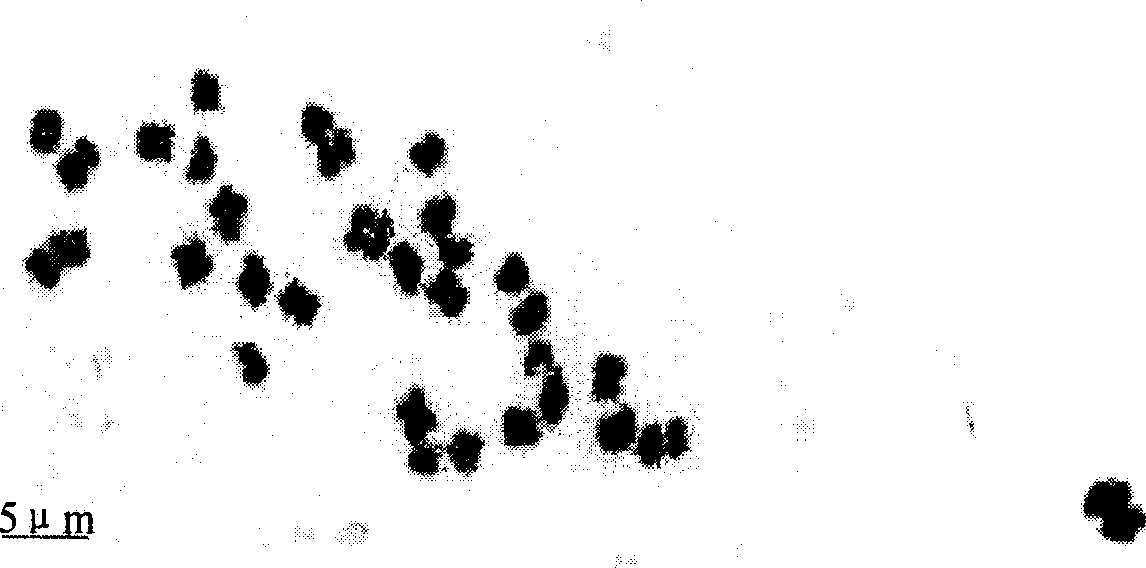
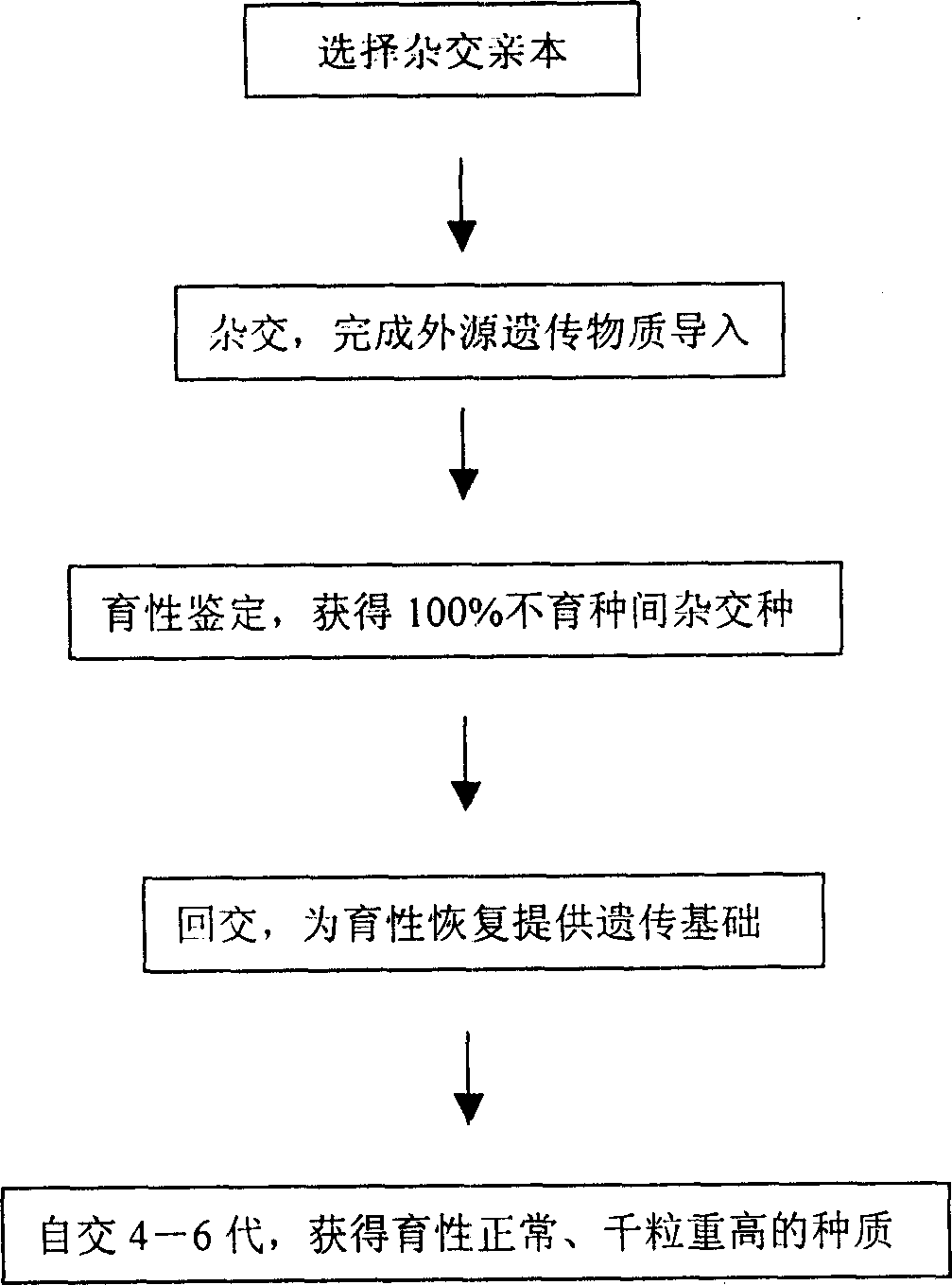
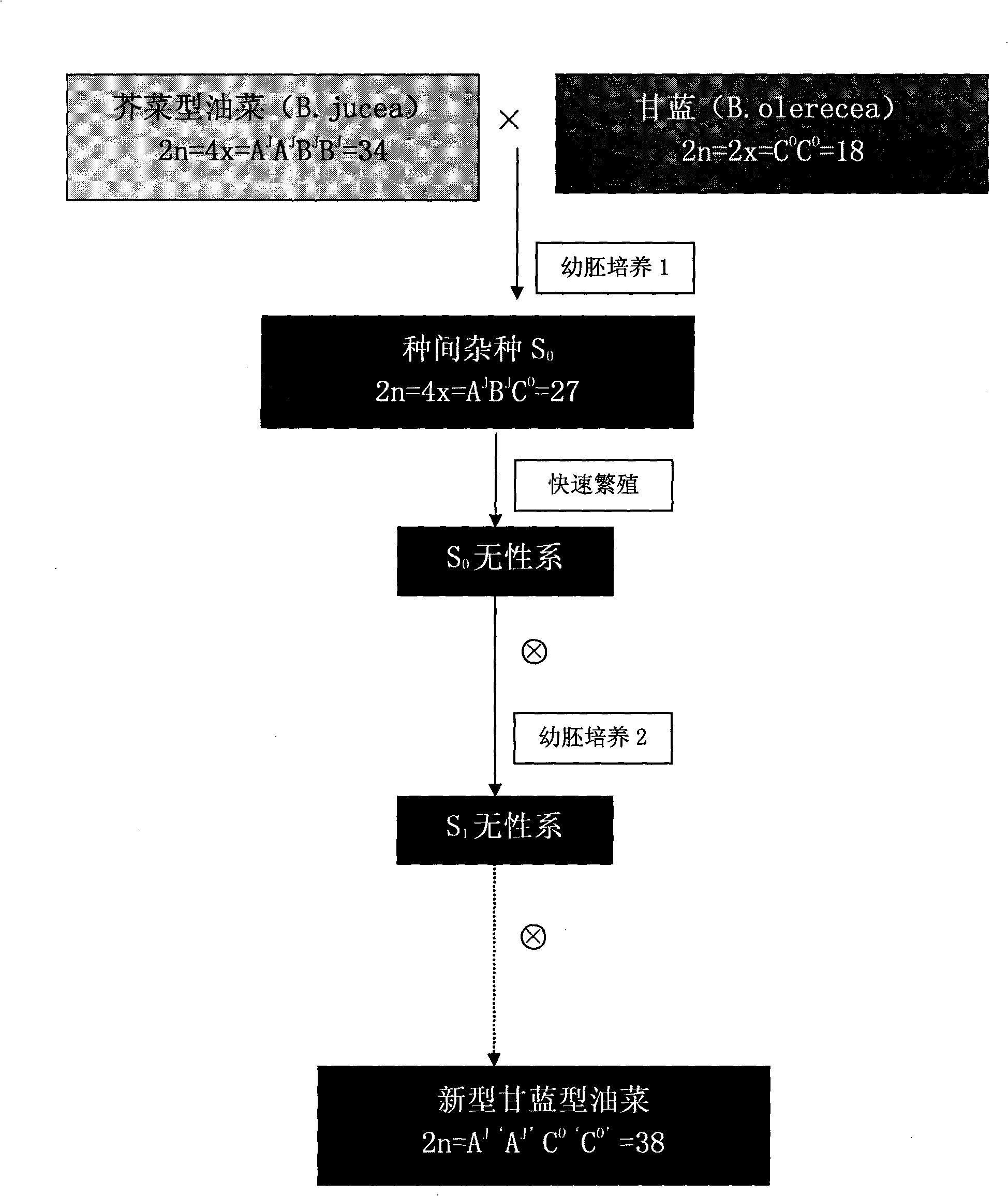
Patents
Literature
214 results about "Interspecific hybridization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Interspecific hybridization is hybridization between organisms treated as distinct species. Use of the term has, however, been problematic since the biological species concept (BSC) says species can't interbreed. For example, many biologists would say two forms should not be treated as distinct species if they are able...
Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration technology for hybridized Chinese tuliptree
The invention is characterized by that on the basis of choice of parents of basswood generic cross and breeding of interspecfic hybridization, the immature embryo of limited quantities got respectively from normal, reciprocal an rotation cross is engaged in induction and cultivation of embryo somatric cell, produces large quantities of embryo of somatic cell in synchronizing development, and leads to cultivate embryo of somatic cell into whole tree characteristics.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Industrialized hybrid fry breeding method for saladfish and lanceolatus
InactiveCN105123580AAchieve reproductive regulationReduce the chance of vertical transmissionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPlant Germ CellsEpinephelus fuscoguttatus
The invention discloses an industrialized hybrid fry breeding method for saladfish and lanceolatus. Female parents of the saladfish and male parents of the lanceolatus are selected; the female parents and the male parents are placed in different breeding ponds; the breeding water temperature of the saladfish is kept between 20 DEG C and 26 DEG C, and the breeding water temperature of the lanceolatus is kept between 25 DEG C and 30 DEG C; through sperm ultralow-temperature cryopreservation and female parent spawning induction, ultralow-temperature cryopreservation is carried out on sperms of the lanceolatus, the sperms are added to freezing diluent according to the volume ratio of the sperms to the freezing diluent of 1 to 1, and the sperms and the freezing diluent are placed in liquid nitrogen to be stored for use; female fishes with obviously expanding abdomens and ovaries developing to the period IV are selected to be bred in the breeding ponds, water temperature is maintained between 22 DEG C and 24 DEG C, medicine injection is carried out on female epinephelus fuscoguttatus for spawning induction, and finally artificial insemination is carried out. Through hybridization of the saladfish and the lanceolatus, interspecies cross species are obtained. Germ cells are safely disinfected, and bacteria and virosis are prevented from being vertically propagated to fry from the germ cells.
Owner:莱州明波水产有限公司
Breeding method for new cabbage type rape line
InactiveCN106134982AEasy to viewReduce erucic acid contentPlant genotype modificationSocial benefitsAgricultural science
The invention discloses a breeding method for a new cabbage type rape line, and belongs to the field of a plant new variety breeding method. According to the breeding method disclosed by the invention, a cabbage type rape line is synthesized by interspecific hybridization of cabbages and Chinese cabbages, and the synthesized cabbage type rape line is subjected to quality genetic improvement of economical characters, erucic acid and glucosinolate so as to breed one new ornamental rape line with a bran-new petal color and a bran-new stalk color; the new cabbage type rape line meets both requirements for ornamental value and oil use, and brings greater economic benefits and social benefits for rape production and the tour and sightseeing industry.
Owner:INST OF IND CROPS HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Interspecific hybridization and propagation method for deep sea scallops and chlamys farreri
ActiveCN104770319AFast growthImprove the quality of breedingClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaInterspecific hybridizationZoology
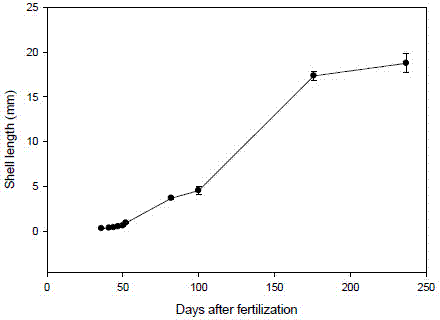
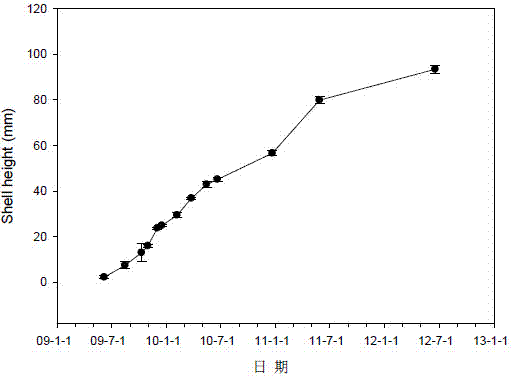
The invention discloses an interspecific hybridization and propagation method for deep sea scallops and chlamys farreri. The interspecific hybridization and propagation method comprises the following steps: a first step of breeding parent scallops: selecting deep sea scallops and chlamys farreri, separating the male and the female of the two scallops respectively, promoting maturity according to a normal parent scallop breeding method and using the mature scallops for cross experiment after synchronously maturing the mature scallops; a second step of laying eggs and performing hybridization: inducing spawning of the male and female groups of the two scallops respectively, fertilizing obtained eggs with conspecific or heterogeneous sperms respectively to obtain pure-bred self-bred progenies of the deep sea scallops and chlamys farreri as well as two hybrid fertilized eggs of female deep sea scallops and male chlamys farreri, female chlamys farreri and male deep sea scallops; hatching the obtained fertilized eggs at 13 to 14 DEG C, observing and measuring the proportion of D type larvas at regular times after the D type larvas appear until the maximum hatching rate is reached; a third step of cultivating scallops, wherein at a larval phase, the average shell height growth speed of the hybrid scallops is 6 to 6.3m per day, and the shell height, the shell length, the shell width and the weight are increased in a cultivating phase. According to the interspecific hybridization and propagation method disclosed by the invention, the deep sea scallops are effectively utilized through interspecific hybridization, so that the scallop breeding species are increased.
Owner:DALIAN CHANGHAI ZHENLU AQUATIC PROD
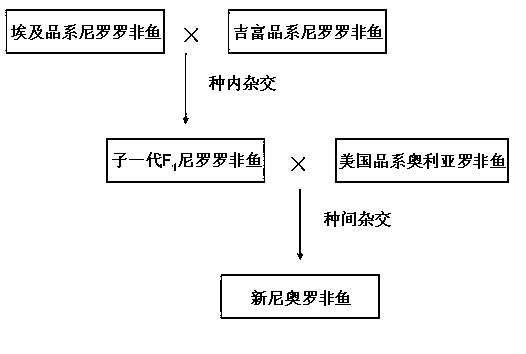
Method for producing seeds of new Nero-Aurea tilapia
InactiveCN102696520AFast growthIncrease male rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPhenotypic traitInterspecific hybridization
The invention discloses a method for producing seeds of new Nero-Aurea tilapia. The method comprises the following steps: (a) carrying out intraspecific hybridization by taking a female of an Egypt strain in Nile tilapia as a female parent and a male of a Gift strain in the Nile tilapia as a male parent to obtain first filial generation F1 of Nile tilapia; and (b) carrying out interspecific hybridization propagation by taking the female in first filial generation F1 of the Nile tilapia as the female parent and the male of American strain of oreochromis aurea as the male parent to obtain hybrid generation, namely the new Nero-Aurea tilapia. With the adoption of the method provided by the invention, a seed producing technique combining intraspecific hybridization with interspecific hybridization is utilized, excellent characters are combined, and the growth speed and the male rate of the tilapia are improved, thereby the cultural output and benefits of the tilapia are improved.
Owner:GUANGXI INST OF FISHERIES
Cultivation method of new germplasm of ornamental Dendrobium spp.
ActiveCN103718948AExcellent ornamental propertiesSolve hybrid parentPlant genotype modificationIntellectual propertyGermplasm
The invention discloses a cultivation method of a new germplasm of ornamental Dendrobium spp. The cultivation method comprises the following steps: an inventor chooses a good single plant of Dendrobium pendulum Roxb. as a female parent, and a good single plant of Dendrobium wardianum Warner as a male parent to conduct artificial interspecific hybridization; conducting artificial pollination and management after pollination; picking fruits; sterilizing the surfaces of the fruits; conducting sprouting cultivation, proliferation and differentiation cultivation, strong seedling rooting cultivation, and acclimatization and transplant to obtain a plurality of strongly grown hybrid filial generation grown-up seedlings. The interspecific hybridization filial generation seedlings gather respective good genetic background of the male parent and female parent, and the new germplasm is provided for culturing the ornamental Dendrobium spp. with proprietary intellectual property rights. According to the invention, the problems that the interspecific cross-compatibility of the Dendrobium pendulum Roxb. and the Dendrobium wardianum Warner is relatively low, and the hybrid seedlings are low in germination ratio and difficult to proliferate are solved, so that a foundation is laid for further culturing the new variety of the ornamental Dendrobium spp. with both a stem and a flower are beautiful and good comprehensive characters, and an effective way is provided for breeding the new variety of the ornamental Dendrobium spp.
Owner:GUANGXI FORESTRY RES INST
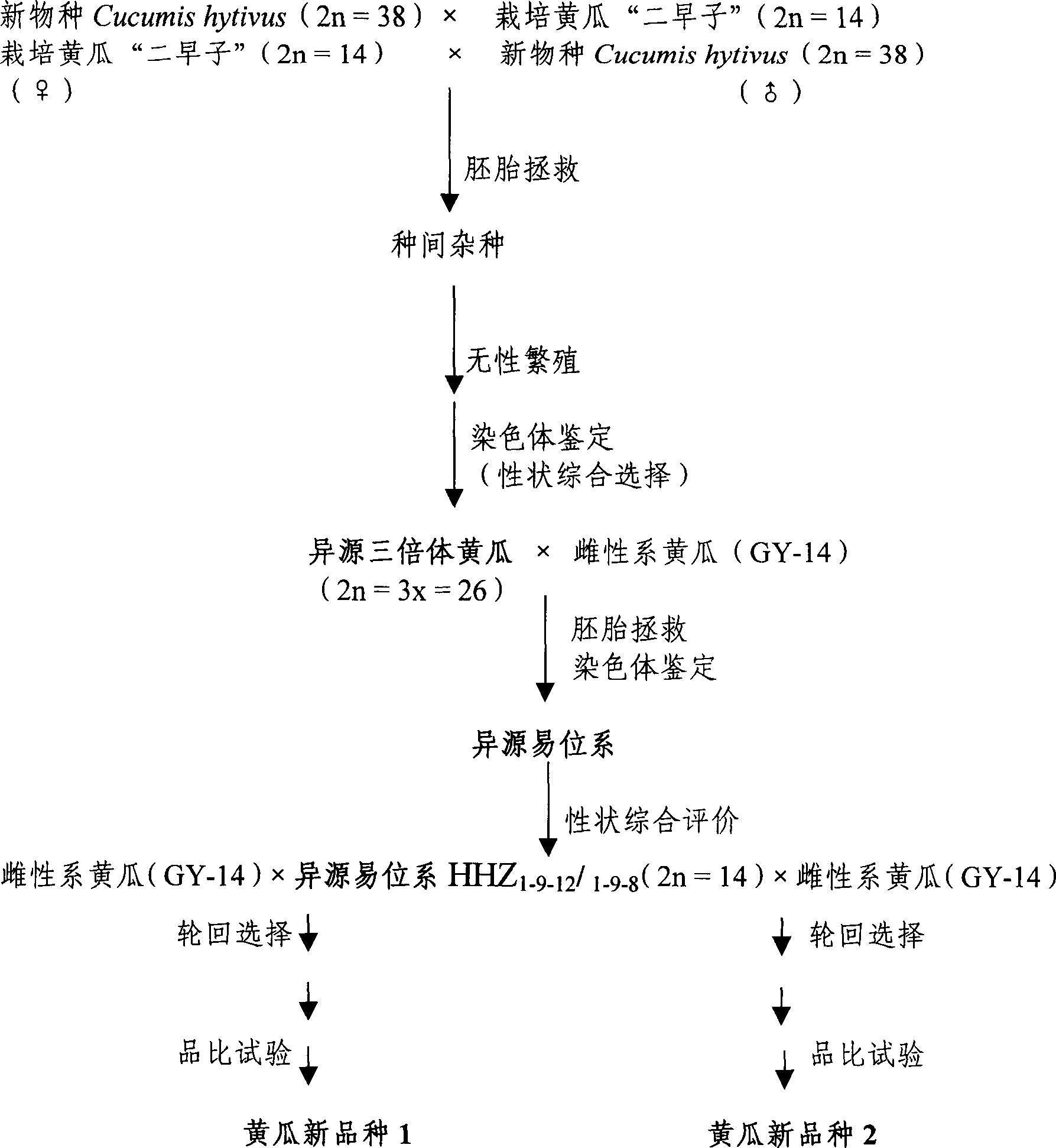
Cucumis allostriploid cucumber and used for method of cucumber breeding
InactiveCN1413447AIncrease varietyImprove economyPlant genotype modificationRoot-knot nematodeInterspecific hybridization
A muskmelon-family allotripolid cucumber without seed is bred by interspecific hybridization between the interspeiescrossed didiploid muskmelon and ordinary cucumber. An alloheterotopic line of cucumber with weak light tolerance and the resistance to root nematoda is obtained by the backcross between said allotriploid cucumber and ordinary cucumber. A new variety of cucumber is obtained by the hybridization between said alloheterotopic line and the female-line cucumber.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for obtaining chrysanthemum distance hydrid using goung embryo rescue
InactiveCN1561694ABroaden the genetic baseDistant hybridizationPlant genotype modificationGermplasmInterspecific hybridization
A method for preparing the distant hybrid of chrysanthemum by embryo rescue includes hybridization between wild diplontic chrysanthemum and cultured hexaplontic 'Huang Ying', embryo rescue by ovary culture, discriminating their descendants by different approaches, and choosing the descendant with new characters.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Wheat interspecific distant hybrid, secondary backcross and selfing breeding method
InactiveCN1813523AGood genetic stabilityReduce manufacturing costPlant genotype modificationGermplasmInterspecific hybridization
The present invention provides a wheat breeding method, including interspecific distant hybridization, secondary back cross and self-cross. Said method includes the following several procedures: a), parents selection; b), distant hybridization; c), hybridization combination and fertility identification; d), backcross; and e) self-cross. Besides, said invention provides the concrete steps and requirements of the above-mentioned every procedure.
Owner:DRY LAND FARMING INST OF HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Haliotis sieboldii and Haliotis discus hannai interspecific hybridization seed production method
ActiveCN101167444AImprove hybrid fertilization rateImprove hatchabilityAnimal reproductionClimate change adaptationInterspecific hybridizationBinary division
An interbreeding producing method of haliotis sieboldii and haliotis discus hannai relates to a cultivation method for seashells and provides a high-fertilization-ratio and high-hatching-ratio interbreeding producing method of haliotis sieboldii and haliotis discus hannai. haliotis sieboldii are taken as parent ormers and haliotis discus hannai are taken as parent ormers when the temperature of natural seawater is 22-26 DEG C, ormers are respectively arranged in different cultivation pools of parent ormers according to sex for cultivation, individuals with mature gonad are expedited to produce with shade drying combined with the stimulation method of using ultraviolet to irradiate seawater until female and male parent ormers lay ova and sperm. The sperm of haliotis sieboldii and the ova of haliotis discus hannai are taken and combined, the pH of seawater for fertilized ova is adjusted, and then ova are washed when fertilized ova divide to the binary division period. Fertilized ova produced by interbreeding female haliotis sieboldii and male haliotis discus hannai can be achieved by that the sperm of haliotis discus hannai and the ova of haliotis sieboldii are taken and combined, the pH is adjusted, and then ova are washed when fertilized ova divide to the binary division period. Finally, ova are cultivated according to normal batching and carry-on cultivation methods.
Owner:福建闽锐宝海洋生物科技有限公司
Method for artificially developing novel brassica napus
InactiveCN101513168AIncrease production levelsEfficient use ofClimate change adaptationPlant genotype modificationBrassicaInterspecific hybridization
The present invention provides a method for artificially developing novel brassica napus. The excellent characters of cabbage and mustard type rape are integrated for obtaining novel brassica napus. The hybridization compatibility when the mustard type rape and cabbage are used for executing interspecific hybridization is higher than the hybridization compatibility when the Chinese cabbage and cabbage are used for executing interspecific hybridization. The interspecific hybrid is easily obtained, and simultaneously, the advantages of drought resistance, cold resistance, excellent strain type, etc. of the mustard type rape can be introduced into the brassica napus. The method of the invention also has the advantages of stable heredity, high speed, large area of character variation and facilitation for selecting the brassica napus with excellent charcter. Furthermore, the chromosomes of AC chromosome set of brassica napus obtained from the method of the invention respectively come from the mustard type rape and cabbage, have larger difference from the prior brassica napus. The use of hybrid vigor of genome of brassica napus is facilitated and the production level of cabbage is increased.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Interspecific hybrid embryo rescuing and seedling forming method of sweet cherries in southern China and Chinese cherries
PendingCN110050690ALearn about developmental statusDetermine the best time for developmentCultivating equipmentsPlant tissue cultureAnthriscus cerefoliumShoot
The invention relates to the field of cross breeding of plants and particularly relates to an interspecific hybrid embryo rescuing and seedling forming method of sweet cherries in southern China and Chinese cherries. The method combines advantages of European sweet cherries and the Chinese cherries, and takes the 'European sweet cherries' as a female parent and the 'Chinese cherries' as a male parent to carry out interspecific distant hybridization. Aiming at the abortion problem of a distant hybrid embryo, the hybrid embryo is subjected to embryo rescuing. A proper sampling period of the embryo rescuing of each hybrid combination, concentrations and ratios of respective exogenous growth regulators for hybrid young embryo germination, subculture propagation and rooting culture, and a proper acclimatization and transplanting method are determined. By applying an interspecific hybrid embryo rescuing system of the sweet cherries in southern China and the Chinese cherries, which is established by the technology, the embryo germination rate reaches 80.00 percent, the multiplication coefficient of subculture hybridized new shoots reaches 5.0, the rooting rate of rooting culture is 90.91percent, the growth vigor of embryo culture seedlings is good and the seedlings grow robustly and have green leaves, and the acclimatization and transplanting survival rate reaches 77.27 percent.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Development and applications of Indel marker capable of distinguishing five pepper cultivated species
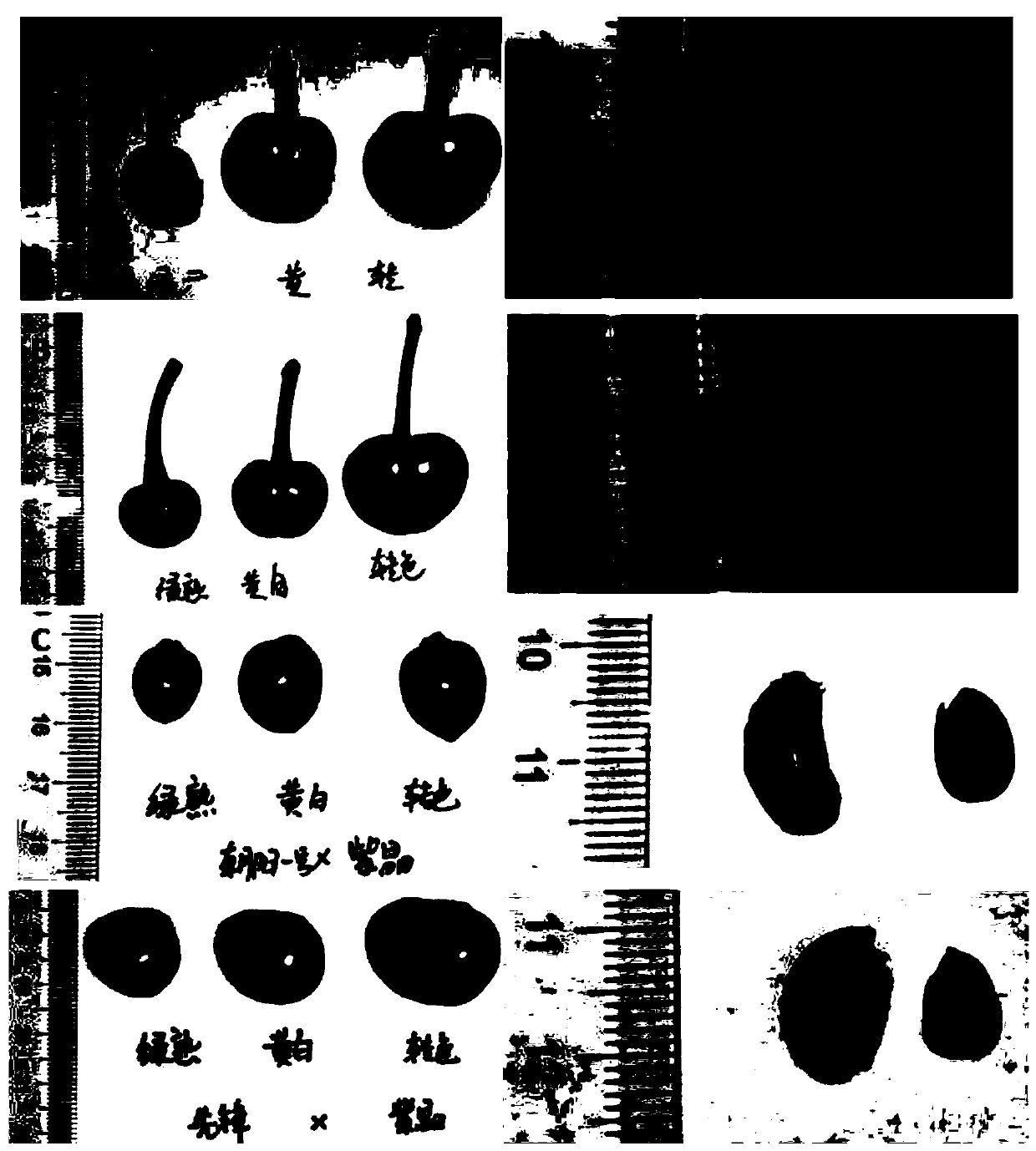
ActiveCN108588255AEasy to operateBelt type is simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerAgricultural science
The invention discloses development and applications of an Indel marker capable of distinguishing five pepper cultivated species. An Indel marker primer capable of distinguishing five pepper cultivated species is composed of a forward primer as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and a reverse primer as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The genome DNA of the five pepper cultivated species materials is subjected to PCR amplification by adopting the primer provided by the invention, the five pepper cultivated species can be rapidly and accurately distinguished, the five pepper cultivated species can be distinguished, andthe inter-species hybrid variety of the five cultivated species can be identified.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Mutagenized tobacco plant as seed culture for the production of oil for energetic, industrial and alimentary uses
ActiveUS20100058655A1High productMaximisation of seed productionMutant preparationBiofuelsBiodieselNicotiana tabacum
The present invention relates to the development of tobacco plants, modified through mutagenesis techniques, interspecific hybridisation followed by poliploidisation and recombinant DNA technologies, characterised by the fact of being capable of producing a very high amount of seeds and their use for the production of oil for energetic and industrial scopes, such as combustion oil, biodiesel and lubricating oil, and for animal and human alimentation.
Owner:AEP ADVANCED ECOPOWER PATENTS
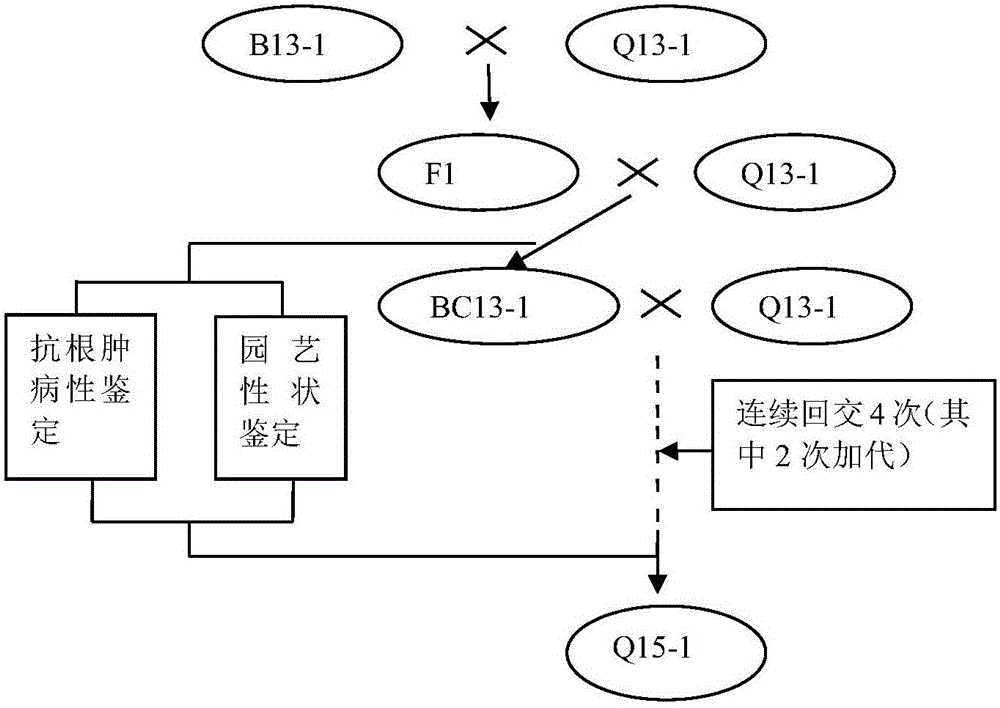
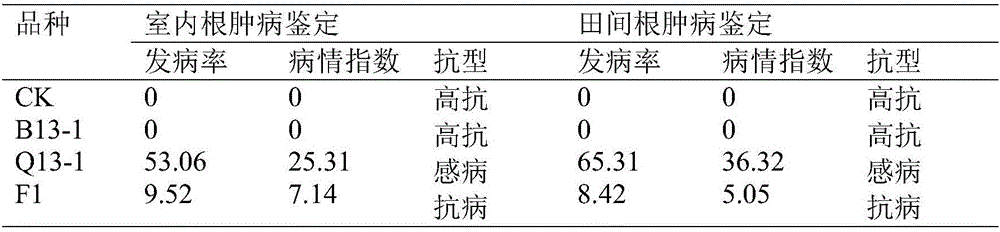
Method for acquiring non-heading Chinese cabbage clubroot resistance germplasm resources
InactiveCN105850717ADig extensivelyExclusion of biohazardsPlant genotype modificationInterspecific hybridizationPhenotypic trait
The invention discloses a method for obtaining germplasm resources of non-heading Chinese cabbage resistant to clubroot, comprising: selecting introduced Chinese cabbage resistant to clubroot and susceptible non-heading Chinese cabbage with excellent agronomic properties; Interspecific hybridization was used to obtain F1 seeds of the first generation of hybridization; the screened F1 generation was continuously backcrossed for 4 generations, and a new non-heading Chinese cabbage resistant germplasm Q15‑1 with stable phenotype and resistance to clubroot was initially obtained. The present invention adopts the method of interspecific hybridization, and carries out artificial inoculation identification on each backcross offspring, screens the resistant single plant of clubroot disease, and finally obtains new germplasm. The present invention utilizes Brassicaceae Chinese cabbage The hybrid vigor between the two varieties of non-heading Chinese cabbage and its variant non-heading Chinese cabbage, the resistance gene of clubroot Chinese cabbage is transferred to non-heading Chinese cabbage through hybridization and backcrossing at the bud stage, which is simple and easy. Biological risks caused by other methods such as genetic modification and genetic engineering technology are excluded.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Tissue culture rapid propagation method of ornamental lily
ActiveCN102405845AEasy to trainIncrease production capacityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureCulture mediumsNutrient
The invention discloses a tissue culture rapid propagation method of an ornamental lily The method comprises the following steps: selecting a scale without injuries at an intermediate layer of the ornamental lily, washing and cleaning the scale with clear water, sequentially processing the cleaned scale with 75% alcohol and 0.1% mercuric chloride, and then washing with sterile water for 5-7 times; cutting the scale which is well sterilized into small pieces with the area of 1-2cm<2>, inoculating the small pieces onto an induction culture medium, performing induction for 23-27 days under induction conditions, and budding and becoming a patch of bulb; cutting 2-3 single buds from the induced patch of bulb, and transferring to a propagation culture medium for performing propagation culture for 25-35 days; selecting the clumpy buds with the blade height of 2-4cm from the propagated patch of bulb, cutting into the single buds and inoculating the single buds onto a rooting culture medium for culturing and rooting for 20-26 days so as to become test-tube plantlets; and performing acclimatization on the test-tube plantlets, then cleaning, and transplanting into a nutrient matrix formed by mixing yellow soil with vermiculite in a volume ratio of 1: 1 for cultivation and management. By adopting the method, the propagation coefficient is increased, the propagation speed is accelerated, the effects of detoxification and rejuvenation are achieved, and the problems of degradation, incompatibility of interspecific hybridization and the like, which are often caused by multi-generation propagation, can be avoided.
Owner:珠海慧洁生物有限公司
Breeding method of early-ripe and disease-resistant broccolini
ActiveCN103168681ANormal inbred lineGood production capacityPlant genotype modificationEarly generationShoot
The invention relates to a breeding method of crops, and particularly to a breeding method of broccolini, belonging to the technical field of plant breeding. The breeding method has the advantages that 1. the male sterility line belongs to cytoplasmic male sterility and maternal inheritance, and is stable in sterility, the sterile plant rate and the sterility are 100 percent, nectary is developed, more nectars grow, stigma is normal, flowering and fruiting characters are good, and a seedling does not yellow under the condition of low temperature and can not deteriorate after multi-generation backcross, transform is easy, growth is vigorous, and combining ability is strong; 2. a transformation early generation sterile line is stronger in growth vigor in comparison with a maintainer line and has the advantage of interspecies cross; 3. a later producing shoot of the transformation early generation sterile line is stronger than that of the maintainer line, and thus the transformation early generation sterile line material is early planted by 5 days in comparison with a backcross male parent; 4. F1 is prepared by using the sterile line, the seed yield is high, the seed producing cost is low and the labor is saved; and 5. a new variety prepared by using the sterile line is strong in disease resistance, and is remarkable in production increasing.
Owner:安徽省凤阳县御膳油脂有限公司
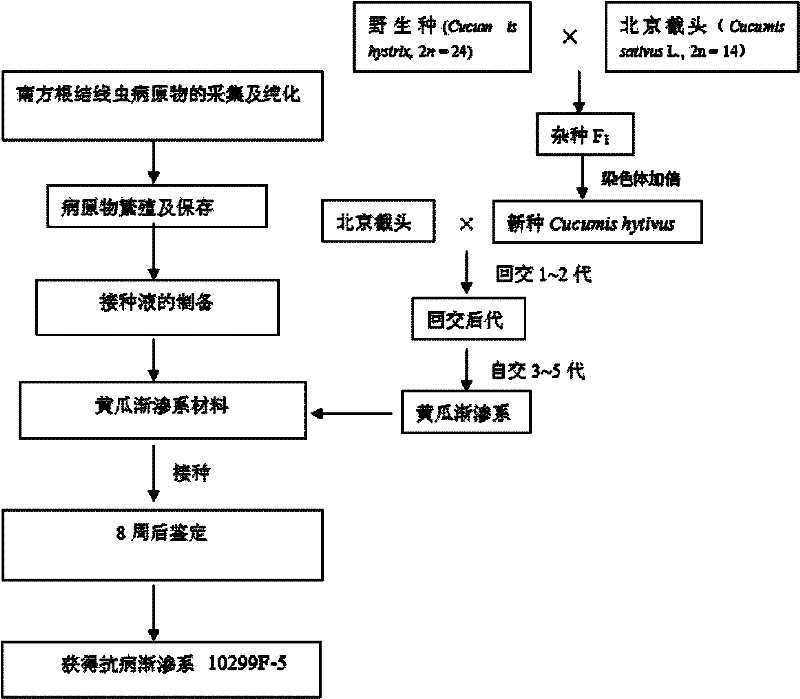
Cultivation Method of Cucumber Introgression Line Material Resistant to Meloidogyne incognita
InactiveCN102257953ABroaden the genetic baseStrong plant growthHorticulture methodsPlant genotype modificationWild speciesGenetic Materials
The invention belongs to the field of seed breeding in biotechnology, and relates to a method for cultivating cucumis sativus L introgression line material for resisting meloidogyne incognita. The method comprises the following steps of: performing the interspecific hybridization of wild species and cultivated species, doubling chromosomes to obtain new amphidiploid species, and performing backcross and selfing to obtain an interspecific introgression line; identifying the cucumis sativus L introgression line by a method of inoculating artificial seedling stage spawn liquid to obtain the cucumis sativus L interspecific hybridization introgression line material for resisting meloidogyne incognita, wherein an identification result indicates that disease indexes of the introgression line 10299F-5 are 2.0, and the introgression line 10299F-5 has disease-resistant expression. The cultivating cucumis sativus L interspecific hybridization introgression line material for resisting meloidogyneincognita is high in an economical character, and can be used as a breeding material directly, so the blank of cucumis sativus L resources for resisting meloidogyne incognita is filled, a reference is provided for the inoculation identification of other plants, and useful genetic materials are provided for improvement on cucumis sativus L species, the transfer of disease-resistant genes, gene positioning, molecular marks, gene cloning and the like in future.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Hybridizing and breeding method of dwarf winter wheat
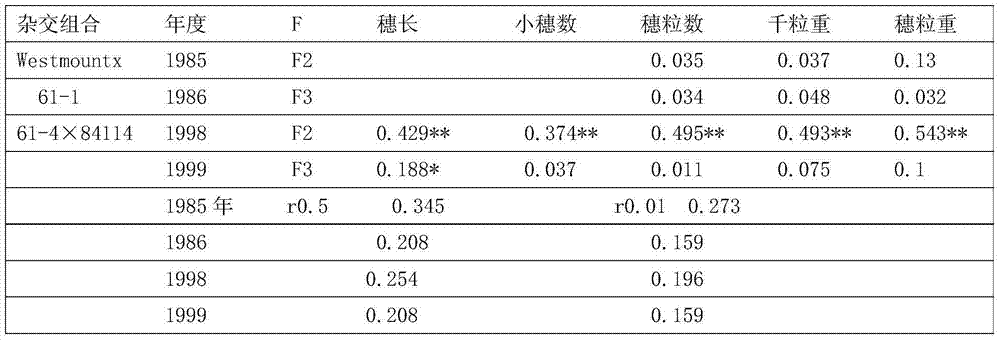
The invention disclose a hybridizing and breeding method of dwarf lodging-resistant winter wheat with high photosynthetic efficiency of wheat and low seed charge and fertilizer feed. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out interspecific hybridization of varieties of Masutuo wheat and big heat wheat; selecting a 61-1 wheat strain from a hybrid generation as a cross parent; carrying out hybridization with Westmount wheat variety; then, selecting a 61-4 wheat strain from the hybrid generation of Westmount wheat variety and 61-1 wheat variety as the cross parent again; and carrying out hybridization with the wheat strain 84114 to obtain the dwarf winter wheat. The method provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that according to the hybridizing and breeding method of the dwarf winter wheat, the bred winter wheat is named as Yinong 61 wheat variety which has the advantages of late seeding time, quick mature, tiller productive in spring, high percentage of earbearing tiller, dwarf, more spikes, more grains, high thousand seed weight, excellent weak gluten, large leaf area, high photosynthetic efficiency and strong cold resistance and lodging resistance.
Owner:邓世雄
Cabbage hybrid breeding method
InactiveCN1895030ADisease resistantWith high qualityPlant genotype modificationAngiosperms/flowering plantsInterspecific hybridizationGermplasm
A method for selectively culturing the cytoplasmic male sterility line of Chinese cabbage includes such steps as choosing the cytoplasmic male sterility line of cabbage-type rape (or radish) RC97-1 as female parent and the selfing line of Chinese cabbage '1138' as male parent, hybridizing, choosing excellent plant as the female parent for backcrossing, backcrossing by continuous 7 generations while choosing the high-yield and disease-resistant plants for backcrossing to obtain RC7, and hybridization between the resultant RC7 as female parent and selfing line of Chinese cabbage 03 S1207.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV +1
Breeding method of continuously and directly seeding carly and late rice breed
InactiveCN1679390AHarm reductionReduce pollutionPlant genotype modificationRice cultivationHigh resistanceInterspecific hybridization
A method for selectively culturing the excellent variety of rice includes such steps as choosing parent rices which has high resistance to low temp, high temp and oxygen lack, short dormant period and low optical and temp sensitivities, hydridizing, backcrossing ion beam mediated distant hybridizing for genetic recombination, and genetic modifying to its descendants.
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Breeding method of brassica napus capable of being specially adopted as green manure
The invention relates to a breeding method of brassica napus variety capable of being specially adopted as a green manure. The method comprises that brassica oleracea type hybrid brassica campestris is selected as the female parent and is subjected to interspecific hybridization with white brassica parachinensis to obtain a F1 generation hybrid species; the F1 generation hybrid species and the female parent are subjected to backcrossing to obtain BC1F1 seeds; the seeds are cultivated and are subjected to selfing to obtain BC1F2 seeds; the single plant having the chromosome number close to the brassica campestris female parent is selected to carry out selfing to obtain BC1F3 seeds; the single plant having the chromosome number n of 19 is further selected to carry out selfing to obtain BC1F4 seeds; and the BC1F4 seeds are subjected to subsequent multi-generation selfing, wherein the short growth period of the plant is adopted as the main limiting target character during the multi-generational selfing process and the consistent directional system selection in the line is performed until the brassica napus variety capable of being specially adopted as the green manure is obtained. With the breeding method of the present invention, the brassica napus variety capable of being specially adopted as the green manure and with characteristics of short growth period, strong adaptability, high biological yield and low seed production cost can be bred out.
Owner:湖南省作物研究所
Novel rucola plants with cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS)
InactiveUS20100122371A1Facilitates therefore efficient crop improvementIncrease resistanceSeed and root treatmentPlant phenotype modificationBiotechnologyBrassica oleracea var botrytis
The present invention discloses rucola plants, including an E. sativa plant, with cytoplasmic inherited male sterility (CMS) for hybrid breeding purposes. The present invention includes plants that comprise CMS-cytoplasm from cauliflower (S. oleracea var. botrytis) transferred to E. sativa by a wide interspecific cross.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Seed production method by interspecific crossing of green abalone and Pacific abalone
ActiveCN103109765AObvious hybrid vigorClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaRipeningSemen
The invention relates to a seed production method by interspecific crossing of green abalone and Pacific abalone and relates to a hybrid seed production method for aquatic shellfishes. Pacific abalone and green abalone are used as parent abalones. Sea water temperature is controlled to 24 DEG C-26 DEG C through a temperature control facility to allow for synchronous accelerated ripening of gonads of the parent abalones. The male abalones and female abalones are placed in different culture ponds for breeding. Sex character of the parent abalones in each culture pond needs to be equal. The individuals with maturely developed gonads are induced for spawning by drying in the shape, ultraviolet irradiation and sea water stimulation until the female and male abalones lay eggs and discharge semen. Insemination is allowed at the water temperature of 20 DEG C to 22 DEG C. Inseminated hybrid abalone fry are obtained by direct cross combination, namely female Pacific abalone with green abalone, or by reciprocal cross combination, namely female abalone with Pacific abalone. The inseminated hybrid abalone fry are bred by conventional larva, offspring and intermediate breeding methods, and direct-cross or reciprocal-cross fry of green abalone and Pacific abalone are obtained finally.
Owner:福建闽锐宝海洋生物科技有限公司
Chinese cabbage hybrid breeding process
InactiveCN1887061ACompact plantStrong disease resistancePlant genotype modificationAngiosperms/flowering plantsDiseaseInterspecific hybridization
The Chinese cabbage hybrid breeding process features that the process includes interspecific crossing with cabbage type rape radish cytoplast male sterile material RC97-1 as female parent and Chinese cabbage self-bred line 1138 as male parent to obtain transfer bred primary generation seed, selecting the excellent single plant as the backcross female parent for the next turn; continuous seven-generation backcross transfer breeding, economic character selection, disease resistance identification to obtain Chinese cabbage cytoplast male sterile material RC7 with stable sterility and economic character the same as that of corresponding maintainer line; and the further crossing with the Chinese cabbage cytoplast male sterile material RC7 as male parent and Chinese cabbage self-bred line 04S245 as male parent to obtain the Chinese cabbage hybrid. The Chinese cabbage hybrid Jingqiu-70, or RC7*04S245, has the features of early ripening, compact plant, high disease resistance, etc.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV +1
Hybrid breeding method of Lutmria maxima jonas and Lutraria philippinarum
InactiveCN102835341APromote domesticationEasy to reinforceClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaNatural resourceLutraria
The invention discloses a hybrid breeding method of lutmria maxima jonas and Lutraria philippinarum. The lutmria maxima jonas grows rapidly and is high in price, but cultivation is affected by bottom tide, storm and diseases, and annual fluctuation of the output is large. The breeding mode for Lutraria philippinarum is simpleand economic effect is obvious, but the disease resistance of the young Lutraria philippinarum is poor, and it is difficult to artificially breed. The method comprises the steps of: carrying out interspecific hybridization according to the situation that lutmria maxima jonas and Lutraria philippinarum are geographically isolated and different in reproductive biology characteristics, and breeding filial generation with merits such as strong disease resistance and fast growth speed. According to the invention, the measures such as purchasing and transporting of parent shellfish, domesticating of the parent shellfish, artificial fertilization and hybridization, incubation and superior varity selection, cultivation of planktonic larvae, larval metamorphosis, juvenile mollusk cultivation and intermediate cultivation in a sear area are adopted. The hybrid breeding method is scientific and reasonable in technological process and strong in maneuverability, and hybridization of two types of geographically isolated clams belonging to Lutraria is achieved. The method disclosed by the invention is fewer in occupied resources and low in cost, and natural resources are fully utilized.
Owner:广西海洋研究所有限责任公司
Artificial-bursting cross pollination method for cassava
InactiveCN103461096AImprove result rateEnough time for pollination and conceptionPlant genotype modificationBurstingInterspecific hybridization
The invention belongs to the technical field of cassava intervarietal hybridization breeding and provides an artificial-bursting cross pollination method for cassava. 2-3 days before flowering of cassava female flowers, the female flowers are subject to artificial bursting, so that female flower stigmas are exposed; then the male flower pollen or the bud of a newly-flowered male flower, prepared in advance, is aligned to the female flower stigmas to sweep back and forth, so that the stigmas are stained with the pollen; the pollinated cassava female flowers are covered by a bag; 3-4 days after pollination, the bag is removed. The condition of mucus (nectar) secreted on the female flower stigmas is utilized as an artificial pollination medium to judge the best pollination time, so that the female flowers and the male flowers have enough time for pollination and impregnation, and the cassava fruitage ratio is improved. The artificial-bursting cross pollination method can be used for intervarietal hybridization of cassava and lays foundations for cultivating new cassava varieties.
Owner:SOUTH ASIAN TROPICAL AGRI SCI RES INST OF GUANGXI
Pickle and purple cabbage trigenomic species allohexaploid vegetable germplasm and acquisition method
ActiveCN103651111AShorten the timeEasy to operateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureGermplasmOperability
The invention discloses a pickle and purple cabbage tri-genome species allohexaploid vegetable germplasm and an acquisition method, which fill in the blank of lack of brassica trigenomic species allohexaploid vegetable germplasm. The acquisition method comprises the steps that pickle and purple cabbages of brassica vegetable germplasm are cross-fertilized; an ovary is picked at the seventh day after pollination; mature seeds are obtained by embryo rescue; a large quantity of propagated progenies are obtained through subculture and propagation after seed germination; duplication treatment is carried out on a haploid by a liquid culture medium with colchicine to obtain the multi-genome allohexaploid vegetable germplasm. The pickle and purple cabbage tri-genome species allohexaploid vegetable germplasm and the acquisition method, disclosed by the invention, have the advantages of strong operability, simpleness and practicality, save the time for obtaining multi-genome polyploidy material, can be widely used for embryo rescue for interspecies cross of cruciferous brassica vegetable germplasm, and have great significance to cultivation and breeding of new species of special plants.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Methods for assaying gene imprinting and methylated CpG islands
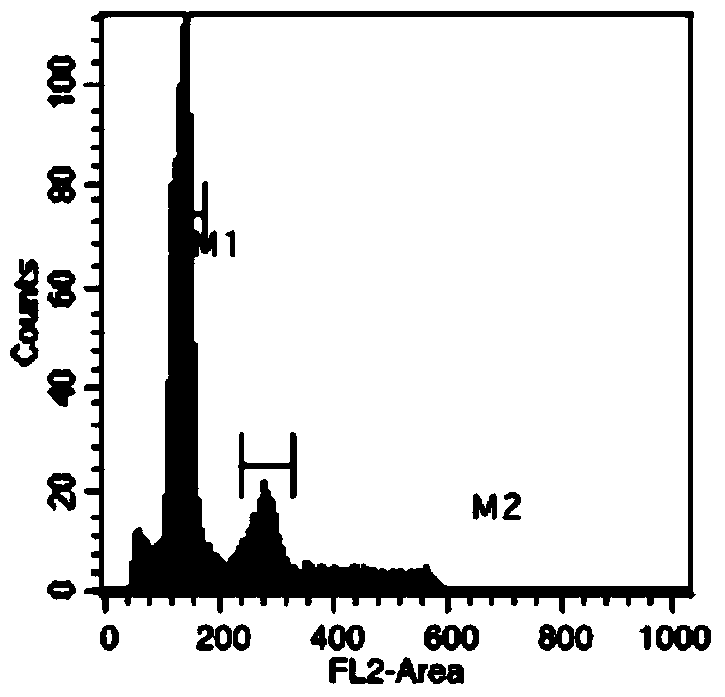
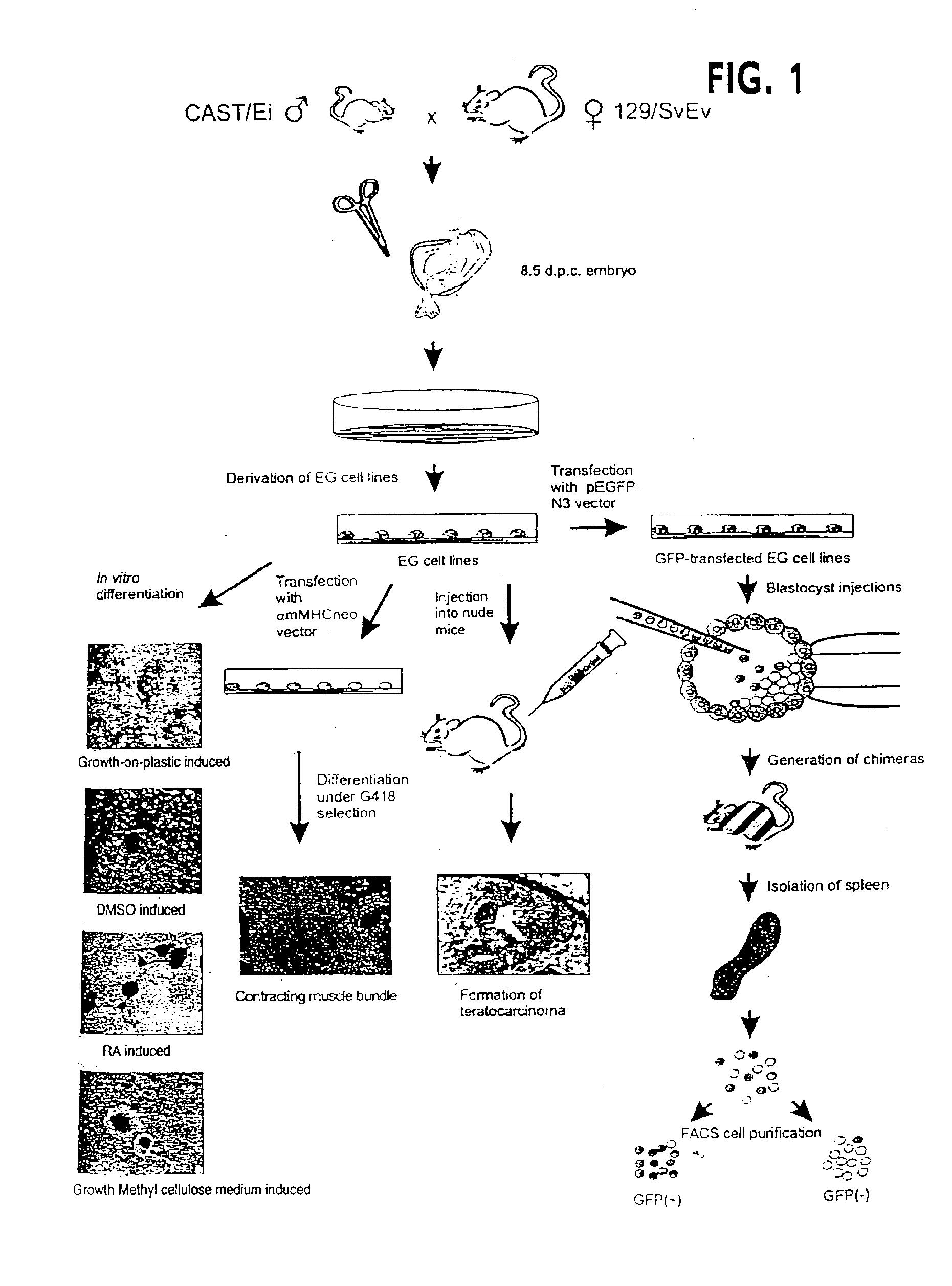
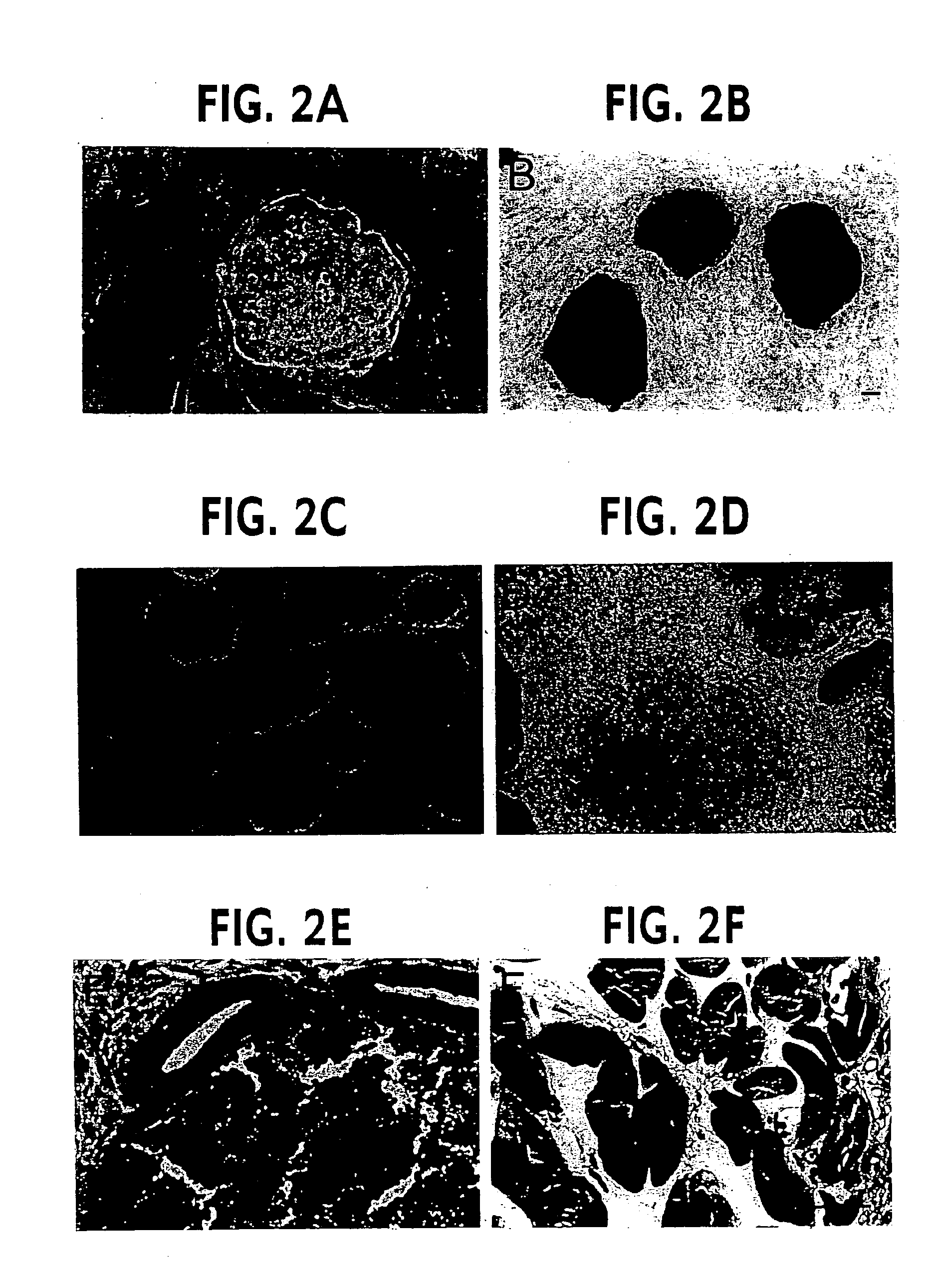
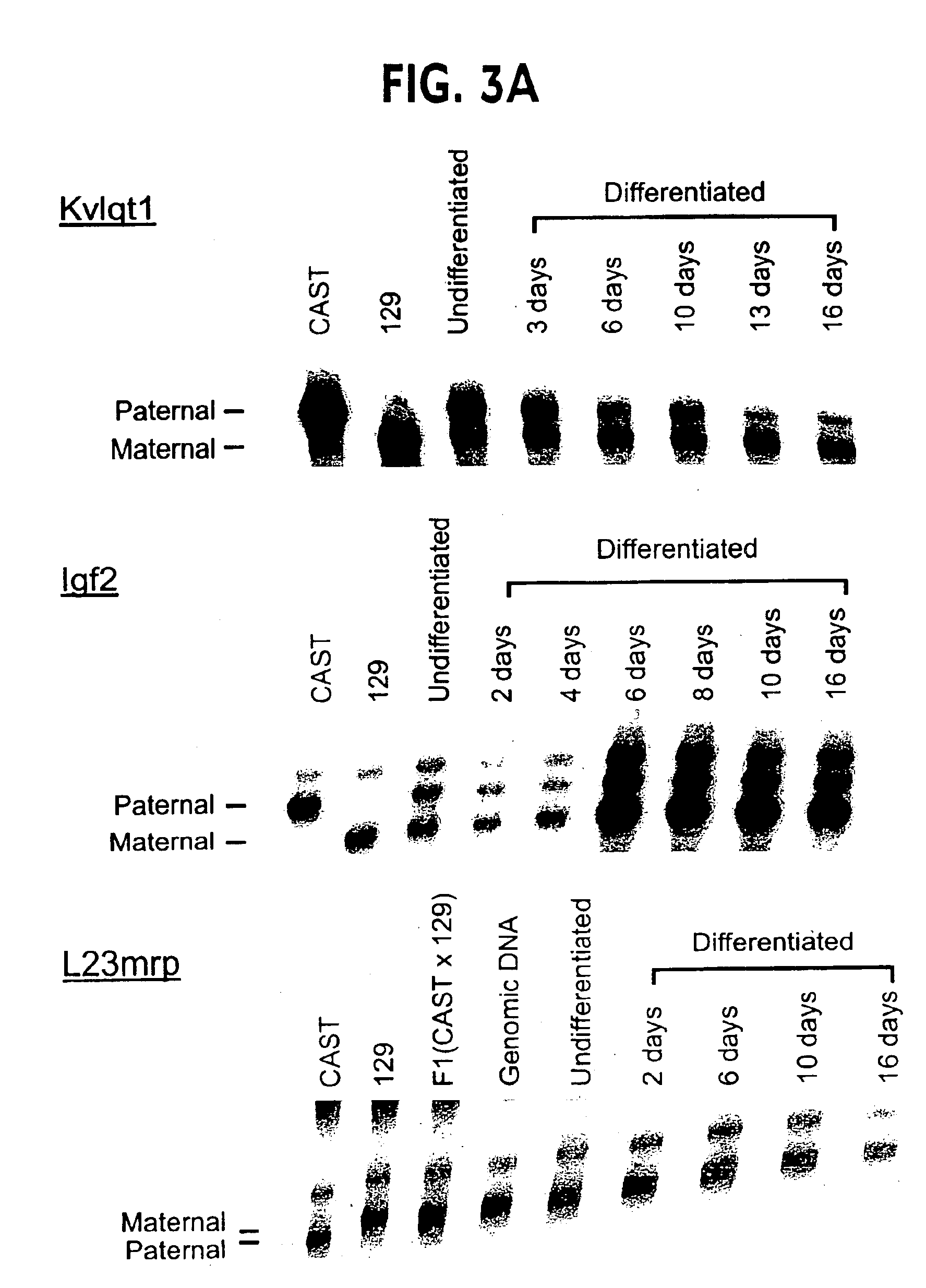
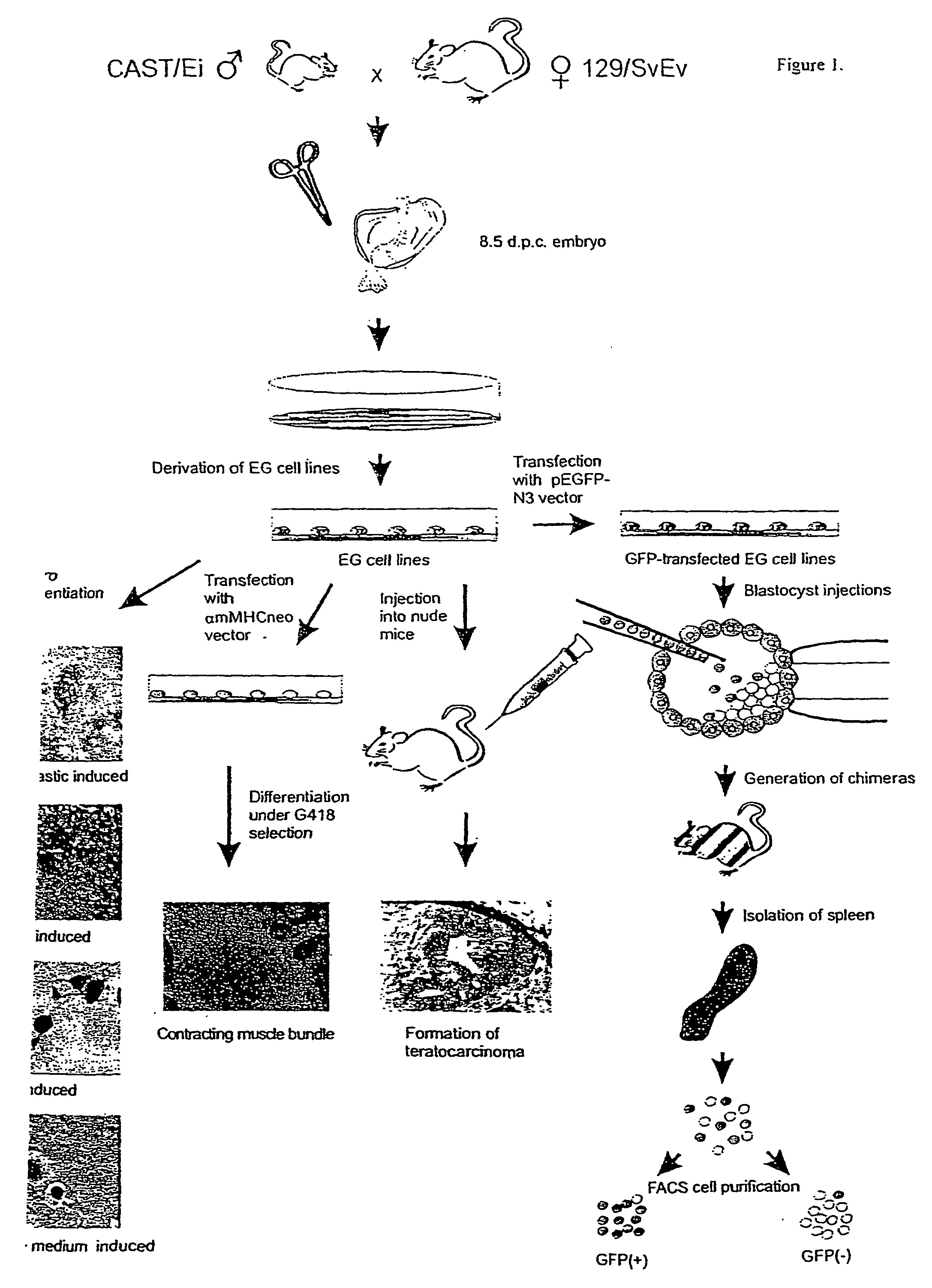
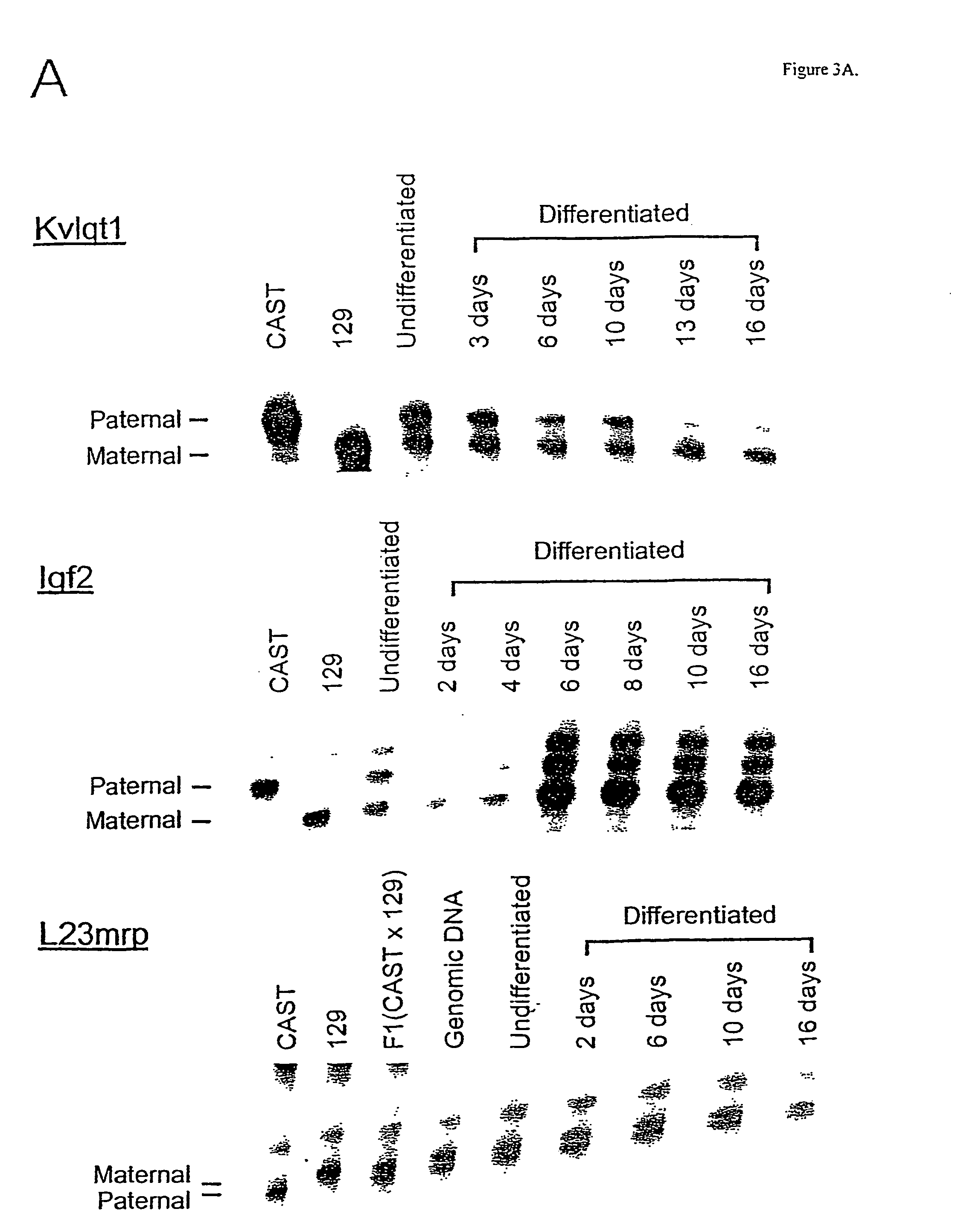
Genomic imprinting is a parent of origin-dependent gene silencing that involves marking of alleles in the germline and differential expression in somatic cells of the offspring. Imprinted genes and abnormal imprinting have been implicated in development, human disease, and embryonic stem cell transplantation. We have established a model system for genomic imprinting using pluripotent 8.5 d.p.c. mouse embryonic germ (EG) cell lines derived from an interspecific cross. We find that allele-specific imprinted gene expression has been lost in these cells. However, partial restoration of allele-specific silencing can occur for some imprinted genes after in vitro differentiation of EG cells into somatic cell lineages, indicating the presence of a gametic memory that is separable from allele-specific gene silencing. We have also generated a library containing most methylated CpG islands. A subset of these clones was analyzed and revealed a subdivision of methylated CpG islands into 4 distinct subtypes: CpG islands belonging to high copy number repeat families; unique CpG islands methylated in all tissues; unique methylated CpG islands that are unmethylated in the paternal germline; and unique CpG islands methylated in tumors. This approach identifies a methylome of methylated CpG islands throughout the genome.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Methods for assaying gene imprinting and methylated cpg islands
InactiveUS20050153440A1Drug screeningSkeletal/connective tissue cellsAbnormal tissue growthModel system
Genomic imprinting is a parent of origin-dependent gene silencing that involves marking of alleles in the germline and differential expression in somatic cells of the offspring. Imprinted genes and abnormal imprinting have been implicated in development, human disease, and embryonic stem cell transplantation. We have established a model system for genomic imprinting using pluripotent 8.5 d.p.c. mouse embryonic germ (EG) cell lines derived from an interspecific cross. We find that allele-specific imprinted gene expression has been lost in these cells. However, partial restoration of allele-specific silencing can occur for some imprinted genes after in vitro differentiation of EG cells into somatic cell lineages, indicating the presence of a gametic memory that is separable from allele-specific gene silencing. We have also generated a library containing most methylated CpG islands. A subset of these clones was analyzed and revealed a subdivision of methylated CpG islands into 4 distinct subtypes: CpG islands belonging to high copy number repeat families; unique CpG islands methylated in all tissues; unique methylated CpG islands that are unmethylated in the paternal germline; and unique CpG islands methylated in tumors. This approach identifies a methylome of methylated CpG islands throughout the genome.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com