Method for artificially developing novel brassica napus
A new type of Brassica napus technology, applied in botany equipment and methods, plant genetic improvement, angiosperms/flowering plants, etc., can solve the problem of narrow genetic basis of Brassica napus, unfavorable utilization of heterosis among genomes, and difficult selection of plants traits and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
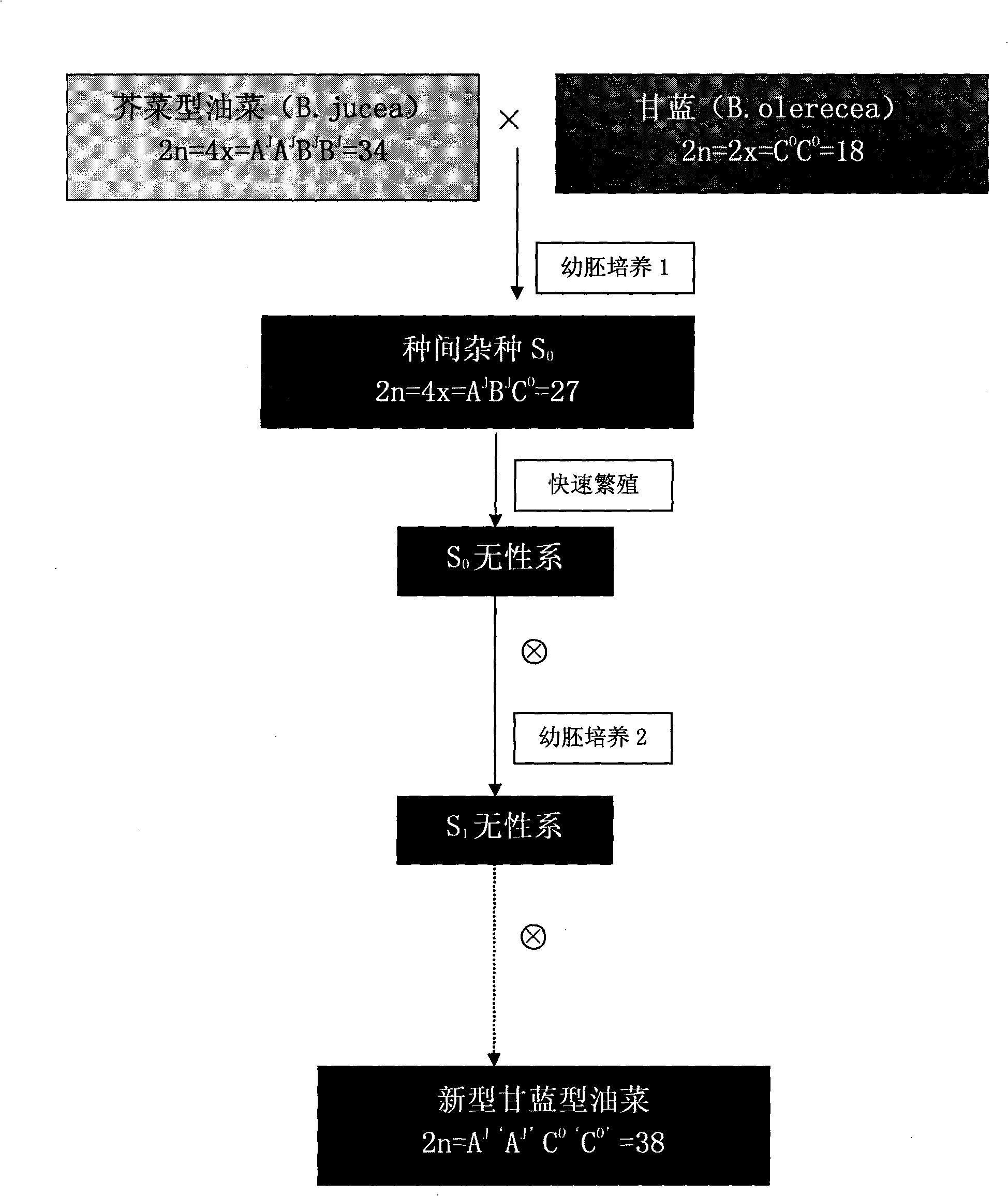
[0018] When rapeseed is in full flowering stage in February-April, select the vigorous mustard type rape as the female parent, remove the flower buds that have bloomed and are too small, and emasculate the flower buds that will bloom in the past 1-2 days, and use a mass percentage concentration of 10%. Apply NaCl to the stigma, wait for the salt water to dry naturally, and then infuse pollen taken from healthy kale plants. After pollination, quickly cover the stigma with a paper bag to prevent the introduction of foreign pollen. Repeat pollination the next day.
[0019] About 20 days after pollination, take immature young ovules, disinfect the surface with 75% alcohol under aseptic conditions, and then disinfect with sodium hypochlorite with a mass percentage concentration of 10%-15% for 15-20 minutes, and then inoculate into MS On the medium, after it germinates, it is transferred to the rapid propagation medium for rapid propagation to obtain clones. Around October-November...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Embodiment 2: Cabbage is selected from head cabbage, and the above-mentioned example operations are carried out at the same time.
Embodiment 3
[0024] Embodiment 3: Brassica kale is selected as the cabbage, and the above-mentioned example operations are carried out at the same time.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com