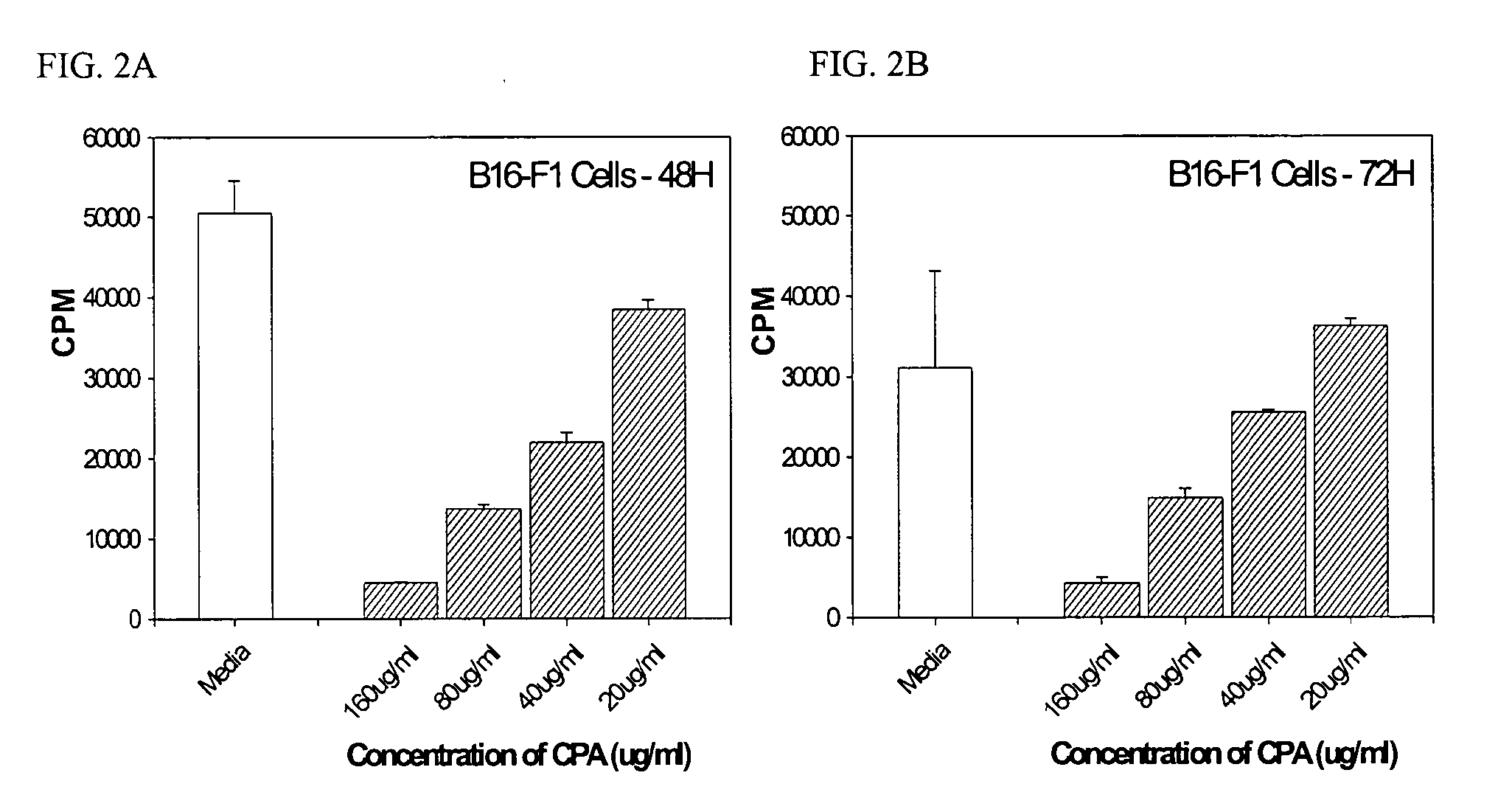
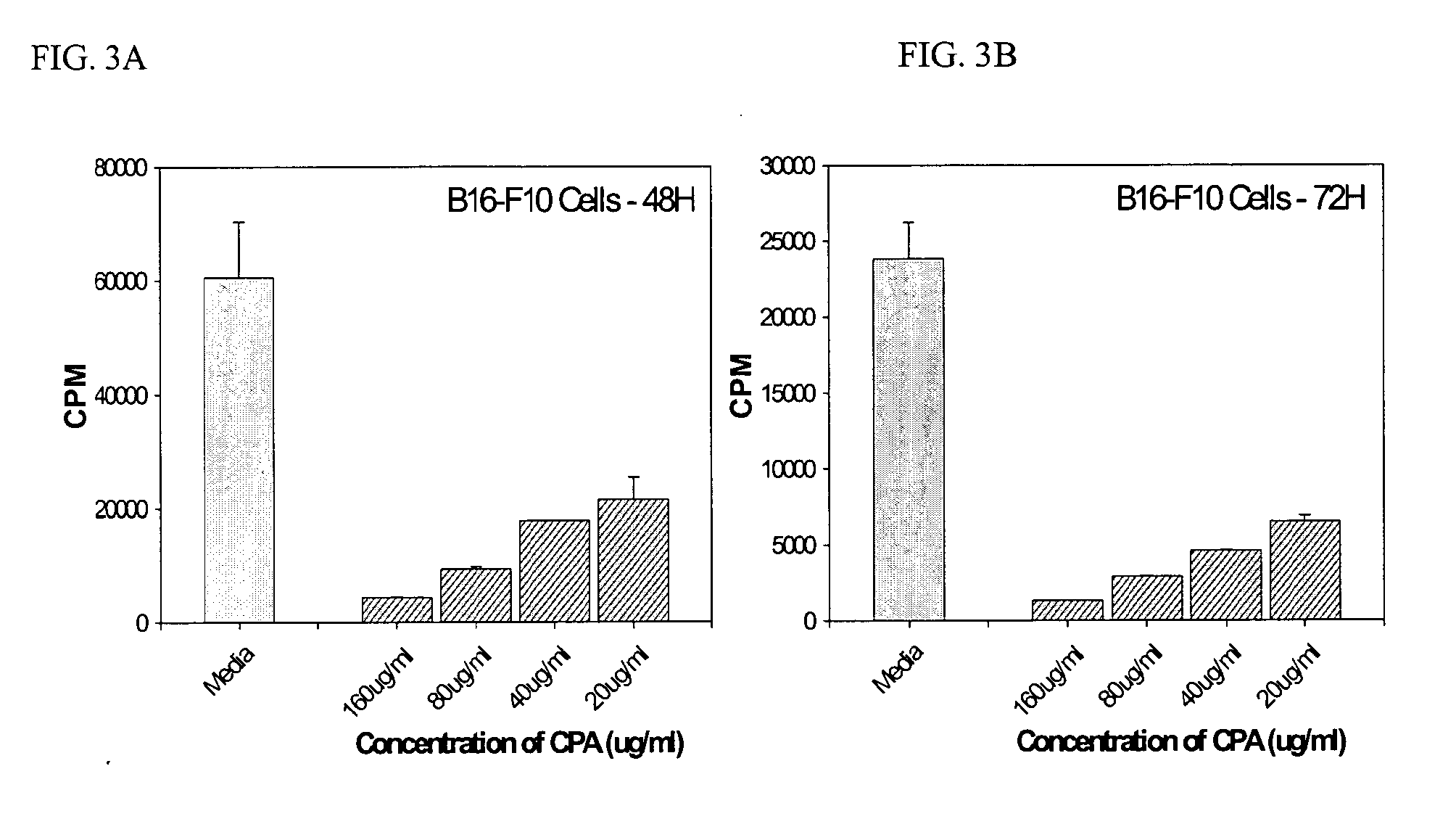
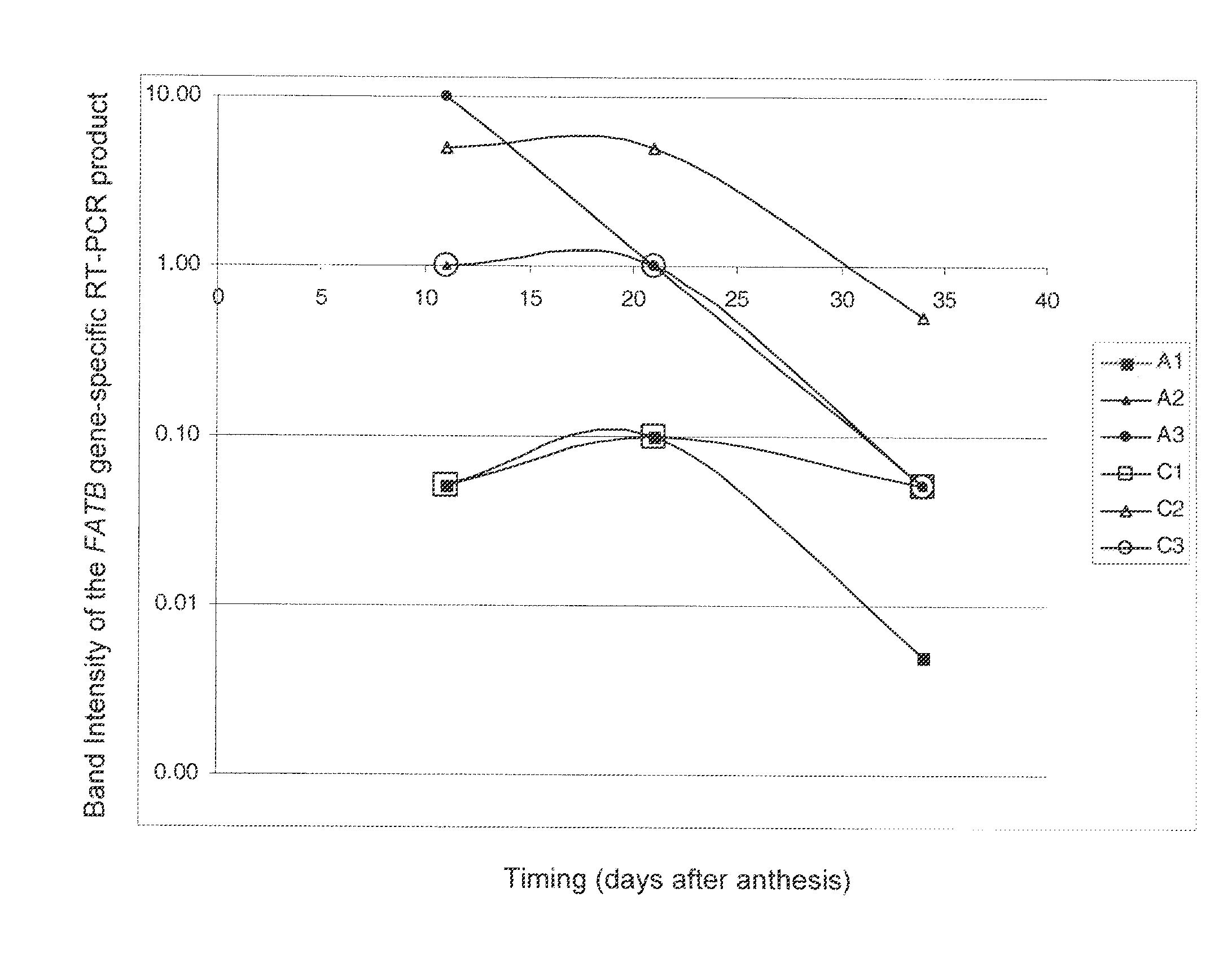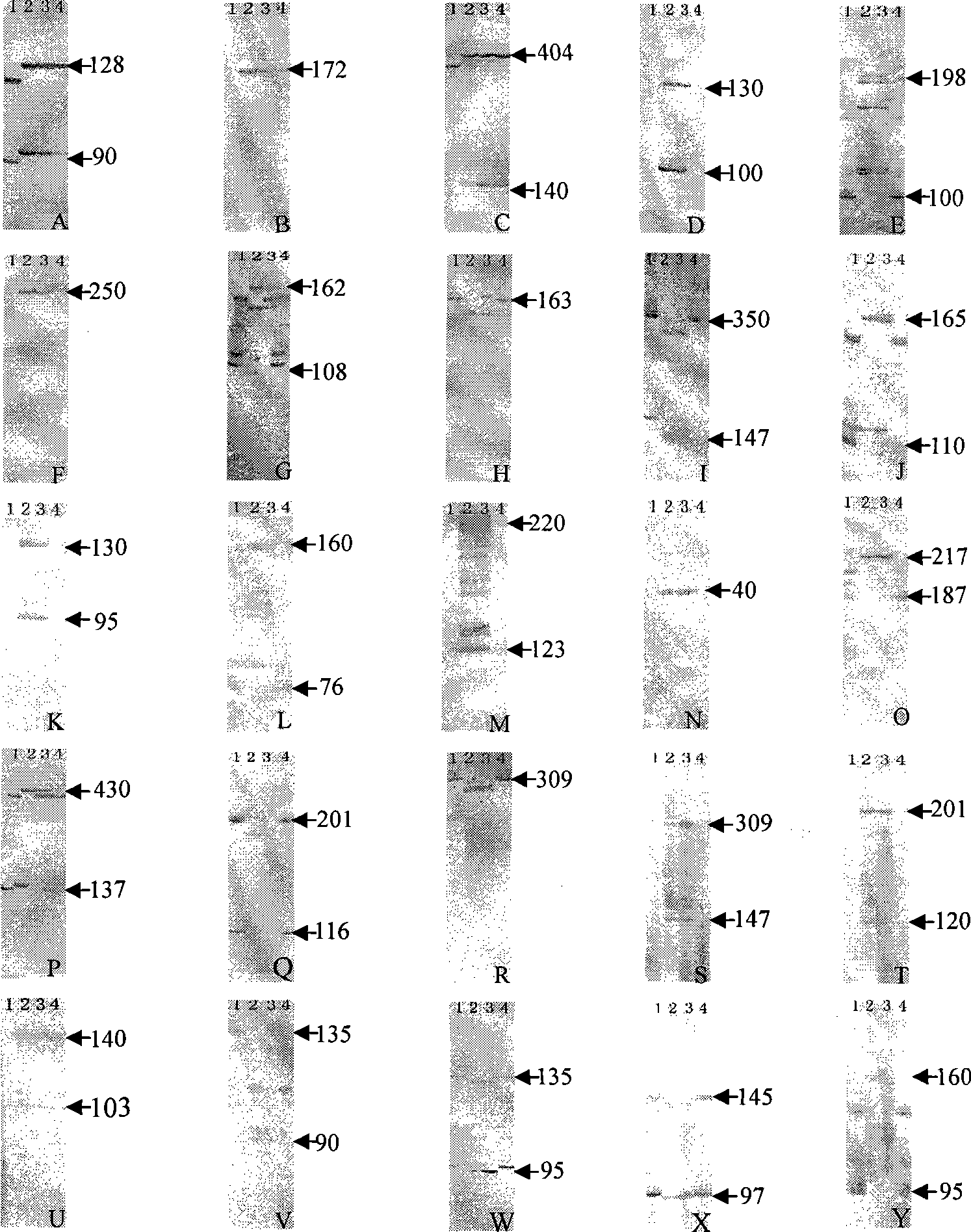Patents
Literature
277 results about "Brassica oleracea" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Brassica oleracea is a plant species that includes many common foods as cultivars, including cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower, kale, Brussels sprouts, collard greens, savoy, kohlrabi, and gai lan. In its uncultivated form, it is called "wild cabbage,” and is native to coastal southern and western Europe. A hardy plant in its uncultivated form, its high tolerance for salt and lime, and its intolerance of competition from other plants, typically restrict its natural occurrence to limestone sea cliffs, like the chalk cliffs on both sides of the English Channel, and the windswept coast on the western side of the Isle of Wight.
Brassica plant comprising mutant fatty acyl-acp thioesterase alleles
ActiveUS20110145944A1Reduce the amount requiredMinimal level of functional FATB proteinHydrolasesImmunoglobulinsAcyl carrier proteinWild type
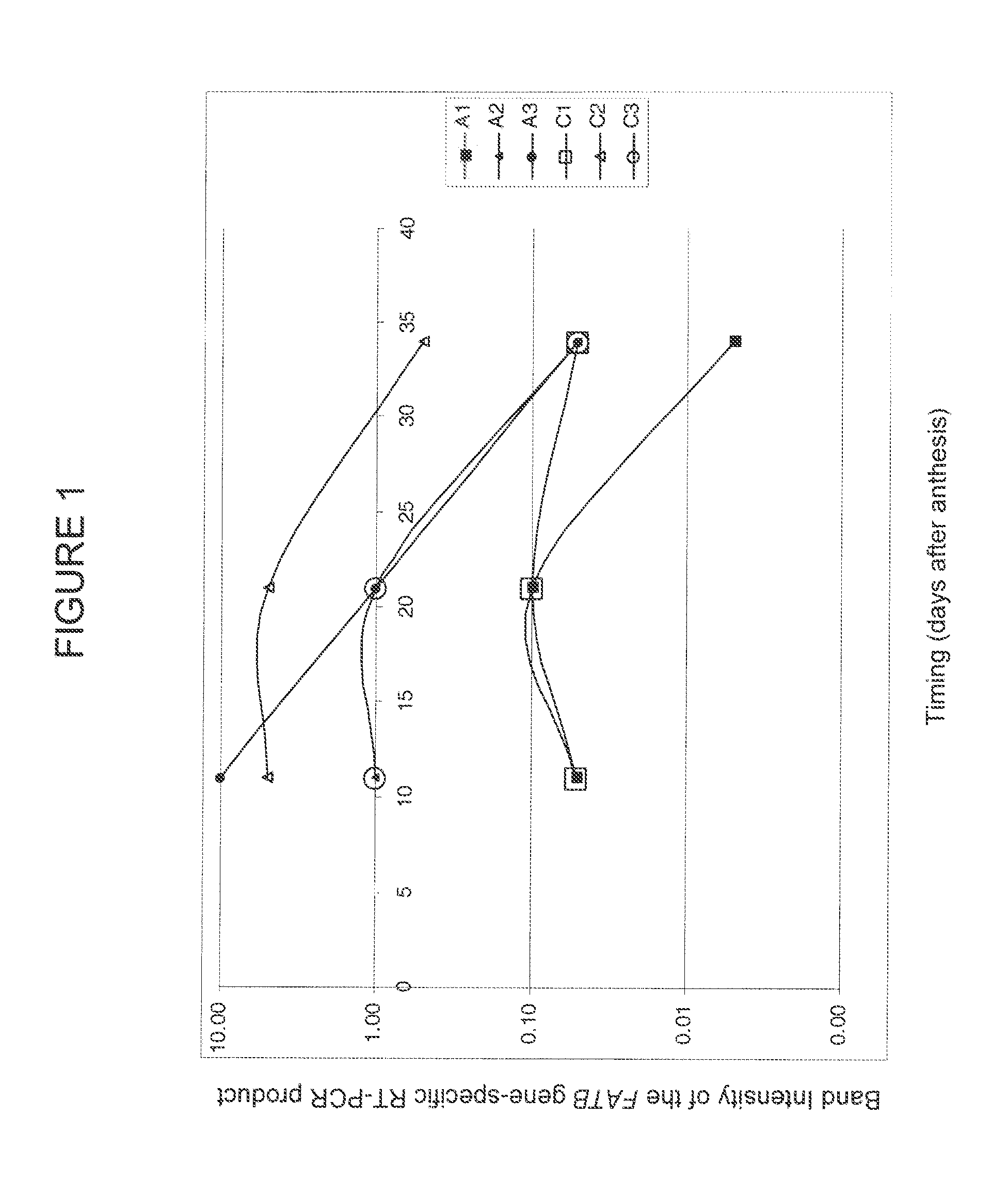
The invention relates to crop plants comprising novel seed lipid compositions. Provided are both wild type and mutant nucleic acid molecules encoding Brassica fatty acyl-acyl carrier protein (ACP) thioesterase B proteins (FATB) and the proteins as such. Also provided are Brassica plants, tissue and seeds comprising at least three mutant fatB alleles in their genome, whereby the seed oil fatty acid composition or profile is significantly altered.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCIENCE NV
Canola cultivar NQC02CNX25
ActiveUS20060075517A1DegreeImprove nutritional qualityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationCultivarBrassica oleracea
A canola cultivar, designated NQC02CNX25, plants and seeds of the NQC02CNX25 canola cultivar, methods for producing a canola plant produced by crossing the NQC02CNX25 cultivar with itself or with another canola plant, and hybrid canola seeds and plants produced by crossing the NQC02CNX25 cultivar with another canola cultivar or plant are provided.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Canola cultivar NQC02CNX25
ActiveUS7348473B2Improve nutritional qualityQuantitative precisionOther foreign material introduction processesTissue cultureCultivarBrassica oleracea
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Canola cultivar NQC02CNX12
InactiveUS7355100B2Improve nutritional qualityQuantitative precisionOther foreign material introduction processesTissue cultureCultivarBrassica oleracea
A canola cultivar designated NQC02CNX12, plants and seeds of the NQC02CNX12 canola cultivar, methods for producing a canola plant produced by crossing the NQC02CNX12 cultivar with itself or with another canola plant, and hybrid canola seeds and plants produced by crossing the NQC02CNX12 cultivar with another canola cultivar or plant are provided.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Novel canola cultivars having high yield and stabilized fatty acid profiles
ActiveUS20080260930A1Improve nutritional qualityFood preparationAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyΑ-linolenic acid
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
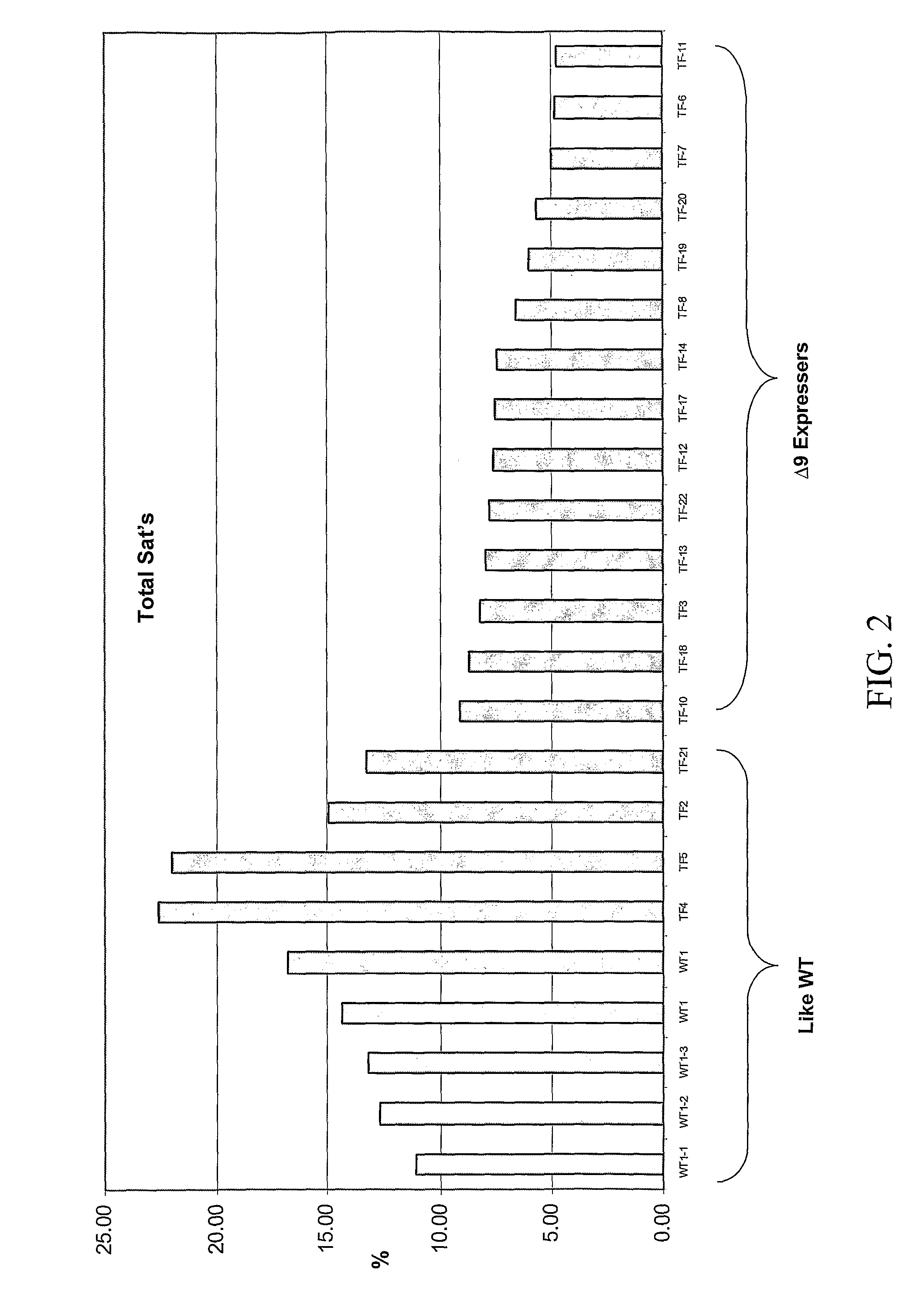
Certain Plants with "No Saturate" or Reduced Saturate Levels of Fatty Acids in Seeds, and Oil Derived from the Seeds
InactiveUS20080260933A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologySaturated Level
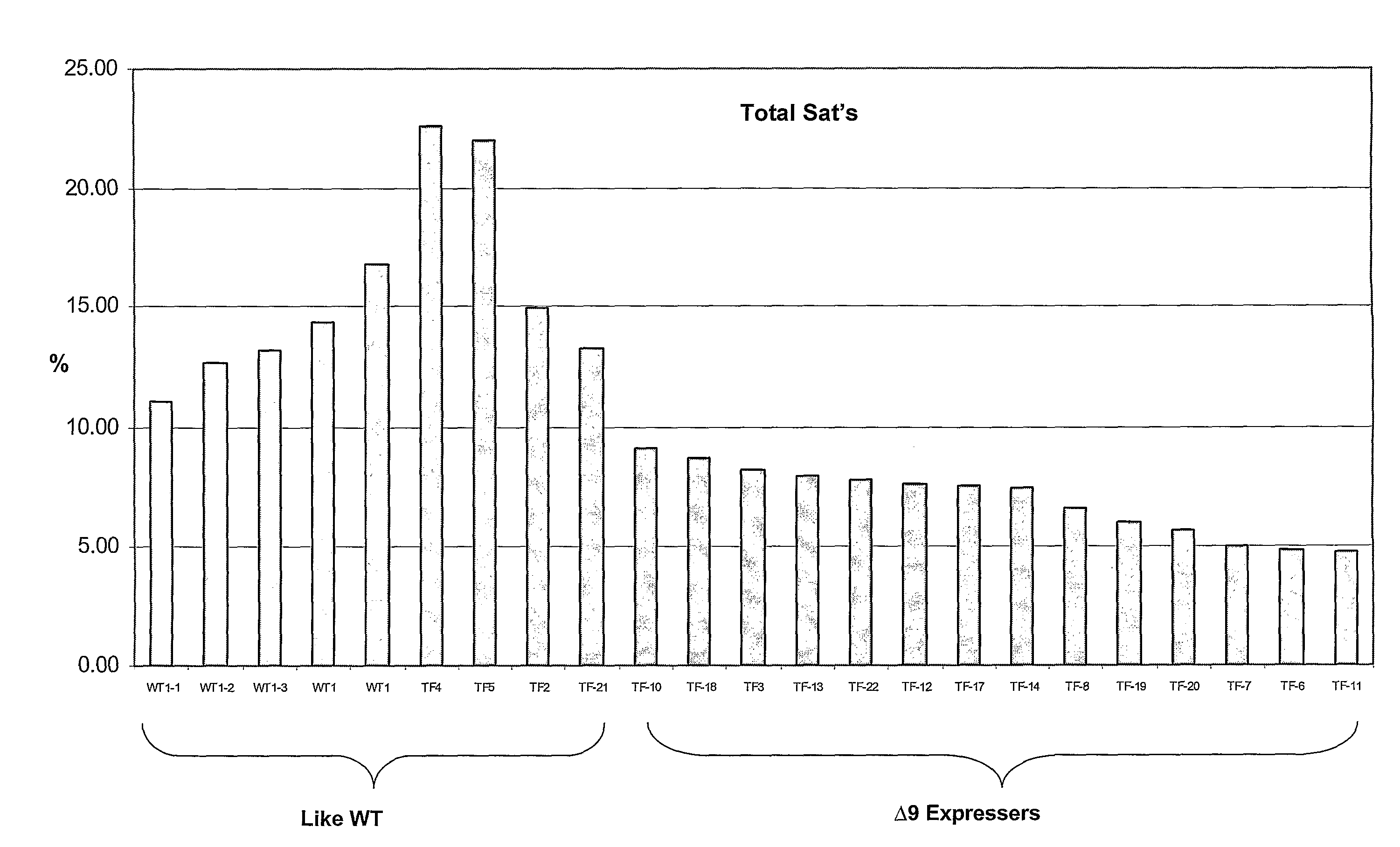
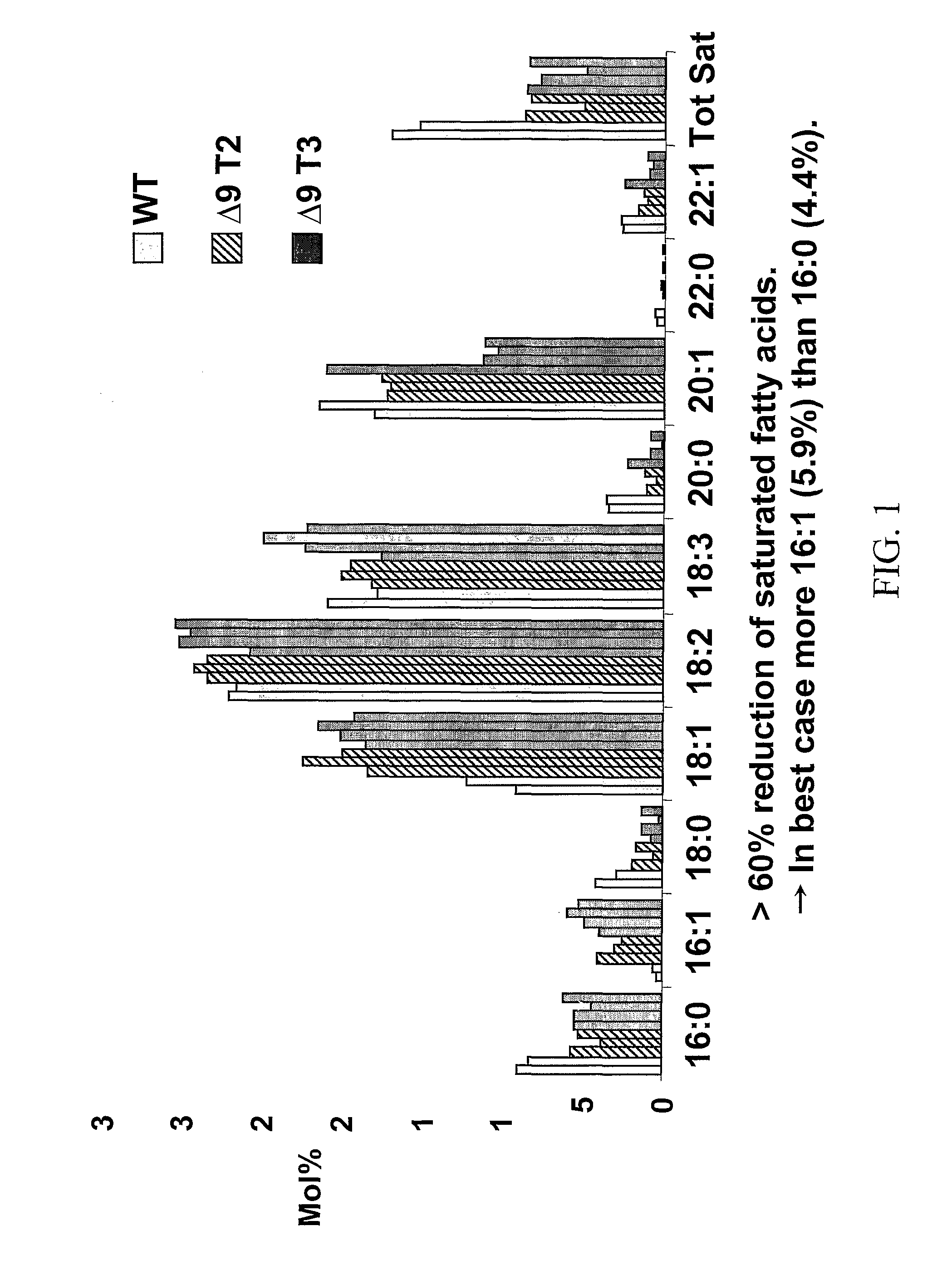
The subject invention provides “no sat” canola oil. The subject invention also provides seeds that can be used to produce such oils. Plants that produce these seeds are also included within the subject invention. All of this was surprisingly achieved by using a delta-9 desaturase gene in canola. This technology can be applied to other plants as disclosed herein. Oils of the subject invention have particularly advantageous characteristics and fatty acid profiles, which were not heretofore attained. The subject invention still further provides a plant-optimized delta-9 desaturase gene. The subject invention still further provides a plant-optimized delta-9 desaturase gene. In some preferred embodiments, a preferred plant comprises at least two copies of a delta-9 desaturase gene of the subject invention. Seeds produced by such plants surprisingly do not exhibit effects of gene silencing but rather have further surprising reductions in levels of total saturates.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Novel canola cultivars having high yield and stabilized fatty acid profiles
ActiveUS20120174266A1Improve nutritional qualityFruit and vegetables preservationOrganic chemistryΑ-linolenic acidOleic Acid Triglyceride
According to the invention, there are provided novel canola cultivars, seeds of canola cultivars, to the plants, or plant parts, of novel canola cultivars and to methods for producing a canola plants produced by crossing the novel canola cultivars with themselves or another canola cultivar, and the creation of variants by mutagenesis or transformation of the canola cultivars. The novel canola cultivar(s) include canola plants having a desired trait that includes an oleic acid value of about 70% and a yield greater than about 2100 kg / ha, and oils canola seeds having an oleic acid content of greater than about 70% and an α-linolenic acid value of less than about 3%.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Canola cultivar DN040244A
ActiveUS8563810B2Improve nutritional qualityTissue cultureVector-based foreign material introductionCultivarBrassica oleracea
The present invention relates to a new and distinctive canola cultivar, designated DN040244A. Also included are seeds of canola cultivar DN040244A, to the plants, or plant parts, of canola DN040244A and to methods for producing a canola plant produced by crossing the canola DN040244A with itself or another canola cultivar, and the creation of variants by mutagenesis or transformation of canola DN040244A.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Canola cultivar DN040839
ActiveUS7723578B2Improve nutritional qualityTissue cultureVector-based foreign material introductionCultivarCanola
The present invention relates to a new and distinctive canola cultivar, designated DN040839. Also included are seeds of canola cultivar DN040839, to the plants, or plant parts, of canola DN040839 and to methods for producing a canola plant produced by crossing the canola DN040839 with itself or another canola cultivar, and the creation of variants by mutagenesis or transformation of canola DN040839.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Canola cultivar DN051505
ActiveUS8324461B2Improve nutritional qualityTissue cultureVector-based foreign material introductionCultivarCanola
The present invention relates to a new and distinctive canola cultivar, designated DN051505. Also included are seeds of canola cultivar DN051505, to the plants, or plant parts, of canola DN051505 and to methods for producing a canola plant produced by crossing the canola DN051505 with itself or another canola cultivar, and the creation of variants by mutagenesis or transformation of canola DN051505.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
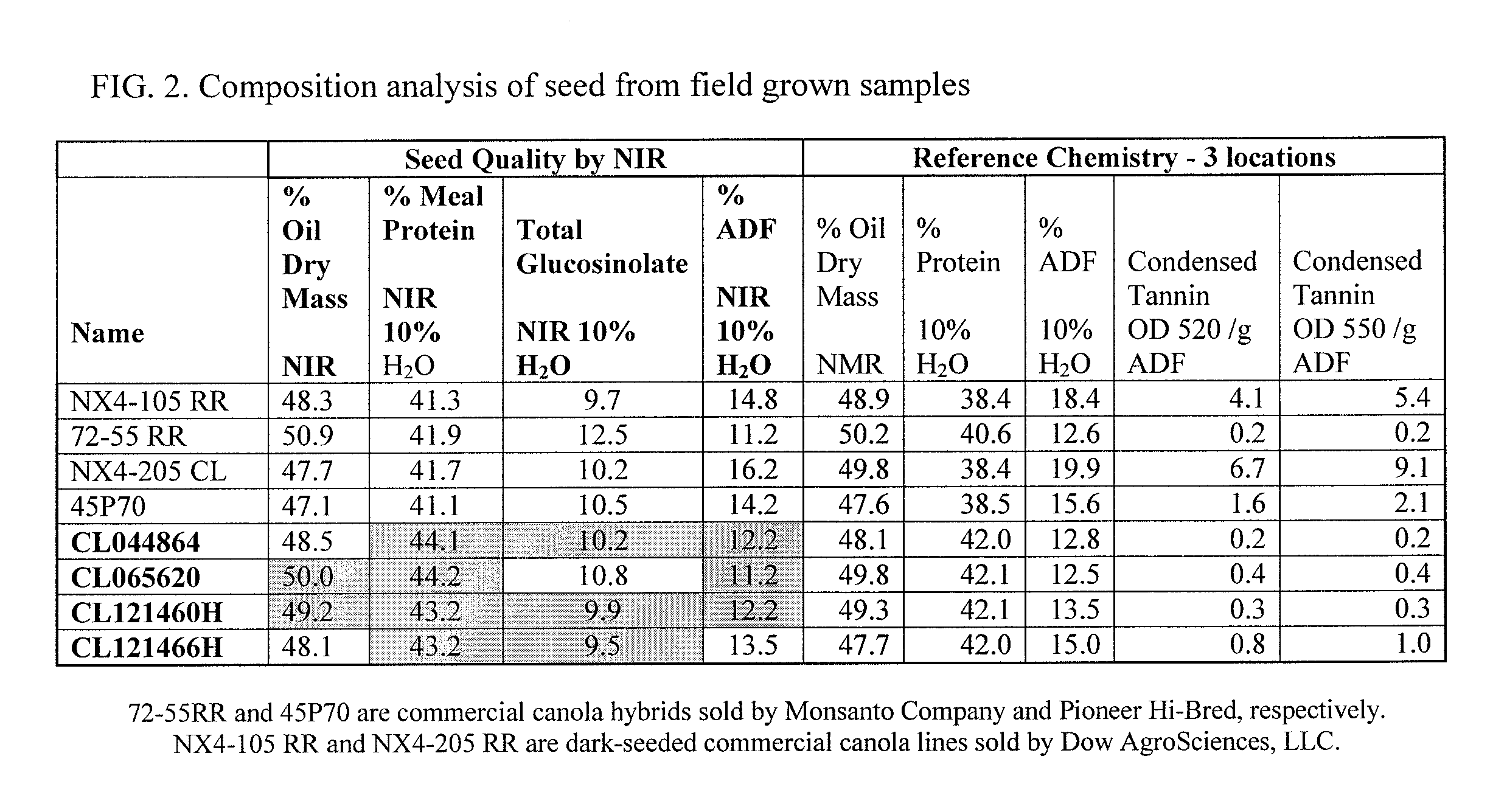
Canola Germplasm Exhibiting Seed Compositional Attributes That Deliver Enhanced Canola Meal Nutritional Value
ActiveUS20120216307A1High nutritional valueIncrease heightFood processingAnimal feeding stuffGermplasmPolyphenol
The present invention concerns a canola germplasm comprising at least 45% crude protein and not more than 18% acid detergent fiber content on an oil-free, dry matter basis. Certain embodiments further comprise one or more traits selected from the group consisting of reduced polyphenolic content and increased phosphorous content. In particular embodiments, the invention concerns canola plants comprising such germplasm and plant commodity products (e.g., seeds) produced therefrom. Canola plants comprising a germplasm of the invention may exhibit favorable seed composition characteristics that make them particularly valuable as a source for canola meal, and for methods of introducing at least one trait selected from the group consisting of high protein content, low fiber content, reduced polyphenolic content and increased phosphorous contentinto a canola variety in a seed coat color-independent manner.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Canola Germplasm Exhibiting Seed Compositional Attributes That Deliver Enhanced Canola Meal Nutritional Value Having Omega-9 Traits
ActiveUS20120213909A1High nutritional valueIncrease heightFruit and vegetables preservationFood processingFiberGermplasm
A canola germplasm confers on a canola seed the traits of high protein content and low fiber content, wherein the canola plant produces a seed having, on average, at least 68% oleic acid (C18:1) and less than 3% linolenic acid (C18:3). The canola seed traits may also include at least 45% crude protein and not more than 18% acid detergent fiber content on an oil-free, dry matter basis. Certain embodiments further comprise one or more traits selected from the group consisting of reduced polyphenolic content and increased phosphorous content. In particular embodiments, the invention concerns canola plants comprising such germplasm and plant commodity products (e.g., seeds) produced therefrom. Canola plants comprising a germplasm of the invention may exhibit favorable seed composition characteristics that make them particularly valuable as a source for canola meal.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Plants and seeds of spring canola variety scv384196
ActiveUS20090285968A1Improve nutritional qualityAnimal feeding stuffOther foreign material introduction processesGenetic MaterialsTransgene
A canola line designated SCV384196 is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of canola line SCV384196, to the plants of canola SCV384196, to plant parts of canola line SCV384196 and to methods for producing a canola plant produced by crossing canola line SCV384196 with itself or with another canola line. The invention also relates to methods for producing a canola plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic canola plants and plant parts produced by those methods. This invention also relates to canola lines or breeding lines and plant parts derived from canola line SCV384196, to methods for producing other canola lines, lines or plant parts derived from canola line SCV384196 and to the canola plants, varieties, and their parts derived from use of those methods. The invention further relates to hybrid canola seeds, plants and plant parts produced by crossing the line SCV384196 with another canola line.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Plants and seeds of spring canola variety scv328921
ActiveUS20090288184A1DegreeImprove nutritional qualityOther foreign material introduction processesFatty-oils/fats productionGenetic MaterialsTransgene
A canola line designated SCV328921 is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of canola line SCV328921, to the plants of canola SCV328921, to plant parts of canola line SCV328921 and to methods for producing a canola plant produced by crossing canola line SCV328921 with itself or with another canola line. The invention also relates to methods for producing a canola plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic canola plants and plant parts produced by those methods. This invention also relates to canola lines or breeding lines and plant parts derived from canola line SCV328921, to methods for producing other canola lines, lines or plant parts derived from canola line SCV328921 and to the canola plants, varieties, and their parts derived from use of those methods. The invention further relates to hybrid canola seeds, plants and plant parts produced by crossing the line SCV328921 with another canola line.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Plants and seeds of spring canola variety scv354718
ActiveUS20090288185A1DegreeImprove nutritional qualityOther foreign material introduction processesTissue cultureTransgeneBrassica oleracea
A canola line designated SCV354718 is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of canola line SCV354718, to the plants of canola SCV354718, to plant parts of canola line SCV354718 and to methods for producing a canola plant produced by crossing canola line SCV354718 with itself or with another canola line. The invention also relates to methods for producing a canola plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic canola plants and plant parts produced by those methods. This invention also relates to canola lines or breeding lines and plant parts derived from canola line SCV354718, to methods for producing other canola lines, lines or plant parts derived from canola line SCV354718 and to the canola plants, varieties, and their parts derived from use of those methods. The invention further relates to hybrid canola seeds, plants and plant parts produced by crossing the line SCV354718 with another canola line.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
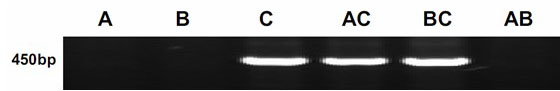
Method for rapidly detecting expression of ANS (Anthocyanidin Synthetase) genes from different sources in rape seed capsule and application thereof
InactiveCN102433379AEasy to detectQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyHeterologous
The invention discloses a method for rapidly detecting expression of ANS (Anthocyanidin Synthetase) genes from different sources in rape seed capsules. In the method, a specific primer capable of distinguishing ANS genes from chromosome sets A, B and C by cloning and analyzing sequences of ANS genes in three elementary species of rape (cabbage: the chromosome set is AA, and 2n=20; brassica oleracea: the chromosome set is CC, and 2n=18; and brown mustard: the chromosome set is BB, and 2n=16) and three allotetraploids (mustard type rape: the chromosome set is AABBA, and 2n=36; cabbage type rape: the chromosome set is AACC, and 2n=38; brassica carinata: the chromosome set is BBCC, and 2n=34) according to the nucleotide polymorphic loci of ANS genes from the chromosome sets A, B and C, and the ANS gene types expressed in the seed capsules of rape of different chromosome set types are identified in combination with an RT-PCR (Reverse Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction). The method plays a role in further researching the molecular adjusting mechanism for the color formation of rapeseed capsules and accelerating the variety breeding of yellow seed rape; and meanwhile, a novel methodfor detecting the source of a rape ANS gene is provided.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Supplement composition and method of use in enhancement of methylation process
InactiveUS20070021376A1Increase heightIncrease of methylationBiocideSulfur/selenium/tellurium active ingredientsS-Adenosyl-l-methionineMethylsulfonylmethane
A supplement composition for enhancement of methylation process is provided, which contains vitamin B6 (as pyridoxine HCl), folic acid, vitamin B12 (as cyanocobalamin), betaine HCl, and methylsulfonylmethane; and also contains S-adenosylmethionine. The supplement composition further includes silymarin (from milk thistle seed extract), N-acetyl L-cysteine, and cruciferious blend which includes broccoli (brassica oleracea var. talica), kale (brassica oleracea var. acephala), and radish (raphanus sativus). Further provided is a method of using the supplement composition for enhancement of methylation process.
Owner:SURACELL
Method for identifying celery cabbage-brassica oleracea alien addition lines
InactiveCN101423867AFacilitate communicationImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresisMolecular level
The invention discloses a method for identifying Chinese cabbage-cabbage addition lines. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting 91 pairs of primers in different linkage groups of cabbage according to a published cabbage genetic map; (2) extracting genetic groups DNA of different Chinese cabbages and cabbages to carry out PCR amplification; (3) electrophoretically separating an amplified product in modified polyacrylamide gel of 6 percent to carry out silver staining; (4) screening SSR primers in the linkage groups of the cabbage different from the Chinese cabbage; and (5) identifying the Chinese cabbage-cabbage addition lines by the SSR primers in the linkage groups of the cabbage different from the Chinese cabbage. The method has the advantages that the method can quickly and accurately identify important genetic analysis materials for the Chinese cabbage and the cabbage, such as coenospecies, addition lines, alien substitution lines, translocation lines and the like on molecular level, and lays foundation for modifying Chinese cabbage genetic background by cabbage gene.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Canola Extracts Containing High Levels of Phenolic Acids
ActiveUS20100143275A1Preventing and minimizing sunburnBiocideCosmetic preparationsMedicineSinapic acid
Disclosed in certain embodiments is a canola extract comprising greater than 30% sinapic acid, pharmaceutical compositions thereof, and methods thereof
Owner:1242753 ONTARIO INC
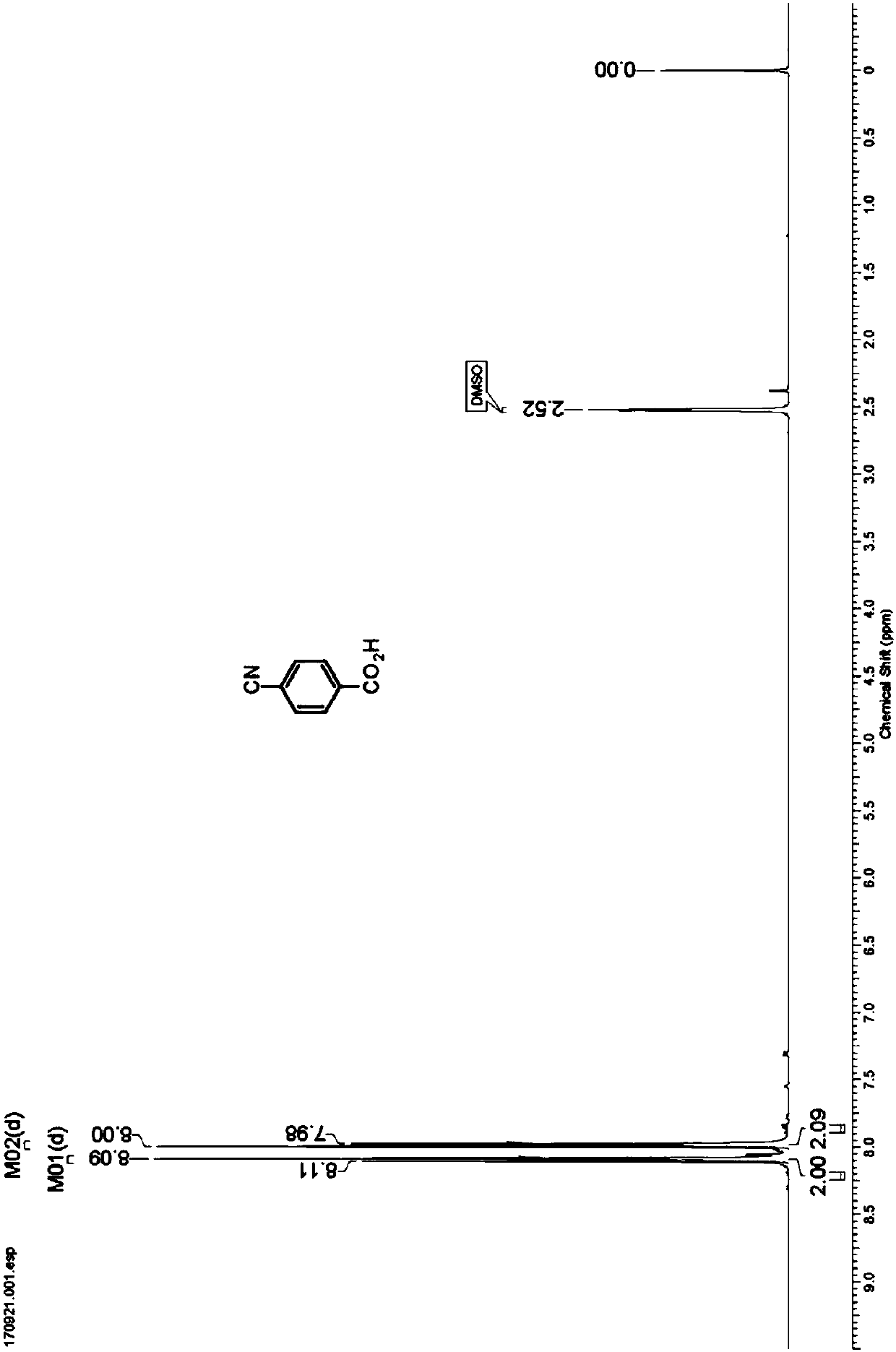
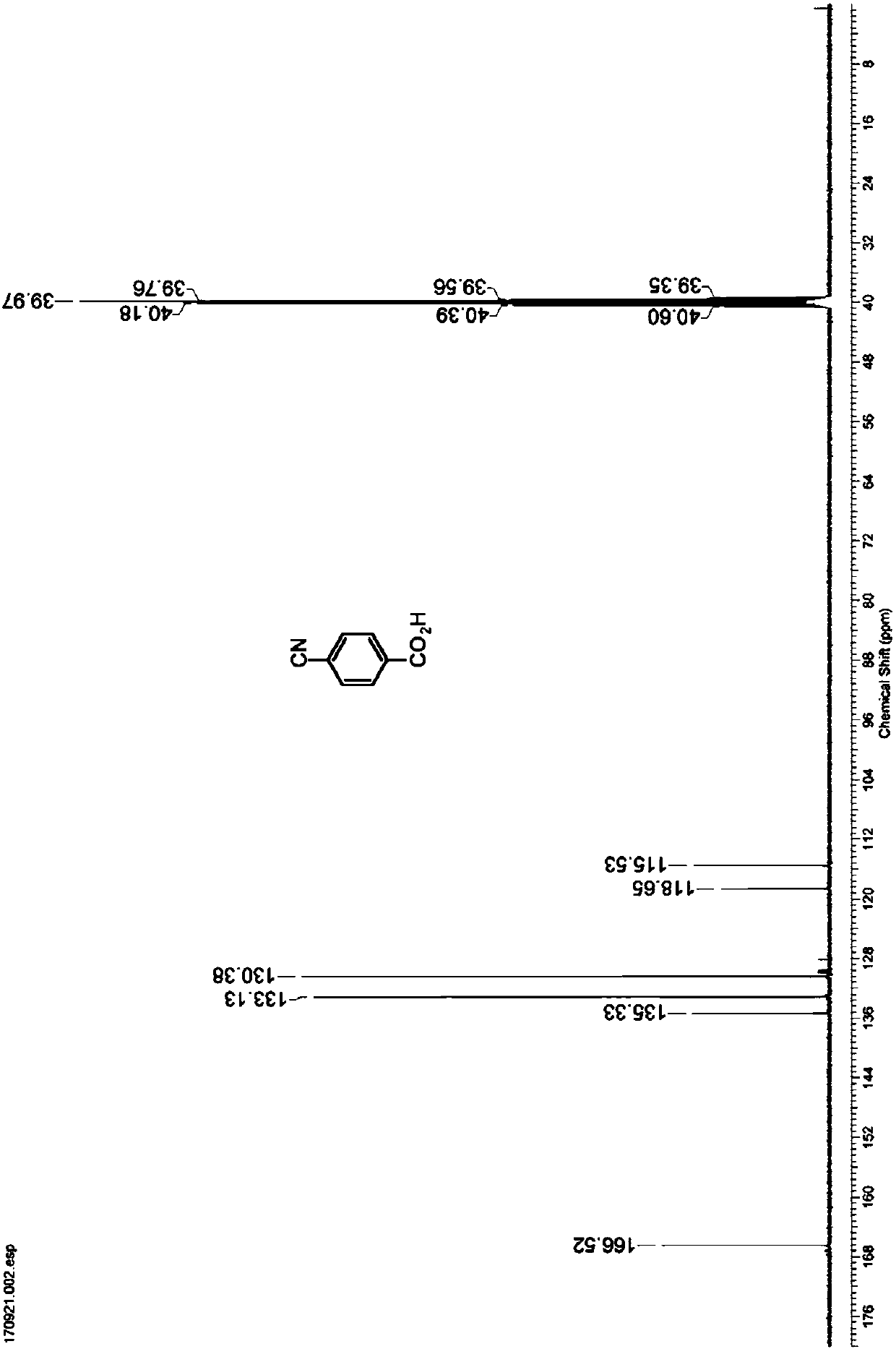
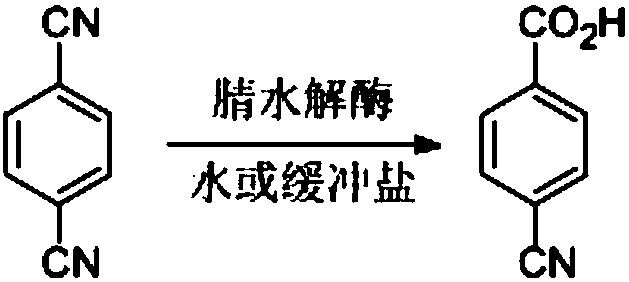
Nitrilase capable of preparing paracyanobenzoic acid by hydrolyzing p-benzenedicarbonitrile
ActiveCN107641622AMild reaction conditionsQuick responseHydrolasesFermentationArabidopsis thalianaPollution
The invention discloses a nitrilase N1 derived from pantoea sp.AS-PWVM4 and a gene thereof, a nitrilase N2 derived from arabidopsis thaliana and a gene thereof, a nitrilase N3 derived from acidovoraxfacilis 72W and a gene thereof, a nitrilase N4 derived from leptolyngbya sp. and a gene thereof, a nitrilase N5 derived from brassica oleracea var.oleracea and a gene thereof and a nitrilase N6 derived from camelina sativa and a gene thereof, and a method for preparing paracyanobenzoic acid as p-aminomethylbenzoic acid intermediate by using the nitrilase as a biological catalyst; resting cells ofthe corresponding nitrilases can be used for catalyzing 100g / L of substrate; the conversion rate is greater than 99%; the method has the obvious characteristics of mild reaction conditions, no pollution and simple process route, and has broad industrial application prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Molecular marker and specific primers for assisting in test of wilt disease resistance in brassica oleracea and use thereof
InactiveCN102108407AAchieve early selectionMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceSheath blight
The invention discloses a molecular marker and specific primers for assisting in test of wilt disease resistance in brassica oleracea and use thereof. The invention provides a reagent for assisting in the test of wilt disease resistance in brassica oleracea and / or assisting in screening brassica oleracea with wilt disease resistance, which is a specific primer pair formed by nucleotides represented by a sequence 2 and a sequence 3 in a sequence table. The invention also provides a specific gene fragment which is at a genetic distance about 2.87cM to the wilt disease resistance gene in brassica oleracea and is formed by nucleotides represented by a sequence 1 in a sequence table. The result of the identification of wilt disease resistance in brassica oleracea and / or screening of the brassica oleracea with wilt disease resistance with assistance from the reagent (primer pair) or sequence characterized amplified region (SCAR) marker, which are provided by the invention, is 97 percent consistent with that of field identification. When used in breeding, the reagent, molecular marker or method has the advantages of accuracy, quickness, capability of realizing early breeding and the like and has a bright application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES +1
Method for planting brassica oleracea L.var .botrytis L.
ActiveCN105766277APrevent diseaseEasy to transportBio-organic fraction processingMagnesium fertilisersDiseaseMoisture
The invention relates to the field of vegetable plantation, in particular to a method for planting brassica oleracea L.var .botrytis L..The method for planting brassica oleracea L.var .botrytis L.comprises the following steps of 1, variety selection; 2, seedling culture; 3, soil preparation and soil moisture regulation; 4, fertilizer application; 5, transplanting and field planting; 6, field management; 7, disease and insect pet prevention; 8, leaf binding and flower protection; 9, harvesting conducted in good time.The method is simple and convenient to operate, brassica oleracea L.var .botrytis L.can grow vigorously, resist to diseases and be high in quality and yield, cost can be saved, and synergism, ecological efficiency and environmental protection can be achieved.
Owner:通海高原农产品有限公司
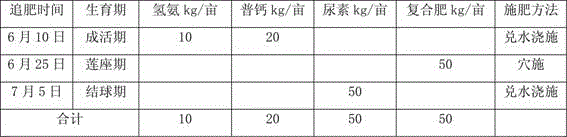
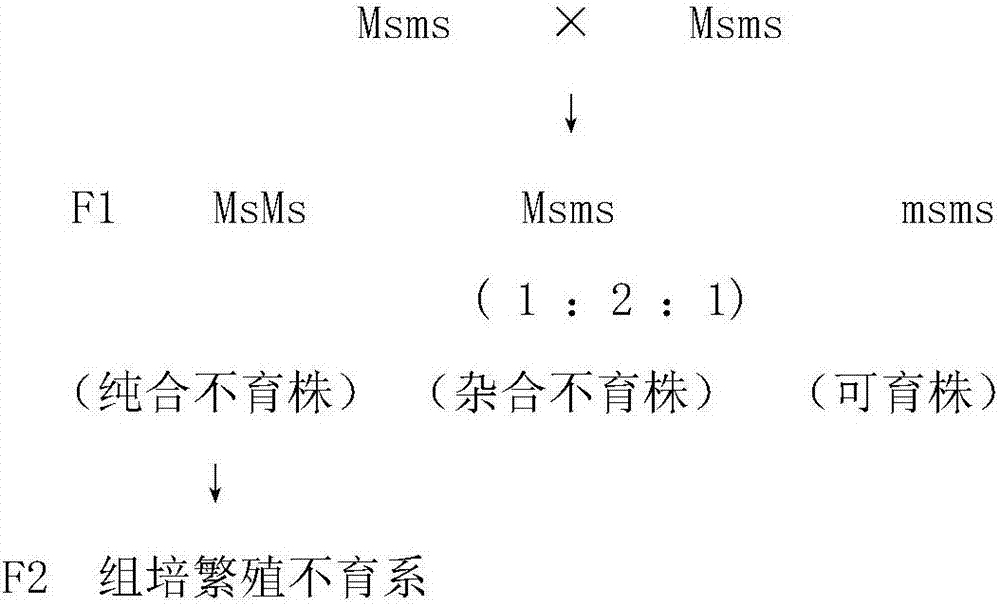
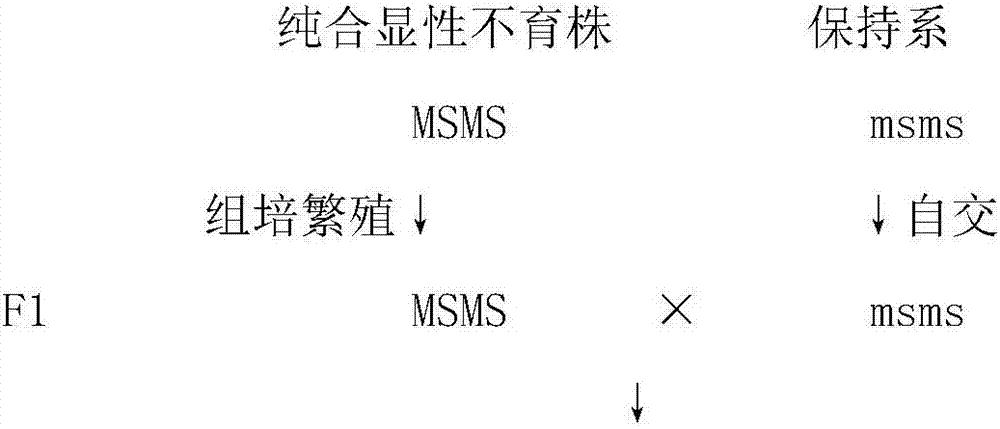
Brassica oleracea seed production technology
ActiveCN106962195AIncrease productionStable productionPlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsDiseasePollination
The invention discloses a brassica oleracea seed production technology, an adopted seed production method comprises the steps that a lateral bud is cut from a knot position and cultured on a culture medium, and subculture is performed in a lab continuously to obtain an original mother plant; seed reproduction of a sterile line is performed; a sun bed is prepared; a seeding tray is prepared; provisonal planting of the mother plant is performed; maintainer line seedling growing is performed; field planting is performed; pollination is performed; ventilation harvesting is performed; in the podding mid-term, maintainer line rows are removed; the row space is increased to facilitate ventilation and light transmitting, 70% of pods are cut when yellowing and dried for threshing after ripening; male parent seed reproduction is performed; the bud selection standard is strictly required, the bud stripping and pollination operation is standardized, and pollination marks are made; coeno-species seed reproduction is performed. According to the seed production technology, the yield can reach 65-75 kg / mu, the germination rate and the germination potential can reach up to 85% or above, the seed yield is high, and a foundation is laid for brassica oleracea stable production; after planting, the species has remarkable advantages over the other species on whether the disease resistance, the cold resistance, the physical shape or the yield, and the brassica oleracea is convenient to popularize, promote and plant.
Owner:ZHANGJIAKOU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for obtaining Brassica oleracea var. acephala DC. small spore regenerated plants and special culture medium
InactiveCN1922986AWide adaptabilityImprove embryo emergence rateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSporePlantlet
The invention relates to a method for obtaining collard regenerated plant and special cultivation base. Wherein, said method comprises (1), planting the collard into induced cultivation base, until the density is 5*10<4-5*10<5n / mL, at 30-35Deg.C and in dark, treating it at high temperature for 24-72hours, and under 24-26Deg. C and in dark, inducing idiosome; (2), when the idiosome has been formed, under 24-26Deg. C, 1500-2500Lux, cultivating for 5-10days while each day lights 14-18hours; then grafting the seed into differentiation cultivation base, to be cultivated in same conditions; (3) when grows out branch and leaf, transplanting it into rooting cultivation base, under 24-26Deg. C, 1500-2500Lux, lighting 14-18hours each day, to root, to obtain the collard regenerated plant.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
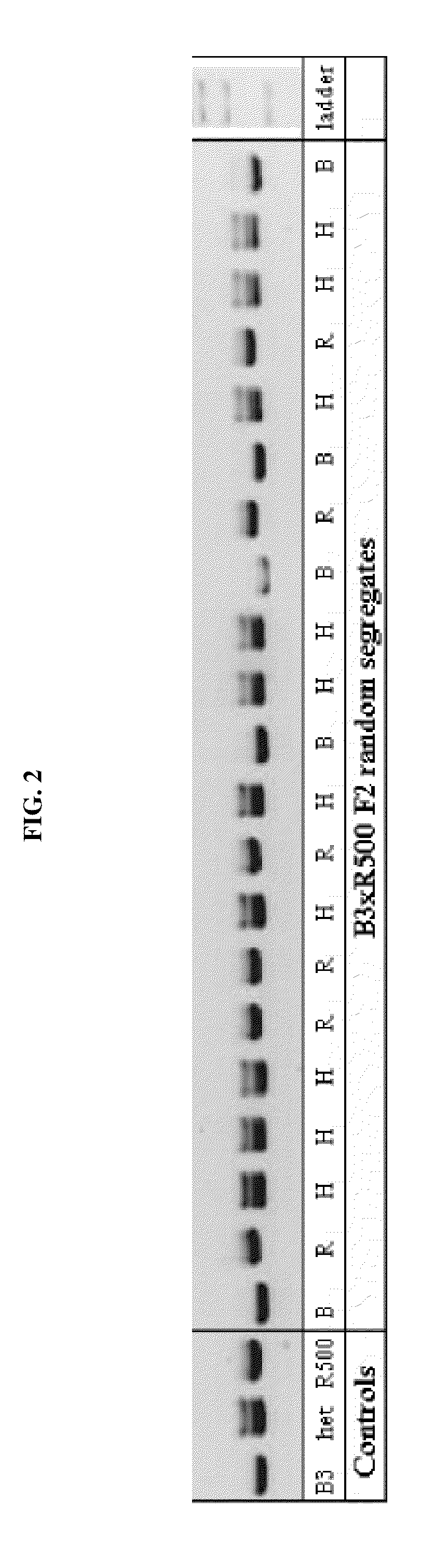
Self-compatible, rapid-cycling brassica rapa plants lacking inbreeding depression
The invention provides Brassica rapa plants and seeds thereof that are self-compatible, rapid-cycling and lack inbreeding depression. For instance, the invention provides plants and seeds of the Brassica rapa line designated B3. The invention thus relates to plants, seeds and tissue cultures of Brassica rapa plants that are self-compatible, rapid-cycling and lack inbreeding depression, such as Brassica rapa line B3, and methods to produce and propagate said plants by crossing such a Brassica rapa plant with itself, or another Brassica rapa plant. The invention further relates to seeds and plants produced by such crossing. Educational materials, such as a kit comprising said Brassica rapa plants are also provided by the invention.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Culture method for brassica oleracea L. var. acephala microspore regeneration plant
InactiveCN102228003AImprove embryo emergence rateImprove utilization efficiencyHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSporeHeat shock
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Method for efficiently obtaining regeneration plant by cultivating isolated microspores of brassica oleracea L.var.capitata L.
ActiveCN104429952AIncrease incidenceQuality improvementHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSporeGermplasm
The invention discloses a method for efficiently obtaining a regeneration plant by cultivating isolated microspores of brassica oleracea L.var.capitata L.. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing embryogenesis; and (2) performing embryo germination, thereby obtaining the regeneration plant, wherein the separated microspores are subjected to dark culture in a culture box at the temperature of 18+ / -0.5 DEG C until an embryoid visible to the naked eyes is generated in the step (1) of performing embryogenesis; and then the small embryoid is transferred to a dark shaking table at a speed of 50-55 revolutions per minute at the temperature of 25+ / -0.5 DEG C to perform shake culture until the cotyledonous embryoid is formed. According to the method, the genetically homogenous double-haploid plant materials can be obtained in batches, the germplasm resource innovation is accelerated, and the breeding progress is shortened. The method disclosed by the invention can be popularized and applied in the research field of molecular marker assisted breeding, mutant screening and cell totipotency mode systems of the brassica oleracea L.var.capitata L..
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Method for rapid propagation of brassica oleracea by grafting technique
The invention discloses a method for rapid propagation of brassica oleracea by a grafting technique. The method includes: selecting appropriate scions and stocks, adopting a bud grafting method for grafting, creating an integral moisture-preserving heat-preserving high-irradiation environment after grafting, managing properly after greening of scion brassica oleracea axillary buds, and finally subjecting scion brassica oleracea to rooting and transplanting. According to the method, brassica oleracea is easy in bolting, grafting to rachises is simpler and more convenient in operation than grafting to dwarf stems, bolts are easy to form lateral bolts, and more stock sources can be provided. By adoption of the bud grafting method, simplicity in operation is achieved, pollution procedures are reduced, and scion survival rate can be increased. White brassica oleracea axillary buds are subjected to strong light exposure after grafting, the white axillary buds can be induced to generate chlorophyll, and accordingly grafting survival rate can be increased. By adoption of tin foil paper for making a simple funnel-shaped rooting device, a moisture preserving environment can be created, induction for rooting is facilitated, and the survival rate is increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Vegetable interplanting method
InactiveCN102668839ATake advantage ofThe benefit of increasing production and income is obviousClimate change adaptationHorticultureLand resourcesSpinacia
The invention discloses a vegetable interplanting method which can be implemented all year around. According to the technical scheme, spinach is planted at the beginning of November, Malabar spinach is planted in the middle of November, and spinach and Malabar spinach are interplanted; next year, after spinach is harvested from early March to the middle of March, rape is planted; after Malabar spinach is harvested from early March to the beginning of April, bitter chrysanthemum is planted and rape and bitter chrysanthemum are interplanted; after rape is harvested from the beginning of May to the late May, lettuce is planted; after bitter chrysanthemum is harvested from the beginning of June to the end of July, brassica oleracea is planted and the lettuce and the brassica oleracea are interplanted; after lettuce is harvested from early August to the beginning of September, leaf lettuce is planted, the brassica oleracea is harvested from the early October to late October, and the leaf lettuce is harvested at the beginning of November. According to the method disclosed by the invention, various vegetables can be produced all year round after being combined and interplanted, thus fully utilizing land resources, and having obvious benefits in both production increase and income increase.
Owner:屯留县五里庄绿源方舟蔬菜种植专业合作社
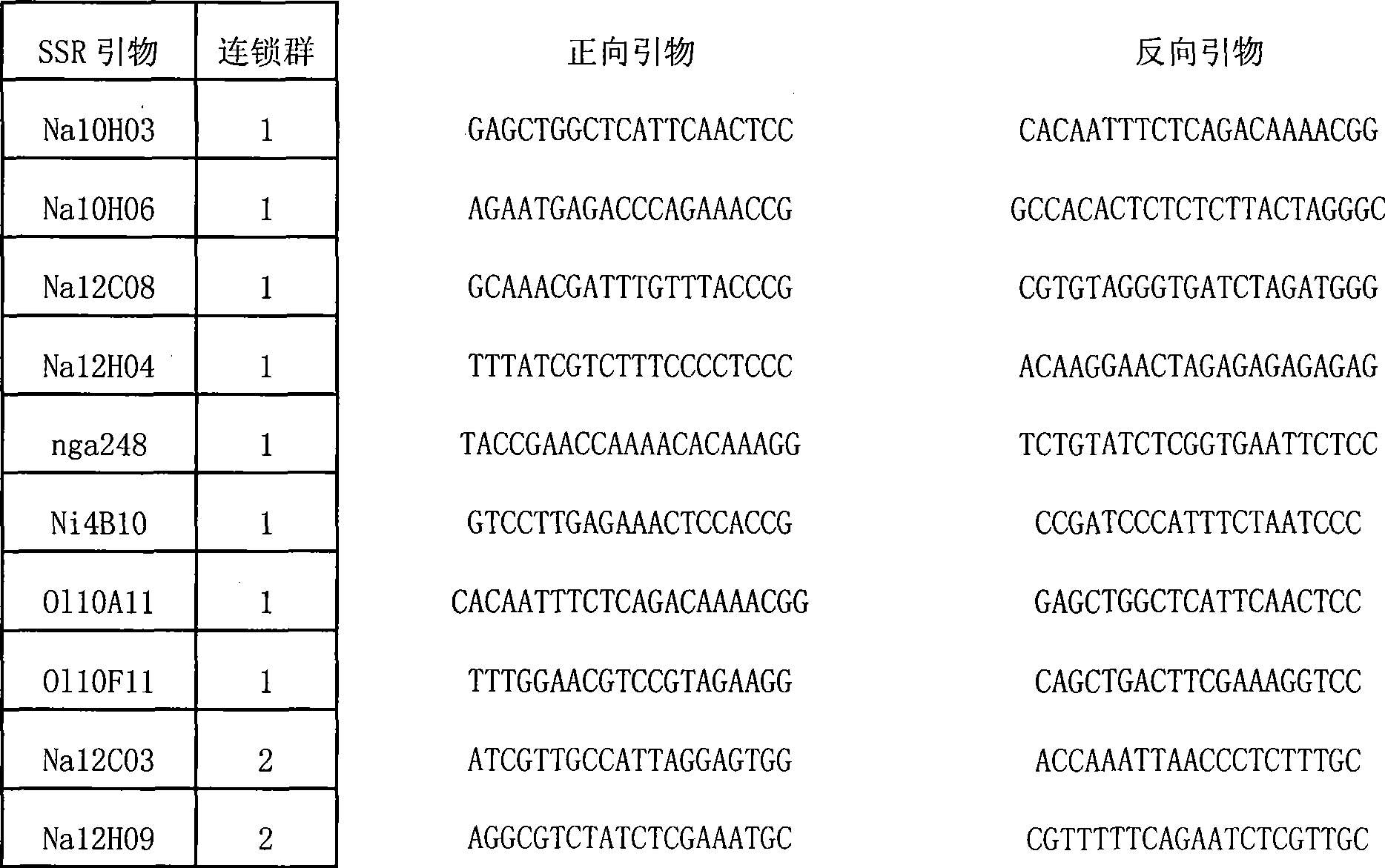
SSR labels of brassica oleracea red leaf gene Re and application thereof
InactiveCN104846081AImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention provides two SSR labels that located on both sides of the brassica oleracea red leaf gene Re and are closely linked to the gene, i.e. C9Z90 and C9Z94. The genetic distances between the two labels and the Re gene are 0.3cM and 2.0cM respectively. According to the nucleotide sequences of the two labels, two pairs of specific amplification primers are designed respectively for molecule assisted selection of brassica oleracea white leaf gene. In the assistant selection process, the two labels can be used at the same time, and have the characteristics of good repeatability, high reliability, low detection cost, and time saving and labor saving.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com