Patents
Literature
98 results about "Interspecific hybrids" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An interspecific hybrid is a cross between plants in two different species. Many times they will be from the same genus, but not always. The resulting plant may or may not be sterile. Crop yields increase dramatically when hybridization is used to exceed one or more of the parents in size and reproductive potential.
Novel method for improving achievement rate of first backcross hybrid generation of oryza sativa and oryza minuta
InactiveCN102668973AEasy to shatterReduced shatteringHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureOryzaAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the technical field of cross breeding of plants and relates to a novel method for improving an achievement rate of a first backcross hybrid generation of oryza sativa and oryza minuta. The method includes that firstly, the oryza sativa is used as a female parent, the oryza minuta is used as a male parent, and the oryza sativa and the oryza minuta are subjected to hybridization and embryo rescue to obtain an interspecific hybrid F1 plant; secondly, the interspecific hybrid F1 plant is used as a female parent, the corresponding oryza sativa is used as a male parent, the interspecific hybrid F1 plant and the corresponding oryza sativa are subjected to backcross, by means of a method which is similar to a method of hybrid rice seed production, and the pollination is directly performed for 3 consecutive days to obtain a plurality of young embryos of a first wide cross and backcross hybrid generation; and finally, the plurality of young embryos are subjected to the embryo rescue to obtain the first backcross hybrid generation BC1F1 plant. According to the novel method for improving the achievement rate of the first backcross hybrid generation of the oryza sativa and the oryza minuta, the method is simple in operating and low in cost, the achievement rate can be stably improved from current 0.02% -0.03% to 0.32%-0.35%, and the problem that the first backcross hybrid generation BC1F1 of the oryza sativa and the oryza minuta is difficult to achieve is solved.
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院水稻研究所
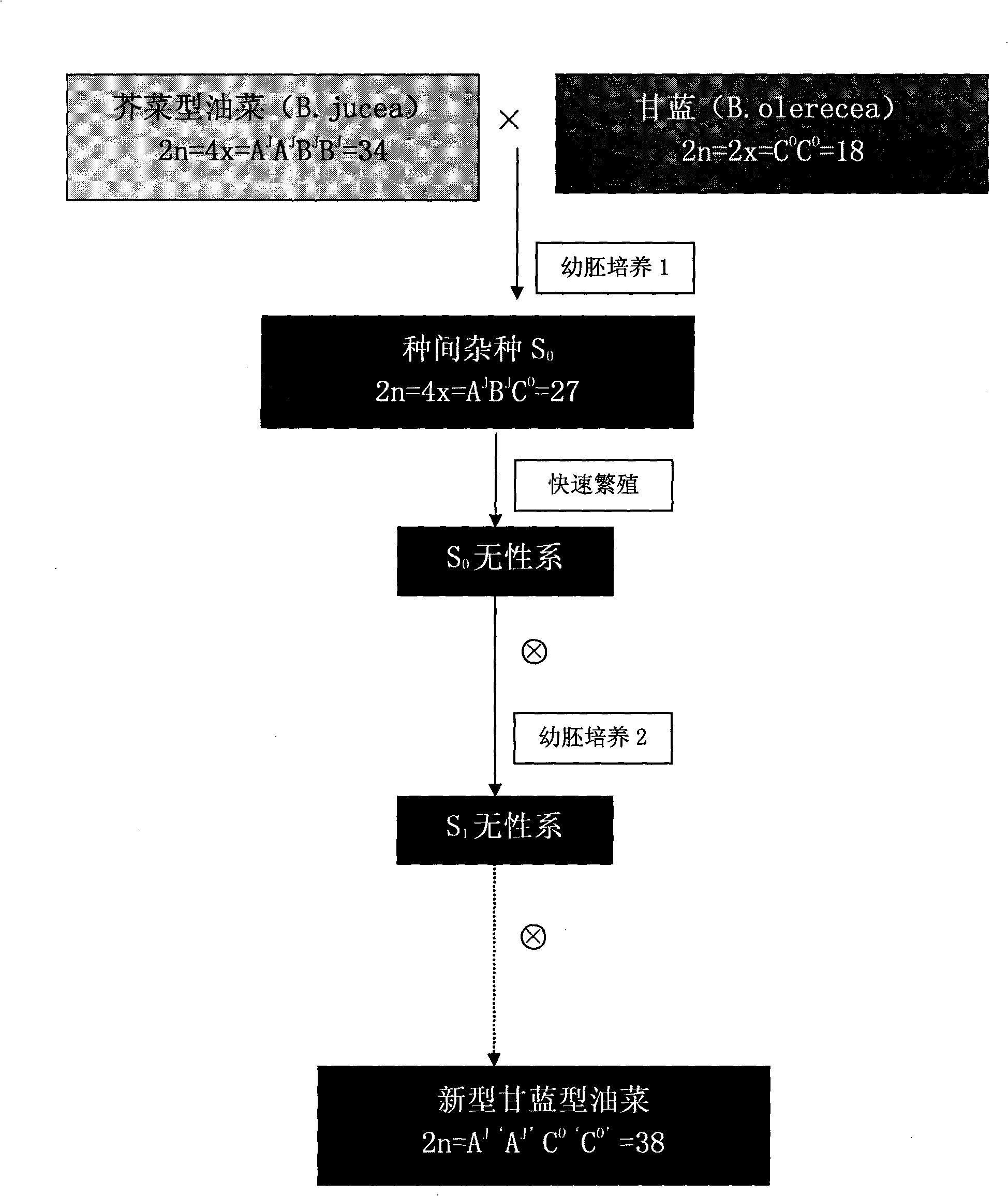
Method for artificially developing novel brassica napus
InactiveCN101513168AIncrease production levelsEfficient use ofClimate change adaptationPlant genotype modificationBrassicaInterspecific hybridization
The present invention provides a method for artificially developing novel brassica napus. The excellent characters of cabbage and mustard type rape are integrated for obtaining novel brassica napus. The hybridization compatibility when the mustard type rape and cabbage are used for executing interspecific hybridization is higher than the hybridization compatibility when the Chinese cabbage and cabbage are used for executing interspecific hybridization. The interspecific hybrid is easily obtained, and simultaneously, the advantages of drought resistance, cold resistance, excellent strain type, etc. of the mustard type rape can be introduced into the brassica napus. The method of the invention also has the advantages of stable heredity, high speed, large area of character variation and facilitation for selecting the brassica napus with excellent charcter. Furthermore, the chromosomes of AC chromosome set of brassica napus obtained from the method of the invention respectively come from the mustard type rape and cabbage, have larger difference from the prior brassica napus. The use of hybrid vigor of genome of brassica napus is facilitated and the production level of cabbage is increased.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Interspecific hybrid embryo rescuing and seedling forming method of sweet cherries in southern China and Chinese cherries
PendingCN110050690ALearn about developmental statusDetermine the best time for developmentCultivating equipmentsPlant tissue cultureAnthriscus cerefoliumShoot
The invention relates to the field of cross breeding of plants and particularly relates to an interspecific hybrid embryo rescuing and seedling forming method of sweet cherries in southern China and Chinese cherries. The method combines advantages of European sweet cherries and the Chinese cherries, and takes the 'European sweet cherries' as a female parent and the 'Chinese cherries' as a male parent to carry out interspecific distant hybridization. Aiming at the abortion problem of a distant hybrid embryo, the hybrid embryo is subjected to embryo rescuing. A proper sampling period of the embryo rescuing of each hybrid combination, concentrations and ratios of respective exogenous growth regulators for hybrid young embryo germination, subculture propagation and rooting culture, and a proper acclimatization and transplanting method are determined. By applying an interspecific hybrid embryo rescuing system of the sweet cherries in southern China and the Chinese cherries, which is established by the technology, the embryo germination rate reaches 80.00 percent, the multiplication coefficient of subculture hybridized new shoots reaches 5.0, the rooting rate of rooting culture is 90.91percent, the growth vigor of embryo culture seedlings is good and the seedlings grow robustly and have green leaves, and the acclimatization and transplanting survival rate reaches 77.27 percent.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
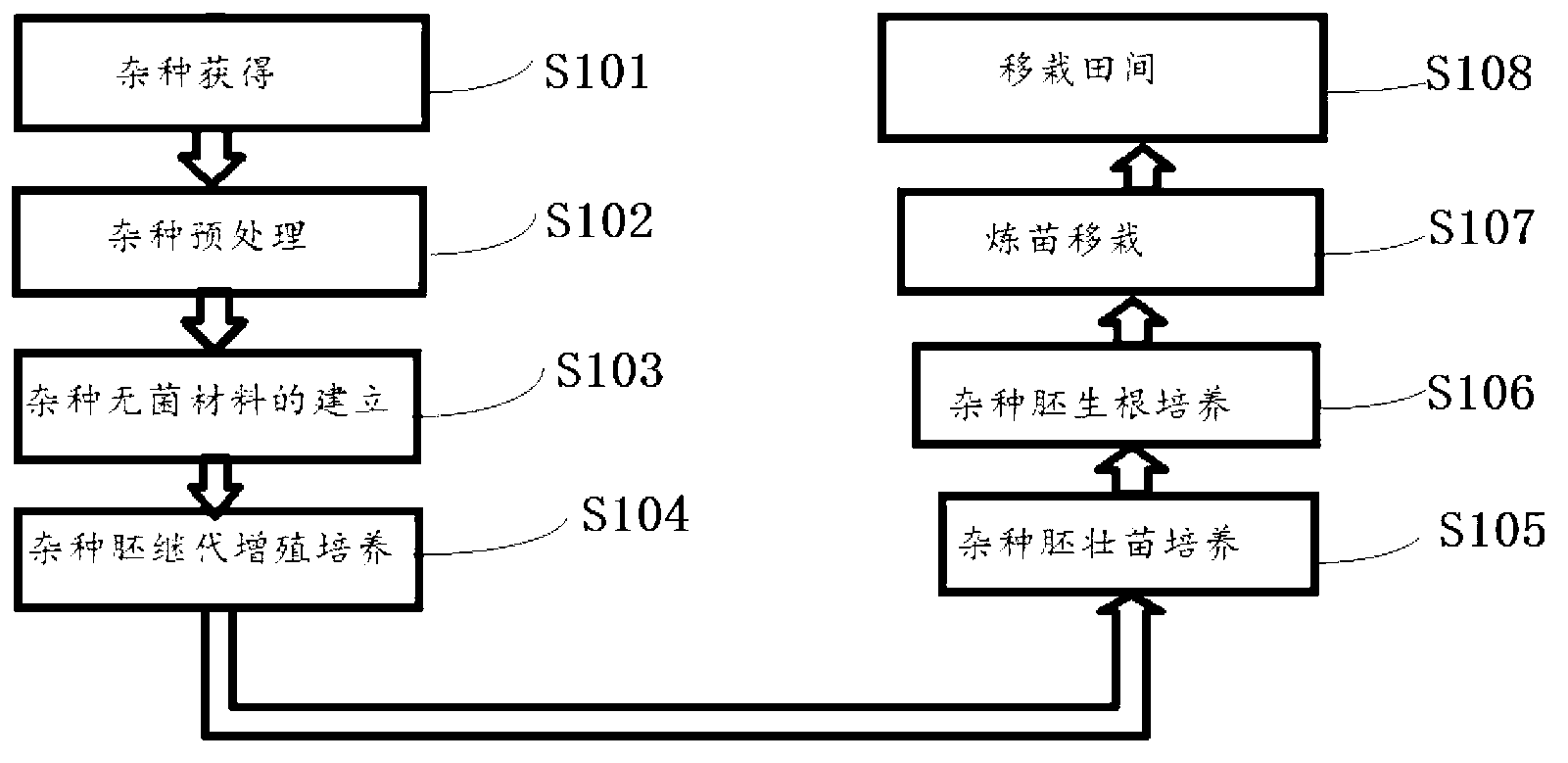
Novel isolated culture method for cherry intraspecies and intraspecific hybrid embryo
InactiveCN103283606AInterest activityInterest productivityPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsEconomic benefitsEmbryo
The present invention discloses a novel isolated culture method for cherry intraspecies and intraspecific hybrid embryo. The novel isolated culture method comprises: hybrid obtaining, a hybrid pretreatment, hybrid sterile material establishment, hybrid embryo subculture, hybrid embryo strong seedling culture, hybrid embryo rooting culture, seedling exercising transplantation, and transplanting into field. According to the present invention, the hybrid embryo isolated culture method is utilized, such that a male parent for new cherry variety breeding and having excellent characteristics and a female parent for new cherry variety breeding and having excellent characteristics can be effectively screened, it is ensured that the bred filial generation has the same excellent characteristics of the male parent and the female parent, and the bred hybridization variety has targeting property and universality; and a large number of cherry seedlings can be rapidly bred in a low cost manner, and a production period is short, such that economic benefits are good, and good market prospects are provided.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Cultivated rice hybrid infertility gene S1 and application thereof
InactiveCN104561062AVerify accuracyIncrease productionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPhysiologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a cultivated rice hybrid infertility gene S1 and application thereof. The S1 gene comprises two alleles S1-j and S1-g; the nucleotide sequence of S1-j is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1; and the nucleotide sequence of S1-g is shown as SEQ ID NO. 2. A plurality of molecular markers suitable for positioning the S1 gene are firstly developed by a map-based cloning method to construct an ultra-large positioning colony suitable for positioning, the cultivated rice hybrid infertility gene S1 is positioned and cloned to obtain a candidate gene ORF12, and respective full length sequences of S1 alleles of hybrid parents are further measured, to discover that the S1 genes of the hybrid parents show allelic similarity and difference of hybrid infertility reasons. The S1 gene is a first cloned rice hybrid infertility gene at home, and can provide a firm theoretical basis for solving the problem of rice hybrid male and female sterility, guiding rice breeding and further improving the yield of rice.
Owner:LINGNAN NORMAL UNIV
Method for constructing collard cytoplasmic male sterility near-isogenic lines
The invention discloses a method for constructing collard cytoplasmic male sterility near-isogenic lines, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: A, selecting the variety of collard, performing selfing to the ninth generation, and using the ninth generation as a receptor; B, selecting a cytoplasmic male sterile Chinese cabbage selfed line as an CMS donor; C, using the donor as a female parent, using the receptor as a male parent, performing interspecific hybridization to obtain interspecific hybrid, and successfully transforming the CMS genes to collard; D, performing authenticity identification on the interspecific hybrid; E, using the interspecific hybrid in the interspecific hybridization as a female parent, using a receptor collard selfed line as a recurrent parent, and performing back crossing to the sixth generation to breed a collard cytoplasmic male sterility line which forms a pair of near-isogenic lines with the recurrent male parent; and F, analyzing the near-isogenic property between the back-crossed sixth generation and the recurrent parent. The invention provides a method for constructing collard cytoplasmic male sterility near-isogenic lines, obtains the collard cytoplasmic male sterility near-isogenic lines, and provides a parent material for producing advantageous hybrid of the collard.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Method for interspecific hybrid genome in-situ hybridization of crambe cordifolia
InactiveCN104745695AEasy to shapeGood dispersionMicrobiological testing/measurementDispersityConcentration ratio
The invention belongs to the technical field of crop molecular breeding, and in particular relates to a method for interspecific hybrid genome in-situ hybridization of crambe cordifolia. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a probe marker, preparing a slide, performing in-situ hybridization, performing signal detection and the like. In the slide preparation process, a chromosome slide which is good in morphology and good in dispersity in the meiosis period of crambe cordifolia can be obtained under appropriate enzymolysis conditions by using an acetic acid extension flame drying method. When probes and chromosomes are modified, appropriate temperature and time can be selected, appropriate blocking DNA and a probe concentration ratio can be confirmed, fluorescent in-situ hybridization images with clear signals can be obtained, and different interspecific chromosomes of hybrid crambe cordifolia species can be clearly identified, so that genome in-situ hybridization can be well applied to cytological detection of crambe cordifolia species with characteristics of a large number of chromosomes, small morphology and the like, and novel techniques and methods are provided for identification and structural research on crambe cordifolia chromosomes, evolution research on crambe cordifolia, and the like.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Identifying method for pleurotus nebrodensis-pleurotus eryngii interspecific hybrid
InactiveCN102618663AShort detection timeImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementPleurotus nebrodensisBio engineering
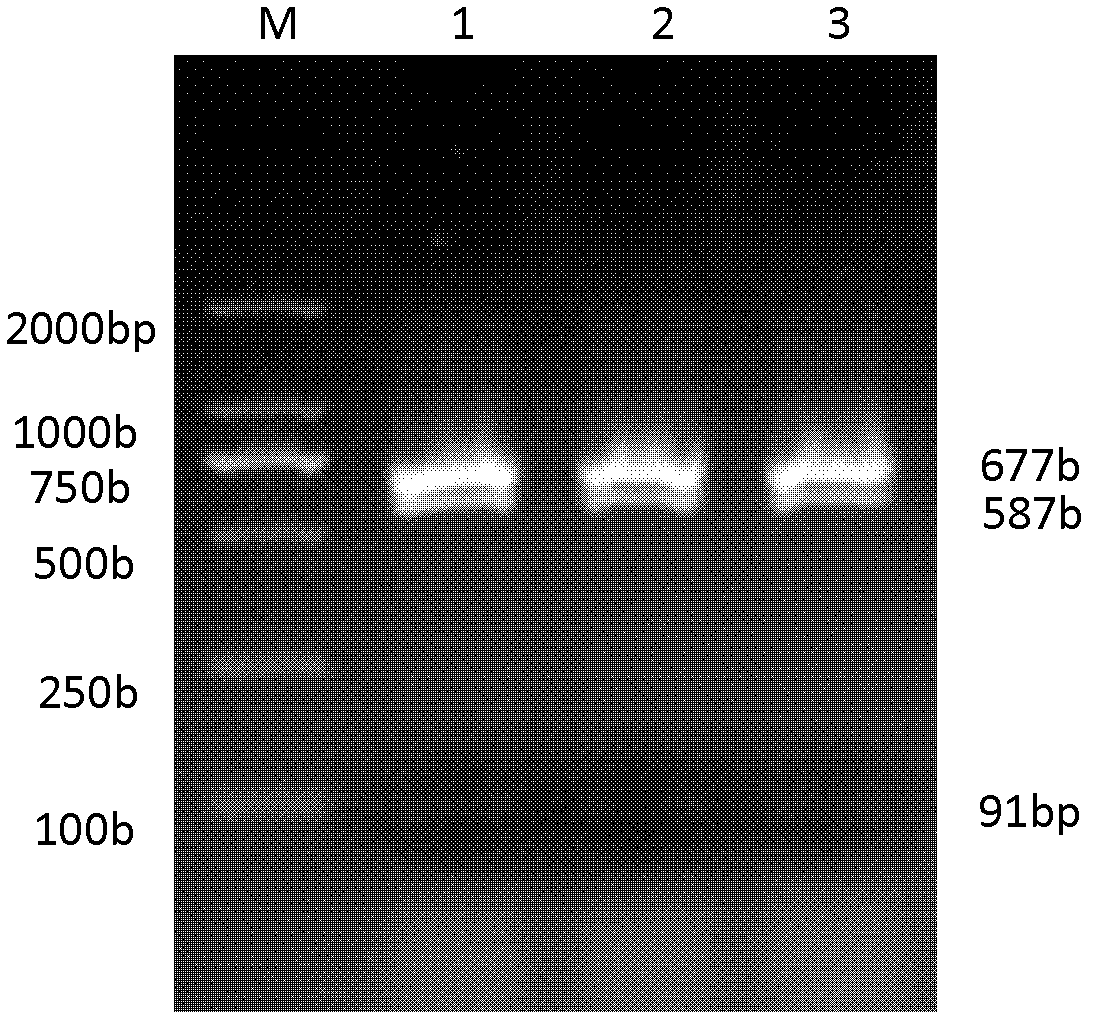
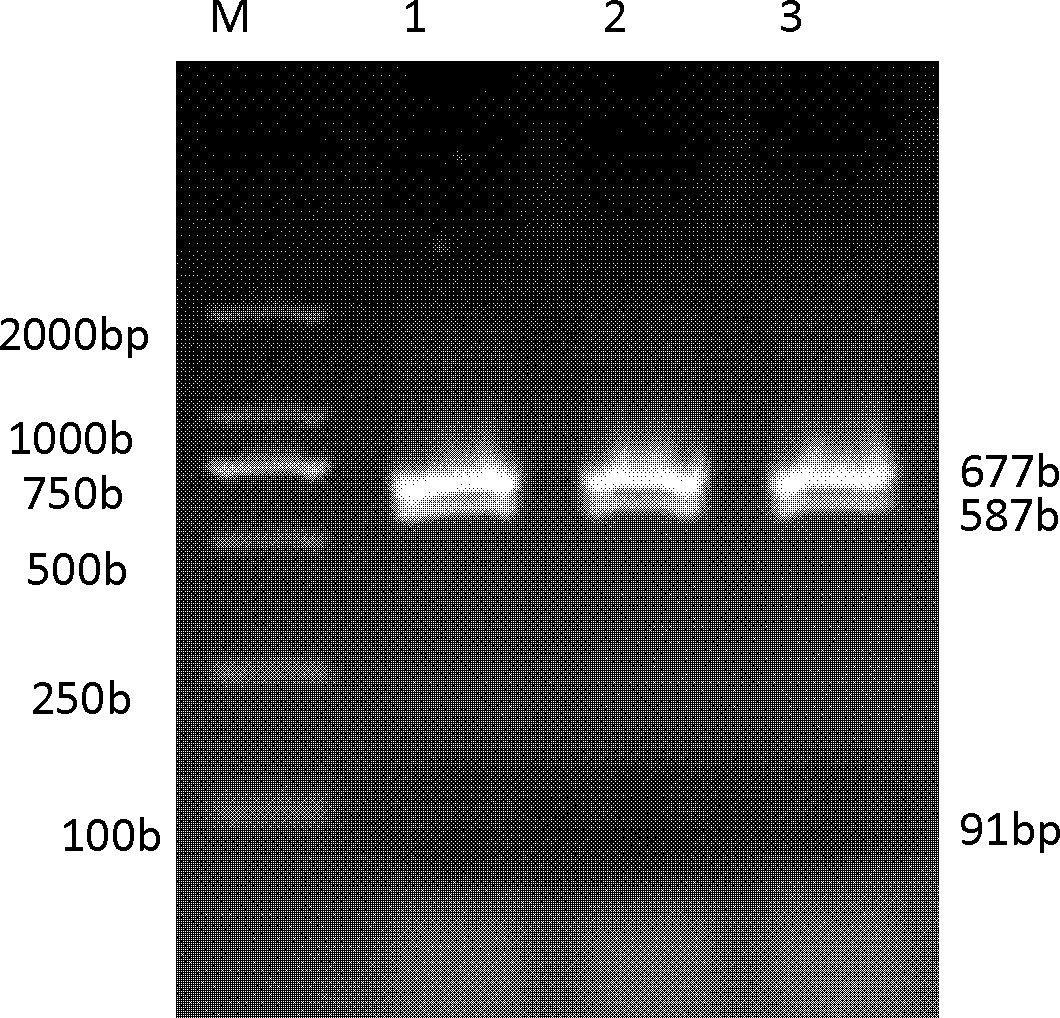
The invention belongs to the field of biological engineering, and is used for solving the technical problem of difficulty in screening a pleurotus nebrodensis-pleurotus eryngii interspecific hybrid in the prior art. The invention provides an identifying method of the pleurotus nebrodensis-pleurotus eryngii interspecific hybrid. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a strain protoplast; culturing the protoplast; culturing and collecting hyphae in the protoplast; extracting genome DNAs (Deoxyribonucleic Acids) in the hyphae; performing ITS-PCR (Internal Transcribed Spacer-Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on the extracted DNAs; performing specific enzyme splicing on an amplification product; and performing electrophoresis on an enzyme splicing product. If DNA marking strips of which the molecular weights are 675-685bp, 585-595bp and 85-95bp are generated according to electrophoresis detection, the strain is an interspecific hybrid of pleurotus nebrodensis and pleurotus eryngii. The identifying method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of short detection time, high accuracy, easiness for judging and high stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI BAIRONG VELVET MUSHROOM
Haliotis discus hannnai and haliotis iris interspecific hybrid production method
InactiveCN105494187AOptimize fertilization conditionsImprove hybrid fertilization rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaFully developedHigh fertility
The invention relates to a haliotis discus hannnai and haliotis iris interspecific hybrid production method with a higher fertility rate and a higher hatching rate. According to the interspecific hybrid production method, Chinese haliotis discus hannnai is taken as female parent abalone, and Zelanian haliotis iris is taken as father parent abalone; the female parent abalone and the father parent abalone are put into different parent abalone cultivation ponds for cultivation; the female haliotis discus hannnai with the gonad fully developed is subjected to spawning induction with a method combining shady drying and ultraviolet irradiation seawater stimulation until the female haliotis discus hannnai lays eggs, and the male Zelanian haliotis iris with the gonad fully developed is subjected to spawning induction with a method combining shady drying and hydrogen peroxide seawater soaking until the male Zelanian haliotis iris releases sperms; fertilized eggs of haliotis discus hannnai and haliotis iris hybrids are obtained in the following steps: the eggs of the haliotis discus hannnai and the sperms of the haliotis iris are taken respectively and mixed, the temperature of seawater where fertilization is performed is adjusted, and the eggs are washed after the fertilized eggs are split to two cell stages; the haliotis discus hannnai and haliotis iris hybrid fries can be obtained with conventional hatching and later cultivation methods.
Owner:山东大学(威海)
Petunia mutant allele
The present invention relates to a petunia plant, seed, variety and hybrid. More specifically, the invention relates to a petunia plant having an allele which results in a petunia plant with altered flower color and / or altered flower color pattern. The invention also relates to crossing petunia plants containing the allele with petunia or Calibrachoa plants lacking the allele to produce novel types of petunia and Calibrachoa-petunia inter-generic hybrid plants.
Owner:BALL HORTICULTURAL
Osteospermum and dimorphoteca plants having an altered flower phenotype
The present invention relates to an Osteospermum and Dimorphoteca plant, seed, variety, and hybrid. Another aspect of the present invention relates to an Osteospermum and Dimorphoteca plant having a mutant allele designated KLEDF which results in an altered flower phenotype. The invention also relates to crossing Osteospermum and Dimorphoteca plants containing the KLEDF mutant allele with other Osteospermum and Dimorphoteca plants lacking the KLEDF mutant allele to produce intergeneric and interspecific hybrids. This invention further relates to specific lines of Osteospermum varieties exhibiting the altered-flowering phenotype. Furthermore, the invention relates to pollen, seed, and sexual, as well as asexual progeny of such plants with altered flowers. In addition, the invention relates to methods for propagating said plants and to uses of said plants.
Owner:KLEMM SOHN
Method of producing euphorbia interspecific hybrid plants by cutting and then culturing the hybrid embryos
InactiveUS20060218679A1Efficiency of viableImprove efficiencyBryophytesSeed and root treatmentEuphorbia colorataDigenea
A method for producing an interspecific hybrid Euphorbia plant. The method comprises: (a) providing a first plant which is a Euphorbia pulcherrima plant and a second plant which is a species of Euphorbia selected from the group consisting of Euphorbia cornastra, Euphorbia radians, Euphorbia colorata and Euphorbia fulgens; (b) pollinating a flower of the second plant with pollen from the first plant or a flower of the first plant with pollen from the second plant in a manner which permits formation of an embryo in at least one ovule of the pollinated plant; (c) cutting the embryo; and (d) culturing the cut embryo by placing the cut embryo in contact with culture medium to permit growth of the embryo to thereby produce a primary plant.
Owner:BONZA BOTANICALS
Multi-parental hybrid breeding method of tilapia
ActiveCN104542397AIncrease emergenceIncrease the male rate of offspringClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaAquaculture of tilapiaInterspecific hybrids
The invention provides a breeding method of tilapia. The breeding method comprises the steps of performing intra specific hybrid breeding for new Gift tilapia and Sudan tilapia to obtain the first filial generation tilapia; performing interspecific hybrid breeding by using raun of the first filial generation tilapia as a female parent and milter of blue tilapia as a male parent to obtain the hybrid generation which is the tilapia. According to the method, the breeding technology combining specific hybrid breeding and interspecific hybrid breeding of tilapia is adopted; various outstanding properties are collected; therefore, the output of fries and male rate of the later generations are increased, and as a result, the breeding output and benefits of tilapia are increased. The invention further provides tilapia bred through the breeding method; the tilapia has the advantages of being high in output of fries and male rate of the later generations.
Owner:广东伟业罗非鱼良种有限公司 +1
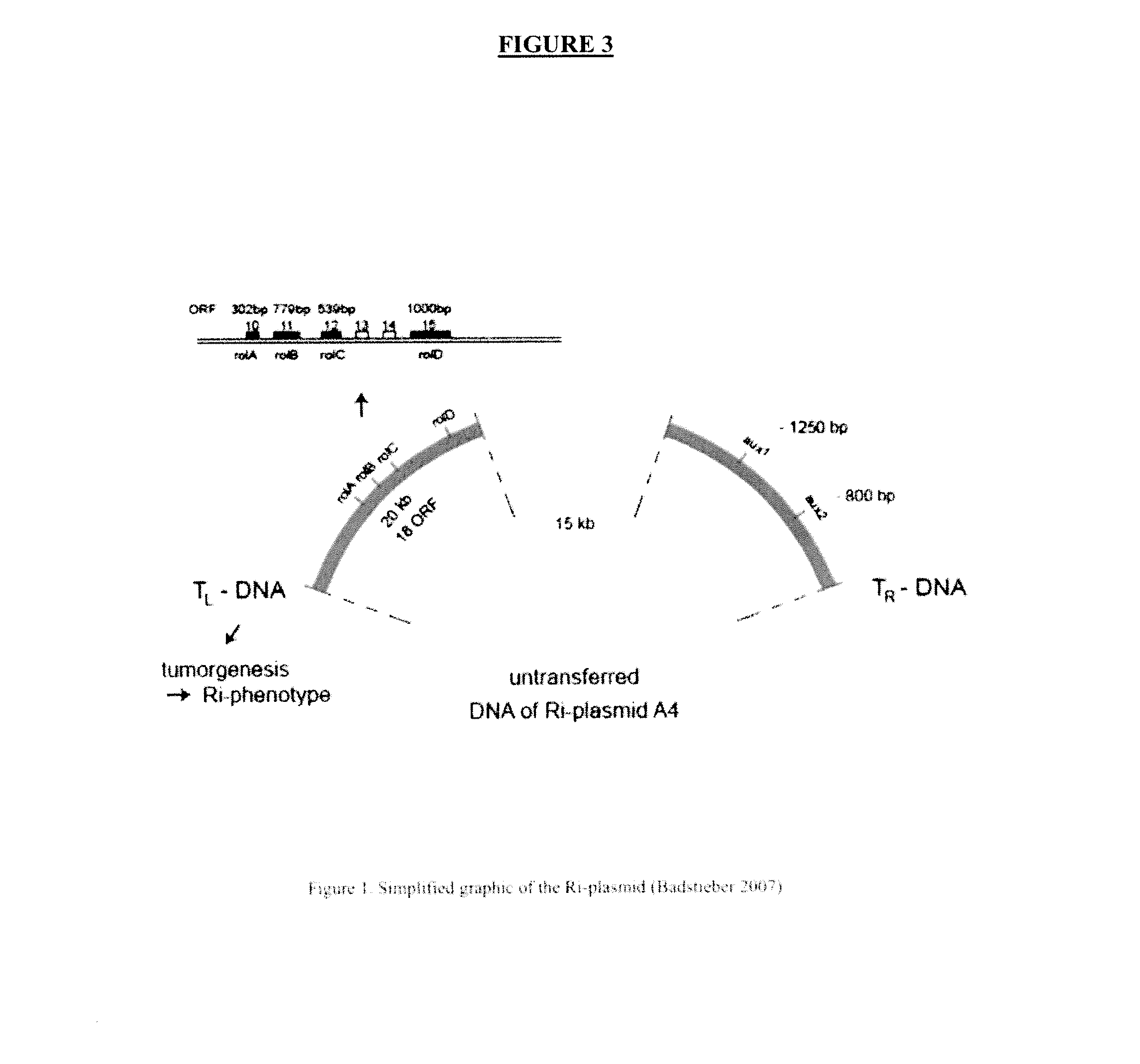
Agrobacterium rhizogenes transformation and expression of rol genes in kalanchoë
ActiveUS20140053297A1Reduce the overall heightClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesRhizobium rhizogenesPhenotype
The present disclosure embraces Kalanchoë interspecific hybrid plants, and considers rol transformation in Kalanchoë species and hybrids. Disclosed herein are methodology and the like for producing rot-transformed Kalanchoë interspecific hybrid plants, as well as resultant rot-transformed Kalanchoë interspecific hybrid plants with novel phenotypes.
Owner:KNUD JEPSEN +1
Interspecific cross breeding method for cucurbit (melon rootstock)
InactiveCN102204508ANot easy to growNot easy to hollowPlant genotype modificationHigh resistanceDying back
The invention belongs to the technical field of breeding of cucurbitaceae vegetable. An interspecific hybrid F1 (Yong rootstock No. 6) of cucurbit (a melon rootstock) is obtained by hybridizing a female parent of a stable inbred line J03-2-3-2-1-5-7-4 by multi-generation of directed autocopuation screening of cucurbit materials originated from Japan and a male parent of a stable inbred line YH2-3-3-2-1-4-2-6 by multi-generation of directed autocopuation screening of local Lagenaria species produced in Ningbo. The melon rootstock selectively bred with the method provided in the invention meets objectives of breeding and has moderate growth potential, high resistance to die-back and root rot, well-developed roots, strong stalks, strong ability in absorbing nutrient, low degree of vain growth and robust hypocotyls which are not easy to become hollow, and therefore the melon rootstock is favorable for grafting. The melon rootstock has good grafting affinity and strong symbiosis affinity, and a survival rate over 95% is obtained for the grafting of the rootstock onto the watermelon specie ''Zaojia'' (8424). The engrafted melon rootstock is low temperature-resistant, moisture-resistant and barren-resistant; after field planting, the root and overground part of a grafted seedling grows fast and has sound growth potential, and the period of first harvest of the grafted seedling is 5 days earlier than that of a self-rooted seedling, the fruition rate is high and stable, weight of single fruit and fruit shape can substantially maintain the same, melon skin is not thickened, sugar degree of the grafted seedling is higher than that of the self-rooted seedling, sugar degree gradient is small, quality of the watermelon is not affected, and good adaptability is obtained.
Owner:NINGBO ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Seed selection method of oryza glaberrima cytoplasmic male sterile line
InactiveCN103704124ARich source of cytoplasmAvoid the potential risk of single sourcePlant genotype modificationDiseaseAgricultural science
The invention discloses a seed selection method of an oryza glaberrima cytoplasmic male sterile line. The method comprises a step of subjecting oryza glaberrima used as a maternal plant and a common cultivated non-glutinous rice variety to distant hybridization to obtain interspecific hybrid F1 seeds; a step of subjecting interspecific F1 plans used as the maternal plant and a selected non-glutinous rice variety (recurrent parent) to backcross; a step of performing continuous multi-generation character selection and nucleus substitution backcross to obtain the genetically stable oryza glaberrima cytoplasmic male sterile line, with the recurrent parent being a maintainer line; and a step of performing distant hybridization seed selection and test-cross selection to obtain a strong restoring line, thus achieving a three-line complete set of the non-glutinous-type oryza glaberrima cytoplasmic male sterile line, the maintainer line and the restoring line. The oryza glaberrima cytoplasmic male sterile line has advantages of complete pollen abortion, stable male sterility and good restorability, and is suitable for seed production of three-line hybrid rice, thus facilitating further enlargement of cytoplasmic inheritance diversity of the three-line hybrid rice and avoiding a potential risk of specialization disease outbreak.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for acquiring cucumis melo wild species and cultivating thick skin cucumis melo hybrid species
ActiveCN107306788AExcellent geneBroaden the genetic basePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsWild speciesInterspecific hybridization
Belonging to the technical field of plant breeding, the invention relates to a method for acquiring cucumis melo wild species and cultivating thick skin cucumis melo hybrid species. The main technical measures include: conducting cucumis melo interspecific hybridization, then conducting aseptic treatment on an ovary pollinated for 15-21d, taking out immature embryos, then putting the immature embryos in a hormone added 1 / 2MS medium for culture, then carrying out subculture to obtain seedlings, controlling the culture temperature at 26DEG C, the daily illumination time at 10-12h, and the illuminance at 1600-2000lx. The method provided by the invention can solve the key technical problem of cucumis melo interspecific hybridization reproductive disorder, and also can acquire cucumis melo interspecific hybrid seedlings.
Owner:南京利华农业科技有限公司
Creation method of pumpkin interspecific crossing recombinant inbred line
The invention discloses a creation method of a pumpkin interspecific crossing recombinant inbred line. The method comprises the steps that winter squash is used a female parent, cucurbita moschata isused as a male parent, F1 hybrid seeds are obtained, then winter squash is used as a recurrent parent, and the interspecific crossing recombinant inbred line is obtained through a backcross and selfing method; the interspecific crossing recombinant inbred line has the performance of progeny reproduction. Along with increasement of the selfing generation number, the progeny fertility is gradually restored, the fertility of high-generation inbred lines of the fourth inbred generation and the fifth inbred generation is basically close to a normal level, and the reproductive performance of the interspecific crossing recombinant inbred line is good. By adopting the method, the problems can be solved that hybridization of cucurbita moschata and winter squash is difficult, and interspecific crossing hybrids and selfed progeny thereof are difficultly obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Stock screening method of interspecific hybrid loquat
The invention discloses a stock screening method of an interspecific hybrid loquat. Excellent strains are selected from a group of interspecific hybrids; three strains with the best roots are selected from these hybrid progenies as candidate stocks; more than 10,000 strains can be bred from each bud every year. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the stock with a deep root can be obtained; the disease of a hollow root of the cultivated loquat is overcome; the stock material of which the graft compatibility is better than that of a wild loquat can be obtained; the phenomenon of graft incompatibility is also overcome.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
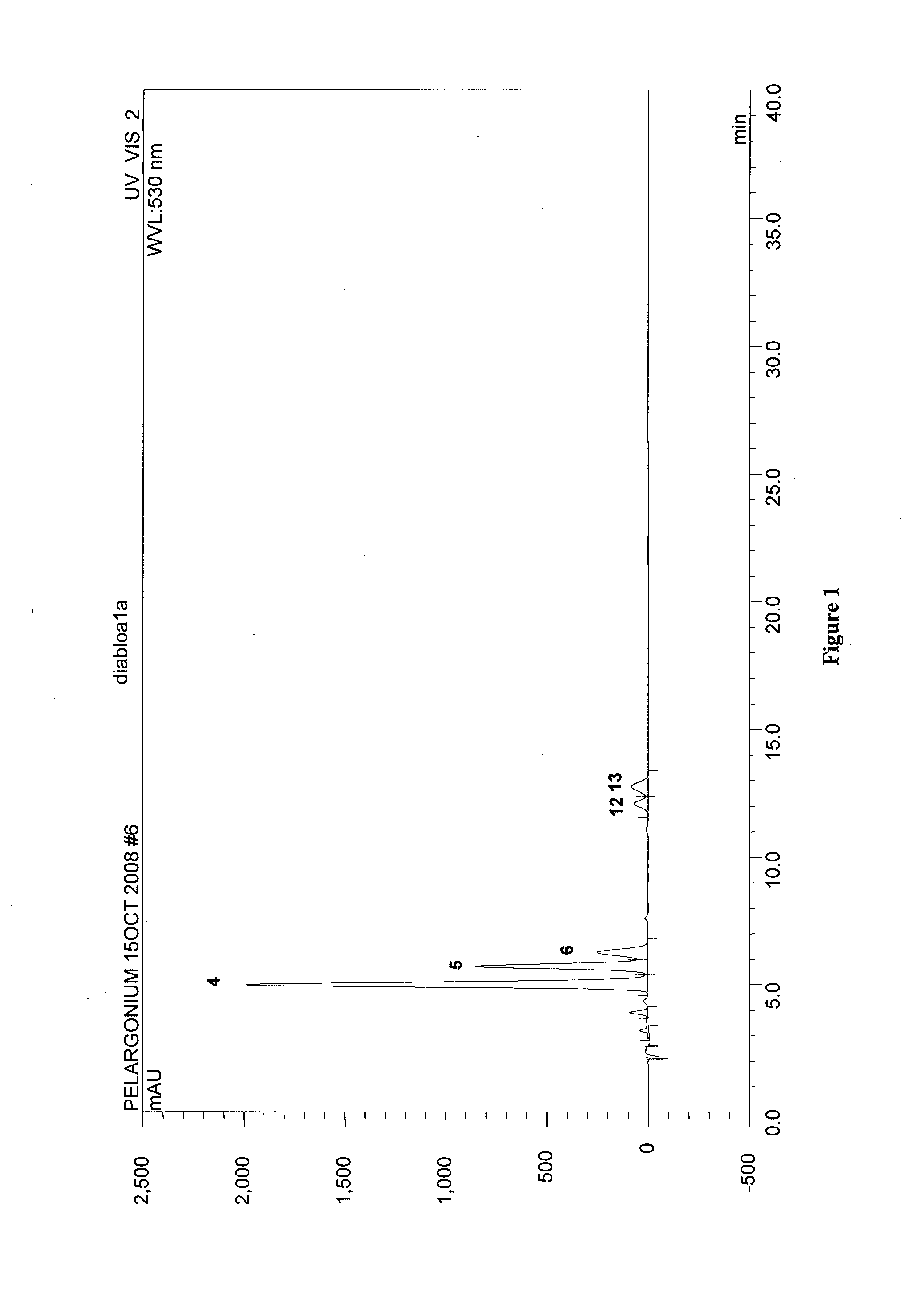
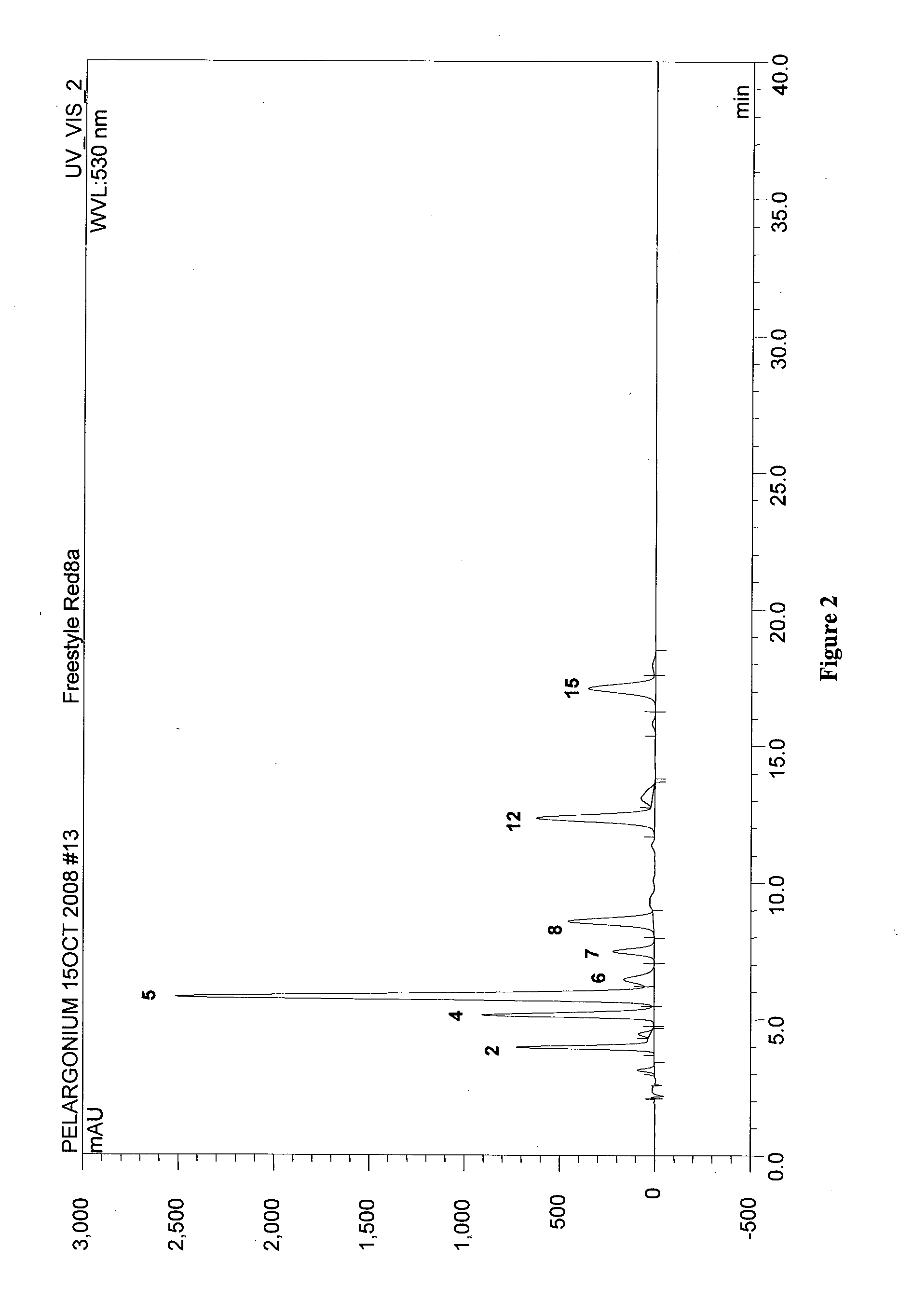
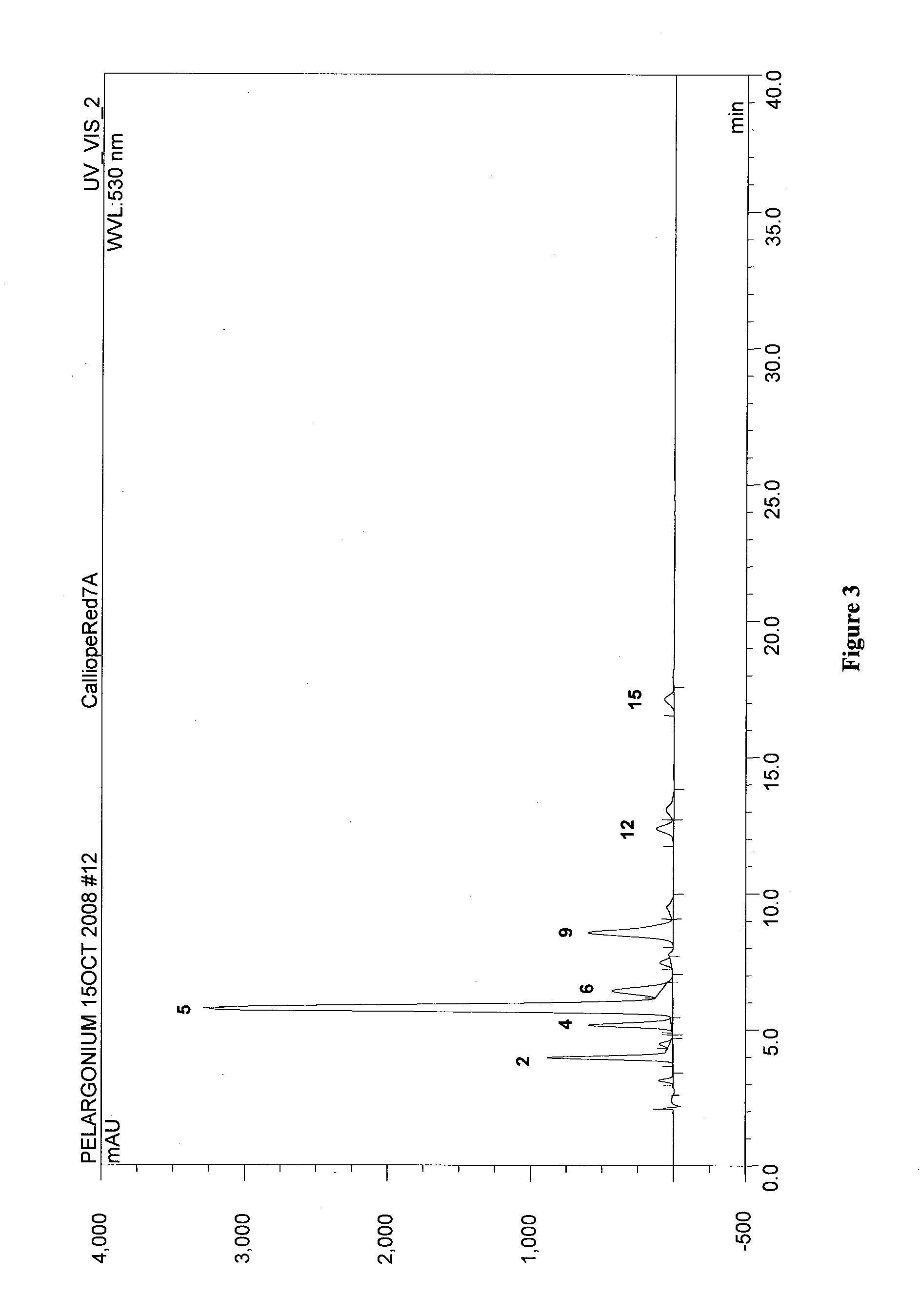
Flower pigmentation in pelargonium hortorum
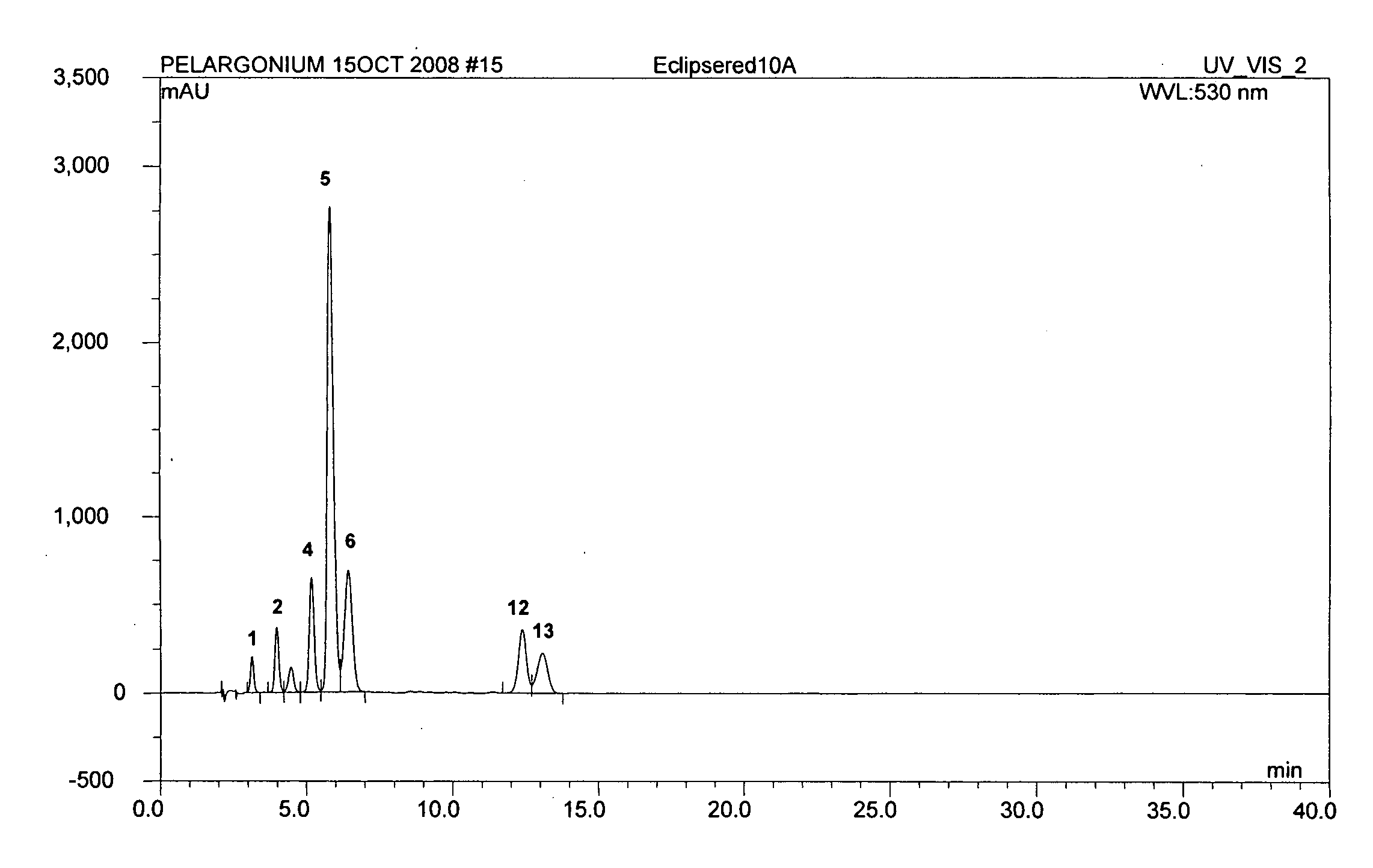
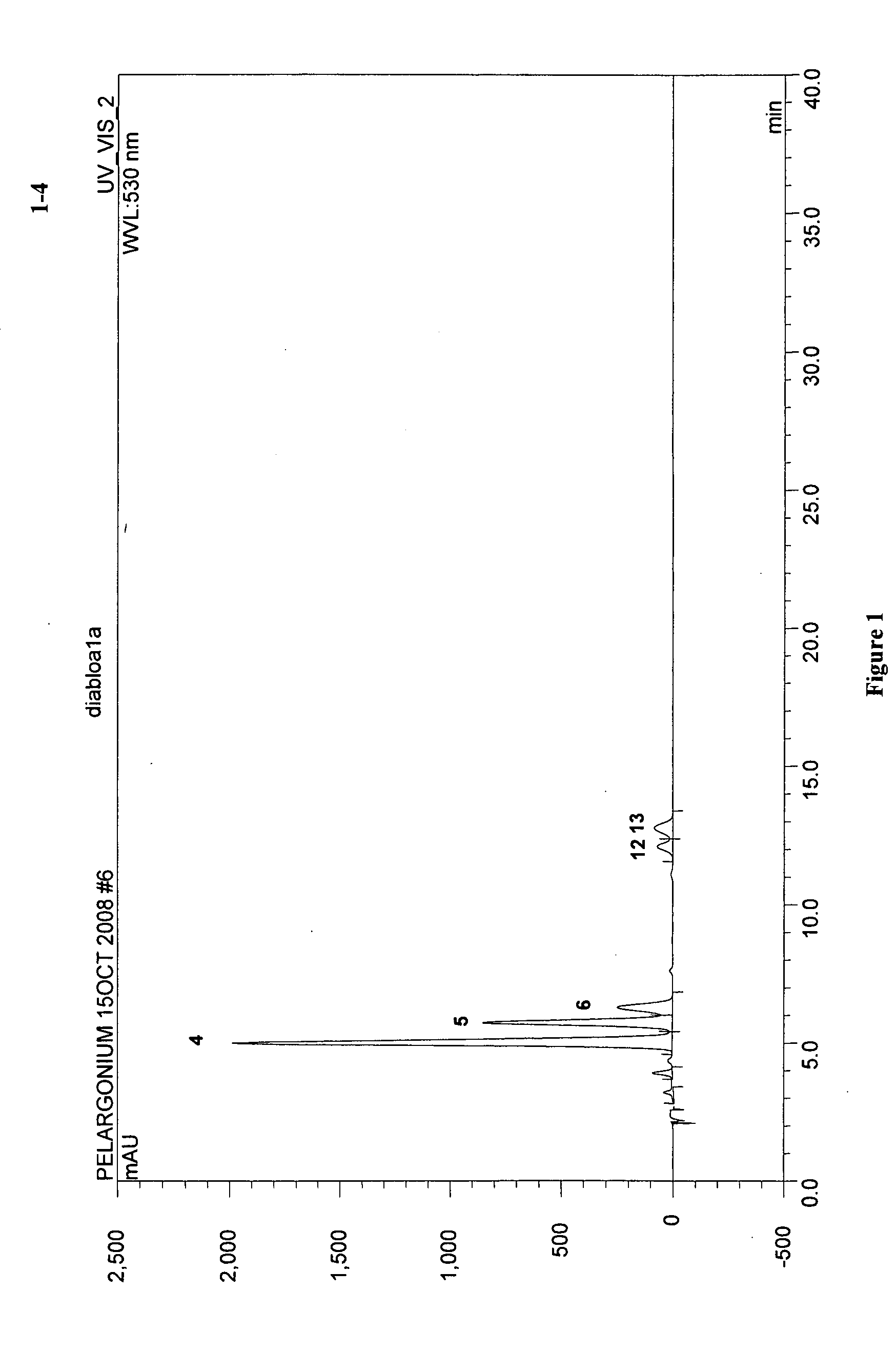
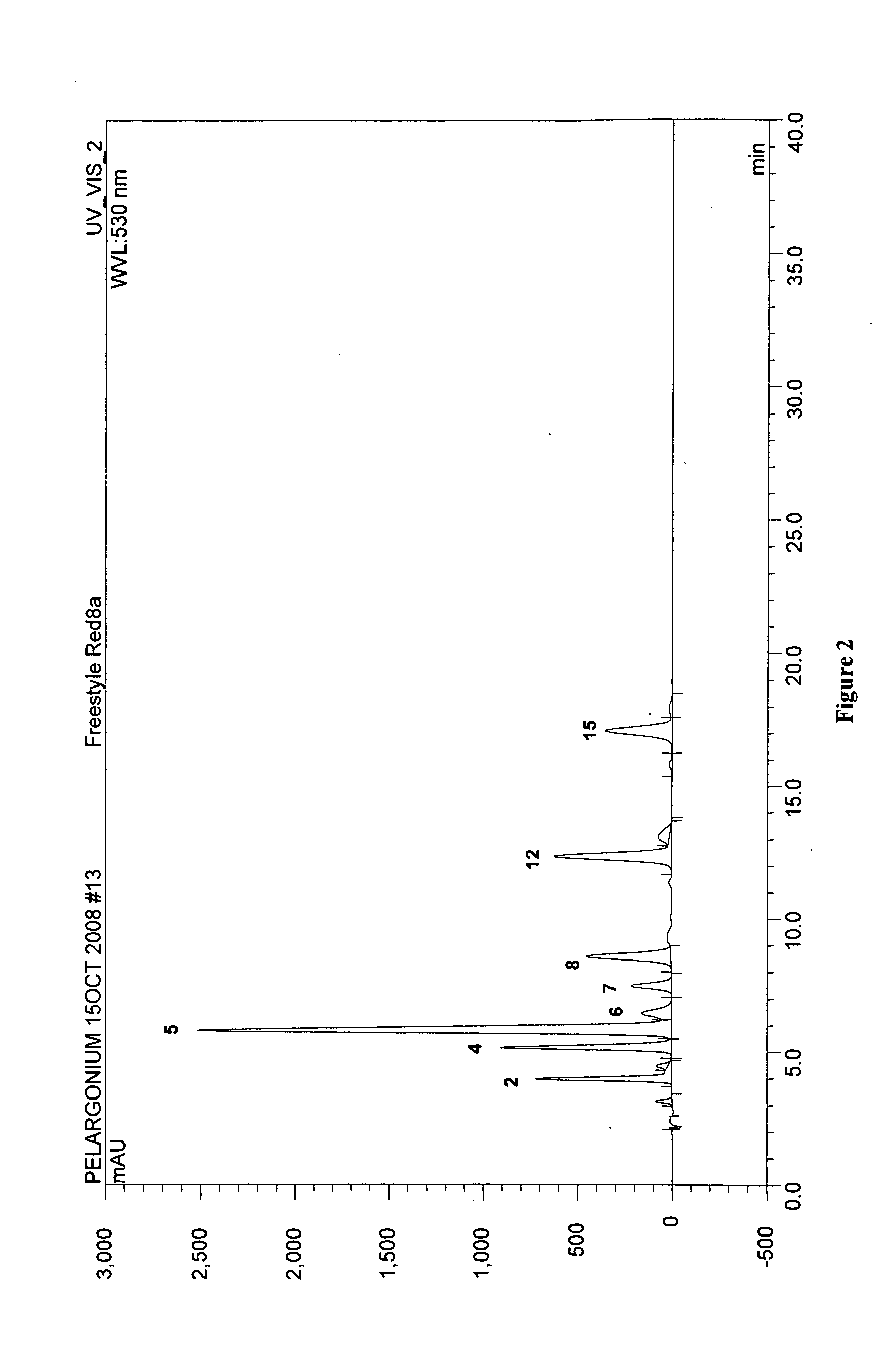
InactiveUS20110041198A1Plant genotype modificationAngiosperms/flowering plantsPelargonium x hortorumPetal
The present invention relates to novel Pelargonium hortorum-interspecific plants having dark red to burgundy or darker pigmented flower petal, a trailing growth habit, dark leaf color and tolerance to high temperatures, high light and edema. The present invention also relates to methods for creating novel Pelargonium hortorum-interspecific hybrid plants having dark red to burgundy or darker pigmented flower petals, a trailing growth habit and tolerance to high temperatures, high light and edema.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
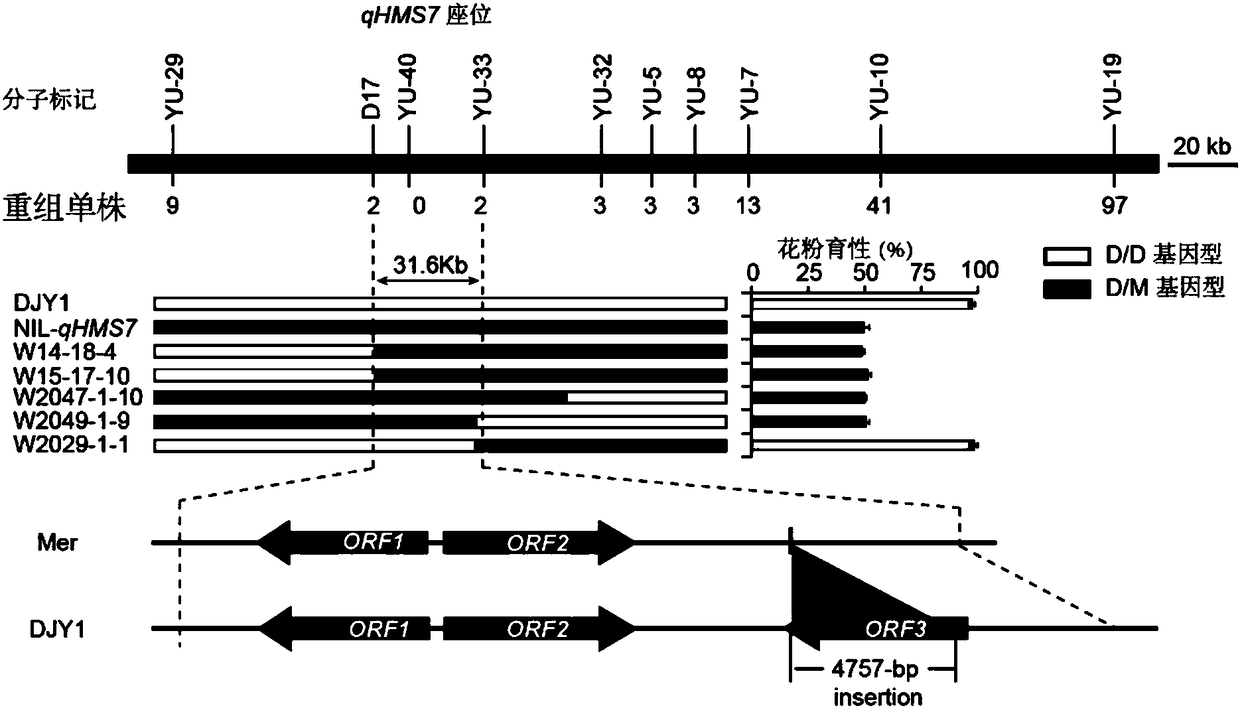
Paddy rice interspecific hybrid pollen fertility gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a paddy rice interspecific hybrid pollen fertility gene and an application thereof. The gene concretely relates to a paddy rice interspecific hybrid pollen fertility related locus qHMS7, is positioned at a 7th chromosome long arm, and accurately positioned in a 31.6 kb area between molecule marks D17 and YU-33, and a DNA fragment of the related gene of the paddy rice interspecific sterility site qHMS7 is provided, a protein sequence coded by the hybrid pollen fertility gene is provided, a concrete application method of the hybrid pollen fertility gene in a seed selection affinity system during a paddy rice heredity improvement process is provided, and the tight linkage molecule mark generated according to the hybrid pollen fertility gene sequence and an applicationof the tight linkage molecule mark in the paddy rice cross breeding are provided.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Identification method of interspecific hybrids of Brassica campestris and Brassica napus
InactiveCN102768210AImprove accuracyAccurate identificationInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsStomaCuticle
The invention discloses an identification method of interspecific hybrids of Brassica campestris and Brassica napus, falling into the technical field of plant cytology. The method includes collecting the 4th-7th leaves of a plant in the seedling stage, tearing to collect hypoderm tissues of lower parts of the leaves, staining with iodine-potassium iodide solution, observing stomata under an optical microscope, measuring major / minor axis values of guard cells, calculating perimeter values of the guard cells with an ellipse model while observing and counting chloroplasts, recording 15 data per leaf, and identifying with parents as controls. For Brassica campestris, stoma guard cells have perimeter smaller than 58.90 micrometer and chloroplast count of 9-11; for Brassica napus, stoma guard cells have perimeter greater than 75.83 micrometer and chloroplast count of 19-20; while, for the to-be-identified material, if more than ten stomata simultaneously satisfy that guard cells have perimeter of 58.90-75.83 micrometer and chloroplast count of 14-16, it is determined that the plant is interspecific hybrids F1 of Brassica campestris and Brassica napus, otherwise it is false hybrid.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Flower Pigmentation in Pelargonium hortorum
The present invention relates to novel Pelargonium hortorum—interspecific plants having dark red to burgundy or darker pigmented flower petal, a trailing growth habit, dark leaf color and tolerance to high temperatures, high light and edema. The present invention also relates to methods for creating novel Pelargonium hortorum—interspecific hybrid plants having dark red to burgundy or darker pigmented flower petals, a trailing growth habit and tolerance to high temperatures, high light and edema.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Cultivation method of virus-resistant sweet potato interspecific introgression line
ActiveCN108308017ABroaden the genetic baseReduce manpowerPlant genotype modificationWild speciesAgricultural science
The invention discloses a cultivation method of a virus-resistant sweet potato interspecific introgression line. The method comprises the following steps: performing interspecific hybridization on broad affinity parent Xu potatoes 18 and virus-resistant sweet potato wild species to obtain interspecific hybrid seedling seeds on the basis of guaranteeing the hybridization quantity and performing treatment by using hybridization treatment liquid; performing tracking identification on the obtained hybrid F1 group, selecting an SPVD-resistant true hybrid as a female parent and cultivated species asa recurrent parent, and performing continuous back cross for three generations and establishing a BC3F1 group; and performing resistance identification and labeling analysis on the BC3F1 group to obtain a virus-resistant introgression group BC3F1. The traditional genetic group construction method of the sweet potatoes is broken through, the sweet potato genetic basis is broadened, a high-densitygenetic map can be constructed by a small group scale, and manpower and material resource expenditures caused by application of too much marks are reduced. Meanwhile, the method can be applied to improvement of an anti-SPVD variety.
Owner:XUZHOU INST OF AGRI SCI IN JIANGSU XUHUAI DISTRICT (JIANGSU XUZHOU SWEETPOTATO CENT)
Interspecific cross breeding method of fagopyrum dibotrys and tartary buckwheat and application
PendingCN111480570AImprove featuresImprove multiple regeneration capabilitiesPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyHeterosis
The invention relates to an interspecific cross breeding method of fagopyrum dibotrys and tartary buckwheat and application. According to the interspecific cross breeding method of the fagopyrum dibotrys and the tartary buckwheat and application, with tetraploid tartary buckwheat as female parents and a diploid fagopyrum dibotrys complex plant doubled line and / or tetraploid fagopyrum dibotrys which naturally exists as male parents, crossing is conducted, and a cross breed obtained by adopting the interspecific cross breeding method of the fagopyrum dibotrys and the tartary buckwheat can live through the winter in warm southern areas, so that years of asexual propagating expanding production and cultivation are achieved. According to the breeding method, not only is the interspecific heterosis of the fagopyrum dibotrys and the tartary buckwheat used, but also the heterosis among different fagopyrum dibotrys lines is used, the perennial characteristic and the multiple regeneration capability of the interspecific cross breed fagopyrum dibotrys are further improved, and thus the regeneration capability of branch cutting and multiple cutting of cross breed plants is strong enough to support overwintering and propagating expanding of multiple branch cutting, so that the heterosis of the cross breed is maintained permanently, and the cross breed can be widely applied and popularized in production.
Owner:GUIZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for quickly obtaining interspecific hybrids of incompatible wide species and cultivated species of peanuts
InactiveCN102577930AEfficiently obtainedEasy to getPlant genotype modificationMolecular identificationPollination
The invention relates to a plant distant hybridization technology, in particular to a method for quickly obtaining a large amount of interspecific hybrids of an incompatible wide species and a cultivated species of peanuts through medicine induction after pollination. The method for quickly obtaining the interspecific hybrids of the incompatibility wide species and the cultivated species of the peanuts comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing a hormone mixed solution; (2) collecting incompatible peanut wide species pollen and pollinating a peanut cultivated species female parent; (3) dipping the hormone mixed solution and applying on a base of each pollinated cultivated species female parent flower; and (4) carrying out molecular identification on the harvested seeds. According to the invention, the method can be operated in the field and a large amount of interspecific hybrids can be effectively obtained, a long-winded complicated tissue cultivation step is omitted, and the incompatible hybrids of the peanuts can be simply and easily obtained.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
Agrobacterium rhizogenes transformation and expression of rol genes in kalanchoe
ActiveUS20160032311A1Climate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesKalanchoe speciesPhenotype
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF COPENHAGEN +1
Method using young embryo to save and obtain interspecies hybrid of hydrangea macrophylla
InactiveCN105494078ADistant hybridizationAvoid premature agingPlant genotype modificationPremature agingHydrangea macrophylla
The invention provides a method using young embryo to save and obtain distant hybrid of hydrangea macrophylla. According to the provided method, non-hardy hydrangea macrophylla (diamond) is taken as the female parent and hardy H. arborescence Annabelle is taken as the male parent to carry out interspecies hybridization; ovary culture is performed to rescue young embryo; and the obtained hybrid offspring is subjected to morphological identification and SSR identification. The provided method can prevent the phenomenon of embryo premature senility, which is caused by incompatibility, of distant hybrid. A large amount of interspecies hybrid offspring can be obtained through tissue culture. The interspecies distant hybridization of hydrangea macrophylla is achieved; novel species, which have a strong performance on resisting cold and a high ornamental value, are created; and the breeding period of hydrangea macrophylla is largely reduced.
Owner:杨玉勇 +2
Method for producing tetraploid oysters and interspecific hybridization triploid oysters
ActiveCN113678764AStable productionGood characterClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPolar bodyOyster
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic breeding of aquaculture varieties, and relates to a method for producing tetraploid oysters and a method for interspecific hybridization of triploid oysters by using the tetraploid oysters. The triploid oysters are stimulated for 5-8 days at the high temperature of 26-28 DEG C, ripening is promoted for 30-40 days at the water temperature of 22-24 DEG C after stimulation, and ova of female oysters with the largest diameter are selected after ripening; the selected ova and sperms of diploid oysters are fertilized for 5-8 minutes, then an inhibitor is added to inhibit first polar body discharge of the fertilized ova, and then a large number of tetraploid oysters are stably obtained for optimization. After strong optimization, high-concentration sperms are used for carrying out hybrid fertilization on excellent tetraploid oysters and excellent diploid oysters in different species, and interspecific hybrid triploid oysters with excellent breeding traits are obtained. According to the method for producing the tetraploid oysters and the method for interspecific hybridization of the triploid oysters by using the tetraploid oysters, the method for producing the tetraploid oysters and the method for interspecific hybridization of the triploid oysters by using the tetraploid oysters can be used for stably and efficiently producing the tetraploid oysters and the hybrid triploid oysters with the excellent breeding traits, can be widely applied to genetic breeding of oysters and shellfishes, and improves the shellfish breeding industry.
Owner:青岛前沿海洋种业有限公司
Method of obtaining primula forbesii and primula saxatilis interspecific hybrid by utilizing immature embryo rescue technology
ActiveCN103563749AImproved germplasmFacilitate genetic exchangeHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureInterspecific hybridizationPrimula
The invention provides a method of obtaining a primula forbesii and primula saxatilis interspecific hybrid by utilizing an immature embryo rescue technology. The method comprises the following steps: selecting primula primula forbesii and primula saxatilis which are originated in China to carry out hybridization; carrying out immature embryo rescue by adopting an ovary culture means; carrying out hybrid morphological identification on obtained progeny materials; selecting the progeny material which has morphological characteristics, such as stems, leaves, flowering phase and inflorescence, similar to parents at the same time, and has novel properties not owned by the parents as a interspecific crossing new variety. The method disclosed by the invention realizes the interspecific distant hybridization of the primula, and obtains a batch of new hybrid germplasms.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com