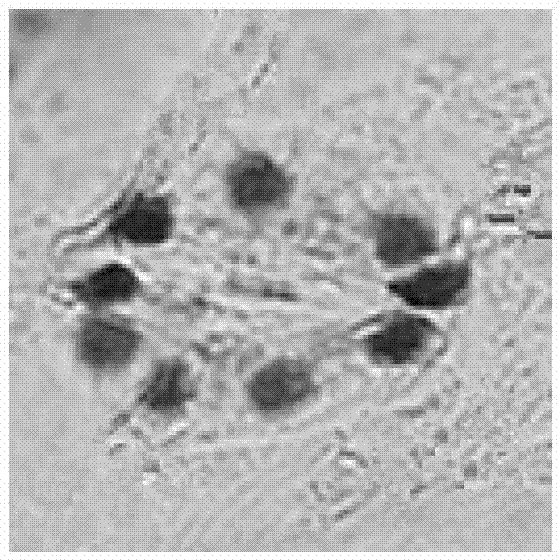
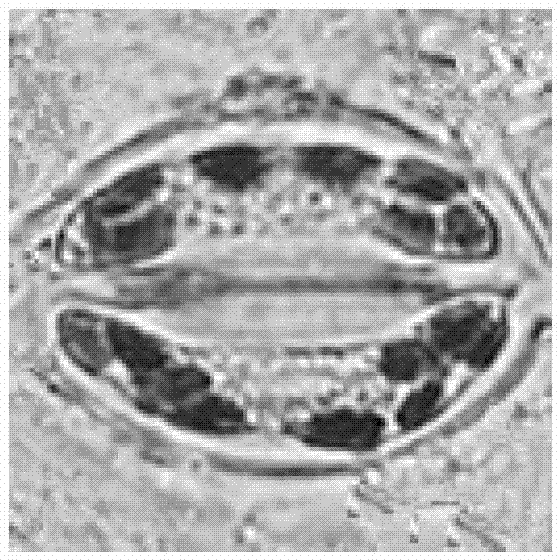
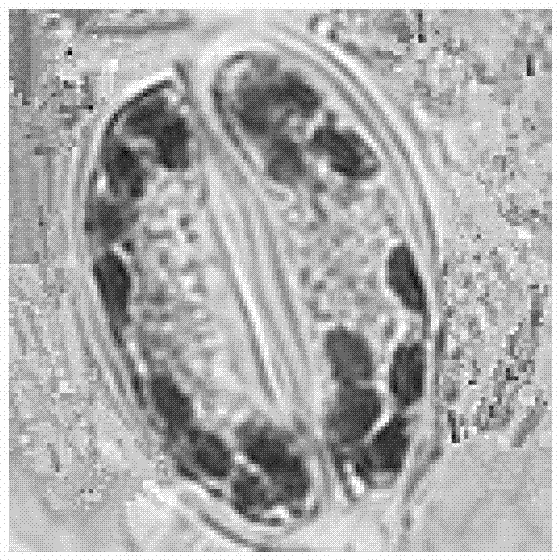
Identification method of interspecific hybrids of Brassica campestris and Brassica napus
A technology of Brassica napus and Brassica napus, applied in the field of plant cytology, achieves the effects of simple technology, improved accuracy, and high identification efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Embodiment 1: a kind of method for interspecific hybrid identification of Chinese cabbage-type rape and Brassica napus, it comprises the following steps:
[0022] (1) For the configuration of 1% iodine-potassium iodide staining solution, weigh 1g of iodine and pour it into a small beaker, add 80ml of distilled water to dissolve, then add 2g of potassium iodide; set the volume to 100ml for later use;
[0023] (2) Pick the flat leaves at the sixth leaf position of the interspecific hybrid F1 of Chinese cabbage-type rapeseed Longyou No. 9, Brassica napus vision and the interspecific hybrid F1 of Chinese cabbage-type rapeseed No. 9 and Brassica napus at the seedling stage, and put them into plastic bags , put it in a prepared ice box below 0°C within 5-10 minutes, and bring it back. After the leaves are washed with distilled water, put them in a fume hood to dry the water on the surface of the leaves, cut the lower part of the leaves with a blade, and tear them off with twee...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2: A method for identification of interspecific hybrids between Chinese cabbage-type rape and Brassica napus, in step (2), picking Chinese cabbage-type rape Longyou No. 9, Brassica napus vision and Brassica napus Longyou 9 at the seedling stage No. and Brassica napus vision interspecific hybrid F1 The flattened leaves at the 4th leaf position were packed into plastic bags; the rest were the same as in Example 1.
[0047] Verification example:
[0048] The identification method is as in Example 1. The existing 40 interspecific hybrids of Chinese cabbage-type rape Yanyou 2 and Brassica napus Qinchuan Donggan 1 were identified by the above-mentioned method.
[0049] Experimental steps:
[0050] This 40 seeds are placed in the petri dish, spray a small amount of water, allow it to germinate, when the root grows to about 4mm, move into the nutrient bowl, put the tissue culture room to grow, room temperature is controlled at about 25 ℃. At the seedling stage, the yo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com