Patents
Literature
56 results about "Guard cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Guard cells are specialized cells in the epidermis of leaves, stems and other organs that are used to control gas exchange. They are produced in pairs with a gap between them that forms a stomatal pore. The stomatal pores are largest when water is freely available and the guard cells turgid, and closed when water availability is critically low and the guard cells become flaccid. Photosynthesis depends on the diffusion of carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the air through the stomata into the mesophyll tissues. Oxygen (O₂), produced as a byproduct of photosynthesis, exits the plant via the stomata. When the stomata are open, water is lost by evaporation and must be replaced via the transpiration stream, with water taken up by the roots. Plants must balance the amount of CO₂ absorbed from the air with the water loss through the stomatal pores, and this is achieved by both active and passive control of guard cell turgor and stomatal pore size.
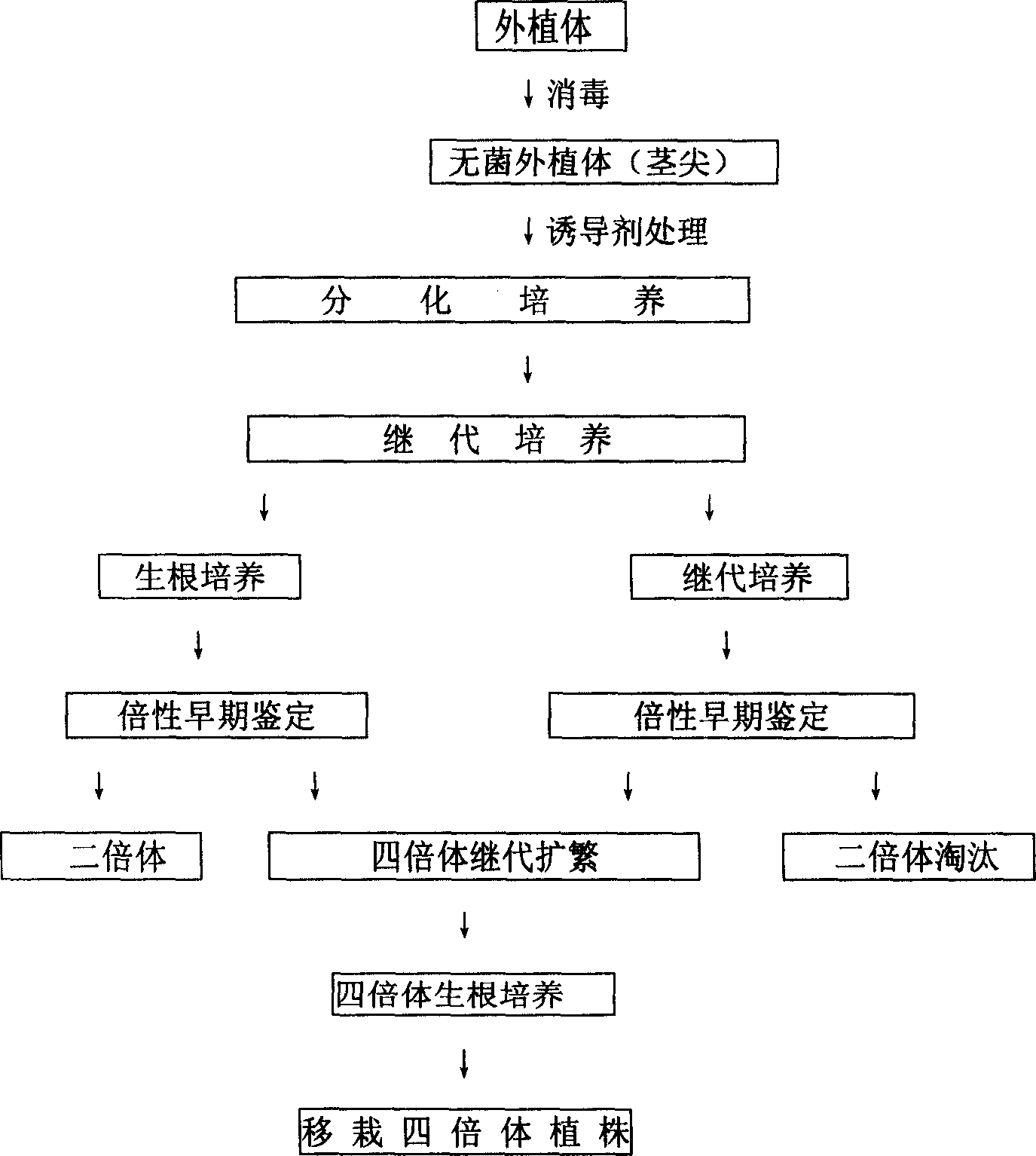
Excised mutagenesis tetraploid method of water melon and ploidy early stage certification technique
InactiveCN1631101AInduction frequency is highLow toxicityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureFluorescenceColchicine
The invention provides an excised mutagenesis tetraploid method of water melon and ploidy early stage certification technique, wherein dinitro toluene herbicide (DNH) is employed to substitute the conventional colchicines as inducer, whose function is to suppress the Mitosis in the metaphase of cell division through the mechanism of interfering spindle, so as to double the tissue cell chromosome. The method has the advantages of increased inducement success rate and substantially shortened time required for inducement.
Owner:刘文革 +1
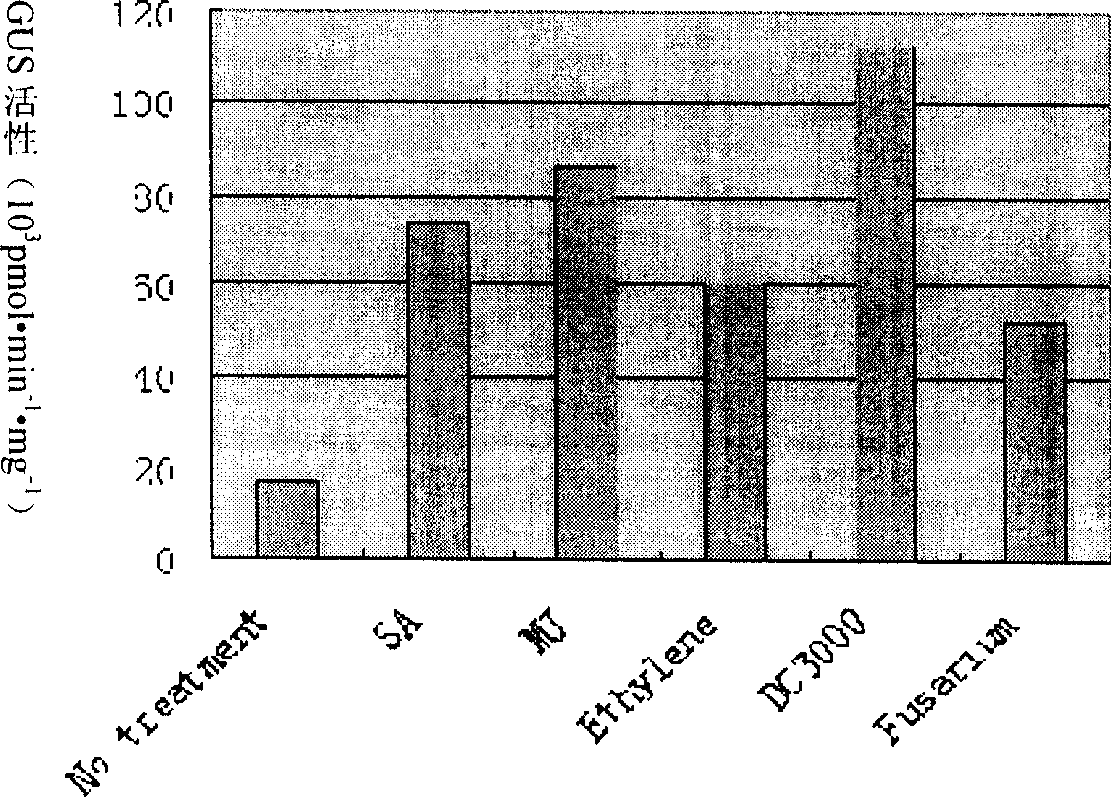
Cotton tissue specific and pathogenic bacterium inducing promoter and its use
InactiveCN1900281AUnderstand interactionReduce outputFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBudGuard cell
The present invention relates to cotton tissue specific and pathogenic bacterium inducing promoter and their application, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The promoter contains CAAT-box, TATA-box, ethylene, methyl jasmonate, abscisic acid response element, pathogenic bacterium inducer response elements W boxes, GT-1, MYB, MYBST1, MYB1LEPR, etc. There are also specific root expressing elements to enhance the expression of GUS gene, which expresses specifically in the phloem of root, bud and stem, the vein of foliage and the guard cell of air pore. Paraffin section observation shows that GHNBS promoter expresses in phloem companion cell. After treatment with SA, MeJA, Ethylene, pathogenic bacteria of blight and pseudomonas syringae DC3000, GUS will have obviously raised activity, so that it is one organ specific and pathogenic bacterium relevant promoter.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
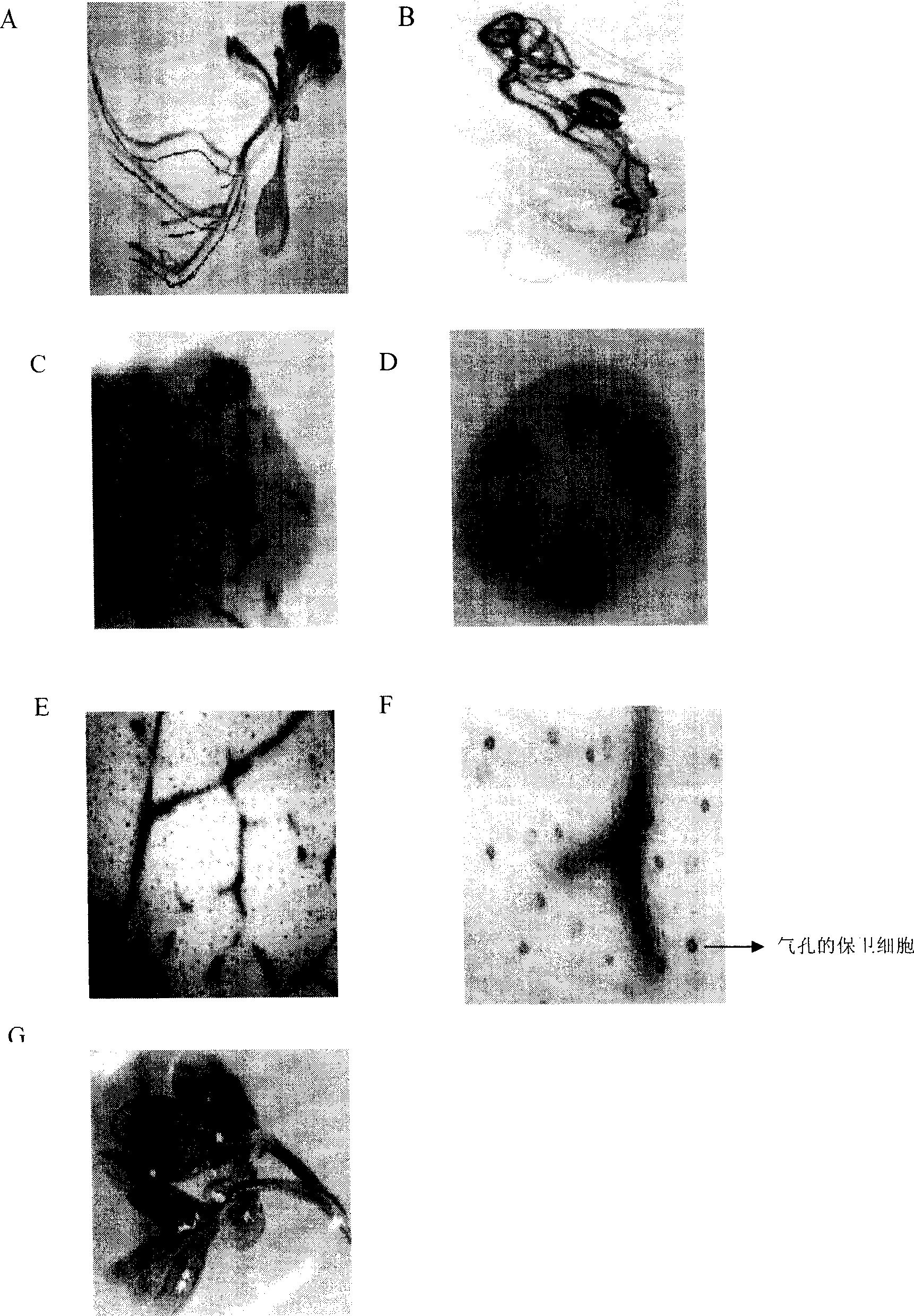
Preparation method for wheat leaf stomata guard cell observation samples
InactiveCN103076217AHas a preservation effectLong storage timePreparing sample for investigationMicroscopic observationDistilled water
The invention discloses a preparation method for wheat leaf stomata guard cell observation samples, and relates to the plant research technology. The method comprises the steps of preparation of a material to be treated, fixation of the material to be treated, dehydration and whole transparency. The method is characterized in that a transparent reagent adopted by the whole transparency is obtained by mixing chloral hydrate, distilled water and glycerol according to the weight ratio of 4 g: 1 ml: (0-0.5) ml (the ratio can be rationally widened to a range). For preparing the wheat leaf stomata guard cell observation samples, clear microscopic observation images are obtained.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Application of GRMZM2G417164 in stomata development
ActiveCN107723296AImprove stress resistancePlant peptidesFermentationAgricultural scienceGene engineering
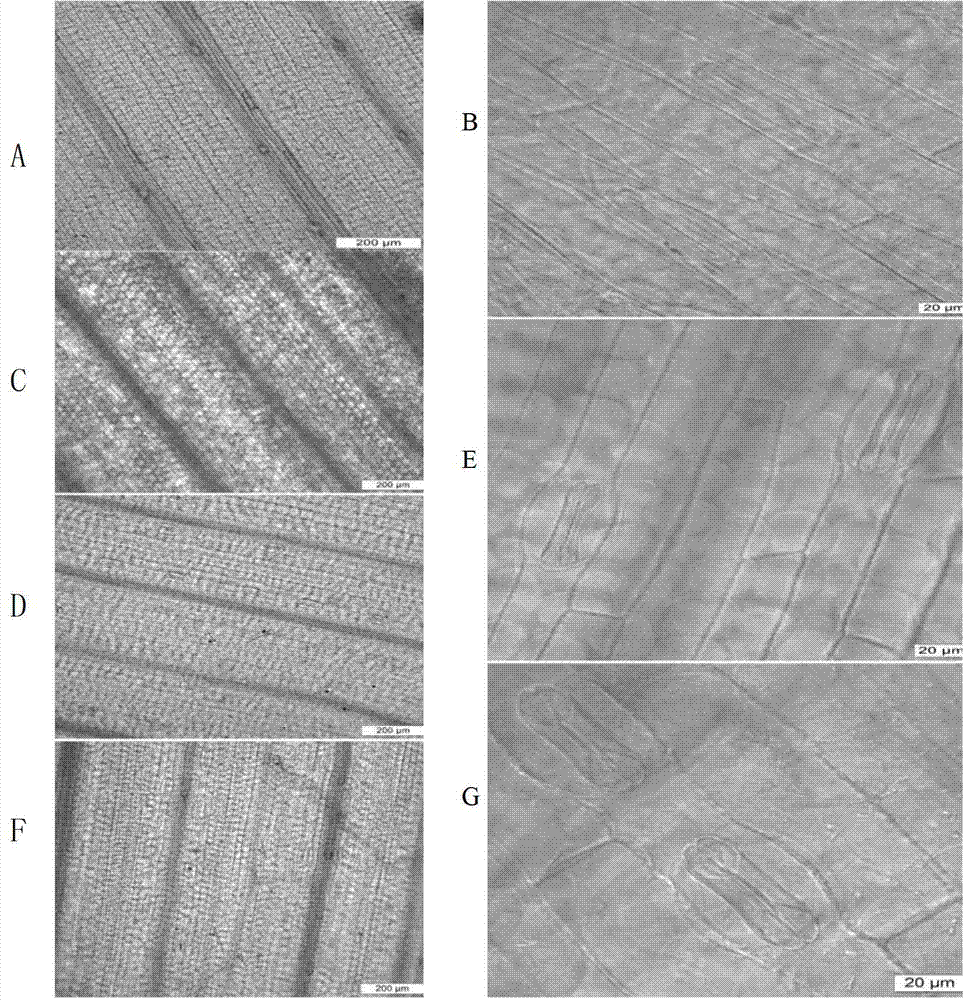
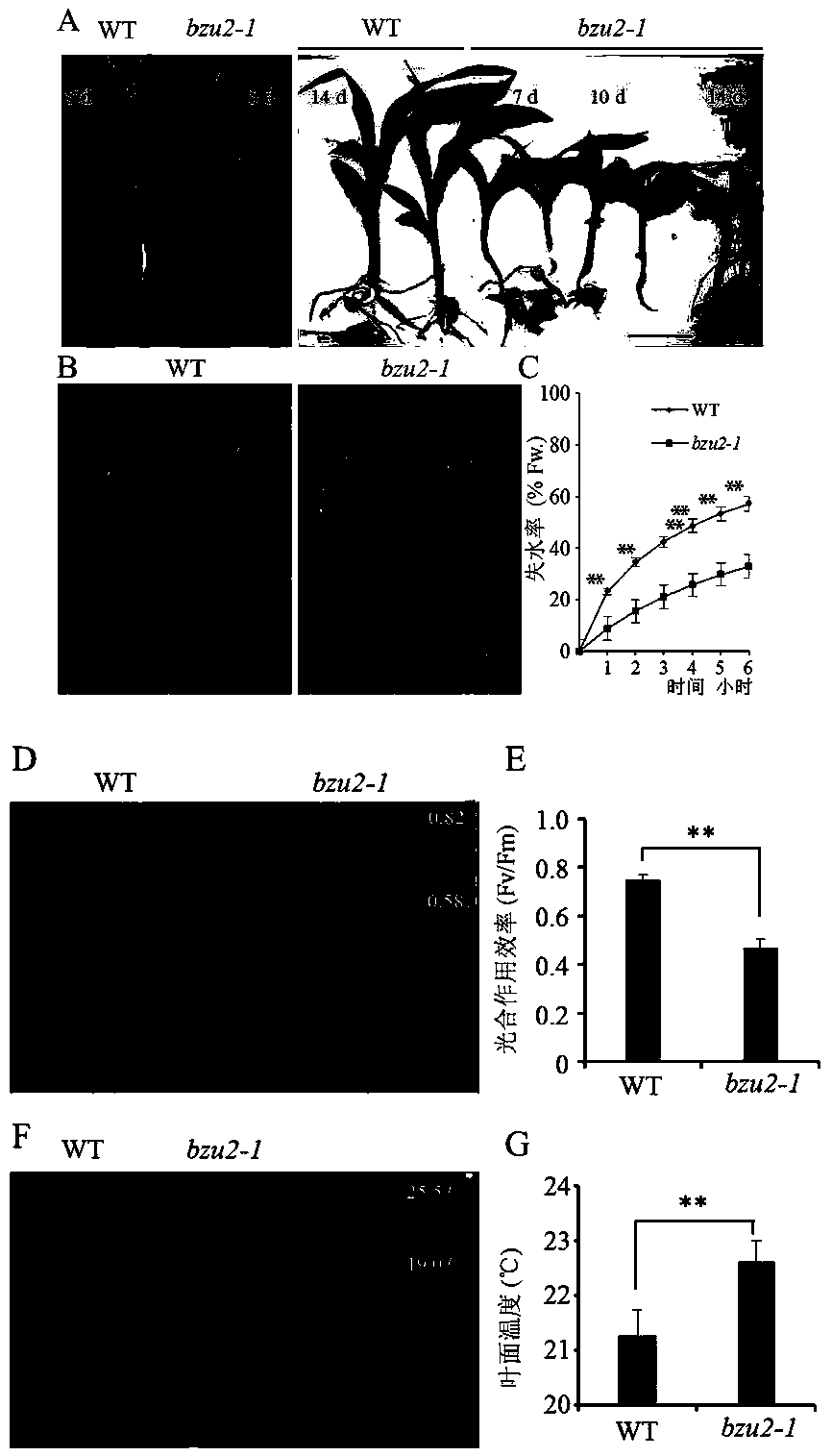
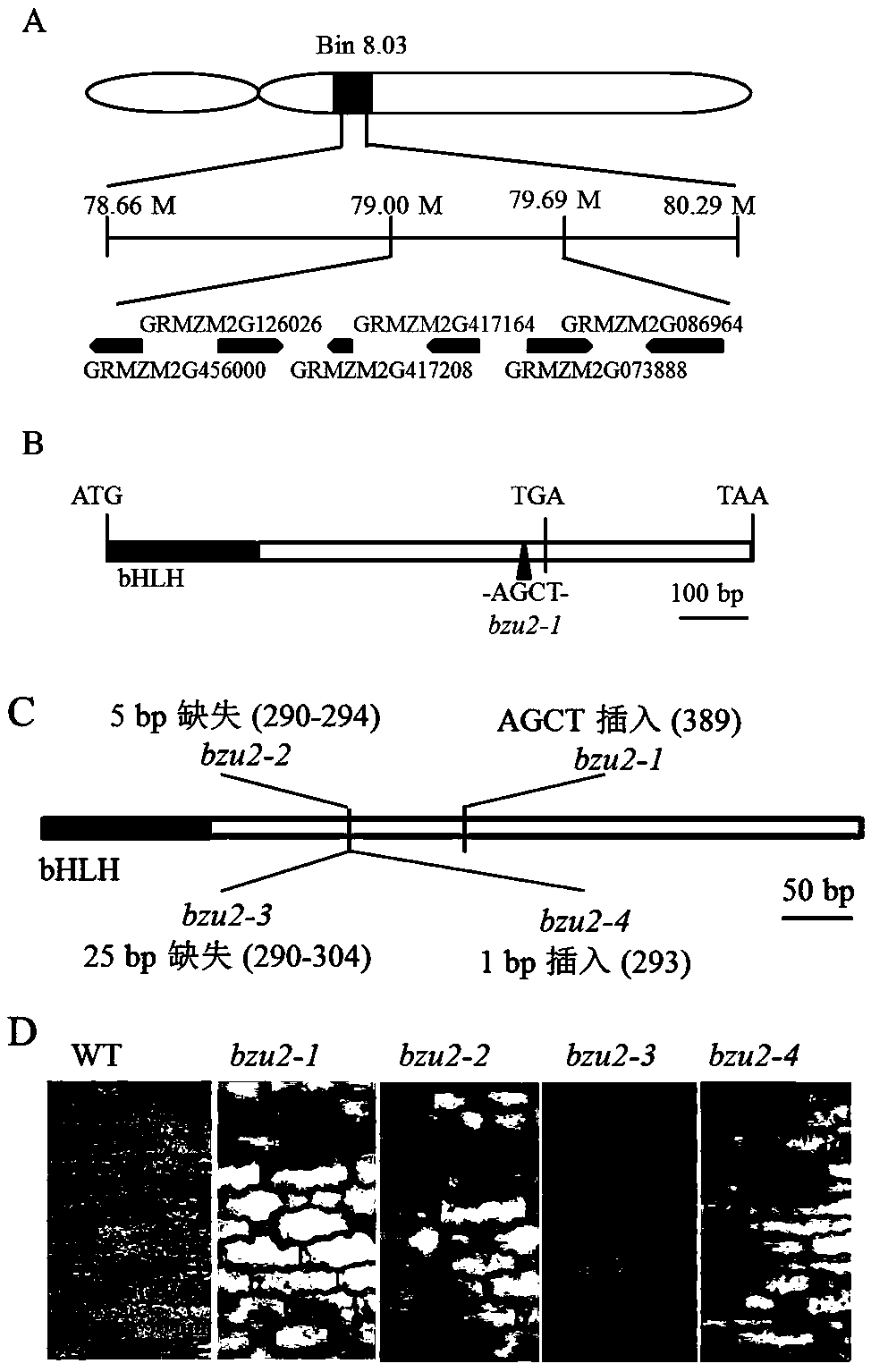
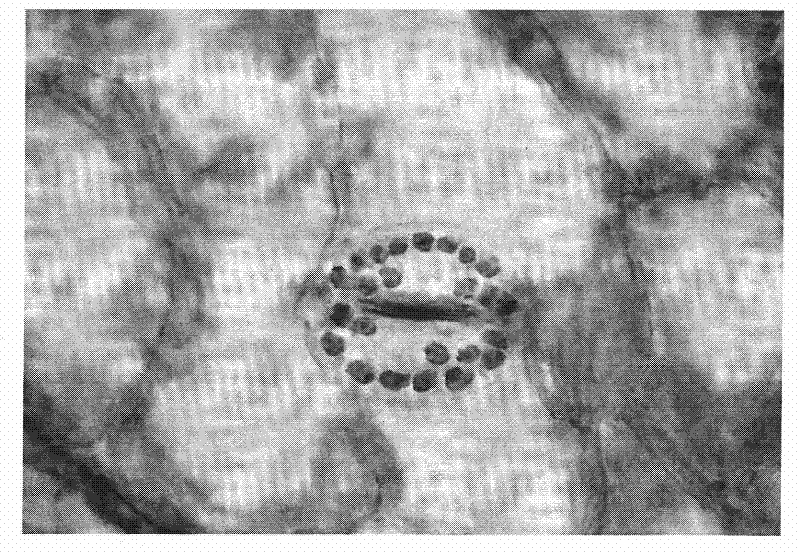
The invention relates to the technical field of maize gene engineering, in particular to application of a maize GRMZM2G417164 gene in adjustment of stomata development. The maize GRMZM2G417164, serving as a transcription factor, regulates some genes associated with the stomata development, and adjusts an associated process of maize stomata development. A series of experiments prove that a proteincoded by the GRMZM2G417164 gene controls transfer of a signal from a guard mother cell to a subsidiary mother cell and a final longitudinal division of the guard mother cell to form a guard cell. After the gene is mutant, a plant cannot form a normal guard cell and a normal subsidiary cell. Therefore, deep research and analysis on GRMZM2G417164 gene functions has an important theoretical significance and a practical application value for exploring a maize stomata development mechanism and improving maize resistance.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Method for identifying haploid regenerated by brassica napus microspores simply, conveniently and quickly
InactiveCN102304561AImprove application efficiencyUse impactMicrobiological testing/measurementCuticlePlant cell
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant cytology, and particularly relates to a method for identifying haploid regenerated by brassica napus microspores simply, conveniently and quickly in batch in the early stage in a method of chloroplast counting. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: inoculating an embryoid cultured by in-vitro microspores onto a B5 culture medium; when the embryoid is grown into a complete plant, cutting the fifth even leaf sterilely; dyeing the lower epidermis tissue in the middle of the leaf by using iodine-potassium iodide; observing chloroplasts of guard cells of air vents by using an optical microscope; and recording the number of the chloroplasts of 10 air vents on each prepared leaf (namely the same leaf), wherein more than 7 air vents have 6 to 8 chloroplasts, and the plants of the chloroplasts are the haploid. By the method, the problem of long-time subculture of the haploid is solved, and in ten thousands of plants, the cost of reagents, lands and labors can be saved by 19,083 RMB. The method has a simple process, is easy to operate and low in cost and can be used for identifying the ploidy of a large number of plants, and one plant of seedling is identified only for 5 minutes, so the application efficiency of the double haploid (DH) technology is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
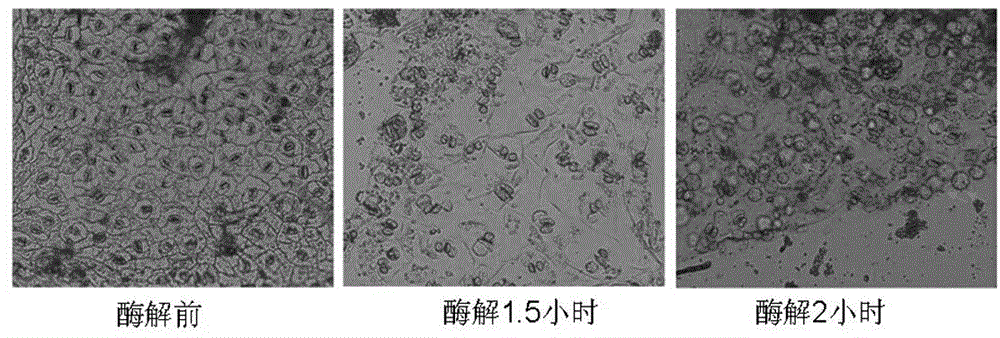
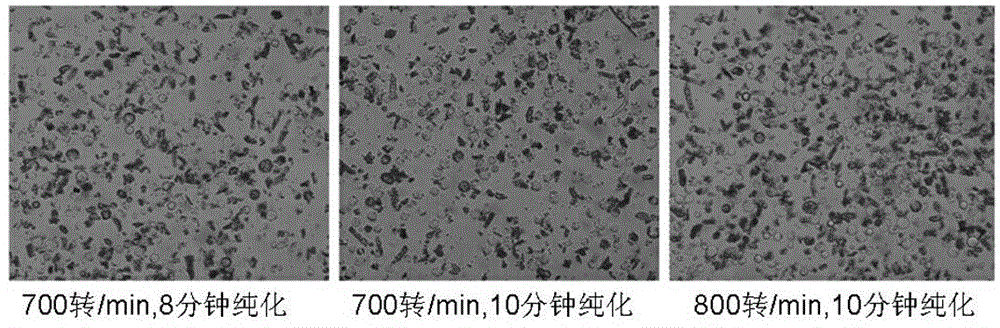
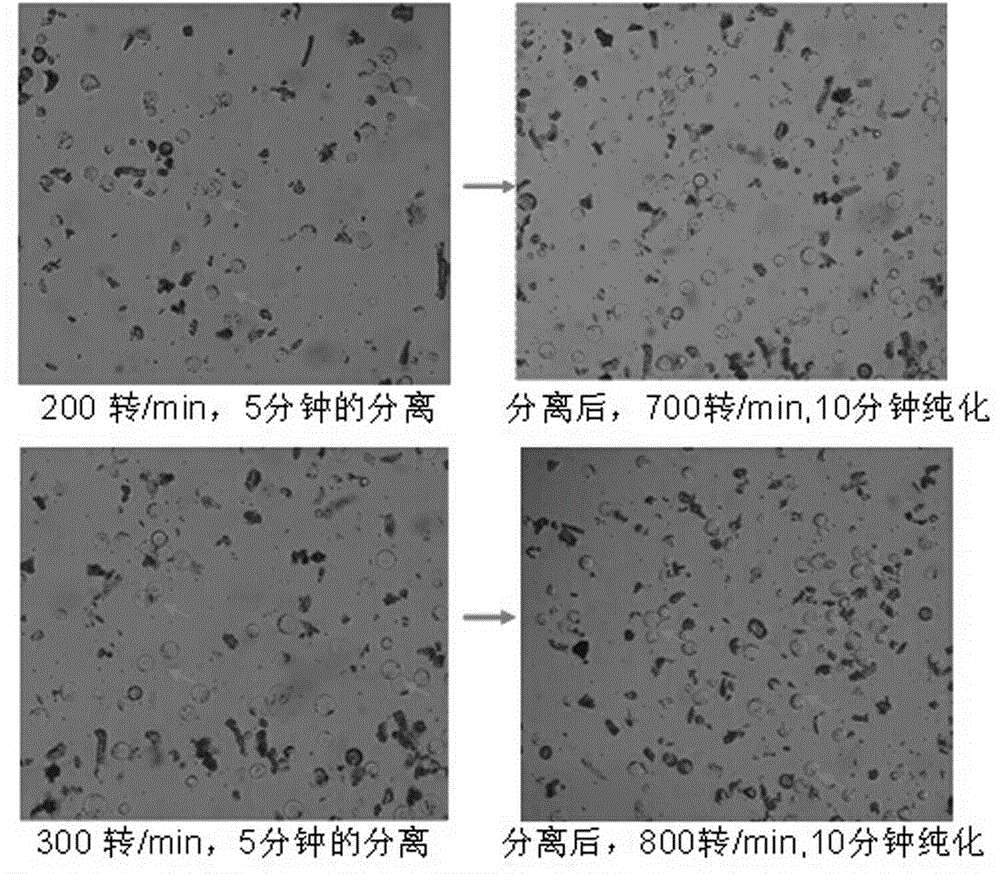
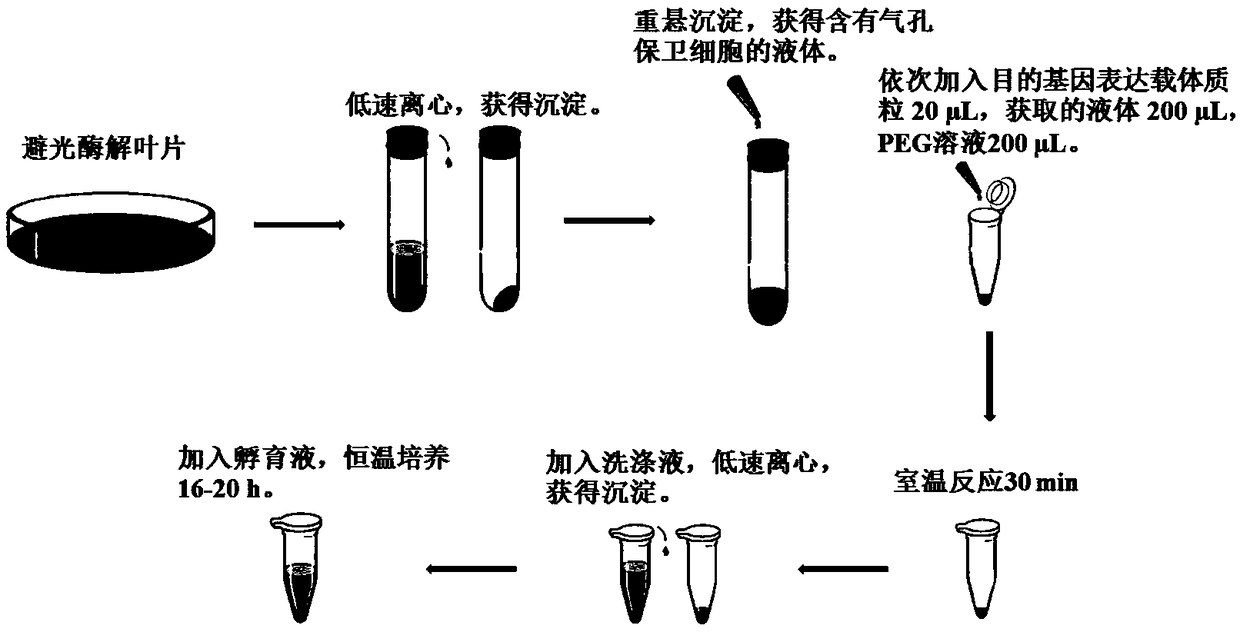
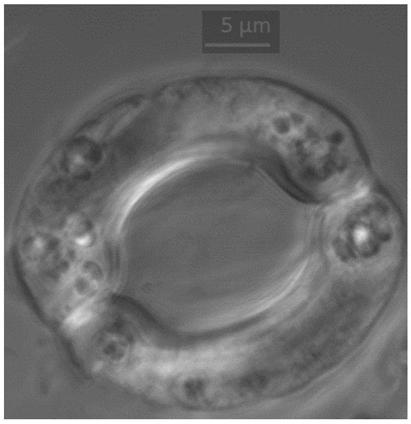
Method for separating cotton guard cell protoplast
The invention particularly relates to a method for separating a cotton guard cell protoplast. The method comprises the following steps: inducing germination of cotton seeds, carrying out enzymolysis and separation on the guard cell protoplast, centrifuging and the like. According to the method for separating the cotton guard cell protoplast provided by the invention, guard cells of cotton leaves are processed by adopting a one-step enzymolysis approach. Compared with a two-step enzymolysis approach, the experimental period is greatly shortened, the experimental operation process is simplified, the experiment efficiency is improved, high physical activity of the protoplast is kept, the problem of separation of the cotton guard cell protoplast is solved, and a good experimental foundation is provided for research of guard cell permeability, ion transportation and the mechanism of stomatal movement by successful separation of the cotton guard cell protoplast.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
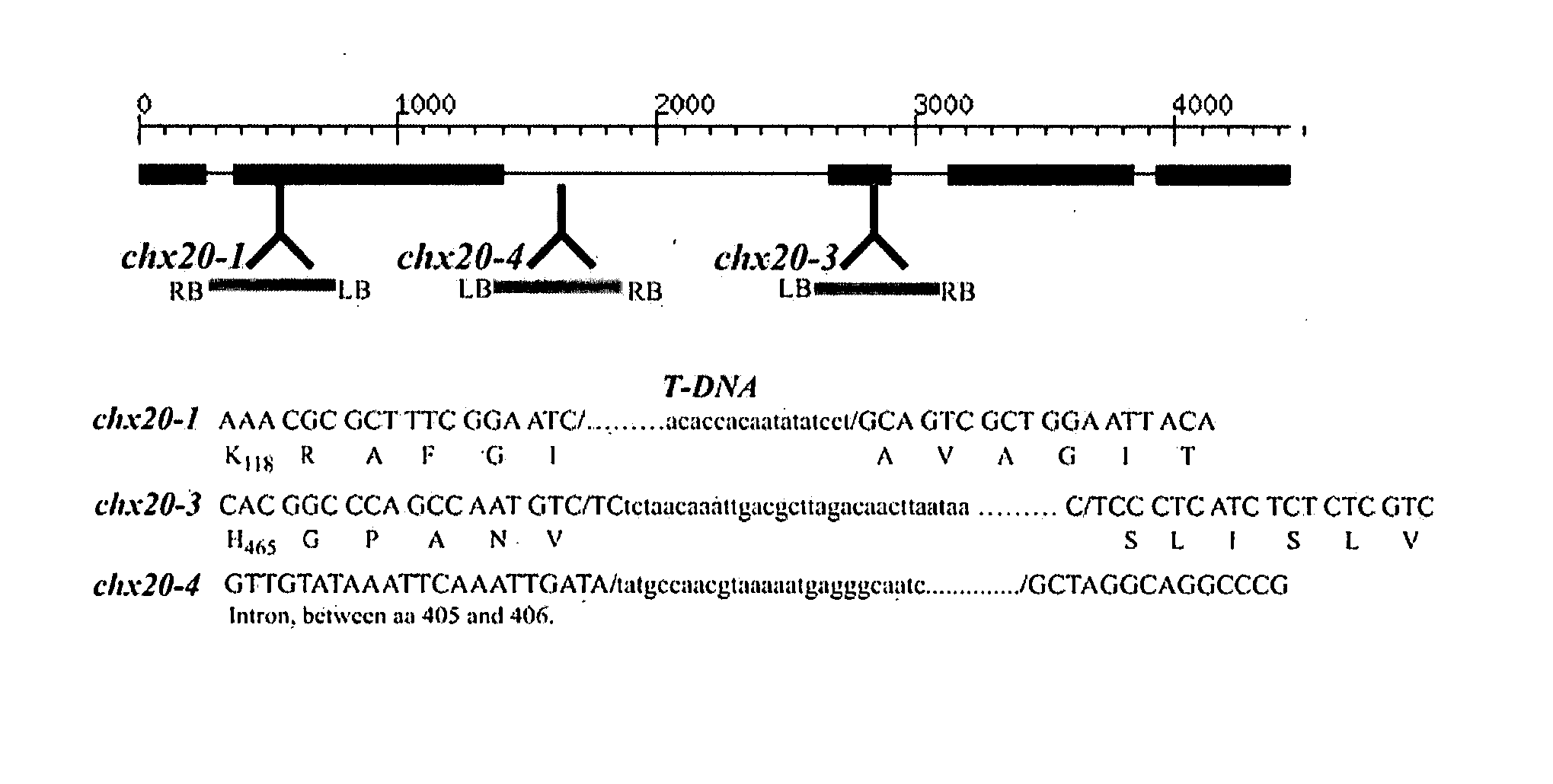
Guard cell-specific tool for molecular manipulation of drought avoidance/water loss in plants
InactiveUS20080028489A1Improve scalabilityGrowth of yeastSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesGas exchangeBiology
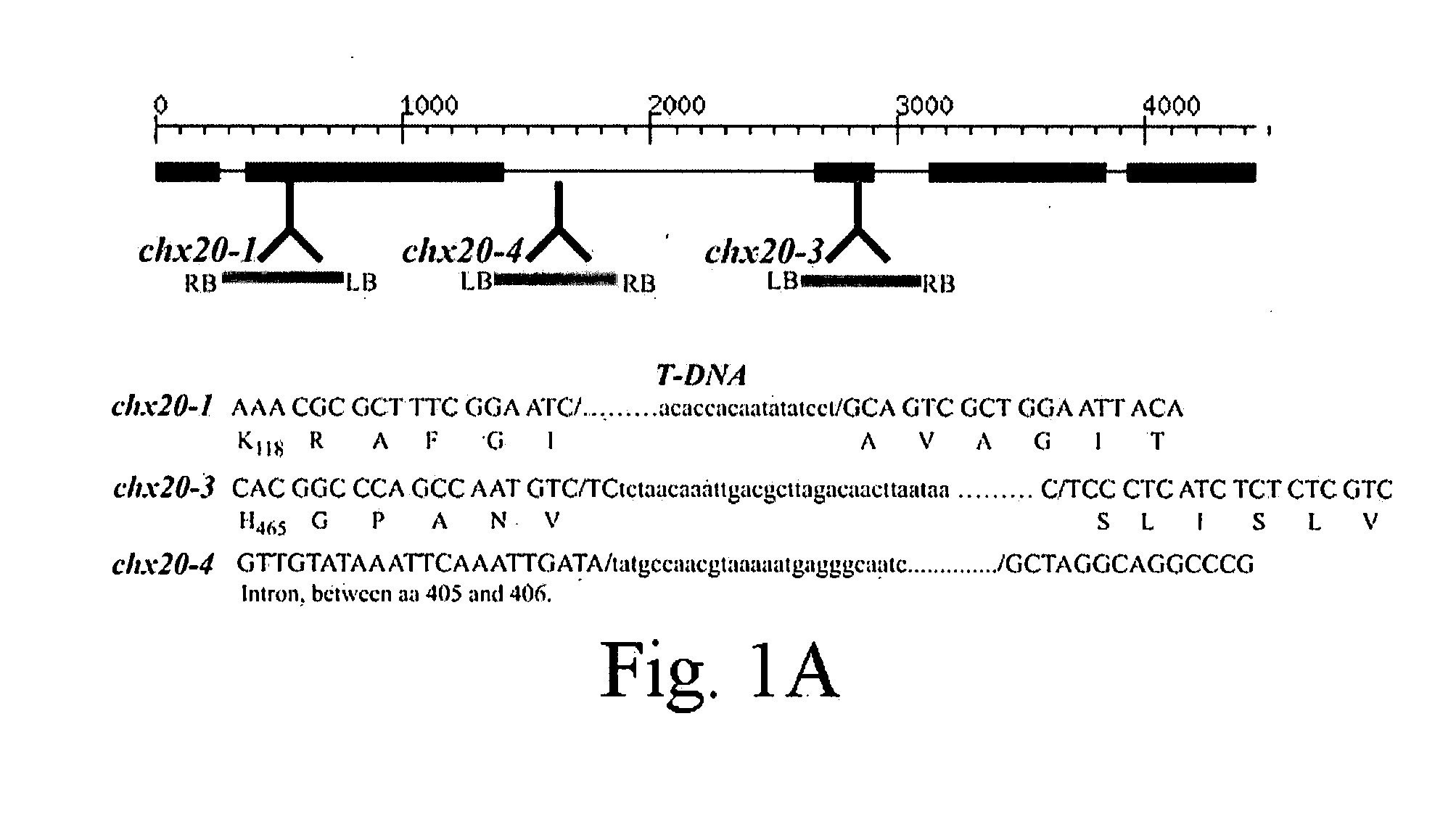
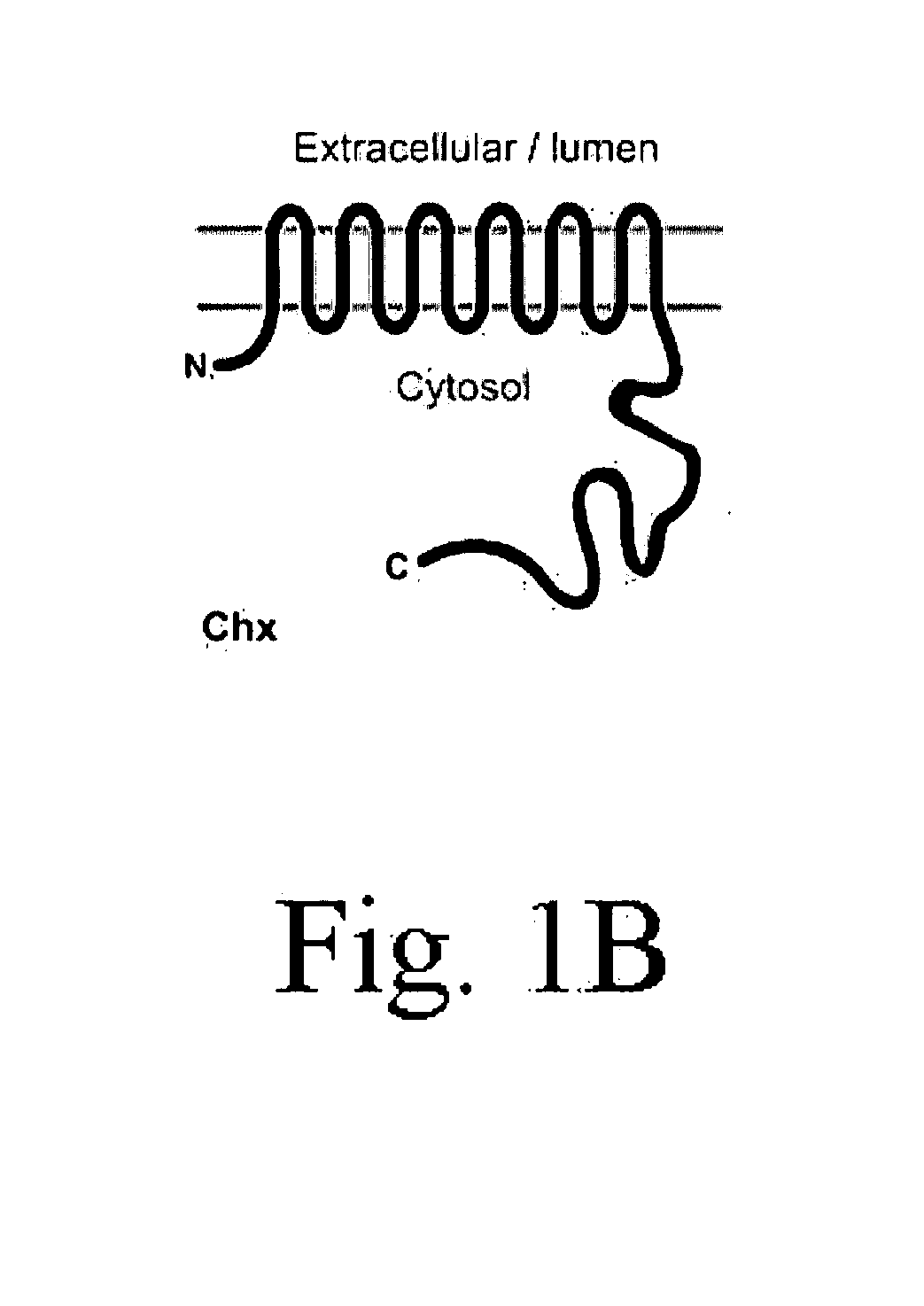
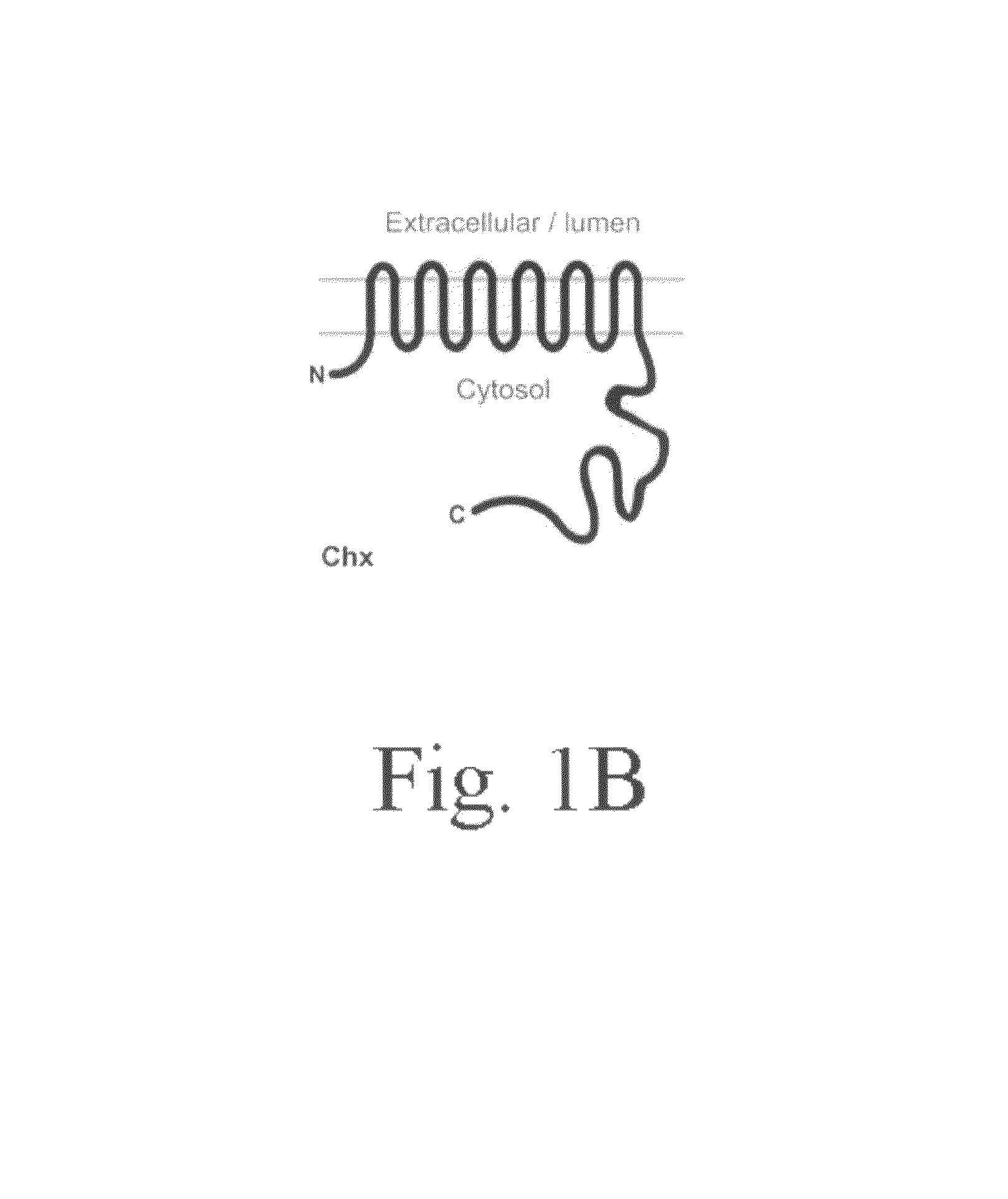
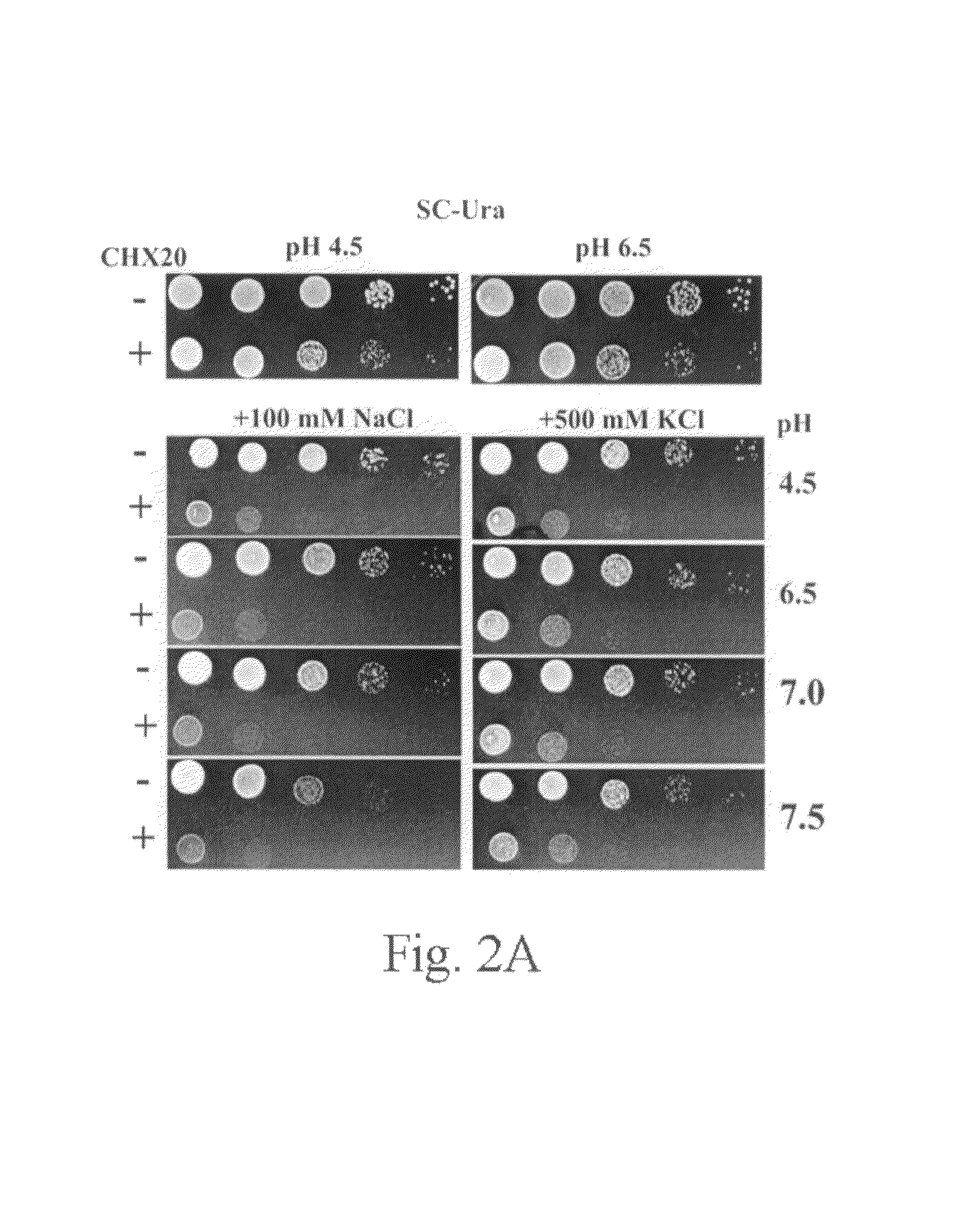
The inventors herein disclose a new transporter that participates in guard cell movement. The inventors have now found that AtCHX20 is preferentially expressed in guard cells using microarray and promoter TGUS analyses. The inventors have also found a guard cell specific promoter which serves as a powerful tool to manipulate the opening and closing of guard cells and thus the ability to control water loss and gas exchange of plants. Such a tool can be particularly useful when applied to crops and other plants of economic importance, thus the present inventors have identified homologous genes in several other plants that fall within the scope of this invention.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Fluorescent indicator detection method for concentration of free calcium ion in guard cell of tomato blade
InactiveCN106770127AAccurate detectionEasy to operatePreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceLaser scanning
The invention discloses a fluorescent indicator detection method for concentration of a free calcium ion in a guard cell of a tomato blade. The method comprises the steps of 1, preparing a fluorescent indicator working solution, 2, obtaining a tomato blade hypoderm, 3, loading the prepared fluorescent indicator solution on the obtained tomato blade hypoderm, and 4, acquiring a fluorescent image on the tomato blade hypoderm loaded with the fluorescent indicator solution by a laser-scanning confocal microscopy and determining an optimum method of fluorescent indicator detection for the concentration of the free calcium ion Ca<2+> in the guard cell of the tomato blade according to the acquired fluorescent image.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF AGRI
Arabidopsis-stomatal-specific promoter and a genetic construct containing the promoter for expression of nucleic acids in plants
InactiveUS7662947B2High degreeAvoid lostSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesArabidopsisFhit gene
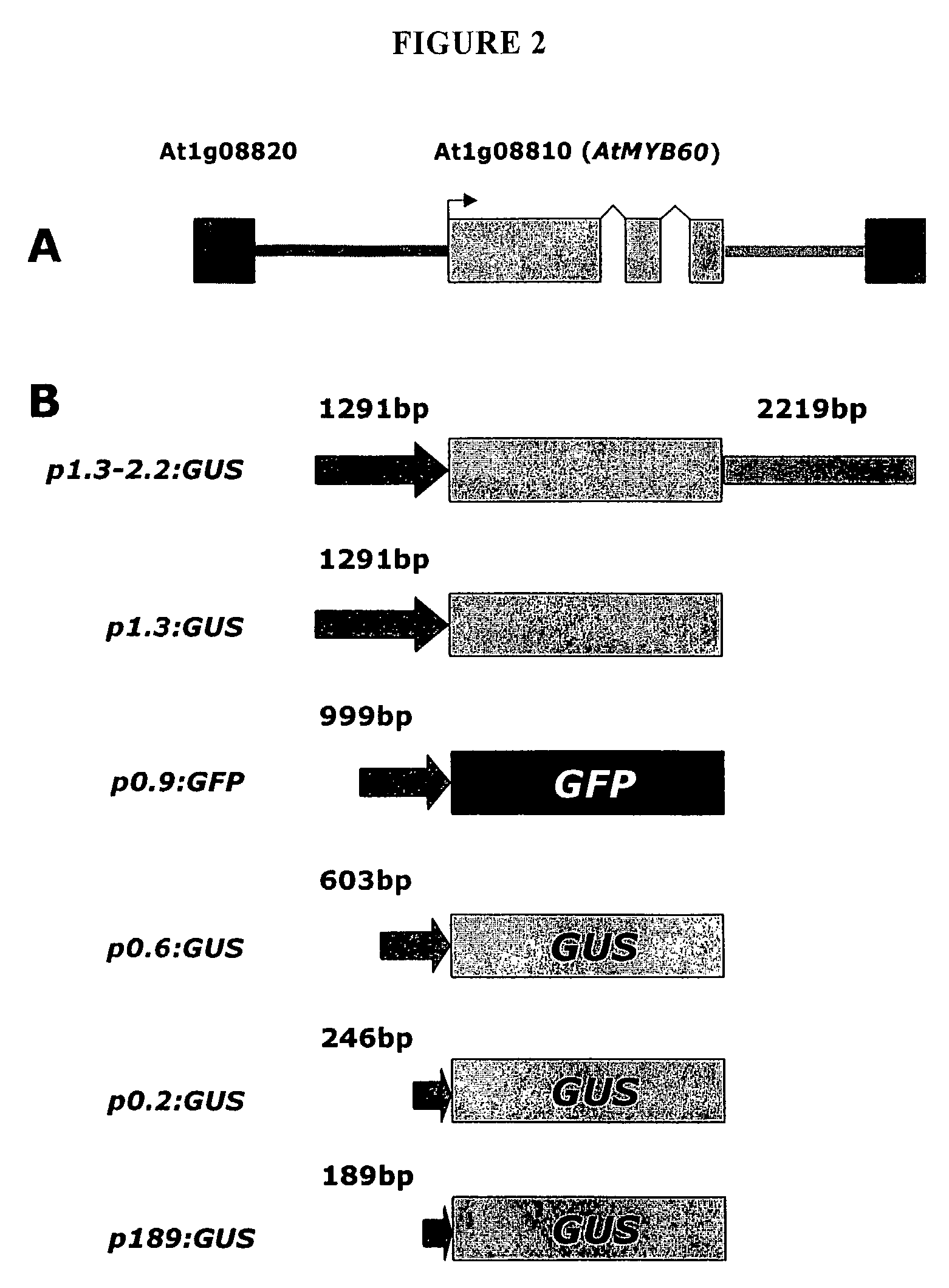
The present invention relates to the expression of recombinant nucleic acids in plants. More specifically, the invention provides an Arabidopsis stomatal-specific promoter (AtMYB60 promoter—SEQ ID NO: l)for the selective expression of nucleic acids in stomatal guard cells, gene constructs containing the promoter, expression vectors carrying such and plants transfected therewith. The selective expression of nucleic acids in plant guard cells allows the regulation of stomatal opening / closing states thereby modulating, e. g. increasing, the plant ability to resist to adverse environmental or climatic conditions.
Owner:GALBIATI 50 PERCENT INTEREST MASSIMO +1
The method for doubling haplobiont of gerbera
The invention discloses a method for doubling a haplobiont of gerbera. The method for doubling the haplobiont of the gerbera comprises the following steps: double haplobiont plants are finally determined when tissue-cultured breeding seedlings of the haplobiont of the gerbera go through strong seedlings and multiplication culture, chemical mutagenesis culture, rejuvenation culture, variant plantsscreening, breed conservation of primary plants, propagation, rooting culture, mutagenic strains reselection, identification of stomata guard cells chloroplast counting method, and identification of root tip chromosome counting method. The ploidy doubling cultivation of haplobiont of the gerbera and identification processes are optimized, while mutation rate of the haplobiont is increased, and theaccuracy of ploidy identification is guaranteed. The method for doubling the haplobiont of the gerbera can effectively reduce the formation and interference of chimeras, reduce the damage of chemicaldrugs to the plants to reduce death rate of the haplobiont, and keep variation rate of the haplobiont between 60-80%, and provides the double haplobiont with excellent traits and high stability for breeding of new variety of the gerbera.
Owner:FLOWER RES INST OF YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI +2
Foliage fertilizer
InactiveCN101423441AImprove wetting abilityLow costAmmonium salt fertilisersFertilizer mixturesSulfateStratum corneum
The invention relates to a foliage fertilizer. The foliage fertilizer is characterized in that the foliage fertilizer comprises the following compositions in weight percent: 20 to 30 percent of potassium citrate, 1 to 2 percent of ferrous sulfate, 1 to 5 percent of manganese sulfate, 1 to 2 percent of bluestone, 1 to 5 percent of ammonium molybdate, 1 to 5 percent of surfactant, 1 to 5 percent of complexing agent and the balance being water. The potassium citrate, micro-fertilizer and the surfactant are compounded to form the foliage fertilizer which has nutritive substances essential to the growth of plants. The compounded foliage fertilizer has strong wetting capacity, is sprayed on the leaf surface of the plant and is absorbed by the plant through corneum, or unkeratinized guard cells or pores of the leaf surface, thereby improving the utilization rate of the fertilize effect and the supplementation of the micro-fertilizer; and the fertilization method has low cost and rapid effect, and is simple and convenient.
Owner:孙立民
Expression cassettes for guard cell-preferential expression in plants
InactiveUS20060117408A1Less stringentAffect processSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAArabidopsis
The present invention relates to expression cassettes comprising transcription regulating sequences with guard cell-preferential or guard cell-specific expression profiles in plants obtainable from Arabidopsis thaliana gene At5g58580, or from Arabidopsis genomic DNA sequences as described by SEQ ID NO: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 12, 13, 14, or 15.
Owner:SUNGENE
Application of combination of chemical mutagenesis method and negative pressure method in chionanthus retusus polyploid breeding
ActiveCN110036907APromote rootingImprove breathabilityAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersDiseaseChloroplast
The invention discloses application of a combination of a chemical mutagenesis method and a negative pressure method in chionanthus retusus polyploid breeding. The application includes following steps: collecting chionanthus retusus seeds, germinating through sand storage, putting germinating seedlings into a culture dish with a mutagenic agent, putting the culture dish into a negative pressure pump, treating under negative pressure, and transplanting when the treated germinating seedlings grow to have about 4-5 leaves; spraying nutritional liquid to the leaves after transplanting, spraying liquid fertilizer to roots of chionanthus retusus seedlings, correcting chionanthus retusus plants at proper time, and timely removing diseased stems and weak stems; timely preventing and controlling pest and disease when chionanthus retusus seedlings grow. The method can increase probability of chromosome doubling; formed polyploid plants are thicker in leaf, darker in leaf color, bigger in air hole size and fewer in air hole in unit leaf area, and number of guard cell chloroplasts is obviously increased.
Owner:TAISHAN RES INST OF FORESTRY
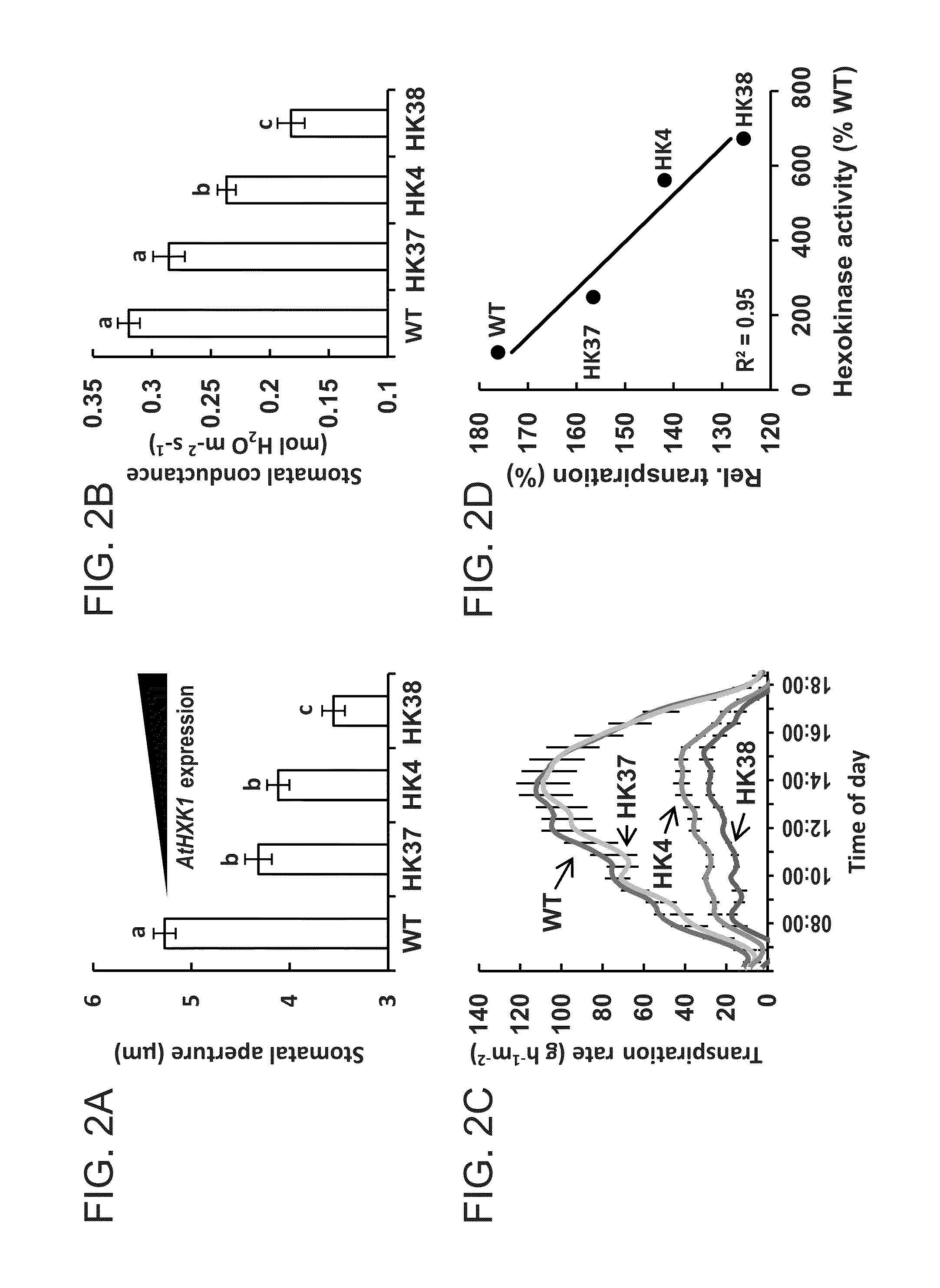
Methods of modulating stomata conductance and plant expression constructs for executing same
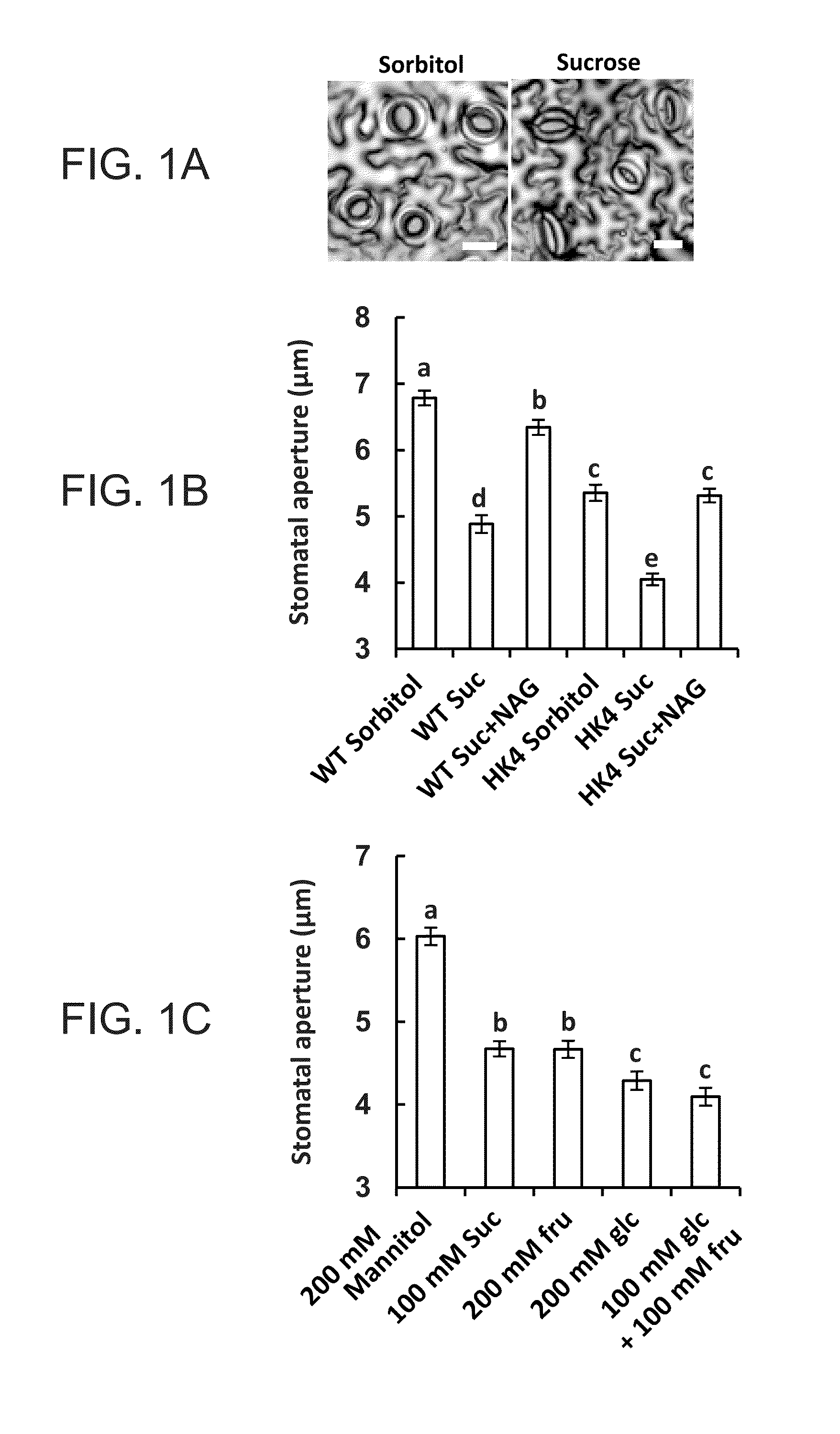
InactiveUS20140345000A1Decreasing stoma conductanceDecreasing the stomata conductance of the plantClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesPlant cellNucleic acid sequencing
Plant expression construct are provided. According to an embodiment, the plant expression construct comprises a nucleic acid sequence encoding a hexokinase under a transcriptional control of a guard cell-specific cis-acting regulatory element. Also provided are methods of using the constructs and transgenic plants, plant cells and plant parts expressing same.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD +1
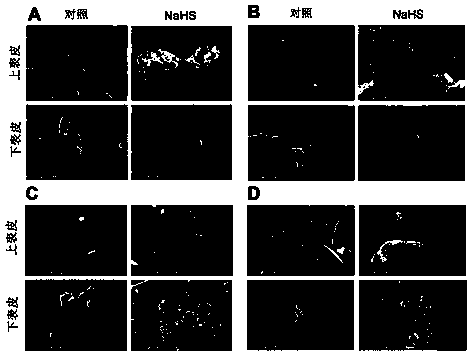
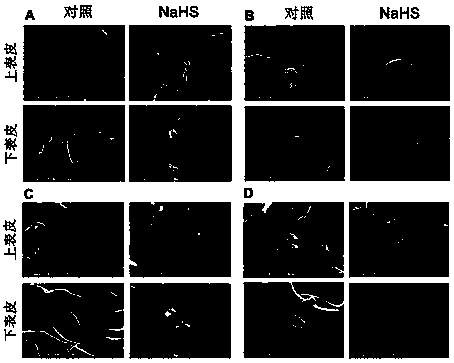
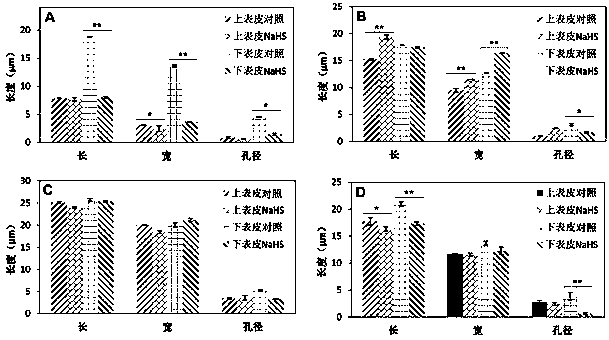
Application of sodium bisulfide as plant stress-resisting agent
The invention discloses an application of sodium bisulfide as a plant stress-resisting agent. The plant stress-resisting agent is instantly prepared for use. NaHS is prepared into an aqueous solutionin concentration of 50-100umol.L-1, and then the aqueous solution is sprayed onto mature leaves of plants. The NaHS aqueous solution utilizes NaHS to slowly release H2S / HS- in water, so as to achievethe functions of restraining development of stomata guard cells and boosting compound of waxes on plant surface. The plant stress-resisting agent has the advantages of obvious effect, high water solubility, low cost, safety, non-toxicity and simple preparation. The plant stress-resisting agent according to the invention also can supplement sulfur (S) and sodium (Na) required by plants and has thefunction of leaf fertilizers.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Composite foliar fertilizer
InactiveCN101734965AImprove wetting abilityLow costPotassium fertilisersFertilizer mixturesSulfateStratum corneum
The invention discloses a composite foliar fertilizer, and is characterized by comprising the following components in weight percent: 20-30% of potassium sulfate, 1-2% of ferrous sulfate, 1-5% of manganese sulfate, 1-2% of copper sulfate, 1-5% of zinc sulfate, 1-5% of surfactant, 1-5% of complexing agent and the balance water, wherein, the potassium sulfate compounds with tiny fertilizer and the surfactant to manufacture the foliar fertilizer which has nutrient substances needed for the growth of the plants. The compounded foliar fertilizer has strong moistening capacity, and is absorbed by plants through foliar surface cuticula or non-keratinized guard cells and pores when being sprayed on the foliar surfaces of plants, thus improving the use ratio of fertilizer efficiency and the supplement of the tiny fertilizer, and being a fertilizing method with low cost, quick effect and simple method.
Owner:孙立华
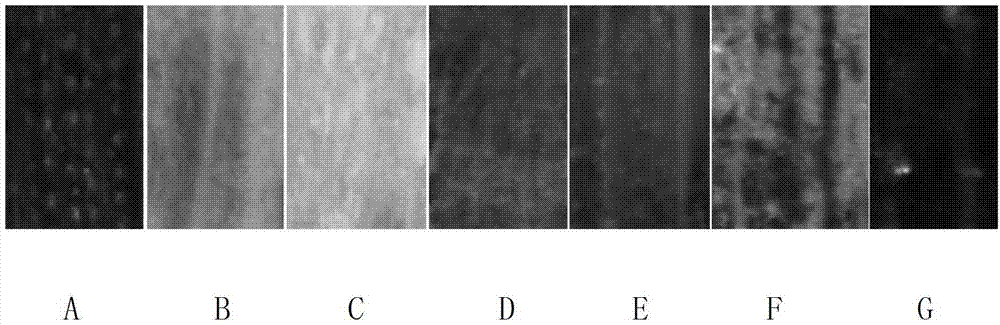
Method for observing distribution and dynamic states of proteins on stomatal guard cell membrane at single-molecule level
ActiveCN108195801AAvoid damageHigh resolutionFluorescence/phosphorescenceCell membraneMolecular level
The invention provides a method for observing the distribution and dynamic states of proteins on a stomatal guard cell membrane at a single-molecule level, belonging to the field of biotechnology. Themethod comprises the following steps: A, acquiring a transgenic material in which a target gene is fluorescently labeled; B, acquiring the real-time images of proteins on a guard cell membrane by using a total internal reflection fluorescence microscope; C, processing the time series images by using the Image J software; D, carrying out single-particle tracing analysis on target proteins via Matlab R2014a so as to determine the dynamic state of each individual protein polymer; E, calculating the dwell time of the proteins on the cell membrane; and F, subjecting the dwell time parameters of the target proteins to Gaussian Fitting so as to determine the dwell time and changes of the target proteins. The method has the advantages of capacity of improving the signal-to-noise ratio of imagingand realizing high-resolution observation, fast imaging speed, in-vivo visibility and high repeatability. The method has practical application value in the research of the functions of plant genes.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
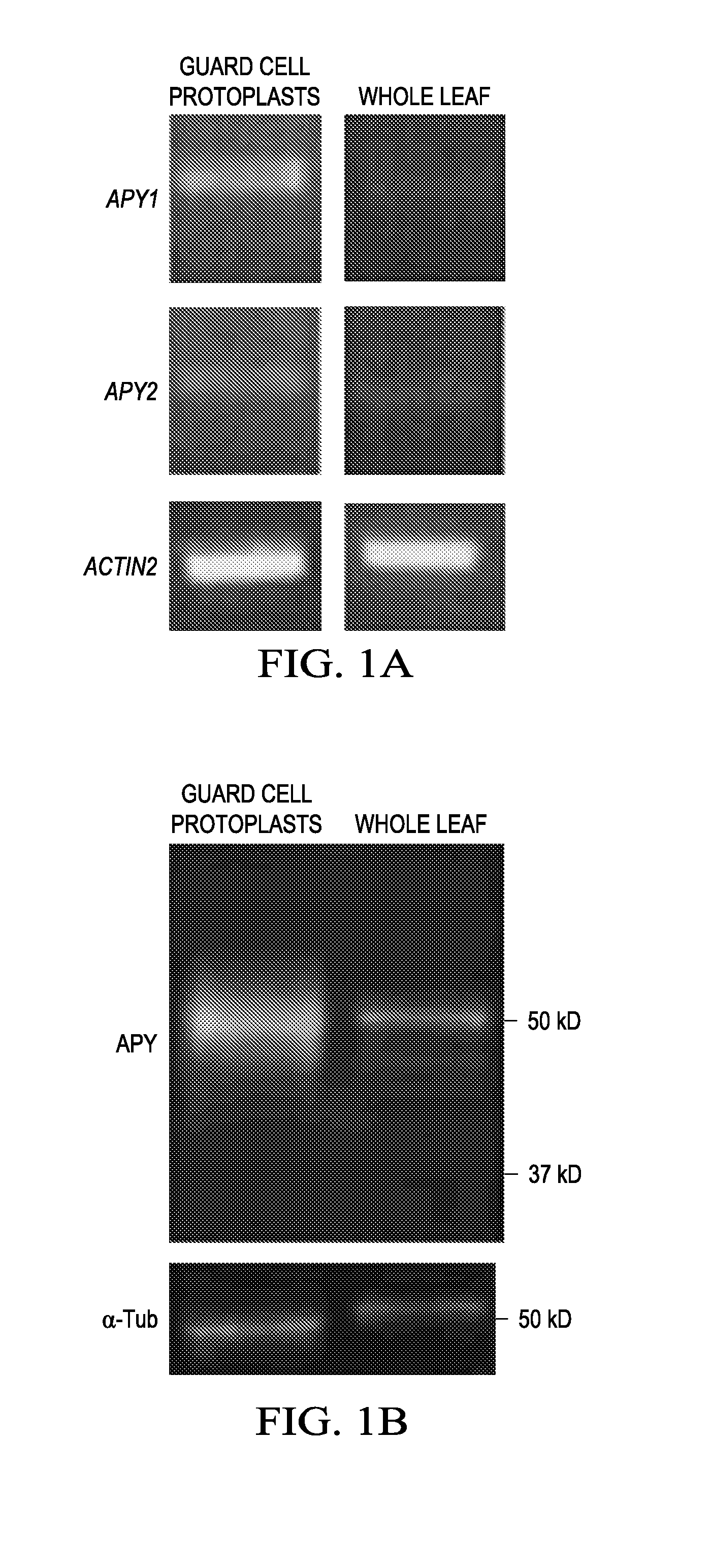
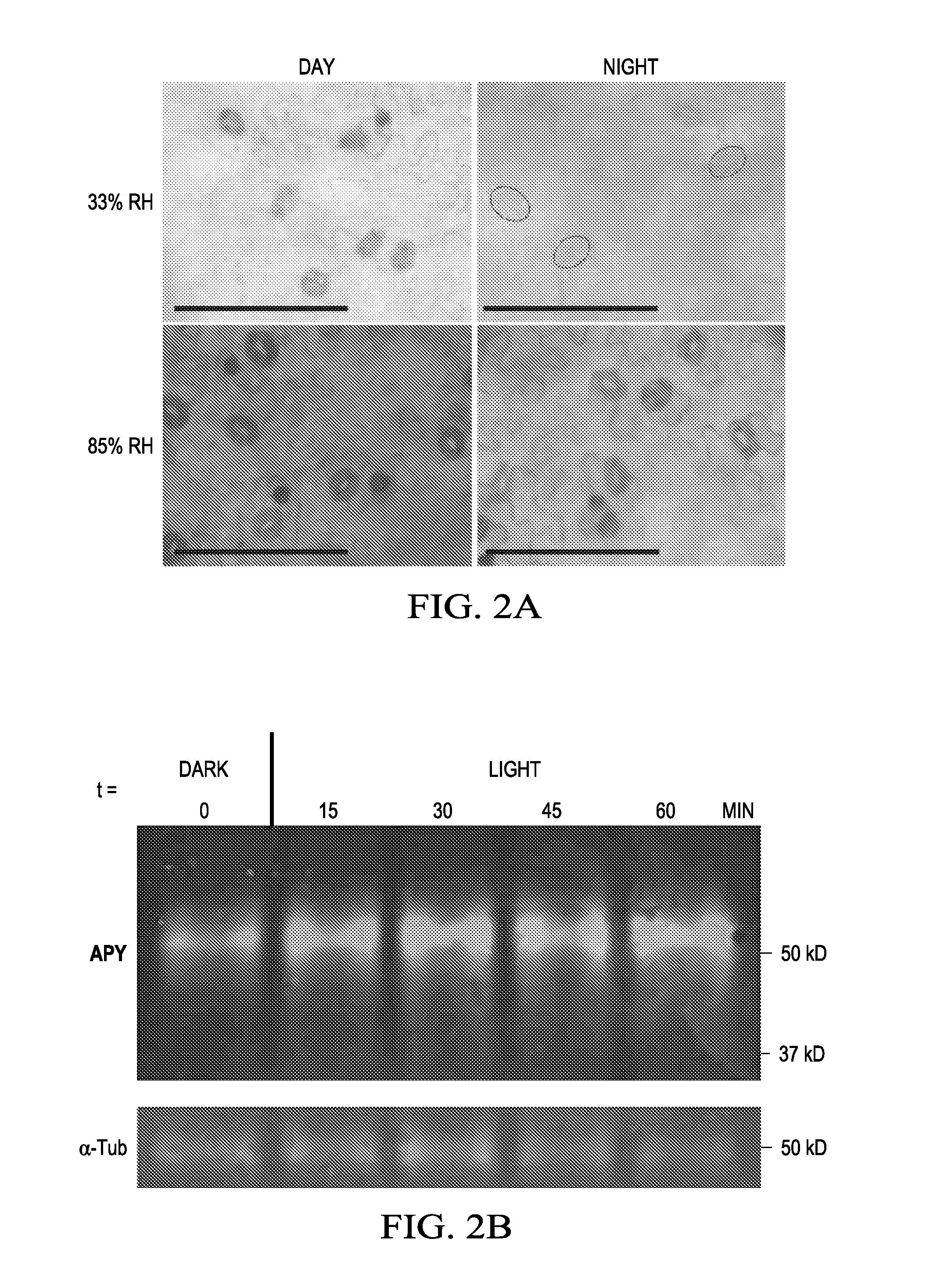
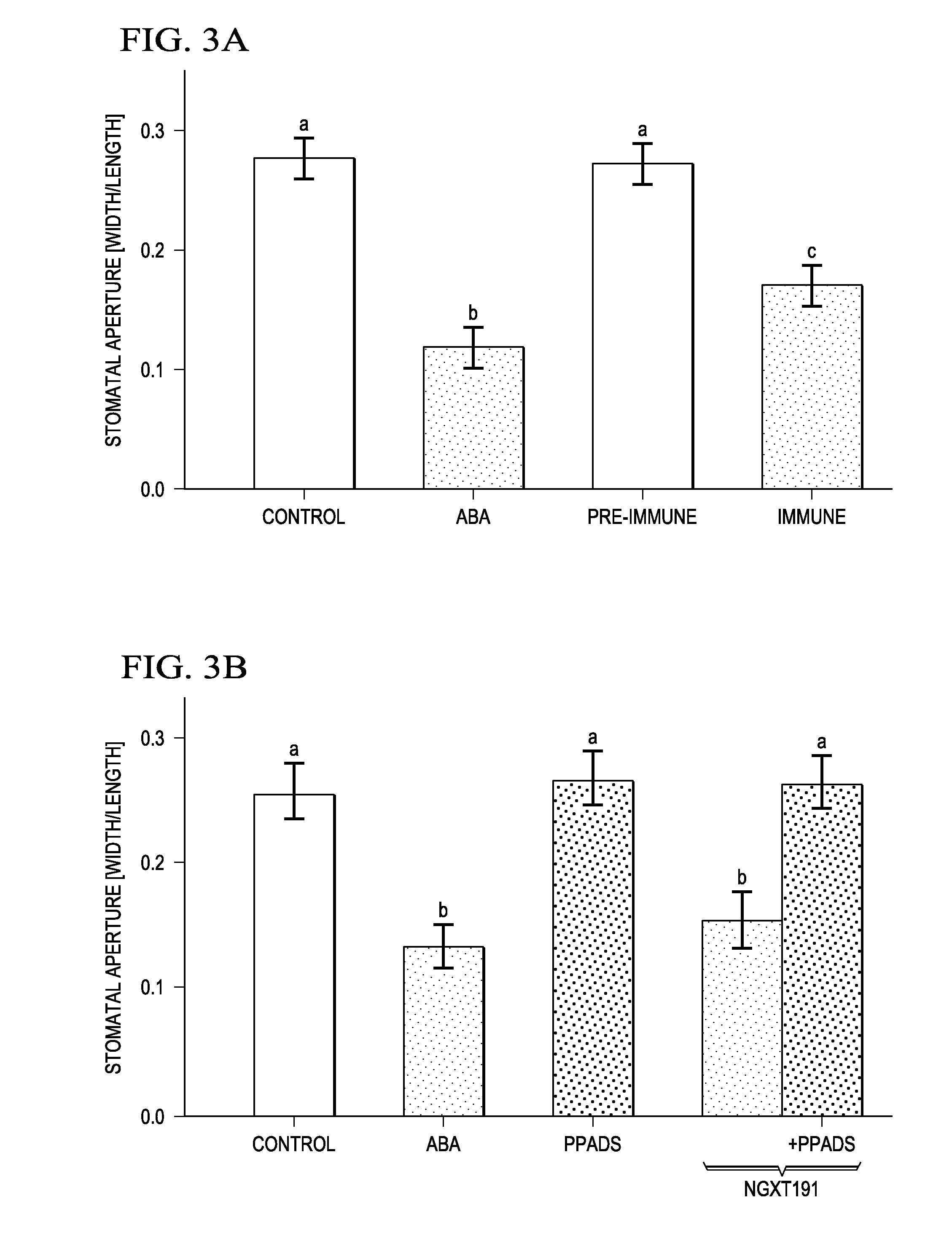
Regulation of Stomatal Apertures by Apyrases and Extracellular Nucleotides
The role of extracellular nucleotides and apyrase enzymes in the guard cells that border stomata in regulating stomatal aperture and the plant's resistance to drought and pathogens is disclosed herein. Expression of apyrases APY1 and APY2, in guard cell protoplasts is strongly correlated with cell growth, cell secretory activity and with conditions that favor stomatal opening. Both short-term inhibition of ectoapyrase activity and long-term suppression of APY1 and APY2 transcript levels significantly disrupt normal stomatal behavior in light. Furthermore, two punnoceptor inhibitors in mammals, pyridoxalphosphate-6-azo-phenyl-2′,4′-disulphonic acid (PPADS) and Reactive Blue 2, block ATPS- and ADPβS-induced opening and closing, and also partially block the ability of abscisic acid (ABA) to induce stomatal closure, and light-induced stomatal opening. Treatment of epidermal peels with ATPyS induces increased levels of nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species, and genetically suppressing the synthesis of these agents blocks the effects of nucleotides on stomatal aperture.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Identification method of interspecific hybrids of Brassica campestris and Brassica napus
InactiveCN102768210AImprove accuracyAccurate identificationInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsStomaCuticle
The invention discloses an identification method of interspecific hybrids of Brassica campestris and Brassica napus, falling into the technical field of plant cytology. The method includes collecting the 4th-7th leaves of a plant in the seedling stage, tearing to collect hypoderm tissues of lower parts of the leaves, staining with iodine-potassium iodide solution, observing stomata under an optical microscope, measuring major / minor axis values of guard cells, calculating perimeter values of the guard cells with an ellipse model while observing and counting chloroplasts, recording 15 data per leaf, and identifying with parents as controls. For Brassica campestris, stoma guard cells have perimeter smaller than 58.90 micrometer and chloroplast count of 9-11; for Brassica napus, stoma guard cells have perimeter greater than 75.83 micrometer and chloroplast count of 19-20; while, for the to-be-identified material, if more than ten stomata simultaneously satisfy that guard cells have perimeter of 58.90-75.83 micrometer and chloroplast count of 14-16, it is determined that the plant is interspecific hybrids F1 of Brassica campestris and Brassica napus, otherwise it is false hybrid.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Method for obtaining callus tissue of stevia rebaudiana bertoni
InactiveCN107980630AImprove separation efficiencyShorten the timeHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureCuticleGuard cell
The invention belongs to the field of plant cell culture, and particularly relates to a method for obtaining callus tissue of stevia rebaudiana bertoni. The method for obtaining the callus tissue of the stevia rebaudiana bertoni comprises steps as follows: induced culture of stomatal guard cells of the stevia rebaudiana bertoni, suspension culture and induced culture of the callus tissue. With theadoption of the method for obtaining the callus tissue of the stevia rebaudiana bertoni, a large quantity of epithelial fragments containing the stomatal guard cells can be quickly obtained, a high-purity suspension cell culture system is rapidly established, cell screening and culture time is shortened, the obtained callus tissue is high in quality, the percentage of embryonic callus is high, and weight increment is fast.
Owner:BEIJING AGRO BIOTECH RES CENT
Guard cell-specific tool for molecular manipulation of drought avoidance/water loss in plants
InactiveUS7993926B2Improve scalabilityPromote growthSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesGas exchangeHomologous gene
The inventors herein disclose a new transporter that participates in guard cell movement. The inventors have now found that AtCHX20 is preferentially expressed in guard cells using microarray and promoter TGUS analyses. The inventors have also found a guard cell specific promoter which serves as a powerful tool to manipulate the opening and closing of guard cells and thus the ability to control water loss and gas exchange of plants. Such a tool can be particularly useful when applied to crops and other plants of economic importance, thus the present inventors have identified homologous genes in several other plants that fall within the scope of this invention.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Method for rapidly identifying cassava autotetraploid
InactiveCN107748097ARapid identificationSimple and fast operationPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansVisual field lossCuticle
The invention relates to a method for rapidly identifying cassava autotetraploid, and belongs to the technical field of autotetraploid identification. The method for rapidly identifying the cassava autotetraploid comprises the following steps: 1) immersing a cassava leaf in a Carnot fixer to obtain a fixed cassava leaf; 2) taking the lower epidermis of the fixed cassava leaf obtained in step 1), and staining the lower epidermis in an iodine-potassium iodide staining solution to obtain a stained lower epidermis; and 3) microscopically observing the stained lower epidermis obtained in step 2), counting the number of chloroplasts in the guard cells, determining the cassava as an autoteraploid if the number of chloroplasts in more than 90% of the guard cells in the visual field is 7 or more, and determining the cassava as a diploid if the number of chloroplasts in more than 90% of the guard cells in the visual field is less than 7. The identification method has the advantages of low cost,high speed, high accuracy, and realization of efficient and rapid detection of the cassava autotetraploid.
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院经济作物研究所
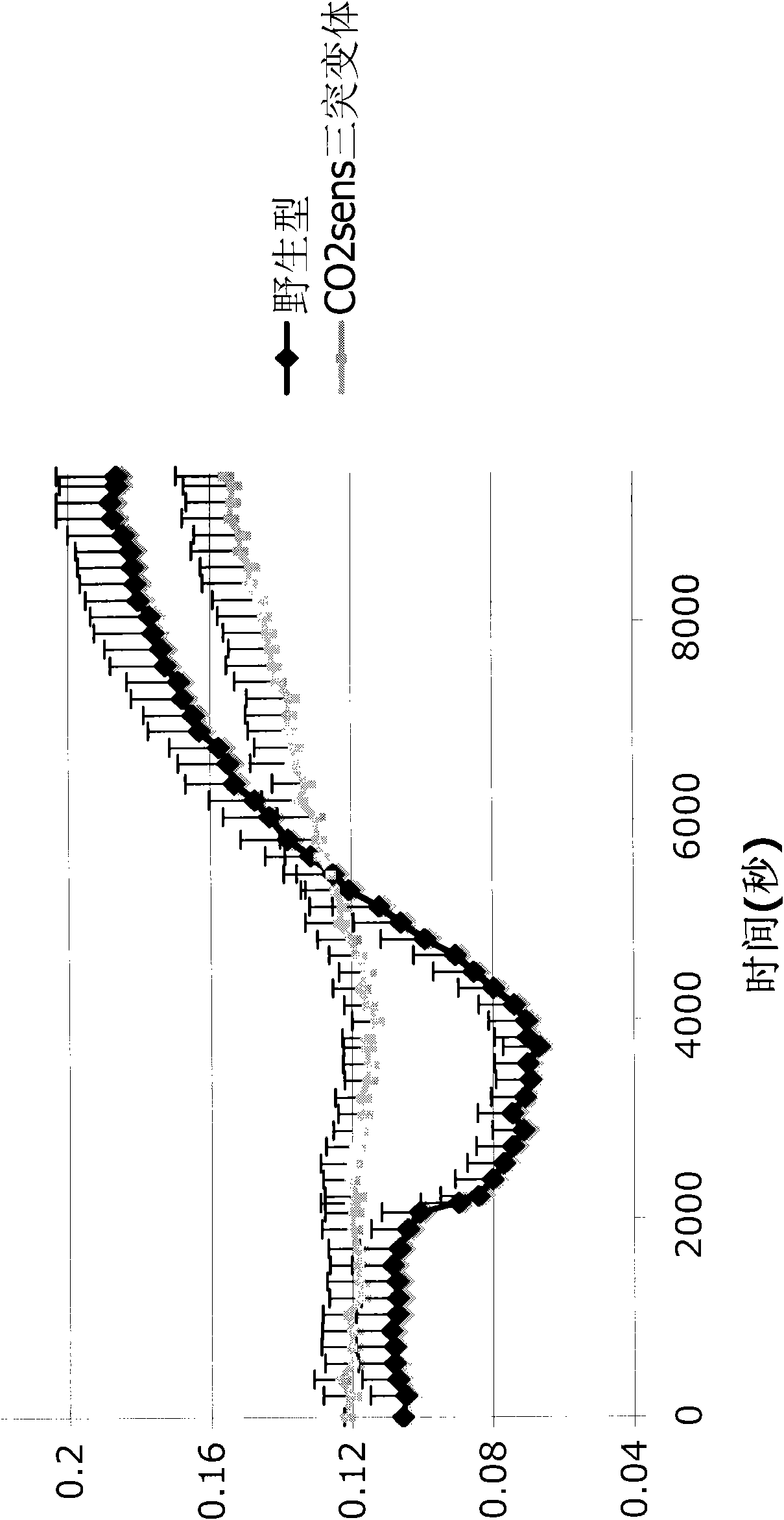
Plant CO2 sensors, nucleic acids encoding them, and methods for making and using them
The invention provides compositions and methods for manipulating the exchange of water and / or carbon dioxide (CO2) through plant stomata by controlling CO2 sensor genes. The invention provides compositions and methods for enhancing or optimizing biomass accumulation in a plant. The invention provides compositions and methods for opening or closing a stomatal pore on a guard cell in the epidermis of a plant. The invention provides compositions and methods for increasing or decreasing oxygenation efficiency and / or carbon fixation in a guard cell in the epidermis of a plant by manipulating expression of a ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase / oxygenase. The invention provides promoters for regulating expression of a nucleic acid in a plant guard cell.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
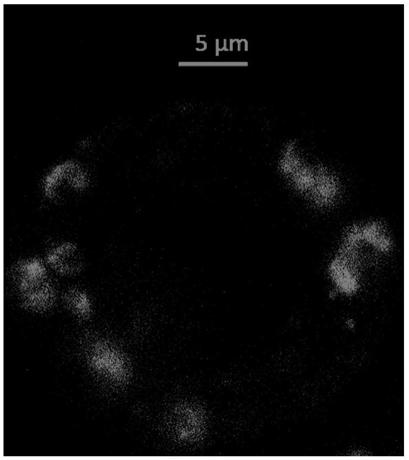
Method for rapidly locating protein position in guard cell of plant leaf
InactiveCN109266669AEasy to observe and locateLow technical requirementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceVector-based foreign material introductionPlant cellProtein subcellular location
The invention relates to a method for rapidly locating the position of a protein in a guard cell of a plant leaf, belonging to the field of a method for locating the protein in a plant cell, in particular to the field of a method for locating the protein in a plant guard cell. The invention aims at solving the problems of long cycle and complex operation of protein subcellular localization by thetraditional method. The method for quickly locating the position of the protein in the guard cell of the plant leaf comprises the following steps: 1, construction of a plant expression vector; 2, separation of the guard cell of the plant leaf; 3, transformation of the guard cell; 4, incubation and culture of the guard cell; and 5, localization of the protein in the guard cell. The method providedby the invention is used for localization of proteins in plant guard cells.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Application of corn Zm00001d029151 gene in regulation and control of morphogenesis of guard cells
ActiveCN113755511AGuaranteed correctnessConfirmed thickeningIsomerasesRacemaces/epimerasesNucleotideCell wall
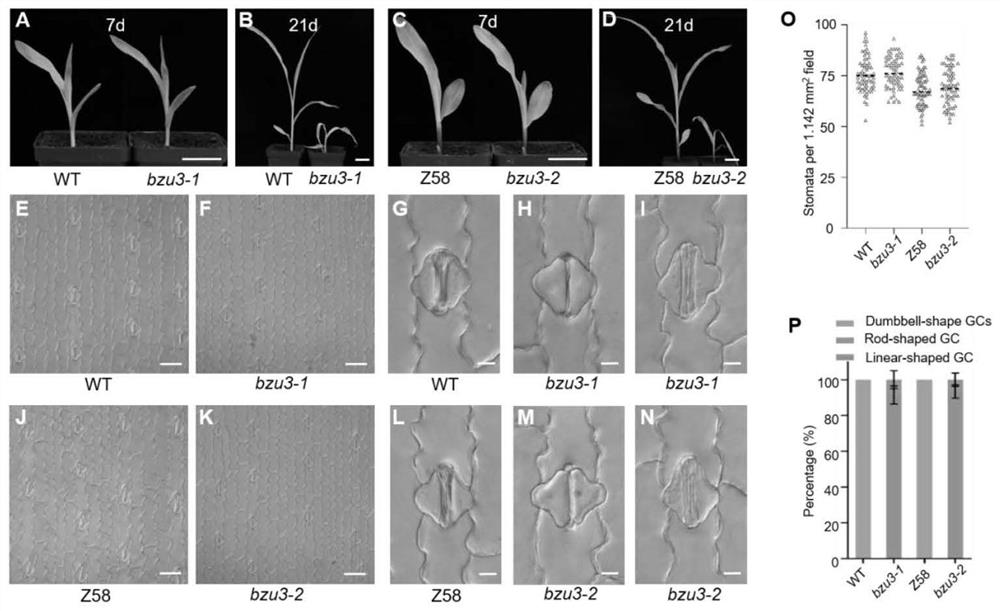
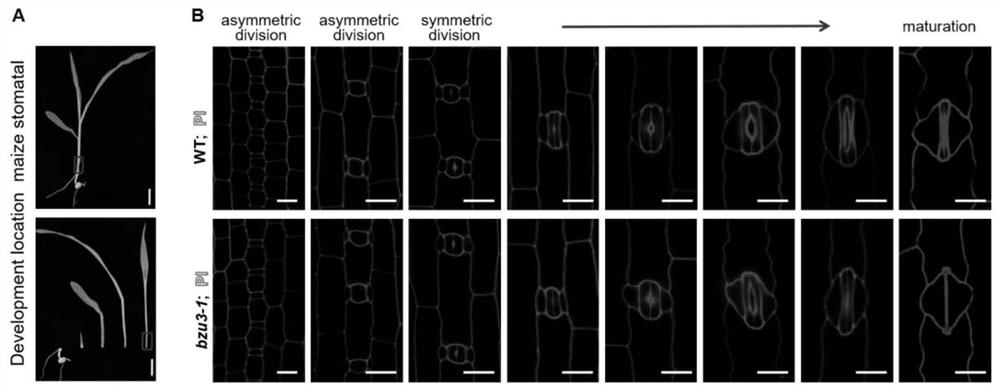
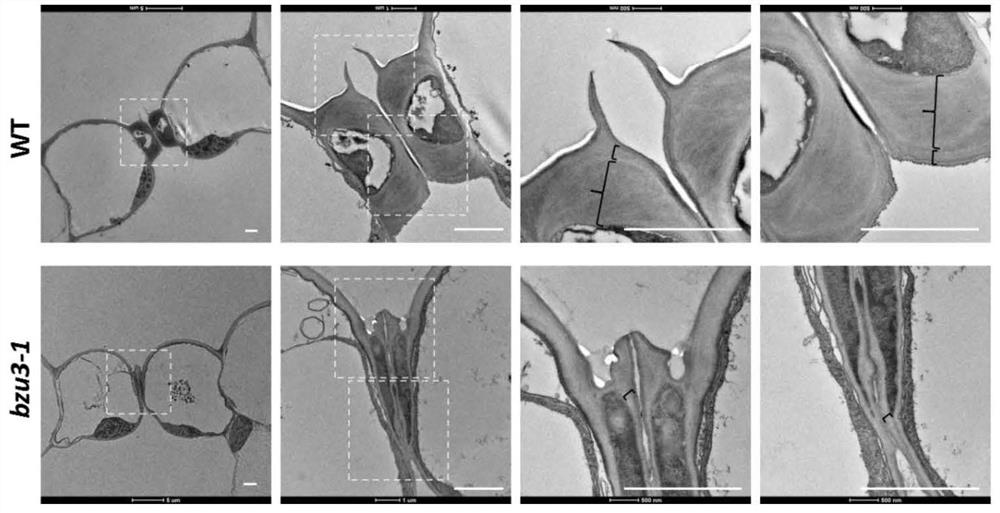
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, and particularly discloses application of a corn Zm00001d029151 gene in regulation and control of morphogenesis of guard cells, the nucleotide sequence of the Zm00001d029151 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, the amino acid sequence of protein coded by the Zm00001d029151 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.2, and the Zm00001d029151 gene is specifically expressed in the guard cells and participates in regulation and control of the thickening process of cell walls of the guard cells. The Zm00001d029151 gene is used for regulating and controlling morphogenesis of dumbbell-shaped guard cells, and has important theoretical significance and practical application value for exploring a molecular mechanism of morphogenesis of corn stomatal guard cells and improving stress resistance of corn.
Owner:SANYA INST OF HENAN UNIV +1
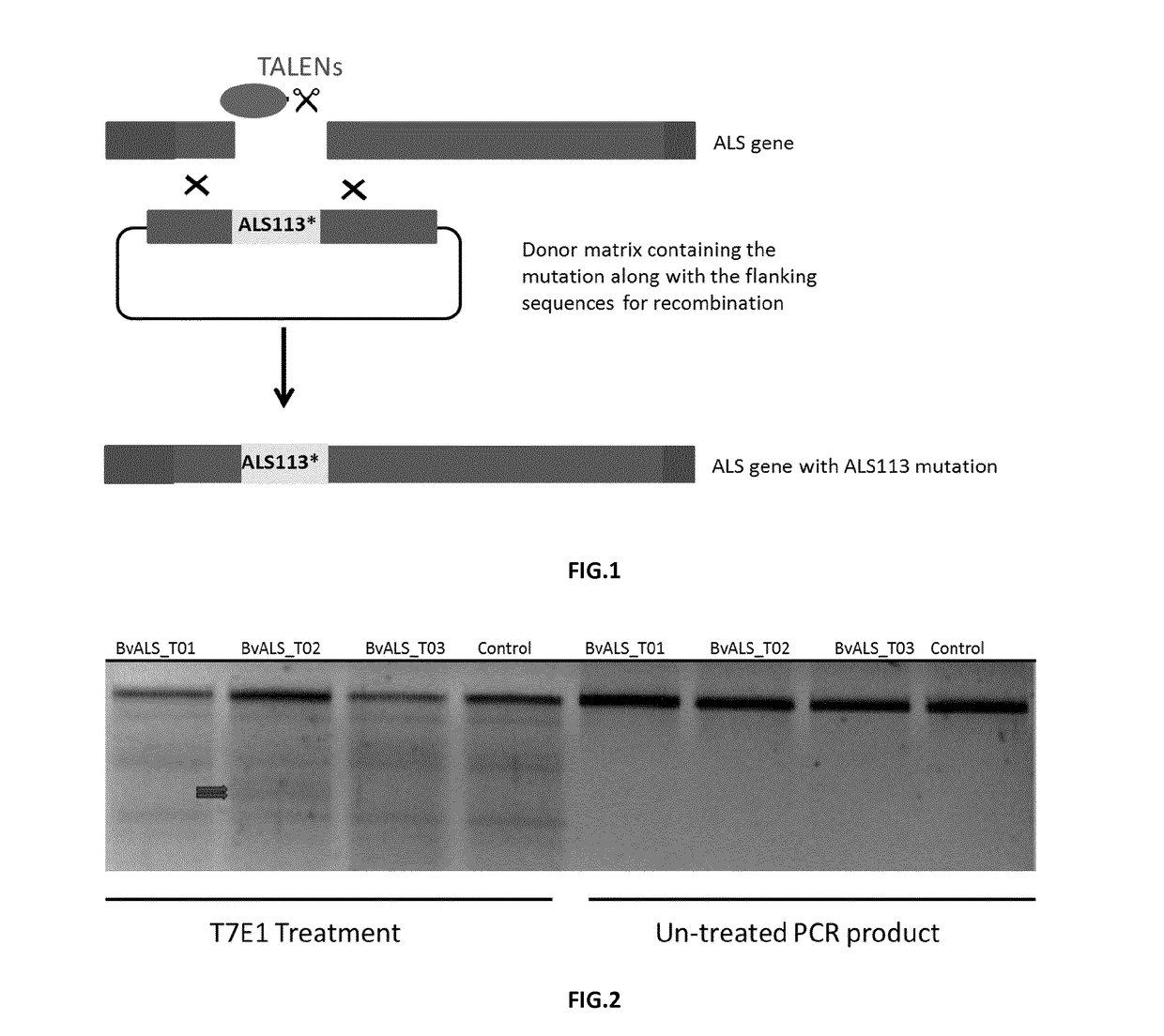
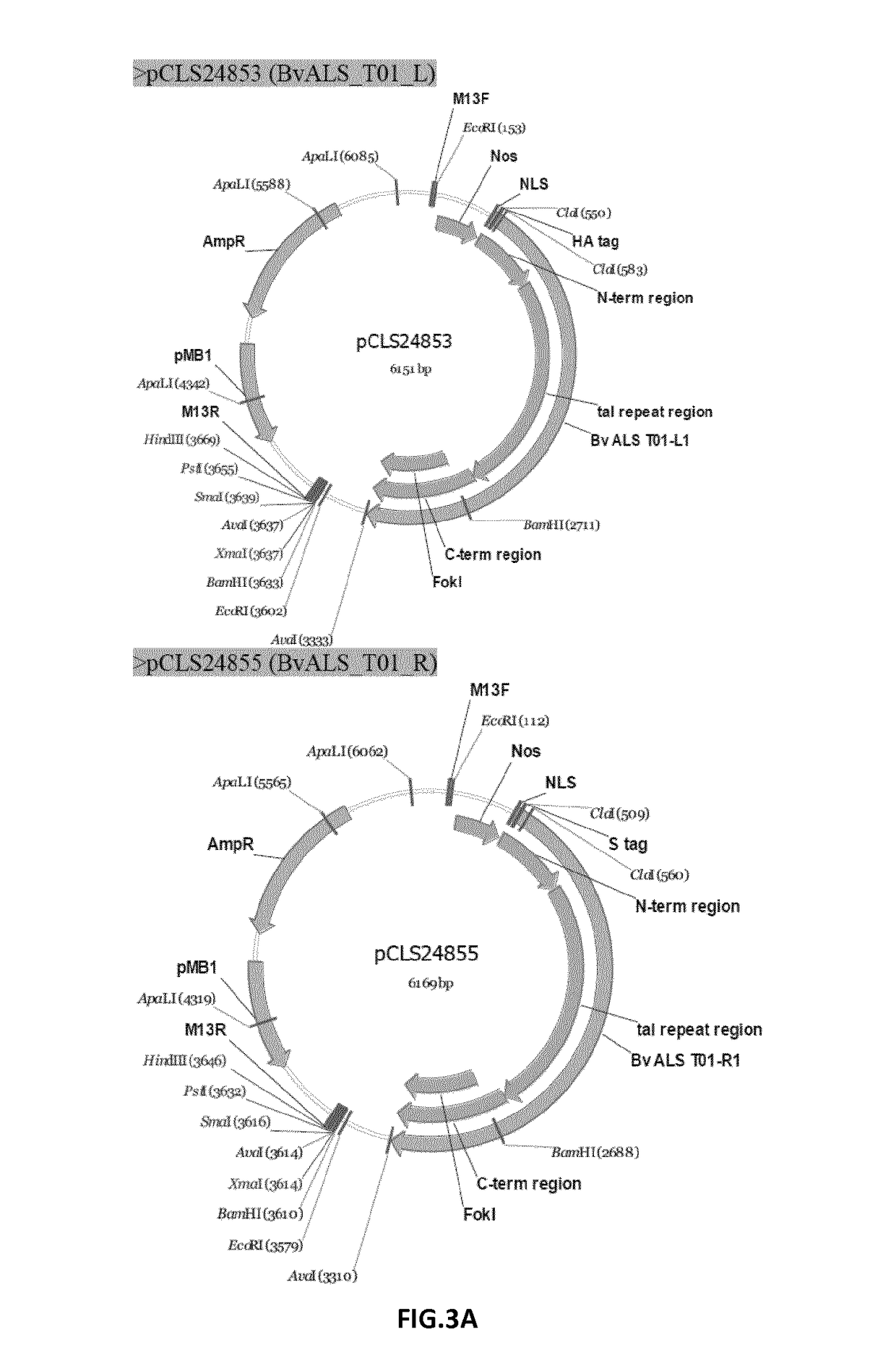
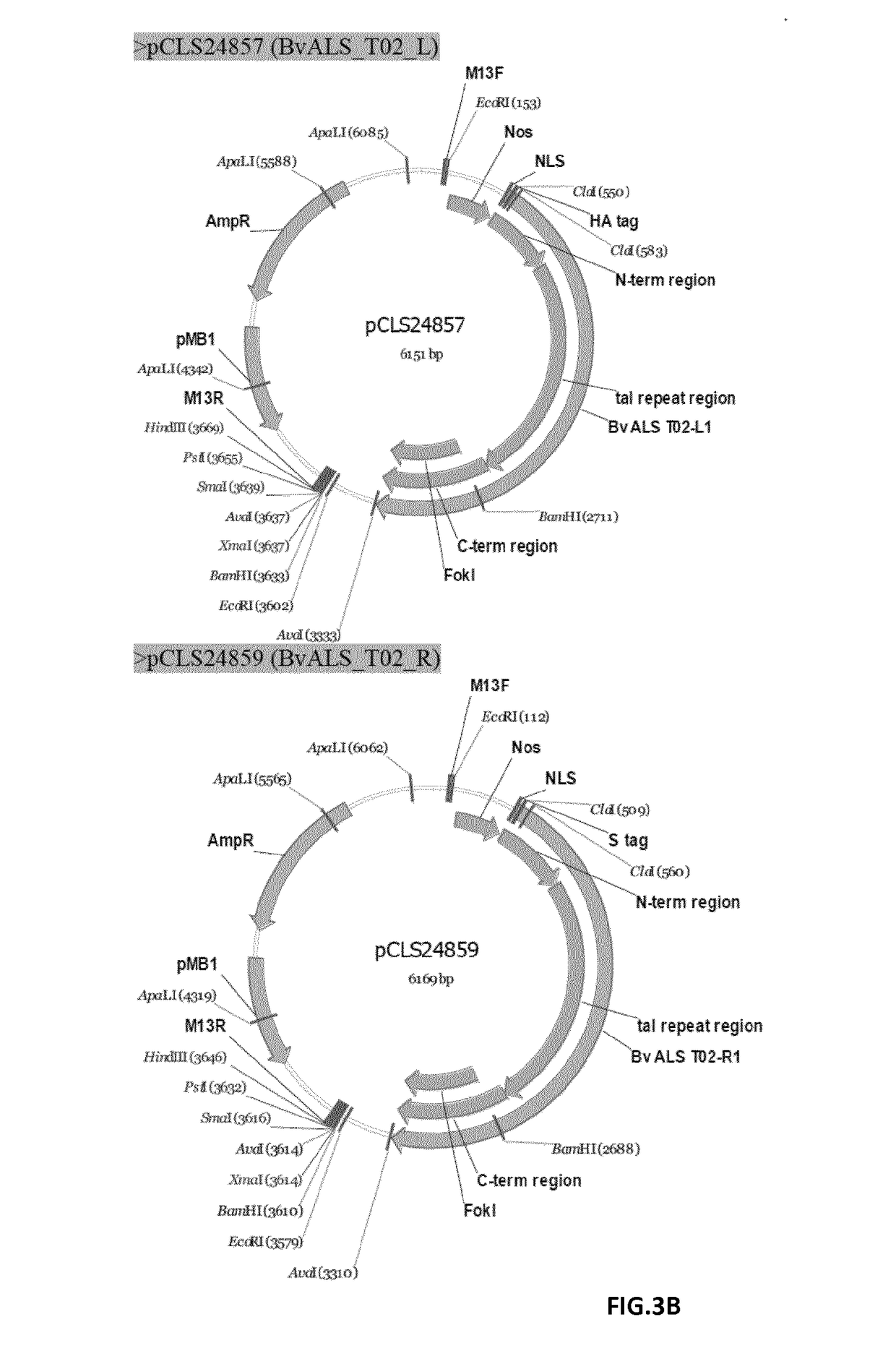
Transformation method of sugar beet protoplasts by talen platform technology
InactiveUS20170121723A1Vector-based foreign material introductionLyasesNucleotideTransformation cell
A method for transformation of sugar beet protoplasts includes obtaining protoplasts from stomatal guard cells isolated from a sugar beet plant. The protoplasts are transformed with a nucleic acid construct including a nucleotide sequence of interest and Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases (TALEN) or one or more vectors including sequences encoding these Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases (TALEN)sequences. The TALEN target and process a target sequence and replace the target sequence through homologous recombination with the nucleic acid construct including the nucleotide sequence of interest, -possibly applying to an in vitroculture of the protoplasts, a medium that is toxic, preferably lethal to the in vitroculture of the protoplasts. Sugar beet plants are regenerated from the cell culture, preferably from the surviving protoplasts having integrated the nucleic acid construct including the sequence of interest that possibly renders the transformed cell resistant to the toxic activity of the applied medium.
Owner:SESVANDERHAVE
Guard cell expression cassettes compositions and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20160032301A1Modulate its functionImproving response to water deficit waterBacteriaSugar derivativesBiotechnologyPhenotypic trait
The invention is directed to artificial transcription regulating polynucleotides that confer guard cell regulated expression and methods of use thereof. The present invention further provides methods of using the transcription regulating polynucleotides and plants and plant parts thereof comprising the transcription regulating polynucleotides. In agricultural biotechnology, plants can be modified according to one's needs. One way to accomplish this is by using modern genetic engineering techniques. For example, by introducing a gene of interest into a plant, the plant can be specifically modified to express a desirable phenotypic trait.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Plant stomata specific promoter and application thereof
InactiveCN102433338AImprove photosynthetic efficiencyIncrease productionFungiBacteriaDiseasePlant Stomata
The invention discloses a plant stomata specific promoter and an application thereof. The promoter provided in the invention comprises the following nucleotide sequences: 1) a sequence 1 in a sequence table; 2) a nucleotide sequence still has the function of a stomata specific promoter after the 5' terminal and / or 3' terminal of the nucleotide sequence of the sequence 1 in the sequence table are deleted; and 3) a nucleotide sequence with the function of a stomata specific promoter when one or more deoxynucleotide residues of the nucleotide sequence in 1) or 2) is substituted, added or deleted. Experiments prove that: the promoter provided in the invention has excellent stomata specificity, and the specificity can be stably transferred to the next generation, which has important significance to molecular biological researches of stomata and guard cells, stomata motion and other theories, and has great application value and a wide market prospect in improving the photosynthetic efficiency of crops by culturing drought and disease resisting crops so as to improve yield, quality and other fields.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Ammopiptanthus mongolicus guard cell specific expression promoter and application thereof
InactiveCN108588070AStrong specificityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
Disclosed are an ammopiptanthus mongolicus guard cell specific expression promoter and application thereof. The ammopiptanthus mongolicus guard cell specific expression promoter is a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No.1 and can be used for screening specific genes related to guard cells. The promoter capable of realizing specific expression in the ammopiptanthus mongolicus guard cells is provided for the first time and is quite high in specificity, and thus an effective tool is provided for research of the functions of plant guard cells.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application and expression vectors of paddy rice stomata open type potassium ion channel gene OsK2-1
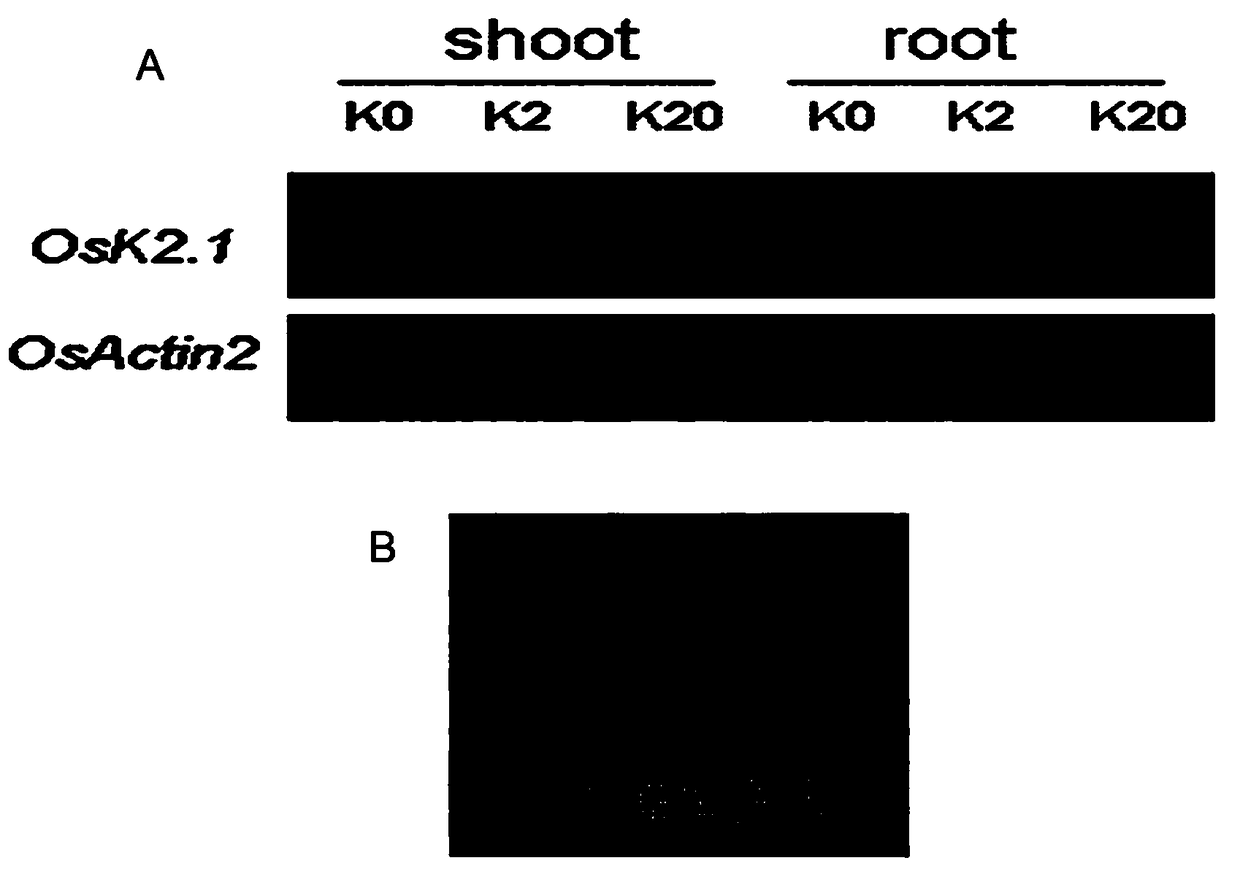
ActiveCN109082428AImprove effective utilizationStomatal opening increasedPlant peptidesFermentationAgricultural scienceINCREASED EFFECT
The invention relates to application and expression vectors of a paddy rice stomata open type potassium ion channel gene OsK2-1. The paddy rice stomata open type potassium ion channel gene OsK2-1 is obtained through cloning. The gene is mainly expressed in paddy rice overground part mesophyll and stomatal guard cells, and the gene protein has transport activity for mediating potassium ion inward absorption. The invention discovers the application of the paddy rice stomata open type potassium ion channel gene OsK2-1 in the increasing of crop photosynthetic rate, stomatal conductance and transpiration rate and in the increasing of nitrogen utilization efficiency in crop high-nitrogen environments for the first time. The animal expression vector and the plane overexpression vector of the paddy rice stomata open type potassium ion channel gene OsK2-1 evidently increase the biomass and grain yield of paddy rice modified by the OsK2-1 gene and especially has a good yield increasing effect and promising application prospect under a high-nitrogen condition.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com