Method for rapidly identifying cassava autotetraploid
An autotetraploid and identification method technology, applied in the field of autotetraploid identification, can solve the problems of expensive experimental instruments, toxic reagents, harmful to the body, etc., and achieve rapid identification, easy operation, and high accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
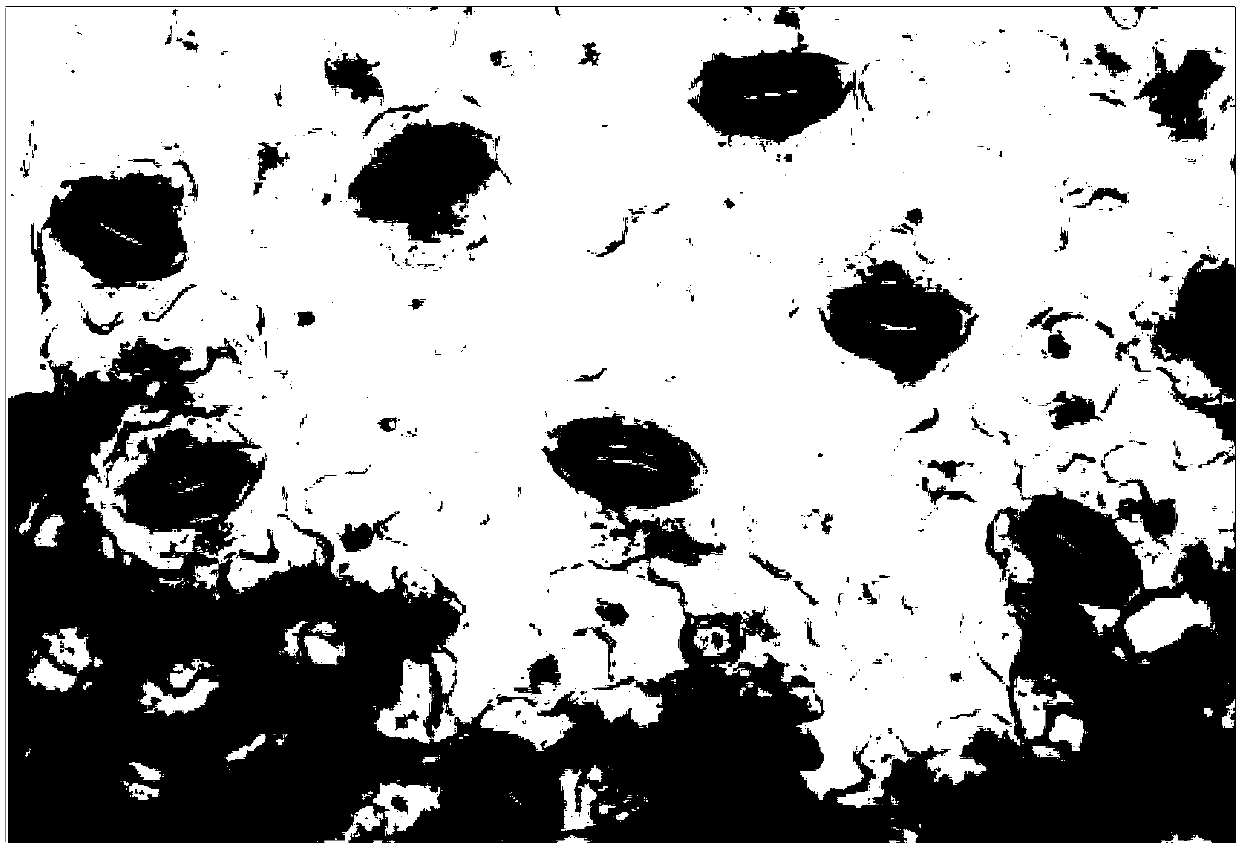
[0032] (1) Material collection: When the cassava plant grows to 0.8 meters, the sixth expanded leaf of cassava variety Xinxuan 048 with unknown ploidy is taken as the material for identifying the autotetraploid of the plant.
[0033] (2) Film production: After wiping off the dust on the leaves, place them on the operating table. Use a scalpel to draw a cross on the lower epidermis of the leaf avoiding the veins, lift up the corner of the cross with tweezers, slowly tear off the lower epidermis of the leaf, immerse the lower epidermis of the leaf in Carnot’s fixative solution for 2 seconds, then take it out quickly, and dry the lower epidermis with filter paper Finally, place the lower epidermis on a clean glass slide, and stain with a drop of iodine-potassium iodide staining solution for 60 seconds. Cover with a coverslip and blot excess liquid with filter paper.
[0034] (3) Counting: Place the prepared sheet under a 40 times objective lens of an ordinary optical microscope ...
Embodiment 2
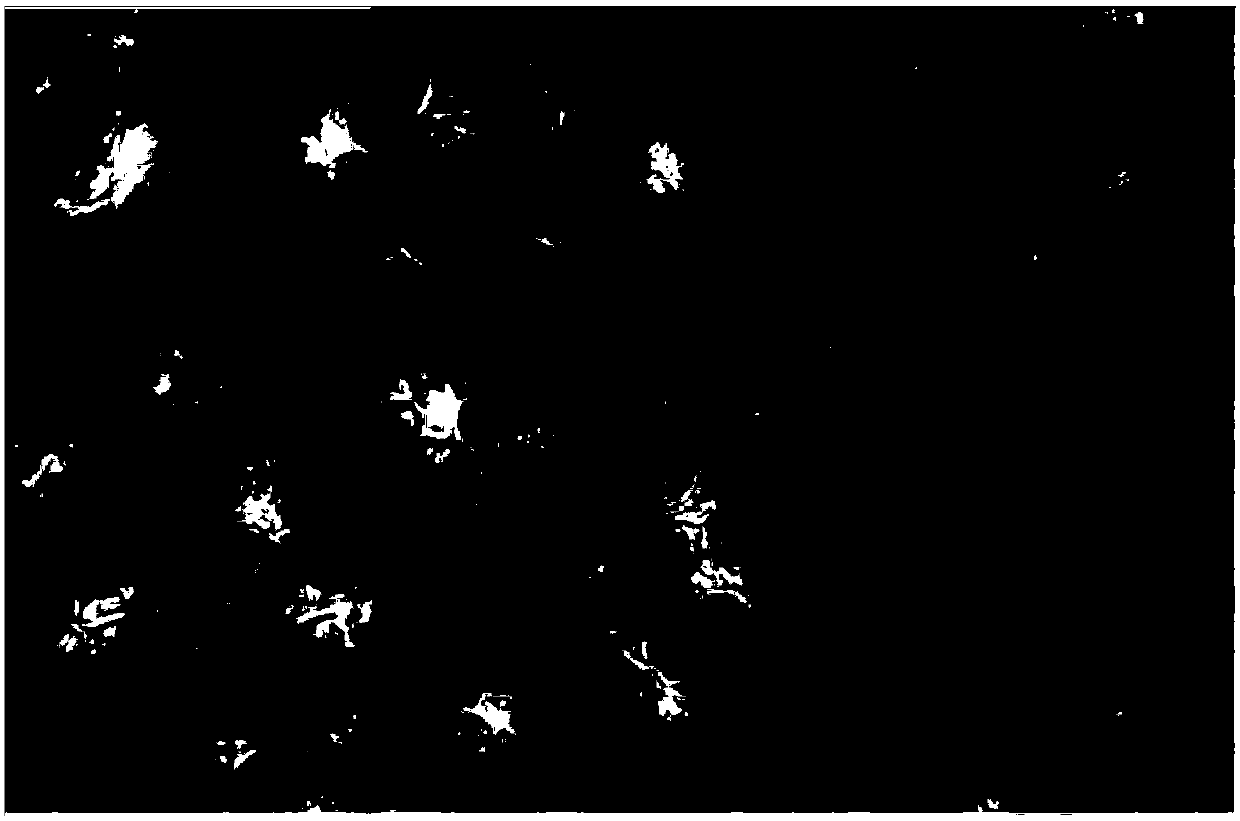
[0037] (1) Material collection: when the cassava plant grows to 0.6 meters, the seventh unfolded leaf of cassava variety Huanan 205 with unknown ploidy is taken as the material for identifying the autotetraploid of the plant.
[0038] (2) Film production: After wiping off the dust on the leaves, place them on the operating table. Use a scalpel to draw a cross on the lower epidermis of the leaf avoiding the veins, lift up the corner of the cross with tweezers, slowly tear off the lower epidermis of the leaf, immerse the lower epidermis of the leaf in Carnot’s fixative solution for 2 seconds, then take it out quickly, and dry the lower epidermis with filter paper Afterwards, place the lower epidermis on a clean glass slide, and stain with a drop of iodine-potassium iodide staining solution for 120s. Cover with a coverslip and blot excess liquid with filter paper.
[0039] (3) Counting: Place the prepared sheet under a 40 times objective lens of an ordinary optical microscope fo...
Embodiment 3
[0042] (1) Material collection: When the cassava plant grows to 1.0 m, the fifth expanded leaf of cassava variety Nanzhi 199 with unknown ploidy is taken as the material for identifying the autotetraploid of the plant.
[0043](2) Film production: After wiping off the dust on the leaves, place them on the operating table. Use a scalpel to draw a cross on the lower epidermis of the leaf avoiding the veins, lift up the corner of the cross with tweezers, slowly tear off the lower epidermis of the leaf, immerse the lower epidermis of the leaf in Carnot’s fixative solution for 2 seconds, then take it out quickly, and dry the lower epidermis with filter paper Afterwards, place the lower epidermis on a clean glass slide, and stain with a drop of iodine-potassium iodide staining solution for 30 seconds. Cover with a coverslip and blot excess liquid with filter paper.
[0044] (3) Counting: Place the prepared sheet under a 40 times objective lens of an ordinary optical microscope for ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com