Patents
Literature
255results about How to "Simplified management" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
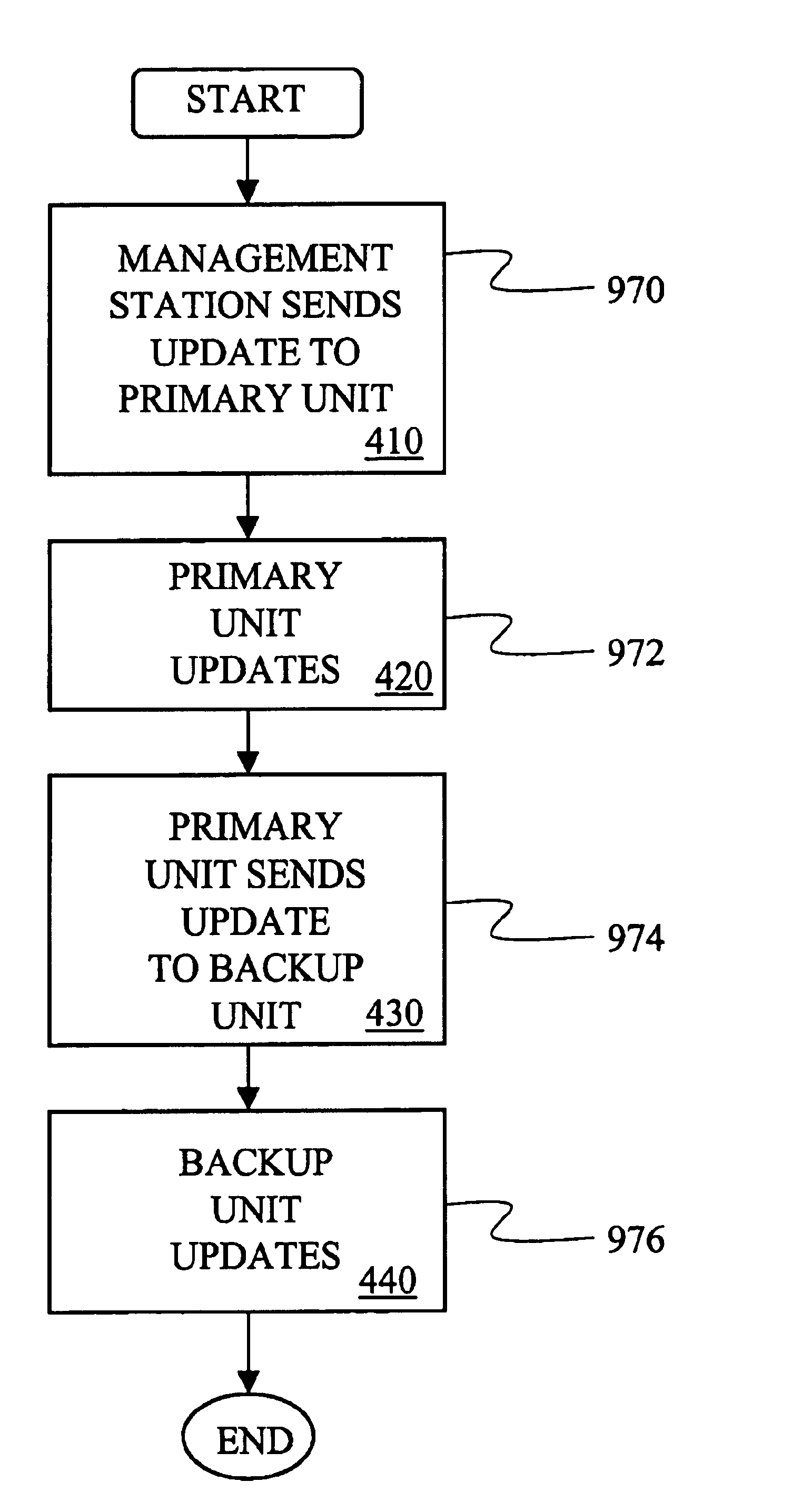
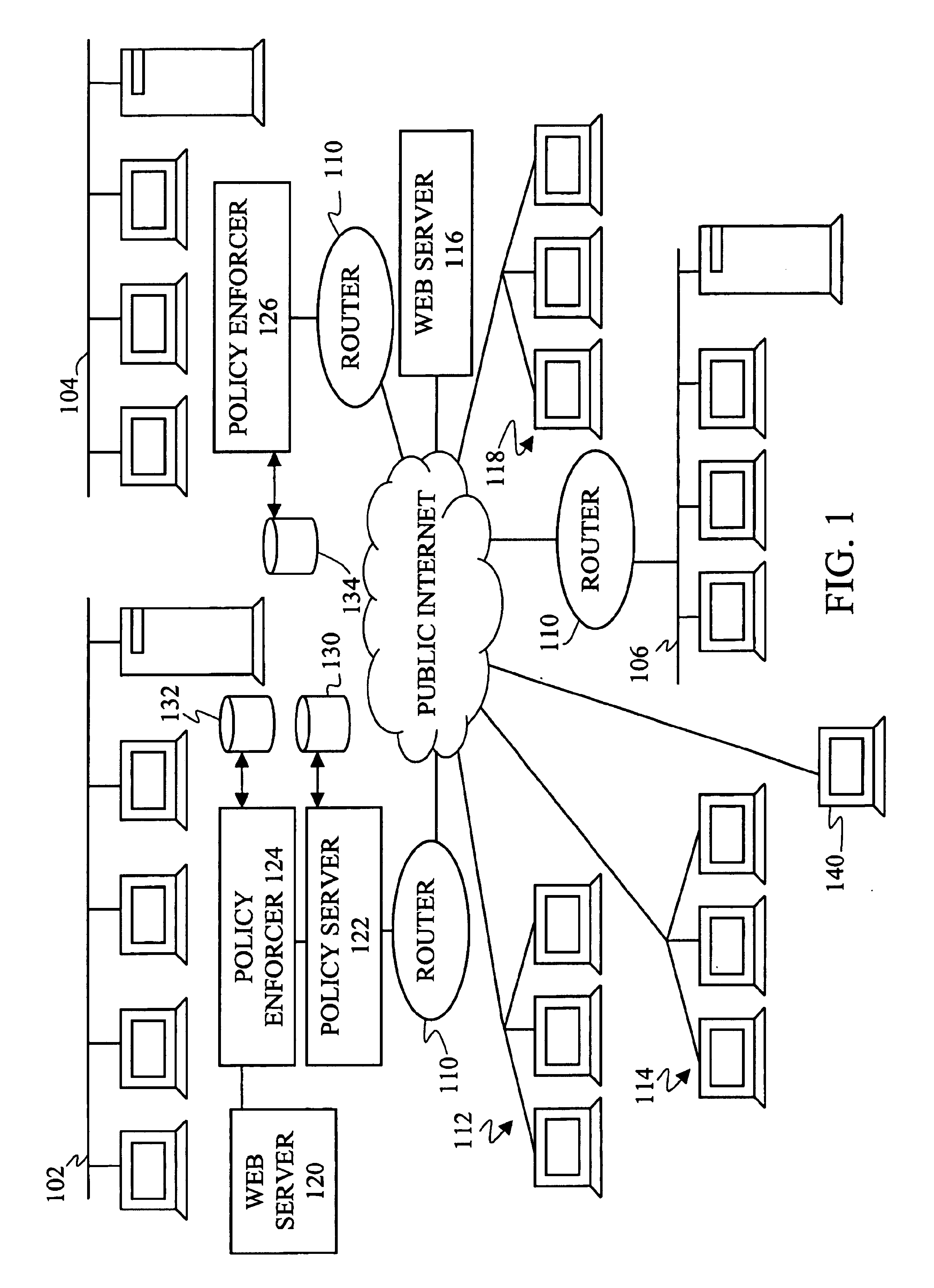
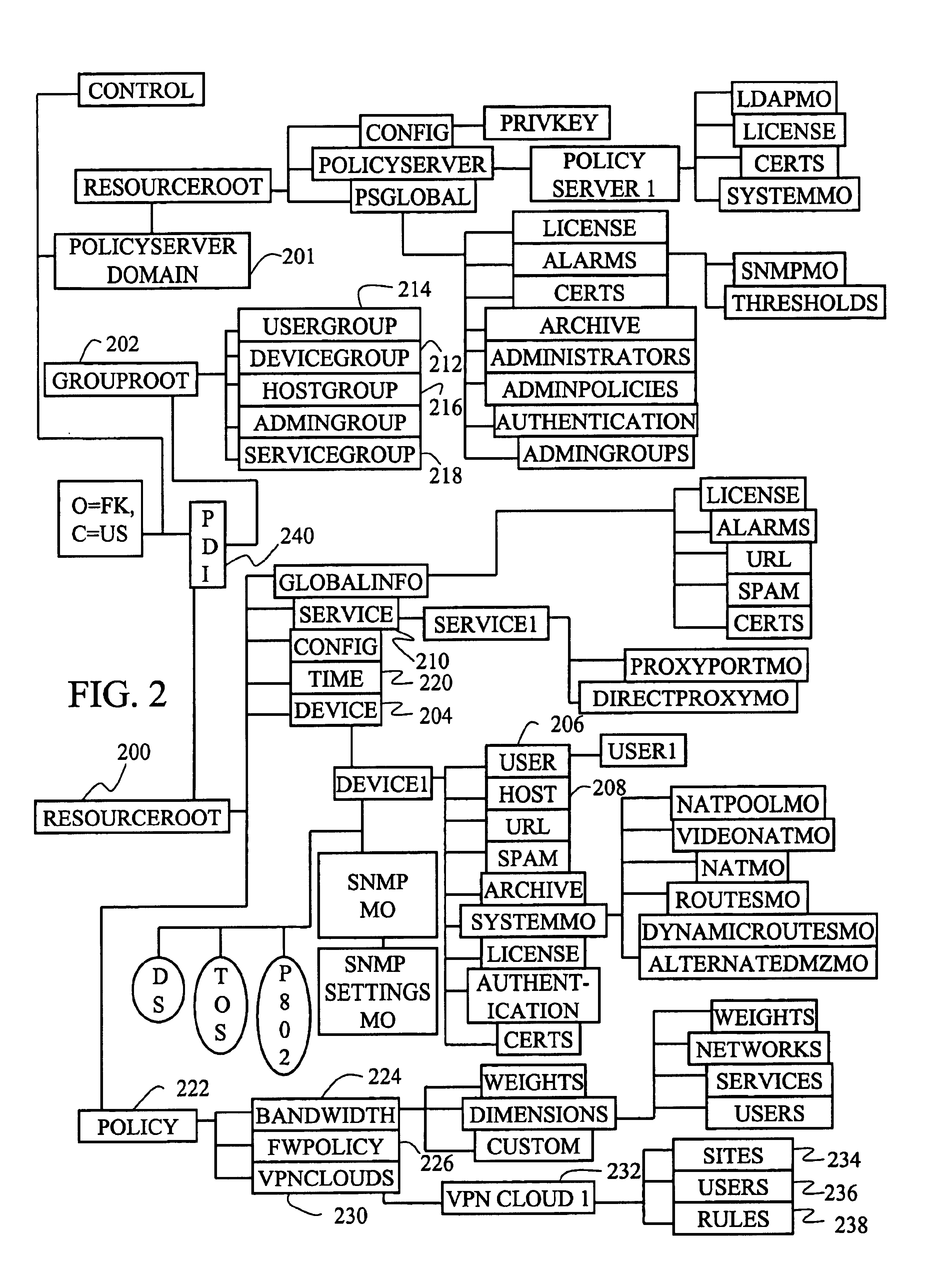
Object model for network policy management
InactiveUS6944183B1Simplified managementEnergy efficient ICTDigital computer detailsNetwork managementAdaptive routing
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
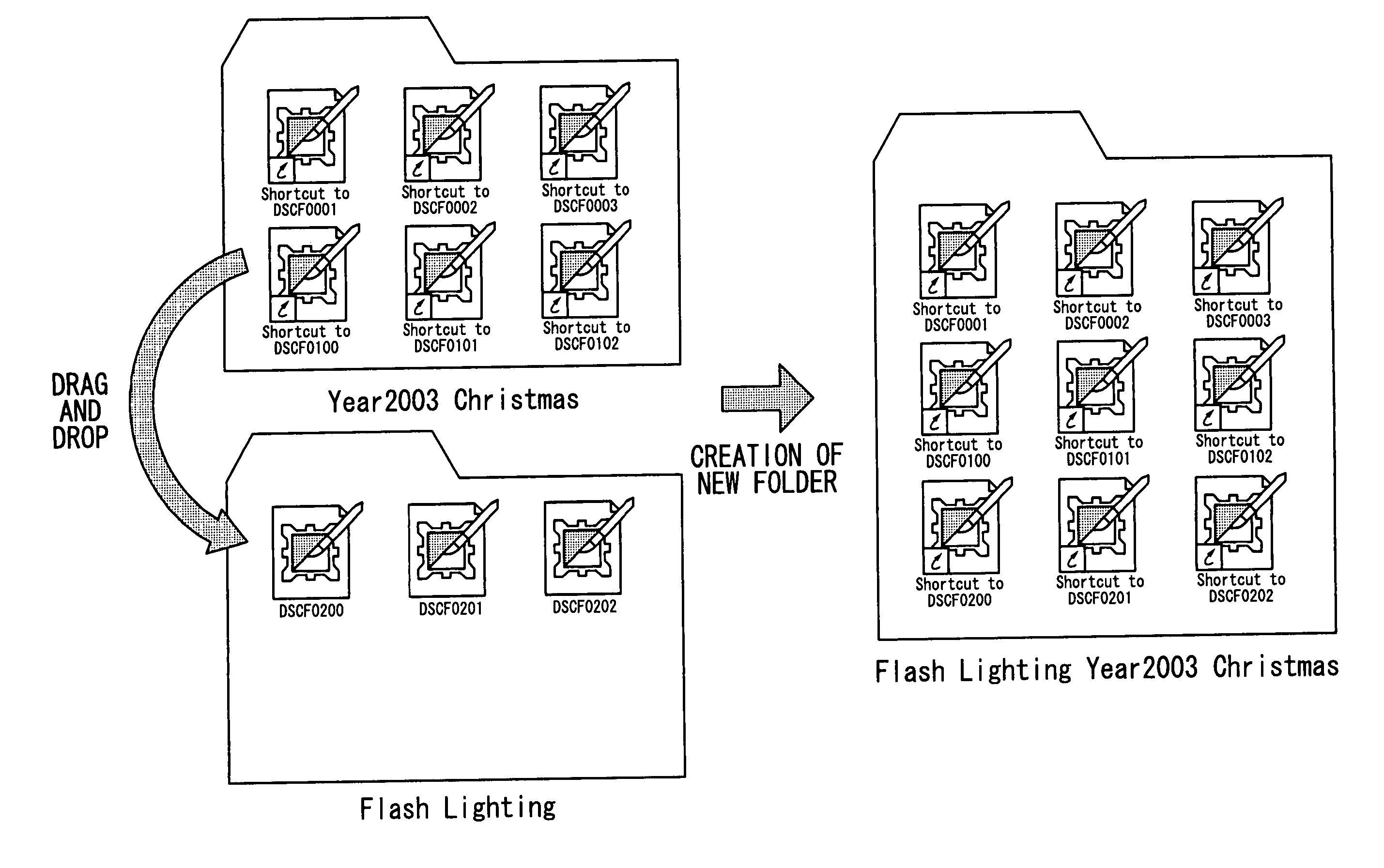
File management program
InactiveUS20050177796A1Simplified managementEasy to manageTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDrag and dropComputer science
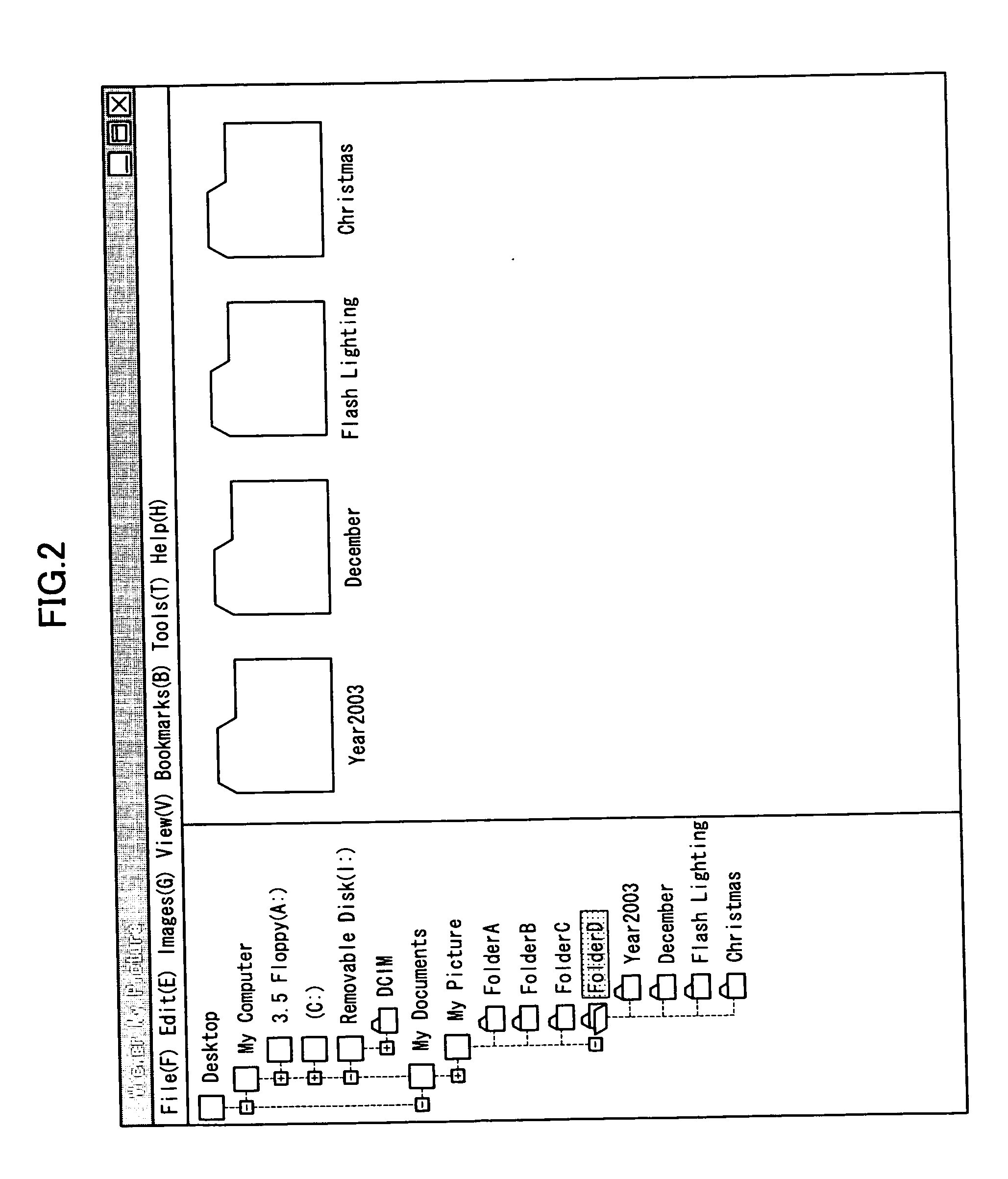
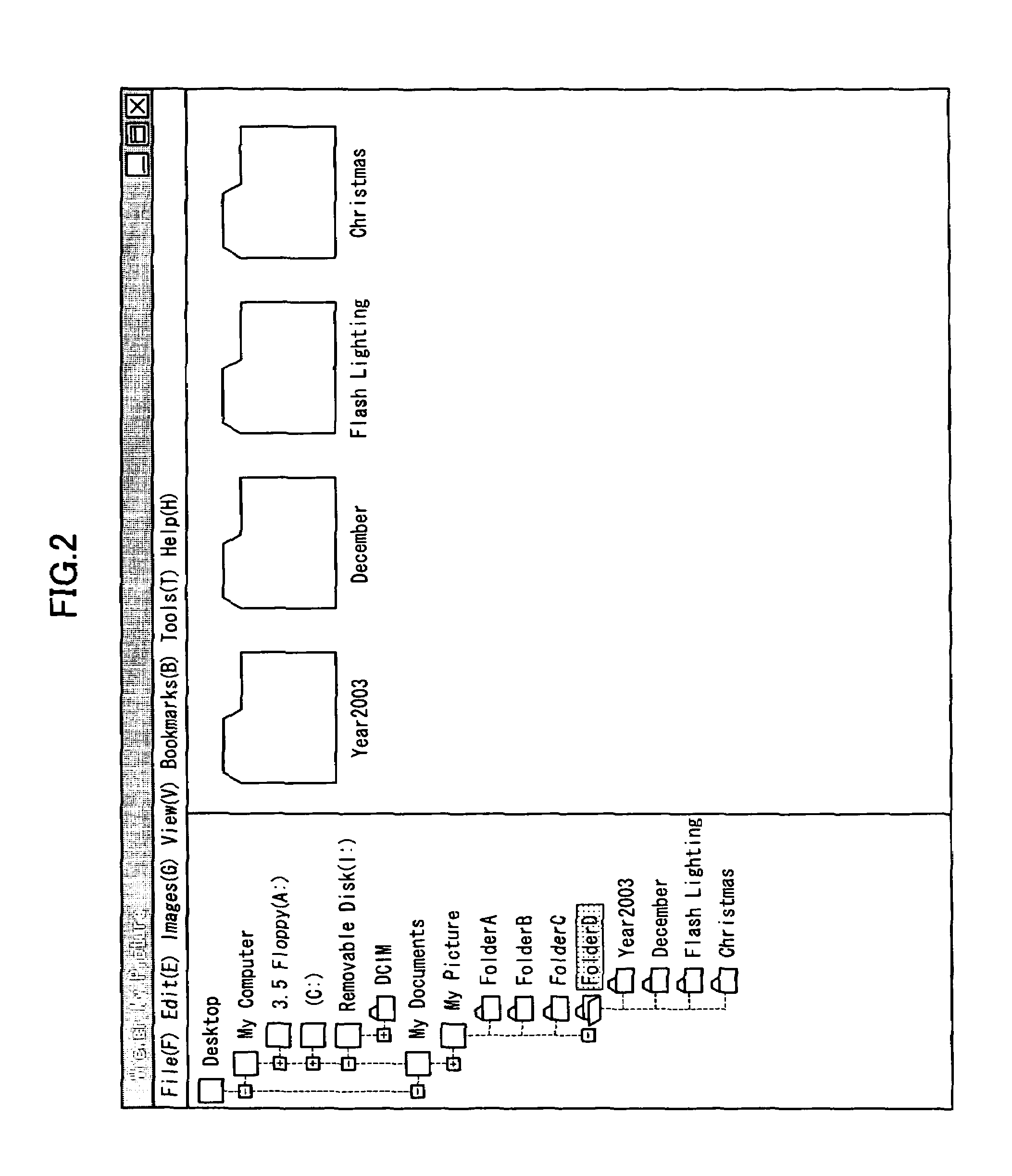
The computer readable medium has embodied thereon a file management program for processing by a computer, the file management program comprising: a first code segment for, when an icon of a first folder displayed on a display apparatus is dragged and dropped onto another icon of a second folder displayed on the display apparatus, creating a third folder at the same level as the second folder; and a second code segment for copying a file stored in the first folder and a file stored in the second folder into the third folder.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Building integrated photovoltaic devices as smart sensors for intelligent building energy management systems
ActiveUS20140330538A1Increase flexibilityImprove usabilityOptical radiation measurementSolar heating energyBuilding energyEngineering
Building-integrated photovoltaic devices can be provided, which function as sensors, wherein the output parameters from the device are used to provide information about light intensity and ambient temperature, in addition to providing power, to an intelligent building energy management system.
Owner:SOLARWINDOW TECH
Network data model for relational database management system
ActiveUS20050097108A1Reduce maintenance costsSimplified managementDigital data processing detailsRelational databasesRelational database management systemNetwork data
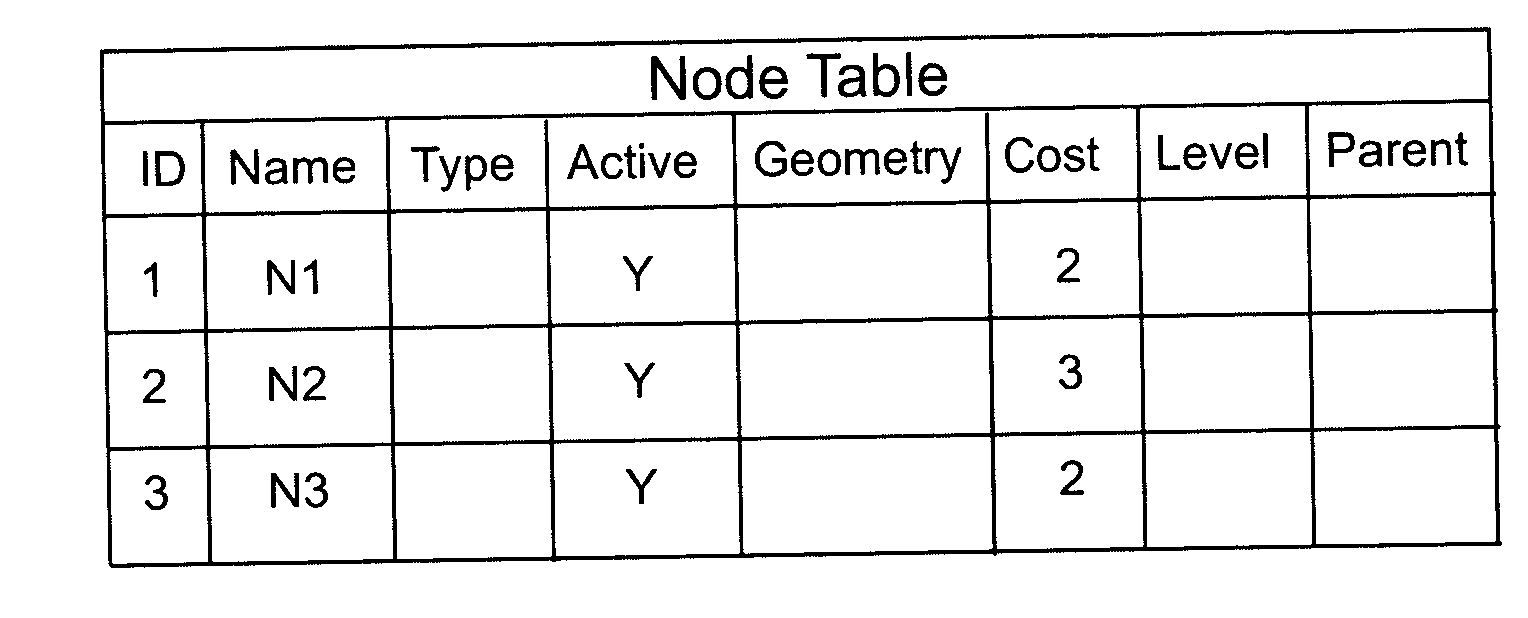
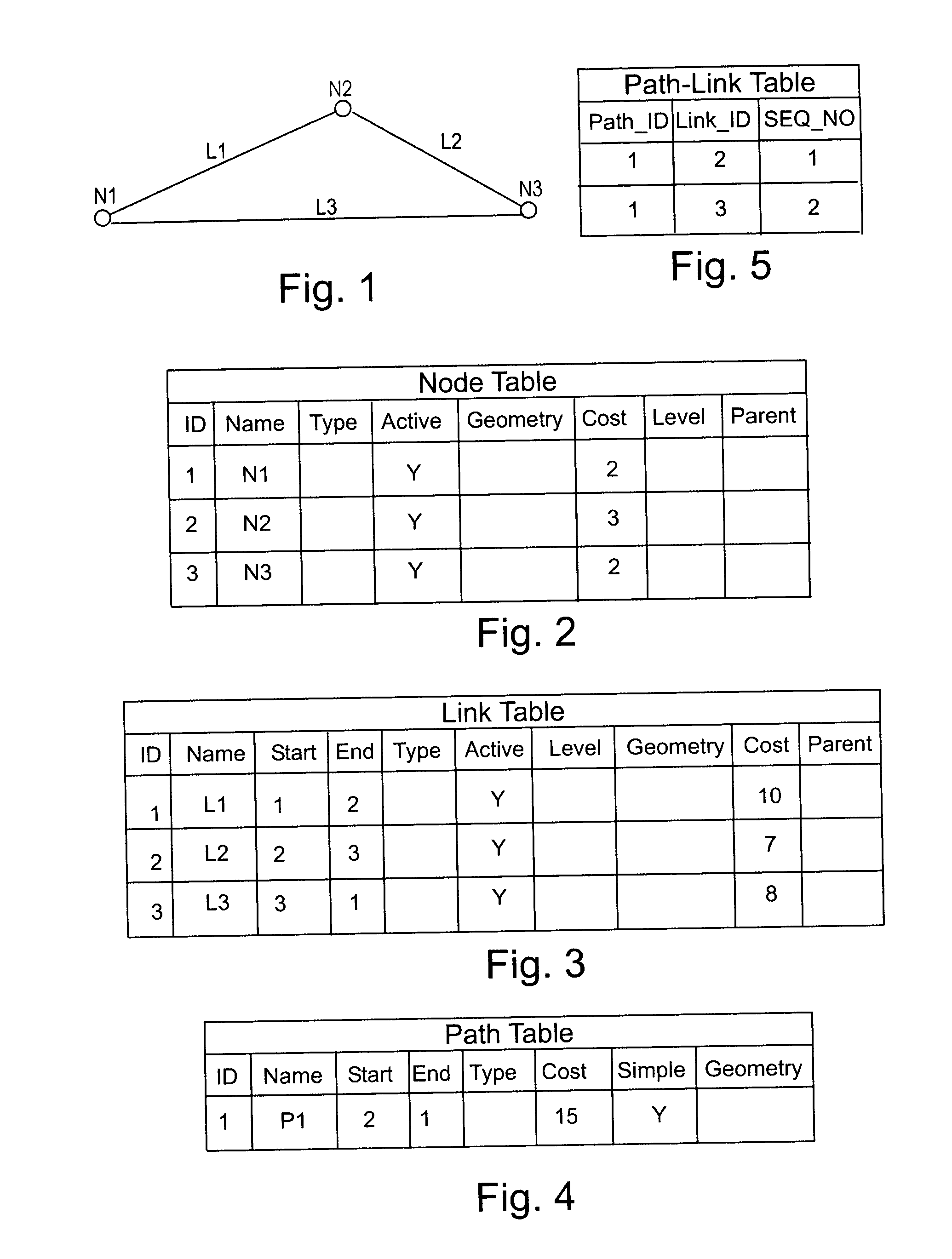
A shareable application program interface (API) and network data model infrastructure which is used in combination with a relational database to provide data storage and processing functions for network data. The network data model is stored in relational tables that describe a set of nodes and links forming a network wherein each of node represents an object of interest and link represents a relationship between two nodes. A generic node table contains a row describing each node in the network, and a generic link table contains row data describing each link. In addition, a path table whose contents are commonly generated by network analysis procedures contains rows which describe corresponding paths each consisting of an alternating sequence of nodes and links. The sequence of links in each path are identified in a separate path-link table. The system provides two application program interfaces, a PL / SQL API and a Java API, which executing application programs to use stored procedures for creating the node and link tables, store data describing nodes and links in the tables, and perform standard operations on the network data.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
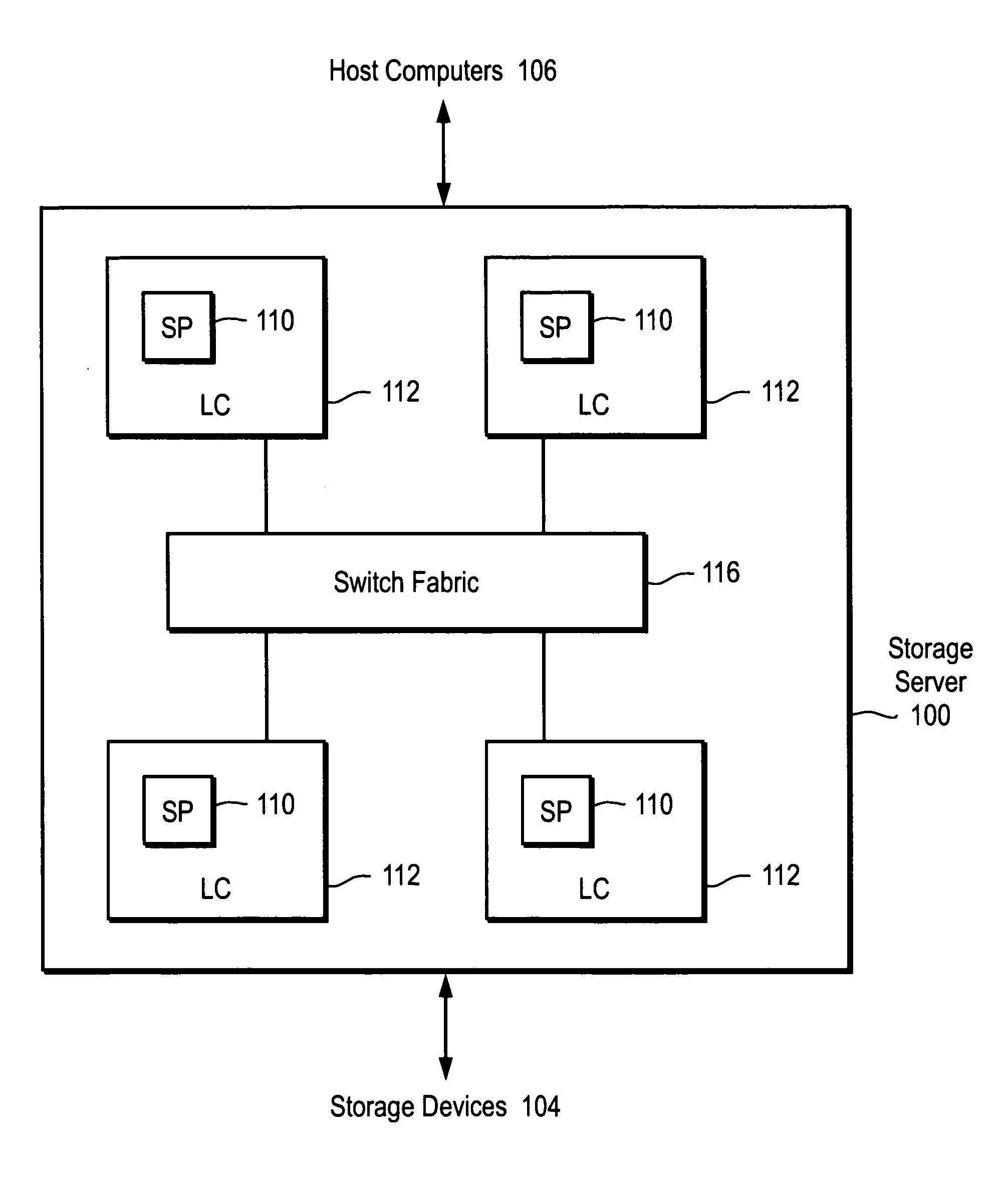
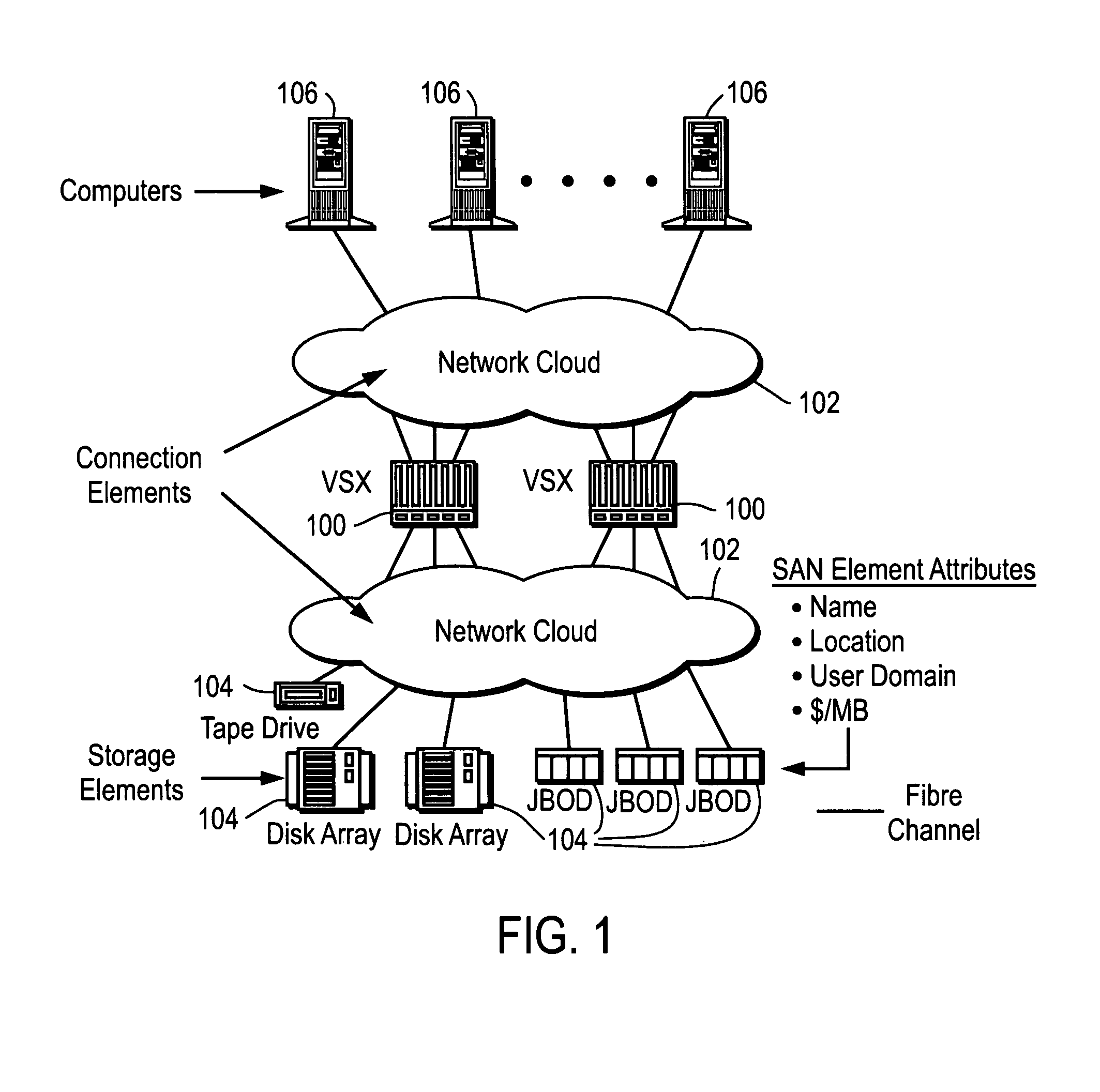
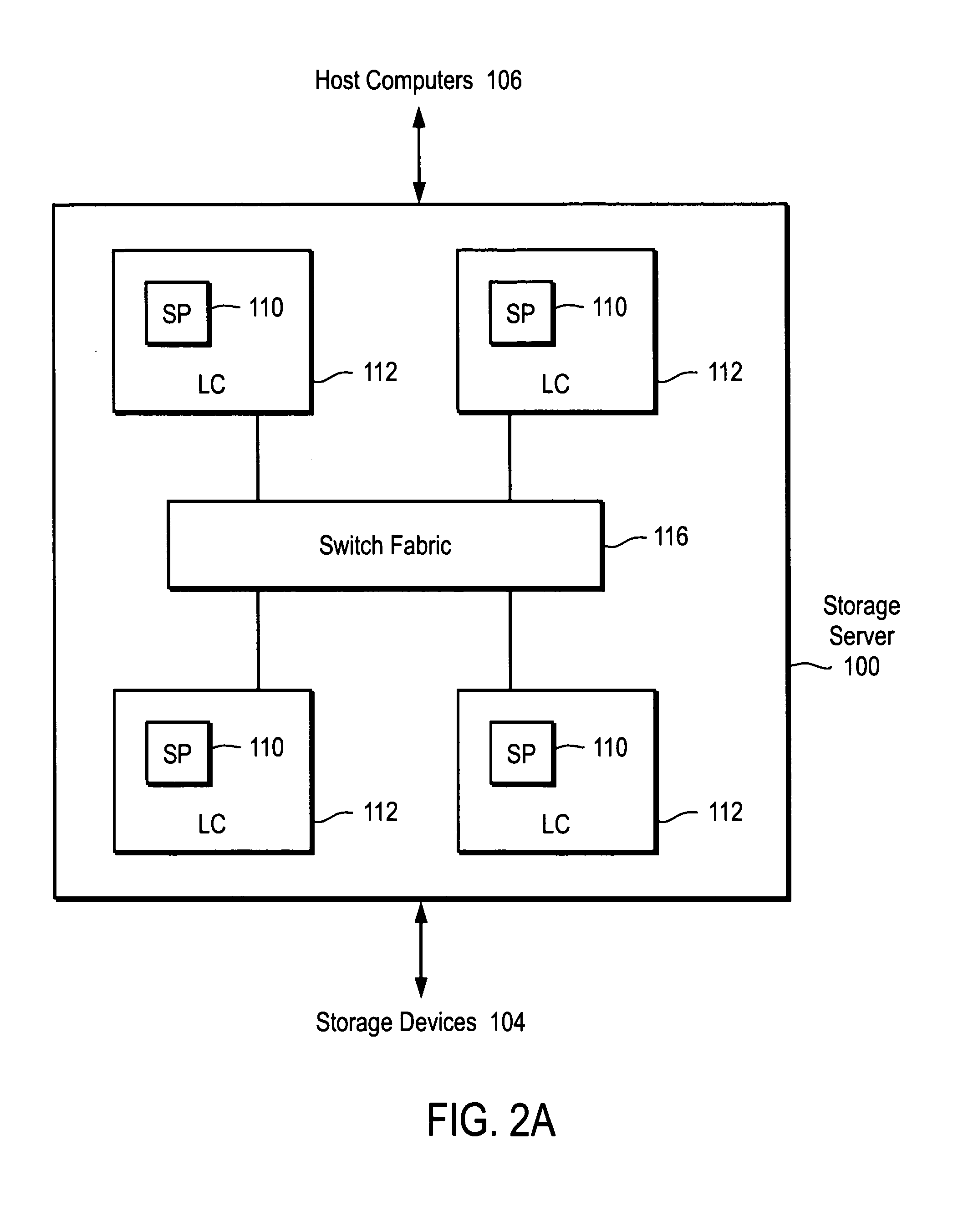
Method and apparatus for identifying storage devices
InactiveUS7203730B1Simplifying SAN storage managementSimplified managementDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationStorage area networkComputerized system
Embodiments according to the invention perform functions including discovery, classification, and profiling of storage devices, computer systems, connection elements, and other components relating to a storage area network (SAN). Changes to the SAN topology are tracked in order to show growth patterns.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
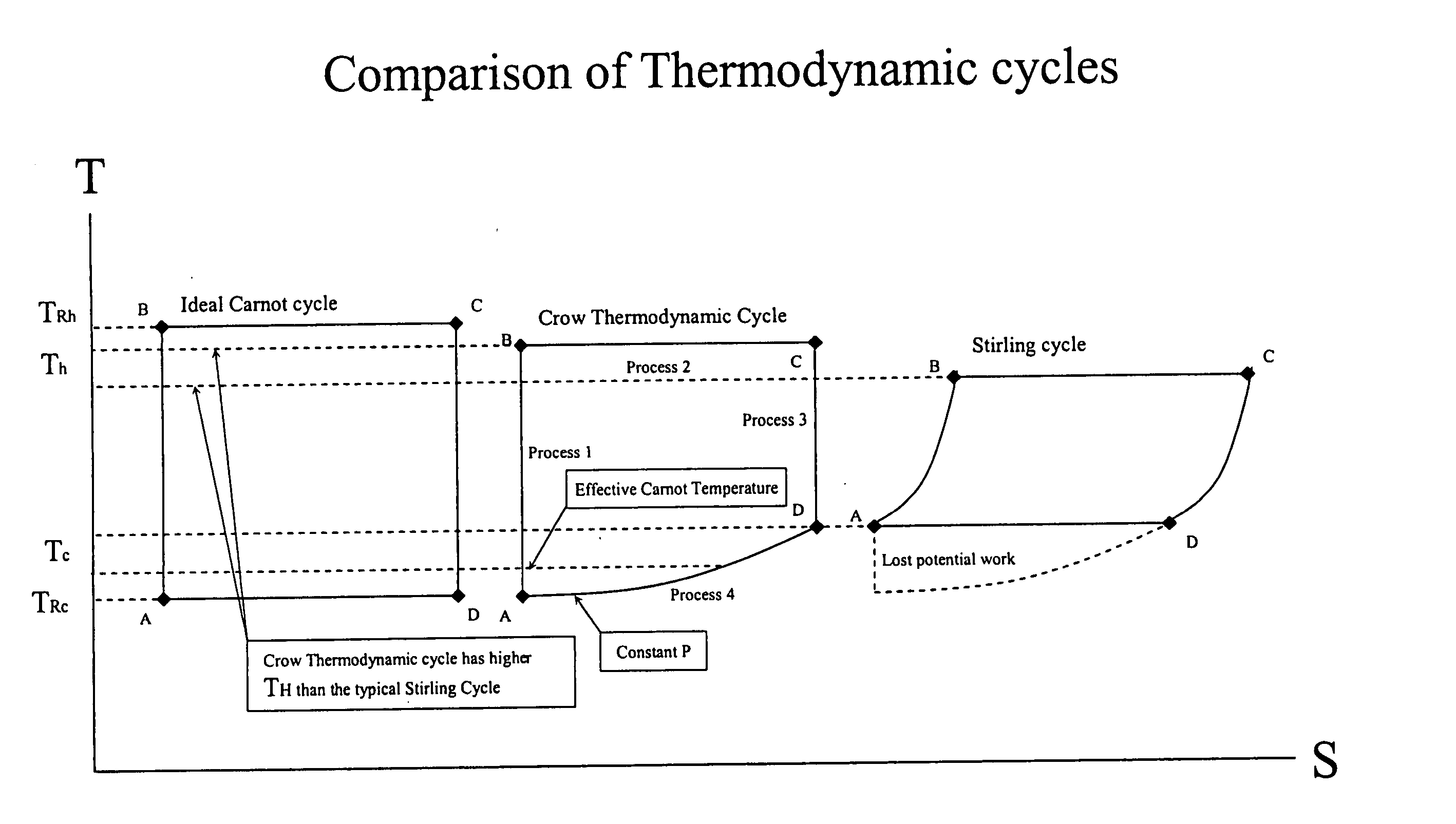
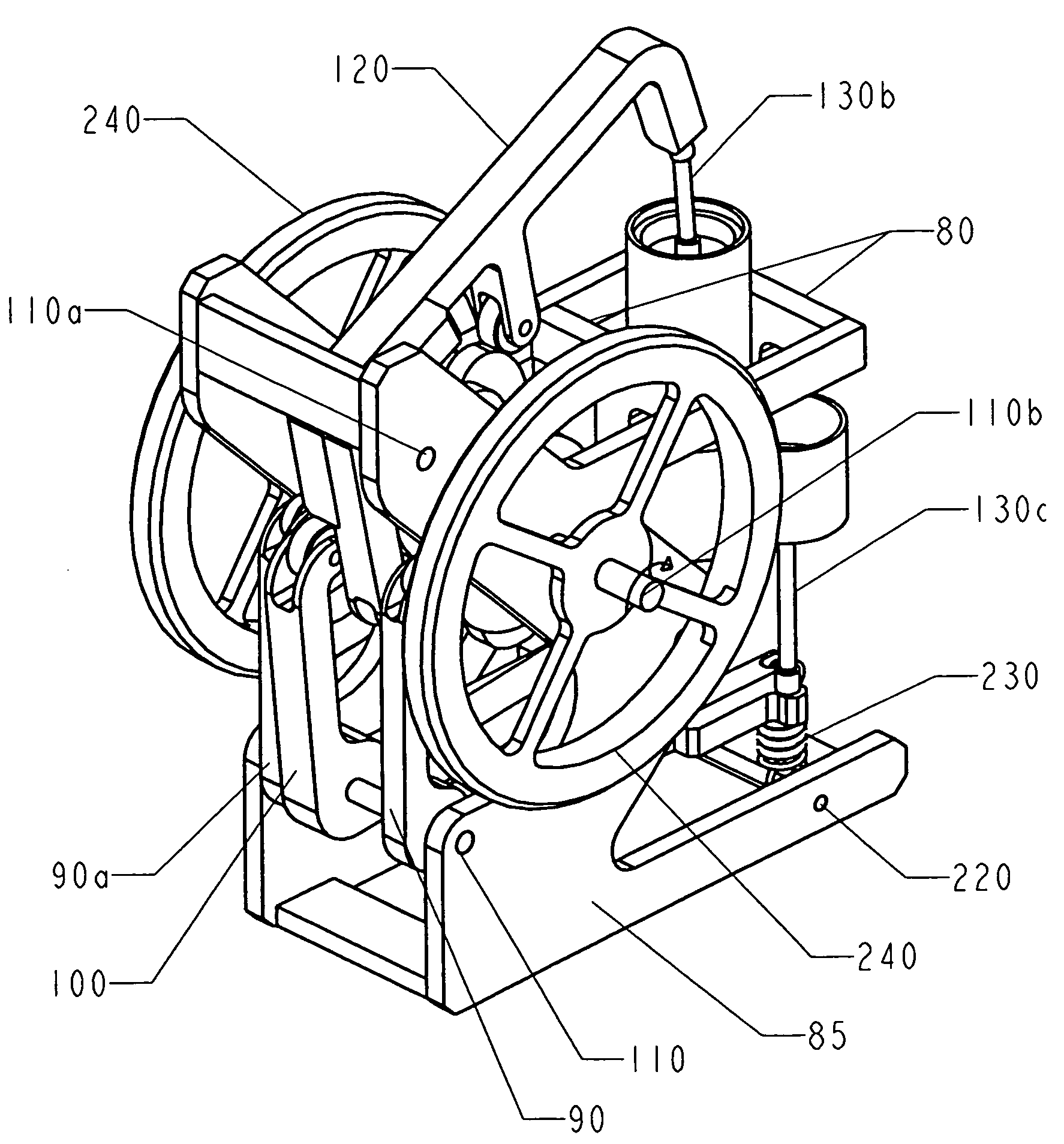
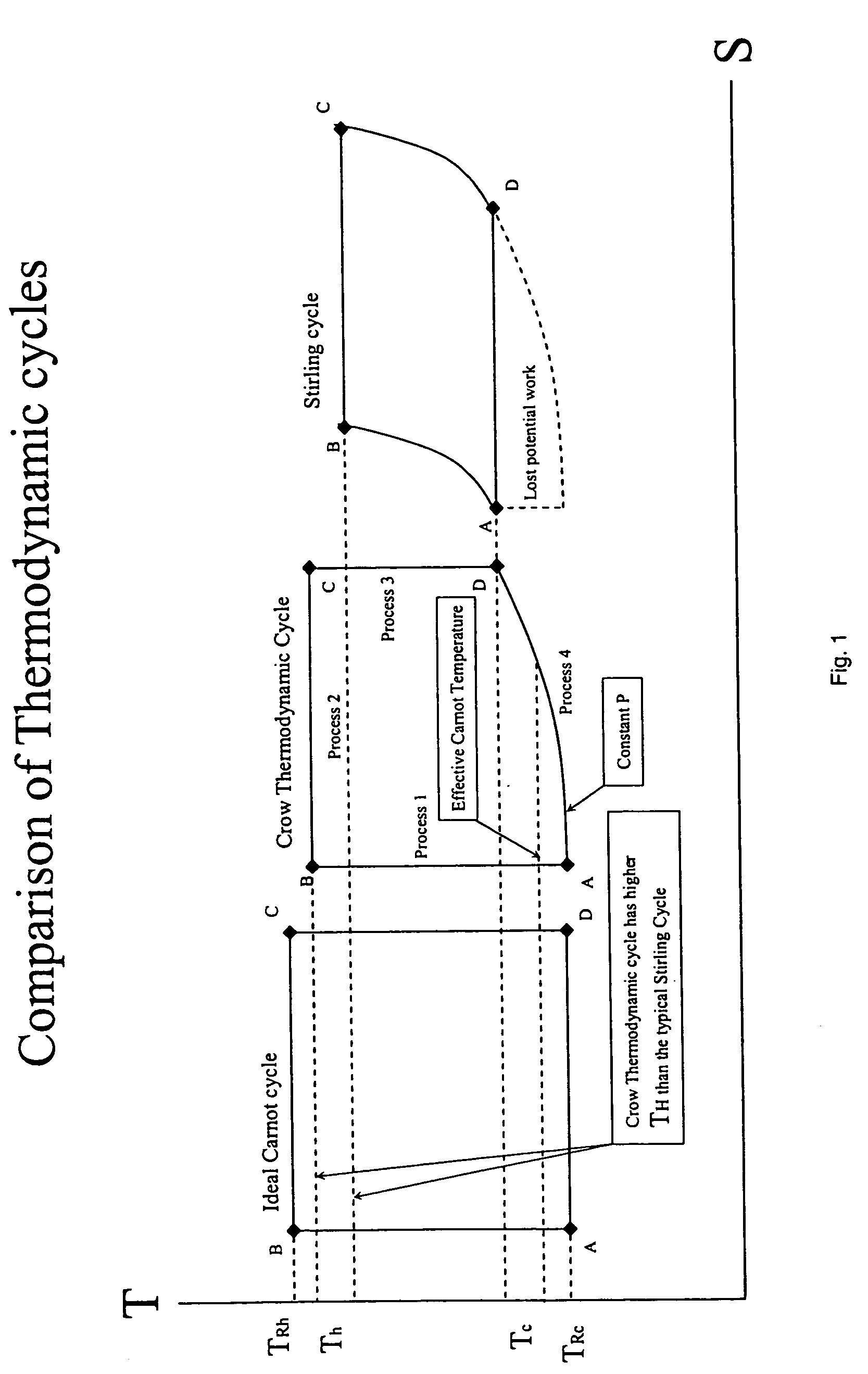
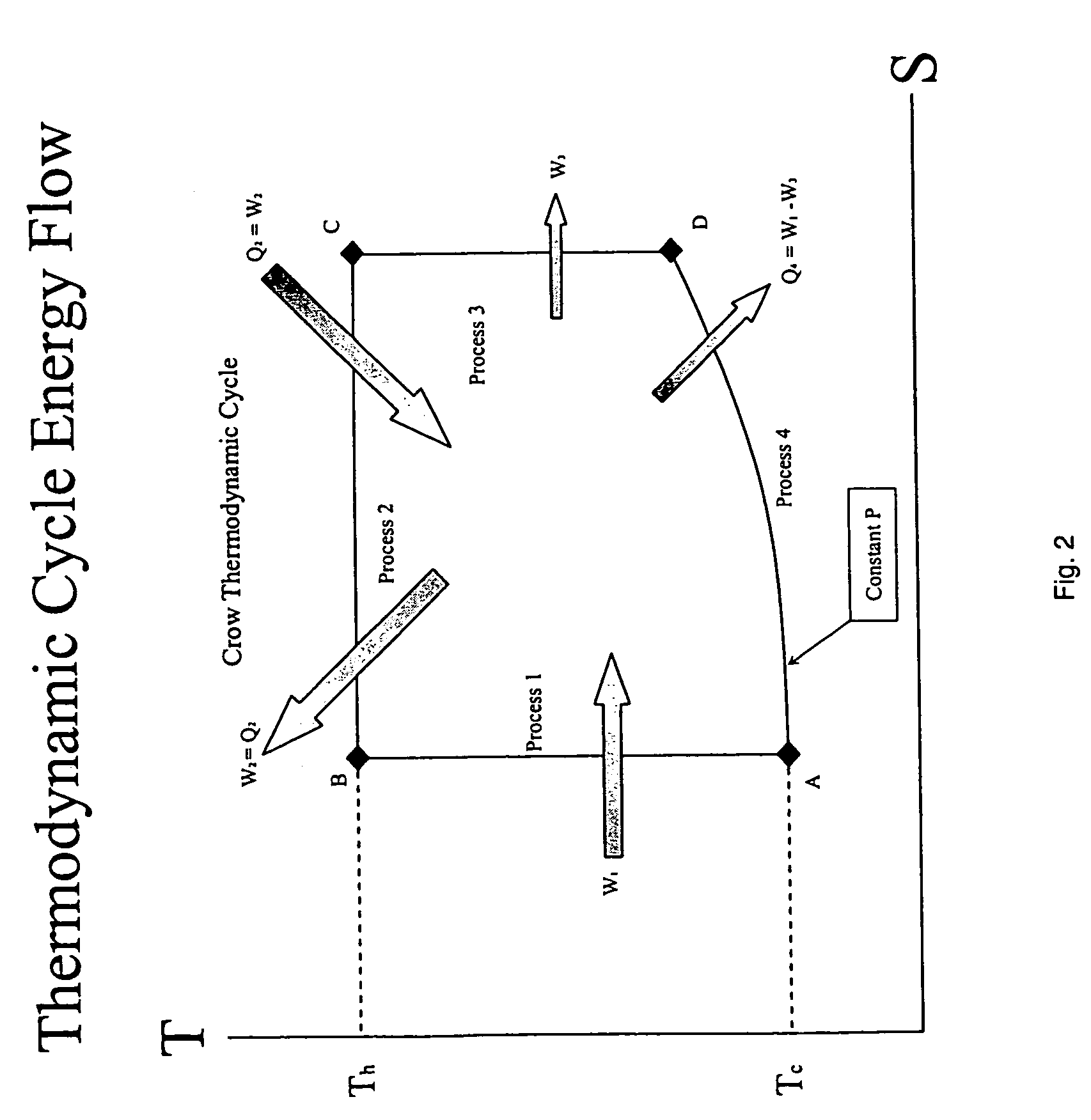
Method and apparatus for converting thermal energy to mechanical energy
InactiveUS20060090467A1Improve efficiencyEfficient regenerationEricsson type enginesSteam engine plantsThermal energyWorking fluid
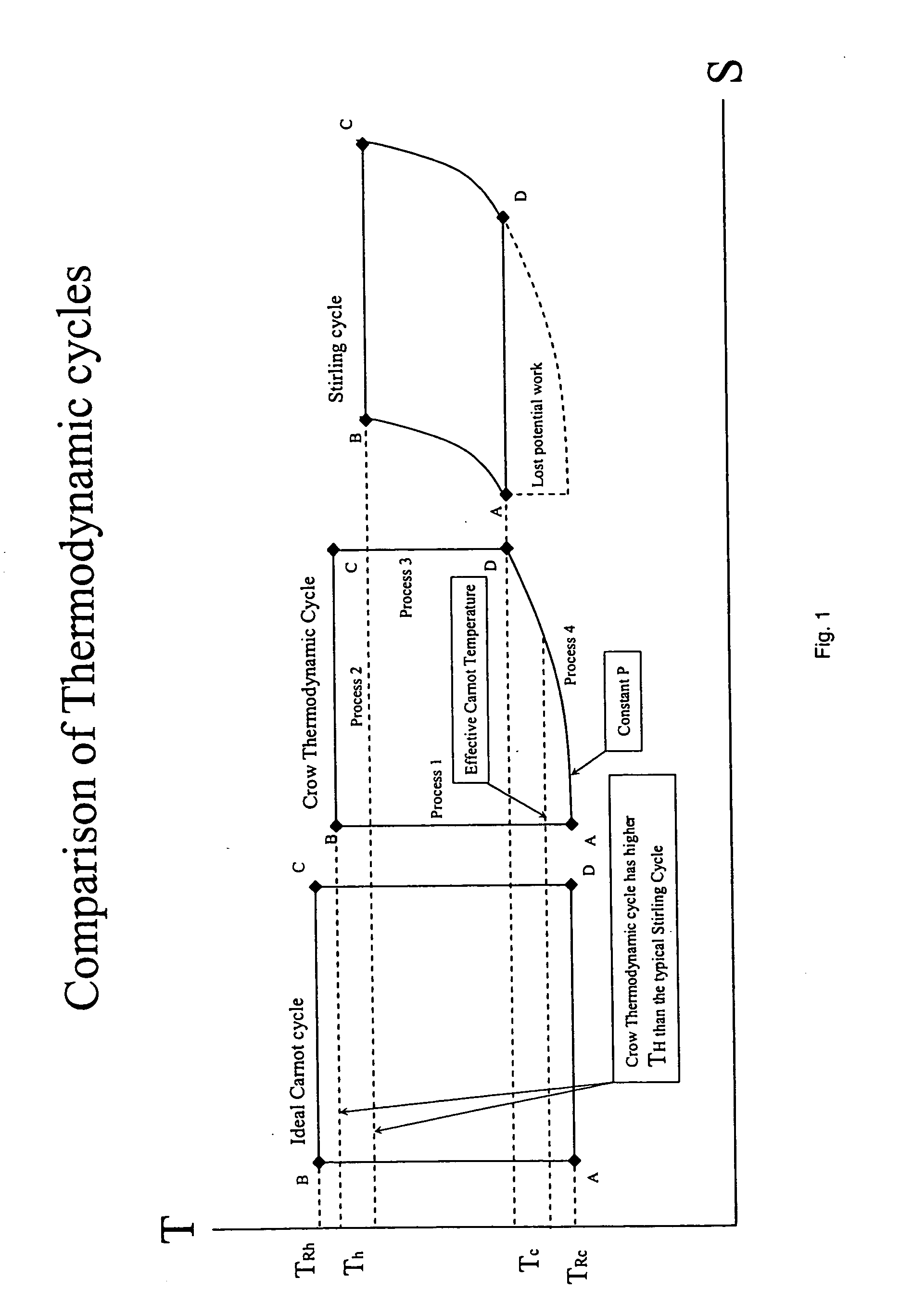
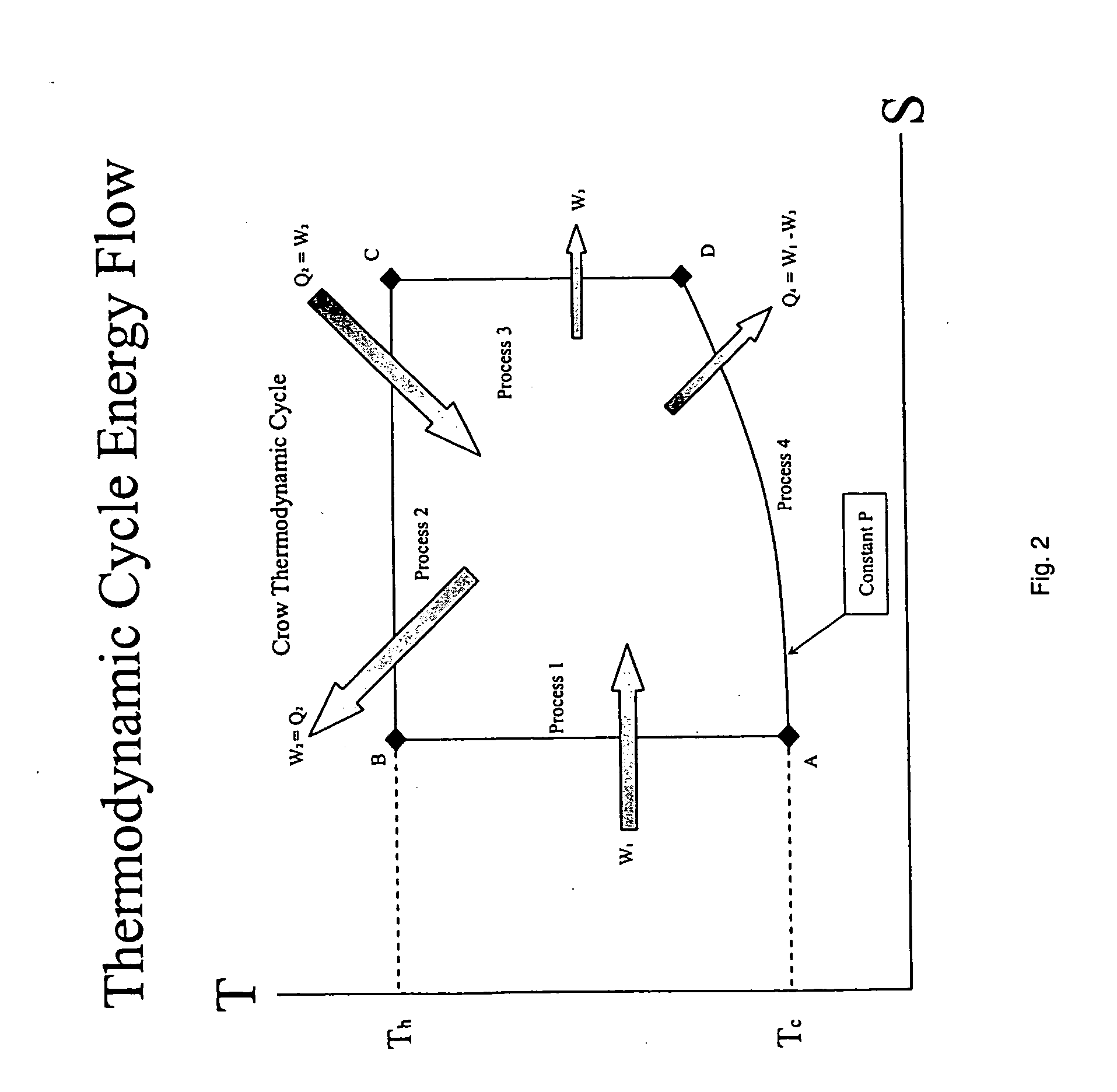
A method and apparatus for converting thermal energy to mechanical energy which can use a wide range of fuels and perform with a high efficiency. Operating on a little utilized thermodynamic cycle of isentropic compression, isothermal expansion, isentropic expansion and finally constant pressure cooling and contraction. The external heat engine utilizes a heat exchanger carrying heat from the external energy source to the working parts of the engine. Pistons and cylinders are activated by appropriate means to adiabatically compress the working fluid, for example ambient air, to transfer the entire mass of the air through the heat exchanger to accomplish isothermal expansion followed by adiabatic expansion and, finally, exhaust the air to ambient to allow for constant pressure cooling and contraction. Valve pistons in conjunction with the cylinders form valves that allow for the exchange of working fluid with ambient. Energy is added to the engine during isothermal expansion, whereby the energy of compression is added by a flywheel or other appropriate energy storage means, said flywheel stores energy recovered during adiabatic expansion. The thermodynamic cycle described and the engine embodiments disclosed, when run in reverse, perform as a heat pump or refrigeration device.
Owner:CROW DARBY
Storage device, computer system, and storage device access method
ActiveUS20070124531A1Technique is effectiveSwift and flexible access makingMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRead-only memoriesAccess methodEquipment computers
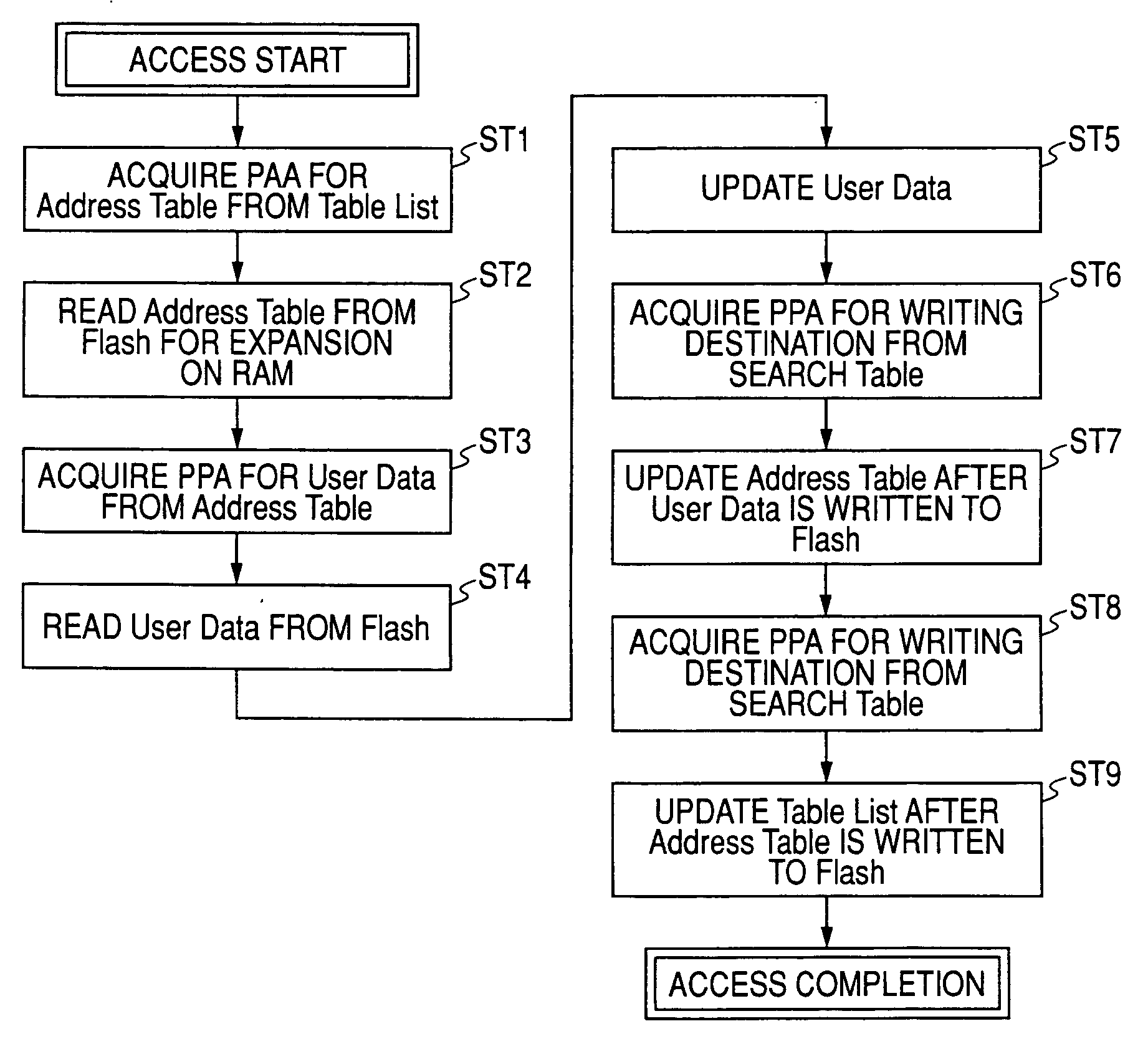
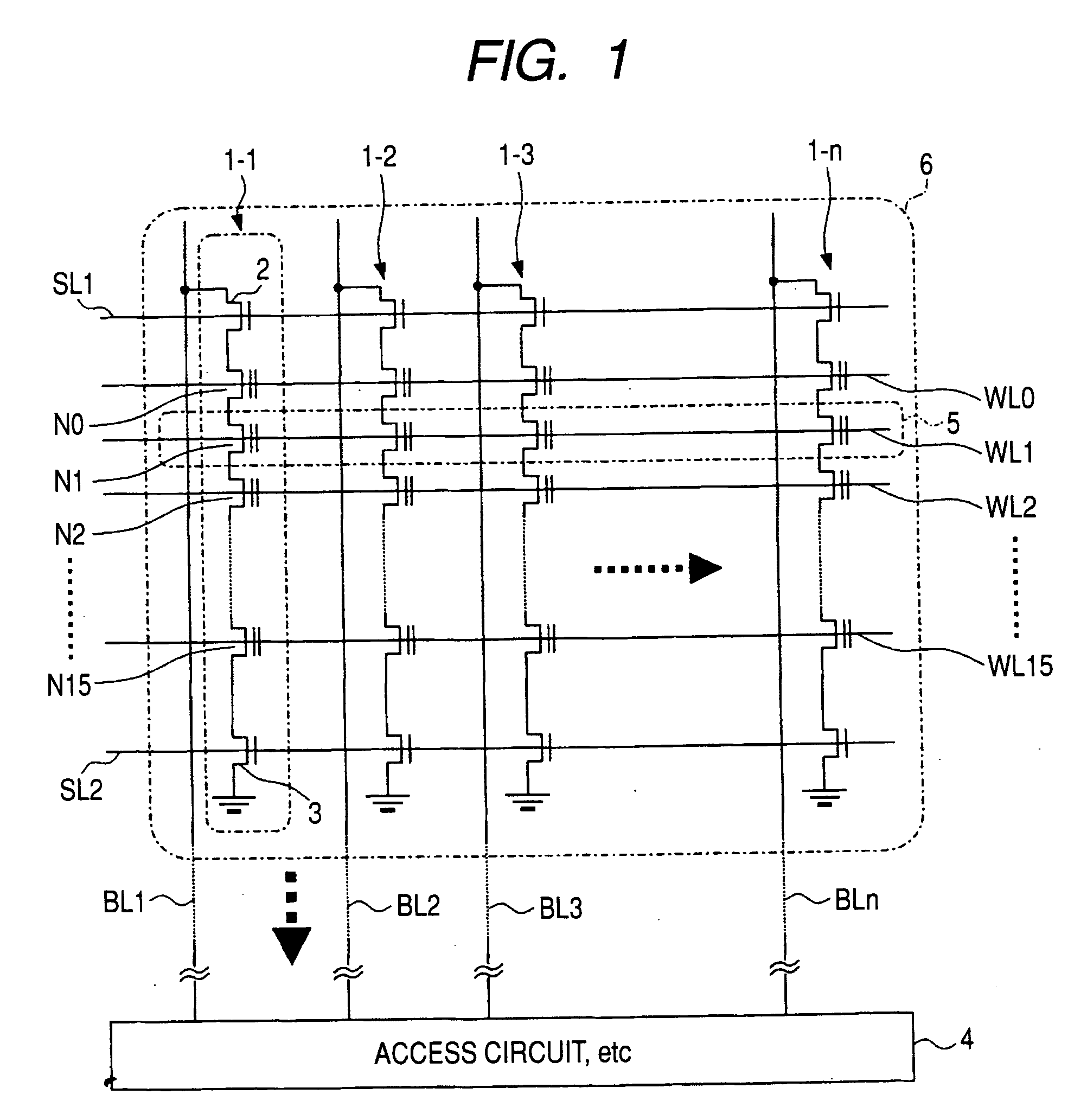
A storage device that includes: an address table; a cache memory; a flash memory device being a storage medium for user data; and a control circuit that is in charge of access management for the flash memory device. In the storage device, the control circuit makes access to the user data on the flash memory device via an address table, in the address table, with an index of an address value generated from an initial logical address, location information is acquired for the user data on the flash memory device corresponding to the index, and the address table is segmented in its entirety into a plurality of small address tables for every area of the index, and the small address tables being segmentation results are stored in the flash memory device, read as required when the user data is accessed, and expanded on the cache memory with entries of the small address tables.
Owner:SONY CORP
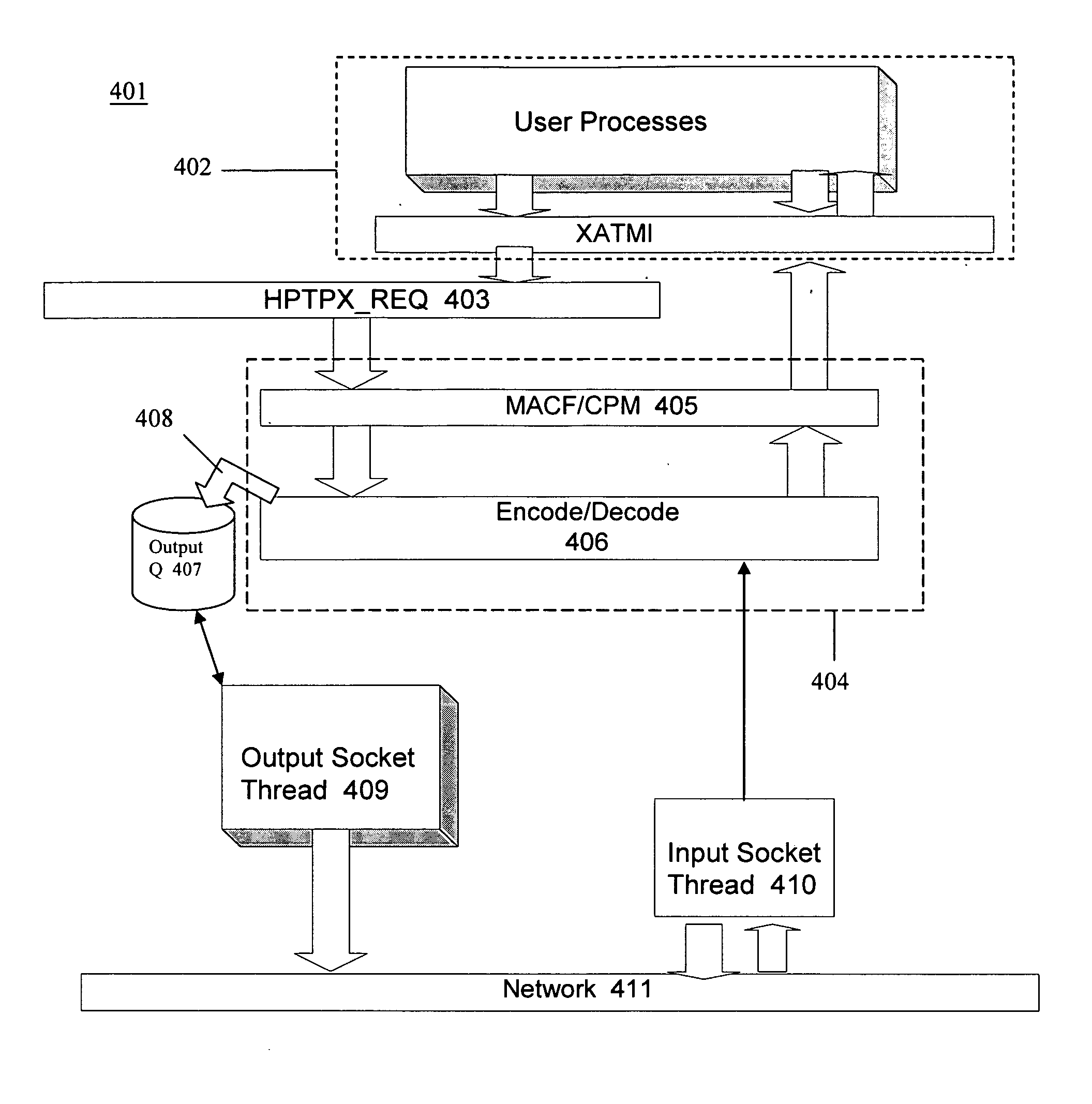
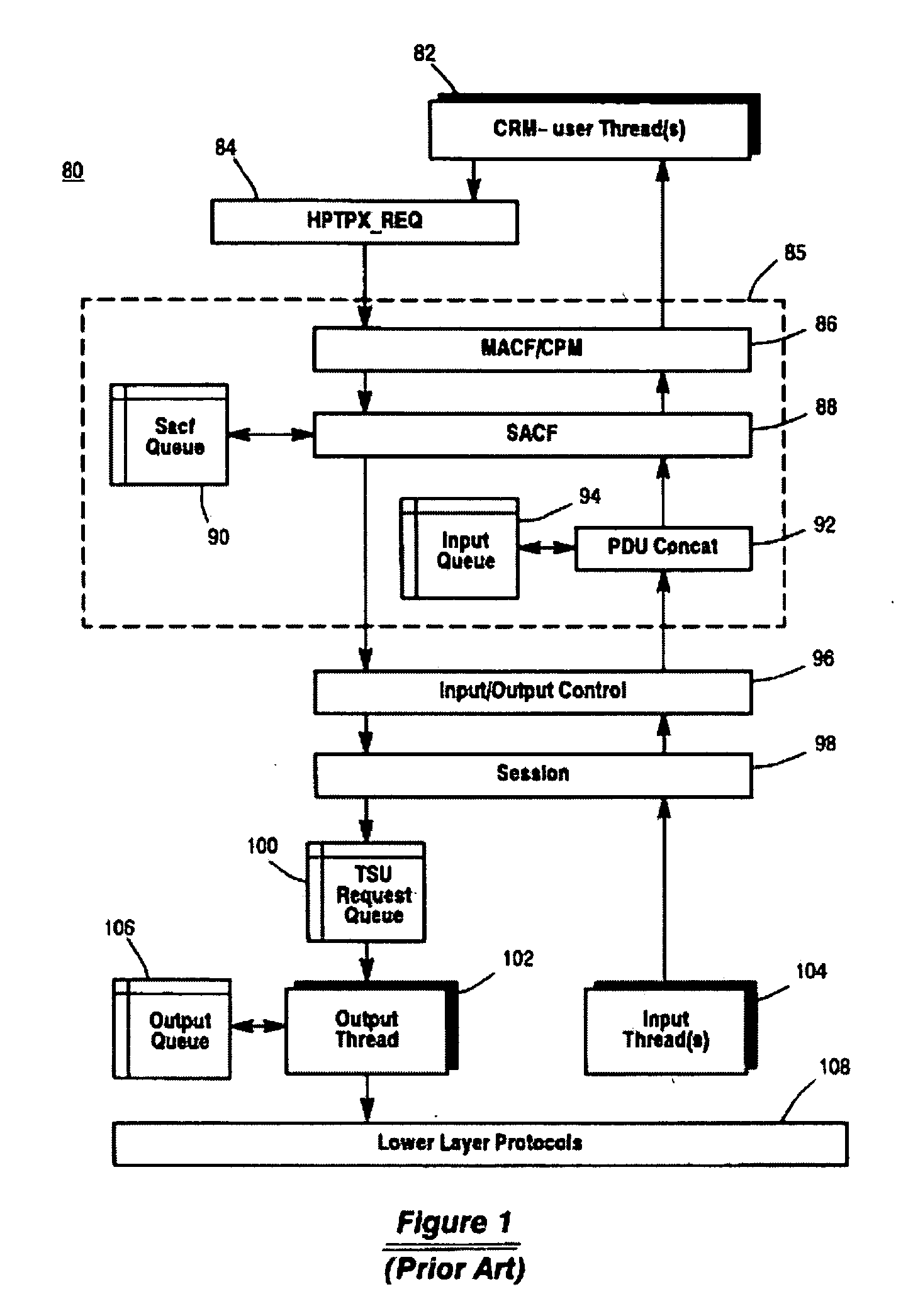
Message transfer using multiplexed connections in an open system interconnection transaction processing environment
InactiveUS20050193056A1Less complexSimpler connection creationMultiple digital computer combinationsSecuring communicationMessage lengthMultiplexing
Novel message formats for use in a distributed transaction environment are disclosed. Each message includes a message type field, a message length field, and a data field, typically in the foregoing order, and each field in the message has a fixed number of bytes. The message type and data length fields may be comprised of a single header. The data field may include novel groups of OSI TP PDUs where each grouping characterizes the content of the data in the PDU. A novel apparatus for use in a distributed transaction environment also is disclosed. The apparatus may include a peer processing machine and a multiplexed TCP / IP connection for exchanging messages with other peer processing machines in the distributed transaction environment.
Owner:UNISYS CORP
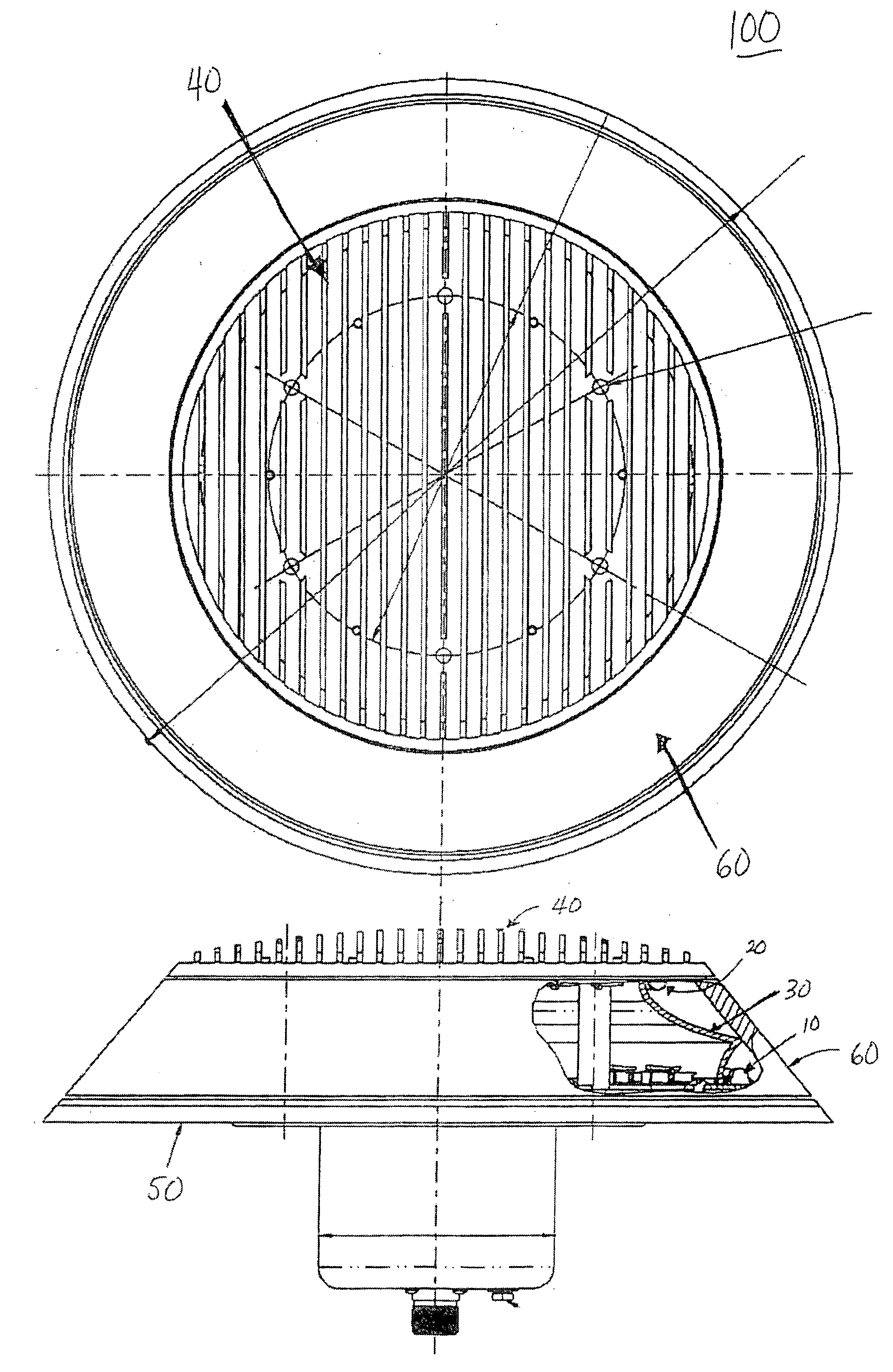
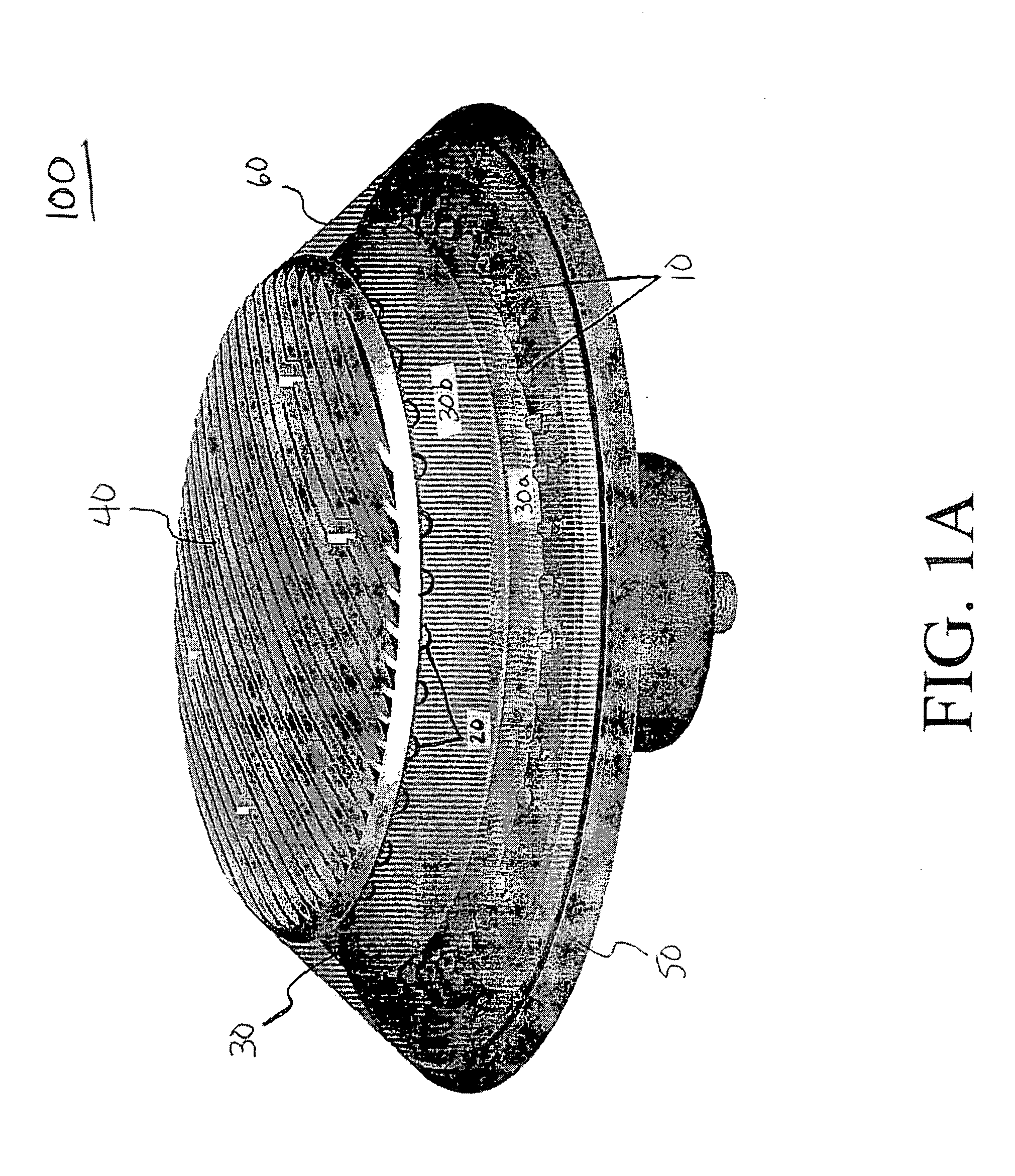
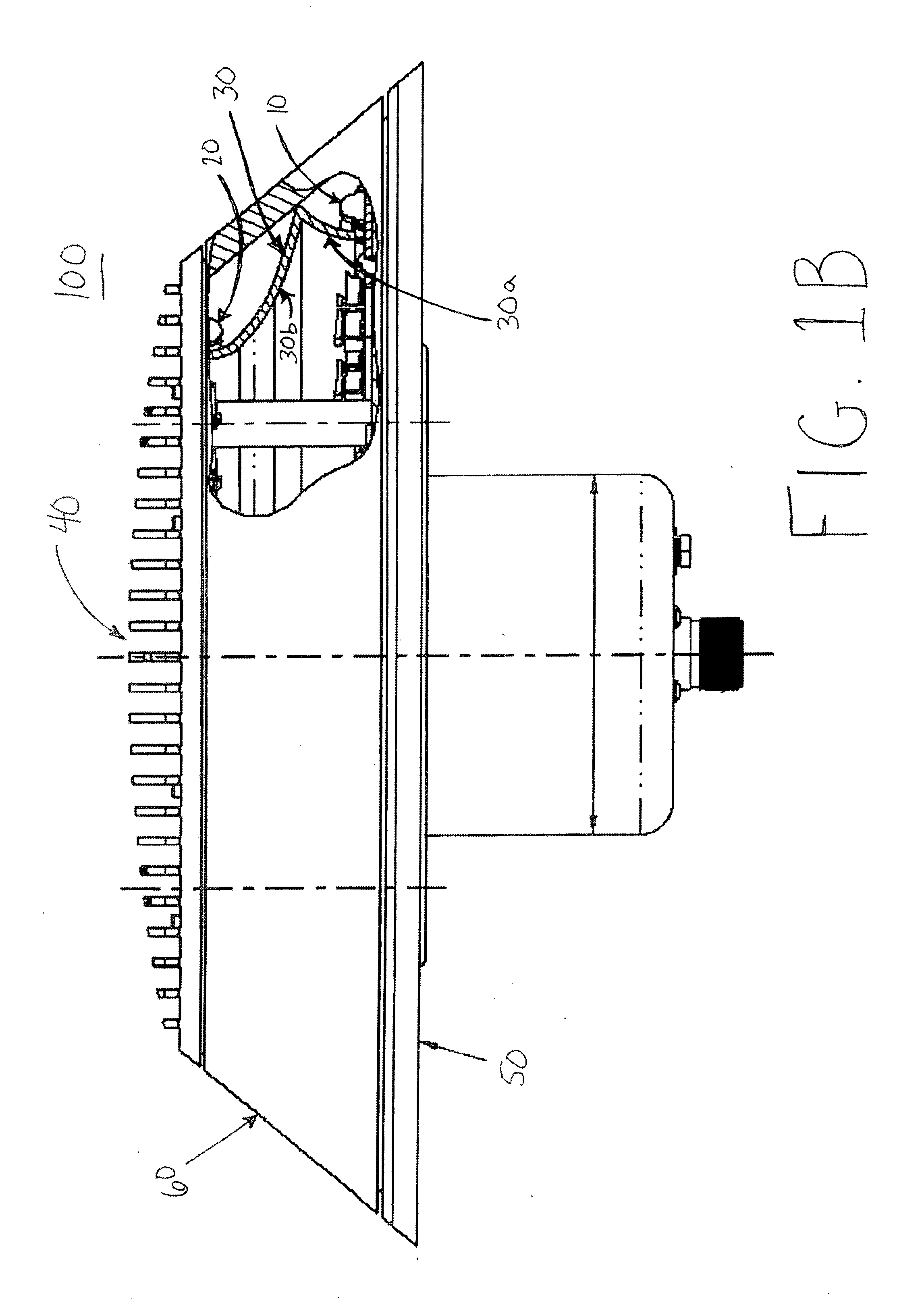
Body mounted LED-based anti-collision light for aircraft
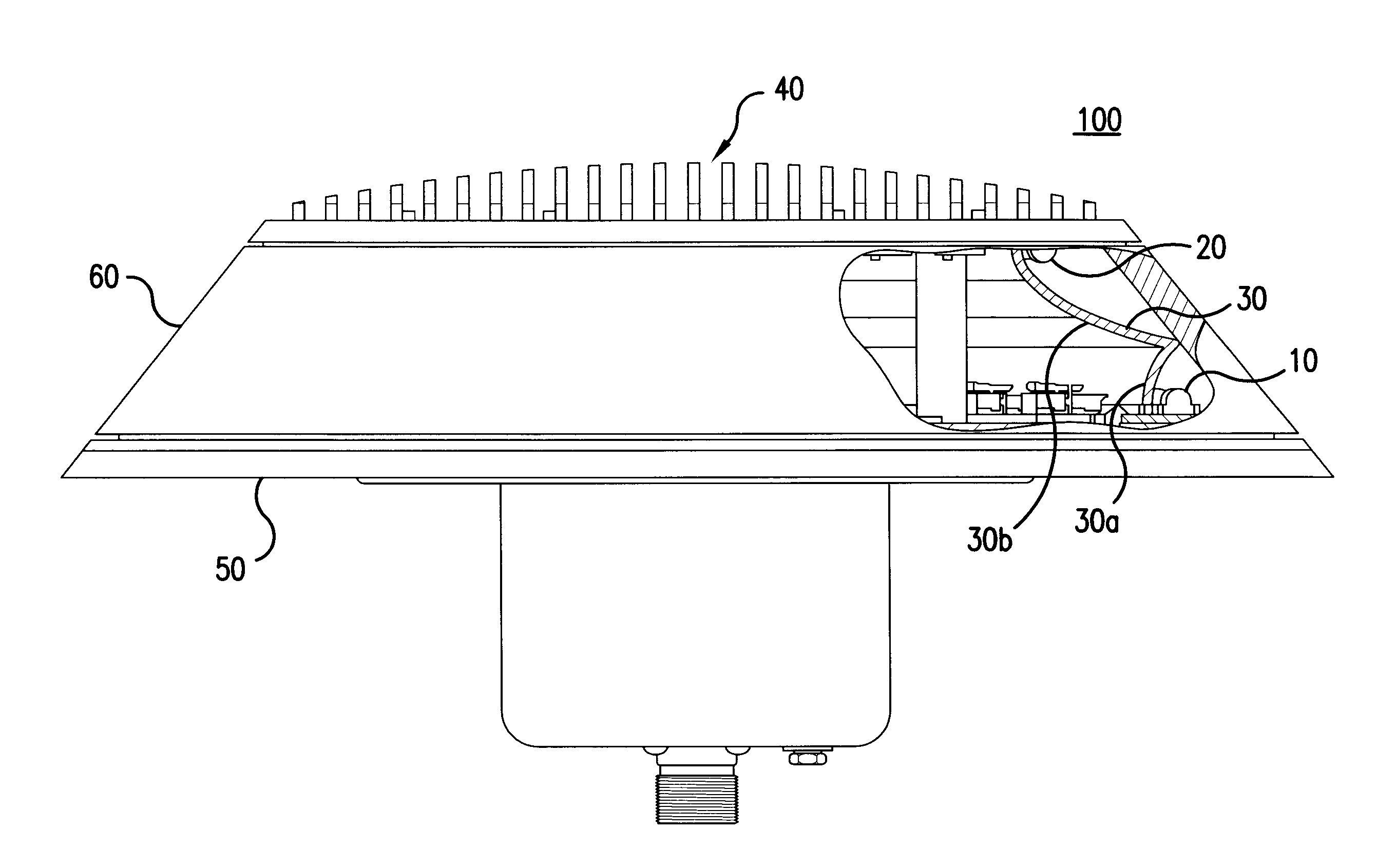
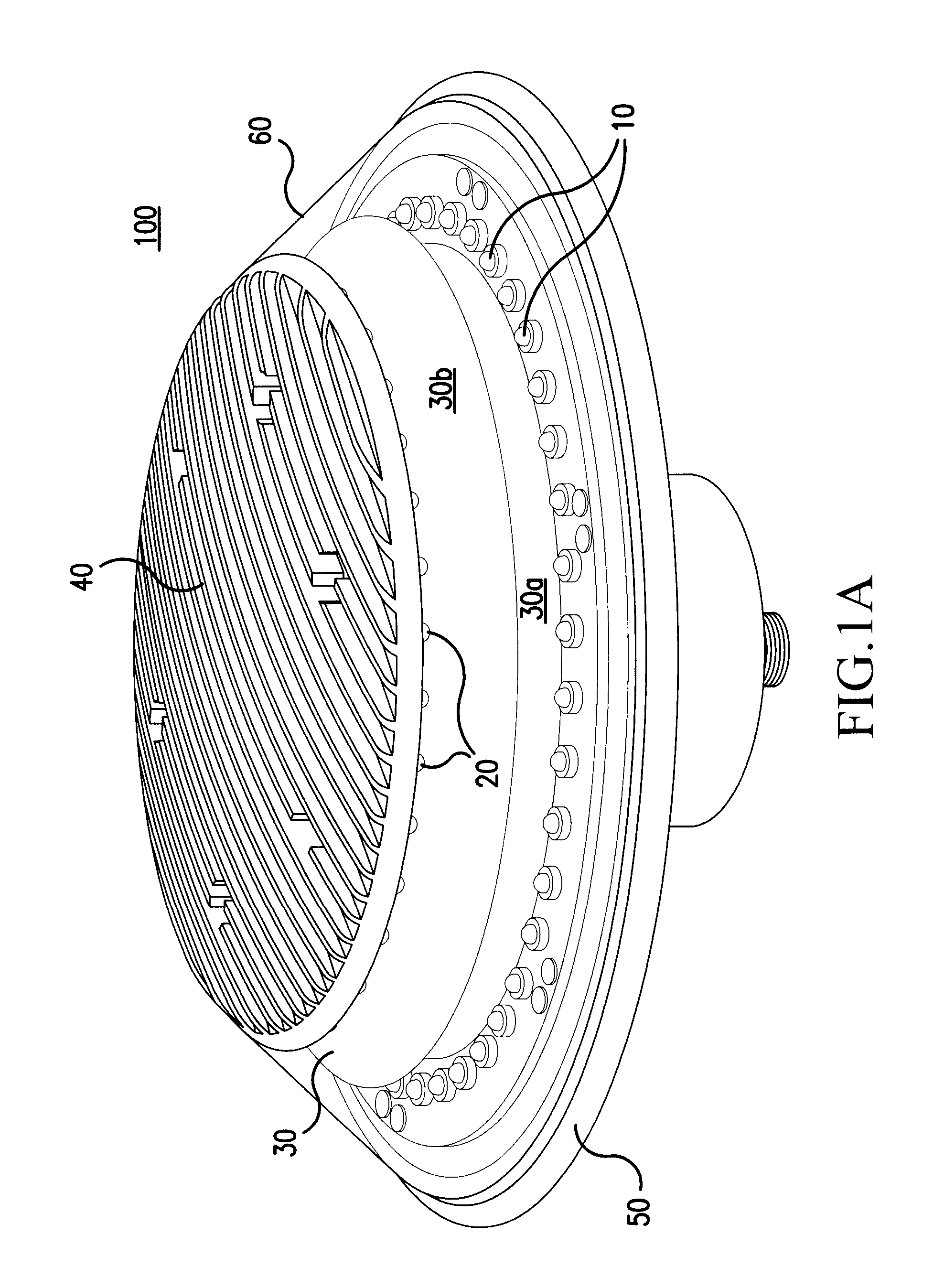
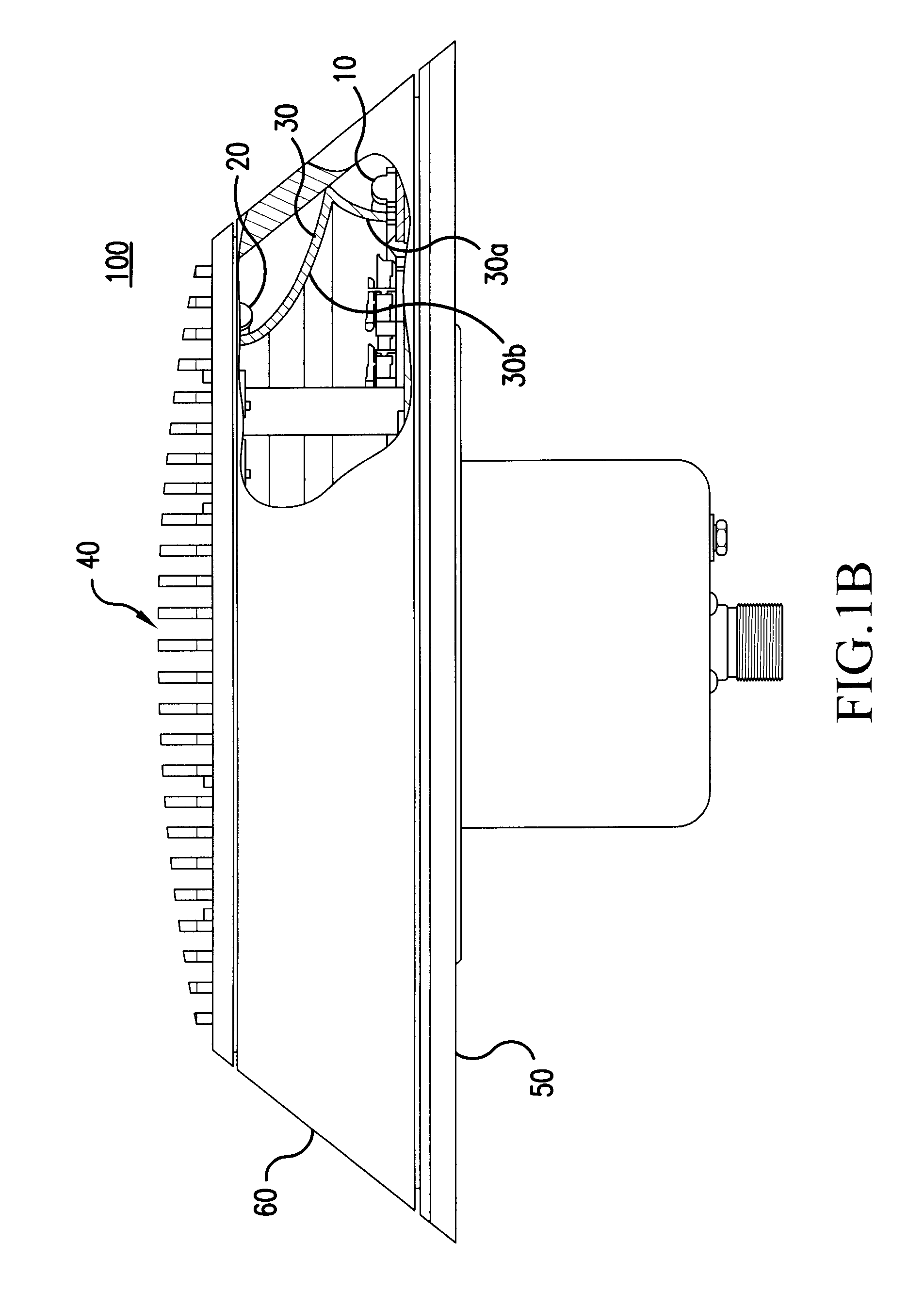
ActiveUS20060007012A1Reduce in quantityLow costLighting support devicesPoint-like light sourceEngineeringLight-emitting diode
A rotationally symmetrical anti-collision light (100, 200) for an aircraft utilizing light-emitting diodes (LEDs) is mounted to the fuselage of an aircraft. The LEDs (10, 10′, 20, 20′) may be configured in one or more concentric rings. The anti-collision light includes a reflector (30, 30′) configured to redirect the light emitted by at least one of the rings, so that the light pattern satisfies predetermined specifications.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
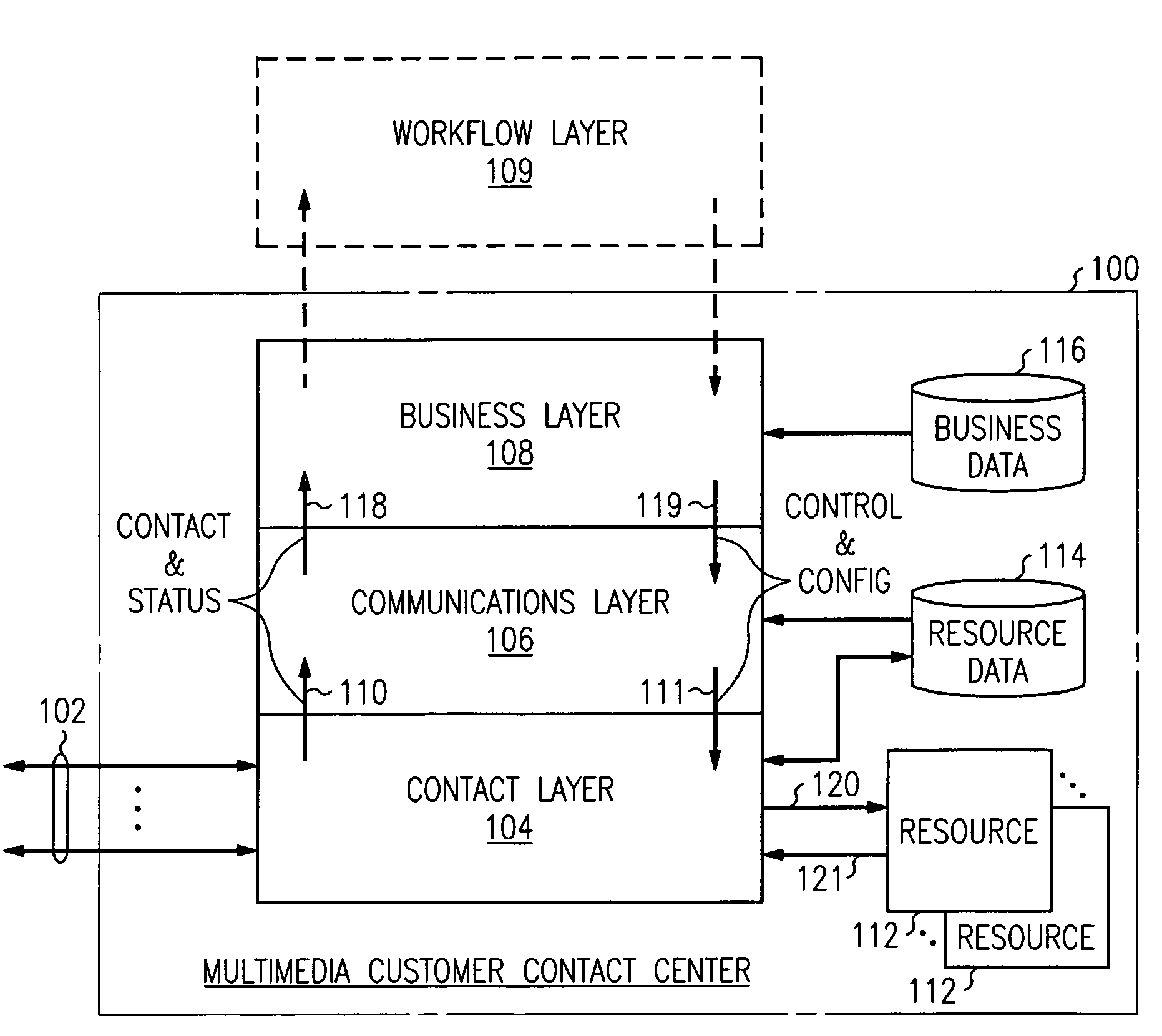
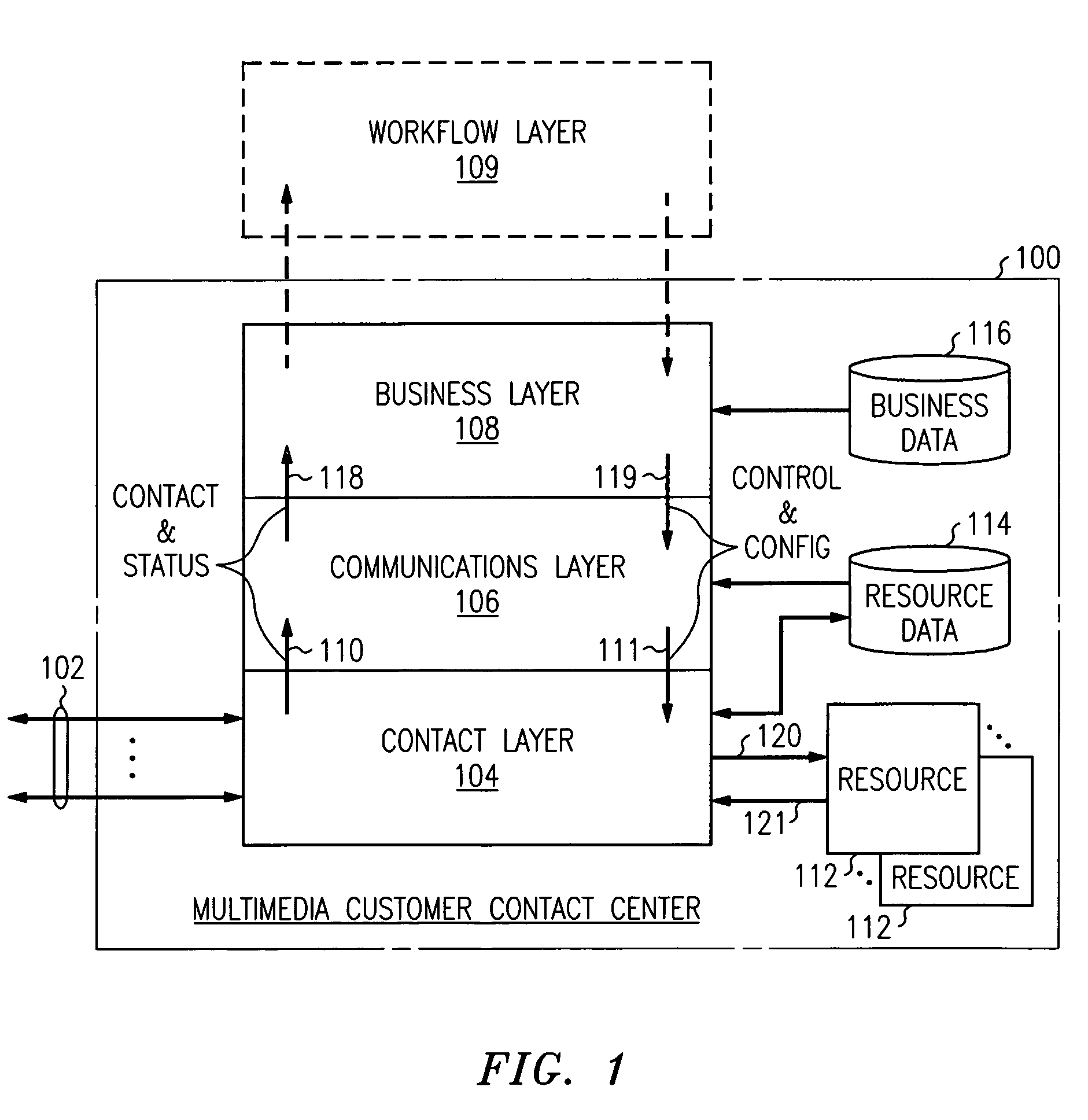
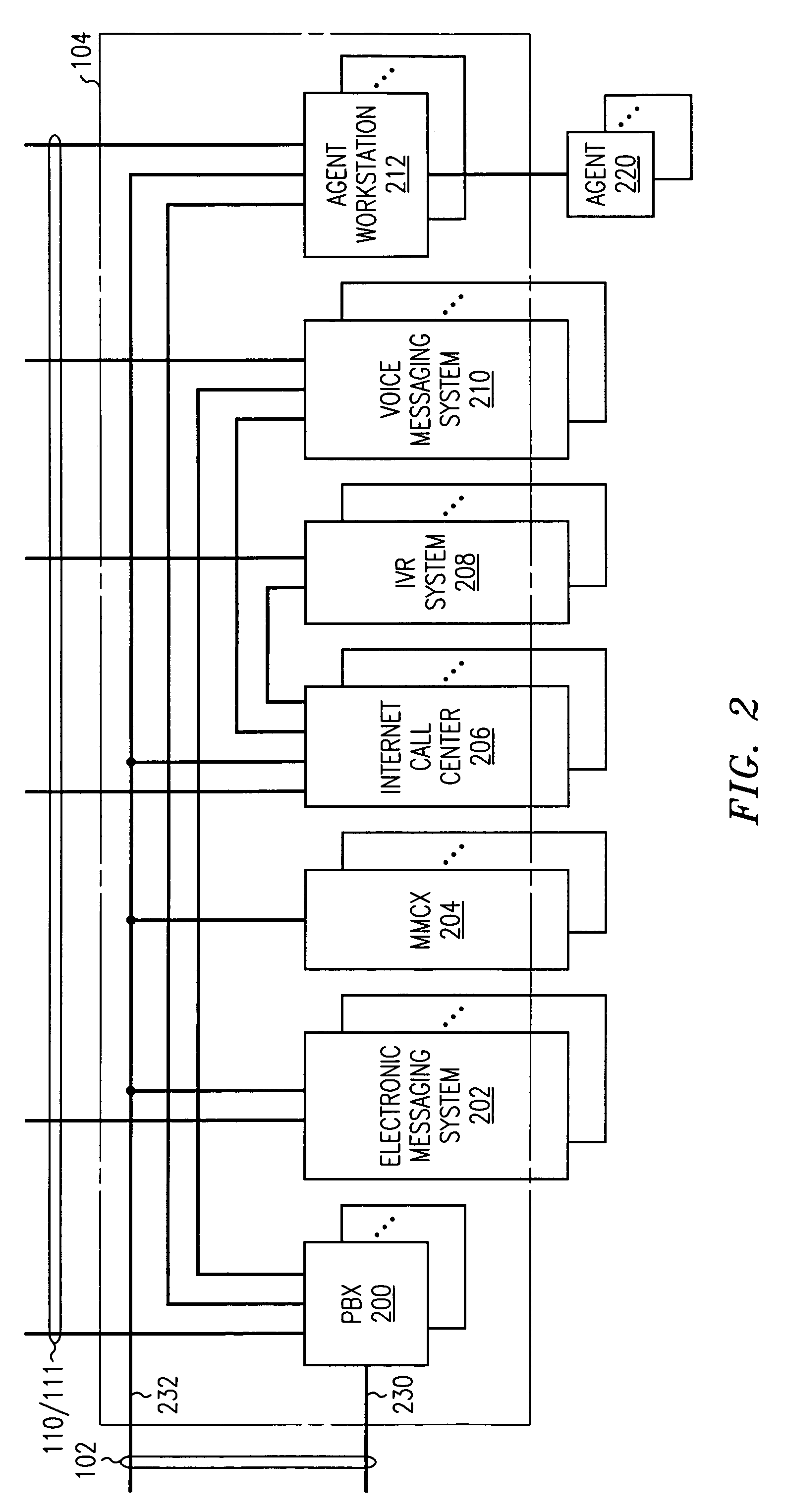
Multimedia customer care center having a layered control architecture
InactiveUS6978247B1Easy to integrateImprove simplicitySpecial service for subscribersOffice automationCare centerPre-existing
The architecture of a multimedia customer care center (100) is divided into three separate application layers: a contact layer (104), a communications layer (106) and a business layer (108). The contact layer comprises media-specific handlers (200–212) that manage their media-specific resources, connect customer contacts to resources (220) and report events, including status to the communications layer. The communication includes media-independent software (106) that manages shared resources, that tracks, accumulates, and reports events reported by the contact layer, and that directs handling of events by the contact layer according to business information. The business layer includes software (108) that provides an interface to the customer contact center for the business that is served by the center. It manages business services by supplying business information that defines the services and business goals to the communications layer, and generates reports from information accumulated by the communications layer. It effects scheduling and adherence tracking of resources. It also provides workflow control capability or interfaces to pre-existing workflow systems.
Owner:AVAYA INC
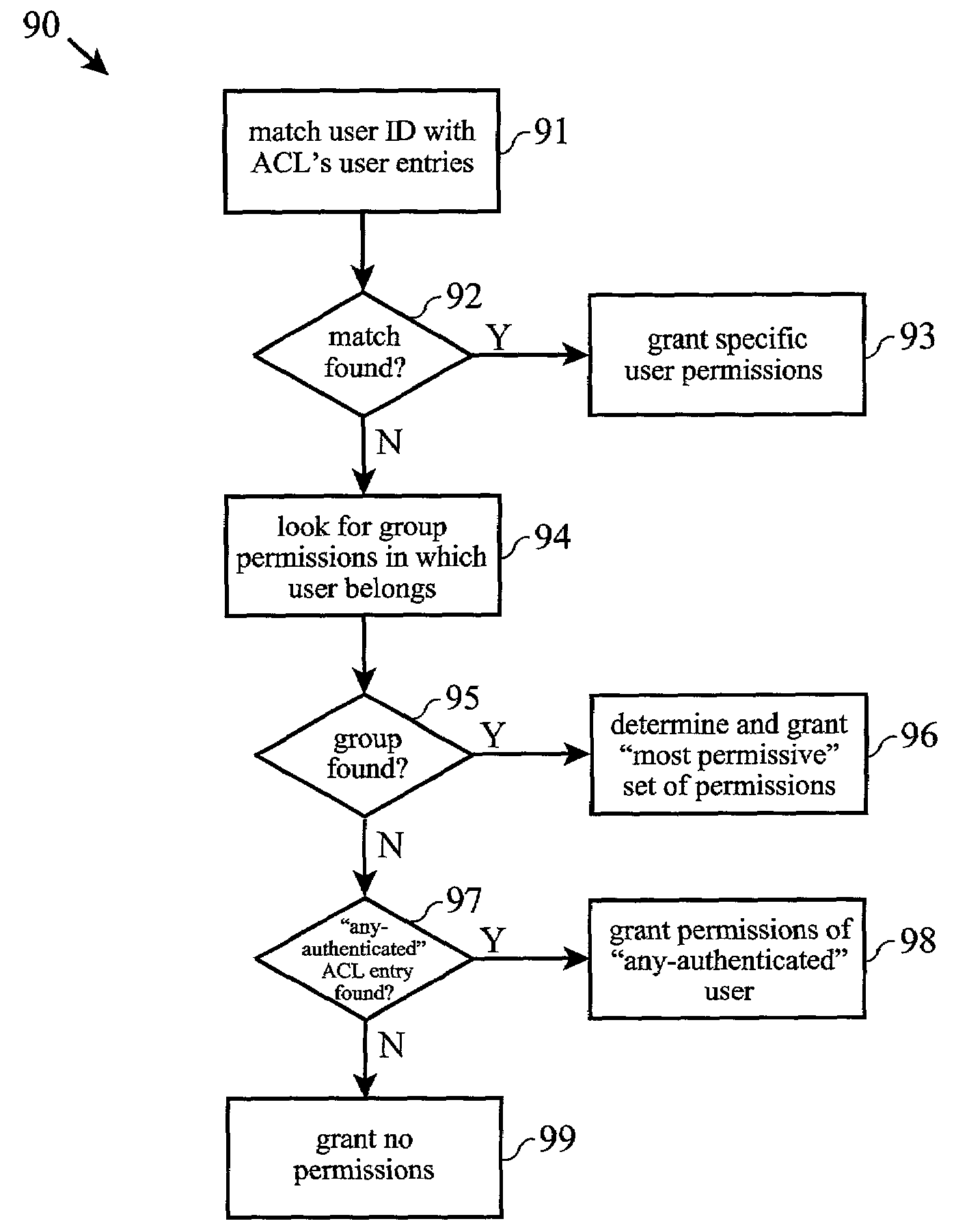
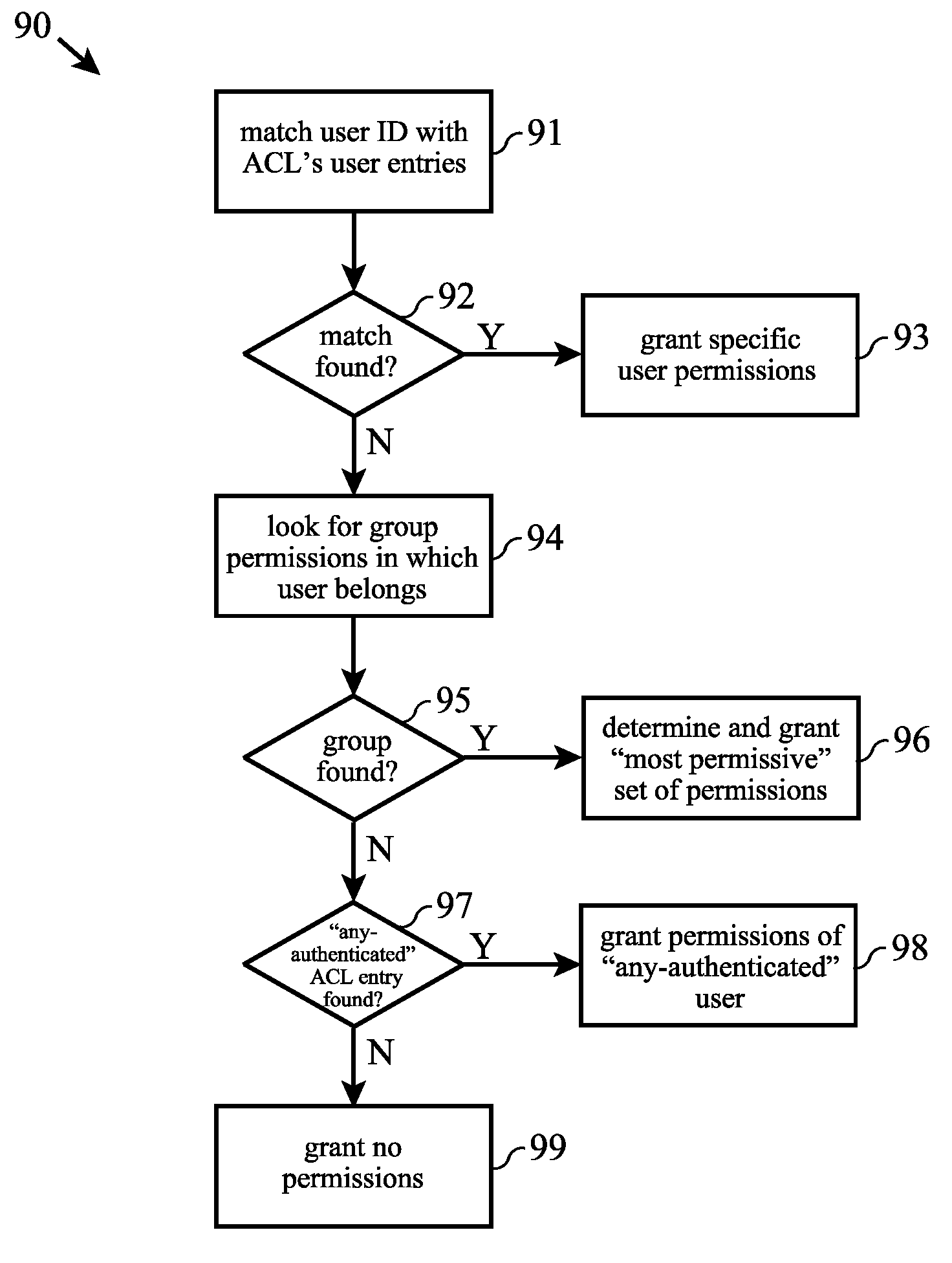
Grouped access control list actions
ActiveUS7380271B2Simple definitionSimplified managementDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationAccess methodOperational definition
Access Control Lists (ACLs) are used to describe the permitted actions (permissions) on protected network computer system resources or objects associated with an client or user identity. An identity may be an individual user or group of users. The actions are used to represent the different access methods available on a particular projected object or resource. A new action grouping mechanism is provided which tags each action with an action group name. The grouping of actions facilitates a larger permission set to be defined in an ACL, whereas action permission indicators can be reused for unique action definitions within various action groups. This effectively extends the finite total number of permissions available within a security system, allows a more descriptive and extensible permission mechanism in an Access Control List, as well as aiding in the simplification of management and definition of security policies.
Owner:SAILPOINT TECH HLDG INC
STREAMING BRIDGE DESIGN WITH HOST INTERFACES AND NETWORK ON CHIP (NoC) LAYERS
ActiveUS20150188847A1High degreeSimplified managementData switching by path configurationTraffic volumeTraffic profile
Systems and methods described herein are directed to streaming bridge design implementations that help interconnect and transfer transaction packets between multiple source and destination host interfaces through a Network on Chip (NoC) interconnect, which includes a plurality of NoC router layers and virtual channels (VCs) connecting the router layers. Implementations are configured to support a variety of different traffic profiles, each having a different set of traffic flows. Streaming bridge design implementation can divide streaming bridge into a streaming TX bridge and a streaming RX bridge, wherein TX bridge is operatively coupled with host TX interfaces and RX bridge is operatively coupled with host RX interfaces, and where TX bridge forwards transaction packets from host TX interfaces to different router layers / VCs of NoC, and RX bridge, on the other hand, receives packets from NoC router layers / VCs and transmits the packets to host RX interfaces based on Quality of Service.
Owner:INTEL CORP
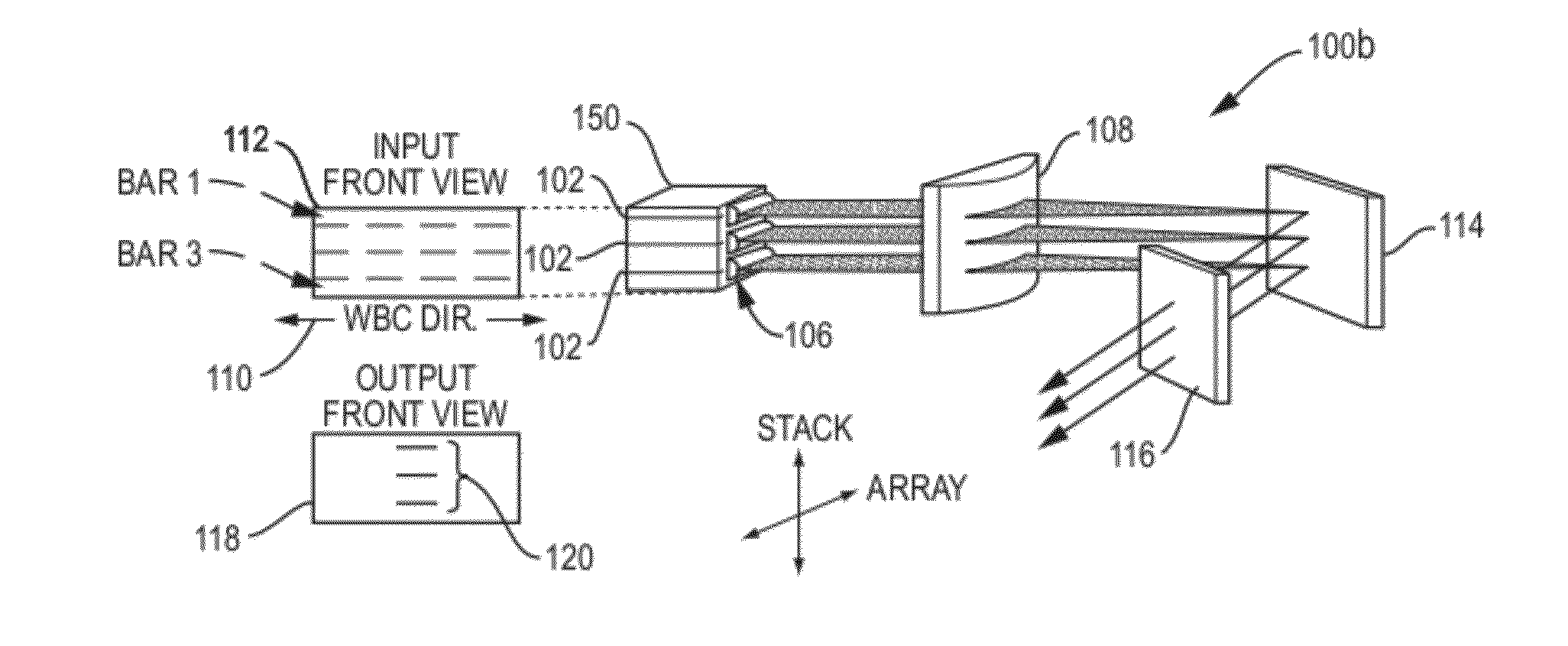
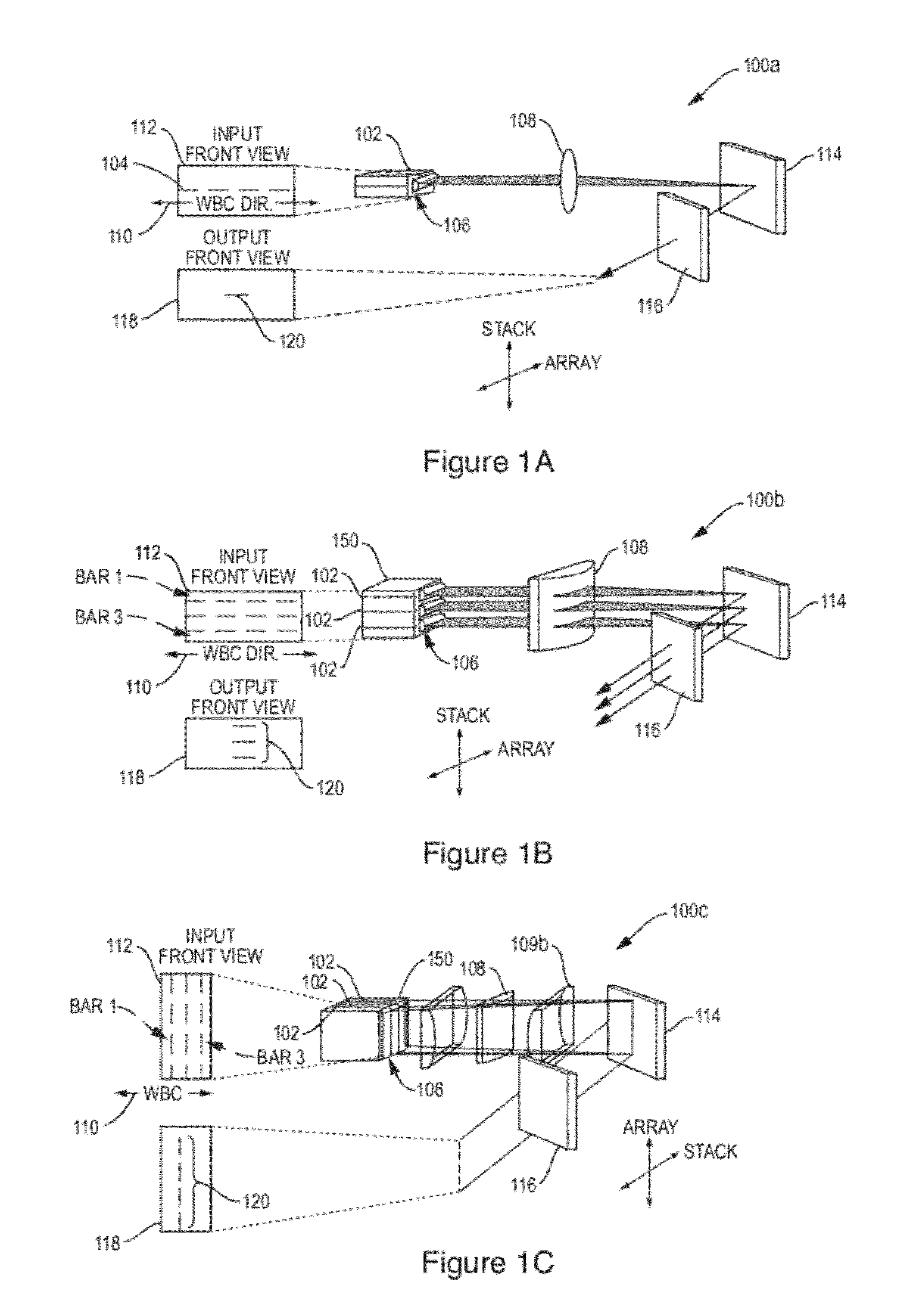
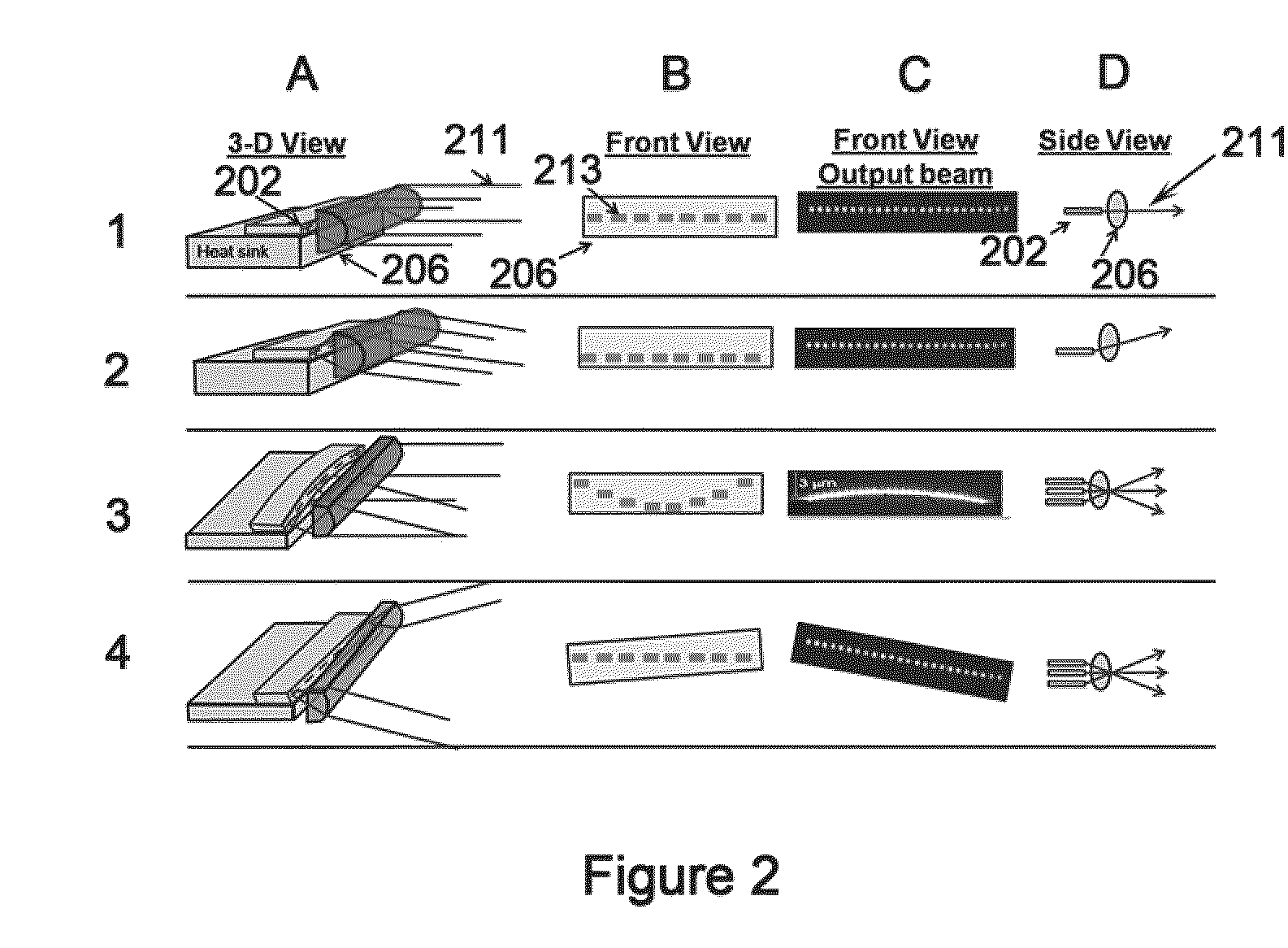
Compact Interdependent Optical Element Wavelength Beam Combining Laser System and Method
ActiveUS20120105968A1Small footprintSimplified managementLaser detailsSemiconductor laser optical deviceLight beamLength wave
A Compact Interdependent Optical Laser System and Method is designed for use with wavelength beam combining (WBC) systems that utilize both slow-axis and fast-axis WBC. Multiple optical elements having individual and interdependent functionality allow for the system to compact reducing the overall footprint of the system. Additional, configurations incorporating the compact system described herein allow for high-power and brightness scaling.
Owner:PANASONIC OF NORTH AMERICA
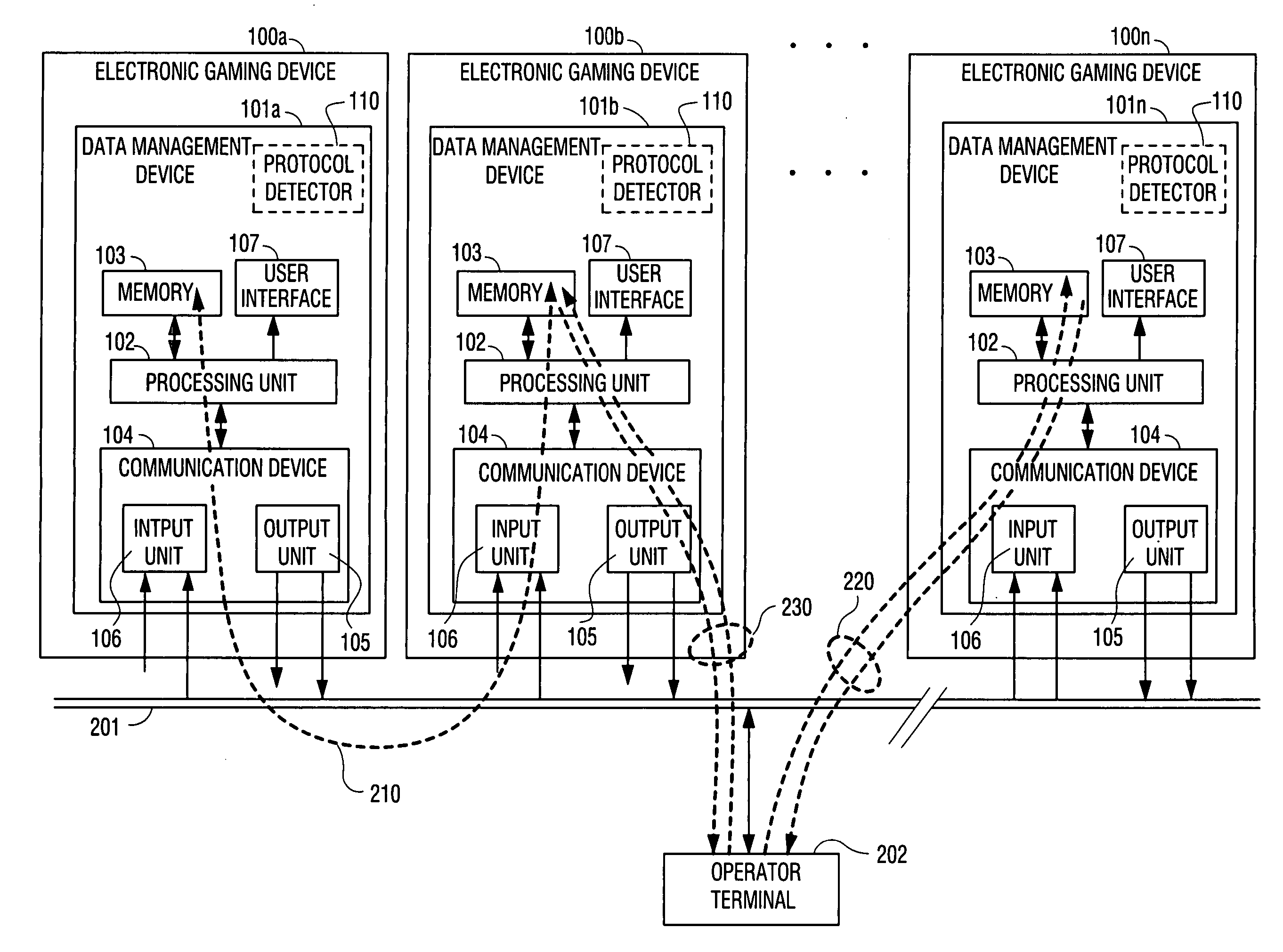
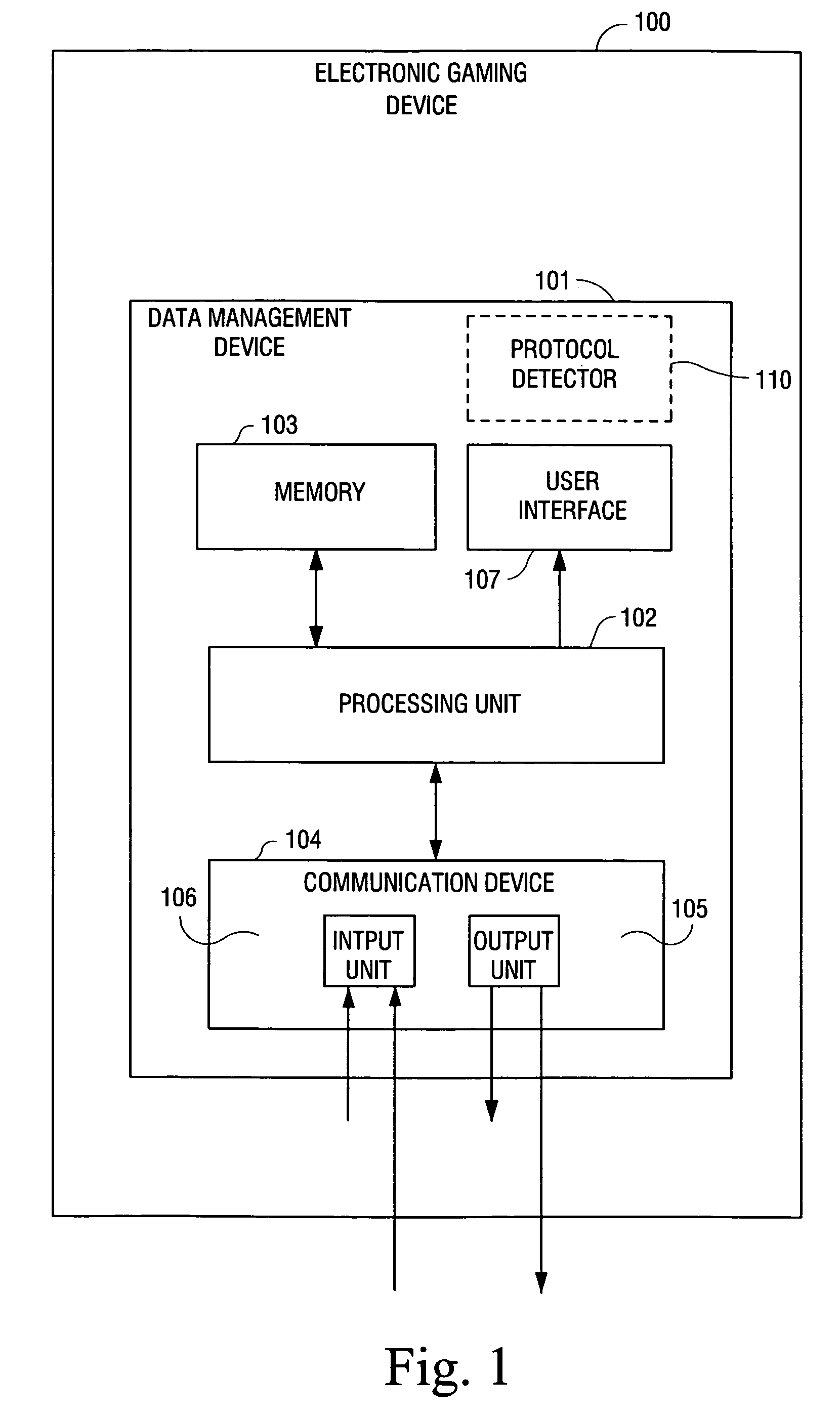
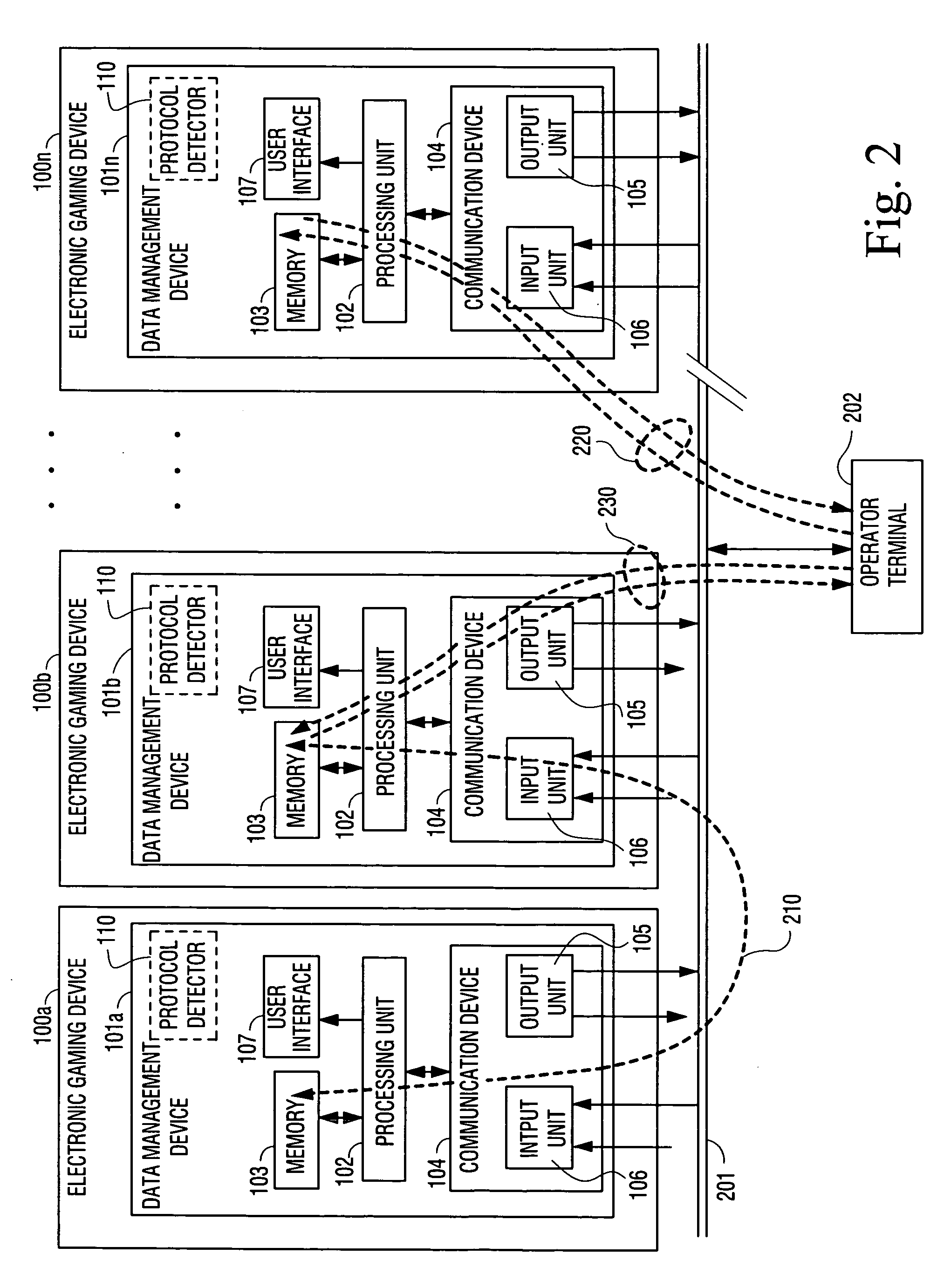
Data management device within an electronic gaming device and a method for monitoring electronic gaming devices
InactiveUS20060030409A1Reduced failure rateLow failure rateApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesStorage cellComputer hardware
An electronic gaming system comprises a plurality of gaming devices (100a-100n) including respective data management devices (101a-101n) having a processor unit (102) for processing gaming data in the respective electronic gaming device (100a-100n) in response to a gaming sequence being performed using the electronic gaming device, a memory unit (103) for storing the gaming data generated in the electronic gaming device (100a-100n) and a communication device (104) for communicating gaming data with at least one other data management device, and a databus device (201) for connecting the plurality of data management devices (101a-101n) with each other through the communication devices (104) provided in each of the electronic gaming devices (100a-100n) for exchanging gaming data between the data management devices (101a-101n).
Owner:SYST & PROGRESS HLDG
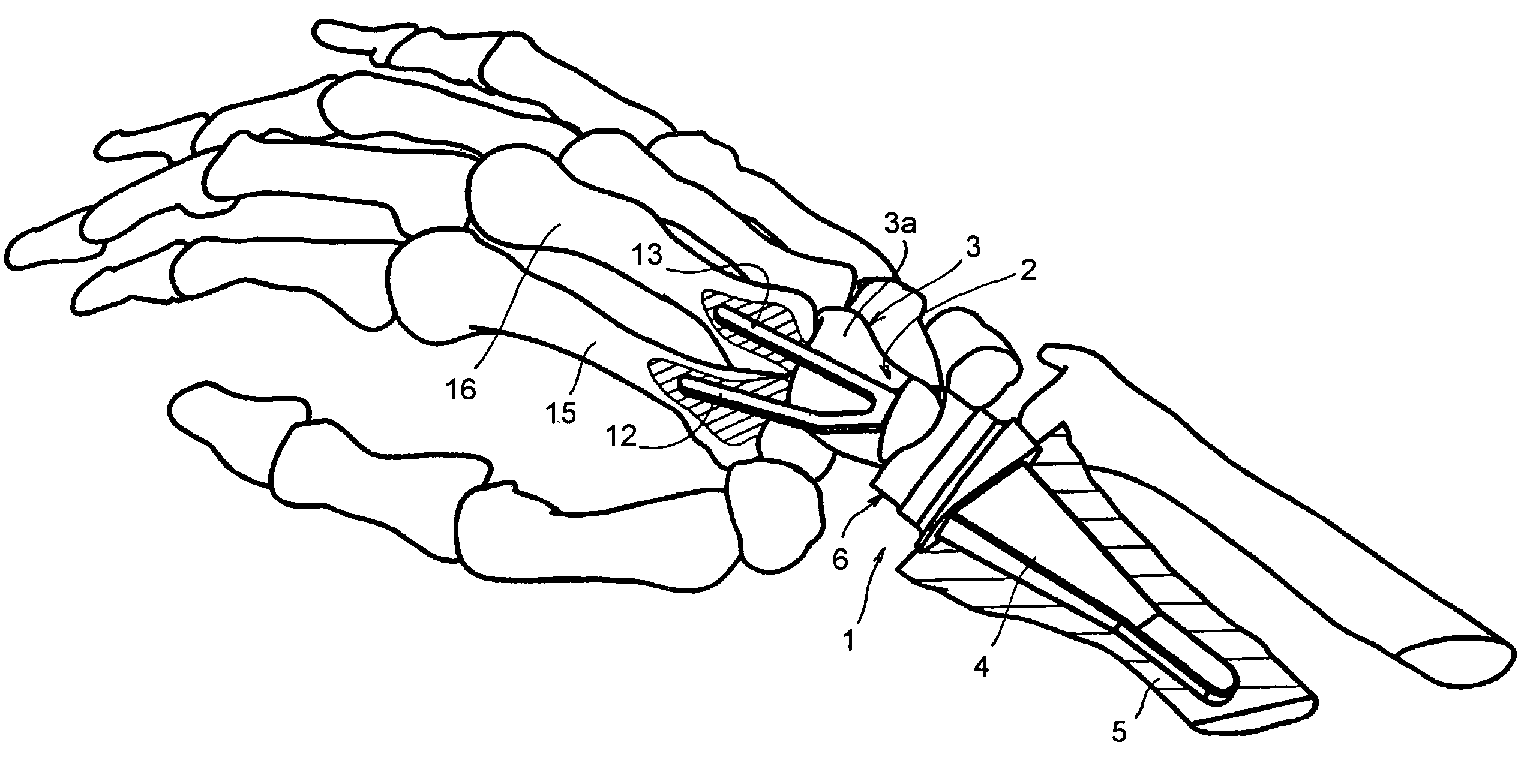
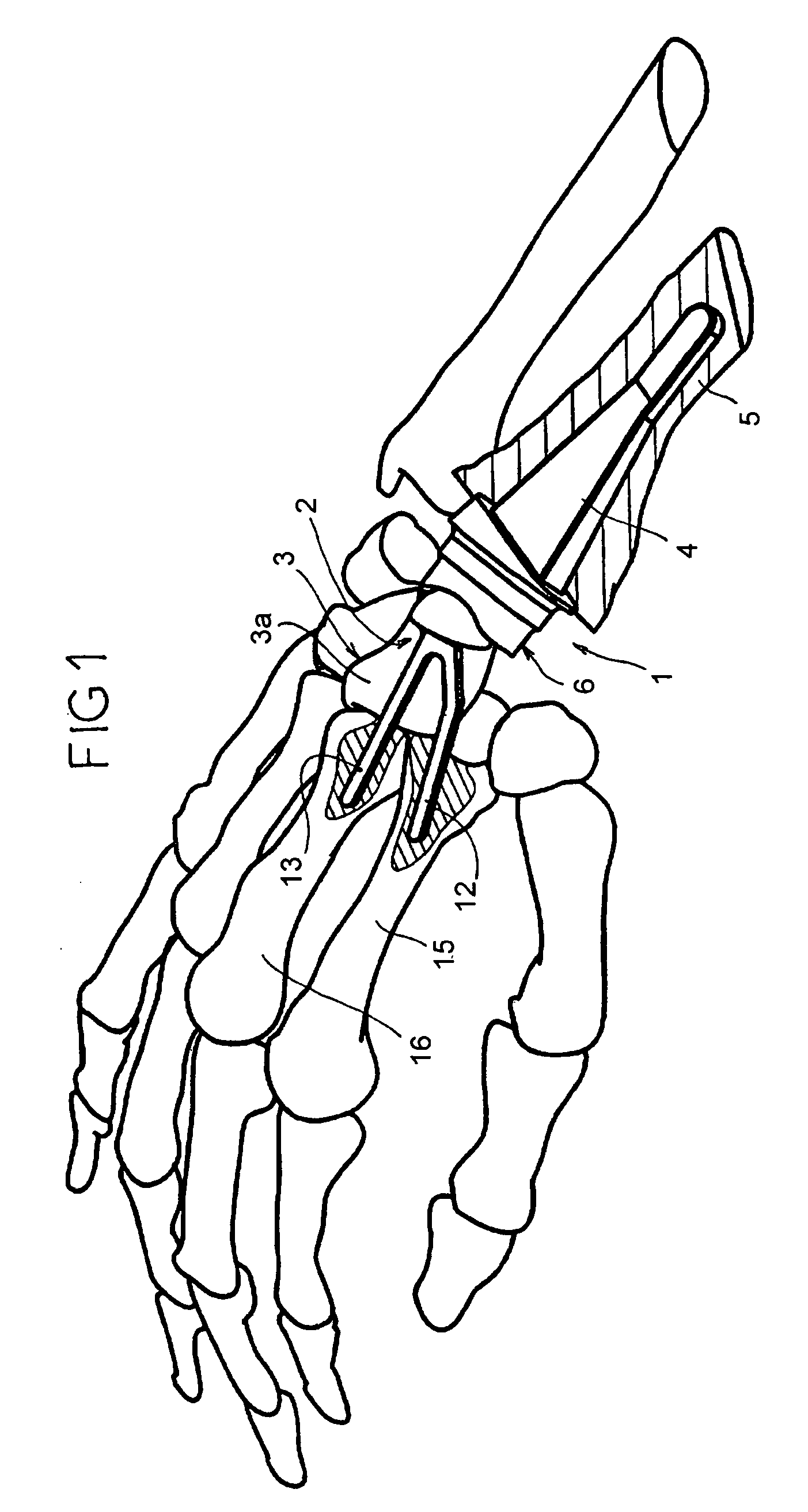
Wrist articulation prosthesis and set of elements allowing building of this prosthesis
InactiveUS20050171613A1Simplify inventory managementRestores anatomical movementWrist jointsAnkle jointsSacroiliac jointEngineering
The prosthesis includes a main element wherein one part forms an articulation side, an element called the “radial” element and an intermediate sliding element. The articulation side that delimits the part of the main element is convex and presents a round form. The intermediate element forms a concave articulation side appropriate for cooperating with the convex articulation side that forms the main element, this concave articulation side presenting, in sectional view in the sagittal plane, that is in the plane in which the flexion and extension movement of the wrist takes place, a rounded circle form very slightly larger than that of the convex articulation side, and presenting, in sectional view in the frontal plane, that is in the plane in which the abduction and adduction of the hand takes place, a rounded circle form markedly larger than that of the convex articulation side.
Owner:SMALL BONE INNOVATIONS INT
File management program
InactiveUS7636898B2Simplified managementEasy to manageTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDrag and dropFile copying
The computer readable medium has embodied thereon a file management program for processing by a computer, the file management program comprising: a first code segment for, when an icon of a first folder displayed on a display apparatus is dragged and dropped onto another icon of a second folder displayed on the display apparatus, creating a third folder at the same level as the second folder; and a second code segment for copying a file stored in the first folder and a file stored in the second folder into the third folder.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Allocating and deallocating portions of memory
ActiveUS20130088501A1Reduce in quantityShorten the timeMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computing
Owner:ARM LTD
Pressure measuring system for vacuum chamber using ultrasonic wave
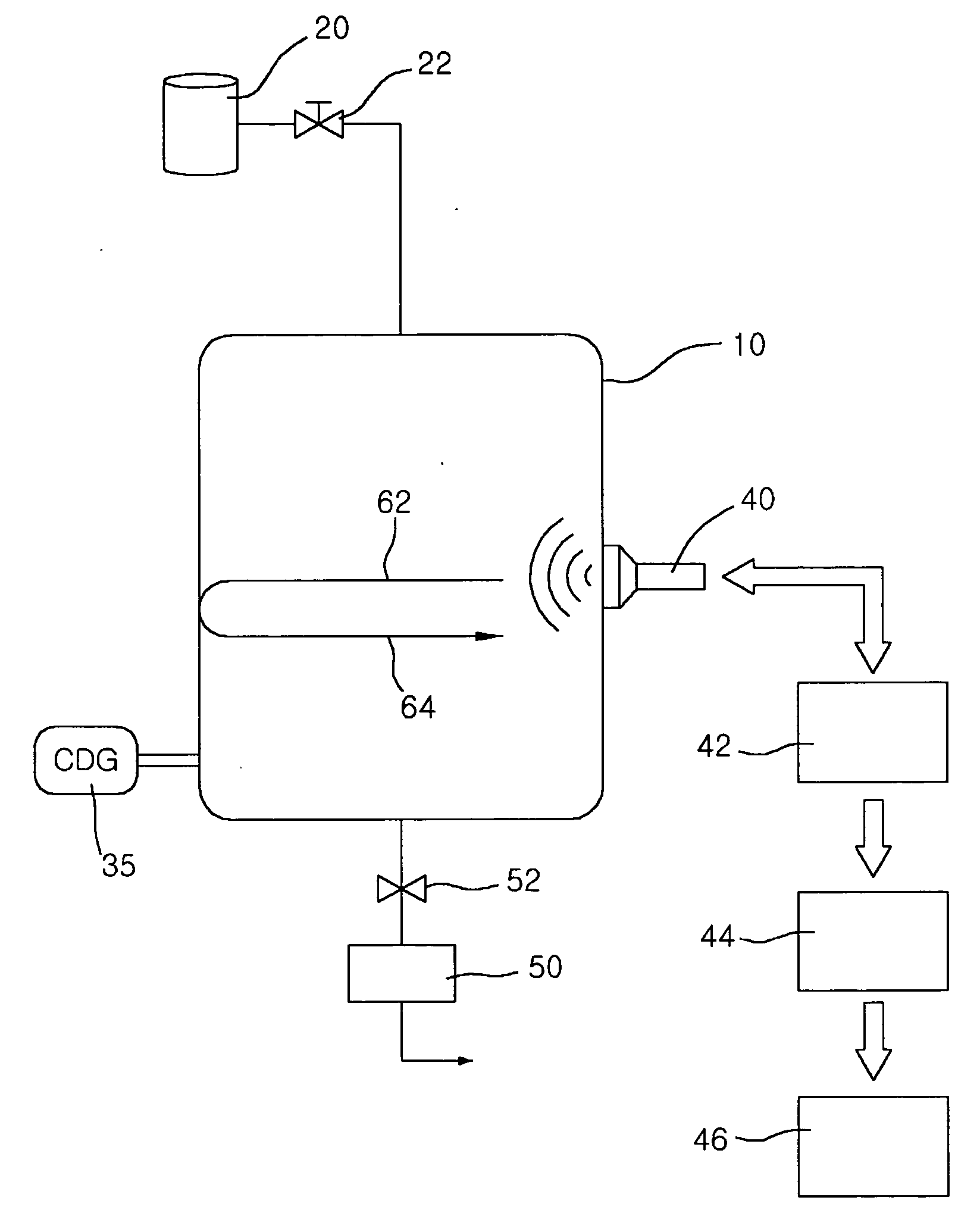
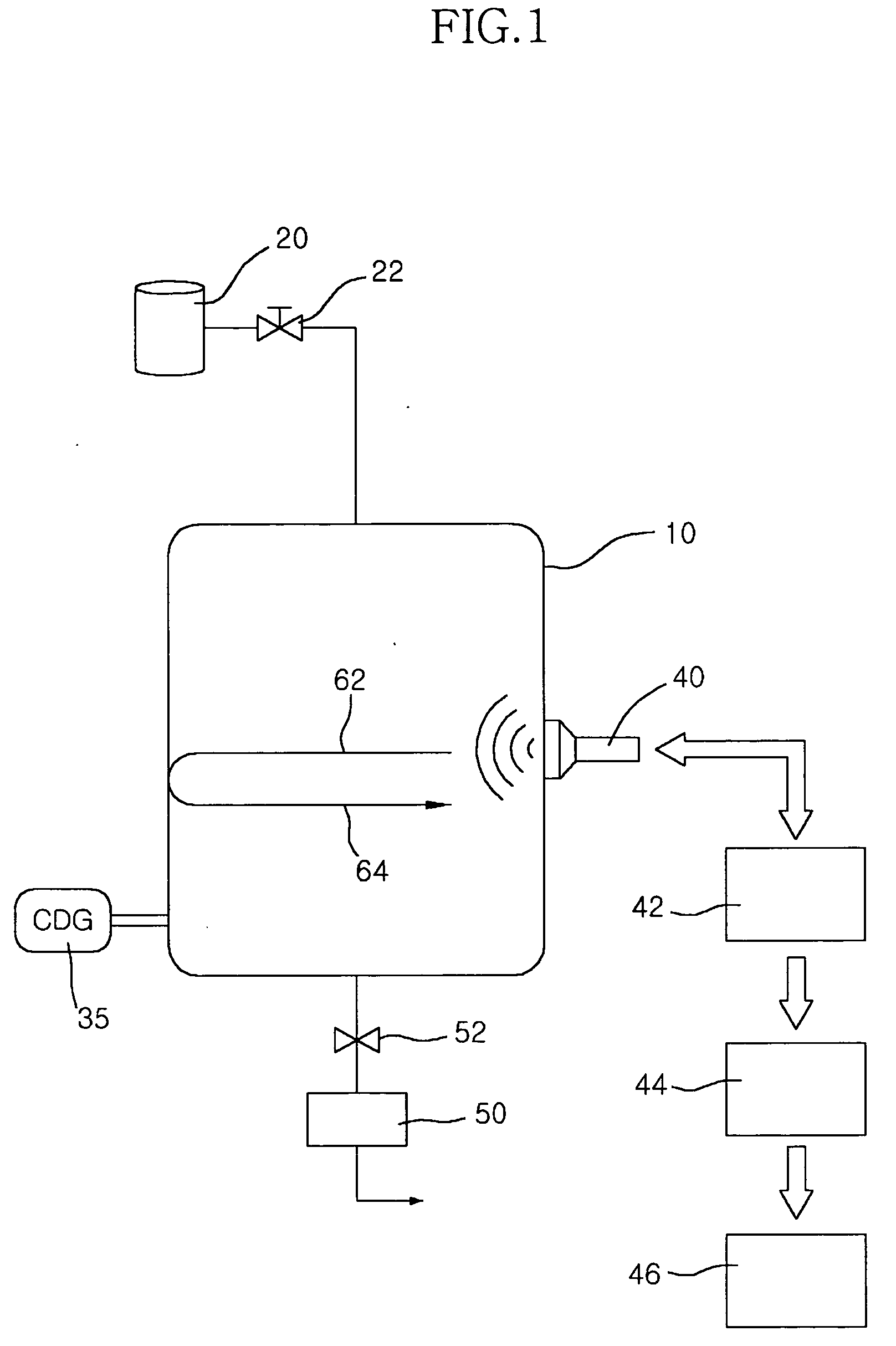
InactiveUS20070068260A1Reduce vacuumEasy to measureVacuum gaugesPressure difference measurement between multiple valvesReflected wavesVacuum chamber
Disclosed is a pressure measuring system for a vacuum chamber, in particular, a pressure measuring system for a vacuum chamber using ultrasonic wave. In this regard, there is provided a pressure measuring system for a vacuum chamber using ultrasonic wave, comprising a vacuum chamber 10 formed with desired vacuum at the inside thereof; ultrasonic wave-emitting means mounted close to an outer peripheral surface of the vacuum chamber 10 for emitting an ultrasonic wave 62 to the inside of the vacuum chamber 10; ultrasonic wave-receiving means for receiving a reflection wave 64 reflected after the striking of the ultrasonic wave 62 emitted from the ultrasonic wave-emitting means to the vacuum chamber; reflection wave-detecting means for detecting the reflection wave 64 from the ultrasonic wave-receiving means; and amplitude-analyzing means for analyzing the amplitude of the reflection wave 64 detected by the reflection wave-detecting means.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Time-based cache control
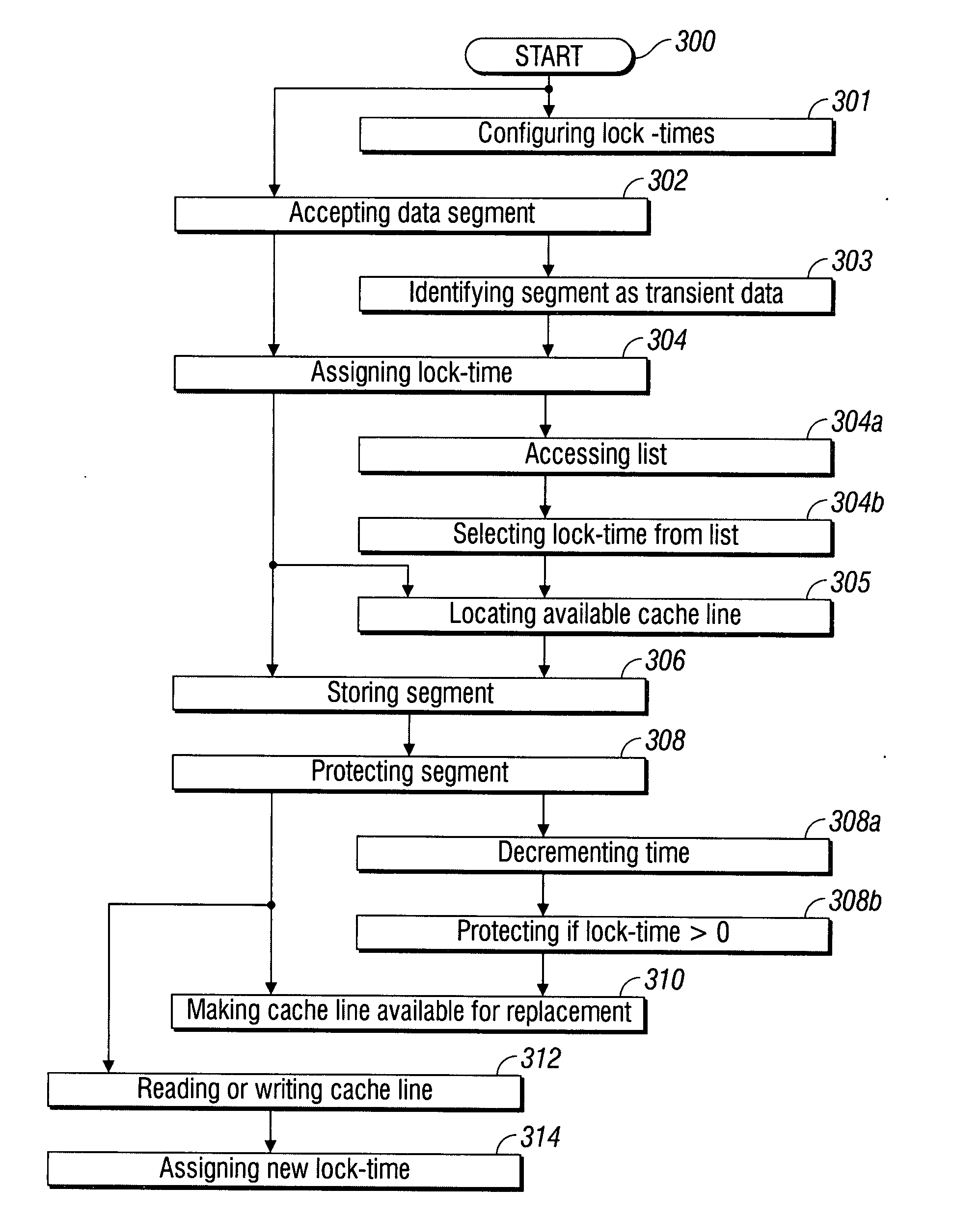
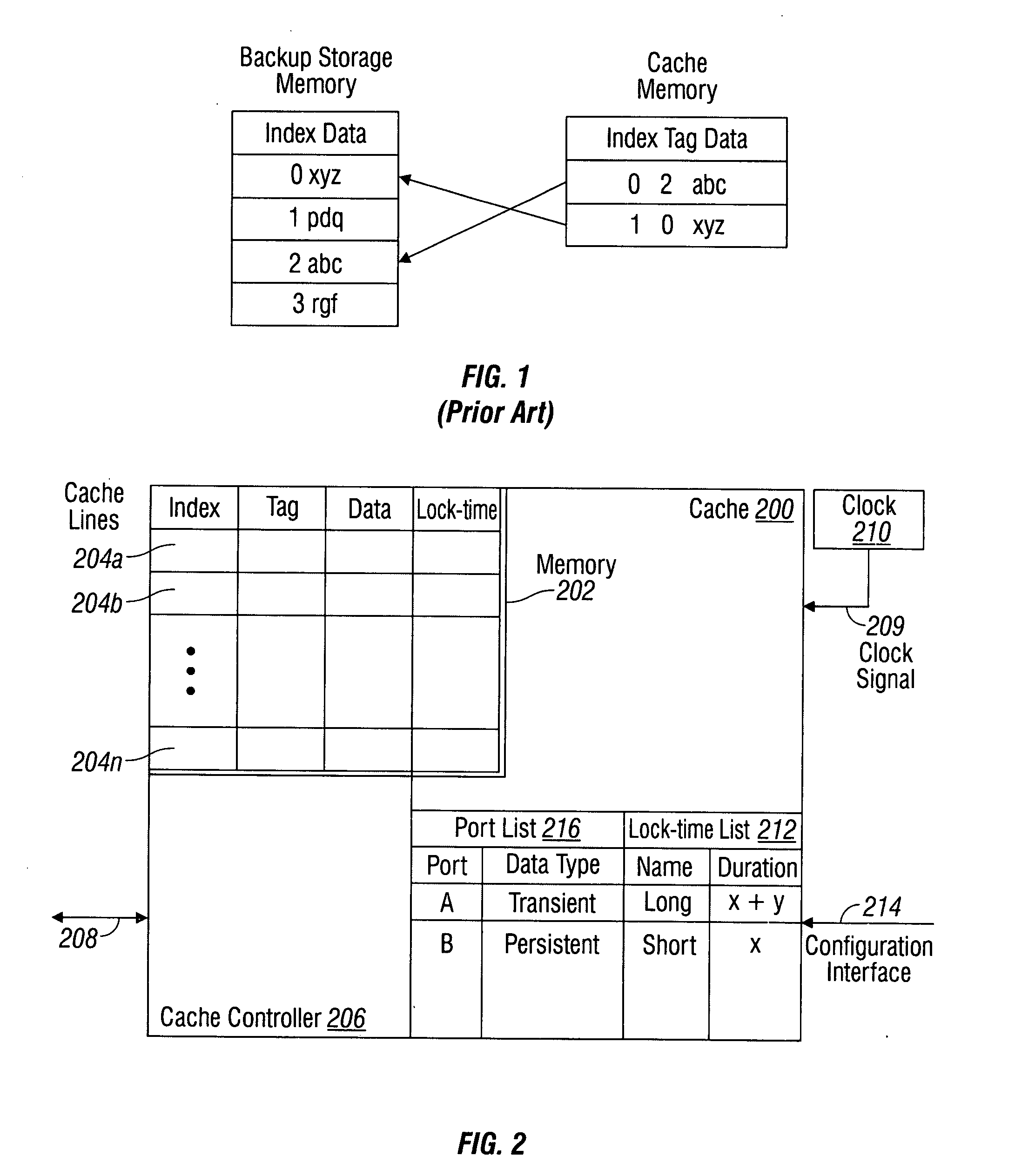
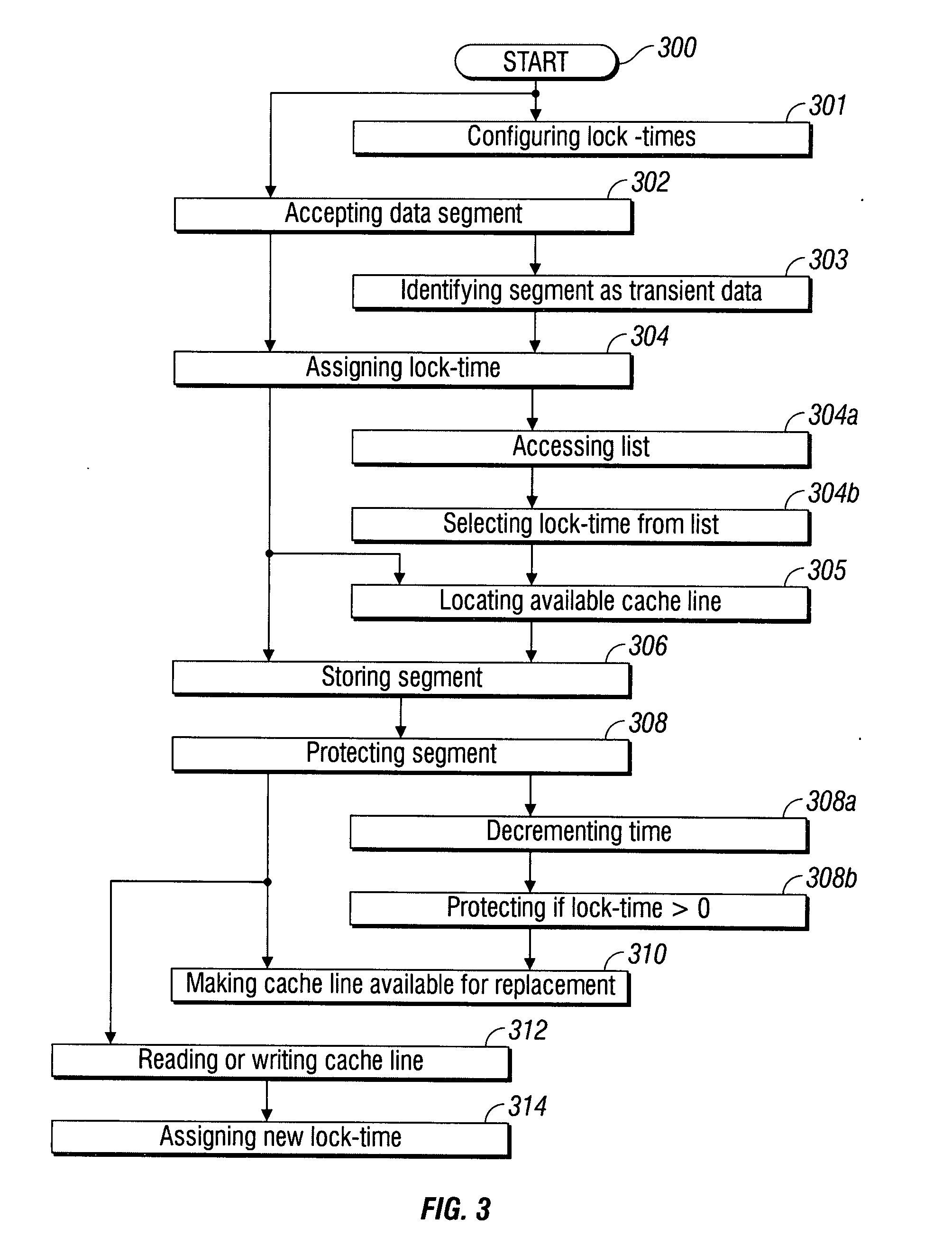
InactiveUS20090037660A1Improve performanceSimplifies cache managementMemory systemsParallel computingLock time
A time-based system and method are provided for controlling the management of cache memory. The method accepts a segment of data, and assigns a cache lock-time with a time duration to the segment. If a cache line is available, the segment is stored (in cache). The method protects the segment stored in the cache line from replacement until the expiration of the lock-time. Upon the expiration of the lock-time, the cache line is automatically made available for replacement. An available cache line is located by determining that the cache line is empty, or by determining that the cache line is available for a replacement segment. In one aspect, the cache lock-time is assigned to the segment by accessing a list with a plurality of lock-times having a corresponding plurality of time duration, and selecting from the list. In another aspect, the lock-time durations are configurable by the user.
Owner:APPLIED MICRO CIRCUITS CORPORATION
Rotationally symmetrical LED-based anti-collision light for aircraft
ActiveUS7645053B2Reduce in quantityReduce consumptionPoint-like light sourceLighting support devicesEngineeringLight-emitting diode
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Irradiation device and use thereof
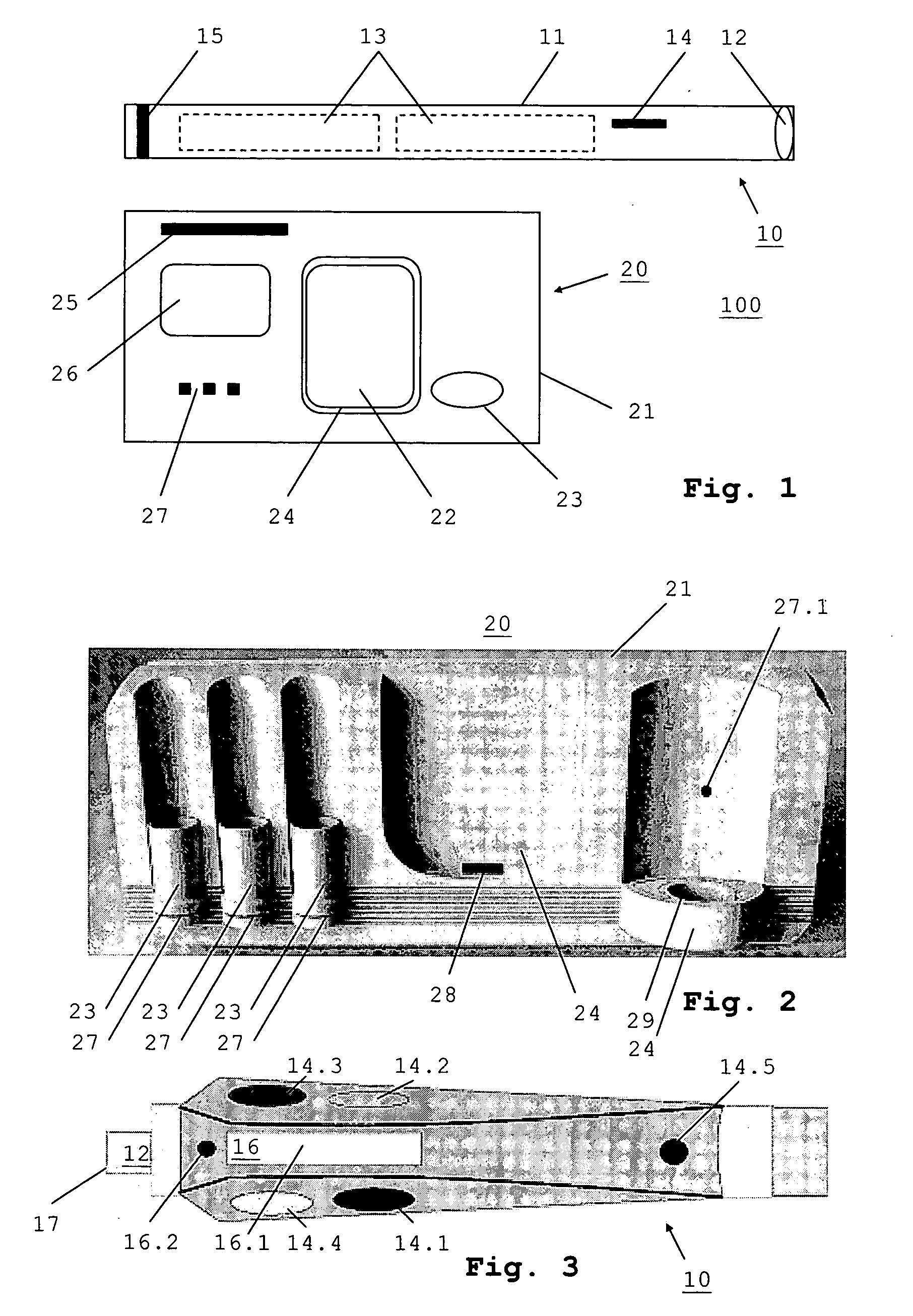
InactiveUS20050203592A1Easy to operateImprove securitySurgical instrument detailsLight therapyControl signalEngineering
An irradiation device (100) includes at least one laser light source (10) with a housing (11) wherein a laser device (12) is arranged, and a base unit (20) which includes a device body (21) and a control device (22), wherein the operating state of the laser device (12) can be set depending on control signals of the control device (22), and wherein the control device (22) is arranged so as to be separable from the device body (21).
Owner:TEICHERT KLAUS
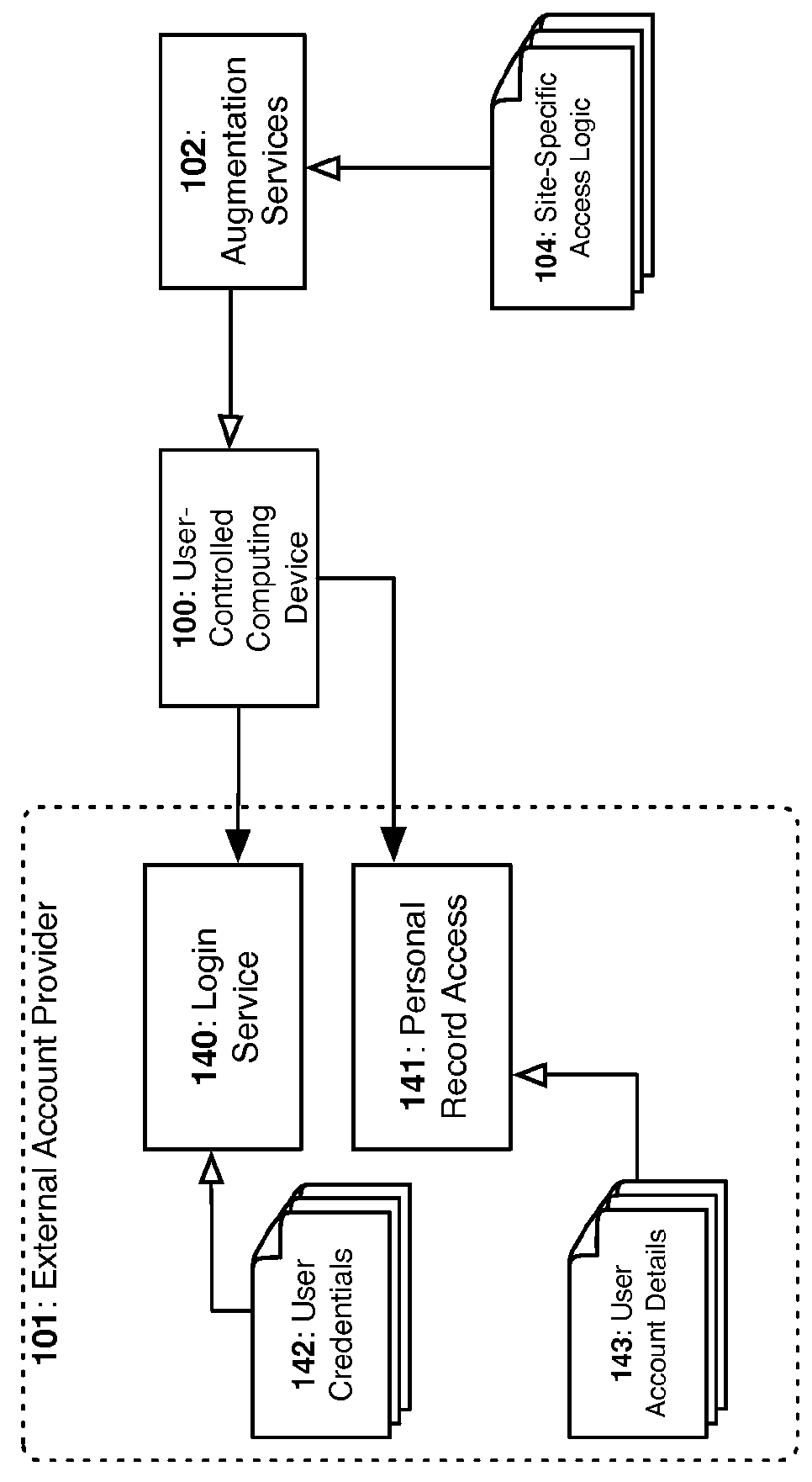
Decentralized Systems and Methods to Securely Aggregate Unstructured Personal Data on User Controlled Devices
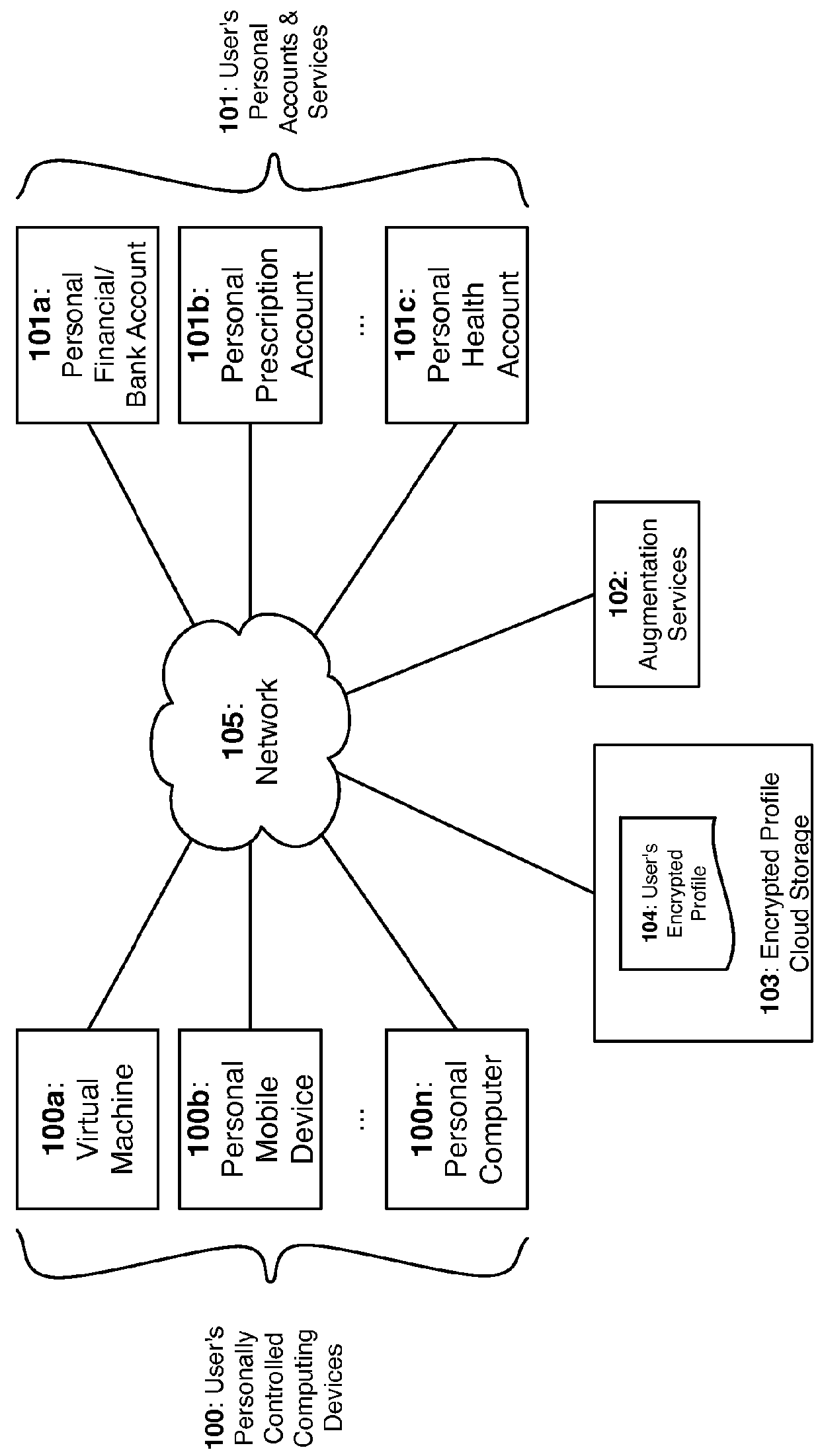
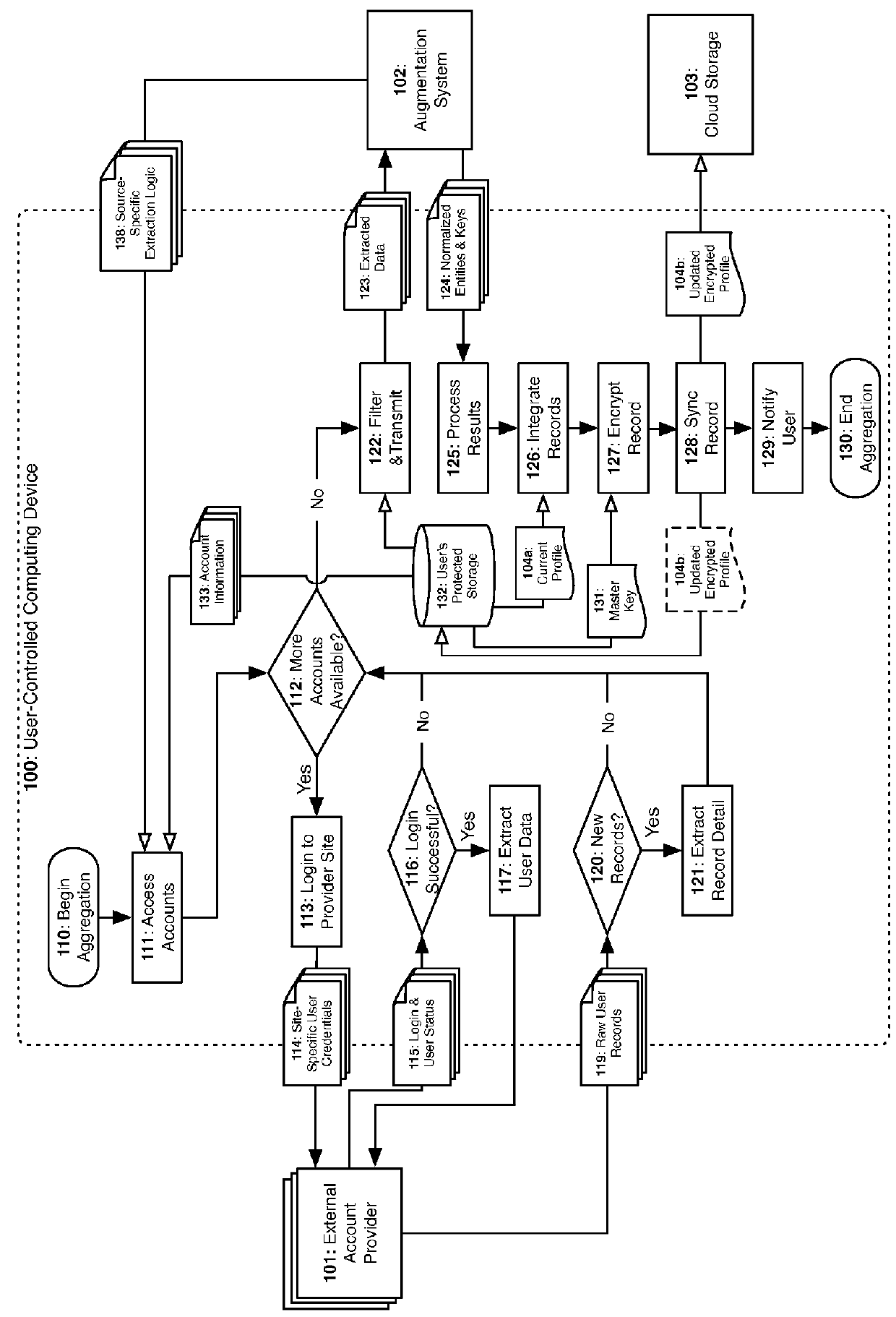
InactiveUS20160034713A1Simplify key managementImprove securityDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationInternet privacyPrivacy preserving
A privacy-preserving decentralized computer-implemented system and method for securely aggregating an individual's personal data by extracting, redacting, normalizing, and linking data from a plurality of the individual's personal accounts and services.
Owner:APOTHESOURCE
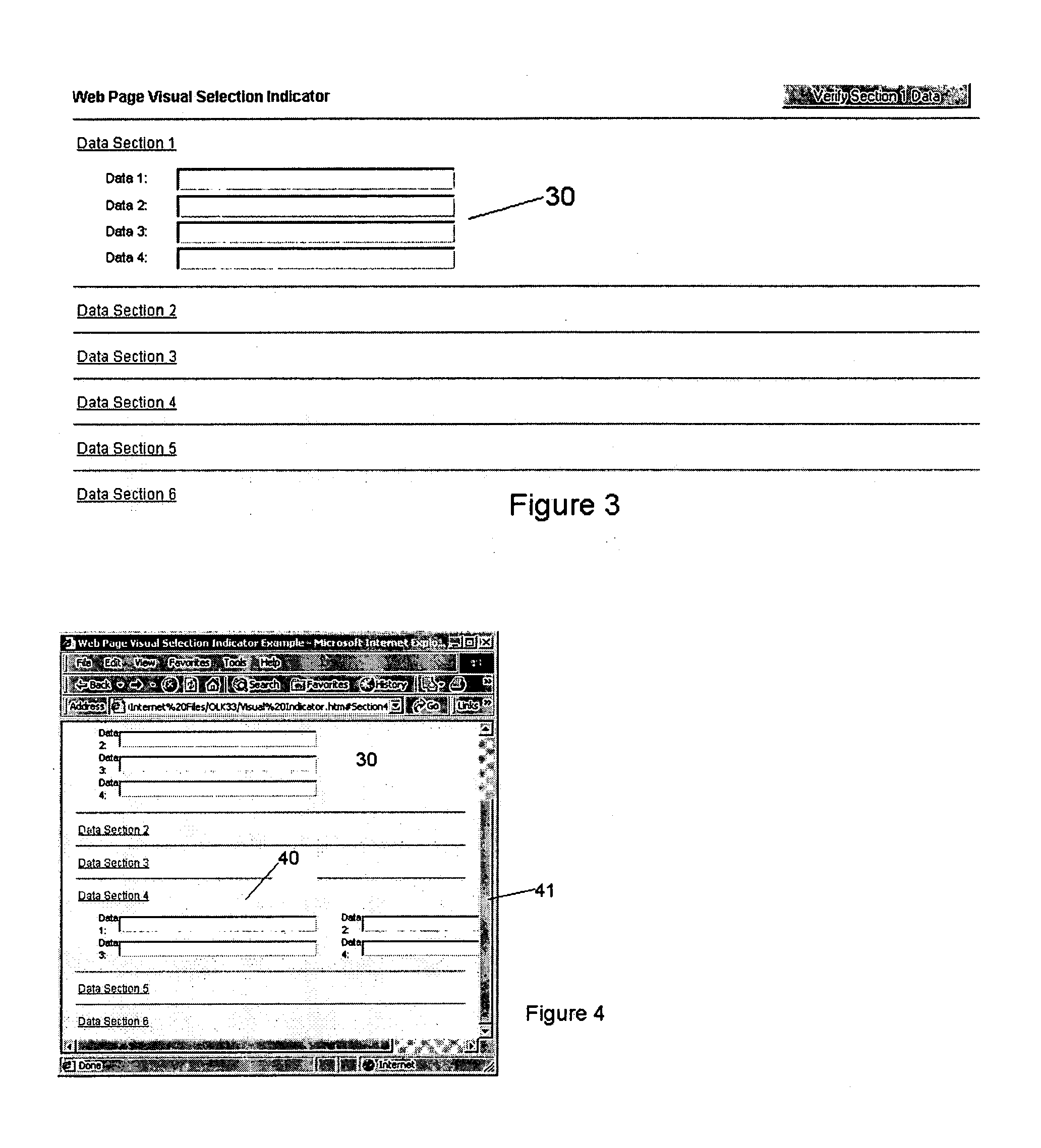
User interface
InactiveUS20050114790A1Simple to referenceSimplified managementDigital computer detailsInput/output processes for data processingGraphical user interfaceUser input
A graphical user interface displays a plurality of sections of information. Each section has a heading which comprises a link. The links can be selected by a user to collapse or expand information in the section. In addition, automatic scrolling takes place to scroll expanded information substantially into view. When a section is collapsed or expanded the associated heading is marked for a pre-specified time to aid the user in returning his or her attention to the appropriate region of the display, despite the use of the automatic scrolling. In addition, marks are used to indicate regions of the display where user entered information needs to be added or corrected.
Owner:APPLE INC
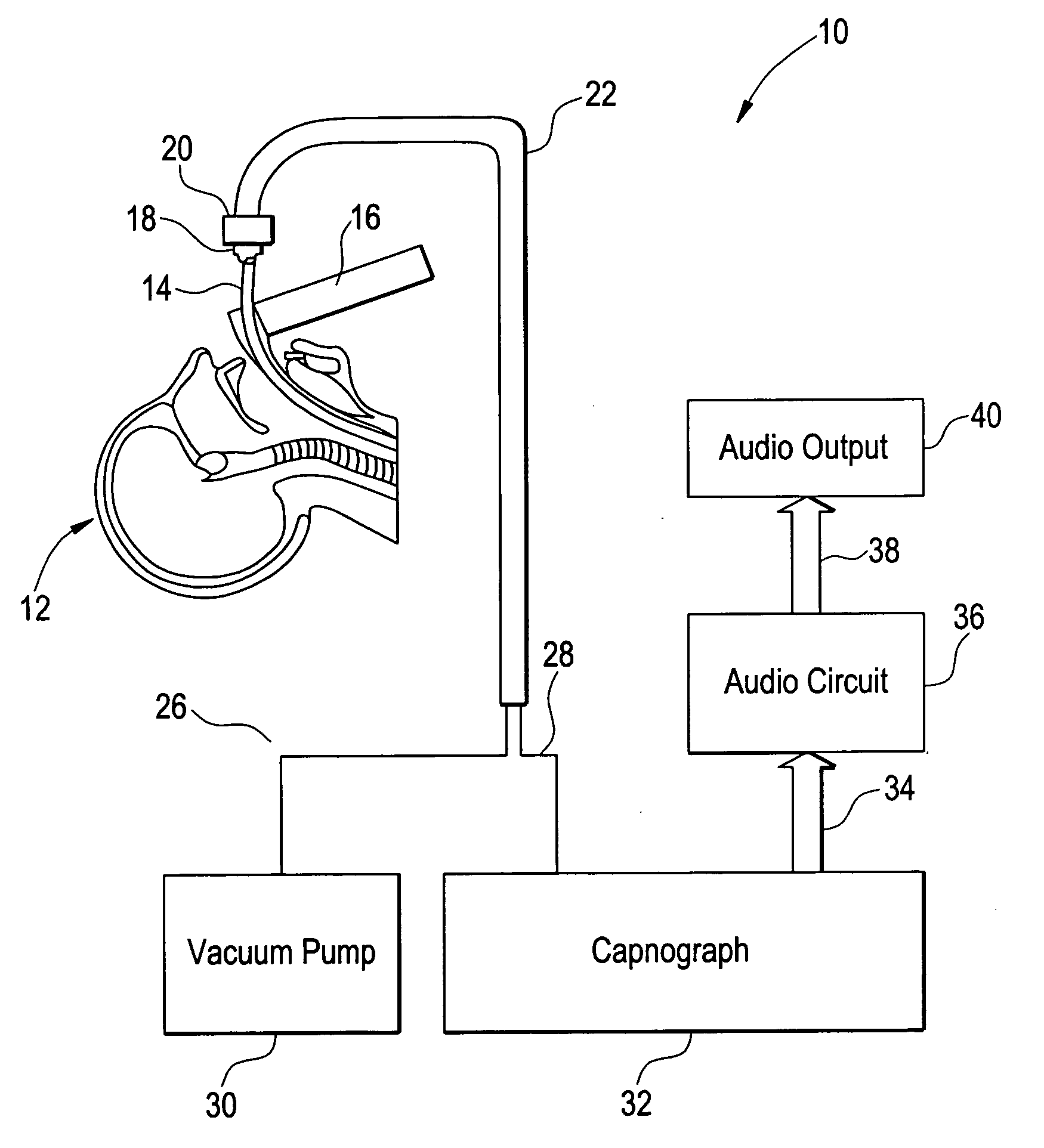
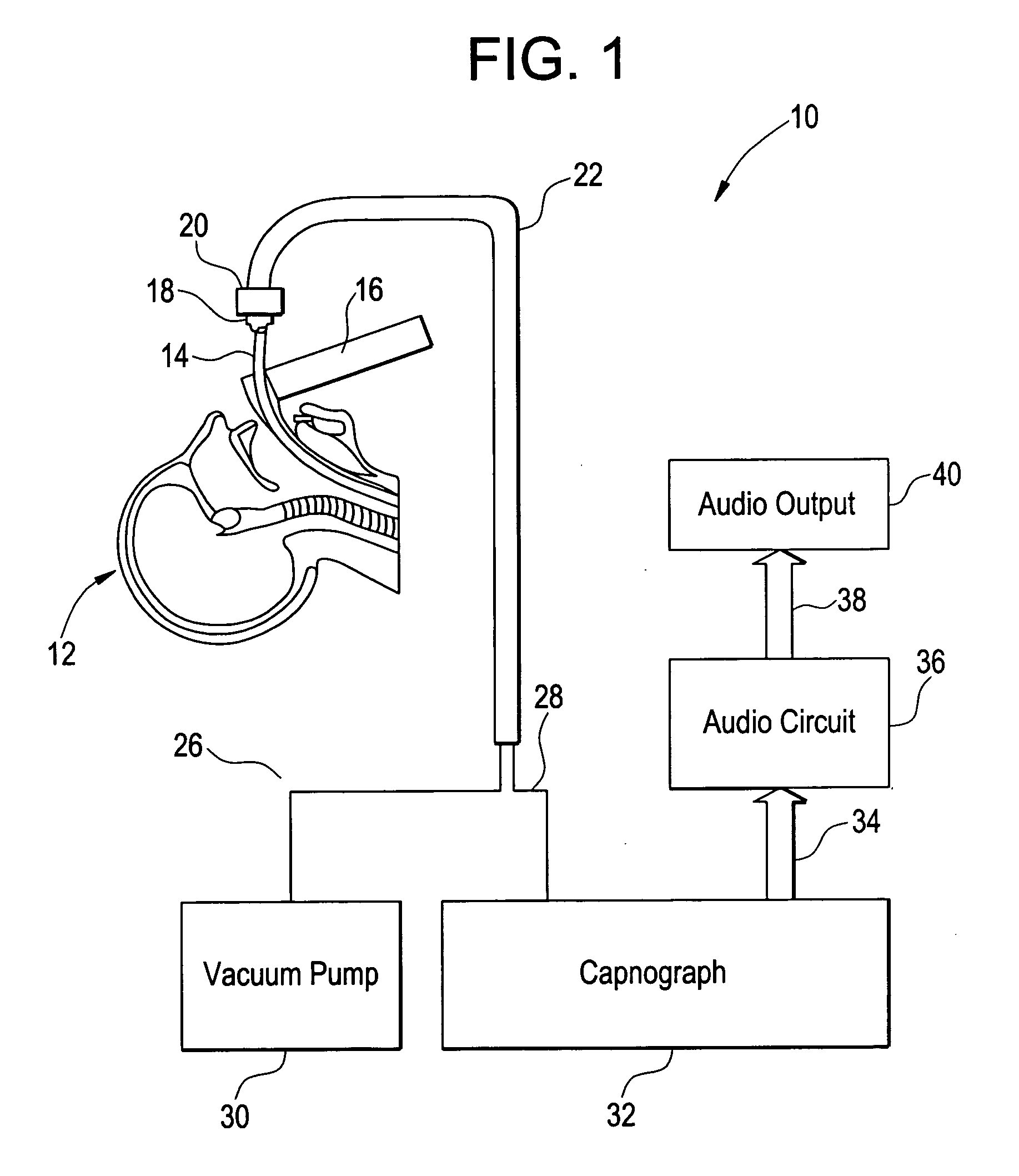
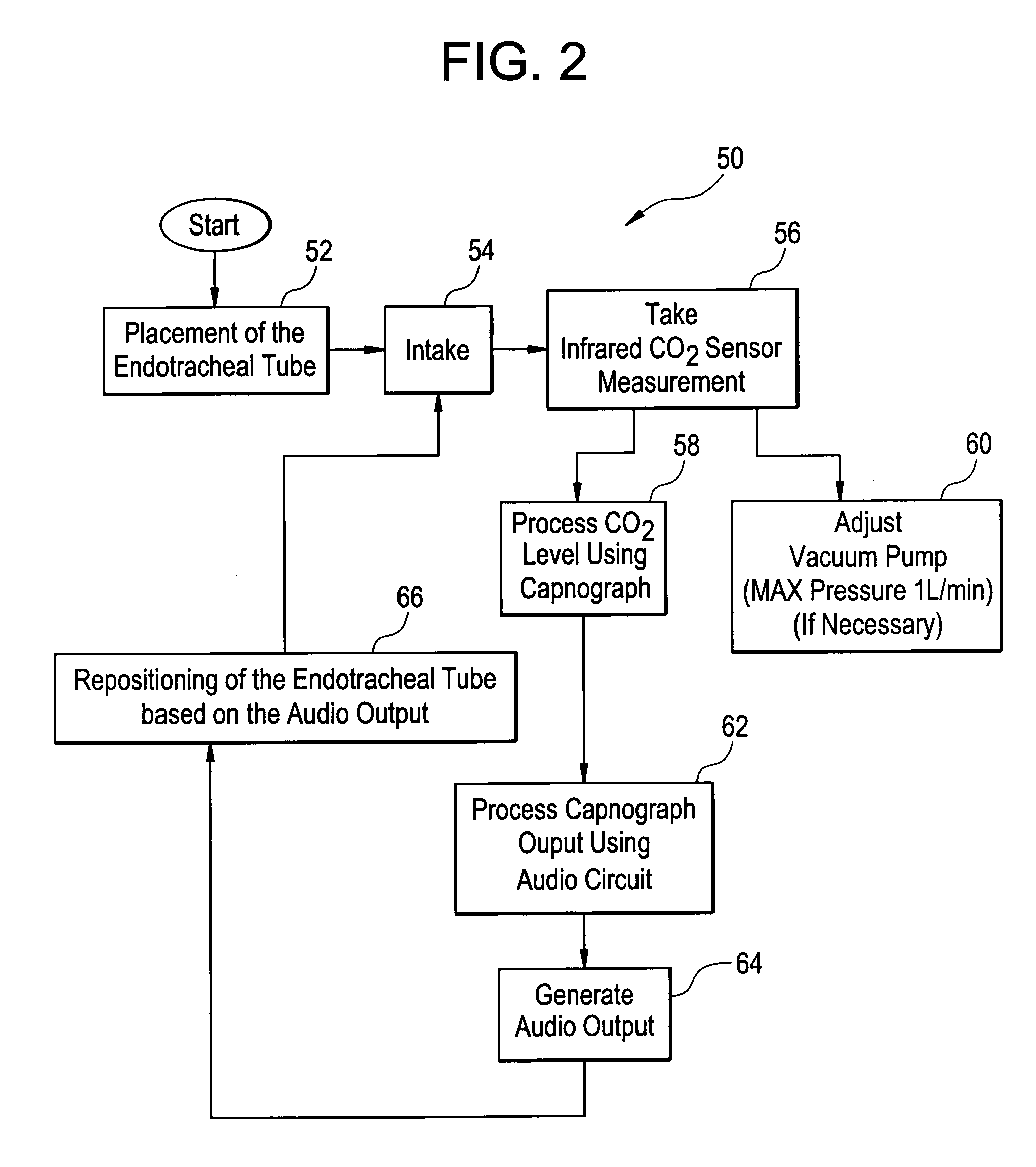
Method and apparatus for capnography-guided intubation
InactiveUS20080251070A1Easy to transportSimplified managementTracheal tubesRespiratory device testingVibratory signalOmni directional
A method and apparatus for qualitative sensory signal, capnography-guided intubation is provided. A qualitative sensory signal, such as an audible signal, is generated during intubation of a patient to provide an audible indication of carbon dioxide levels, so as to facilitate proper placement of an intubation tube. The frequency of the audible signal corresponds to measured carbon dioxide levels, thereby providing a simple, easy-to-interpret, audible indication of the current position of an endotracheal tube during intubation, as well as confirmation of proper placement of the tube. Alternatively, the qualitative sensor signal may be an omni-directional visual signal or a palpable vibratory signal.
Owner:UNIV OF MEDICINE & DENTISTRY OF NEW JERSEY +1
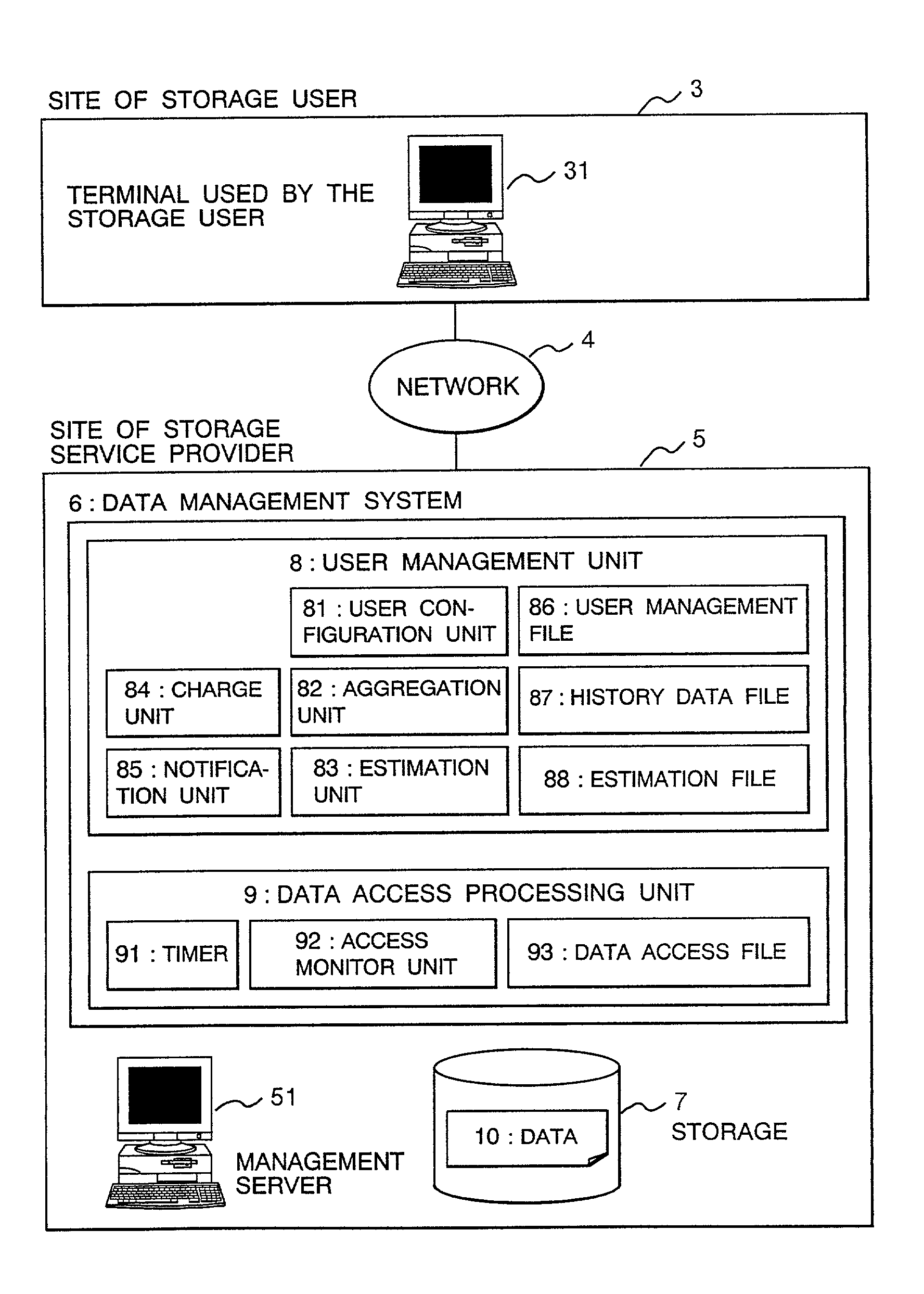
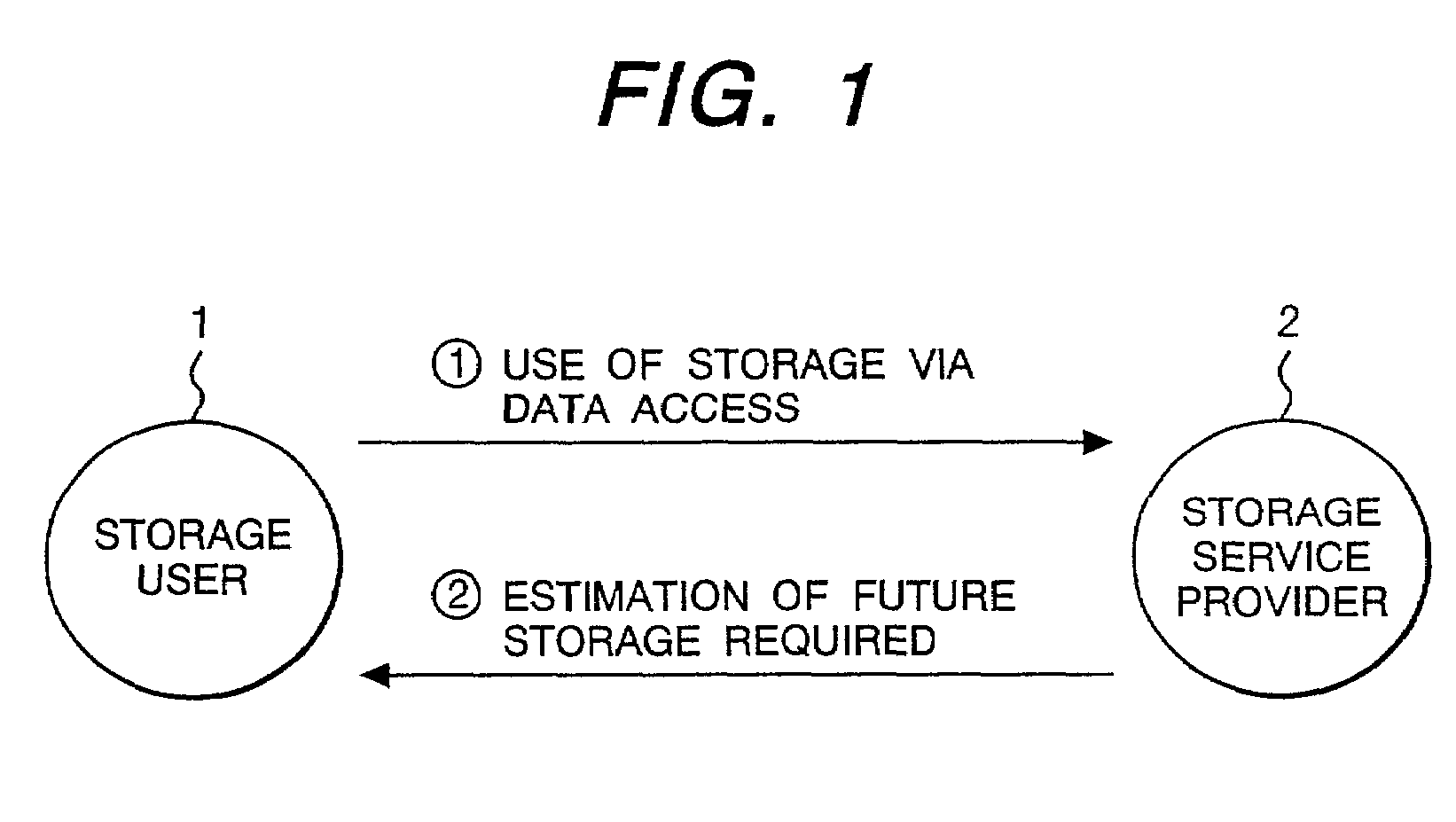
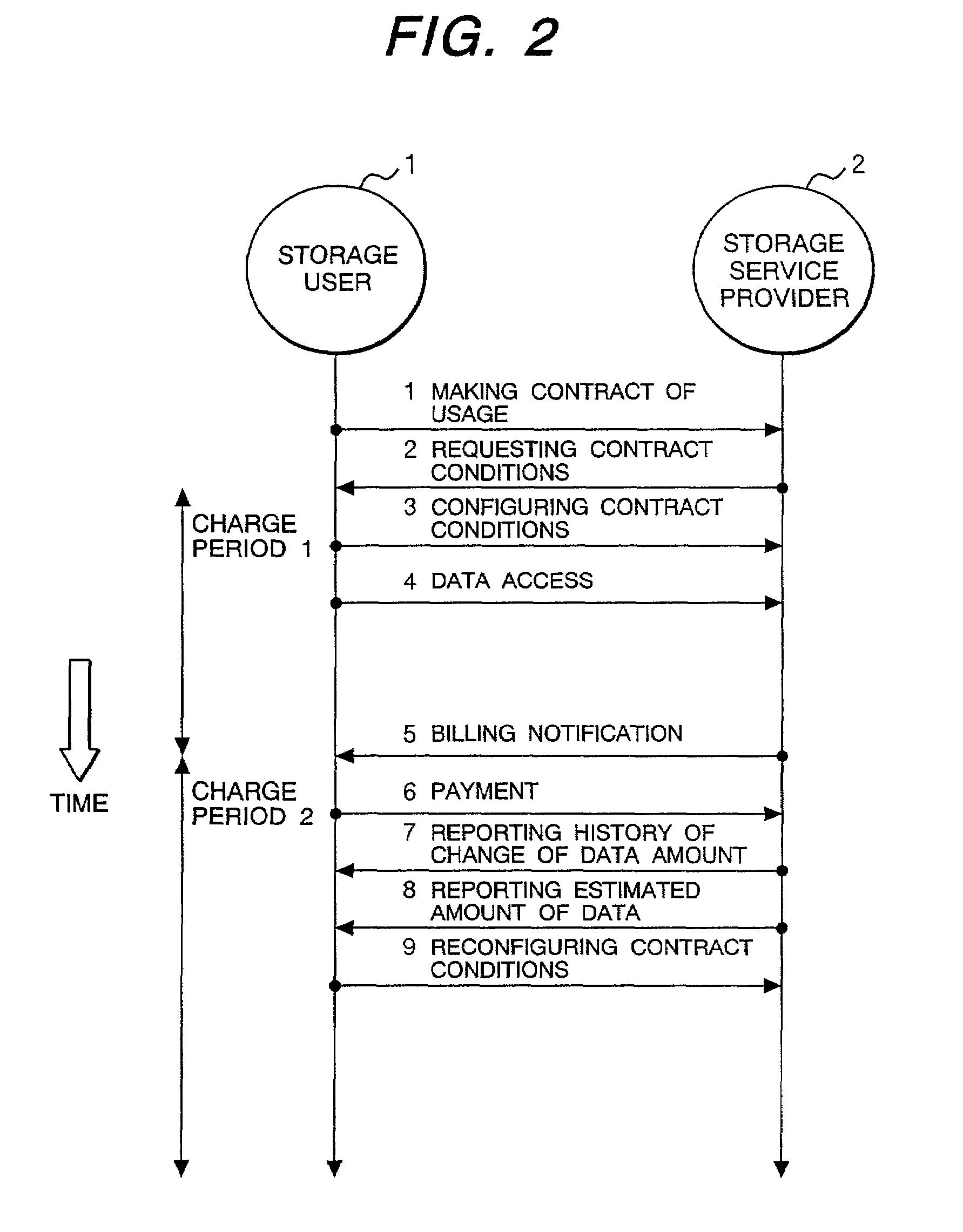
Service method of a rental storage and a rental storage system
InactiveUS6988087B2Reduce management costsReduce capacityPayment architectureBilling/invoicingService provisionNetwork connection
The present invention provides a service method of rental storage, which, when a rental storage service provider provides a rental storage for rental storage service users, allows ideal use of storages in correspondence with the billing charge to the users by proposing the most optimum contract options to the users, and which allows suppressing the management cost of the users.The service method of rental storage through network connection, the storage provider will estimate the future usage of storage based on the history of usage of storage by the rental storage service user to report the estimation to the user. The rental storage service user will update the contract by expanding or reducing the amount of data usage so as to receive the most optimum contract conditions of rental storage service.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
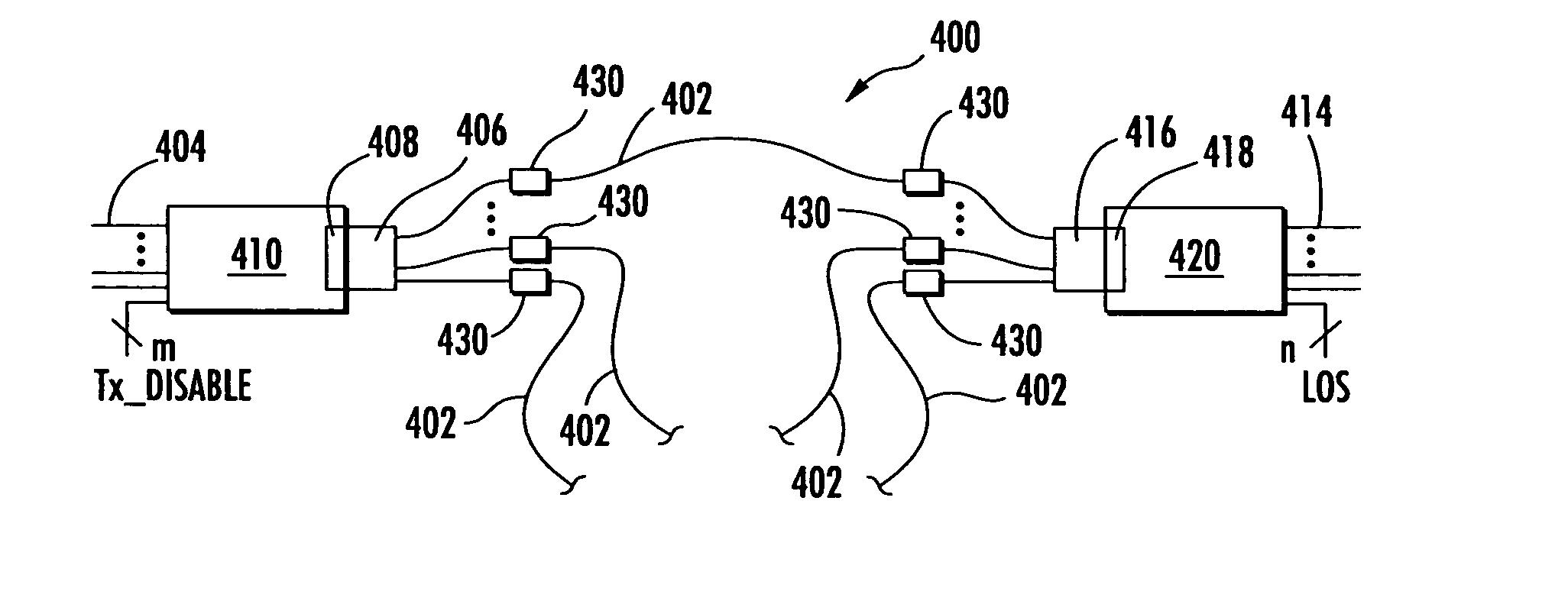
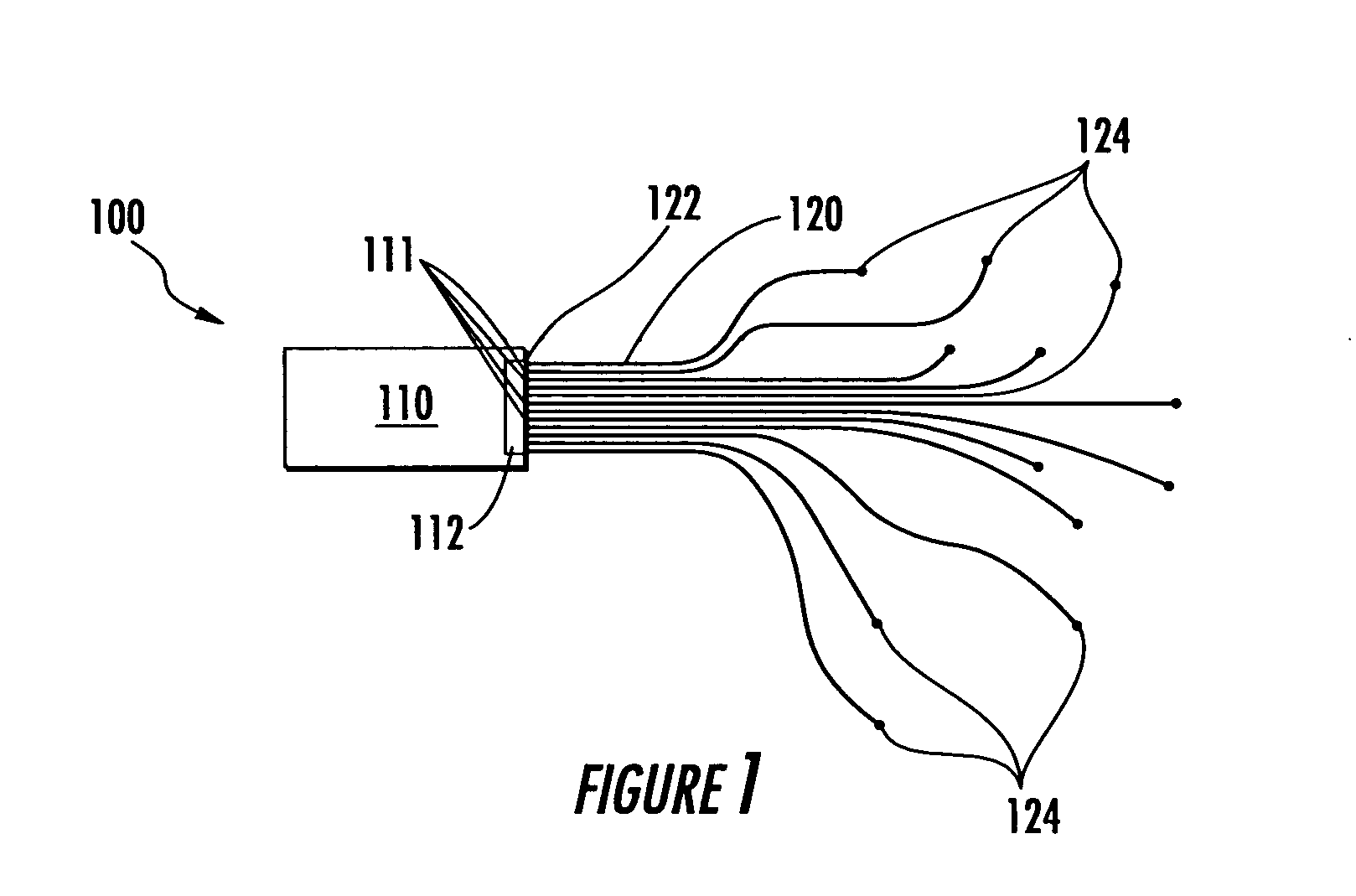
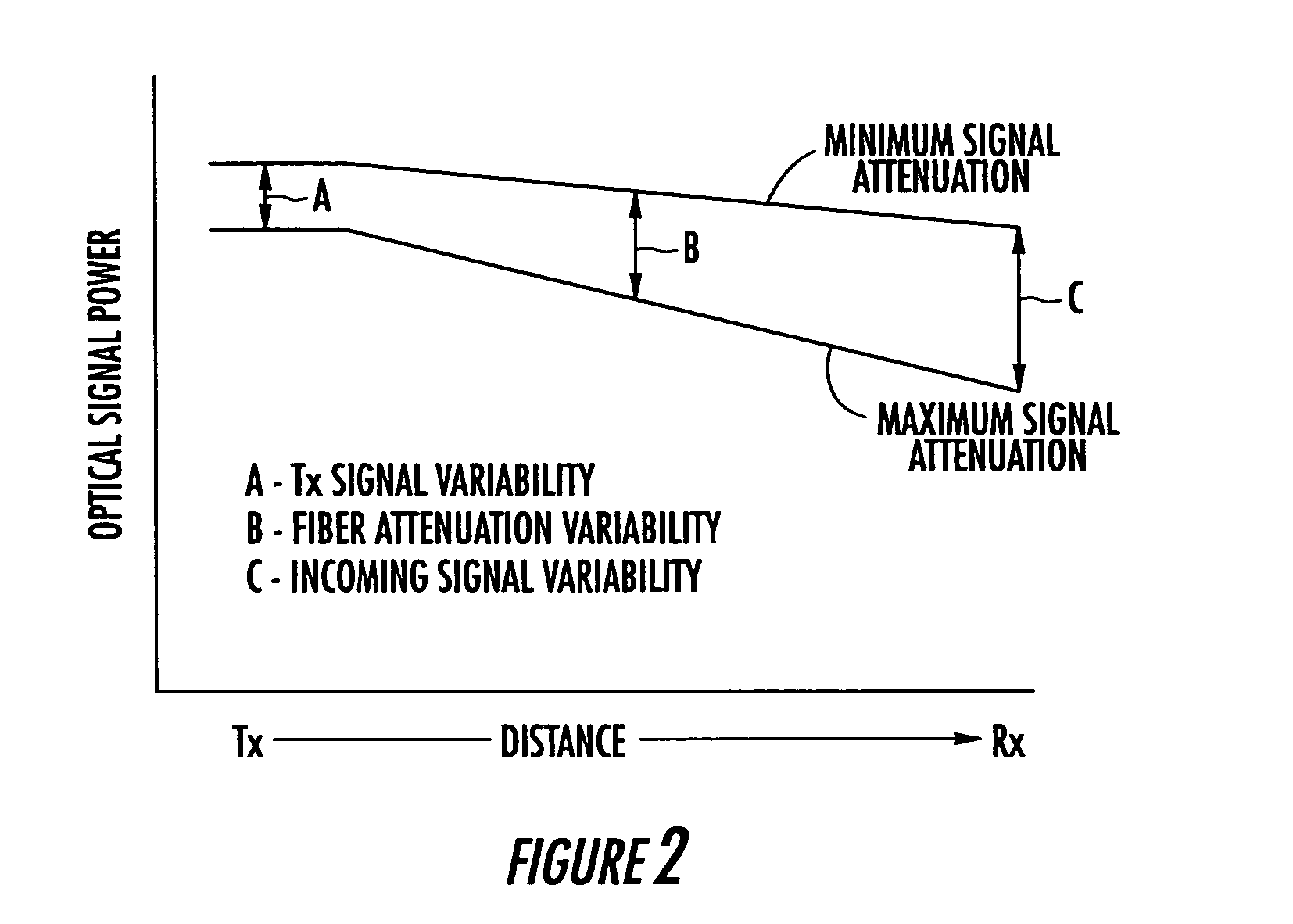
Apparatus and methods for using fiber optic arrays in optical communication systems
InactiveUS7020359B2Increased battery back up timeHigh densityCoupling light guidesFibre mechanical structuresCommunications systemFiber array
Systems and methods for optical communication that may be employed to couple together fiber optic arrays of two or more optical communication modules using parallel fiber optic connectors and physically distinct and signal-independent optical communication paths. The disclosed systems and methods may be employed to provide separate signal-independent communication paths having signal transport characteristics that meet standards required for single fiber single point-to-single point applications.
Owner:OPTICAL COMM PRODS
Method and apparatus for converting thermal energy to mechanical energy
InactiveUS7284372B2Improve efficiencyEfficient regenerationEricsson type enginesSteam engine plantsThermal energyExternal energy
A method and apparatus for converting thermal energy to mechanical energy which can use a wide range of fuels and perform with a high efficiency. Operating on a little utilized thermodynamic cycle of isentropic compression, isothermal expansion, isentropic expansion and finally constant pressure cooling and contraction. The external heat engine utilizes a heat exchanger carrying heat from the external energy source to the working parts of the engine. Pistons and cylinders are activated by appropriate means to adiabatically compress the working fluid, for example ambient air, to transfer the entire mass of the air through the heat exchanger to accomplish isothermal expansion followed by adiabatic expansion and, finally, exhaust the air to ambient to allow for constant pressure cooling and contraction. Valve pistons in conjunction with the cylinders form valves that allow for the exchange of working fluid with ambient. Energy is added to the engine during isothermal expansion, whereby the energy of compression is added by a flywheel or other appropriate energy storage means, said flywheel stores energy recovered during adiabatic expansion. The thermodynamic cycle described and the engine embodiments disclosed, when run in reverse, perform as a heat pump or refrigeration device.
Owner:CROW DARBY
Grouped Access Control List Actions
InactiveUS20080109897A1Simplification of management and definitionSimple definitionDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionSafe systemSecurity policy
Access Control Lists (ACLs) are used to describe the permitted actions (permissions) on protected network computer system resources or objects associated with an client or user identity. An identity may be an individual user or group of users. The actions are used to represent the different access methods available on a particular projected object or resource. A new action grouping mechanism is provided which tags each action with an action group name. The grouping of actions facilitates a larger permission set to be defined in an ACL, whereas action permission indicators can be reused for unique action definitions within various action groups. This effectively extends the finite total number of permissions available within a security system, allows a more descriptive and extensible permission mechanism in an Access Control List, as well as aiding in the simplification of management and definition of security policies.
Owner:IBM CORP
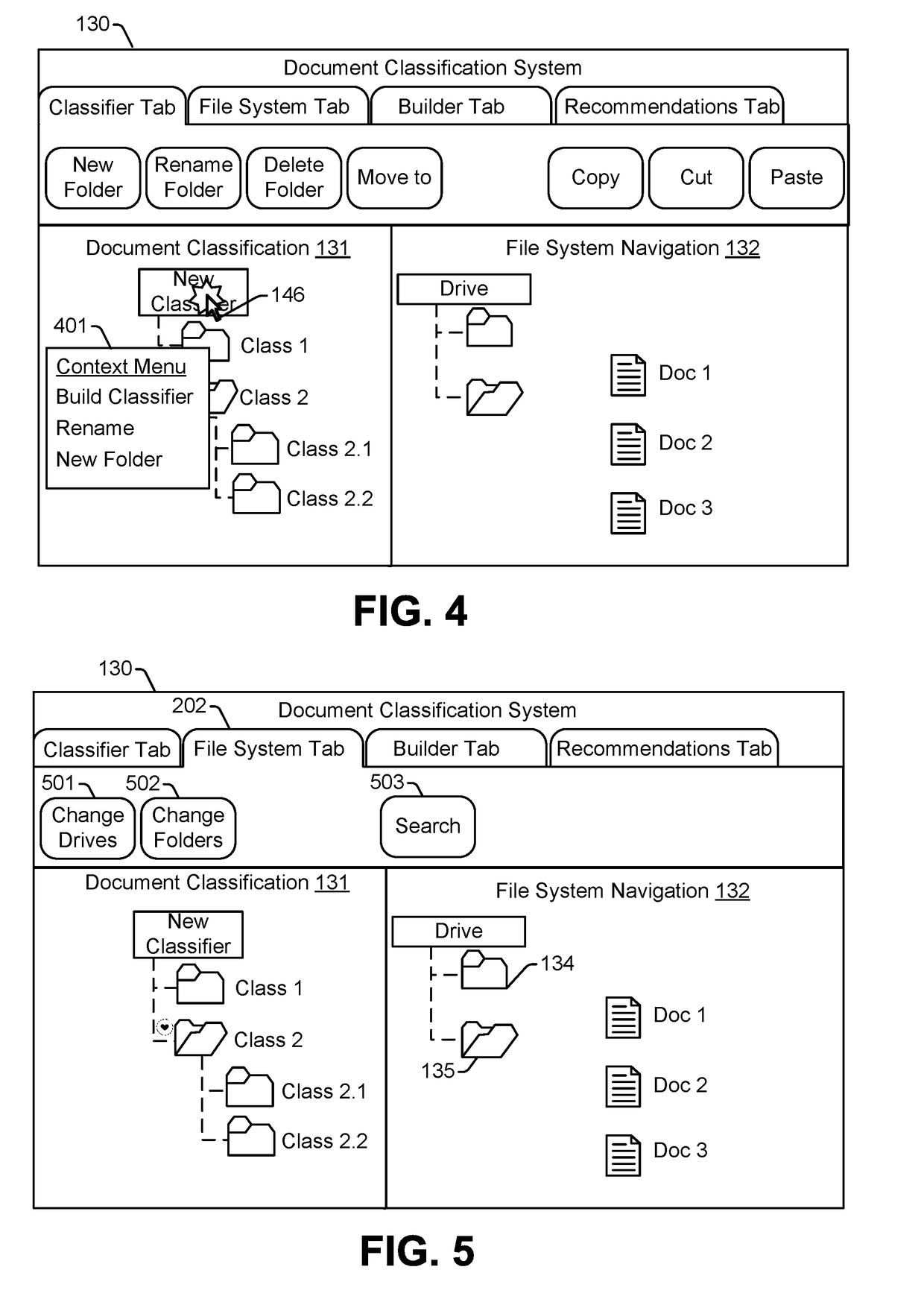
Generation of document classifiers
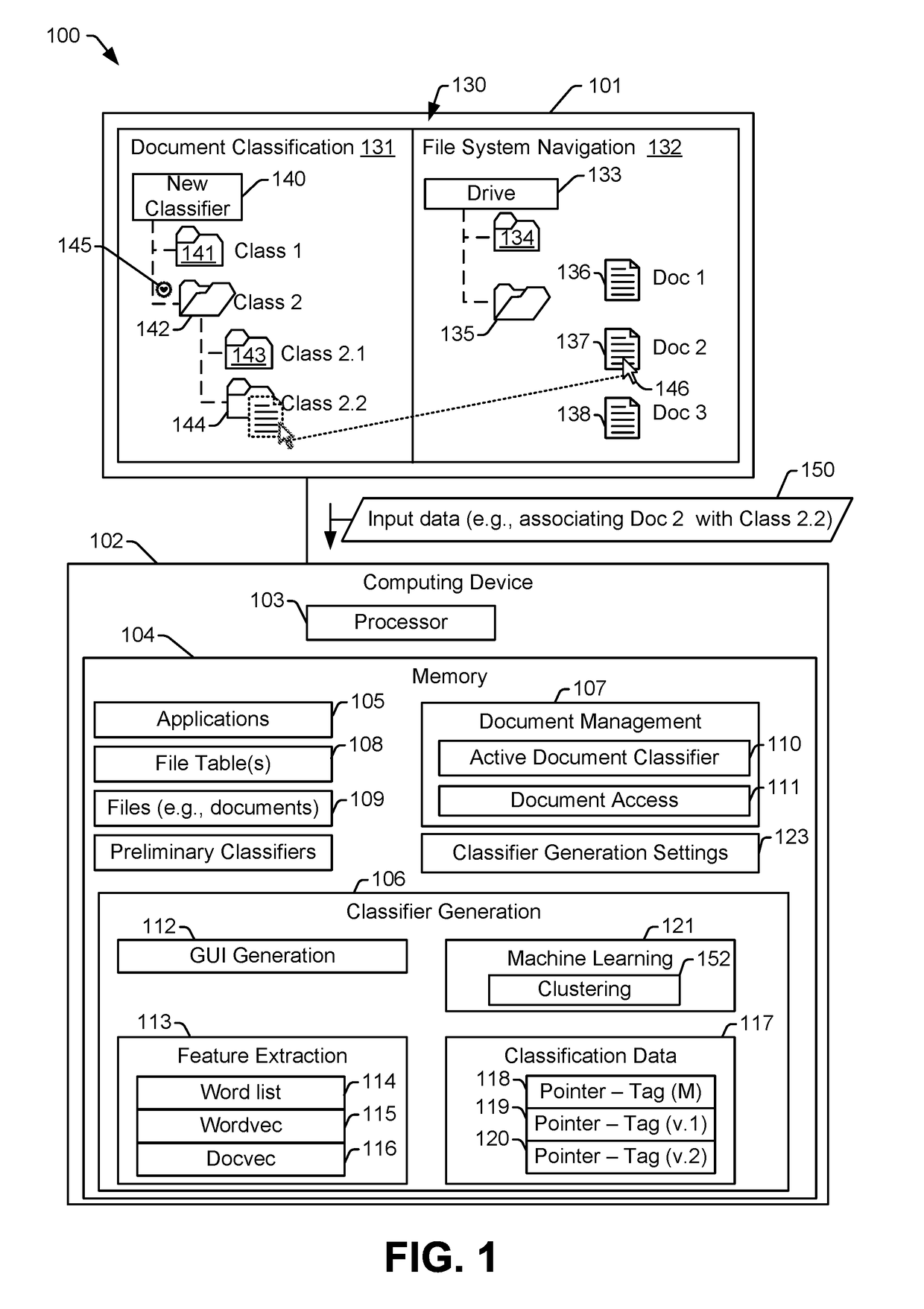
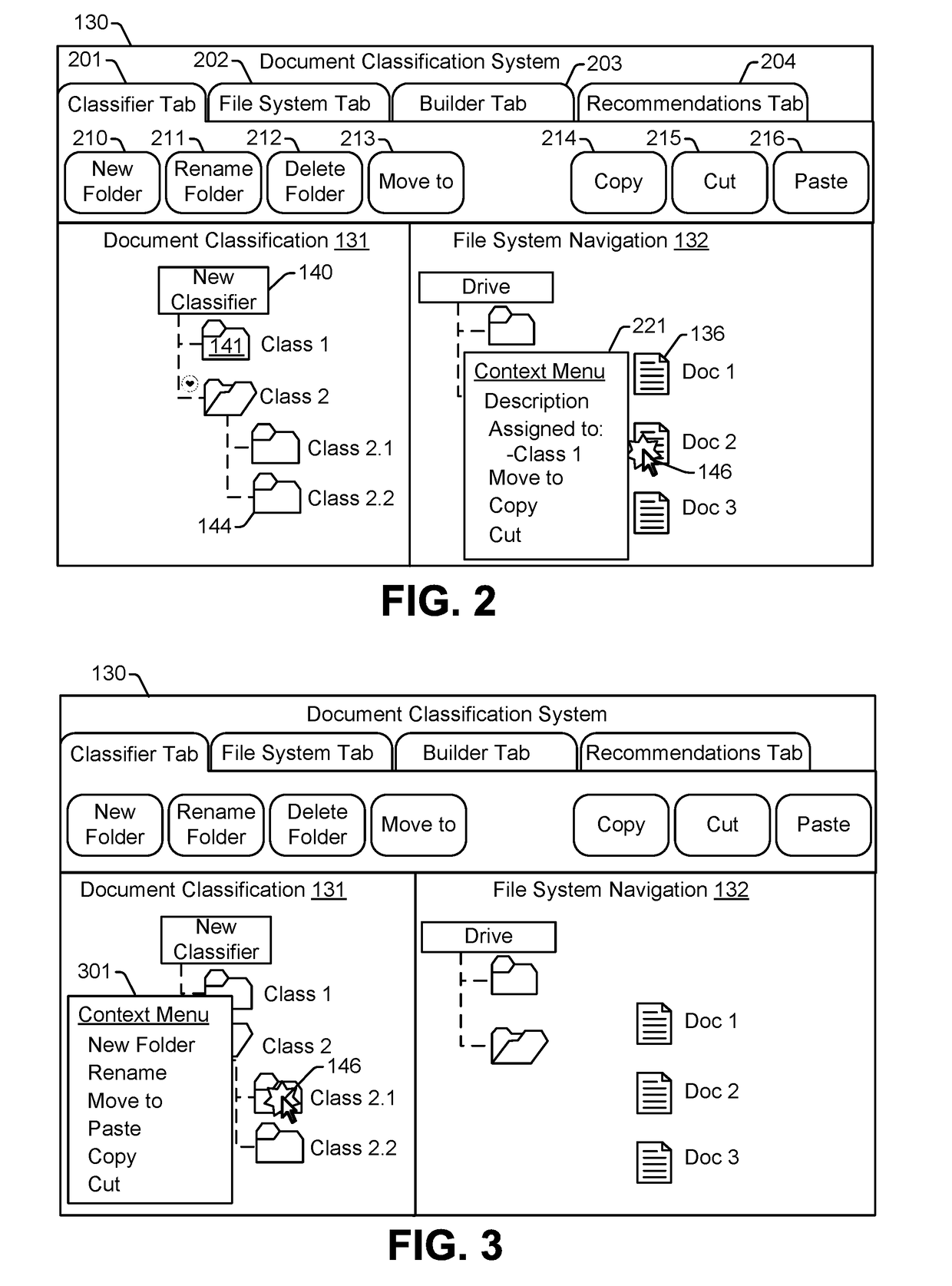
ActiveUS20180349388A1Simplified generationSimplified managementMathematical modelsDigital data information retrievalFeature vectorDocument classification
A method includes performing, by a computing device, a clustering operation to group documents of a document corpus into clusters in a feature vector space. The document corpus includes one or more labeled documents and one or more unlabeled documents. Each of the one or more labeled documents is assigned to a corresponding class in classification data associated with the document corpus, and each of the one or more unlabeled document is not assigned to any class in the classification data. The method also includes generating, by the computing device, a prompt requesting classification of a particular document of the document corpus, where the particular document is selected based on a distance between the particular document and a labeled document of the one or more labeled documents.
Owner:SPARKCOGNITION INC
Apparatus and methods for using fiber optic arrays in optical communication systems
InactiveUS20050053337A1Small sizeReduce power consumptionCoupling light guidesFibre mechanical structuresOptical fiber connectorFiber array
Systems and methods for optical communication that may be employed to couple together fiber optic arrays of two or more optical communication modules using parallel fiber optic connectors and physically distinct and signal-independent optical communication paths. The disclosed systems and methods may be employed to provide separate signal-independent communication paths having signal transport characteristics that meet standards required for single fiber single point-to-single point applications.
Owner:OPTICAL COMM PRODS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com