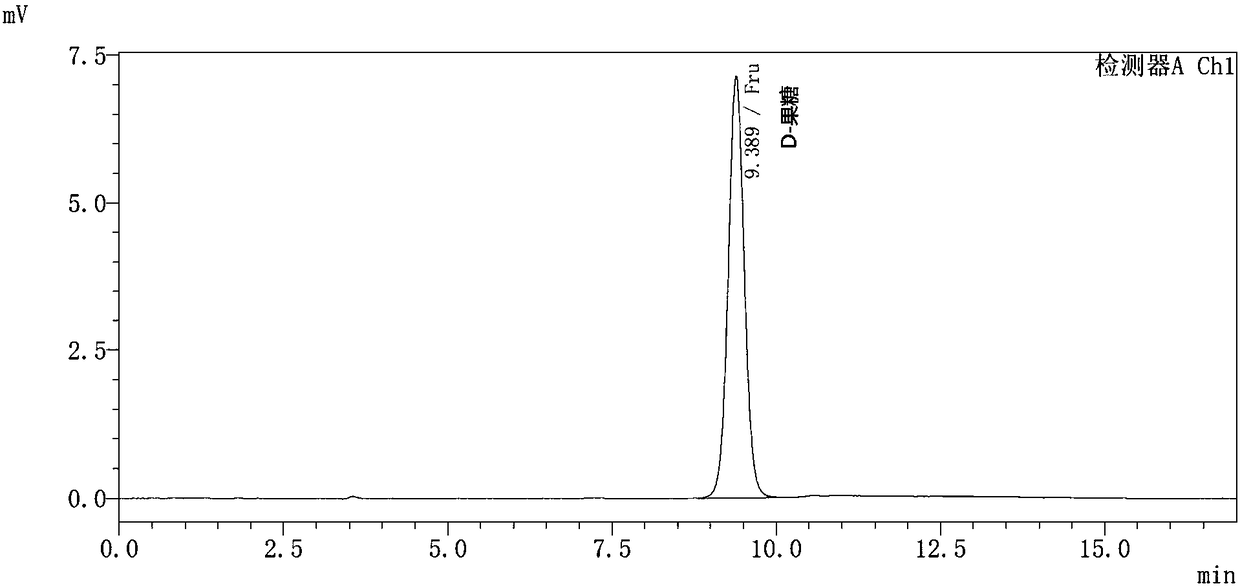
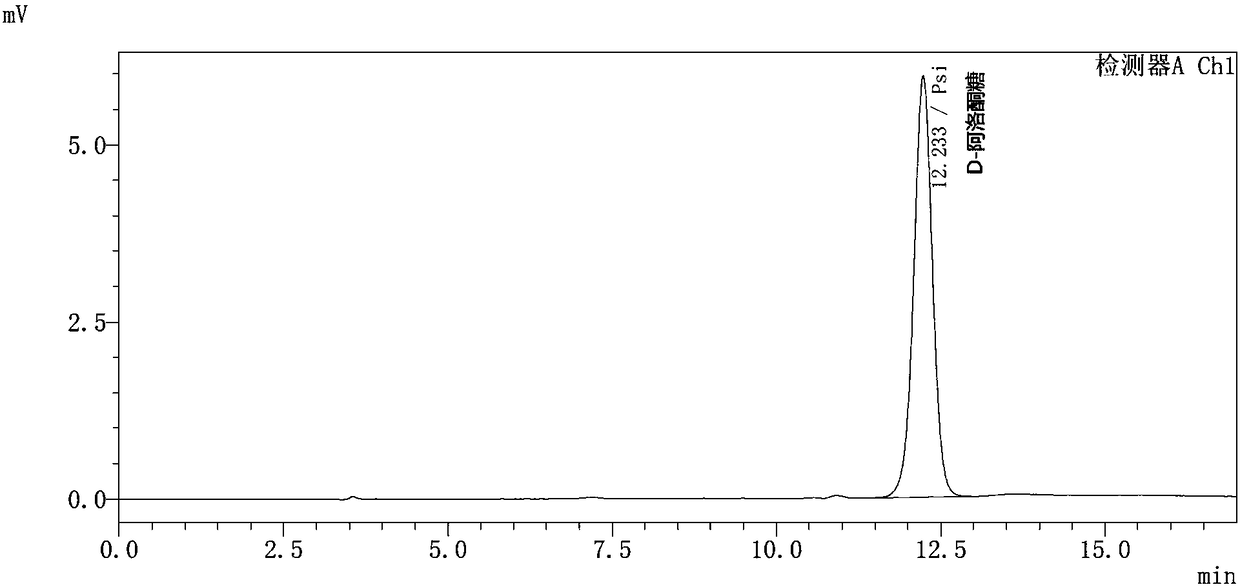
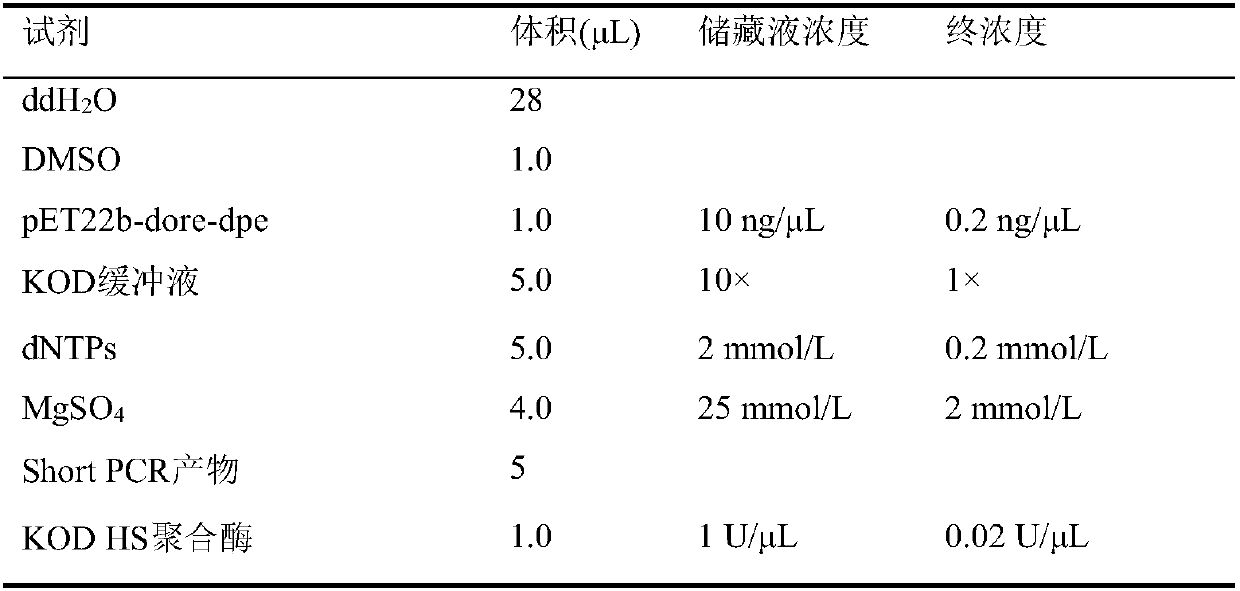
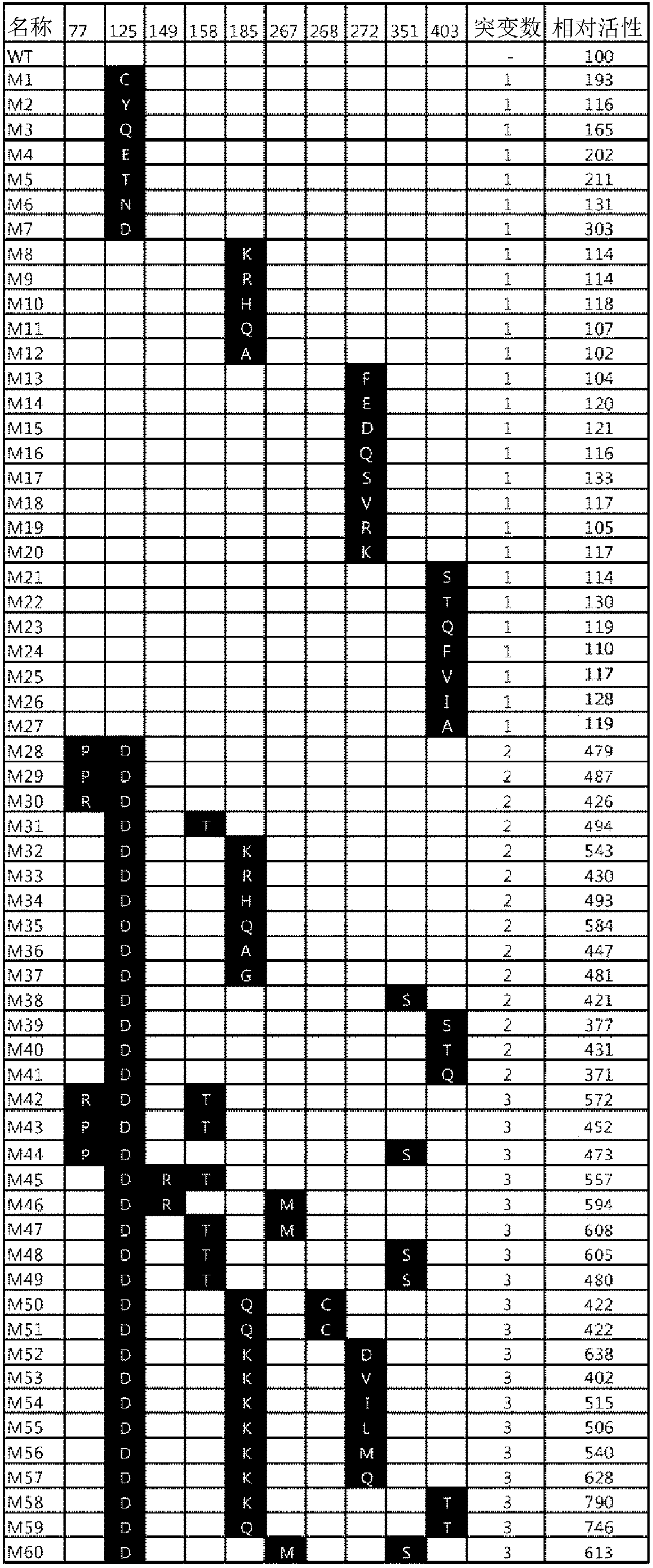
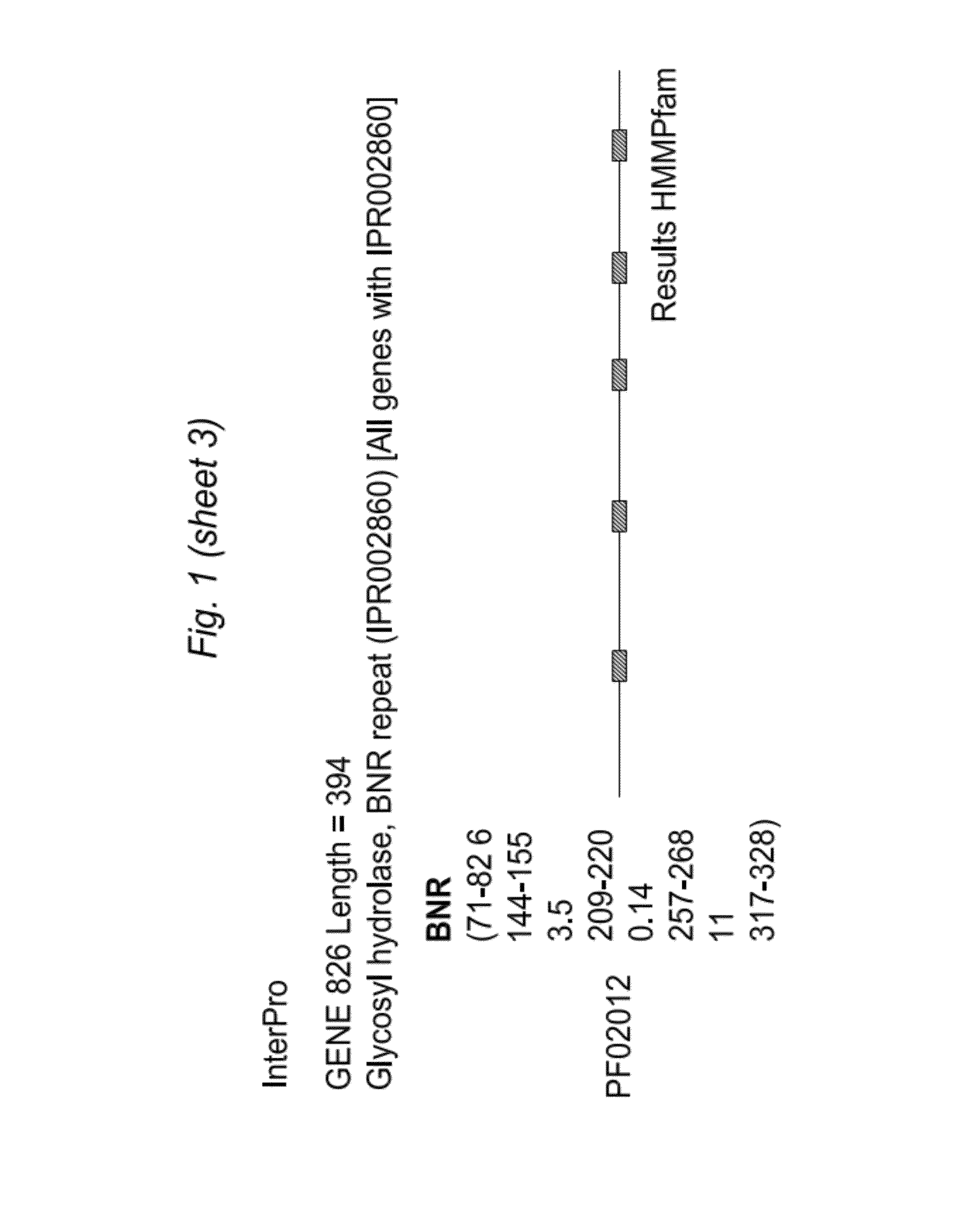
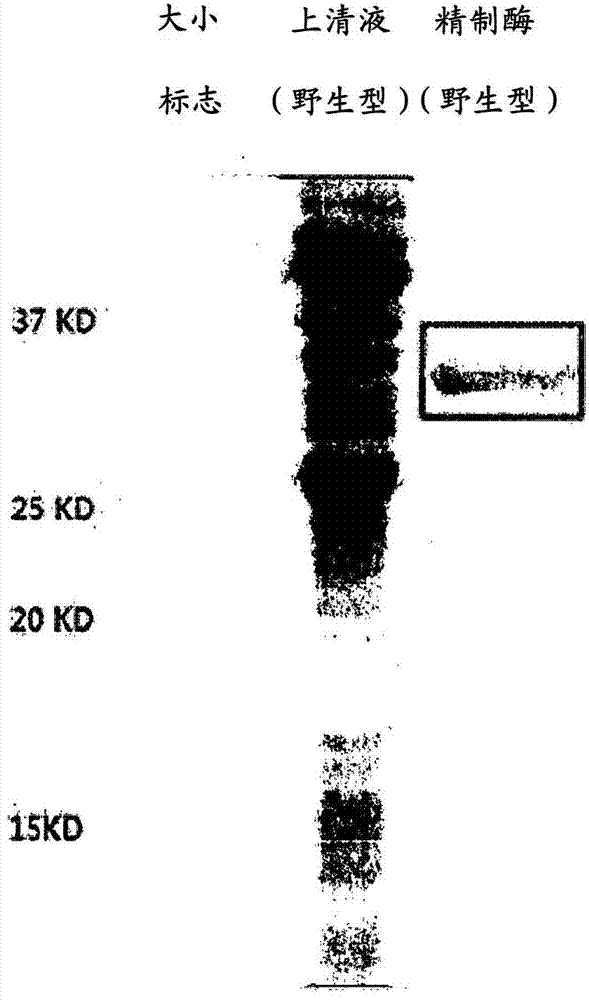
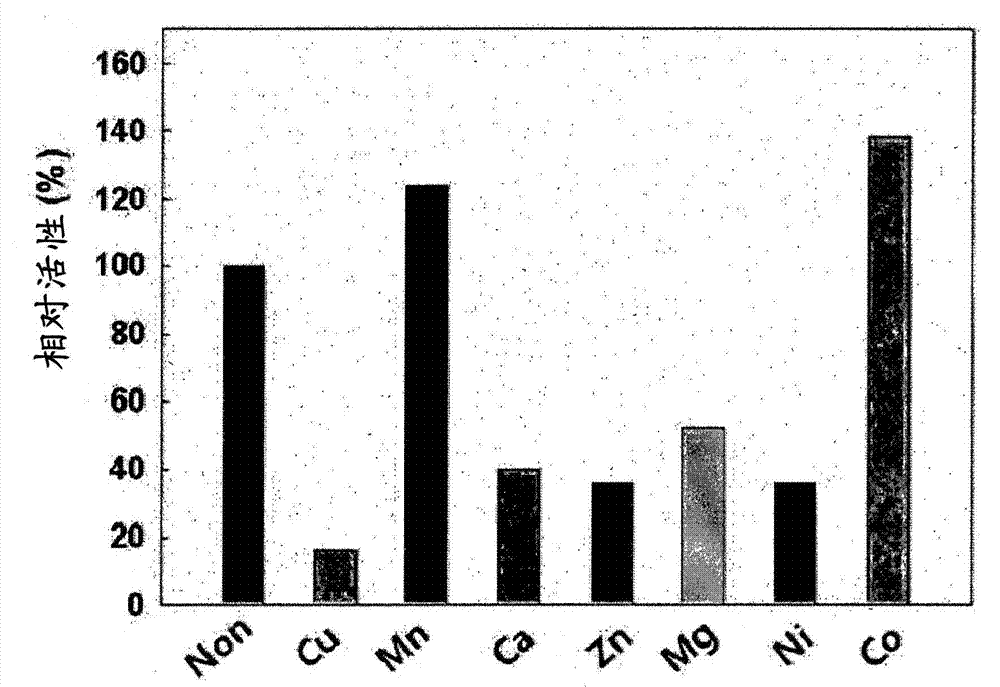
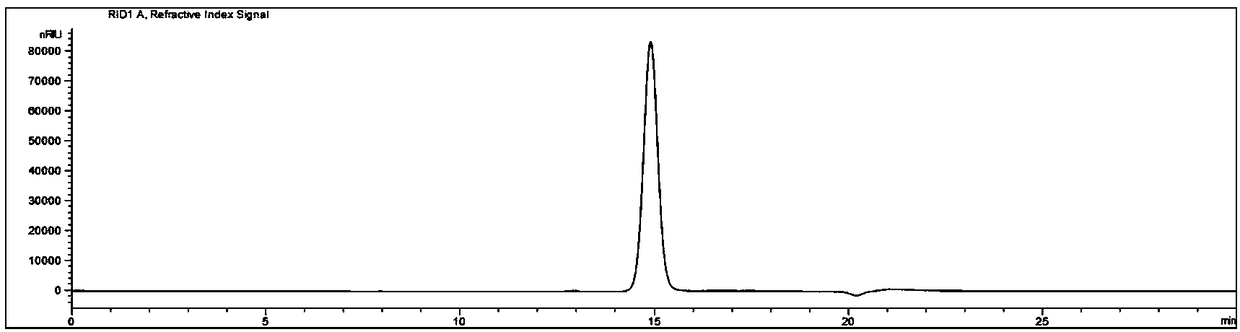
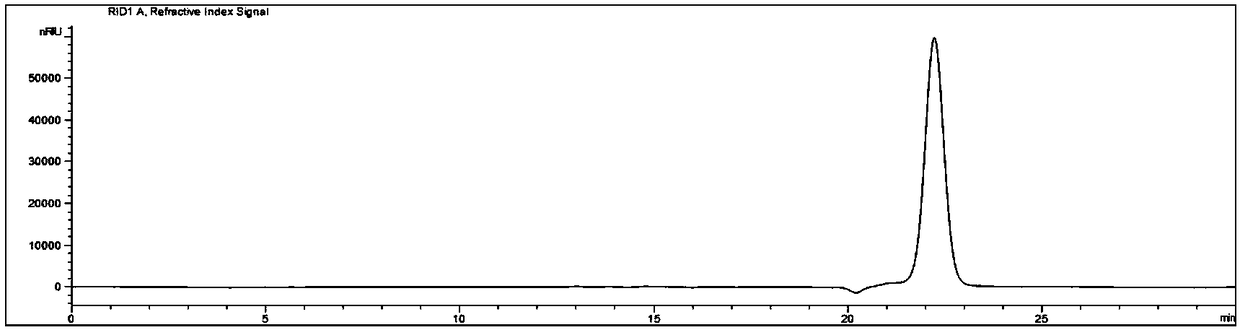
Patents
Literature
363results about "Racemaces/epimerases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of engineering a cytidine monophosphate-sialic acid synthetic pathway in fungi and yeast
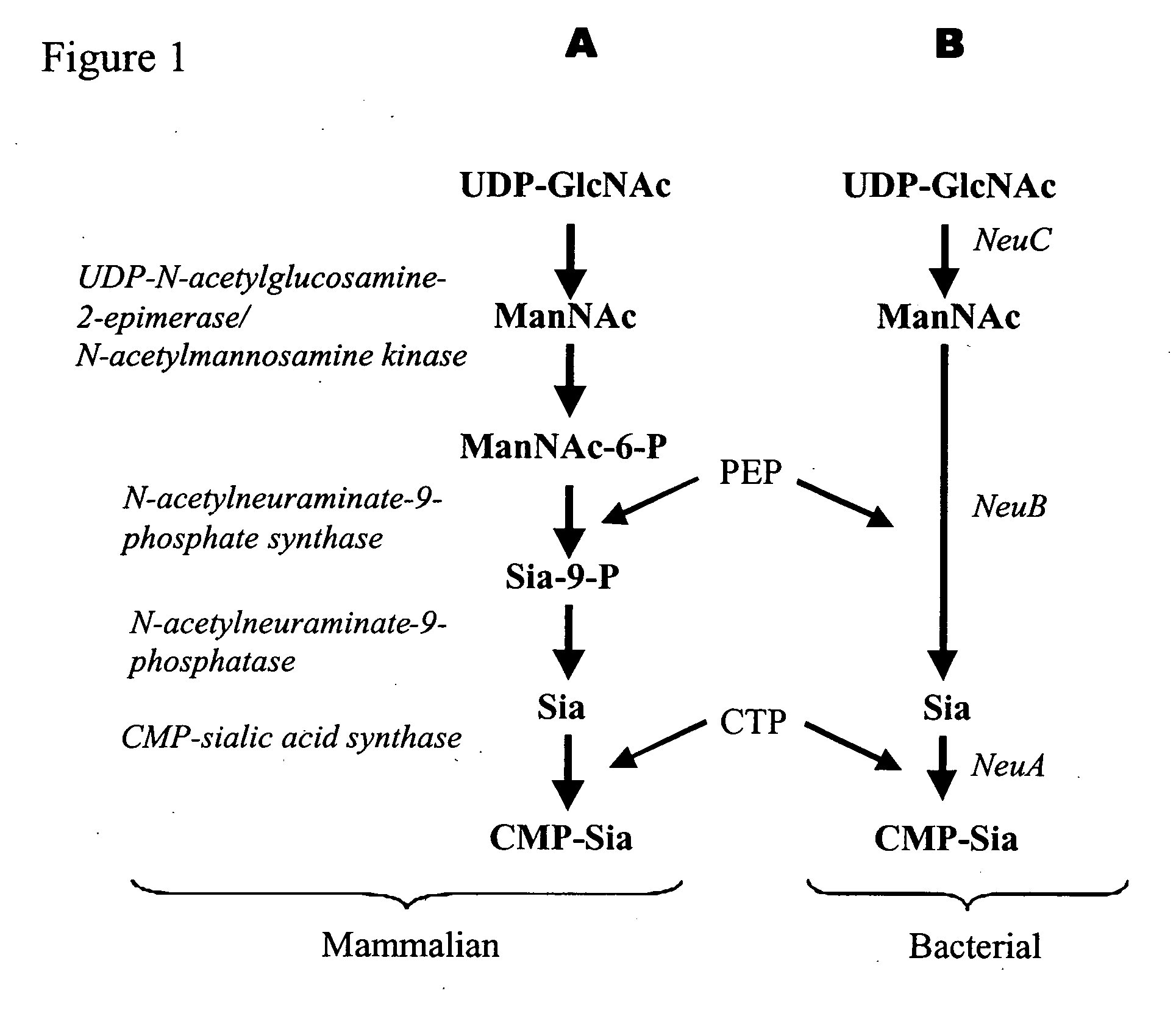
The present invention provides methods for generating CMP-sialic acid in a non-human host which lacks endogenous CMP-Sialic by providing the host with enzymes involved in CMP-sialic acid synthesis from a bacterial, mammalian or hybrid CMP-sialic acid biosynthetic pathway. Novel fungal hosts expressing a CMP-sialic acid biosynthetic pathway for the production of sialylated glycoproteins are also provided.
Owner:GLYCOFI
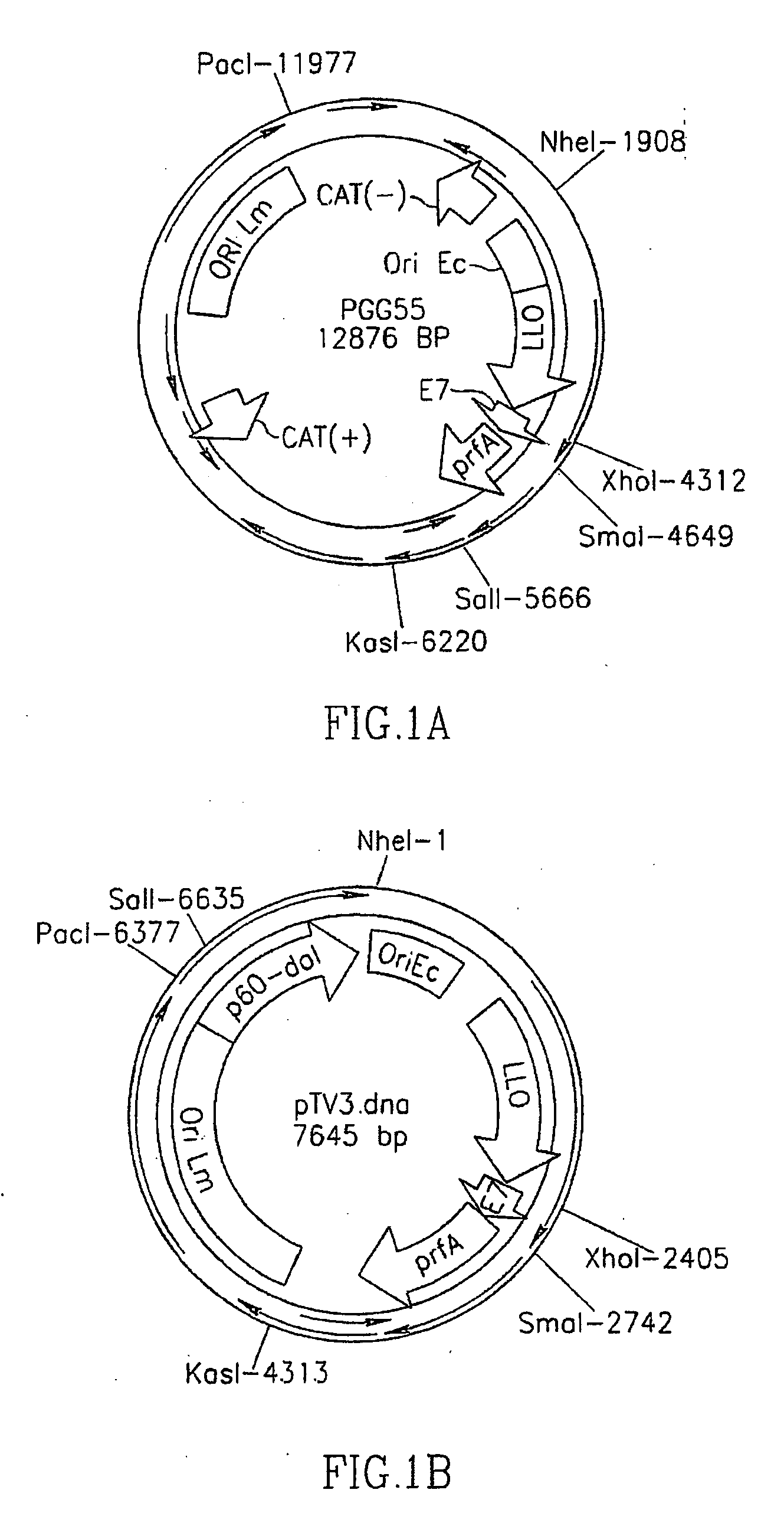
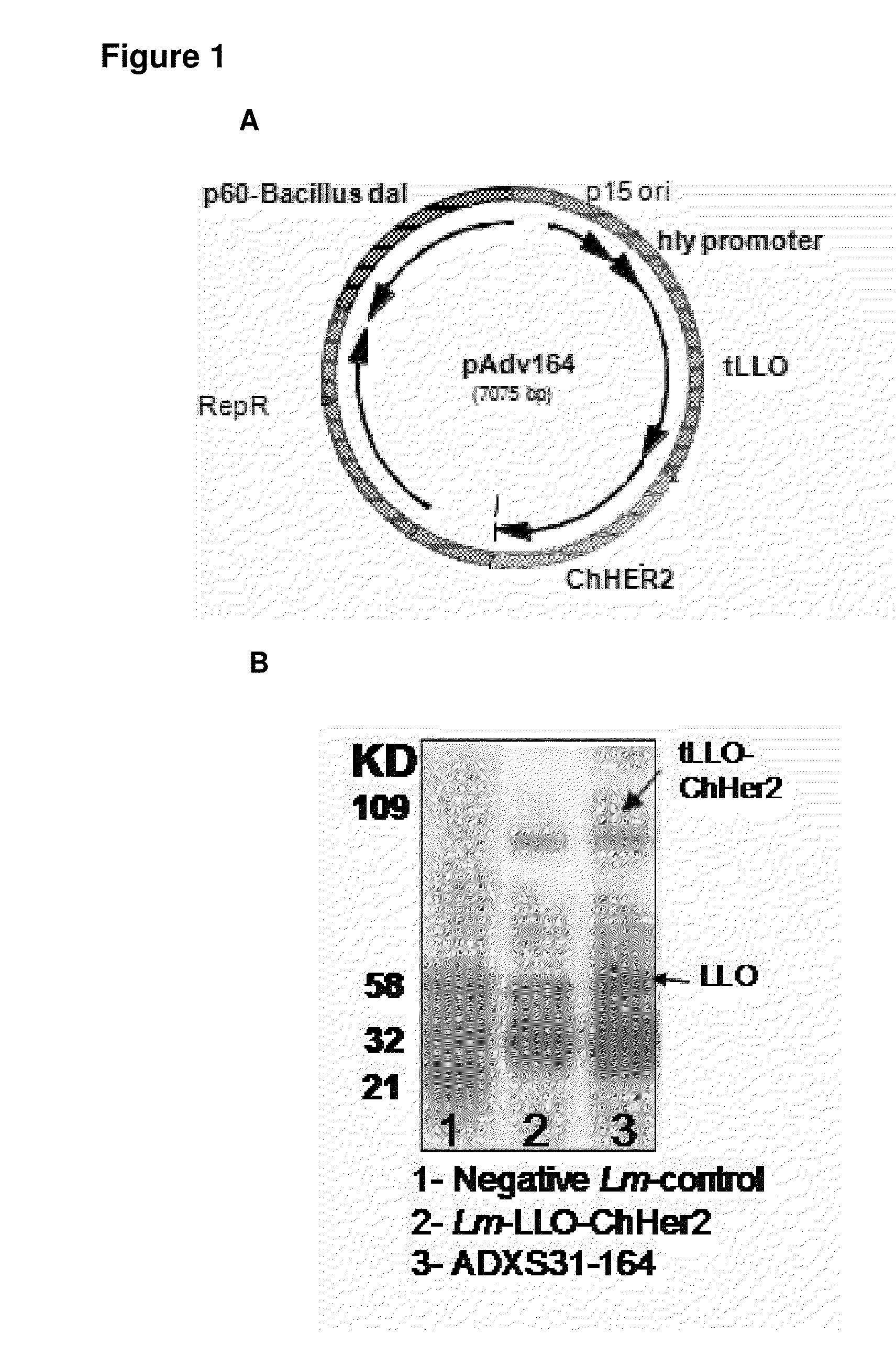
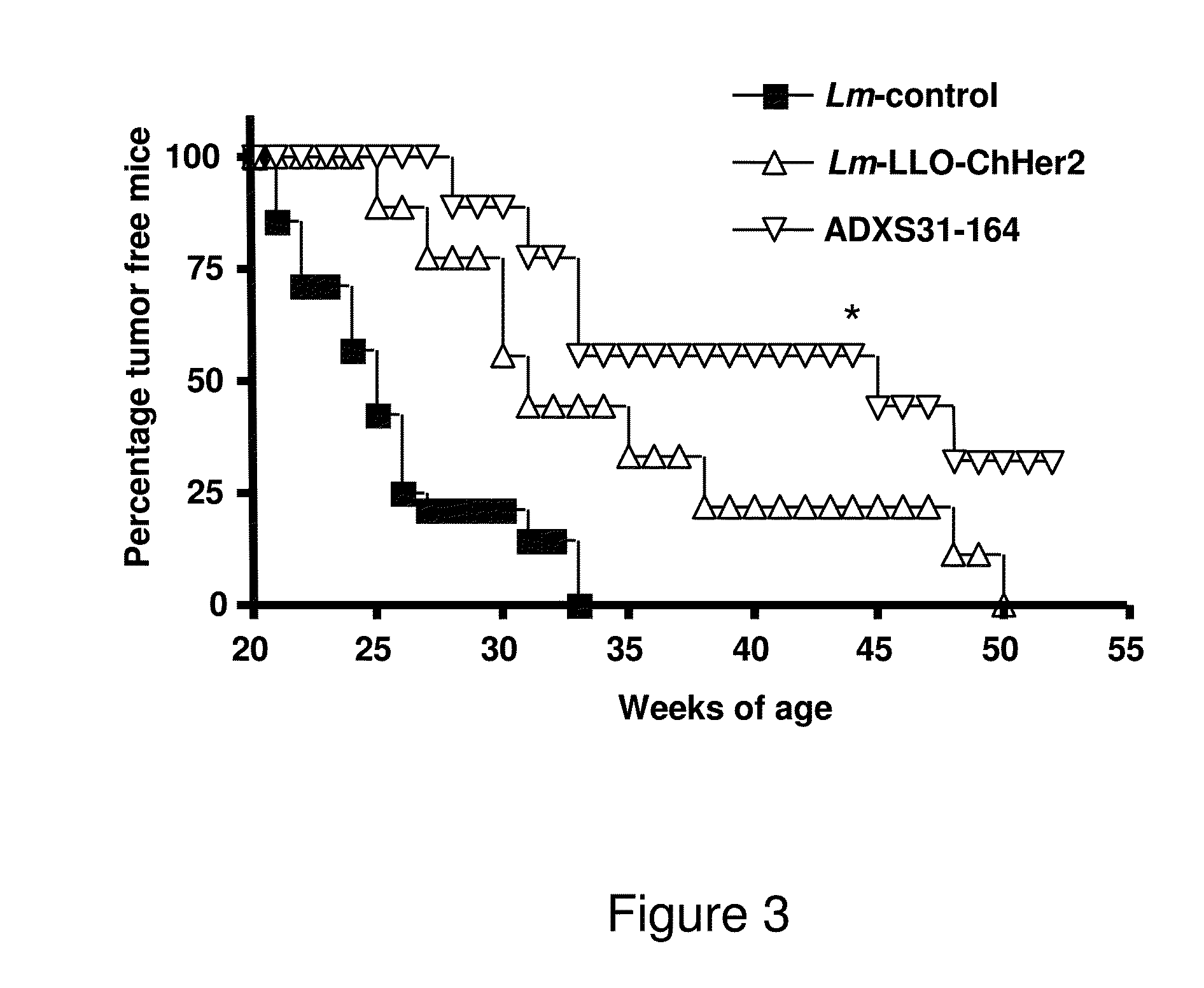
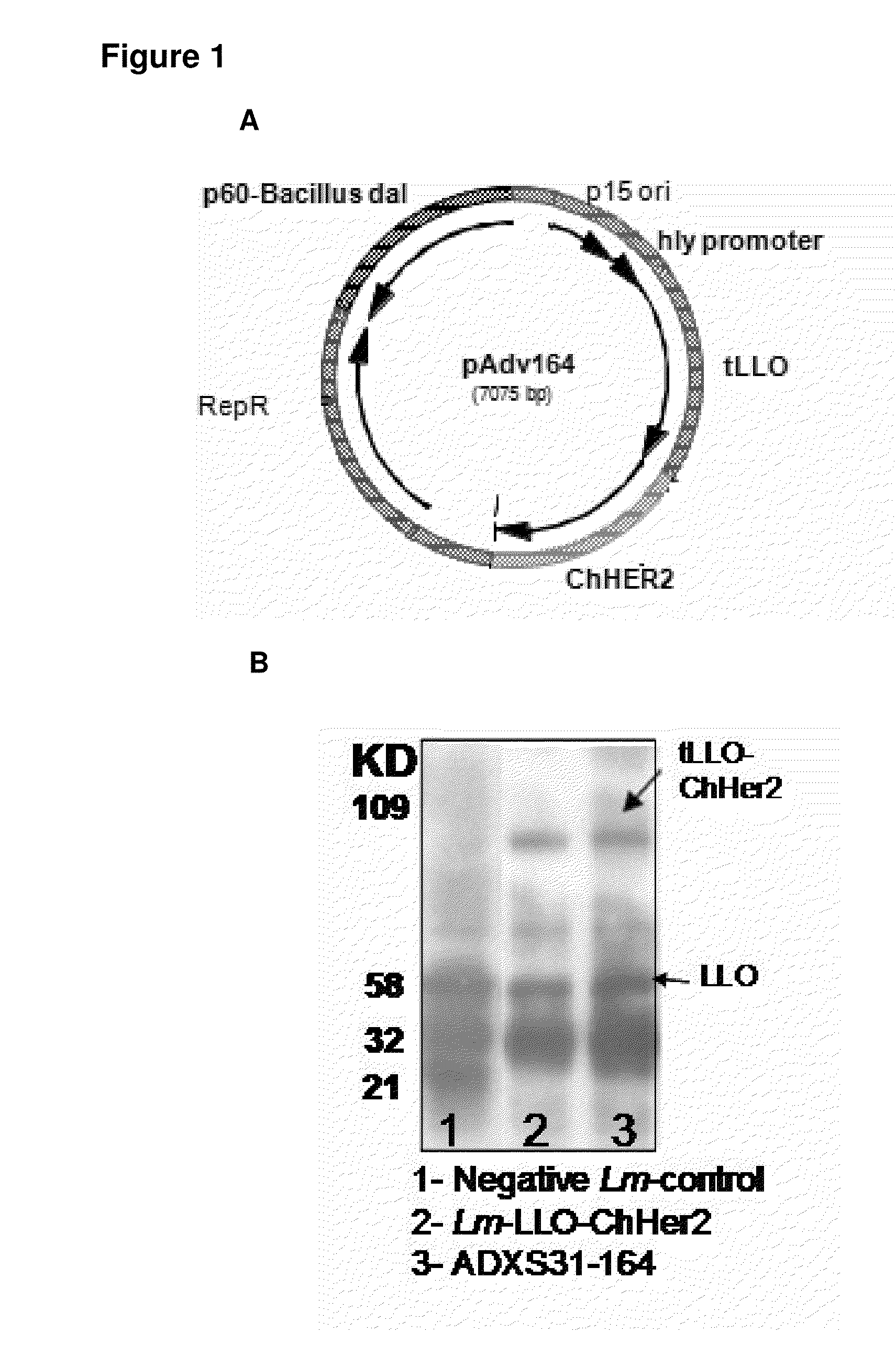
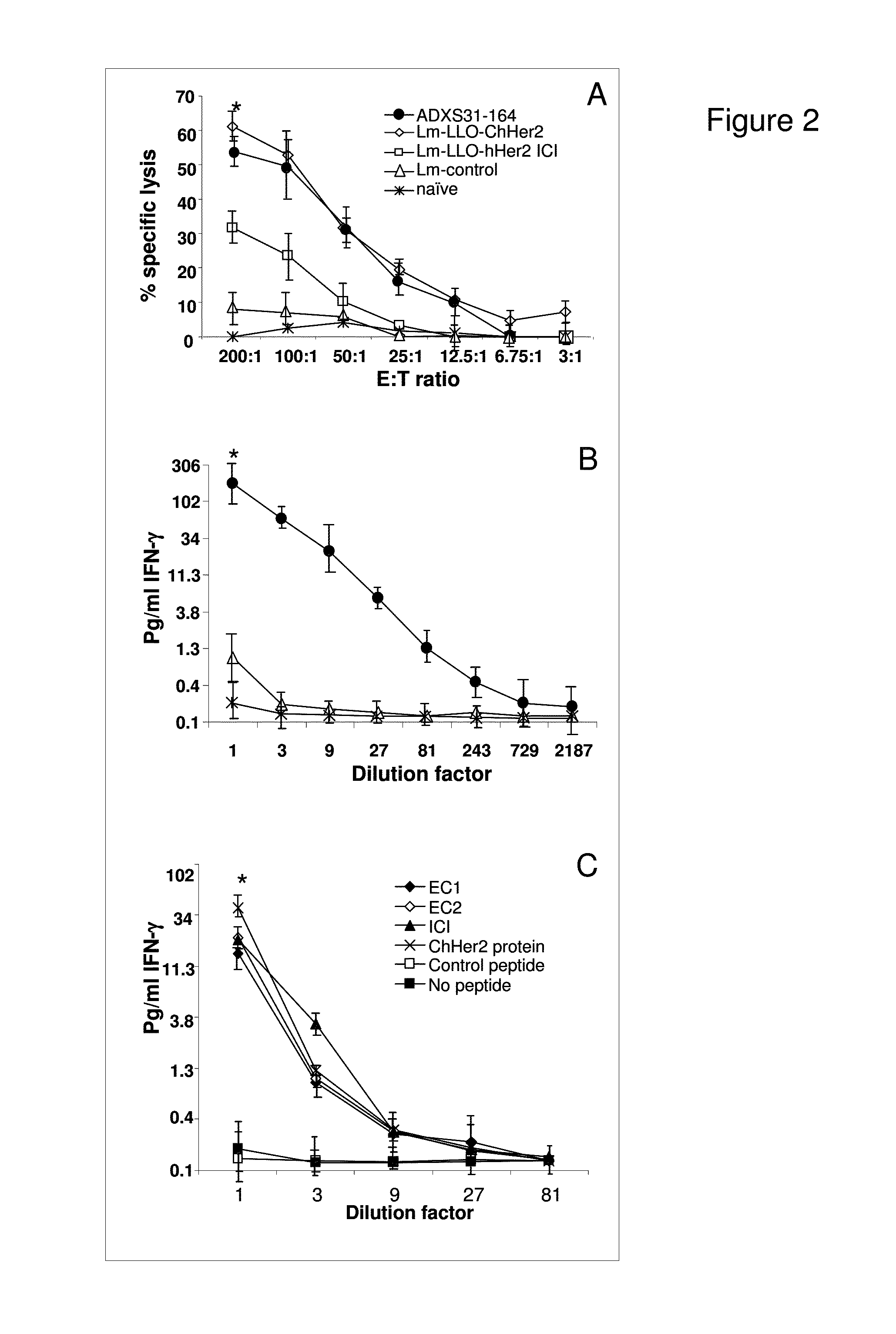
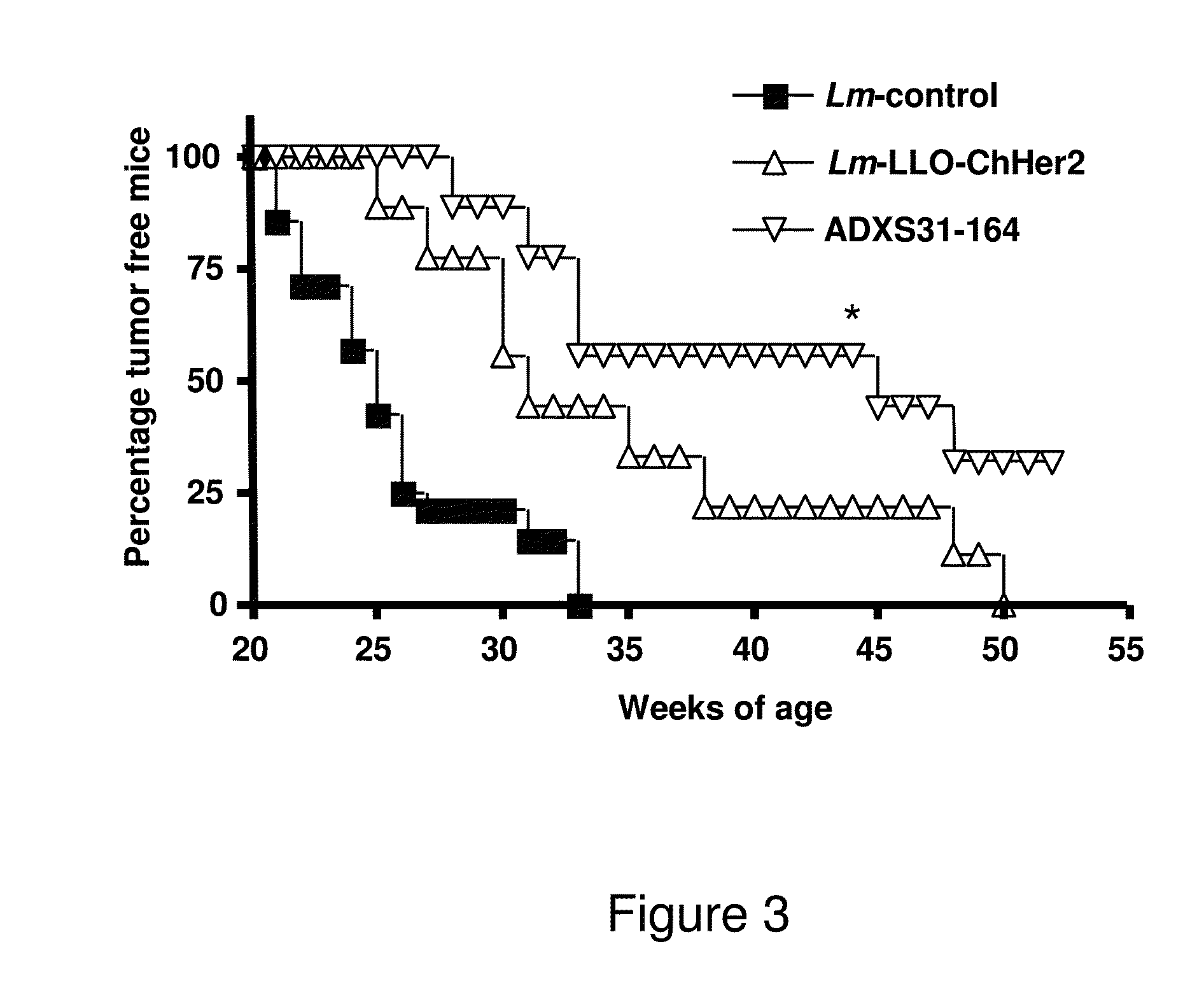
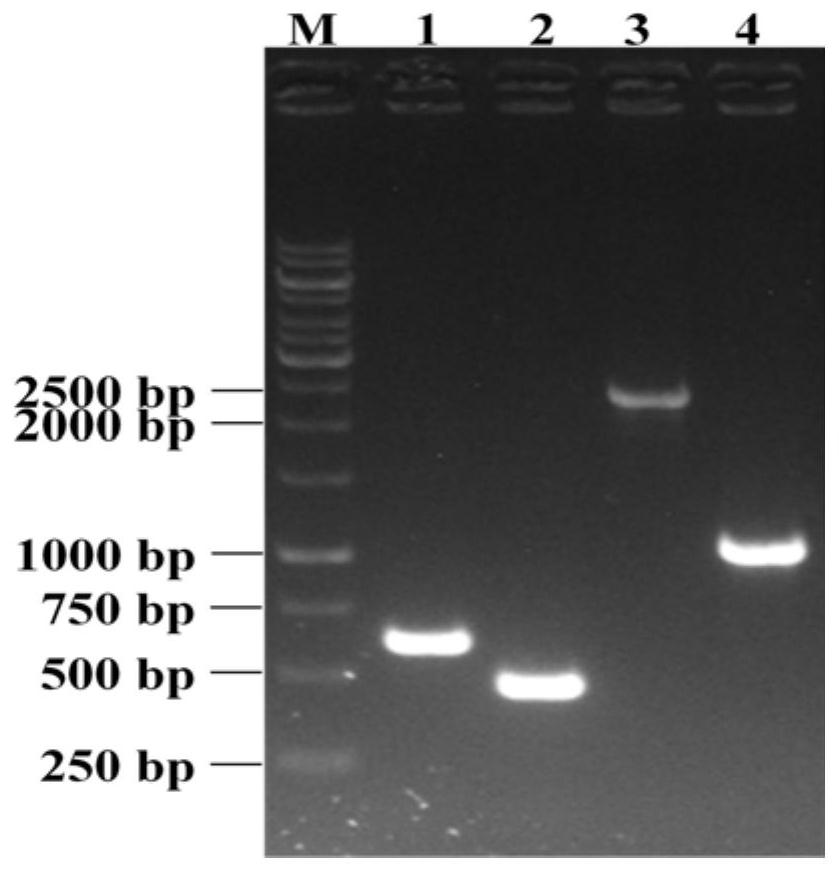
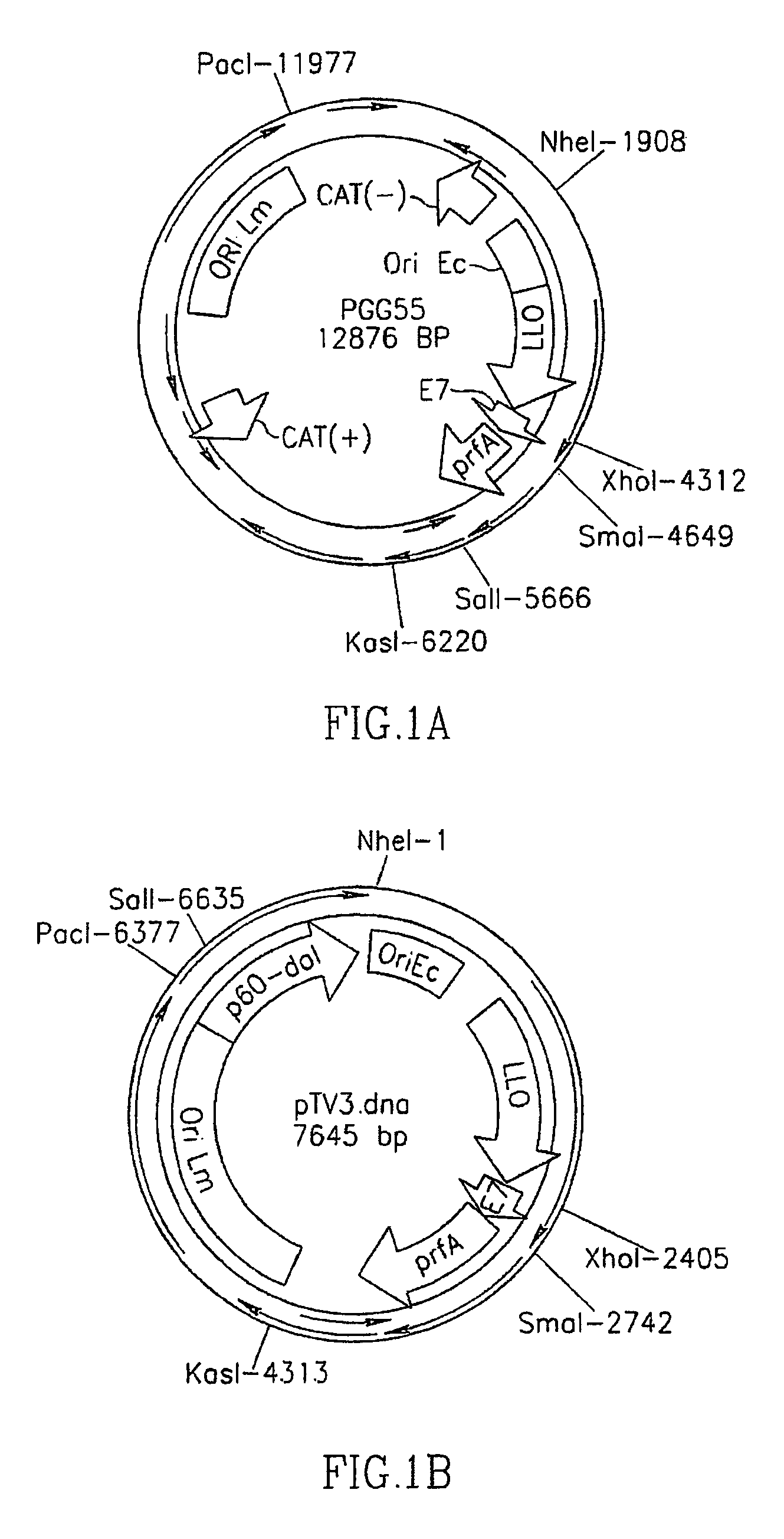
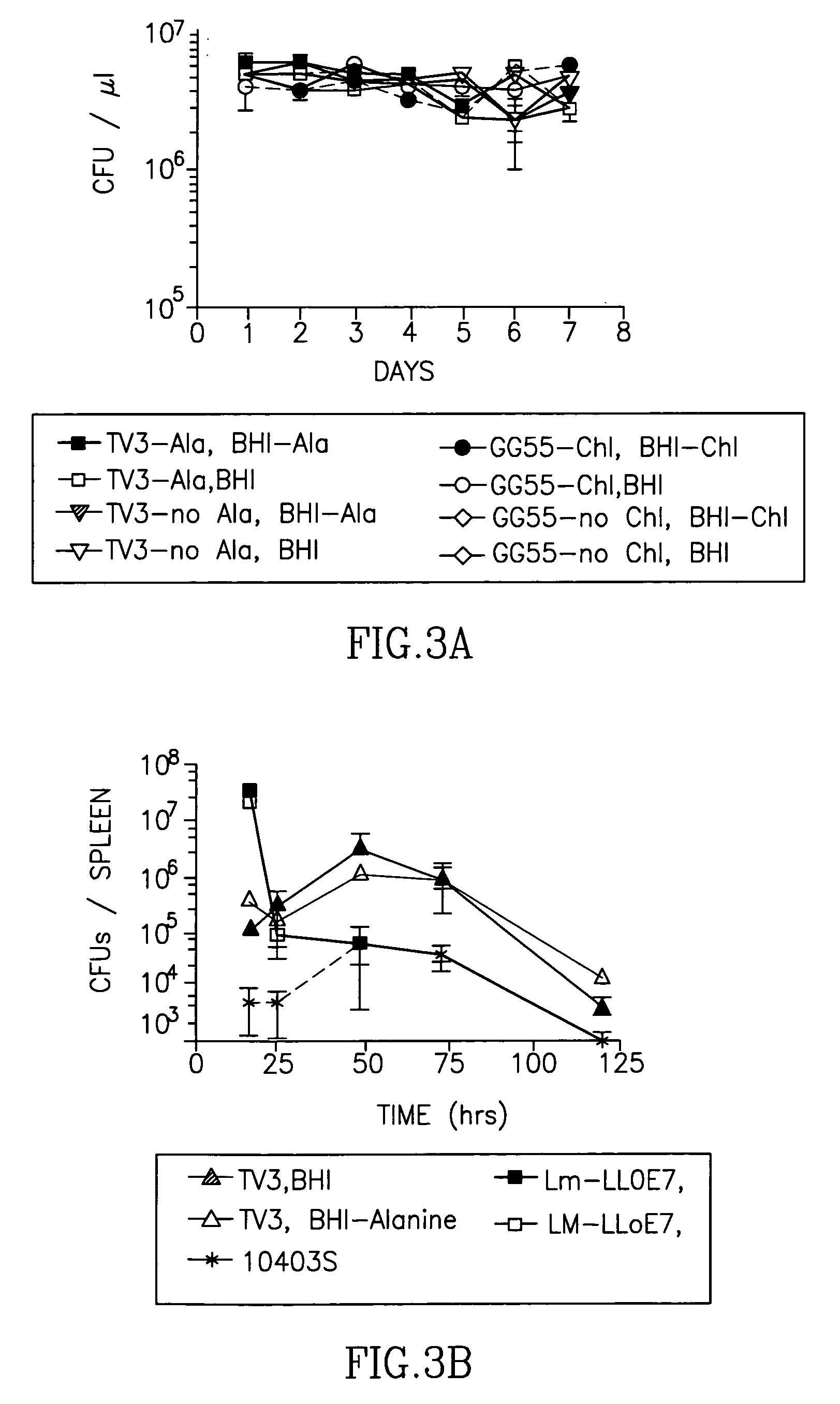
Methods for constructing antibiotic resistance free vaccines
The present invention provides Listeria vaccine strains that express a heterologous antigen and a metabolic enzyme, and methods of generating same.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Genes, compositions, kits, and methods for identification, assessment, prevention, and therapy of prostate cancer
InactiveUS20060068425A1Reduced expression levelHigh expressionCompound screeningTumor rejection antigen precursorsOncologyHuman prostate
The invention relates to newly discovered nucleic acid molecules and proteins associated with prostate cancer including pre-malignant conditions. Compositions, kits, and methods for detecting, characterizing, preventing, and treating human prostate cancers are provided.
Owner:MILLENNIUM PHARMA INC
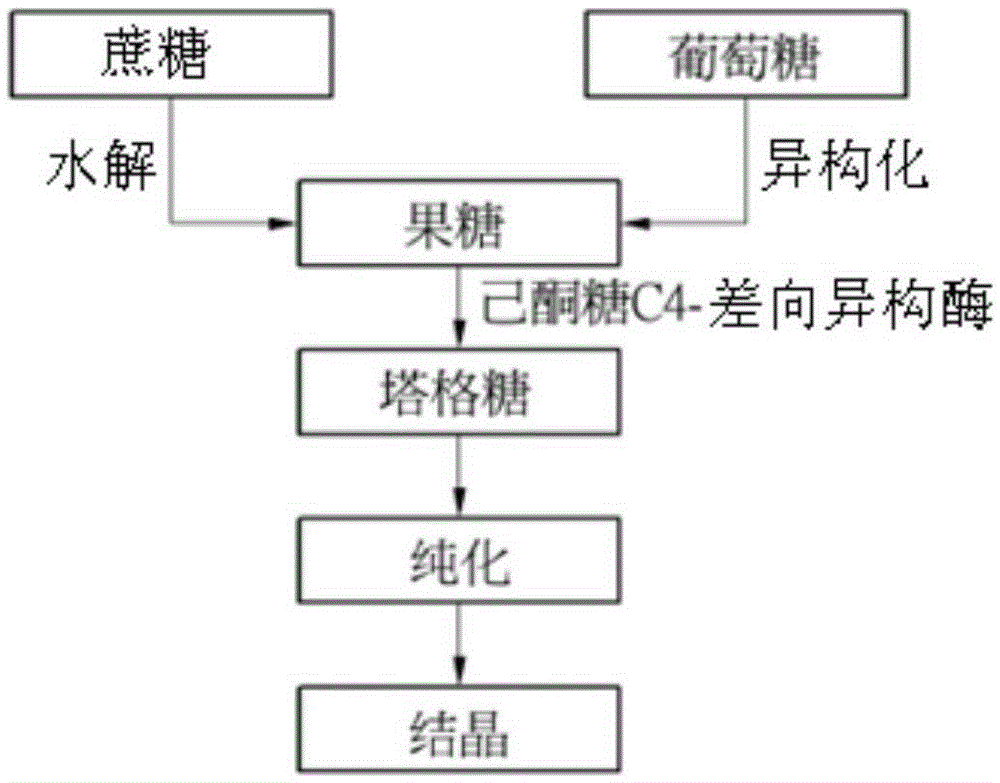
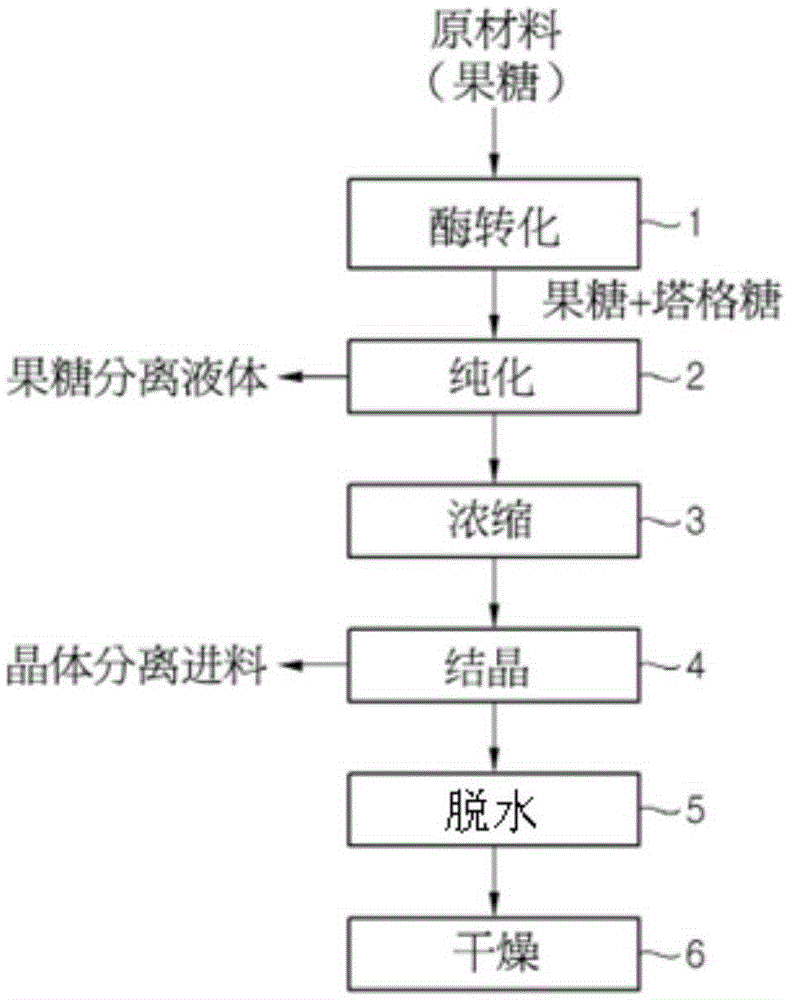
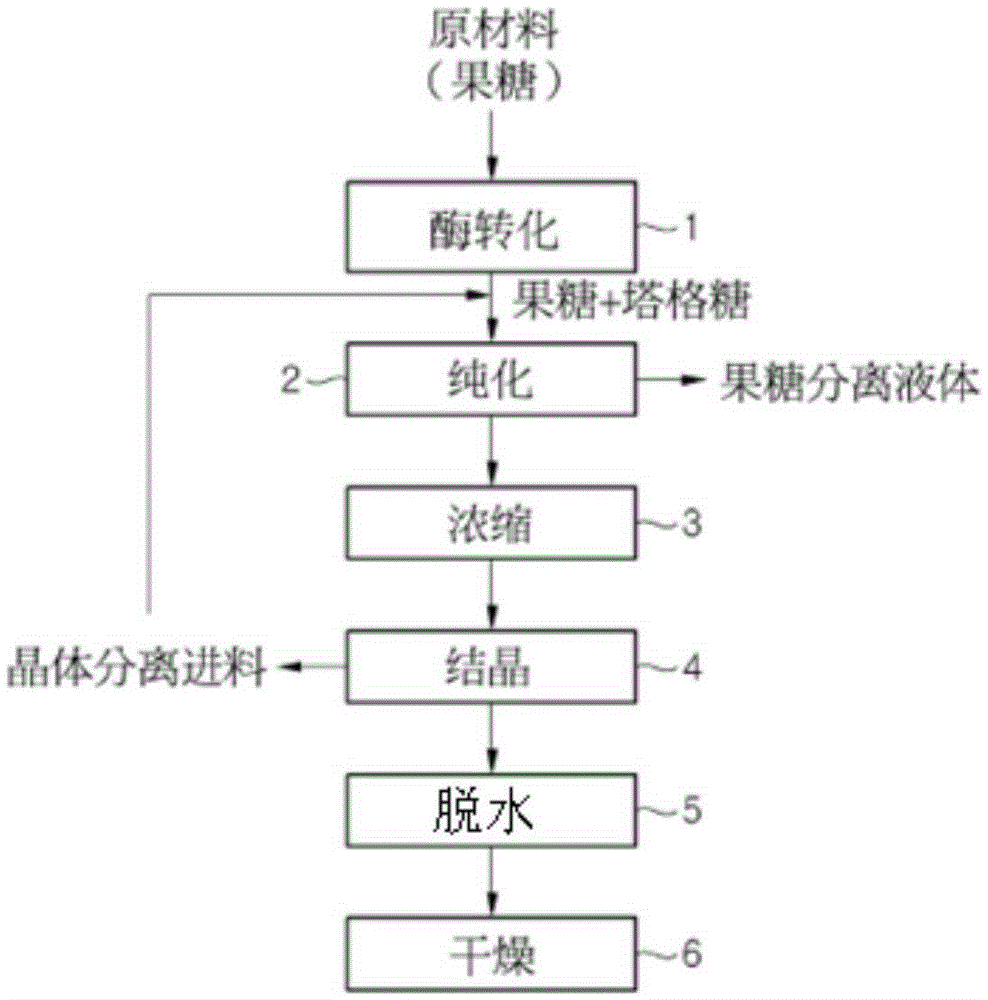
Production method for tagatose
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
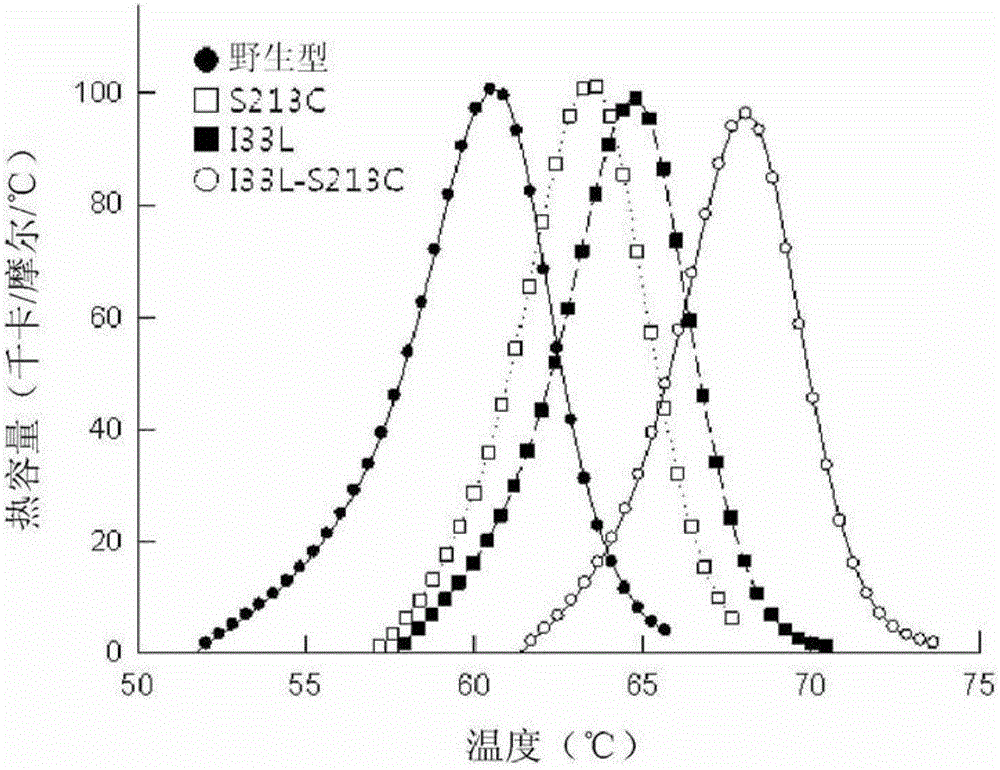
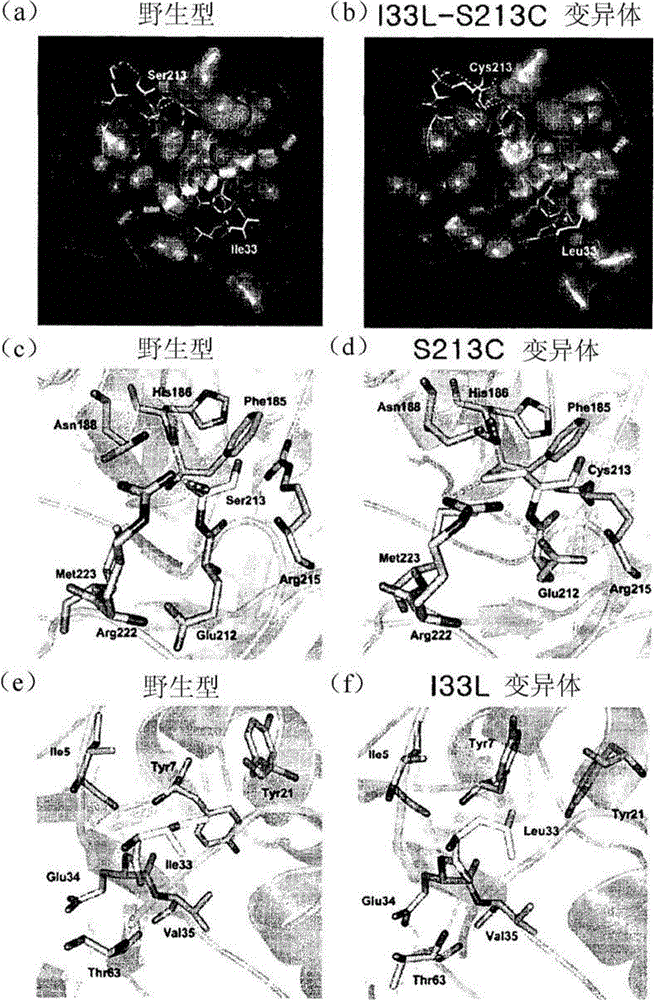
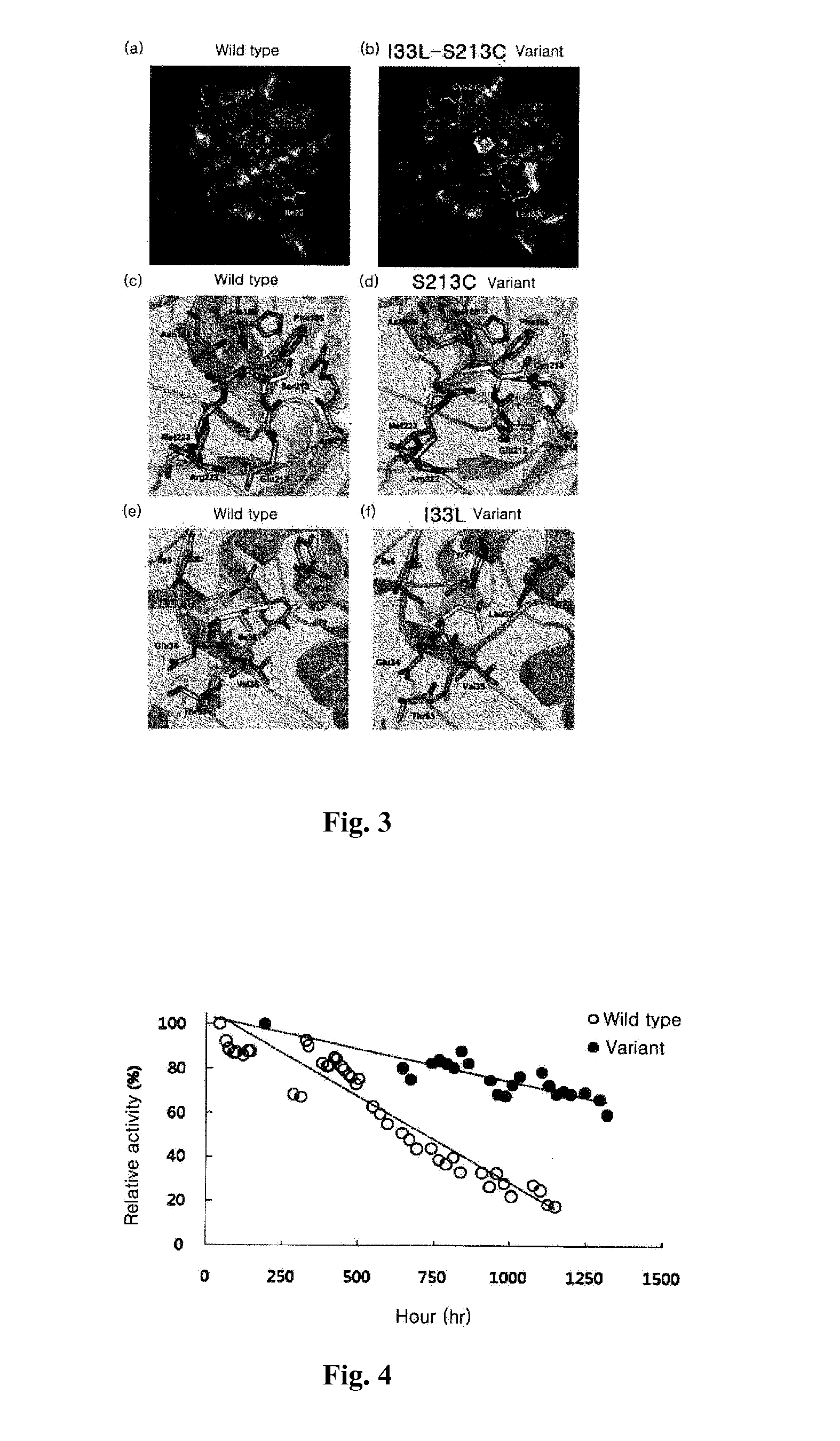
D-psicose 3-epimerase mutant with improved thermal stability, and continuous production of d-psicose using same
ActiveCN104160023AEfficient large-scale industrial preparationMaintain enzymatic activityRacemaces/epimerasesIsomerasesPsicoseMutant
The present invention relates to a D-psicose 3-epimerase mutant of which the thermal stability is improved by substituting an amino acid of a specific sequence number. In addition, the present invention relates to a recombinant vector comprising the gene of the D-psicose 3-epimerase mutant, and a recombinant strain transformed with the recombinant vector. Further, the present invention relates to an immobilized reactor prepared using the enzyme mutant or the recombinant vector, and a method for producing D-psicose using the immobilized reactor.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Novel arabinose-fermenting eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS20100304454A1Improve stabilityAvoid recombinationFungiHydrolasesPropanoic acidGlucose repression
The present invention relates to eukaryotic cells which have the ability to convert L-arabinose into D-xylulose 5-phosphate. The cells have acquired this ability by transformation with nucleotide sequences coding for an arabinose isomerase, a ribulokinase, and a ribulose-5-P-4-epimerase from a bacterium that belongs to a Clavibacter, Arthrobacter or Gramella genus. The cell preferably is a yeast or a filamentous fungus, more preferably a yeast is capable of anaerobic alcoholic fermentation. The may further comprise one or more genetic modifications that increase the flux of the pentose phosphate pathway, reduce unspecific aldose reductase activity, confer to the cell the ability to directly isomerise xylose into xylulose, increase the specific xylulose kinase activity, increase transport of at least one of xylose and arabinose into the host cell, decrease sensitivity to catabolite repression, increase tolerance to ethanol, osmolarity or organic acids; and / or reduce production of by-products. The cell preferably is a cell that has the ability to produce a fermentation product such as ethanol, lactic acid, 3-hydroxy-propionic acid, acrylic acid, acetic acid, succinic acid, citric acid, amino acids, 1,3-propane-diol, ethylene, glycerol, -lactam antibiotics and cephalosporins. The invention further relates to processes for producing these fermentation products wherein a cell of the invention is used to ferment arabinose into the fermentation products.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV +1
Preparation method for high-purity D-psicose
ActiveCN106520746AImprove the ability to convert into D-psicoseEasy to controlSugar derivativesOrganic chemistry methodsChromatographic separationCentrifugation
The invention relates to a preparation method for high-purity D-psicose. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) subjecting the fermentation broth of Bacillus subtilis to centrifugation and then subjecting obtained thalli to homogenization so as to obtain a mixed solution containing D-psicose 3-epimerase; (2) preparing a fructose solution, adding the mixed solution containing D-psicose 3-epimerase, adjusting a pH value, carrying out a reaction under a heat insulation condition, then adding the fructose solution into the reaction solution in a fed-batch manner, continuing the reaction, and then stopping the reaction so as to prepare a crude D-psicose solution; and (3) subjecting the crude D-psicose solution to decoloring, filtering, ion exchange, chromatographic separation and concentration, and then to crystallization or drying so as to prepare D-psicose. The preparation method provided by the invention uses Bacillus subtilis fermentation broth for direct production and omits the process of enzyme extraction, so production cost is greatly reduced, a reduction of 25% or so compared with traditional production methods, so the competitiveness of prepared D-psicose is greatly improved.
Owner:SHANDONG BAILONG CHUANGYUAN BIO TECH
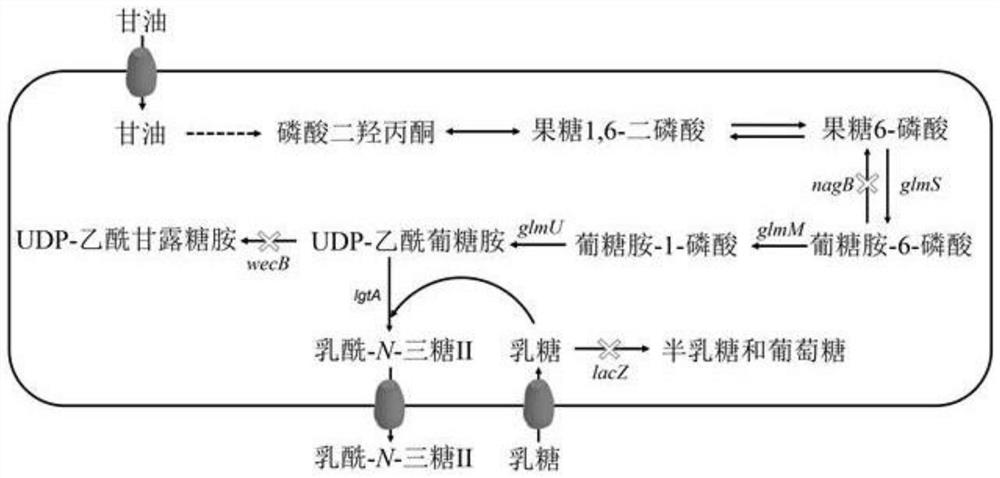
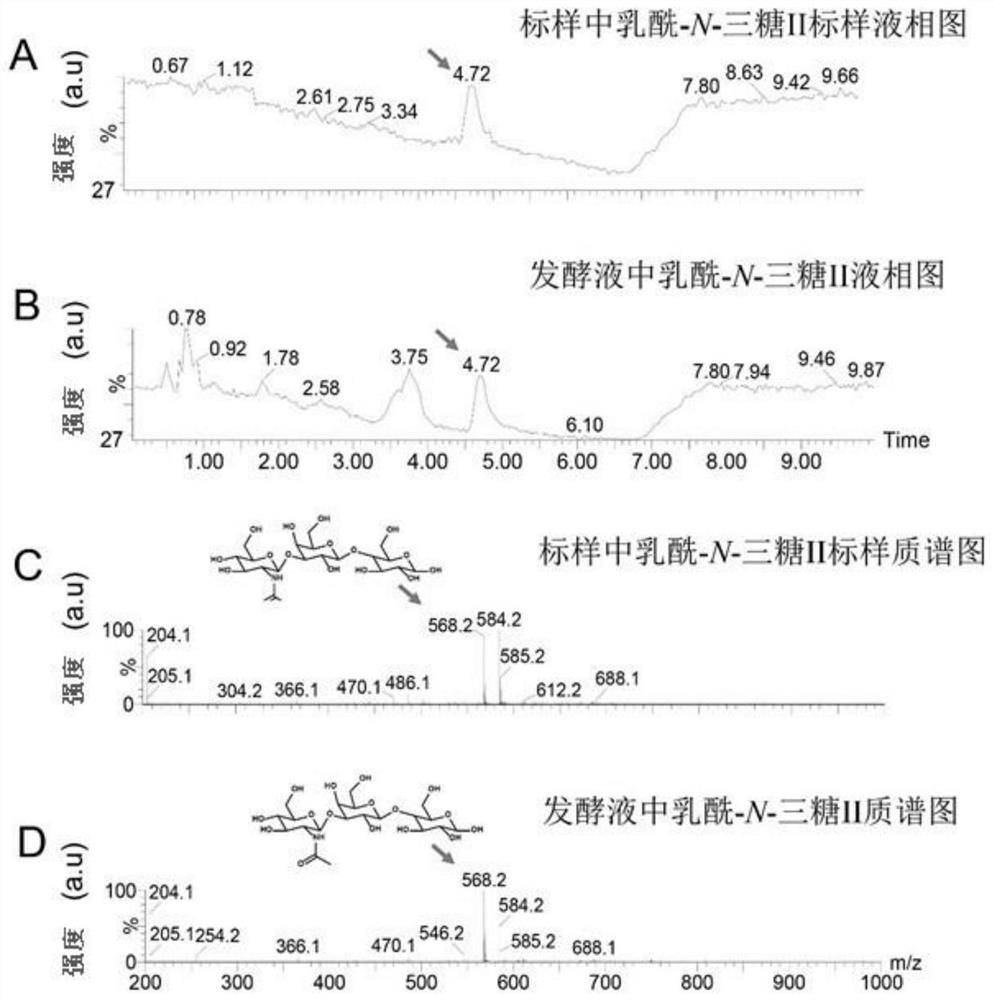
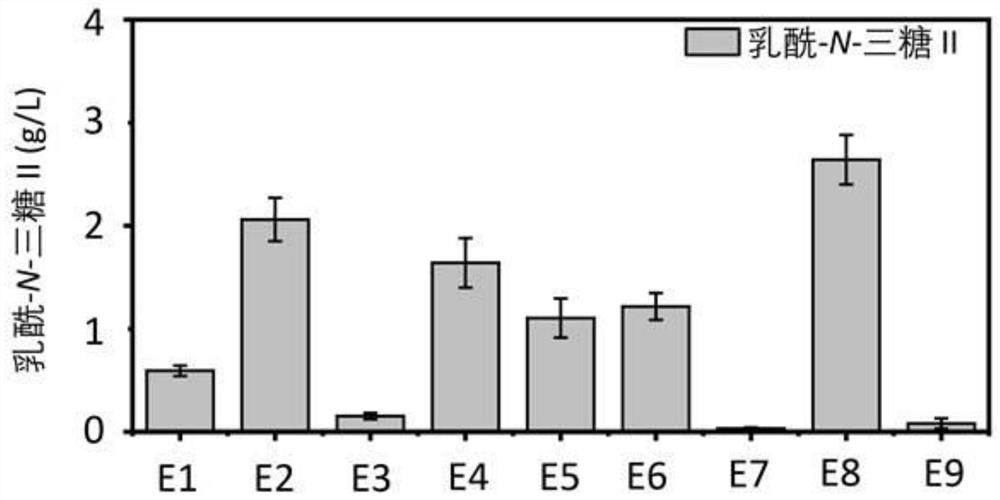
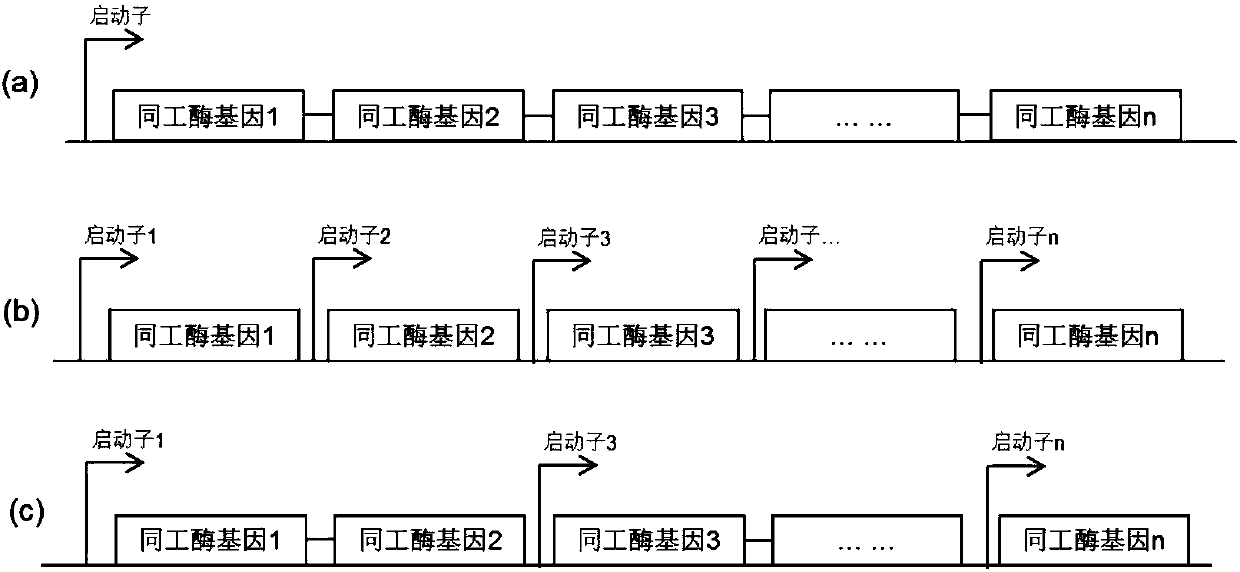
Genetically engineered bacteria capable of increasing yield of lactoyl-N-trisaccharide II and production method for genetically engineered bacteria
ActiveCN111979168AIncrease productionPrecise regulation of carbon fluxBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses genetically engineered bacteria capable of increasing the yield of lactoyl-N-trisaccharide II and a production method, and belongs to the field of microbial genetic engineering. According to the invention, the expression of glmM, glmU, glmS and lgtA in a lactoyl-N-trisaccharide II synthetic pathway is regulated and controlled in a combined manner, so the carbon flux of a metabolic pathway is accurately regulated and controlled, and the metabolic pressure is relieved; the expression of wecB, nagB and lacZ in an escherichia coli host, namely the lactoyl-N-trisaccharide IIsynthetic pathway is knocked out, so the yield of the lactoyl-N-trisaccharide II is further increased; in a flask shaking experiment, the capacity of escherichia coli for producing the lactoyl-N-trisaccharide II is increased to 4.82 g / L from 0.53 g / L; in a fermentation tank with a volume of 3 L, the yield of the lactoyl-N-trisaccharide II reaches 46.2 g / L; and thus, thegenetically engineered bacteria have industrial application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for efficiently preparing D-psicose 3-epimerase and use of D-psicose 3-epimerase
InactiveCN107723307ALow costHigh catalytic efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesIsozymePsicose
The invention discloses a method for efficiently preparing D-psicose 3-epimerase and a use of the D-psicose 3-epimerase and provides a method for efficiently preparing an enzyme catalyst for catalyzing the same reaction through isozyme combined expression. The method utilizes corynebacterium glutamicum as a host cell to construct a recombinant strain expressed by plasmid dissociation and chromosomal integration, measures D-fructose catalytic efficiency, improves enzyme catalytic efficiency by 2-4 times than that of single expression of D-psicose 3-epimerase through combined expression and hasa conversion ratio of 29% when 70% of fructose is a substrate. The method improves D-psicose production efficiency and is suitable for industrial production of D-psicose. The invention also disclosesa novel use of the D-psicose 3-epimerase in psicose synthesis. The enzyme is derived from Paenibacillus senegalensis, has catalytic activity of about 25 U / mg and can be used to convert D-fructose intoD-psicose.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
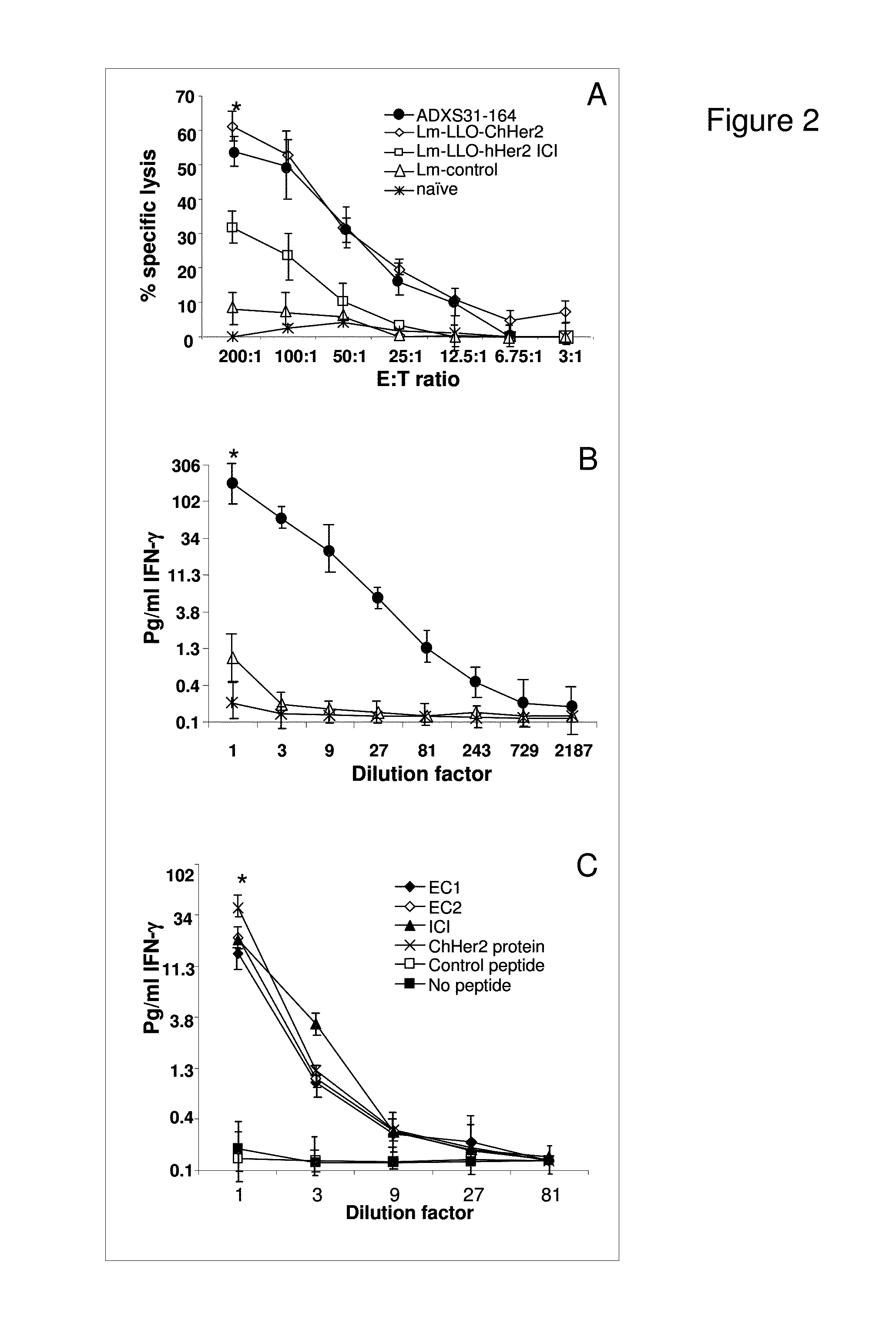
Compositions and methods for prevention of escape mutation in the treatment of her2/neu over-expressing tumors
This invention provides compositions and methods for treating and vaccinating against a Her2 / neu antigen-expressing tumor and inducing an immune response against dominant in a non-human animal.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
Constructed recombinant escherichia coli and method for biosynthesis of 3'-sialyllactose
ActiveCN106190938ANo other features changedDoes not affect growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesEscherichia coli
The invention discloses constructed recombinant escherichia coli and a method for biosynthesis of 3'-sialyllactose. The recombinant escherichia coli is named as E.coli-XYY which has a synthesis pathway of the 3'-sialyllactose. Meanwhile, the invention also discloses a constructing method. At the same time, the invention solves the problems of the prior art and provides an efficient gene knockout scheme; an original strain, after undergoing genetic engineering transformation, can produce the 3'-sialyllactose only, without changing other properties of the strain, so that influence on fermentation production is avoided; since mature escherichia coli plasmid is adopted by the strain, bacterium growth and normal metabolism do not affected in a metabolic process. The recombinant escherichia coli constructed by the invention has a good application prospect; therefore, a new thought is provided for the production of the 3'-sialyllactose by virtue of a biological method.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
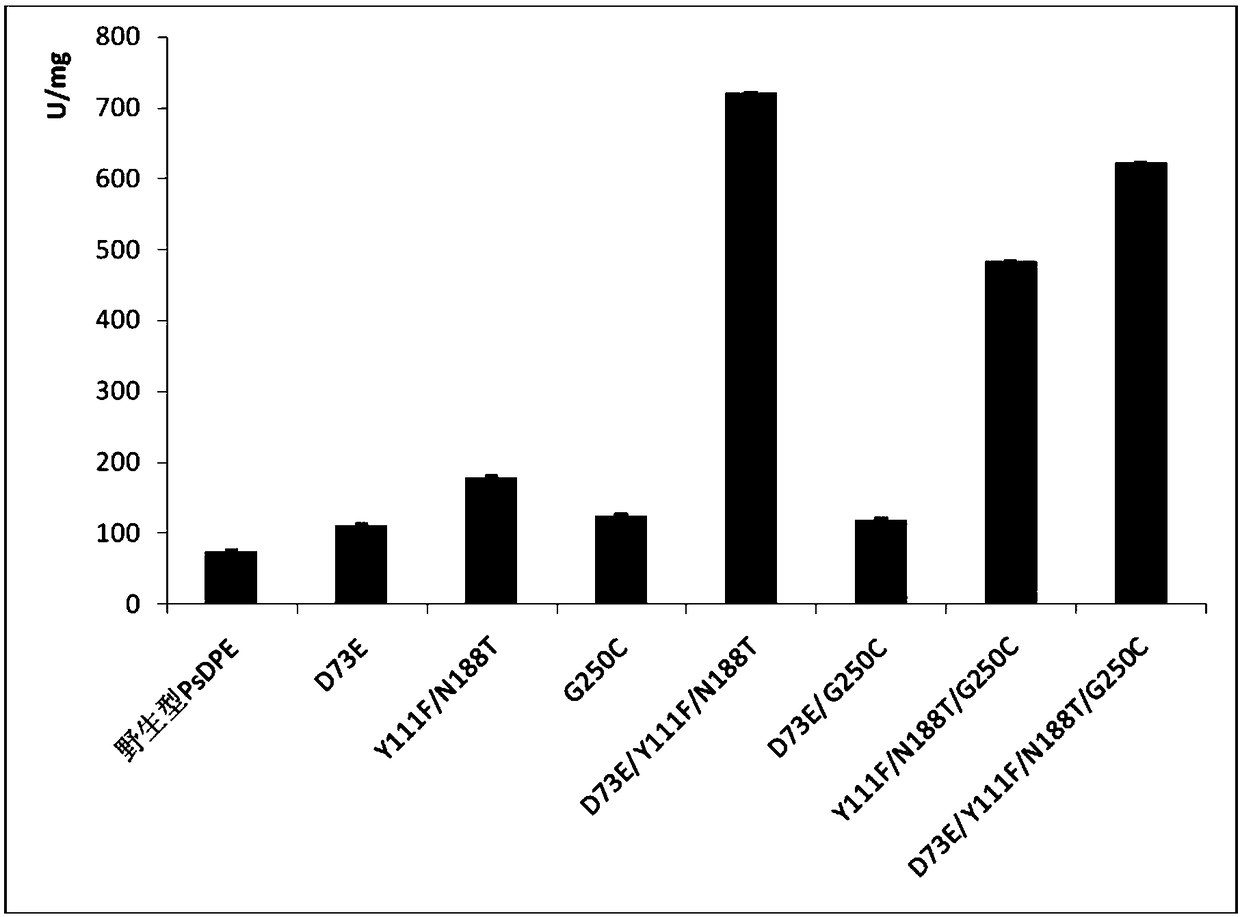
D-psicose-3-epimerase mutant with improved catalytic activity and application of mutant
The invention provides a D-psicose-3-epimerase mutant with improved catalytic activity and an application of the mutant and particularly provides mutational D-psicose-3-epimerase. The mutational D-psicose-3-epimerase is obtained by mutation in at least three loci selected from the following groups: the 73rd aspartic acid (D), the 111st tyrosine (Y), the 188th asparaginate (N) and the 250th glycine(G) of wild D-psicose-3-epimerase corresponding to SEQ ID NO:1. The mutational D-psicose-3-epimerase has very high catalytic activity and catalytic efficiency (reaching up to 29.6%).
Owner:LIVINGZONE SHANGHAI BIO CHEM TECH CO LTD
D-psicose 3-epimerase mutant with improved thermal stability, and continuous production of d-psicose using same
ActiveUS20140199732A1Improve thermal stabilityEfficient productionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWild typePsicose
The present invention relates to a D-psicose 3-epimerase variant with improved thermostability by substituting an amino acid at a specific position of an amino acid sequence of a wild type D-psicose 3-epimerase. Further, the present invention provides a recombinant expression vector including a gene of the D-psicose 3-epimerase variant, and a recombinant strain transformed with the recombinant expression vector. Furthermore, the present invention provides an immobilized reactor prepared using the D-psicose 3-epimerase variant or the recombinant strain, and a method of continuously producing D-psicose using the immobilized reactor.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Preparation method of high-purity D-psicose
InactiveCN107699557AImprove conversion efficiencyReduce manufacturing costMicroorganism based processesIsomerasesChromatographic separationGlucose polymers
The invention relates to a preparation method of high-purity D-psicose. The method comprises the following steps: (a) preparing a D-psicose epimerase crude enzyme preparation; (b) immobilizing the crude enzyme preparation prepared in the step (a) and glucose isomerase; (c) preparing a mixed solution containing D-psicose, fructose and glucose; (d) decolorizing, filtering and hybridizing the mixed solution prepared in the step (c) to obtain a D-psicose solution and a mixed solution of the fructose and the glucose; (e) performing chromatographic separation, concentration, crystallization or drying on the D-psicose solution prepared in the step (d) to obtain D-psicose.
Owner:SHANDONG BAILONG CHUANGYUAN BIO TECH
Compositions and methods for prevention of escape mutation in the treatment of her2/neu over-expressing tumors
This invention provides compositions and methods for treating and vaccinating against a Her2 / neu antigen-expressing tumor and inducing an immune response against dominant in a non-human animal.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
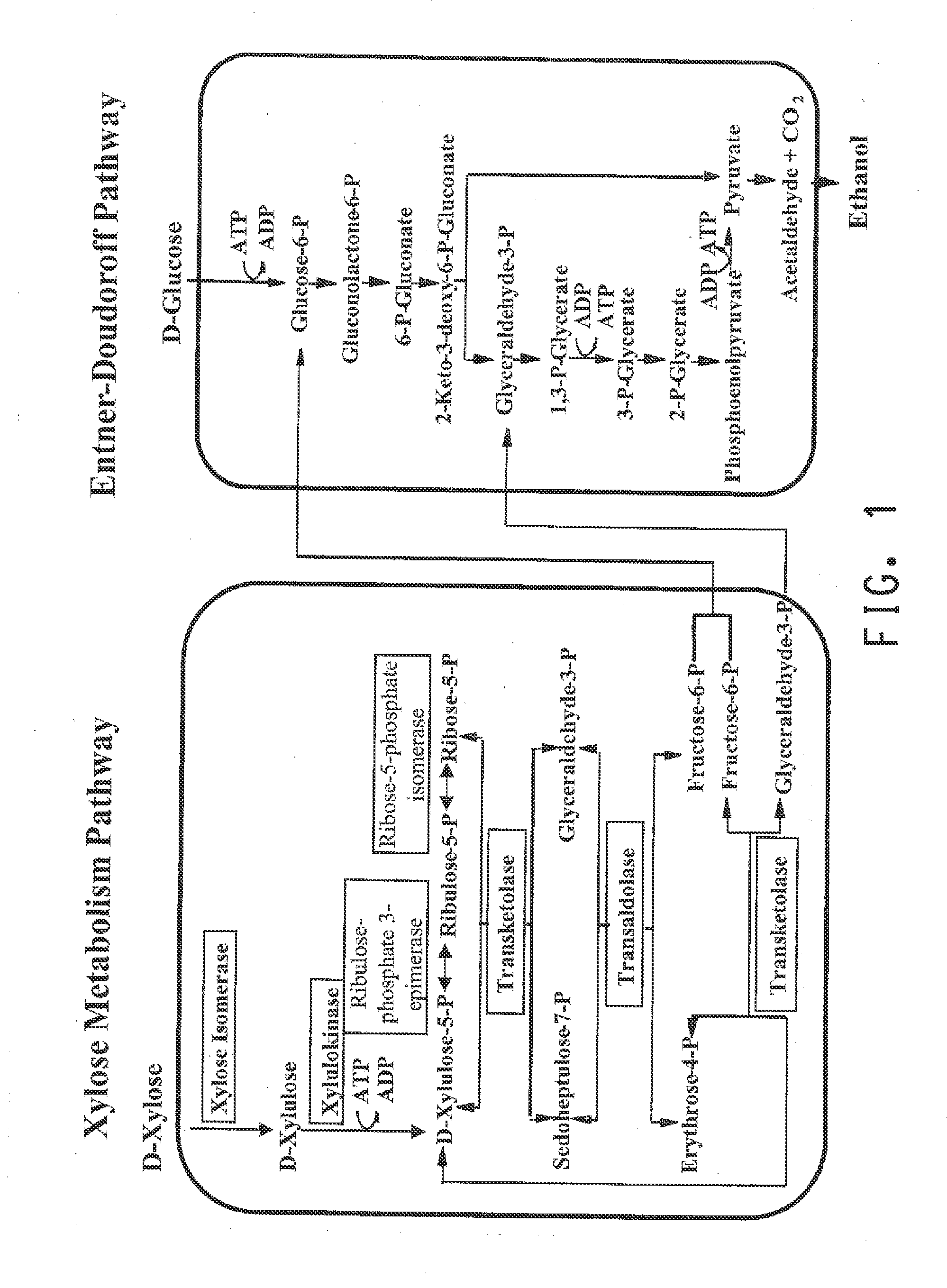
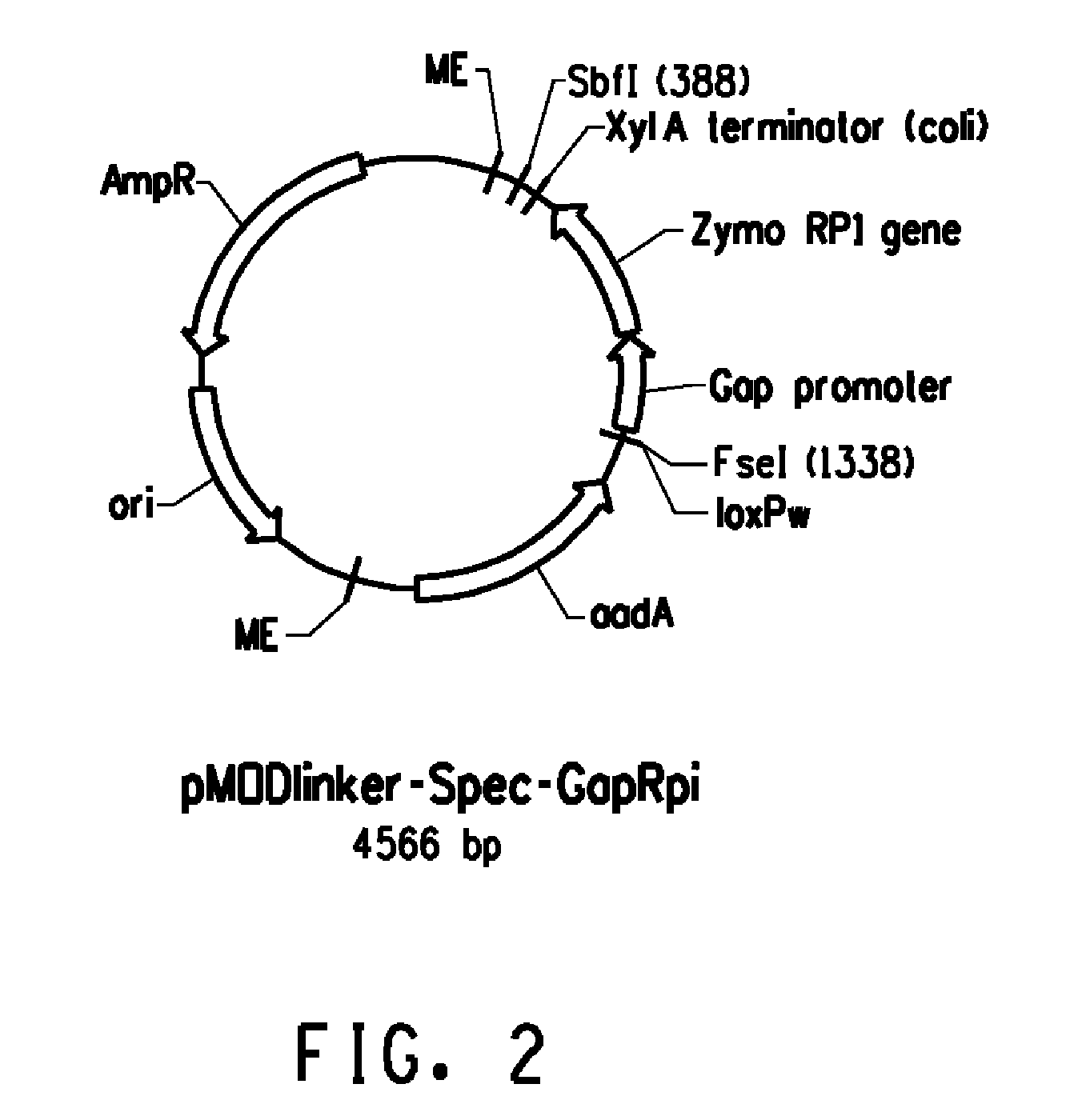
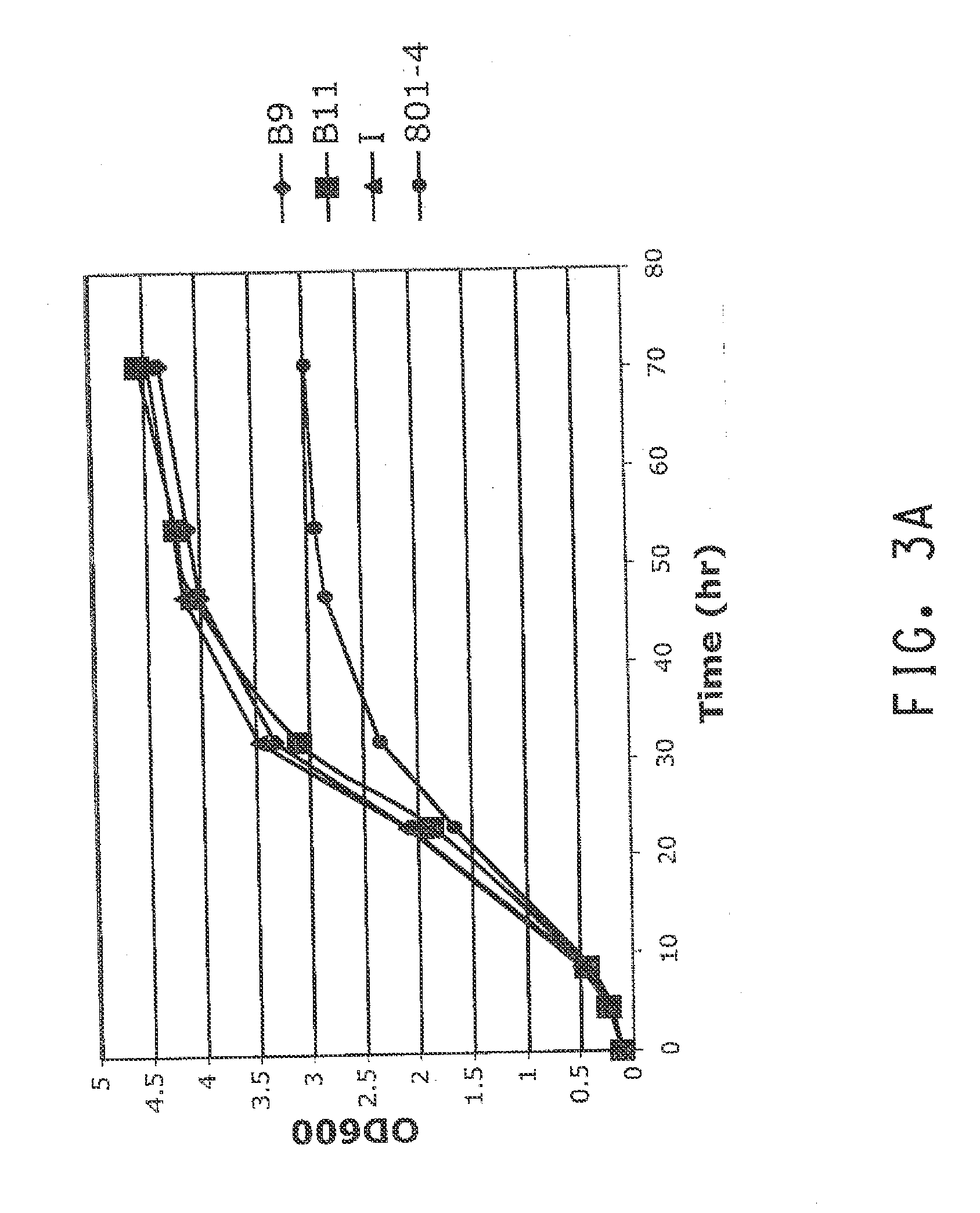
Pnp gene modification for improved xylose utilization in zymomonas
InactiveUS20130157331A1High activityNon-limiting xylose isomerase activityBacteriaTransferasesRibose-5-phosphate isomeraseZymomonas
The endogenous pnp gene encoding polynucleotide phosphorylase in the Zymomonas genome was identified as a target for modification to provide improved xylose utilizing cells for ethanol production. The cells are in addition genetically modified to have increased expression of ribose-5-phosphate isomerase (RPI) activity, as compared to cells without this genetic modification, and are not limited in xylose isomerase activity in the absence of the pnp modification.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE TECH CORP
D-psicose 3-epimerase mutant with improved catalytic efficiency
ActiveCN108018278AHigh catalytic efficiencyIncreased relative enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPsicoseMutant enzyme
The invention discloses a D-psicose 3-epimerase mutant with improved catalytic efficiency and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering. The Dorea sp. DPEase mutant enzyme A38E / G105A keepsthe optimal catalytic conditions. Under the optimal catalytic conditions, the relative enzyme activity of the enzyme for catalytic conversion of D-fructose as a substrate into D-psicose is improved by38.6%. The discovery has an important research value for the industrial production of D-psicose.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Hexuronate C4-epimerase mutant with improved conversion activity, and method for producing D-tagatose by using same
ActiveCN108138161AIncrease productionEfficient manufacturingBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTagatoseHexuronate
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Bifidobacterial gene sequences and their use
This invention provides nucleic acids and proteins involved in oligosaccharide modification in the species Bifidobacteria. The invention provides methods for utilizing the proteins of the invention to generate human milk oligosaccharides or oligosaccharide mimics. The invention also provides compositions containing the human milk oligosaccharides or oligosaccharide mimics and methods for use.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
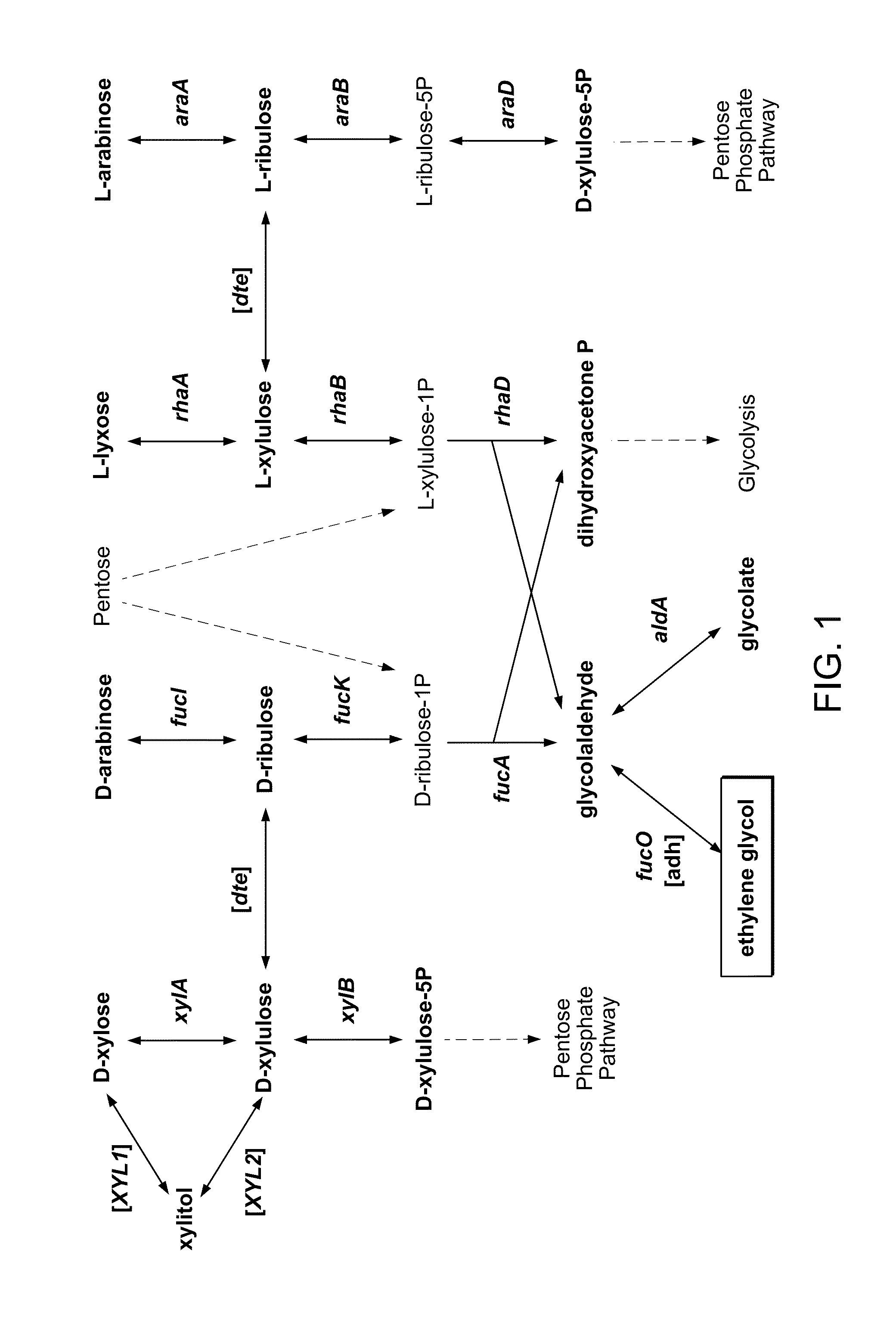
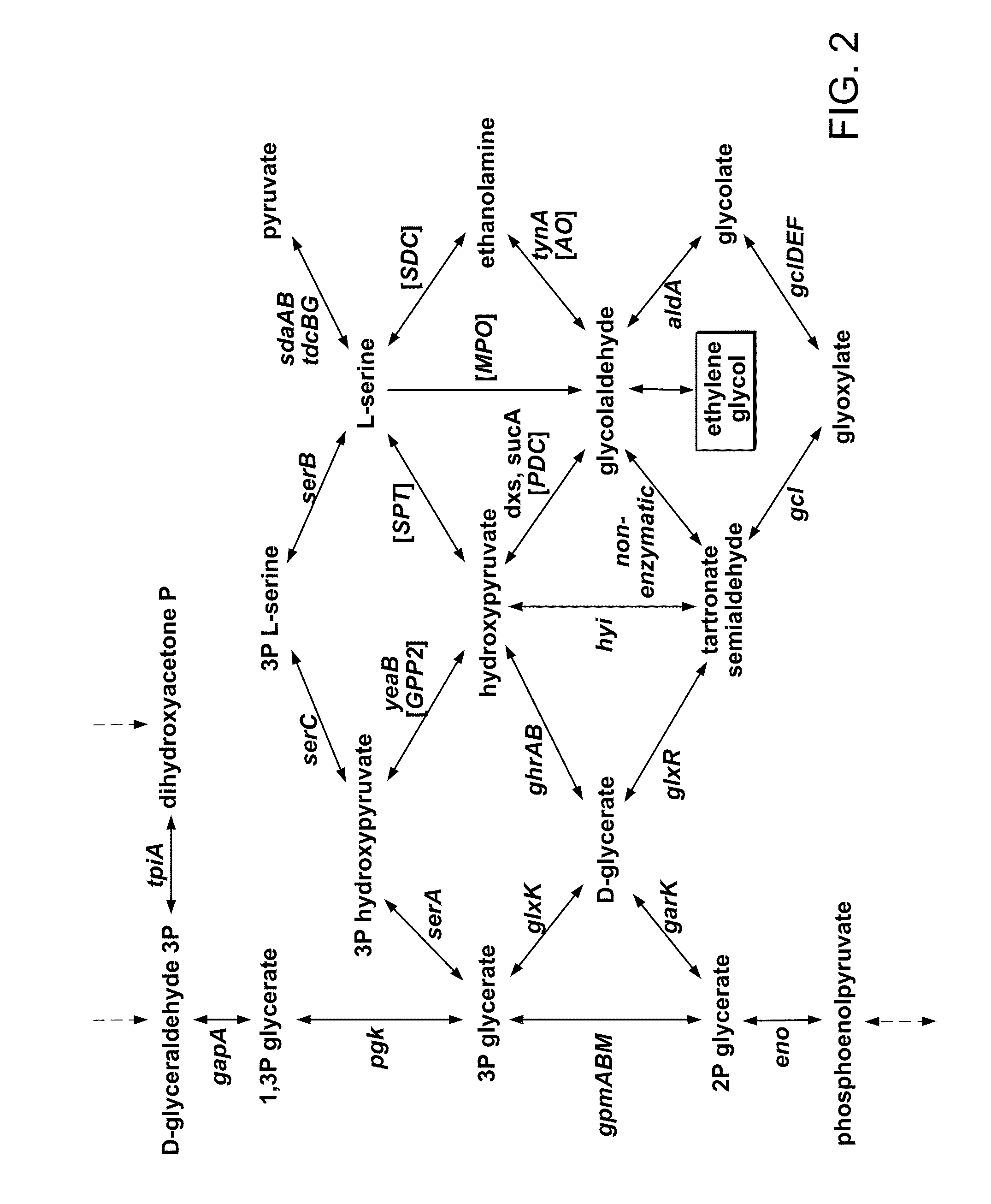
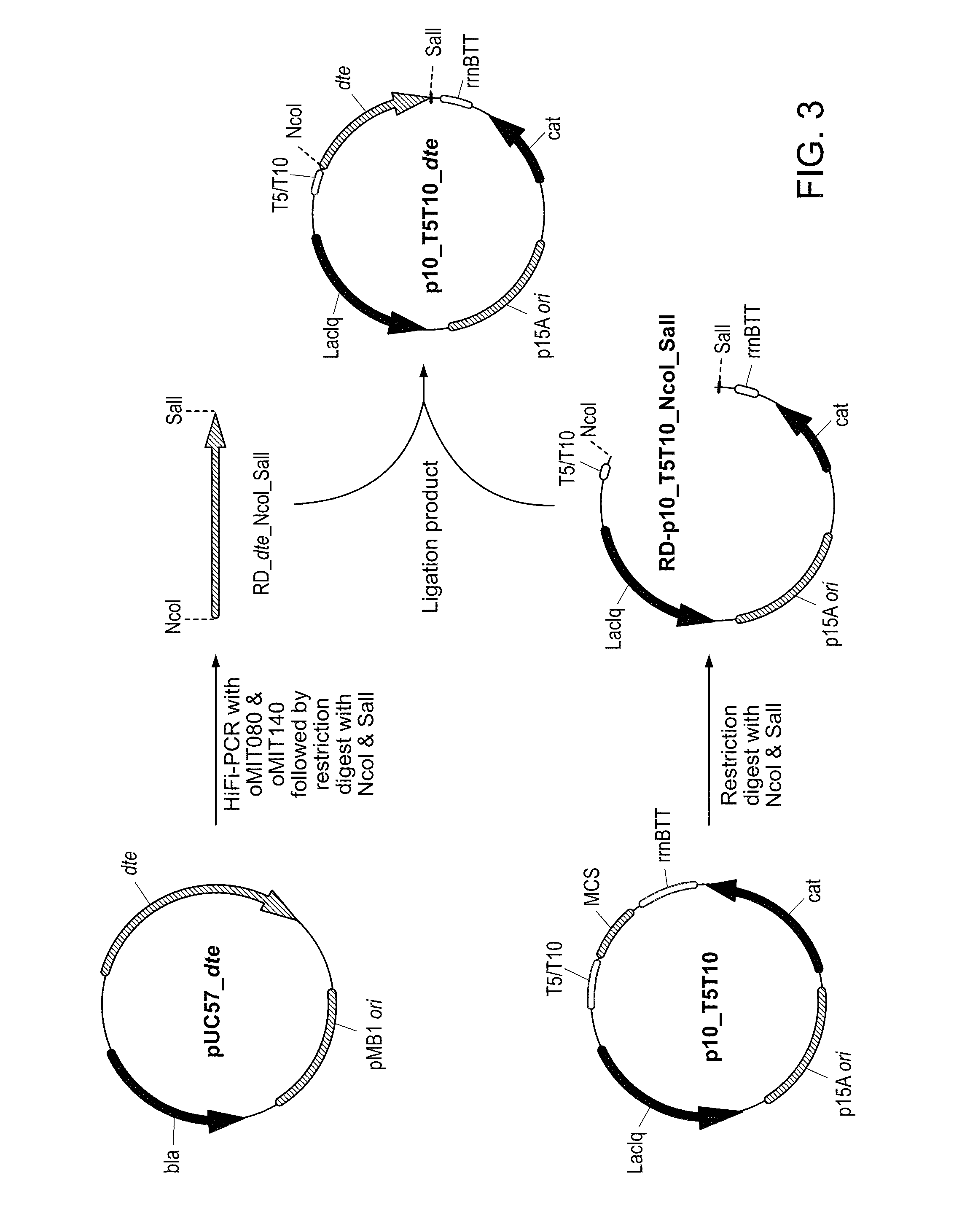
Engineering microbes and metabolic pathways for the production of ethylene glycol
InactiveUS20130316416A1Increasing the amount of 3-phosphoglycerateReducing flux to 2-phosphoglycerateBacteriaHydrolasesMicrobiologyBiochemistry
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
D-psicose 3-epimerase production strain and immobilization method thereof
ActiveCN108102995AGood continuous conversion abilityRealize continuous productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFructoseMicrobiology
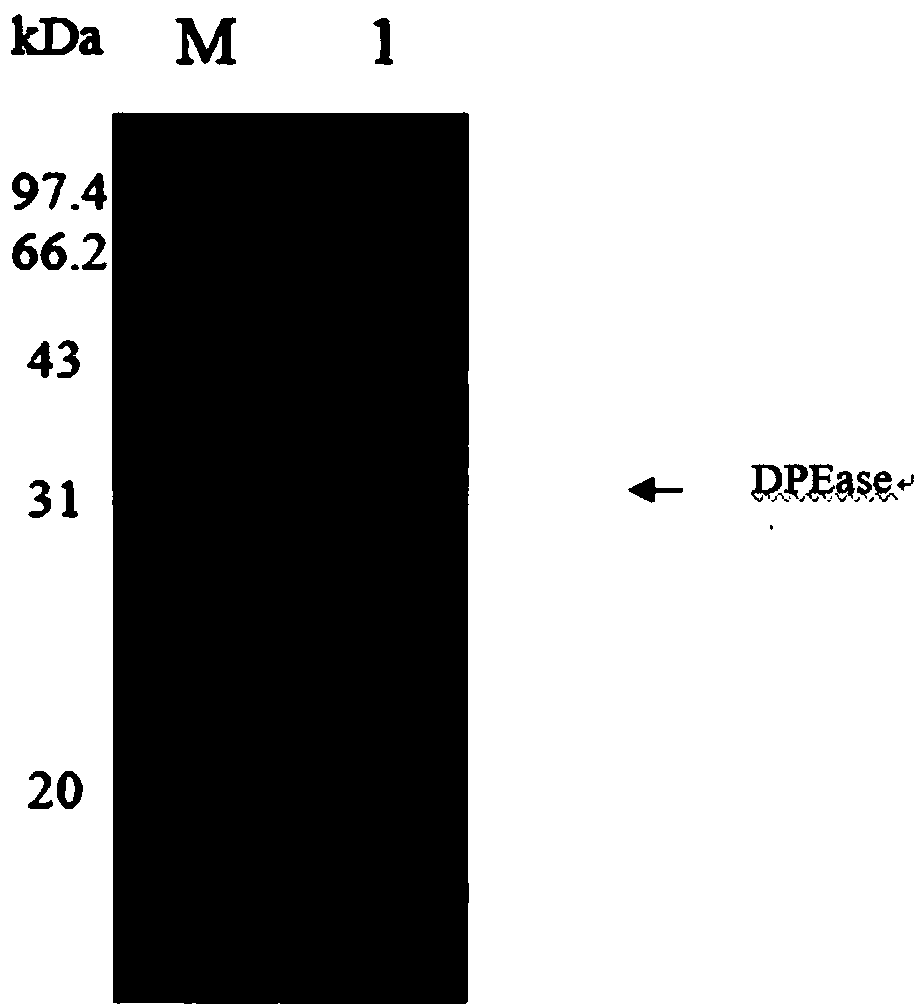
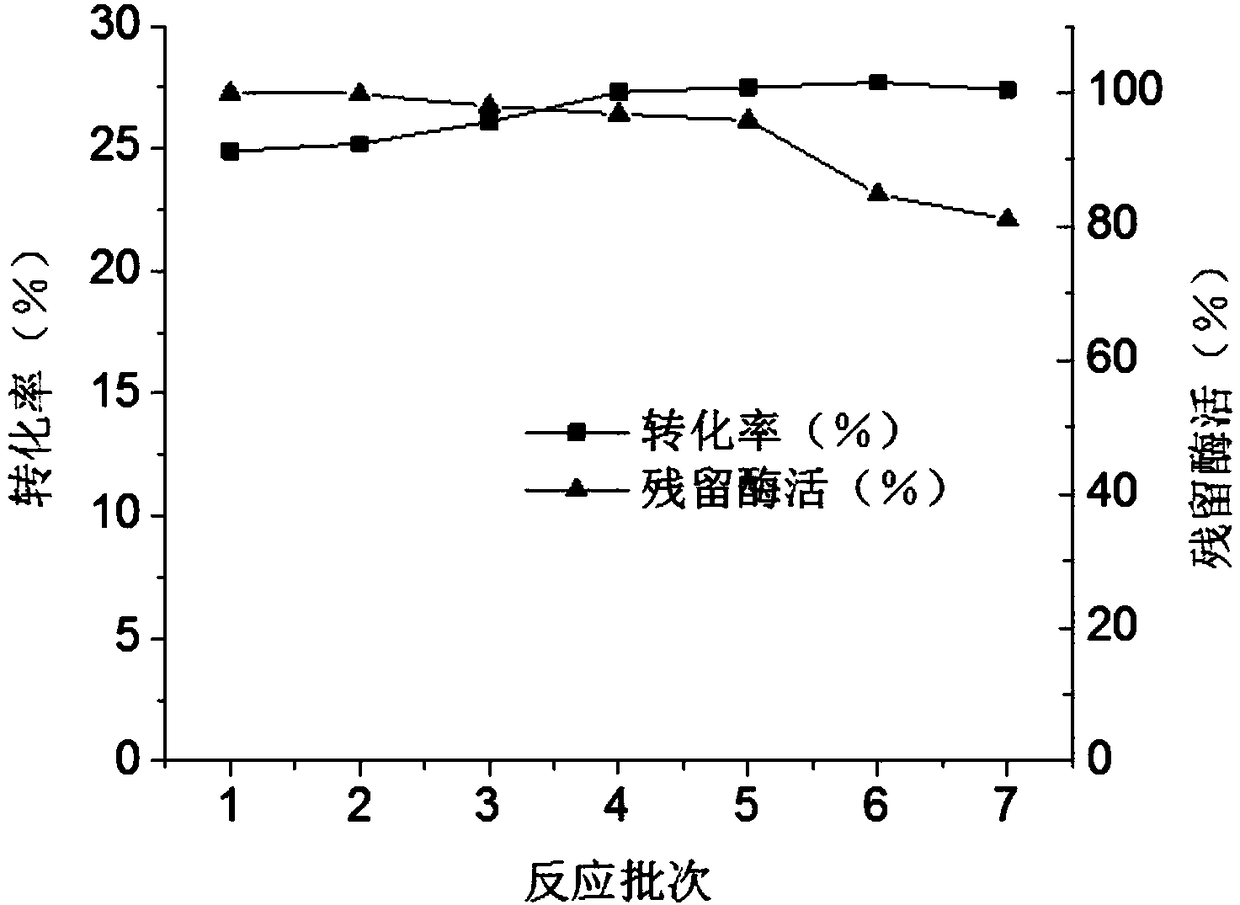
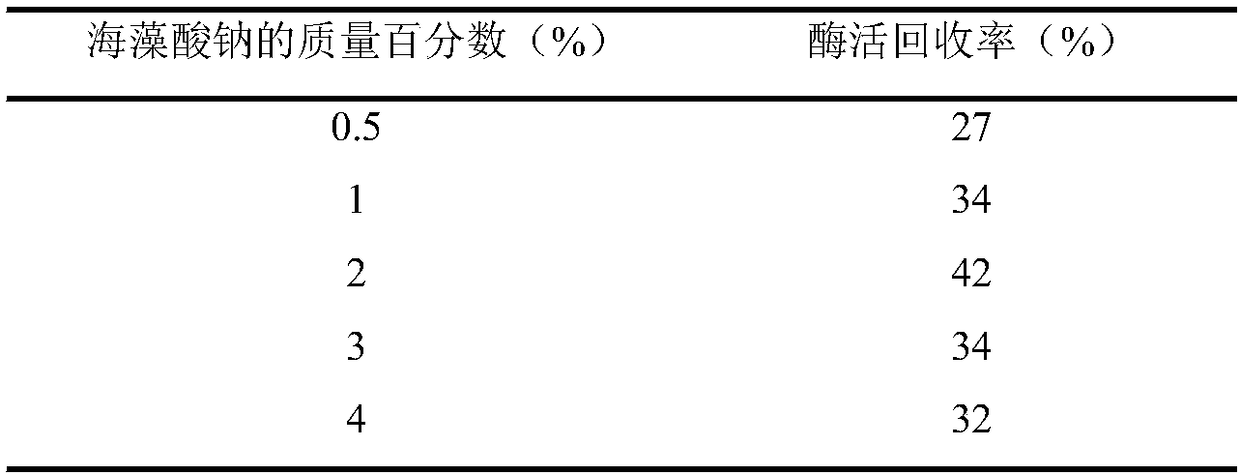
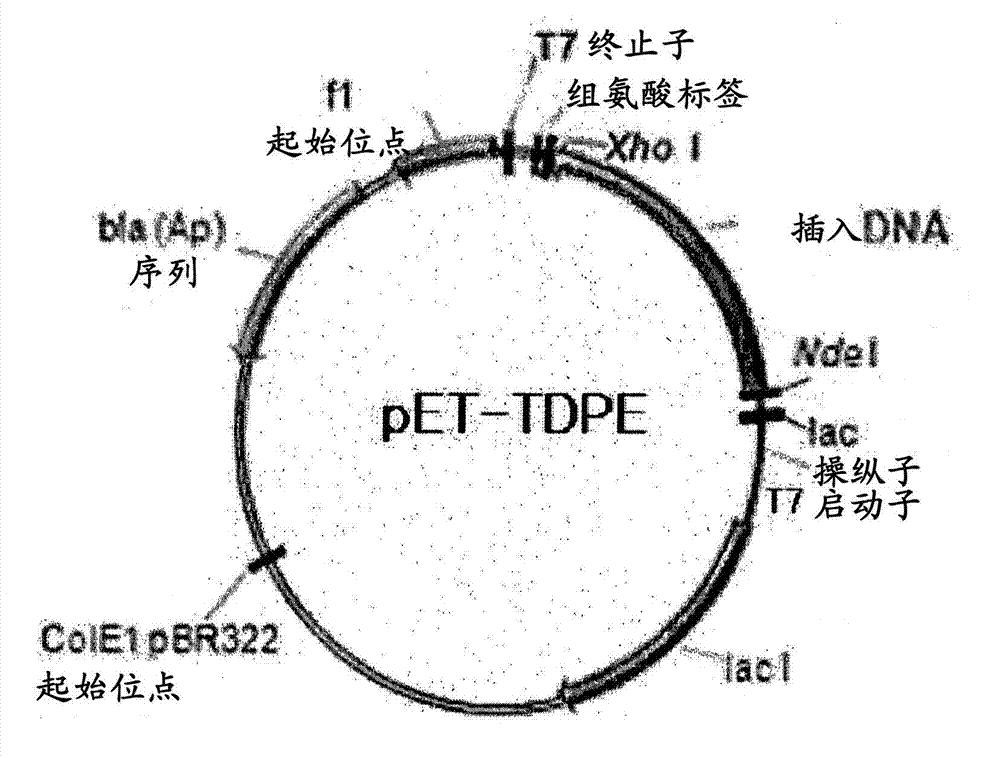
The invention discloses a D-psicose 3-epimerase production strain and an immobilization method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. According to the invention, recombinant bacillus subtilis pHY300PLK-DPEase for producing D-psicose 3-epimerase is constructed, and the recombinant bacterium (the recombinant bacillus subtilis) serves as the production strain; an enzyme activity recovery rate of immobilized cells reaches 64%, the optimum temperature of the immobilized cells is improved by 5 DEG C in comparison with that of whole cells and the optimum pH value of the immobilized cells is free from obvious change; and after continuous conversion with 300g / L of fructose as a substrate for seven times, a conversion rate can be still kept at 28% and residual enzyme activitycan be still kept at 81%. The immobilization method is simple and easy to implement and immobilized particles are excellent in performance; therefore, a quite high industrial application value is achieved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Psicose epimerase and composition for conversion to psicose using same
A D-psicose 3-epimerization enzyme of the present invention is an enzyme with excellent activity for producing psicose by epimerizing a third carbon location of fructose. By applying the enzyme based on the wide pH range useful for industries and stability at high temperatures, the psicose with high economic feasibility can be mass-produced. The enzyme can be applied for producing functional saccharide, and for health food materials, medicines, and cosmetics using the same.
Owner:SAMSANG CORP
Engineering strain for generating allulose, construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN110079488AHigh yieldSuitable for large-scale productionBacteriaHydrolasesO-Phosphoric AcidPhosphate
The invention discloses a construction method of an engineering strain for generating allulose and an application thereof. The construction method comprises the following steps: increasing content ofintracellular fructose 6-phosphoric acid by reducing enzymatic activity of fructose 6-phosphokinase and glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase in corynebacterium glutamicum and enhancing enzymatic activityof glucokinase and glucose 6-phophate isomerase by regulating glucose intracellular metabolism; constructing a synthetic route of allulose composed of 6-aloxone phosphate 3-epimerase and 6-aloxone phosphate phosphorylase; constructing a metabolic pathway of fructose composed of fructose transmittase and fructokinase; constructing a metabolic pathway of glycerinum composed of glycerol transmittase, glycerol dehydrogenase and dihydroxyacetone kinase, thereby acquiring a corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant strain. The strain is capable of metabolizing glycerinum, glucose, fructose or saccharose for synthesizing allulose. Compared with the present reported method for compounding allulose through bioconversion of fructose, the construction method provided by the invention has the advantagesof high conversion rate, low production cost, and the like, and is suitable for large-scale production of allulose.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Novel D-allulose 3-epimerase and application thereof
ActiveCN109306347AImprove conversion rateImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyThermal stability
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and in particular relates to novel D-allulose 3-epimerase, DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) for encoding the novel D-allulose 3-epimerase, an expression vector and a transformant containing the DNA and application of the enzyme to production of D-allulose. The D-allulose 3-epimerase is derived from thermoacidophile mesoaciditoga lauensis of a deep-sea spring and has relatively high conversion rate and thermal stability when being used for converting D-fructose into the D-allulose.
Owner:JILIN COFCO BIOCHEM +1
Hexuronate C4-epimerase mutant with improved conversion activity, and method for producing D-tagatose by using same
A hexuronate C4-epimerase with improved conversion activity and a method for producing D-tagatose using the hexuronate C4-epimerase. The hexuronate C4-epimerase includes an amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1, in which serine (S) at position 125, serine (S) at position 185, valine (V) at position 267, serine (S) at position 268, threonine (T) at position 272, tryptophan (W) at position 306, arginine (R) at position 386 and tyrosine (Y) at position 403 from an N-terminal of hexunorate C4-epimerase are mutated.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
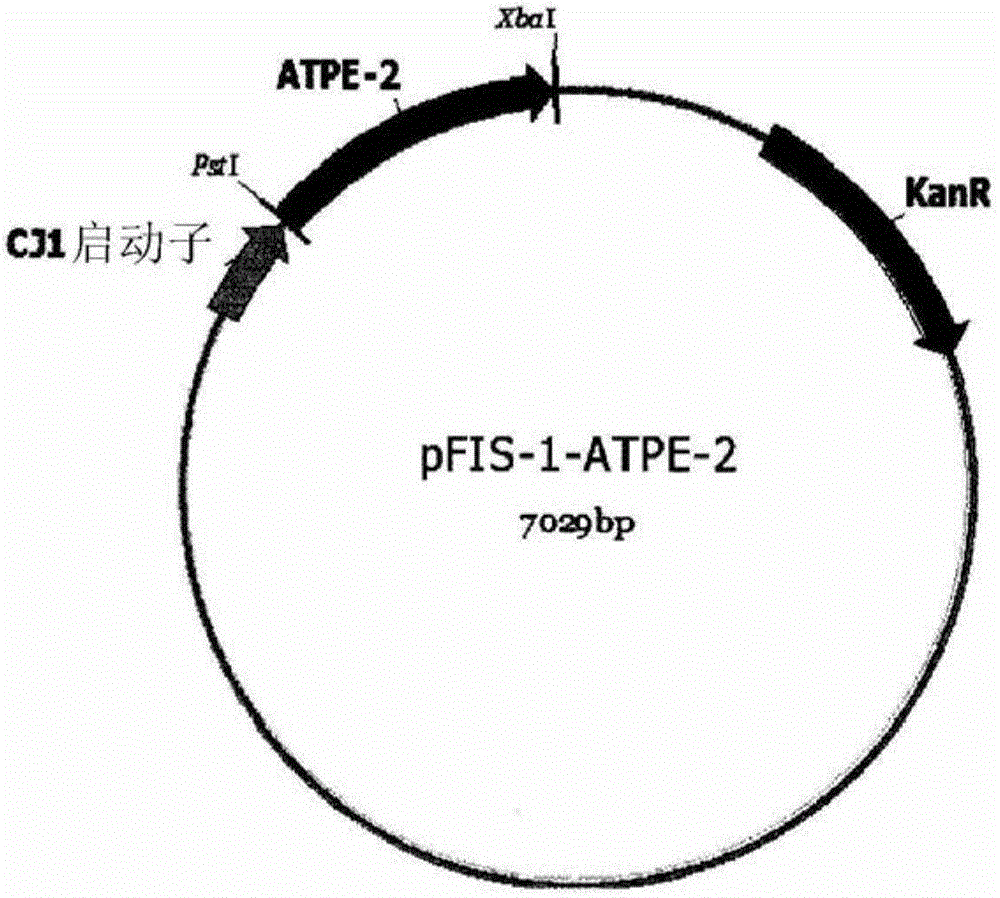
Chassis system for ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) regeneration and application
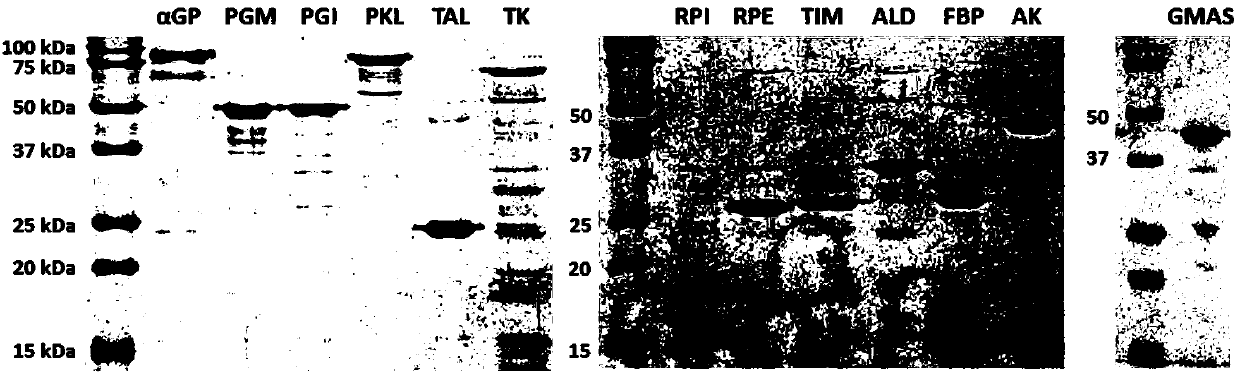
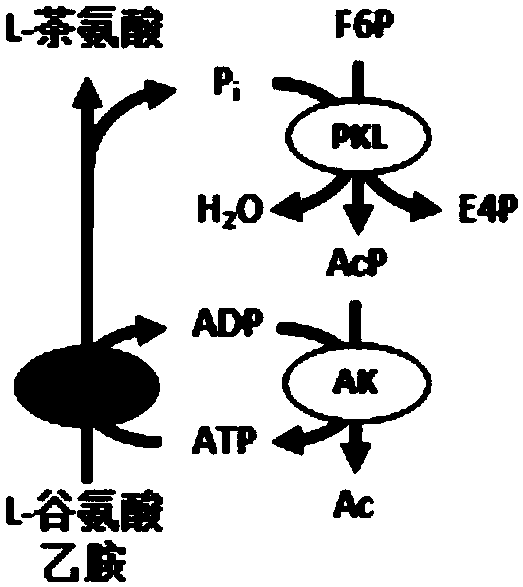
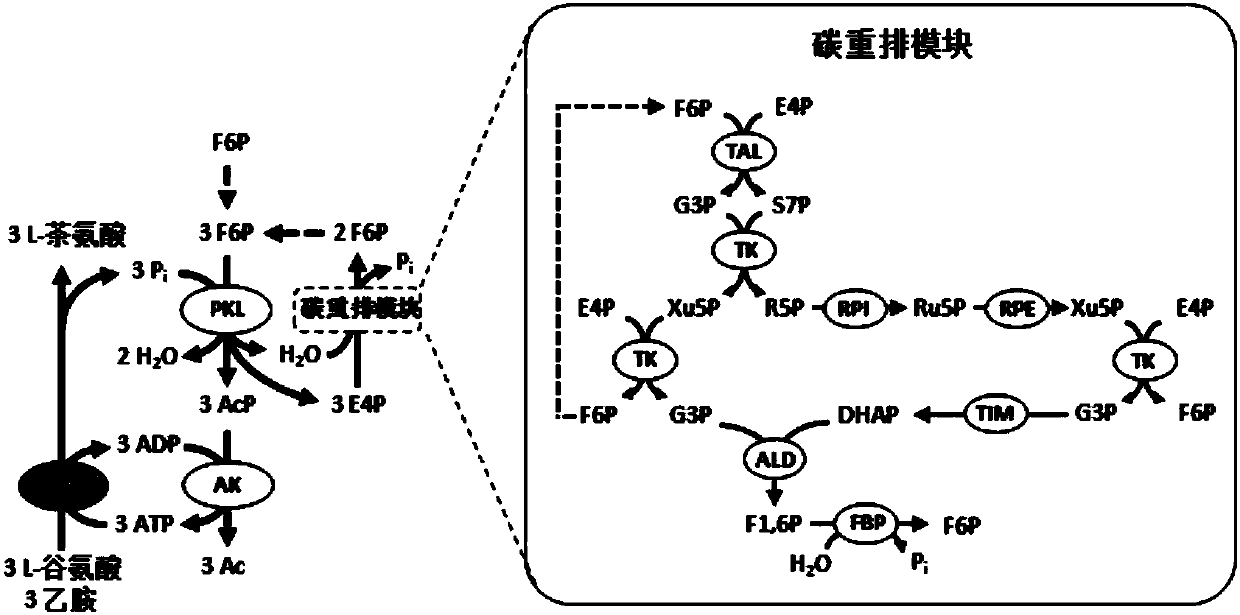
The invention provides a chassis system for ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) regeneration and application. The chassis system for ATP regeneration comprises the following five enzymes: alpha-glucan phosphorylase, glucophosphomutase, phosphoglucose Isomerase, phosphoketolase and acetokinase. In addition, the chassis system can further comprise the following seven enzymes: transaldolase, transketolase,ribose-5-phosphate isomerase, ribulose-3 epimerase, triosephosphate isomerase, fructose-bisphosphate aldolase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. The chassis system can be coupled to an enzymic catalyticreaction needing ATP, utilizes starch or maltodextrin as energy, is not added with any coenzyme, can efficiently regenerate the ATP at low cost through a one-pot reaction and is an economical, highlyefficient, stable and sustainable ATP regeneration system.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Psicose Epimerase and Psicose Production Method Using Same
ActiveUS20170101637A1Little or no activityImprove thermal stabilityRacemaces/epimerasesIsomerasesFructosePsicose
The present invention provides a novel psicose epimerase derived from Flavonifractor plautii and capable of converting fructose to psicose. The novel psicose epimerase according to the present invention possesses an activity producing psicose by epimerizing the carbon-3 position of fructose, and has maximal activity for the conversion of fructose to psicose at a relatively high temperature and a pH less than or equal to neutral, has excellent thermal stability, and can mass-produce psicose from fructose in a high yield for a short amount of time. Therefore, the psicose epimerase according to the present invention is advantageous in the industrial production of psicose, and it is expected that the psicose produced thereby can be usefully utilized in the functional sugar industry and also as materials for health food, medicine, cosmetics, and the like using the psicose.
Owner:DAESANG
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid as well as construction and application of genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN113817658AIncrease production intensityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a genetically engineered bacterium for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid through xylose induction. Escherichia coli is used as a starting strain, an N-acetylglucosamine synthesis pathway is integrated on a genome, an N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase gene bAGE and an N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase gene neuB from collar algae are introduced, an N-acetylneuraminic acid synthesis pathway is constructed, and a key gene nano ATEK of a catabolism pathway of the N-acetylneuraminic acid is knocked out. Meanwhile, metabolic pathways of precursor substances required by synthesis of the N-acetylneuraminic acid are subjected to multi-copy reinforcement, part of bypass metabolic pathways are knocked out, key enzyme genes for producing GlcNAc and Neu5Ac are optimized according to different copy numbers, the optimal proportion of the key enzyme genes is finally determined, and the high-yield strain of the N-acetylneuraminic acid is obtained. The highest yield of the N-acetylneuraminic acid can reach 28g / L, the highest production intensity can reach 0.67 g / (L*h) which is the highest value reported at present, and the N-acetylneuraminic acid has important industrial application value.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Methods for constructing antibiotic resistance free vaccines
The present invention provides Listeria vaccine strains that express a heterologous antigen and a metabolic enzyme, and methods of generating same.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
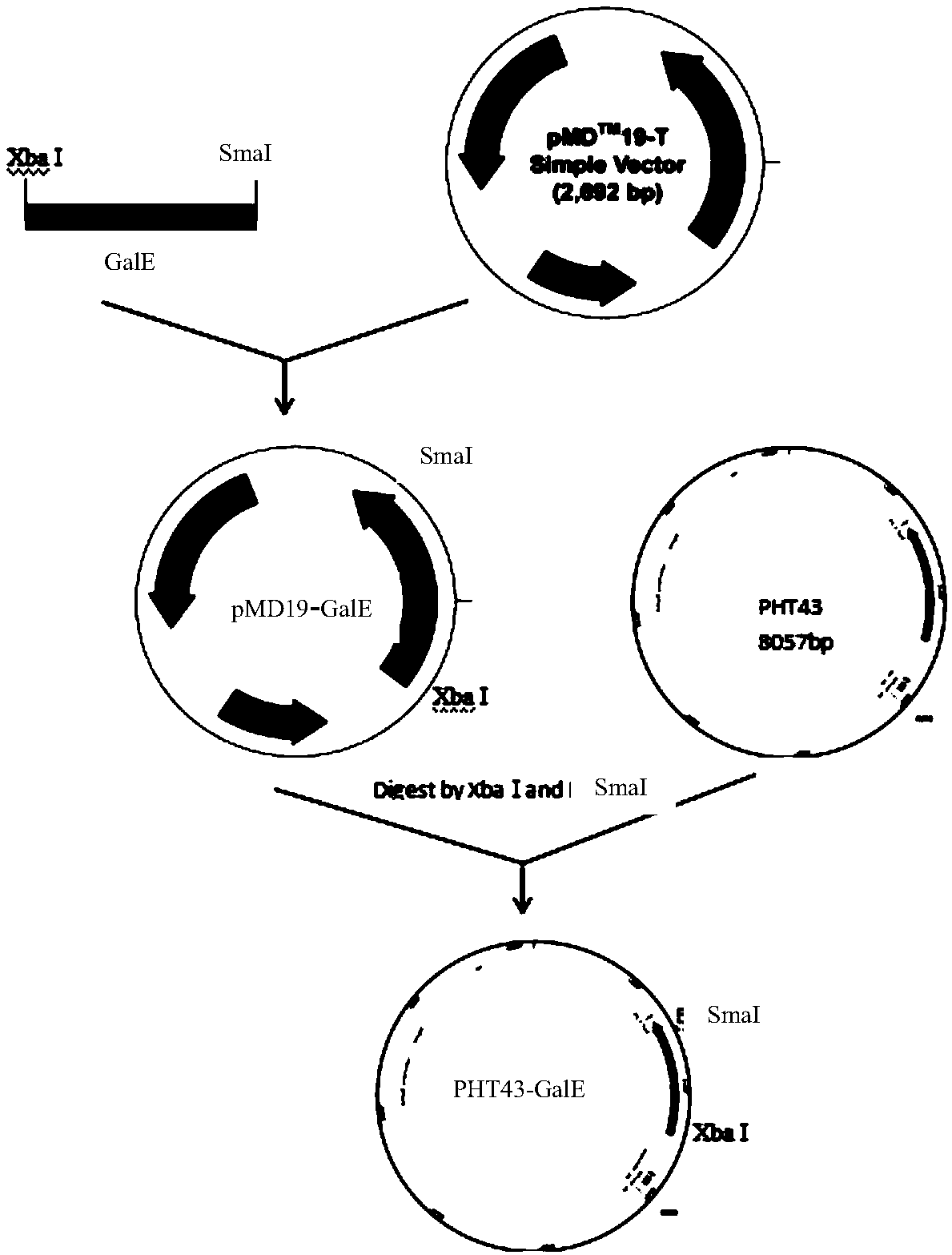
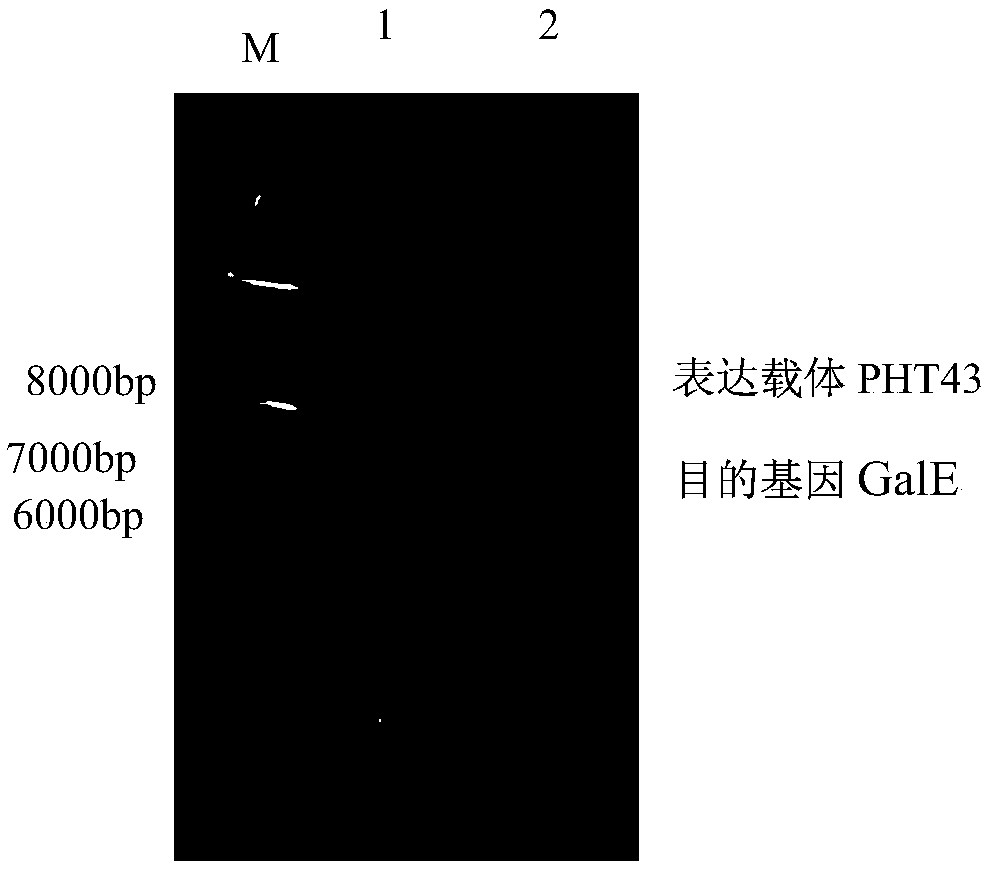
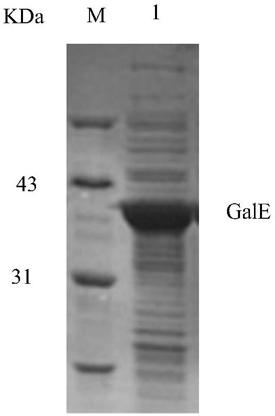
Method for efficiently expressing preparation of UDP-glucose-4-epimerase
ActiveCN109402152AStrong ability to secrete proteinEasy to trainBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFood industry
The invention relates to a method for efficiently expressing preparation of UDP-glucose-4-epimerase. The method comprises the steps that a recombinant expression vector is constructed by using a UDP-glucose-4-epimerase (GalE) gene and a carrier of bacillus subtilis; the recombinant expression vector is then transformed into the bacillus subtilis to construct recombinant engineered bacteria; and the recombinant engineering bacteria are induced to culture in a liquid medium, bacterial liquid is centrifuged, and liquid supernatant is taken. The method has a high yield of the UDP-glucose-4-epimerase, relatively pure proteins, easy recovery and purification and simple production operation, and provides convenience for industrial large-scale production of GalE, output is improved, time and laborare saved, and the cost is saved. In particular, security assurance is provided for the application of the UDP-glucose-4-epimerase in the food industry, and great significance is achieved.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com