Chassis system for ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) regeneration and application
A chassis, glucose phosphate technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, enzymes, isomerases, etc., can solve problems such as increasing the production cost of target products, and achieve sustainable ATP regeneration, low production costs, and low separation costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
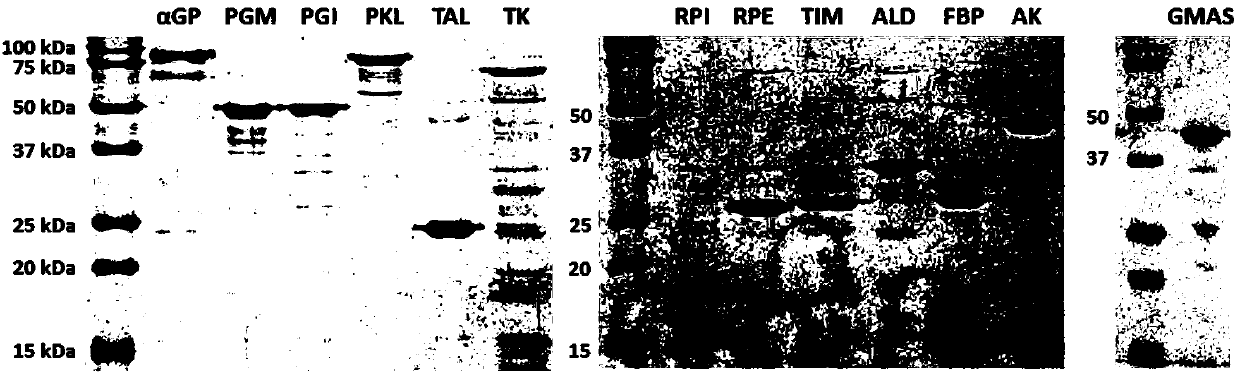
[0042] The enzyme involved in the ATP regeneration system of embodiment 1 and the enzyme used to produce L-theanine - Preparation of glutamine synthetase.
[0043] The construction of the expression vector of the enzyme of the ATP regeneration chassis system: using the corresponding genomic DNA (purchased from ATCC) as a template, using PCR to obtain the gene of the enzyme, and by simple cloning (Simple Cloning) method (You et al.ApplEnviron Microbiol 2012 78(5):1593-5) respectively cloned the genes into pET vectors (Novagen, Madison, WI) to obtain the corresponding expression vectors for each enzyme.
[0044] - Glutamine synthetase from Methylovorus mays. After preparing the expression vector gmas / pET21a according to the method of Liu et al. (ProcessBiochemistry 2016 51(10):1458-63), the terminator of the gmas gene was removed by site-directed mutagenesis, and the C-terminus of GMAS with a histidine tag was obtained. Expression vector. The primers used for site-directed...
Embodiment 2
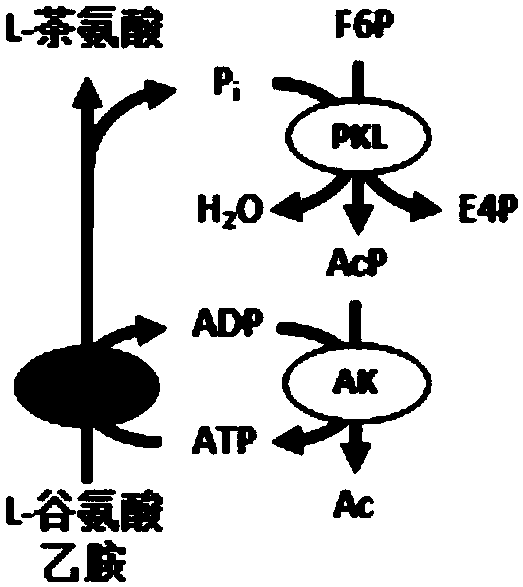
[0054] Example 2 uses fructose 6-phosphate and phosphate as energy sources to regenerate ATP and produce L-theanine. Fructose 6-phosphate is one of the intermediate products of the ATP regeneration chassis system in the present invention, and can replace maltodextrin as an energy substrate for ATP regeneration.
[0055] Configure a 1ml reaction system in a screw bottle, the system contains 200mM HEPES buffer at pH 7.2, 5mM sodium phosphate at pH 7.2, 10mM magnesium chloride, 0.5mM manganese chloride, 1mM thiamine pyrophosphate, 1mM ADP, 30 mM sodium glutamate, 60 mM ethylamine hydrochloride, 5 mM fructose 6-phosphate. Experimental group 1 was an ATP regeneration system containing only PKL, AK, and GMAS enzymes ( figure 2 ), the concentration of each enzyme in the reaction system (concentration of enzyme activity unit) is 2U / ml. Experimental group 2 is an ATP regeneration system with carbon rearrangement modules added. In addition to the above three enzymes at the same conce...
Embodiment 3
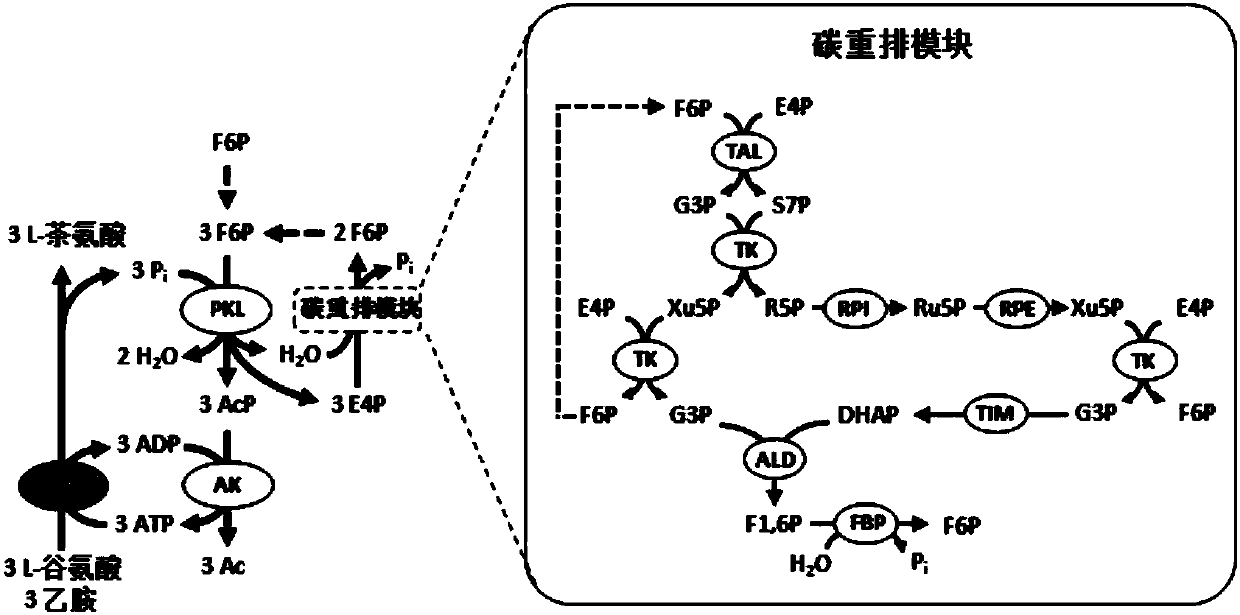
[0057] Example 3 uses maltodextrin and phosphate as energy sources to regenerate ATP and produce L-theanine.
[0058] Configure a 1ml reaction system in a screw bottle, the system contains 200mM HEPES buffer at pH 7.2, 5mM sodium phosphate at pH 7.2, 10mM magnesium chloride, 0.5mM manganese chloride, 1mM thiamine pyrophosphate, 1mM ADP, 30 mM sodium glutamate, 60 mM ethylamine hydrochloride, contains 6.3 mM glucose equivalent maltodextrin (DE 4-7). Experimental group 1 was an ATP regeneration system containing only αGP, PGM, PGI, PKL, AK and GMAS ( Figure 5 ), the concentration of each enzyme in the reaction system was 2U / ml. Experimental group 2 is an ATP regeneration system with carbon rearrangement modules added. In addition to the above 6 enzymes at the same concentration, TAL, TK, RPI, RPE, TIM, ALD, FBP ( Figure 6), the concentration of each enzyme in the carbon rearrangement module in the reaction system is 1U / ml. Samples were taken at 37°C for 0, 1, 3, 6, and 8 ho...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com