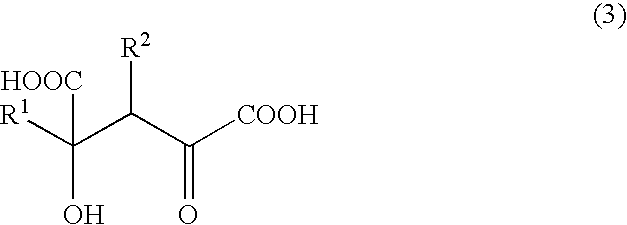Patents
Literature
80 results about "Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase (EC 4.1.2.13), often just aldolase, is an enzyme catalyzing a reversible reaction that splits the aldol, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, into the triose phosphates dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P). Aldolase can also produce DHAP from other (3S,4R)-ketose 1-phosphates such as fructose 1-phosphate and sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphate. Gluconeogenesis and the Calvin cycle, which are anabolic pathways, use the reverse reaction. Glycolysis, a catabolic pathway, uses the forward reaction. Aldolase is divided into two classes by mechanism.
Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase regulatory sequences for gene expression in oleaginous yeast
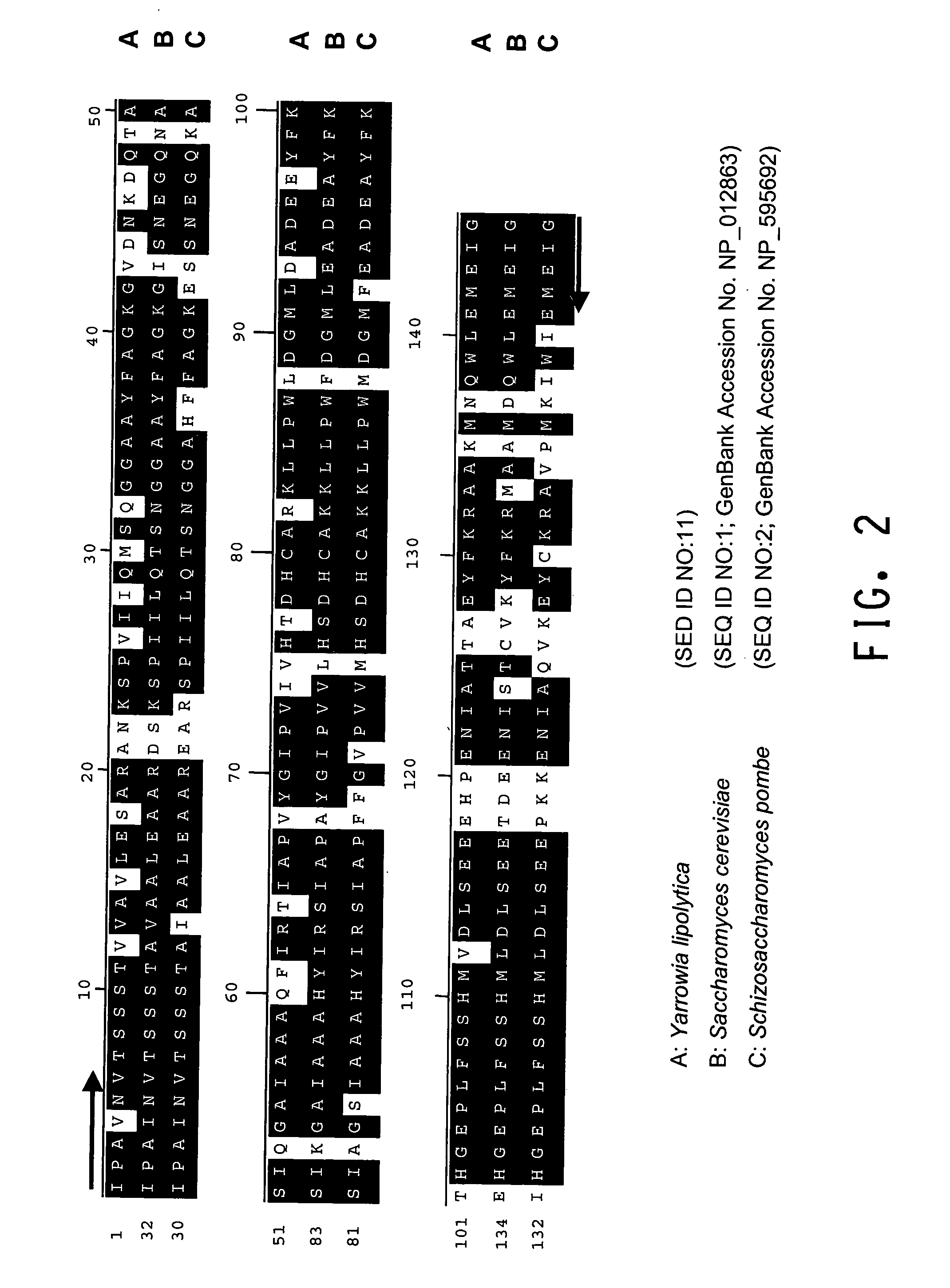
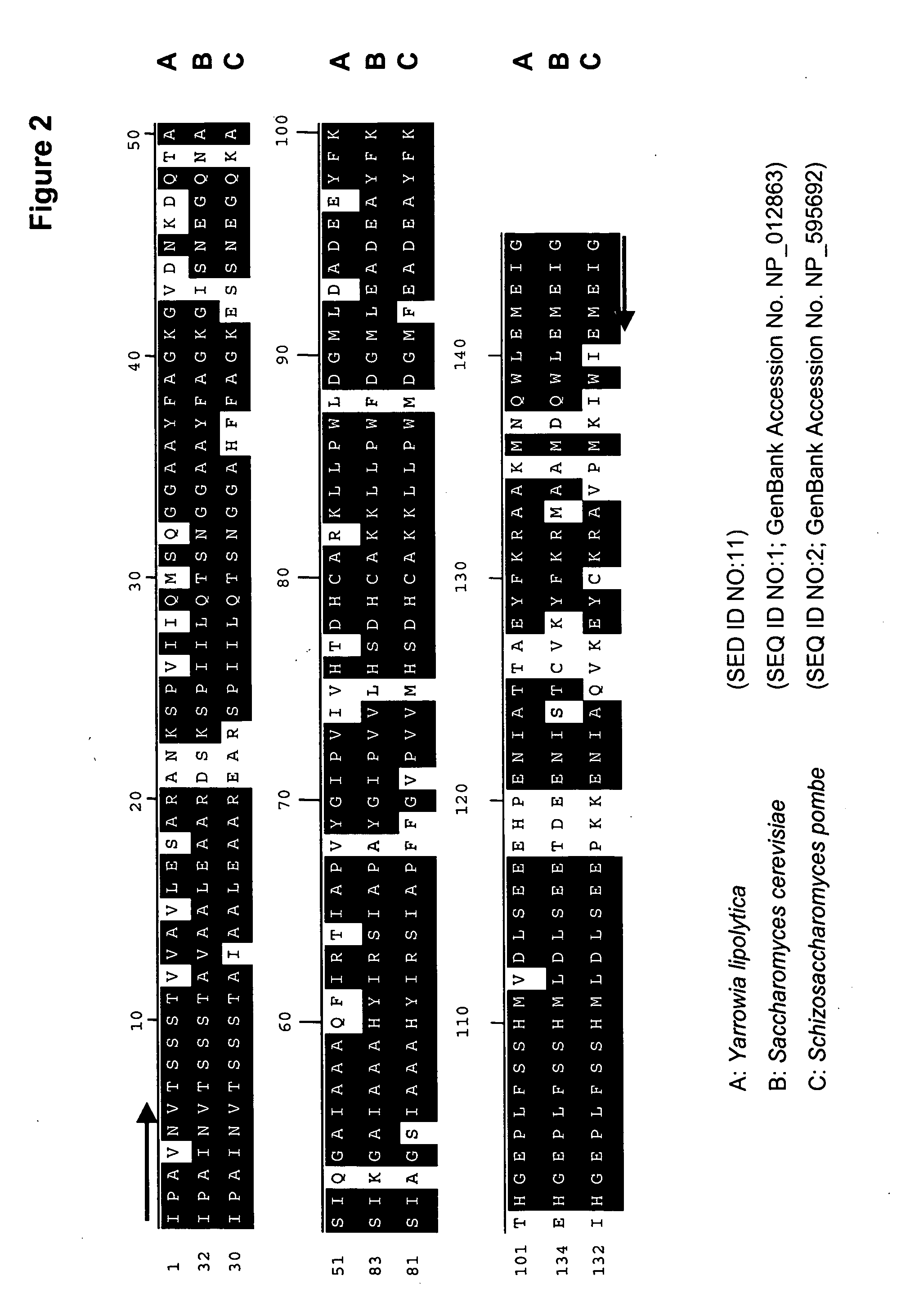
The regulatory sequences (i.e., promoter regions, introns and enhancers) associated with the Yarrowia lipolytica gene encoding fructose bis-phospate aldolase (FBA1) have been found to be particularly effective for the expression of heterologus genes in oleaginous yeast. The promoter regions of the invention have been shown to drive high-level expression of genes involved in the production of ω-3 and ω-6 fatty acids.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
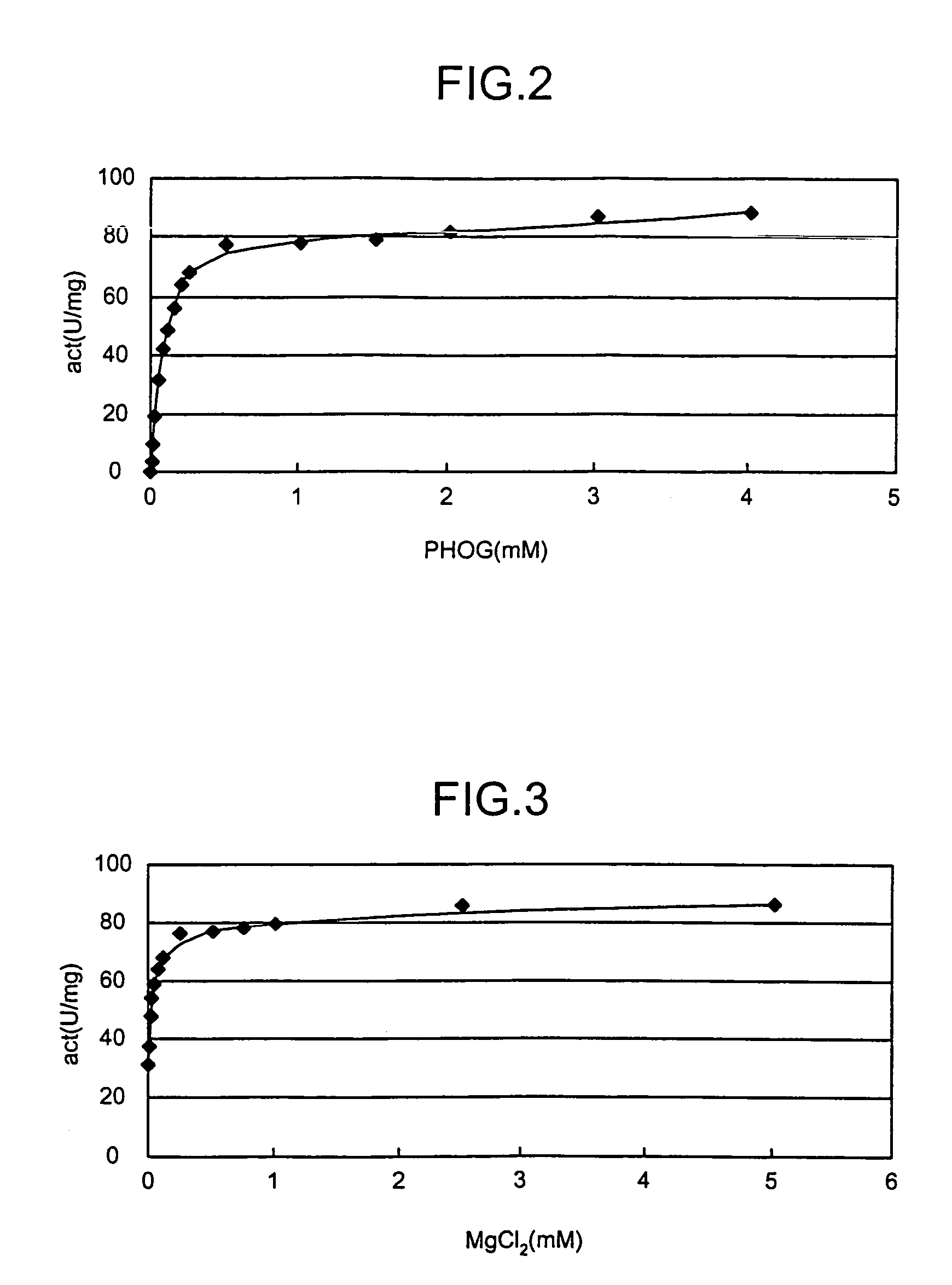
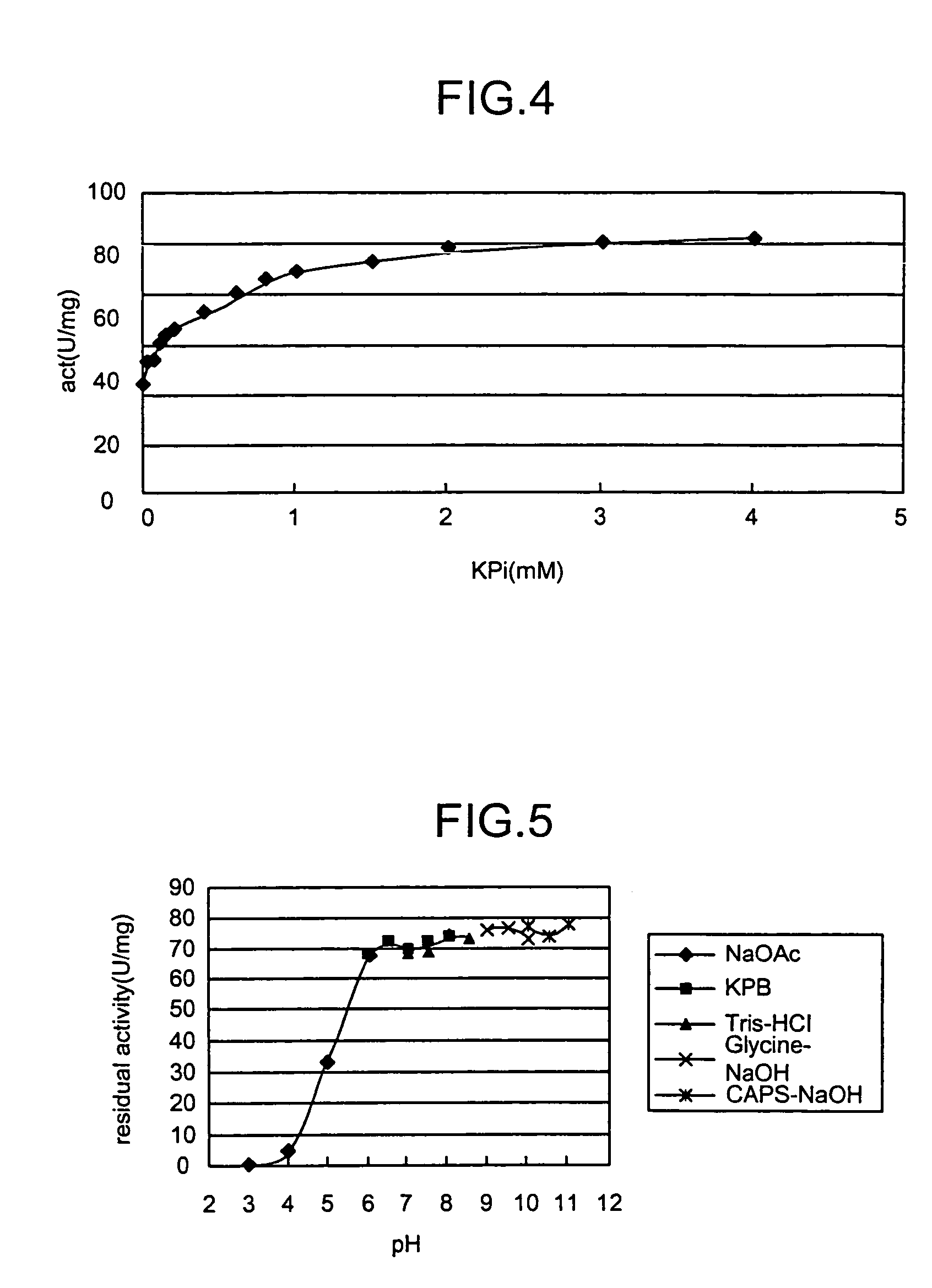
Novel aldolase and production process of substituted alpha-keto acids
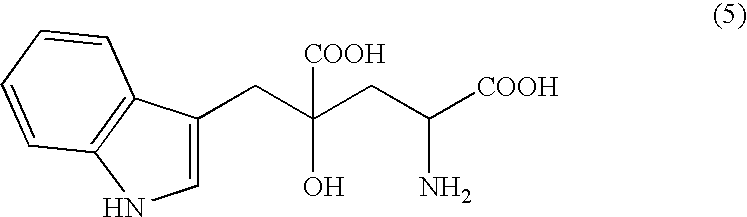
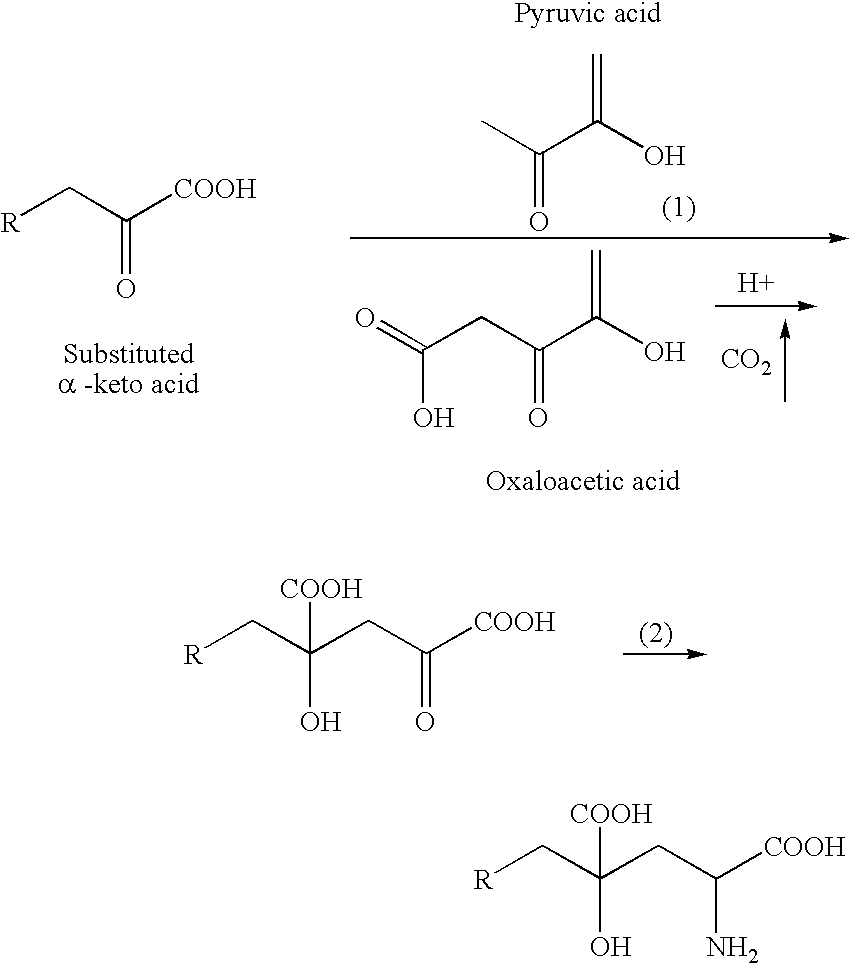
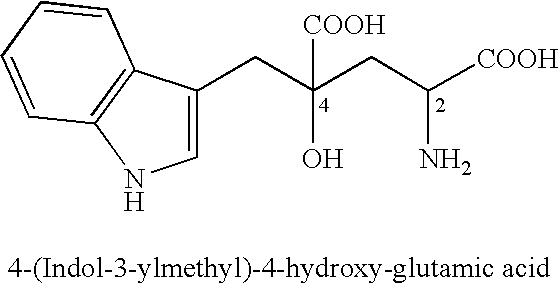
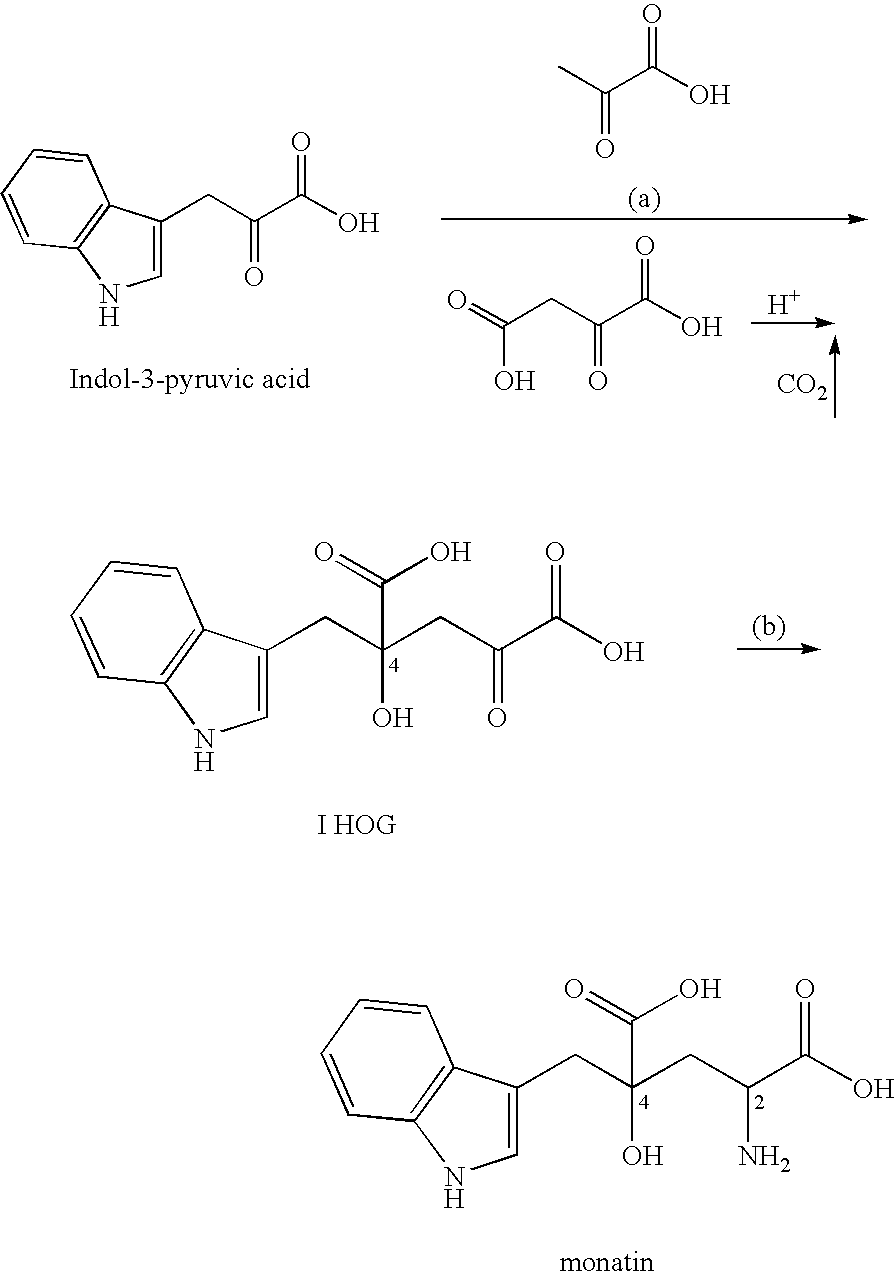
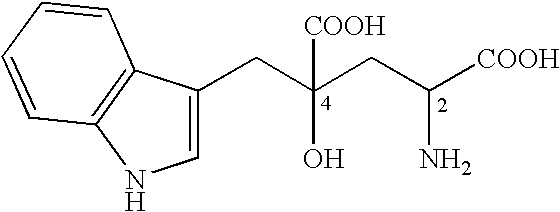
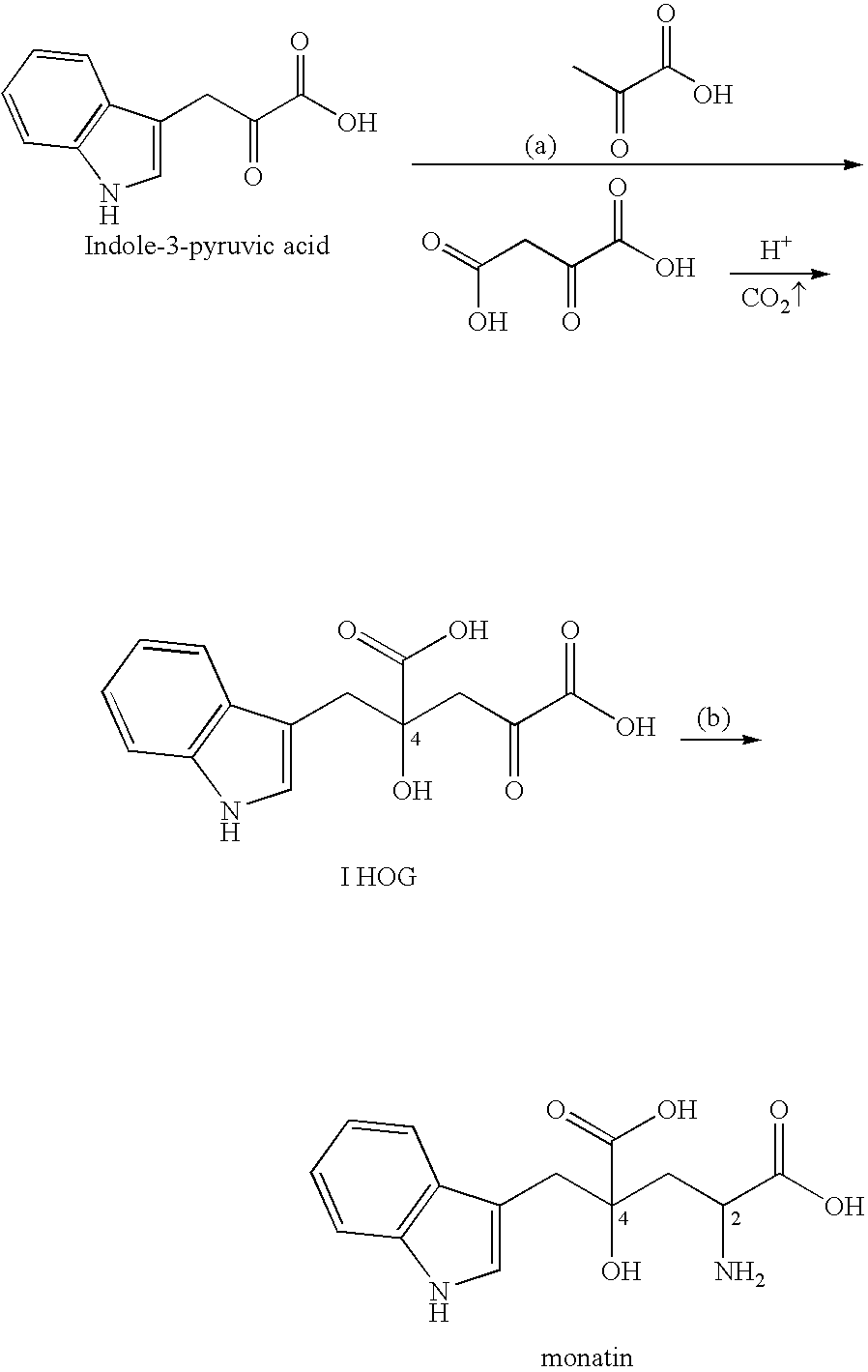
4-(Indol-3-ylmethyl)-4-hydroxy-2-oxoglutarate, which is useful as an intermediate in the synthesis of monatin, may be synthesized from indole pyruvic acid and pyruvic acid (and / or oxaloacetic acid) by using a novel aldolase derived from the genus Pseudomonas, Erwinia, Flavobacterium, or Xanthomonas.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
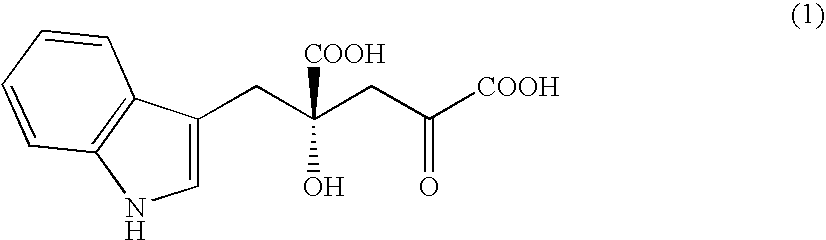
Novel aldolase, and method for producing optically active IHOG and monatin
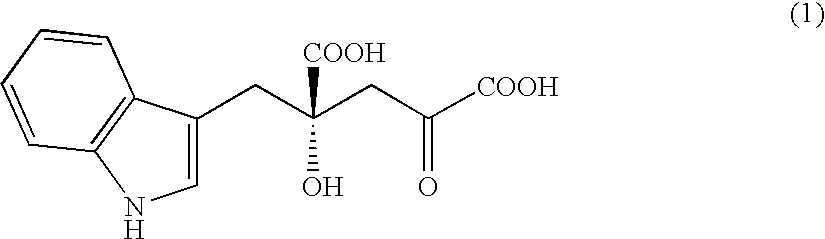
The present invention relates to a method for producing optically active IHOG, which can in turn be used for the production of monatin. The present invention further relates to a method for producing optically active monatin, and aldolase used for these methods. As such, the present invention enables the synthesis of 4-(Indole-3-ylmethyl)-4-hydroxy-2-oxoglutaric acid with high optical purity, which is useful as an intermediate in the synthesis of optically active monatin, from indole pyruvic acid and pyruvic acid (or oxaloacetic acid).
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Novel aldolase, and method for producing optically active IHOG and monatin
The present invention relates to a method for producing optically active IHOG, which can in turn be used for the production of monatin. The present invention further relates to a method for producing optically active monatin, and aldolase used for these methods. As such, the present invention enables the synthesis of 4-(Indole-3-ylmethyl)-4-hydroxy-2-oxoglutaric acid with high optical purity, which is useful as an intermediate in the synthesis of optically active monatin, from indole pyruvic acid and pyruvic acid (or oxaloacetic acid).
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase regulatory sequences for gene expression in oleaginous yeast
The regulatory sequences (i.e., promoter regions, introns and enhancers) associated with the Yarrowia lipolytica gene encoding fructose bis-phospate aldolase (FBA1) have been found to be particularly effective for the expression of heterologus genes in oleaginous yeast. The promoter regions of the invention have been shown to drive high-level expression of genes involved in the production of ω-3 and ω-6 fatty acids.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Aldolase and production process of substituted alpha-keto acids
4-(Indol-3-ylmethyl)-4-hydroxy-2-oxoglutarate, which is useful as an intermediate in the synthesis of monatin, may be synthesized from indole pyruvic acid and pyruvic acid (and / or oxaloacetic acid) by using a novel aldolase derived from the genus Pseudomonas, Erwinia, Flavobacterium, or Xanthomonas.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Aldolase and production process of 4-hydroxy-L-isoleucine
A novel aldolase is described. 4-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-keto-pentanoic acid, which is useful as an intermediate in the synthesis of 4-hydroxy-L-isoleucine, may be synthesized from acetaldehyde and α-ketobutyric acid using a novel aldolase, which is derived from the genus Arthrobacter.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
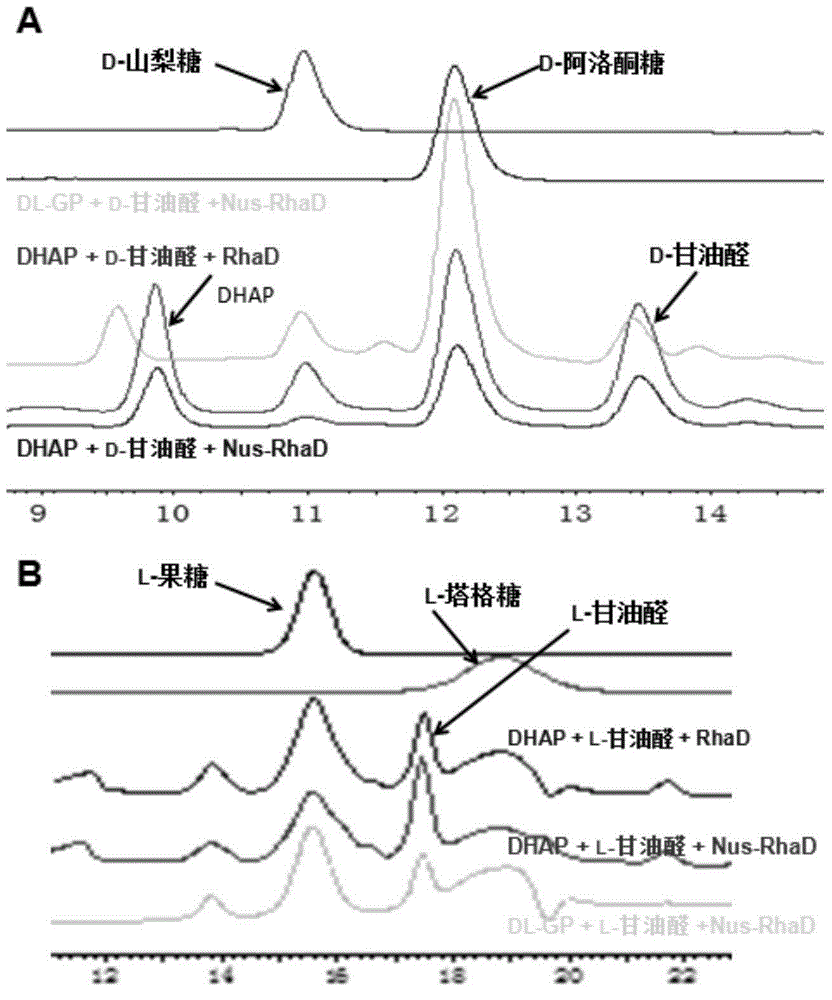
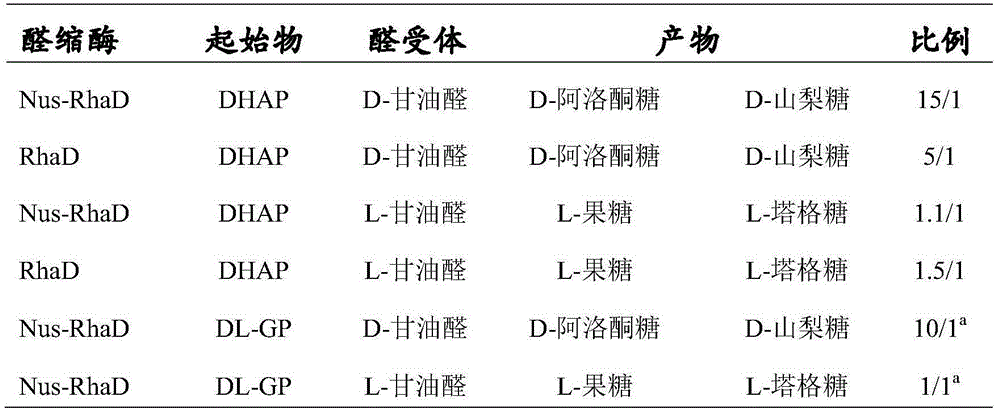
Application of L-rhamnulose-1-phosphate aldolase in catalytic synthesis of rare sugars
The invention discloses application of L-rhamnulose-1-phosphate aldolase in catalytic synthesis of rare sugars. In order to avoid the direct use of DHAP (dihydroxyacetone phosphate) and greatly decrease the synthesis cost of rare sugars, a 'single kettle with four enzymes' strategy is adopted, the L-rhamnulose-1-phosphate aldolase derived from Thermotoga maritima MSB8 is used for synthesizing a series of rare sugars such as D-allulose, D- sorbose, L-fructose and L-tagatose. Experiments show that the aldolase has good thermal stability and can be used for highly selectively synthesizing D-allulose having important application value while D-glyceraldehyde is used as a receptor.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
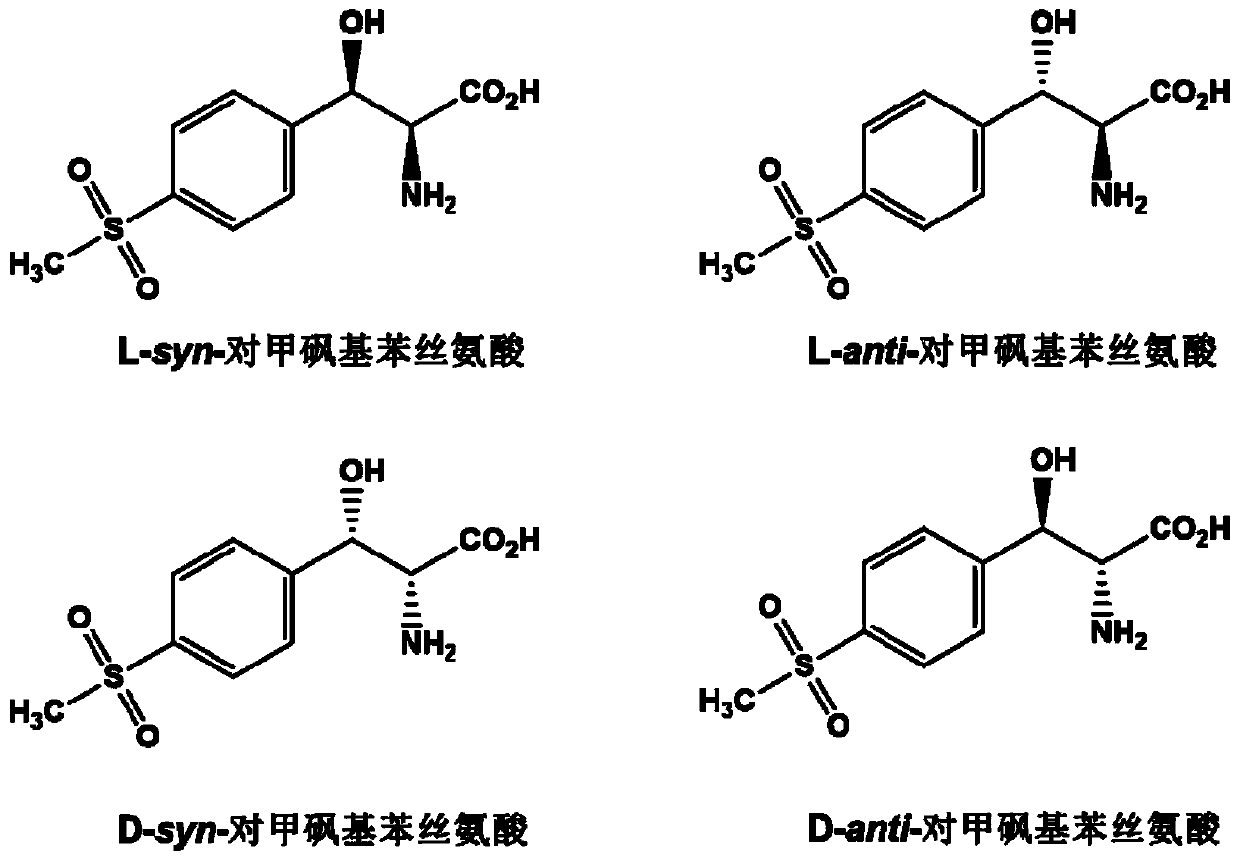
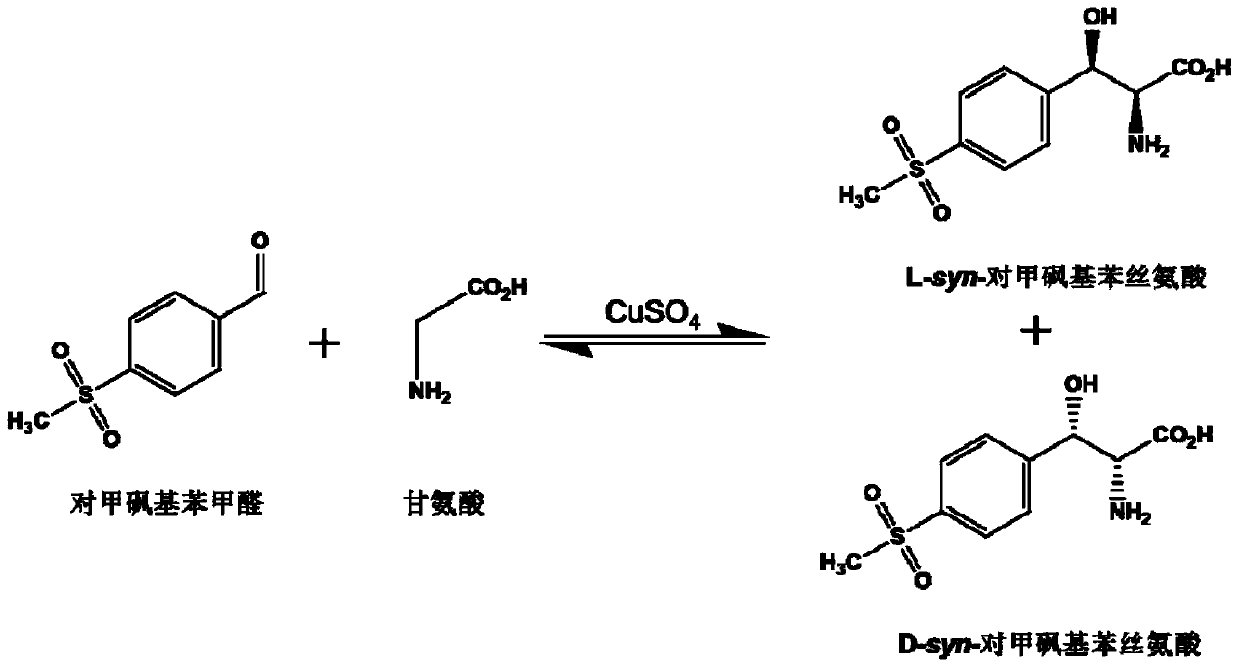
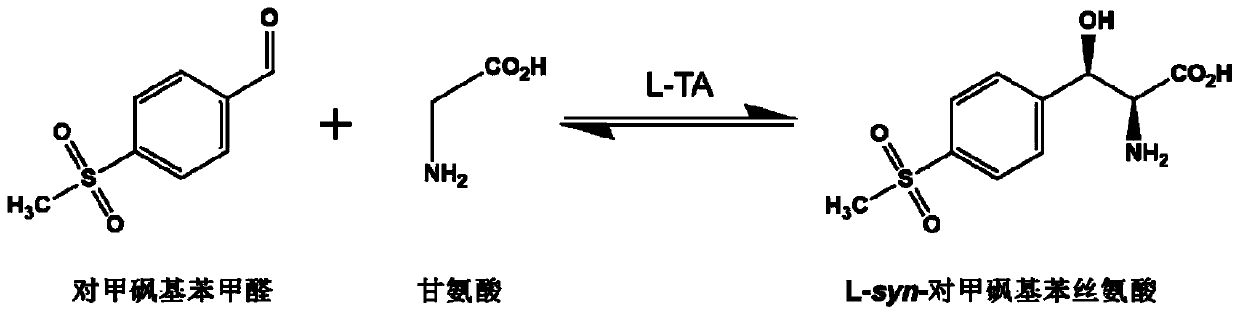
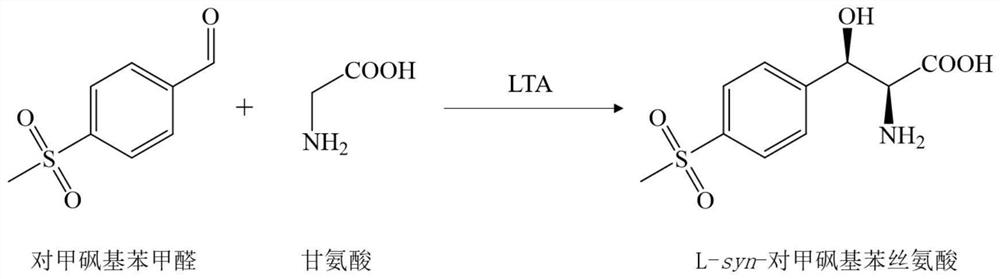
L-threonine aldolase mutant, gene and method for preparing L-syn-p-methylsulfonylphenylserine
ActiveCN111139230AIncrease profitEasy to separate and purifyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMutantPyridoxine phosphate
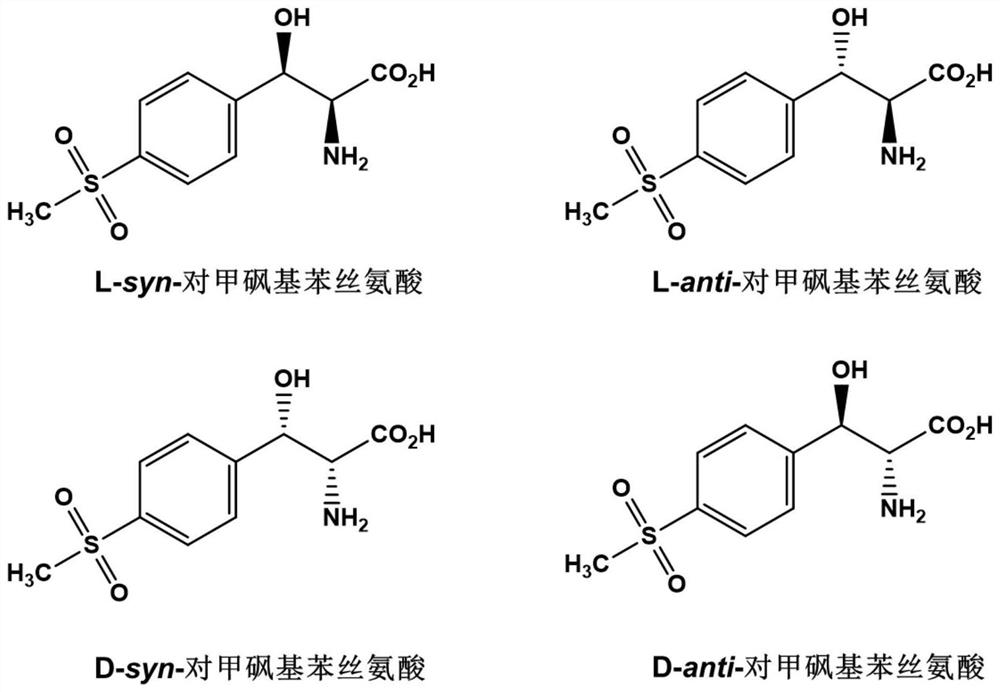
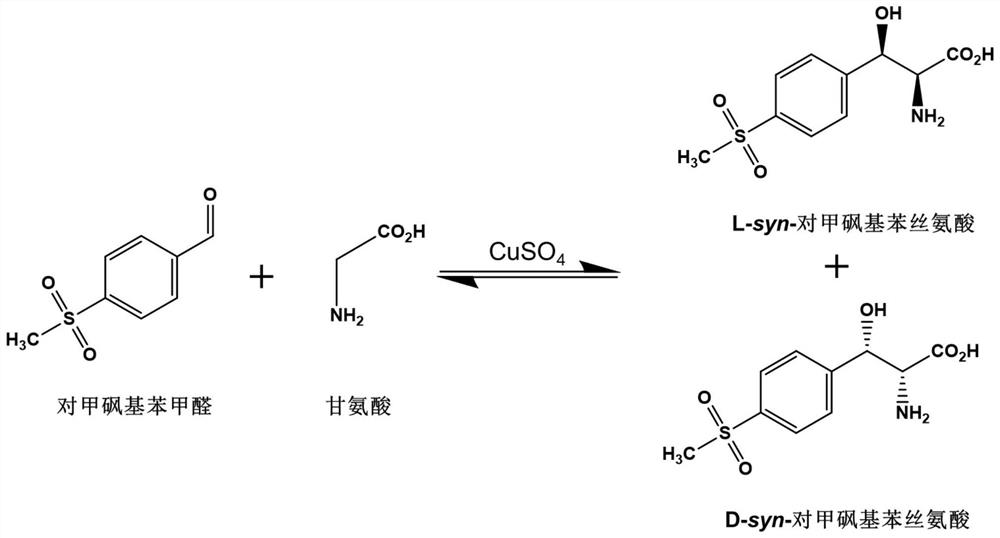
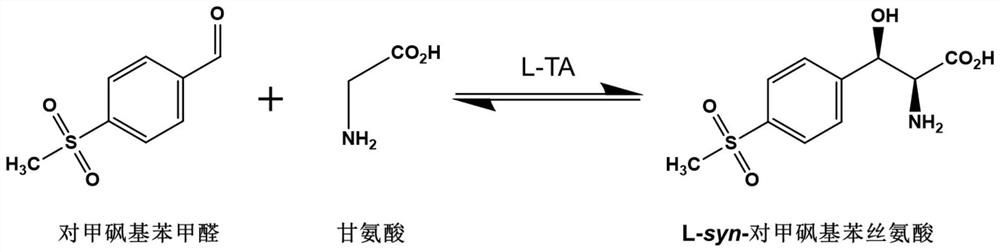
The invention discloses an L-threonine aldolase mutant, a gene and a method for preparing L-syn-p-methylsulfonylphenylserine. The L-threonine aldolase mutant is obtained by mutation of wild type L-threonine aldolase; and with glycine and p-methylsulfonylbenzaldehyde as substrates and pyridoxal phosphate as a coenzyme, the L-syn-p-methylsulfonylphenylserine can be generated from the L-threonine aldolase mutant through a catalytic condensation reaction. The L-syn-p-methylsulfonylphenylserine produced by using the L-threonine aldolase mutant disclosed by the invention has the following advantages: 1, the production process is simple, and the reaction conditions are mild; 2, the L-threonine aldolase has high selectivity and high optical purity and does not need to be split; 3, the atom utilization rate is high and theoretically can reach 100%; 4, the production process is environment-friendly and less in pollution, and conforms to the concept of green chemistry; and 5, product separation and purification are simple.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for synthesis of D-psicose by aldolase whole cell
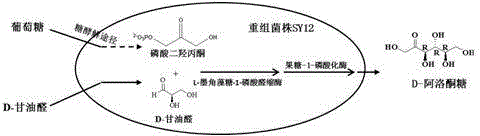
The invention discloses a method for synthesis of D-psicose by microbiological fermentation, specifically a method for synthesis of D-psicose by aldolase whole cell. The method includes: firstly constructing recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum SY12 carrying L-fucose-1-phosphate aldolase gene and fructose-1-phosphorylase gene (i.e. with aldehyde condensation approach), then adding glucose and D-glyceraldehyde into a basic salt medium, synthesizing dihydroxyacetone phosphate from glucose by means of intracellular glycolysis, synthesizing a single product D-psicose from D-glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) under the action of the L-fucose-1-phosphate aldolase and fructose-1-phosphorylase carried by the corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant strain SY12, with the conversion rate of D-glyceraldehyde being 53%. Therefore, compared with the existing method for in vitro synthesis of D-psicose by ketose3-epimerase, the biosynthesis method of D-psicose provided by the invention has the advantages of high conversion rate, single product, easy separation and the like, and lays certain foundation for mass production of D-psicose.
Owner:天津怡和生物科技有限责任公司
Method for preparing levodopa with one-pot enzymatic method
The invention discloses a method for preparing levodopa with a one-pot enzymatic method. The method is characterized in that formaldehyde, glycine and catechol are taken as substrates; formaldehyde and glycine are subjected to a catalytic reaction in the presence of aldolase and other enzymes to be converted into serine, then, serine is converted into pyruvic acid and ammonia under the action of anhydrase, and finally, pyruvic acid and catechol react under the action of tyrosine phenol lyase to produce levodopa. The method adopts novel catalysis routh design and has the advantages of being simple to operate, short in production cycle, low in production cost, high in yield, low in environmental protection pressure, suitable for mass industrial production and the like.
Owner:CHANGXING PHARMA
Chassis system for ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) regeneration and application
The invention provides a chassis system for ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) regeneration and application. The chassis system for ATP regeneration comprises the following five enzymes: alpha-glucan phosphorylase, glucophosphomutase, phosphoglucose Isomerase, phosphoketolase and acetokinase. In addition, the chassis system can further comprise the following seven enzymes: transaldolase, transketolase,ribose-5-phosphate isomerase, ribulose-3 epimerase, triosephosphate isomerase, fructose-bisphosphate aldolase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. The chassis system can be coupled to an enzymic catalyticreaction needing ATP, utilizes starch or maltodextrin as energy, is not added with any coenzyme, can efficiently regenerate the ATP at low cost through a one-pot reaction and is an economical, highlyefficient, stable and sustainable ATP regeneration system.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Novel aldolase and production process of 4-hydroxy-l-isoleucine
InactiveUS20090104659A1High expressionHigh copy numberBacteriaSugar derivativesArthrobacterL-Isoleucine
A novel aldolase is described. 4-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-keto-pentanoic acid, which is useful as an intermediate in the synthesis of 4-hydroxy-L-isoleucine, may be synthesized from acetaldehyde and α-ketobutyric acid using a novel aldolase, which is derived from the genus Arthrobacter.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Aldolase mutant as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN111876404AAldehyde reactivity improvementHigh catalytic efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChloroacetaldehydePhenylalanine
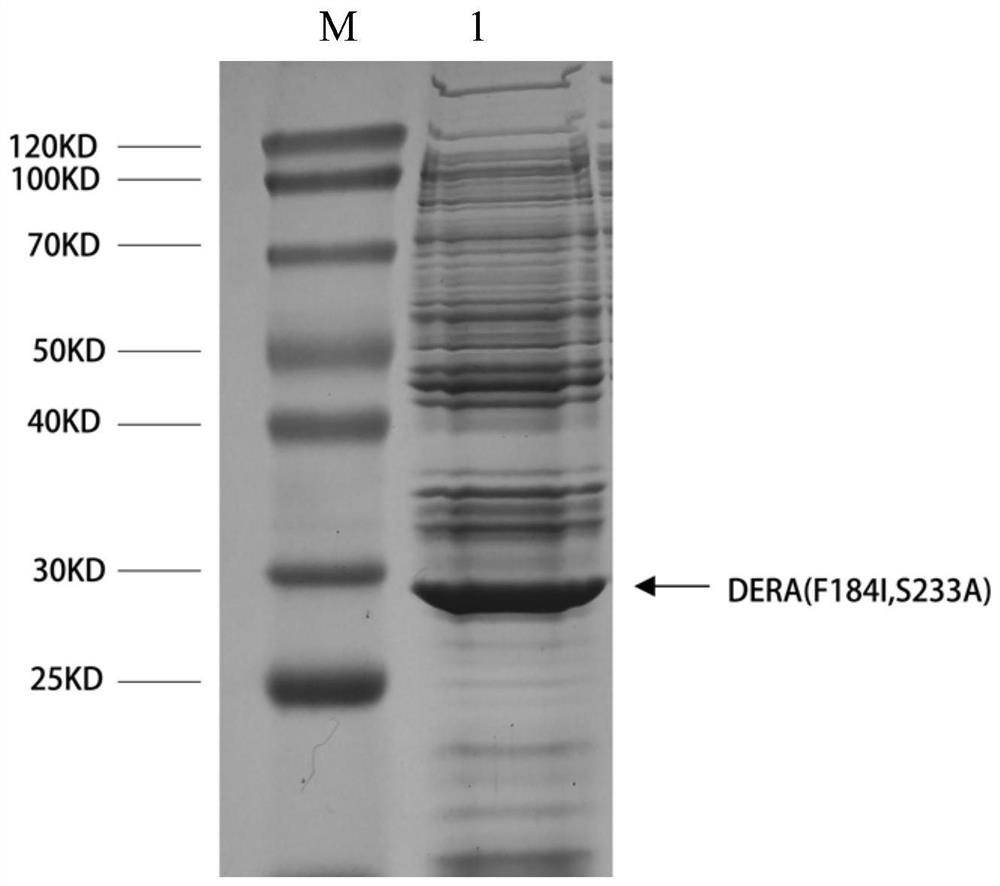
The invention discloses an aldolase mutant, a coding gene thereof and an application of the aldolase mutant in production of statins intermediates, and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. The amino acid sequence of the aldolase mutant is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. According to the invention, on the basis of thermophilic bacteria Thermoga maritima wild aldolase, site-specific mutagenesis is introduced into the coding gene of the thermophilic bacteria Thermoga maritima wild aldolase, a codon (TTT) for coding phenylalanine at the 184 site is mutated into a codon (ATT) for coding isoleucine, and serine (Ser) at the 233 site is mutated into alanine (Ala). The activity of the obtained aldolase mutant in an acetal reaction by using acetaldehyde and chloroacetaldehyde as substratesis remarkably improved, catalytic efficiency is improved by 0.86 times, the mutant has a good industrial application prospect, and the problems of low aldolase catalytic conversion rate, insufficientactivity, poor substrate affinity and the like of wild thermophilic bacteria are solved.
Owner:浙大宁波理工学院
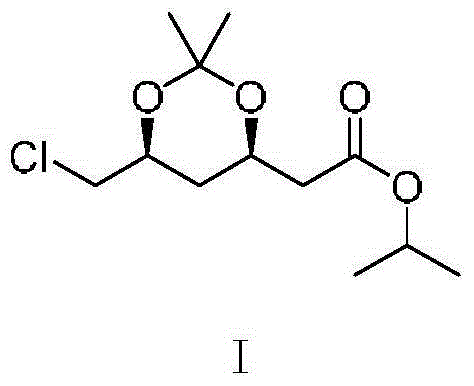
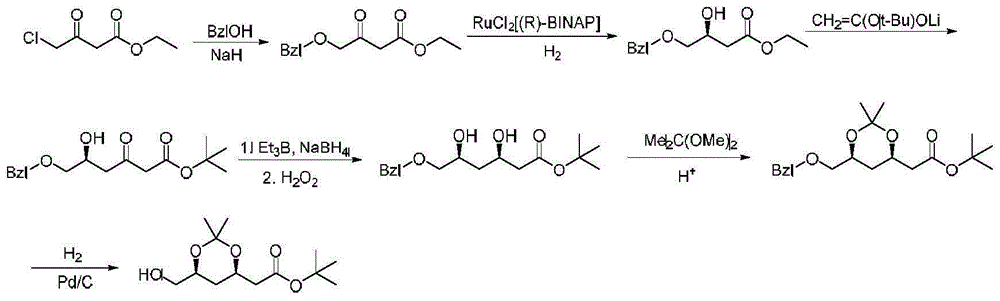
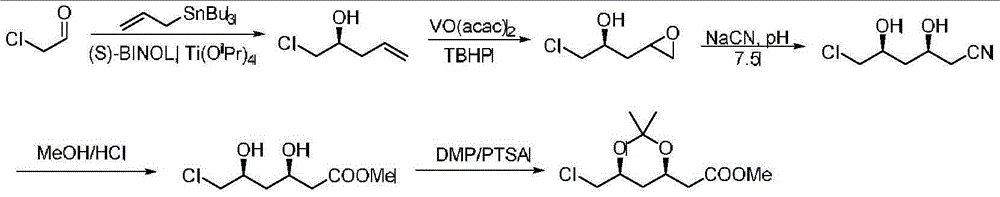
Preparation method of (4R-cis)-6-chloromethyl-2, 2-dimethyl-1, 3-dioxane-4-acetic acid isopropyl ester
The invention discloses a preparation method of (4R-cis)-6-chloromethyl-2, 2-dimethyl-1, 3-dioxane-4-acetic acid isopropyl ester. The preparation method has the advantages that chloroacetaldehyde and acetaldehyde serve as reaction substrates to complete a condensation reaction under the action of aldolase, an open-loop esterification reaction between an oxidative obtained product and isopropanol is achieved in the presence of a catalyst, and ester exchange between the product and 2, 2-dimethoxy propane is completed to obtain a target product, so that synthetic route is short, highly toxic products are not used in the whole reaction process, and raw materials are low in cost.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
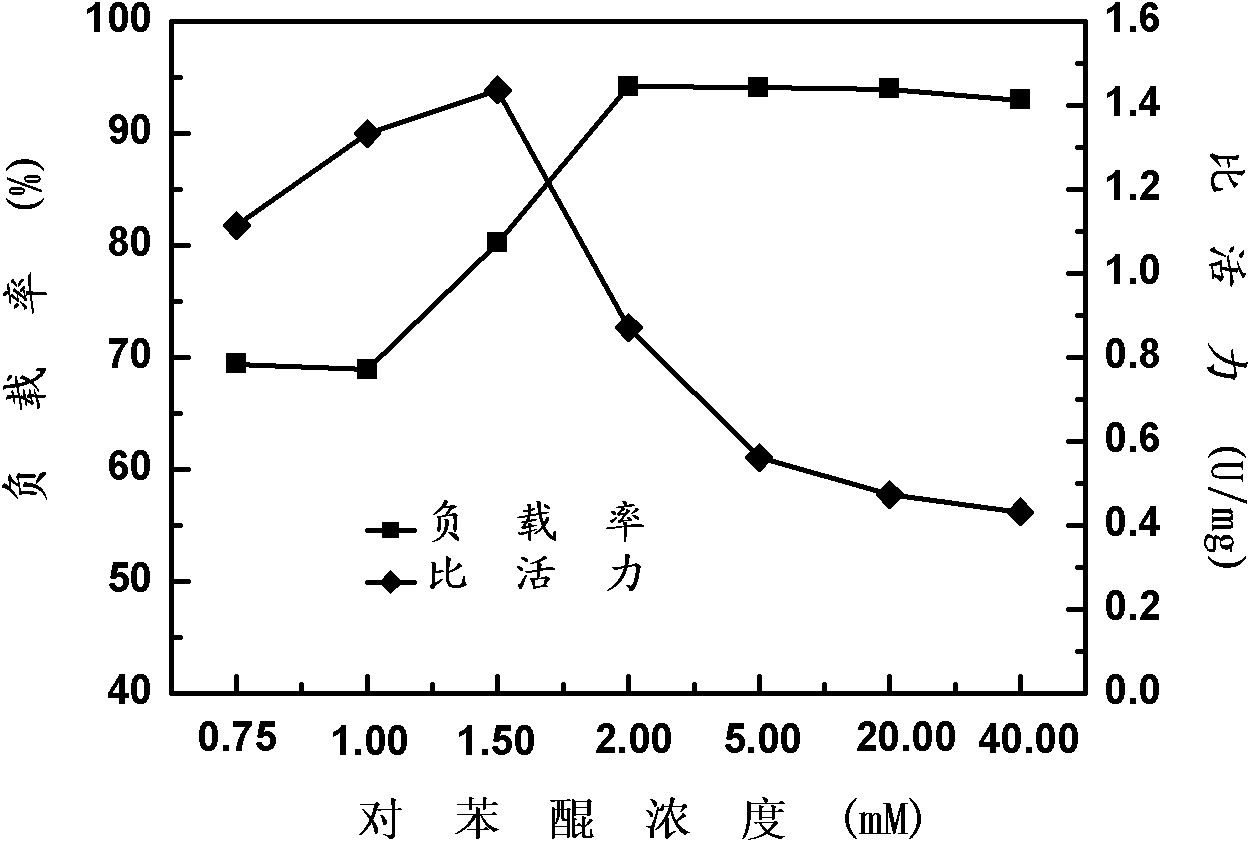
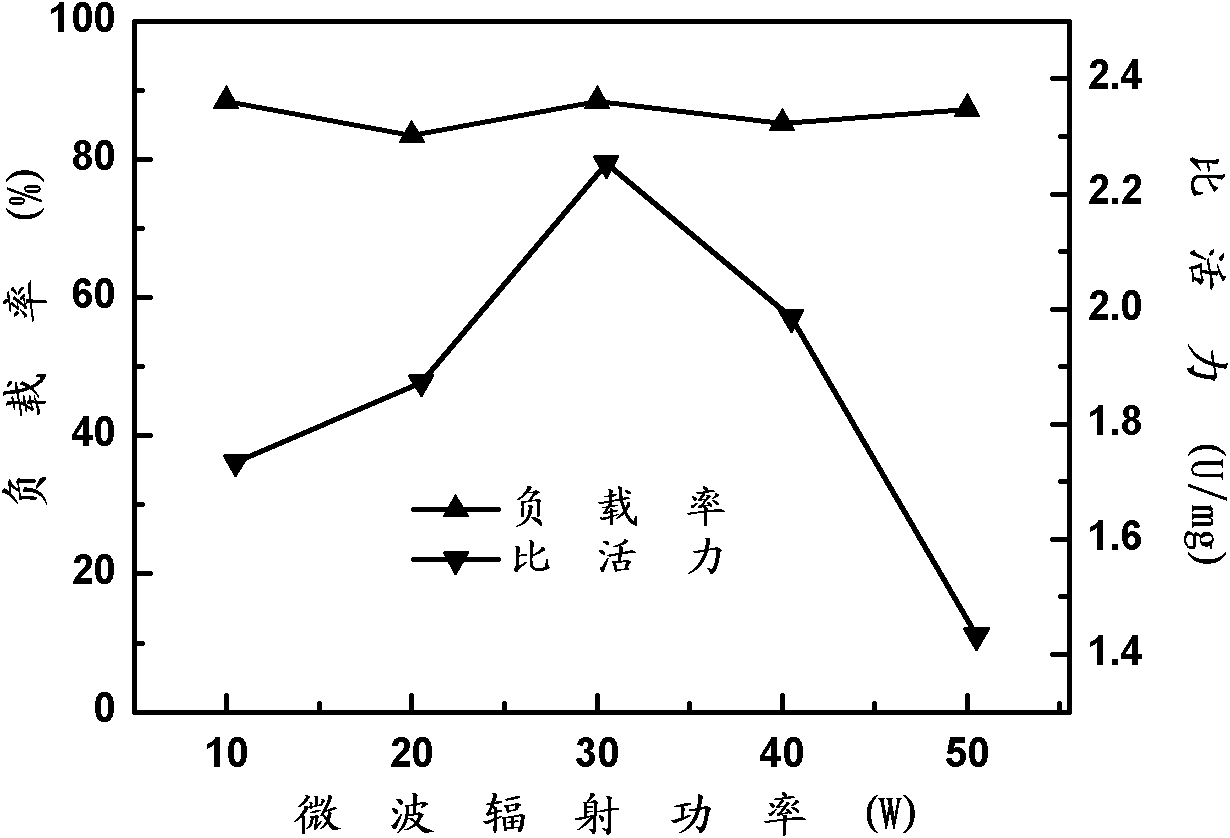
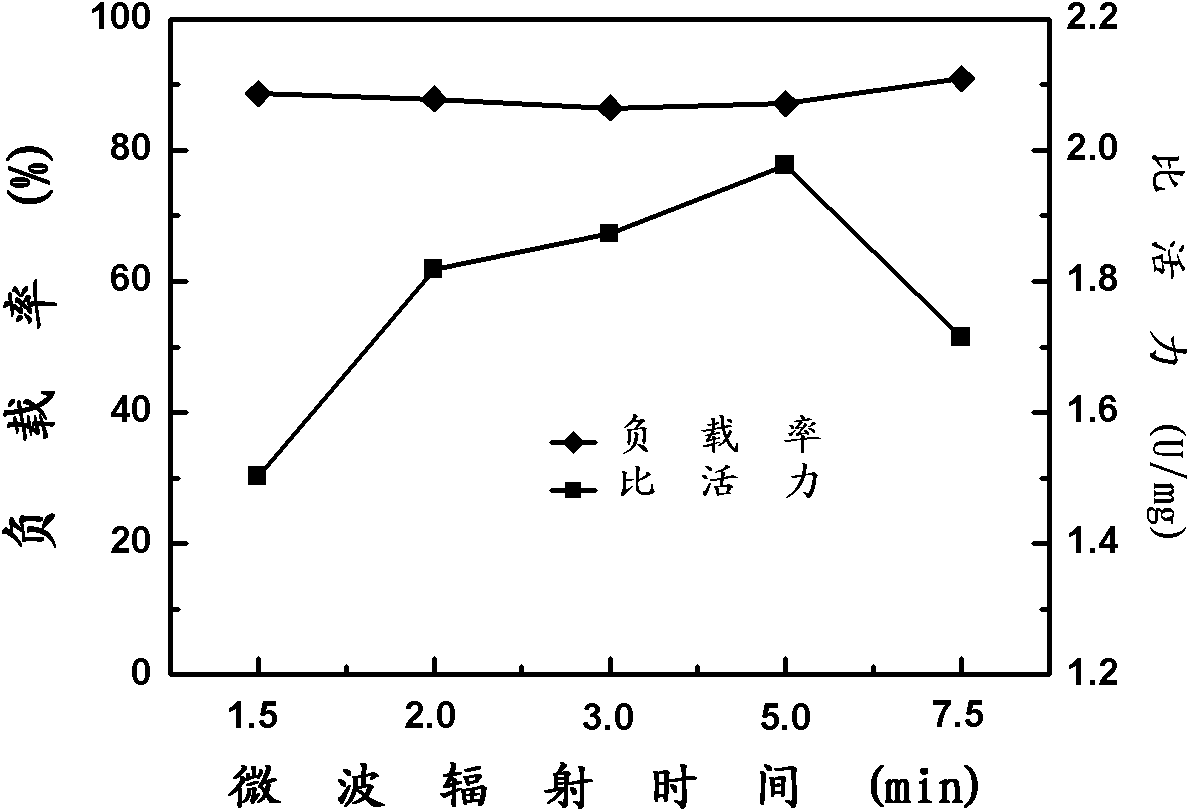
Microwave-assisted immobilization method of aldolase
InactiveCN101892218AImprove temperature stabilityMicroorganism based processesElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentCatalytic effectSubstrate concentration
The invention relates to a method for preparing immobilized aldolase, in particular to a microwave-assisted immobilization method of aldolase. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) activating a carrier; (2) taking an activated carrier liquid obtained in the step (1), adding aldolase free enzyme according to an adding amount of 50mg of aldolase free enzyme / gMCFs-NH2 to obtain a mixed liquid; and (3) irradiating the mixed solution obtained in the step (2) for 1.5 to 7.5 minutes under the conditions of 5 DEG C and 10 to 50W of microwave, centrifuging the mixed solution, and washing precipitate with 0.01 M of PBS solution with the pH of 7.0 to obtain the microwave immobilized aldolase. The immobilized aldolase prepared by the method has higher temperature stability than that of the aldolase free enzyme under the conditions of 70 DEG C of preserved temperature, and particularly the catalytic effect of the microwave-immobilized aldolase immobilized by microwaves under the low substrate concentration can reach that of the aldolase free enzyme and the immobilized aldolase obtained by the conventional immobilization method under the action of high substrate concentration.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Substituted imidazolium compounds, and preparation method, pharmaceutical compositions and application thereof
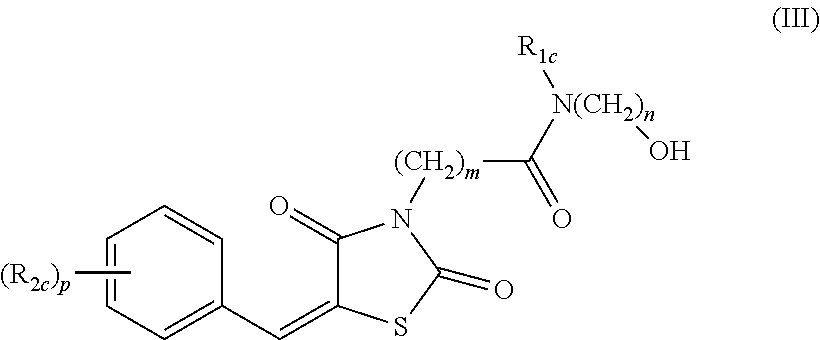
The invention relates to compounds with selective inhibitory activity against aldolase and a preparation method thereof, pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds, and application of the compounds to preparation of drugs for inhibiting the synthesis of triglyceride and cholesterol, drugs for reducing the synthesis of fatty acid, drugs for preventing and / or treating obesity and type 2 diabetes, drugs for preventing and / or treating tumors, drugs for preventing and / or treating Parkinson's disease, drugs for preventing and / or treating Alzheimer's disease, or drugs for prolonging the life of mammals. The general structure of the compounds is as described in the specification.
Owner:XIAMEN VIVOHEALTHS TECH CO LTD
D-fructose-6-phosphate aldolase A mutant, recombinant expression vector, genetically engineered bacterium and application and reaction product thereof
ActiveCN106701723AHigh catalytic activityEasy to manufactureFermentationLyasesMutated proteinNucleotide
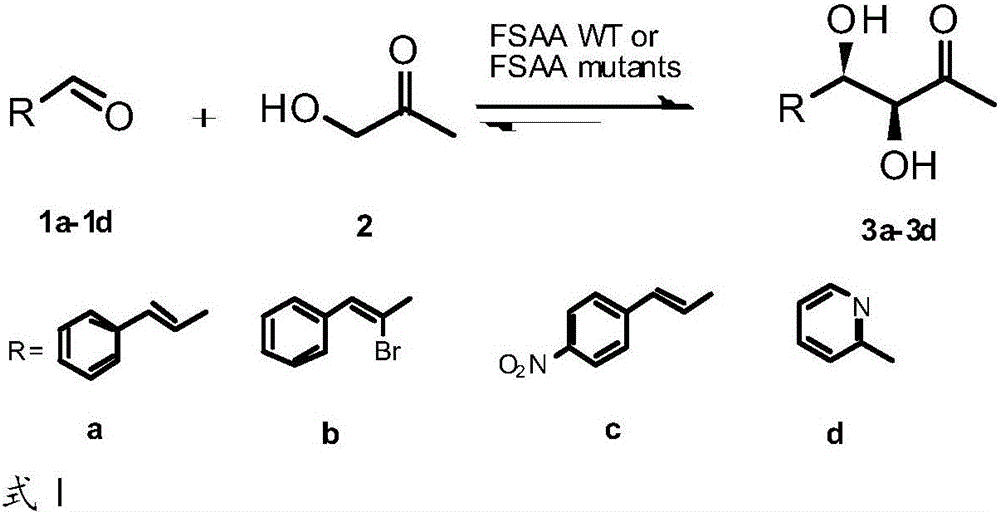
The invention provides an FSAA mutant with remarkably increased catalytic activity, a nucleotide sequence thereof, a recombinant expression vector containing a corresponding mutant gene and a genetically engineered bacterium. A chiral product with high optical purity can be prepared by aldol condensation reaction in which cinnamyl aldehyde / alpha-bromocinnamaldehyde / 4-nitrocinnamaldehyde / pyridine-2-formaldehyde and hydroxyacetone (HA) are asymmetrically catalyzed by the FSAA mutants or the genetically engineered bacteria containing a corresponding mutant protein, the chiral product can serve as a valuable chiral building block, and important potential application value in the field of medicines is realized.
Owner:杭州馨海酶源生物科技有限公司
N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase as well as coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN103060300AIncrease enzyme activityHigh development valueFungiBacteriaEscherichia coliN-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase
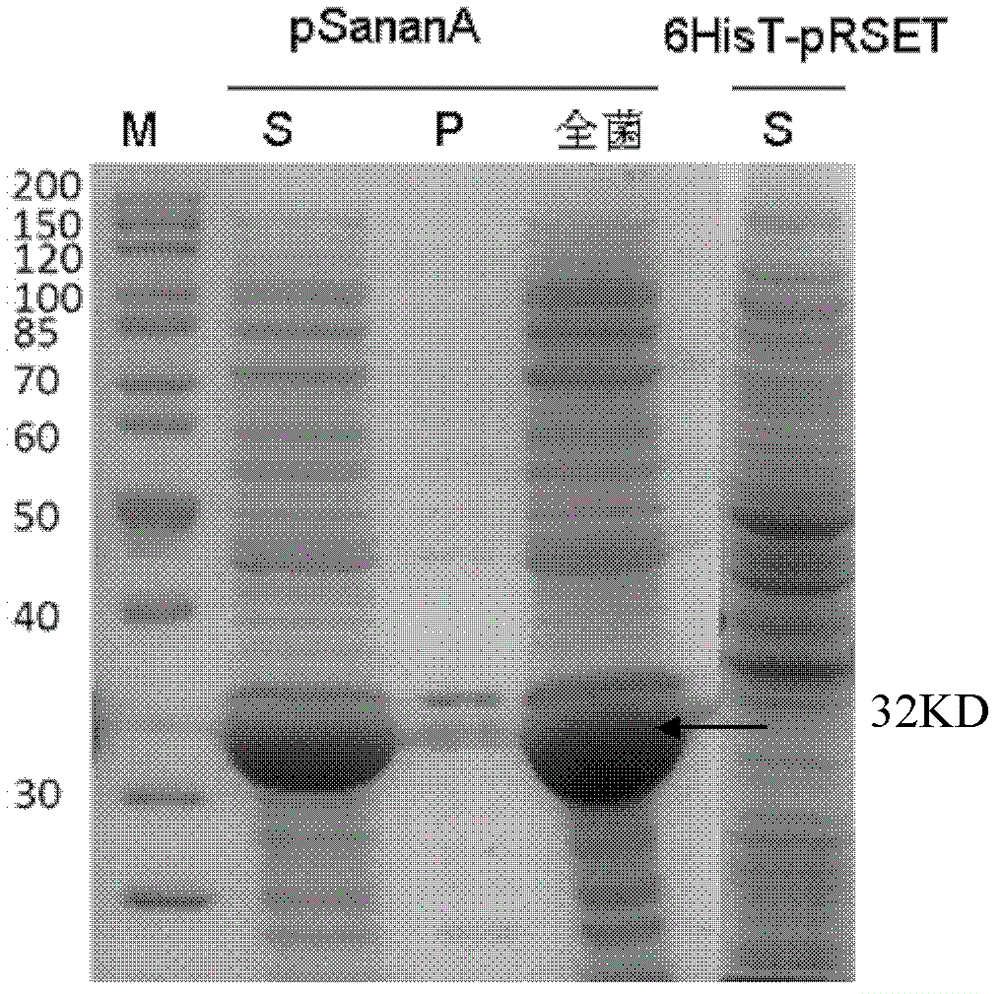
The invention discloses an N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase as well as a coding gene and an application thereof. The N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase provided by the invention is a protein of the following a) or b): a) a protein consisting of an ammonia acid sequence represented by a sequence 2 in a sequence table; and b) a protein with an activity of N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase, wherein the ammonia acid sequence represented by the sequence 2 is subjected to substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more of ammonia acid residues so as to obtain the protein derived by the protein in the a). According to the invention, a new gene SananA for coding the N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase is obtained, and the gene SananA is cloned to a prokaryotic expression vector 6HisT-pRSET plasmid, so that a high-efficiency expression of a N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase protein (SaNanA) can be carried out in escherichia coli. The obtained recombinant N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase protein provided by the invention can catalyze N-acetylmannosamine and pyruvic acid to generate N-acetylneuraminic acid, so that the N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase protein has high enzyme activity, application foreground and development value.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
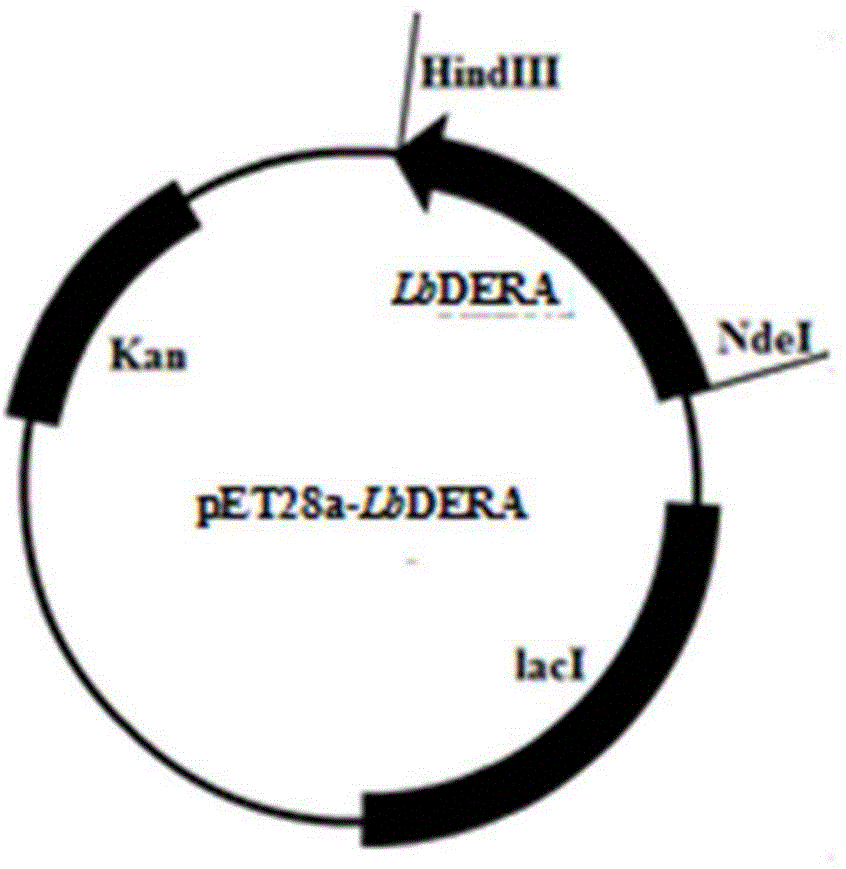
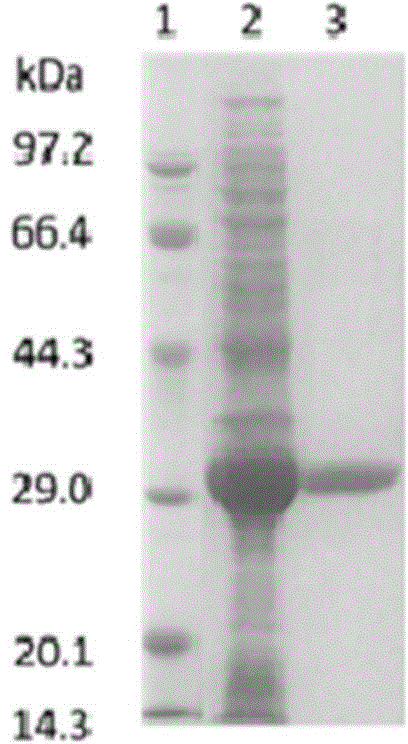
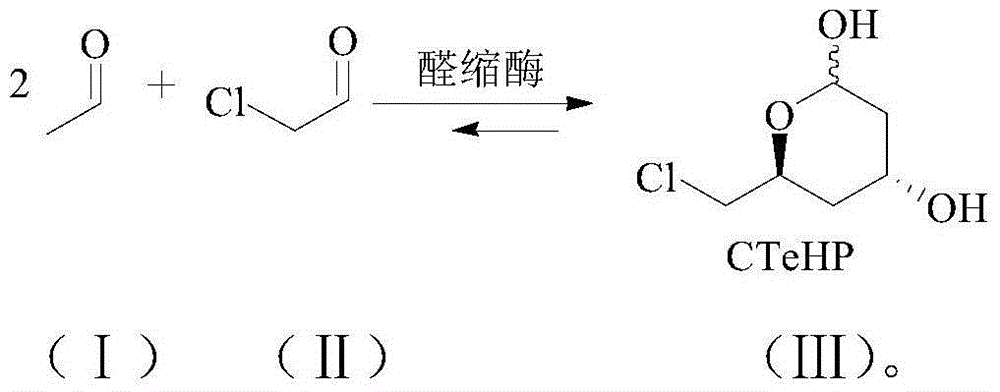
Lactobacillus brevis, aldolase, genes of aldolase and method of preparing statin intermediate
ActiveCN104560832AHigh activityMild reaction conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismHeat stability
The invention discloses lactobacillus brevis, aldolase, a gene of the aldolase and a method of preparing a statin intermediate. The lactobacillus brevis is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with a preservation number of CGMCC NO.10135 and is capable of producing the aldolase. Compared with prior art, the aldolase is high in activity, heat stability and substrate tolerance; the method for catalytically preparing (3R, 5S)-6-chloro-2, 4, 6-trideoxy-D-ribofuranose-pyranoside, serving as the statin intermediate, by the aldolase and a mutant of the aldolase has the advantages of mild reaction condition, high substrate concentration, little amount of a catalyst and the like, so that the aldolase has good application prospect in the industrial production.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Biosynthesis method of 2-deoxy scarce aldose by using aldolase
ActiveCN104017795ALow costNo generationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme biosynthesis
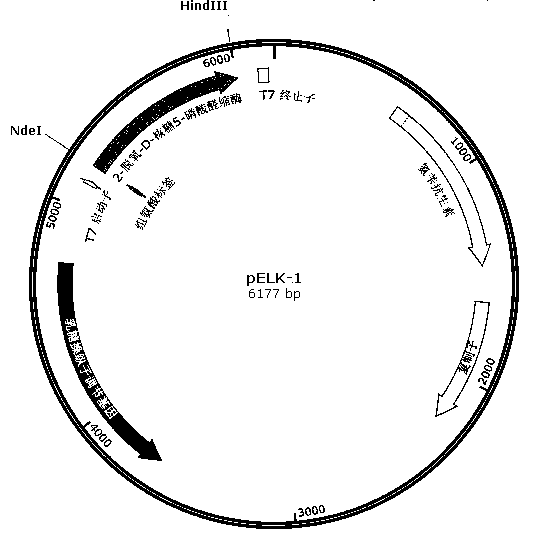
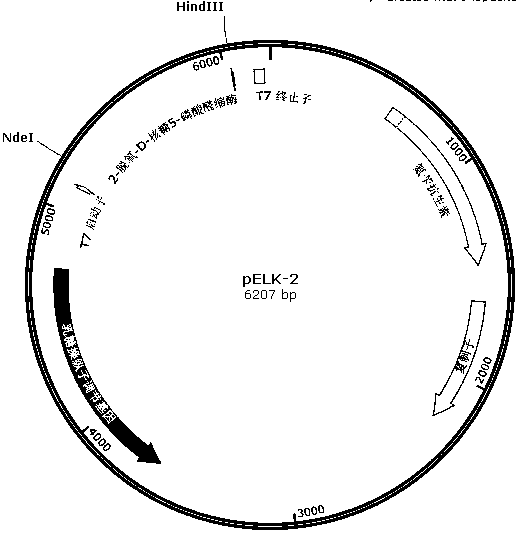
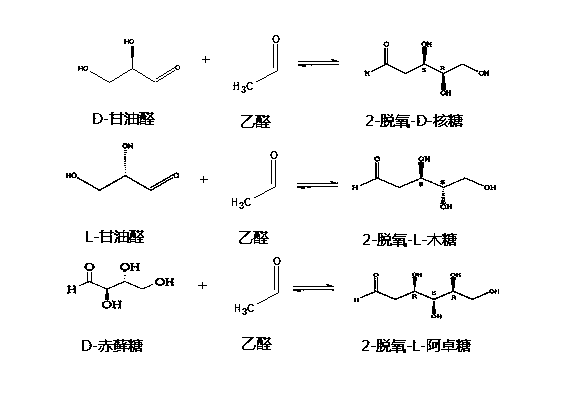
The invention relates to a biosynthesis method of 2-deoxy scarce aldose such as 2-deoxy-D-ribose aldolase by using aldolase, and discloses protein sequences of two 2-deoxy-D-ribose 5-phosphate aldolase mutants, and a constructed Escherichia coli recombinant bacterial strain L1 containing encoding genes of the 2-deoxy-D-ribose 5-phosphate aldolase mutants. Experiments show that the recombinant strain can catalyze reaction of acetaldehyde and a variety of aldehyde groups to produce 2-deoxy aldose by using resting cells, and has strong substrate tolerance. For example, recombinant strain can synthesize 2-deoxy-D-ribose by using aldehyde and D-glyceraldehyde as substrates, synthesize 2-deoxy-L-ribose by using acetaldehyde and L-glyceraldehyde as substrates, and synthesize 2-deoxy-D-altrose by using acetaldehyde and D-erythrose as substrates. Therefore, the Escherichia coli recombinant bacterial strain L1 provided by the invention can be applied to the production of deoxidation deoxy scarce aldose, and the obtained deoxy aldose has wide application prospect in the industries of food and medicine.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Cubilose acid aldolase mutant as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN103881997AHigh catalytic activityReduce manufacturing costGenetic engineeringFermentationSialic acidSodium pyruvate
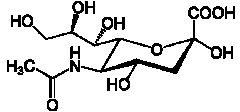
The invention discloses a cubilose acid aldolase mutant as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The cubilose acid aldolase mutant is obtained from sequence 2 in a sequence list through point mutation, and the point mutation is at least one mutation at the 25th site and 275th site of the sequence. Through site directed mutation on the cubilose acid aldolase, cubilose acid aldolase mutant with high catalytic activity is finally obtained. Besides, the mutant uses N-acetylmannosamine, sodium pyruvate and trinosin (ATP) as the substrate and has the cubilose acid aldolase catalytic activity which is at least 50% higher than that of the parent. Thus, the cubilose acid aldolase mutant can be used for producing cubilose acid (sialic acid), the production cost is lowered, and the market competitiveness of the corresponding product is enhanced.
Owner:BONTAC BIO ENG SHENZHEN
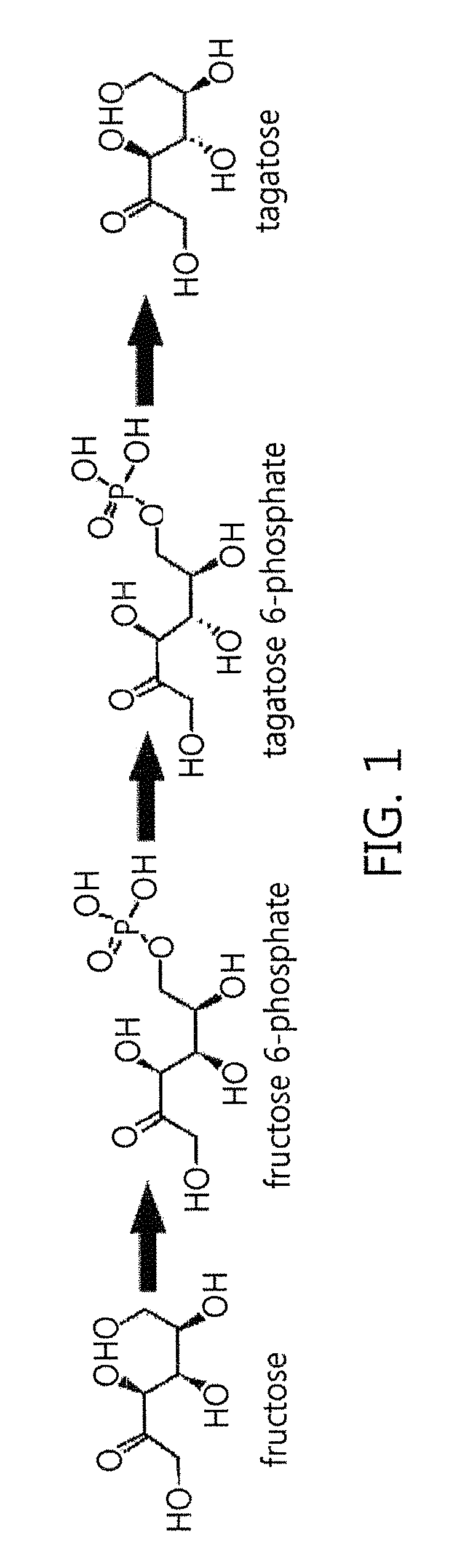
Aldolase, aldolase mutant, and method and composition for producing tagatose by using same
ActiveUS9914919B2Improve productivityEasy to useFermentationCarbon-carbon lyasesBiotechnologyTagatose
Owner:SAMSANG CORP
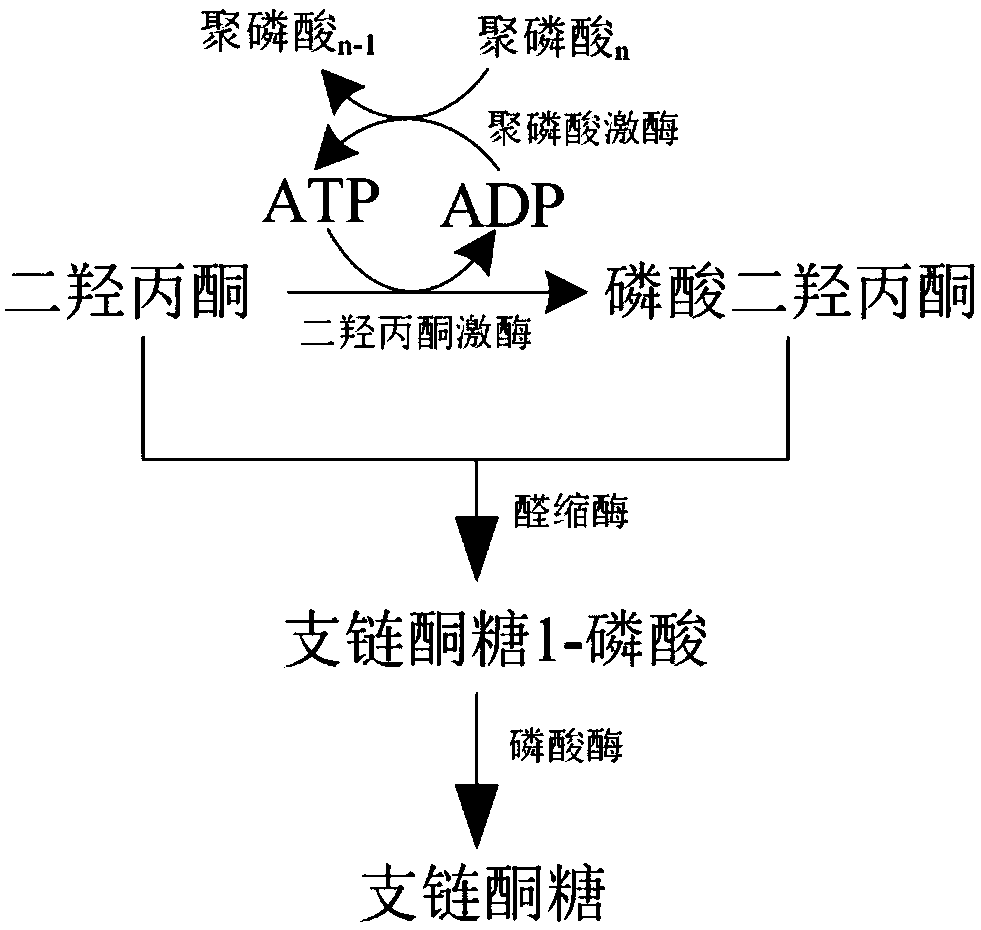
Biological synthesis method of branched ketose
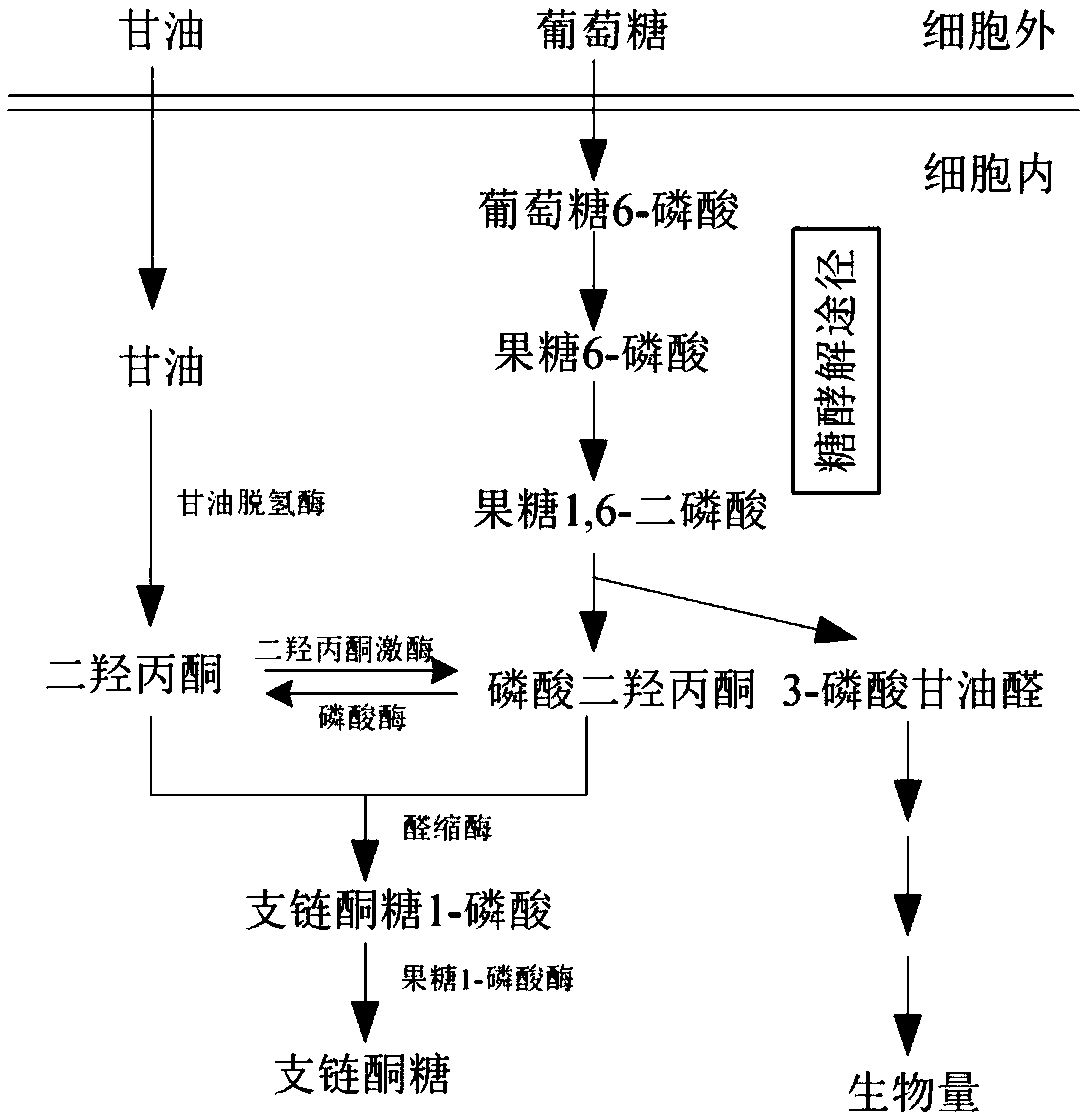
The invention discloses a branched ketose method. According to the invention, the new function of known aldolase is provided, wherein the aldolase can catalyze an aldol condensation reaction between dihydroxyacetone phosphate and dihydroxyacetone to synthesize branched ketose, so that the invention discloses a method for synthesizing branched ketose by constructing an in-vitro multi-enzyme cascadereaction system to catalyze dihydroxyacetone on the basis, and the conversion rate is 90%; the invention also discloses a construction method of a corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant strain for producing branched ketose, wherein the branched ketose is synthesized by fermenting a cheap substrate glucose or glycerol with the obtained recombinant strain, and the yield reaches 36.3 g / L; and compared with the existing chemical method for synthesizing branched ketose, the branched ketose synthesis method provided by the invention has the advantages of cheap substrate, environmental friendliness,high product synthesis efficiency, single product and convenience in separation, has industrial application potential, and provides a basis for synthesis of 4-hydroxymethylfurfural.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Diesel oil improver component containing biological enzyme and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103421552AImprove catalytic performanceHigh-speed catalytic performanceLiquid carbonaceous fuelsFuel additivesAldehyde oxidasePeroxidase
The invention provides a diesel oil improver component containing biological enzyme, which comprises cetane number improver and biological enzyme, wherein the weight part ratio of the cetane number improver to the biological enzyme is 1:(0.01-1); the biological enzyme is the mixture of sulpho enzyme, alcohol oxidase, aldehyde oxidase, amine oxidase, sulfhydryl oxidase, methyl mercaptan oxidase, methyl naphthoquinone oxidase, peroxidase, ferrochelatase, decarboxylase, aldolase, oxyacid lyase, demethylase, alcohol dehydratase, acid dehydratase, esters dehydratase, desulfhydrase, desulfurization methyl enzyme, cobalt chelating enzyme and magnesium chelating enzyme. According to the diesel oil improver component containing the biological enzyme, provided by the invention, the high speed catalytic performance can be realized under the temperate environment through utilizing properties of the biological enzyme, and the component is combined with the conventional cetane number improver for use, the catalytic combustion efficiency of the cetane number improver in diesel oil is greatly improved, and the combustion performance of the diesel oil is further improved.
Owner:英杰惠能(北京)能源新技术有限公司
L-threonine aldolase mutant and method for preparing L-syn-p-methylsulfonyl phenyl serine
ActiveCN113249365ASimple production processMild reaction conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBenzaldehydeEnzyme catalysis
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for increasing yield of sialic acid and application
ActiveCN113337495AEfficient catalytic activityEfficient productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliCatalytic transformation
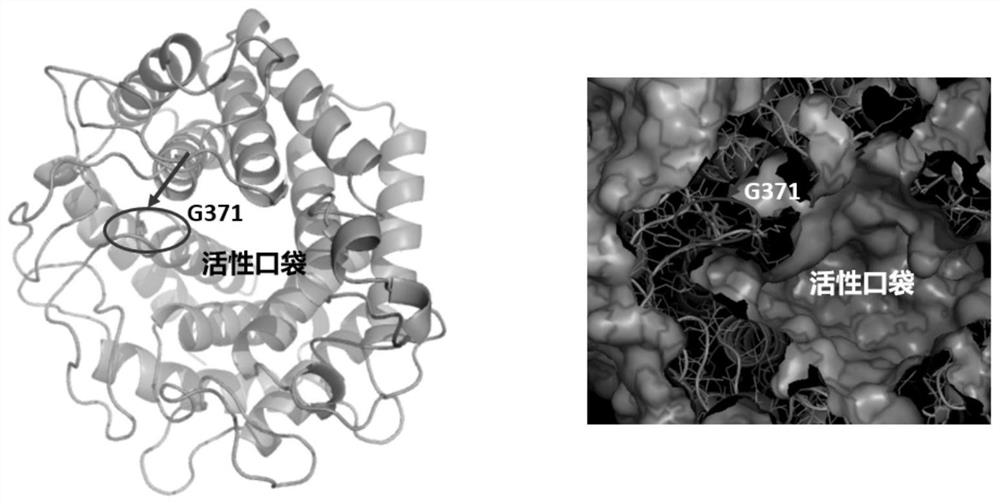
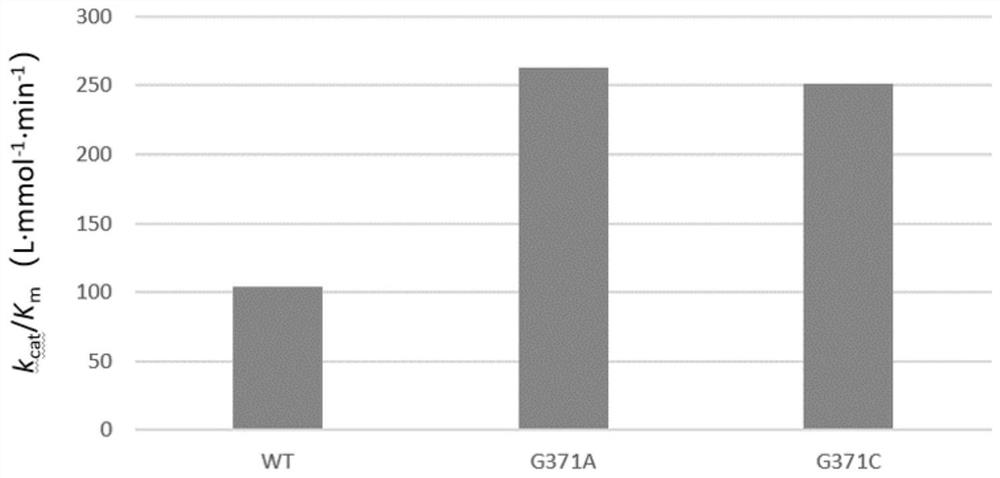
The invention discloses a method for increasing the yield of sialic acid and an application, and belongs to the field of enzyme engineering and microbial engineering. According to the invention, the enzyme catalytic activity key amino acid site Gly371 of N-acetylglucosamine-2-epimerase is subjected to saturated mutation, and an enzyme mutant capable of improving the catalytic efficiency is screened. Through overexpression of the N-acetyl glucosamine-2-epimerase mutant and the N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase with improved catalytic efficiency, the production efficiency of the recombinant escherichia coli for catalytic production of sialic acid is improved. The yields of Neu5Ac prepared by whole-cell catalysis of the recombinant escherichia coli containing G371C and the recombinant escherichia coli containing G371A, which are constructed by the invention, are respectively 352.0 and 353.6 mmol.L <-1 >, which are obviously higher than those of wild recombinant bacteria. Besides, the conversion efficiency of the Neu5Ac generated by converting GlcNAc under catalysis of a recombinant strain containing a mutant is obviously higher than that of a control strain.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Modified microorganisms and methods for production of useful products
InactiveUS20170356016A1Improve the level ofReduce accumulationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsOxidoreductasesMicroorganismBiological body
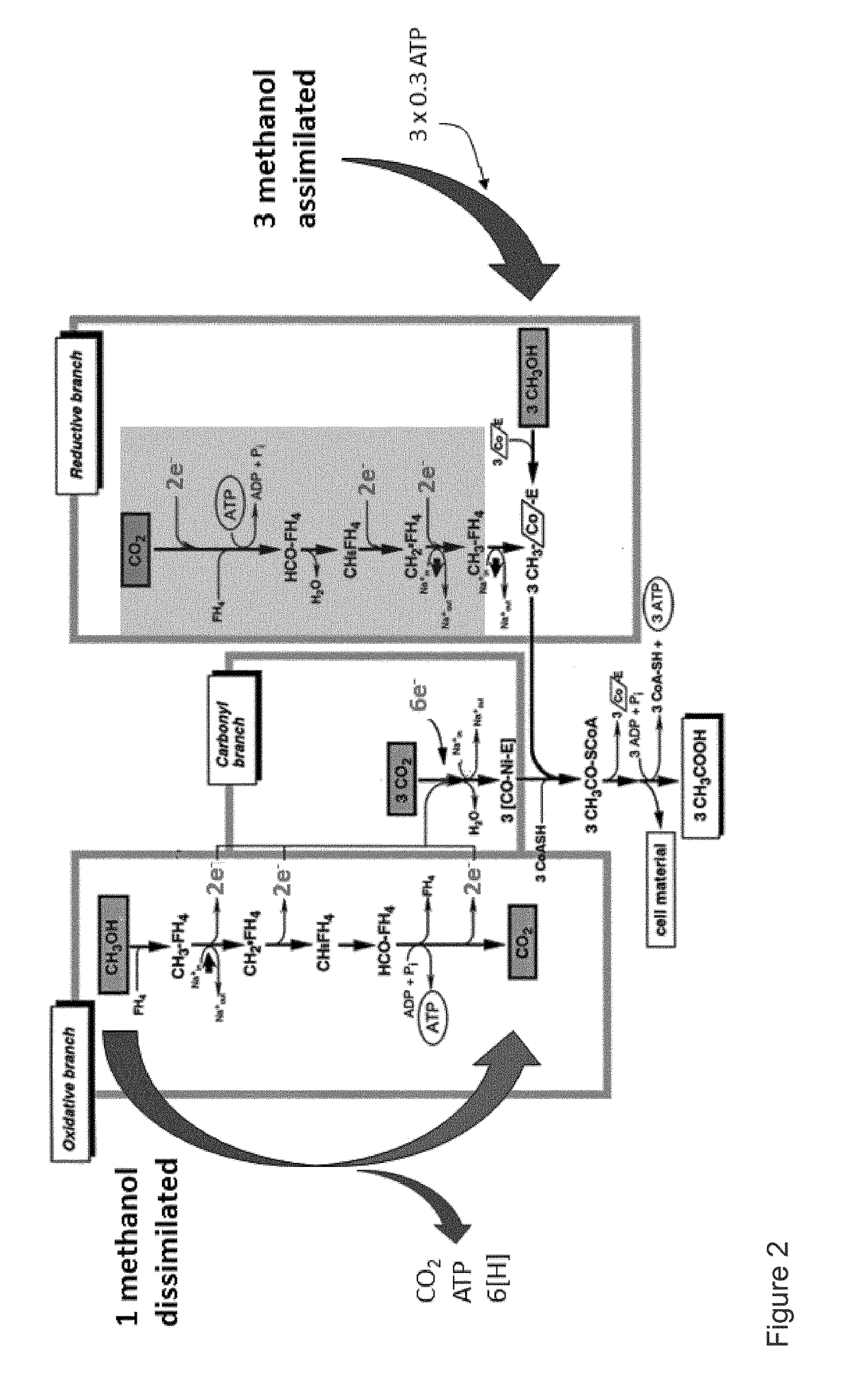
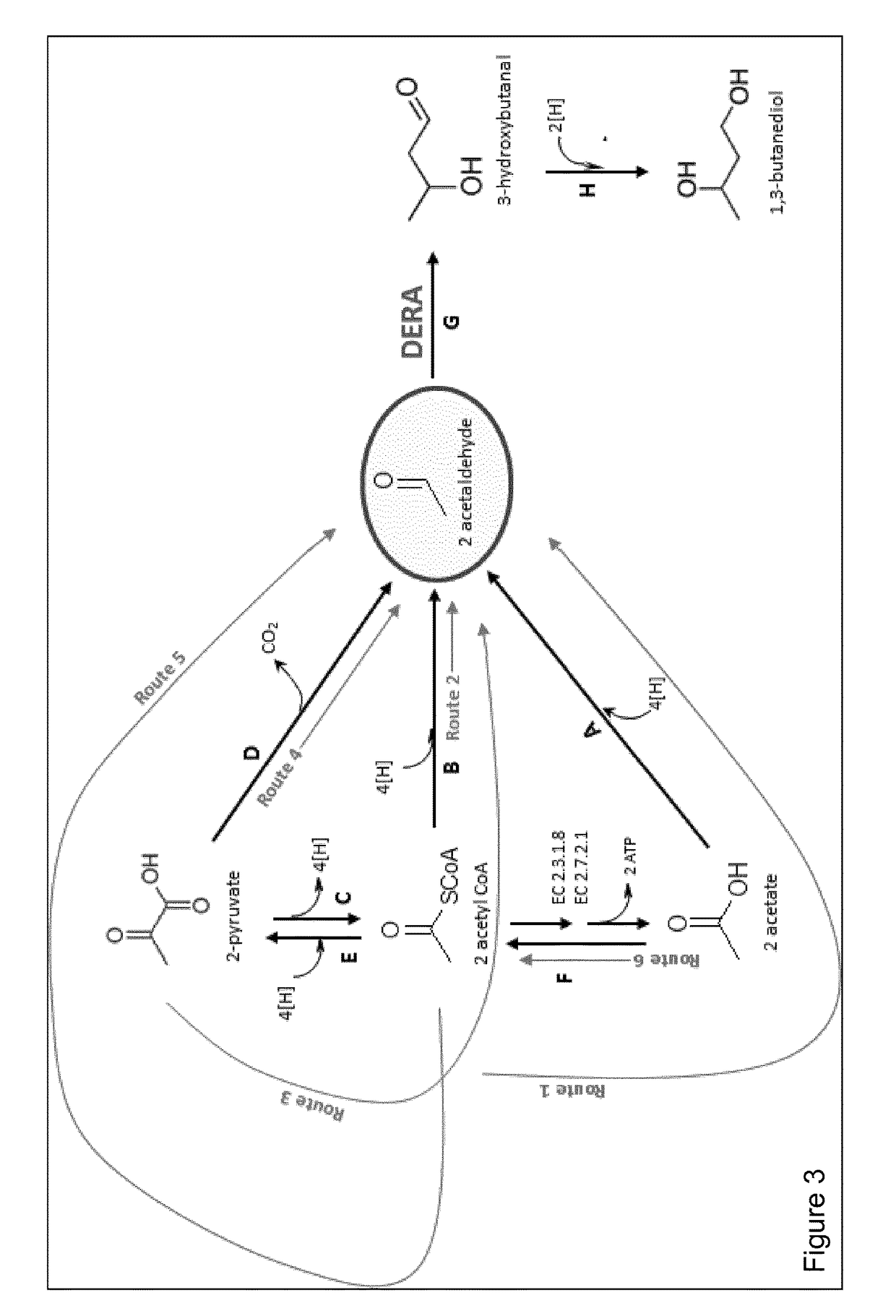
Non-naturally occurring microbial organisms and related methods, processes and materials are for microbial organisms that include a genetic modification which enhances production of 3-hydroxybutanal or a downstream product of 3-hydroxybutanal such as 1,3-butanediol from endogenous central metabolic intermediates such as acetyl CoA or pyruvate which are converted to acetaldehyde. Two molecules of acetaldehyde are condensed to form the 3-hydroxybutanal using an aldolase capable of accepting acetaldehyde as both the acceptor and donor in an aldol condensation. The aldolase may be a deoxyribose phosphate aldolase type enzyme, and is typically introduced into the organisms. Energetically favorable pathways produce 3-hydroxybutanal or downstream products thereof.
Owner:ZUVASYNTHA
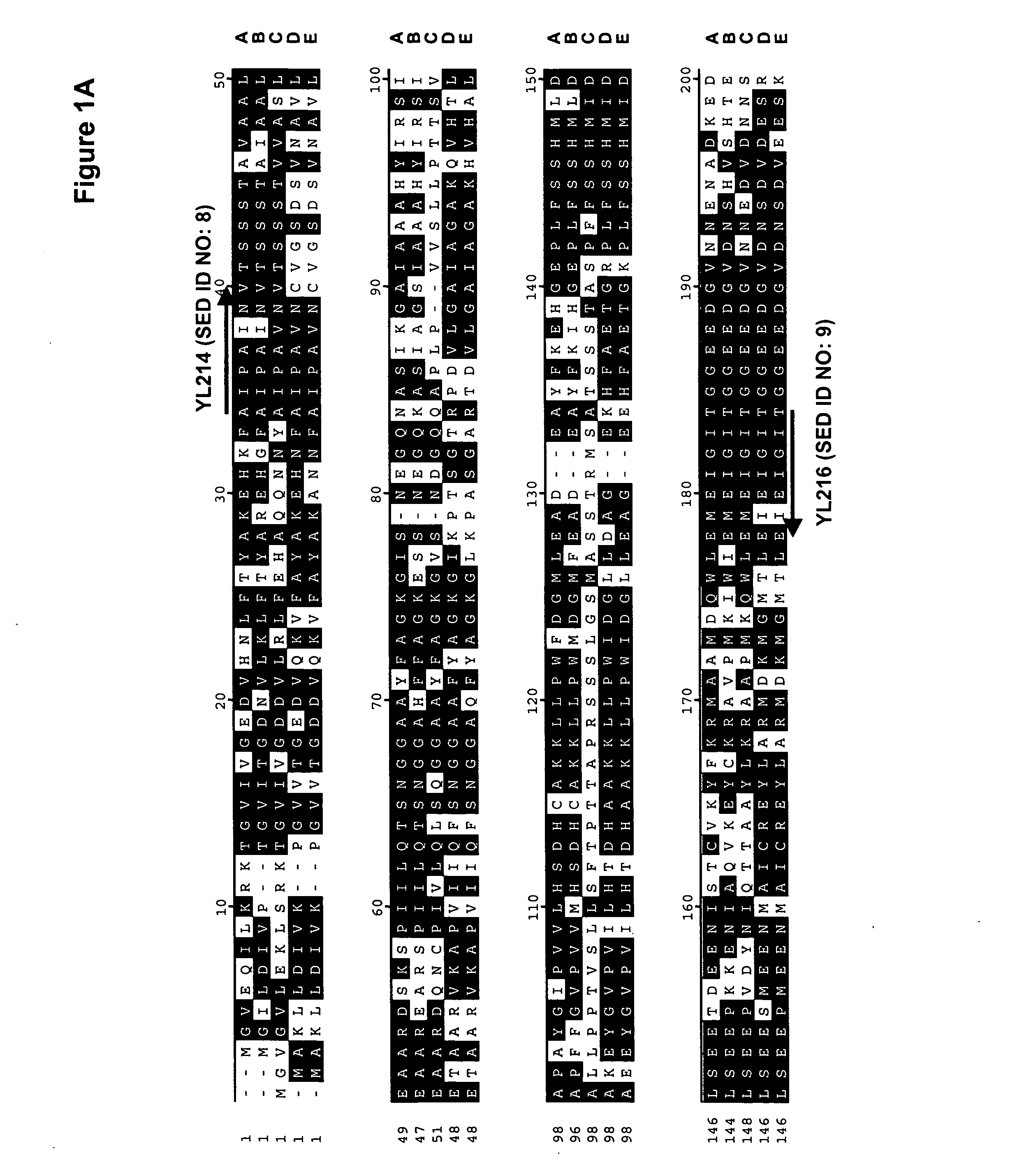
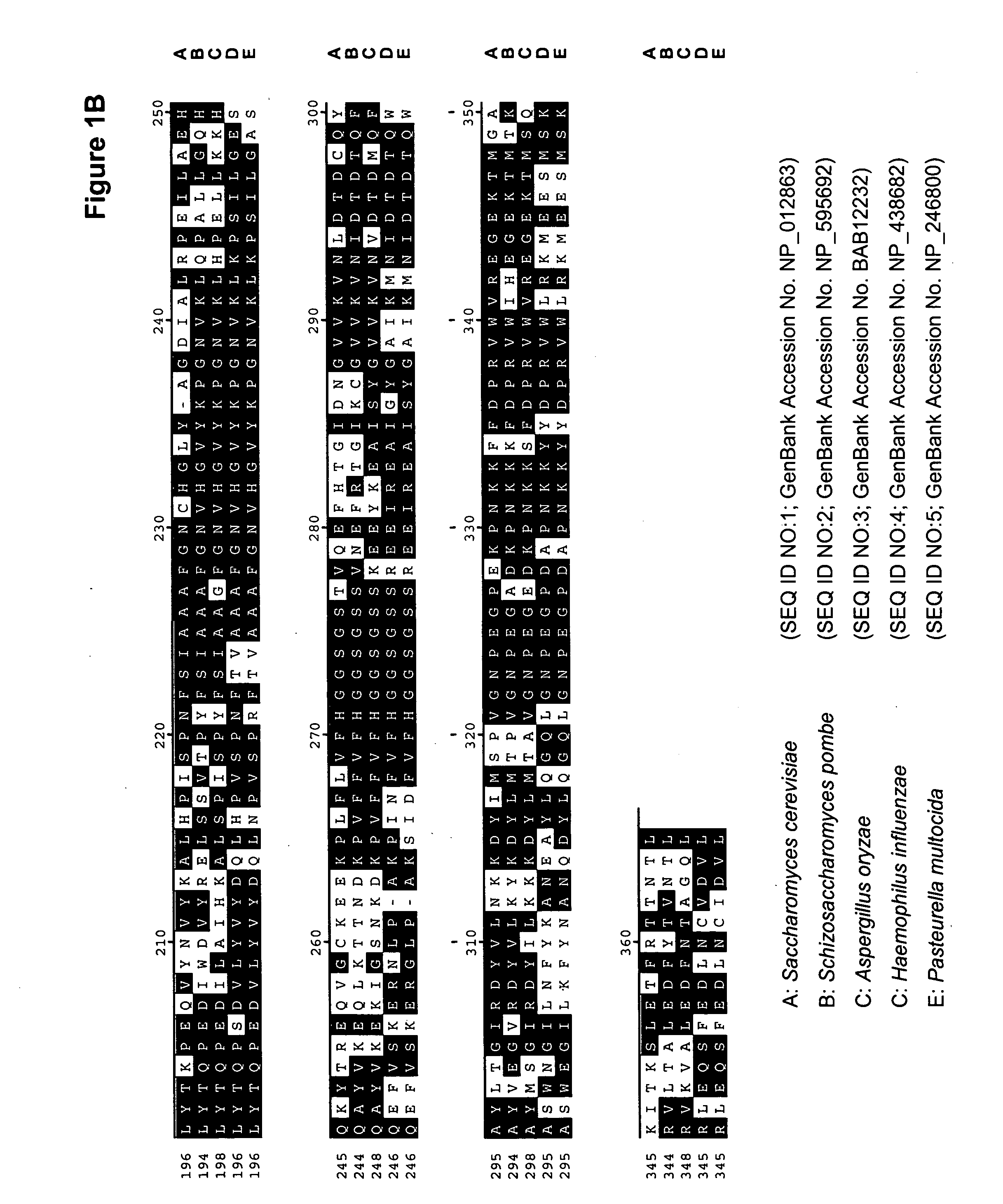
Small molecule malarial aldolase-trap enhancers and glideosome inhibitors
In one aspect, the present invention relates to a method of identifying compounds useful in modifying the activity of Aldolase. The method includes providing a first model comprising Aldolase or residues of the amino acid sequence corresponding to SEQ ID NO: 1 said residues being at amino acid positions selected from the group consisting of 10-13, 26, 27, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 37, 39, 40, 41, 43, 44, 47, 48, 51, 52, 60, 63, 66, 79, 84, 85, 92, 93, 103, 106-109, 112-117, 138, 142, 146, 148, 151, 153, 179, 182, 183, 185, 186, 194, 196, 197, 198, 199, 208, 226-228, 231-269, 270, 272, 277-283, 285-289, 294, 295, 297-299, 301-304, 306-310 312, 313, 316, 317, 319, 321, 323, 326, 330, 344, 345, and 347, providing one or more candidate compounds, evaluating contact between the candidate compounds and the first model to determine which of the one or more candidate compounds have an ability to bind to and / or fit in the first model, and identifying compounds which, based on said evaluating, have the ability to bind to and / or fit in the first model as compounds potentially useful for modifying the activity of Aldolase. The present invention also discloses compounds and compositions which modify the activity of Aldolase, or a complex between Aldolase and TRAP. Methods of treating or preventing malaria, or an infection by apicomplexan organisms are also disclosed.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
L-threonine aldolase mutant and application of L-threonine aldolase mutant in synthesis of L-synn-p-methylsulfonylphenylserine
ActiveCN114134134ASimple production processMild reaction conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme catalysisThreonine aldolase
The invention discloses an L-threonine aldolase mutant and an application of the L-threonine aldolase mutant in synthesis of L-syn-p-methylsulfonyl phenyl serine. The L-threonine aldolase mutant is obtained by mutating wild type L-threonine aldolase, and L-syn-p-methylsulfonyl phenyl serine can be generated by a catalytic condensation reaction by taking glycine and p-methylsulfonyl benzaldehyde as substrates and taking pyridoxal phosphate as a coenzyme. When the L-threonine aldolase mutant is used for producing L-synn-p-methylsulfonylphenyl serine, the L-threonine aldolase mutant has the following advantages: 1, the production process is simple, and the reaction conditions are mild; 2, the selectivity of the L-threonine aldolase is high, the optical purity of the product is high, and resolution is not needed; 3, the atom utilization rate is high and can reach 100% theoretically; the production process is environmentally friendly, pollution is small, and the green chemistry concept is met; 5, the product is simple to separate and purify.
Owner:宁波泓森生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com