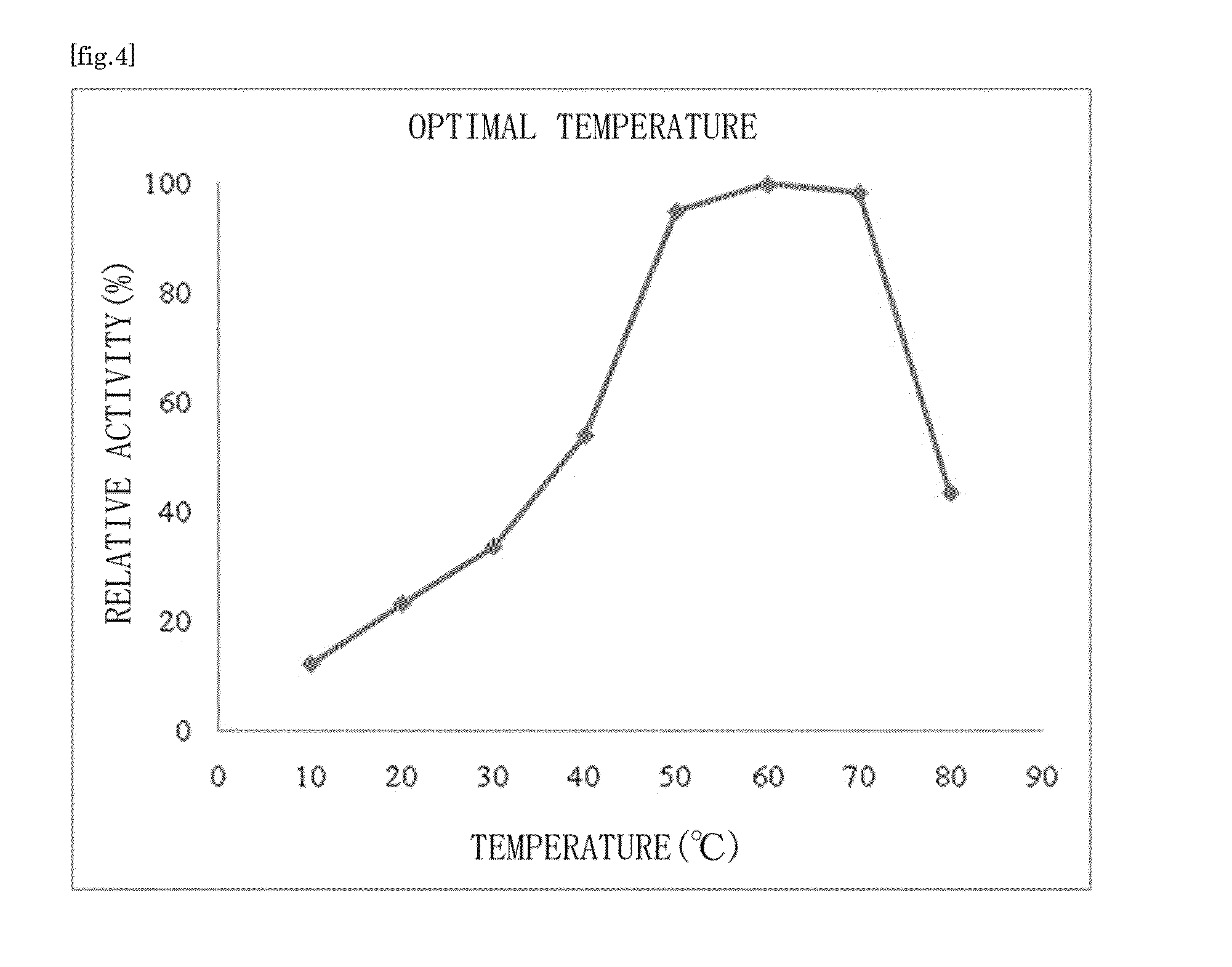
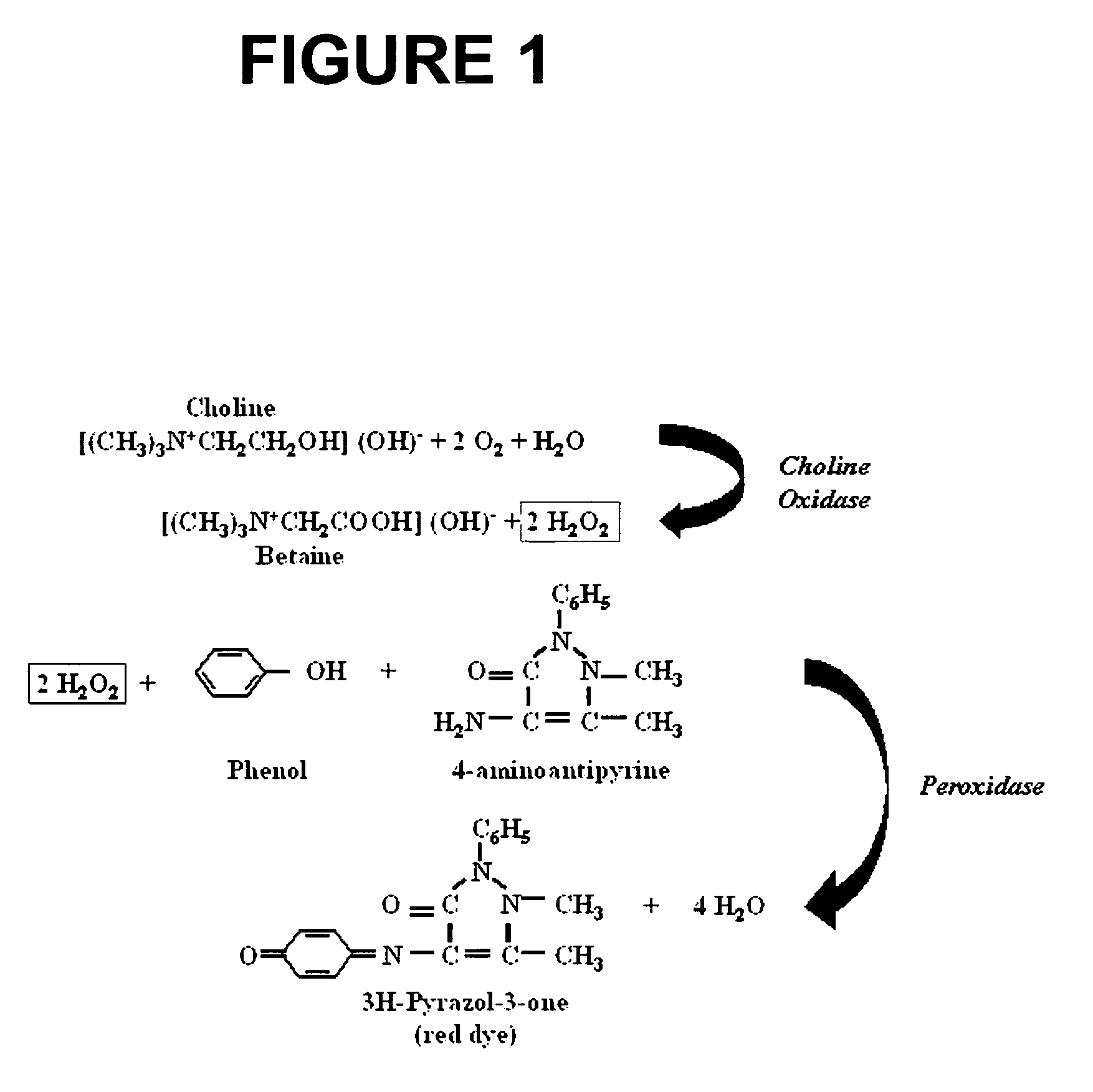
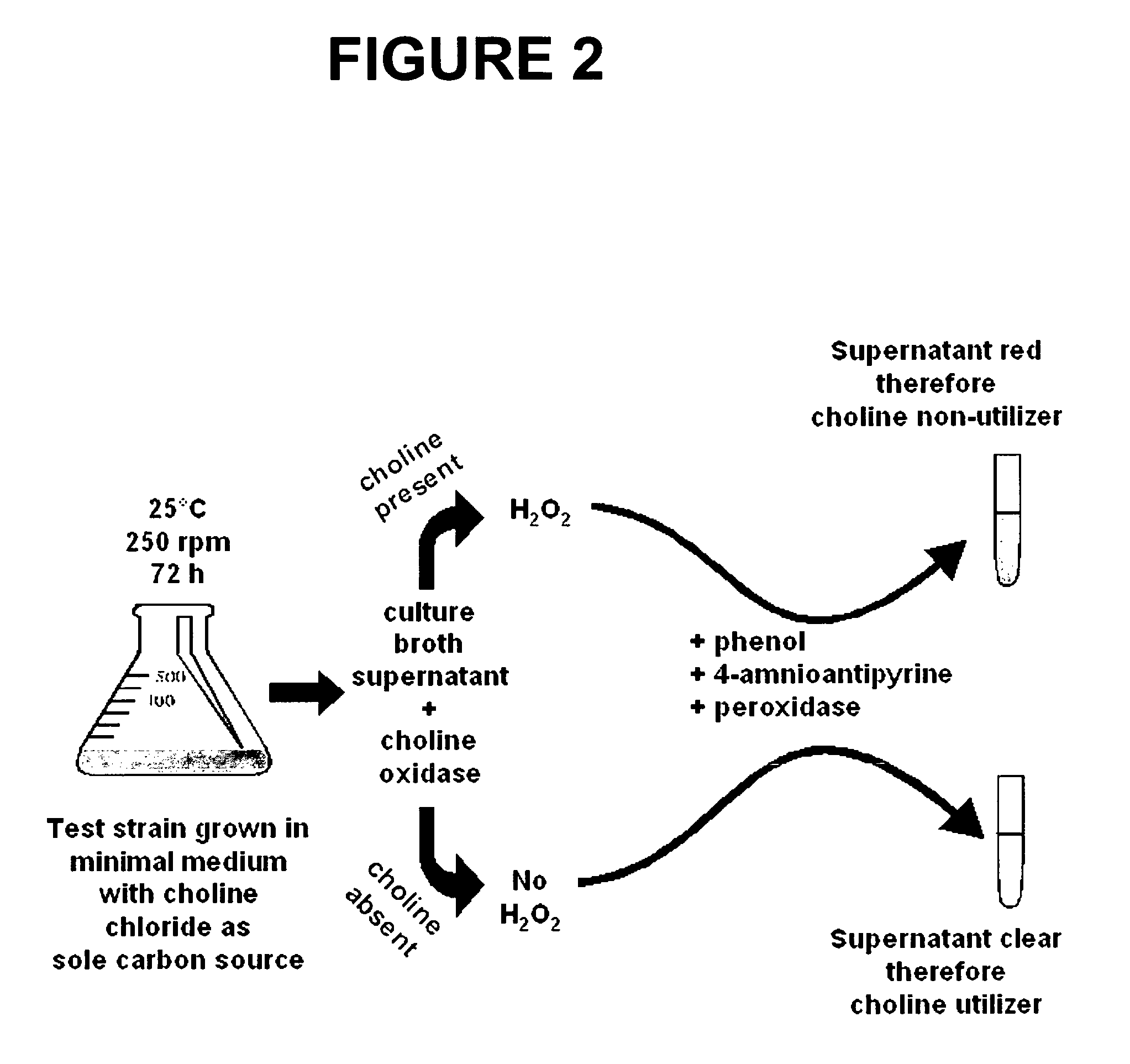
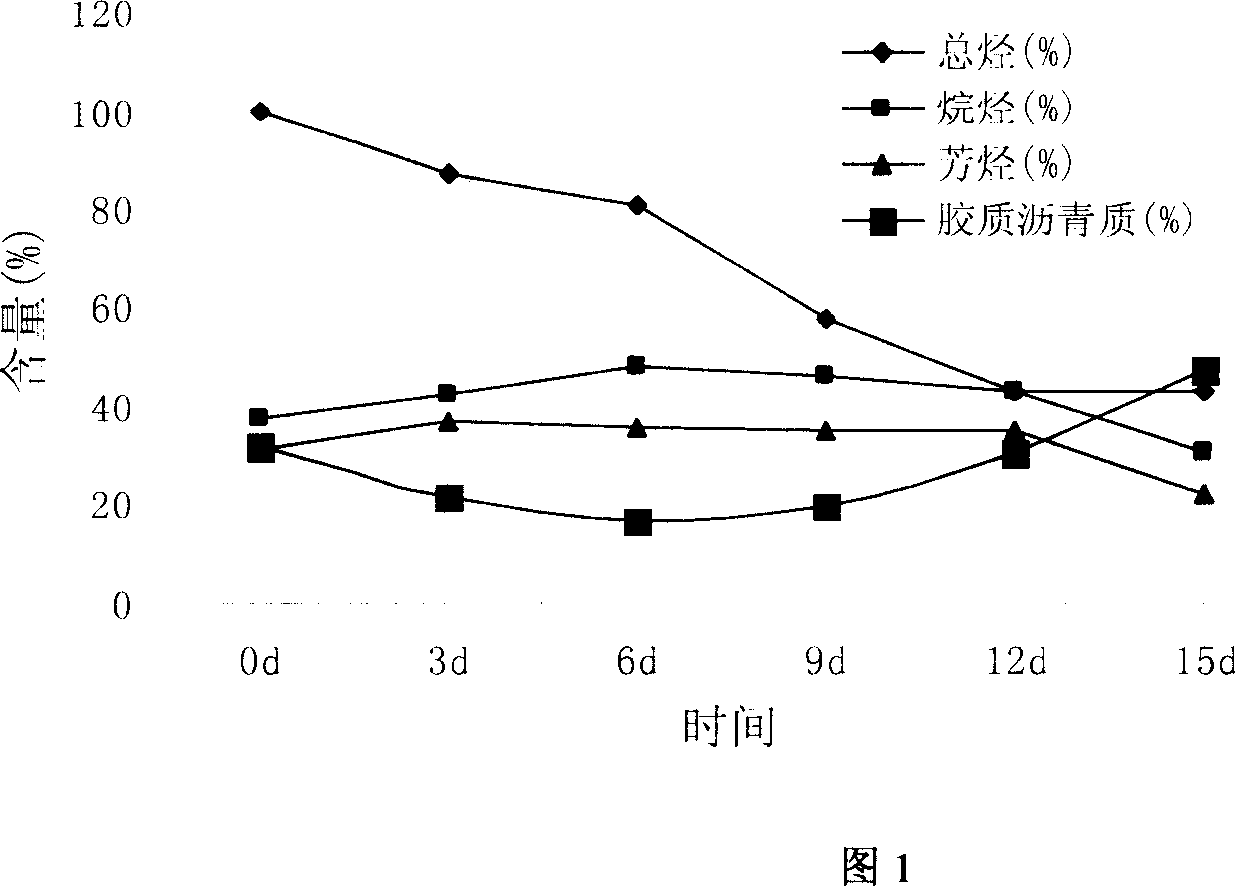
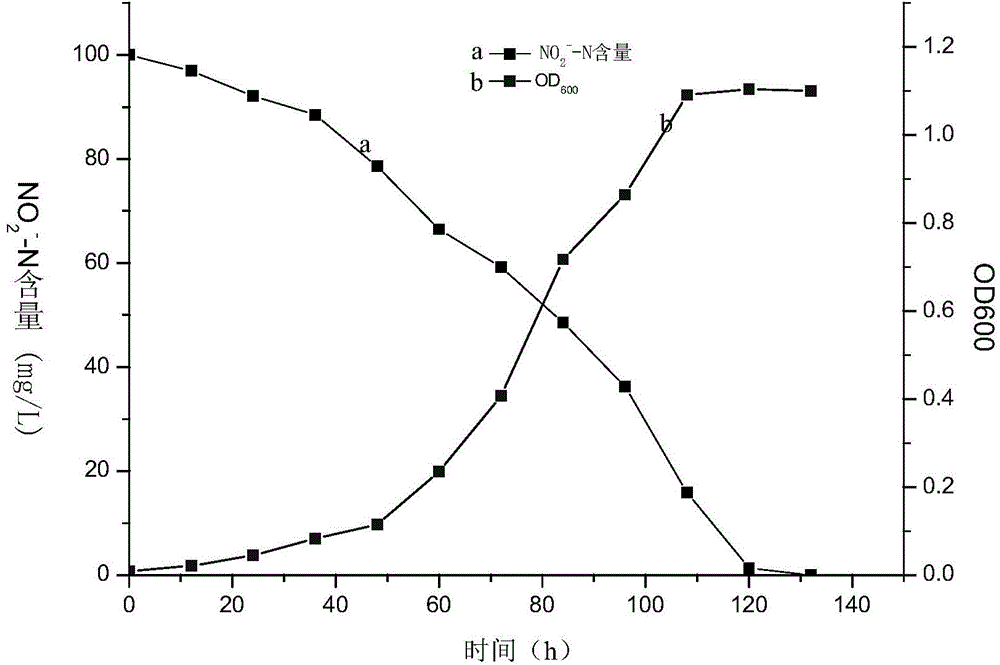
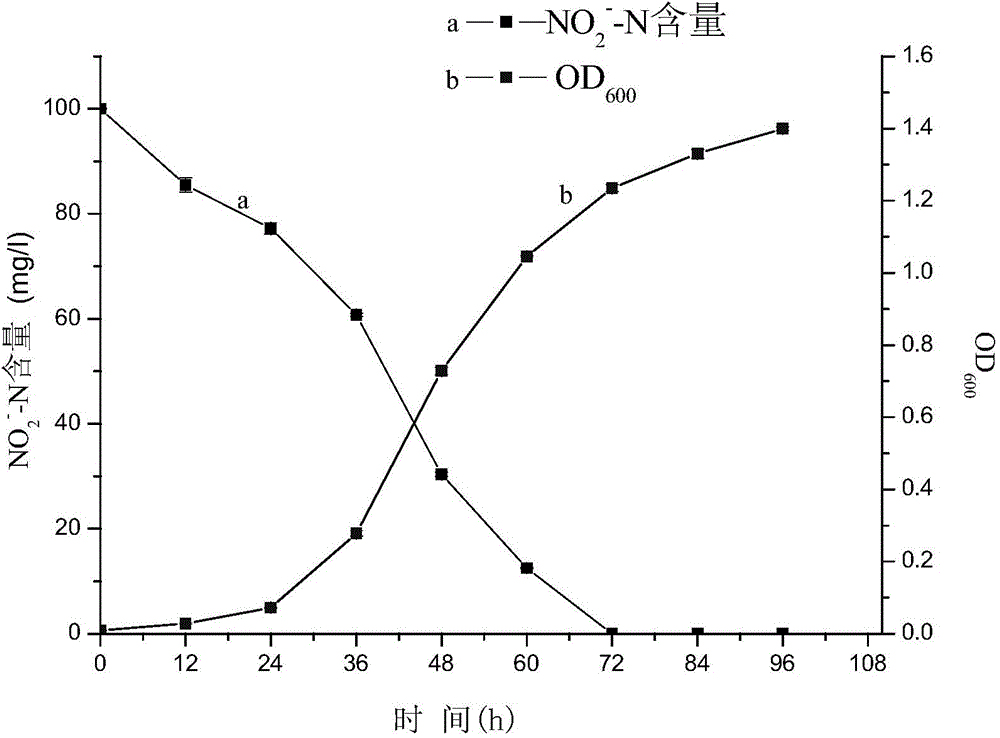
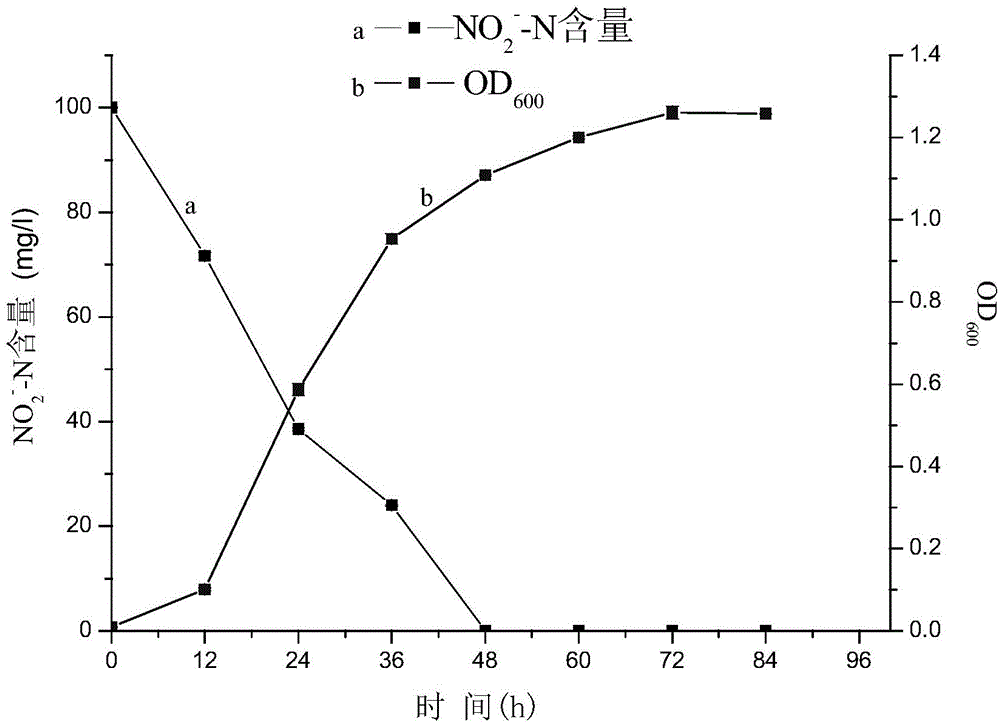
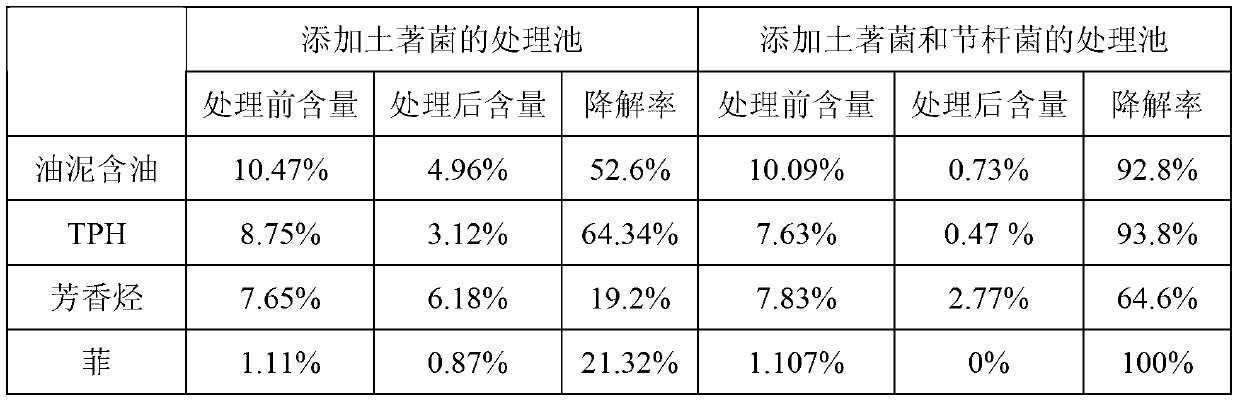
Patents
Literature
196 results about "Arthrobacter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Arthrobacter (from the Greek, "jointed small stick”) is a genus of bacteria that is commonly found in soil. All species in this genus are Gram-positive obligate aerobes that are rods during exponential growth and cocci in their stationary phase. Arthrobacter have a distinctive method of cell division called "snapping division" or reversion in which the outer bacterial cell wall ruptures at a joint.
Composite microbial inoculum organic multielement compound fertilizer and production method thereof
ActiveCN102690151AImprove physicsGood biological propertiesFertilizer mixturesThiobacillus ferrooxidansBran
The invention discloses a composite microbial inoculum organic multielement compound fertilizer which is prepared from microbial inoculum, organic component and inorganic fertilizer. The microbial inoculum is a composite microbial inoculum which comprises the following three types of microbial inocula: resource type microbial inoculum, which contains Bacillus megaterium, thiobacillus thiooxidans, Bacillus mucilaginosus and Bacillus circulans; environment-friendly microbial inoculum, which contains Arthrobacter and Alcaligenes; and antibiotic microbial inoculum, which contains Streptomycs micuoflavus and Streptomyces jingyangensis. The organic component is one or more of cereal crop straw, subsidiary agricultural product dreg, sugar mill bagasse, bran coat, municipal and rural domestic waste, and livestock and poultry dung. The inorganic fertilizer is one or more of nitrogen fertilizer, phosphate fertilizer, potash fertilizer and medium / micro-nutrient element fertilizer. The weight proportion of microbial inoculum to organic constituent to inorganic fertilizer is (5-25):(18-28):(47-77).
Owner:赵大伟
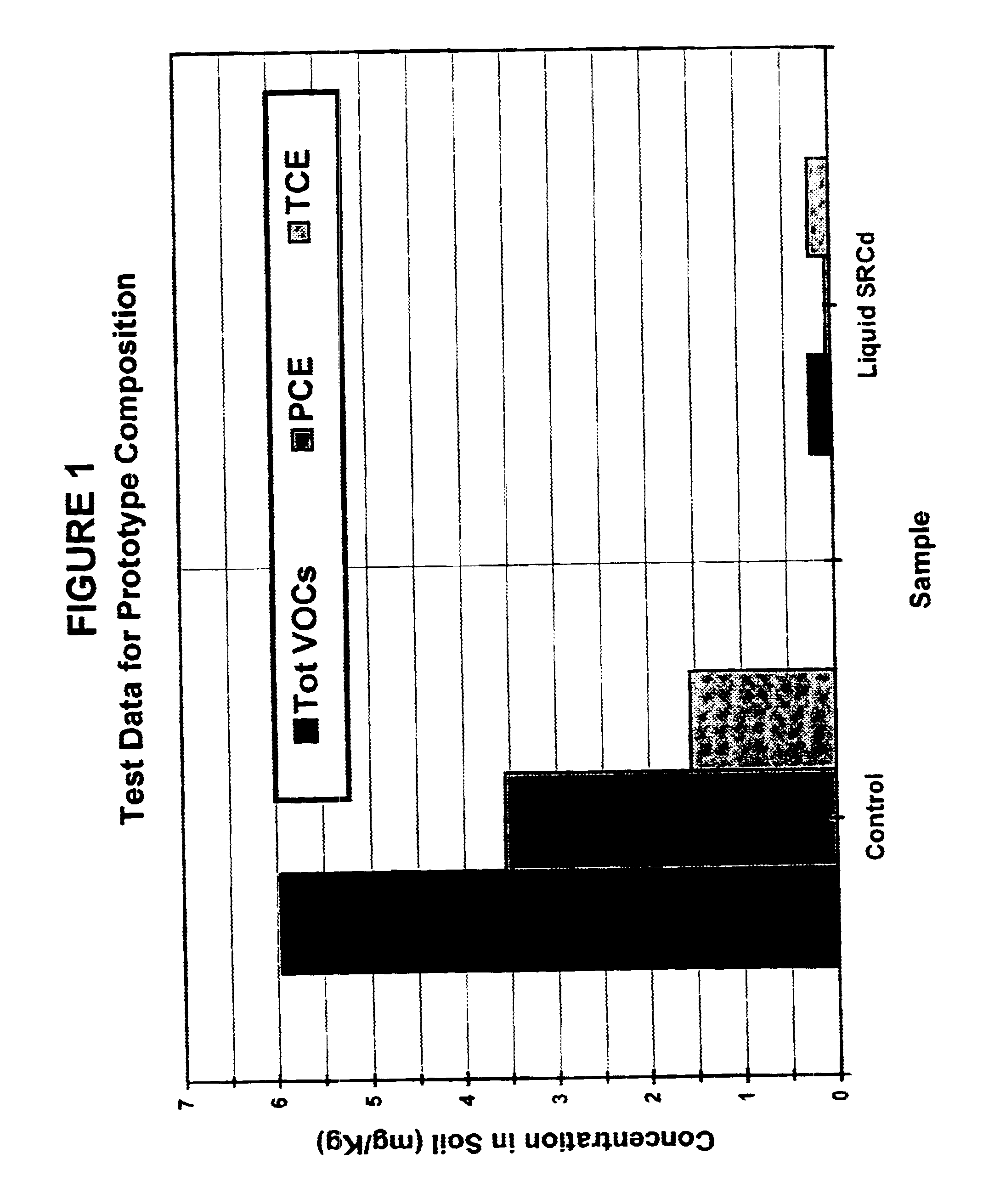
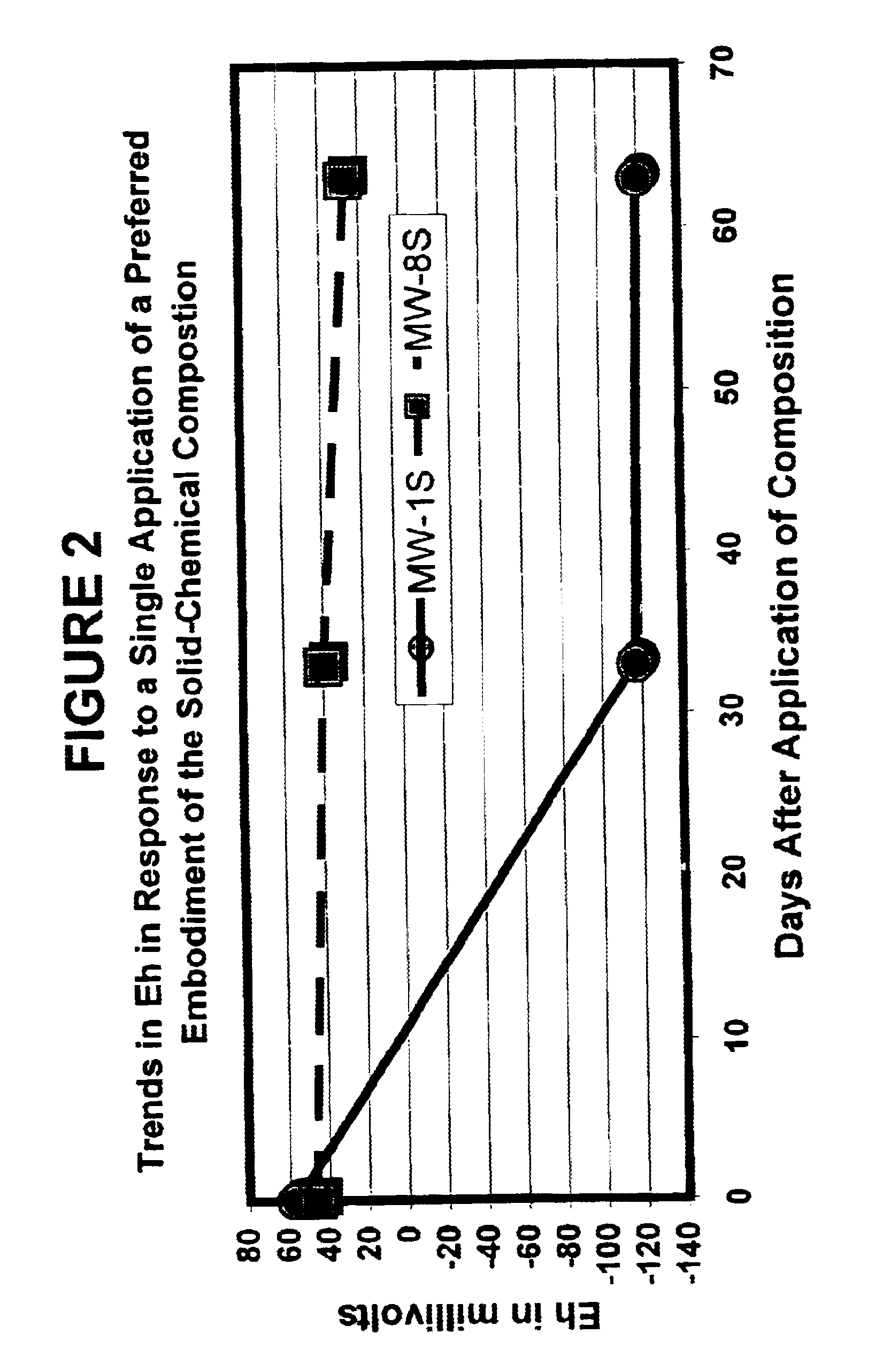
Solid-chemical composition for sustained release of organic substrates and complex inorganic phosphates for bioremediation
InactiveUS6620611B2Improve solubilityIncreasing speed and effectivenessBacteriaWater treatment compoundsPseudomonasTrichoderma spp
A slow-release solid chemical composition for environmental bioremediation is provided. The composition comprises a source of soluble organic substrates which include sugars, soluble organic polymers and mixtures of them in an amount of 7% to 90%, insoluble organic substrates an amount of 10% to 70%, complex inorganic phosphates in an amount of 0.5% to 7% and soluble organic salts in an amount of 2% to 70%. The insoluble organic substrates include fibrous plant materials, starches, cellulosic materials and mixtures of these substrates. The complex inorganic phosphates include ringed metaphosphates, linear polyphosphates and mixtures. The organic salts include lactates, formates, acetates, citrates, etc. Also the composition further comprises microorganisms which include Bacillus spp., Rhizobium spp., Bradyrhibzobium spp., Fibrobacter spp., Clostridium spp., Pseudomonas. spp., Geobacter spp., Arthrobacter spp., Nocardia, spp., aspergillus spp., Trichoderma spp., Candida spp., Yarrowia spp. and combinations of these microorganisms. The composition can be prepared in various forms, including granules, briquettes, pellets, tablets or capsules.
Owner:HINCE ERIC CHRISTIAN MR
Ketose 3-epimerase produced by arthrobacter globiformis
There are provided a highly safe epimerase usable in food industry, and a method for producing a ketose. The epimerase is a ketose 3-epimerase obtainable from a microorganism of the genus Arthrobacter, and having the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 of the Sequence Listing, and (1) substrate specificity whereby a D- or L-ketose is epimerized at position 3 to produce a corresponding D- or L-ketose, and (2) the highest substrate specificity for D-fructose and D-psicose among D- and L-ketoses. The ketose 3-epimerase is also represented by SEQ ID NO: 3 or SEQ ID NO: 4 of the Sequence Listing, and epimerizes a D- or L-ketose at position 3 to produce a corresponding D- or L-ketose.
Owner:MATSUTANI CHEM INDS CO LTD +1
Choline-utilizing microbial strains for biologically controlling fusarium head blight
InactiveUS7601346B1Effective suppressionEffective controlBiocideBacteriaTriticeaeFusarium ear blight
Three choline utilizing strains of microorganisms isolated from the anthers of wheat, Aureobasidium pullulans strain AS 55.2, Arthrobacter species strain OH 221.3, and Pseudomonas species strain AS 64.4, are superior antagonists of F. graminearum. These microorganisms are effective for suppression and control of FHB in cereals, particularly in wheat and barley.
Owner:AGRI THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICAS AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF +1
Microorganism bacterium agent for processing thick oil sewage and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN1990854AImprove biodegradabilityAvoid incomplete treatmentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCitrobacterAnaerobic bacteria
The invention relates to the biological treatment for oil extraction wastewater, which in detail relates to a bacterial agent for treating thick oil wastewater and the method for preparing the same. The comprised components and their proportion by weight are as follows: pseudomonas aeruginosa 5-10%, bacillus subtilis 10-15%, lichen bacilli 5- 15%, Citrobacter propionate tumefaciens 10- 15%, liquid gold tumefaciens 10- 20%, annular gemma bacillus 5- 10%, wilting Bacillus pumilus 5- 10%, spherical arthrobacter 5- 10%, crabstick tumefaciens 5- 10%, and hot ground anaerobic rod baceria 10- 15%. It is prepared by activating bacteria, shake-flask culturing, expanding propagating and mixing. The cooperation action is strong, the biological surface activating agent generating- bacteria can enlarge the dissolution of hydrocarbon petroleum in water and make it is easier for hydrocarbon petroleum to contact with bacteria; the anaerobic bacteria can improve the biodegradation of thick oil wastewater; the degradation perfomace of aerobic bacteria is good and suitable for biological treatment for thick oil wastewater.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
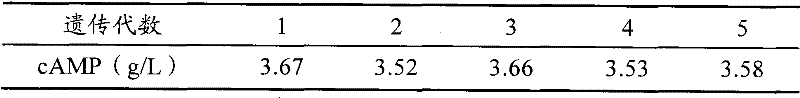
Arthrobacter for fermentative production of cyclic adenosine monophosphate and application thereof
ActiveCN102268385AAvoid damageHigh mutation rateBacteriaFermentationArthrobacterAdenosine monophosphate.cyclic
The invention provides arthrobacter for producing cyclic adenosine monophosphate through fermentation and application thereof. With a preservation number of CGMCC No.3584, the arthrobacter of the invention has a A302 strain which is three times higher than an original strain in terms of the cyclic adenosine monophosphate output. Undergoing over 10 generations of passage, the A302 strain of the invention is stable in producing cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
Owner:NANJING BIOTOGETHER
Environment-friendly straw fermenting agent
InactiveCN102517217APromote growth and developmentHigh in nutrientsFungiBacteriaCelluloseStreptomyces hygroscopicus
The invention relates to an environment-friendly straw fermenting agent. The environment-friendly straw fermenting agent is prepared from the following seven raw materials in percentage by weight: 25 percent of bacillus subtilis, 15 percent of trichoderma viride, 18 percent of saccharomyces cerevisiae, 12 percent of aspergillus niger, 10 percent of streptomyces hygroscopicus, 10 percent of trichoderma koningii and 10 percent of arthrobacter. The environment-friendly straw fermenting agent can accelerate the decomposition speed of cellulose and can completely decompose crop straws within aboutten days to return to the field, so that the straws are corroded, blackened and composted. The environment-friendly straw fermenting agent can accelerate release of nutrient elements in the straws, provides more nutrients for growth of the crops at the later stage, maintains and improves soil fertility, improves soil organic matter, improves physicochemical property of the soil, increases the yield of the crops by about 10 percent, and can be widely applied to returning straws of the crops such as rice, wheat, corn and the like to the field.
Owner:宋保德
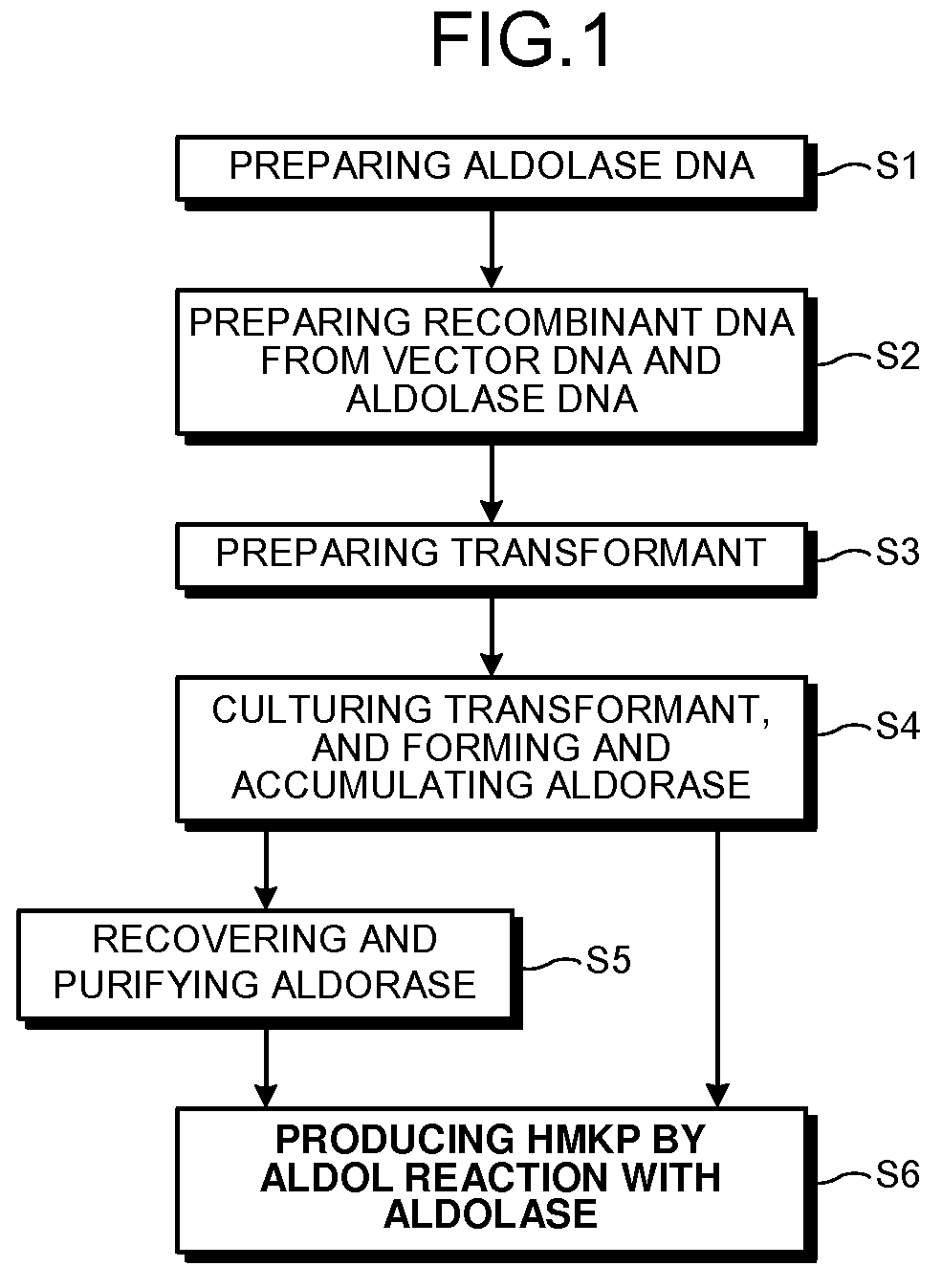
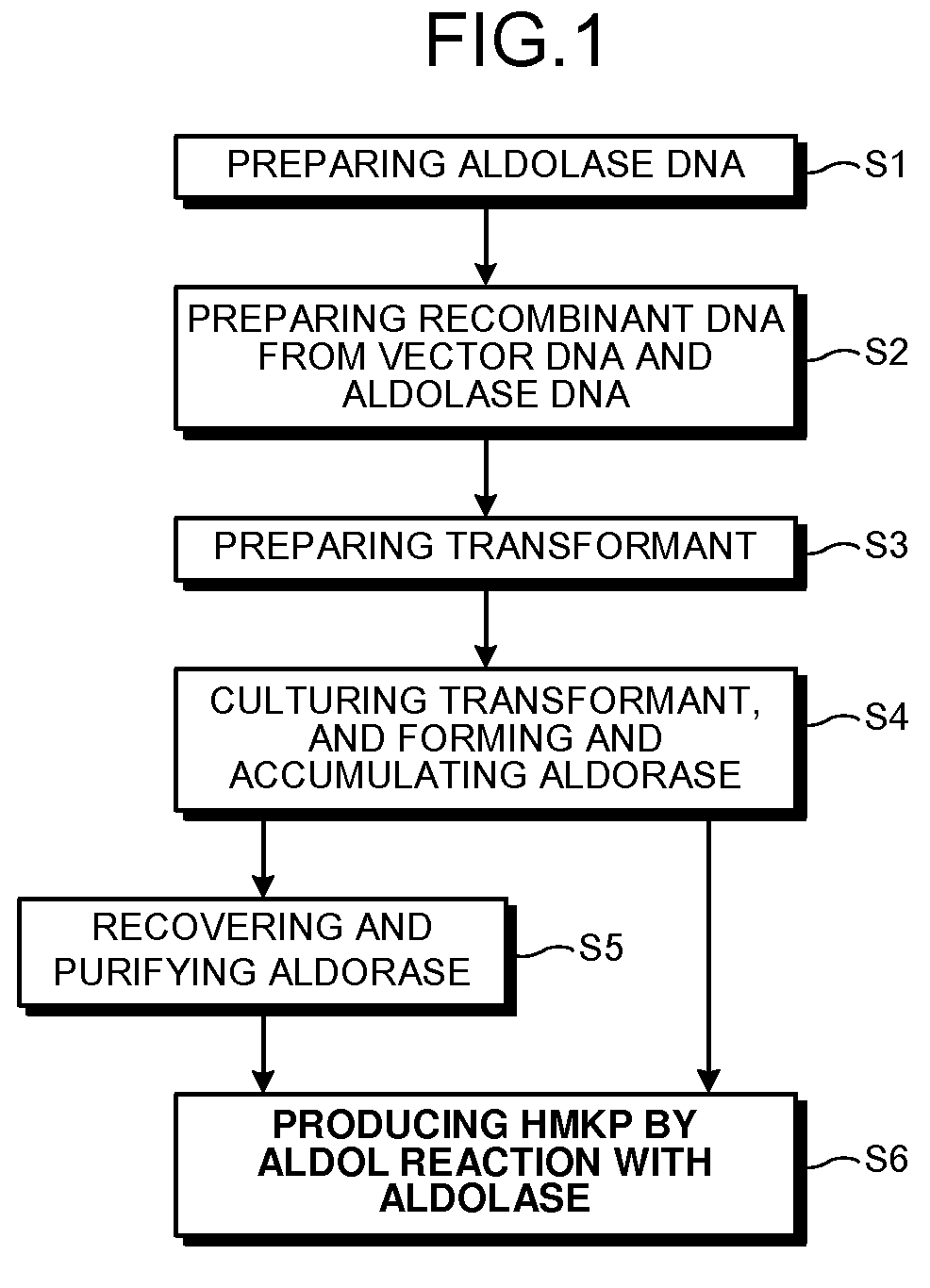
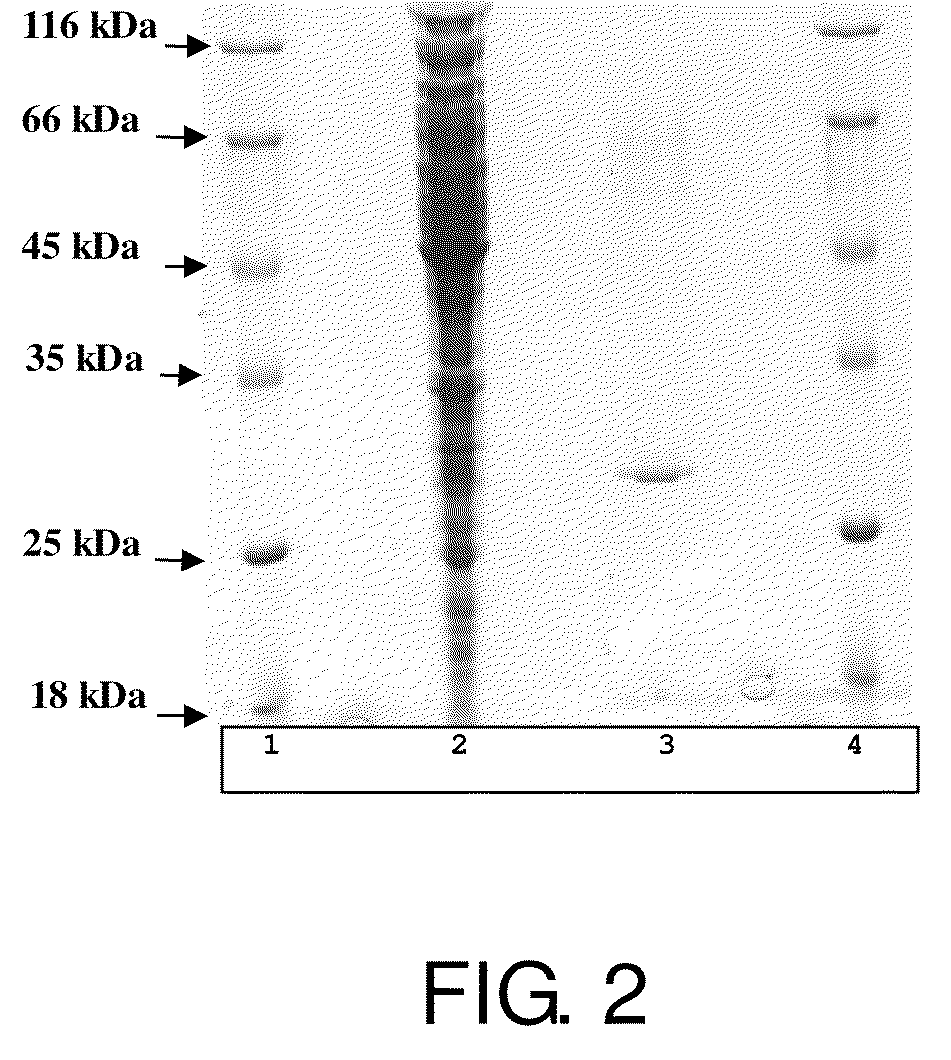
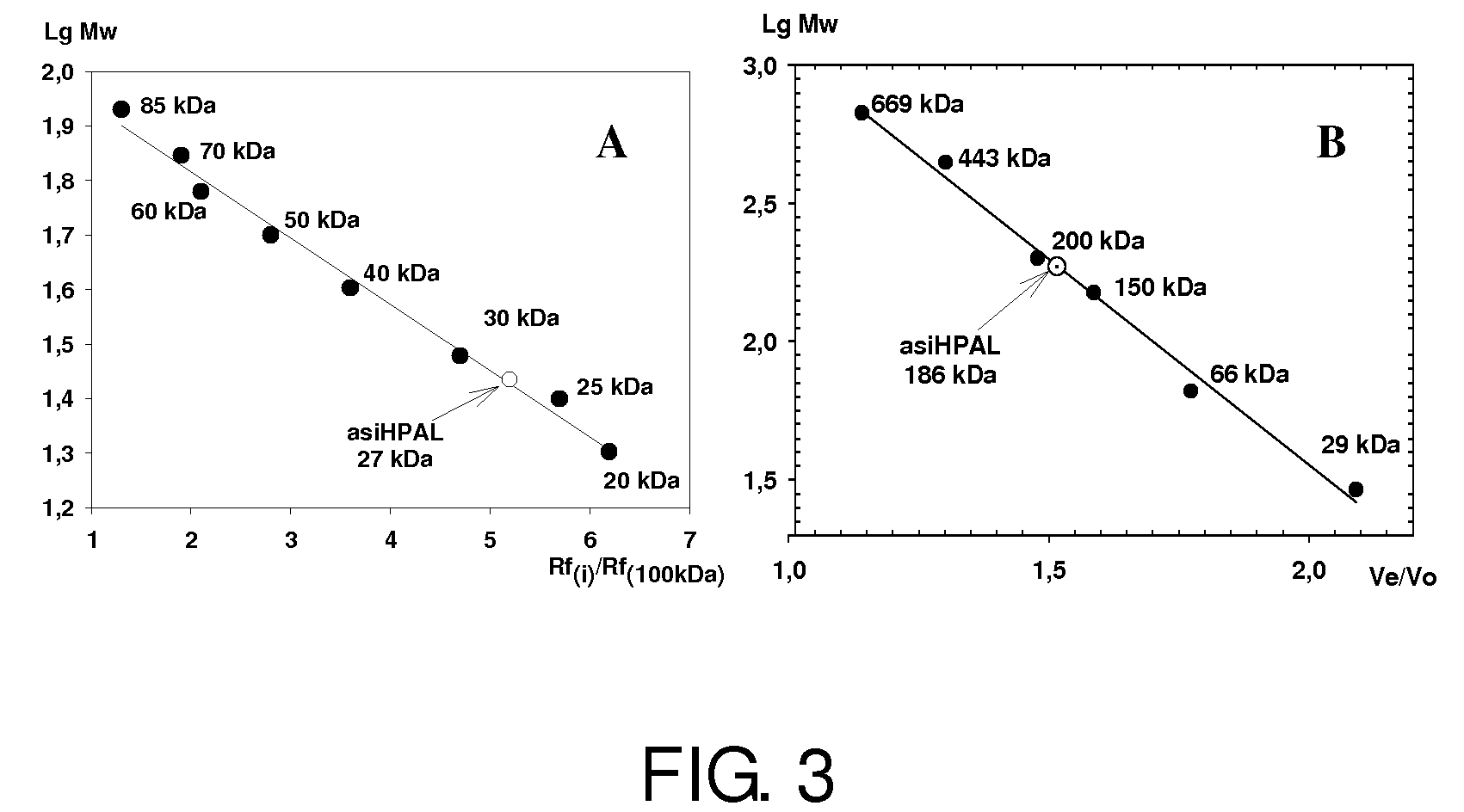
Aldolase and production process of 4-hydroxy-L-isoleucine
A novel aldolase is described. 4-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-keto-pentanoic acid, which is useful as an intermediate in the synthesis of 4-hydroxy-L-isoleucine, may be synthesized from acetaldehyde and α-ketobutyric acid using a novel aldolase, which is derived from the genus Arthrobacter.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Novel arabinose-fermenting eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS20100304454A1Improve stabilityAvoid recombinationFungiHydrolasesPropanoic acidGlucose repression
The present invention relates to eukaryotic cells which have the ability to convert L-arabinose into D-xylulose 5-phosphate. The cells have acquired this ability by transformation with nucleotide sequences coding for an arabinose isomerase, a ribulokinase, and a ribulose-5-P-4-epimerase from a bacterium that belongs to a Clavibacter, Arthrobacter or Gramella genus. The cell preferably is a yeast or a filamentous fungus, more preferably a yeast is capable of anaerobic alcoholic fermentation. The may further comprise one or more genetic modifications that increase the flux of the pentose phosphate pathway, reduce unspecific aldose reductase activity, confer to the cell the ability to directly isomerise xylose into xylulose, increase the specific xylulose kinase activity, increase transport of at least one of xylose and arabinose into the host cell, decrease sensitivity to catabolite repression, increase tolerance to ethanol, osmolarity or organic acids; and / or reduce production of by-products. The cell preferably is a cell that has the ability to produce a fermentation product such as ethanol, lactic acid, 3-hydroxy-propionic acid, acrylic acid, acetic acid, succinic acid, citric acid, amino acids, 1,3-propane-diol, ethylene, glycerol, -lactam antibiotics and cephalosporins. The invention further relates to processes for producing these fermentation products wherein a cell of the invention is used to ferment arabinose into the fermentation products.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV +1
Composite heterotrophic nitrifying bacterial agent and application of same in nitrogen removal treatment of waste water containing ammonia and nitrogen
ActiveCN102443558AStrong toleranceGood removal effectBacteriaWater contaminantsHigh concentrationWater quality
The invention relates to a composite heterotrophic nitrifying bacterial agent. The composite heterotrophic nitrifying bacterial agent is characterized by comprising pseudomonas CCTCC M 2011416, pseudomonas CCTCC M 2011417 and arthrobacter CCTCC M 2011418. The composite heterotrophic nitrifying bacterial agent also comprises domestication bacteria liquid. The invention also protects application ofthe composite heterotrophic nitrifying bacterial agent in nitrogen removal treatment of waste water containing ammonia and nitrogen, and the application is characterized in that: the composite heterotrophic nitrifying bacterial agent with an inoculation amount of 0.1 to 5% is inoculated into a water body containing ammonia and nitrogen; the number of live bacteria in the composite heterotrophic nitrifying bacterial agent is 109 to 1010 / mL; treating conditions are that temperature is 20 to 35 DEG C, pH is 6 to 9 and aeration time is 48 to 72 h. The composite heterotrophic nitrifying bacterial agent provided in the invention has strong ability in enduring waste water with a high concentration of ammonia and nitrogen, can be used for nitrogen removal treatment of waste water with a concentration of ammonia and nitrogen greater than 400 mg / L, has a high removal capability to waste water with a high concentration of ammonia and nitrogen, with a removal rate of ammonia and nitrogen being more than 99%, substantially reduces the content of ammonia and nitrogen in a water body and improves water quality.
Owner:JIANGSU JIANGDA ECOLOGICAL SCI & TECHCO +1
Arthrobacter, uses for produced xanthine oxidase and production method thereof
InactiveCN101402922AHigh activitySimple nutritional requirementsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesArthrobacterNitrogen
The invention provides an Arthrobacter and an application of the Arthrobacter for generating xanthine oxidase and a preparation method thereof. The Arthrobacter XL2006 derives from nature and the16S rRNA sequence of the Arthrobacter XL2006 is shown in a sequence table SEQ ID NO.1. The Arthrobacter XL2006 is applied to producing, extracting and purifying the xanthine oxidase and preparing a diagnostic kit. The Arthrobacter XL2006 is characterized by the production of the xanthine oxidase and can adopt hypoxanthine or xanthine as a unique source of carbon and nitrogen and a unique energy source. The fermentation and the production of the xanthine oxidase are characterized by simple nutritional requirements, easy culture and short fermentation time; the produced xanthine oxidase has quite high activity, and strains provided by the invention are utilized to ferment and extract the xanthine oxidase and the prepared diagnostic kit can be applied to clinically testing the levels of hypoxanthine and xanthine in blood serum of patients.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Method for preparing biochemical preparations for treating threonine fermentation wastewater
ActiveCN106082532ALarge specific surface areaHigh tensile strengthTreatment using aerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentBiotechnologyThreonine
The invention relates to a method for preparing biochemical preparations for treating threonine fermentation wastewater. The method includes preparing physical adsorbents and complex microbial inoculants. The complex microbial inoculants comprise, by volume, 6-7 parts of yeast, 5-6 parts of arthrobacter, 5-6 parts of pseudomonas, 4-5 parts of rhodococcus, 4-5 parts of bacillus amyloliquefaciens, 4-5 parts of clostridium and 3-4 parts of scenedesmus obliquus. The method has the advantages that the biochemical preparations contain diversified microorganisms with excellent degradation capacity for refractory pollutants, various strains are reasonably compatible with one another, accordingly, excellent degradation effects can be realized, and the method has a broad application prospect.
Owner:内蒙古阜丰生物科技有限公司
Environmentally-friendly fertilizer and making method thereof
InactiveCN106588466AIncrease profitAvoid pollutionSuperphosphatesMagnesium fertilisersBacillus megateriumPseudomonas
The invention belongs to the technical field of fertilizers, and concretely discloses an environmentally-friendly fertilizer and a making method thereof. The making method of the environmentally-friendly fertilizer comprises the following steps: mixing an organic fertilizer, a charcoal fertilizer, a composite fertilizer, modified starch, a phosphate compound and a composite biological inoculant according to a certain mass fraction ratio, standing the obtained mixture, drying the mixture, granulating the dried mixture, and drying obtained granules, wherein the charcoal fertilizer is prepared from hickory shells, rice straws, rice husks, corn stalks and corncobs according to a certain weight ratio; and the composite bacterial inoculant is prepared by mixing ferment bacteria, Arthrobacter globiformils, Bacillus megaterium, Pseudomonas pseudoacaligenes, polysorbate and sodium dodecyl sulfate according to a certain weight ratio. The environmentally-friendly fertilizer prepared in the invention has the characteristics of comprehensive and balanced nutrition, high utilization rate, no pollution, effective increase of the output of crops, and effective absorption and degradation of heavy metals and organic pollutants from soil, so the absorption of pollutants by crops is reduced, thereby guaranteeing the health of human bodies.
Owner:兴业县保旺生物肥有限公司
Microbial inoculum for repairing amino benzenes polluted water and its preparation method and using method
InactiveCN101165167AContinuously strengthen the purification effectCutting costsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationAeromonas
The present invention relates to microbiology technology, and is especially microbial preparation for repairing aniline contaminated water and its preparation process and usage. The microbial preparation consists of aerobes Pseudomonas, Alealigenes, Zoogloea, Aeromonas, Arthrobacter and Bacillus in the weight ratio of 8-10 to 3-4 to 1-2 to 1-3 to 1-2 to 1-2, as well as culture liquid containing aniline. It is applied into aniline contaminated water to reach aniline degrading rate up to 80-100 %. It is prepared through domestication in relatively high concentration nitro arene compound and nutritious compound and screening. It has high growth and reproduction capacity, powerful adaptability, high biomass, low cost, powerful water purifying effect and no secondary pollution.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Arthrobacter with aerobic denitrification capability and application thereof
ActiveCN104862260AStrong toleranceGood removal effectBacteriaWater contaminantsMicroorganismArthrobacter
The invention discloses an arthrobacter with aerobic denitrification capability and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of microorganism application. The arthrobacter DYS3-4 with aerobic denitrification ability is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, the preservation date is 29th, April, 2015 and the preservation number is CCTCC M 2015 264. The arthrobacter DYS3-4 can be applied to nitrogenous effluent biological denitrification, mariculture nitrite removal, freshwater aquaculture nitrite removal and low temperature denitrification microorganism preparation. Under an aerobiotic condition, the nitrate and the nitrite in the water environment can be rapidly and effectively removed. The arthrobacter growth temperature scope is wide, the denitrification effect at the temperature of 10-35 DEG C is good, and the arthrobacter has good application prospect in the nitrogenous effluent biological denitrification and the freshwater aquaculture nitrite removal.
Owner:THIRD INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY STATE OCEANIC ADMINISTATION
Arthrobacter strain highly effectively degrading phenanthrene, and application thereof
ActiveCN103215204AReduce contentRealize harmless disposalBacteriaWater contaminantsPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonArthrobacter
The invention provides an arthrobacter strain highly effectively degrading phenanthrene, and an application thereof. The phenanthrene-degrading arthrobacter strain has a preservation number of CGMCC No. 6581. The strain provided by the invention can effectively degrade polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and heterocyclic substances in soil and oil sludge, and can be effectively applied in biodegradation treatments of petroleum-contaminated soil and PAHs pollutants in soil in loess highlands. Especially a phenanthrene degradation rate can be higher than 98%. The invention also provides a formula of a nutrient solution for the growth and degradation of the strain, and a method for applying the strain in petroleum-contaminated soil field reparation.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Protein extracted from perinereis aibuhitensis, its preparation method and use
InactiveCN1521188AHigh antibacterial activityPrevent proliferationAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliPerinereis aibuhitensis
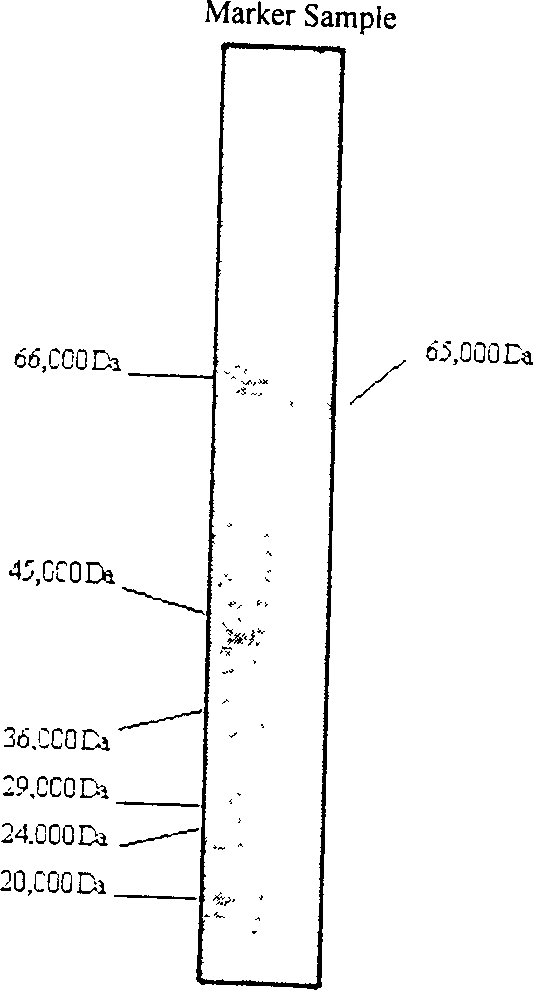
The present invention is one kind of protein extracted from Perinereis aibuhiteris and its preparation process and use. The protein is alkali protein with molecular weight 65000 Da and isoelectric point of 8.3. The protein preparing process includes raising Perinereis aibuhiteris in artificial sea water for 24-48 hr to make it become clean, electrically striking Perinereis aibuhiteris with 5-10 V DC to obtain body fluid, centrifugally filtering body fluid, reverse concentration, gel filtering, and chromatographic elution in anionic exchange column to collect active protein. The protein is used in preparing antibiotic medicine resisting escherichia coli, verdigris pseudomonad, staphylococcus aureus and arthrobacter and anticancer medicine for suppressing human liver cancer cell strain proliferation and producing alpha-fetoglobulin, and has high antibiotic activity and obvious anticancer effect.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Composition of bacterial strains, bioremediation mixture and use of this composition for the removal of contaminants from the soil and the method for purifying the soil contaminants
InactiveUS20140141494A1Low costFacilitates quick acquisition of appropriate amountBacteriaBiochemical fibre treatmentBacteroidesFood contaminant
The object of the present invention is a composition of bacterial strains which may comprise Stenotrophomonas sp. strain 2L, Stenotrophomonas sp. strain 5L, Stenotrophomonas sp. strain 6L, Stenotrophomonas sp. strain 3N, Achromobacter sp. strain 4P, Arthrobacter sp. strain 1N, Brevundimonas sp. strain 2N, Brevundimonas sp. strain 5N, Brevundimonas sp. strain 6N, Pseudomonas sp. strain 3G, and Pseudomonas sp. strain 4, deposited under the number KKP 2041p (IAFB Collection of Industrial Microorganisms—Institute of Agricultural and Food Biotechnology in Warsaw), a bioremediation vaccine (bioremediation mixture) which may comprise the composition of these strains, the use of the vaccine in the removal of contaminants from the soil, and the method for the treatment of contaminated soil.
Owner:UNIWERSYTET WARSZAWSKI
Arthrobacter mutant strain, method for producing lactase from mutant strain and method for preparing lactulose by using lactase
InactiveCN102168028ANot generatedHigh purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCatalytic methodLactase
The invention belongs to the technical fields of food and biology, and discloses an Arthrobacter mutant strain (Arthrobacter sp.jnsb-2), a method for producing lactase by fermentation culturing of the mutant strain and a catalytic method for synthesizing lactulose from lactose and levulose by using the lactase as a catalyst. In the invention, the Arthrobacter mutant strain jnsb-2 is used as the strain of which the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M209210, and is subjected to fermentation culturing on a fermentation culture medium composed of a carbon source, a nitrogen source and inorganic salt, thus obtaining the lactase; and by using the lactase as a catalyst, lactose and levulose can be used as substrates and converted into the lactulose by an enzyme method. The lactase produced by the fermentation of the strain has the advantages of extensive culturing conditions, short enzyme production cycle and convenient operation process; and by using the enzyme method to convert the lactase into the lactulose, the defects that the product is easy to degrade and the colored byproduct is difficult to remove in the lactulose preparation process based on the chemical method are overcome, and a high product purity is achieved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
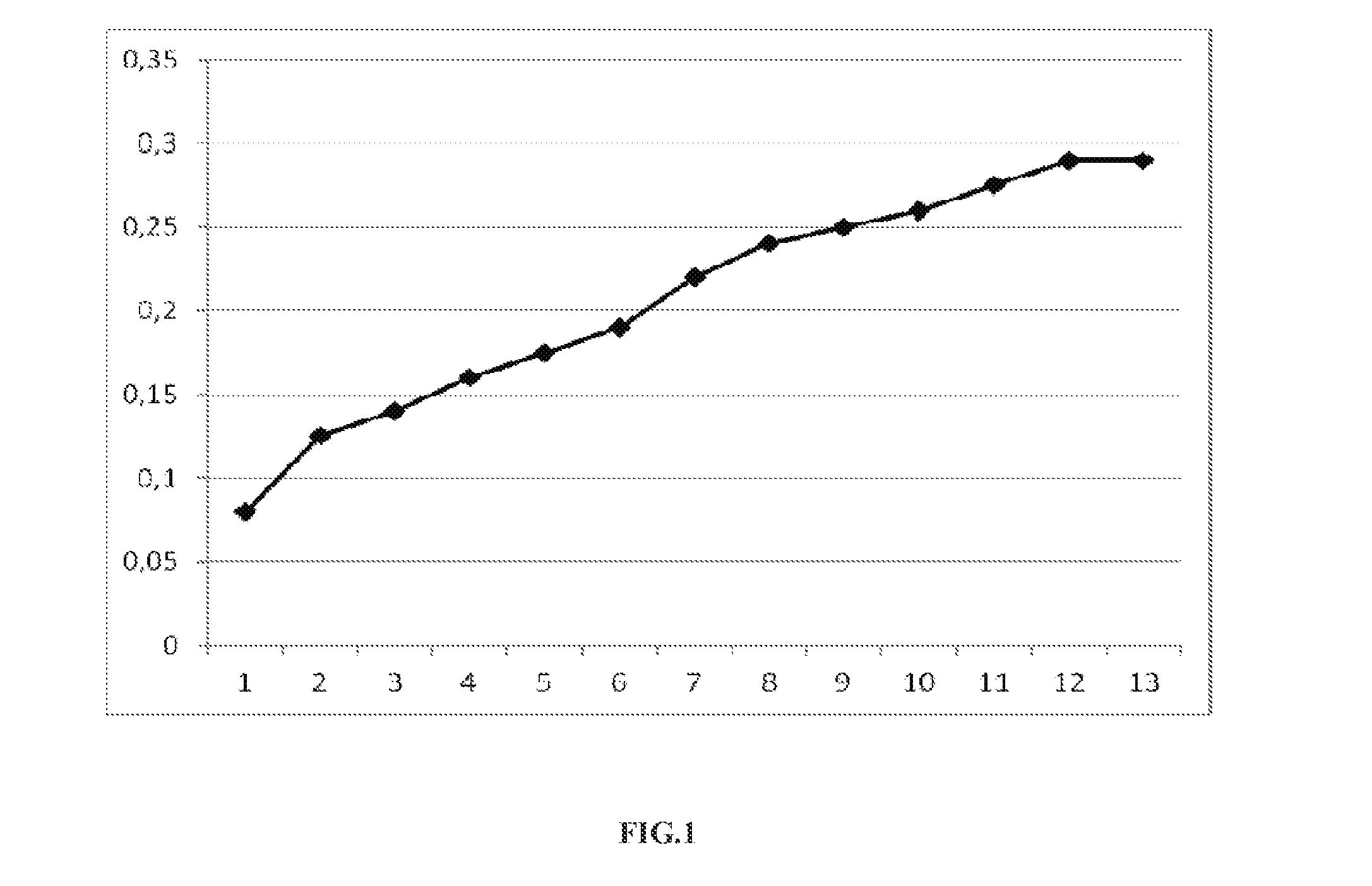
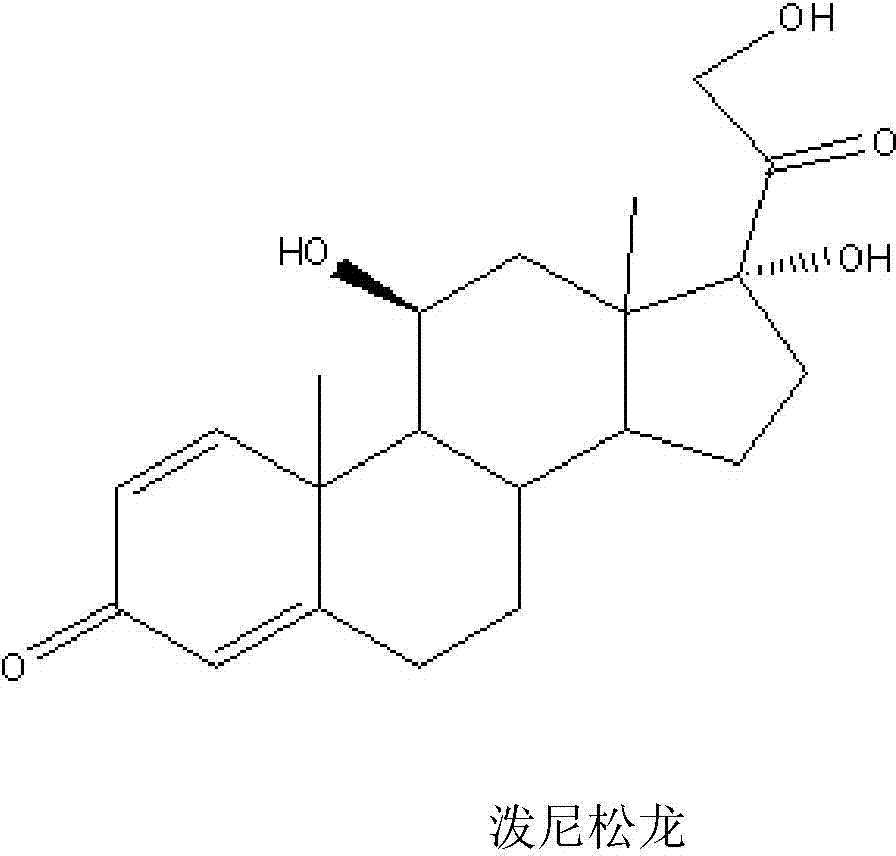
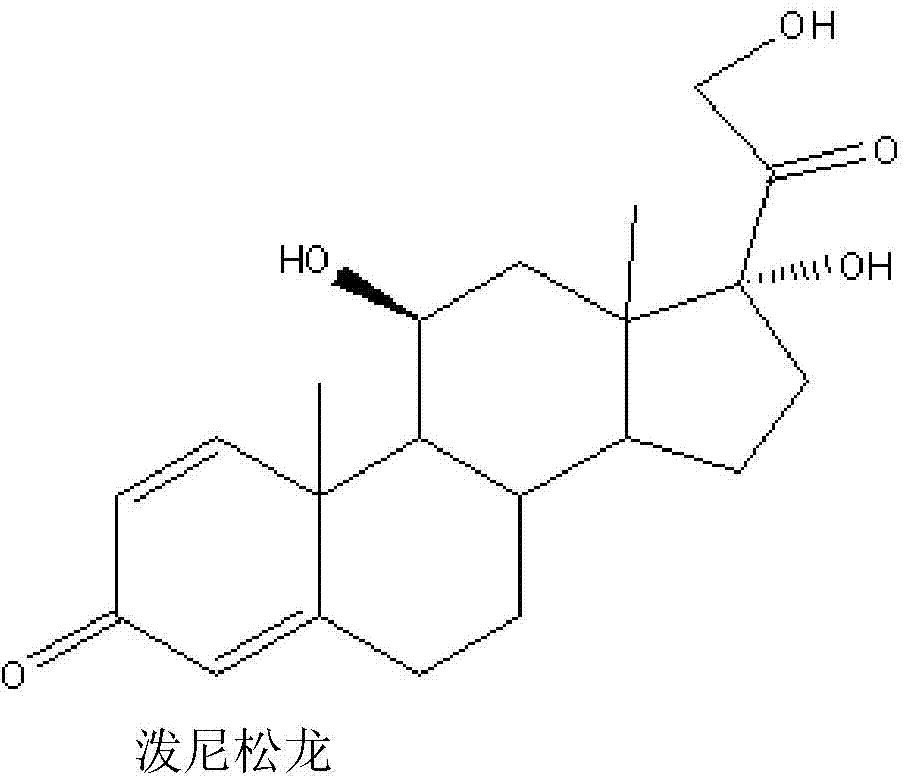
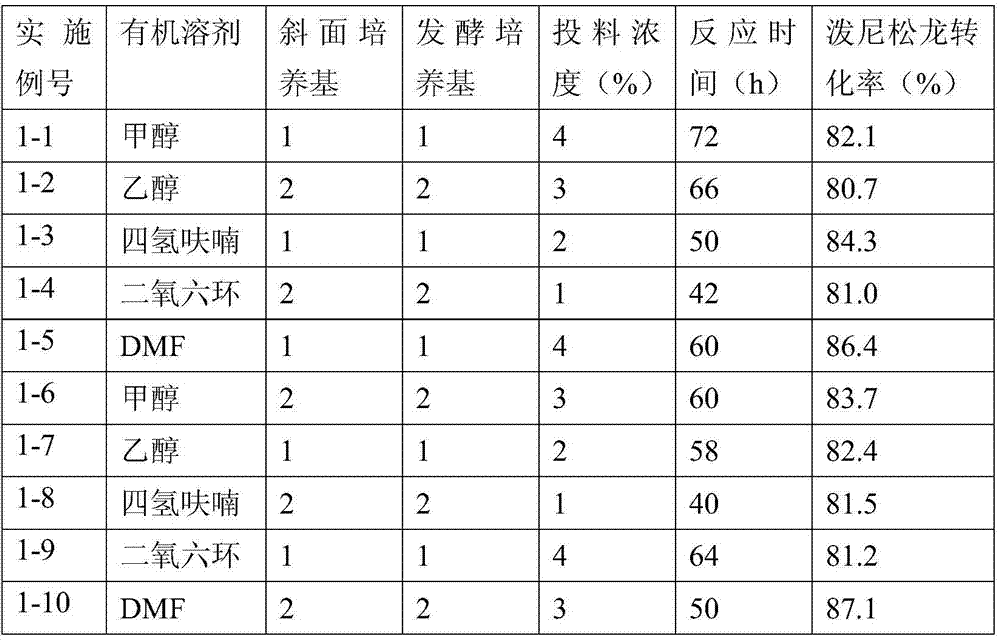
Method for preparing prednisolone through bio-fermentation in one step
The invention relates to a method for directly generating prednisolone through bio-fermentation in one step by using cortisone acetate as a raw material and Arthrobacter Simple ATCC 21032.
Owner:TIANJIN JINYAO GRP
Method for preparing small-molecule hyaluronic acid by enzymatic digestion method, obtained small-molecule hyaluronic acid and application thereof
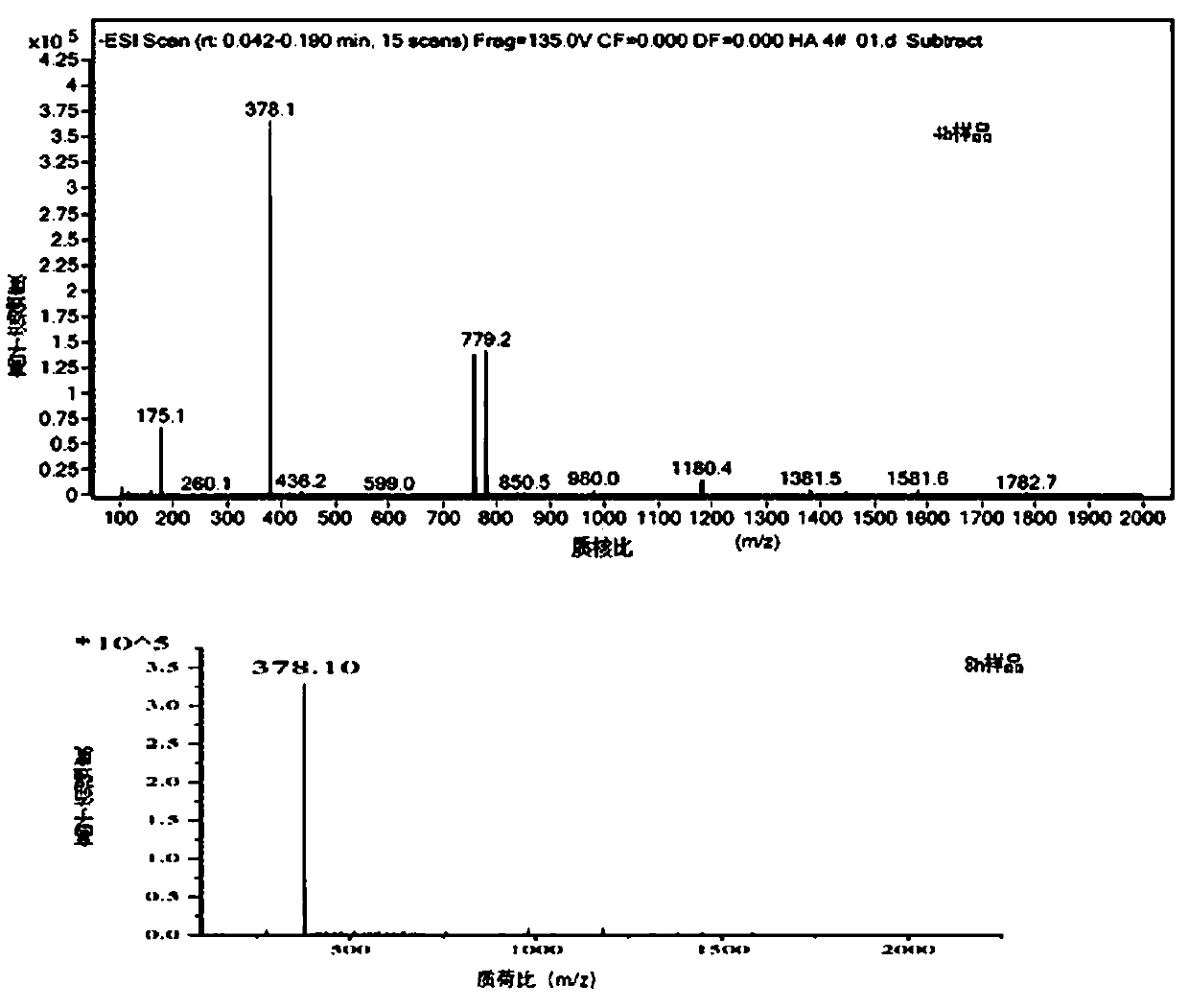
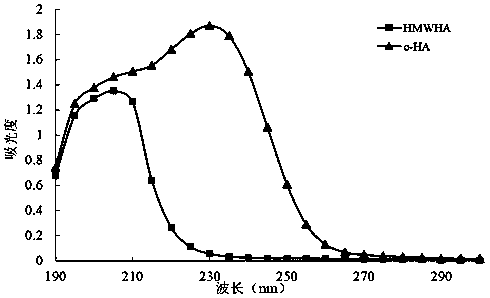
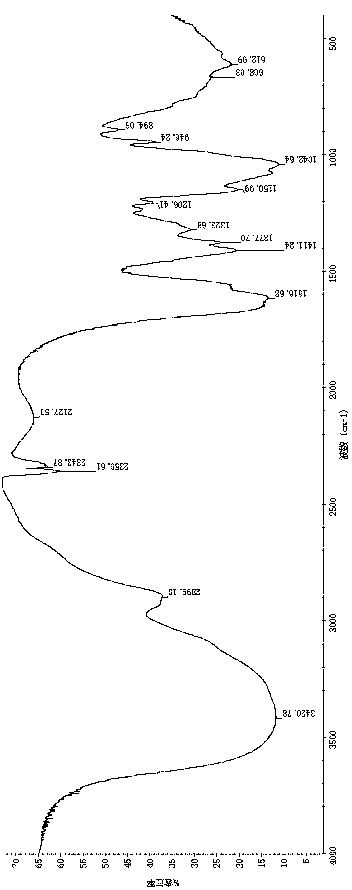
ActiveCN110331178AEasy to operateMild conditionsCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsEnzymatic digestionNon toxicity
The invention provides a method for preparing small-molecule hyaluronic acid by an enzymatic digestion method, the obtained small-molecule hyaluronic acid and application thereof. According to the method for preparing the small-molecule hyaluronic acid by the enzymatic digestion method, the obtained small-molecule hyaluronic acid and the application thereof, hyaluronic acid with a molecular weightgreater than 600 kDa or salts of the hyaluronic acid are degraded by using hyaluronidase prepared by fermentation of arthrobacter globiformils HL6 with the preservation number being CCTCC NO:M 2018452 or hyaluronidase as shown in SEQ ID NO:1, the small-molecule hyaluronic acid or salts of the small-molecule hyaluronic acid are prepared, the process of the method is easy to operate, the conditionis mild, no environmental pollution and animal source virus pollution exist, no damage is caused to a product structure, the product homogeneity is good, and environmentally friendly industrial production of the small-molecule hyaluronic acid is realized. The prepared small-molecule hyaluronic acid has the advantages of high purity, safety and non-toxicity, good moisturizing, transdermal absorption, anti-oxidation and anti-inflammatory activities, is widely used in the fields of food, cosmetics and medicine, can further be used as a standard product for the research on the structure and quality of hyaluronic acid, and has broad research and application prospects.
Owner:MARINE BIOMEDICAL RES INST OF QINGDAO CO LTD
Compound microecological preparation for prawn
InactiveCN1620892ANo adverse effects on palatabilityImprove the body's immunityAnimal feeding stuffVector-based foreign material introductionBacillus licheniformisArthrobacter
The composite micro ecological preparation for prawn consists of live bacteria bead and carrier, and features that the live bacteria bead contains Bacillus subtilis in 1-2 billion CFU / g, Bacillus licheniformis in 0.5-10 billion CFU / g, double microcapsule coated lactic acid bacterian in 0.3-0.5 billion CFU / g, and double microcapsule coated tobacco arthrobacter in 0.2-0.5 billion CFU / g, with the total live bacteria being in the range of 2-4 billion CFU / g. The present invention has the advantages of: small added amount of 0.1-0.2 %, obvious effect of raising immunity and survival rate of prawn, obvious function of raising the digestion and absorption of prawn and lowering the feed coefficient, no bad effect on the taste of feed, stable material source, low cost and simple production process.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Arthrobacter and application thereof
ActiveCN104946556ANo pollution in the processNo pollutionBacteriaWater contaminantsInorganic saltsArthrobacter
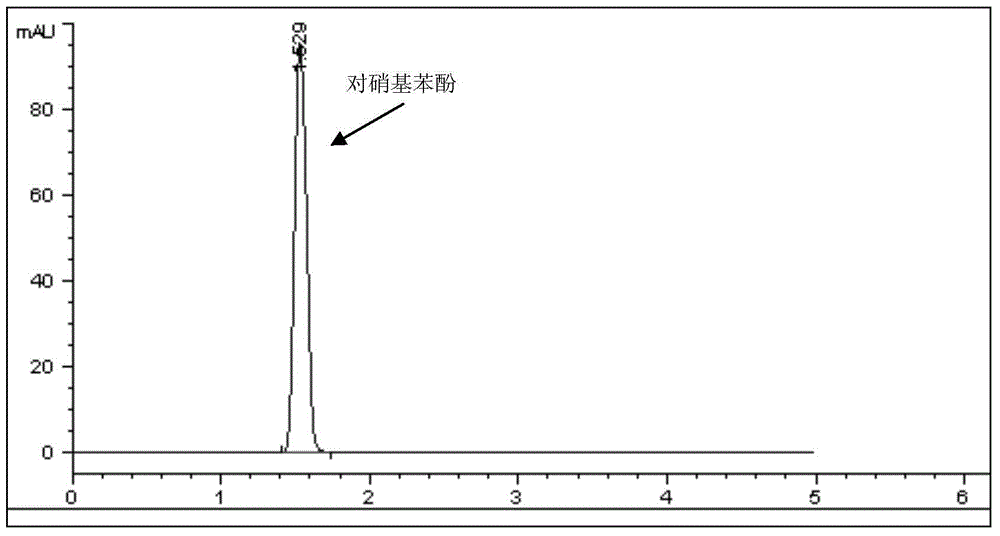
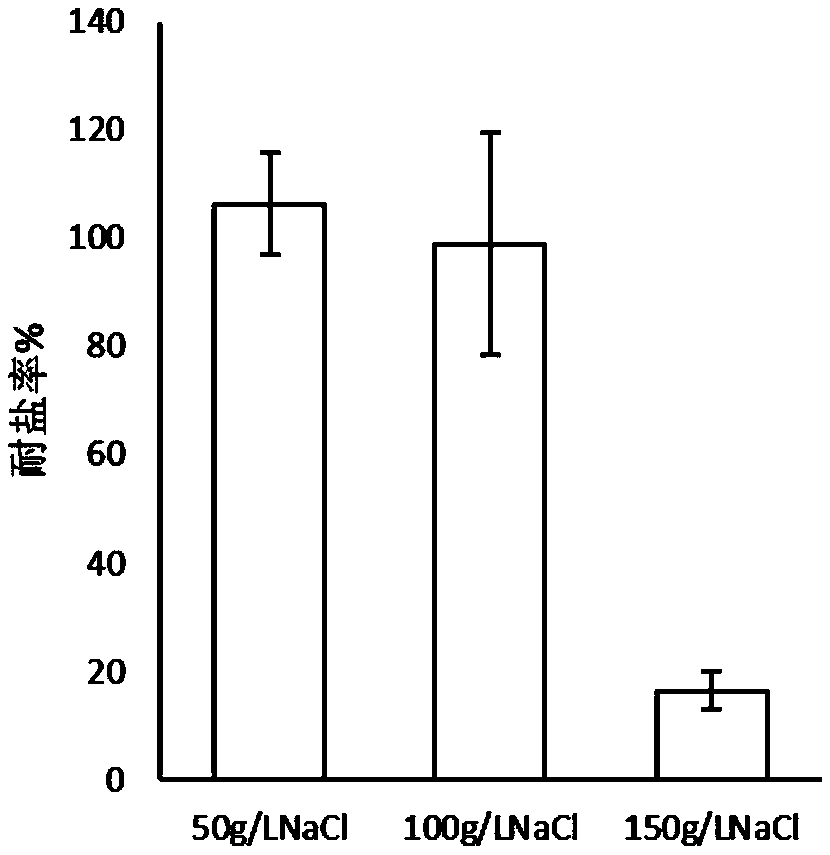
The invention provides an arthrobacter and an application thereof. The arthrobacter is YC-RL1 collected with the serial number of CGMCC No.10611 and can be used for simultaneously degrading a mixture composed of 100mg / L naphthalene, 100mg / L fluorene, 100mg / L biphenol, 100mg / L 1, 2, 3, 4-tetrachlorobenzene and 100mg / L p-nitrophenol in an inorganic salt within 4 days. The arthrobacter has a relatively-wide tolerance range for salt ion concentration and can be used for simultaneously degrading a mixture composed of five 100mg / L compounds in an inorganic salt ion culture medium with the NaCl concentration of 0-60g / L within 5 days. YC-RL1 can be applied to biological remediation of an environment polluted by naphthalene, fluorene, biphenol, 1, 2, 3, 4-tetrachlorobenzene and p-nitrophenol and an environment simultaneously polluted by various pollutants, also has a favorable application potential for high-salt industrial production wastewater treatment of the pollutants and also has a relatively-high economic value and a relatively-good application prospect.
Owner:中国农业科学院研究生院
Vancomycin production wastewater treatment method
ActiveCN106746160AEfficient removalImprove processing efficiencyMultistage water/sewage treatmentStaphylococcus cohniiTotal nitrogen
The present invention relates to a vancomycin production wastewater treatment method, which comprises: (1) carrying out coagulation precipitation treatment on vancomycin production wastewater, and filtering to remove precipitate; (2) carrying out anaerobic biochemical treatment on the effluent obtained in the step (1), and pouring Pseudomonas stutzeri FSTB-5; and (3) carrying out aerobic biochemical treatment on the effluent obtained in the step (2), and pouring a COD removing denitrogenation bacterial agent, wherein the COD removing denitrogenation bacterial agent comprises at least one selected from Pseudomonas stutzeri FSTB-5, Paracoccus denitrificans DN-3 and Methylobacterium SDN-3, at least one selected from Arthrobacter FDN-1 and Flavobacterium aquatile FDN-2, and at least one selected from Kocuria palustris FSDN-A and Staphylococcus cohnii FSDN-C. According to the present invention, the coagulation precipitation-anaerobic biochemical treatment-aerobic biochemical treatment combination treatment process is used, the specific COD removing bacterial agent is poured into the anaerobic unit, and the specific COD removing denitrogenation bacterial agent is poured into the aerobic unit, such that the efficient removal of the COD and the total nitrogen from wastewater is achieved, and the treatment method has characteristics of simple process, high treatment efficiency, low treatment cost, and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Biological agent prepared by Arthrobacter AS-1 strain and its application
InactiveCN1654632AImprove qualityShort fermentation cycleTobacco treatmentBacteriaBacteroidesBiotechnology
The present invention relates to biological preparation prepared with arthrobacter AS-1 strain and its application, and belongs to the field of microbial technology. The microbial strain is preserved in the preservation number of CGMCC No. 1281. The biological preparation is prepared through the process including the steps of: test seed culture, shaker culture, seeding tank culture and liquid fermentation in fermenting tank. The culture process has strain inoculating amount of 0.5-2 %, adopts the culture medium comprising beef paste, yeast extractum, peptone and glucose and of pH 6.8-7.2. The fermentation is controlled in 28-30 deg.c and pH 7.0-7.2, the fermentation time in the seeding tank is 16-20 hr, the fermentation time in the fermenting tank is 24-48 hr, and the biological preparation is obtained after the bacteria number in the fermentation liquid reaches 7.0 E8 / ml. The present invention has the advantages of short fermentation period, saving in power, low cost, no pollution, etc.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Method of removing recalcitrant organic pollutants
InactiveUS20130334135A1Efficient biodegradationReducing the recalcitrant chemical oxygen demand (COD)Treatment using aerobic processesBacteriaChemical oxygen demandComamonas
Recalcitrant chemical oxygen demand (COD) of a liquid is reduced in a water treatment system. The method includes pretreating the liquid in a pretreatment unit to remove indigenous bacteria or microbes to a population level below which the indigenous organisms can interfere with the screened and externally introduced microorganisms. The liquid is then provided to a reactor that has a filter bed formed with a carrier material. Special microbes are screened and used to colonize the carrier material to remove recalcitrant COD. A biofilm is cultured on the surface of the carrier material to immobilize the screened microbes in the reactor. The method further includes percolating the liquid from the pretreatment unit through the filter bed colonized with the screened microbes to degrade at least part of the recalcitrant COD under aerobic conditions. In one embodiment, the filter is formed with biological granular activated carbon (GAC) as the carrier material and the screened microbes comprise at least one microbial species selected from the group consisting of Bacillus, Comamonas, Arthrobacter, Micrococcus, Pseudomonas, Pediococcus, Achromobacter, Flavobacterium, Mycobacterium, Rhodanobacter, Stenotrophomonas and Yeast.
Owner:BL TECH INC
Novel aldolase and production process of 4-hydroxy-l-isoleucine
InactiveUS20090104659A1High expressionHigh copy numberBacteriaSugar derivativesArthrobacterL-Isoleucine
A novel aldolase is described. 4-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-keto-pentanoic acid, which is useful as an intermediate in the synthesis of 4-hydroxy-L-isoleucine, may be synthesized from acetaldehyde and α-ketobutyric acid using a novel aldolase, which is derived from the genus Arthrobacter.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
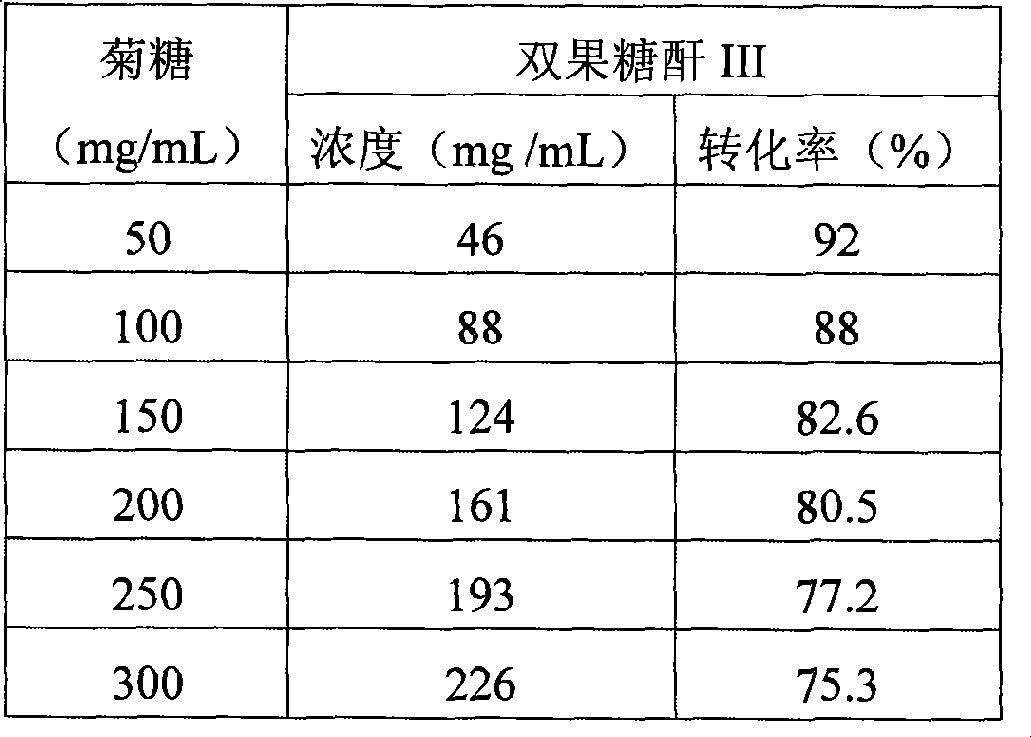
Bacterial strain for producing inulin fructose transferase and method for producing difructose anhydride III using said transferase
The invention relates to a strain for producing an inulin fructosyltransferase and a method for using the fructosyltransferase to produce a difructose anhydride III, the strain and the method belong to the biotechnology field of foods. The invention relates to an Arthrobacter aurescens SK 8.001 which is sieved from soil, the collection serial No. is CCTCC NO: M 208120, the Arthrobacter is taken as a starting strain, insulin is taken as a carbon source, thereby composing a fermentation culture medium with a nitrogen source and inorganic salt; and the inulin fructosyltransferase is produced by fermentation. The fermentation culture medium takes the insulin and sodium nitrate as the main carbon source and the nitrogen source, and the enzyme activity of the inulin fructosyltransferase in fermentation broth can achieve 2 to 100U / ml through the detection after the fermentation. A catalyst of the inulin fructosyltransferase is added in the insulin solution with 1 percent to 50 percent for producing the difructose anhydride III, the conversion is carried out for 3 to 24h, and the conversation rate can be more than 75 percent. The obtained difructose anhydride III product is safe and reliable, thereby being a functional sweetener with great market potentiality.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
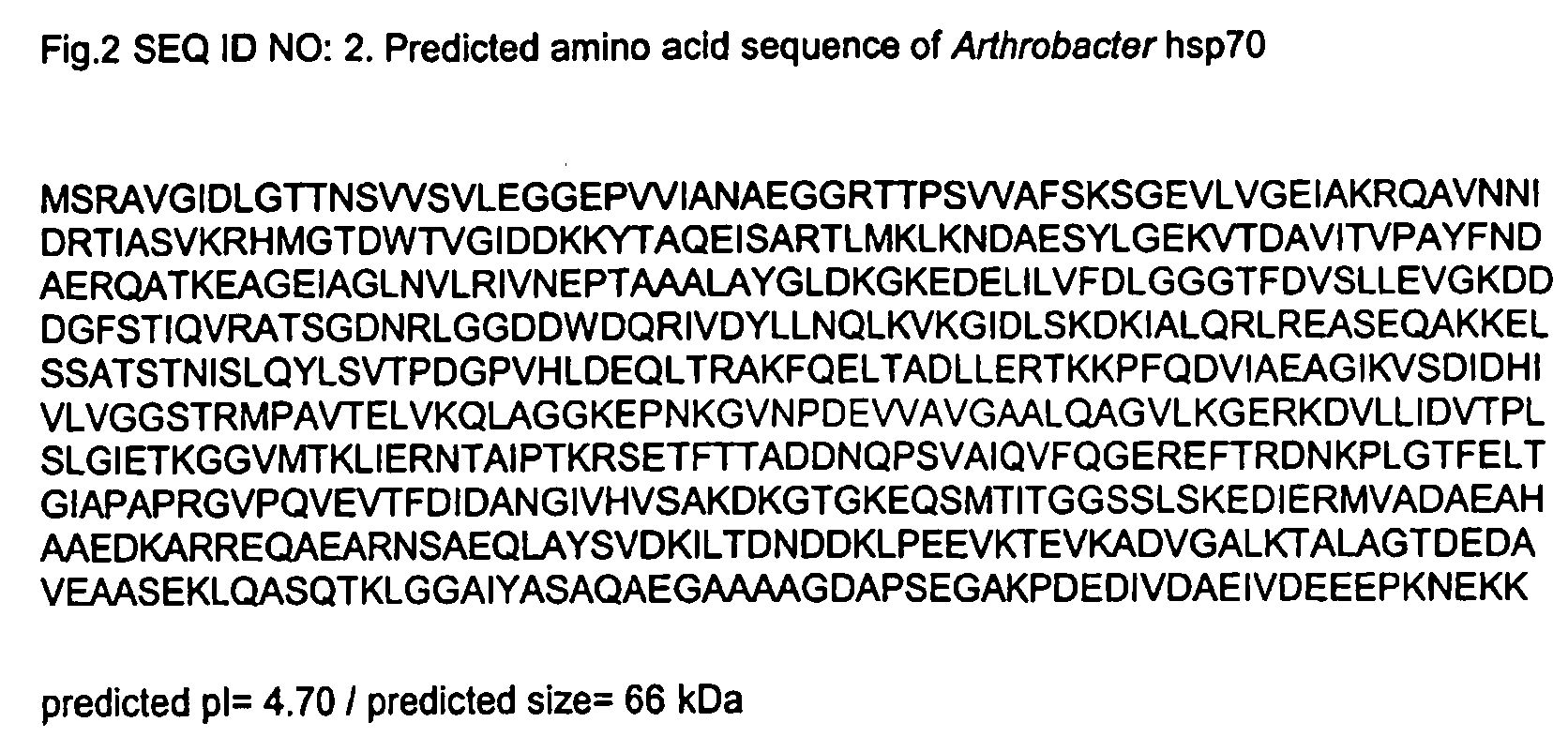
Hsp70 from Arthrobacter
The hsp70 gene from an Arthrobacter species has been isolated and sequenced. The encoded protein is believed to be highly immunogenic, especially in fish, and also has utility as a non-specific adjuvant, and as an adjuvanting carrier for heterologous antigens.
Owner:NOVARTIS TIERUNDHEIT
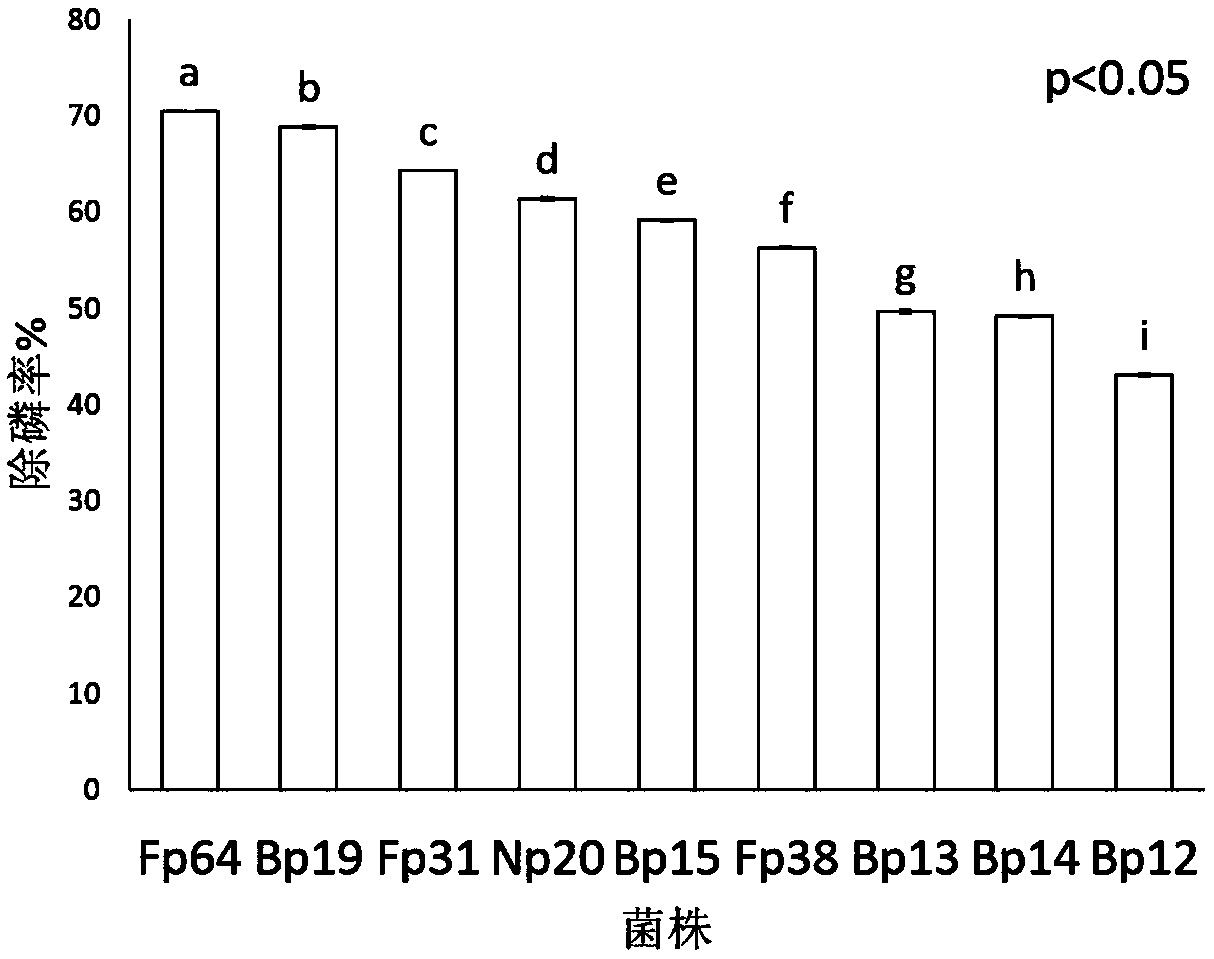
Multi-functional arthrobacter Fp64 for controlling soil phosphorus loss and application thereof
ActiveCN108795799AStop lossReduce in quantityAgriculture tools and machinesBacteriaMicroorganismArthrobacter
The invention relates to multi-functional arthrobacter Fp64 for controlling soil phosphorus loss and application thereof. The arthrobacter Fp64 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on April 26, 2018, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.15644. The arthrobacter Fp64 is used as a phosphorus regulating agent or the like in agricultural production, hasgood environmental adaptability and has the ability to resist pathogenic bacteria. When the arthrobacter Fp64 is added to soil, the loss of phosphorus in the soil can be effectively prevented.
Owner:ECOLOGY INST SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com