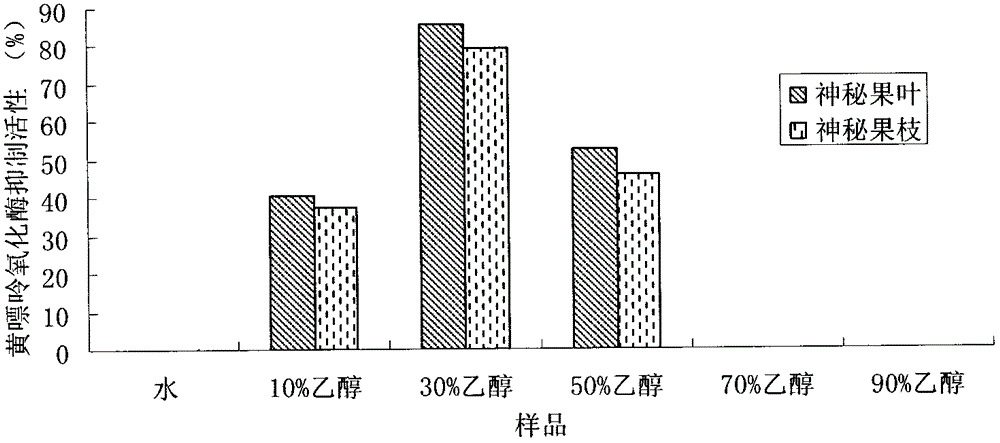
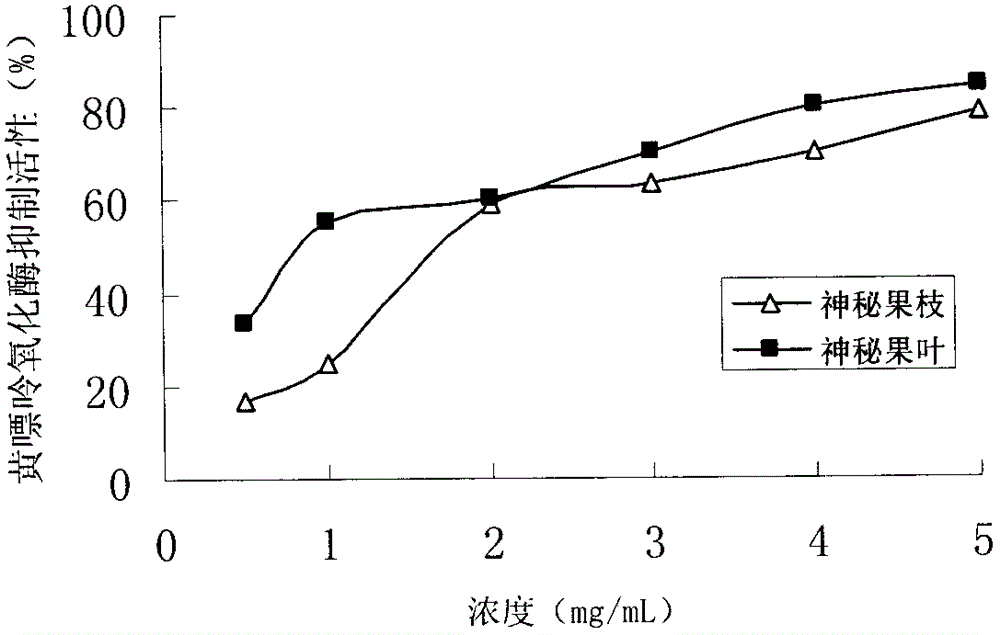
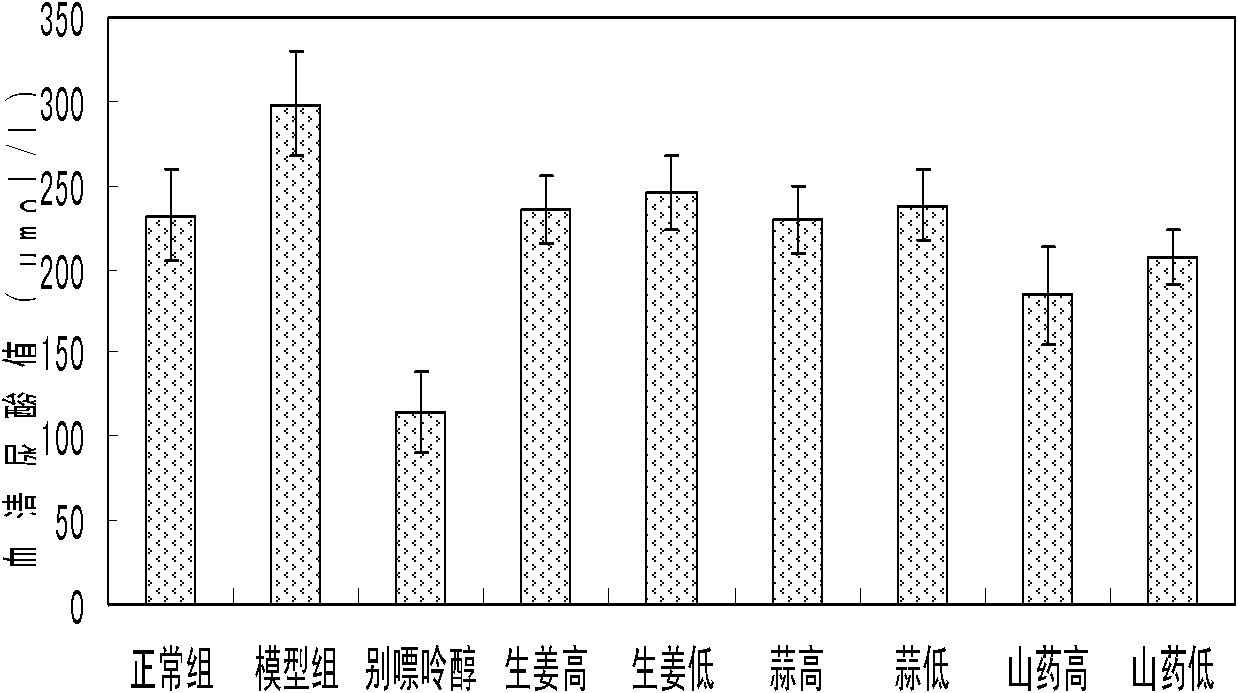
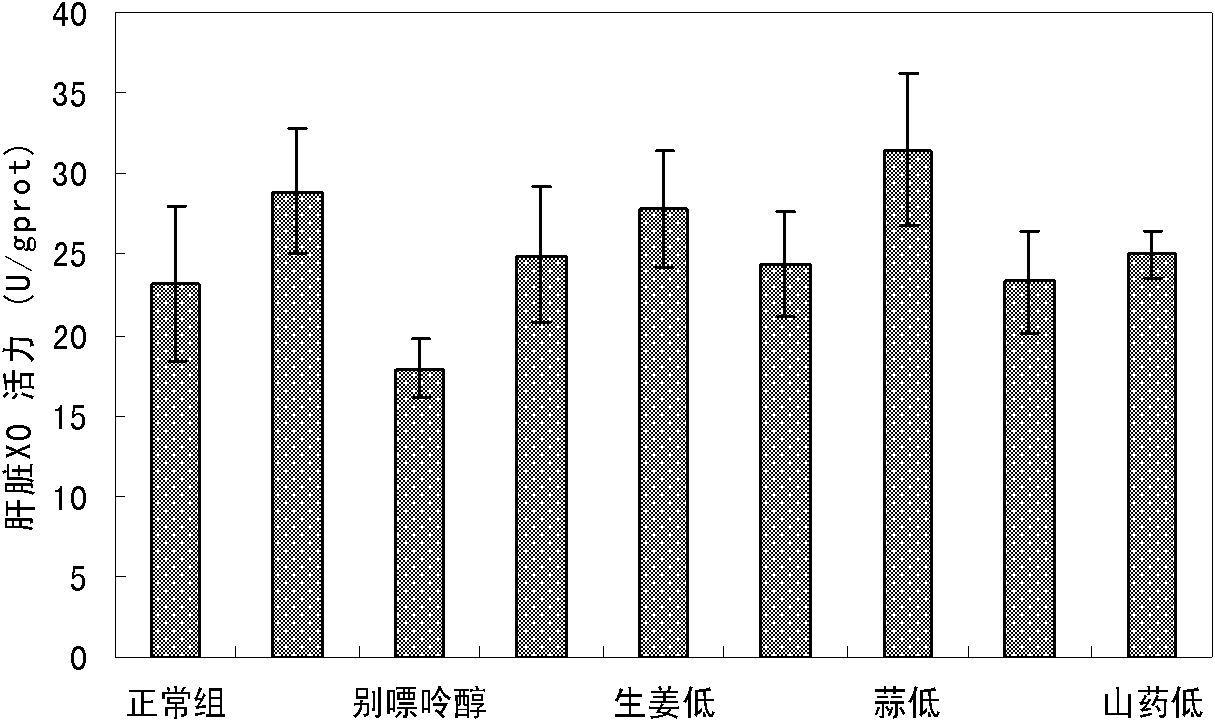
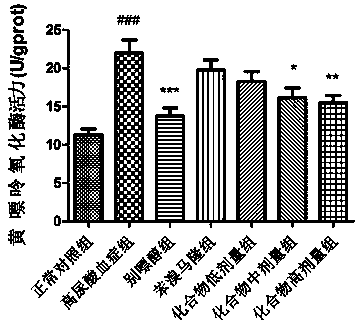
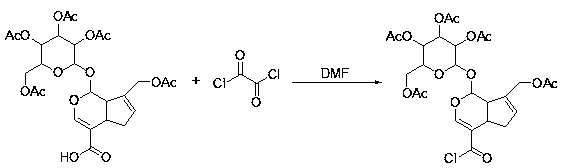
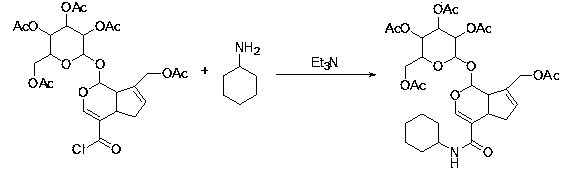
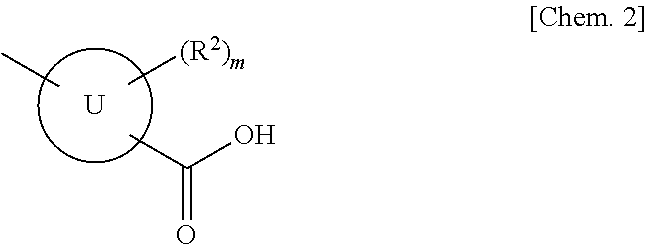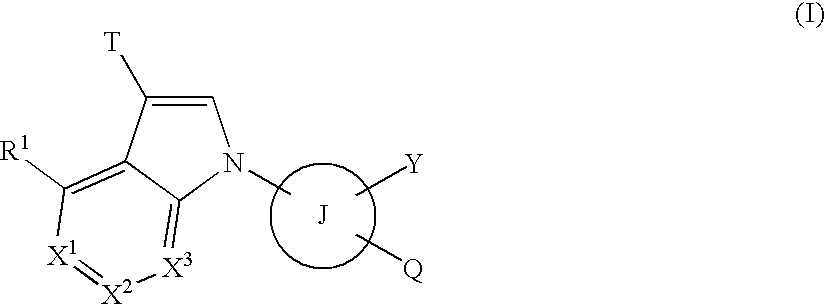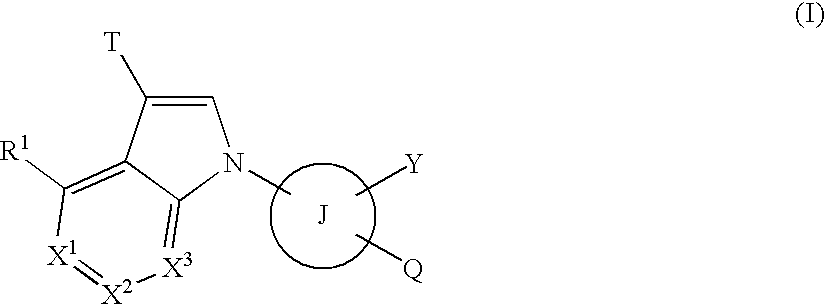Patents
Literature
260 results about "Xanthine oxidase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
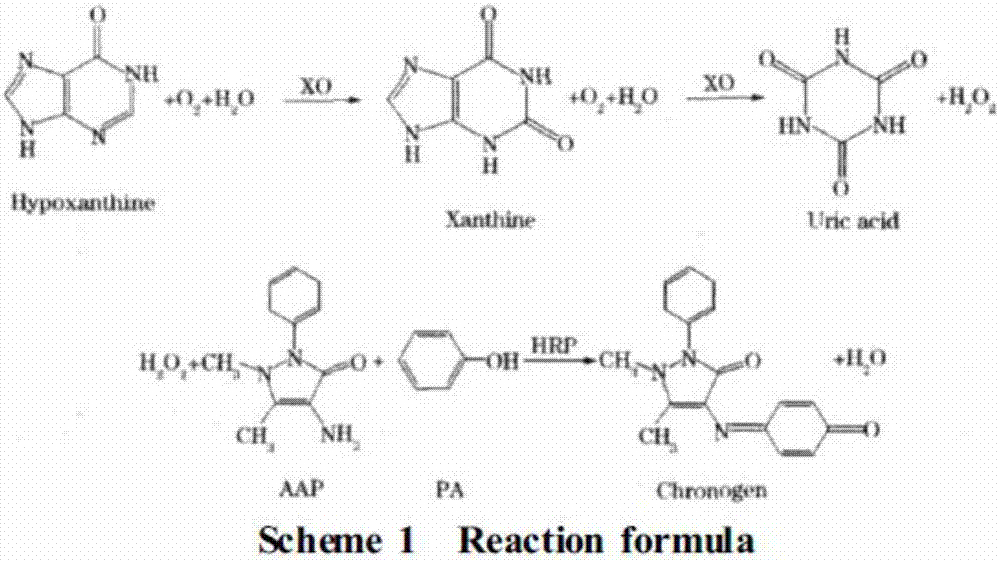
Xanthine oxidase (XO, sometimes 'XAO') is a form of xanthine oxidoreductase, a type of enzyme that generates reactive oxygen species. These enzymes catalyze the oxidation of hypoxanthine to xanthine and can further catalyze the oxidation of xanthine to uric acid. These enzymes play an important role in the catabolism of purines in some species, including humans.
Material containing metal ion ligand complex producing nitric oxide in contact with blood
InactiveUS7128904B2Good biocompatibilityPeptide/protein ingredientsOther blood circulation devicesPolymer thin filmsNitric oxide
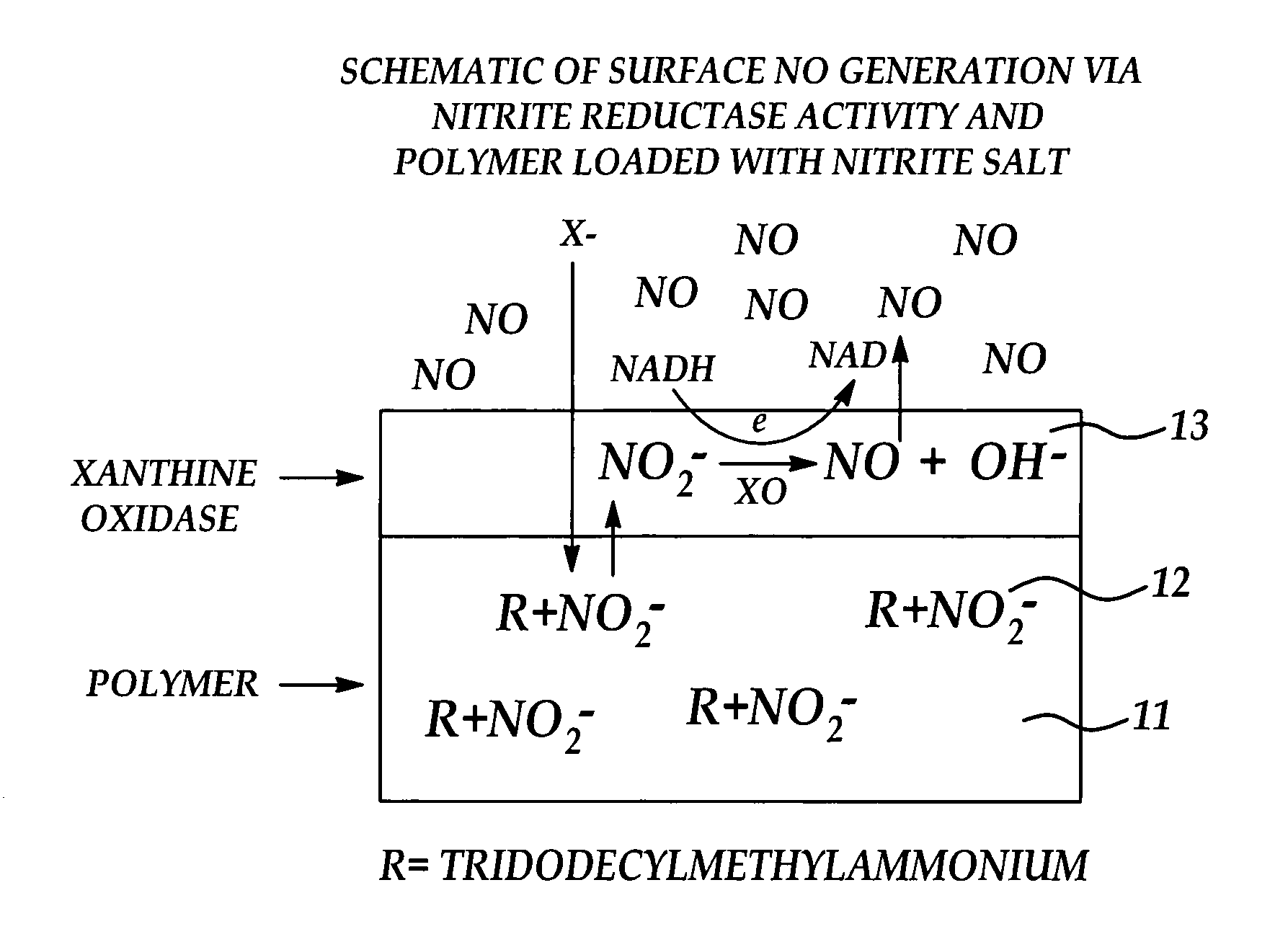
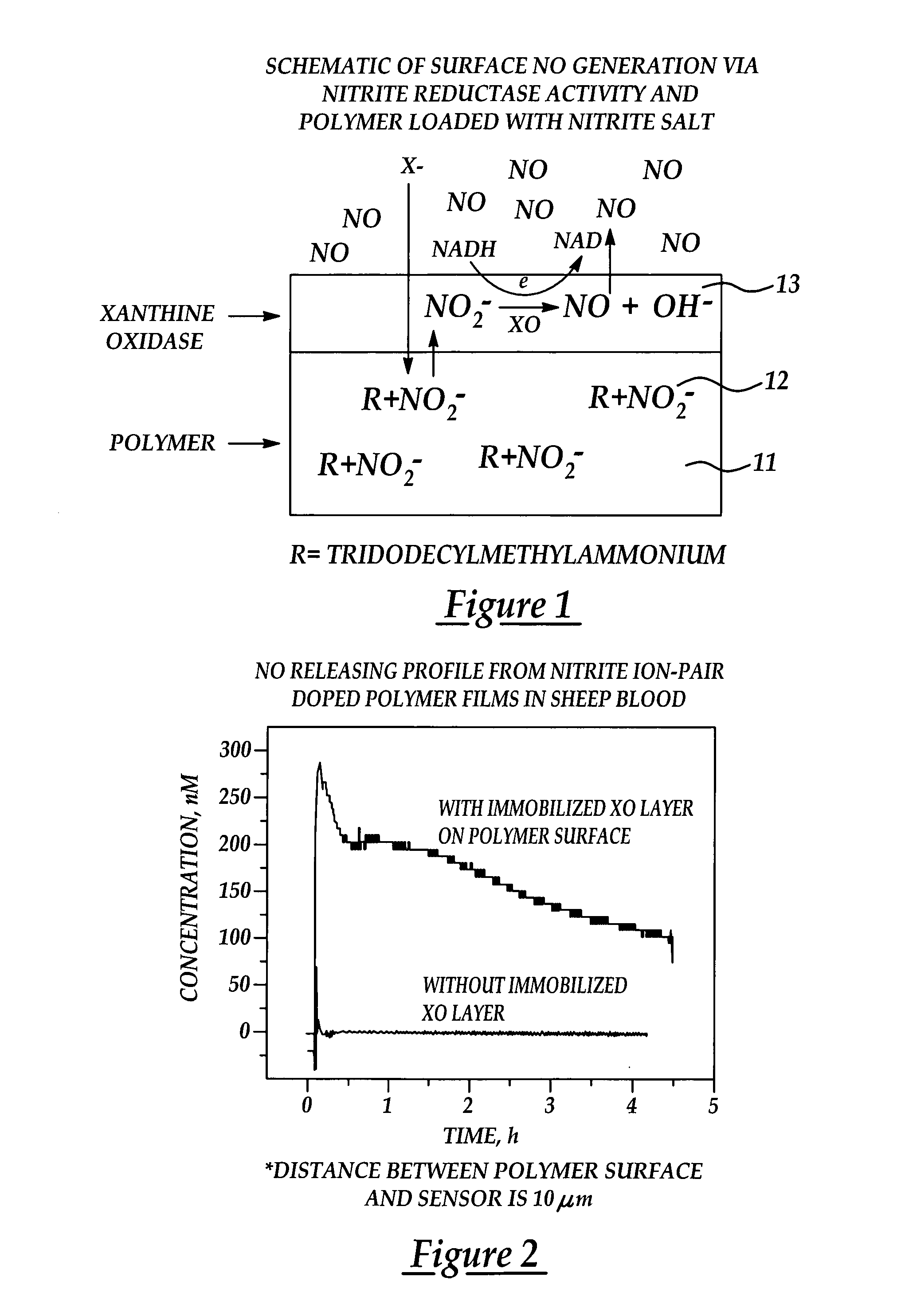
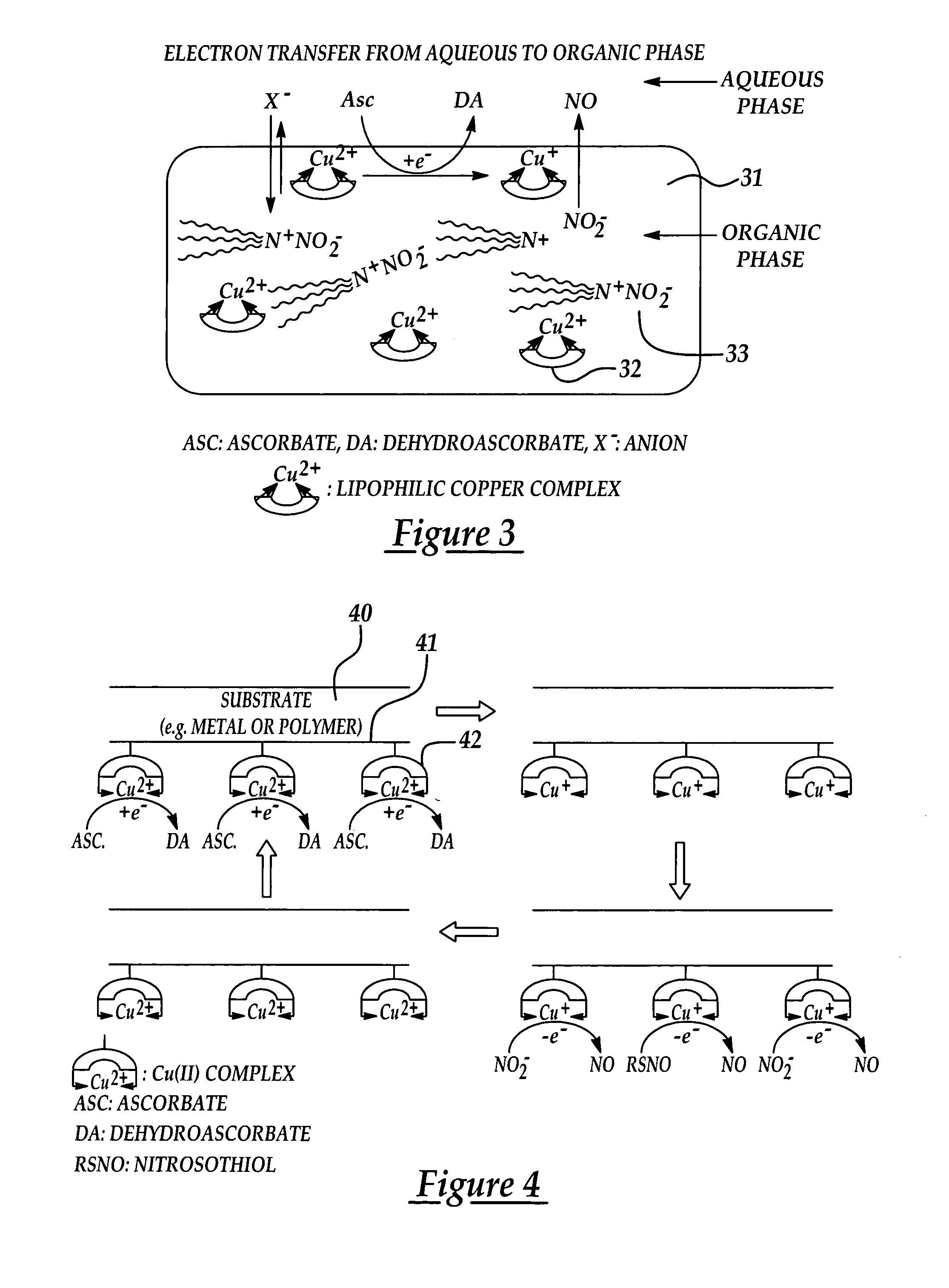
Biocompatible materials that have the ability to release nitric oxide (NO) in situ at the surface-blood interface when in contact with blood. The materials which may be polymers (e.g., polyurethane, poly(vinyl chloride), silicone rubbers), metals, such as stainless steel, carbon, and the like are provided with biocatalysts or biomimetic catalysts on their surface that have nitrite, nitrate, and / or nitrosothiol-reducing capability. Illustratively, the catalysts are adsorbed or immobilized at the surface of the material. The catalysts can act on endogenous nitrite, nitrate, or nitrosothiols within the blood creating a local increase in the NO levels at the surface of the material. An illustrative enzymatic biocatalyst is mammalian xanthine oxidase. In another illustrative embodiment, a biomimetic catalyst is a copper (Cu(II)-ligand complex, e.g. dibenzo[e,k]-2,3,8,9-tetraphenyl-1,4,7,10-tetraaza-cyclododeca-1,3,7,9-tetraene. In some cases, lipophilic salts of nitrite / nitrate (e.g., tridodecylmethylammonium nitrite (TDMA+NO2− / NO3−)) or certain salts of nitrosothiols can be doped within a polymer material, or an underlying polymeric film, to create a reservoir of nitrite or nitrosothiol that continuously leaks into the immobilized catalytic layer. Adequate levels of endogenous reducing equivalents are present within blood to provide catalytically-generated surface levels of NO that are above the threshold reportedly required to prevent platelet adhesion or activation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
(AZA)indolizine derivative and pharmaceutical use thereof
InactiveUS20130217878A1Inhibit productionExcellent xanthine oxidase inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseaseXanthine
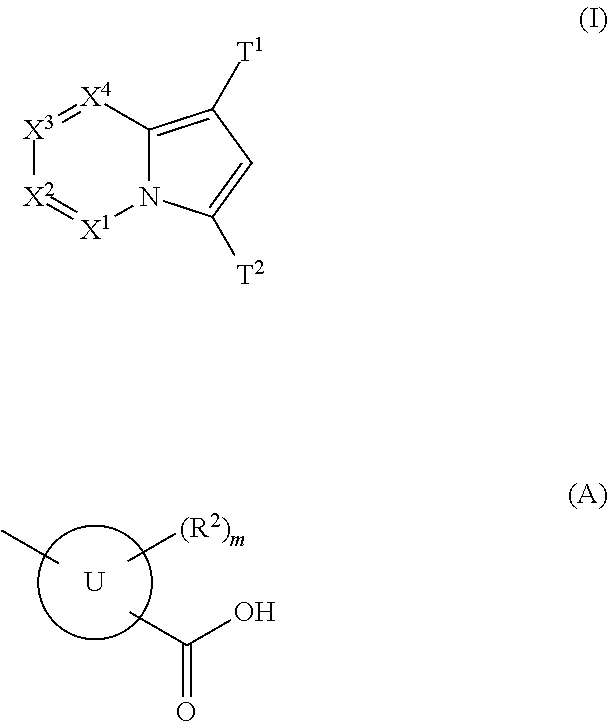
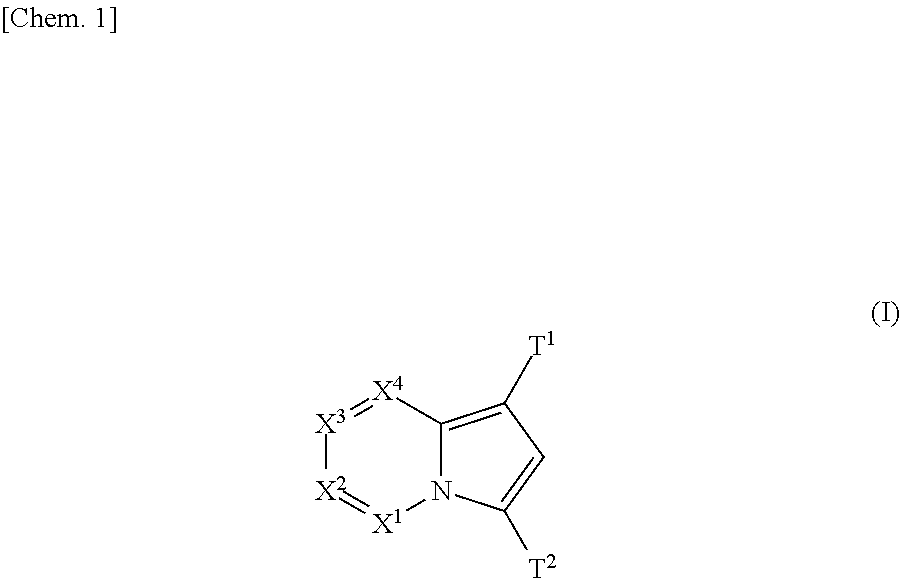
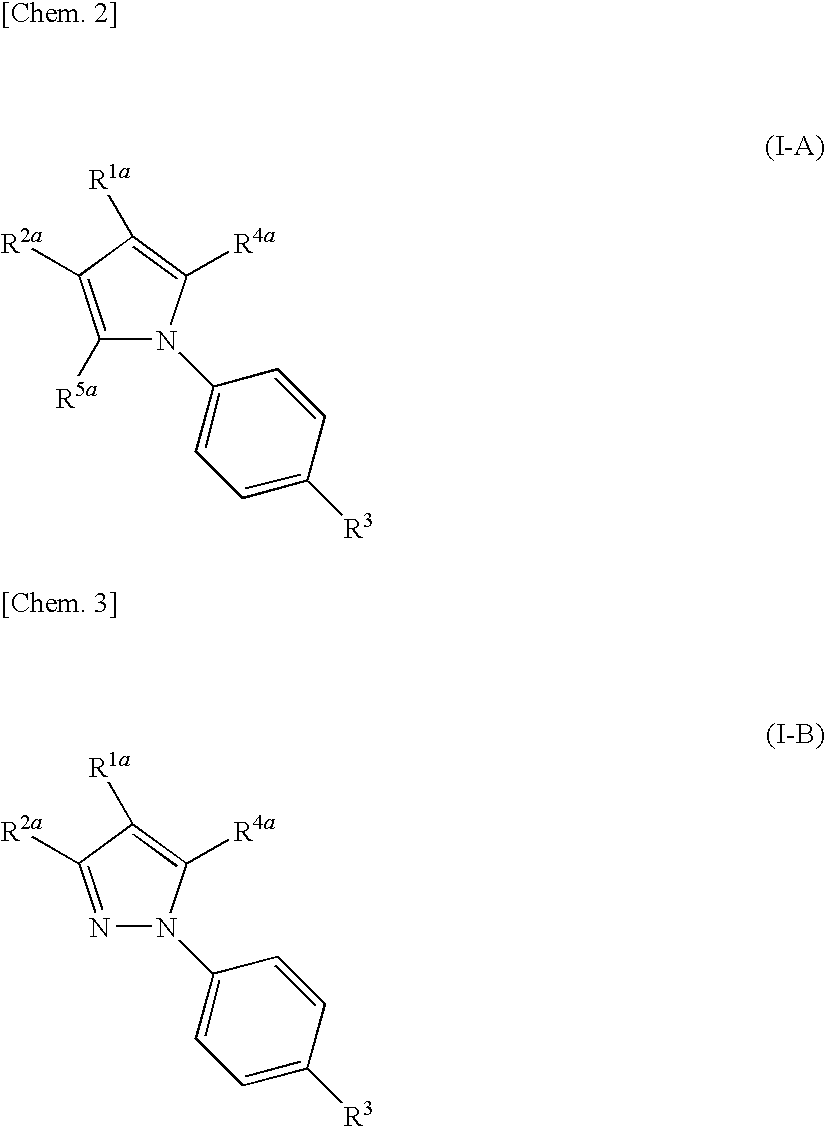
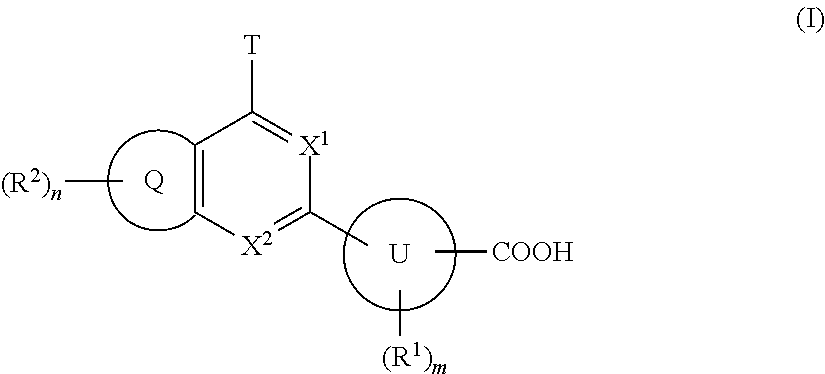
(Aza)indolizine derivatives represented by Formula (I) having xanthine oxidase inhibitory activities and useful as agents for the prevention or treatment of a disease associated with abnormality of serum uric acid level, prodrugs thereof, salts thereof or the like. In Formula (I), 0 to 2 of X1, X2, X3 and X4 are a nitrogen atom and the others are CR1; one of T1 and T2 represents cyano and the other represents a group represented by Formula (A), with the proviso that when T1 is cyano, at least one of X1 to X4 is a nitrogen atom; R1 independently represents a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, a hydroxy group, C1-6 alkyl, C1-6 alkoxy or the like; ring U represents a benzene ring or the like; m represents integral number from 0 to 2; R2 independently represents a fluorine atom, a hydroxy group or the like.
Owner:KISSEI PHARMA
Nitrogenated heterocyclic compound and pharmaceutical composition comprising the same
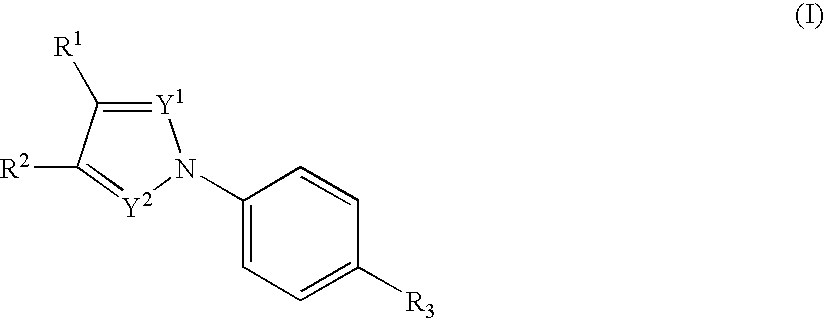
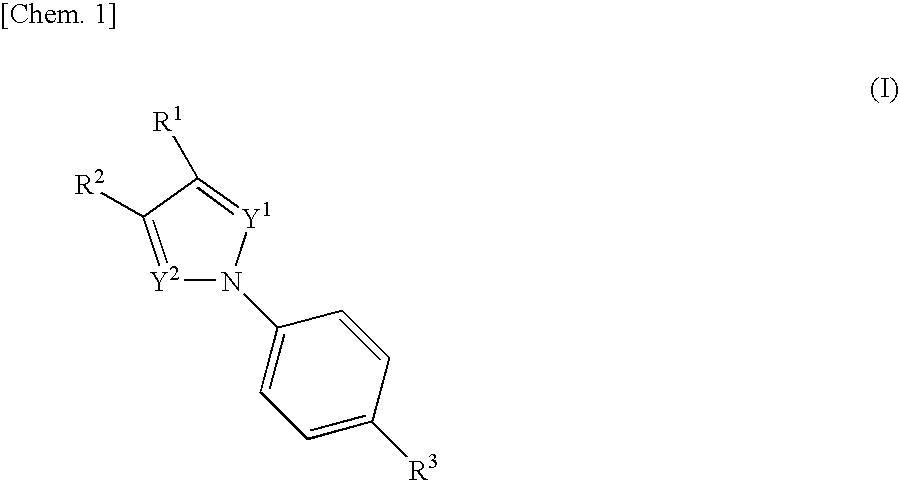
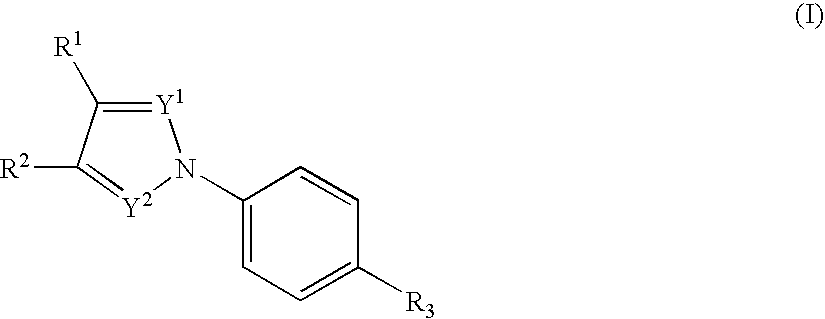
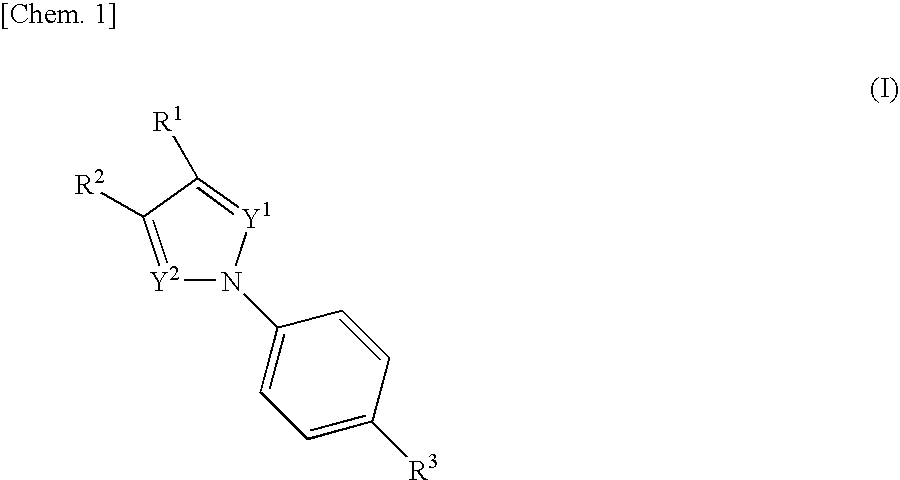
The present invention relates to novel compounds having a xanthine oxidase inhibitory effect and an uricosuric effect and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same as an active ingredient. That is, the present invention relates nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds represented by the following general formula (I):wherein Y1 represents N or C(R4); Y2 represents N or C(R5); R4 and R5 independently represent an alkyl group, a hydrogen atom etc.; one of R1 and R2 represents an optionally substituted aryl group, an alkoxy group or an optionally substituted heterocyclic group; the other of R1 and R2 represents a haloalkyl group, a cyano group, a halogen atom etc.; and R3 represents a 5-tetrazolyl group or a carboxy group, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same as an active ingredient.
Owner:KISSEI PHARMA
Preparation method and use of moringa oleifera leaf polysaccharides
InactiveCN104829743AHigh purityHigh deproteinization rateOrganic active ingredientsSkeletal disorderBiotechnologyXanthine
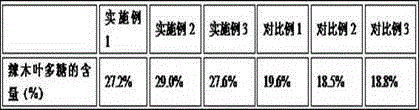
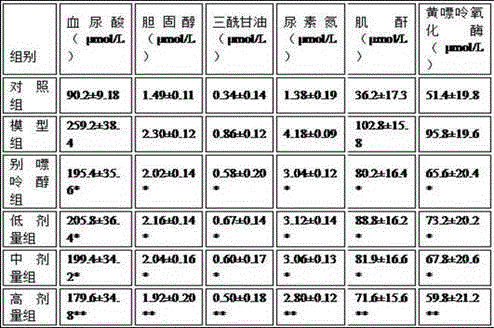
The invention belongs to the chemical field of natural products and particularly relates to a preparation method and use of moringa oleifera leaf polysaccharides. The preparation method comprises the steps of carrying out combined microwave-ultrasound extraction, hydrochloric acid method deproteinization, hydrogen peroxide method decoloration and AB-8 macroporous adsorption resin column separation, so as to prepare the moringa oleifera leaf polysaccharides. The preparation method of the moringa oleifera leaf polysaccharides has the advantages of short extraction time, low extraction temperature, low energy consumption and high extraction rate and purity. Besides, an animal experiment proves that the prepared moringa oleifera leaf polysaccharides have remarkable treatment effect to hyperuricosuria; by decreasing the content of cholesterol, triacylglycerol, urea nitrogen, creatinine and xanthine oxidase, the production of uric acid is achieved; meanwhile, by directly decomposing uric acid, renal functions are improved, the excretion of uric acid is promoted, and blood vessels are protected, thereby being favorable to the recovery of patients with the hyperuricosuria. The preparation method has a wide medical application prospect.
Owner:隽觅(广州)生物科技有限公司
Synsepalum dulcificum Denill tree branch and leaf extract and extraction method and application of extract
InactiveCN102743421AImprove cleanlinessStrong absorption capacityAntinoxious agentsSkeletal disorderFreeze-dryingOxygen radical absorbance capacity
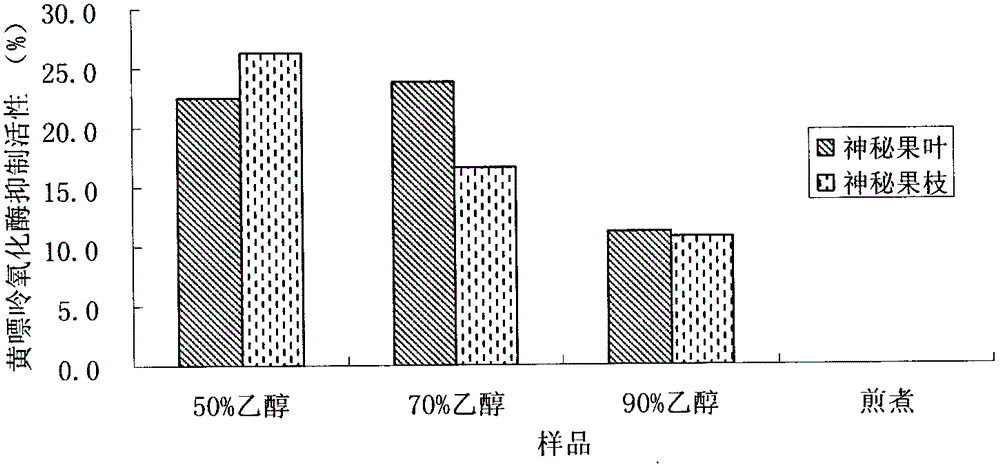
The invention relates to an extraction method for a Synsepalum dulcificum Denill tree branch and leaf extract. The extraction method comprises the following steps of: crushing Synsepalum dulcificum Denill tree branches and leaves to obtain an extracted raw material; adding ethanol water; performing reflux extraction for 2-5 hours; filtering; performing reduced pressure distillation on supernate; performing freeze drying to obtain branch and leaf crude extract dry powder; dissolving the branch and leaf crude extract dry powder in water; performing macroporous resin treatment; then, eluting by using the ethanol water to obtain drips; and respectively performing vacuum concentration and the freeze drying to obtain a refined branch and leaf extract. The total phenol content of the obtained extract is 66.5 percent, and the total phenol content of a branch extract is 84.1 percent. The diphenylpicrylphenylhydrazine (DPPH) scavenging activity of the extract is 7.9 and 7.8 times of that of glutathione, and the oxygen radical absorbing capacity of the extract is 7.0 and 6.2 times of that of the glutathione. The extract is good in inhibitory activity on xanthine oxidase and can be used for preparing antioxidants, gout suppressants and health-care products.
Owner:万福群
High-sensitivity kit for detecting 5'-nucleotidase
InactiveCN104388534AEasy to operateHigh precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementPurine nucleoside phosphorylaseNucleotidase
The invention relates to the field of an external diagnostic reagent, and particularly relates to a high-sensitivity kit for detecting 5'-nucleotidase. The kit for detecting 5'-nucleotidase comprises a 5'-nucleotidase R1 reagent, a 5'-nucleotidase R2 reagent and a 5'-nucleotidase calibration product, wherein the 5'-nucleotidase R1 reagent comprises a buffer solution, a stabilizing agent, a preservative agent, an enzyme activator, 4-AAP(4-aminoantipyrine), 18-crown ether-6 and UAO (Uricase), PNP (Purine Nucleoside Phosphorylase), XOD (Xanthine Oxidase) and POD (Peroxidase) reaction enzyme systems; the 5'-nucleotidase R2 reagent comprises a buffer solution, a stabilizing agent, a preservative agent, PO3- and a Trinder developing system; and the 5'-nucleotidase calibration product comprises a buffer solution, a stabilizing agent, a preservative agent and 5'-nucleotidase. The detection kit provided by the invention is enhanced in detection sensitivity by 40% compared with a 'PNP-XOD-POD' enzyme system, and has good application prospects.
Owner:CHONGQING ZHONGYUAN BIOLOGICAL TECH
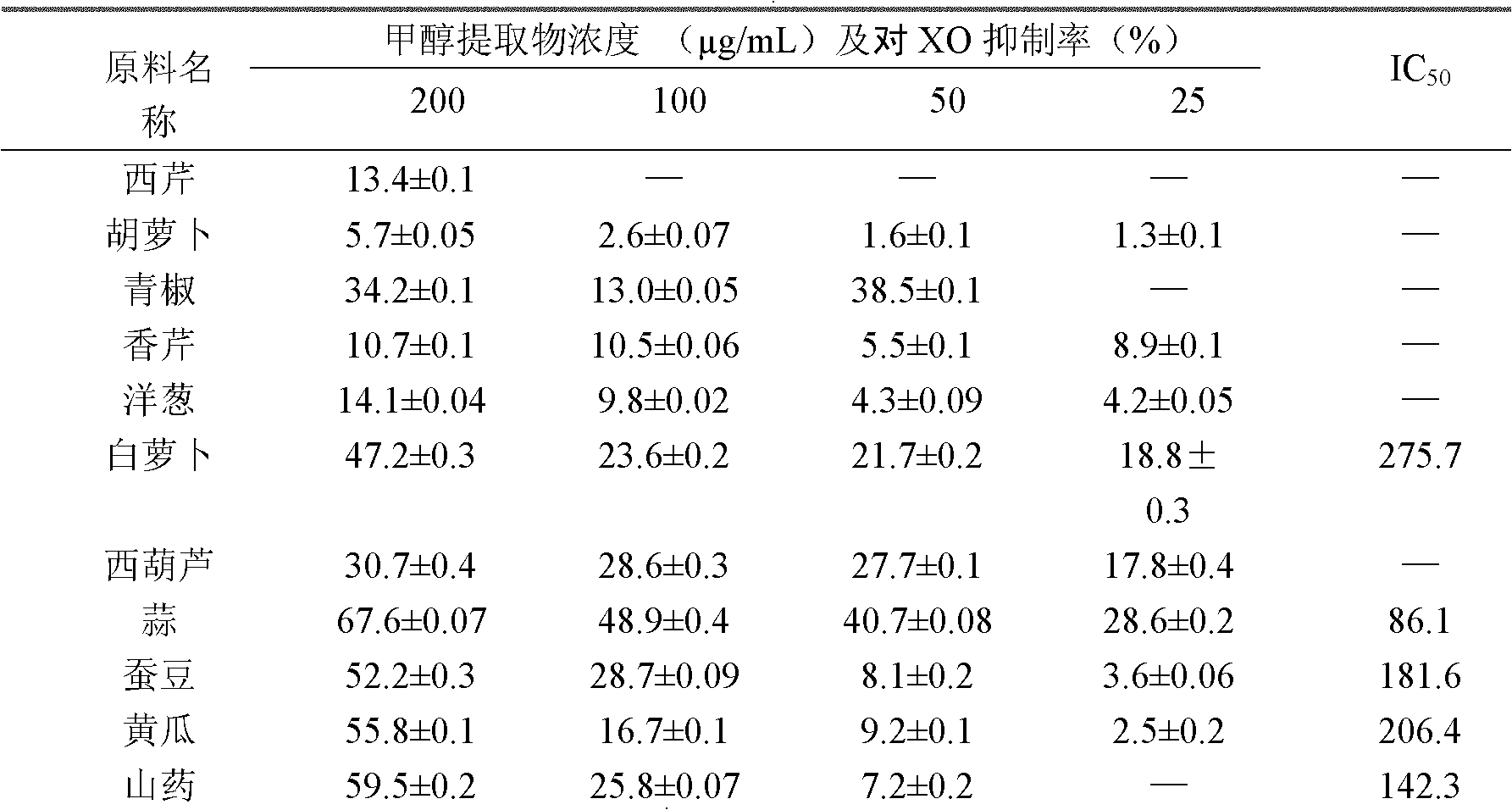
Use of vegetable extract in inhibiting xanthine oxidase (XO) and application in preparing food for preventing and treating hyperuricemia or gout
The invention relates to use of vegetable extract in inhibiting xanthine oxidase (XO) and application in preparing food for preventing and treating hyperuricemia or gout. The vegetable extract is prepared by the following steps: a methanol extraction process: removing impurities from fresh vegetable, and removing moisture in an electrothermal blowing drying box at 40 DEG C; crushing the vegetableinto powder by a crusher; weighing a certain amount of dry vegetable into a conical flask, and extracting by methanol ultrasonic wave twice for 45 minutes in each extraction; filtering to remove the filter residue; recycling the solvent from the filtrate by a rotary evaporator, and drying the remainder in an electrothermal vacuum drying box to obtain extractum; and applying the vegetable methanolextract to an in vitro XO inhibition test so as to screen out the vegetable crude extract with the effect on inhibiting the XO. The invention provides an reference on diet for preventing and treatinggout or hyperuricemia.
Owner:广东南龙嶂农林科技有限公司
Method for the preparation of a protein peptide, a protein peptide and use thereof
ActiveUS20160316794A1Reduce generationLowering plasma uric acid levelProtein composition from fishPeptide/protein ingredientsImpurityXanthine oxidase
The present invention discloses a method for the preparation of a protein peptide, peptide powder prepared thereby, and use of the peptide powder in hypouricemic food products or health care products. The peptide powder is capable of inhibiting the activity of xanthine oxidase and effectively reducing uric acid. The method in an example of the present invention comprises: mincing the tuna, heating with steam or water to obtain a pretreated tuna, enzymolysing the pretreated tuna, deactivating the enzyme, centrifuging, removing impurities to obtain a supernatant, concentrating, and drying to obtain the peptide powder of interest.
Owner:INFINITUS (CHINA) CO LTD
Arthrobacter, uses for produced xanthine oxidase and production method thereof
InactiveCN101402922AHigh activitySimple nutritional requirementsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesArthrobacterNitrogen
The invention provides an Arthrobacter and an application of the Arthrobacter for generating xanthine oxidase and a preparation method thereof. The Arthrobacter XL2006 derives from nature and the16S rRNA sequence of the Arthrobacter XL2006 is shown in a sequence table SEQ ID NO.1. The Arthrobacter XL2006 is applied to producing, extracting and purifying the xanthine oxidase and preparing a diagnostic kit. The Arthrobacter XL2006 is characterized by the production of the xanthine oxidase and can adopt hypoxanthine or xanthine as a unique source of carbon and nitrogen and a unique energy source. The fermentation and the production of the xanthine oxidase are characterized by simple nutritional requirements, easy culture and short fermentation time; the produced xanthine oxidase has quite high activity, and strains provided by the invention are utilized to ferment and extract the xanthine oxidase and the prepared diagnostic kit can be applied to clinically testing the levels of hypoxanthine and xanthine in blood serum of patients.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Fused heterocyclic derivative and use thereof for medical purposes
InactiveUS20110201815A1Inhibit productionStrong inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseaseAryl
Owner:KISSEI PHARMA
(AZA)indole derivative and use thereof for medical purposes
ActiveUS20100056521A1Excellent xanthine oxidase inhibitory activityInhibit productionBiocideOrganic chemistryDiseaseAlkoxy group
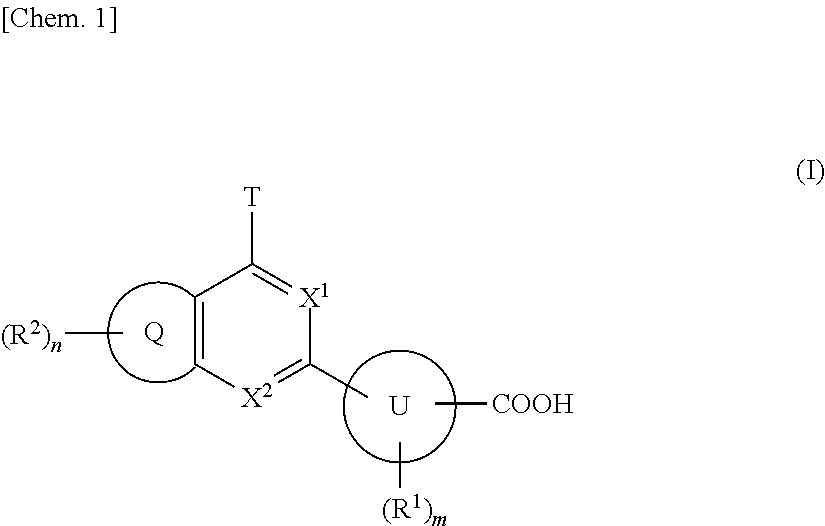
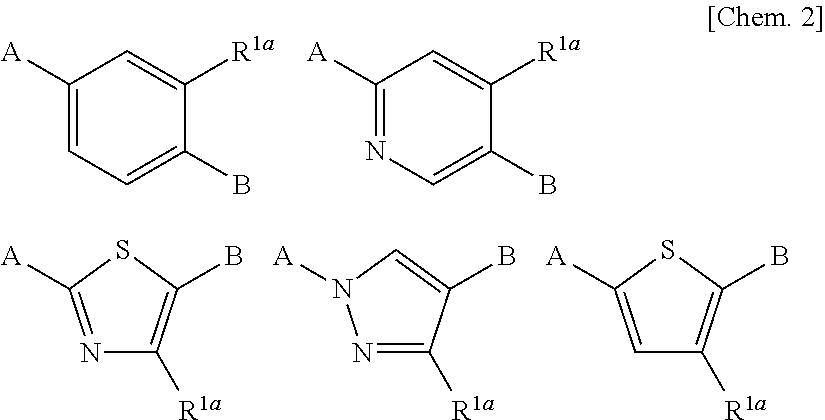
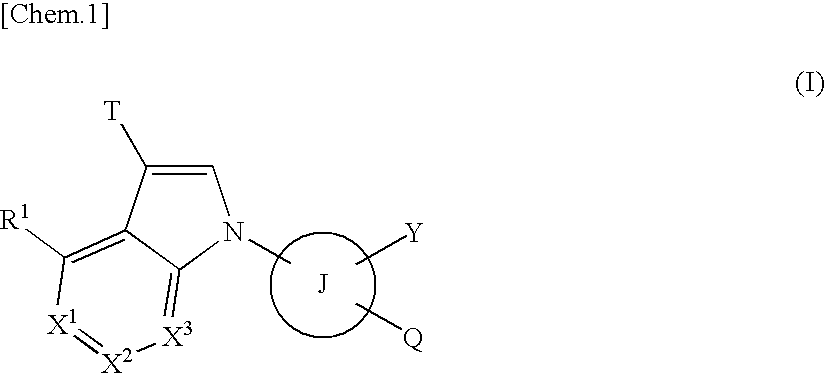
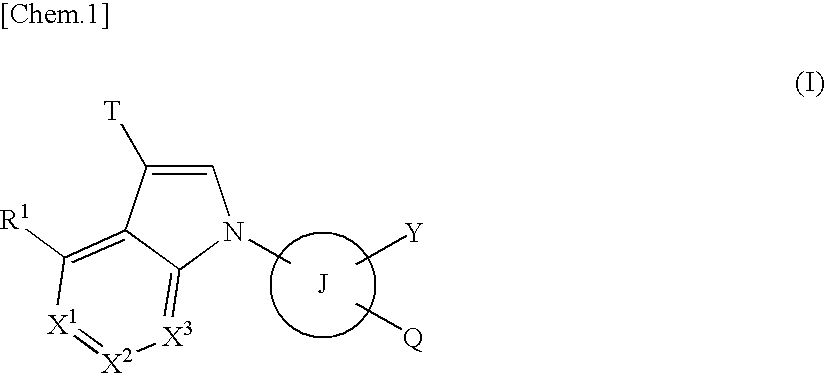
The present invention provides compounds useful as agents for the prevention or treatment of a disease associated with abnormal serum uric acid level which has a uricosuric activity or the like. The present invention relates to (aza)indole derivatives represented by the following general formula (I) having xanthine oxidase inhibitory activities and useful as agents for the prevention or treatment of a disease associated with abnormality of serum uric acid level, prodrugs thereof, or salts thereof. In the formula (I), T represents nitro or cyano and the like; ring J represents aryl or heteroaryl and the like; Q represents carboxy or 5-tetazolyl and the like; Y represents H, OH, NH2, halogen, nitro, alkyl, alkoxy and the like; X1, X2 and X3 independently represent CR2 or N; R1 and R2 independently represent halogen, cyano, haloalkyl, A-D-E-G, —N(-D-E-G)2 and the like, in the formula, A represents a single bond, O, S and the like; D and G independently represent optionally substituted alkylene, cycloalkylene, heterocycloalkylene, arylene, heteroarylene and the like; E represents a single bond, O, S, COO, SO2 and the like.
Owner:KISSEI PHARMA
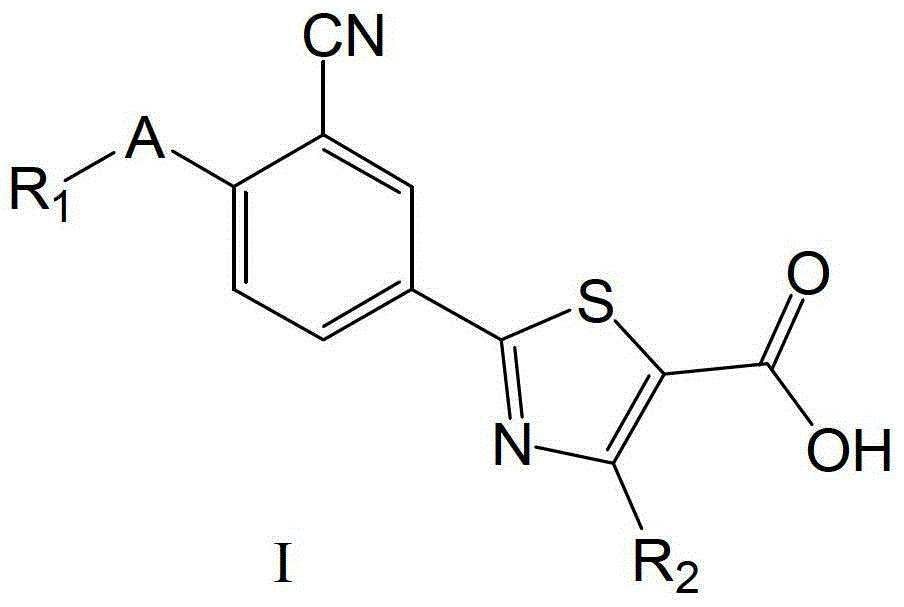
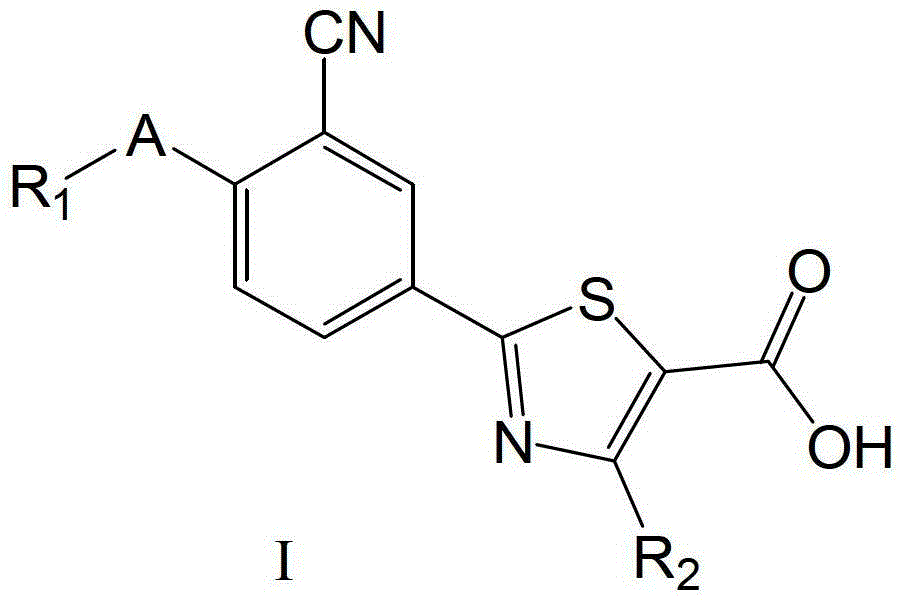
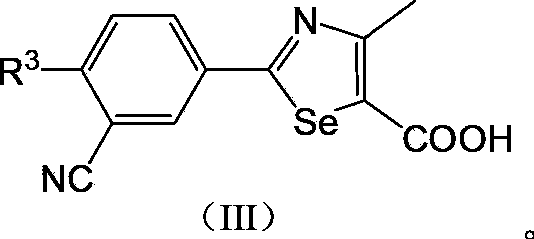
2-(3-cyano-4-alkoxy) phenyl-4-substituted thiazole-5-formic acid compound, composition as well as preparation methods and applications thereof
InactiveCN103333134ASimple manufacturing methodOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryArylThiazole
The invention relates to a 2-(3-cyano-4-alkoxy) phenyl-4-substituted thiazole-5-formic acid compound which has xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity and is shown in a general formula I, a composition and preparation methods thereof. The invention also relates to applications of the compound and the composition thereof to preparation of medicaments for treating and / or preventing hyperuricemia and gout diseases. In the formula I, R2 is substituted or unsubstituted phenyl or a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaromatic radical, R1 is a substitutive aliphatic group of a straight chain or a branched chain, substituted or unsubstituted alicyclic hydrocarbonyl or substituted or unsubstituted aryl alkyl and A is an oxygen atom, a sulfur atom or a nitrogen atom.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
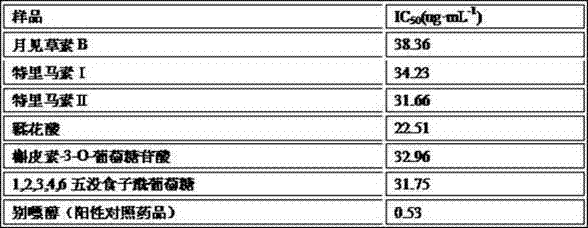
Folium eucalypti extractive with uric acid reduction effect as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103919857AAbundant resourcesLow priceSkeletal disorderUrinary disorderXanthineOxidative enzyme
The invention discloses an application of a folium eucalypti extractive serving as an active ingredient in preparation of medicines for treating hyperuricemia, and also provides a preparation method of the folium eucalypti extractive. Main active ingredients of the folium eucalypti extractive are 6-12% of scabish essence B, 1-2% of tellimagrandin I, 1-1.5% of quercetin-3-O-glucoside acid, 0.8-1.2% of ellagic acid, 0.2-0.5% of tellimagrandin II, 0.1-0.15% of 1,2,3,4,6 pentagalloylglucose and 25-50% of total phenols. The pharmacological experiment shows that the folium eucalypti extractive has an inhibiting effect on xanthine oxidase and relatively strong effects of reducing uric acid, protecting renal injury caused by the hyperuricemia and the like in bodies.
Owner:曹庸
Nitrogenated heterocyclic compound and pharmaceutical composition comprising the same
The present invention relates to novel compounds having a xanthine oxidase inhibitory effect and an uricosuric effect and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same as an active ingredient. That is, the present invention relates nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds represented by the following general formula (I):wherein Y1 represents N or C(R4); Y2 represents N or C(R5); R4 and R5 independently represent an alkyl group, a hydrogen atom etc.; one of R1 and R2 represents an optionally substituted aryl group, an alkoxy group or an optionally substituted heterocyclic group; the other of R1 and R2 represents a haloalkyl group, a cyano group, a halogen atom etc.; and R3 represents a 5-tetrazolyl group or a carboxy group, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same as an active ingredient.
Owner:KISSEI PHARMA
Extraction method and application of moringa oleifera leaf total flavones
The invention belongs to the chemical field of natural products and in particular relates to an extraction method and an application of moringa oleifera leaf total flavones. The extraction method adopts microwave and ultrasound to synergistically extract the moringa oleifera leaf total flavones, and has the advantages of high efficiency, time saving, energy conservation, low energy consumption, simple operation and good repeatability. Besides, an animal test proves that the extracted moringa oleifera leaf total flavones have a significant treatment effect on hyperuricosuria and Alzheimer's disease. The total flavones provided by the invention can reduce uric acid, and can also reduce cholesterol, triacylglycerol, urea nitrogen, creatinine and xanthine oxidase, reduce the generation of uric acid, directly decompose uric acid, improve the renal function, promote uric acid excretion, and protect multiple levels of blood vessels to reduce uric acid, so that the moringa oleifera leaf total flavones are beneficial for healing of lithemia patients and have a broad medical application prospect.
Owner:萧丽雅
2-Arylselenazole compounds and medicinal composition thereof
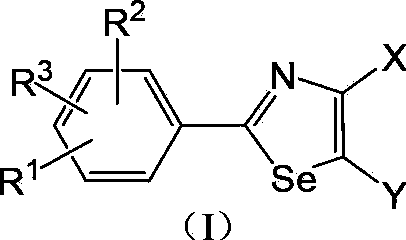
The invention discloses 2-arylselenazole compounds and a medicinal composition thereof. The 2-arylselenazole compounds are compounds represented by formula (I) or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. The 2-arylselenazole compounds have a xanthine oxidase inhibition activity. The compounds or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof can be applied to prepare medicines for preventing or treating hyperuricemia, gout, diabetic nephropathy, inflammatory diseases and neurological system diseases.
Owner:NANJING LIFECARE PHARM CO LTD
Allopurinol derivative and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102746306AGrowth inhibitionEasy to prepareOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryUse medicationTrial drug
The invention provides an allopurinol derivative as shown in Formula I, and a preparation method and application thereof. Tumor growth can be effectively suppressed by the allopurinol derivative provided by the invention, the activity of the allopurinol derivative is equivalent to that of 17-AGG (17-allylamide-17-demethoxygeldanamycin) to which phase III clinical trial is performed, and the allopurinol derivative has a good antitumor effect. The activity of xanthine oxidase can be effectively suppressed by the allopurinol derivative, and the allopurinol derivative can be used for treating gout and provides a new drug choice for clinically treating cancer and gout. Additionally, the preparation method of the compound provided by the invention has the advantages of simplicity, lower cost, high yield and good industrial application prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN GUOKANG PHARMA
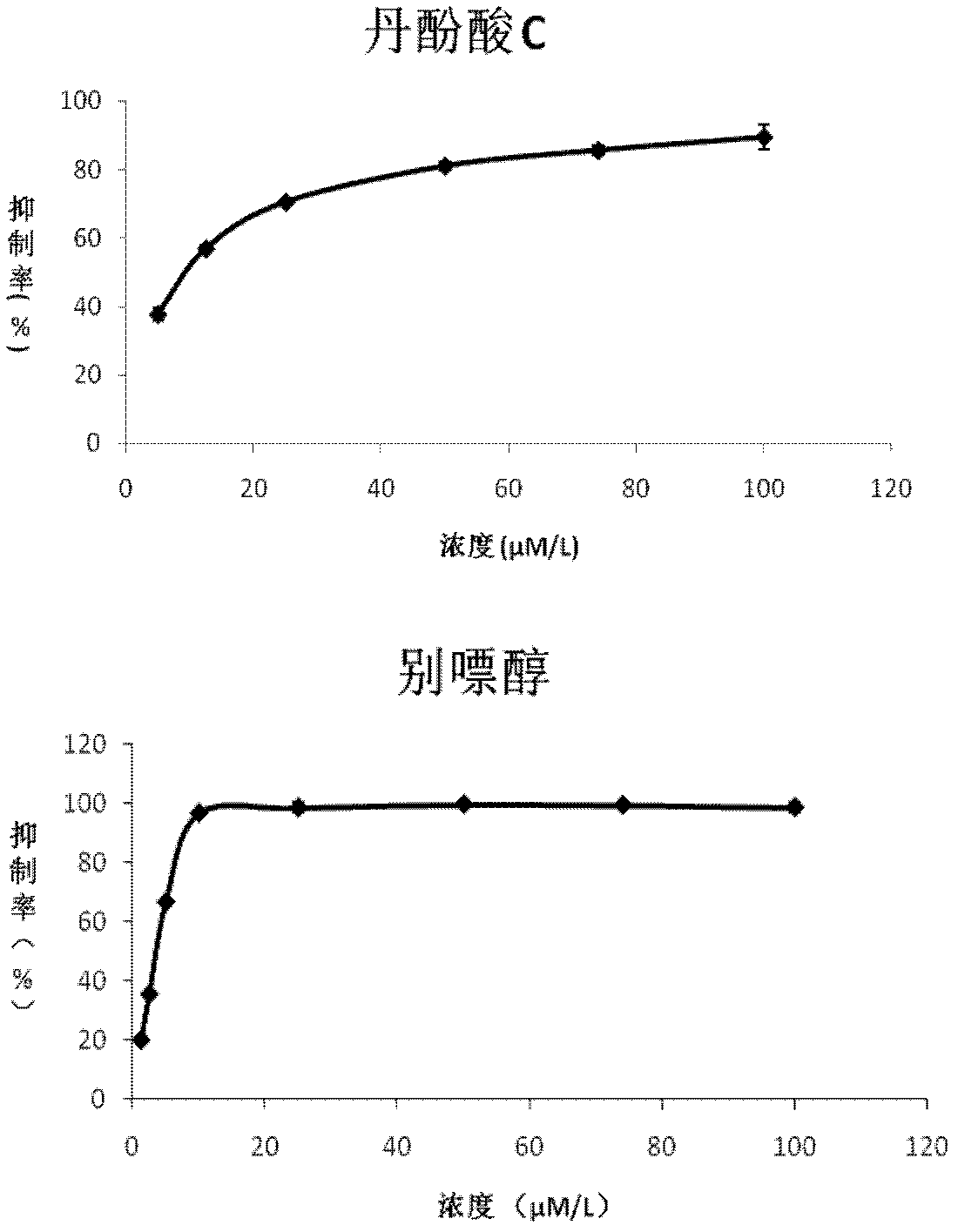
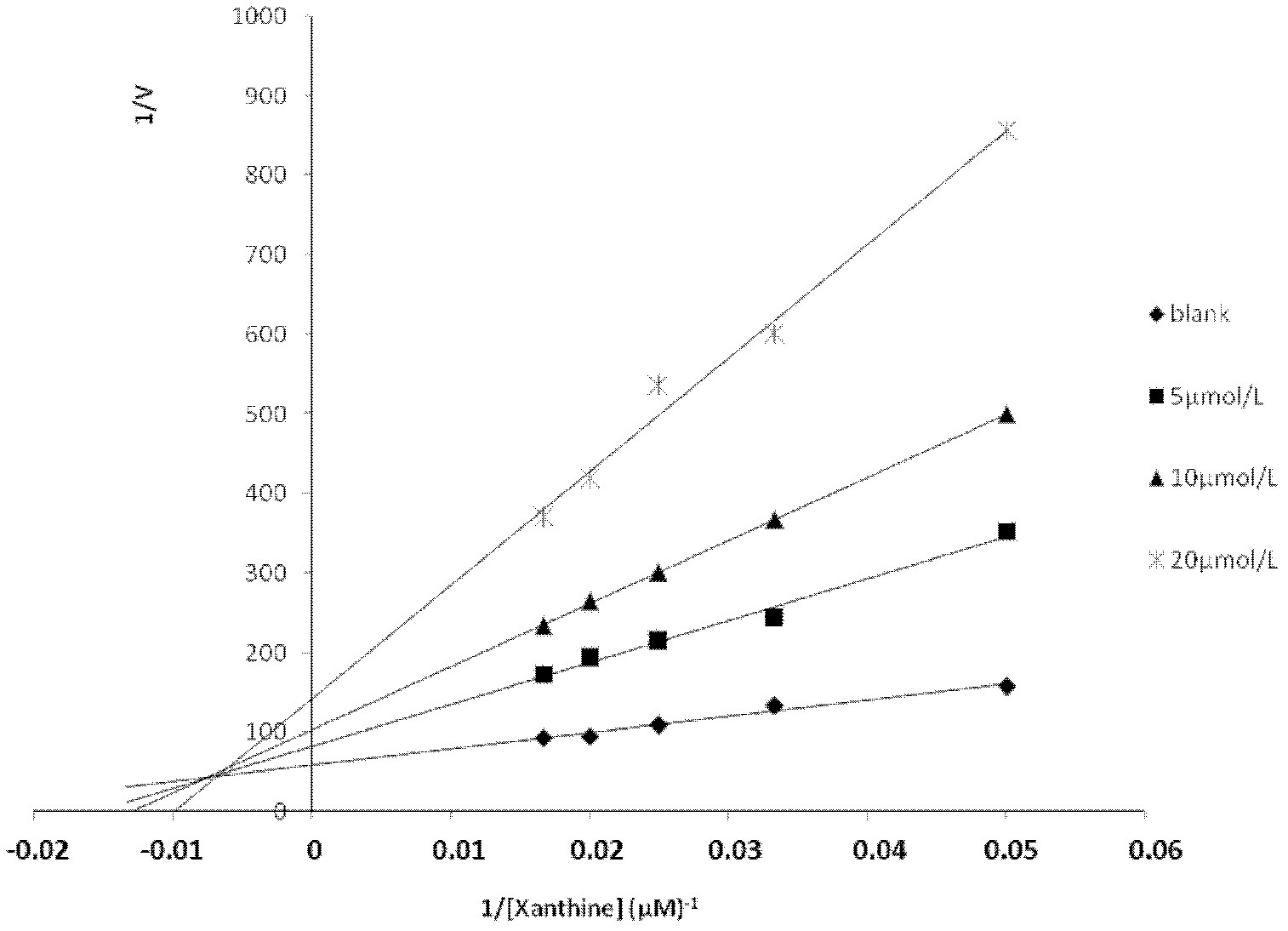
Application of salvianolic acid C in preparation of drugs for prevention and treatment of hyperuricemia
The present invention relates to the technical field of medicine, specifically to an application of salvianolic acid C in preparation of drugs for prevention and treatment of hyperuricemia. The results of the pharmacological test show that: the salvianolic acid C can be adopted as a xanthine oxidase (XO) inhibitor to prevent and treat hyperuricemia and complications of the hyperuricemia, wherein the complications caused by the hyperuricemia comprise: gout, gouty arthritis, gouty nephropathy, lithangiuria, cardiovascular diseases and other diseases.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Acacia extracts and their compounds on inhibition of xanthine oxidase
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Composition with rhizoma alpiniae officinarum extract, flos chrysanthemi extract and uric acid reducing function and application of composition
InactiveCN108404020ARaw materials are easy to getHas uric acid-lowering activitySkeletal disorderNatural extract food ingredientsEnrichment methodsFlos chrysanthemi
The invention discloses a composition with rhizoma alpiniae officinarum extract, flos chrysanthemi extract and a uric acid reducing function and application of the composition. The composition is a compound of the rhizoma alpiniae officinarum extract and the flos chrysanthemi extract. The rhizoma alpiniae officinarum extract is made of dry rhizoma alpiniae officinarum and is prepared by the aid ofultrasonic auxiliary ethanol extraction methods and macroporous resin separation and enrichment methods, and diphenylheptane and flavone compounds in the rhizoma alpiniae officinarum are pertinentlyextracted; the flos chrysanthemi extract is made of dry Bo flos chrysanthemi, Qi flos chrysanthemi and Jinsihuang flos chrysanthemi and is prepared by the aid of ethanol reflux extraction methods, andflavone substances in the flos chrysanthemi are pertinently extracted. The composition and the application have the advantages that the composition contains the abundant diphenylheptane compounds (more than 30%) and the abundant flavone (more than 7%) compounds, and is obvious in uric acid reducing activity (the in-vitro xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity is higher than 75 micro-mol of allopurinol equivalent weight / g); the composition has excellent flavor, is safe and reliable and can be applied to hyperuricemia prevention and adjuvant therapy healthcare foods or medicines, and raw materials for the composition are easily available.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Xanthine oxidase inhibitory peptide
InactiveCN111925412AClear structureGood potentialTetrapeptide ingredientsSkeletal disorderXanthineOxidative enzyme
The invention particularly relates to a xanthine oxidase inhibitory peptide. The amino acid sequence of the xanthine oxidase inhibitory peptide is Glu-Glu-Ala-Lys (EEAK). The IC50 value of the tetrapeptide EEAK on xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity is 173.00+ / -0.06 [mu]M, the tetrapeptide EEAK has a continuous and stable inhibitory effect on xanthine oxidase, and the tetrapeptide EEAK has the outstanding advantages of safety, no toxic or side effect, easiness in absorption, industrialization and the like. The active tetrapeptide EEAK or the derivative thereof can be used for preparing gout treatment / prevention medicines or used as a functional food additive for long-term treatment and health care of gout patients, and has a wide application prospect and very important significance.
Owner:BOHAI UNIV
Method for detecting content of hypoxanthine in fish
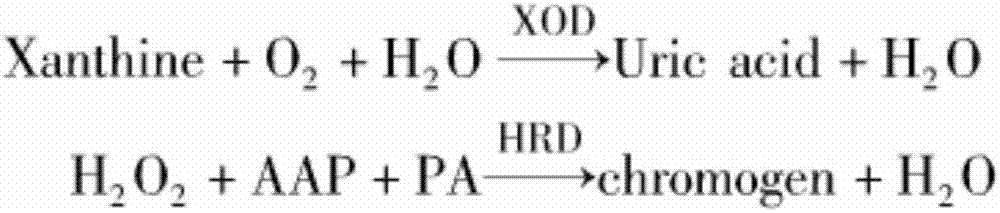
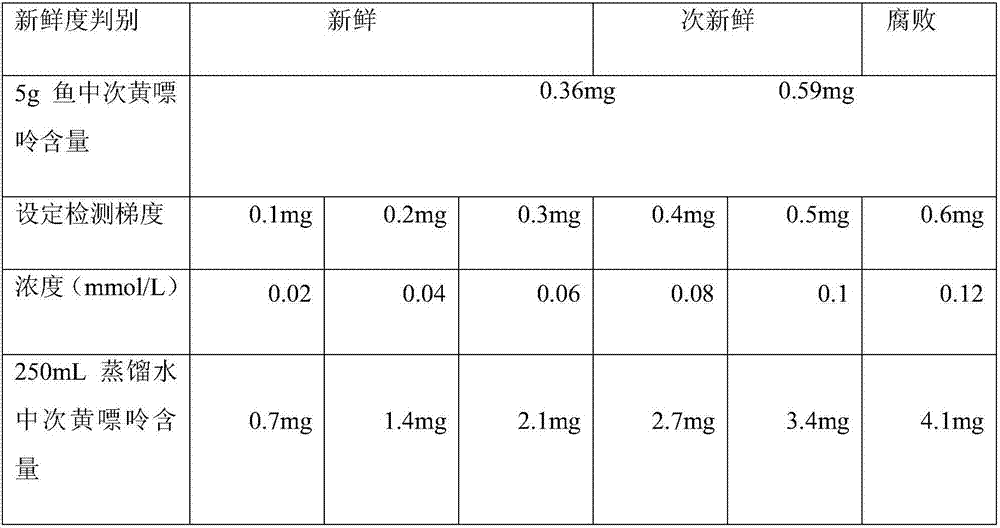
ActiveCN106855508ASimple methodFinish fastPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsHorse radish peroxidaseComputer science
The invention discloses a method for detecting content of hypoxanthine in fish, and relates to a method for detecting hypoxanthine. The method disclosed by the invention is simple, fast in completion speed, reasonable in design, high in accuracy degree, good in data reference and easy to operate, the detection purpose can be achieved without special testing instruments, that is, by using conventional detection instruments, large-scale popularization and application can be facilitated. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: preparing a sample liquid from fish meat, performing coupling catalysis on the sample liquid by using horse radish peroxidase and xanthine oxidase, and detecting by using an ultraviolet spectrophotometer, so as to obtain the content of the hypoxanthine. The method is adopted to judge the freshness of fish.
Owner:BEIJING WUZI UNIVERSITY
Application of 3-methoxy xanthone compound in preparation of medicament for preventing and treating hyperuricemia
InactiveCN102499934ASuitable for preventionSuitable for therapeuticOrganic active ingredientsSkeletal disorderSerum uric acidXanthone
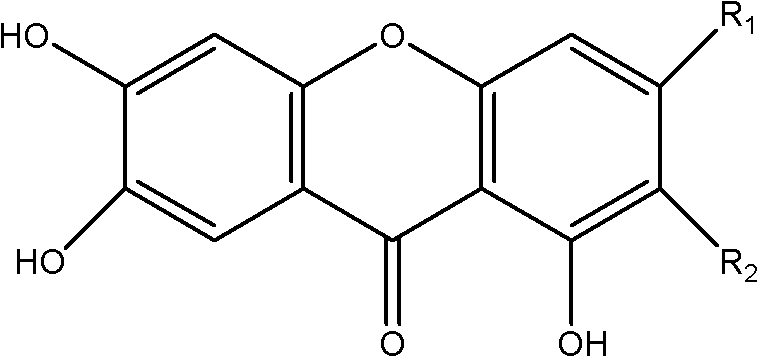
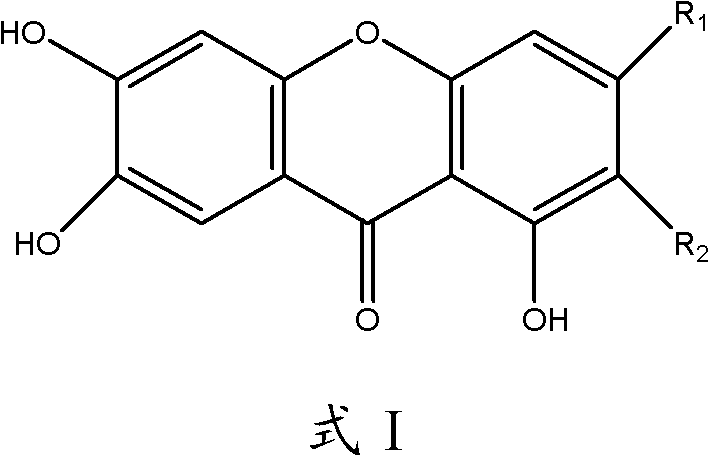
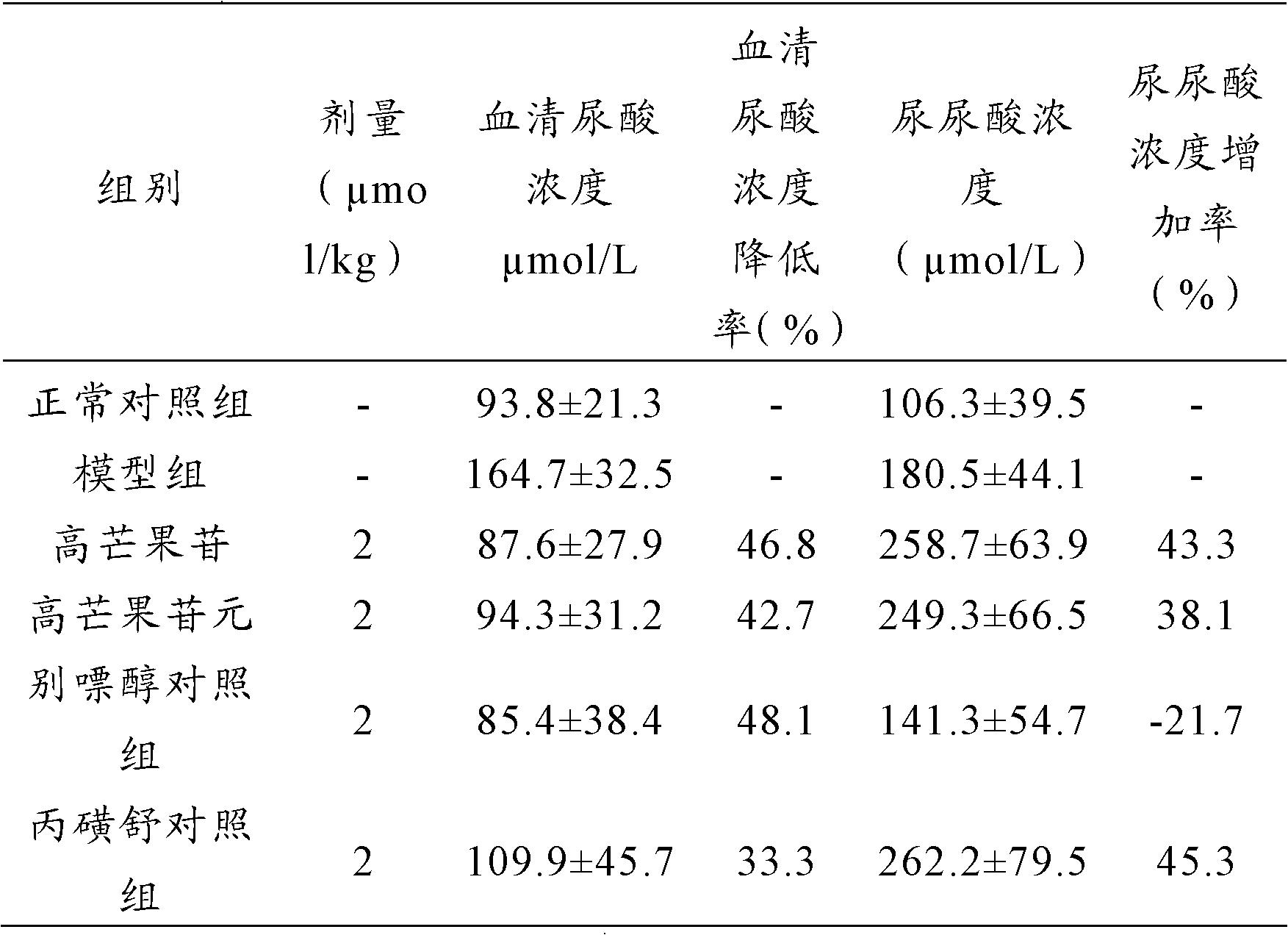
The invention discloses application of high mangiferin and aglycon thereof in preparation of a medicament for preventing and treating hyperuricemia and in particular relates to application of high mangiferin and aglycon thereof in preparation of a medicament for preventing and treating hyperuricemia as well as gout and lithangiuria brought by the hyperuricemia, and a medicine application way. The high mangiferin and aglycon thereof provided by the invention can be used for obviously reducing the concentration of serum uric acid in an animal for experiment and have the serum uric acid inhibition effect similar to that of a xanthine oxidase inhibition medicament allopurinol; and simultaneously, the high mangiferin and aglycon thereof provided by the invention can be used for obviously improving the concentration of uric acid in urine and have the uric acid excretion promoting function similar to that of a uric acid excretion promoting medicament probenecid. The high mangiferin and aglycon thereof provided by the invention are efficient, low in toxicity and high in safety, thus the high mangiferin and aglycon thereof are wide in application prospect.
Owner:KPC PHARM INC
Enzyme biosensor for detecting inosine monophosphate(IMP) and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110501400AExcellent electron transfer abilityQuick responseMaterial electrochemical variablesBovine serum albuminXanthine oxidase
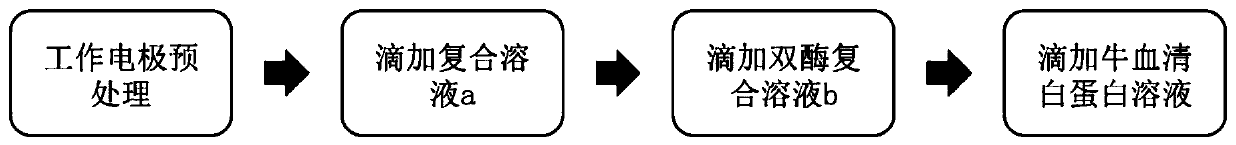
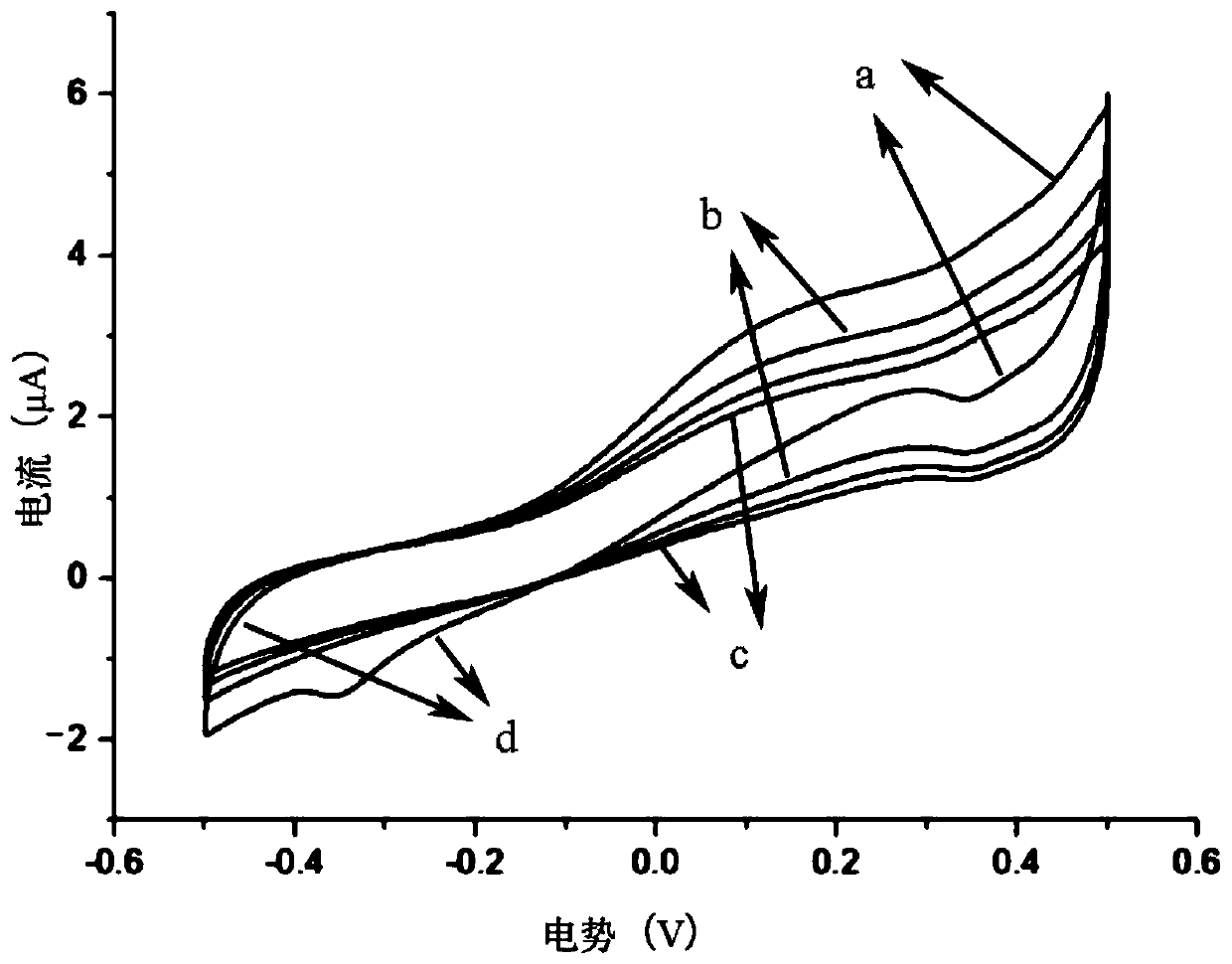
The invention belongs to the technical field of a biosensor, and discloses an enzyme biosensor for detecting inosine monophosphate(IMP) and a preparation method and an application thereof. The lineardetection range of the enzyme biosensor is 0.313-210 microgram / L, and the detection limit is 0.238 microgram / L. The enzyme biosensor is formed by a reference electrode, a counter electrode and a modified electrode obtained by curing an IMP-sensitive substance recognition film on the surface of a working electrode. The substance recognition film is formed by a composite solution a, a double-enzymecomposite solution b formed by a 5'-nucleotidase solution and an xanthine oxidase solution by the volume ratio 1: 1, and a bovine serum albumin solution by the volume ratio of 1: 1: 1, wherein the composite solution a is composed of a MXene-Ti3C2Tx solution (T is selected from OH, O or F), a chitosan solution, a chloroauric acid solution and a chloroplatinic acid solution by the volume ratio of 12:1.2:1:1. The enzyme biosensor is simple, fast and accurate and high in sensitivity, and can be used for quantitative detection of inosine monophosphate(IMP) in food.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
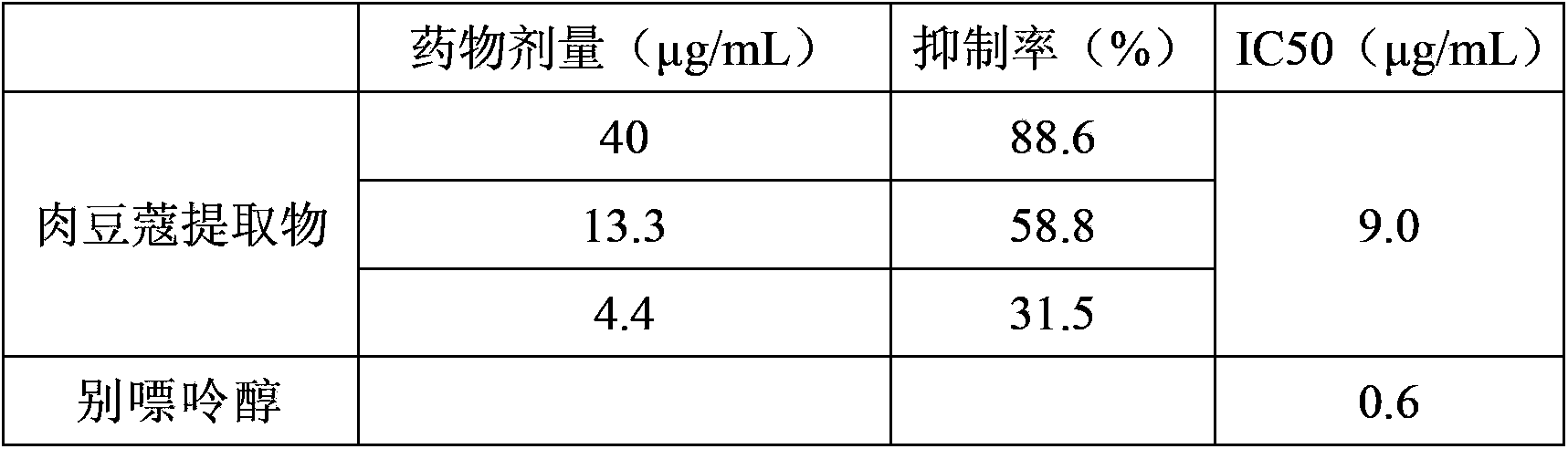
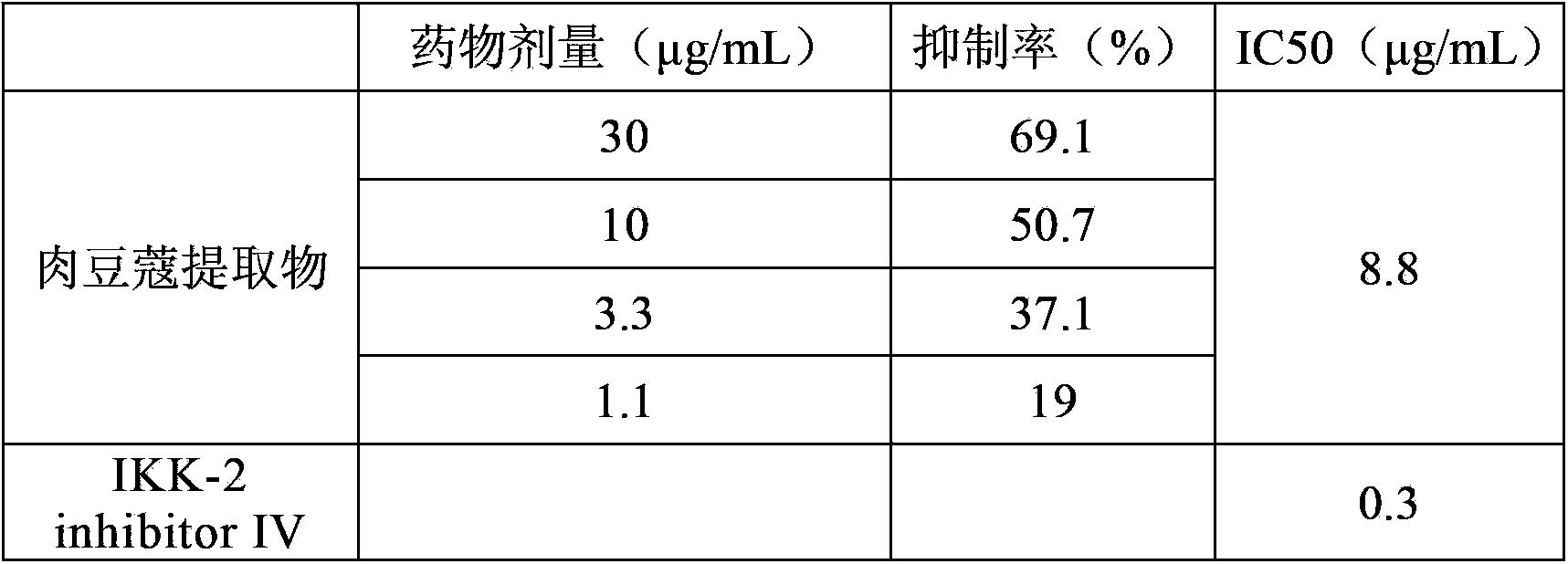
Application of nutmeg extract
InactiveCN103893226AGood anti-gout effectEnhanced inhibitory effectSkeletal disorderFood preparationNutmeg extractMedicine
The invention discloses application of a nutmeg extract in preparing anti-gout medicines, foods or healthcare products. Researches discover that the nutmeg extract has a relatively strong inhibiting effect on xanthine oxidase and a tumor necrosis factor alpha, showing that the nutmeg extract disclosed by the invention has a good anti-gout function; the nutmeg extract can be used for preparing anti-gout medicines, foods or healthcare products as well as a pharmaceutical composition; therefore, a new way is developed for application of the nutmeg extract.
Owner:HUZHOU R & D CENT FOR NUTRITION & HEALTH SHANGHAI INST FOR BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Pentacetylgardenoside cyclohexanamide capable of reducing uric acid activity and preparation method and application of pentacetylgardenoside cyclohexanamide
ActiveCN110437291AImprove biological activityUric acid-loweringSugar derivativesSkeletal disorderKidneyDrug biological activity
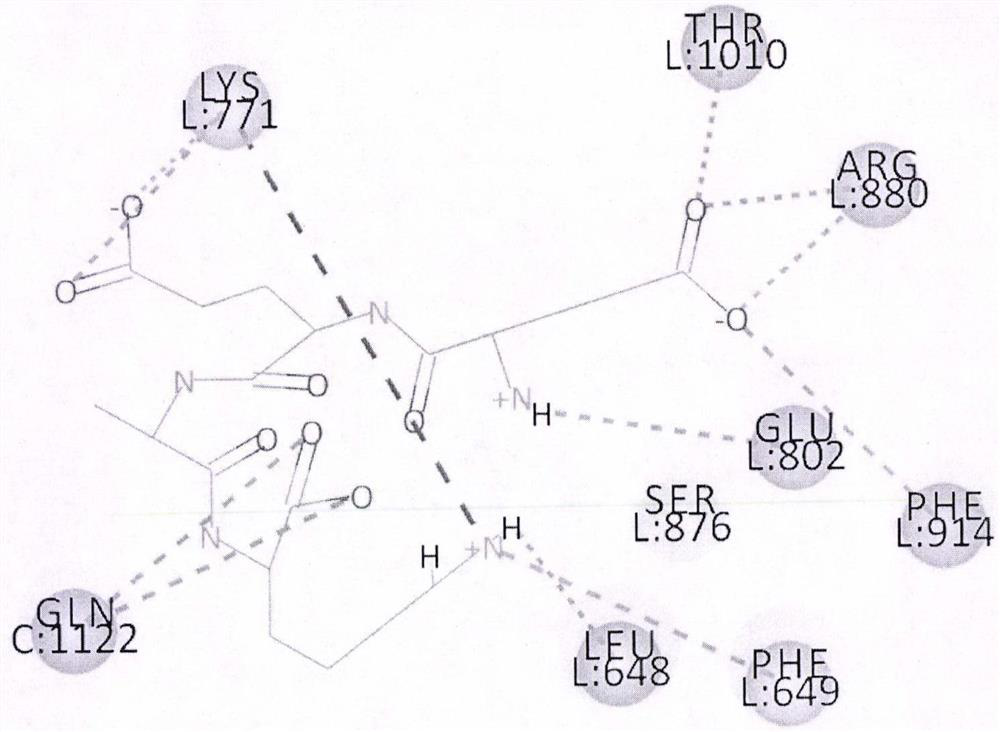
The invention belongs to the technical field of drug synthesis, and particularly relates to pentacetylgardenoside cyclohexanamide capable of reducing uric acid activity and a preparation method and application of the pentacetylgardenoside cyclohexanamide. The molecular structure formula of a compound is as follows (please see the specification of the formula). According to the pentacetylgardenoside cyclohexanamide, structural modification is conducted on gardenoside to improve the biological activity of the gardenoside, the functions of reducing the uric acid and protecting kidney areachieved,through an amide bond, acompound molecule can make the compound to effectively occupy thenarrow hydrophobic cavity of xanthine oxidase, meanwhile the compound further extends in the cavity, and formsMo-O-X coordination with an Mo ion, thus the inhibition activity of xanthine oxidase is enhanced, and the potential for drug formation is achieved. According to the pentacetylgardenoside cyclohexanamide with the functions of reducing the uric acid and protecting the kidney, the synthetic method is easy, the cost of the raw materials is low, and the structure is novel.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
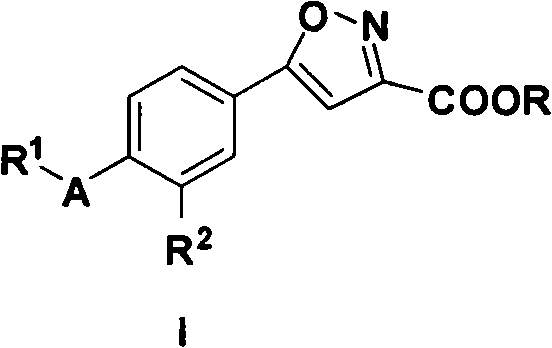
5-substituted phenyl-3-isoxazole carboxylic acid and ester compounds, compositions and preparation method thereof
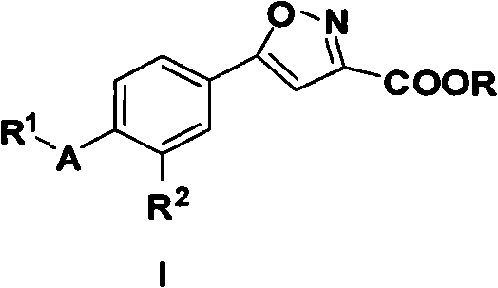
InactiveCN101580495ASimple manufacturing methodOrganic chemistrySkeletal disorderXanthineEthyl group
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicaments, relates to 5-substituted phenyl-3-isoxazole carboxylic acid with xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity shown as in general expression I and ester compounds, tautomer, a pharmaceutical salt and a pharmaceutical solvate thereof and pharmaceutical compositions containing the components and a preparation method of the components, and also relates to application of the compounds and the compositions in preparing a medicament for treating hyperuricemia and gout (wherein R independently is substituted or unsubstituted linear and branched C1-C10 alkyl, C2-C10 alkenyl, C3-C7 naphthenic base, C3-C7 cycloalkenyl groups, an aromatic group, an aralkyl group, a heterocyclic group, heteroaryl, heterocyclic-alkyl, heteroarylalkyl, C3-C7 cycloalkyl-alkyl, aminoalkyl, primary alkyl aminoalkyl, dialkyl aminoalkyl, alkoxyl-alkyl, aryl-oxyalkyl, aralkoxy-alkyl and fully halogenated alkyl; R is a cyano-group, a nitro group, halogen and unsubstituted, monosubstituted or disubstituted aminocarbonyl; R is a hydrogen atom or ethyl; and A is an oxygen atom, a sulphur atom and a nitrogen atom).
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY +1
(Aza)indole derivative and use thereof for medical purposes
ActiveUS8003647B2Inhibit productionExcellent URAT inhibitory activityBiocideOrganic chemistryDiseaseUricosuric Activity
The present invention provides compounds useful as agents for the prevention or treatment of a disease associated with abnormal serum uric acid level which has a uricosuric activity or the like. The present invention relates to (aza)indole derivatives represented by the following general formula (I) having xanthine oxidase inhibitory activities and useful as agents for the prevention or treatment of a disease associated with abnormality of serum uric acid level, prodrugs thereof, or salts thereof. In the formula (I), T represents nitro or cyano and the like; ring J represents aryl or heteroaryl and the like; Q represents carboxy or 5-tetrazolyl and the like; Y represents H, OH, NH2, halogen, nitro, alkyl, alkoxy and the like; X1, X2 and X3 independently represent CR2 or N; R1 and R2 independently represent halogen, cyano, haloalkyl, A-D-E-G, —N(-D-E-G)2 and the like, in the formula, A represents a single bond, O, S and the like; D and G independently represent optionally substituted alkylene, cycloalkylene, heterocycloalkylene, arylene, heteroarylene and the like; E represents a single bond, O, S, COO, SO2 and the like.
Owner:KISSEI PHARMA
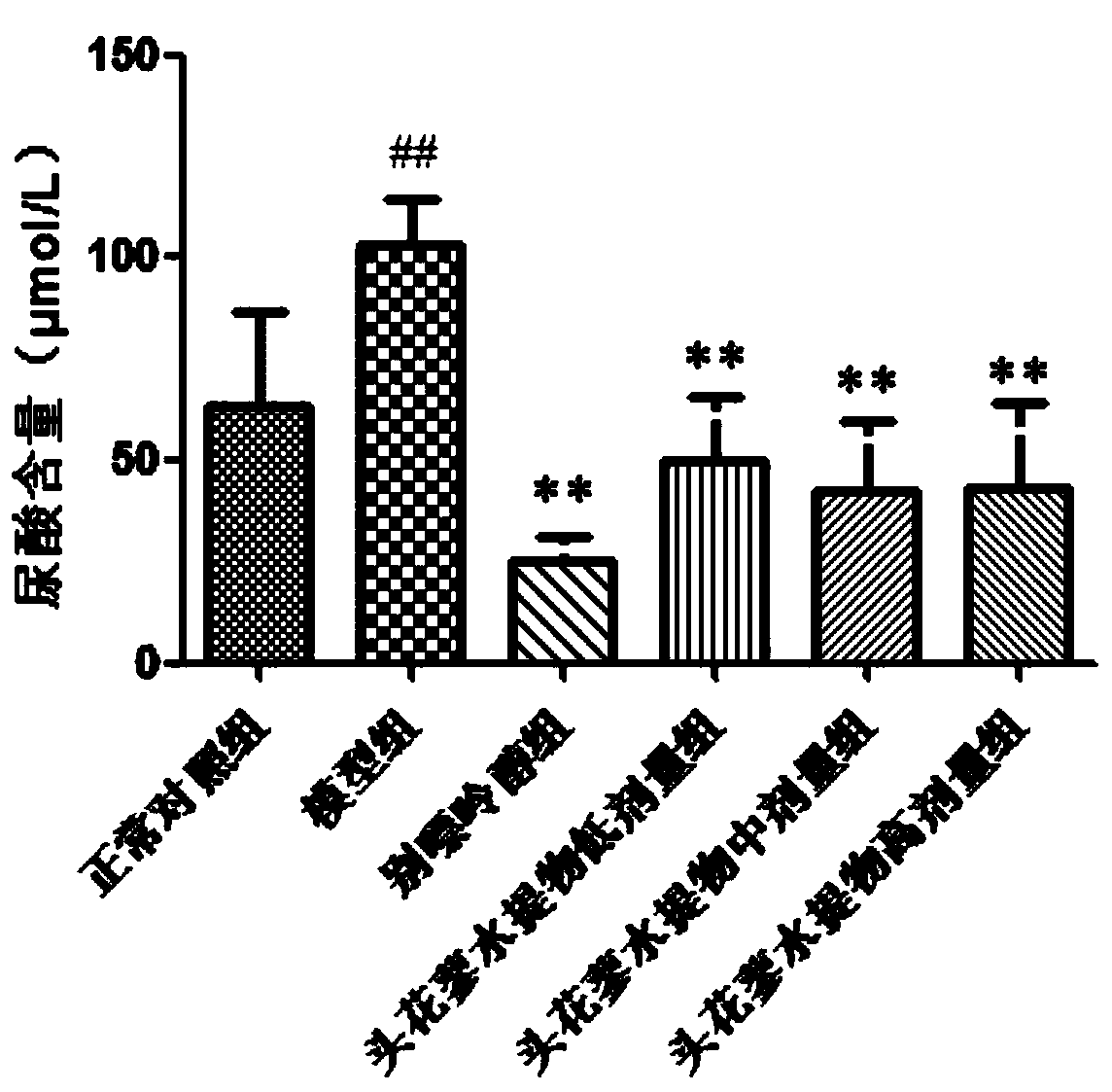
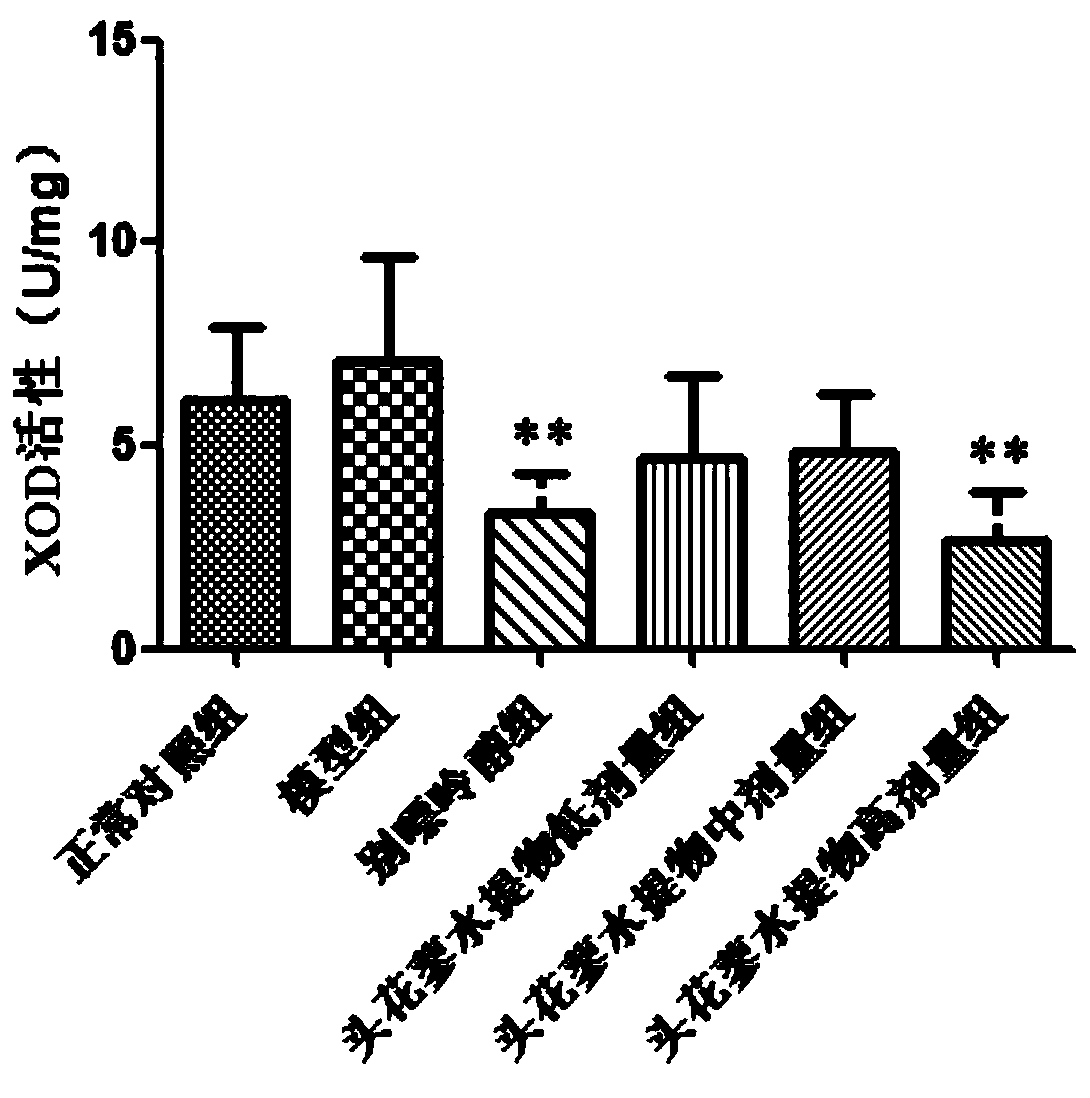
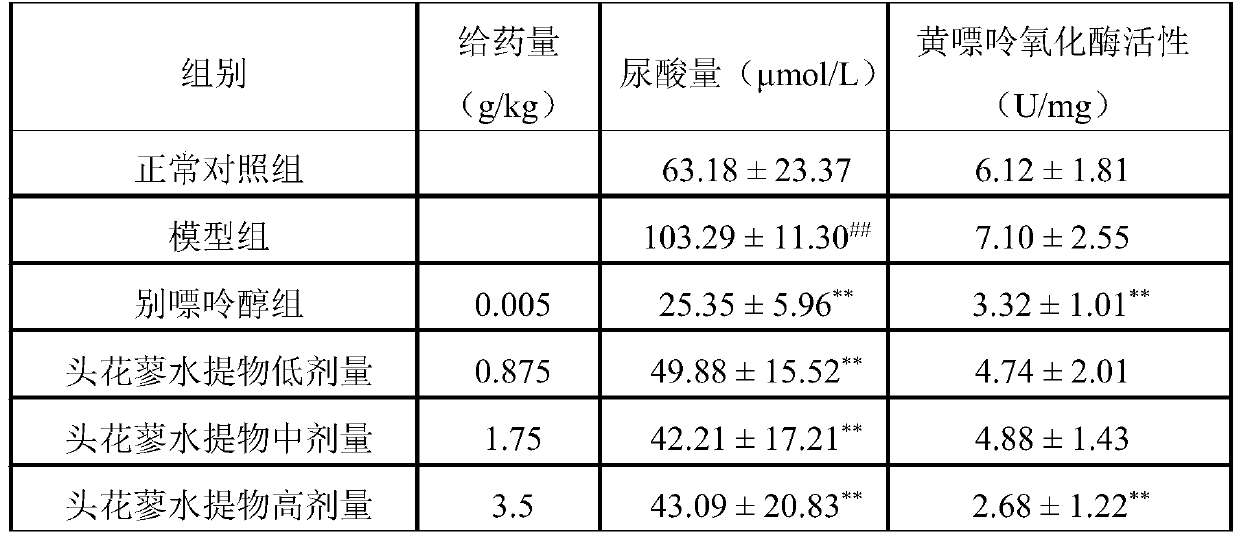
Application of polygonum capitatum in regulation of uric acid
ActiveCN110368419AAnti-hyperuricemiaHas a gout effectSkeletal disorderPlant ingredientsDiseaseMedicine
The invention relates to the technical field of medicines, in particular to application of polygonum capitatum in regulation of uric acid. Through research, it discovers that the polygonum capitatum can reduce uric acid content in serum of individuals with hyperuricemia by inhibiting the activity of xanthine oxidase in the liver, and can be well applied to regulating uric acid, treating diseases related to hyperuricemia or preparing drugs for treating, preventing, reducing and / or relieving diseases related to hyperuricemia. The polygonum capitatum has effects of resisting hyperuricemia and gout, and a brand-new, safe and effective natural drug for treating the hyperuricemia and the gout is provided.
Owner:GUIZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Triarylcarboxylic Acid Derivative
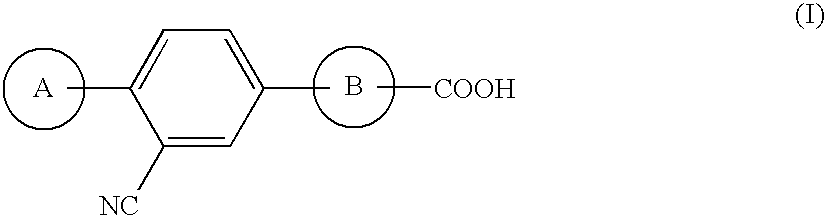
InactiveUS20090018104A1Potent xanthine oxidase inhibiting actionEnhance the imageBiocideSenses disorderArylDiabetic retinopathy
Provided is a triarylcarboxylic acid derivative, or an isomer, a prodrug, a hydrate, a solvate, a polymorph, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, represented by the following general formula (I):wherein A is an optionally substituted aryl or heteroaryl, and B is an optionally substituted monocyclic heteroaryl; and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The triarylcarboxylic acid derivative (I) exhibits potent xanthine oxidase inhibiting action and is therefore useful as a therapeutic agent for preventing or treating hyperuricemia, gout, inflammatory bowel disease, diabetic nephropathy and diabetic retinopathy.
Owner:ASTELLAS PHARMA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com