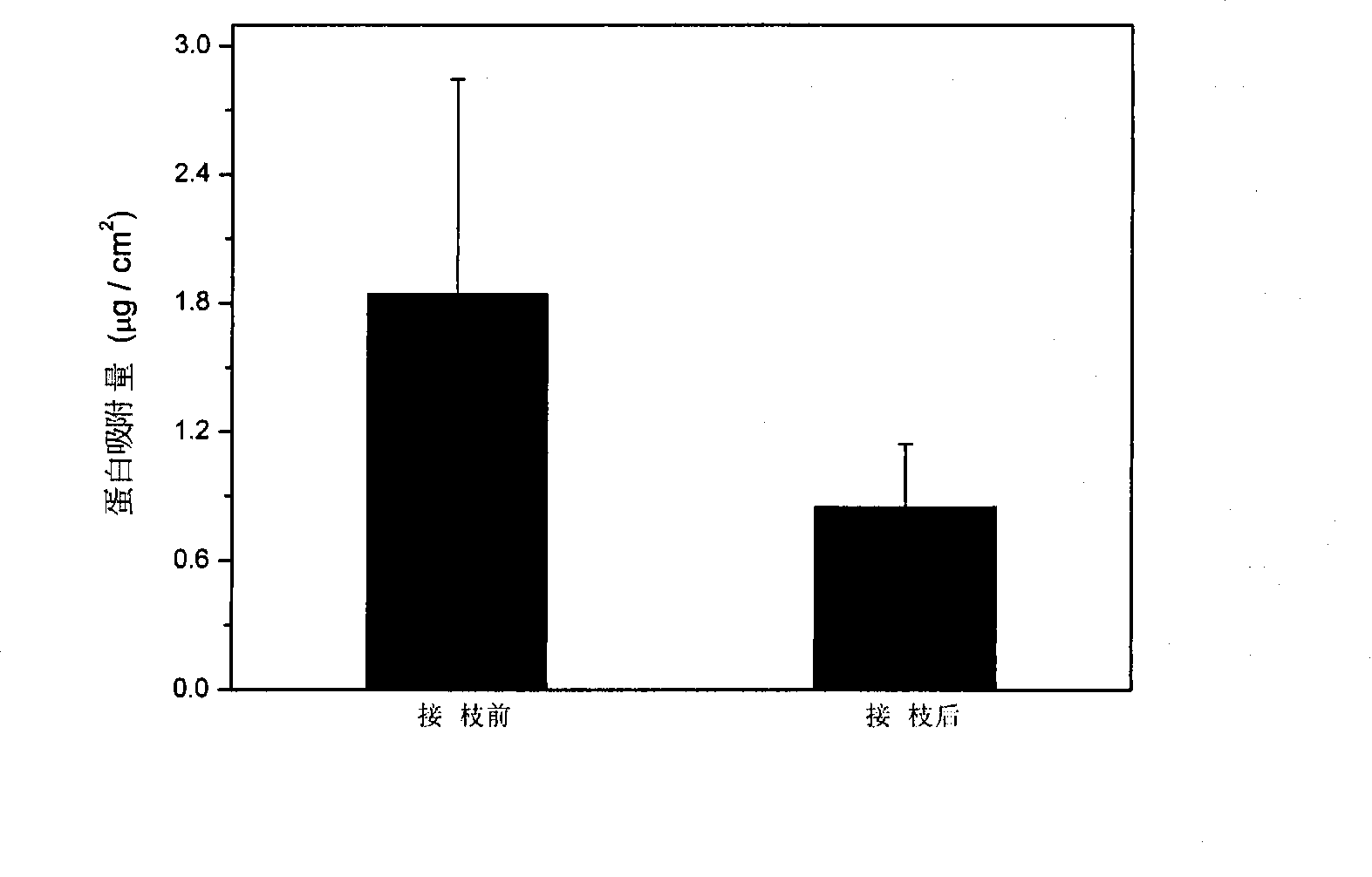
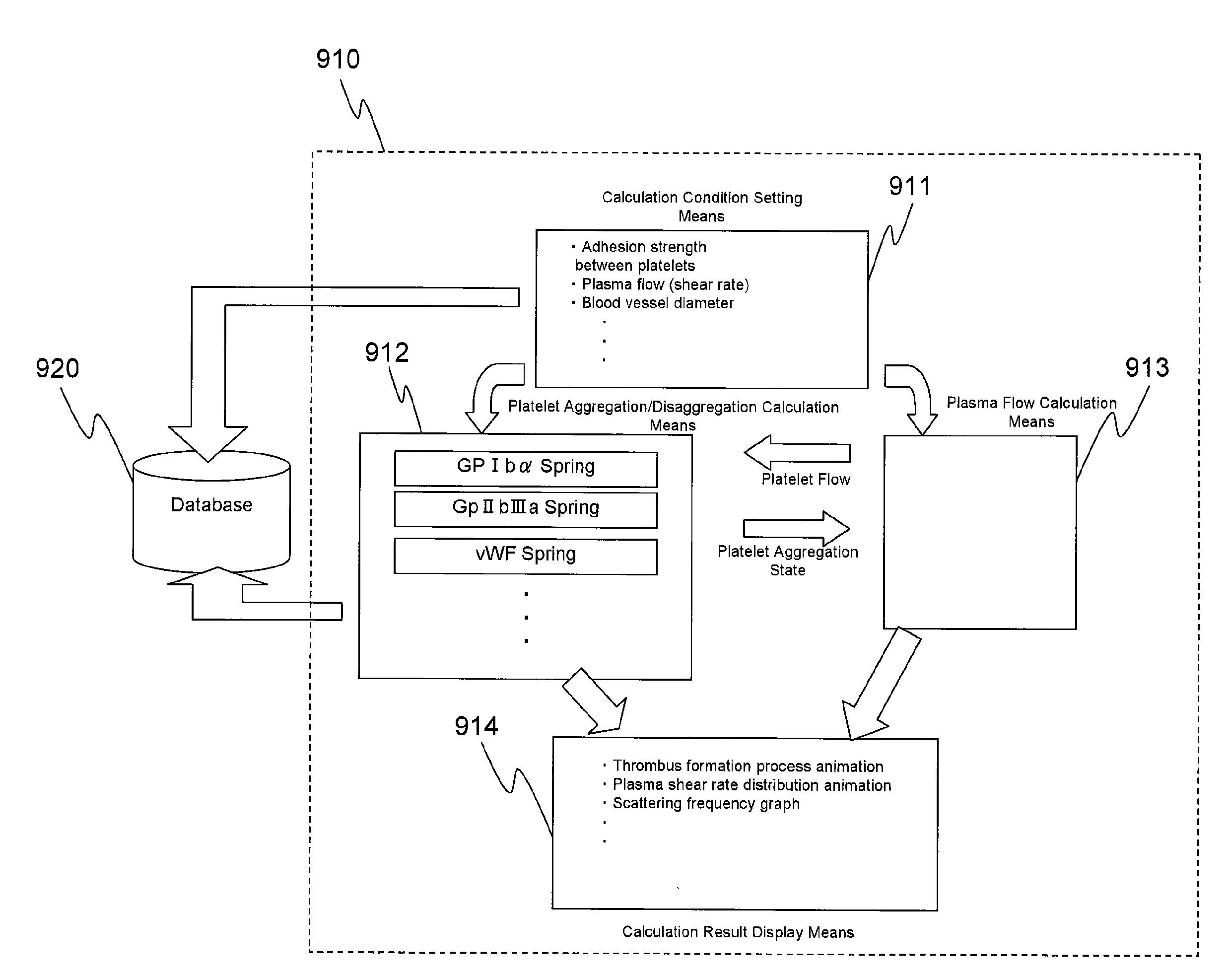
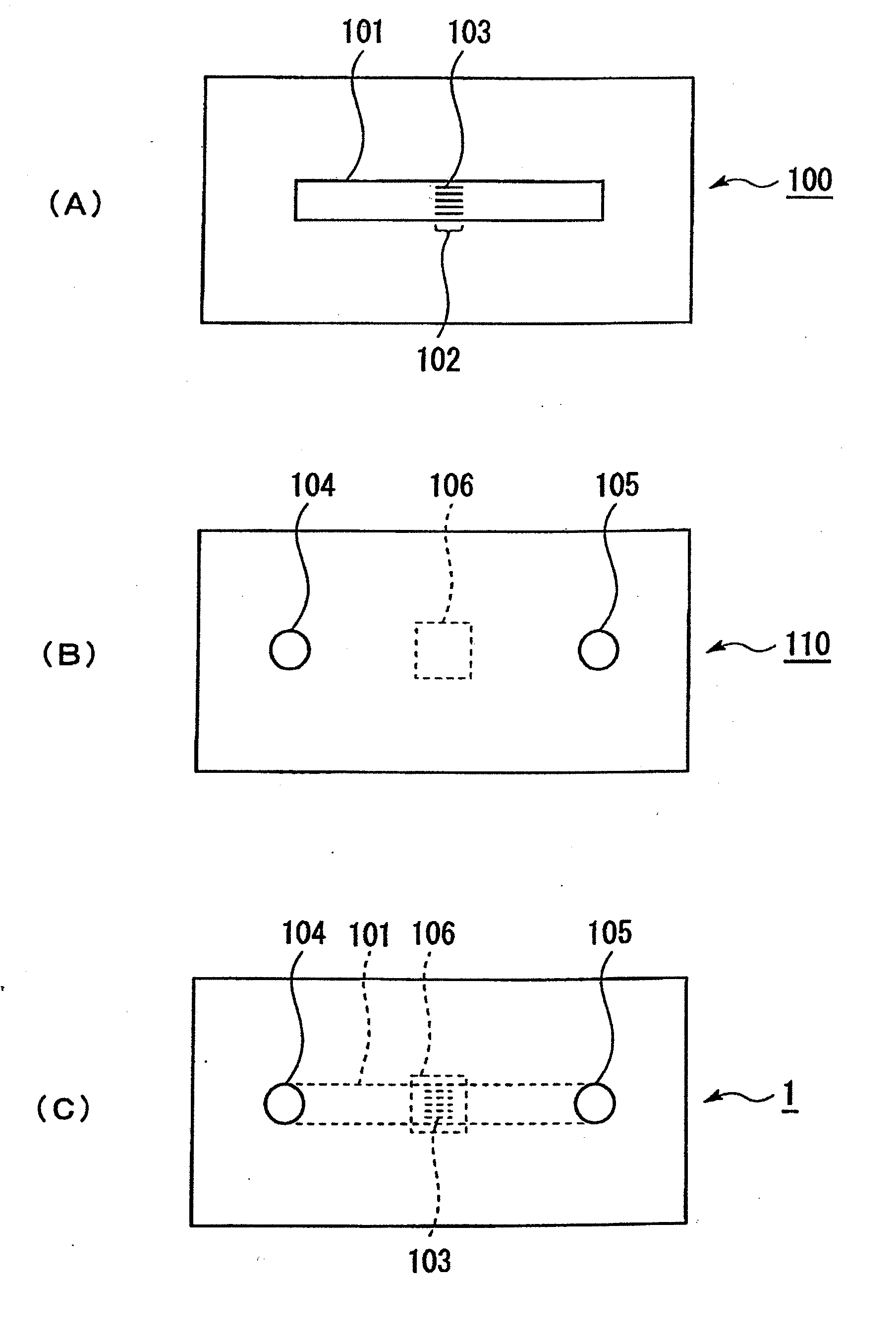
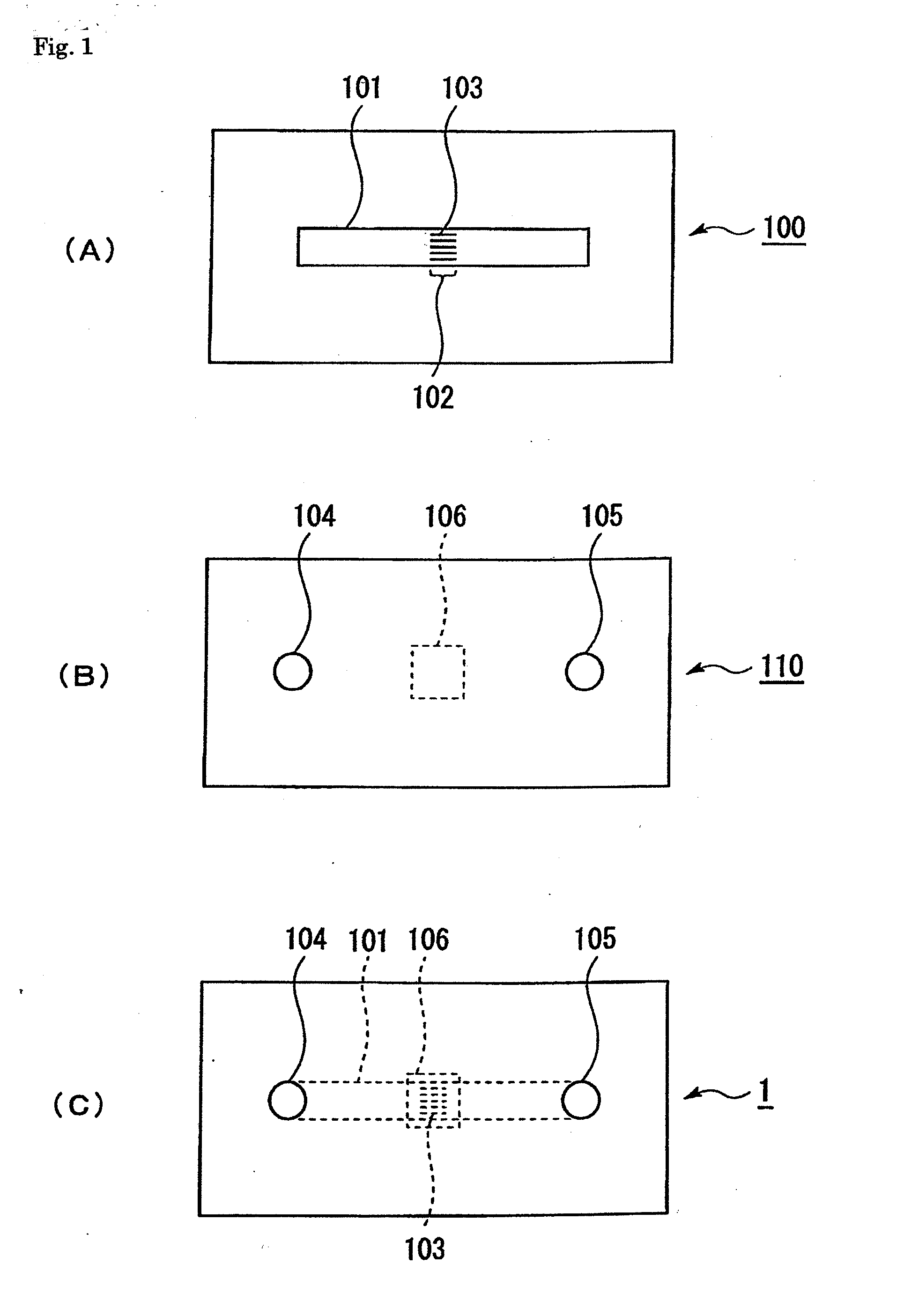
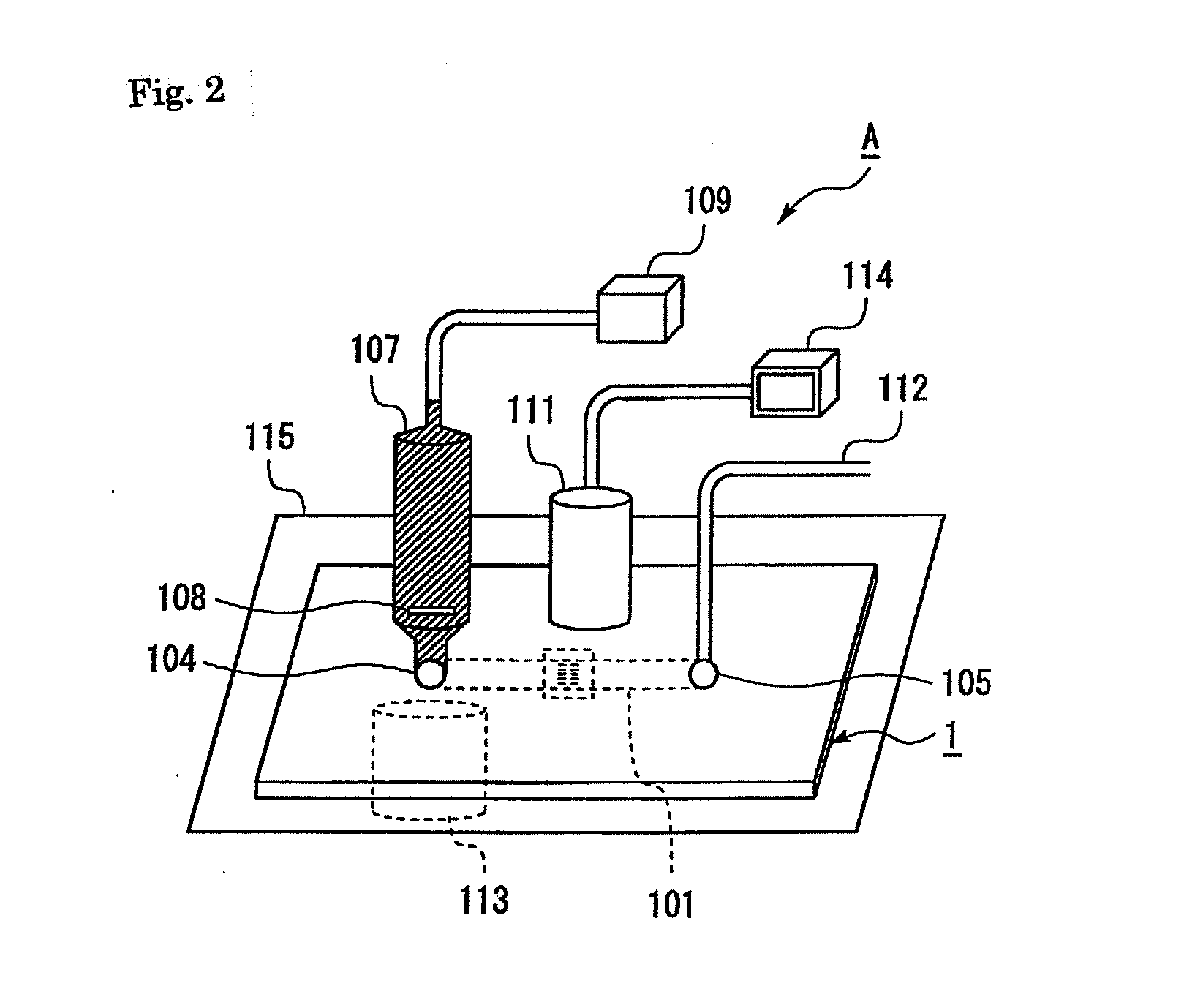
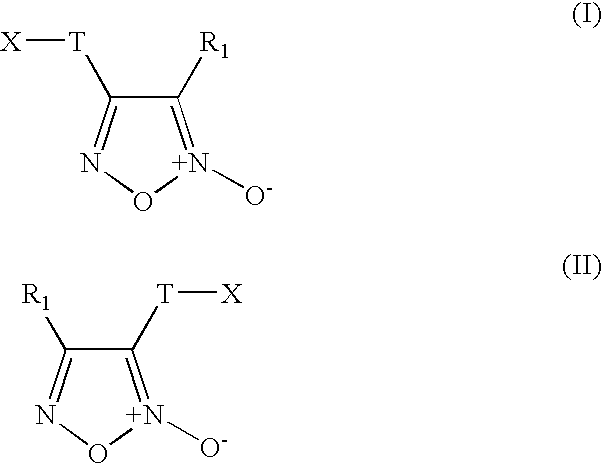
Patents
Literature
150 results about "Platelet adhesion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
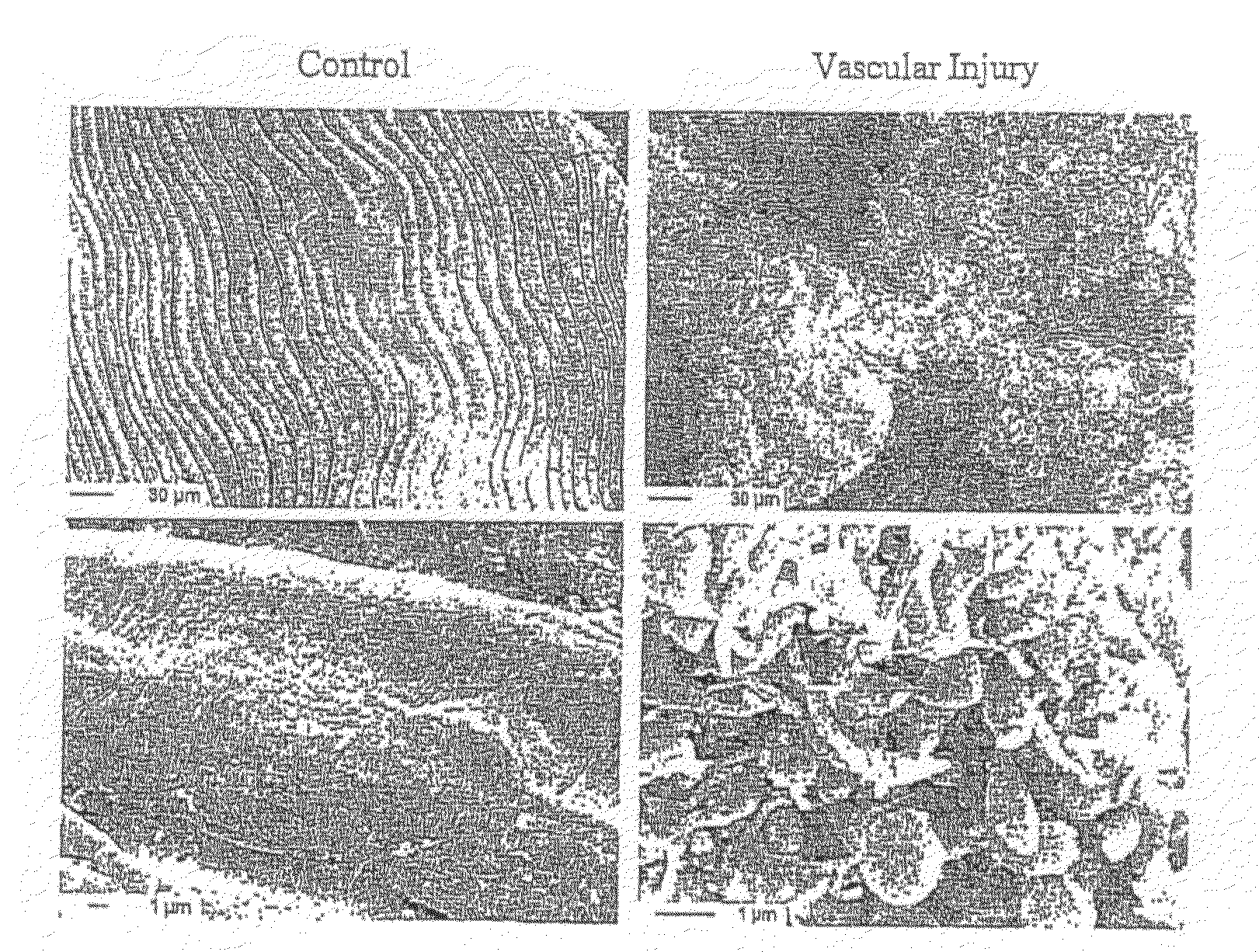
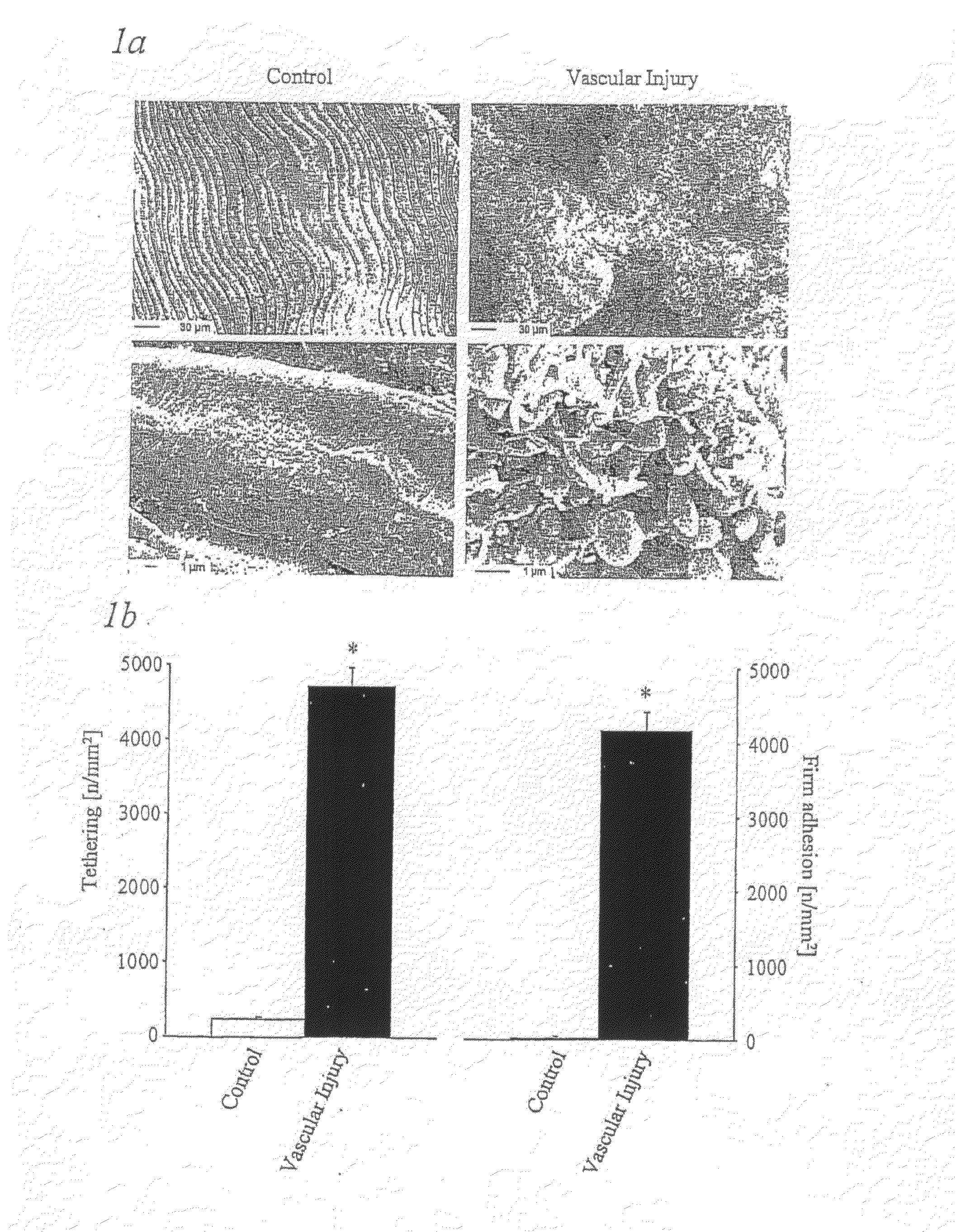
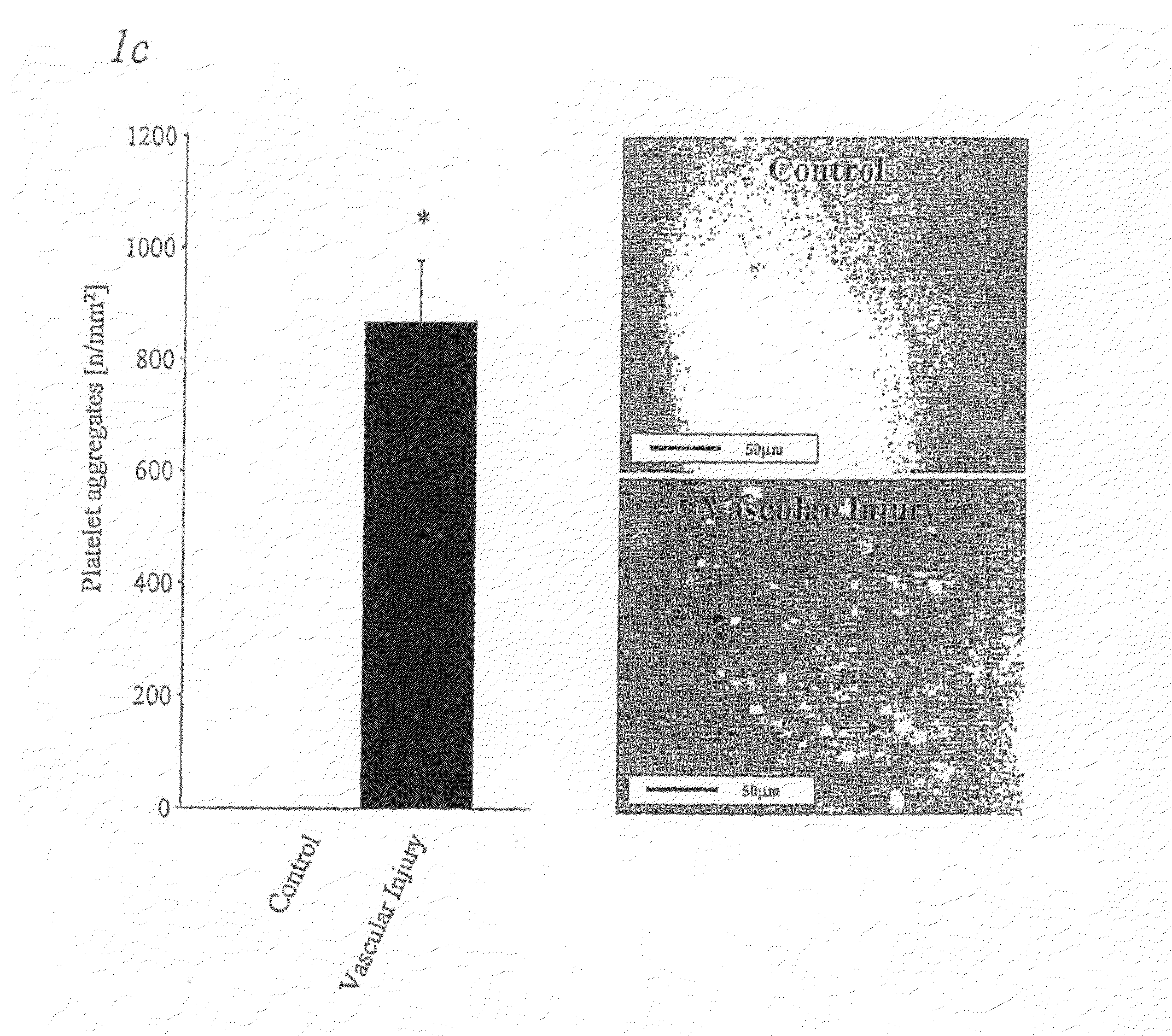
Platelet adhesiveness. Platelet adhesiveness refers to the processes or factors which lead to the adhesion of platelets to other structures. It can be contrasted with platelet aggregation, which refers to the processes or factors which lead to the adhesion of platelets to other platelets.
Methods of using and compositions comprising (+) sibutramine optionally in combination with other pharmacologically active compounds
This invention encompasses methods for the treatment and prevention of disorders that include, but are not limited to, eating disorders; weight gain; obesity; irritable bowel syndrome; obsessive-compulsive disorders; platelet adhesion; apnea; affective disorders such as attention deficit disorders, depression, and anxiety; male and female sexual function disorders; restless leg syndrome; osteoarthritis; substance abuse including nicotine and cocaine addiction; narcolepsy; pain such as neuropathic pain, diabetic neuropathy, and chronic pain; migraines; cerebral function disorders; chronic disorders such as premenstrual syndrome; and incontinence. The invention further encompasses pharmaceutical compositions and dosage forms which comprise optically pure (+) sibutramine, optionally in combination with a phosphodiesterase inhibitor or a lipase inhibitor.
Owner:SEPACOR INC
Devices, articles, coatings, and methods for controlled active agent release or hemocompatibility
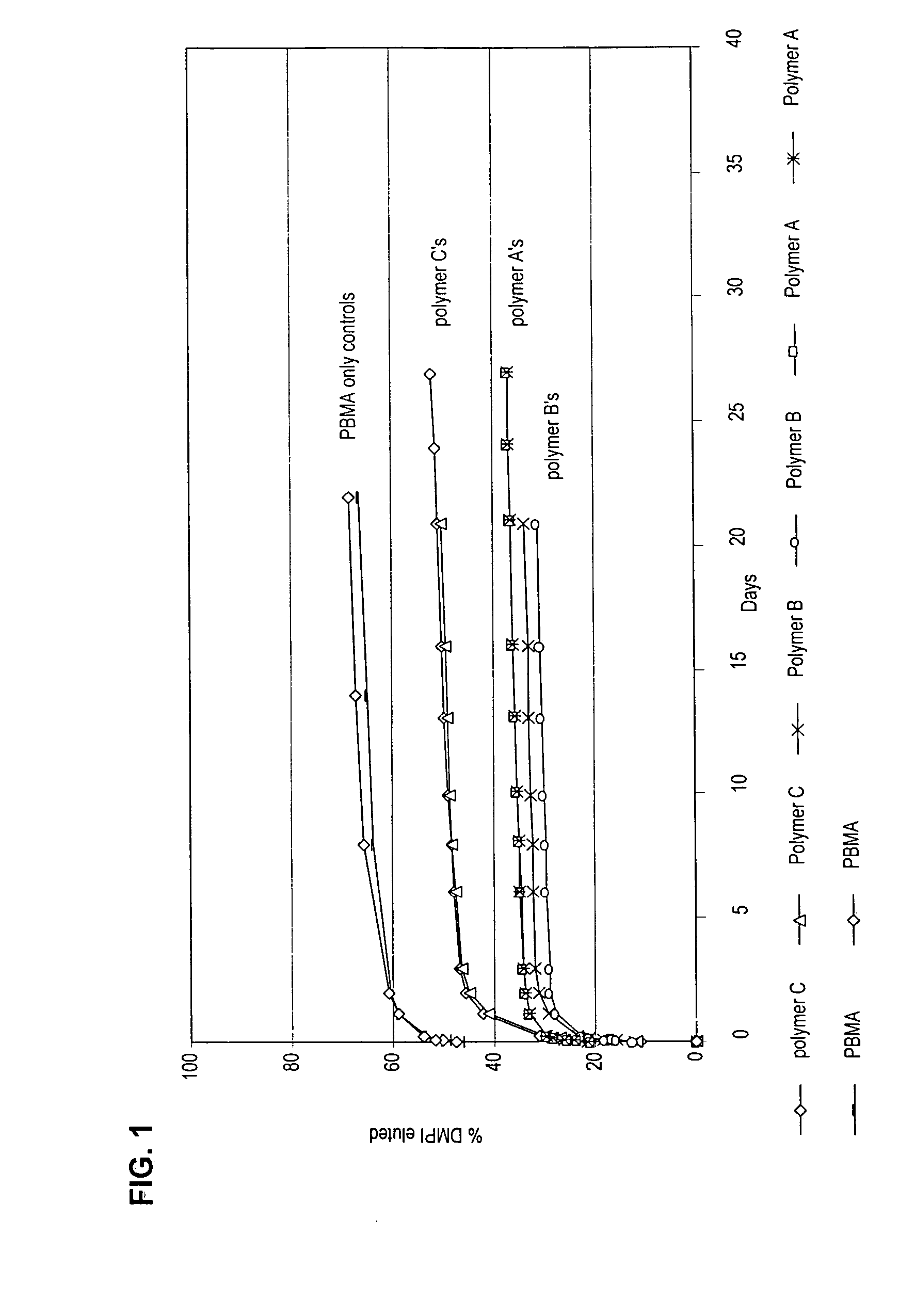
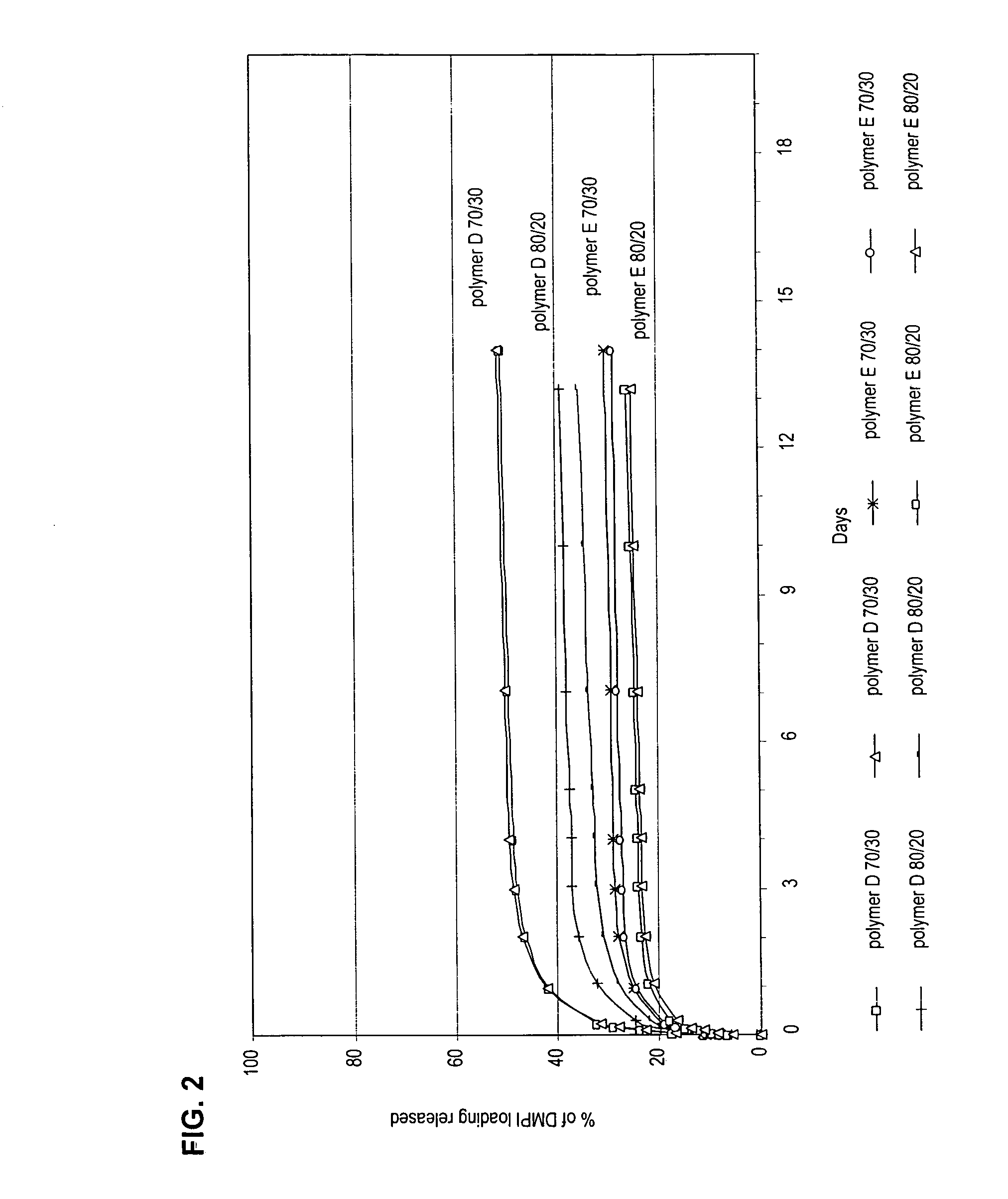
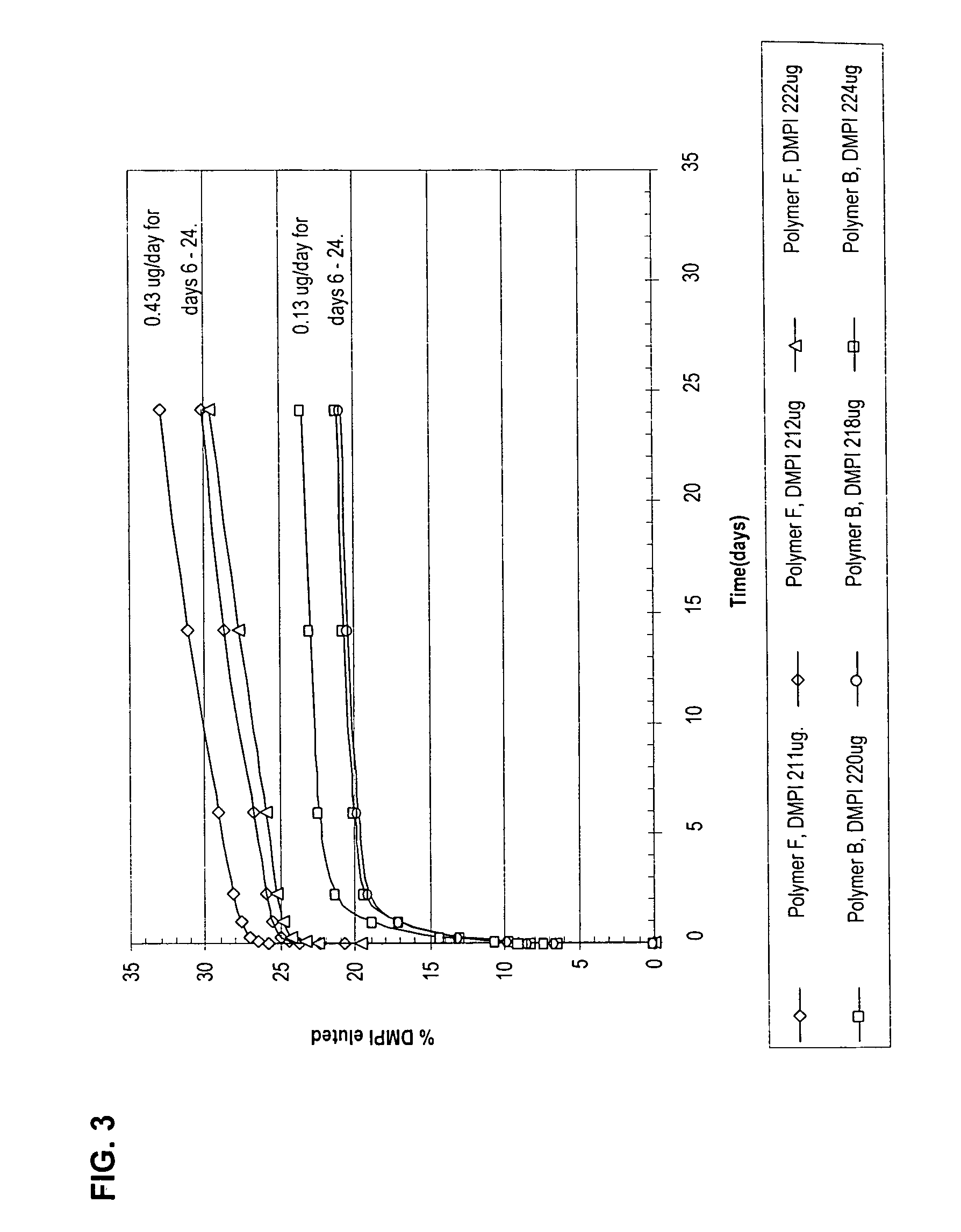
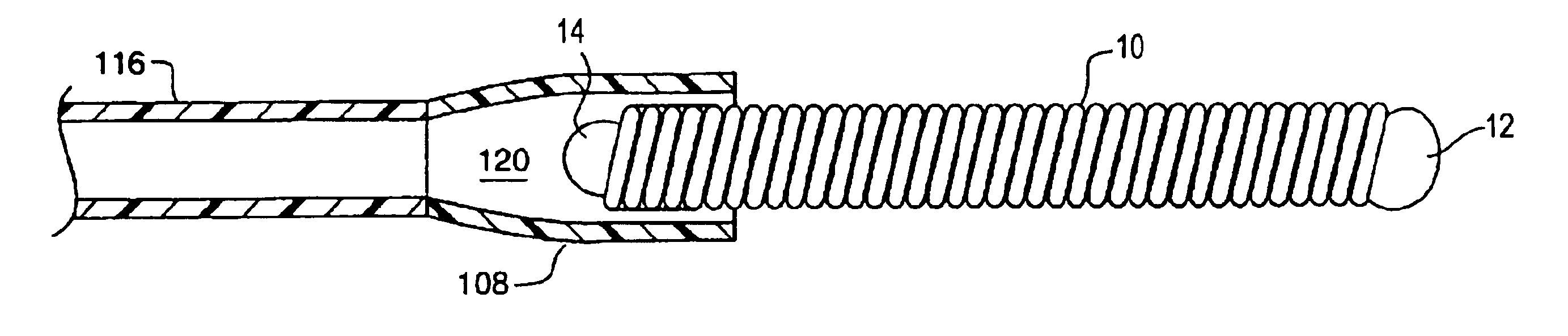
The present invention relates to devices, articles, coatings, and methods for controlled active agent release and / or for providing a hemocompatible surface. More specifically, the present invention relates to copolymer compositions and devices, articles, and methods regarding the same for controlled active agent release. In an embodiment, the present invention includes a copolymer composition. The copolymer composition can include a copolymer and an active agent. In an embodiment, the copolymer includes an effective portion of a monomeric unit including a polar moiety. The active agent can be polar. The active agent can be charged. The active agent can be non-polar. In an embodiment, the copolymer composition includes a random copolymer. In an embodiment, the random copolymer includes butyl methacrylate-co-acrylamido-methyl-propane sulfonate copolymer, which can provide reduced platelet adhesion.
Owner:SURMODICS INC
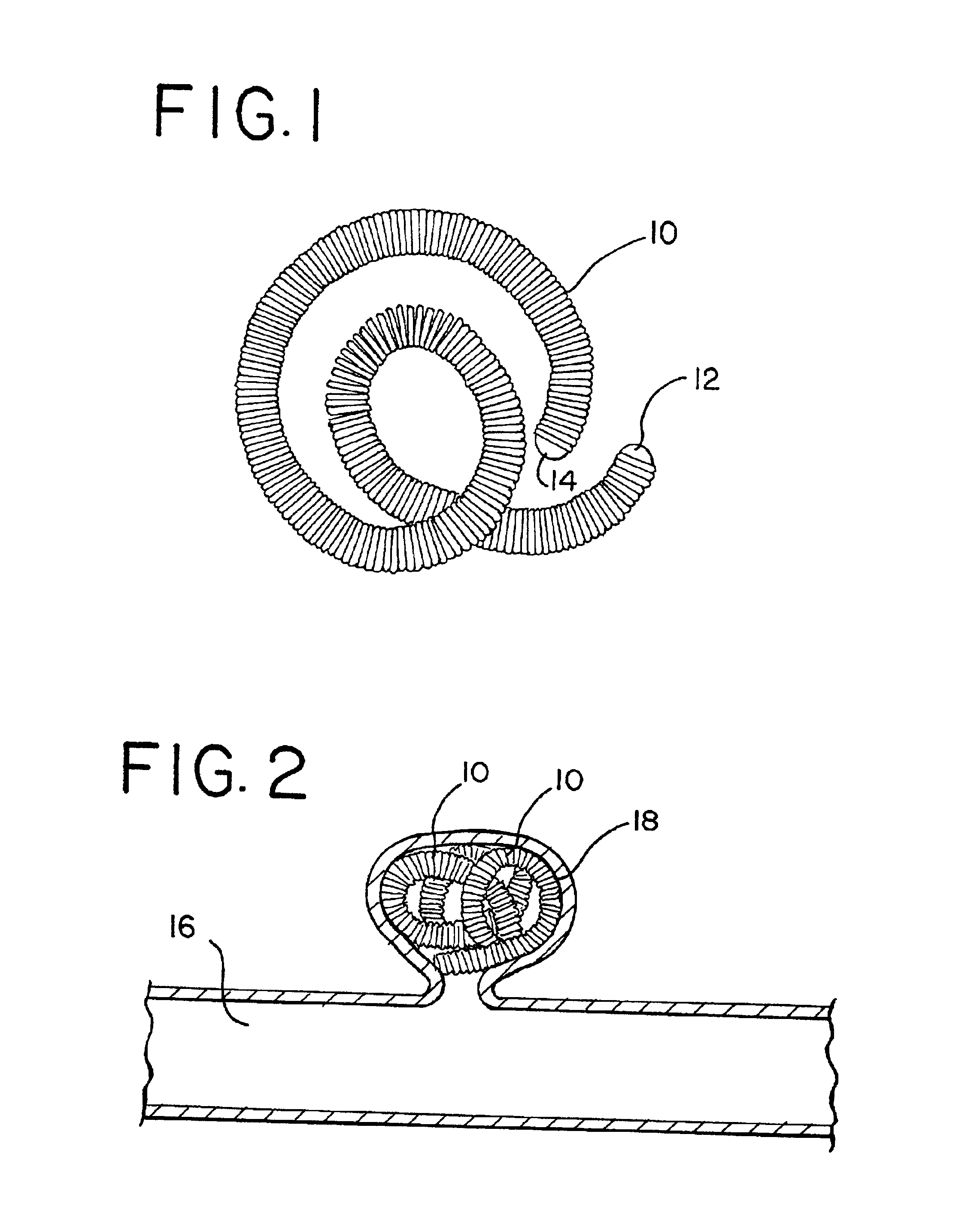
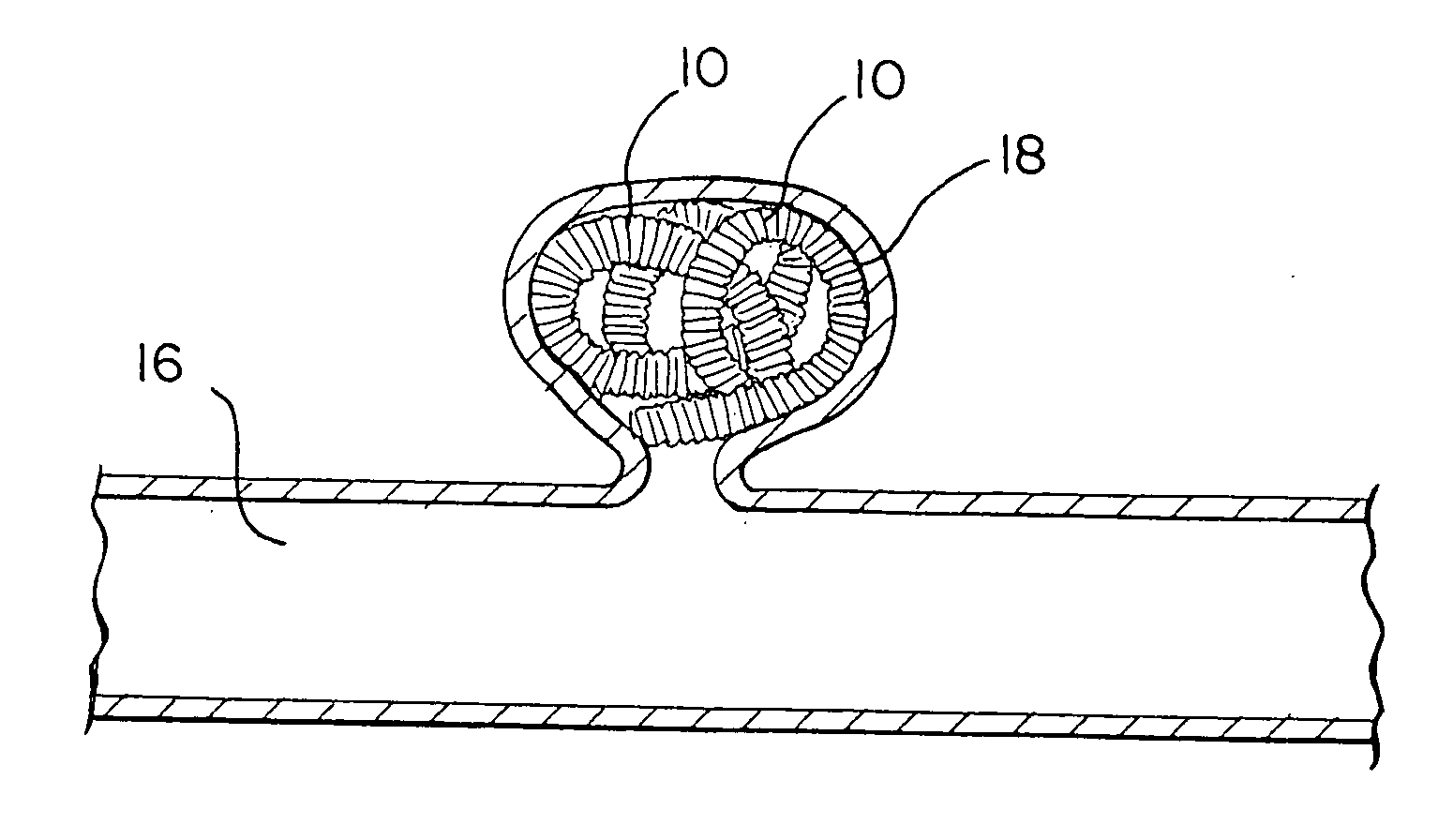
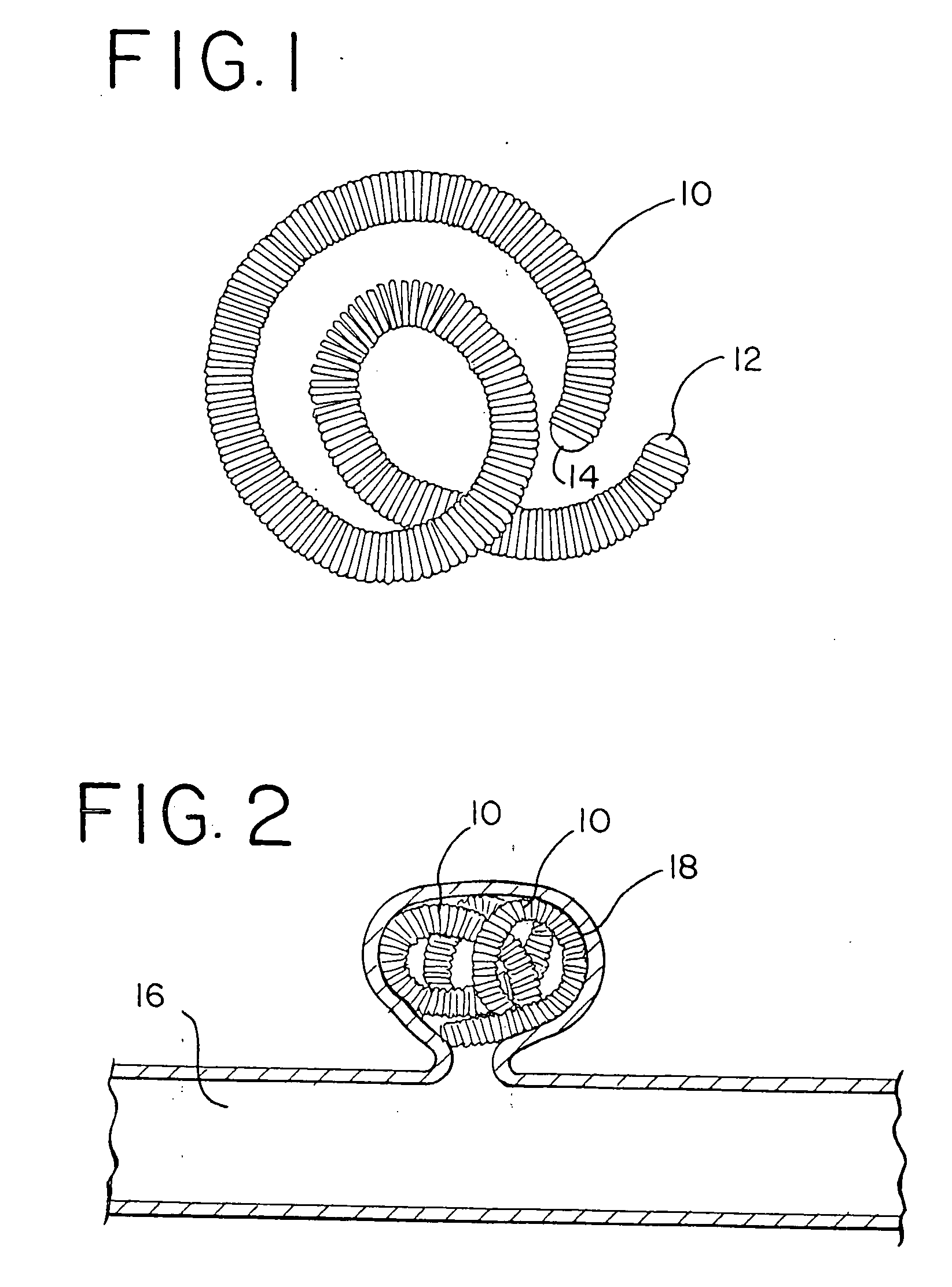
Occluding vasculature of a patient using embolic coil with improved platelet adhesion
InactiveUS6953468B2Improved platelet adhesionGood coagulationDilatorsTissue regenerationPlatinumRadiology
A method as provided for occluding the vasculature of a patient. The method comprises the steps of providing a plurality of embolic coils having a textured surface. The embolic coils are introduced into the patient's vasculature. In this manner, the textured surface provides improved platelet adhesion compared to a non-textured surface, to promote clotting. In the illustrative embodiment, the embolic coil comprises a platinum-tungsten alloy wire and the texturing is performed by abrasion or sandblasting to provide substantially uniform roughness comprising pockets having diameters of about 0.125 microns to about fifty microns and depths of about 0.25 microns to about twenty microns.
Owner:CODMAN & SHURTLEFF INC
Therapeutic morpholino-substituted compounds
Morpholino-substituted pyridopyrimidine, quinolone, and benzopyranone derivatives inhibit phosphoinositide (PI) 3-kinase, an enzyme that regulates platelet-adhesion processes. As a consequence, the compounds in question have anti-thrombotic activity, as well as other pharmaceutical properties. The compounds claimed are represented by formula (I), (II) and (III). PI 3-kinase generates 3-phosphorylated PI second messengers which stimulate platelet adhesion under blood-flow conditions. Because platelet adhesion is a necessary step in the formation of a thrombus, inhibition by these compounds of PI 3-kinase under such conditions inhibits or prevents thrombus formation. The compounds are useful in treating PI 3-kinase-dependent conditions including cardiovascular diseases such as coronary artery occlusion, stroke, acute coronary syndrome, acute myocardial infarction, vascular restenosis, atherosclerosis, and unstable angina; respiratory diseases such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD), and bronchitis; inflammatory disorders; neoplasms including cancers such as glioma, prostate cancer, small cell lung cancer, and breast cancer, and diseases linked to disordered white blood cell function, such as autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Material containing metal ion ligand complex producing nitric oxide in contact with blood
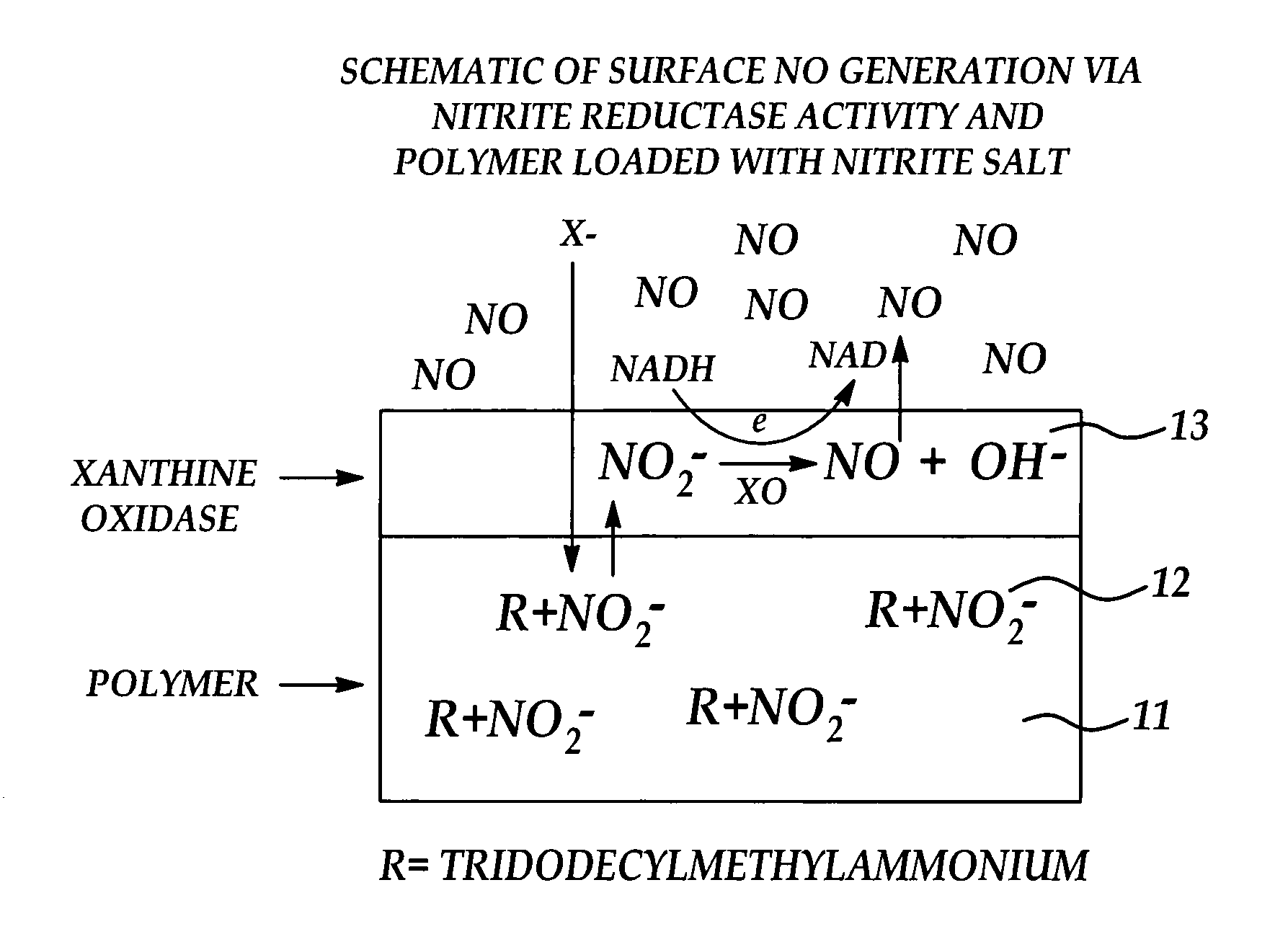
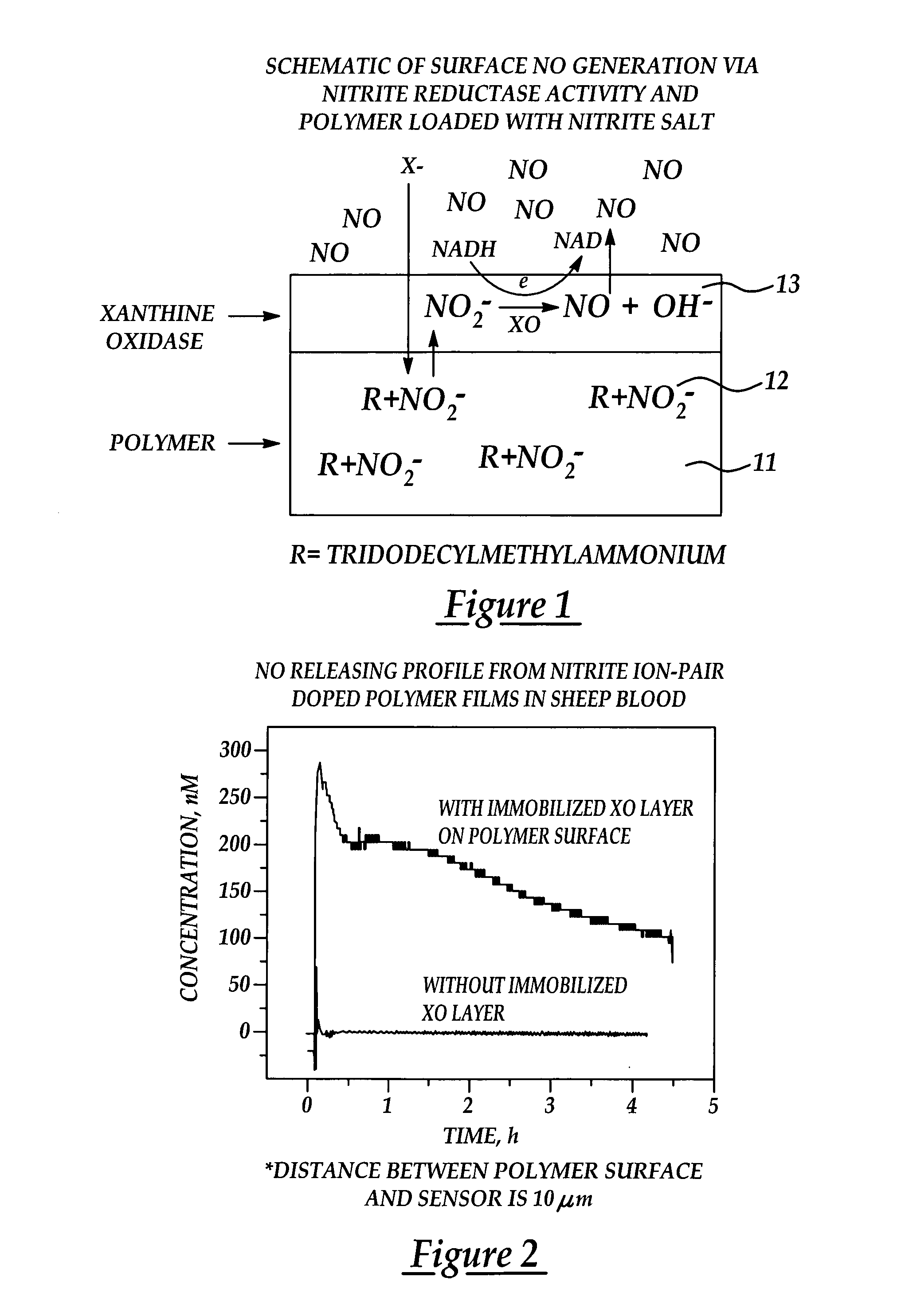
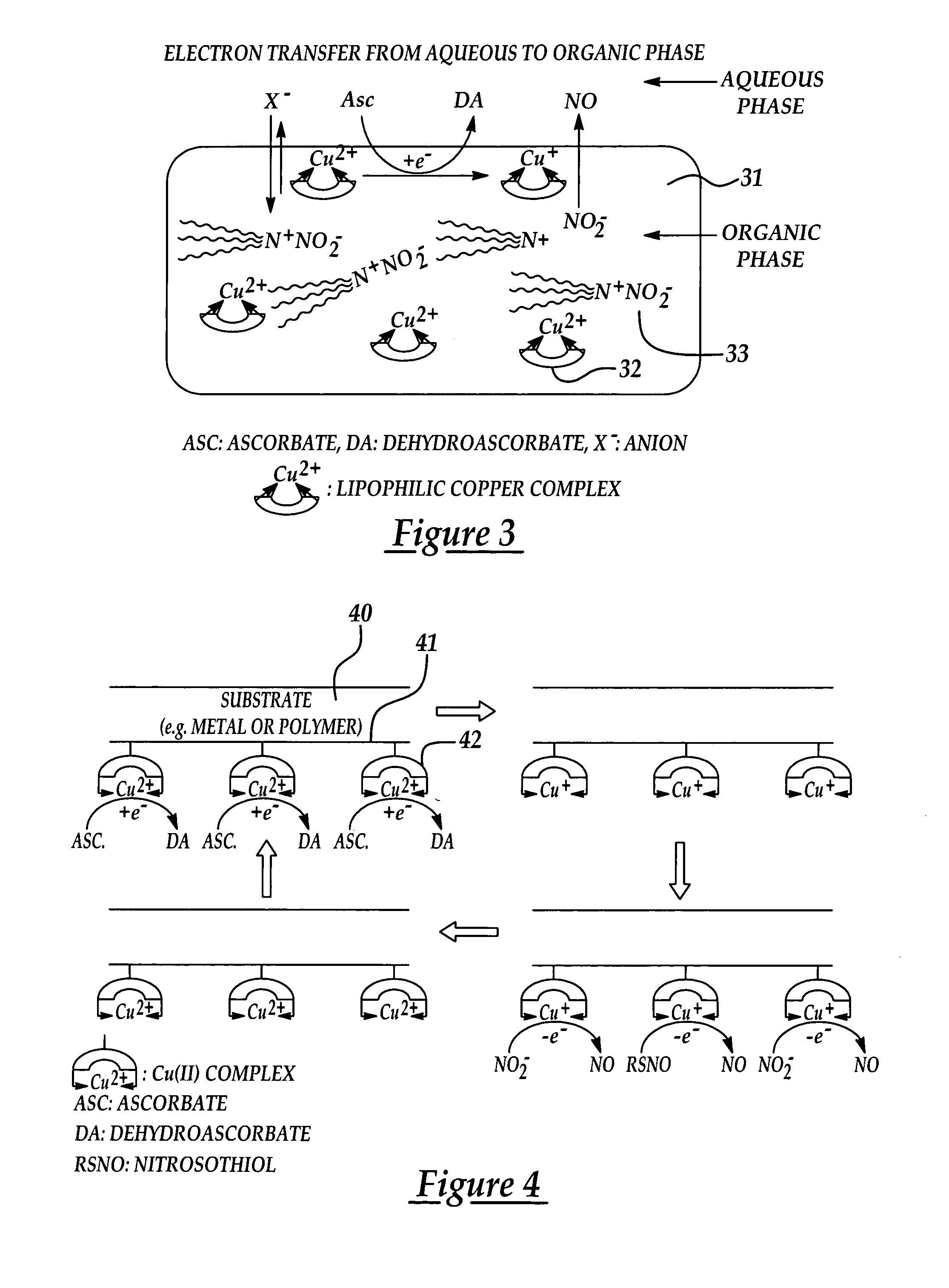
InactiveUS7128904B2Good biocompatibilityPeptide/protein ingredientsOther blood circulation devicesPolymer thin filmsNitric oxide
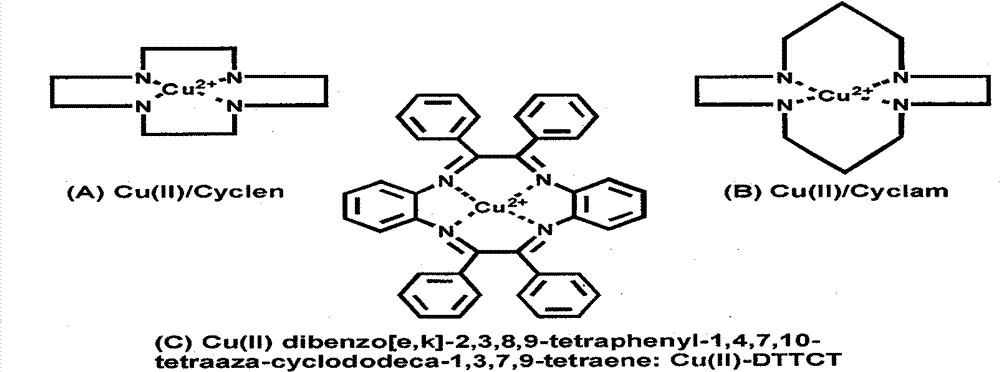
Biocompatible materials that have the ability to release nitric oxide (NO) in situ at the surface-blood interface when in contact with blood. The materials which may be polymers (e.g., polyurethane, poly(vinyl chloride), silicone rubbers), metals, such as stainless steel, carbon, and the like are provided with biocatalysts or biomimetic catalysts on their surface that have nitrite, nitrate, and / or nitrosothiol-reducing capability. Illustratively, the catalysts are adsorbed or immobilized at the surface of the material. The catalysts can act on endogenous nitrite, nitrate, or nitrosothiols within the blood creating a local increase in the NO levels at the surface of the material. An illustrative enzymatic biocatalyst is mammalian xanthine oxidase. In another illustrative embodiment, a biomimetic catalyst is a copper (Cu(II)-ligand complex, e.g. dibenzo[e,k]-2,3,8,9-tetraphenyl-1,4,7,10-tetraaza-cyclododeca-1,3,7,9-tetraene. In some cases, lipophilic salts of nitrite / nitrate (e.g., tridodecylmethylammonium nitrite (TDMA+NO2− / NO3−)) or certain salts of nitrosothiols can be doped within a polymer material, or an underlying polymeric film, to create a reservoir of nitrite or nitrosothiol that continuously leaks into the immobilized catalytic layer. Adequate levels of endogenous reducing equivalents are present within blood to provide catalytically-generated surface levels of NO that are above the threshold reportedly required to prevent platelet adhesion or activation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Methods, products and uses involving platelets and/or the vasculature
InactiveUS20090130021A1Inhibits interactionInhibits GPVI interactionVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseVitronectin
The present disclosure relates to agents which interfere with the binding of GPVI to various components. Agents which interfere with GPVI interaction with one or both of fibronectin and vitronectin or sequences thereof are also disclosed. Methods of treating disorders or diseases which involve pathological, dysfunctional or non-pathological interaction of GPVI with fibronectin and / or vitronectin are included in the present disclosure. The invention also relates to uses of agents for the prevention or treatment of disorders arising from blood platelet adhesion and aggregation.
Owner:MUNCH GOTZ +5
Construction method of anticoagulant artificial blood vessel scaffold material
InactiveCN102961783AInduce and promote regenerationPromote regenerationStentsBlood vesselsFiberSignalling molecules
The invention discloses a construction method of an anticoagulant artificial blood vessel scaffold material. The method includes: taking a rotating stainless steel pipe as a receiver, employing an electrospinning technology to prepare an organic macromolecular polymer, a mixture of a Cu2<+> complex catalyst and the organic macromolecular polymer, and the organic macromolecular polymer successively into a three-layer structured superfine fiber porous tubular scaffold material; and regulating the types and proportion of the Cu2<+> complex catalyst and the organic macromolecular polymer, as well as the electrospinning time of a three-layer electrospinning solution so as to control the release rate of NO. With a three-layer structure, the blood vessel scaffold material formed by the invention not only realizes loading of the Cu2<+> organic complex catalyst, but also improves the phenomenon of NO burst release catalyzed by an ordinary hybrid electrospun structure scaffold material, improves the loading stability of the Cu2<+> complex catalyst, and can leave the biological signal molecule NO to play a better role in inhibiting platelet adhesion, resisting platelet activation and inhibiting smooth muscle cell proliferation so as to improve its anticoagulant property.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Nitrosated and nitrosylated compounds, compositions and methods use
The invention describes novel nitrosated and / or nitrosylated compounds of the invention, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, and novel compositions comprising at least one nitrosated and / or nitrosylated compound of the invention, and, optionally, at least one nitric oxide donor compound and / or at least one therapeutic agent. The invention also provides novel compositions comprising at least one compound of the invention, that is optionally nitrosated and / or nitrosylated, and at least one nitric oxide donor compound and / or at least one therapeutic agent. The compounds and compositions of the invention can also be bound to a matrix. The invention also provides methods for treating cardiovascular diseases, for inhibiting platelet aggregation and platelet adhesion caused by the exposure of blood to a medical device, for treating pathological conditions resulting from abnormal cell proliferation; transplantation rejections, autoimmune, inflammatory, proliferative, hyperproliferative or vascular diseases; for reducing scar tissue or for inhibiting wound contraction, particularly the prophylactic and / or therapeutic treatment of restenosis by administering at least one compound of the invention that is optionally nitrosated and / or nitrosylated, in combination with nitric oxide donors that are capable of releasing nitric oxide or indirectly delivering or transferring nitric oxide to targeted sites under physiological conditions. The compounds of the invention are preferably estradiol compounds, troglitazone compounds, tranilast compounds, retinoic acid compounds, resveratol compounds, myophenolic acid compounds, acid compounds, anthracenone compounds and trapidil compounds.
Owner:NICOX SA
Preparation technique of three-layer artficial blood vessel
ActiveCN106075596AEnhanced Axial MechanicsEnhanced radial mechanicsProsthesisHemodialysisCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention provides a preparation technique of a three-layer (inner, middle and outer layers) artificial blood vessel. The inner layer is composed of a smooth compact thin layer prepared by an ink printing method and can inhibit plasma protein and platelet adhesion, prevent acute thrombosis formation and provide axial mechanical support. The middle layer is formed by winding oriented micro fiber prepared by wet spinning or melt spinning, and mainly functions in guiding tissue cells to grow into gaps of the oriented fiber to realize oriented deposition arrangement of extracellular matrix, and the oriented micro fiber can provide radial mechanical support. The outer layer is formed by winding thick polymer fiber and closely bonded with the middle layer and mainly functions in preventing folding when the artificial blood vessel is bent. The artificial blood vessel prepared by the method can remarkably increase patency rate, can utilize microenvironment at an implanting position to realize quasi-natural reshaping and regeneration and has good application prospect in the aspects of coronary artery bypass surgery, hemodialysis and cerebral and peripheral blood vessel replacement.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Highly blood coagulation resistant cellulose membrane material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a highly ticoagulant cellulose membrane material, wherein an amphichroic ionomer layer is grafted on the surface of a cellulose membrane, and a 'brush'-shaped amphichroic ionomer layer is formed on the surface of the cellulose membrane. The cellulose membrane with good biocompatibility is prepared by grafting of amphichroic ionic molecules on the surface of the material. The neat 'brush'-shaped amphichroic ionomer layer is formed on the surface of cellulose, so that the defects on the surface of the material are overcome, and the action between the material and biomacromolecules is further reduced, thereby nonspecific protein absorption and blood platelet adhesion are reduced to the maximum degree. Therefore, the cellulose membrane material has high nonspecific protein absorption resistance and high ticoagulant performance. The invention discloses a method for manufacturing the highly ticoagulant cellulose membrane material.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Platelet thrombus formation simulator
InactiveUS20100010787A1Avoid disagreementInhibit platelet adhesionMedical simulationSurgeryAdhesion forcePlatelet thrombus
A platelet thrombus formation simulator, said simulator equipped with the following means:(a) a means that selects, from previously stored equations, an equation for the computation of adhesion force according to parallel activation grade;(b) a means that calculates the platelet adhesion force based on the equation depending on the activation grade of each platelet; and(c) a means that outputs the coagulation condition of platelets based on the calculated adhesion force of each platelet.
Owner:KEIO UNIV
Blood-Platelet Test Method and Blood-Platelet Test Device
InactiveUS20110151500A1Clear imagingSimply carry-outBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMedicineReagent
A method for testing platelet function, wherein platelet function is tested by allowing anticoagulated blood, to which a weak platelet-activating reagent has been mixed, to pass through a capillary having a platelet-adhesive surface on at least a part of its inner surface, and observing or measuring the behavior of the blood in the capillary.
Owner:FUJIMORI KOGYO CO LTD
Furoxan compounds, compositions and methods of use
The invention provides novel furoxan compounds, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, and novel compositions comprising at least one compound, and, optionally, at least one nitric oxide enhancing compound and / or at least one therapeutic agent. The compounds and compositions of the invention can also be bound to a matrix. The invention also provides methods for (a) treating cardiovascular diseases; (b) inhibiting platelet aggregation and platelet adhesion caused by the exposure of blood to a medical device; (c) treating pathological conditions resulting from abnormal cell proliferation; (d) treating transplantation rejections, (e) treating autoimmune, inflammatory, proliferative, hyperproliferative or vascular diseases; (f) reducing scar tissue or for inhibiting wound contraction; (g) treating diseases resulting from oxidative stress; (h) treating endothelial dysfunctions; and (j) treating diseases caused by endothelial dysfunctions.
Owner:ARBOR PHARMA LLC
Microfluidic flow assay for measuring hemostatic phenotypes
ActiveUS20110223627A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsClot formationMicrofluidic channel
A microfluidic-based flow assay and methods of manufacturing the same are provided. Specifically, the microfluidic flow assay includes a micropatterned surface that induces clot formation and an array of microfluidic channels though which blood flows. The micropatterned surface contains two clotting stimuli, one for inducing platelet adhesion and another for inducing the coagulation cascade.
Owner:COLORADO SCHOOL OF MINES
Cannula tip for a cardiac assist device
InactiveUS20070049787A1Prevent thrombosisOther blood circulation devicesCannulasInflow cannulaCannula tip
The present invention provides an inflow cannula tip that is shaped to prevent suction with the ventricular wall and adapted to prevent platelet adhesion. In particular, the inlet portion of the cannula tip comprises two projections extending from the cylindrical body of the cannula tip with gaps between the projections. The projections may have beveled edges. The inlet portion of the cannula tip can accept blood flow from either the gaps in the side or from the bottom of the tip. Even if the edge of the cannula tip is close to or even touching ventricle wall, a suction condition will not result, as blood is allowed to flow through the gaps between the projections.
Owner:HITMAC USA +1
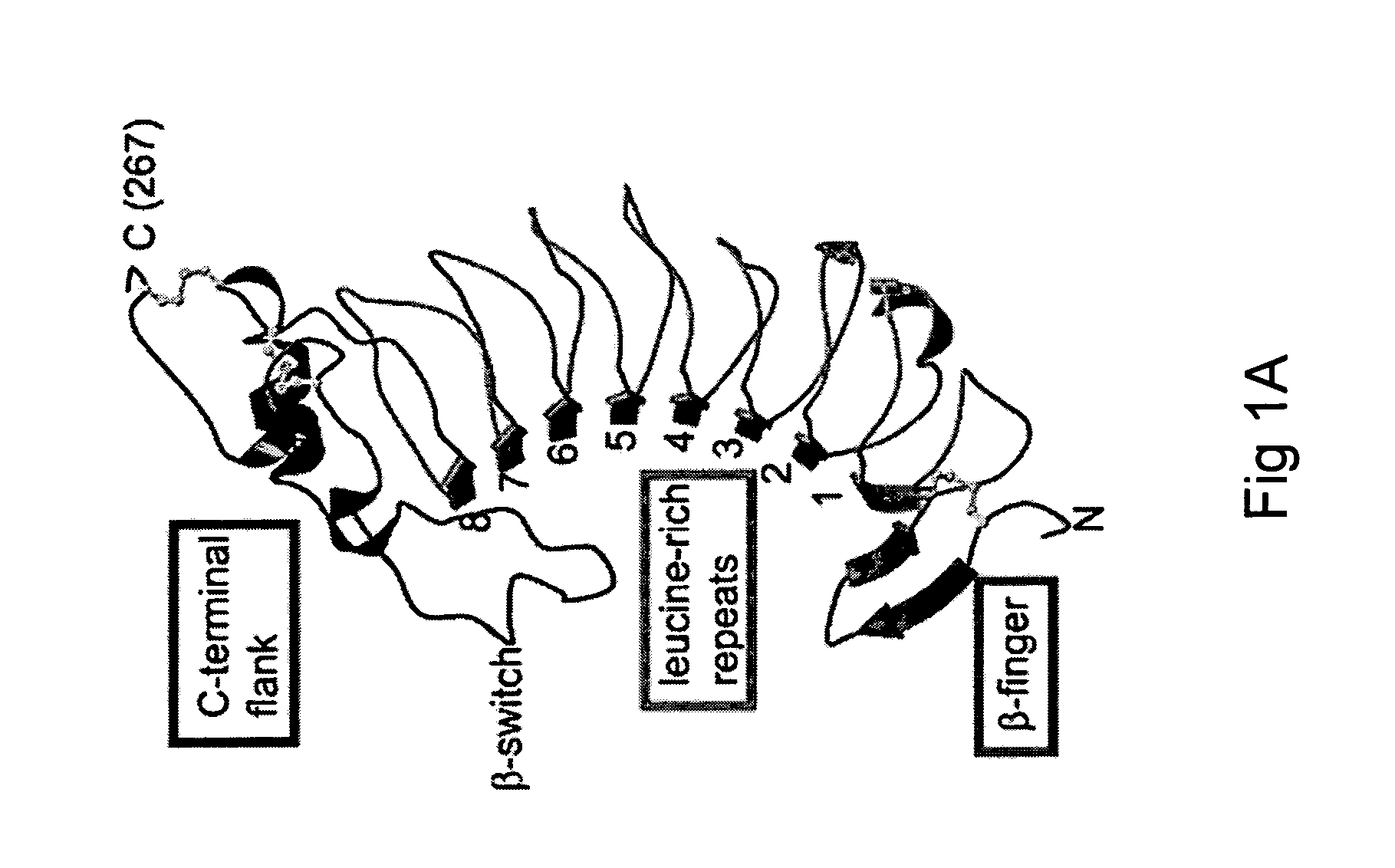
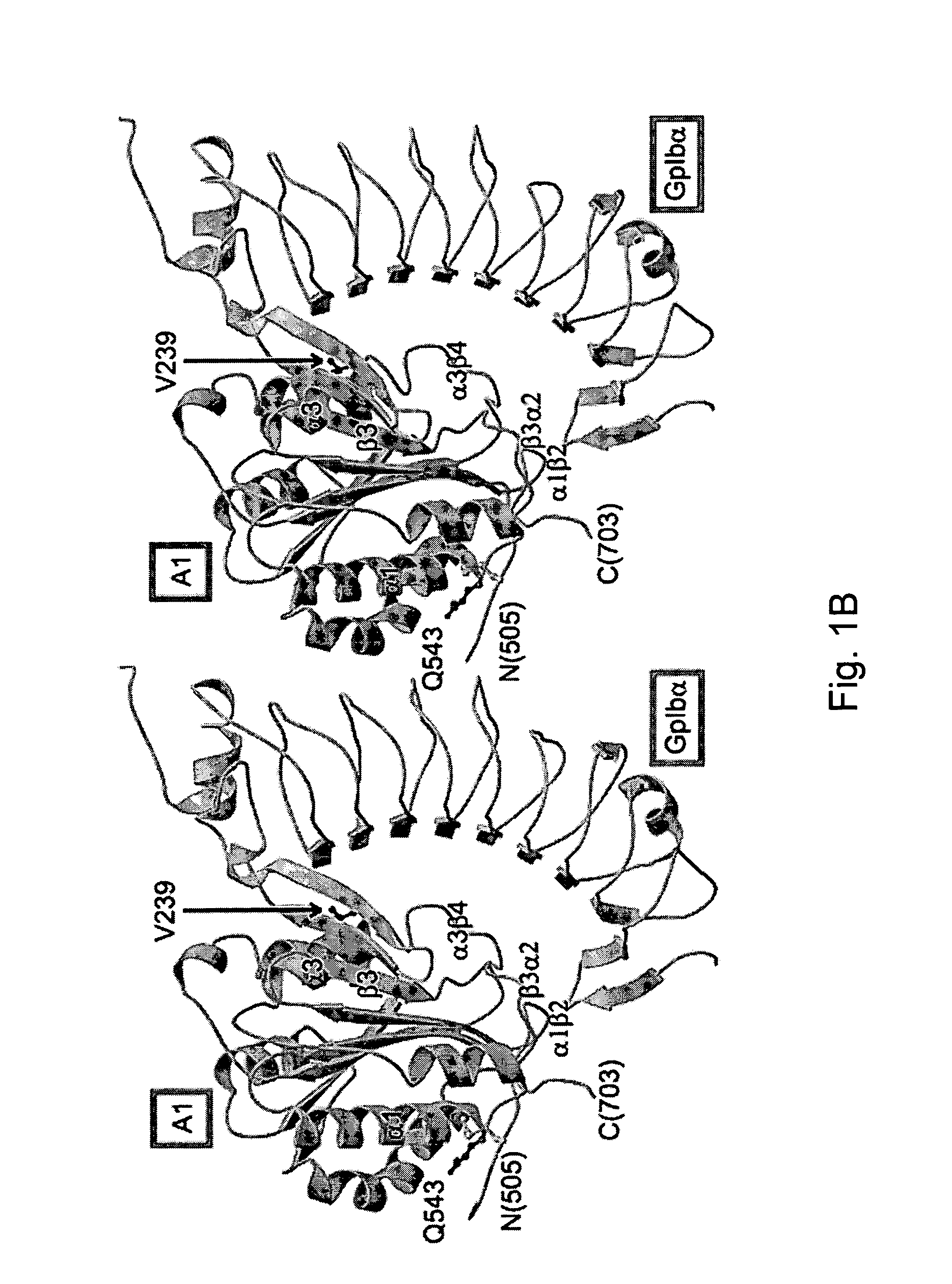
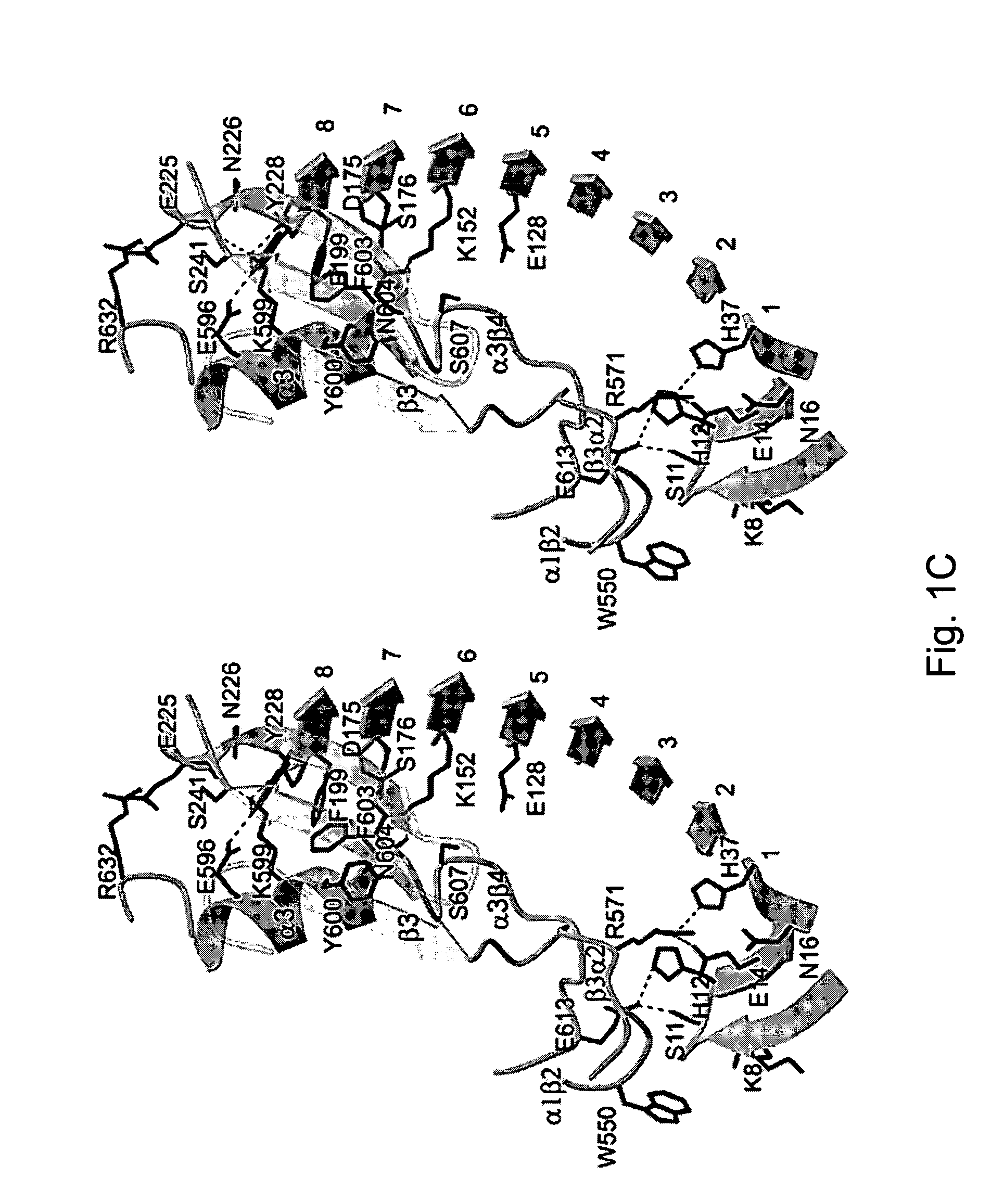
Modulation platelet adhesion based on the surface-exposed beta-switch loop of platelet glycoprotein IB-alpha
ActiveUS20050192224A1Trend downReduce decreaseFactor VIICell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsGlycoprotein IbChemistry
The invention relates to the adhesion of platelet GpIbα to strand β3 of domain A1 of von Willebrand factor (vWF), the strand β3 comprising amino acid residues at amino acid position 560-566 and / or a functional part or equivalent thereof, the platelet GpIbα, the GpIbα region comprising an amino acid sequence corresponding to a beta-switch loop of platelet GpIbα, comprising amino acid residues at amino acid position 227-242 and / or a functional part or equivalent thereof. The invention provides a method of interfering with adhesion of blood platelets to vWF that includes modulating adhesion. The invention further provides proteinaceous compounds, antibodies, medicaments and pharmaceutical compositions to that end. The invention also provides means and methods to increase platelet adhesion by topical application of a compound increasing platelet adhesion.
Owner:ABLYNX NV
Nitrosated and nitrosylated rapamycin compounds, compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS20050209266A1Treating and preventing restenosisTreating and preventing and atherosclerosisBiocideOrganic chemistryPercent Diameter StenosisTherapeutic treatment
The invention describes novel nitrosated and / or nitrosylated rapamycin compounds, and novel compositions comprising at least one nitrosated and / or nitrosylated rapamycin compound, and, optionally, at least one nitric oxide donor compound. The invention also provides novel compositions comprising at least one rapamycin compound and at least one nitric oxide donor compound and / or at least one therapeutic agent. The compounds and compositions of the invention can also be bound to a matrix. The invention also provides methods for treating and / or preventing cardiovascular diseases, for the prevention of platelet aggregation and platelet adhesion caused by the exposure of blood to a medical device, for treating and / or preventing pathological conditions resulting from abnormal cell proliferation; transplantation rejections; autoimmune, inflammatory, proliferative, hyperproliferative or vascular diseases; for reducing scar tissue or for inhibiting wound contraction, particularly the prophylactic and / or therapeutic treatment of restenosis by administering nitrosated and / or nitrosylated rapamycin compounds or rapamycin compounds in combination with nitric oxide donors that are capable of releasing nitric oxide or indirectly delivering or transferring nitric oxide to targeted sites under physiological conditions.
Owner:NICOX SA
Method of using and compositions comprising (-) sibutramine optionally in combination with other pharmacologically active compounds
This invention encompasses methods for the treatment and prevention of disorders that include, but are not limited to, eating disorders; weight gain; obesity; irritable bowel syndrome; obsessive-compulsive disorders; platelet adhesion; apnea; affective disorders such as attention deficit disorders, depression, and anxiety; male and female sexual function disorders; restless leg syndrome; osteoarthritis; substance abuse including nicotine and cocaine addiction; narcolepsy; pain such as neuropathic pain, diabetic neuropathy, and chronic pain; migraines; cerebral function disorders; chronic disorders such as premenstrual syndrome; and incontinence. The invention further encompasses pharmaceutical compositions and dosage forms which comprise optically pure (-) sibutramine, optionally in combination with a phosphodiesterase inhibitor or a lipase inhibitor.
Owner:SEPACOR INC
Method for preparing tissue engineering blood vessel based on 3D bioprinting technology
ActiveCN104490489AGood biocompatibilityStrong mechanical propertiesSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell culture supports/coatingDiseaseThrombus
The invention provides a method for preparing a tissue engineering blood vessel based on a 3D (3-Dimensional) bioprinting technology. The method comprises the following steps:alternately printing a blood vessel shape by virtue of a high-polymer material and a human renascent skin fiber cell column, and removing the high-polymer material after fusion to structure a tissue engineering blood vessel; filling late-outgrowth endothelial progenitor cells into the blood vessel, and performing in-vitro dynamic culturing for 7 days in a bioreactor to obtain a differentiated tissue engineering blood vessel, wherein the high-polymer material is one of pluronic F127, poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), methyl cellulose and sodium alginate. The blood vessel obtained by the method is high in biocompatibility and higher in mechanical property, thrombus formation resistant and platelet adhesion resistance, and can be used for repairing and replacing a damaged or disease blood vessel.
Owner:江苏知聚知识产权服务有限公司
Biological small-diameter artificial blood vessel and preparation method thereof
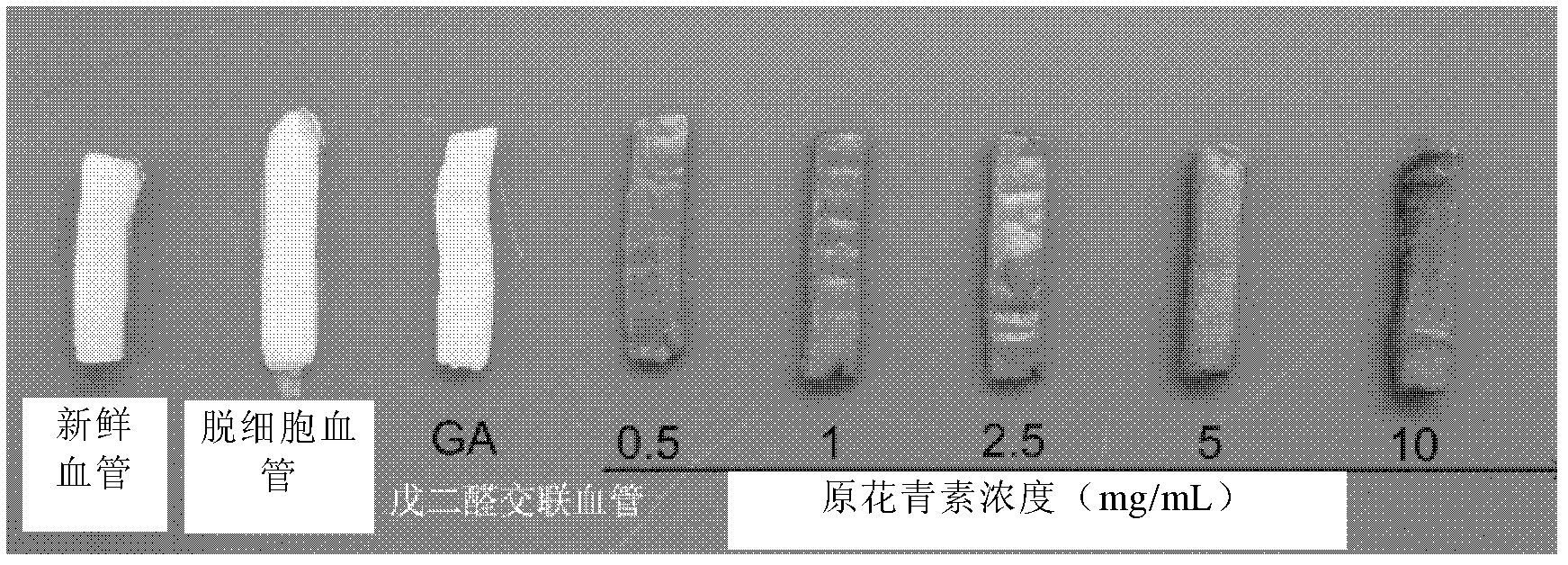
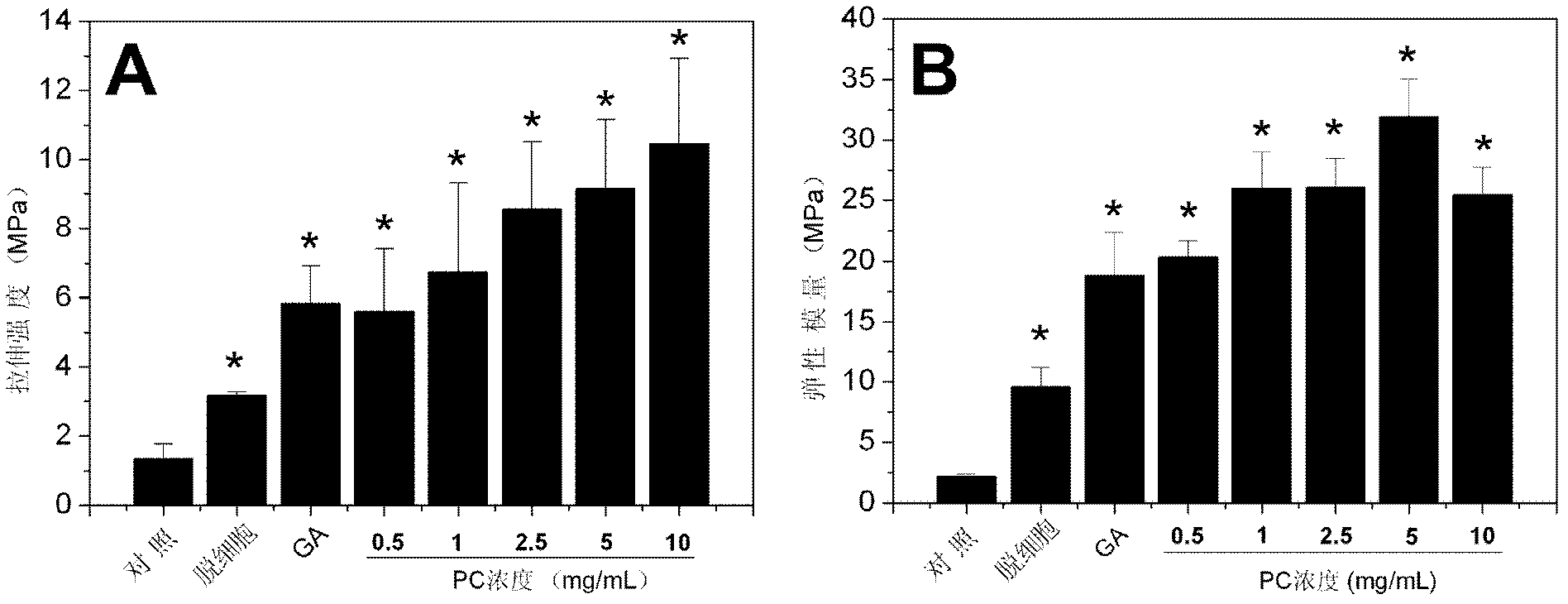
ActiveCN102836464AHigh tensile strengthGood cell compatibilityPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingCell-Extracellular MatrixNon toxicity
The invention discloses a biological small-diameter artificial blood vessel and preparation method thereof. The method comprises a step of crosslinking the natural extracellular matrix of vessels by using procyanidins. The small-diameter artificial blood vessel of the invention has the characteristics of improved mechanical strength and stability, non-toxicity, enzymatic degradation resistance in vivo, anti-calcification, platelet adhesion resistance, low immunogenicity, and very little protein release from cross-linking agent and the small-diameter vessel. These crosslinking characteristics are beneficial for the immigration, prolongation, and long-term anti-calcification of the small-diameter vascular smooth muscle cells and vascular endothelial cells of a human body itself after the small-diameter artificial blood vessel is implanted in the human body.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
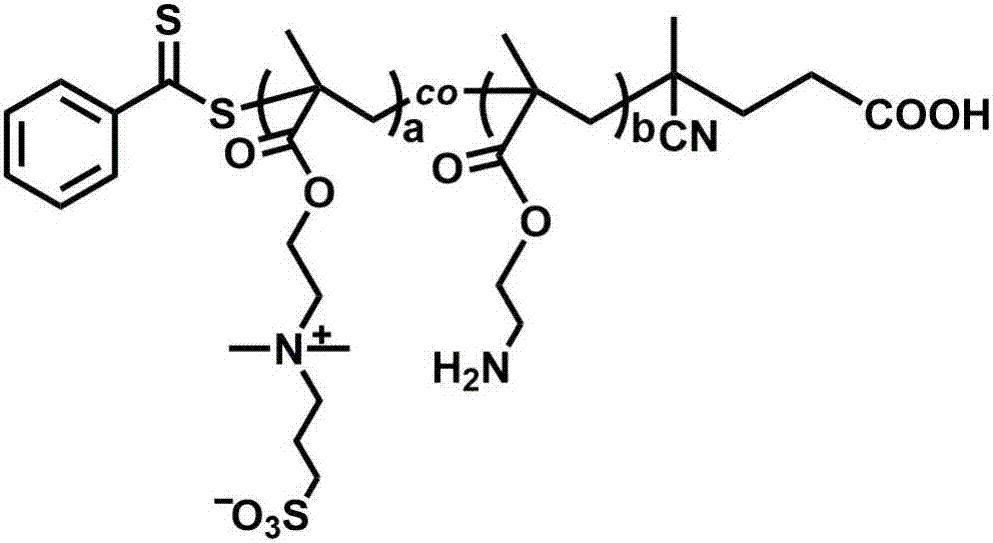
Method for constructing simulated outer cell membrane structure coating on material surface by RAFT (reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer) polymerization technology
ActiveCN102888013AImprove adhesionHigh densityPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingBenzoic acidPolymer science
The invention discloses a method for constructing a simulated outer cell membrane structure coating on a material surface by an RAFT (reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer) polymerization technology, which comprises the following steps of: immobilizing a chain transfer agent 4-cyanopentanoic acid dithiobenzoate on the material surface via primary amino grafting on substrate surface by acylation; then performing free radical polymerization with polymerizable monomers of methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine in solution to obtain the coating modified by grafted polymers on the surface. The method provided by the invention obtains PMPC (polymerized methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) molecular brushes with controllable molecular weight and narrow molecular weight distribution on the surface by grafting and polymerizing the MPC (methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) on the surface through the RAFT polymerization; a good effect of resisting against platelet adhesion is reflected on the modified substrate surface of the prepared simulated outer cell membrane structure; and the prepared coating is useable as the coating on the surface of blood contact materials such as artificial hearts, artificial blood vessels and hemodialyzers.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Hollow fiber membrane for purifying blood
InactiveUS7087168B2Reduced elutionReduced elution amountMembranesSemi-permeable membranesHollow fibre membraneElution
It is intended to provide a blood purification membrane having excellent performance and showing little elution of blood and little adhesion of blood proteins or platelets. The above object can be achieved by using a moisten membrane, which is free from any membrane pore-sustaining agent and has a high water permeation dose and a large pore size, and lessening the pore size by drying the membrane after desolvation.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI MEDICAL CO LTD
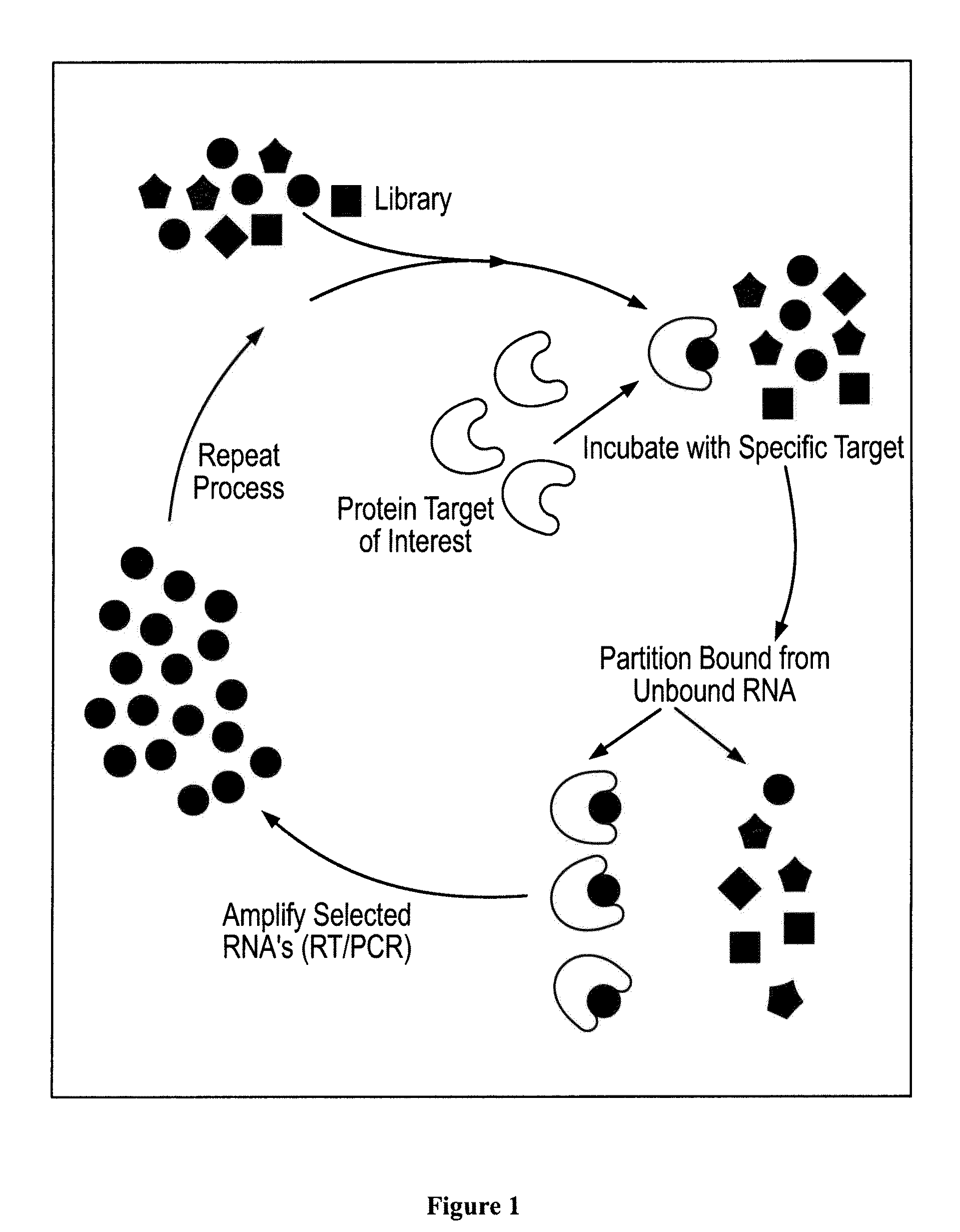
Nucleic acid modulators of glycoprotein vi
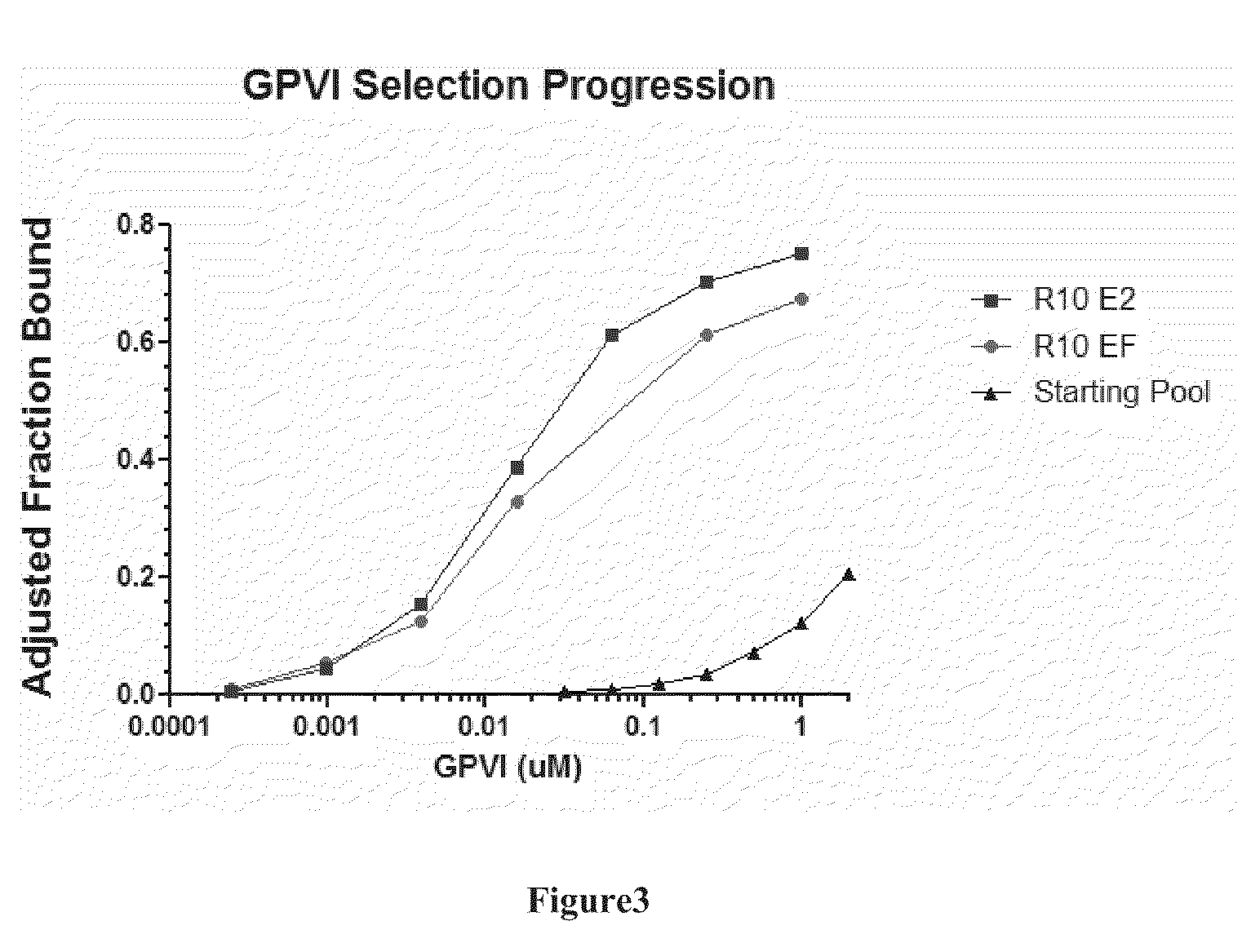
ActiveUS20100311820A1Accelerated destructionReduces eliminates bindingOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderInduced platelet aggregationCollagen VI
The present invention relates, in general, to a pharmacologic system to modulate the biology of platelets based upon a nucleic acid ligand that can interact with and modulate the activity of platelet glycoprotein GPVI to regulate platelet function. These nucleic acid ligands are also actively reversible using a modulator that inhibits the activity of the nucleic acid ligand to neutralize this pharmacologic effect and thereby restore GPVI function, including collagen binding, platelet adhesion, collagen-induced platelet activation, and collagen-induced platelet aggregation. The invention further relates to compositions comprising the nucleic acid ligand, the ligand and a modulator, methods to generate the nucleic acid ligand and its modulator, as well as methods of using these agents and compositions in medical therapeutic and diagnostic procedures.
Owner:TOBIRA THERAPEUTICS
Occluding vasculature of a patient using embolic coil with improved platelet adhesion
A method as provided for occluding the vasculature of a patient. The method comprises the steps of providing a plurality of embolic coils having a textured surface. The embolic coils are introduced into the patient's vasculature. In this manner, the textured surface provides improved platelet adhesion compared to a non-textured surface, to promote clotting. In the illustrative embodiment, the embolic coil comprises a platinum-tungsten alloy wire and the texturing is performed by abrasion or sandblasting to provide substantially uniform roughness comprising pockets having diameters of about 0.125 microns to about fifty microns and depths of about 0.25 microns to about twenty microns.
Owner:CODMAN & SHURTLEFF INC
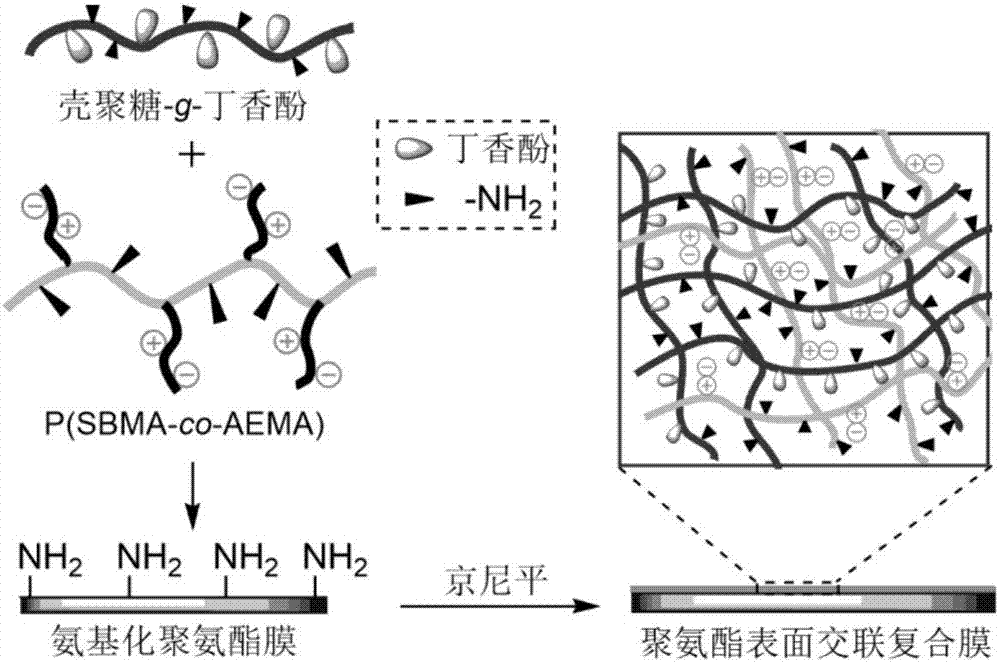
Antibacterial and antifouling double-functional polyurethane surface crosslinking composite film and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107970792AGood antifoulingHas antibacterial propertiesSemi-permeable membranesMembranesComposite filmBetaine
The invention discloses an antibacterial and antifouling double-functional polyurethane surface crosslinking composite film and a preparation method thereof. The polyurethane surface crosslinking composite film is formed by covalently conjugating a natural antibacterial agent eugenol on a chitosan chain to synthesize chitosan-g-eugenol, synthesizing a poly(methacrylic acid sulfonic acid betaine-co-methacrylic acid 2-amino ethyl ester) copolymer by utilizing reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization method and taking a natural biological crosslinking agent genipin as a crosslinking agent to carry out crosslinking on the surface of a polyurethane film. The natural antibacterial agents, i.e., the chitosan and the eugenol, can have a cooperative antibacterial effect; a betaine zwitter ion copolymer can be used for effectively resisting bacterium and platelet adhesion and protein adsorption, so that the composite film has dual functions of antibacterial and antifoulingand has good cell compatibility and blood compatibility. The antibacterial and antifouling double-functional polyurethane surface crosslinking composite film has the advantages that raw materials have a wide source and are easy to obtain and a preparation process is simple and convenient and has a wide application prospect in the field of biomedical implant materials.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Modified SEBS material and preparation method and application thereof
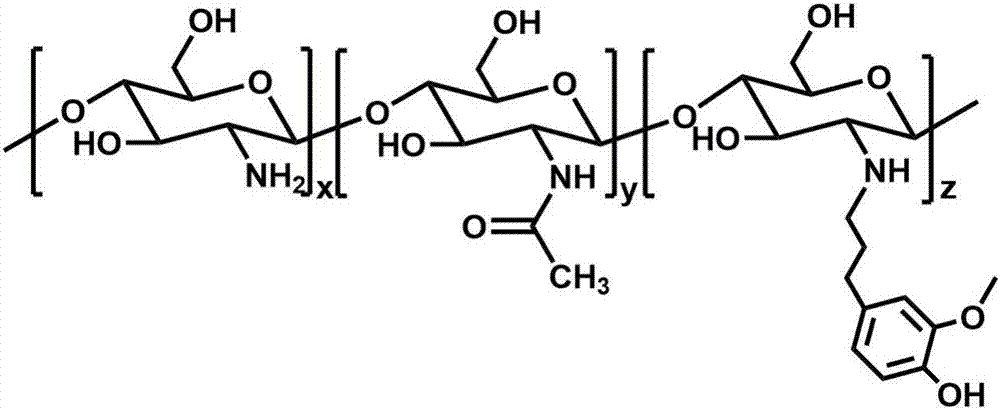
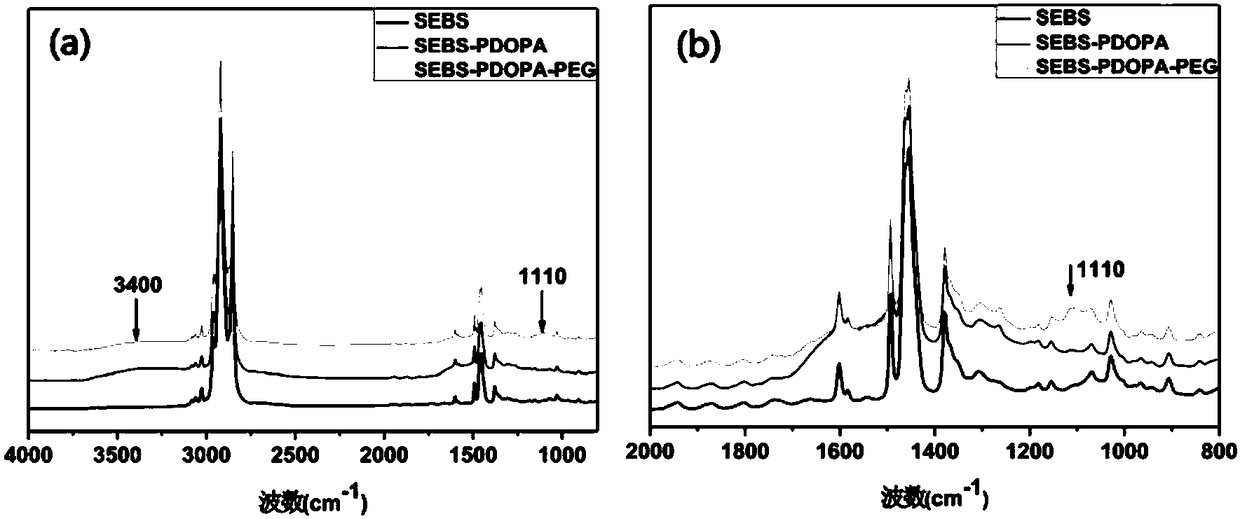
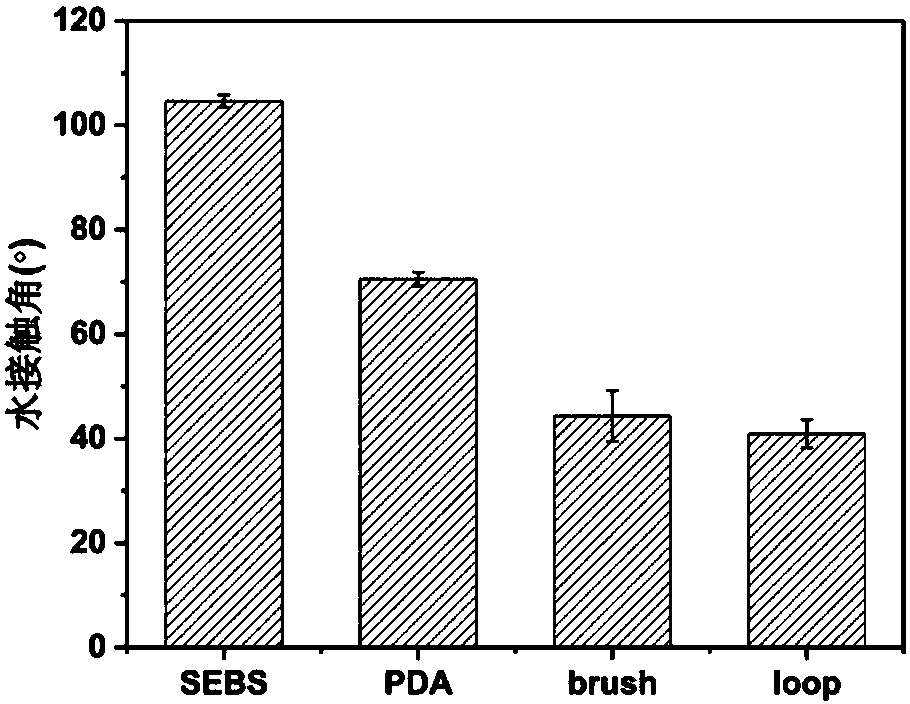
ActiveCN108250477AGood blood compatibilityAvoid pollutionSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPolymer scienceHydrophilic polymers
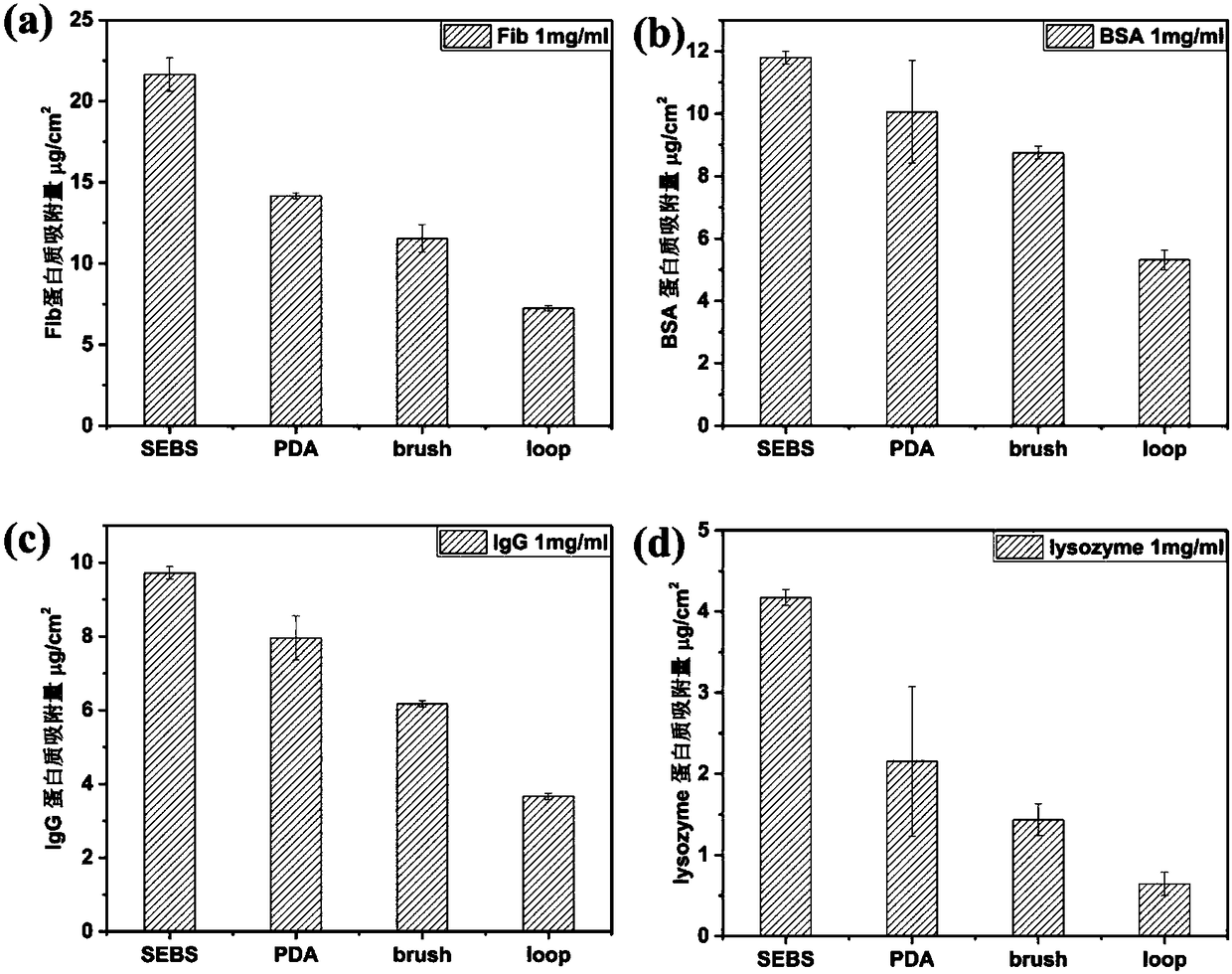
The invention belongs to the field of high molecular materials and particularly relates to a modified SEBS material and a preparation method and application thereof. The material comprises dopamine-modified SEBS and a hydrophilic polymer of which two end groups are grafted on the surface of the SEBS, wherein the two end groups of the hydrophilic polymer are selected from sulfhydryl group, amino group, carboxyl group or sulfonic group. The material provided by the invention is characterized in that dopamine is taken as a bionic adhesive, and two ends of the hydrophilic polymer are fixed on thesurface of the SEBS to construct a loop conformation of the hydrophilic polymer; and the whole surface grafting process does not use an organic solvent, thereby avoiding the pollution and poison of the organic solvent. By constructing the hydrophilic polymer of the loop conformation on the surface of the SEBS, the capability of the SEBS material for resisting protein and platelet adhesion is further improved in comparison with the mode of constructing a hydrophilic polymer of a brush conformation on the surface of the SEBS, and excellent blood compatibility is shown. The material provided by the invention can generate good social and economic benefits when being applied to the field of biomedical materials.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multifunctional tissue adhesion cryogel dressing as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111905143AImprove adhesionHigh activityAntibacterial agentsAerosol deliveryGelatin spongeBiocompatibility
The invention discloses a multifunctional tissue adhesion cryogel dressing as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The multifunctional tissue adhesion cryogel dressing is characterized in that amino-containing polysaccharide and a polysaccharide derivative with blood coagulation promoting capability are used as base materials, and polydopamine formed by dopamine oxidative polymerization is used for crosslinking the amino-containing polysaccharide and the polysaccharide derivative in a cryogel system. so that the hemostatic and wound healing promoting properties of the cryogelcan be further enhanced, and the cryogel is endowed with good oxidation resistance and good photo-thermal properties. A hemostatic adhesive tape has good biocompatibility, bacterium resistance, oxidation resistance, tissue adhesion and other properties, and has better blood cell and platelet adhesion, enrichment, activation and blood coagulation capabilities than medical gauze and gelatin sponge.The multifunctional tissue adhesion cryogel dressing is suitable for hemostasis of various different types of human wounds.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Preparation method of polyester material capable of preventing platelet adhesion without affecting platelet function
ActiveCN105949492AImprove hydrophilicityGood blood compatibilityPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingPolyesterBiological materials
The invention discloses a preparation method of a polyester material capable of preventing platelet adhesion without affecting a platelet function and belongs to the field of surface modification of biological materials. According to the method, firstly, with the adoption of ammonolysis, the surface of the polyester material has positively charged amino or dopamine forms a positively charged dopamine coating on the surface of the material through auto polymerization, the polyester material with positive ions is immersed into a negatively charged biomacromolecule solution, and the processes are performed repeatedly until hydrophilic and biocompatible biomacromolecules are fixed on the surface of the polyester material through layer-by-layer electrostatic self-assembly. By means of the method, static water contact angles of the polyester material can be effectively reduced, the hydrophile of the material is improved, platelet adhesion can be further prevented through introduction of biomacromolecules, and no remarkable influence is caused to gathering and other functions of platelet.
Owner:BLOOD TRASFUSION INST CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Modified sodium alginate electrospun fibre hemostatic membrane and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107737366AIncrease liquid absorptionGood biocompatibilityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAbsorbent padsFiberPolyvinyl alcohol
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical apparatus and instruments, and discloses a modified sodium alginate electrospun fibre hemostatic membrane and a preparation method thereof. Themodified sodium alginate electrospun fibre hemostatic membrane is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 10 to 30 parts of polyvinyl alcohol and 5 to 15 parts of sulfhydrated alginate. According to the modified sodium alginate electrospun fibre hemostatic membrane and the preparation method thereof, the electrospun fibre membrane material prepared by performing electrospinningon the polyvinyl alcohol and the sulfhydrated alginate serving as raw materials is of a porous structure; the soft compressibility and the water absorbability of the material can be improved; space isprovided for adhesion and aggregation of blood platelets. The softness can expand the application range of a hemostatic material and reduce discomfort and pain; the improvement of the water absorbability can quickly absorb moisture in blood and increase the viscosity of the blood, so that the blood flow speed is reduced and the blood is coagulated; the increment of a blood platelet adhesion spaceis beneficial to aggregation of a large number of the blood platelets in a short time and activating blood coagulation factors to stop bleeding quickly.
Owner:GUANGDONG TAIBAO MEDICAL SCI TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com