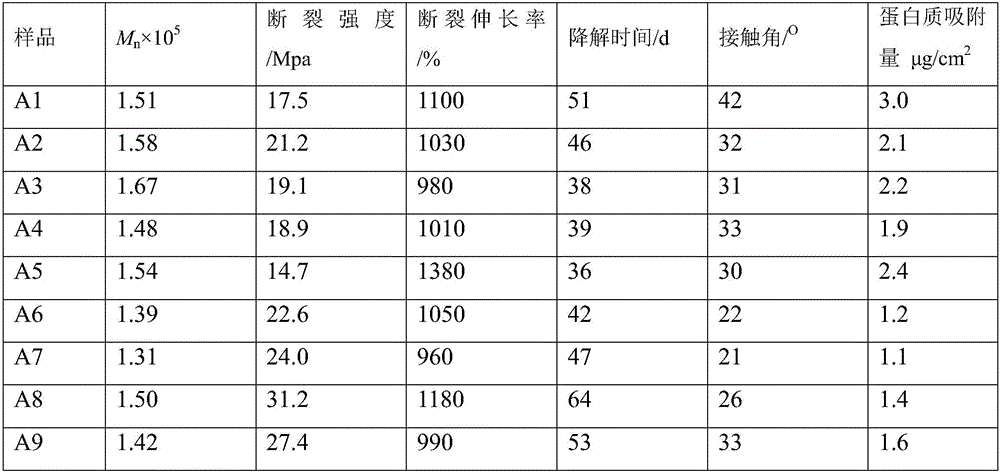
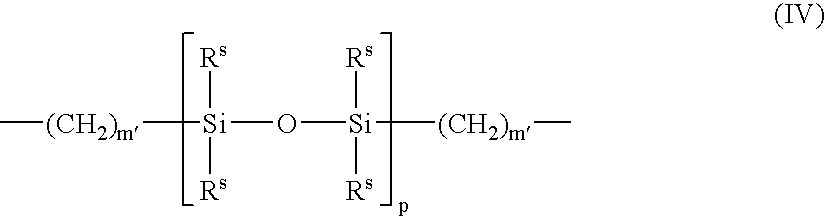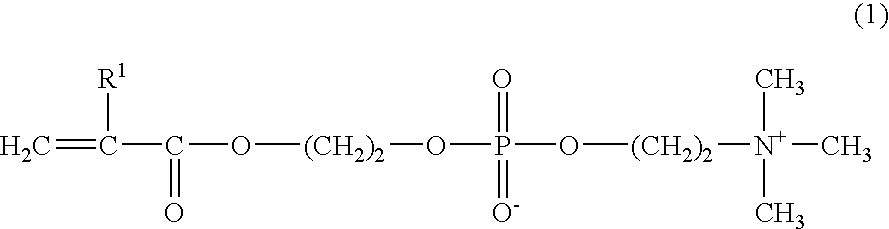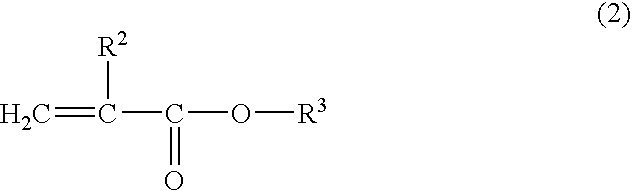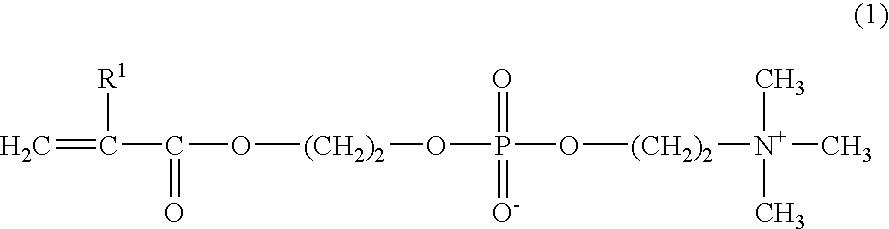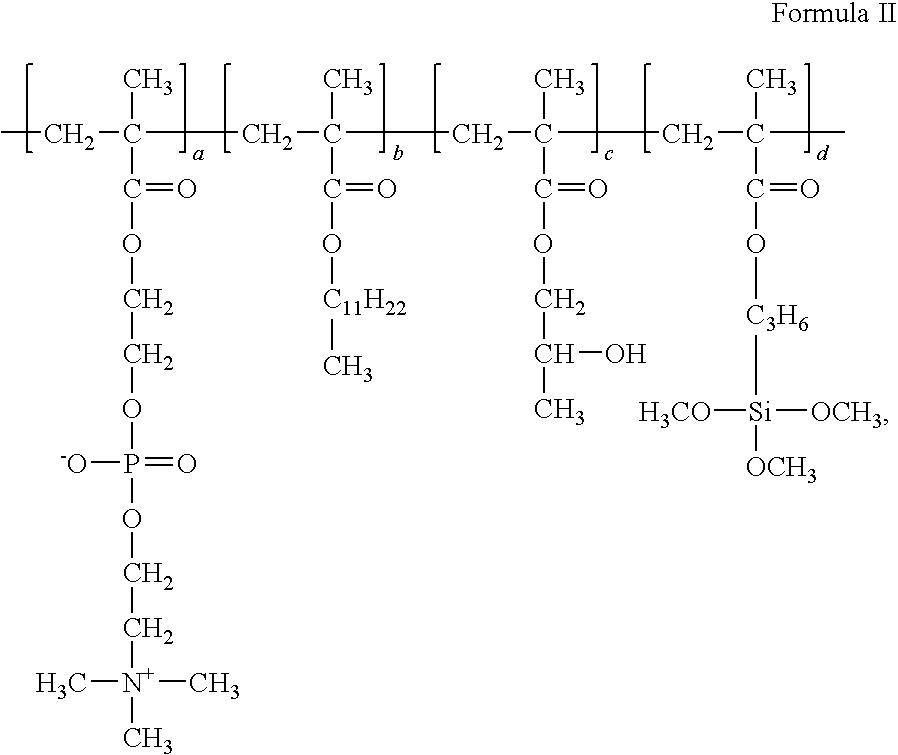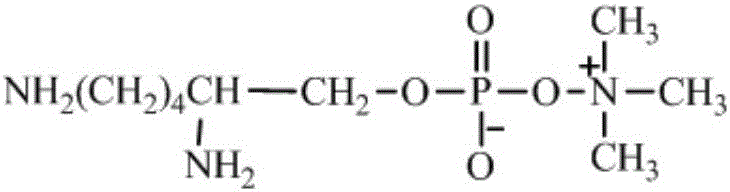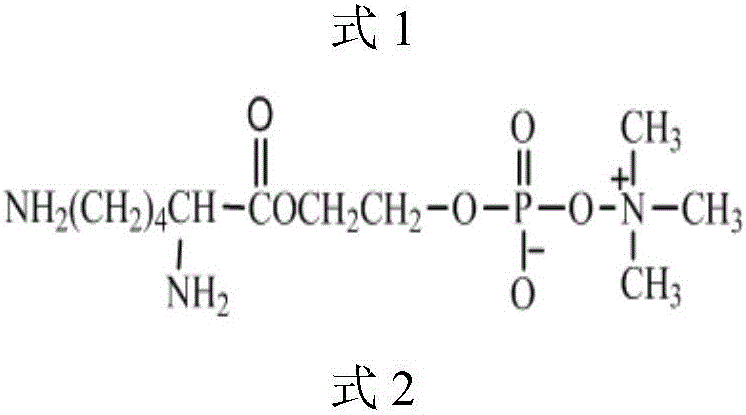Patents
Literature
593 results about "Phosphorylcholine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phosphorylcholine (abbreviated ChoP) is the hydrophilic polar head group of some phospholipids, which is composed of a negatively charged phosphate bonded to a small, positively charged choline group. Phosphorylcholine is part of platelet-activating factor; the phospholipid phosphatidylcholine as well as sphingomyelin, the only phospholipid of the membrane that is not built with a glycerol backbone. Treatment of cell membranes, like those of RBCs, by certain enzymes, like some phospholipase A2 renders the phosphorylcholine moiety exposed to the external aqueous phase, and thus accessible for recognition by the immune system. Antibodies against phosphorylcholine are naturally occurring autoantibodies that are created by CD5+/B-1 B cells and are referred to as non-pathogenic autoantibodies.
Electrochemical luminescence composite material with anti-biofouling properties
InactiveUS20060029979A1Easy to optimizeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMeth-Phosphorylcholine
The present invention relates to the preparation ad application of a high-sensitive electrochemical luminescent composite material which has anti-biofouling properties useful as a sensor material. This material is prepared by immobilization of electrochemical luminescent material into polymer containing phospholipid groups, wherein, the electrochemical luminescent material including ruthenium complex, osmium complex, etc.; the phospholipid containing polymer is the copolymer of 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine (MPC) and other polymerisable monomers. Animal experiment results revealed that this composite material has good anti-biofouling properties; it can be used in producing various sensors for bio-related detections.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Packaging Solutions
ActiveUS20090100801A1Avoid pollutionComfortable to wearPackage sterilisationPackaging corrosive chemicalsPhosphorylcholineOsmolar Concentration
A packaging system for the storage of an ionic, hydrogel contact lens employs an aqueous packaging solution including a phosphorylcholine polymer. Preferably, the solution has an osmolality of at least about 200 mOsm / kg, a pH of about 6 to about 8 and is heat sterilized.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Droplet discharging head and microarray manufacturing method
InactiveUS7438860B2High densityShape stablePump componentsWithdrawing sample devicesElectricityPhosphorylcholine
It is an object of the present invention to provide a droplet discharging head suited to the discharge of a sample solution, and particularly one that contains a bio-related substance. This object is achieved by a droplet discharging head 1 for discharging a sample solution, wherein the portion of the inner walls of the droplet discharging head 1 that comes into contact with the sample solution is covered with a polymer composed of phosphorylcholine group-containing unsaturated compound units, or a copolymer including same. The droplet discharging head is preferably an electrostatic drive or piezoelectric drive type.
Owner:KAZUHIKO ISHIHARA +1
Imitation mussel attachment protein and cell membrane structure copolymer and preparation method and application thereof
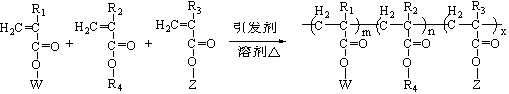
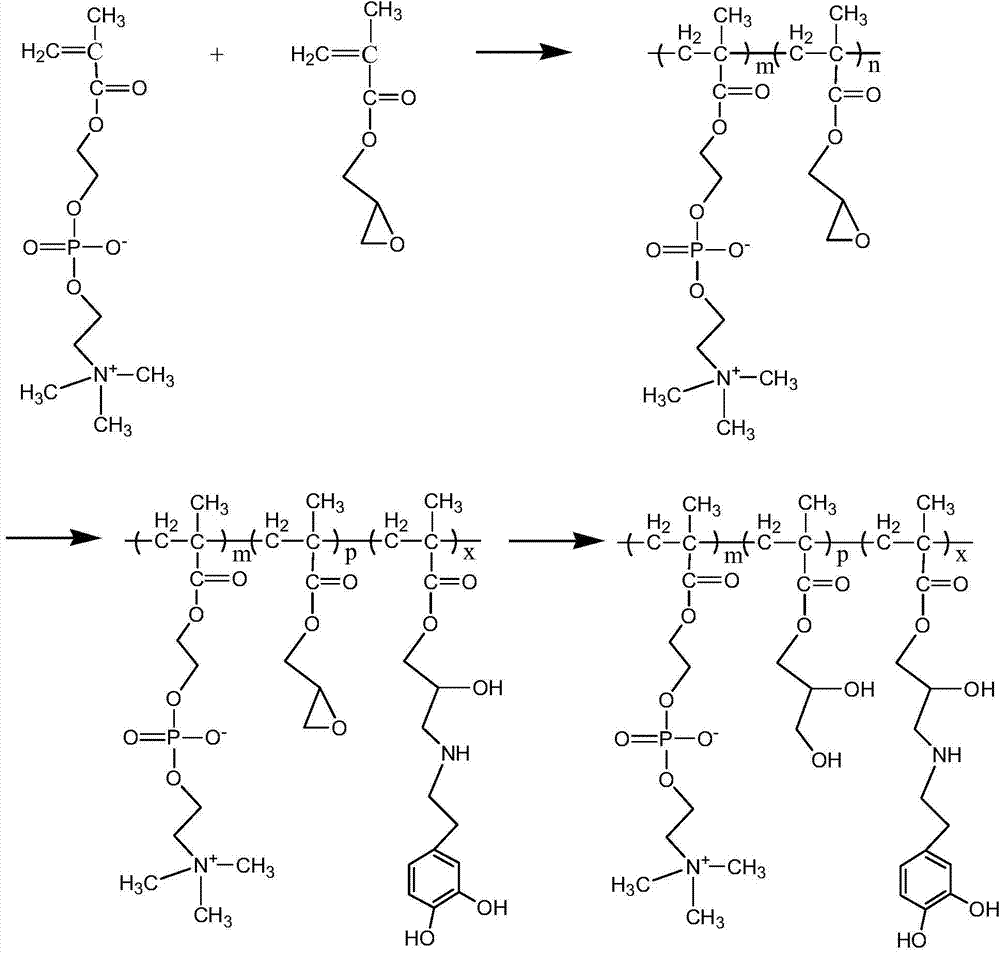
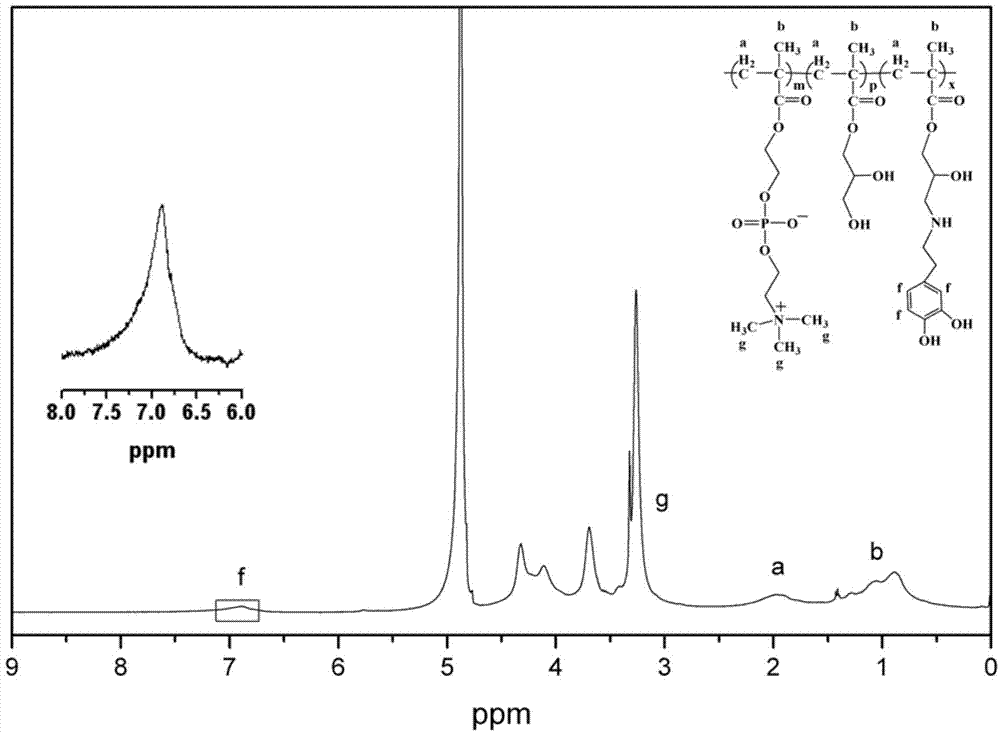
The invention discloses an imitation mussel attachment protein and cell membrane structure double-bionic copolymer shown by the structural formula (I), wherein m is an integer from 10 to 1,000, n is an integer from 0 to 500, and x is an integer from 5 to 500; in the m, n and x, the molar percentage of m is 30-90%, the molar percentage of n is 0-50%, and the molar percentage of x is 10-70%; R1, R2 and R3 are H or CH3; R4 is an alkyl with 4-18 carbon atoms; V is a catechol group with 2-300 carbon atoms in chain connection; W is a hydrophilic group with 2-8 carbon atoms in chain connection; and the hydrophilic group is a quaternary ammonium group, phosphorylcholine group, pyridinium, sulfonic acid group, phosphate group, carboxylic acid group or sulfuric acid group. According to the invention, the coating is in firm combination, the copolymer is almost suitable for an establishment method of a surface imitation cellulosa membrane structure of any material, and the surface hydrophilic performance and biocompatibility of artificial organ and related materials, medicine controlled-release systems, separation materials and other materials can be improved.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Phosphocholine linked prodrug derivatives
InactiveUS7060290B1Increase bioactivity and bioavailabilityImprove bioavailabilityBiocideNervous disorderIndependent groupCarbonyl group
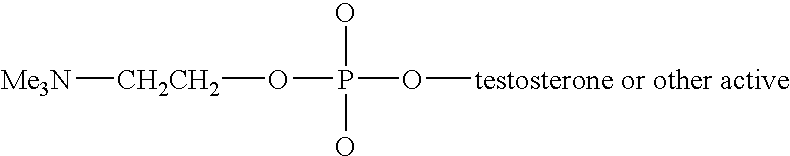
Disclosed are compounds of general formula (I) that function as prodrugs, thereby increasing bioavailabilities of the linked therapeutic agents, wherein the LINKER is (i) substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, (ii) substituted or unsubstituted alkenyl, (iii) substituted or unsubstituted alkanoyl, (iv) substituted or unsubstituted alkenoyl wherein the double bond is cis, and (v) (ortho or para) carbonyl-substituted aryl; and wherein the subtituent is each an independent group or linked together thereby forming a ring; and wherein X is one or more substituted or unsubstituted group containing one or more O, N, or S atom and wherein the substituent is each an independent group or linked together thereby forming a ring; and wherein the therapeutic agent is an alcohol-containing water-insoluble steroids or another alcohol containing compounds and methods to prepare such compounds.
Owner:SUPERGEN
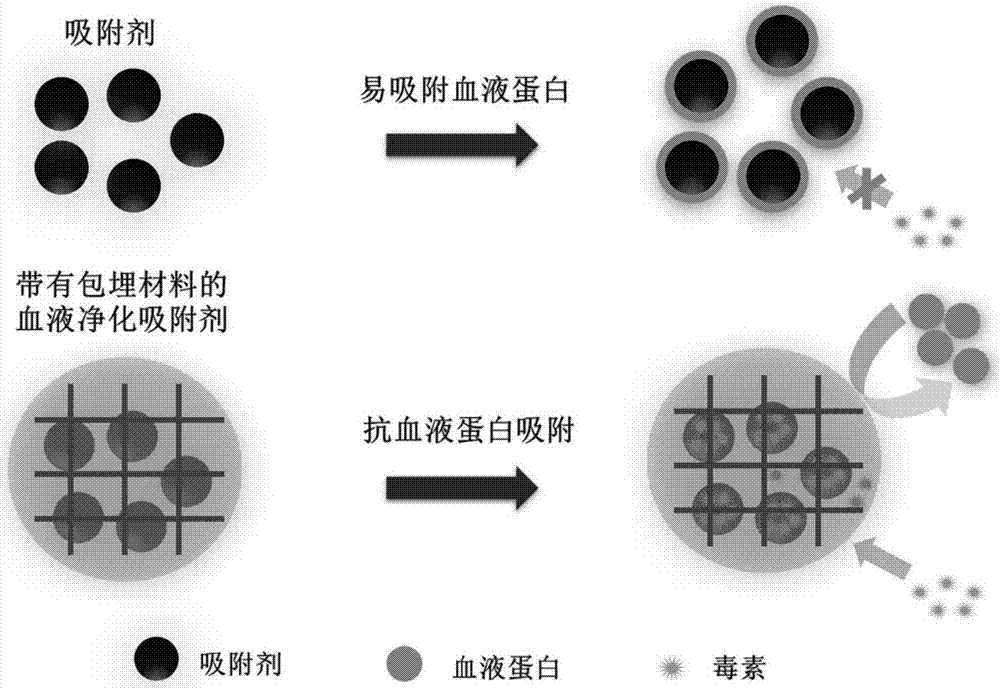
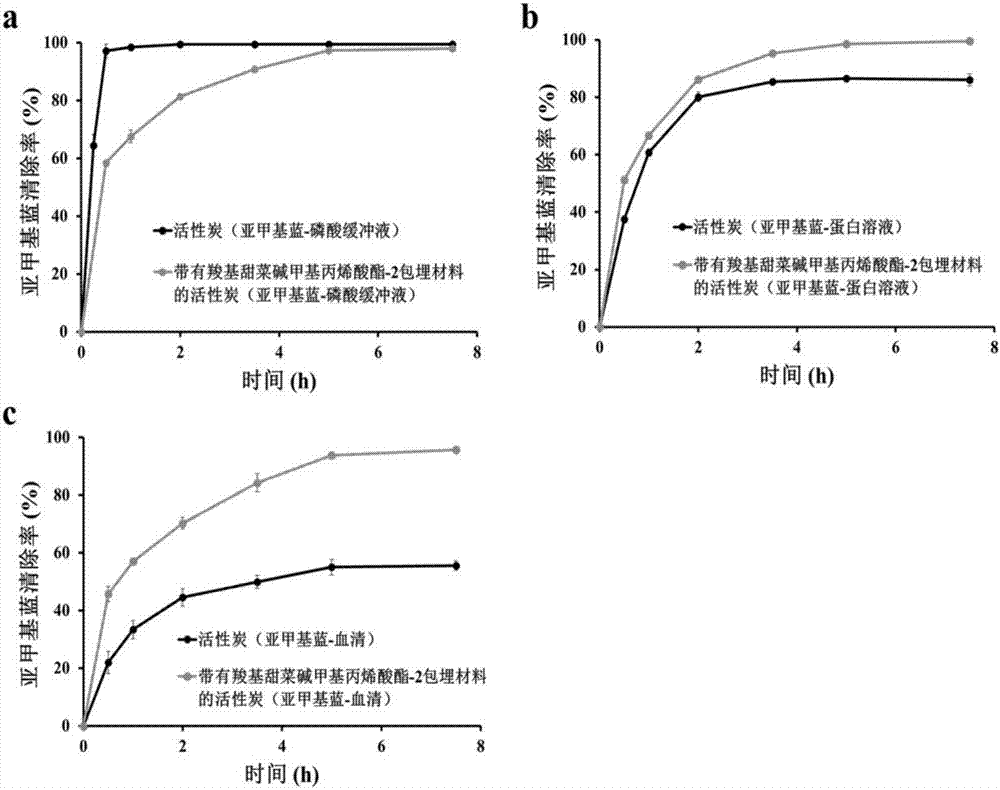
Blood purification adsorbent with embedding material and preparation method of blood purification adsorbent
ActiveCN107126936ARetention of adsorptionExcellent anti-protein adsorption performanceOther blood circulation devicesOther chemical processesCross-linkBetaine
The invention relates to a blood purification adsorbent with an embedding material and a preparation method of the blood purification adsorbent. The embedding material comprises zwitterionic monomer, a cross-linking agent, an initiator and a solvent, and the zwitterionic monomer comprises one or two types of zwitterionic molecules of carboxyl betaine, sulfobetaine and phosphorylcholine. The method includes: mixing the zwitterionic monomer, the cross-linking agent, the initiator and the solvent; adding activated carbon or resin to form mixed solution, wherein the mass of added activated carbon or resin is 6%-50% of that of the zwitterionic monomer; subjecting the mixed solution with activated carbon or resin to ultraviolet radiation or heating or normal-temperature standing to enable curing of the monomer on the surface of the adsorbent through cross-linking polymerization to form the adsorbent with the zwitterionic embedding material. The embedding material is excellent in protein adsorption resistance and biocompatibility and is extremely high in toxin diffusion efficiency in application to blood adsorption. The blood purification adsorbent is easy to store, and the preparation method is simple and feasible.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Medical device and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20110027757A1Good antithrombotic propertiesImprove concentrationDental implantsImpression capsAdhesion processPhosphorylcholine
An object is to provide a medical device having excellent antithrombotic and sliding characteristics, which can exert a cell adhesion inhibitory effect. A medical device comprising: a substrate capable of forming hydroxyl groups; and a biocompatible material layer laminated on the substrate at an appropriate position, wherein the hydroxyl groups are formed on a surface of the substrate at least at a required position by a surface treatment, while the biocompatible material layer is formed from a polymer containing phosphorylcholine groups, and wherein the substrate and the biocompatible material layer are joined via a binder layer formed from silica being covalently bonded with the hydroxyl groups and the biocompatible material, respectively.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP +1
Contact lens wetting solution
InactiveUS20060217276A1Less discomfortReduce frictionInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsSenses disorderCarbon numberMonomer composition
Contact lens wetting solutions for reducing friction between the contact lens and ocular tissues, and maintaining such effect for a long time, are disclosed. The wetting solution is composed only of a particular ratio of a lubricant composed of copolymer (A) obtained by polymerizing a monomer composition comprising 2-(meth)acryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine and alkyl(meth)acrylate, a buffer, an inorganic chloride, a preservative, a chelating agent, and water. The copolymer (A) has a weight average molecular weight of 100,000 to 1,000,000, and satisfies the formula 80≦N×R≦240, provided that 4≦N≦18 and 10%≦R≦60%, wherein N stands for the carbon number of the alkyl group in monomer Y constituting copolymer (A), and R stands for a molar fraction of the unit derived from monomer Y with respect to the sum of the units derived from monomers X and Y.
Owner:NOF CORP +2
Phosphorylcholine Conjugates and Corresponding Antibodies
ActiveUS20070286868A1Increased and decreased riskSignificant positive effectImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsPhosphorylcholineIgm antibody
IgG and IgM autoantibody levels against phosphorylcholine in subjects with hypertension (diastolic pressure>95 mmHg) were determined at baseline in order to determine the importance of antibodies for the development of atherosclerosis. The results show that increases in intima-media thickness (IMT) at a follow-up four years after baseline were significantly less prevalent in subjects having high IgM autoantibodies to phosphorylcholine. The presence or absence of IgM autoantibodies against phosphorylcholine is thus related to an increased or decreased risk of developing ischemic cardiovascular diseases. A method to determine IgM antibodies toward phosphorylcholine is proposed in this invention to identify subjects at risk of developing ischemic cardiovascular diseases. Animal experiments show that medium to high levels of IgM antibodies can be detected in plasma after active immunization with a keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH)-phosphorylcholine conjugate. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a phosphorylcholine conjugate (active immunization) or a monoclonal antibody with specificity to a phosphorylcholine conjugate (passive immunization) is proposed and the use of these compositions as active or passive immunogens in the treatment or prevention of atherosclerosis.
Owner:ATHERA BIOTECH
Biocompatible and low-abrasion member, and artificial joint using the same and method of producing the same
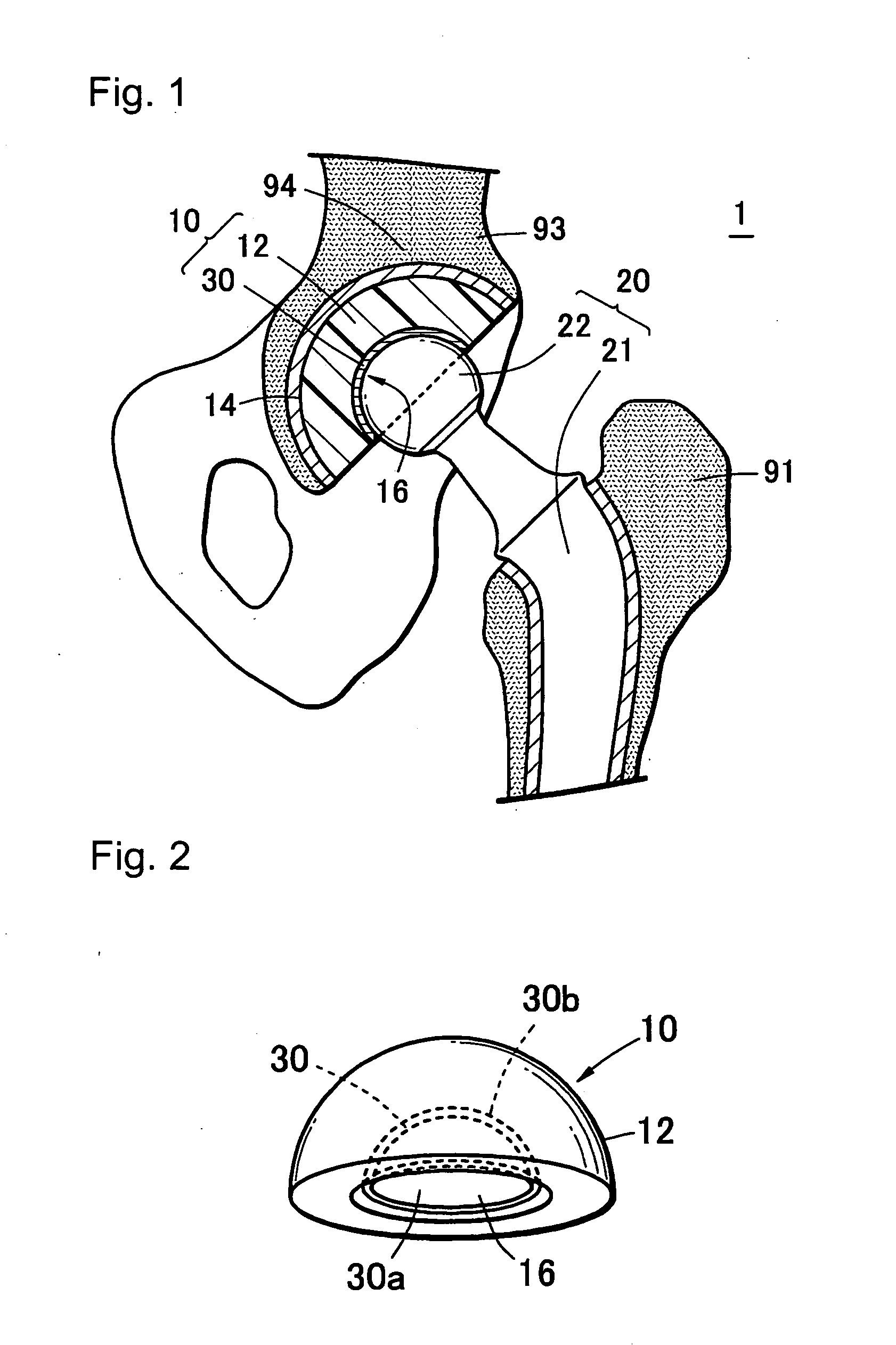
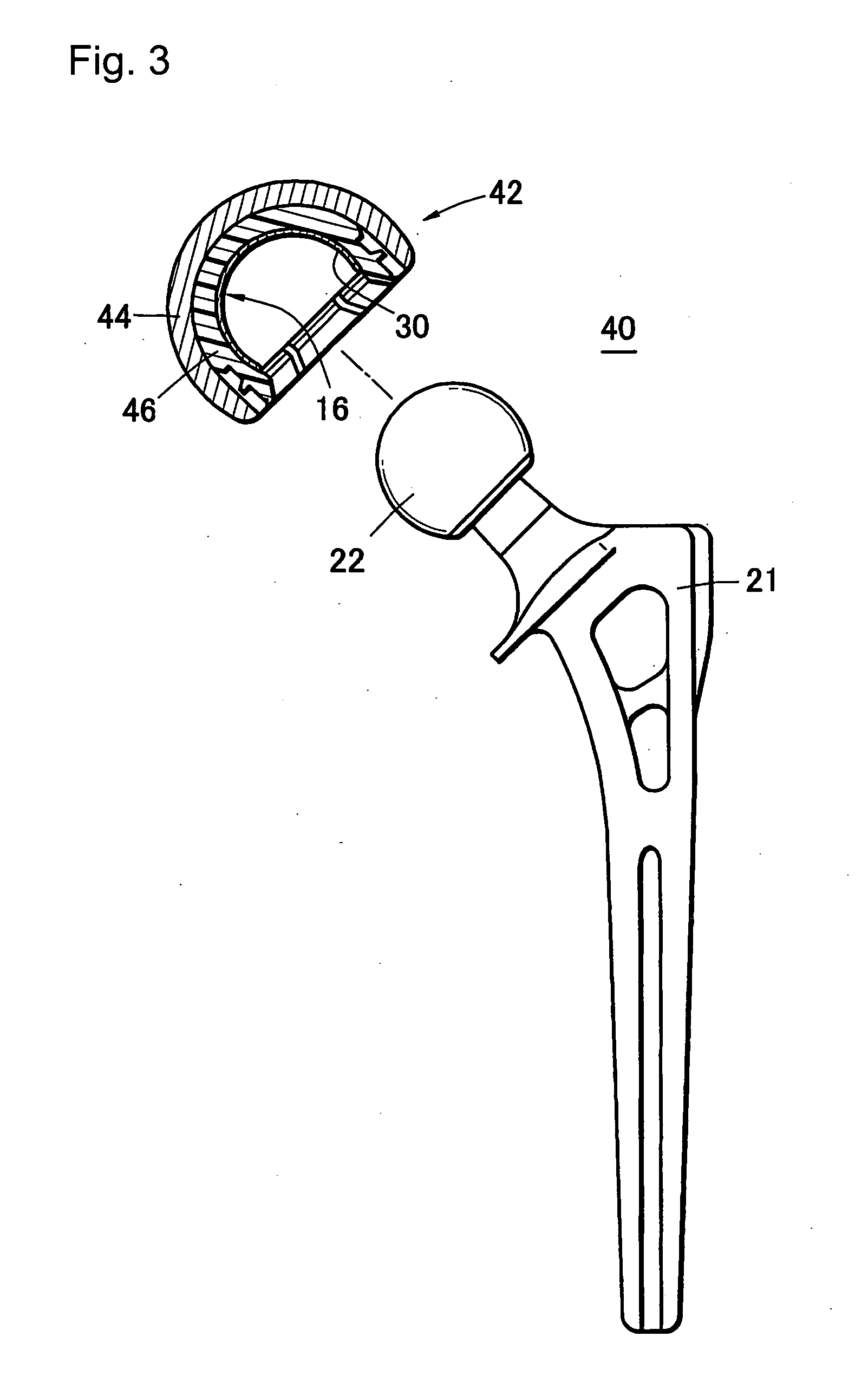
ActiveUS20120197413A1Firmly connectedSatisfactory mechanical characteristicImpression capsAnkle jointsArtificial jointsPhosphorylcholine
The object of the present invention is to provide a sliding member, a prosthesis and a method of producing the sliding member, which can suppress production of abrasive wear debris by suppressing friction of the sliding section, and also can maintain satisfactory mechanical characteristics in vivo. A sliding member comprising: a substrate 1 capable of forming hydroxyl groups; and a biocompatible material layer 4 laminated on appropriate sections of the substrate 1, wherein hydroxyl groups are formed on at least a required section of a surface of the substrate 1 by surface treating to form a surface-treated layer 2, while the biocompatible material layer 4 is formed from a polymer containing phosphorylcholine groups, and wherein the substrate 1 and the biocompatible material layer 4 are joined via a binder layer 3 formed from silica being covalently bonded with the hydroxyl groups and the biocompatible material, respectively.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP +1
Gas-filled microbubbles and systems for gas delivery
InactiveUS20140010848A1Eliminate side effectsLow viscosityBiocideBreathing masksDipalmitoylphosphatidylcholinePhosphorylcholine
Compressible and concentrated suspensions containing gas-filled microbubbles, uses thereof for delivering gas into a subject in need thereof, and systems for delivering the compressible suspensions. The gas-filled microbubbles each comprise a gas core surrounded by a lipid membrane, which includes (a) one or more lipids, such as 1,2-disteroyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DSPC) or dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC), and (b) one or more stabilizing detergents, such as poloxamer 188, Pluronic F108, Pluronic F127, polyoxyethylene (100) stearyl ether, cholesterol, gelatin, polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), and sodium deoxycholate (NaDoc).
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
High Wear-Resistant Bearing Material and Artificial Joint Replacement Using the Same
ActiveUS20090306781A1Increased durabilityLong maintenance periodFinger jointsAnkle jointsArtificial jointsWear resistant
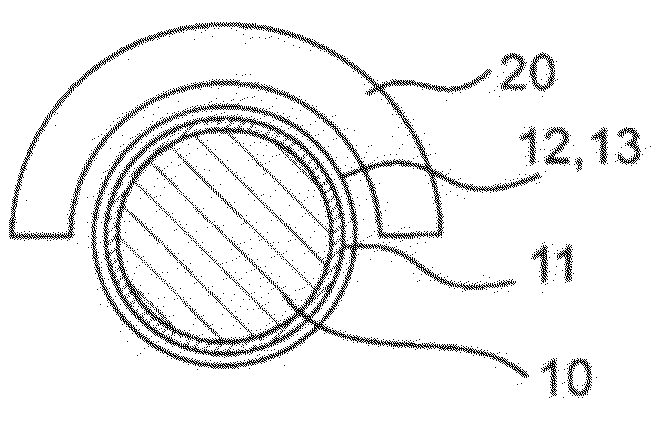
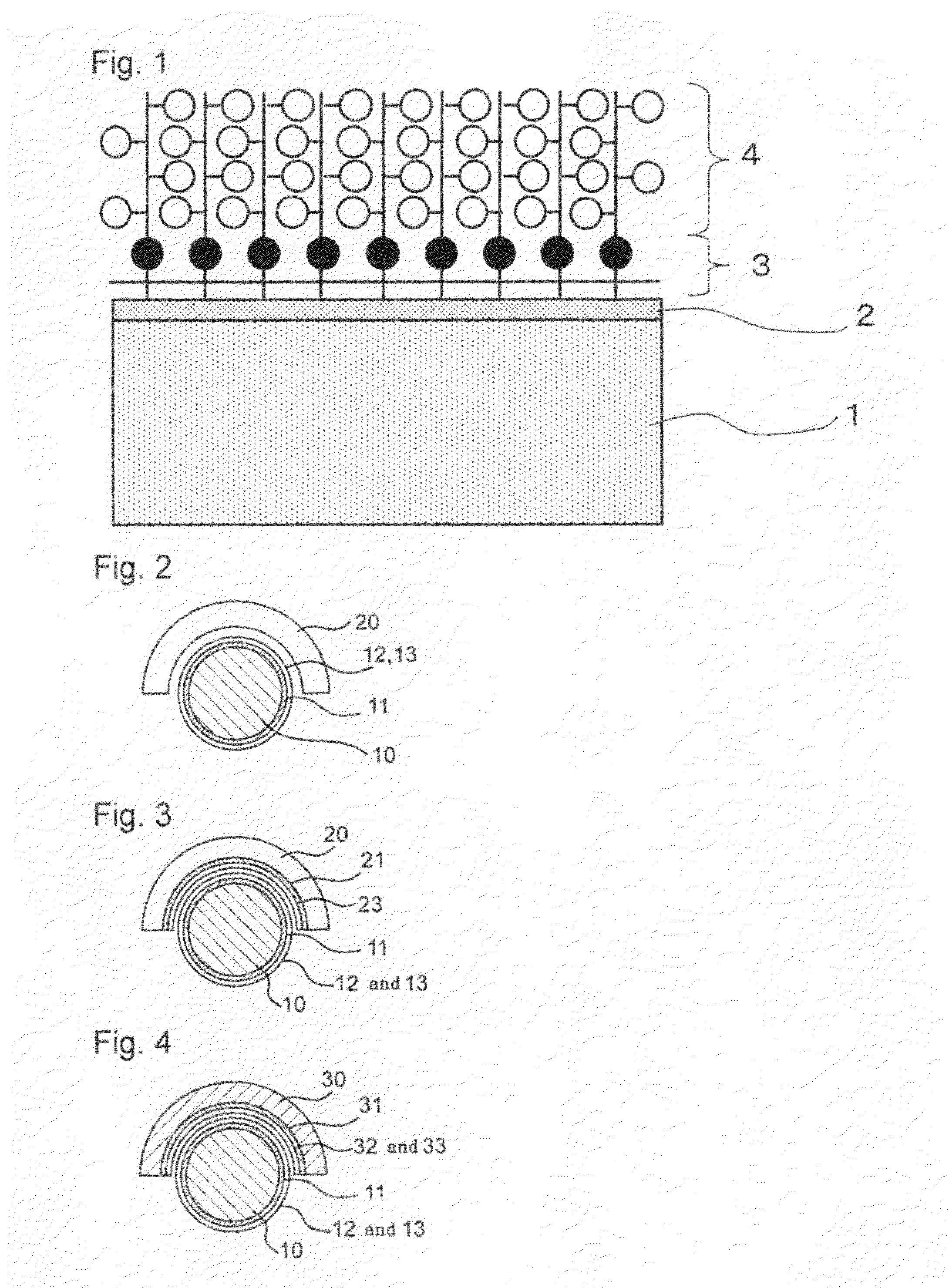
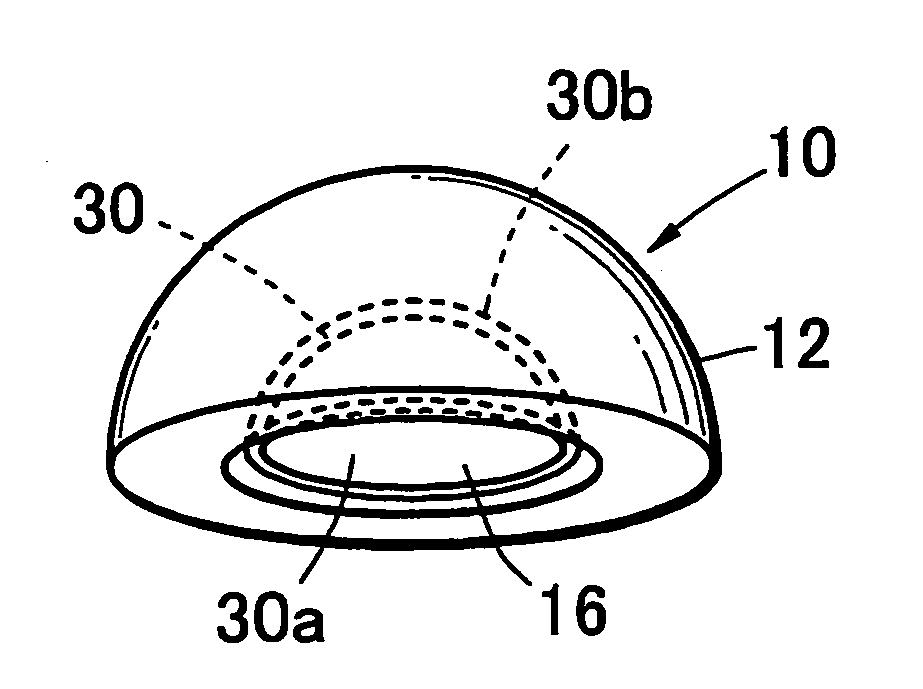
The present invention provides a bearing material that is excellent in durability and is capable of maintaining wear resistance over a long period of time. The bearing material of the present invention is a high wear-resistance bearing material 10 for being used under a humid environment comprising: a base body 12 made of a polymer material having a methylene group; and a polymer layer 30 covering a bearing surface 16 of the substrate 12, the polymer layer 30 comprising polymer chains which have a phosphorylcholine group and are grafted from the bearing surface 16, wherein a phosphoric index of the sliding surface 16 which is calculated by dividing a peak intensity of phosphate group in an infrared spectrum measured on the sliding surface by a peak intensity of the methylene group therein is not less than 0.28.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP +1
Method for improving blood compatibility of material
InactiveCN103881126AHigh densityEasy to prepareLiquid surface applicatorsCoatingsPhosphorylcholineElectrical polarity
The invention discloses a method for improving blood compatibility of a material. The method includes the following steps: 1, synthesizing a polymer containing an amino group; 2, dissolving the polymer containing the amino group in a polar solvent together with dopamine, and stirring uniformly to obtain a costing solution; and 3, coating the costing solution on the surface of a material to be modified to obtain a coating with a simulated cell outer layer membrane structure on the surface of the material to be modified. According to the method, the polymer containing the amino group is coated on the surface of the material to be modified after being mixed with the dopamine, the reaction of the amino group and the dopamine in the coating is controlled by the pH value of the coating solution, so that the density of the coating is increased to fix a phosphorylcholine group on the surface of the material, obtain the surface having the simulated cell outer layer membrane structure, to greatly improve the hydrophilicity of the material, so as to improve the blood compatibility of the material.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
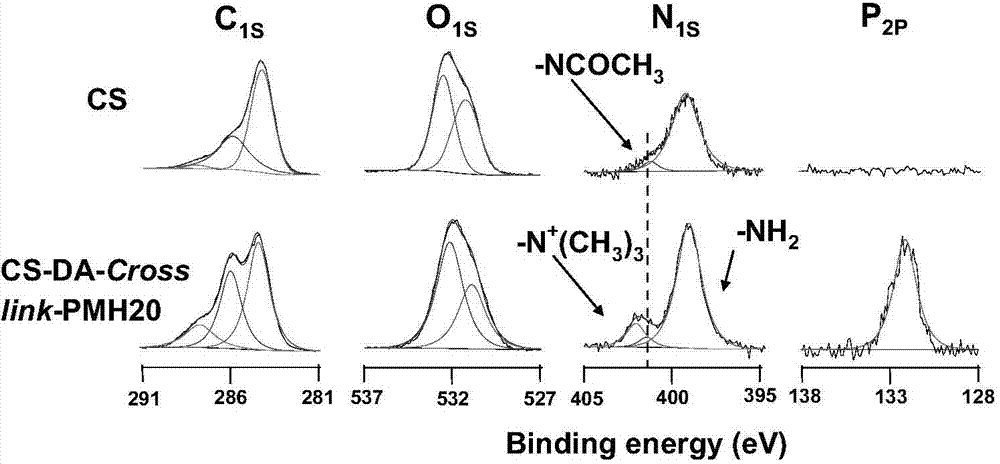
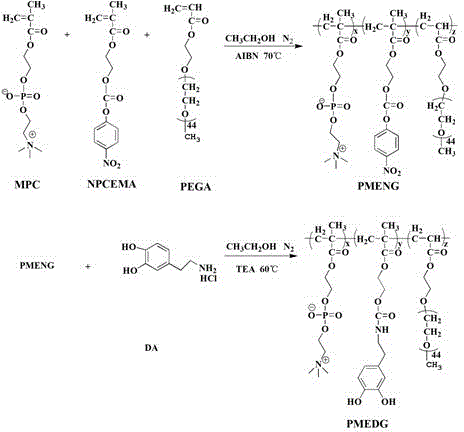
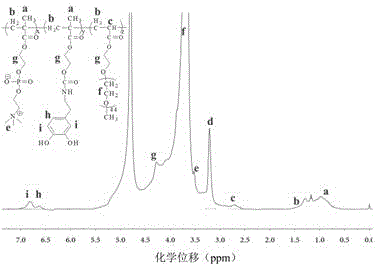
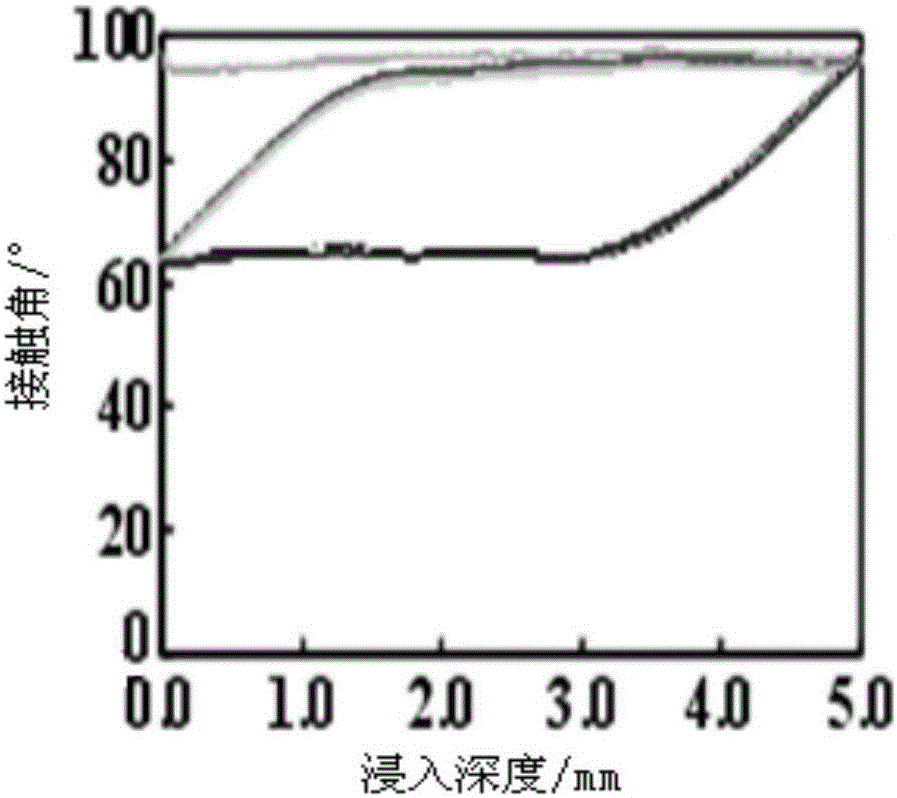
Method for forming simulated cell outer layer membrane structure on surface of cross-linked chitosan
The invention discloses a method for forming a simulated cell outer layer membrane structure on the surface of cross-linked chitosan. The method comprises the following steps that: firstly, the chitosan is cross-linked by glutaraldehyde; and secondly, the surface of the cross-linked chitosan is grafted with phosphinylideyne choline groups to construct the simulated cell membrane structure, the reaction of the grafted phosphinylideyne choline groups is carried out in an anhydrous non-protonic solvent, the reaction temperature is between 40 and 80 DEG C, and the concentration of phosphorylcholine dichloride is between 0.1 and 20mg / ml. The test results show that for the surface modified by the simulated cell outer layer membrane structure, the capabilities of adsorbing protein and blood platelet are obviously reduced, and the blood compatibility is obviously improved. The modified material with the simulated cell outer layer membrane structure has wide application prospect in fields such as blood purification, body implantation materials, tissue engineering, slow release of medicines, biological sensors, and the like.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Functional polymer containing phosphorylcholine and PEG and method for forming anti-pollution coating with functional polymer
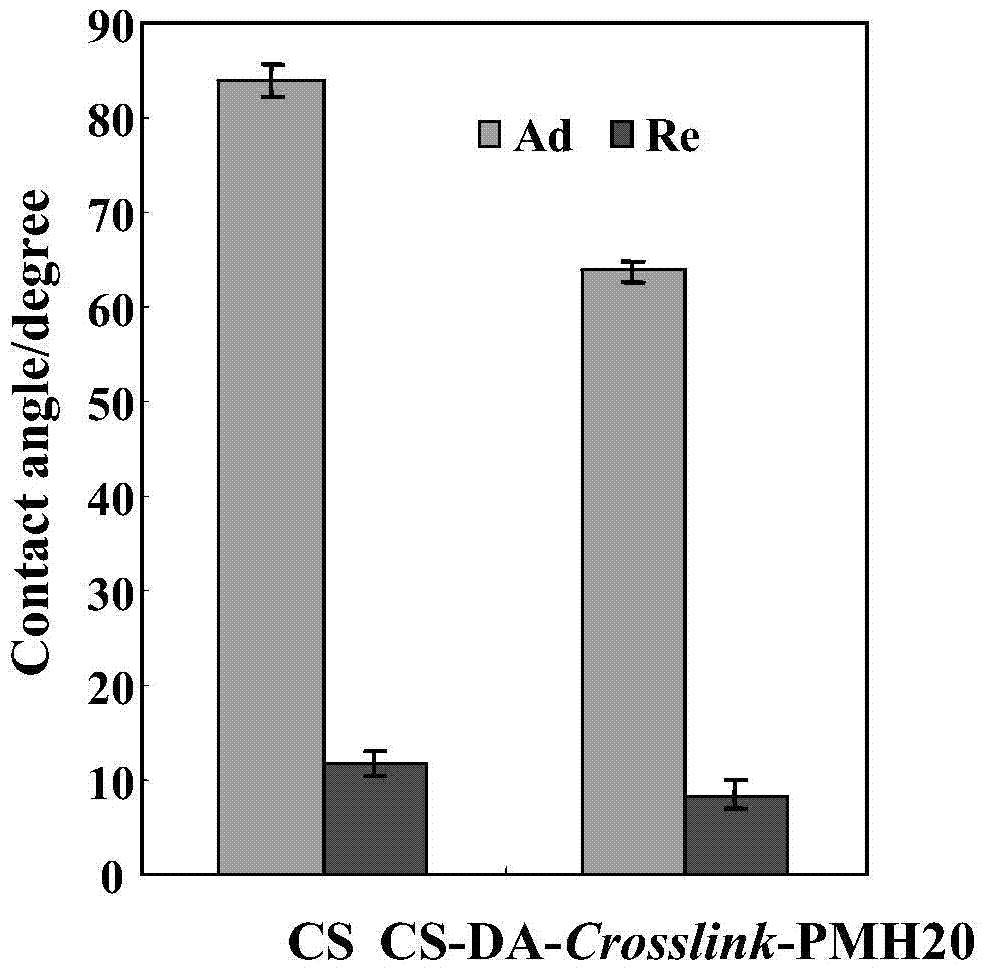
ActiveCN104610516AReduce the amount of adsorptionReduce adhesionAntifouling/underwater paintsPretreated surfacesPhosphorylcholineSide chain
The invention discloses a functional polymer containing phosphorylcholine and PEG and a method for forming a biological pollution resistant interface. The polymer is a functional polymer that contains multiple function groups on a side chain and has a controllable proportion; a PEG flexible chain with larger steric hindrance and outer cell membrane phosphorylcholine hydrophilic group interact to achieve good anti-pollution effect; the polymer contains less than 10% of catechol group, and can be strongly combined with surfaces of various polydopamine-mediated base materials to form a stable hydrophilic monomolecular coating, so that the functional modification of material surfaces is implemented. The method for forming coatings is simple; the coatings can exist on the surface of any base material, so that the ability of resisting adhesion and pollution of multiple biological ingredients of the material surface is improved.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Preparation method of phosphorylcholine bionic coating
The invention discloses a preparation method of a phosphorylcholine bionic coating. The preparation method comprises the following steps of 1, performing free radical polymerization on ethylene monomers containing phosphorylcholine groups and ethylene monomers containing amino groups under the effect of initiators to obtain phosphorylcholine polymers containing amino groups; 2, dissolving the phosphorylcholine polymers containing amino groups into a polar solvent to obtain a polymer solution; then, adding a glutaraldehyde water solution; uniformly mixing the materials to obtain a mixed solution; 3, coating the mixed solution onto the surface of a material to be modified; after drying, putting the material to be modified into distilled water; soaking the materials for 6h to 12h under the condition of the temperature being 40 DEG C to 80 DEG C; after the materials are taken out, obtaining the phosphorylcholine bionic coating on the surface of the material to be modified. The preparation method has the advantages that the method is simple; the conditions are mild; the method is hopeful to become a novel path for regulating and controlling the action of biological materials with biological activity substances such as protein and platelet; important academic significance is realized.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Diazeniumdiolated Phosphorylcholine Polymers for Nitric Oxide Release
ActiveUS20100262238A1Good biocompatibilityBiocideTubular organ implantsPhosphorylcholineBiocompatibility Testing
The present disclosure in a broad aspect provides for diazeniumdiolated phosphorylcholine polymers and associated methods for achieving nitric oxide release. The present polymers have superior biocompatibility and are useful for coating or fabricating medical devices such as a vascular stent.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Polycaprolactone-polyethylene glycol block copolymer, and its preparing method and use
InactiveCN1978492AImprove the effect of surface modificationSurface modification achievedPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPhosphorylcholinePolyethylene glycol
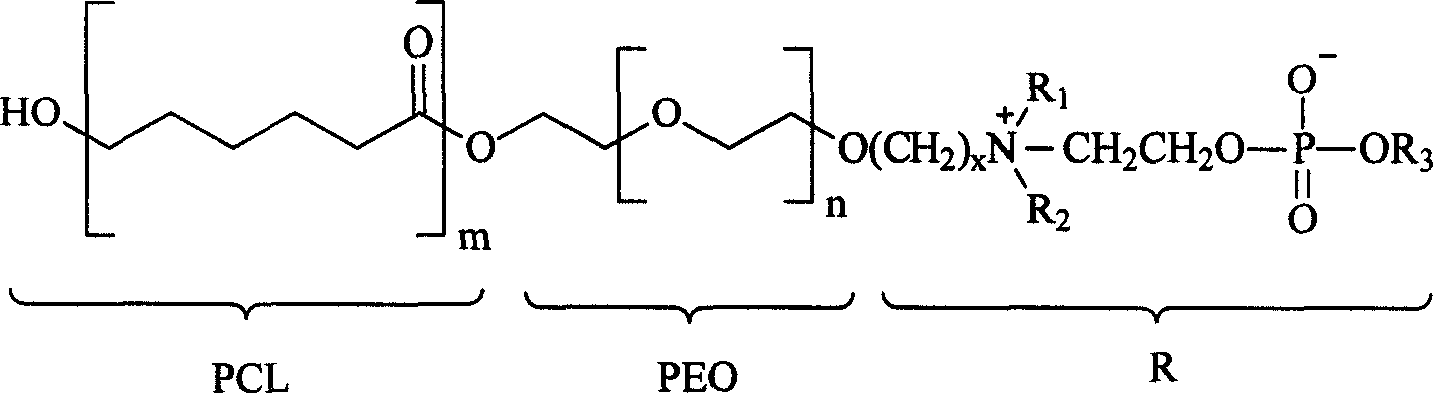
This invention provides the periodic copolymer PCL-PEO-R which was polymerized with poly-epsilon-caprolactone and polyethylene glycol. The polymerization degree of PCL segment is between 10 and 1000, and the corresponding molecular weight is between 1000 and 100000; the polymerization degree of PEO segment is between 10 and 100, and the corresponding molecular weight is between 400 and 5000; the interval group between tertiary amine N and PEO is the alkyl made up of 2-10 carbon atoms, and the selective preference number of carbon atom is 2-4. The other two alkyls on the atom of tertiary amine N may be the same either the different methyl or ethyl. The alkyls which were used to composite phosphorylcholine were made up of the liner chain or the branched chain, and the saturated or the unsaturated alkyls with 1-20 carbon atoms. This invention also provides the preparation of the interpolymer, as well as its application in the preparation of biology medical material.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Biocompatibile monodisperse nano polymer carrier and its preparation and medicine-carrying method
InactiveCN101259279AGood biocompatibilityGood blood compatibilityOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPhosphorylcholineCarrier system
The invention relates to a monodisperse nano-polymer carrier with biological compatibility and a method for preparation and carrying drug thereof. Firstly, a reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization method is used for preparing amphiphilic block copolymers with smaller polydispersity index, wherein the hydrophilic segment is methylacryoyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine (MPC) and the hydrophobic segment is n-butyl methacrylate (BMA). Then through the method of solvent evaporation, the amphiphilic block copolymers are used for preparing nano-polymer micelle, drugs are encapsulated in the micelle through physical action, thus obtaining the monodisperse nano-polymer carrier system with good biological compatibility.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
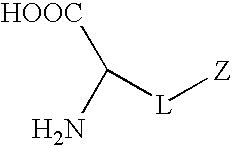
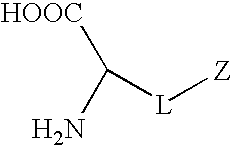
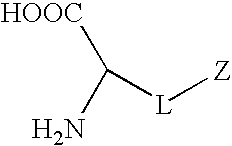
Synthetic non-fouling amino acids
InactiveUS20090149673A1Good biocompatibilityReduce thrombosisOrganic chemistryPhosphorylcholineBiocompatibility Testing
Synthetic amino acids containing one or more non-fouling groups or moieties are described herein. In one embodiment, the amino acid has the following chemical formula:where L is a linker group and Z is a non-fouling group including, but not limited to, polyethylene glycol (PEG); oligoethylene glycol (OEG); zwitterionic group, such as phosphorycholine, carboxybetaine, and sulfobetaine; groups that are hydrogen bond acceptors but not hydrogen bond donors. The non-fouling amino acids can be incorporated into a bioactive peptide as single amino acid residues, multiples amino acid residues, or as blocks of amino acids. The non-fouling amino acids, or peptides containing one or more non-fouling amino acids, can be applied to surfaces in order to improve biocompatibility, reduce thrombogenesis, and / or reduce fouling by proteins or bacteria present in solution.
Owner:ARROW INT INC
Method of modifying surface of material
InactiveUS20060060533A1Easy to adjustIncrease chanceIon-exchange process apparatusOther chemical processesPhosphorylcholinePhosphoric acid
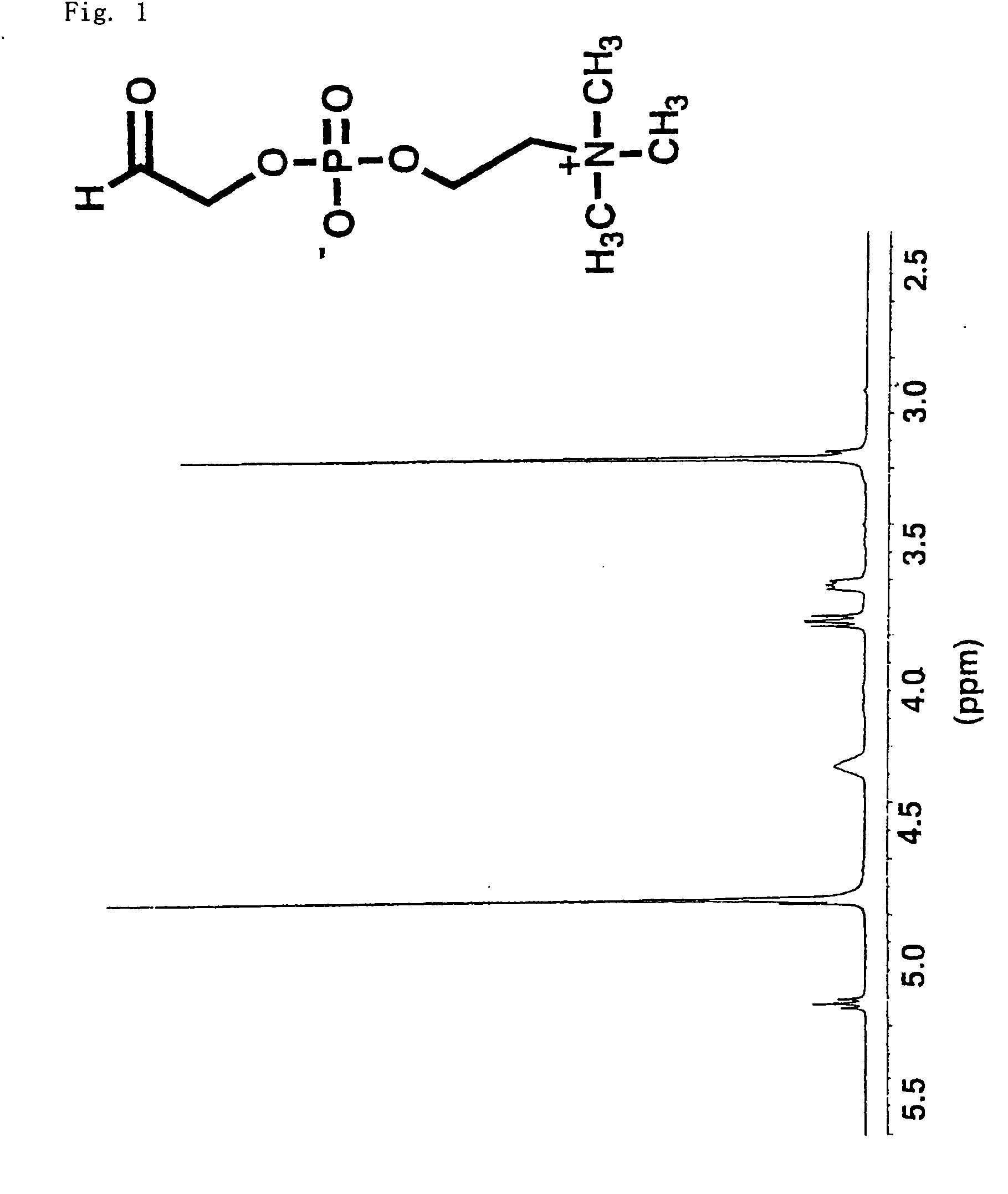
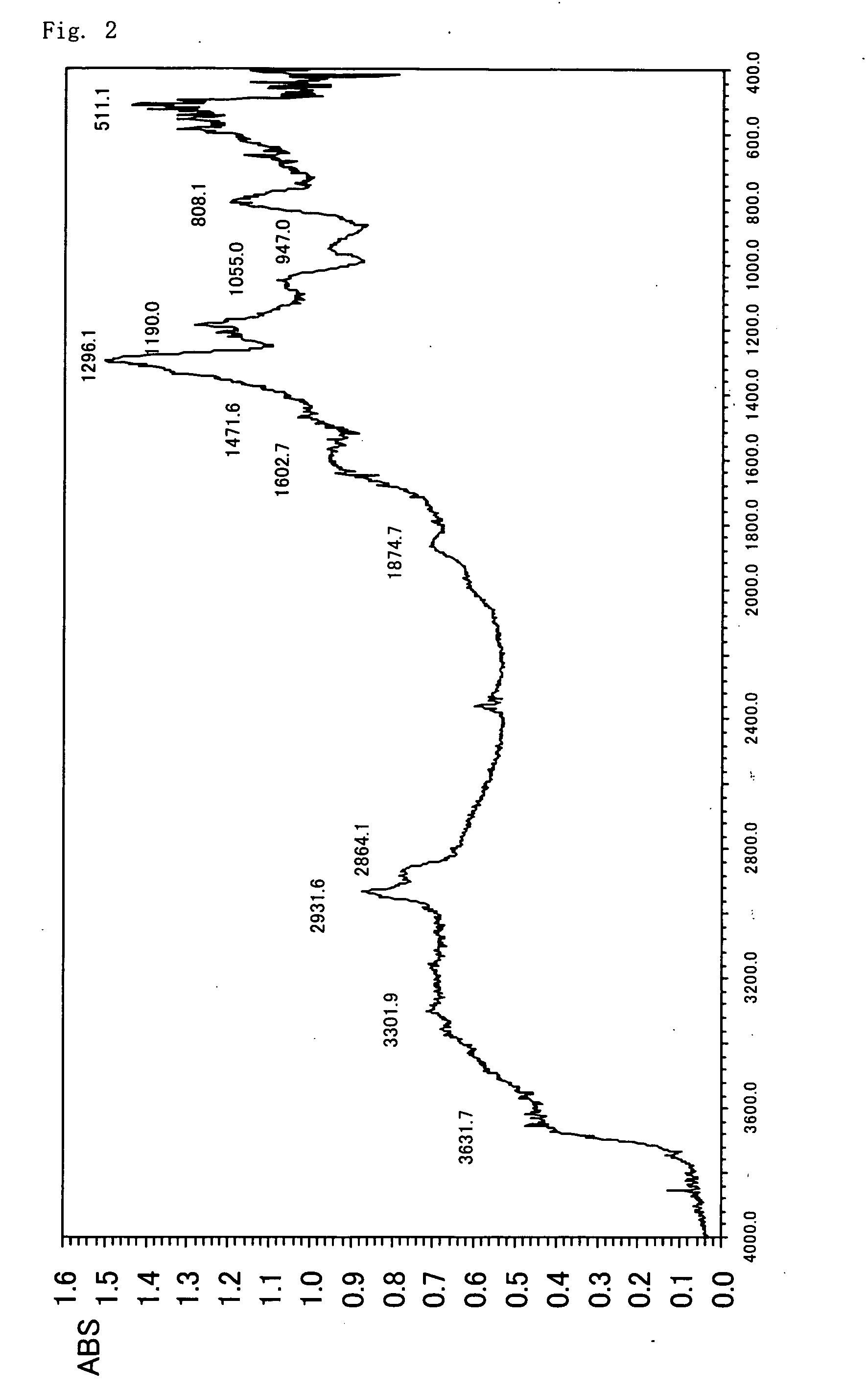
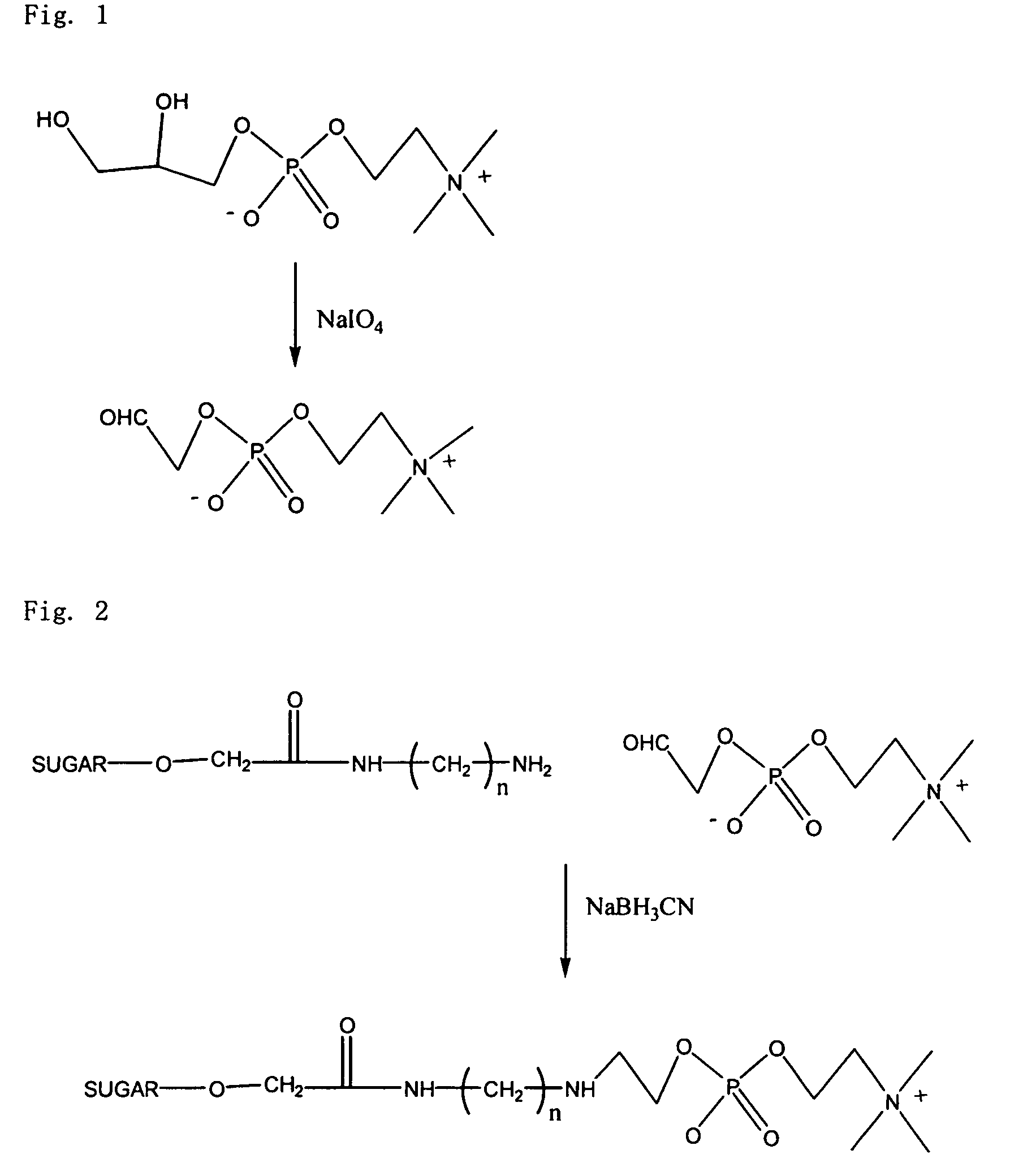
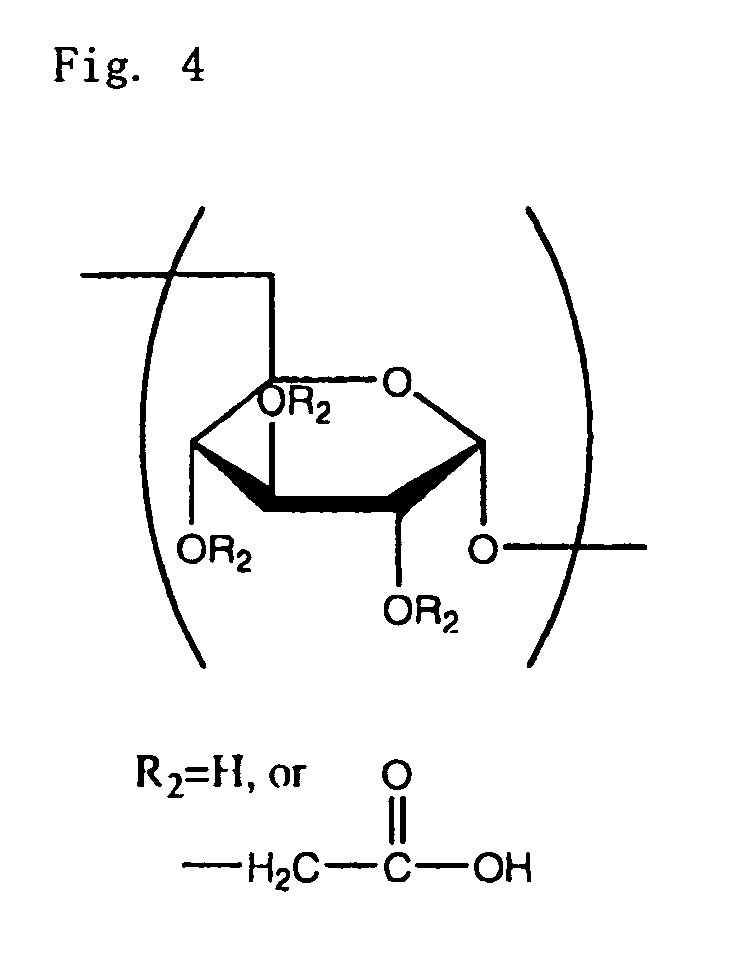
A method for surface modification of a material by means of introducing the phosphorylcholine group represented by the following formula (1-1) onto the surface of the material by treating a material having amino groups with a chemical compound containing an aldehyde derivative obtained by the oxidative ring-opening reaction of glycerophosphorylcholine. The method of the present invention provides various materials such as medical materials having superior biocompatibility and hydrophilicity.
Owner:SANYO FINE IRICA TECH CO LTD
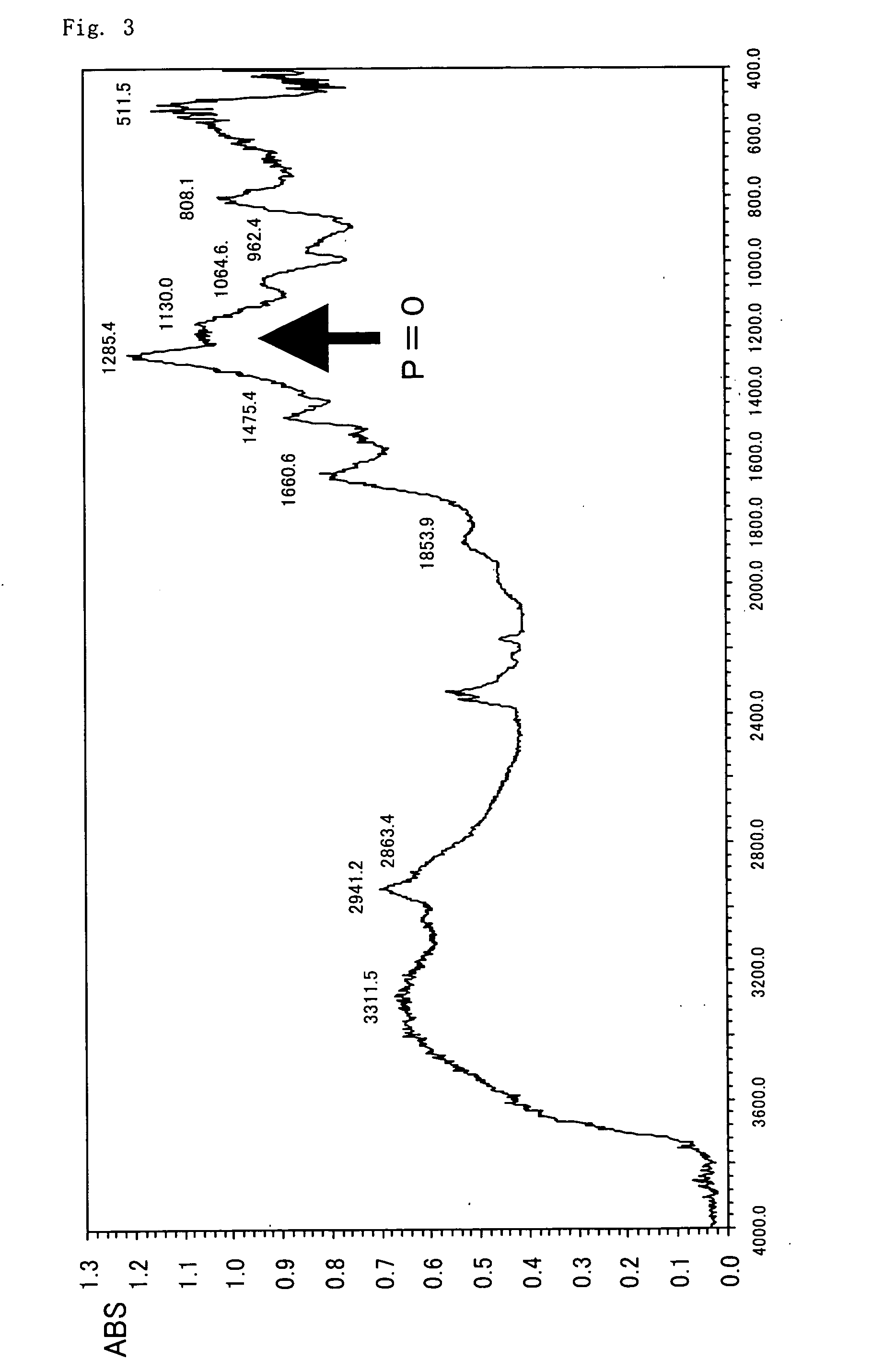
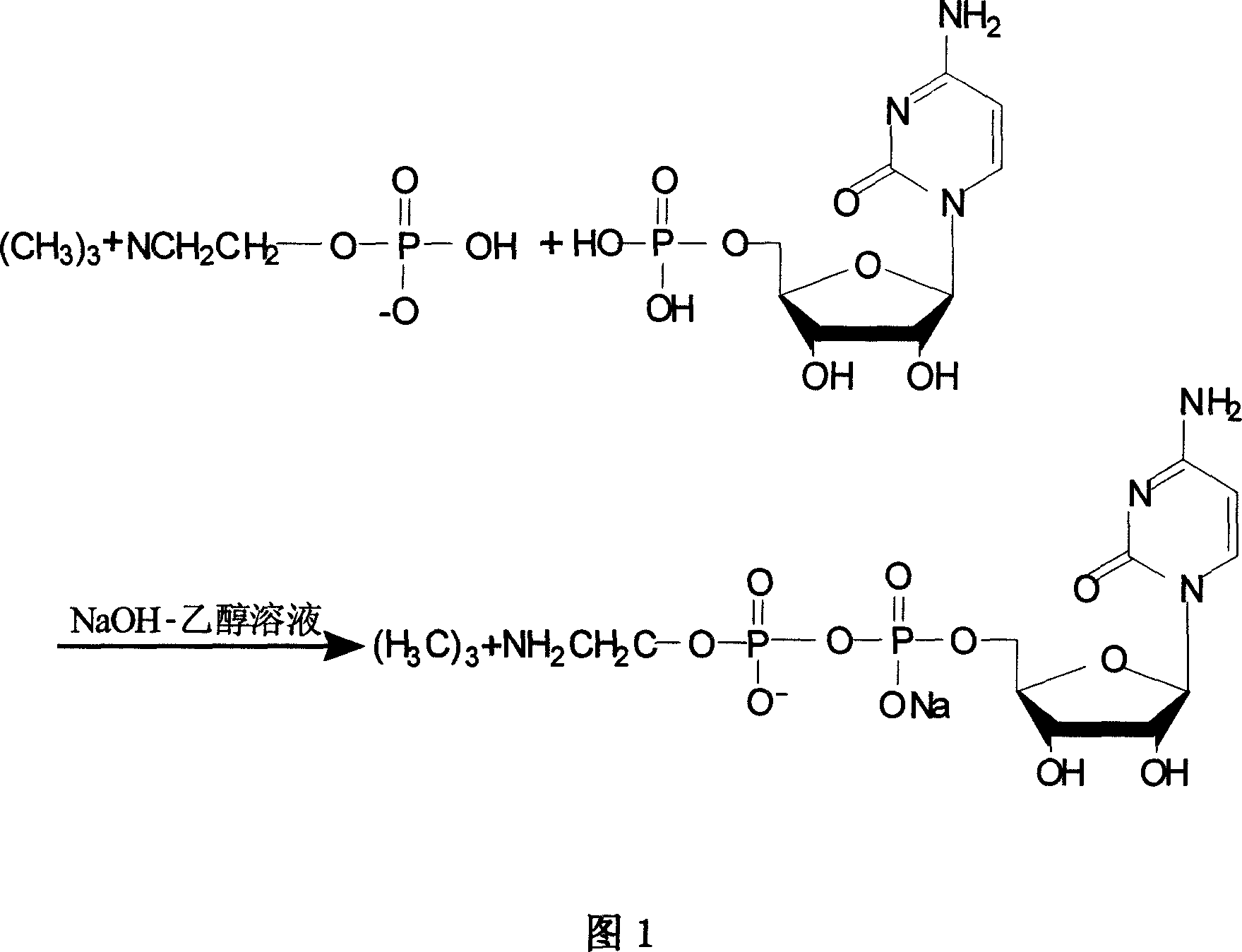
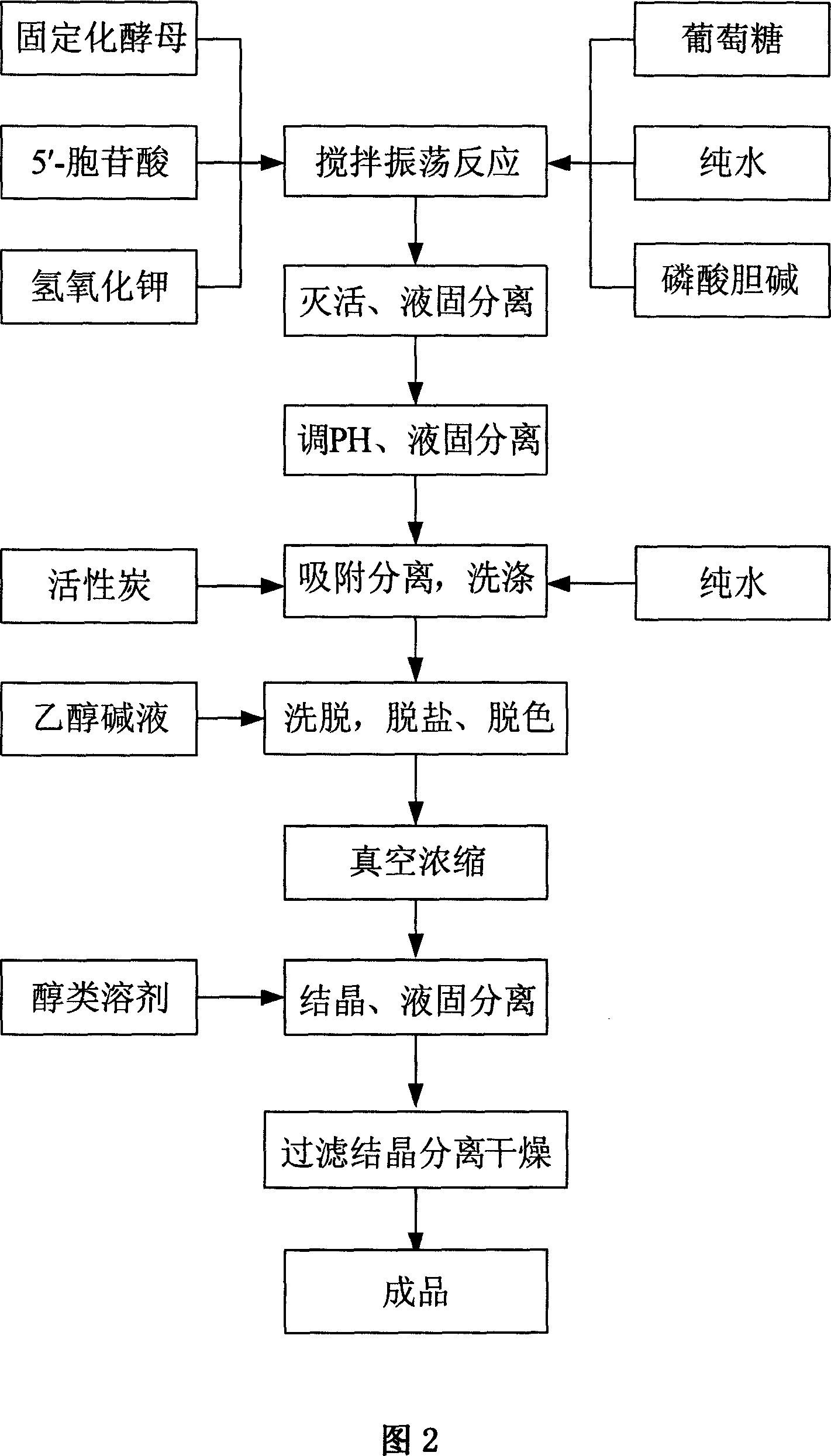
Process for preparing citicoline sodium
The present invention is process of preparing citicoline sodium. The preparation process includes the biotransformation of material including 5'-cytidylate, phosphorylcholine, potassium hydroxide and glucose with yeast as the biocatalyst; extraction and separation with active carbon as the adsorbing carrier, Cl- type ion exchange resin as the separating carrier and re-compounded water-alcohol mixture as the analyzing reagent; and product purification with alcohol solvent as the crystallizing solvent. Compared with available technology, the present invention has the advantages of high product yield and high product purity.
Owner:苏州正济药业有限公司
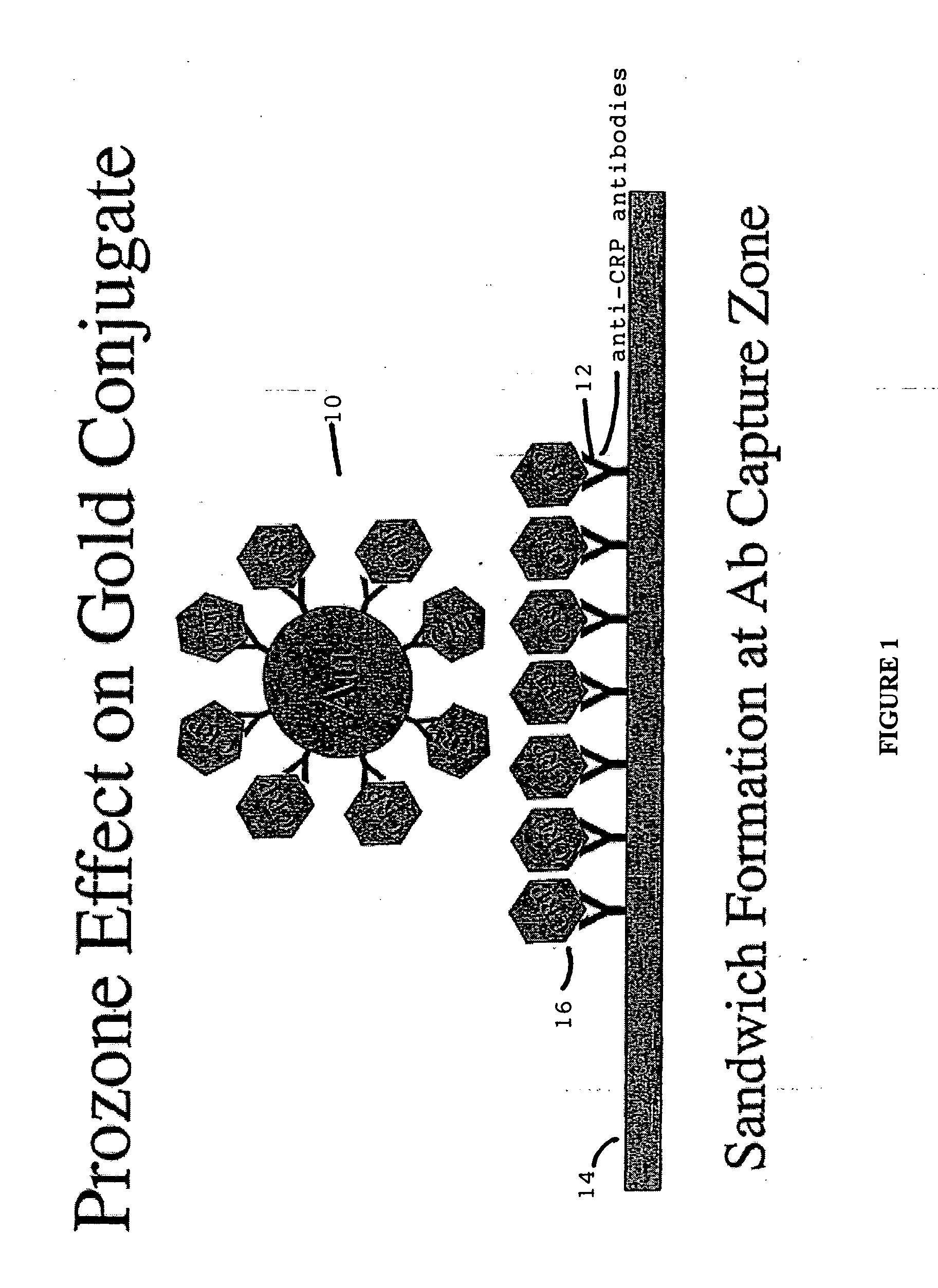
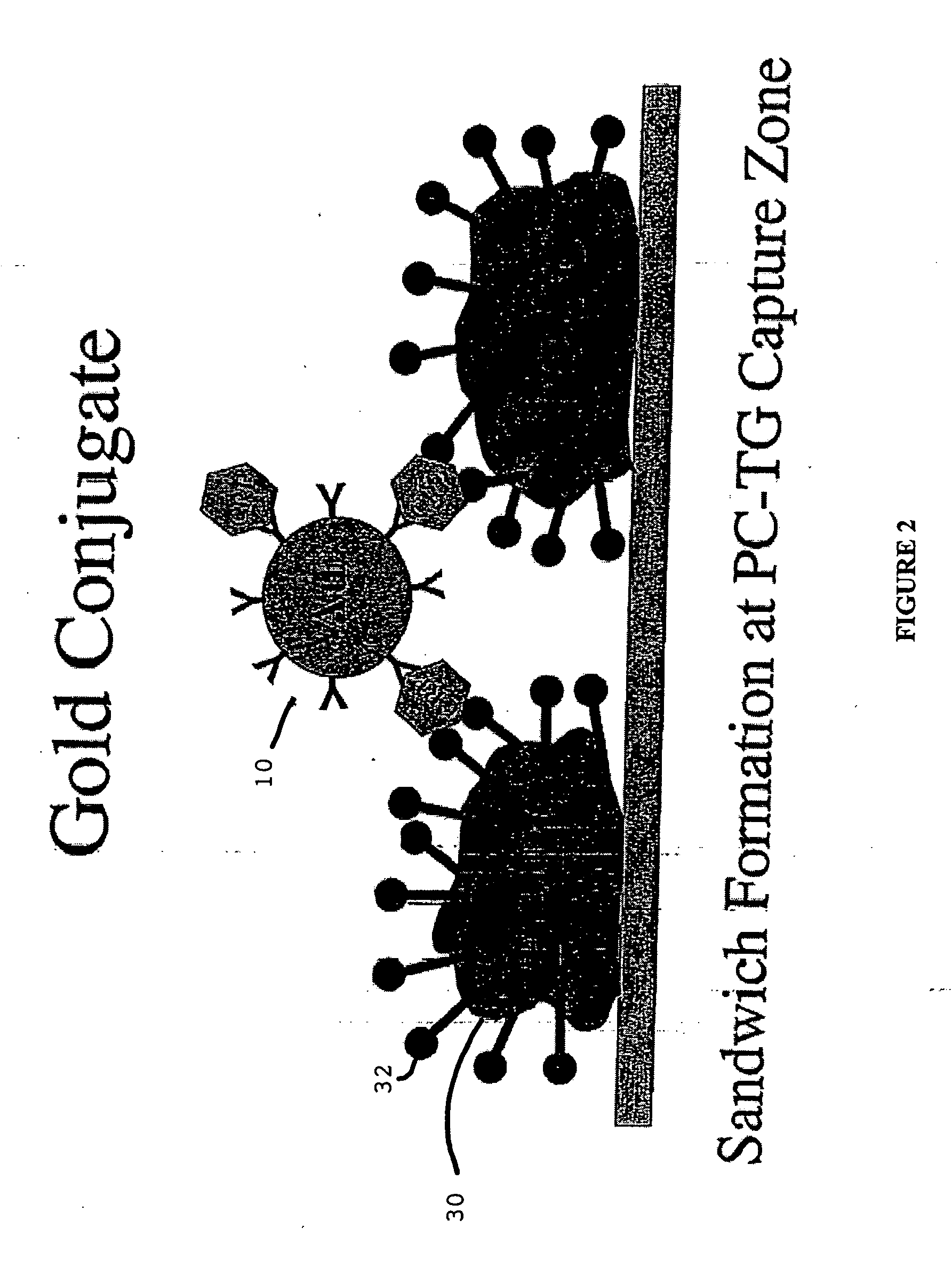
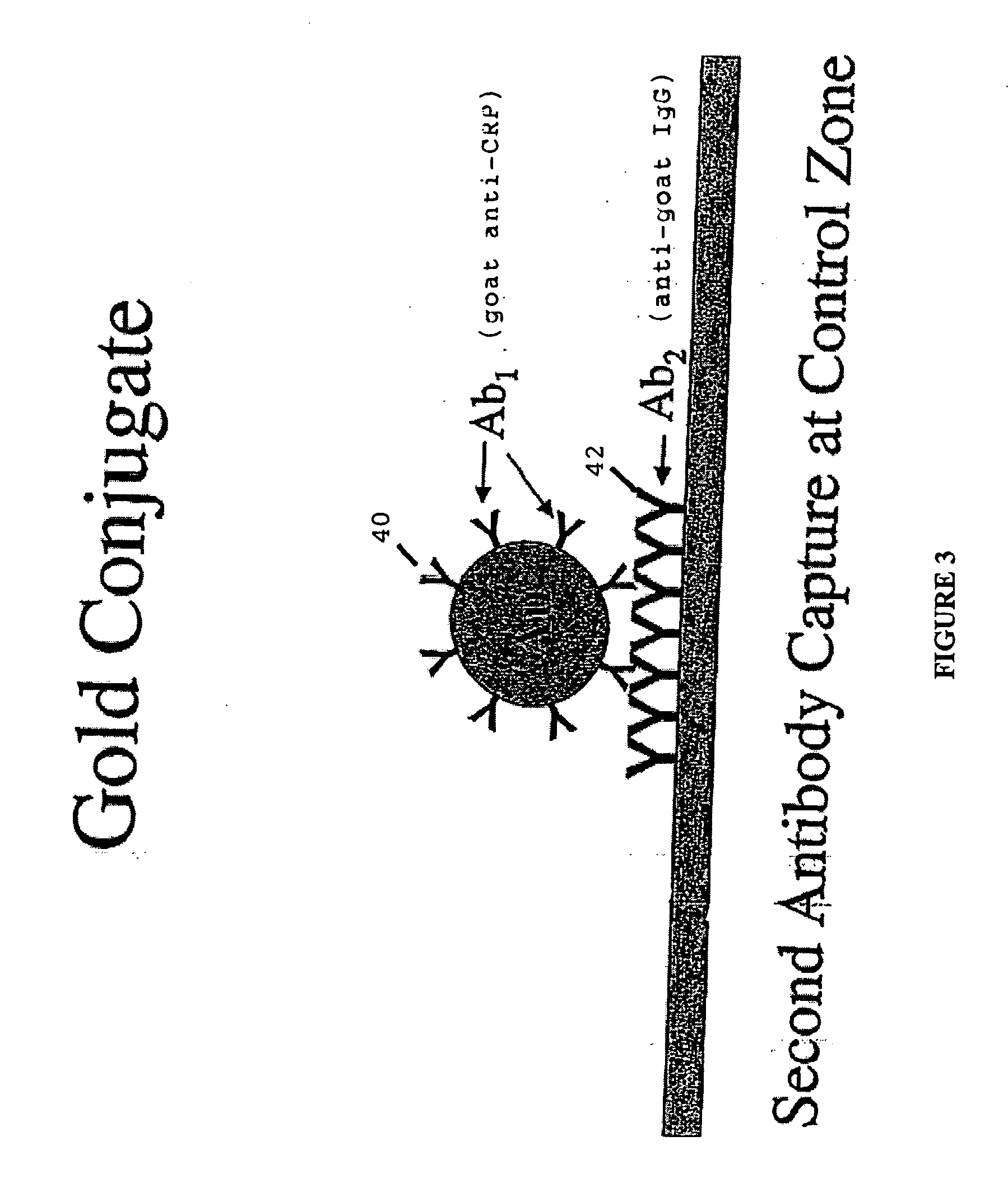
C-reactive protein immunoassay and method
The present invention is directed towards the synthesis and / or use of a mixture of analyte capture reagents comprising antibodies and a non-immunological reagent provided on a solid phase assay, selected to screen for very high and low levels of an analyte. The non-immunological reagent comprising a PC-conjugate that contains multiple copies of covalently coupled phosphorylcholine (PC) moieties, particularly towards a phosphorylcholine-thyroglobulin conjugate assaying for C-reactive protein (CRP), a known inflammatory marker. The mixture of capture reagents function to eliminate hook effect (i.e. false negatives) when CRP is present in sample at high concentrations.
Owner:STRECK INC
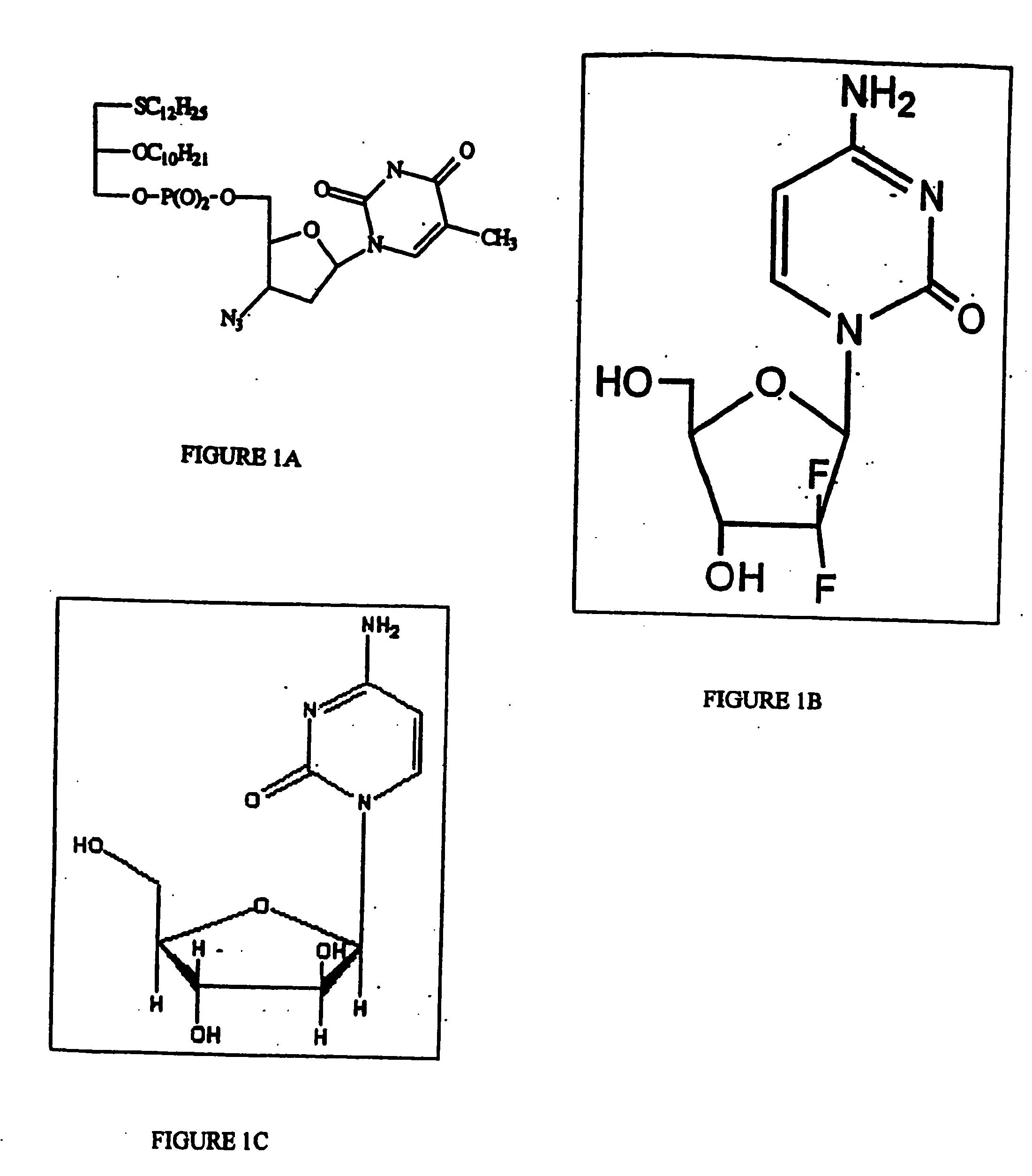
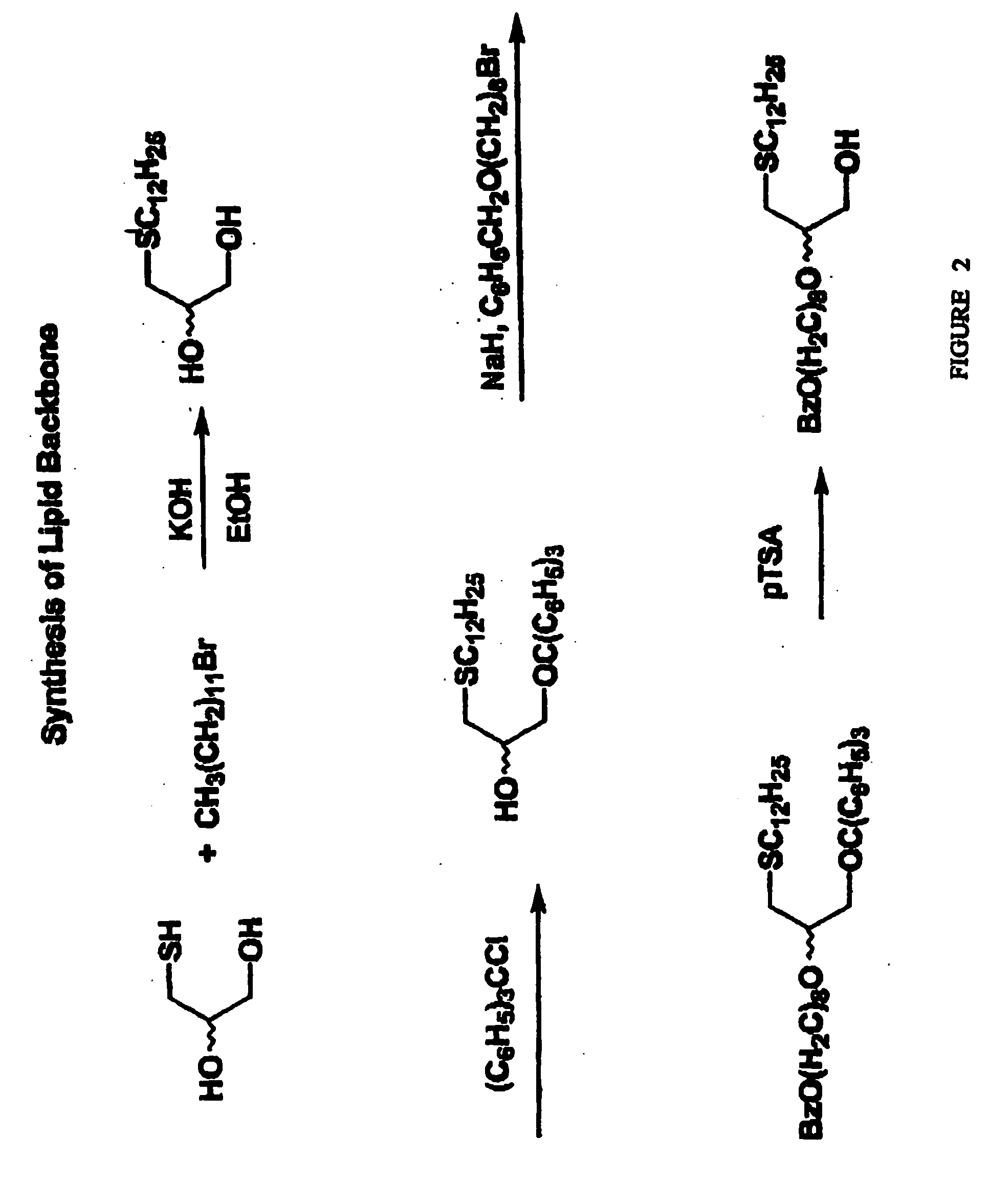
Compositions and methods for targeting cancer cells
The invention includes compositions and methods useful for treatment of a virus infection in a mammal by double-targeting the virus (i.e. targeting the virus at more than one stage of the virus life cycle) and thereby inhibiting virus replication. The compositions of the invention include compounds which comprise a phosphocholine moiety covalently conjugated with one or more antiviral agents (e.g. nucleoside analogue, protease inhibitor, etc.) to a lipid backbone. The invention also includes pharmaceutical compositions and kits for use in treatment of a virus infection in mammals. The methods of the invention comprise administering a compound of the invention, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a pharmaceutical composition of the invention, in an amount effective to treat the infection, to a mammal infected with a virus. Additionally, the invention includes compositions and methods useful for combating a cancer in a mammal and for facilitating delivery of a therapeutic agent to a mammalian cell. The compositions of the invention include compounds which comprise an alkyl lipid or phospholipid moiety covalently conjugated with an anticancer agent (e.g. a nucleoside analogue). The invention also includes pharmaceutical compositions and kits for combating a cancer and for facilitating delivery of a therapeutic agent to a mammalian cell. The methods of the invention comprise administering a compound of the invention, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a pharmaceutical composition of the invention, in an amount effective to combat a cancer or to facilitate delivery of a therapeutic agent to a mammalian cell.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV +1
Zwitterionic polymers with therapeutic moieties
ActiveUS20110319569A1RobustHigh yieldOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDrug deliveryRadical polymerization
The invention generally relates to zwitterionic polymers (including zwitterionic copolymers), such as polymethacrylic structures, with pendent functional moieties, such as therapeutic or biologic moieties. More particularly, the invention relates to phosphorylcholine-substituted methacrylic polymers prepared by free radical polymerization and click chemistry, for example, and compositions and products comprising same, as well as related methods and uses of the compositions, for example, as biological or therapeutic agents and in drug delivery thereof.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
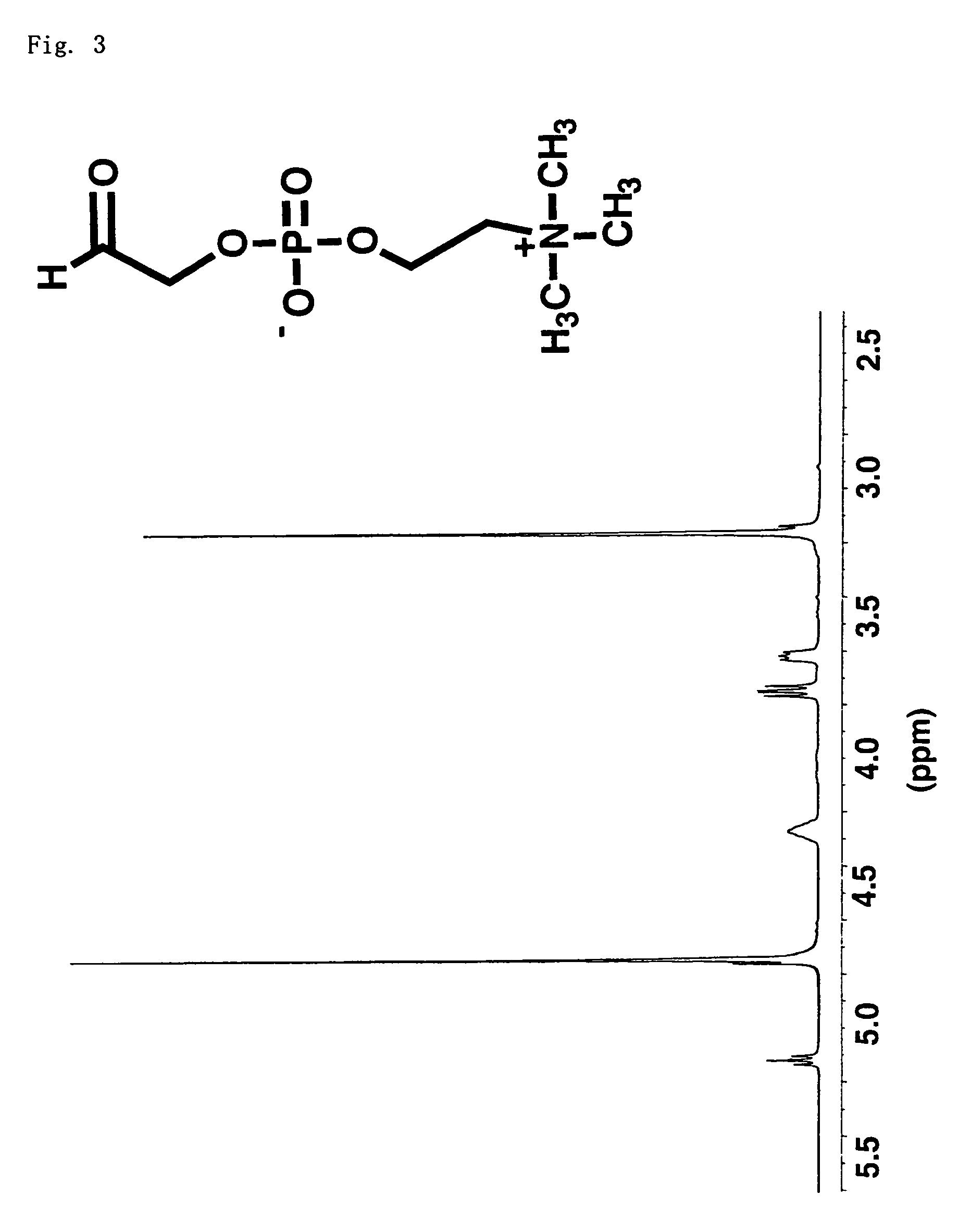
Polysaccharide containing phosphorylcholine group and process for producing the same
The present invention is a method for manufacturing a phosphorylcholine group-containing polysaccharide wherein the aldehyde derivative-containing compound obtained by the oxidative ring-opening reaction of glycerophosphorylcholine is added to a polysaccharide containing amino groups as well as a new polysaccharide having phosphorylcholine groups obtained from this manufacturing method.The object of the present invention is to provide a phosphorylcholine group-containing polysaccharide that is superior in biocompatibility and moisture retention, and is useful as a polymer material for medical use, as well as a simple method of manufacturing it.The polysaccharide of the present invention is utilized, for example, in artificial organs, biomembranes, coating agents for medical tools, drug delivery, and in cosmetics.
Owner:SHISEIDO CO LTD
High-biocompatibility phosphorylcholine-modified polyurethane material and prepration method thereof
The invention relates to a high-biocompatibility phosphorylcholine-modified polyurethane material and a preparation method thereof. The prepration method comprises the following steps that (1) a isocyanate group-terminated prepolymer is prepared, specifically, a hydroxyl-terminated prepolymer is blended with excess diisocyanate for reaction, and the isocyanate group-terminated prepolymer is obtained; and (2) phosphorylcholine-modified polyurethane is prepared, specifically, a propyl dimethicone phosphorylcholine compound is dissolved into a solvent, and dropwise added into the isocyanate group-terminated prepolymer, the isocyanate group-terminated prepolymer is subjected to a chain extension reaction, and the phosphorylcholine-modified polyurethane material is obtained. A membrane prepared through the material is excellent in mechanical property, side-chained phosphorylcholine groups can form a hydrophilic interface in an aqueous solution, and the absorbing capacity for protein in blood is low; and meanwhile, the material has biodegradability. The material can be applied to a living body for a long term as a tissue engineering repair stent material and the like, and degradation products at the later stage can be absorbed by the living body.
Owner:南通药享科技有限公司
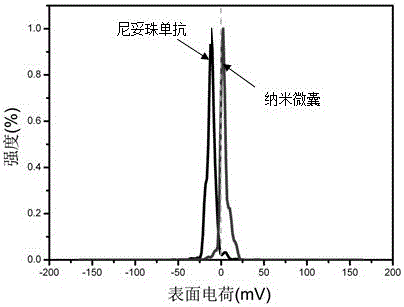
Poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) entrapped nimotuzumab nanocapsule, as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105663084AImprove the defects of low efficiencyAvoid side effectsAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulins2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholineCross-link
The invention discloses a poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) entrapped nimotuzumab nanocapsule, as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The nanocapsule is prepared by polymerizing poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) and nimotuzumab, has a smooth surface and a uniform grain size, and has a brain tumor targeting efficient delivery effect. The preparation method comprises the following steps: weighing 0.1-100mg of a nimotuzumab solution, and sequentially adding a monomer containing carbon-carbon double bond, a cross-linking agent and an initiator respectively according to the molar ratio of the nimotuzumab solution to the monomer containing carbon-carbon double bond, to the cross-linking agent and to the initiator being (1:100)-(1:100000), (1:100)-(1:10000), (1:100-1:10000); and preparing the nanocapsule by an in-situ polymerization method. The nanocapsule can be used for effectively inhibiting reproduction of glioma cells, and the curative effect of nimotuzumab for treating glioma cells can be improved.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
Compound having phosphorylcholine group, polymer thereof and process for producing the same
ActiveUS20060041160A1Easy to processGood biocompatibilityPhosphatide foodstuff compositionsPhosphorus organic compoundsPhosphorylcholinePhosphoric acid
A compound of the invention is a specific compound having a phosphorylcholine group, and a polymer of the invention comprises at least 1 mol % of repeating units with a phosphorylcholine group and has a number-average molecular weight of 1,000 or more, the repeating units with a phosphorylcholine group being represented by the formula (II): wherein A is a bond selected from a single bond, —O—, —COO—, —OOC—, —CONH—, —NH—, —NHCO—, —NR2— and —CH2O— where R2 is an alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms; and m is an integer of 1 to 12.
Owner:NOF CORP +1
Preparation method of di-bionic polymer
The invention discloses a preparation method of a di-bionic polymer. The preparation method comprises the following steps: I, preparing a phosphorylcholine polymer containing epoxy groups; and II, dissolving the phosphorylcholine polymer containing epoxy groups in a polar solvent to obtain a polymer solution; under protection of nitrogen, heating the polymer solution to 35-70 DEG C; then adding dopamine hydrochloride and an acid-binding agent into the polymer solution; carrying out grafting reaction under the insulating and stirring condition; after reaction, dialyzing the reaction product in a dialyzing bag by using an aqueous hydrochloric acid solution with the pH value of 3-4; and finally, freeze-drying the dialyzed reaction product to obtain the di-bionic polymer. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple in method, mild in condition and high in grafting rate of dopamine, the molar ratio of dopamine groups in the prepared di-bionic polymer is greater than 10%, and the di-bionic polymer is strong in adhesive force and hard to fall.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com