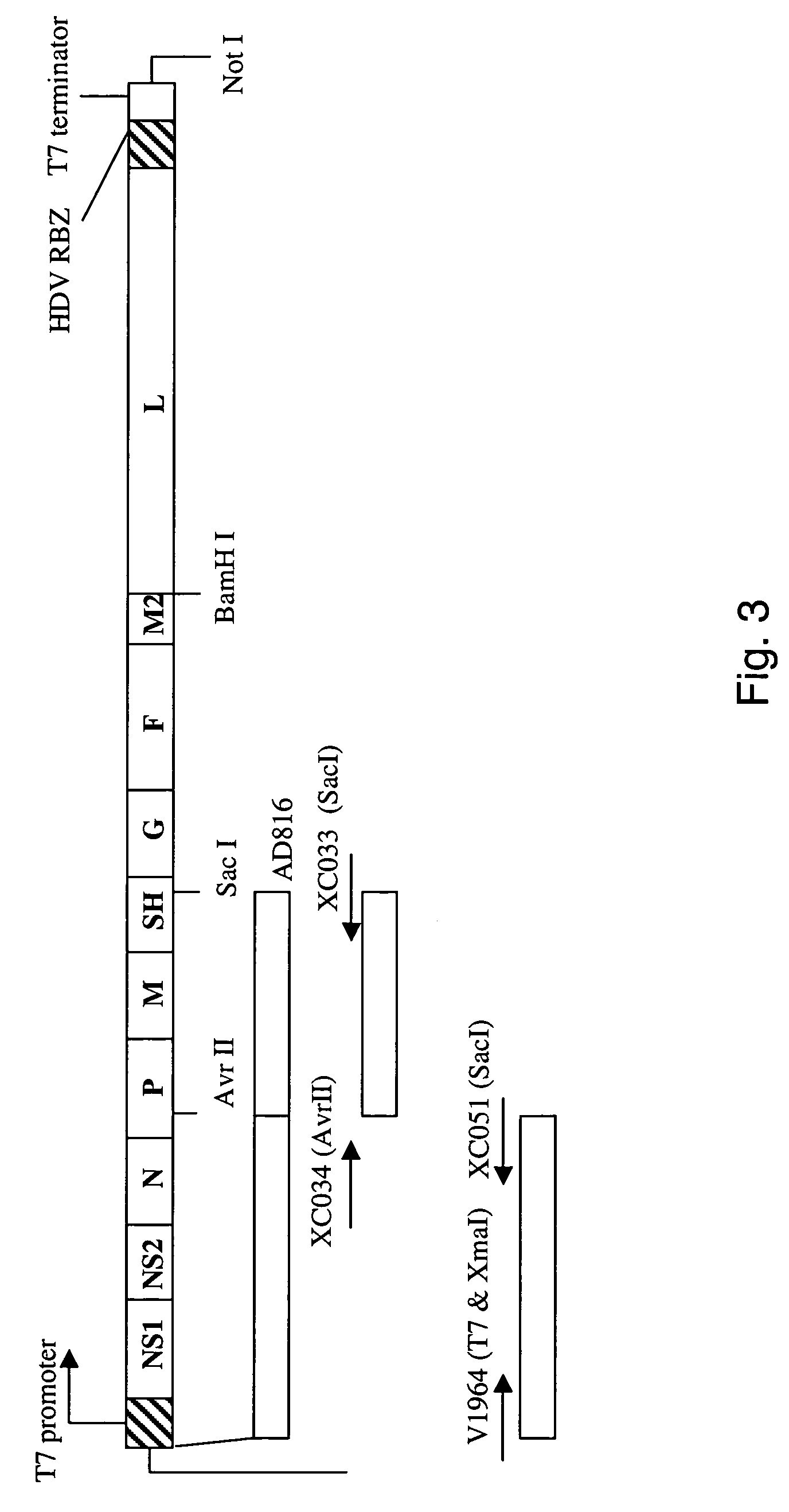
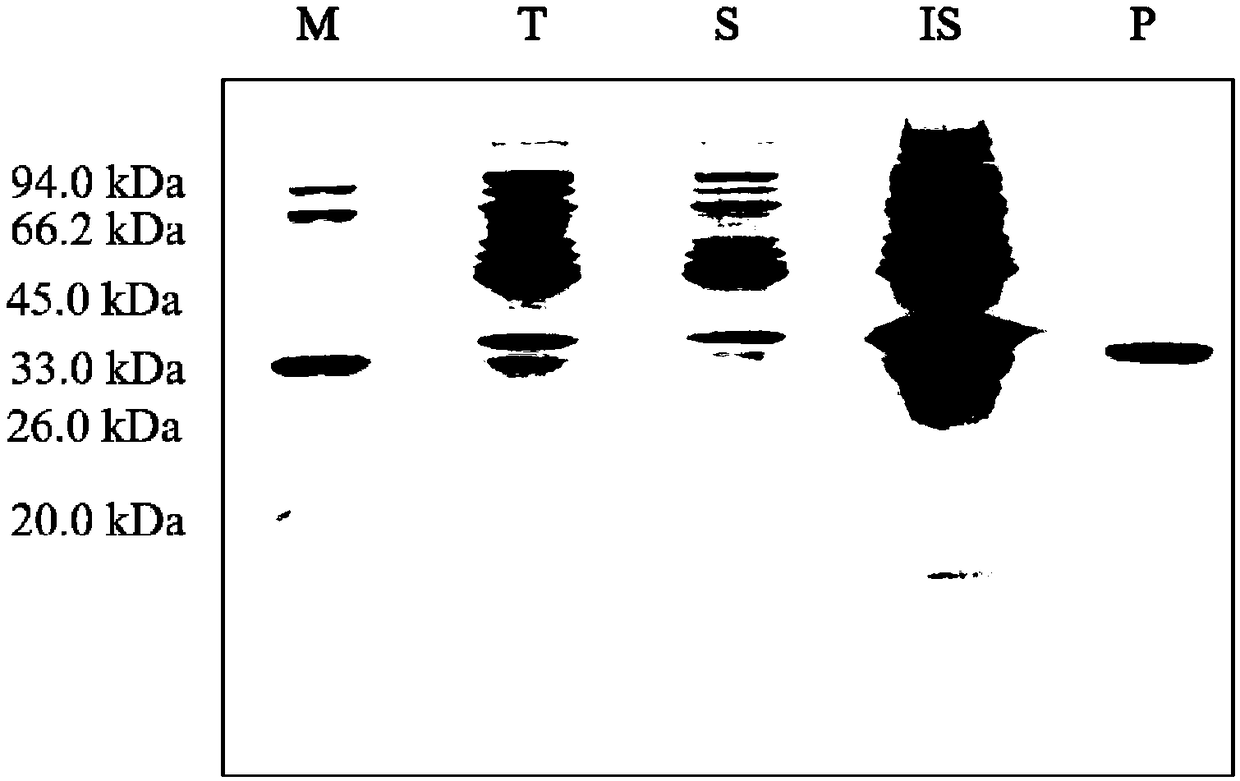
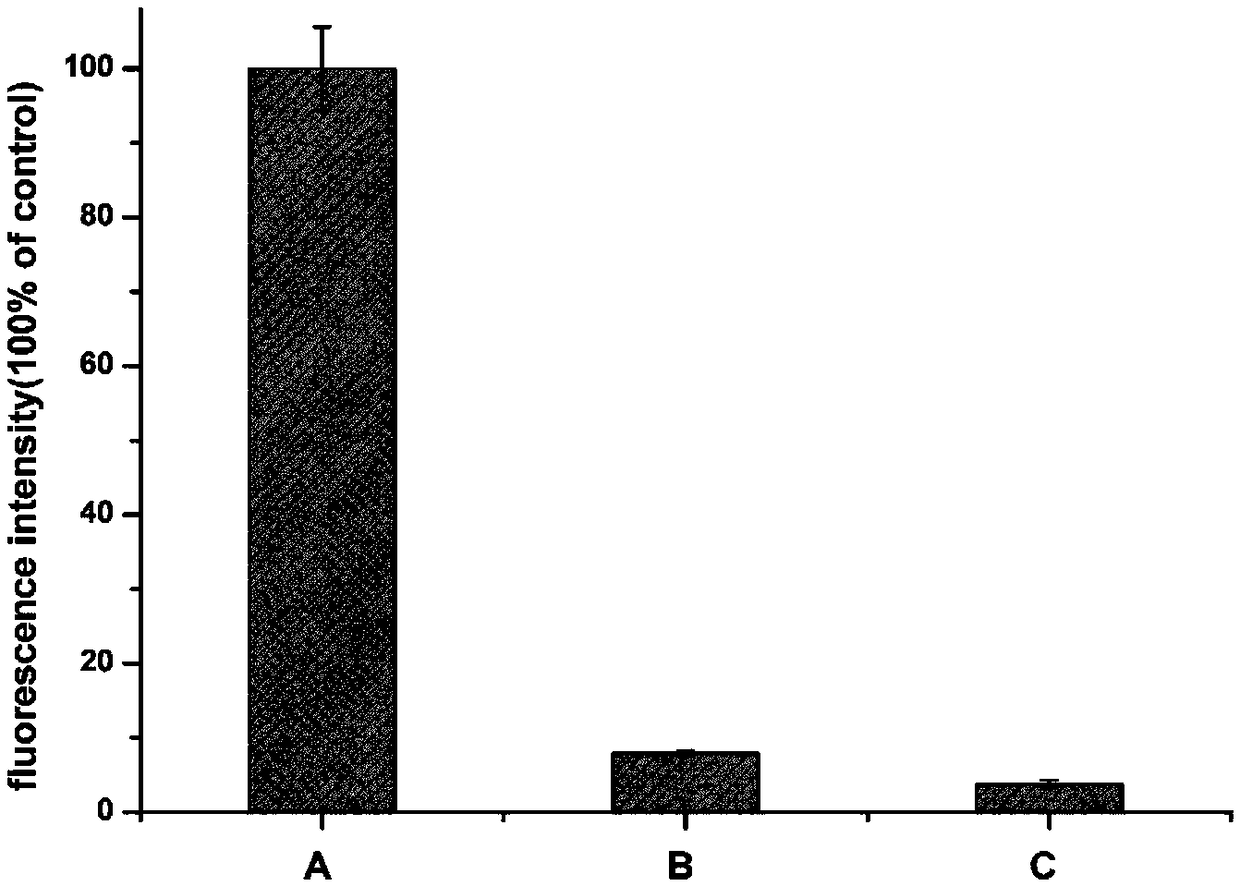
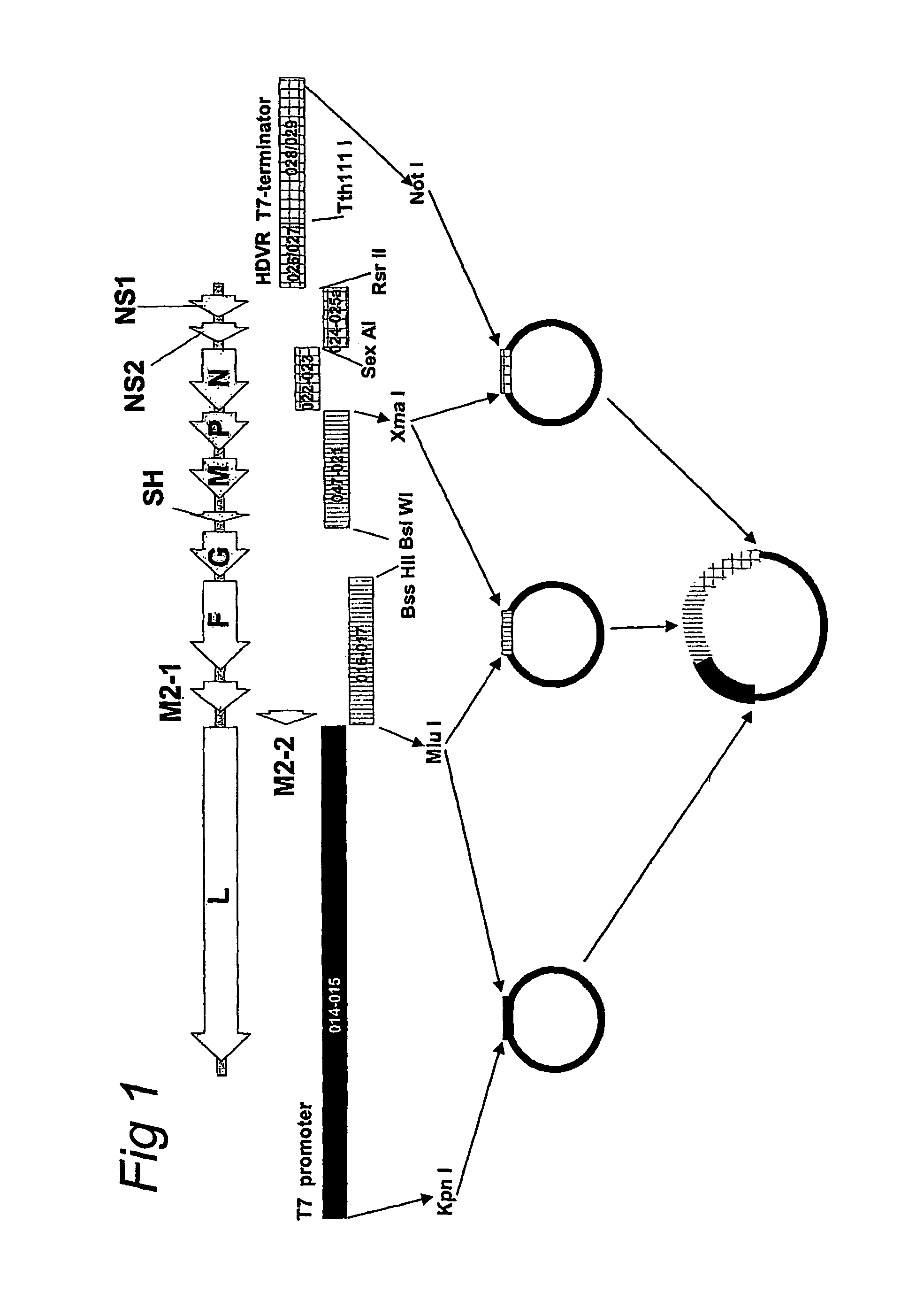
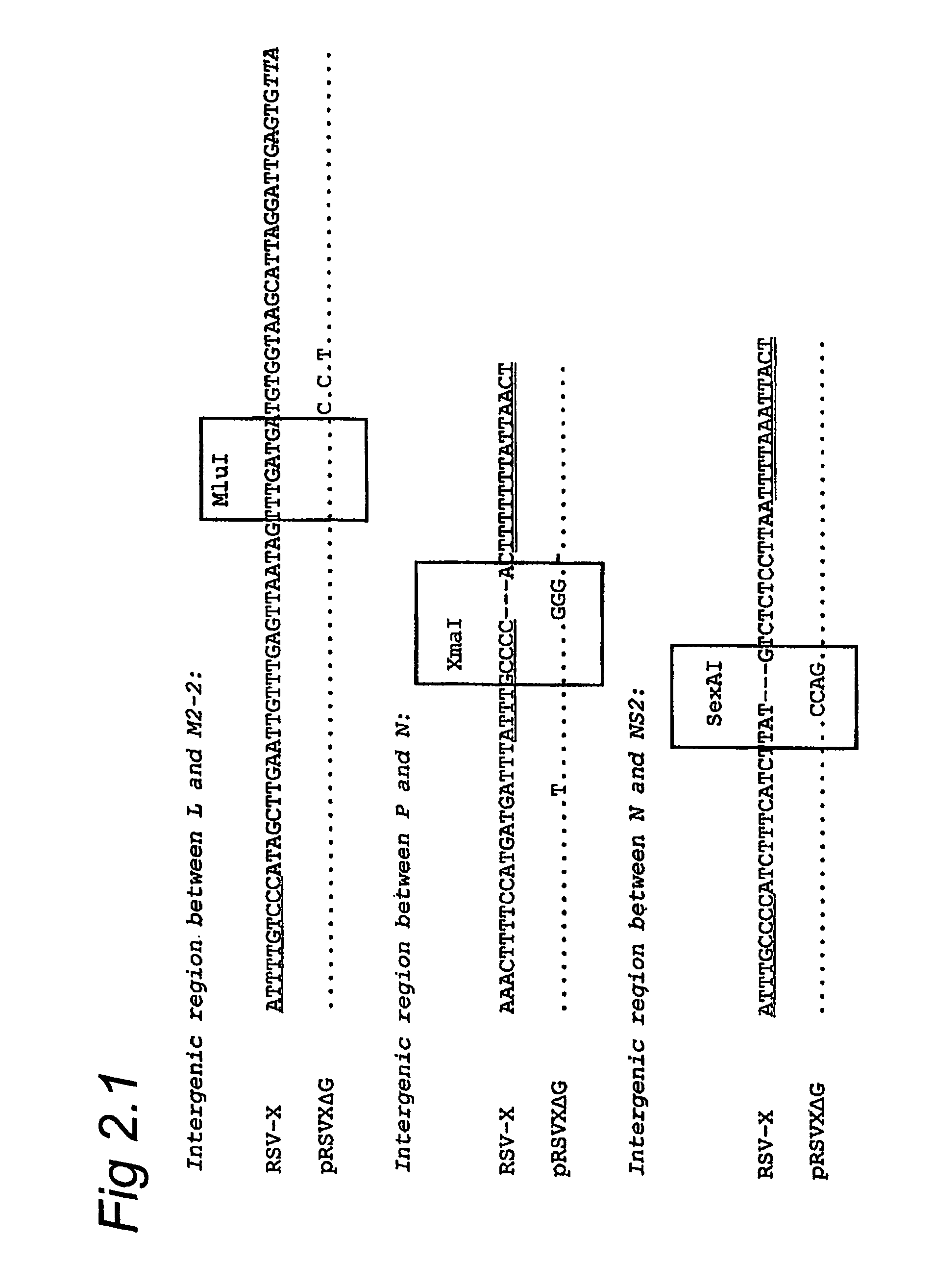
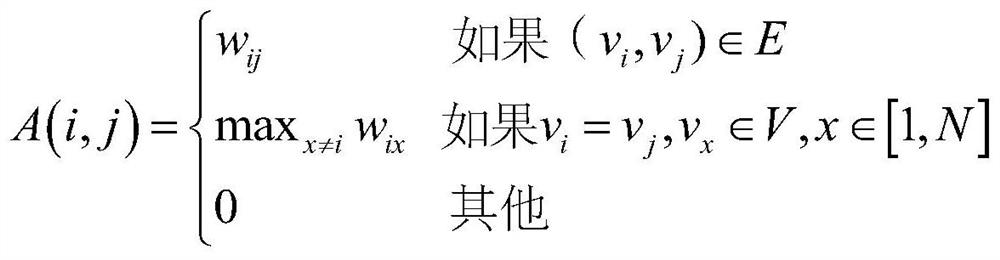
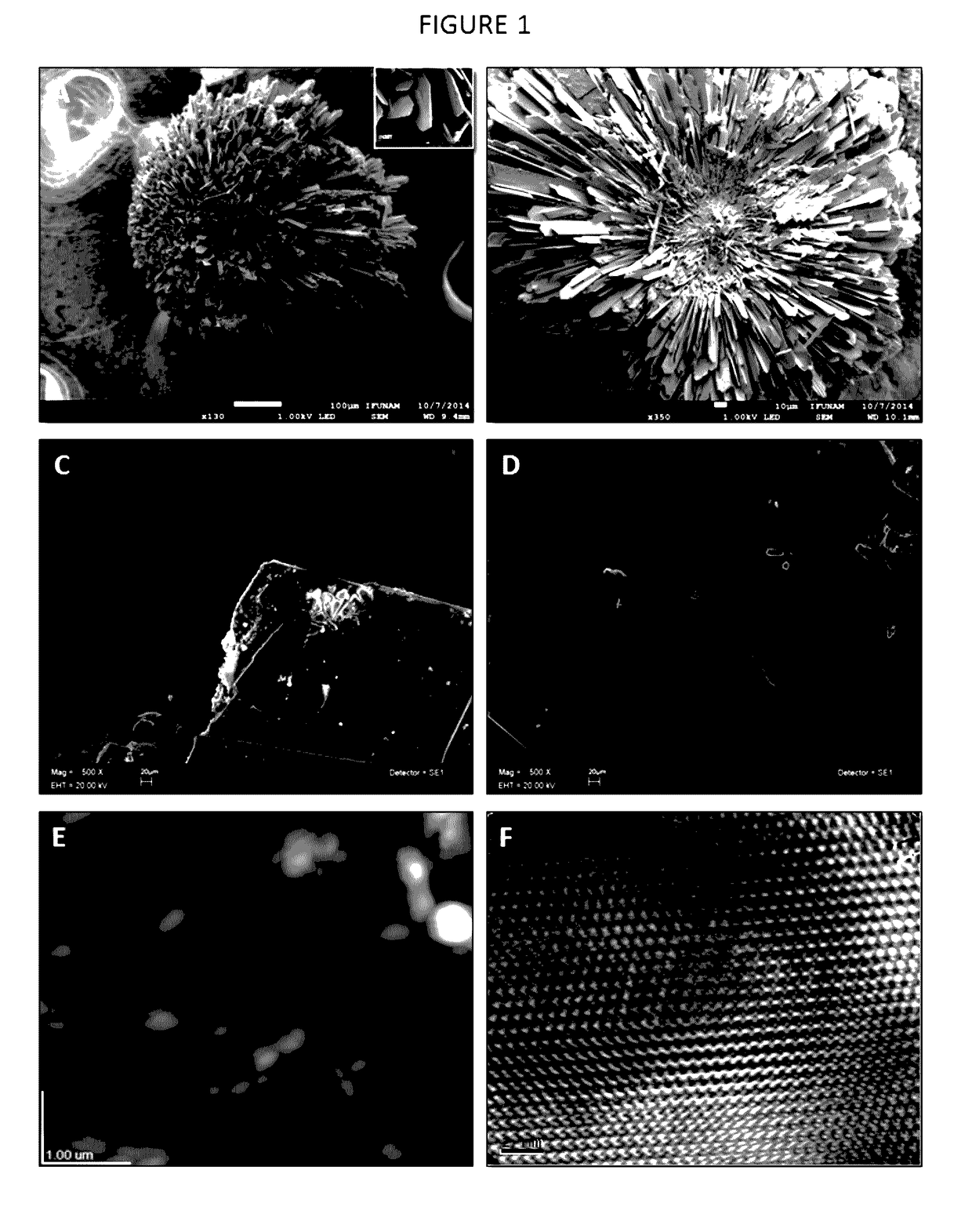
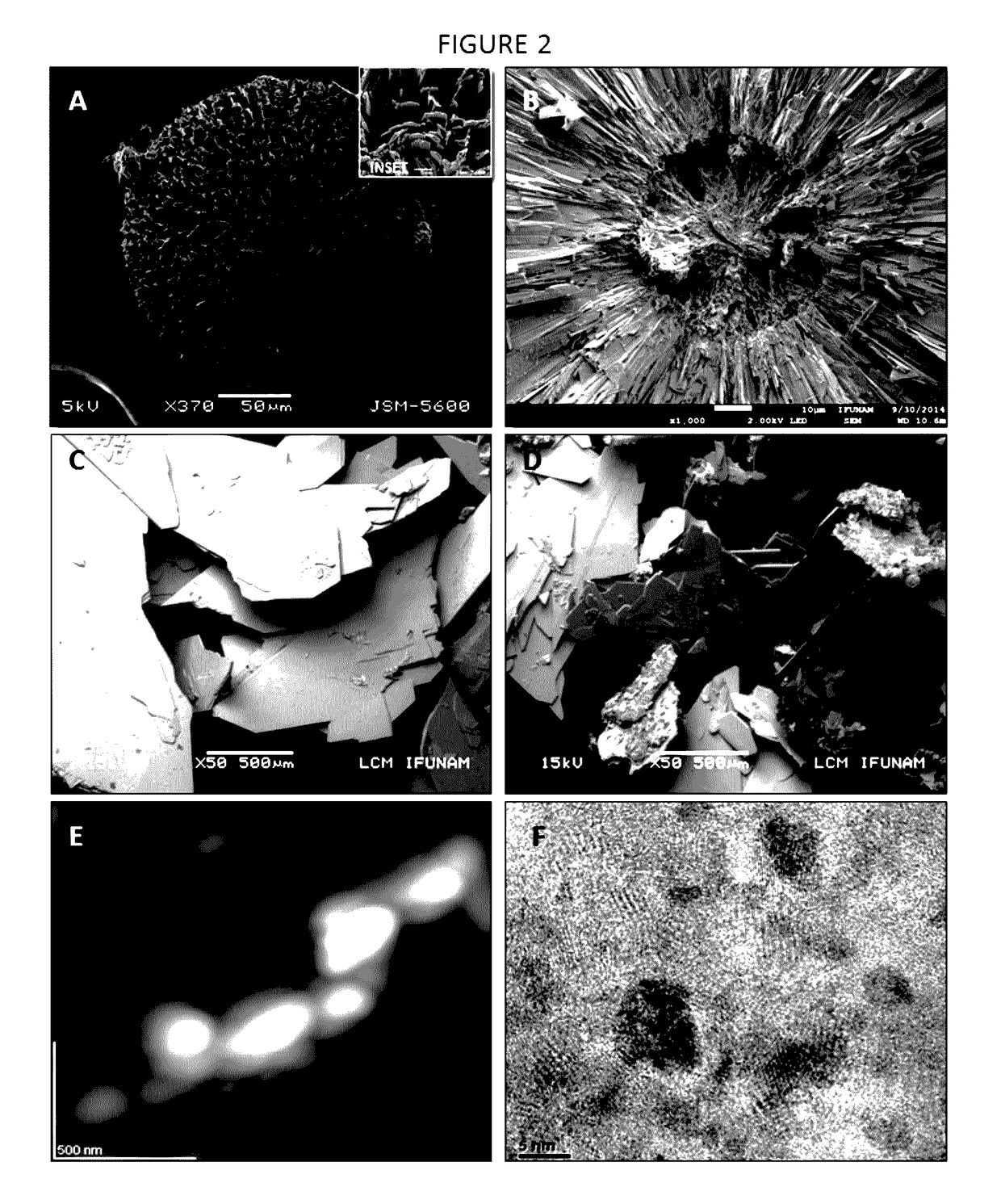
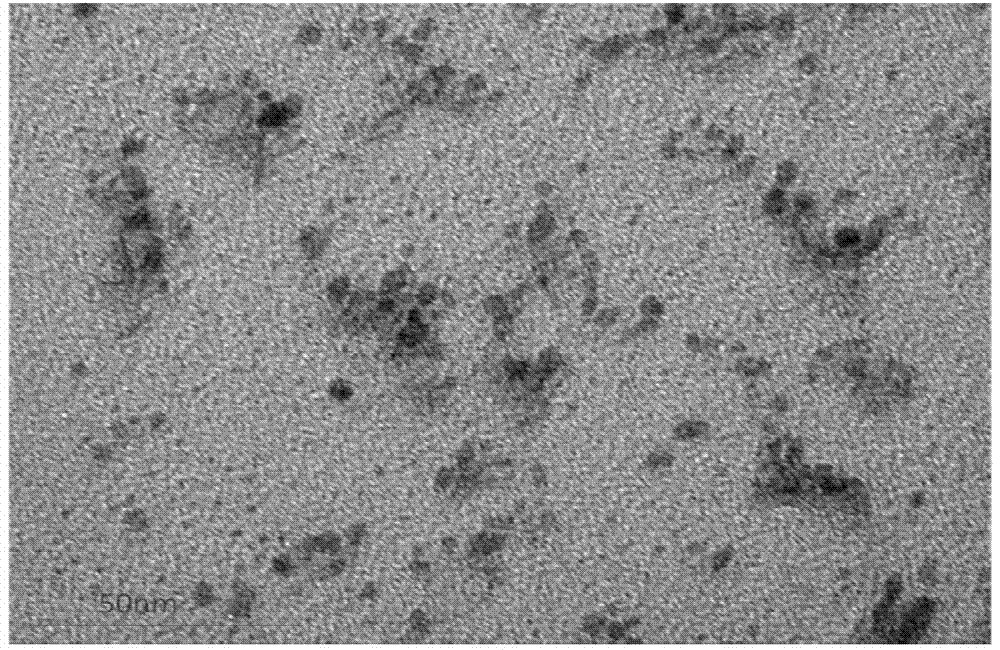
Patents
Literature
40 results about "Attachment protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Attachment proteins can attach the cell to other cells or to other extracellular molecules. Transport proteins allow molecules that are too big or that have a charge to enter into the membrane since only small and uncharged molecules can get through the membrane without the aid of transport proteins.
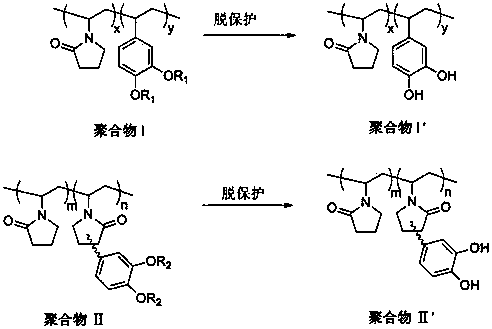
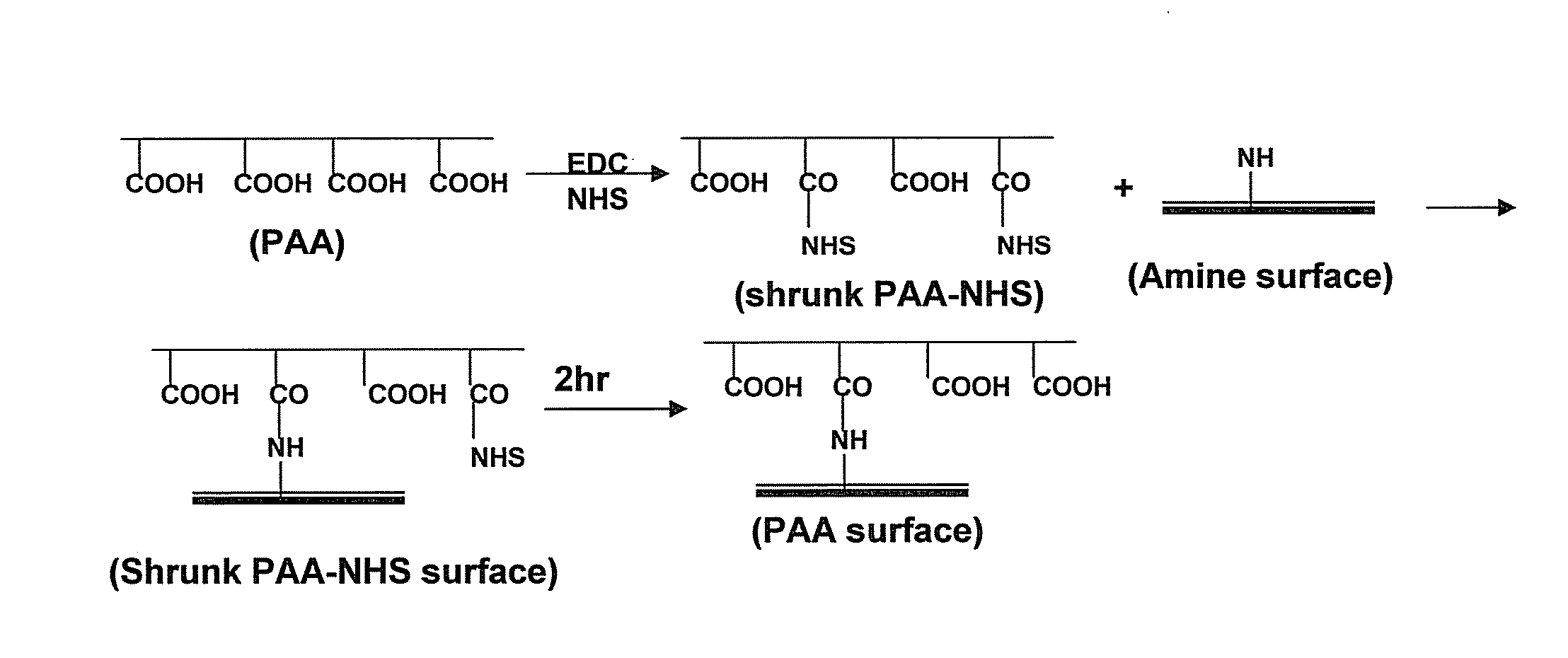
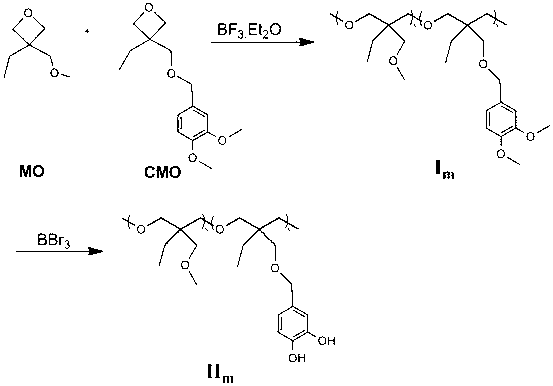
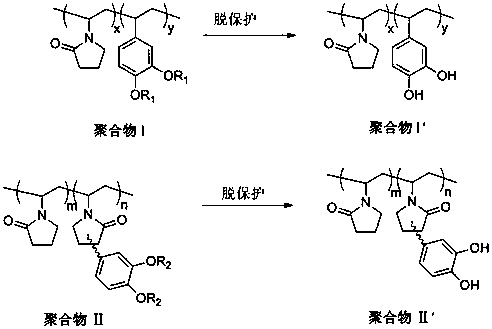
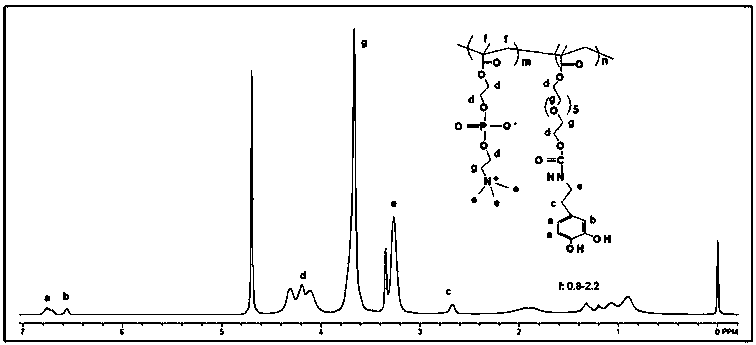
Imitation mussel attachment protein and cell membrane structure copolymer and preparation method and application thereof
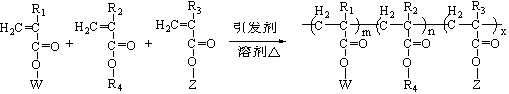
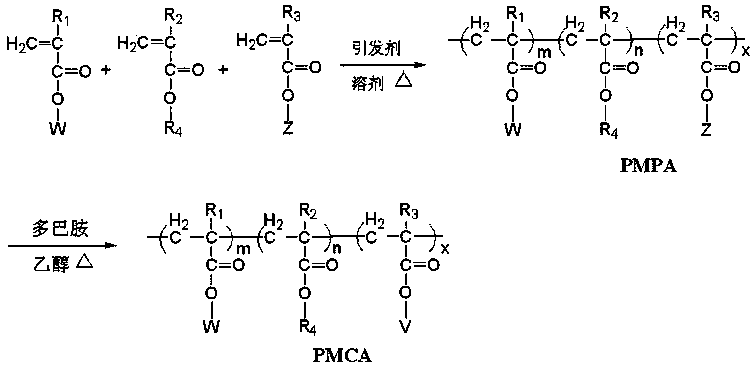
The invention discloses an imitation mussel attachment protein and cell membrane structure double-bionic copolymer shown by the structural formula (I), wherein m is an integer from 10 to 1,000, n is an integer from 0 to 500, and x is an integer from 5 to 500; in the m, n and x, the molar percentage of m is 30-90%, the molar percentage of n is 0-50%, and the molar percentage of x is 10-70%; R1, R2 and R3 are H or CH3; R4 is an alkyl with 4-18 carbon atoms; V is a catechol group with 2-300 carbon atoms in chain connection; W is a hydrophilic group with 2-8 carbon atoms in chain connection; and the hydrophilic group is a quaternary ammonium group, phosphorylcholine group, pyridinium, sulfonic acid group, phosphate group, carboxylic acid group or sulfuric acid group. According to the invention, the coating is in firm combination, the copolymer is almost suitable for an establishment method of a surface imitation cellulosa membrane structure of any material, and the surface hydrophilic performance and biocompatibility of artificial organ and related materials, medicine controlled-release systems, separation materials and other materials can be improved.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Preparation method for biomimetic mussel adhesive used for adhesion on wet surface and underwater curing
InactiveCN103965810AEfficient synthesisImprove bindingNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesPolymer scienceAttachment protein
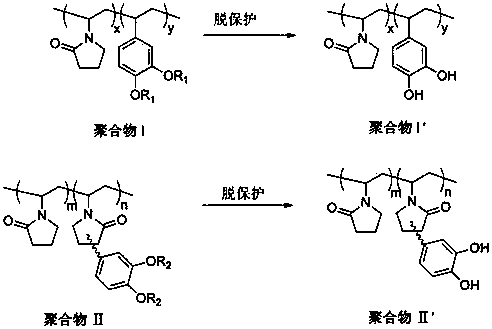
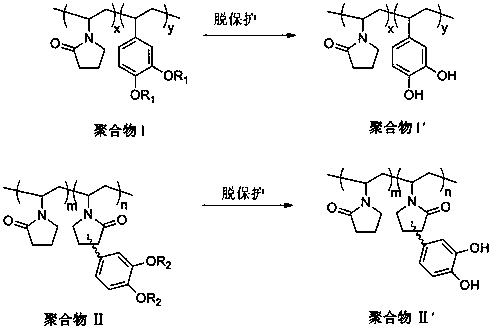
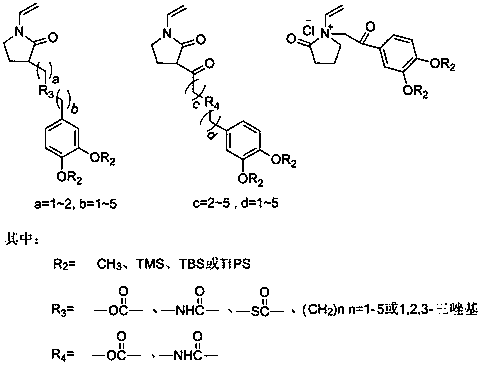
The invention relates to a preparation method for a biomimetic mussel adhesive used for adhesion on a wet surface and underwater curing. The method is characterized in that the biomimetic mussel adhesive is composed of two components including A and B, wherein the component A is a methanol solution of a polymer containing catechol groups; the polymer containing catechol groups is obtained in the manner that N-vinyl pyrrolidone and a polymerizable catechol derivative monomer are subjected to free radical polymerization and further subjected to deprotection; the component B is a crosslinking curing agent. The method has the advantages as follows: 1, the synthetic method is simple and efficient, raw material and reagents used in the reaction process are low in price and easy to get, and amplification in the operation process and industrial production are facilitated; 2, the biomimetic mussel adhesive has certain biocompatibility and initial adhesion performance, can be used for adhesion on the wet surface and underwater curing, and has the bonding strength being over 1 MPa, so as to be applied to adhesion of human tissue and adhesion in the wet environment of commonly-used base material as well as adhesion under the water. According to the invention, perfect combination between synthetic macromolecule and natural mussel attachment proteins is successfully realized, the technical bottleneck about the current biomimetic mussel adhesive is expected to break through, and meanwhile, a new approach for shellfish-based development of biomimetic high polymer material is provided.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
A polymer film material and a preparation method thereof
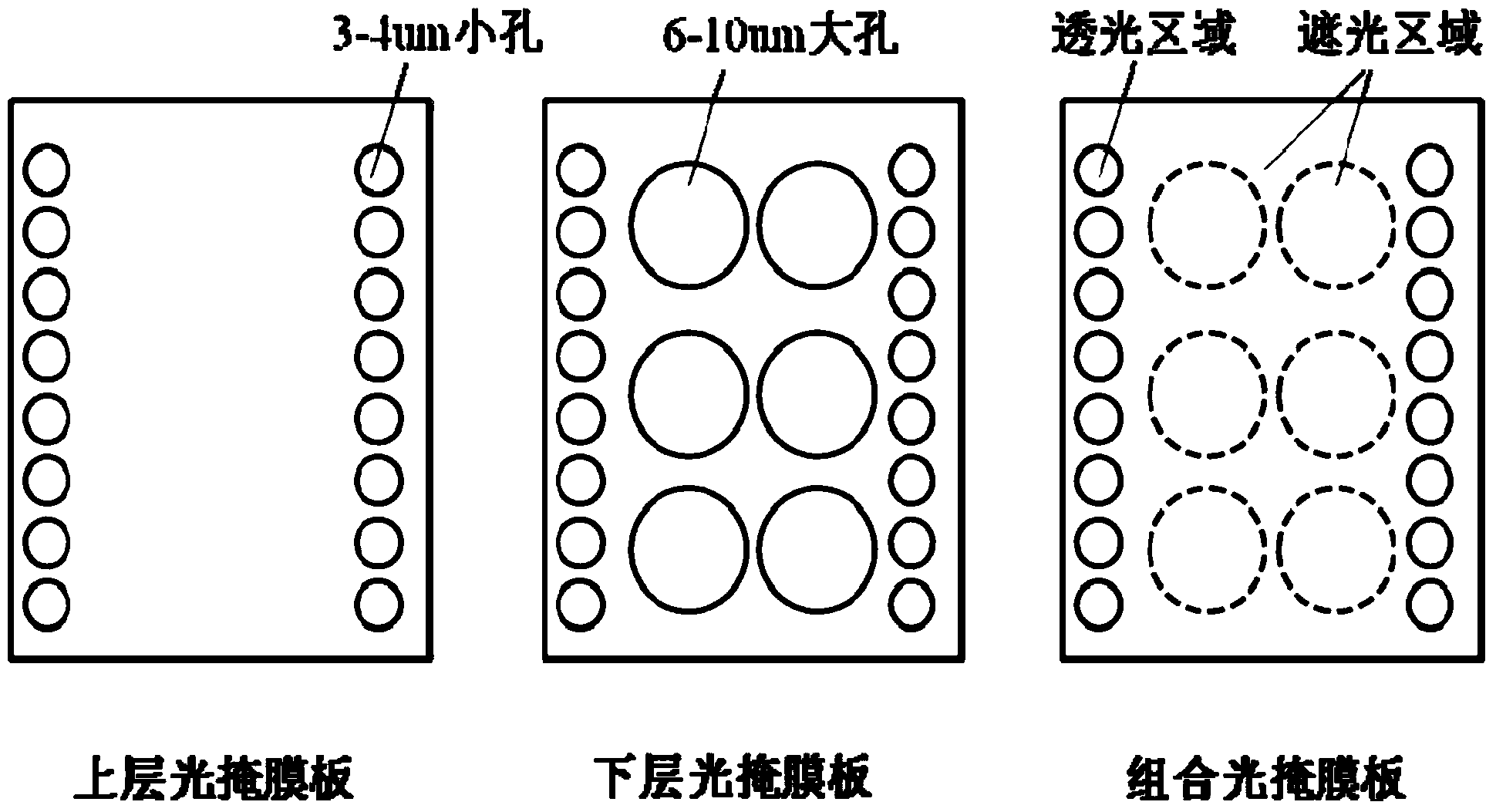
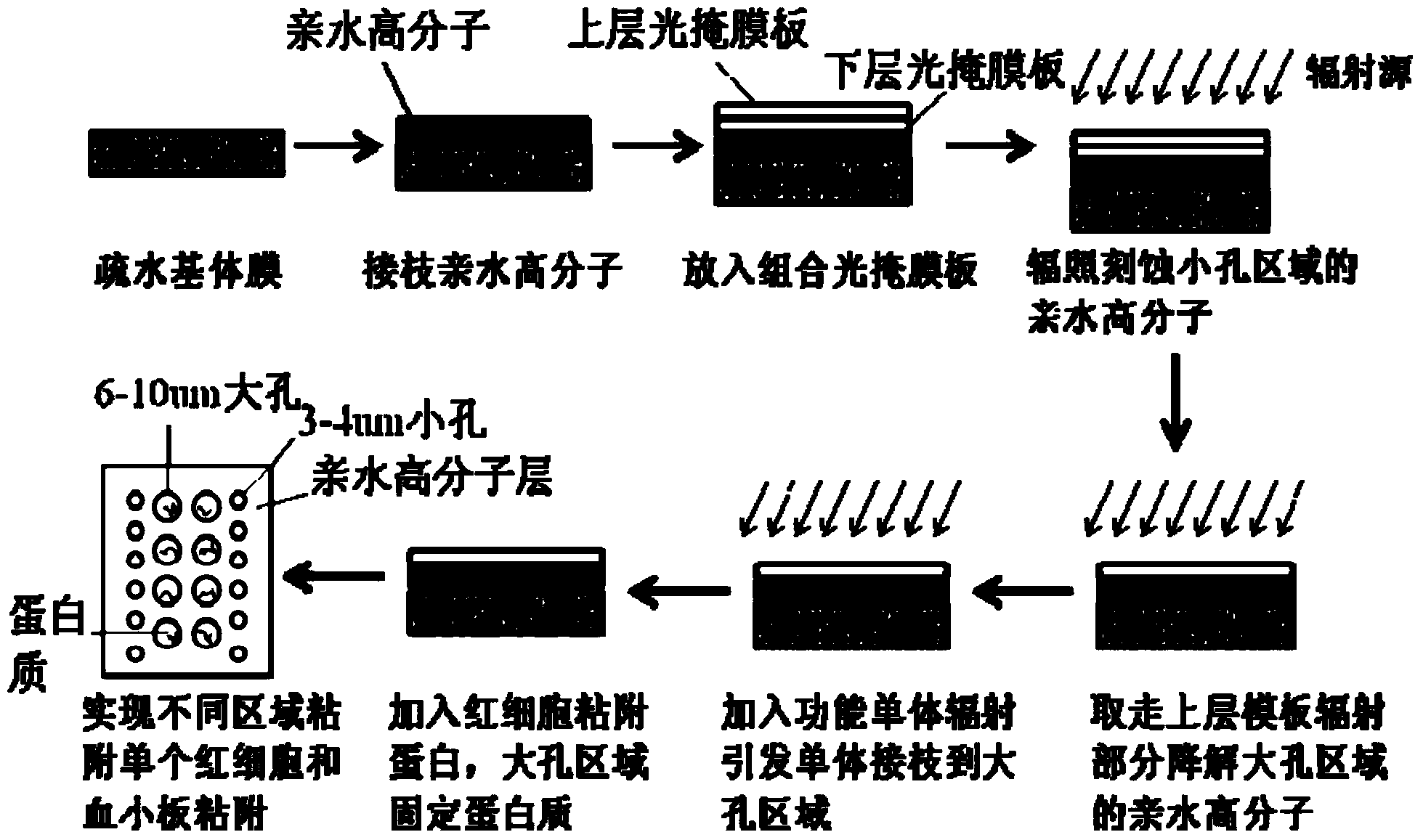
ActiveCN103816816AAchieve adhesionStrong adhesionSemi-permeable membranesFunctional monomerAttachment protein
The invention provides a polymer film material and a preparation method thereof. The polymer film material comprises a hydrophobic polymer layer and a hydrophilic polymer layer. The hydrophilic polymer layer is provided with a hydrophilic adhesive area provided with a functional material fixed to fibronectin. The hydrophilic polymer layer is provided with through holes. The through holes and the hydrophobic polymer layer form a hydrophobic adhesive area. The functional material is a functional monomer or a polymer of the functional monomer. A method of adopting combination of surface grafting and controlled irradiation by utilizing a photomask is adopted, the hydrophilic adhesive area and the hydrophobic adhesive area are formed on the surface of the polymer film and erythrocyte attachment proteins are bonded in the hydrophilic adhesive area, thus obtaining the polymer film material used for separating a single erythrocyte and a single blood platelet from blood.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-density polymer surface coating to immobilize chemical or biological molecules
InactiveUS20120101230A1Peptide preparation methodsMaterial analysisHigh densityComputational chemistry
A method for providing high-density polymer surface for attaching proteins or peptides, and binding proteins, peptides, DNAs, cells, small molecules, and other chemical or biological molecules that are of interests in the areas of proteomic, genomic, pharmaceutical, drug discovery, and diagnostic studies.
Owner:X BODY
Preparation method of biomimetic mussel adhesive based on synthesis of oxetane derivatives
InactiveCN103289074AEfficient synthesisAchieve the perfect combinationPolyether adhesivesPolymer dissolutionPolymer science
The invention relates to a preparation method of a biomimetic mussel adhesive based on the synthesis of oxetane derivatives. The preparation method comprises the following main steps: preparing a phenolic hydroxy protected polymer with a catechol side-chain structure through ring-opening copolymerization of two oxetane derivative monomers; carrying out deprotection on the polymer so as to obtain a catechol structure containing polymer; and after the catechol structure containing polymer is dissolved, adding a certain amount of a crosslinking agent into the polymer, and uniformly mixing so as to obtain the biomimetic mussel adhesive. The method has the characteristics that: 1) the synthesis method is simple and efficient, and raw materials and reagents used in the process of reaction are cheap and easily available, thereby facilitating the amplification of an operating process and industrial production; and 2) the bonding strength is over 5 MPa, so that an effect that a synthetic polymer simulates the attachment protein properties of natural mussels is successfully achieved, and a purpose of integrating certain biocompatibility and high adhesion strength is reached; therefore, the method provides is a novel synthesis technique of biomimetic mussel adhesives and provides a new way for developing novel bionic polymer materials based on the effective protein components of shellfish.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Nucleic acids encoding respiratory syncytial virus subgroup B strain 9320
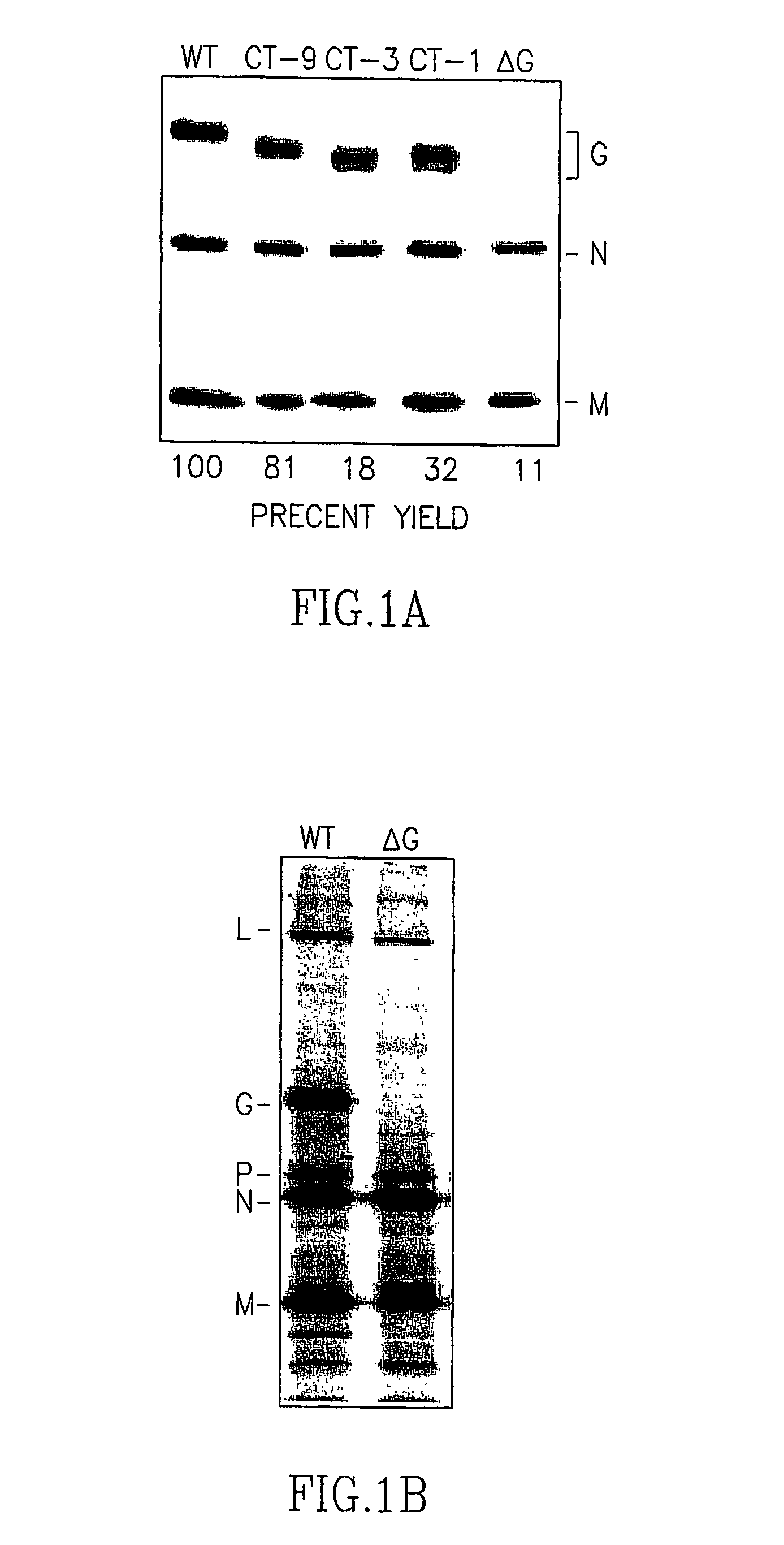
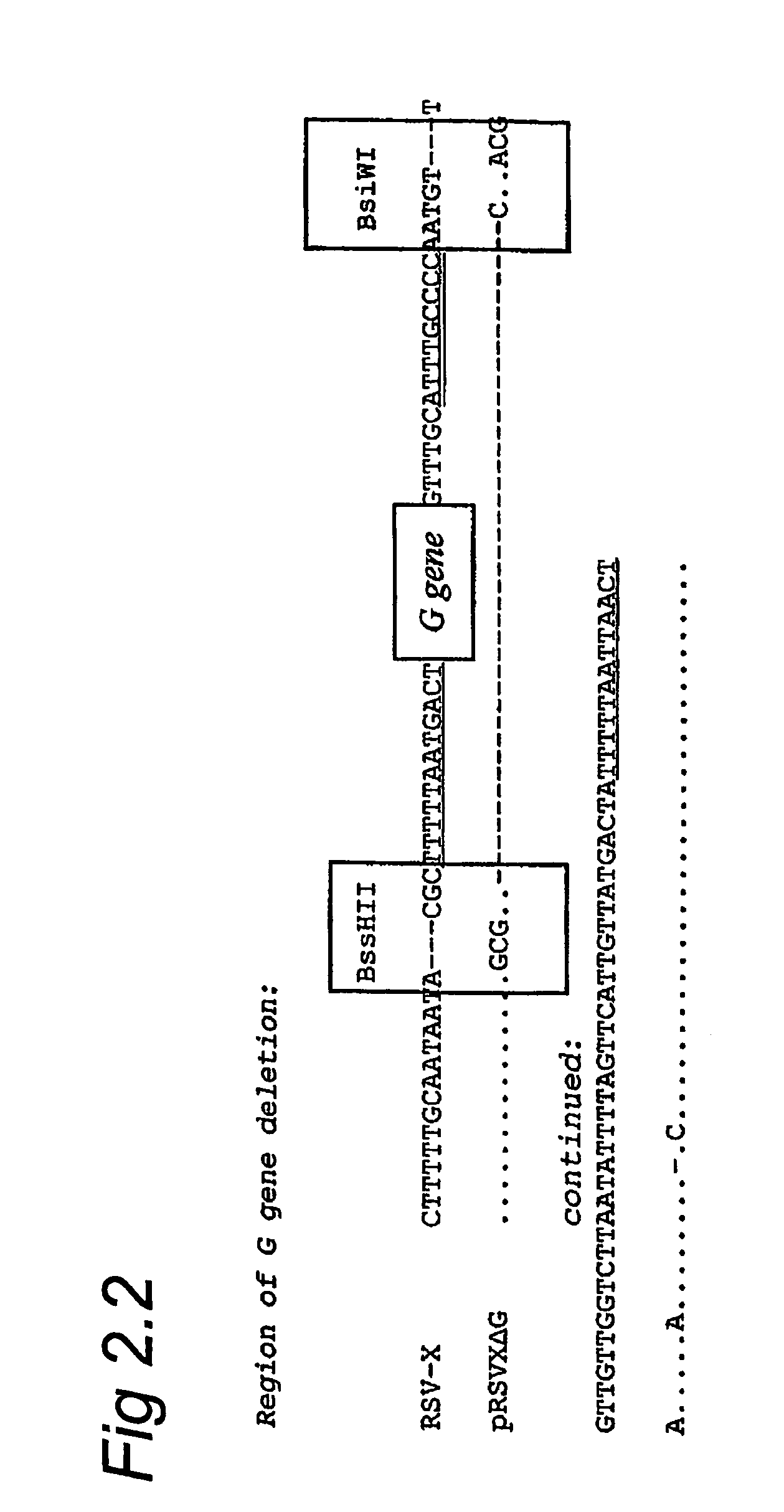
ActiveUS7572904B2SsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesAttachment proteinRespiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
The complete polynucleotide sequence of the human respiratory syncytial virus subgroup B strain 9320 genome is provided. Proteins encoded by this polynucleotide sequence are also provided. Isolated or recombinant RSV (e.g., attenuated recombinant RSV), nucleic acids, and polypeptides, e.g., comprising mutations in the attachment protein G, are also provided, as are immunogenic compositions comprising such isolated or recombinant RSV, nucleic acids, and polypeptides. Related methods are also described.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
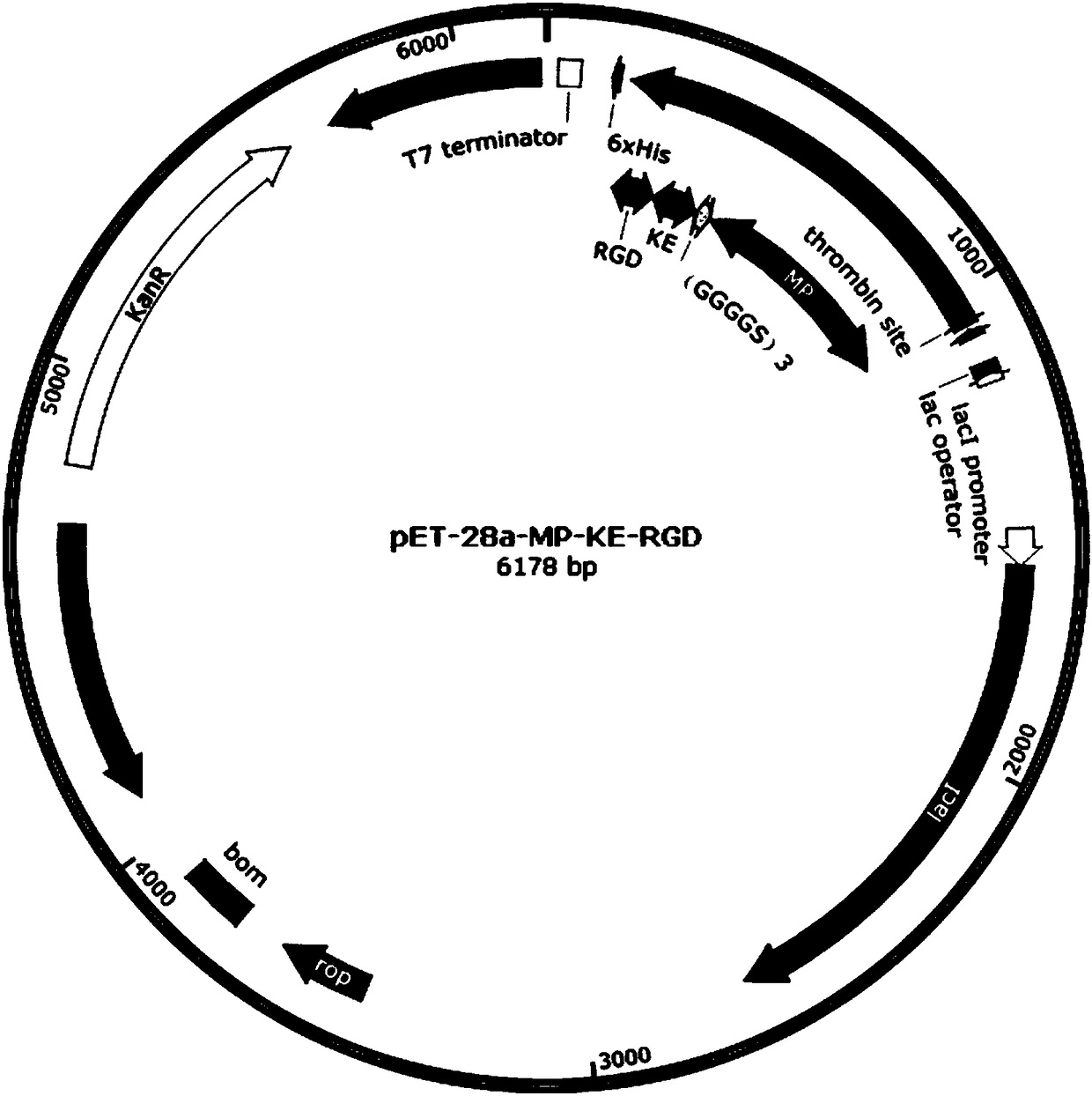
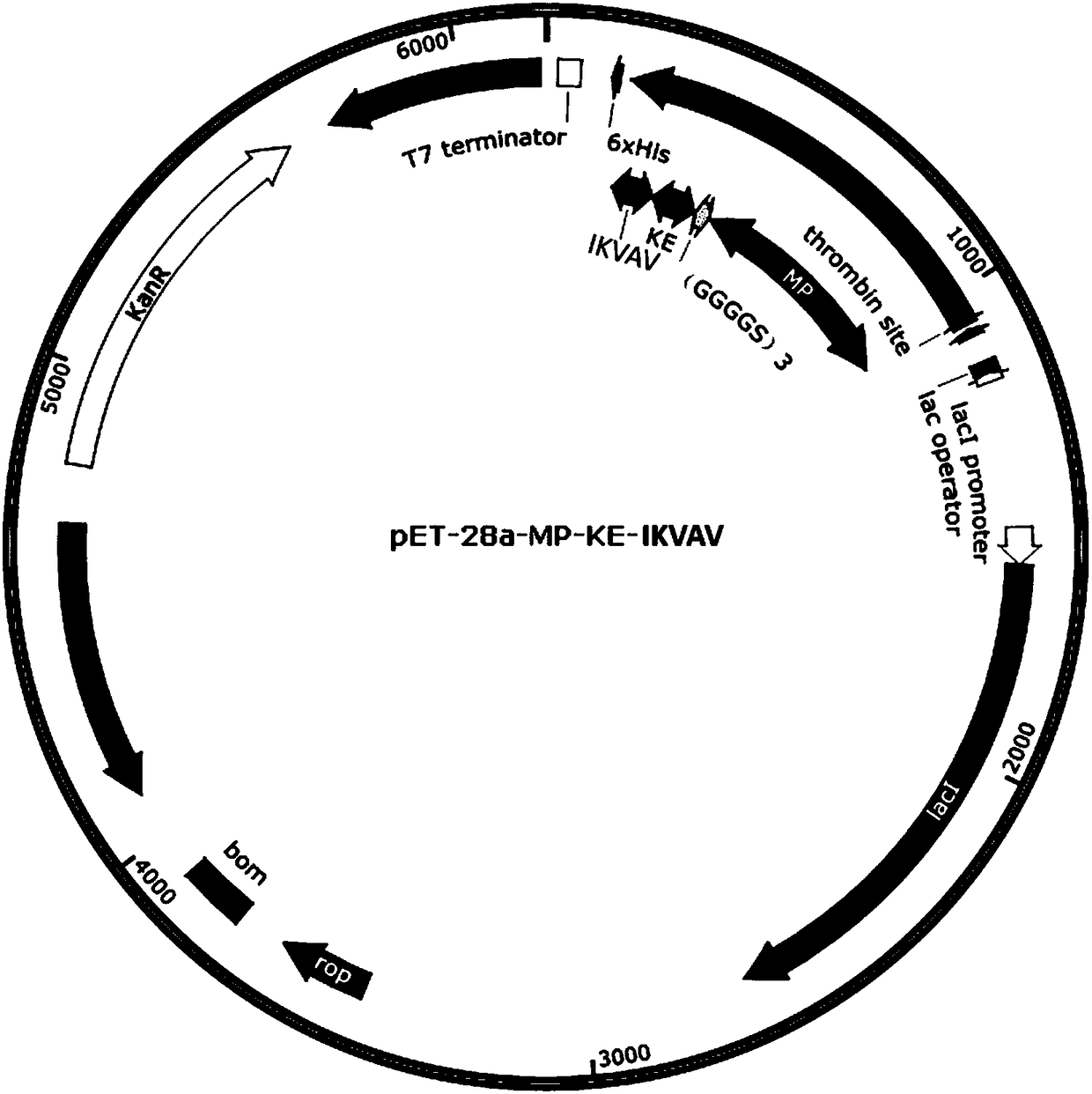
Synthesis method and application of triblock multifunctional fused protein based on mussel attachment protein/zwitter-ion polypeptide
InactiveCN108395483AAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleic acid vectorAttachment proteinSynthesis methods
The invention relates a synthesis method and application of triblock multifunctional fused protein based on mussel attachment protein / zwitter-ion polypeptide. The synthesis method comprises the following steps: cloning a gene of the fused protein to a plasmid vector to obtain a recombinant expression plasmid; after transforming host cells, inducing the host cells by utilizing an induction agent, so as to overexpress the fused protein; after separating and purifying, obtain the fused protein. The mussel attachment protein contains a sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 1, SEQ ID NO. 2, SEQ ID NO. 3, SEQ ID NO. 4, or SEQ ID NO. 5. The zwitter-ion polypeptide contains a sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 6, SEQ ID NO. 7, SEQ ID NO. 8 or SEQ ID NO. 9. Triblock polypeptide contains a sequence shown as SEQ IDNO. 10 (RGD short peptide), SEQ ID NO. 11 (SDE tripeptide), SEQ ID NO. 12 (IKVAV short peptide) or SEQ ID NO. 13 (RADA16-I self-assembled polypeptide). The fused protein is synthesized through microorganisms through a one-step method; the synthesis method has the advantages of moderate and efficient process, low cost and low requirements on equipment and later-period expanded production is facilitated.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
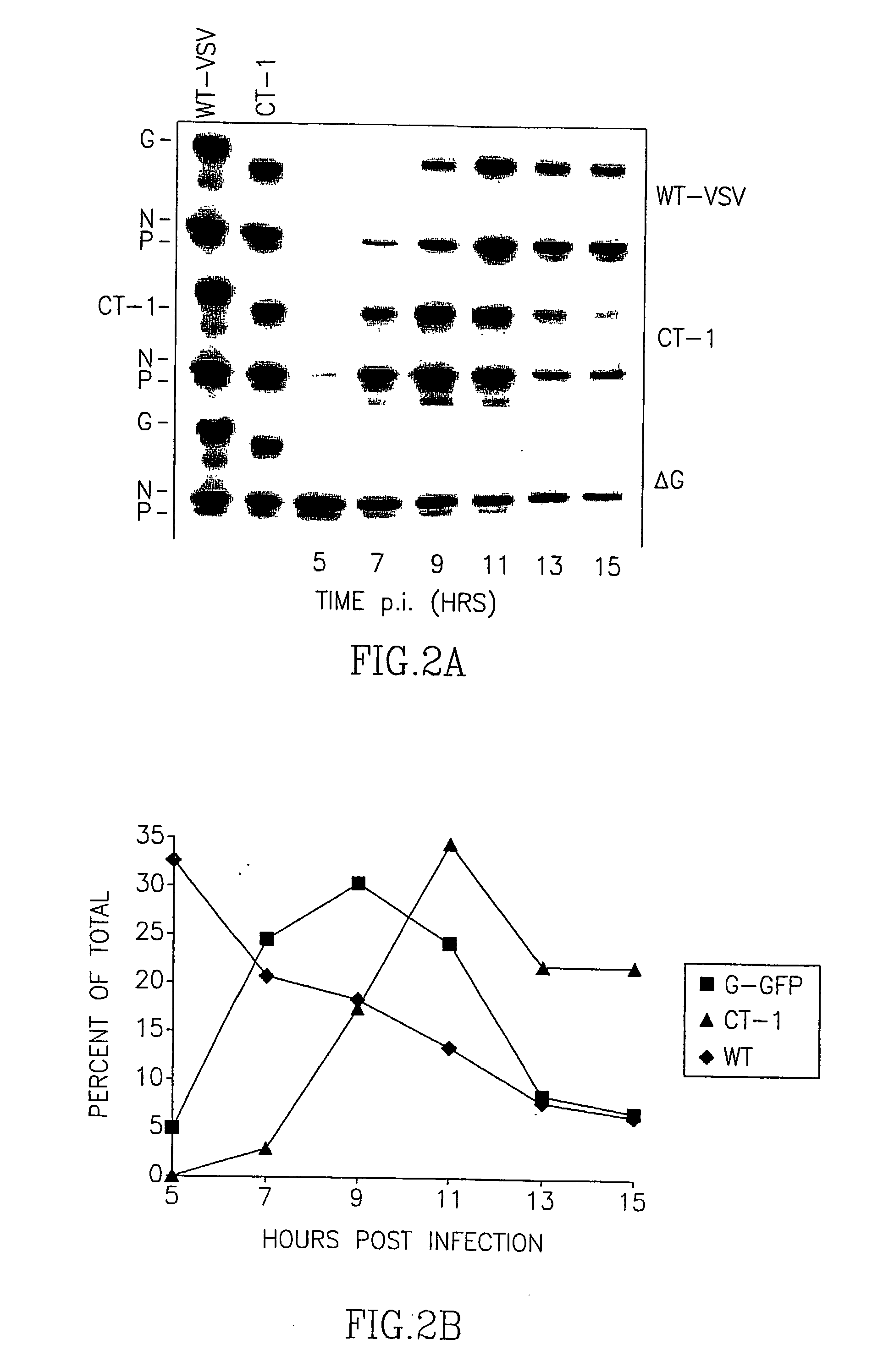
Recombinant Rhabdovirus containing a heterologous fusion protein
InactiveUS20030138457A1Easy to integrateOvercome limitationsSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeterologousAttachment protein
This invention relates to a composition comprising a recombinant or genetically engineered Rhabdovirus that expresses a Fusion Protein, such as the F protein of the Paramyxovirus SV5 strain. This recombinant Rhabdovirus may express other non-Rhabdovirus attachment proteins and / or an enhancer protein. The invention also relates to methods of making recombinant Rhabdoviruses which express an F Protein. These recombinant compositions can be used for purposes of research, as well as for diagnostic and therapeutic compositions for treatment of diseases.
Owner:TENNESSEE RESEARCH CORPORATION
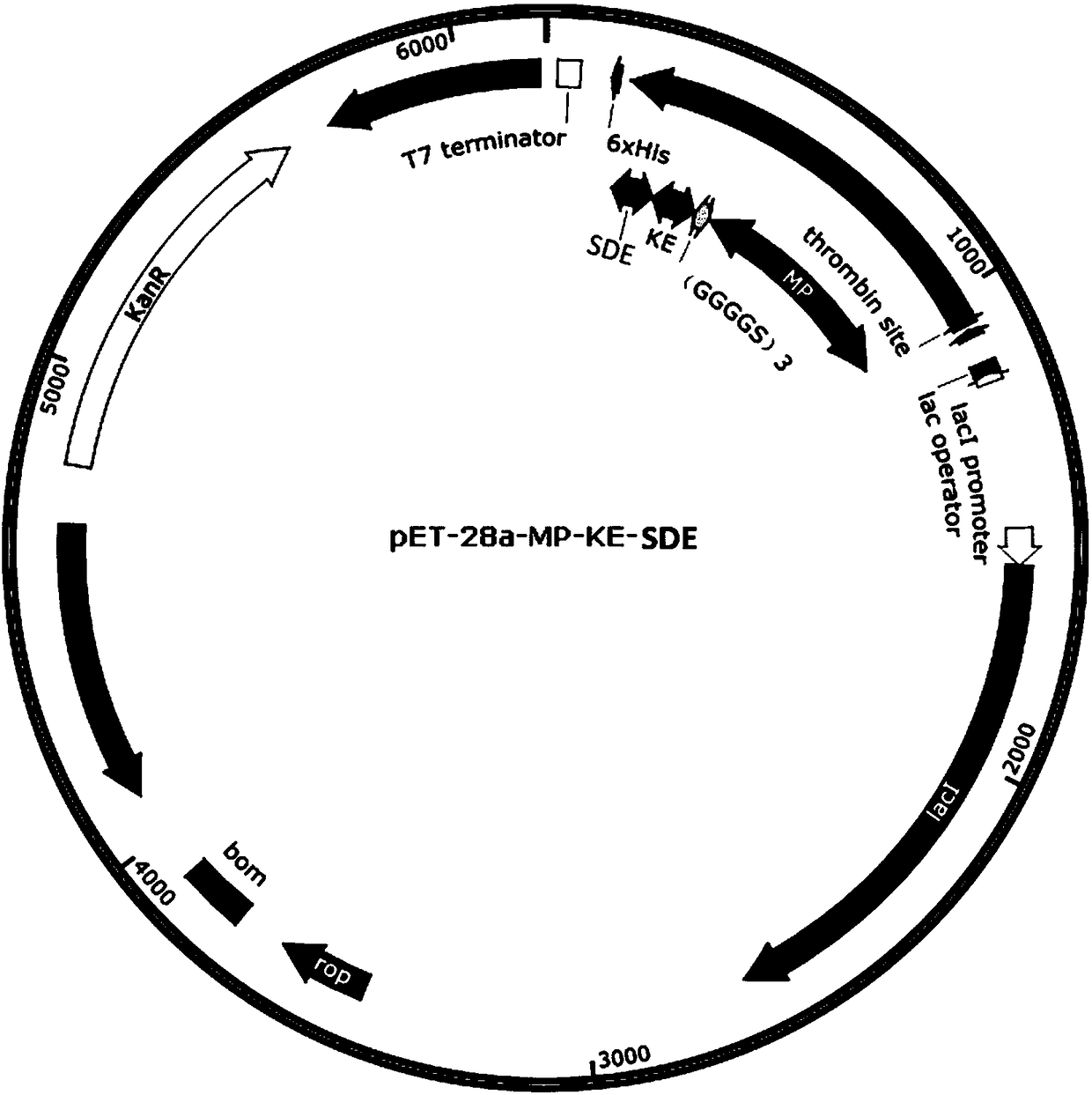
Mussel attachment protein/amphoteric ion polypeptide fusion protein with attachment-anti-staining dual functions and synthesis method
InactiveCN108503712AAdhesiveHas anti-fouling effectAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHybrid peptidesAttachment proteinSynthesis methods
The invention relates to mussel attachment protein / amphoteric ion polypeptide fusion protein with attachment-anti-staining dual functions and a synthesis method. A fusion protein gene with a rationaldesign is cloned to a plasmid vector to obtain a recombinant expression plasmid; furthermore, after host cells are further transformed, the host cells are induced by utilizing an inducer to excessively express the fusion protein; after separation and purification, the fusion protein is obtained. Mussel attachment protein contains a sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 1, SEQ ID NO. 2, SEQ ID NO. 3, SEQ IDNO. 4 or SEQ ID NO. 5. Amphoteric ion polypeptide contains a sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 6, SEQ ID NO. 7, SEQ ID NO. 8 or SEQ ID NO. 9. The fusion protein with the attachment-anti-staining dual functions is synthesized through a microorganism one-step method; a process is moderate and efficient, the cost is low and requirements on equipment are low, so that later-period expanded production is facilitated.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Respiratory syncytial virus with a genomic deficiency complemented in trans
InactiveUS9107939B2Improve efficiencyPrevent lower respiratory tract infection—willSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideDiseaseAttachment protein
Owner:INTRAVACC BV
Nucleic Acids Encoding Respiratory Syncytial Virus Subgroup B strain 9320
ActiveUS20090285853A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesAttachment proteinRespiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
The complete polynucleotide sequence of the human respiratory syncytial virus subgroup B strain 9320 genome is provided. Proteins encoded by this polynucleotide sequence are also provided. Isolated or recombinant RSV (e.g., attenuated recombinant RSV), nucleic acids, and polypeptides, e.g., comprising mutations in the attachment protein G, are also provided, as are immunogenic compositions comprising such isolated or recombinant RSV, nucleic acids, and polypeptides. Related methods are also described.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Surface-controlled and polymerization-modification biological material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102432904AHas antibacterial functionAvoid stickingPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingAttachment proteinAtom-transfer radical-polymerization
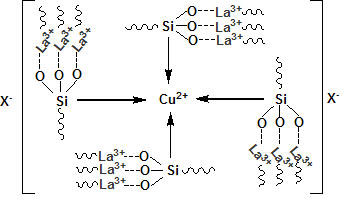
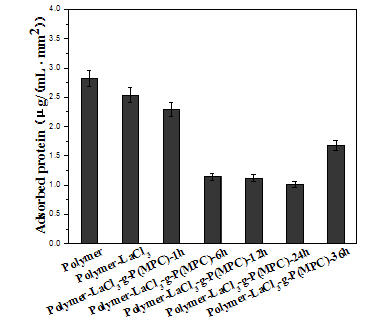
The invention relates to a surface-controlled and polymerization-modification biological material. The biological material is characterized in that a base body is treated by trivalent lanthanum ion / silanization, and the surface of the biological material is grafted with a brush-shaped zwitter-ion polymer layer. Generally, an ATRP (atom transfer radical polymerization) method or an RATRP (reverse atom transfer radical polymerization) method is adopted to use 2, 2'-bipyridyl (Bpy) as ligand, and the prepared grafting materials have the problems of low grafting rate. The surface-controlled and polymerization-modification biological material adopts a special complexing and catalyzing system formed by coordination of free trivalent lanthanum ions / silane coupling agent and copper halide to realize controllable polymerization of the activity of zwitter ions. In the surface-controlled and polymerization-modification biological material, the specificity and the functionality of attachment protein on the surface of the biological material can be effectively adjusted and controlled, the adhesion of blood cells and the multi-path activation of blood can be inhibited, simultaneously, the bacterial adhesion is reduced, and the surface of the biological material with excellent blood compatibility is obtained. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the surface-controlled and polymerization-modification biological material.
Owner:南京周宁琳新材料科技有限公司
Method for in-situ determination of wood fiber biomass enzyme accessibility
ActiveCN102899387AAvoid distortionEvaluation of Enzyme AccessibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFiberAttachment protein
The invention belongs to the field of environmental biological energy and relates to a method for in-situ determination of cellulase accessibility of wood fiber biomass. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) marking general enzyme binding sites of a wood fiber biomass sample; 2) in-situ observing the distribution and the quantity of the general enzyme binding sites, and calculating to obtain the quantity of fiber globule fluorescent protein probes which are attached onto the surface of the sample; 3) releasing the general enzyme binding sites; 4) closing the sample obtained in the step 3 by using lignin attachment proteins, and marking the cellulase binding sites in the sample to obtain the distribution and the quantity of the cellulase binding sites and the quantity of the fiber globule fluorescent protein probes which are attached onto the surface of the sample; and 5) comparing results of the step 4 and the step 2, and evaluating the cellulase accessibility of the wood fiber biomass. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the enzyme binding sites can be observed in situ and counted, visualization is realized and the enzyme accessibility of the wood fiber biomass can be intuitively evaluated.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Waterborne metal coating
InactiveCN106905733AReduce pollutionIncrease brightnessAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesSodium acetateAluminate
Waterborne metal coating is disclosed. The coating includes, by weight, 20-30 parts of an acrylic acid modified emulsion, 5-8 parts of 2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl acetoacetate, 12-18 parts of waterborne amino resin, 6-10 parts of rheological modified resin, 25-30 parts of modified aluminum powder, 10-20 parts of deionized water, 30-40 parts of rear earth aluminate, 1-3 parts of a waterborne silicone defoamer, 2-5 parts of a waterborne silicone leveling agent, 10-20 parts of a waterborne amine type epoxy curing agent, 25-35 parts of mussel attachment protein, 5-15 parts of aluminum type antirust pigment, 7-20 parts of sodium acetate, 5-13 parts of dispersion resin and 9-20 parts of sodium dodecylsulfate.
Owner:德阳森华涂料化工有限公司
Mhc class II haplotype specific immunodominancy of peptides derived from rsv fusion (f) and attachement (g) proteins
InactiveUS20050249744A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsVaccinationAttachment protein
The present invention relates immunodominant peptides derived from human respiratory syncytial virus (H-RSV) that may be used in ex vivo diagnosis of immune responses to H-RSV The immunodominant peptides are derived from the H-RSV Fusion (F) and Attachment (G) proteins and are capable of inducing an antigen specific CD4+ T cell response ex vivo in a MHC class 11 haplotype restricted manner. The immunodominant H-RSV-derived peptides may further be used in methods for vaccination against H-RSV, preferably in a MHC class 11 haplotype specific manner.
Owner:DE STAAT DER NEDERLANDEN VERT DOOR DE MINIST VAN VWS
Atherosclerotic plaque-targeting platelet membrane coated rapamycin bionic nano particles and application thereof
InactiveCN108042510AInhibit progressGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsNanocarriersAttachment protein
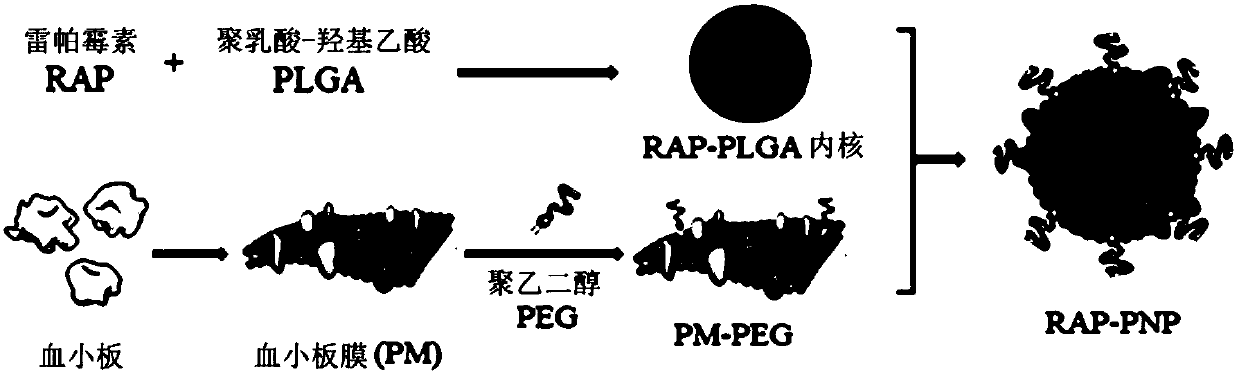
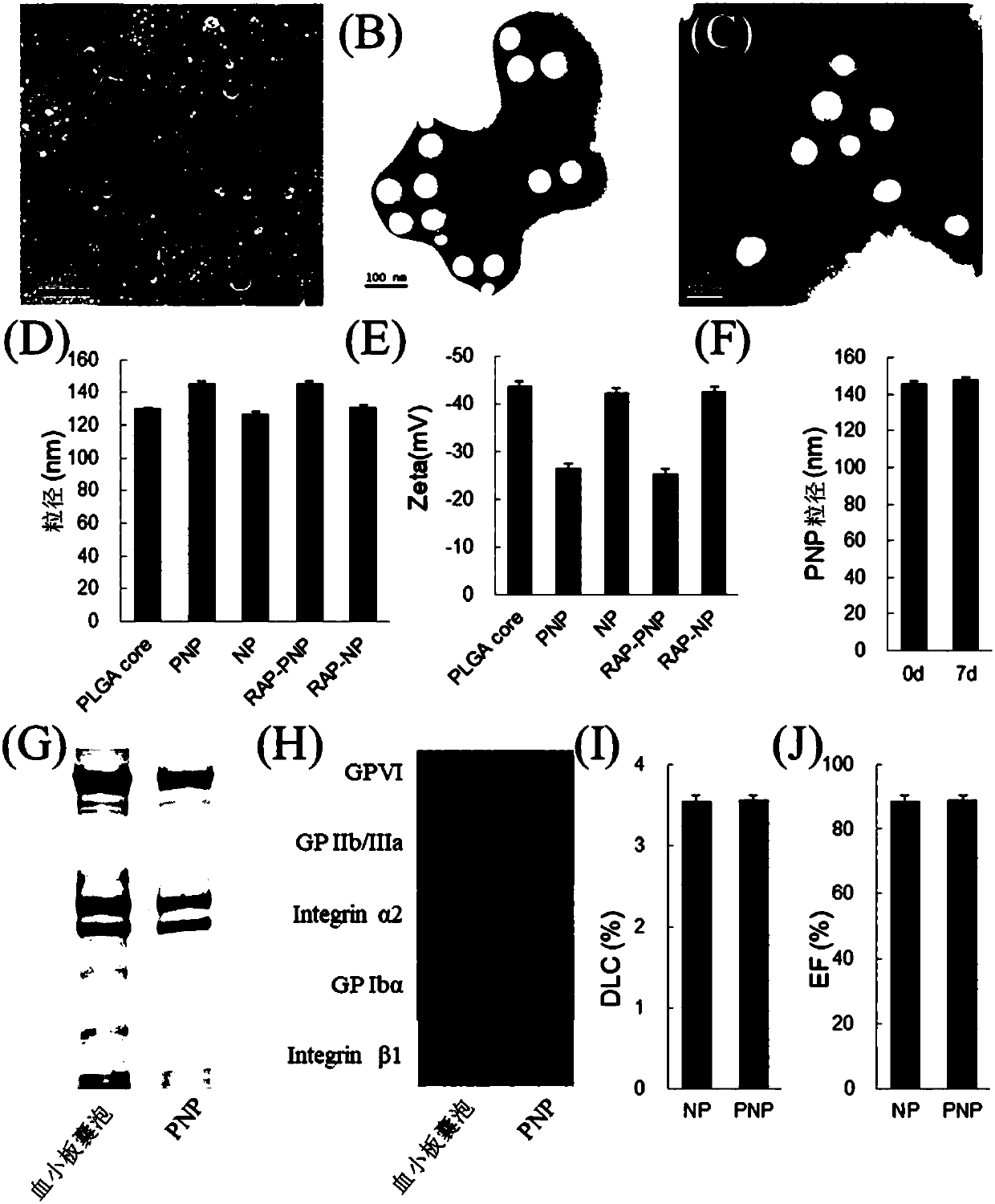
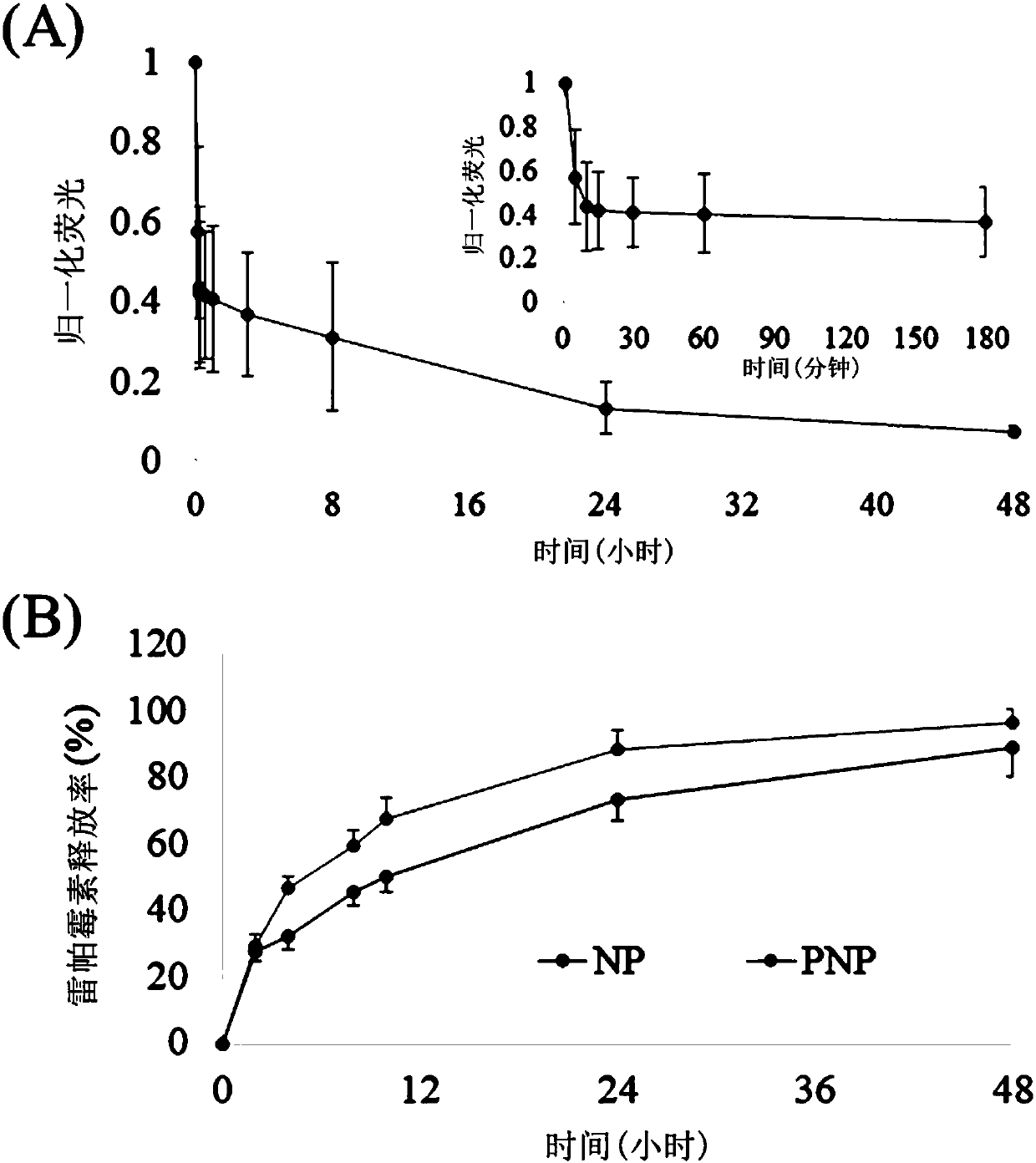
The invention relates to a new dosage form of rapamycin, atherosclerotic plaque-targeting platelet membrane coated rapamycin bionic nano particles. The invention also provides a preparation method andapplication of the new dosage form. The invention has the following advantages: the invention provides atherosclerotic plaque-targeting platelet membrane coated rapamycin bionic nano particles (RAP-PNP), wherein a nano carrier entraps rapamycin, and the surface of the nano carrier is coated with a platelet membrane; the attachment protein on the platelet membrane simulates the natural homing ability of platelet for atherosclerotic plaque, and performs targeted delivery of the rapamycin to part of the atherosclerotic plaque; then, the drug concentration in the plaque is increased, macrophage autophagy is activated, the plaque development is inhibited while the plaque is stabilized, the curative effect of rapamycin against atherosclerosis is improved, and systemic adverse reactions are reduced.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
A kind of preparation method of imitation mussel glue that can be bonded on wet surface and solidified under water
InactiveCN103965810BEfficient synthesisImprove bindingNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesPolymer scienceAttachment protein
The invention relates to a preparation method for a biomimetic mussel adhesive used for adhesion on a wet surface and underwater curing. The method is characterized in that the biomimetic mussel adhesive is composed of two components including A and B, wherein the component A is a methanol solution of a polymer containing catechol groups; the polymer containing catechol groups is obtained in the manner that N-vinyl pyrrolidone and a polymerizable catechol derivative monomer are subjected to free radical polymerization and further subjected to deprotection; the component B is a crosslinking curing agent. The method has the advantages as follows: 1, the synthetic method is simple and efficient, raw material and reagents used in the reaction process are low in price and easy to get, and amplification in the operation process and industrial production are facilitated; 2, the biomimetic mussel adhesive has certain biocompatibility and initial adhesion performance, can be used for adhesion on the wet surface and underwater curing, and has the bonding strength being over 1 MPa, so as to be applied to adhesion of human tissue and adhesion in the wet environment of commonly-used base material as well as adhesion under the water. According to the invention, perfect combination between synthetic macromolecule and natural mussel attachment proteins is successfully realized, the technical bottleneck about the current biomimetic mussel adhesive is expected to break through, and meanwhile, a new approach for shellfish-based development of biomimetic high polymer material is provided.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
PEI-g-HBA prepolymer and vegetable protein composite modified adhesive as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109401726AImprove water resistanceHigh solid contentProtein adhesivesAldehyde/ketone condensation polymer adhesivesEnvironmental resistanceAttachment protein
The invention provides a PEI-g-HBA prepolymer and vegetable protein composite modified adhesive as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The composite modified adhesive is preparedfrom main effective components as follows: vegetable protein meal and a PEI-g-HBA prepolymer. In order to meet the prepress requirement, the PEI-g-HBA component in the adhesive has the structure similar to that of mussel attachment protein DOPA, the prepress requirement of veneers with the moisture content larger than 20% can be met, and bonding strength of manufactured artificial boards can meetthe national standard requirement. The adhesive has the advantages of being simple to manufacture, low in cost, environmentally friendly, pollution-free and the like, the artificial boards adhered bythe adhesive have no formaldehyde release problem, and the problem of formaldehyde in indoor air due to the artificial boards is completely solved.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
MRRP protein, gene, carrier, engineering bacteria and application thereof
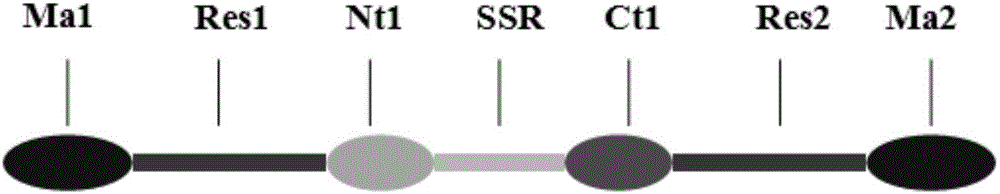
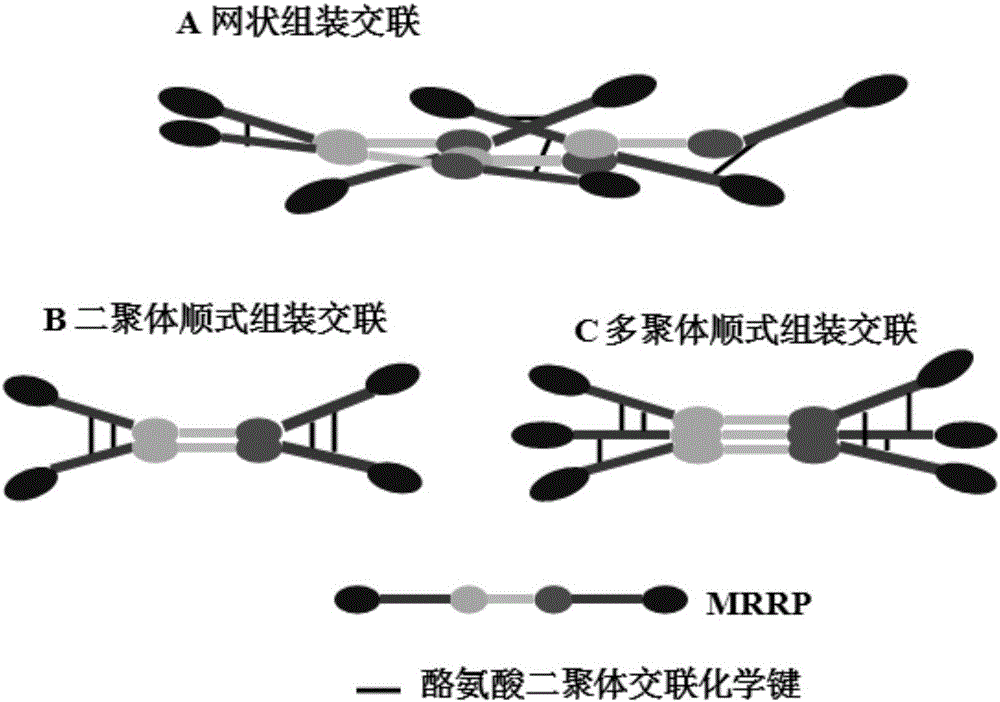
ActiveCN105085685AImprove manufacturing yieldSelf-assembly properties haveBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsAttachment proteinBiology
The invention discloses MRRP protein, a gene, a carrier, engineering bacteria and application of the MRRP protein, the gene, the carrier and the engineering bacteria to preparation of wound healing medicine. The MRRP protein is formed by sequentially connecting mussel attachment protein Ma1, elastic drosophila melanogaster protein Res1, a spider silk protein nitrogen end sequence Nt1, a spider silk protein middle-piece repetitive sequence SSR, a spider silk protein carbon end sequence Ct1, elastic drosophila melanogaster protein Res2 and mussel attachment protein Ma2. The MRRP protein integrates self-assembling performance of spider silk protein, high elasticity of the elastic drosophila melanogaster protein and high viscosity of the mussel attachment protein, comprehensive performance is excellent, lengths are uniform, the MRRP protein can be biodegraded completely, the yield is high by adopting a microorganism method for preparing, and chemical pollution is avoided; the MRRP protein has high elasticity, and can bond wounds, so that the wounds are bonded without using lines.
Owner:山东润土节能环保工程有限公司
Prawn white spot syndrome virus VP37p polypeptide fragment and application thereof
The invention utilizes prawn white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) gene expression technology to obtain a segment which is coded by a prawn white spot bacilliform virus WSV254 gene and is named as VP37p. The invention also relates to a method for manufacturing the VP37p, application of polynucleotide and polypeptide of the VP37p, and an antibody specifically bound with the polypeptide of the VP37p. The invention identifies the function of the VP37p through a biological method for the first time; the VP37p is one of WSSV attachment protein fragments; and the inhibition on the gene and expression products thereof may be one of effective ways of preventing and controlling prawn white spot disease and expects to be applied to the prevention and control of the prawn white spot disease.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
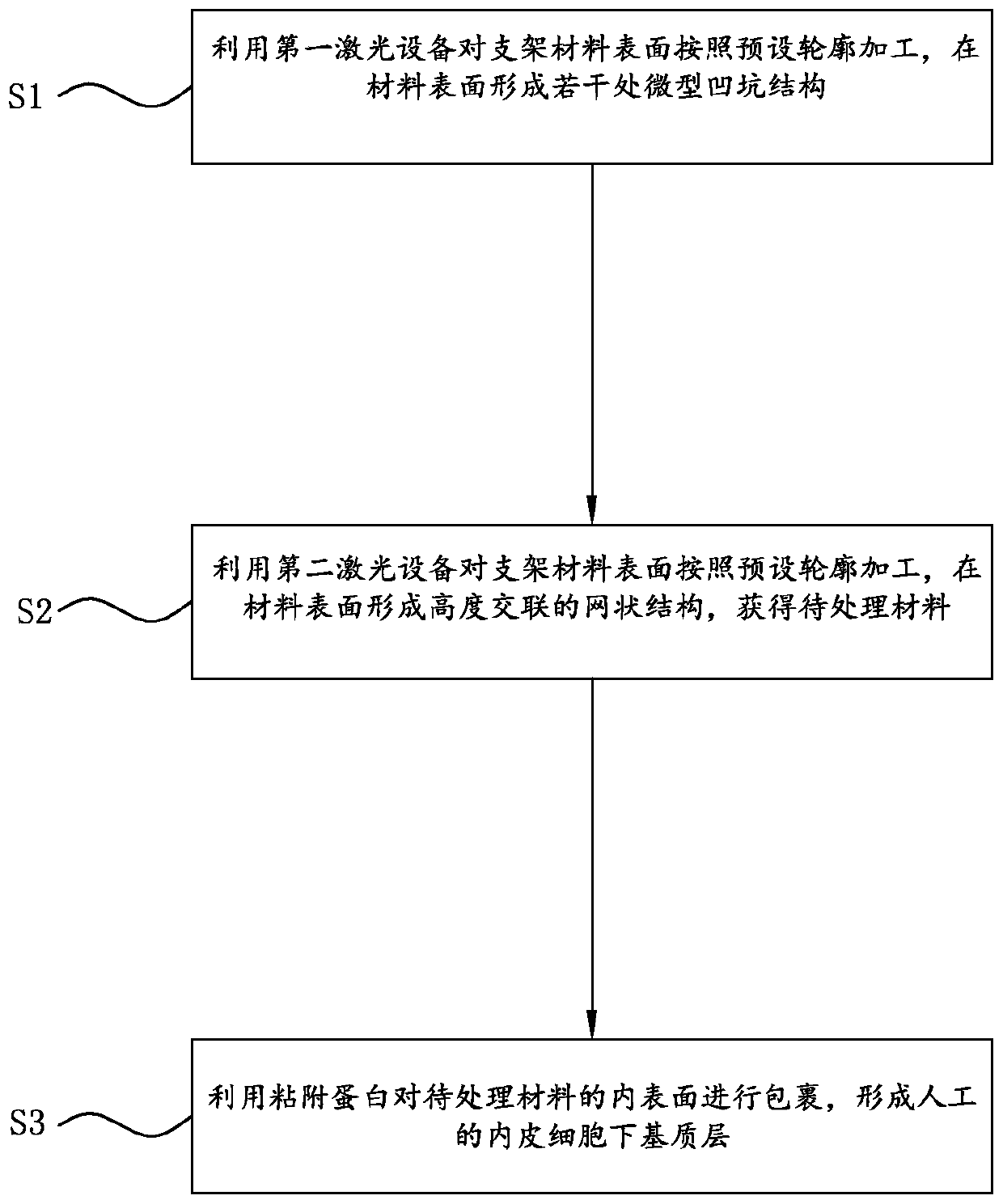
Innovative method for surface modification of biodegradable stent by using laser
ActiveCN110404121AAchieve modificationAccelerates the endothelialization processSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAttachment proteinMedicine
The invention discloses an innovative method for surface modification of a biodegradable stent by using a laser. The innovative method includes the following steps that S1, the surface of a stent material is processed according to a preset contour by using first laser equipment, and a plurality of miniature pits are formed in the surface of the material; S2, the surface of the stent material is processed according to the preset contour with second laser equipment, a highly crosslinked net structure is formed on the surface of the material, and a to-be-processed material is obtained; and S3, the inner surface of the to-be-processed material is coated with attachment proteins, and an artificial substrate layer under endothelial cells is formed, wherein the stent material is a magnesium alloymaterial for manufacturing the biodegradable stent.
Owner:INNO LASER TECH CORP LTD +1
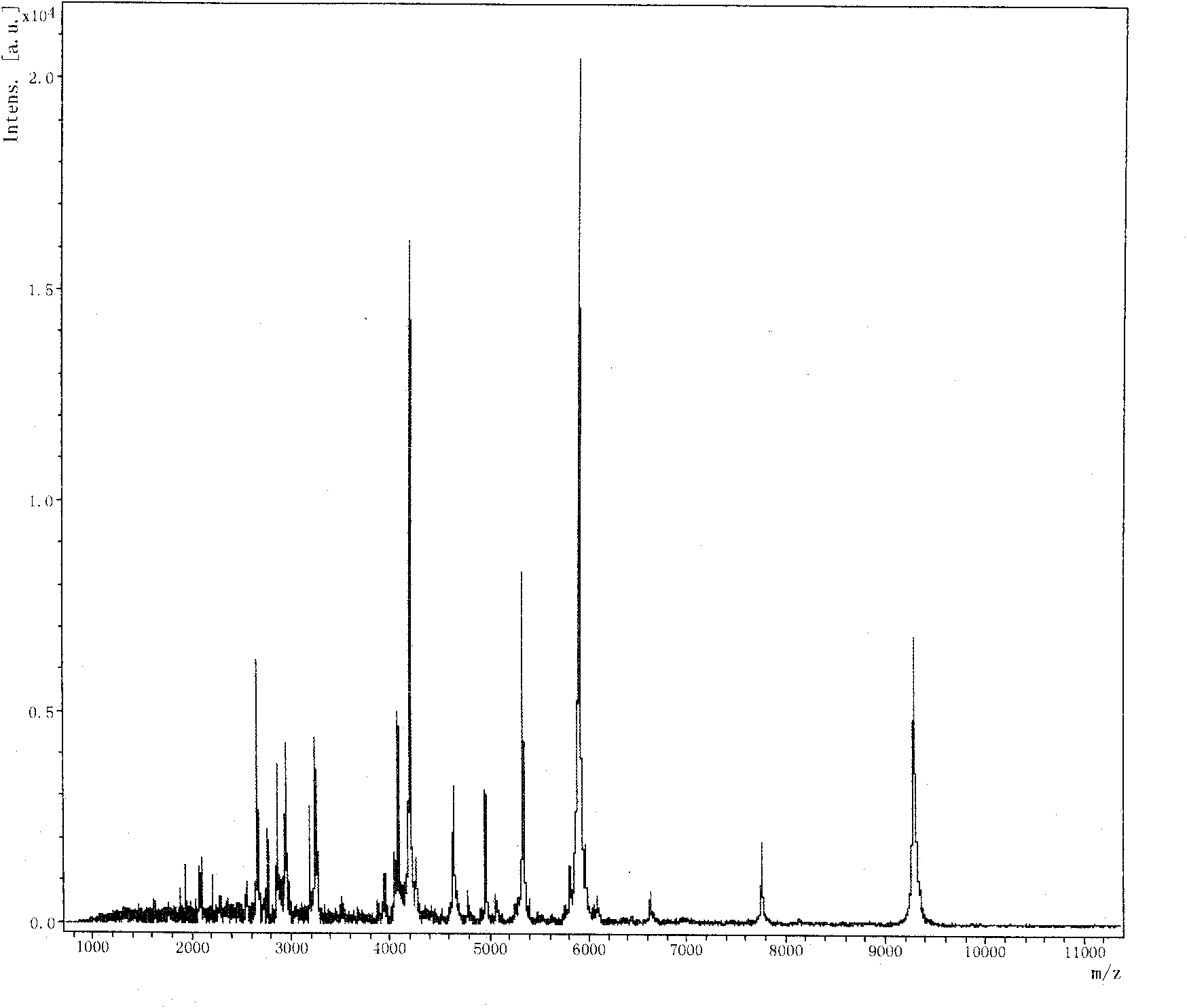
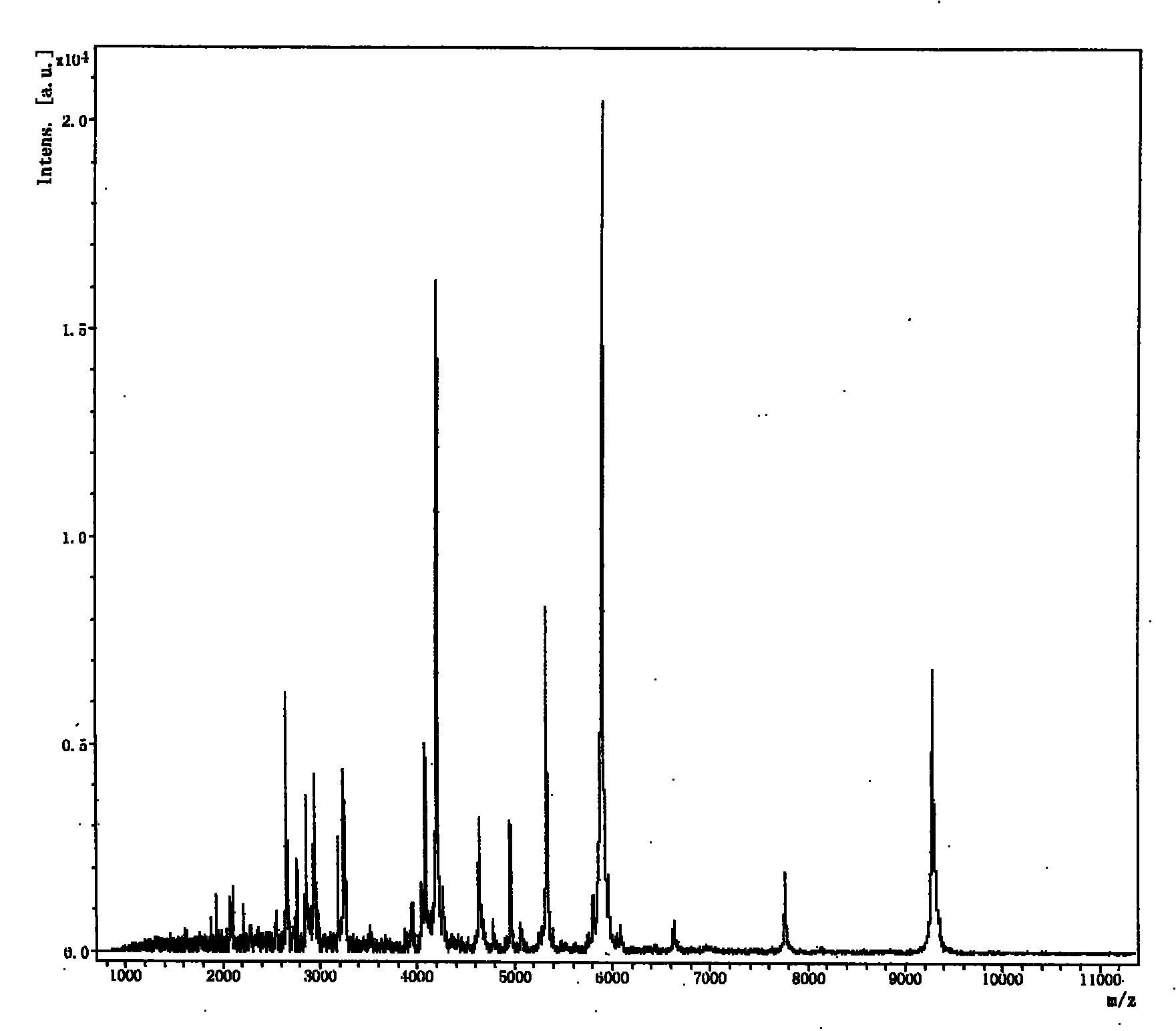
Mass spectrometric detection method for ca-dependent secretory protein 1 in human serum
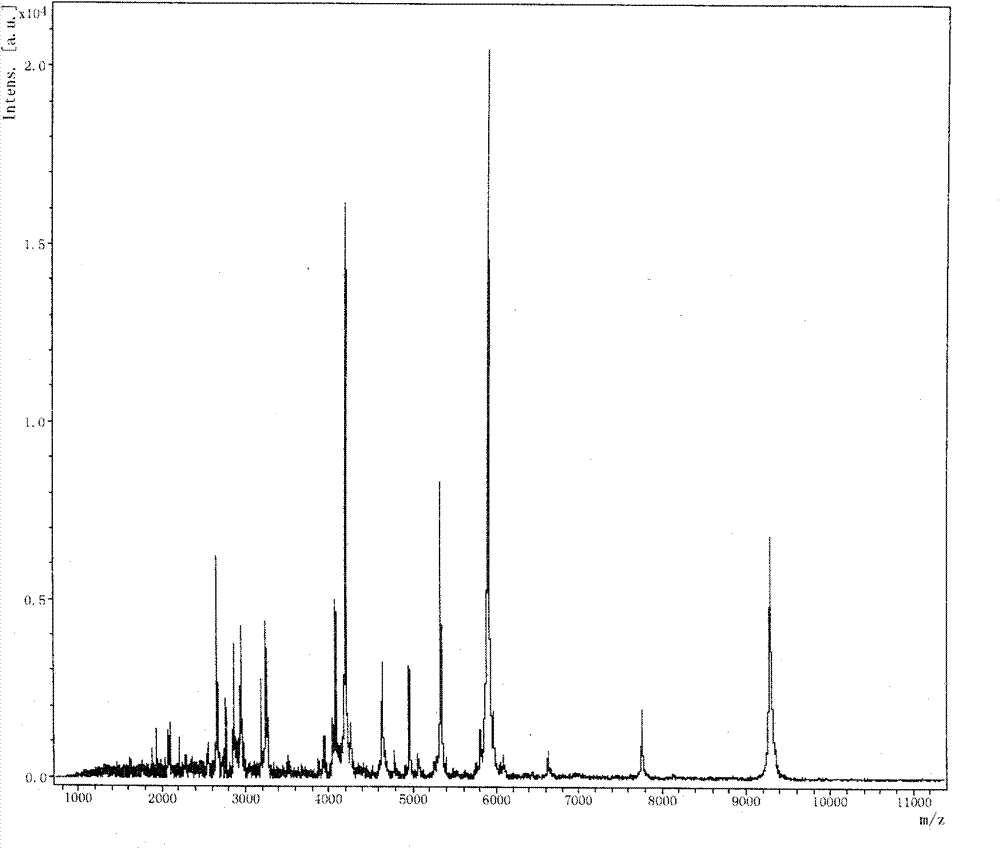
InactiveCN101776642AEasy to detectGood repeatabilityPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMatrix solutionAttachment protein
The invention relates to a mass spectrometric detection method for ca-dependent secretory protein 1 in human serum, which is characterized in that the mass spectrometric detection method comprises the following steps: taking human serum and using magnetic bead attachment protein for obtaining magnetic bead enrichment liquid; adding the magnetic bead enrichment liquid into a matrix solution; carrying out the matrix-assisted laser dissociation ionization flight time mass spectrometric detection according to the following conditions: a first ion source voltage: 20kV; a second ion source voltage: 18.6kV; crystal voltage: 7.6kV; pulse ion time: 320ns; polarity: positive; matrix inhibition mode: gate control; gate control strength: maximum: suppression high limit: 600Da; detector: 1400-1500 V; sample rate: 1.00Gs / s; electrical acquisition: enhancing, 100mV; real-time fluency: high; laser frequency: 20Hz; laser attenuation: closing 73% and ranging 20%; mass to charge ratio is 5336 plus or minus 1; and the peak flowing is the ca-dependent secretory protein 1. The method has the advantages of short time and high sensitivity.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
Swine-derived eperythrozoon detecion kit, method and applications
InactiveCN104152537AQuick checkAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPig farmsAttachment protein
The invention discloses a swine-derived eperythrozoon detecion kit, a method and applications. The kit comprises a TaqMan probe and a primer pair designed aimed at a swine-derived eperythrozoon G1 gene. The probe binds to the 658th-793th nucleotide sequence of the swine-derived eperythrozoon G1 gene specifically. The primer pair is used for amplification of the 658th-793th nucleotide sequence of the swine-derived eperythrozoon G1 gene. The swine-derived eperythrozoon real-time fluorescence quantification PCR detection kit based on the attachment protein G1 gene has characteristics of strong specificity, high sensitivity and good repeatability, can detect whether eperythrozoon is existed in a swine blood sample rapidly, accurately and with high throughput, can be applied at aspects of clinical diagnosis, molecular epidemiological investigation, therapeutic effect evaluation, pig farm purification of swine eperythrozoonosis and the like, and has an important meaning to early state rapid diagnosis, prevention and control and purification of swine eperythrozoonosis.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
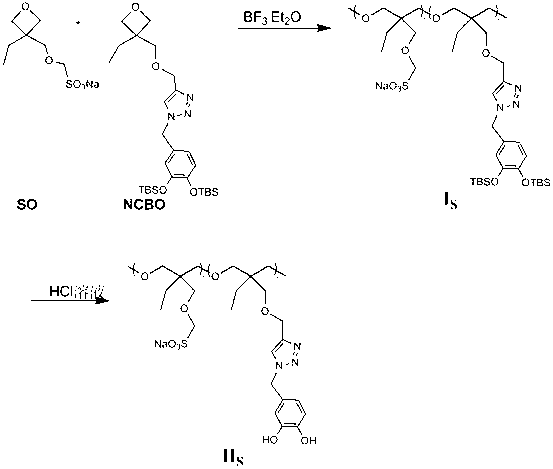
Imitation mussel attachment protein and cell membrane structure copolymer and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses an imitation mussel attachment protein and cell membrane structure double-bionic copolymer shown by the structural formula (I), wherein m is an integer from 10 to 1,000, n is an integer from 0 to 500, and x is an integer from 5 to 500; in the m, n and x, the molar percentage of m is 30-90%, the molar percentage of n is 0-50%, and the molar percentage of x is 10-70%; R1, R2 and R3 are H or CH3; R4 is an alkyl with 4-18 carbon atoms; V is a catechol group with 2-300 carbon atoms in chain connection; W is a hydrophilic group with 2-8 carbon atoms in chain connection; and the hydrophilic group is a quaternary ammonium group, phosphorylcholine group, pyridinium, sulfonic acid group, phosphate group, carboxylic acid group or sulfuric acid group. According to the invention, the coating is in firm combination, the copolymer is almost suitable for an establishment method of a surface imitation cellulosa membrane structure of any material, and the surface hydrophilic performance and biocompatibility of artificial organ and related materials, medicine controlled-release systems, separation materials and other materials can be improved.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Dynamic protein complex recognition method
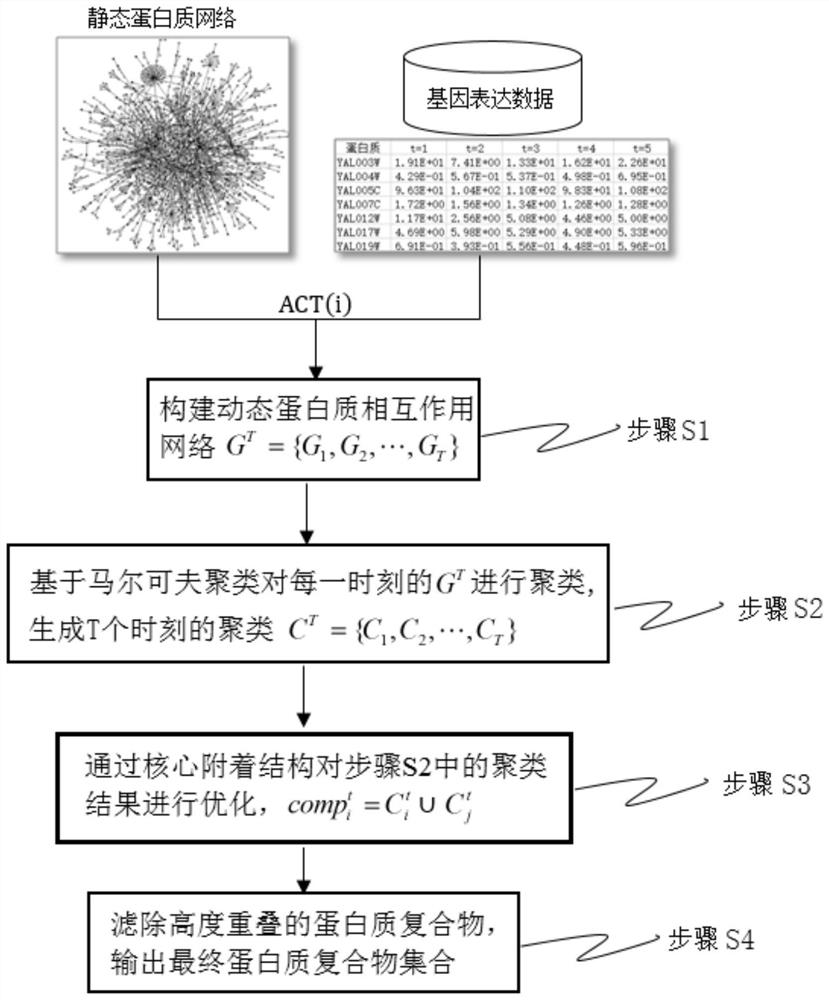
ActiveCN111667886AThe recognition result is accurateInhibitionBiostatisticsProteomicsAttachment proteinMarkov clustering
The invention provides a dynamic protein complex recognition method. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a dynamic protein interaction network in combination with gene expression data and a static PPI network; clustering the dynamic protein interaction network at each moment based on Markov clustering; optimizing the clustering result through a core attachment structure, and combining the cluster with the core protein and the cluster containing the attachment protein; and filtering highly overlapped protein complexes, and outputting a final protein complex set. The method provided by the invention not only can inhibit the generation of subclasses, but also can identify overlapped proteins. The invention provides a calculation method for identifying the protein complex from a dynamic protein interaction network, which is more in line with the PPI network of the actual biological process and provides a more accurate protein complex identification result.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Use of peptidic drugs for osteoporosis treatment and bone regeneration
The present invention provides osteogenic peptides derived from the Cementum-derived attachment protein (HACD1 / CAP) and another derived from the Cementum Protein 1 (CEMP1) and pharmaceutical compositions of these peptides for the prevention and treatment of osteopenia and osteoporosis. These peptides increase bone mineral density in an osteoporotic model and without in vivo side effects, demonstrating clinical effectiveness in the prevention and treatment of osteopenia and osteoporosis in vivo as well as bone repair and / or regeneration.
Owner:UNIV NAT AUTONOMA DE MEXICO
Preparation method for Gd2O3 nanoparticle controllably surface-modified by dopamine and used for positive reinforcement of MRI radiography
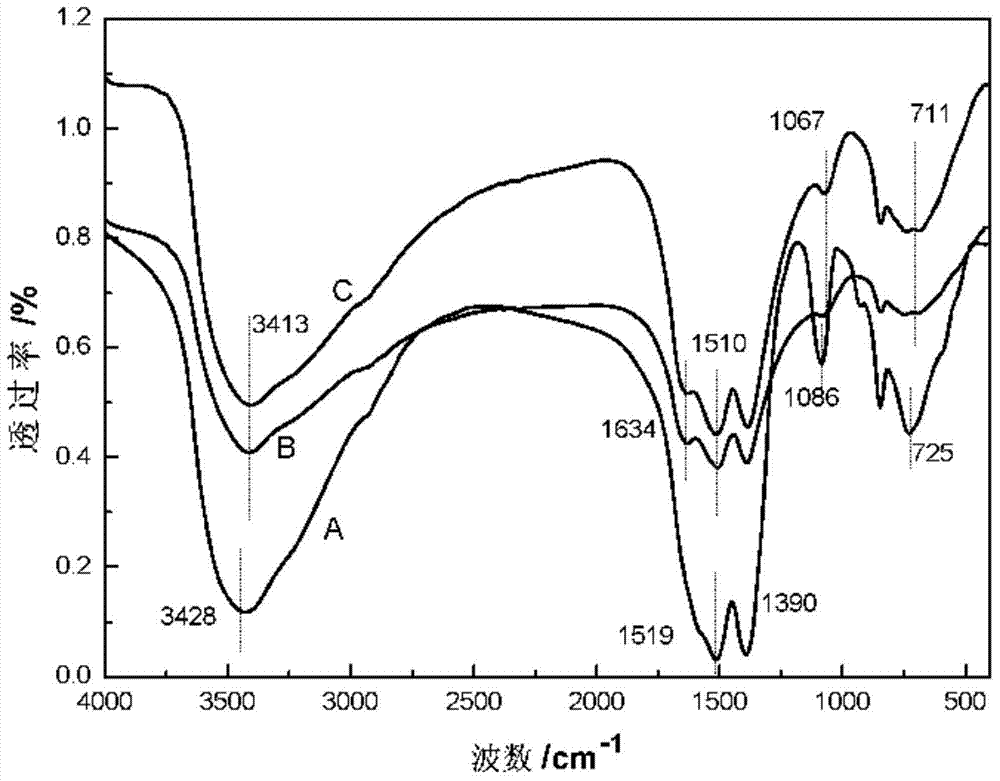
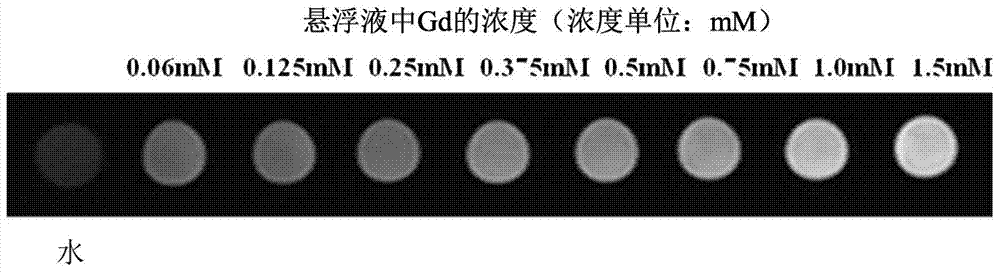
InactiveCN103920167APreparation process safetyIncrease signal strengthMaterial nanotechnologyNMR/MRI constrast preparationsAttachment proteinMRI contrast agent
The invention relates to preparation and application of a Gd2O3 nanoparticle controllably surface-modified by dopamine and used for positive reinforcement of MRI radiography and provides a preparation method and application of such an MRI contrast agent, belonging to the fields of bioimaging technology and nanomedical technology. According to the invention, controllable bionic surface modification of an ultra small Gd2O3 nanoparticle by dopamine is carried out by imitating attachment proteins of marine mussels, employing the property of strong chelating action of dopamine on metal ions and utilizing a certain-strength binding force on metals produced by the strong anchoring effect of an o-dihydroxybenzene group, and thus, the Gd2O3 contrast agent--DA-Gd2O3Gd2O3 / DA which is controllably surface-modified by dopamine and used for positive reinforcement of MRI radiography is obtained. The Gd2O3 contrast agent provided by the invention has an obvious contrast reinforcing effect, can improve intensity of magnetic resonance signals and brighten the image of a related position and is applicable as a contrast agent for MRI T1-weighted positive reinforcement.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV +1
Bifidobacterium longum protein, and preparation method and medical application thereof
ActiveCN105669843AEfficient preparation methodIncreased sensitivityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliAntibiotic sensitivity
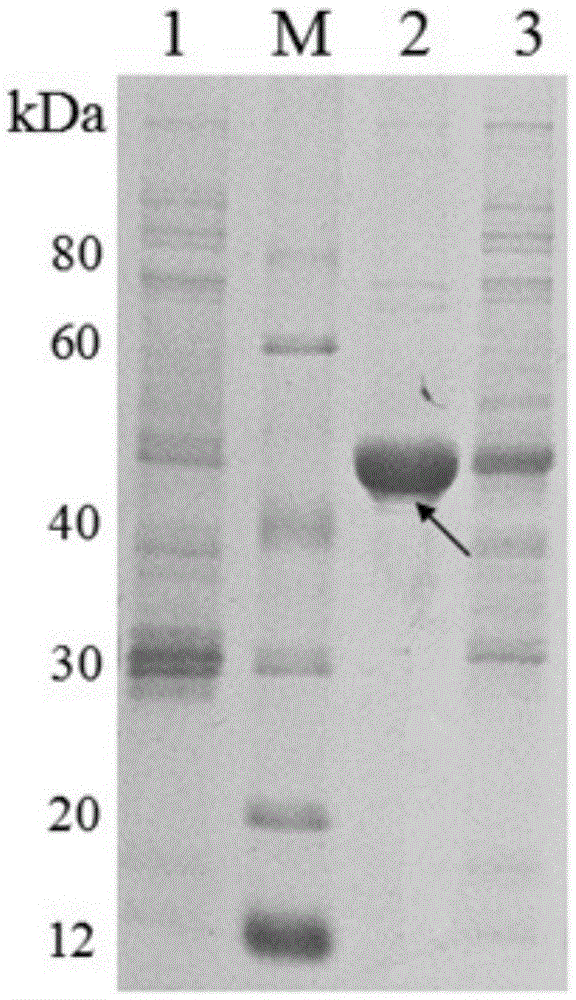
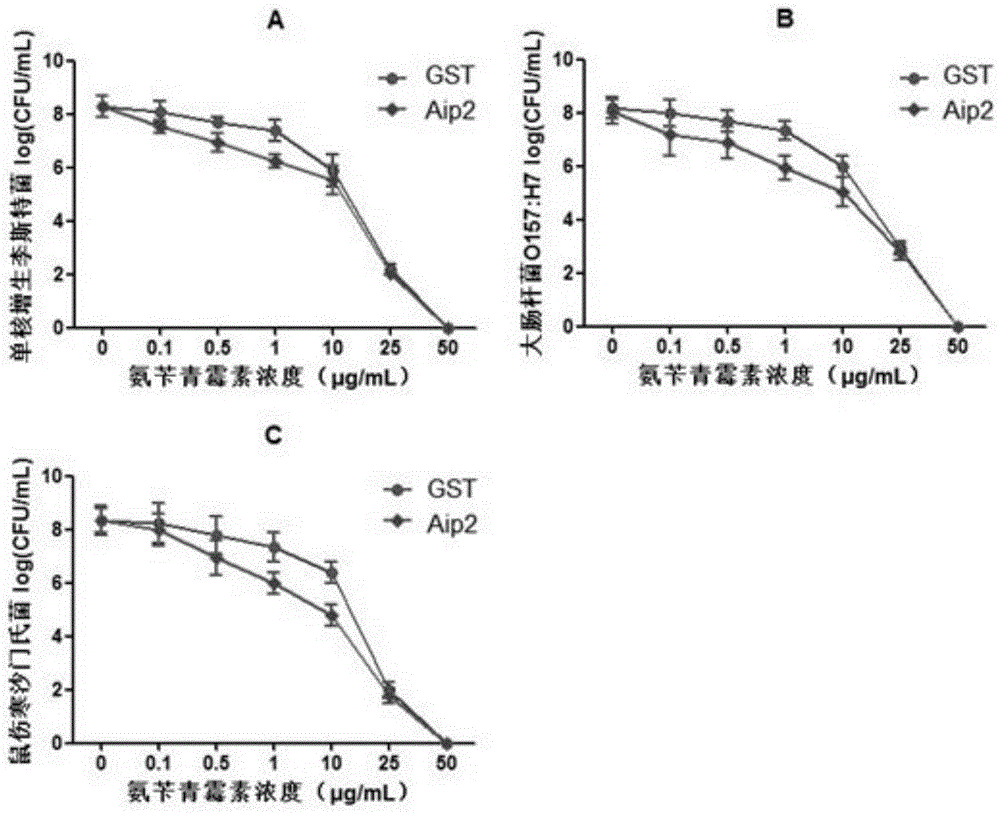
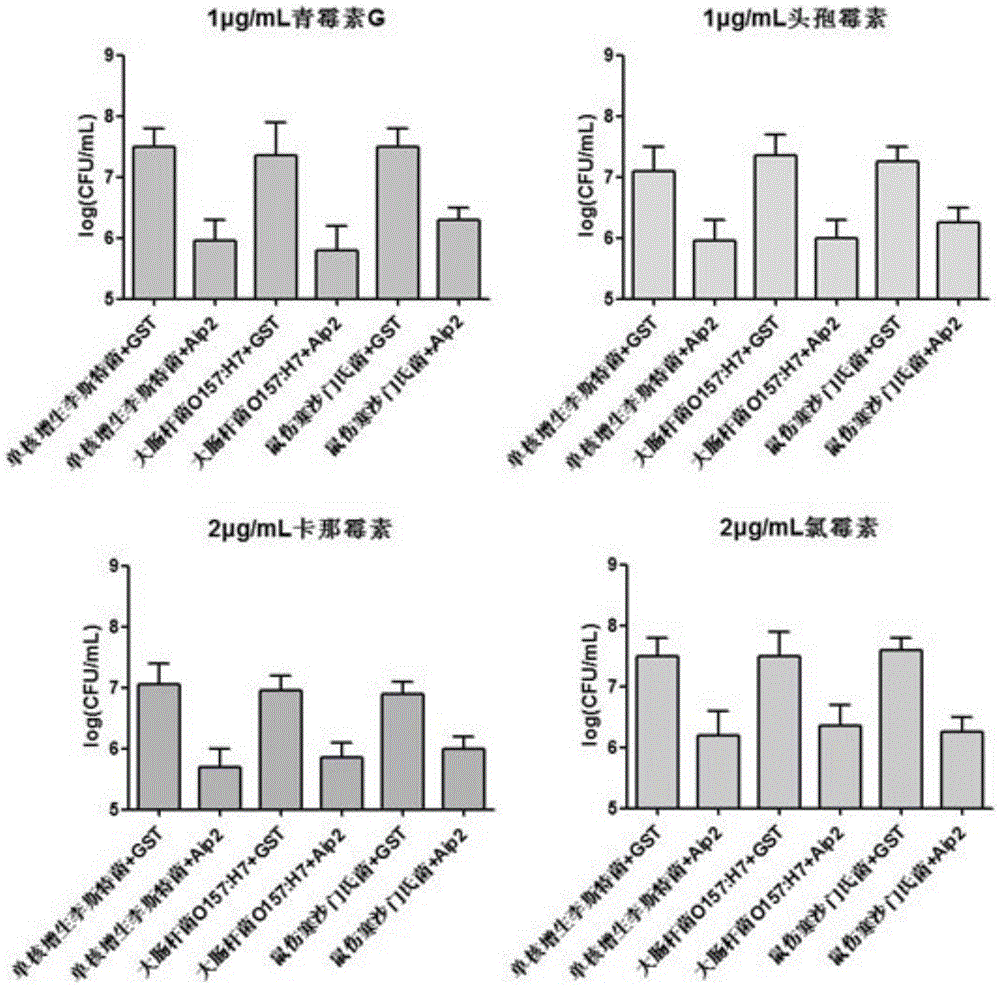
The invention provides an attachment protein derived from bifidobacterium longum, and discloses the amino acid sequence thereof; on the basis, experiments discover that the attachment protein not only can attach to enterocyte, but also has the function of improving microorganism antibiotic sensitivity, and especially for escherichia coli O157:H7, the antibiotic synergy is particularly prominent. Based on the beneficial discovery, the application of the protein as an anti-bacteria synergist, escherichia coli O157:H7, is determined, so that the application range of the protein is expanded, and at the same time, a new approach is provided for improving microorganism drug sensitivity. The prominent technological effect is achieved on the basis of strict experimental measures, and a broad application prospect is obtained.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Treating bladder tumor cells using fibronectin attachment protein as a target
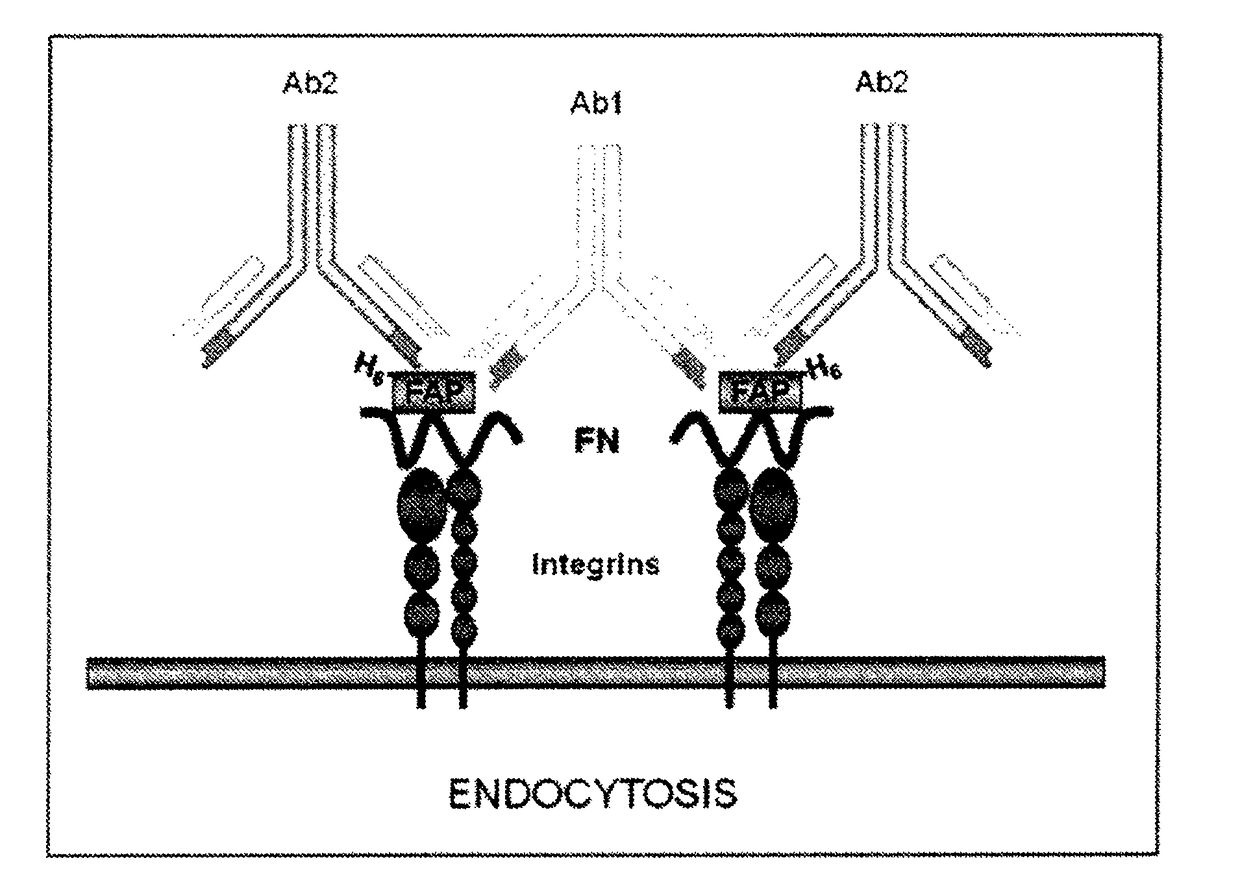
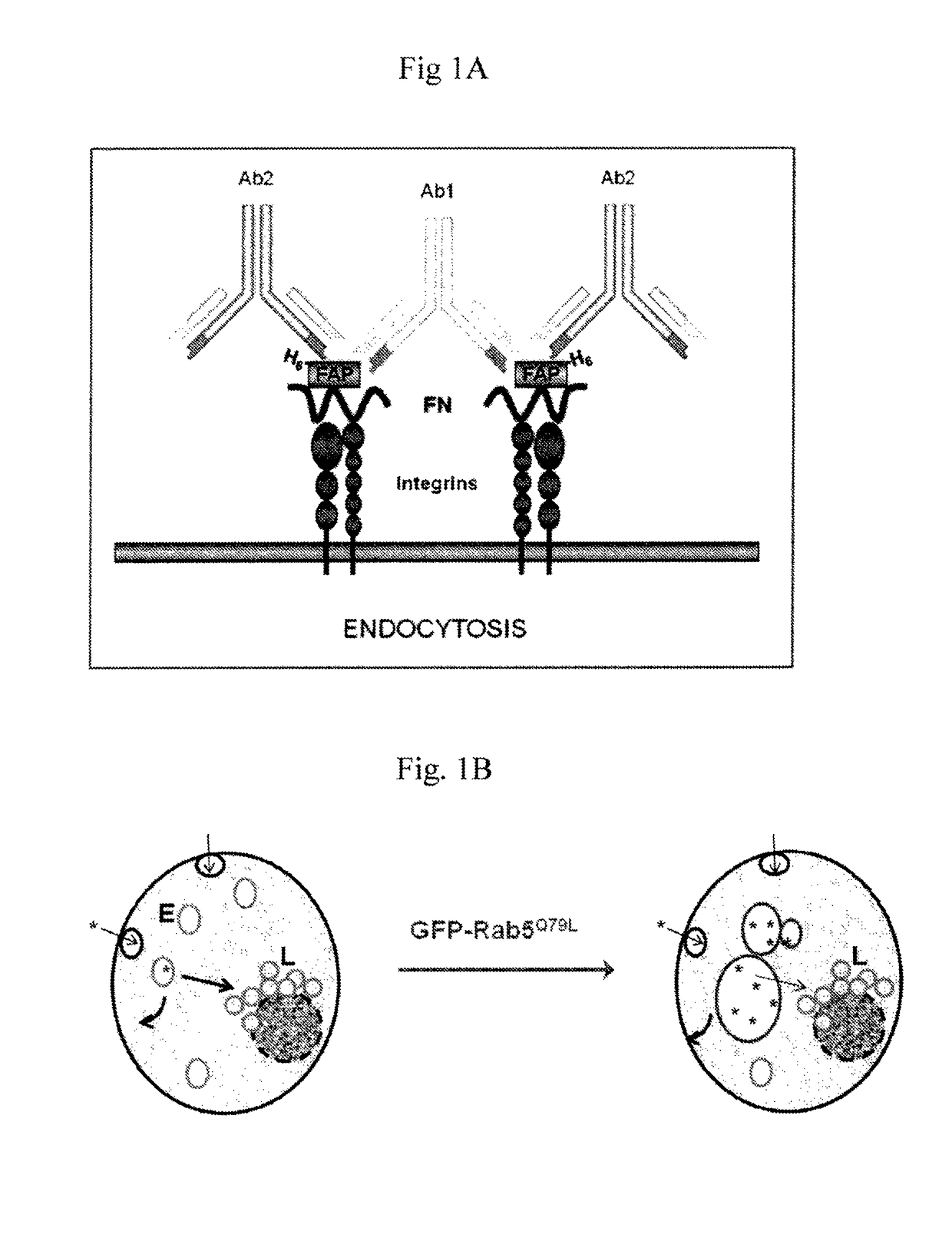
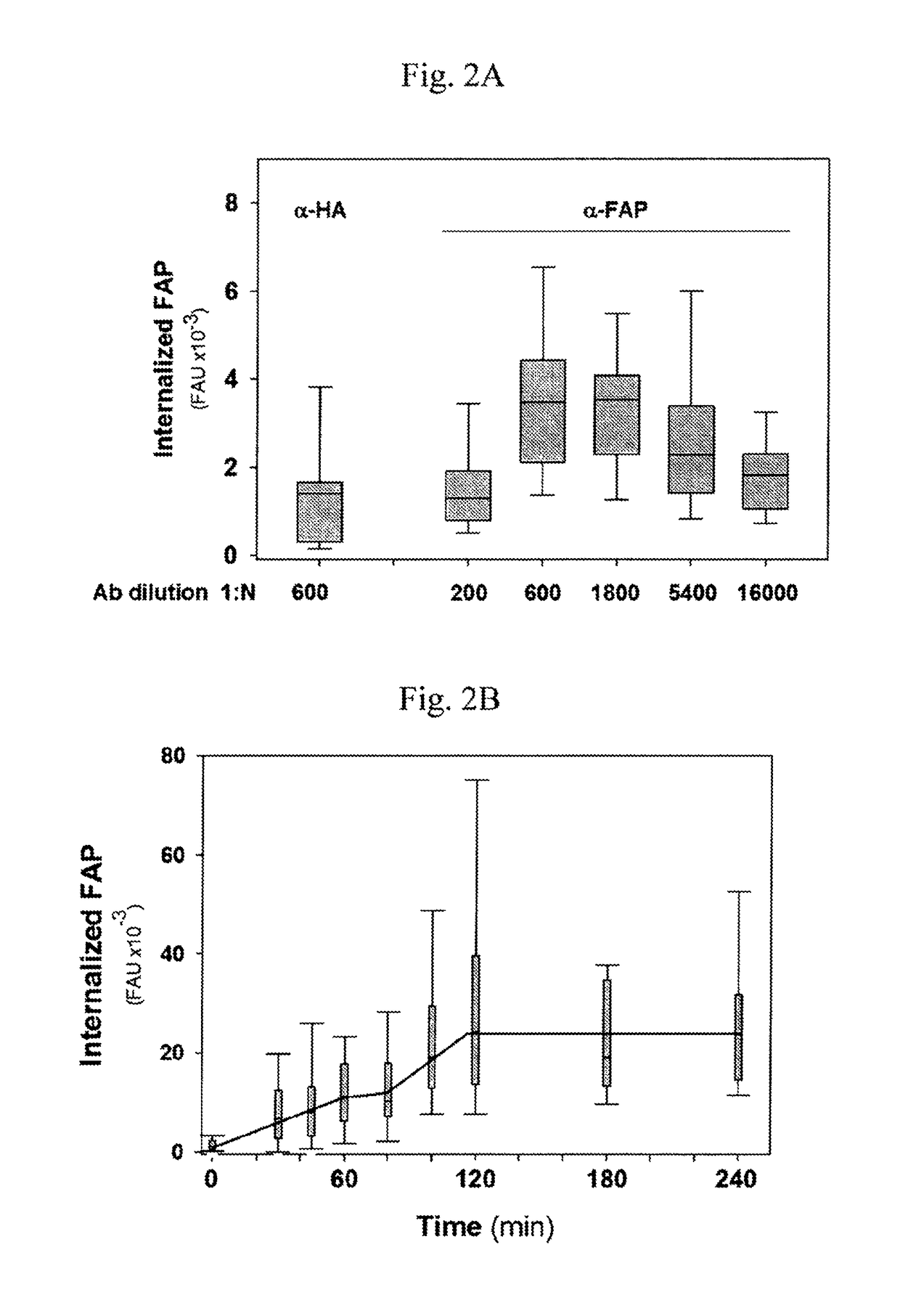
Composition and methods are disclosed for utilizing microaggregation of FAP-containing complexes to promote their fast internalization. This approach allows the uptake of cytotoxic cargo coupled to either FAP-Antibodies or FAP-liposome complexes by tumor bladder cells. Importantly, this approach is efficient even under serum-free conditions such as the ones found in the lumen of the bladder.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Mass spectrometric detection method for ca-dependent secretory protein 1 in human serum
InactiveCN101776642BEasy to detectGood repeatabilityBiological testingAttachment proteinMatrix solution
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com