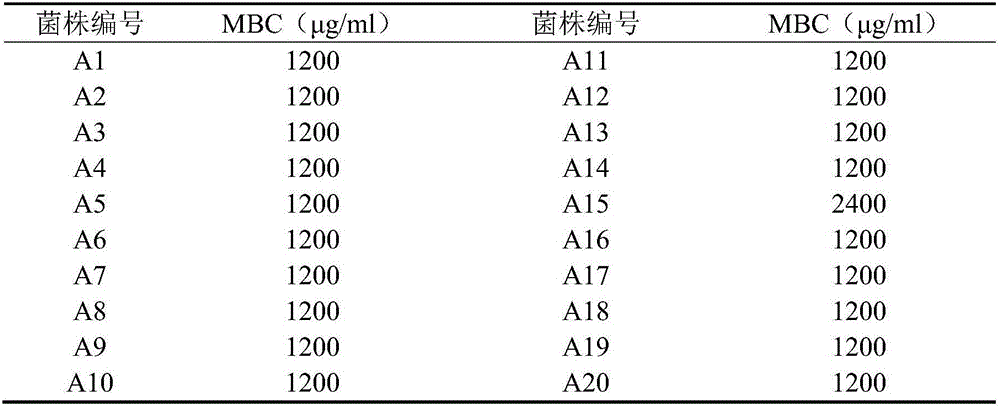
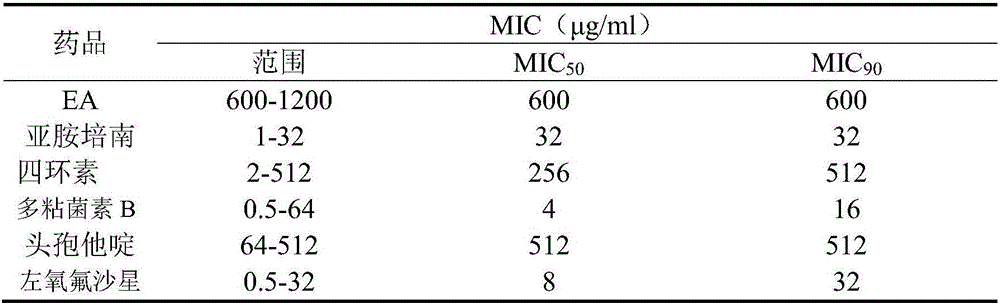
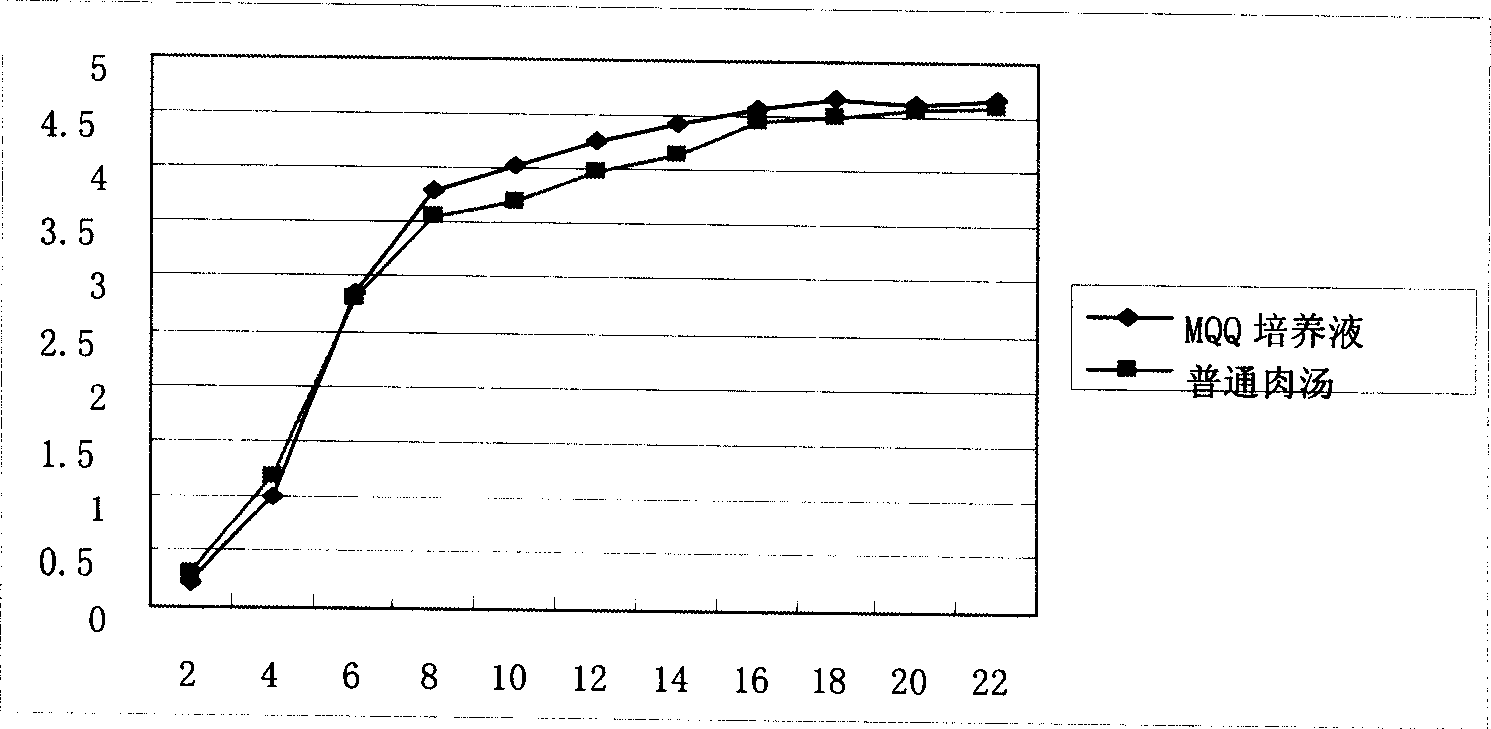
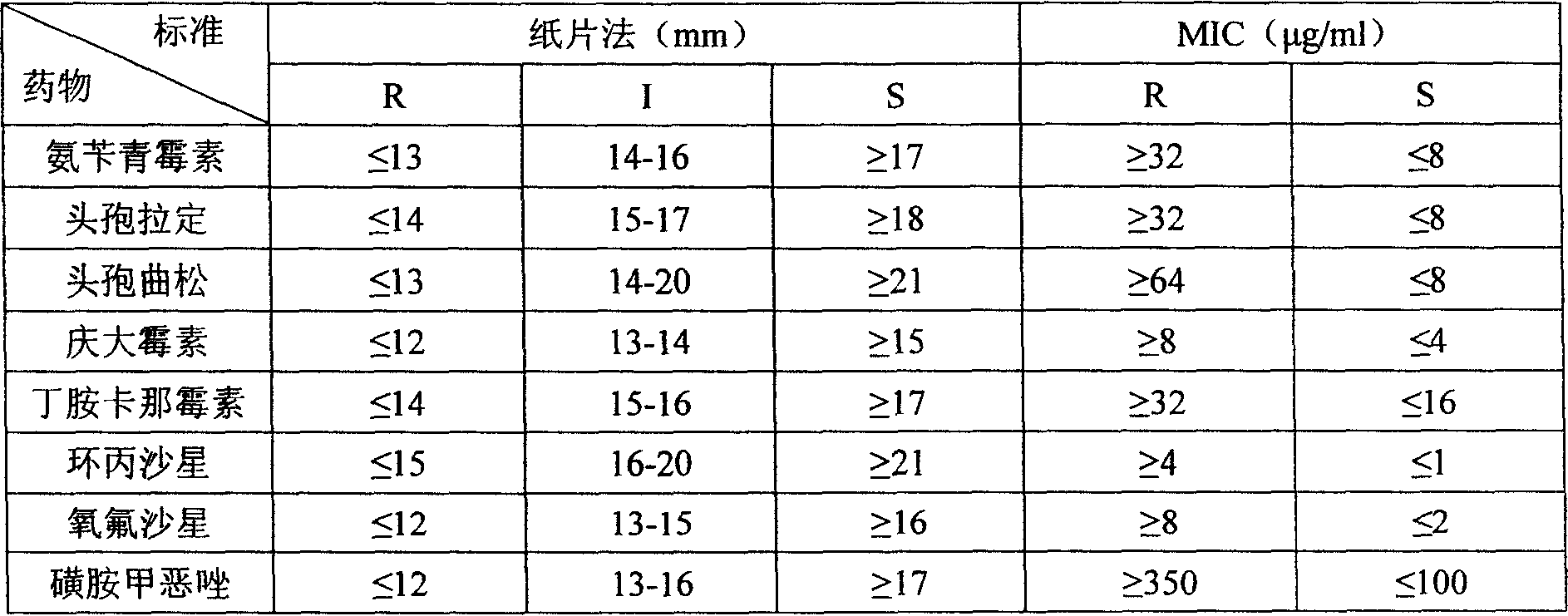
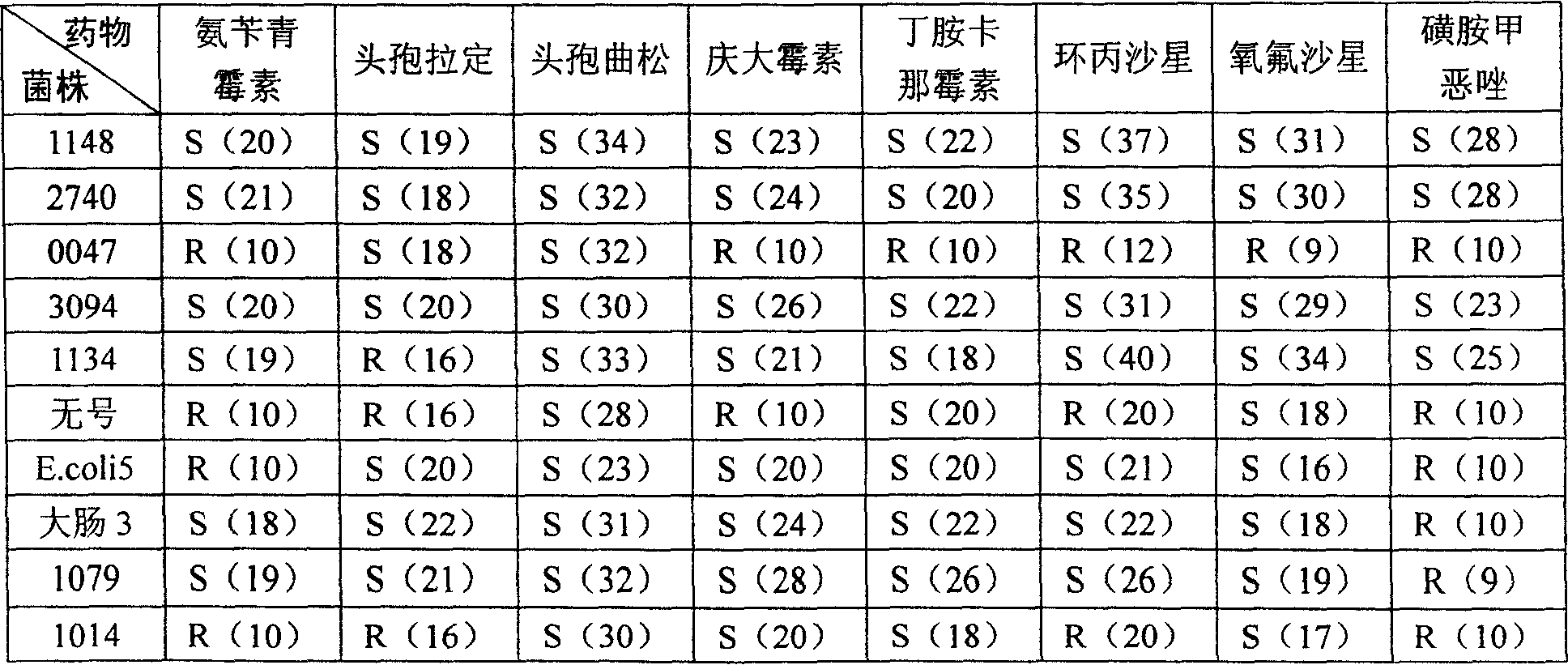
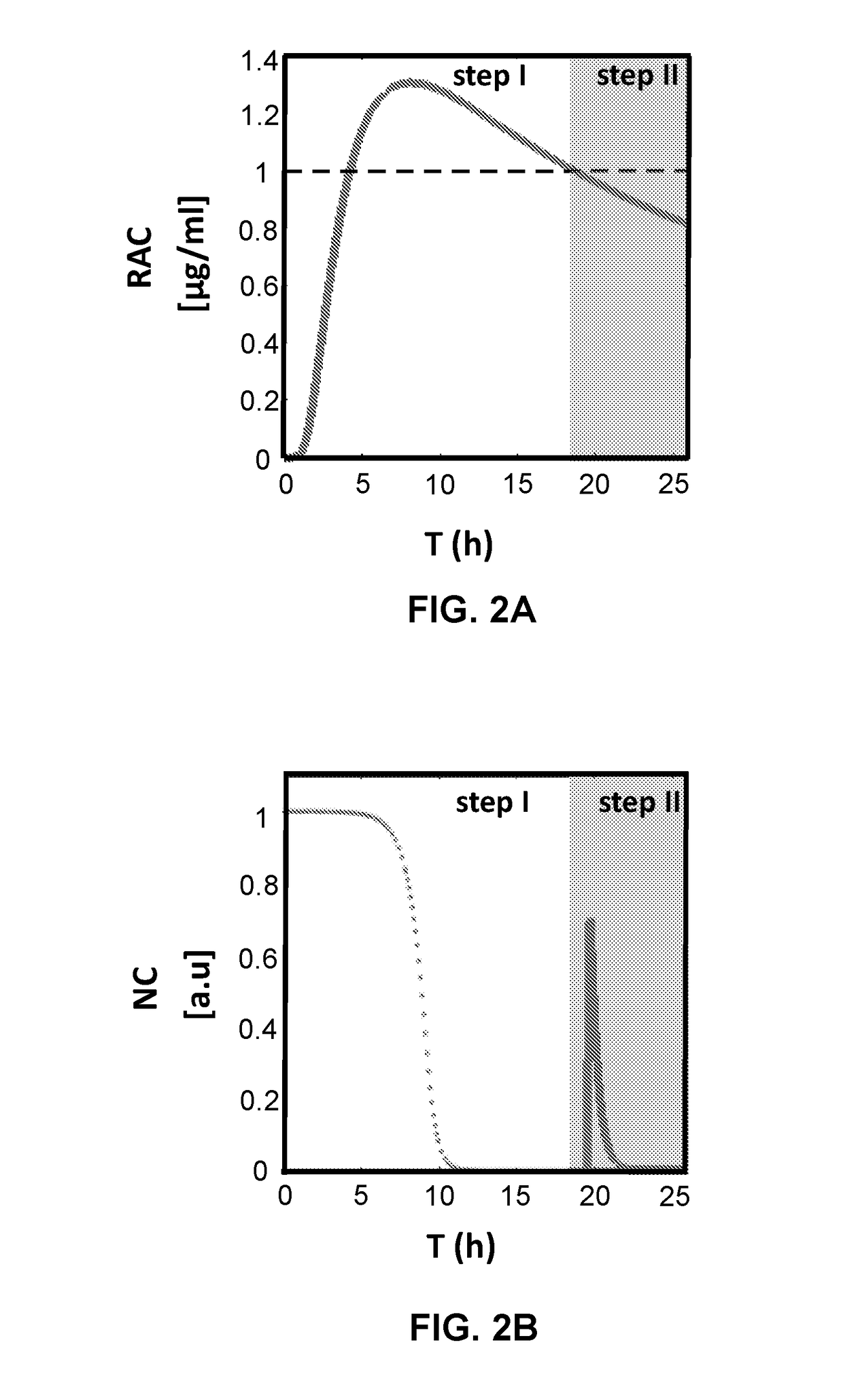
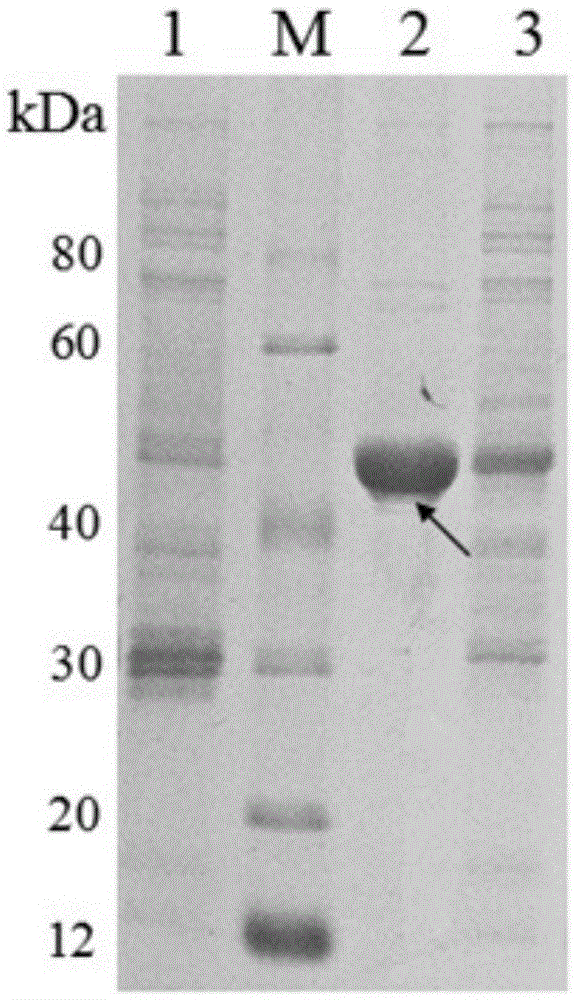
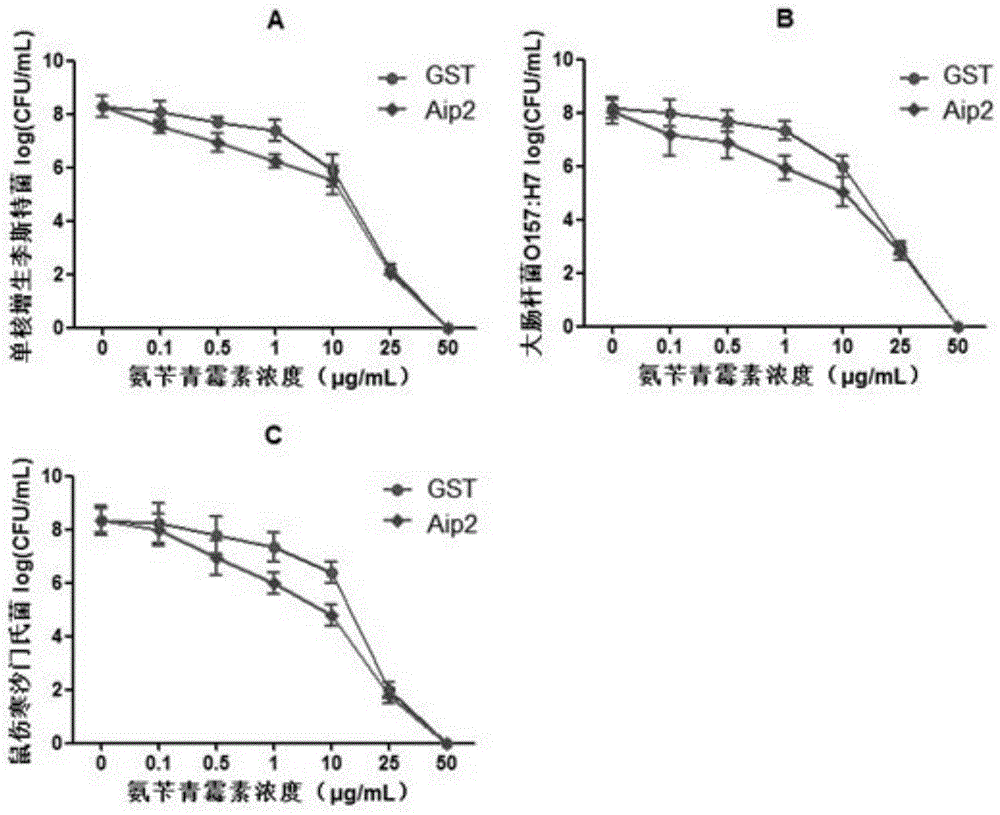
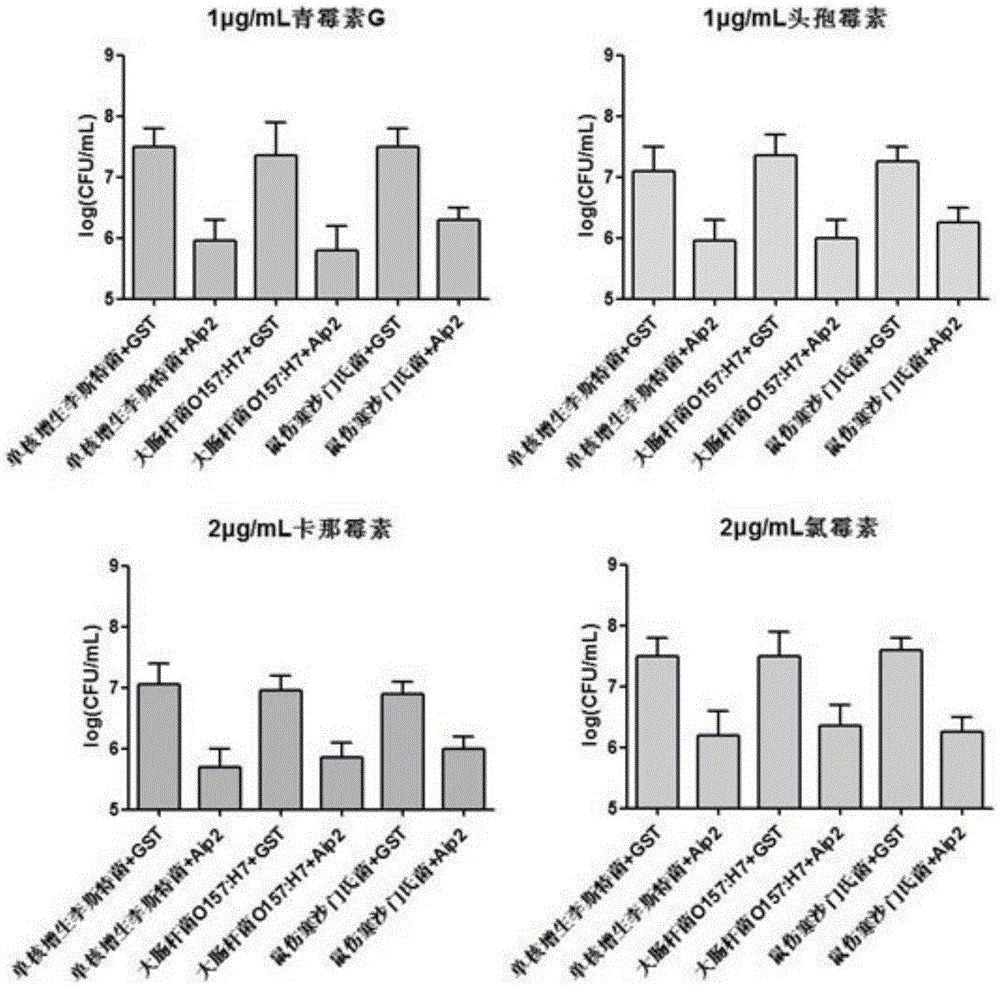
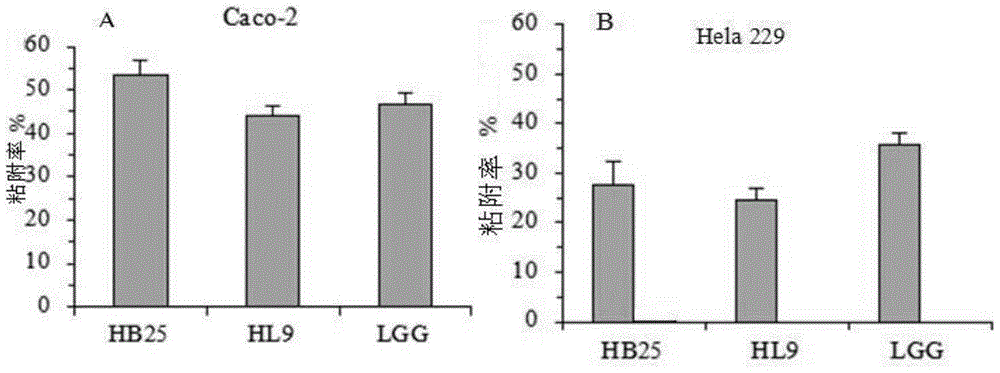
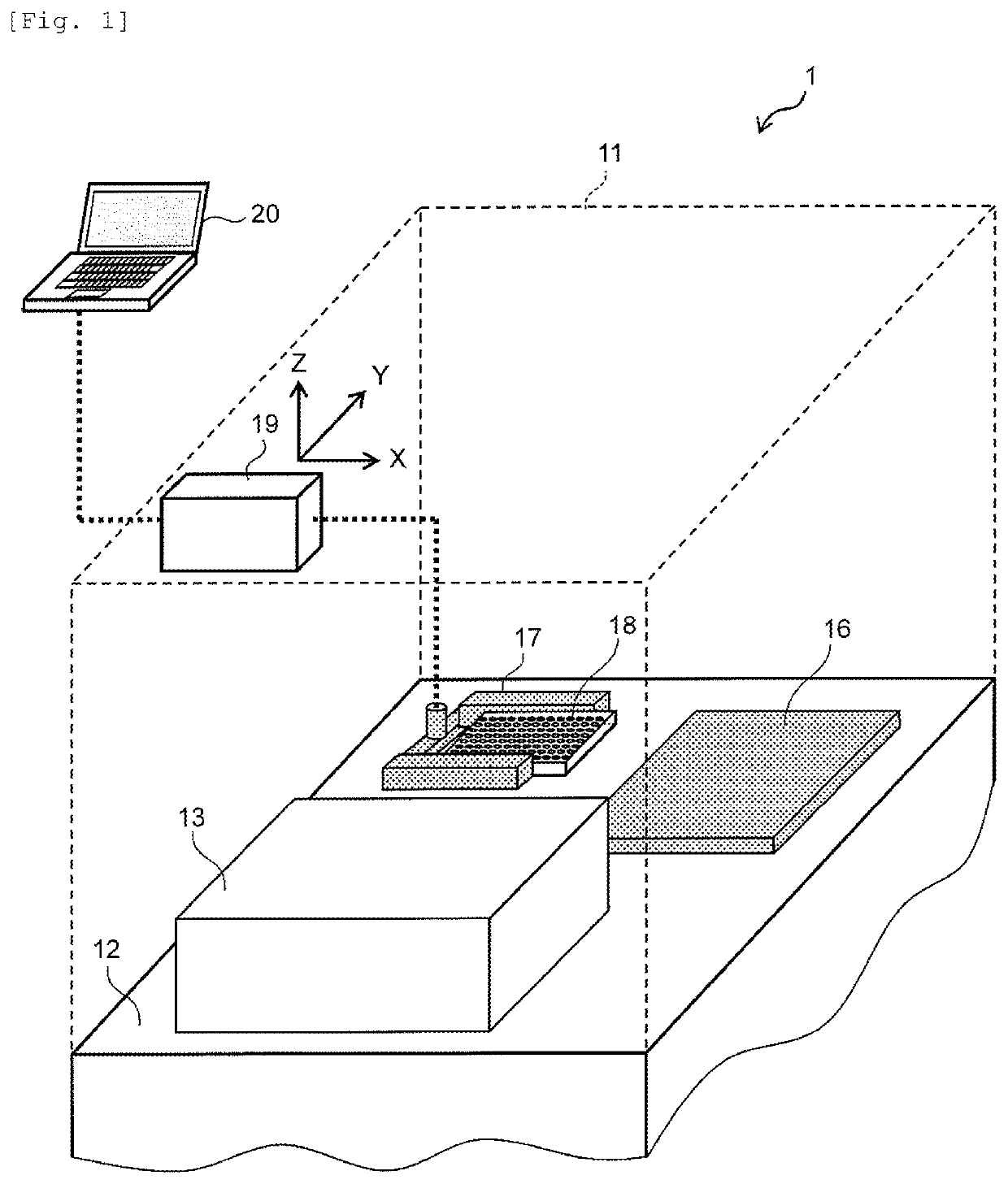
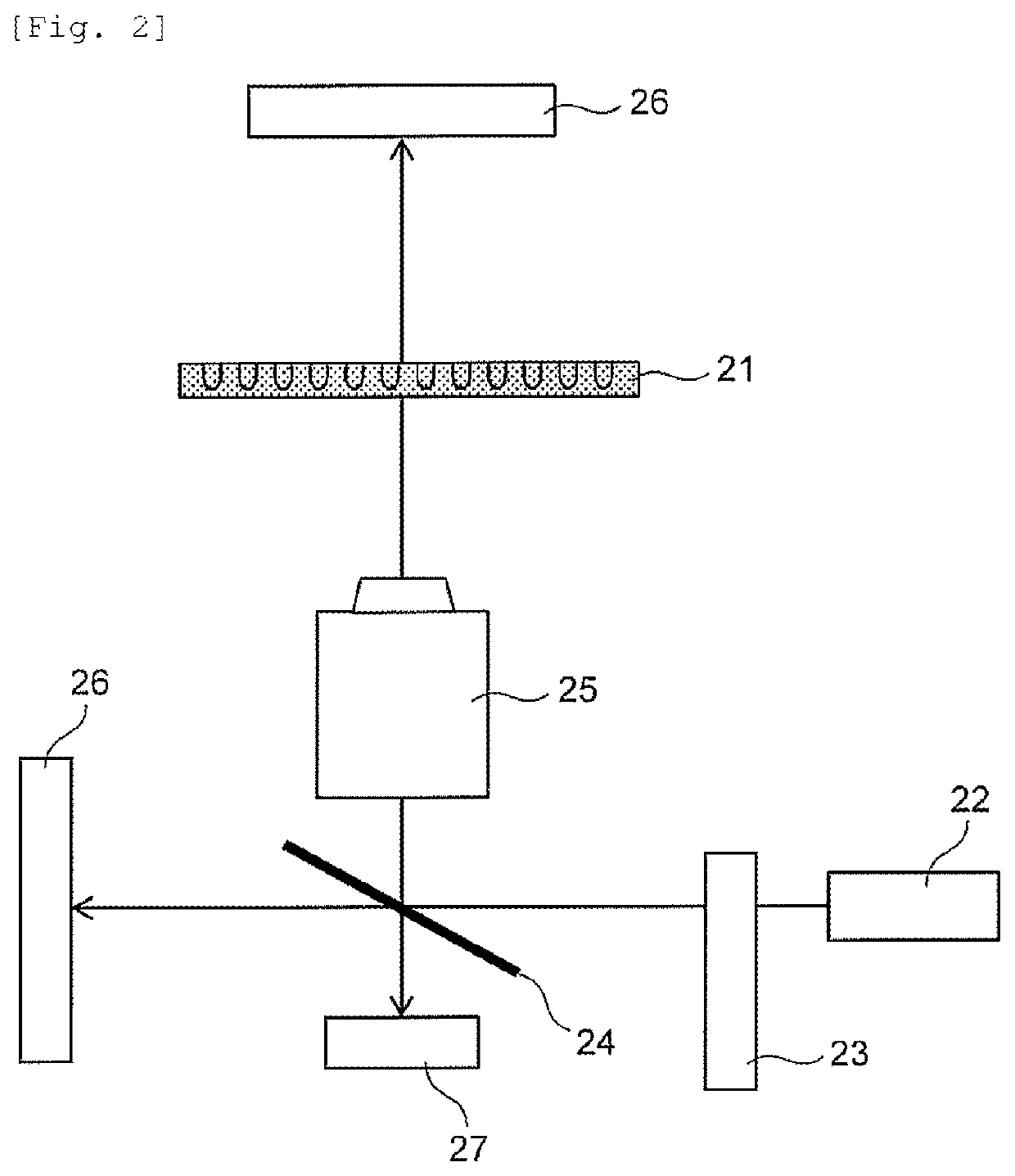
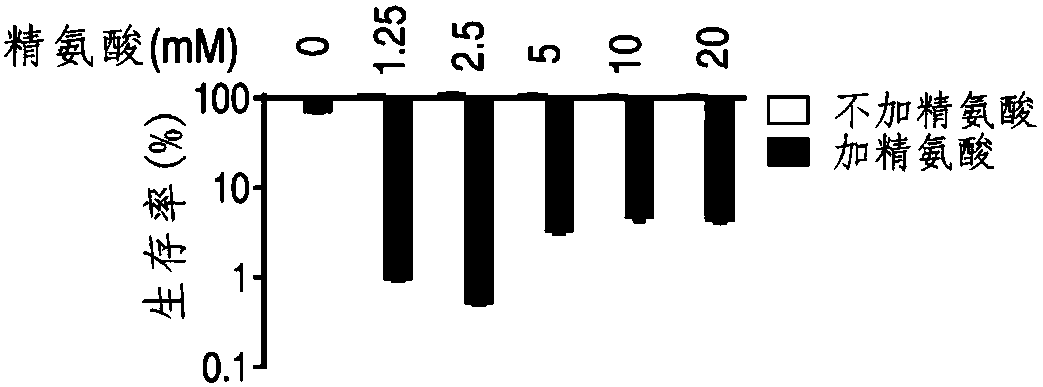Patents
Literature
57 results about "Antibiotic sensitivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Antibiotic sensitivity or antibiotic susceptibility is the susceptibility of bacteria to antibiotics.
Antibiotic Sensitivity Testing Method
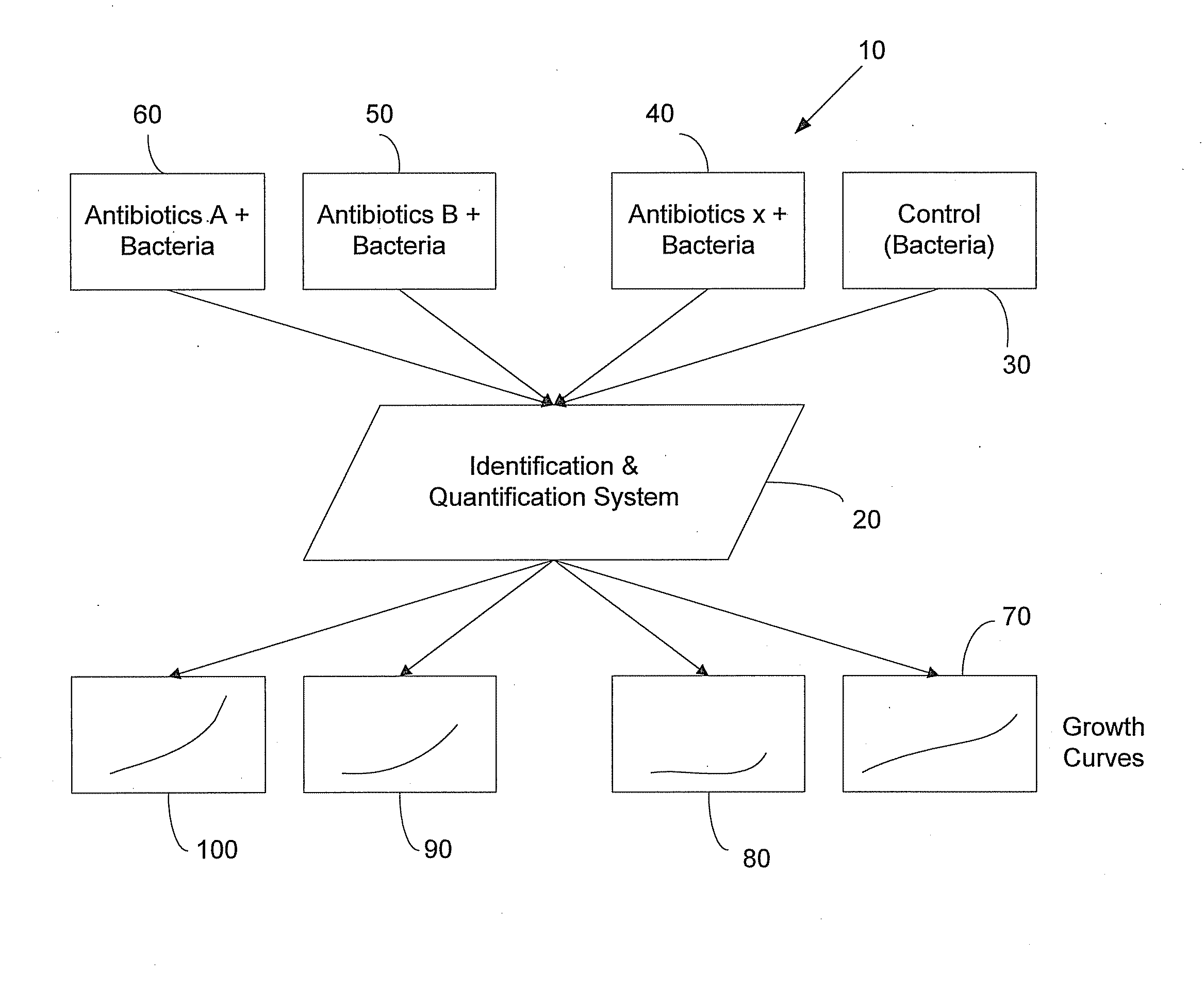
InactiveUS20080220465A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisAntibiotic sensitivityAntibiotic Y
The method includes several steps including obtaining a bacterial sample; identifying the type of bacteria in the bacterial sample; selecting a set of antibiotics based on the identity of the bacteria in the bacterial sample; obtaining a control sample from the bacterial sample; placing the bacterial sample in solutions containing the set of antibiotics; determining concentration of bacteria in the respective antibiotic solutions; determining growth curves for the respective antibiotic solutions based on the determined bacterial concentration; and comparing the growth curves for the respective antibiotic solutions with a growth curve determined from the control sample. An identification and quantification system may be used to select the set of antibiotics, and further may be used in the steps of determining concentration of bacteria in the respective antibiotic solutions and determining growth curves for the respective antibiotic solutions based on the determined bacterial concentration.
Owner:POCARED DIAGNOSTICS
Bacteriophage compositions and uses thereof
InactiveUS20190142881A1Increasing antibiotic sensitivityImpaired efflux pumpAntibacterial agentsViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsAntibiotic sensitivityBiofilm
The present invention includes compositions and methods of bacteriophage to increase antibiotic sensitivity in bacteria. In one aspect, the invention includes a method of increasing antibiotic sensitivity in multi-drug resistant (MDR) bacteria. Another aspect includes a pharmaceutical composition comprising a lytic bacteriophage. Yet another aspect includes a method of treating a multi-drug resistant bacterial infection in a subject. Yet another aspect includes a method of disrupting a pathogenic bacteria associated with a biofilm and compositions for use thereof.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Capacitive biosensor for identifying a microorganism or determining antibiotic susceptibility
InactiveUS20180045725A1Effective treatmentQuick confirmationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionAntibiotic sensitivityMicroorganism
An apparatus for inspecting an antibiotic and a method for determining antibiotic sensitivity using the same is provided. The antibiotic susceptibility inspection time which has conventionally taken longer than 24 hours is shortened to about 2 hours or less, the efficacy of the target substance is monitored in real time, the identification of the microorganism, the kind of the antibiotic capable of treating the microorganism, and the minimum dosage thereof are quickly confirmed. Microbial infections requiring prompt diagnosis and treatment can be effectively treated.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV +1
Gene transfer method of agrobacterium of poplar
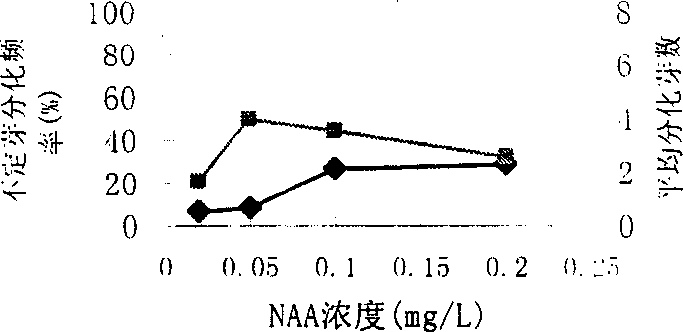
A gene transfer method for the agrobacterium of poplar (Xingjiang poplar) includes explant selection, culture medium screening, hormone addition, antibiotic sensitivity and culture conditions. It can be used for selectively culturing the new stres-resistance variety of Xingjiang poplar within shorter time.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
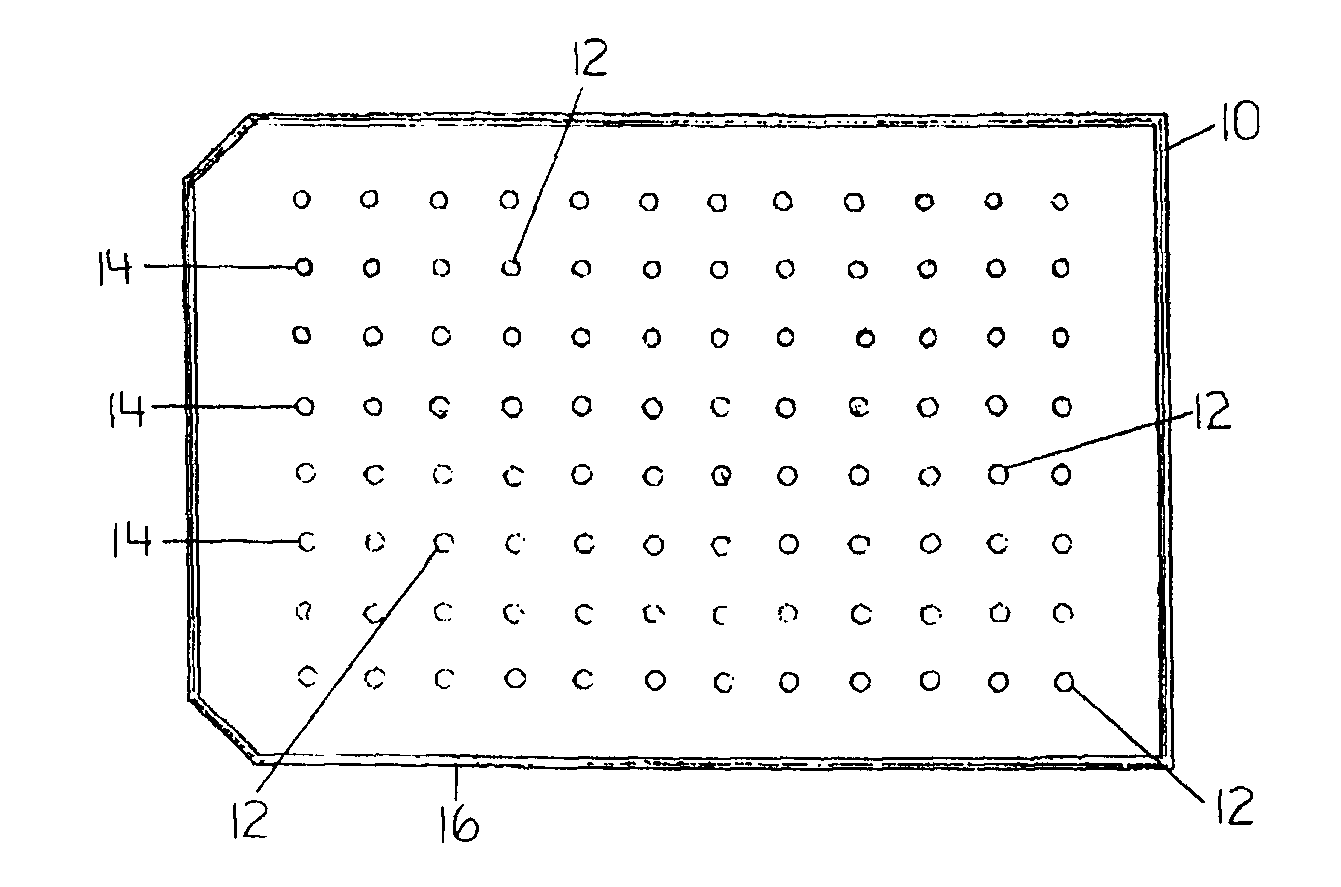
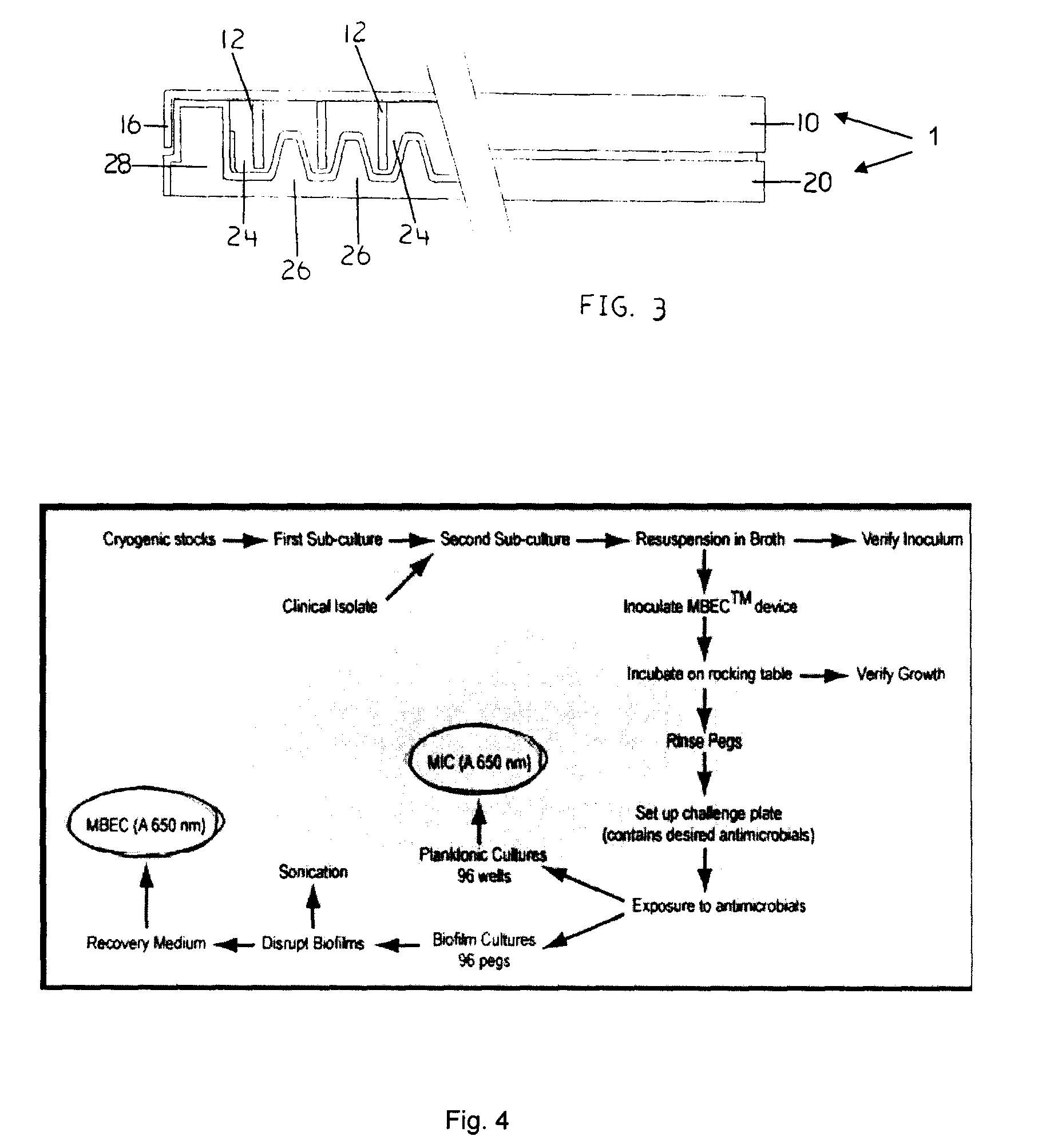
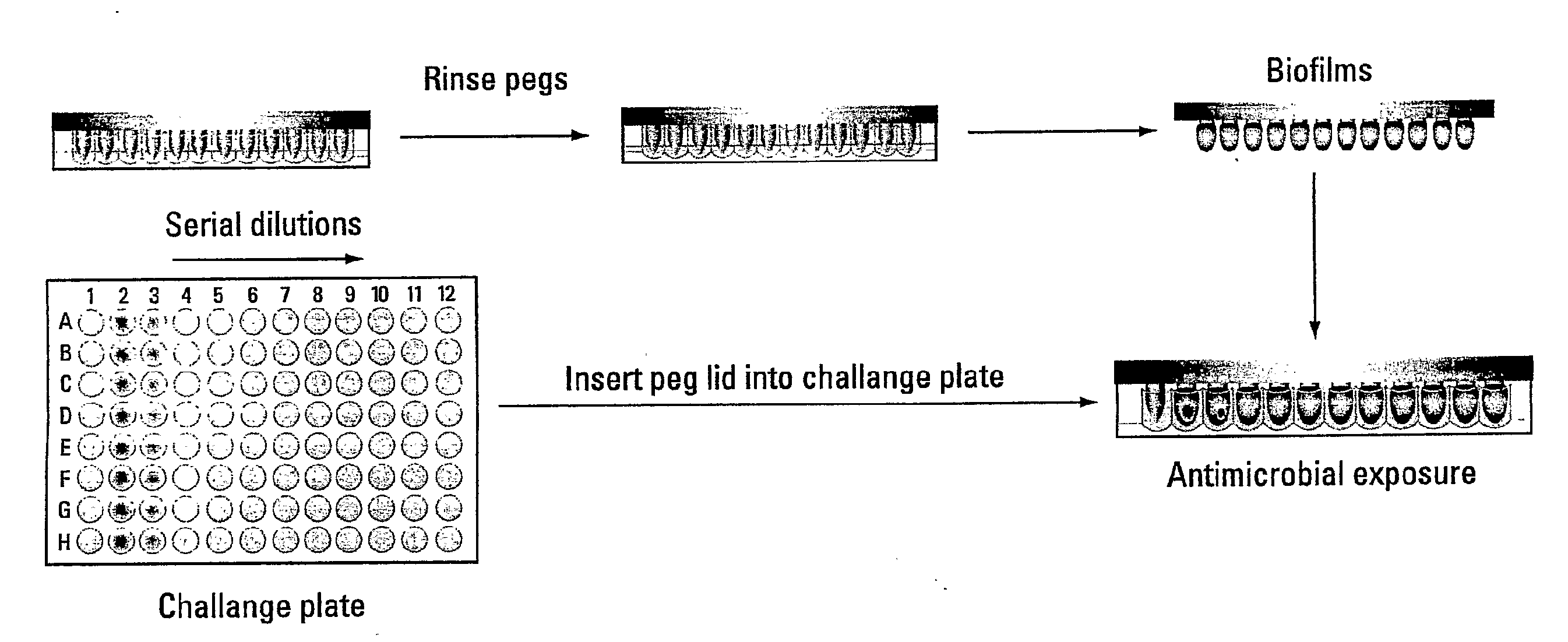
Devices and Methods for the Selection of Agents with Efficacy Against Biofilm
InactiveUS20080318268A1Efficient and cost-effectiveBroaden applicationBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibiotic sensitivityMinimum inhibitory concentration
This invention is a diagnostic plate that can be used to select antibiotic combinations with efficacy against microorganisms growing as a biofilm. The plate allows growth of biofilm on a plurality of projections, and the subsequent simultaneous challenge of biofilms on all projections of the plate to independent concentrations and combinations of anti-biofilm agents. Resistance of microorganisms to antibiotics is higher when they grow as a biofilm, as compared to when they grow in a planktonic state which is usually used to determine their level of antibiotic sensitivity. Growth of microorganisms that slough off the biofilm in the anti-biofilm agent challenge determines the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) which relates to sensitivity of the microorganisms in a planktonic state. Growth of any surviving microorganisms from the biofilm in a subsequent recovery step determines the Minimal Biofilm Eradication Concentration (MBEC) which relates to the sensitivity of the microorganisms growing as a biofilm. Enumeration of the surviving microorganisms in the recovery step determines the Minimum Biocidal Concentration (MBC).
Owner:OLSON MERLE E +1
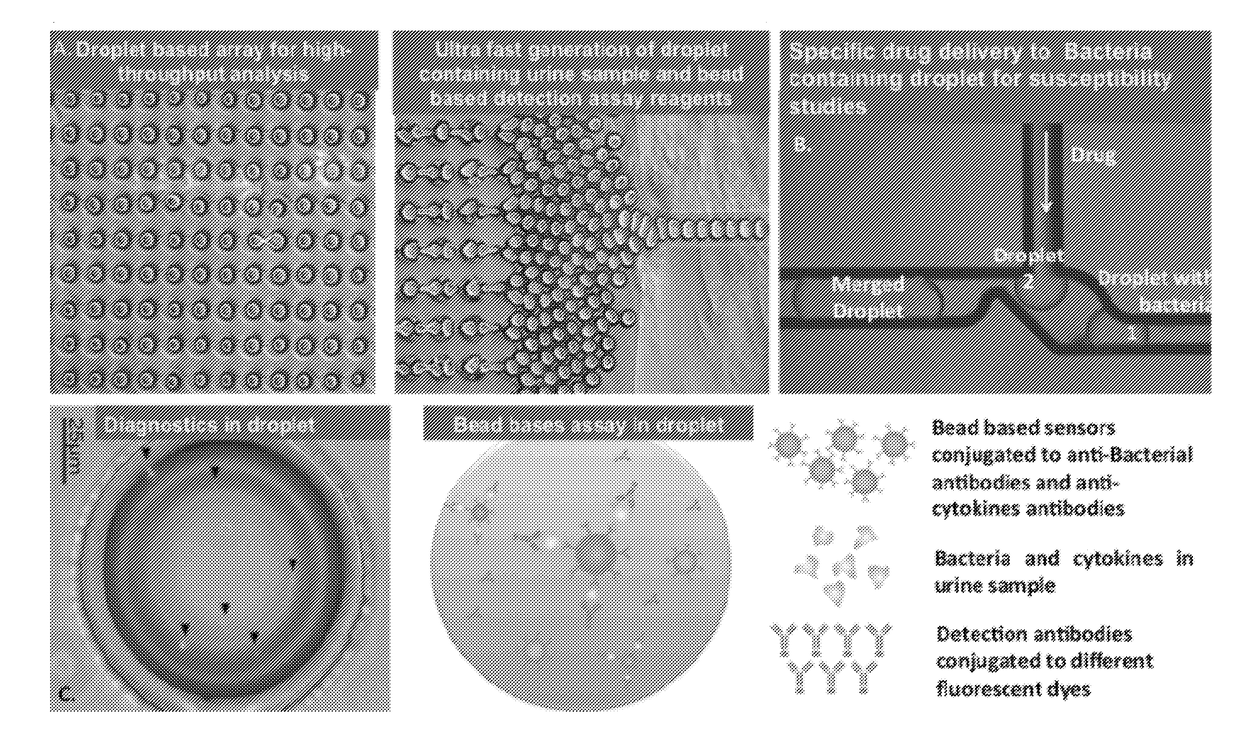
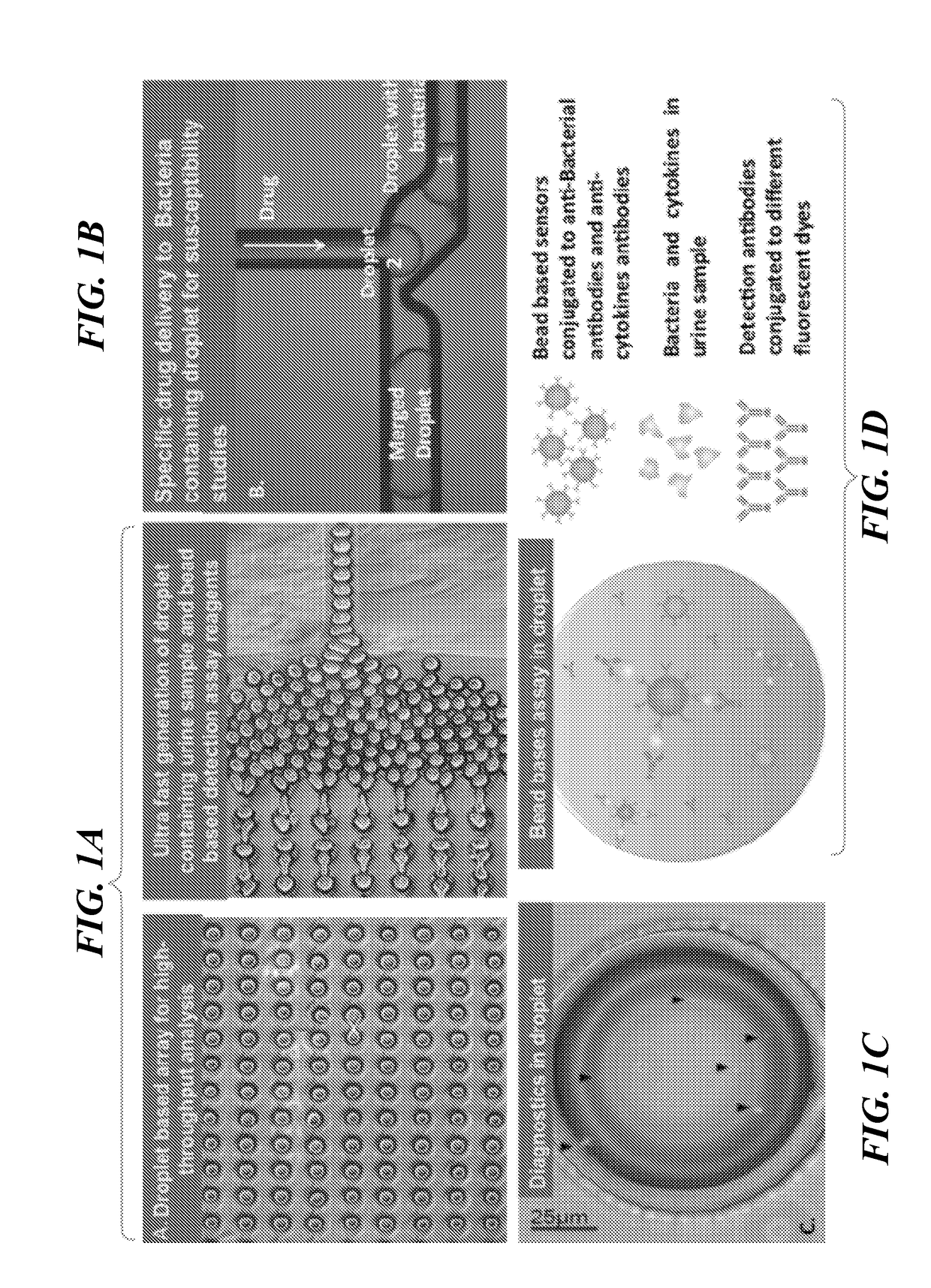
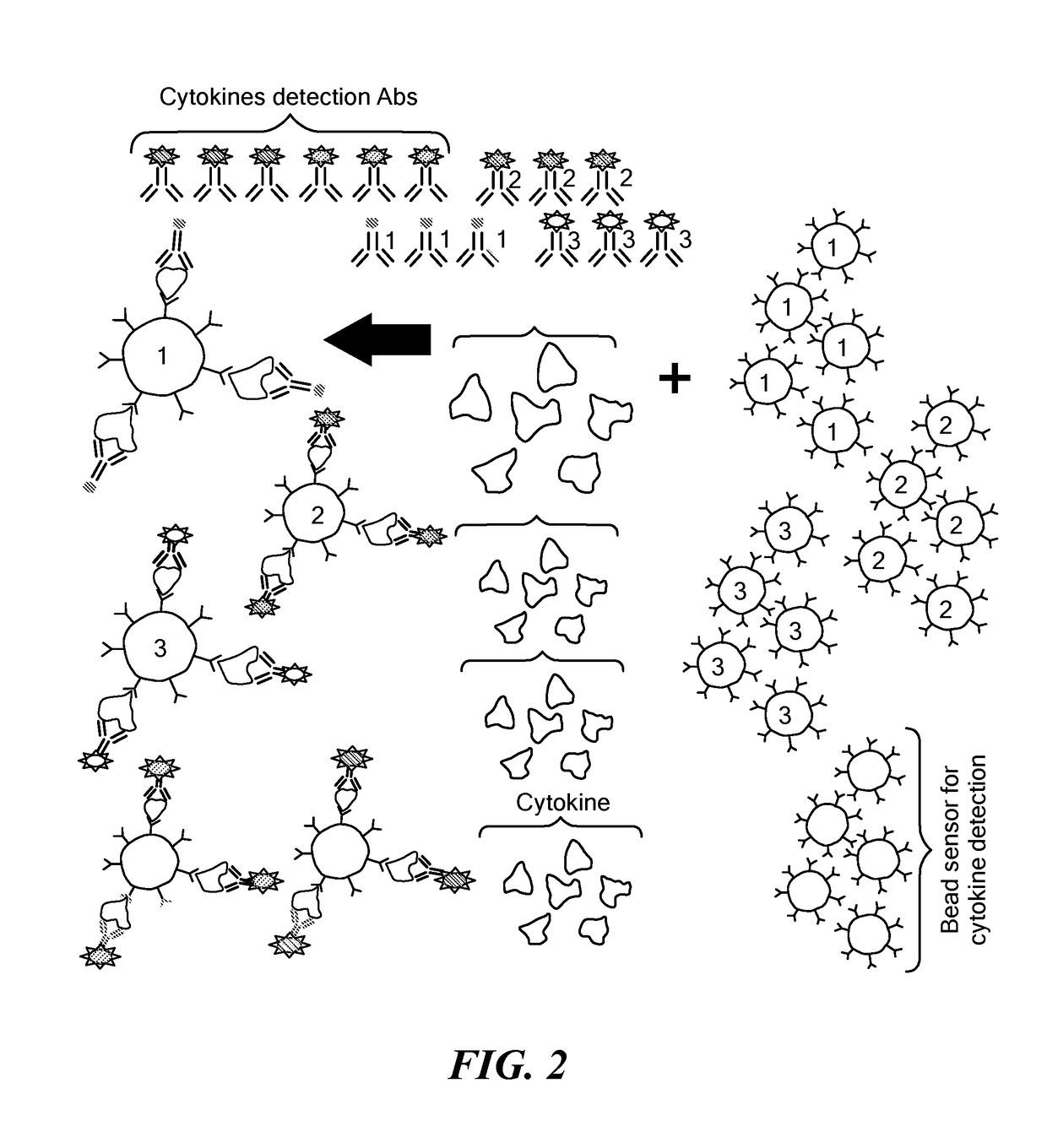
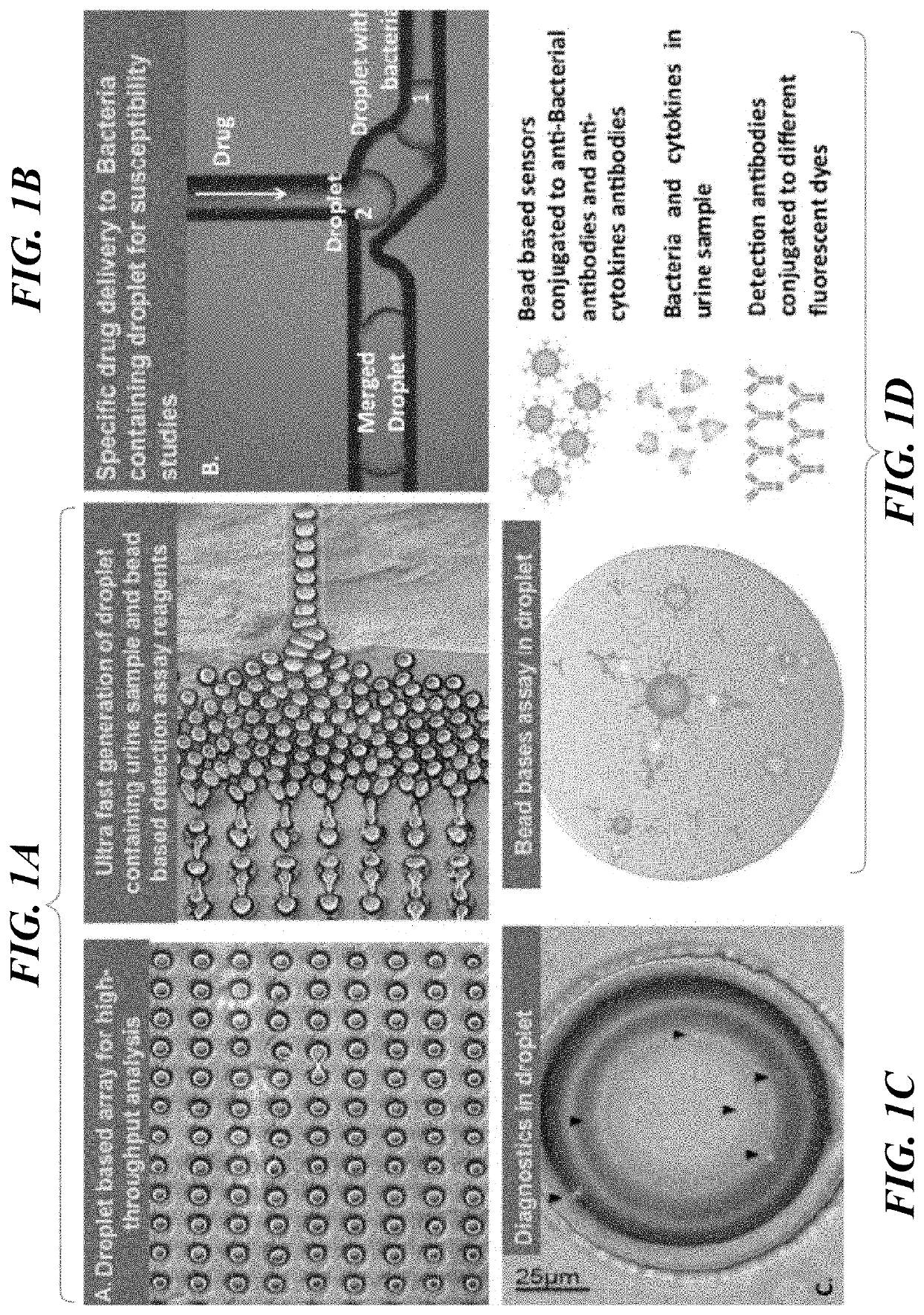
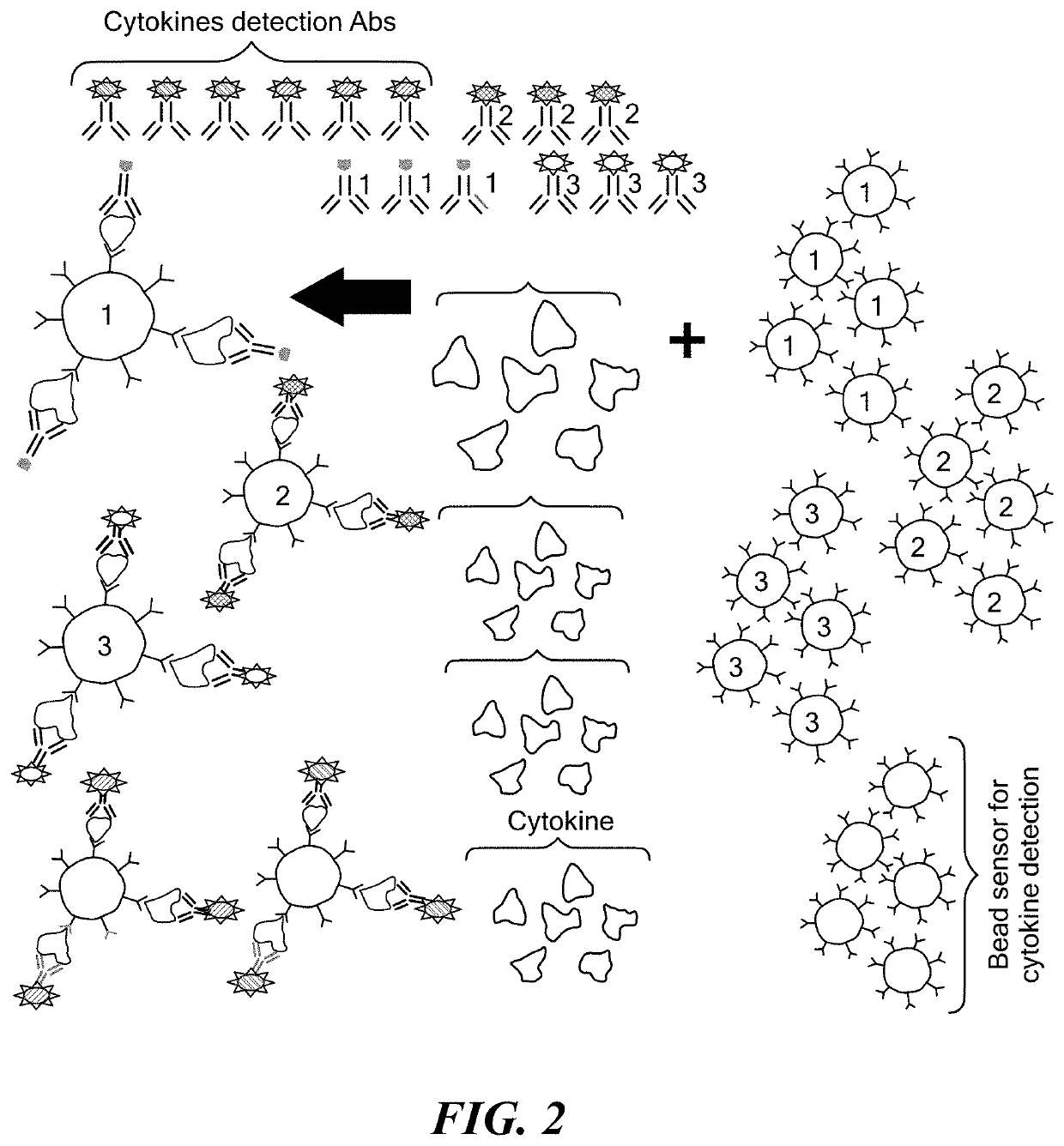
Microdroplet Based Bioassay Platform
ActiveUS20180203005A1Effective monitoringImprove throughputTransportation and packagingMixersAntibiotic sensitivityMicroorganism
Platform technology involving aqueous microdroplet reaction vessels created, arrayed, and characterized by imaging microscopy in a microfluidic device are applied to a wide variety of bioassays involving the detection and phenotypic characterization of single cells. The bioassays include the rapid and automated detection of microbial pathogens and their antibiotic sensitivity from patient samples as well as the characterization of immune responses using a patient's own cells, including the killing of tumor cells.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
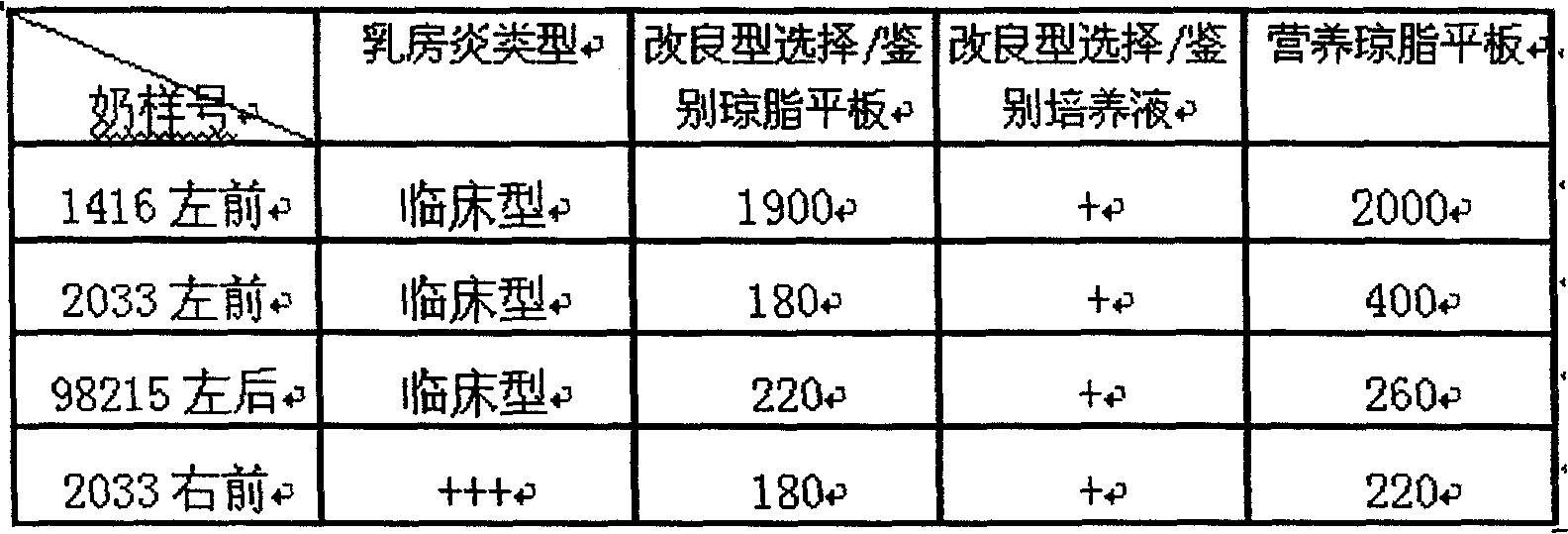
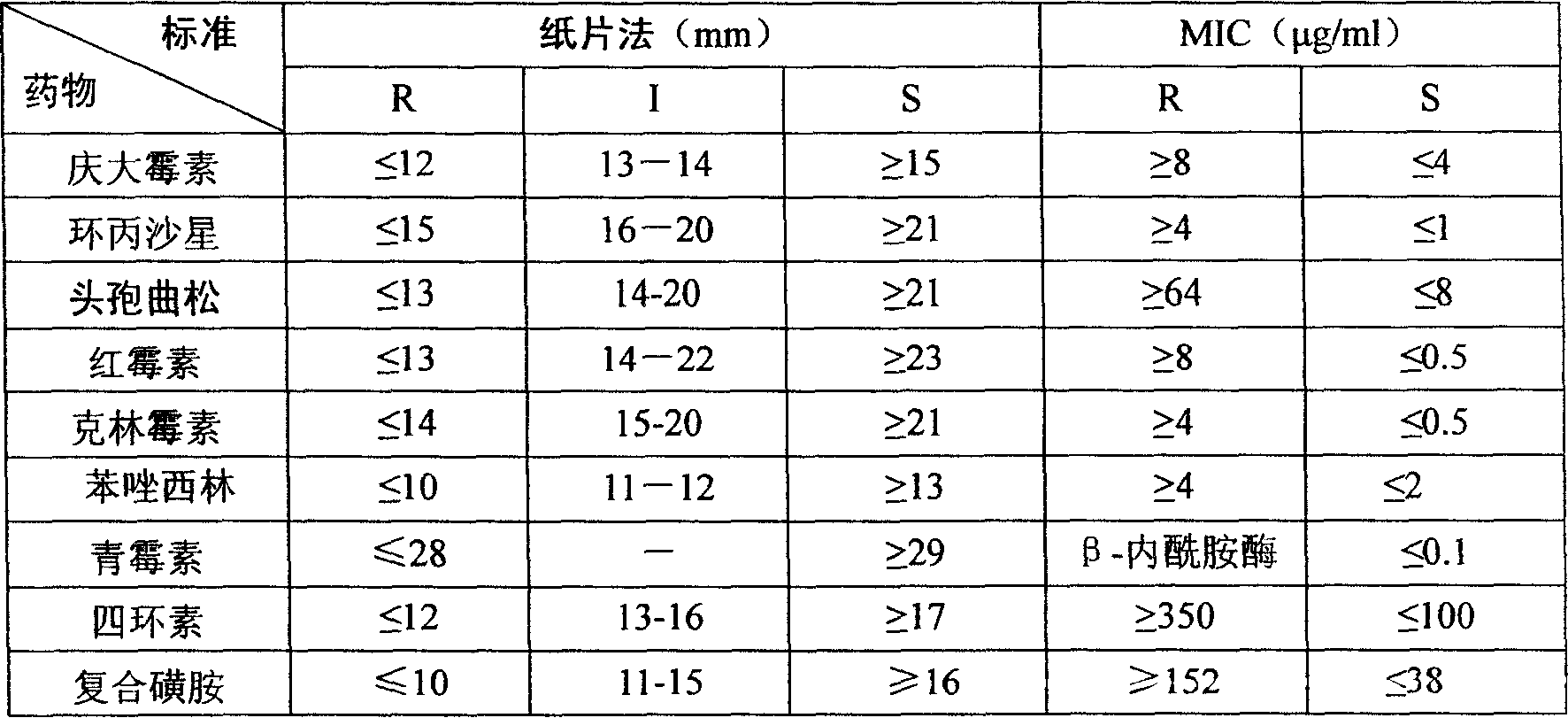
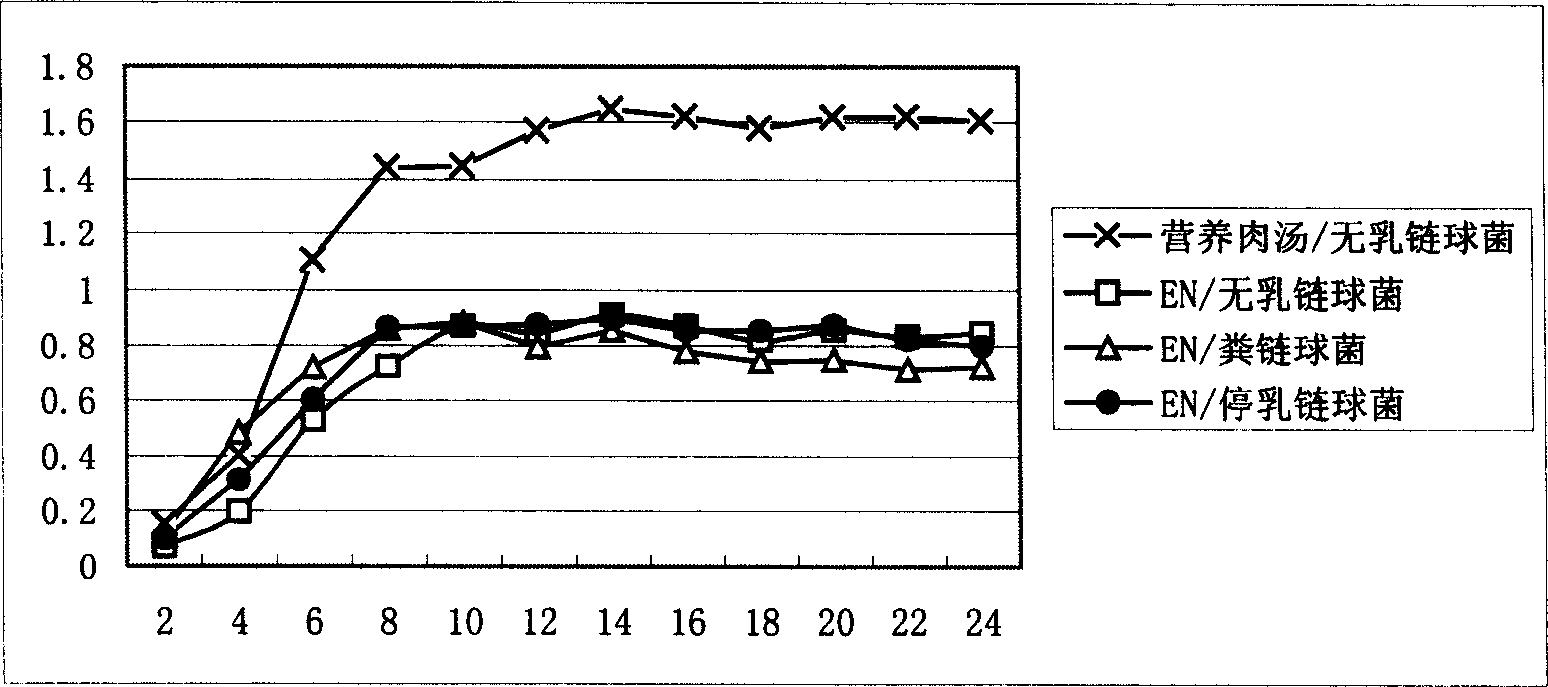
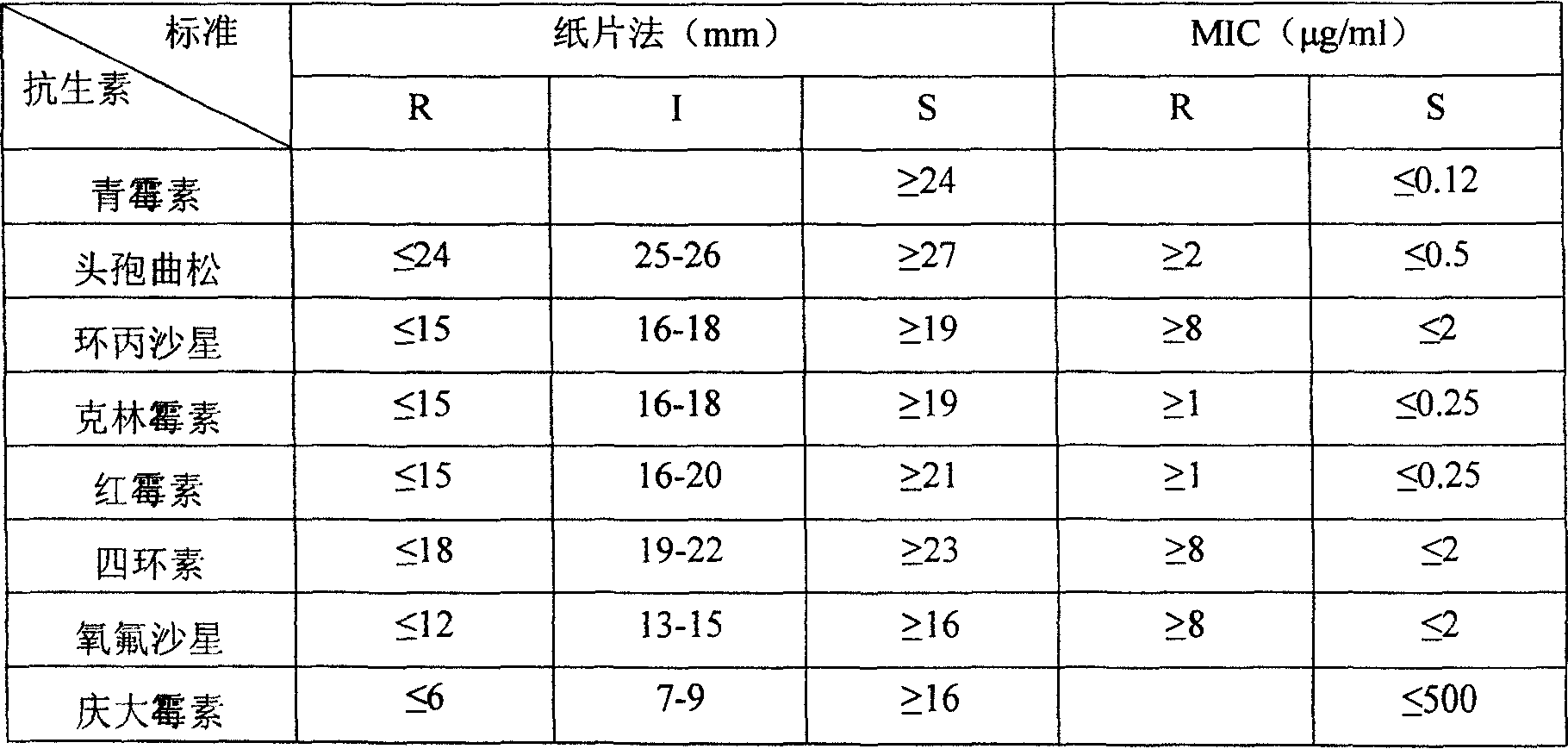
Preparing method for cow mammitis staphylococcus culture fluid and its use
InactiveCN1858234AQuick selection/identificationRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibiotic sensitivityYeast
The preparation process of cow mammitis staphylococcus culture fluid and its use belongs to the field of animal epidemic disease diagnosing, preventing and treating technology. The preparation process includes dissolving peptone 10 g, yeast powder 5 g, sodium pyruvate 10 g, glycin 12 g and lithium chloride 5 g in water of 980 ml; regulating pH to 7.3 with sodium hydroxide; sterilizing at 121 deg.c; cooling to 50+ / -10 deg.c; adding bacteria-free 1% concentration potassium tellurite water solution in 10 ml and Tween-80 in 7 ml, and preservation at 4 deg. c. The culture fluid may be used in the fast identification of cow mammitis staphylococcus and antibiotic sensitivity test.
Owner:兆丰华生物科技(南京)有限公司
Preparing method for cow mammitis streptococcus culture fluid and its use
InactiveCN1858233AGrowth inhibitionExpansion speed is fastMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibiotic sensitivityCulture fluid
The preparation process of cow mammitis streptococcus culture fluid and its use belongs to the field of animal epidemic disease diagnosing, preventing and treating technology. The preparation process includes dissolving peptone 10 g, yeast powder 5 g, sodium chloride 10 g, glucose 5 g and sodium azide 0.5 g in water of 1 L; regulating pH to 7.2 with sodium hydroxide; adding bacteria-free 0.1% concentration crystal violet water solution in 1.3ml and 1% concentration bromocreasol purple water solution in 1.5ml; sterilizing at 121deg.c and preservation at 4 deg. c. The culture fluid may be used in the fast identification of cow mammitis streptococcus and antibiotic sensitivity test.
Owner:南京市天邦生物科技有限公司
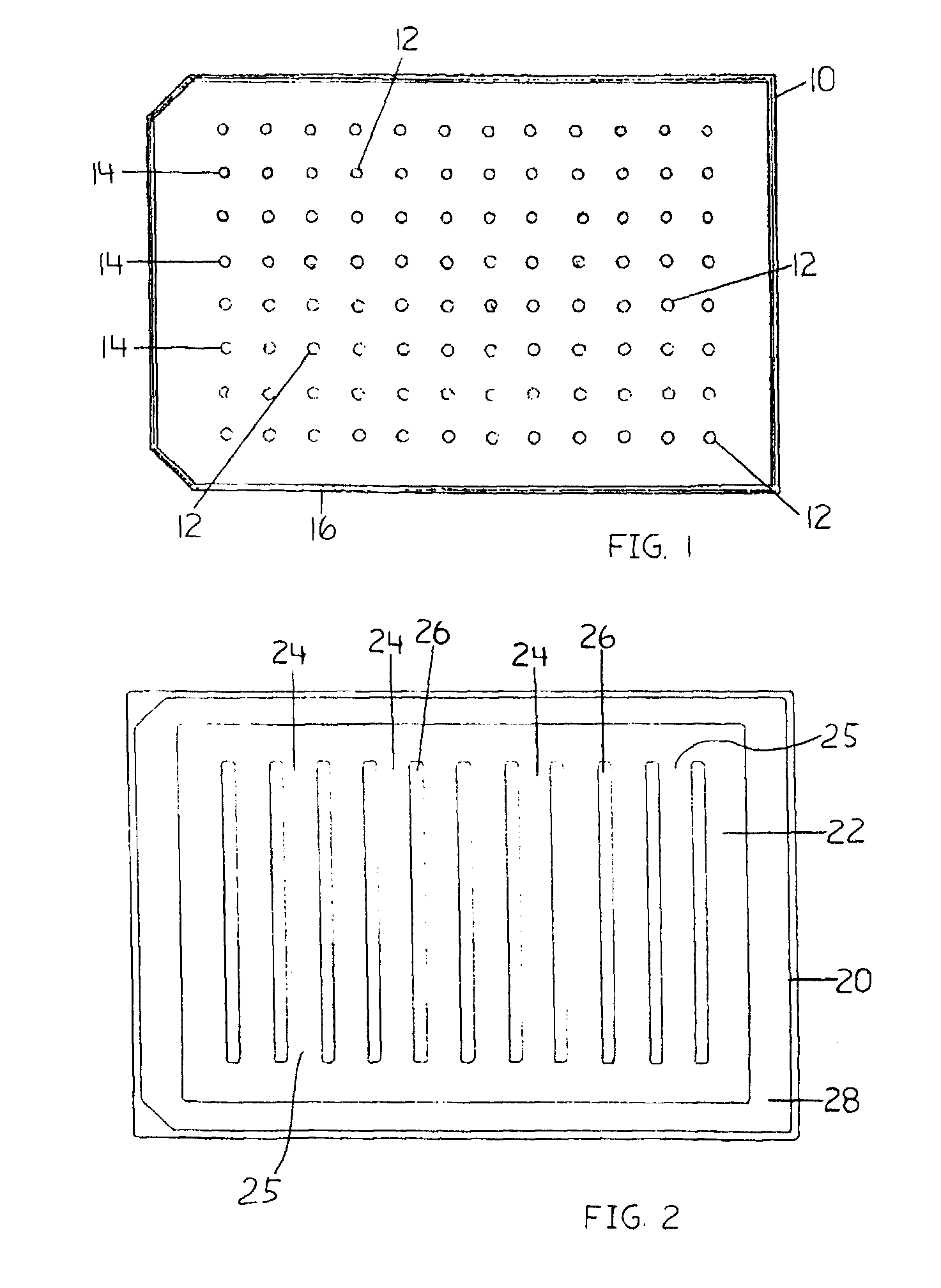
Devices and Methods for the Analysis of Biofilm
InactiveUS20080318269A1Efficient and cost-effectiveBroaden applicationBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyAntibiotic sensitivity
This invention is a diagnostic plate that can be used to select antibiotic combinations with efficacy against microorganisms growing as a biofilm. The plate allows growth of biofilm on a plurality of projections, and the subsequent simultaneous challenge of biofilms on all projections of the plate to independent concentrations and combinations of anti-biofilm agents. Resistance of microorganisms to antibiotics is higher when they grow as a biofilm, as compared to when they grow in a planktonic state which is usually used to determine their level of antibiotic sensitivity. Growth of microorganims that slough off the biofilm in the anti-biofilm agent challenge determines the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) which relates to sensitivity of the microorganisms in a planktonic state. Growth of any surviving microorganims from the biofilm in a subsequent recovery step determines the Minimal Biofilm Eradication Concentration (MBEC) which relates to the sensitivity of the microorganisms growing as a biofilm. Enumeration of the surviving microorganims in the recovery step determines the Minimum Biocidal Concentration (MBC).
Owner:OLSON MERLE E +1
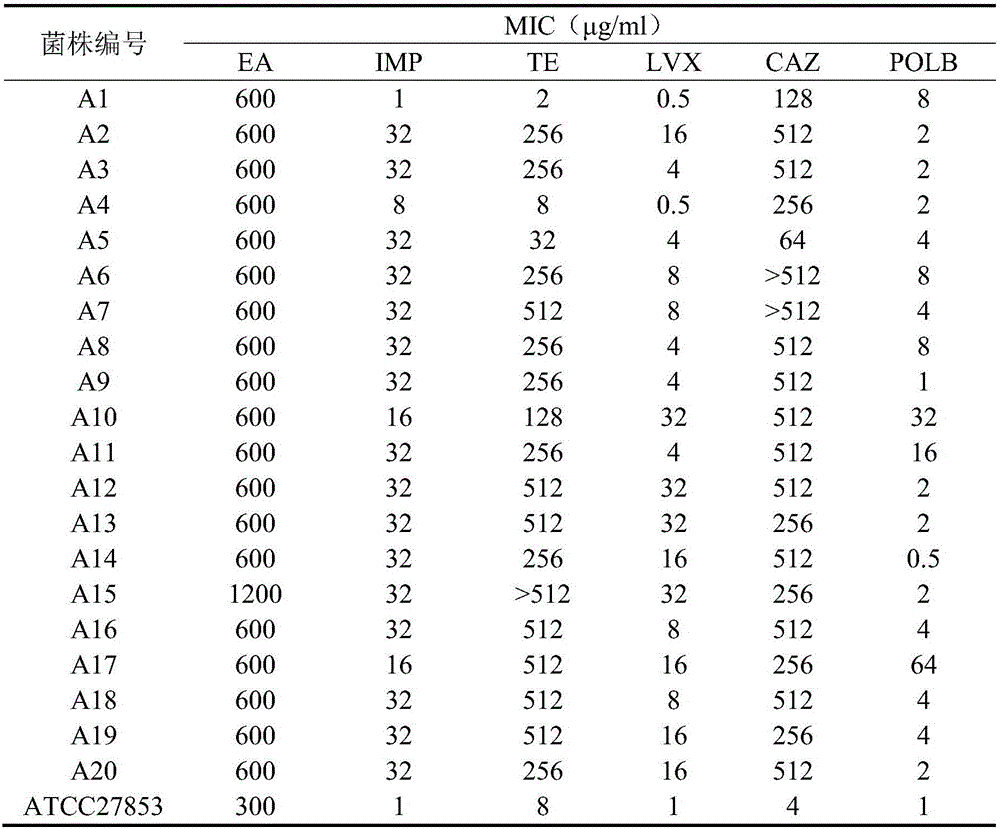
Application of pithecellobium clypearia extracts to preparation of multi-drug resistant acinetobacter baumannii medicine
ActiveCN105816511AReduce dosageAddressing drug resistanceAntibacterial agentsPlant ingredientsAntibiotic sensitivityAntibiotic Y
The invention discloses application of pithecellobium clypearia extracts to preparation of multi-drug resistant acinetobacter baumannii medicine. The pithecellobium clypearia extracts are prepared through the method includes the steps that pithecellobium clypearia coarse powder is extracted with water or an ethyl alcohol solution, the obtained extraction liquid is extracted with ethyl acetate, and the obtained extracts are target products. The antibacterial function of the pithecellobium clypearia extracts to multi-drug resistant acinetobacter baumannii and the sensitivity enhancing function of the pithecellobium clypearia extracts to similar antibiotics are disclosed for the first time. Tests prove that the pithecellobium clypearia extracts and imipenem or tetracycline or polymyxin B or ceftazidime or levofloxacin take effect together, and the use amount of antibiotics can be reduced by 50-87% compared with the mode that only the pithecellobium clypearia extracts are used. The pithecellobium clypearia extracts can serve as natural multi-drug resistant acinetobacter baumannii medicine or an antibiotic sensitivity-enhancing agent, and is applied to treatment of diseases caused by acinetobacter baumannii. A new means and alternative medicine are provided for solving the drug resistance problem of similar antibiotics.
Owner:HUACHENG PHARMA FACTORY GAUNGZHOU
Breeding method using protocorm based on germinated phalaenopsis seeds as receptor
ActiveCN104770294AShortcutImprove performancePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyAntibiotic sensitivity
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
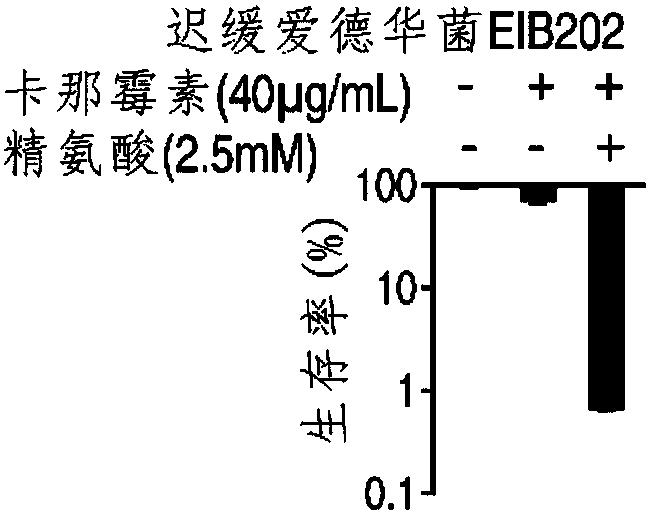
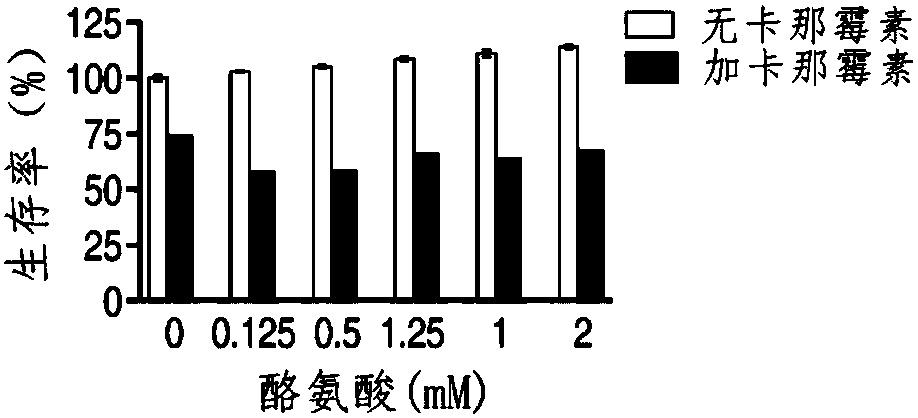
Application of L-arginine in improvement of antibiotics sensitivity of bacteria
ActiveCN108042521AIncreased sensitivityRaise the proton kinetic potentialAntibacterial agentsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsBacteroidesAntibiotic sensitivity
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine and particularly discloses application of L-arginine in improvement of antibiotics sensitivity of bacteria. According to the application, through improving a proton motive force of the bacteria by the L-arginine, the quantity of antibiotics entering interior of the bacteria can be increased, and finally, the bacteria die, so that the L-arginine can be used for improving the sensitivity of the bacteria to the antibiotics, and thus, the problem of bacterial drug resistance is solved. Through jointly using the L-arginine and the antibiotics, the bactericidal action of the antibiotics can be remarkably improved, and the effect is better and the safety and operability are higher compared with that in the prior art that only the antibiotics serve as an antibacterial drug.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Preparing method for cow mammitis E.coli culture fluid and its use
The preparation process of cow mammitis E. coli culture fluid and its use belongs to the field of animal epidemic disease diagnosing, preventing and treating technology. The preparation process includes dissolving peptone 10 g, No. 3 bile salt 1.5 g, lactose 10 g, sodium chloride 5 g and sodium citrate 5 g in water of 1000ml; regulating pH to 7.2 with sodium hydroxide; adding bacteria-free 1% concentration crystal violet water solution in 0.5 ml and 0.4% concentration phenol red water solution in 4 ml; sterilizing at 121 deg.c and preservation at 4 deg. c. The culture fluid may be used in the fast identification of cow mammitis E. coli and antibiotic sensitivity test.
Owner:兆丰华生物科技(南京)有限公司
Populus genetic transformation method
InactiveCN103266131ASimple Genetic Transformation SystemRapid genetic transformation systemHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureAntibiotic sensitivityHormones regulation
The invention discloses a populus genetic transformation method which comprises a step of establishing a genetic transformation technology system taking a populus suspension cell line as a receptor from the aspects of explant selection, callus induction, suspension cell line establishment, suspension cell plant regeneration, culture medium screening, hormone blending, antibiotic sensitivity, culture conditions and the like. By taking the suspension cell line as the receptor of agrobacterium mediation and establishing the suspension cell line with fast growth and good uniformity of cell states, the method disclosed by the invention realizes a simple, convenient and rapid populus genetic transformation system and provides a new way for populus transgenosis operation.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Microdroplet Based Bioassay Platform
ActiveUS20200116709A1Effective monitoringImprove throughputTransportation and packagingMixersAntibiotic sensitivityEngineering
Platform technology involving aqueous microdroplet reaction vessels created, arrayed, and characterized by imaging microscopy in a microfluidic device are applied to a wide variety of bioassays involving the detection and phenotypic characterization of single cells. The bioassays include the rapid and automated detection of microbial pathogens and their antibiotic sensitivity from patient samples as well as the characterization of immune responses using a patient's own cells, including the killing of tumor cells.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
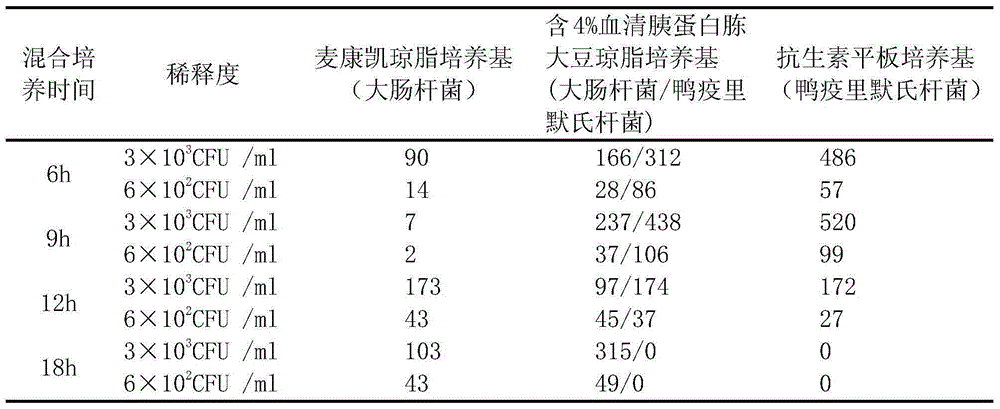
Method for mixed culture and re-separation of riemerella anatipestifer and escherichia coli
ActiveCN105176884AEasy to operateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAntibiotic sensitivityStudy drug
The invention discloses a method for mixed culture and re-separation of riemerella anatipestifer and escherichia coli. The method for mixed culture and re-separation of riemerella anatipestifer and escherichia coli comprises the following steps of (1) performing strain recovery; (2) screening riemerella anatipestifer and escherichia coli with antibiotics sensitivity differences; (3) inoculating the riemerella anatipestifer and the escherichia coli into a culture medium for mixed culture at a certain time interval or different diluting concentration; (4) measuring the minimum inhibitory concentration of antibiotics in the second step on the screened riemerella anatipestifer and escherichia coli; (5) preparing an antibiotic plate culture medium; (6) separating mixed culture bacterium liquid. The method for mixed culture and re-separation of riemerella anatipestifer and escherichia coli has the advantages that two kinds of bacteria are used outside duck poultry bodies and can jointly grow for more than 20 generations; conditions are provided for studying drug resistance transfer and relevant mechanisms of the two kinds of bacteria under the symbiosis condition; important significance is realized on disease prevention and control of duck breeding industry.
Owner:山东绿州动物药业有限公司
Identifying genes involved in antibiotic resistance and sensitivity in bacteria using microcultures
InactiveUS20170342407A1Increase probabilityLoss of fitnessMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein nucleotide librariesTransposon mutagenesisAntibiotic sensitivity
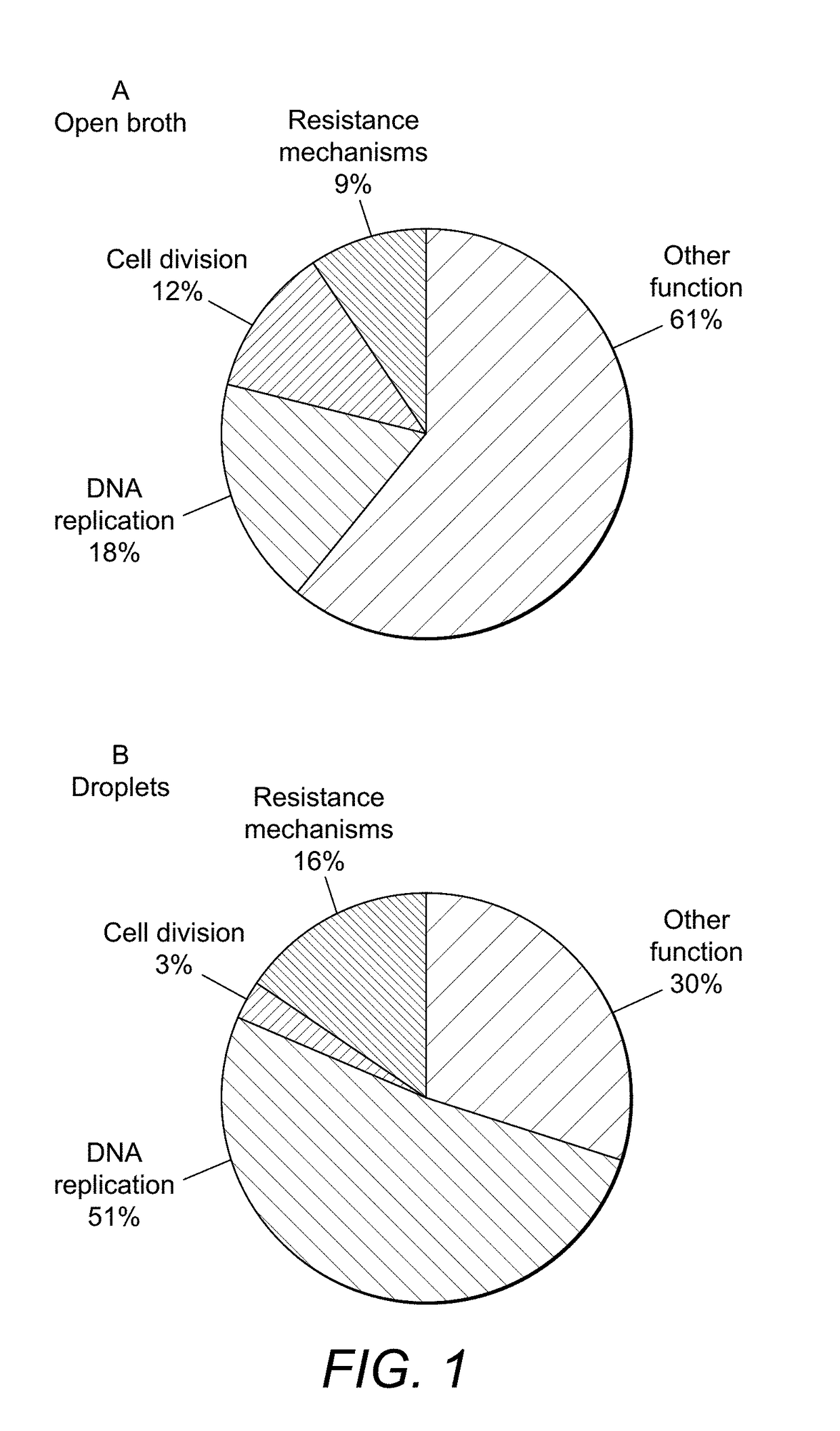
Described is a method for identifying a gene which mediates antibiotic sensitivity or resistance in a target bacterium, the method comprising the steps of: (a) generating a pool of mutant target bacteria by transposon mutagenesis with an activating transposon (TnA), wherein the TnA comprises an outward-facing promoter (TnAP) capable of increasing transcription of a gene at or near its insertion site in the DNA of said target cells; (b) generating a control microdroplet library by encapsulating individual members of the pool of step (a) in microdroplets, the microdroplets comprising a volume of aqueous growth media suspended in an immiscible carrier liquid, each microdroplet comprising a single mutant target cell; (c)generating a test microdroplet library by encapsulating individual members of the pool of step (a) in microdroplets, the microdroplets comprising a volume of aqueous growth media containing the antibiotic and suspended in an immiscible carrier liquid, each microdroplet comprising a single mutant target cell; (d) incubating the control and test microdroplet libraries to produce control and test microcultures; and (e) comparing the distribution of TnA insertions between control and test microcultures to identify a gene which mediates antibiotic sensitivity or resistance in said target bacterium.
Owner:DISCUVA
Method for adjusting antibiotic sensitivity of a test culture
ActiveUS7897365B2Improve stabilityImprove testBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBacteroidesAntibiotic sensitivity
Owner:CHARM SCI
Whole genome sequencing analysis method of pigling diarrhoea Escherichia coli
InactiveCN107245525AUnderstand comprehensivelyReduce abuseMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesAntibiotic sensitivityEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a whole genome sequencing analysis method of pigling diarrhoea Escherichia coli, and belongs to the technical field of biological gene detection. The whole genome sequencing analysis method of pigling diarrhoea Escherichia coli comprises following steps: sample collecting; separation and identification of fecal sample Escherichia coli; serotype identification; virulence factor result detection; whole genome sequencing analysis and whole genome sequence study of Escherichia coli containing a plurality of virulence factors. According to the whole genome sequencing analysis method, whole genome sequencing is adopted for more comprehensive knowing of the genome information of Escherichia coli ST4214, and analysis of the virulence factors contained by Escherichia coli ST4214; genome analysis of pigling diarrhoea Escherichia coli ST4214 possesses significant importance on study of pigling diarrhoea epidemic serotype; study on pigling diarrhoea Escherichia coli ST4214 drug resistance gene is capable of guiding applications of antibiotics based on the antibiotic sensitivity and drug resistance, and avoiding antibiotics abuse; and the whole genome sequencing analysis method is used for providing data base for development of pigling diarrhoea vaccines.
Owner:BEIJING VOCATIONAL COLLEGE OF AGRI
Identifying genes involved in antibiotic resistance and sensitivity in bacteria using microcultures
InactiveUS20180179518A9Increase probabilityLoss of fitnessMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein nucleotide librariesBacteroidesAntibiotic sensitivity
Described is a method for identifying a gene which mediates antibiotic sensitivity or resistance in a target bacterium, the method comprising the steps of: (a) generating a pool of mutant target bacteria by transposon mutagenesis with an activating transposon (TnA), wherein the TnA comprises an outward-facing promoter (TnAP) capable of increasing transcription of a gene at or near its insertion site in the DNA of said target cells; (b) generating a control microdroplet library by encapsulating individual members of the pool of step (a) in microdroplets, the microdroplets comprising a volume of aqueous growth media suspended in an immiscible carrier liquid, each microdroplet comprising a single mutant target cell; (c)generating a test microdroplet library by encapsulating individual members of the pool of step (a) in microdroplets, the microdroplets comprising a volume of aqueous growth media containing the antibiotic and suspended in an immiscible carrier liquid, each microdroplet comprising a single mutant target cell; (d) incubating the control and test microdroplet libraries to produce control and test microcultures; and (e) comparing the distribution of TnA insertions between control and test microcultures to identify a gene which mediates antibiotic sensitivity or resistance in said target bacterium.
Owner:DISCUVA
Method for establishing lily gene transforming receptor system
InactiveCN1561697ASimple methodWith characteristicsHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureAntibiotic sensitivityKanamycin
A method for creating the gene transfer receptor system of lily includes disinfecting the surface of lily bulb or filament, cutting the become segments, culturing in differentiating culture medium to create a high-frequency regeneration system, antibiotic sensitivity test to determine the screening concentrations of cephamycin, hygromycin and kanamycin, inducing the rooting adventitious embryo, and transplanting.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Preparation method of salix suchowensis resistant seedlings
The invention discloses a preparation method of salix suchowensis resistant seedlings. The preparation method comprises preparation and pre-culture of explants; preparation of an infective bacterium solution; infection; co-culture; bacterium washing; differentiation and screening culture till visual kanamycin resistant buds are differentiated; continuous culture of the kanamycin resistant buds in an adventitious bud elongation selection medium; separation of each kanamycin resistant bud when the kanamycin resistant buds are 1 to 2 cm long; culture of each independent kanamycin resistant bud in a rooting selection medium; subculture for a certain time, so as to obtain the integral resistant seedlings. The preparation method is used for preparing the salix suchowensis resistant seedlings from the aspects of explant selection, culture medium optimization, hormone adjustment, antibiotic sensitivity, culture condition and the like, thereby providing a new way for tree gene functional research.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Agrobacterium-mediated method for culturing transgenic populus wutunensis plants
InactiveCN102329817AMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologyAntibiotic sensitivity
The invention relates to an agrobacterium-mediated method for culturing transgenic populus wutunensis plants, and relates to a method for culturing a new anti-reverse populus wutunensis variety by using a gene engineering technology. The method is convenient in material section; populus wutunensis leaves are directly used as explants; factors affecting gene transformation, namely antibiotics sensitivity, are optimized; and an efficient genetic transformation system for populus wutunensis is established. A method with higher transformation efficiency is provided for culturing the new anti-reverse populus wutunensis variety, the time for culturing the new anti-reverse populus wutunensis variety can be shortened, and a new path is provided for genetic improvement of forests.
Owner:DALIAN NATIONALITIES UNIVERSITY
Kit and discs for use in disc diffusion antibiotic sensitivity testing
ActiveUS20180305732A1Eliminate effectiveMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibiotic sensitivityMicrobial Susceptibility
The present invention provides methods and kits for performing microbial sensitivity tests. Specifically, the invention relates to methods for identifying the susceptibility, tolerance or resistance of a microorganism to one or more antimicrobial agents, and the level of tolerance. The method comprises exposing the microorganism grown on a plate surface to one or more antimicrobial agents and to at least one growth promoting agent.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
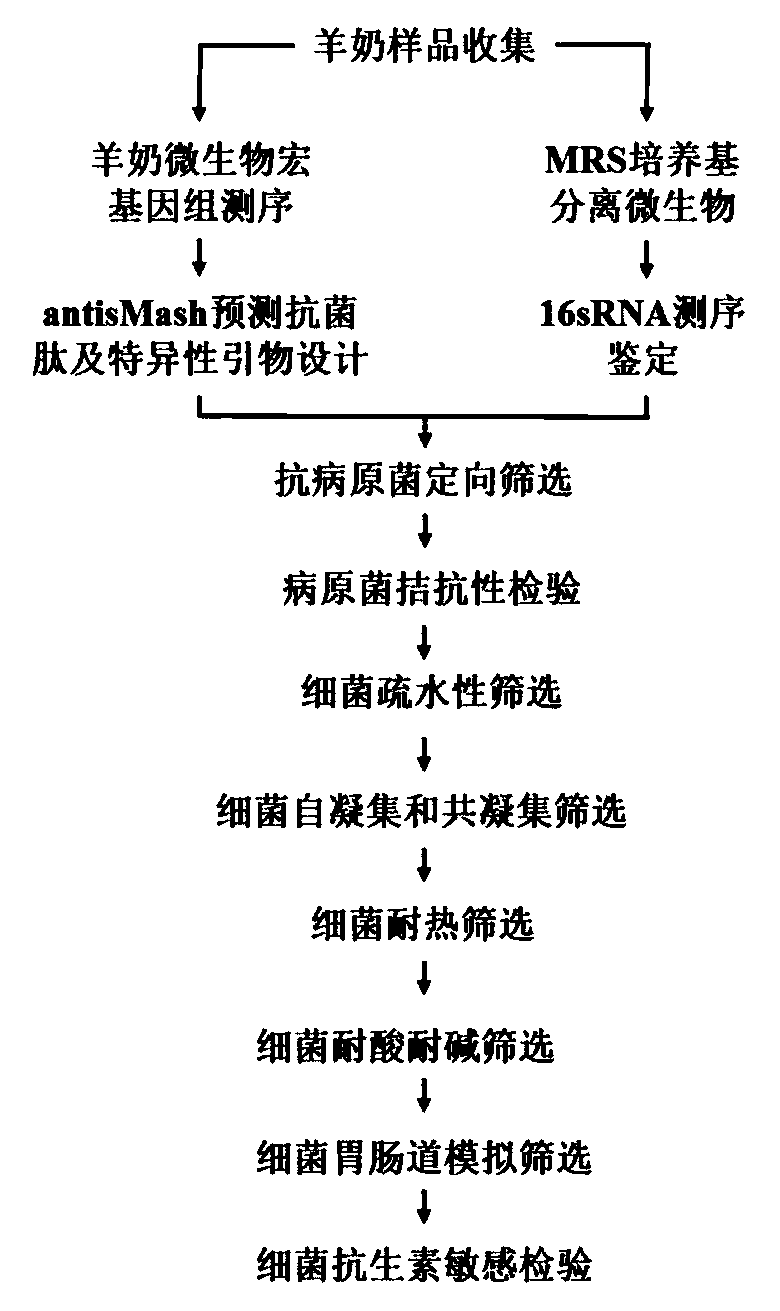
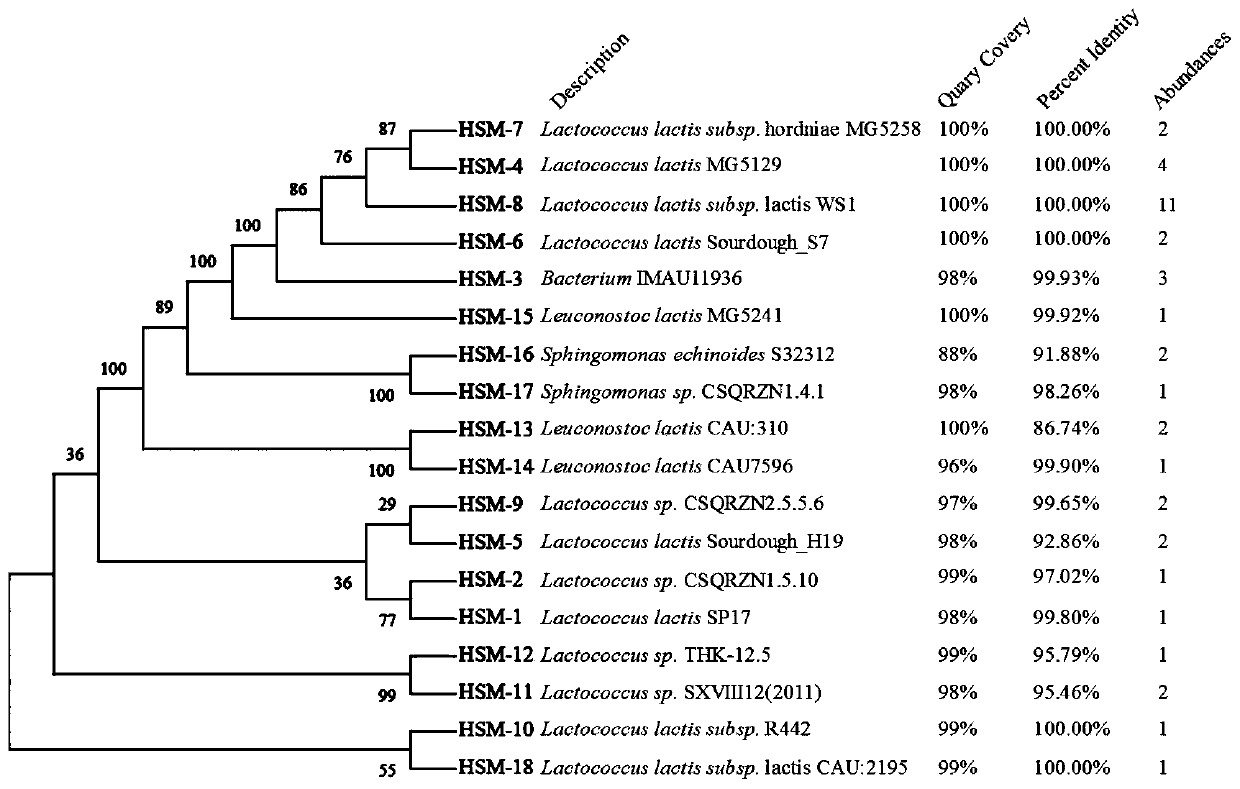
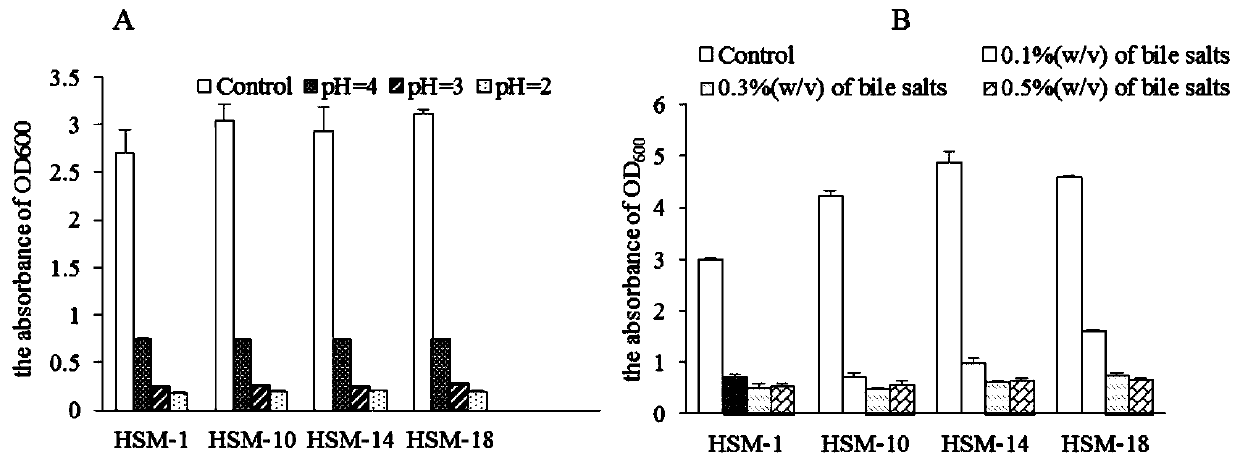
Method for directionally screening probiotic strains from Hu sheep milk
PendingCN111500750AStrong targetingAvoid blindnessMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyAntibiotic sensitivity
The invention discloses a method for directionally screening probiotic strains from Hu sheep milk. The method comprises the following steps: (1) separating microorganisms in an MRS culture medium, andidentifying the strains; (2) sequencing microbial genomes of the Hu sheep milk and designing antibacterial peptide gene primers; (3) directionally screening anti-pathogenic bacteria; (4) carrying outpathogen antagonism test; (5) carrying out hydrophobic screening on the bacteria; (6) carrying out self-agglutination and co-agglutination screening on the bacteria; (7) screening heat-resistant, acid-resistant and alkali-resistant bacteria; (8) simulating and screening bacteria gastrointestinal tracts; and (9) carrying out antibiotic sensitivity inspection. The method for directionally screeningprobiotic strains from Hu sheep milk makes probiotics with specific pathogenic bacteria antagonistic capacity screened from Hu sheep milk microbial flora in a targeted mode, strains to be selected are evaluated and inspected through multiple methods, the pertinence is high, screening blindness is avoided, the screening efficiency is improved, and a foundation is laid for marketization developmentand industrial application of novel probiotics.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Application of Bifidobacterium longum protein in improvement of antibiotics sensitivity of Salmonella typhimurium
ActiveCN105641682AEfficient preparation methodIncreased sensitivityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibiotic sensitivityAntibiotic Y
The invention provides an adhesive protein sourced from Bifidobacterium longum. An amino acid sequence of the protein is determined, on the basis, experiments find that the adhesive protein not only can adhere to an enterocyte, but also has a function of improving antibiotics sensibility of microorganisms, and the antibiotics synergy on Salmonella typhimurium is particularly prominent. On the basis of the beneficial discovery, an application of the protein as an anti-bacterial synergist for Salmonella typhimurium is determined, an application range of the protein is extended, and a new path for improving the drug sensitivity of the microorganisms is provided. Prominent technological effects are obtained on the basis of strict experimental measures, and broad application prospect is provided.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Lactic acid bacteria having ampicillin resistance, and preparation and applications of preparation of lactic acid bacteria having ampicillin resistance
The present invention discloses lactic acid bacteria having ampicillin resistance, and preparation and applications of a preparation of the lactic acid bacteria having ampicillin resistance. According to the present invention, human manure is separated under antibiotic pressure to obtain two strains of lactic acid bacteria have drug resistance, an antibiotic sensitivity test is performed, and whether plasmid DNA exists is detected; PCR amplification is performed to analyze the drug resistance gene localization conditions of the strains and explore the molecular mechanisms of the antibiotic resistance of the lactic acid bacteria, and safety evaluation is performed on the screened lactic acid bacteria having the resistance gene; whether the screened resistance strain provides an adjustment effect on intestinal tract imbalance is verified, and an antibiotic type intestinal tract flora imbalance model is used so as to provide potential treatment methods for diarrhea, flora imbalance and other diseases caused by the use of antibiotics in the clinic; and according to the obtained strain of the present invention, the intestinal tract probiotics can survive under the antibiotic pressure when the antibiotic is clinically used again while the ordinary probiotics can not survive, such that the treatment method can be provided for the diarrhea caused by the antibiotics in the clinic.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Test device
ActiveUS10793821B2Determination of bacterial identification or antimicrobial susceptibilityEasy to determineBioreactor/fermenter combinationsImage enhancementBacteria identificationAntibiotic sensitivity
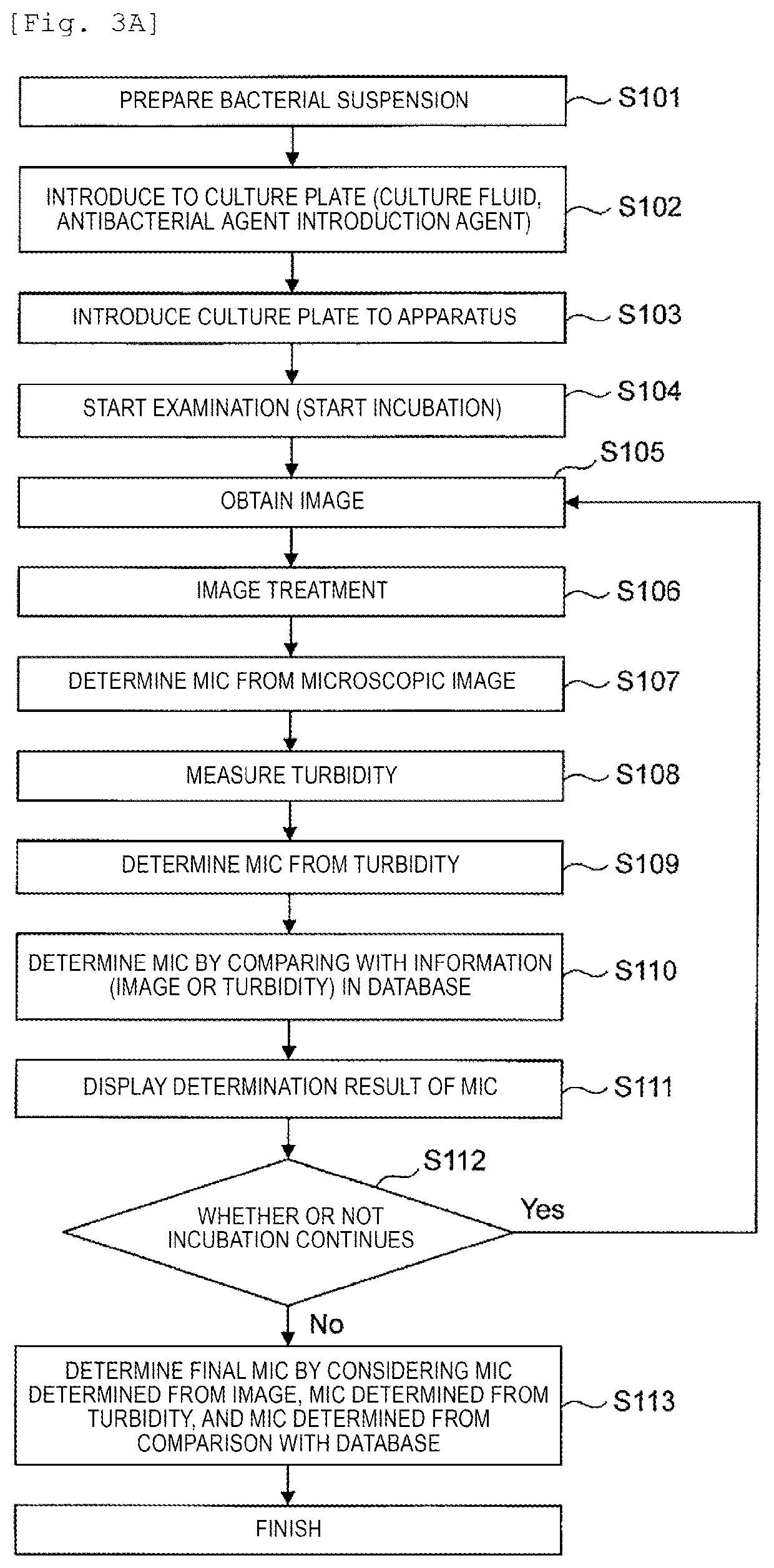
The invention provides a technology for promptly determining bacterial identification or an antimicrobial susceptibility testing. In the invention, first, a state where the bacteria are divided is monitored by performing microscopic observation with respect to the shape or the number of bacteria in each of wells of a culture plate for bacterial identification culture or the antimicrobial susceptibility testing. In addition, the shape, the number or the area of the bacteria are interpreted from the image obtained by the microscopic observation whether or not the bacteria proliferate at a stage from an induction phase to a logarithmic phase, and the time-dependent changes thereof are made into a graph. From the graph, it is determined whether or not the bacteria proliferate for each measurement, the determination results are displayed on the screen, and accordingly, the result of the antimicrobial susceptibility is provided every time when the measurement is performed (FIG. 12).
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Antibiotic sensitivity-restoring and photosensitive agents
ActiveUS9834514B2Delay drug resistanceOrganic chemistryTetracycline active ingredientsAntibiotic sensitivityResistant bacteria
The present disclosure describes a method to treat conditions, including bacterial infections and cancer, using a photosensitive compound that, upon exposure to white light, can be activated. The photosensitive compound can also interact synergistically with antibiotics used concomitantly to kill drug-resistant bacteria. The photosensitive compounds can also be used to inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells.
Owner:NEW MEXICO TECH UNIV RES PARK COPORATION
Analysis method for identifying bacteria and testing antibiotic sensitivity in biological sample
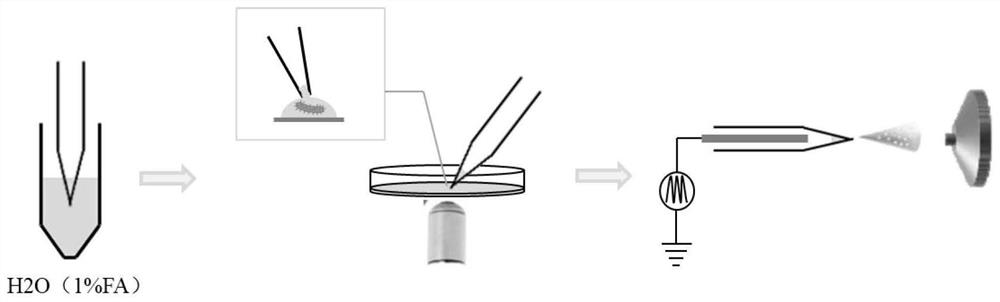
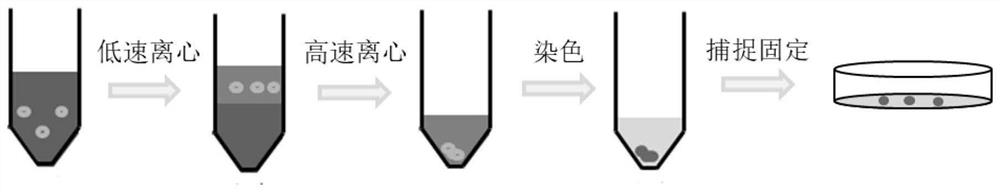
ActiveCN113640365AHigh speedNo incubationPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAntibiotic sensitivityBacteria identification
The invention discloses a method for identifying bacteria in a biological sample and a method for testing antibiotic sensitivity of the bacteria in the biological sample. The method for identifying the bacteria in the biological sample comprises the following steps: (1) centrifugally separating the bacteria in the biological sample; (2) dyeing the bacteria obtained in the step (1); (3) fixing the bacteria dyed in the step (2) through an electrostatic adsorption effect; (4) after an extraction solution is injected into the tip of a capillary tube, extracting metabolite of single live bacteria in an in-situ extraction manner; and (5) inserting an electrode into the capillary tube obtained in the step (4), applying voltage, and carrying out mass spectrometry. The method disclosed by the invention does not need to depend on incubation, can realize bacterial species identification and antibiotic sensitivity test in an initial bacterial infection biological sample, has the advantages of rapidness, high sensitivity, non-targeted analysis and the like, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com