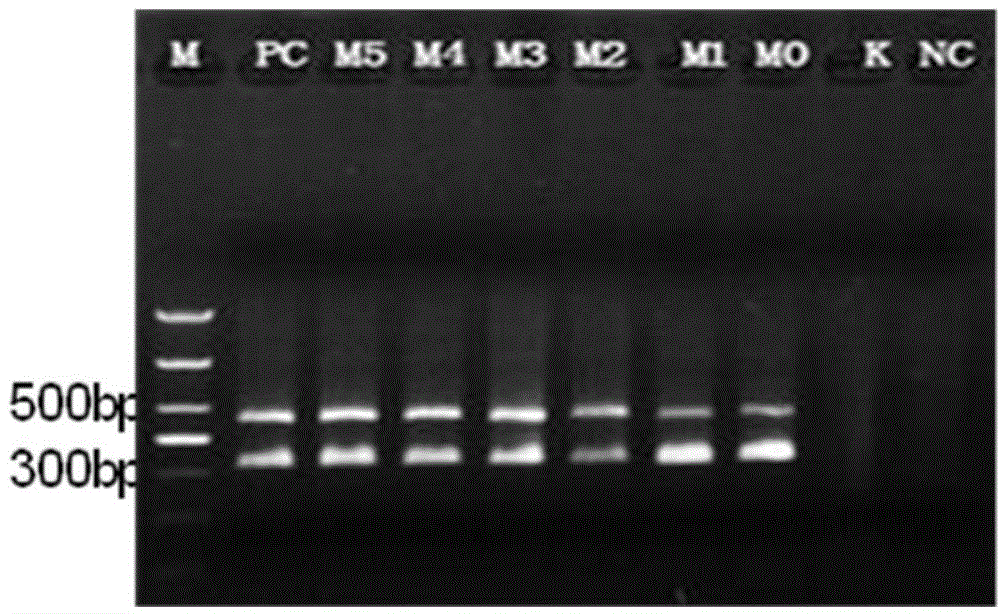
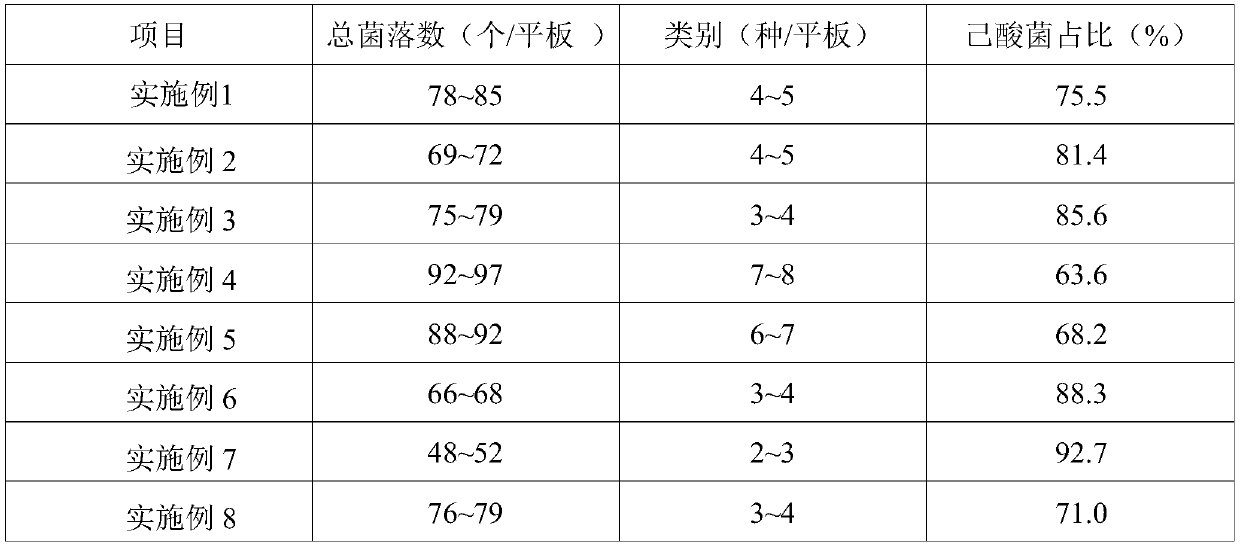
Patents
Literature
78 results about "Bacteria identification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
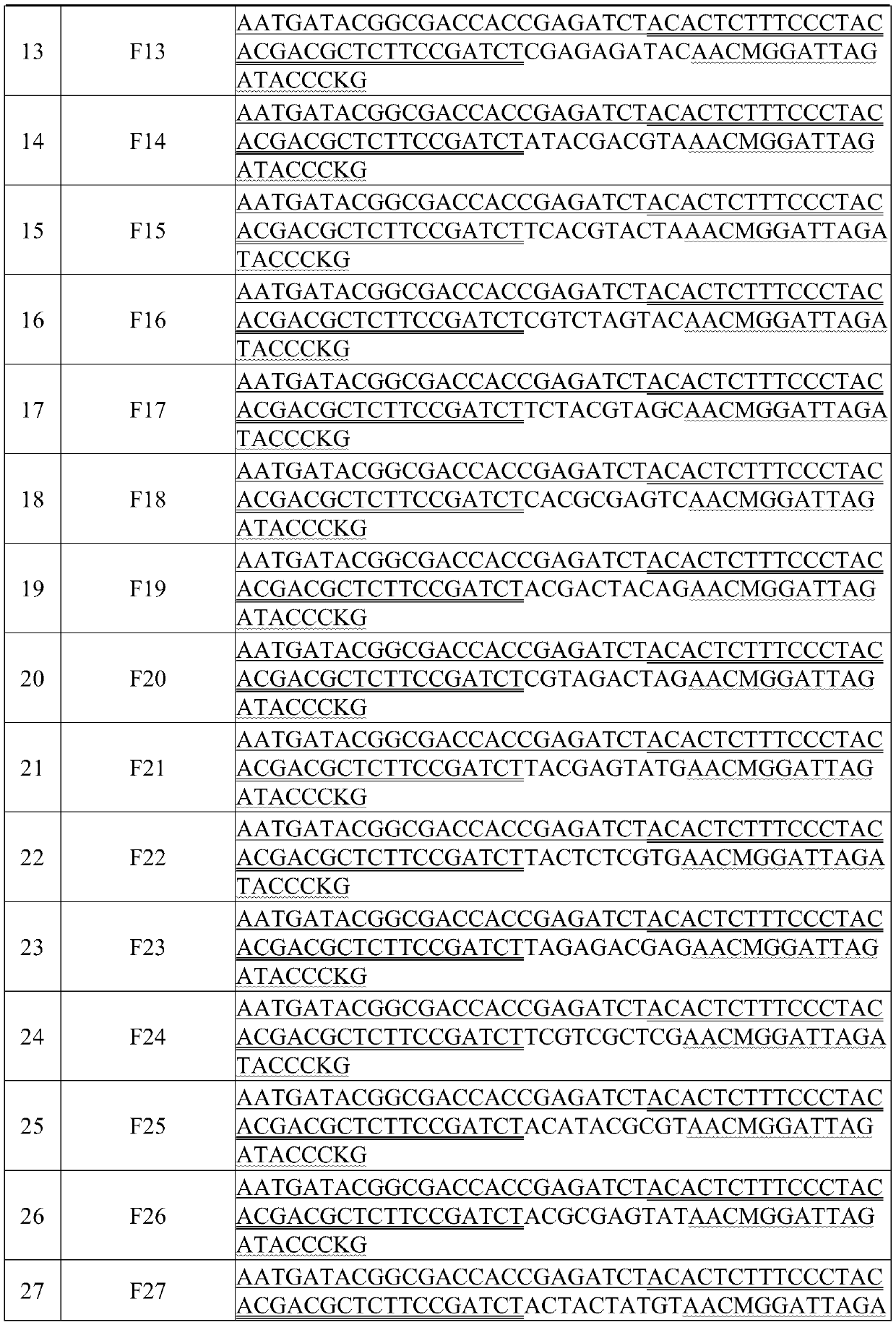
Application Year
Inventor
Bacterial identification is a process which is used to pinpoint the identity of specific bacteria. It is an important part of medical treatment, since many treatments are heavily dependent on the identity of the particular organism causing a medical problem, and it is also an important part of scientific research.
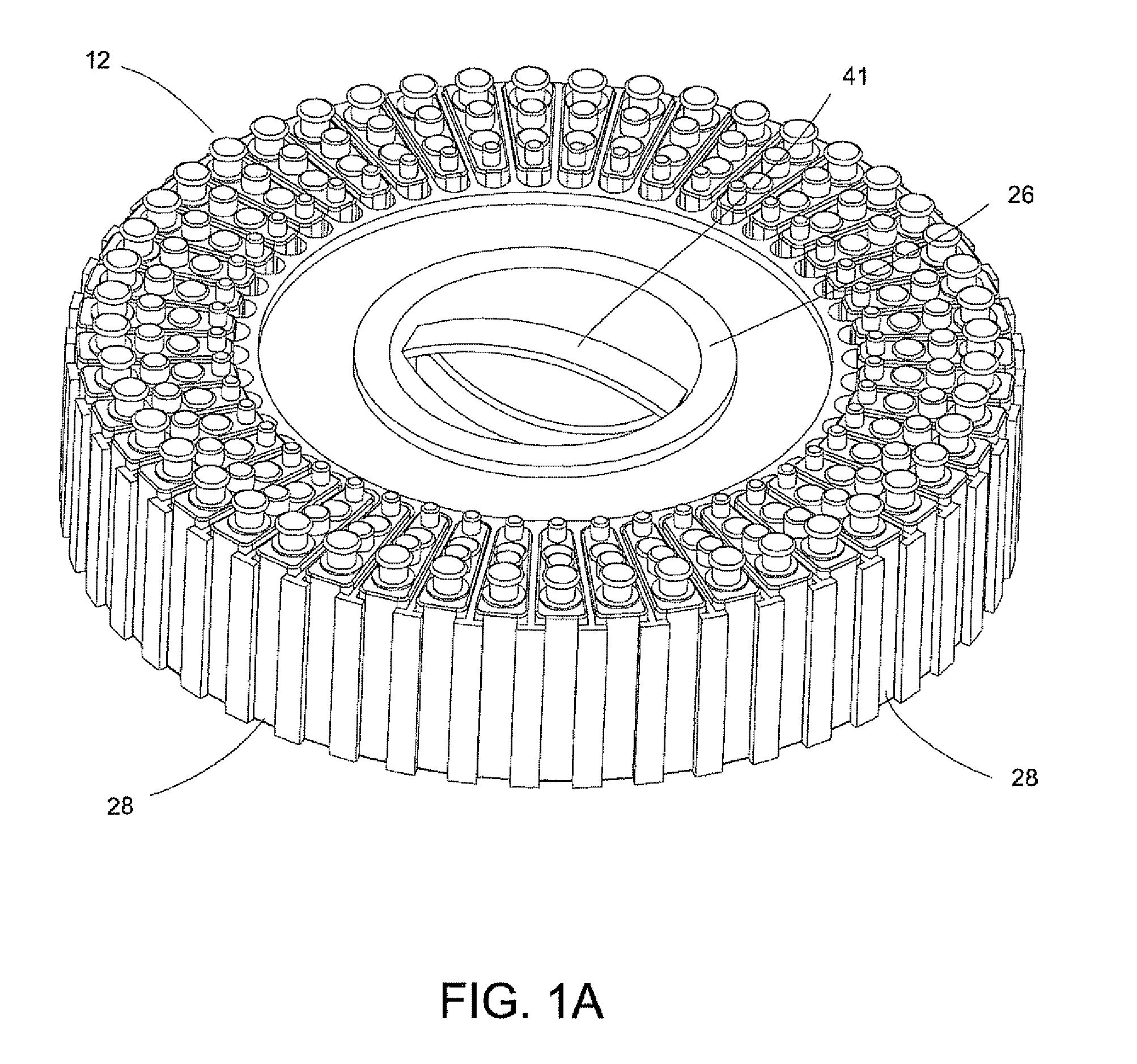
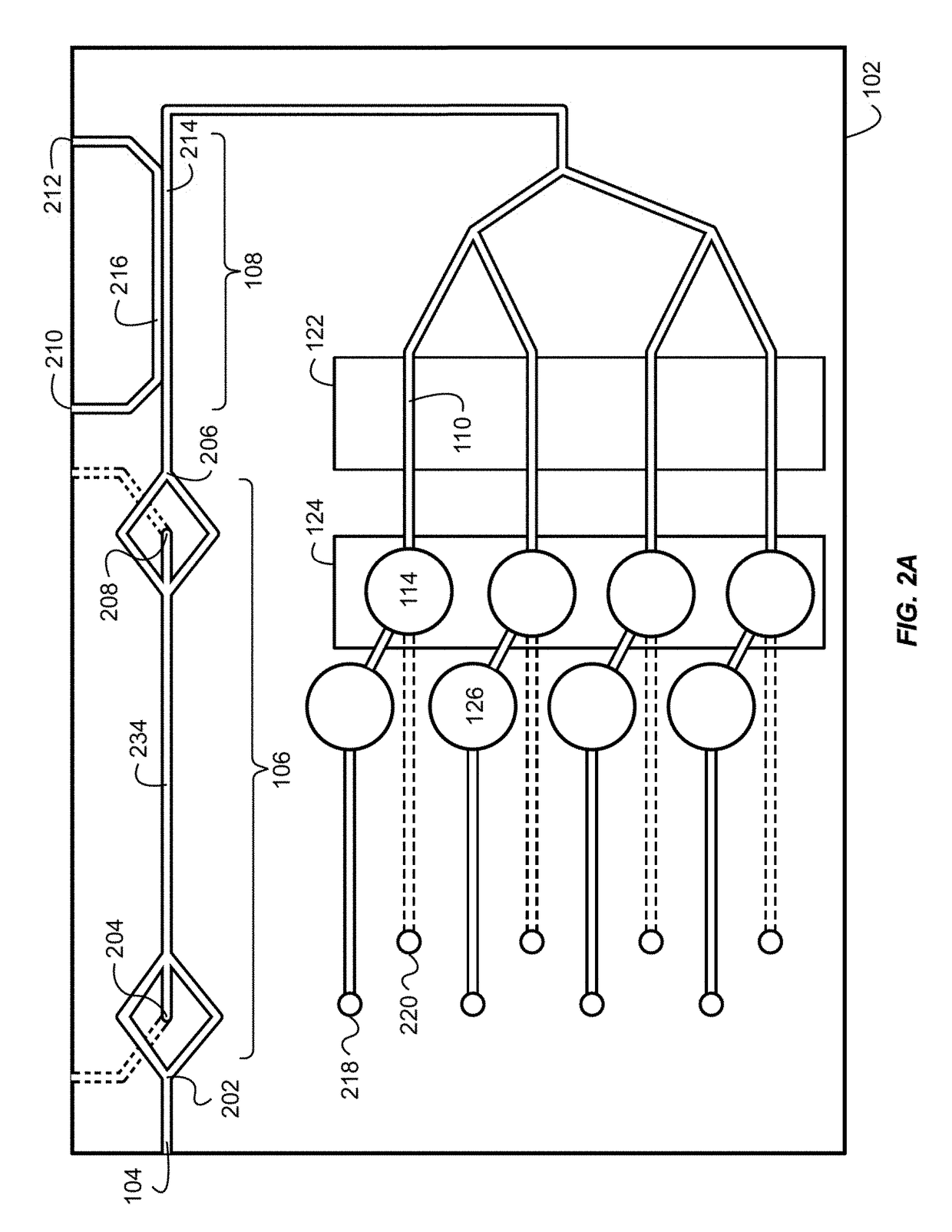
System for Conducting the Identification of Bacteria in Biological Samples
ActiveUS20110093207A1Rapid diagnosisFast resultsDispensing apparatusWithdrawing sample devicesMicroorganismBacteria identification
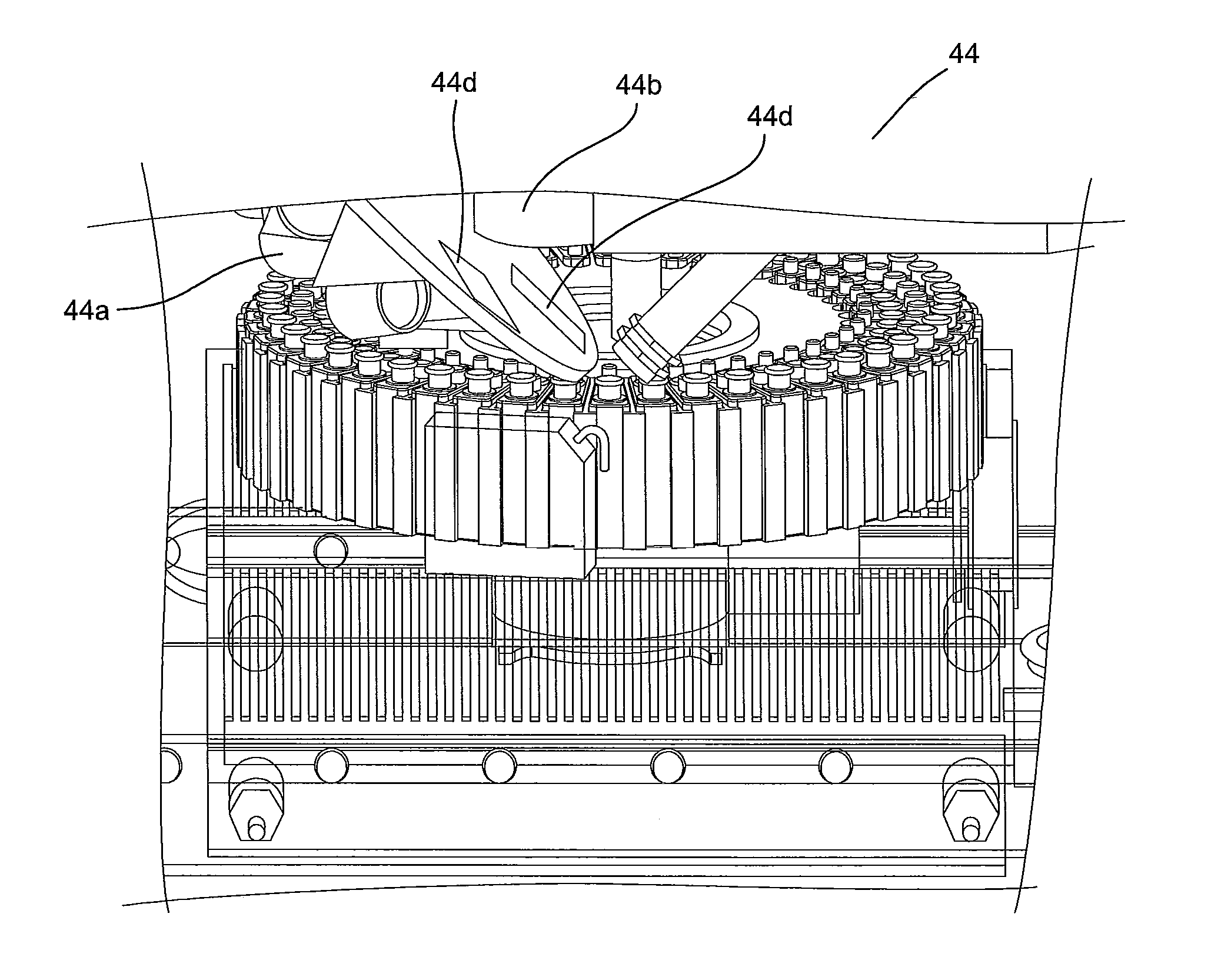
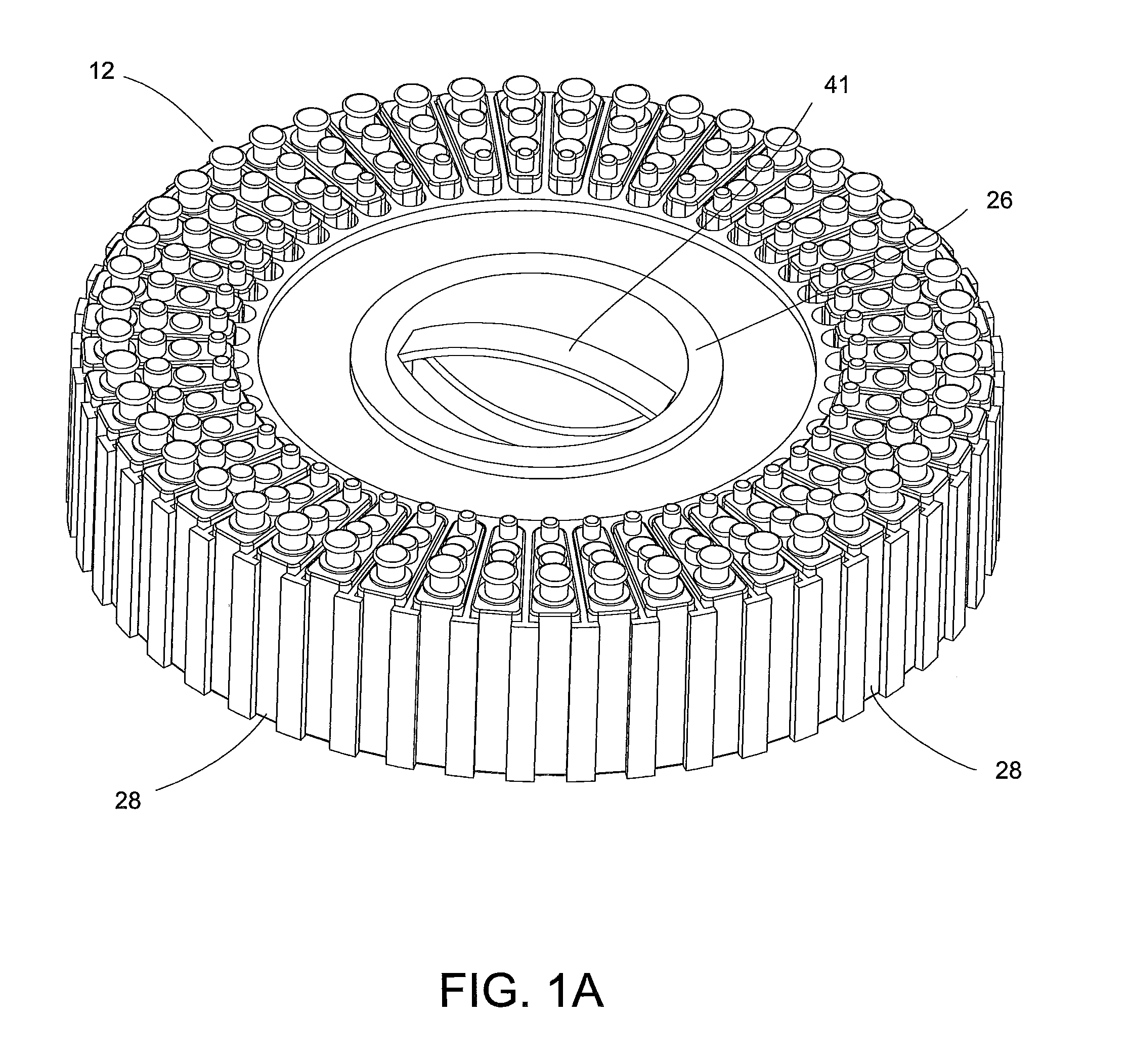
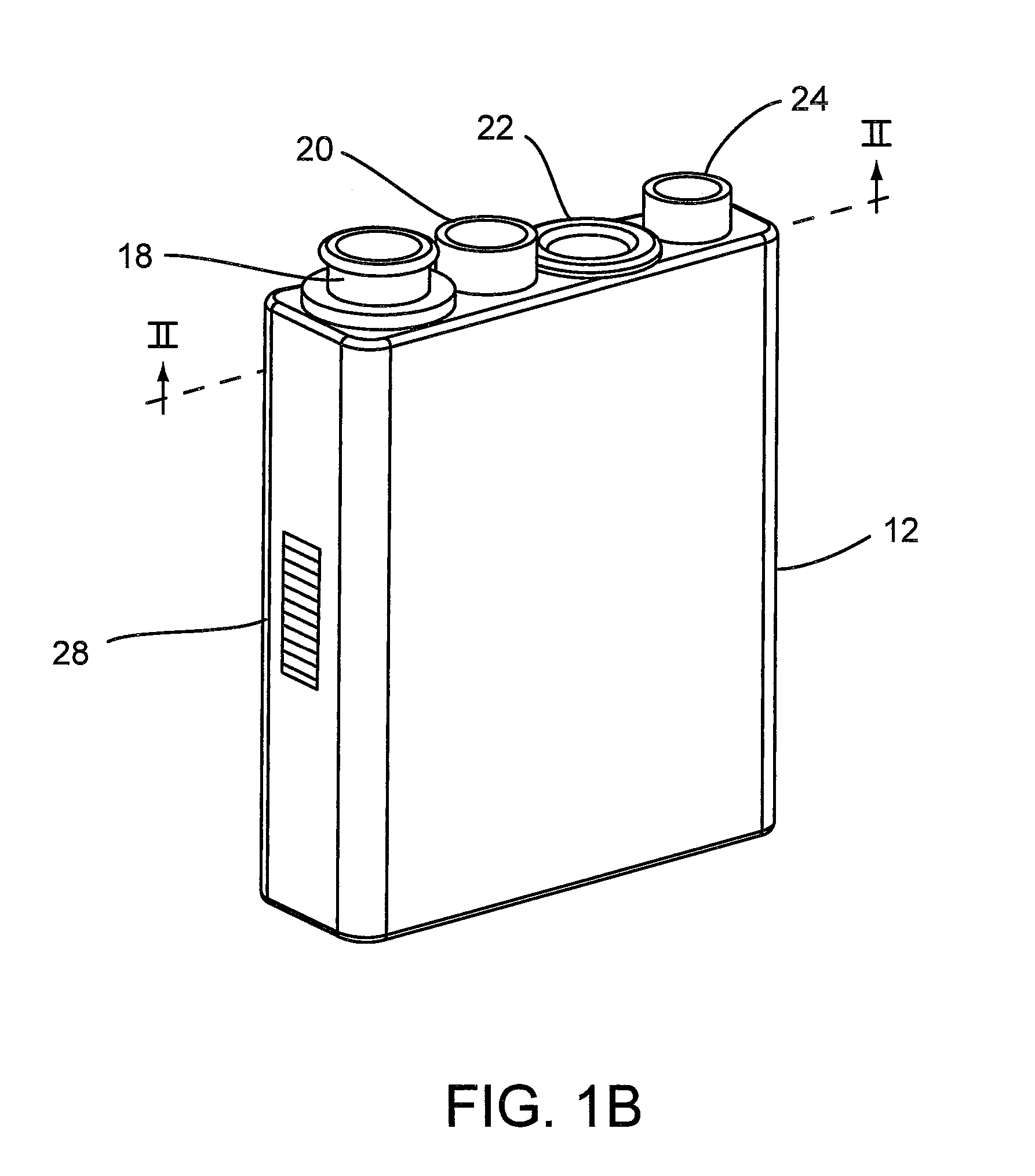
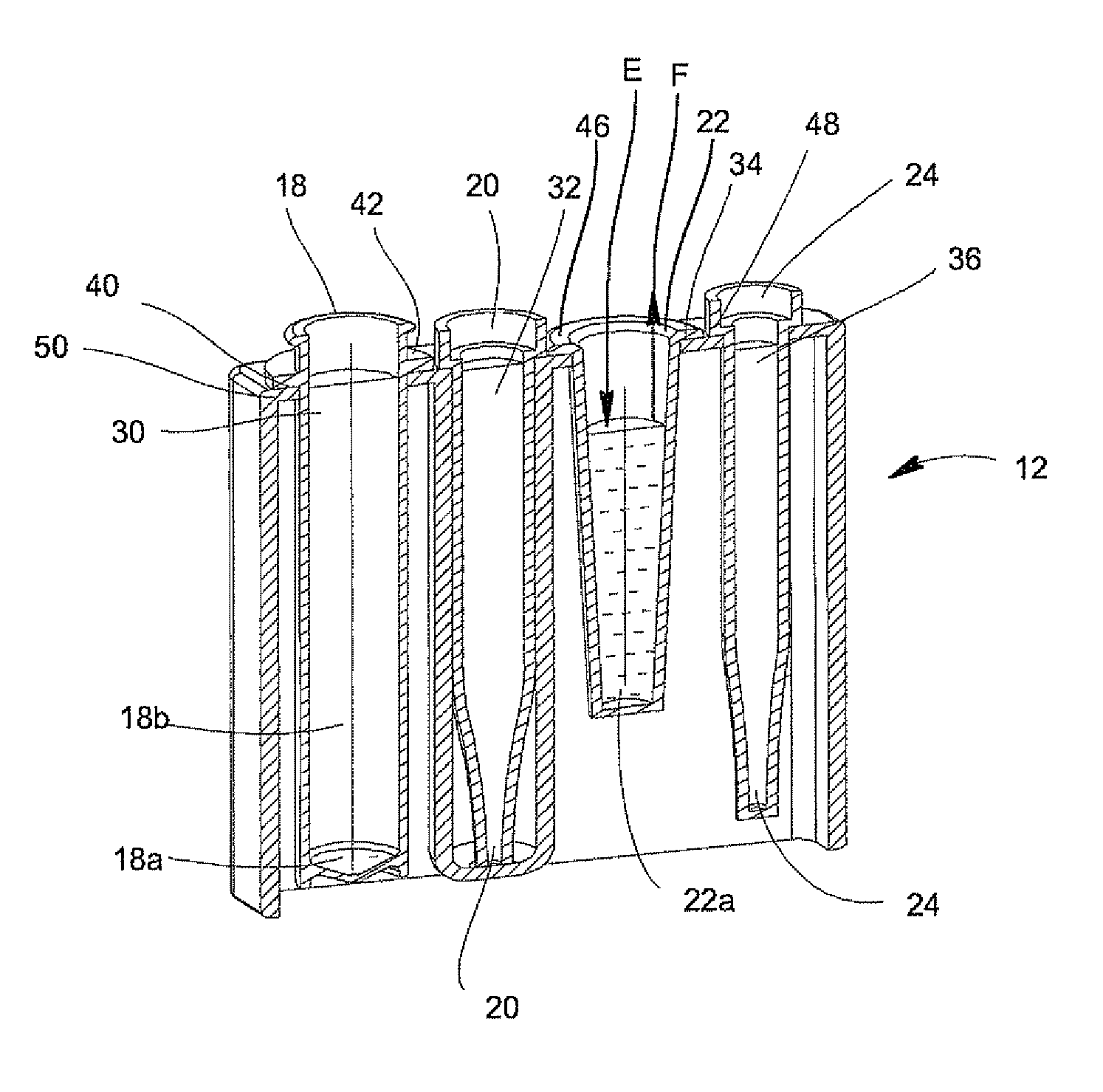
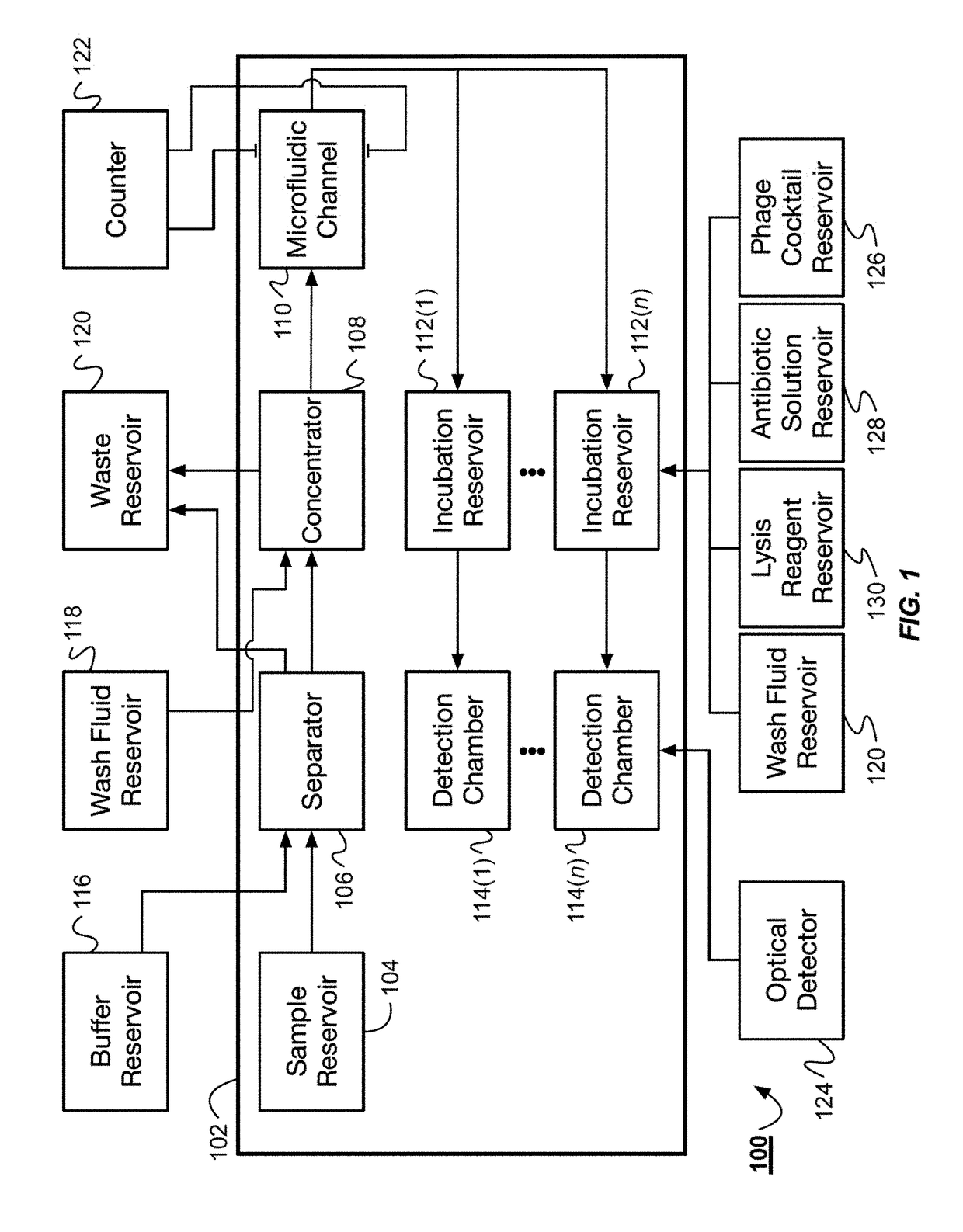
The present invention relates to a system for conducting the identification and quantification of micro-organisms, e.g., bacteria in biological samples. More particularly, the invention relates to a system comprising a cooling, heating and fan arrangement for maintaining a predetermined optimum temperature of the samples during testing; a visual, circumferential and axial alignment system for aligning the samples within the carousel; a transfer system for transferring the samples from the carousel to the centrifuge; a balancing system of minimizing the rotational vibrations of the centrifuge; a safety system and anti-tipping design for the sample containing system; liquid dispensing arms for dispensing the buffered saline solution; and discharge ports for discharging and disposing of the liquid removed from the samples to a location external of the system.
Owner:POCARED DIAGNOSTICS
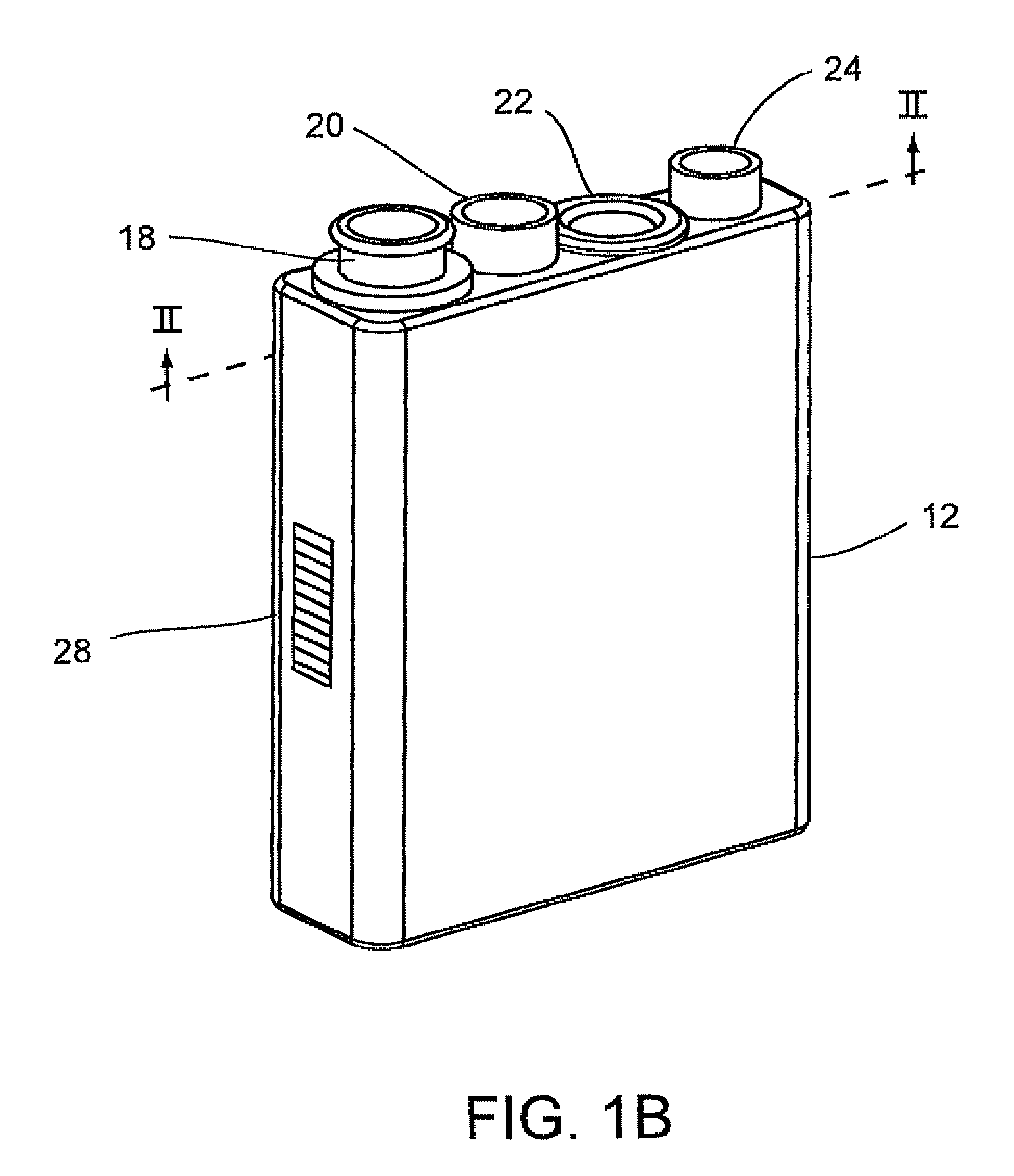
System for conducting the identification of bacteria in biological samples
ActiveUS8519358B2Rapid diagnosisFast resultsWithdrawing sample devicesPhotometryCuvetteBacteria identification
The present invention relates to a system for conducting the identification and quantification of micro-organisms, e.g., bacteria in biological samples. More particularly, the invention relates to a system comprising a disposable cartridge and an optical cup or cuvette having a tapered surface; an optics system including an optical reader and a thermal controller; an optical analyzer; a cooling system; and an improved spectrometer. The system may utilize the disposable cartridge in the sample processor and the optical cup or cuvette in the optical analyzer.
Owner:POCARED DIAGNOSTICS
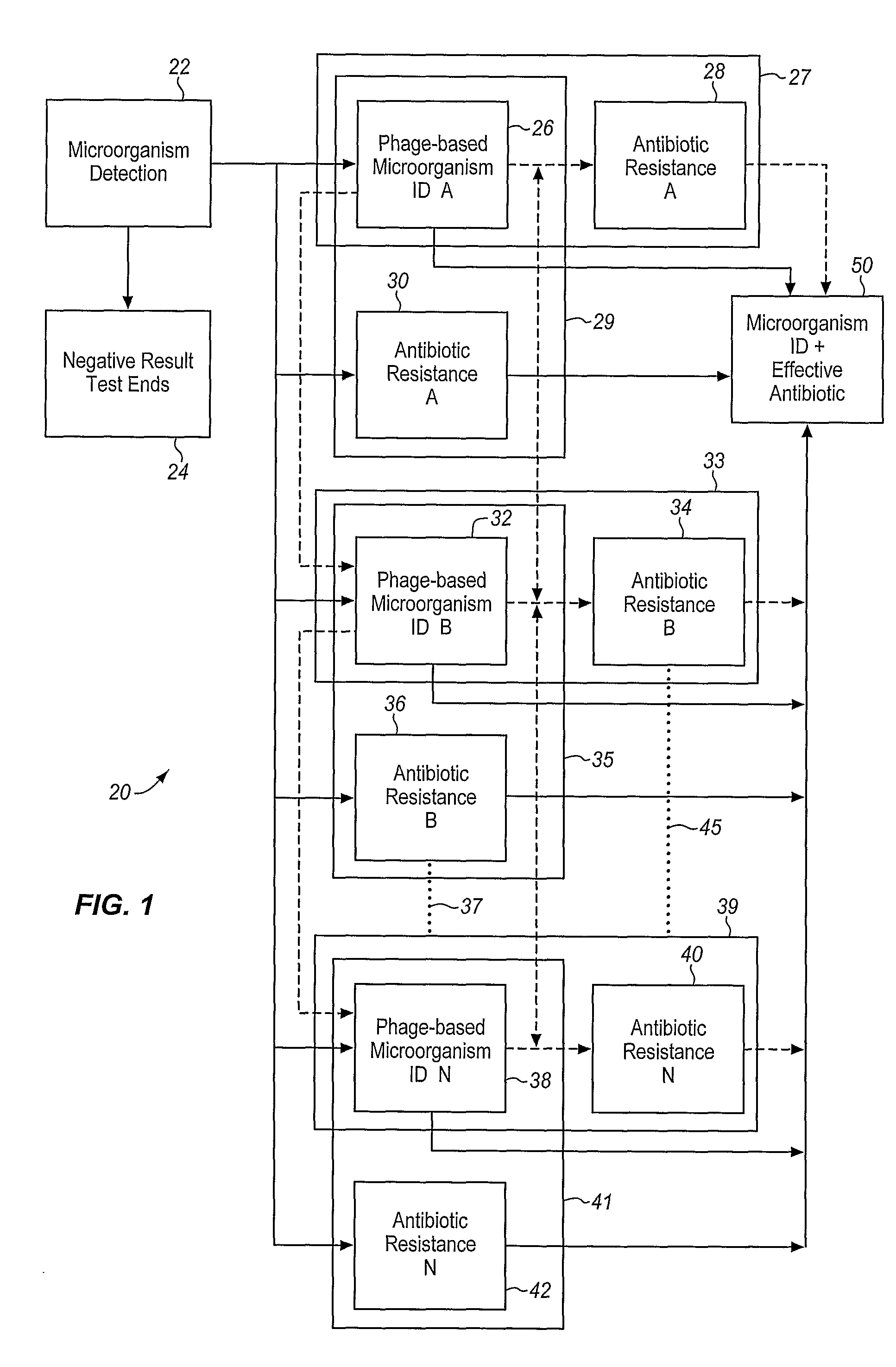
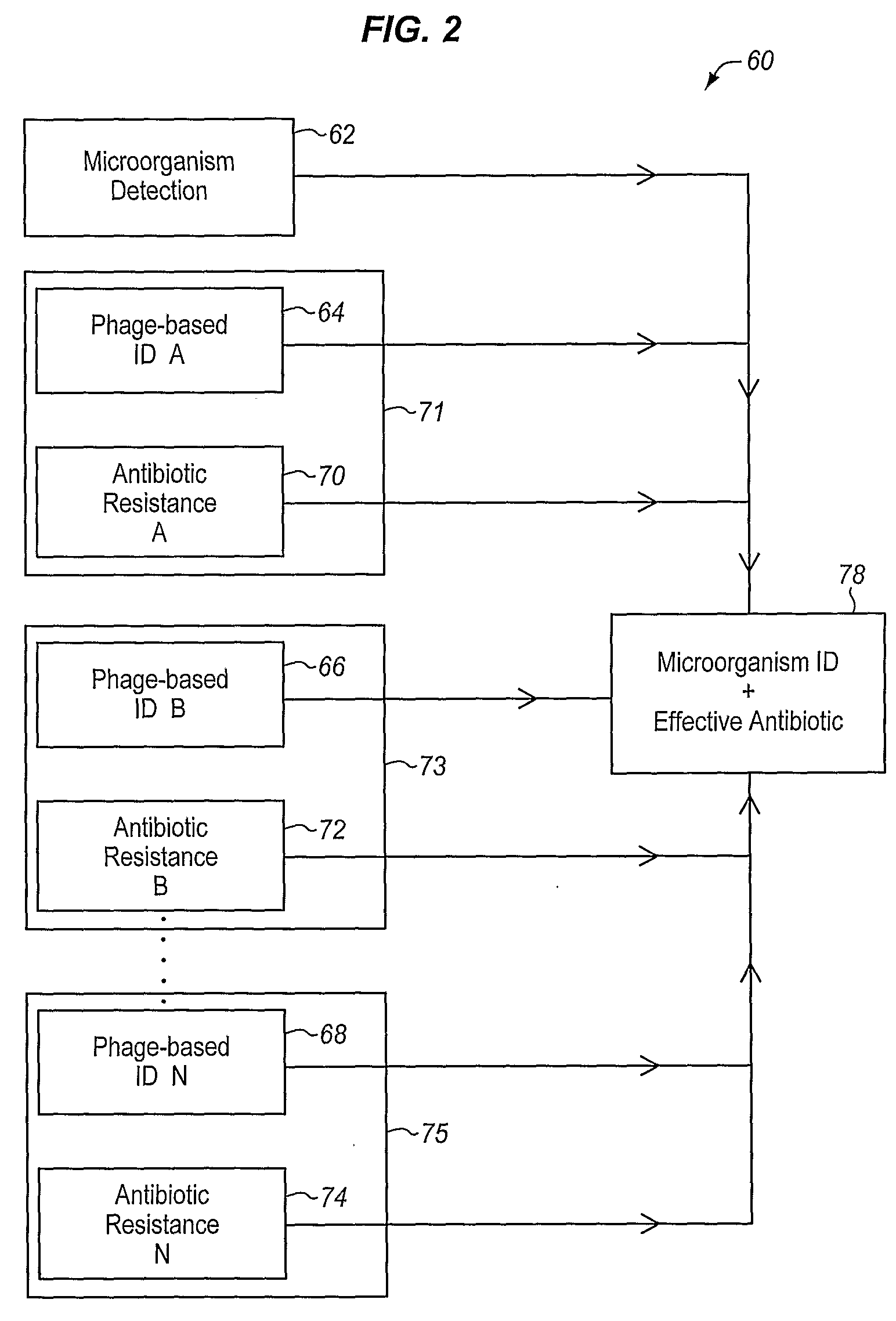
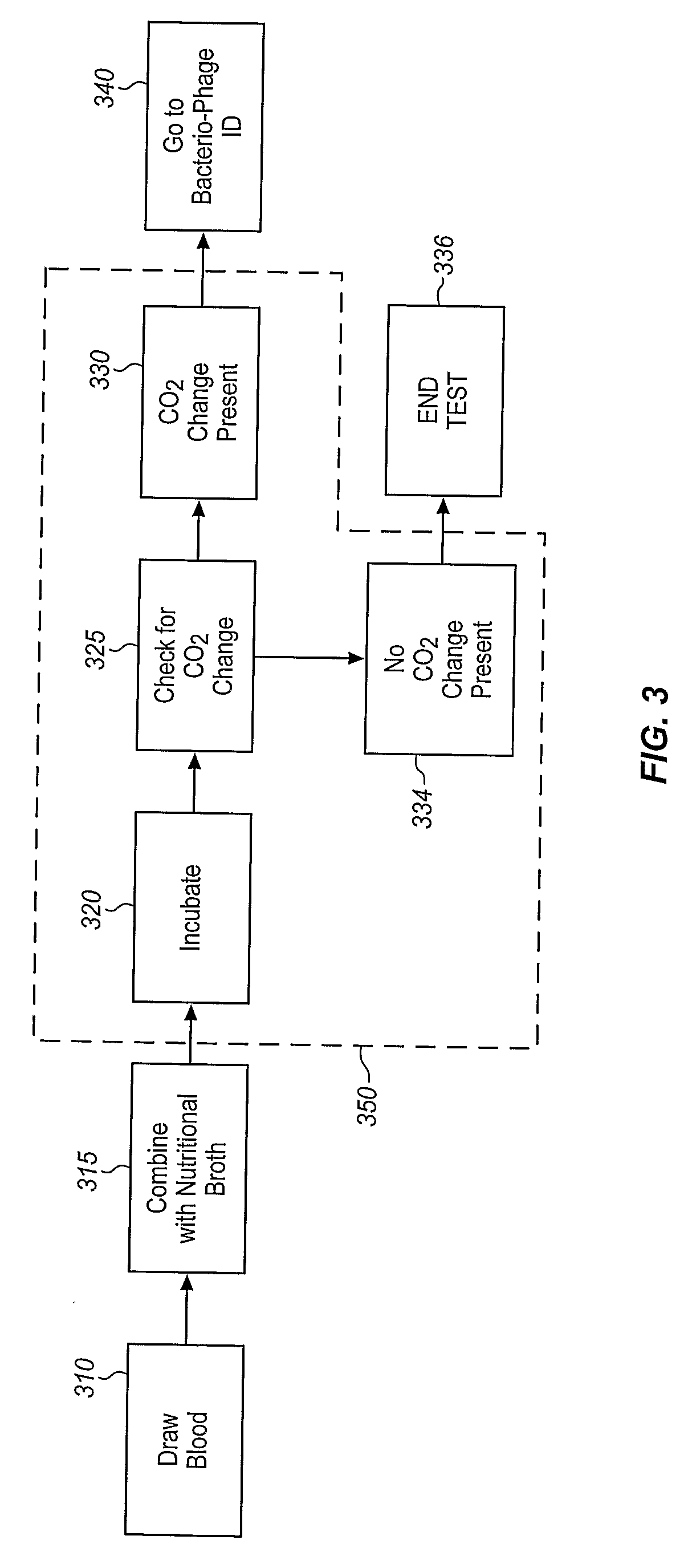
Method and Apparatus for Identification of Microorganisms Using Bacteriophage
InactiveUS20080286757A1Improve reliabilityImprove signal-to-noise ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteria identificationMicroorganism
A sample is tested for the presence of bacteria, such as in an automatic blood culturing apparatus. If bacteria are determined to be present, a bacteriophage-based bacteria identification process is performed to identify the bacteria present. A plurality of bacteria detection processes, such as a blood culture test and Gram stain test may be carried out prior to the bacteria identification process. A bacteriophage-based antibiotic resistance test or antibiotic susceptibility test is also conducted on the sample.
Owner:MICROPHAGETM
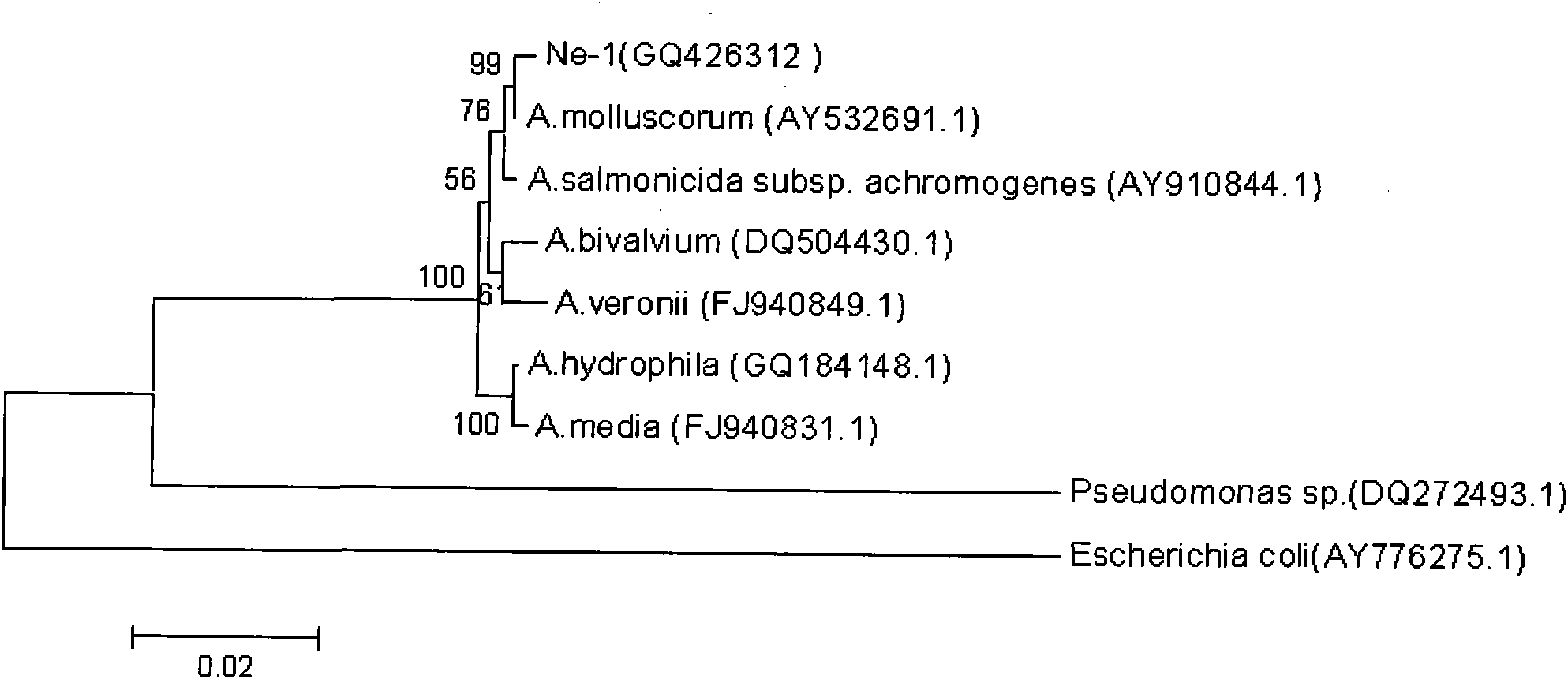
Method for separating Aeromonas molluscorum producing tetrodotoxin from Takifugu fasciatus tissue and fermentation culture method of Aeromonas molluscorum as well as detection method of produced tetrodotoxin
The invention relates to a method for separating Aeromonas molluscorum producing tetrodotoxin from Takifugu fasciatus tissues and a fermentation culture method of the Aeromonas molluscorum as well as a detection method of the produced tetrodotoxin. The method for separating the Aeromonas molluscorum producing the tetrodotoxin from the Takifugu fasciatus tissues comprises a bacteria separation method, a bacteria identification method, a bacteria fermentation culture method, a competitiveness ELISA (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay) detection method and an LC-MS (Liquid Chromatograph-mass Spectrometry) detection method of the tetrodotoxin produced by the Aeromonas molluscorum, and the like. In the invention, by separating bacteria from Takifugu fasciatus ovaries and adopting a TCBS (Thiosulfate Citrate Bile (salt) Sucrose (agar)) culture medium for screening, the Aeromonas molluscorum capable of producing the tetrodotoxin is separated from blowfish bodies for the first time; the separated bacteria is identified by adopting a 16 SrDNA method; the competitiveness ELISA detection method and the LC-MS detection method are both firstly adopted for the tetrodotoxin produced by the separated Aeromonas molluscorum; and the produced tetrodotoxin and tetrodotoxin extracted from the blowfish bodies are determined to be the same substance; in addition, the separated Aeromonas molluscorum can massively separate the tetrodotoxin from the bacteria after being cultured.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Detection method for drug resistant genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae against belta-lactamase
InactiveCN101519688AReduce infection rateReduce mortalityMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisBacteria identification
The invention discloses a detection method for drug resistant genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae against belta-lactamase, pertaining to the technical field of gene detection methods. The detection method comprises the following steps: 1. Klebsiella pneumoniae strains of inpatients are selected and sampling for backup is carried out after strain identification is carried out to all strains using bacteria identifying apparatus; 2. the sensitivity of antibacterials is determined by adopting the micro dilution method so as to judge the sensitivity of antibiotic; and 3. drug resistant genes are detected by adopting a PCR method and belta-lactamase drug resistant genes are checked and DNA positive strains are selected for carrying out sequencing analysis. The detection method finds the drug resistant genes resulting in the resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae to belta lactam drugs by carrying out a systematical and complete research on the drug resistant mechanism of the Klebsiella pneumoniae, thus having important value for instructing the clinical and reasonable use of antibacterials, being capable of reducing the infection rate in a hospital, reducing mortality rate and saving social medical resources, and having good social and economic benefits.
Owner:钟建平
Medicine and bacterium resistant detection chip, method for preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN1635150AEasy to detectQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteria identificationInfective disorder
The invention relates to a detection chip for familiar resistant organisms and its preparation and application methods belonging to microorganism detection field. The invention employs DAN chip method including fixing the synthesized oligonucleotide probes for clinical detection of familiar resistant organisms on the slide surface to form a dot-plot, hybridizing the pending sample DNA with the chip to obtain a great deal of gene sequence information relative to the bacteria identification and drug tolerance, identifying the kinds of the familiar pathogenicbacterias existing in the clinical sample, thus to implement the identification of the clinical familiar pathogenicbacterias and detection of the main drug resistant spectrum. The invention is simple, convenient, quick, sensitive and specific, and can obviously shorten the disease diagnosis time.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV +1
Bacteria identification and antibiotic susceptibility profiling device
The system described herein for bacterial identification can be used as a point-of-care or lab-based diagnostic system. In some implementations, the system can be used to detect other foreign agents within blood or other samples. The system can include disposable microfluidic cartridges that are removable from the system. The microfluidic cartridges can receive a sample, such as a blood sample, that is suspected of containing bacterial cells and separate the bacterial cells from the blood sample. Once the bacterial cells are separated from the blood, the system can introduce the recombinant detector bacteriophages into the system that can infect the bacterial cells. The system can then detect the expression of reporter genes from the recombinant detector bacteriophages.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Multiplex-PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection primer group and kit for various duck-derived pathogenic bacteria
ActiveCN103937892AQuick checkEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesEscherichia coliMultiplex
The invention relates to the technical field of biological detection, and particularly discloses a multiplex-PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection primer group and kit for various duck-derived pathogenic bacteria. The primer group comprises four pairs of primers which are RArpoB-P1 and RArpoB-P2, E.coliphoA-P1 and E.coliphoA-P2, SalminvA-P1 and SalminvA-P2, Strep16srRNA-P1 and Strep16srRNA-P2. The four pairs of primers are used for carrying out multiplex-PCR amplification and can be used for simultaneously, rapidly, conveniently, specifically and sensitively detecting four bacteria which are riemerella anatipestifer, escherichia coli, salmonella and streptococcus. The four pairs of primers can be used for identification of bacteria, disease diagnosis and epidemiological investigation and has broad market prospect and high economic benefits.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Multi-PCR detection kit and detection method for duck-origin common bacteria
ActiveCN102181549AShorten detection timeEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesEpidemiologic surveyPolymerase chain reaction
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological detection, and in particular relates to a multi-polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection kit and a multi-PCR detection method for duck-origin common bacteria. The multi-PCR detection kit for the duck-origin common bacteria comprises three pairs of primers, namely a first pair of primers RADnaBP1 and RADnaBP2, a second pair of primers E.coliphoAP1 and E.coliphoAP2 and a third pair of primers SalminvAP1 and SalminvAP2, wherein the RADnaBP1 has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1; the RADnaBP2 has the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No.2; the E.coliphoAP1 has the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No.3; the E.coliphoAP2 has the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No.4; the SalminvAP1 has the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No.5; and the SalminvAP2 has the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No.6. By the kit and the method, riemerella anatipestifer, escherichia coli and salmonella can be quickly, conveniently, specifically and sensitively detected; and the kit and the method are easy to popularize on a large scale, can be used for bacterial identification, disease diagnosis and epidemiological survey and have wide market prospects and better economic benefits.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Bacterium identification reagent kit as well as preparation method and uses thereof
InactiveCN101200755AHigh sensitivityImprove comparabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteria identificationThiazole
The invention discloses a bacteria identification kit, including indicator, culture medium and testing carbon sources. Thiazole blue is used as the indicator for indicating that whether bacteria can use the testing carbon sources. The invention is a kit which uses a 96-microtitor plate that is prearranged with the culture medium with 95 different carbon sources and is used for the rapid identification of carbon source utilization spectrum. One hole is not added with the carbon source for the comparison. The kit of the invention includes some carbon sources for detecting the specific physiological characteristics and common carbon sources. That using the thiazole blue as the indicator is convenient for naked eyes to observe that whether the bacteria grows and uses the carbon sources. And an eliasa can be used at the wavelength of 600nm to rapidly measure the growing condition of the bacteria. The kit of the invention has the advantages of low cost, short identification time, high sensitivity, convenient operation, accuracy, etc. the result can be made within 20-24 hours. And gram negative bacteria and positive bacteria can be identified.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Pretreatment method for directly detecting infection urine pathogen by MALDI-TOF MS
InactiveCN102749233AReduce lossSimplify detection stepsPreparing sample for investigationBacteria identificationBacteriuria
The invention discloses a pretreatment method for directly detecting infection urine pathogen by MALDI-TOF MS. An urine sample pretreatment part is improved on a methodology, bacteria is washed and collected, formic acid and acetonitrile are used for performing protein digestion on bacteria, and then the detection is carried out, thereby the bacteria identification time is substantially shortened and the identification accuracy is enhanced. The pretreatment method is capable of rapidly and accurately identifying the infection urine sample, and can timely guide the clinical medication with pertinence.
Owner:鲁辛辛 +1
Reagent and method for separating bacteria from positive blood and method for identifying bacteria
InactiveCN107629960ARapid identificationTimely treatmentBacteriaMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBacteria identificationRapid identification
The invention provides a reagent for separating bacteria from positive blood. The reagent comprises an agent A, an agent B and an agent C, wherein the agent A is used for dissolving the hemocyte froma blood sample of a blood culture; the agent B is used as a cleaning agent; the agent C is used for breaking the pathogenic bacteria cytoderm and promoting the protein release in the cells; and the agent A is at least one of saponin solution and SDS or other surface active agent capable of cracking the hemocyte. The invention also provides a method for separating bacteria from positive blood and the method for identifying bacteria. The method comprises the following steps: cracking the hemocyte by using the agent A; cleaning the cell fragments and impurities by using the agent B; breaking thepathogenic bacteria cytoderm by using the agent C, releasing the bacteria protein, taking the supernate containing the bacteria protein and settling a sample to be identified; dropping the sample to be identified into a vacant side on a target plate; drying under room temperature and then covering a substrate on the sample; drying under room temperature; and putting onto a machine for detecting. The bacteria can be quickly identified, the result can be acquired within half an hour, the detection result is high in reliability and the interference is less.
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Compositions and methods for rapid identification of bacteria and fungi and phenotypic antimicrobial drug sensitivity assays
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) as a reporter assay for rapid and simultaneous bacterial identification and antimicrobial drug sensitivity (AST) phenotypic assays. The present invention uses a strategy that has exhibited the ability for multi-reuse as well as processing of a variety of microbiological samples for antimicrobial drug sensitivity tests.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
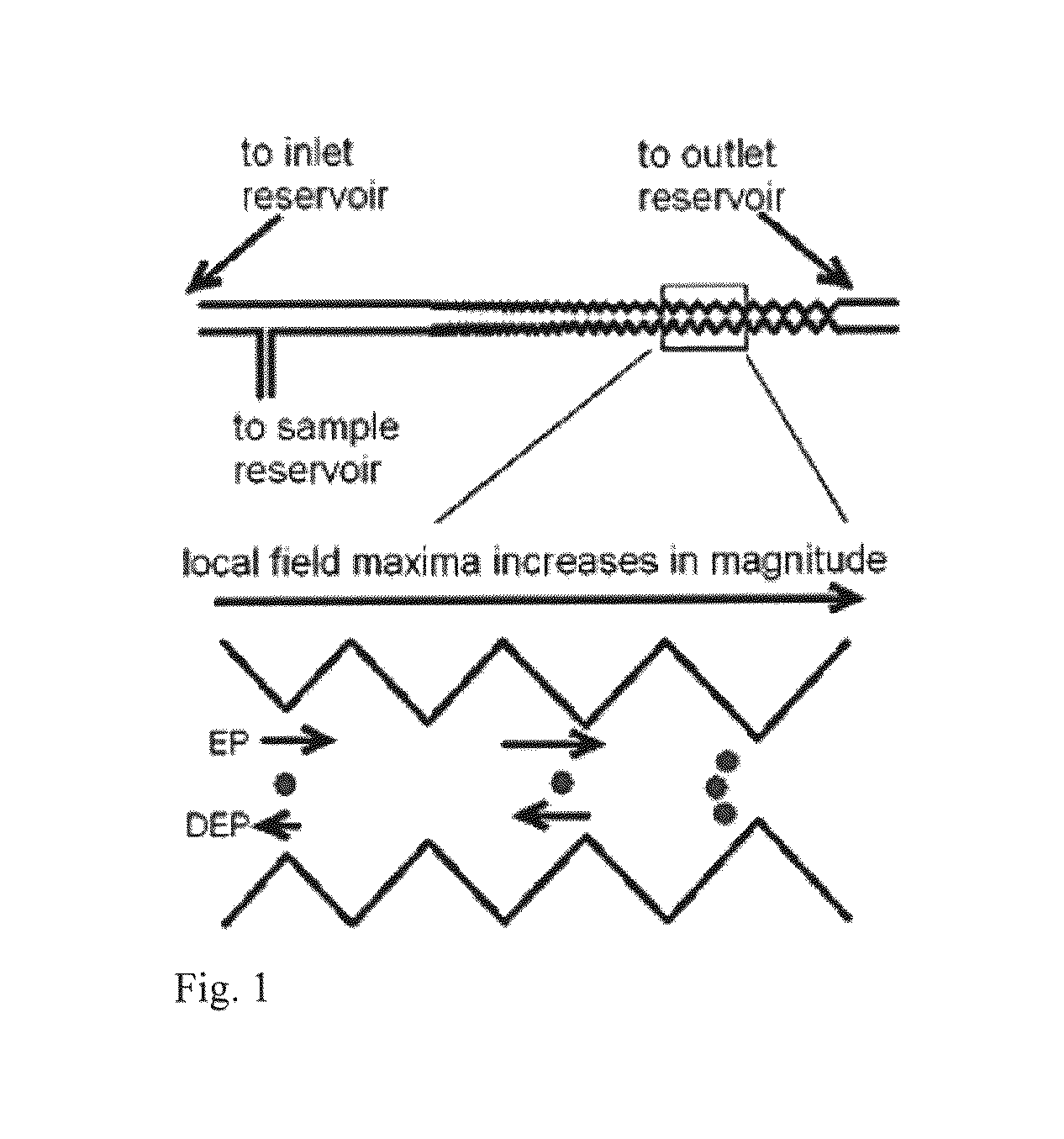
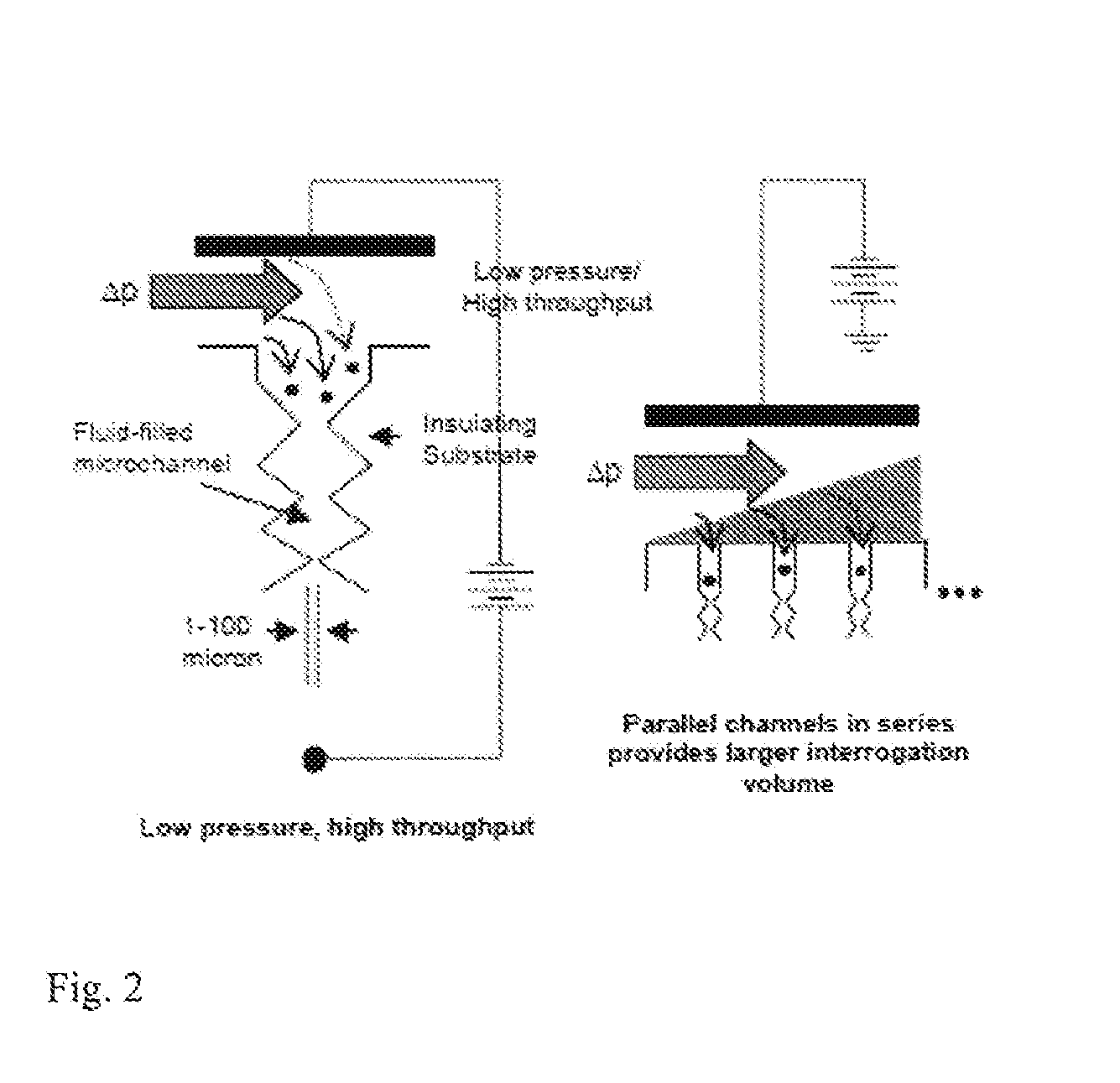
Bacterial identification
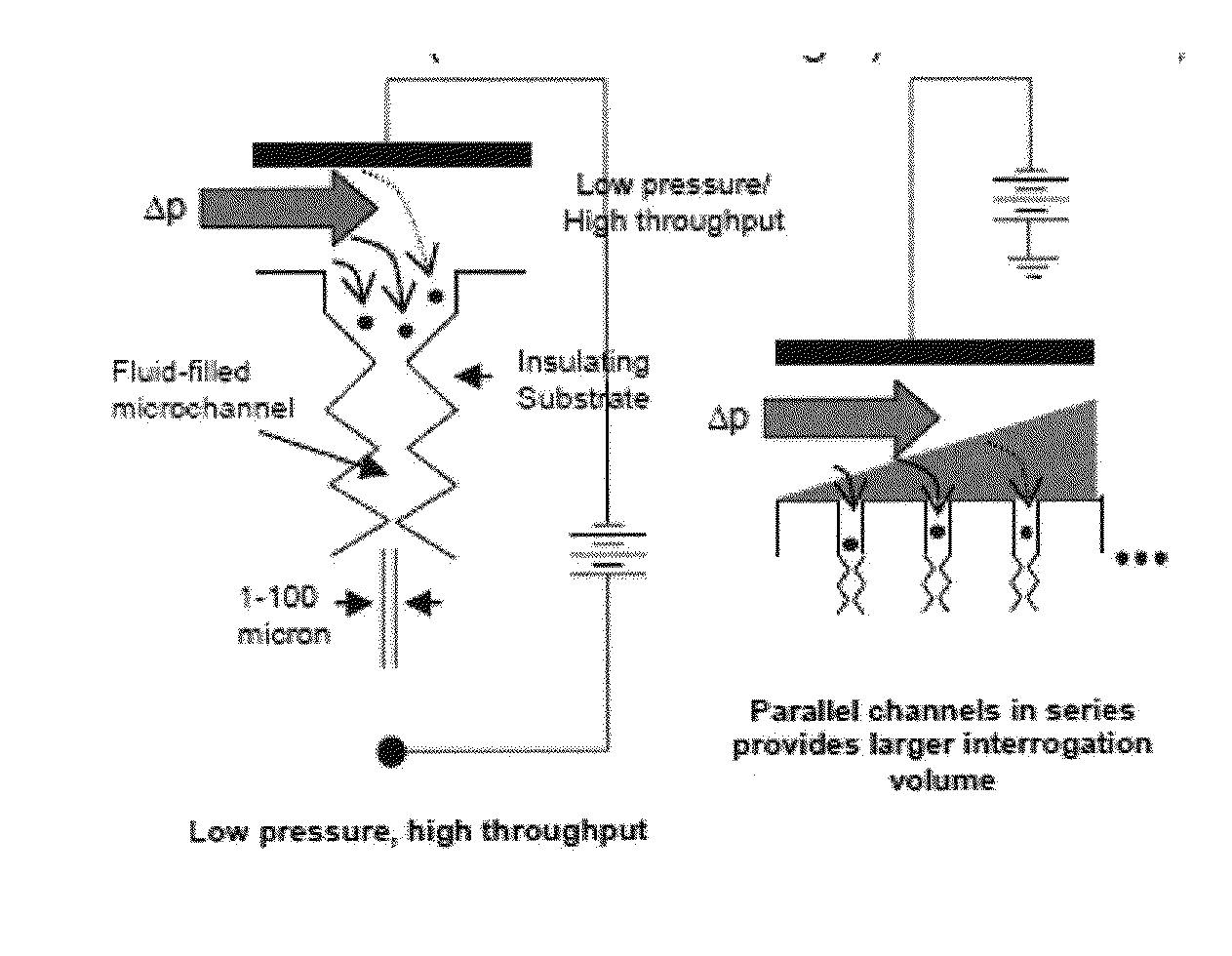
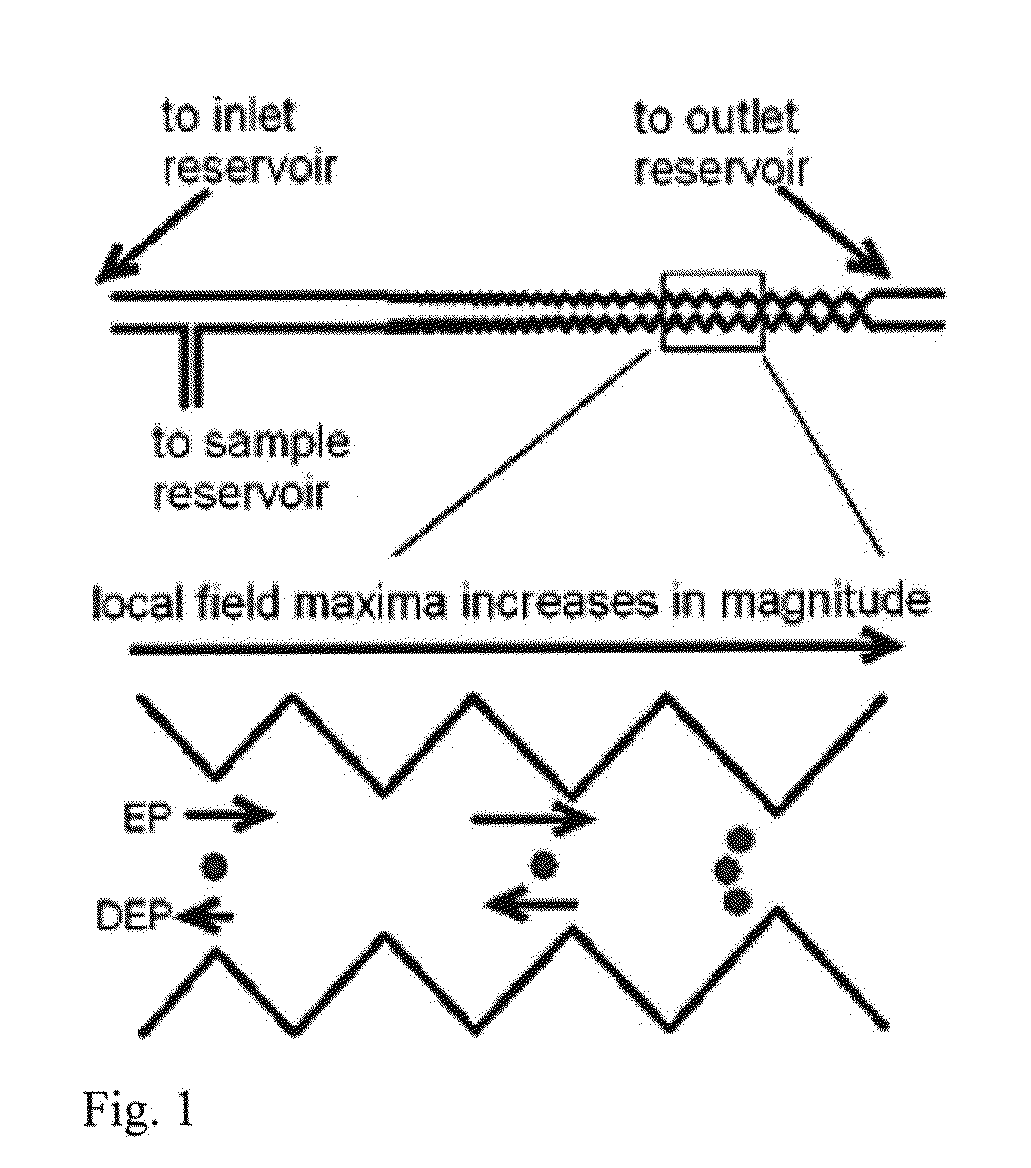
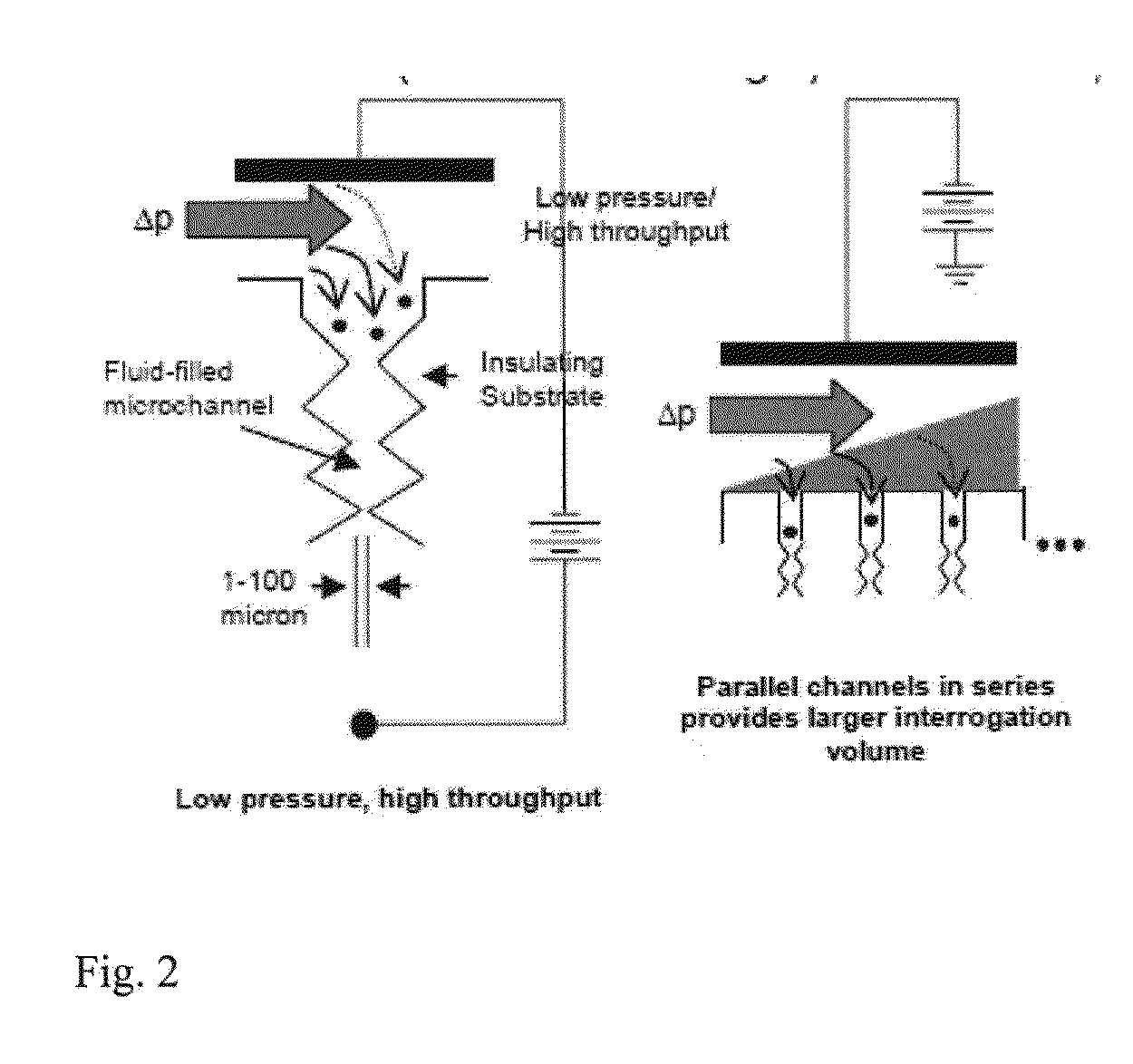
ActiveUS20130286183A1DielectrophoresisMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesBacteria identification
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Dual Tem-PCR quick detection method for salmonella and escherichia coli O78
InactiveCN104946782AQuick checkRapid diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBacteria identificationDisease
The invention discloses a dual Tem-PCR quick detection method for salmonella and escherichia coli O78. According to the dual Tem-PCR quick detection method for the salmonella and the escherichia coli O78, invA gene primer of the salmonella and O-antigen gene primer of the escherichia coli are used for conducting dual Tem-PCR amplification directly on extracted mixing DNA after bacteria enrichment is conducted on a complex sample, and the result is interpreted through gel electrophoresis. A Tem-PCR technology and a dual PCR technology are combined, the problem of enrichment preference of the PCR is solved, the sensitivity degree is improved by 2 to 3 orders of magnitudes compared with an ordinary dual PCR detection, the detection level that the number of sample contaminated bacteria is a single digit can be reached, and the problem that a traditional dual PCR technology is prone to lead to false negative result. According to the dual Tem-PCR quick detection method for the salmonella and the escherichia coli O78, the salmonella and the escherichia coli O78 can be detected quickly, conveniently, excellently and sensitively, wide-range popularization is easy, the salmonella and the escherichia coli O78 can be used for bacteria identification, disease diagnosis and epidemiological investigation, and wide market prospect and comparatively large economic benefits are achieved.
Owner:QINGDAO KANGLAND BIOTECH
Method and apparatus for identification of microorganisms using bacteriophage
InactiveCN101292043AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteria identificationMicroorganism
Owner:MICROPHAGE
Method and system for identifying bacteria and analyzing drug sensitivity
ActiveCN103760159AIdentification/Drug Susceptibility Test AccuracyImprove work efficiencyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicroorganismBacteria identification
The invention provides a method and a system for identifying bacteria and analyzing drug sensitivity, relating to the technical field of medical treatment reagent type detection. Through digital and automatic comparative analysis, a required result is obtained. Compared with the prior art, the invention provides a system for automatically identifying bacteria / experimenting drug sensitivity for the medical microorganism examination work so that the bacteria identification / drug experimenting is more accurate, simpler, micro and rapid.
Owner:聊城市鑫科金诺医疗器械有限公司
Bacterial nucleic acid sequencing identification method and bacterial identification kit based on DNA characteristic sequence
PendingCN108410971AReliable Judgment BasisRapid Integrated IdentificationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBacteria identificationGenomic DNA
The invention relates to a bacterial nucleic acid sequencing identification method and kit based on DNA characteristic sequence. The method comprises the steps: selecting a bacterial strain to be identified, and extracting and purifying a genomic DNA; amplifying a characteristic sequence fragment of the purified genomic DNA by PCR; extracting and purifying the PCR amplified product; determining asequence of the purified PCR amplified product, and removing a primer region by universal sequence splicing software, to obtain a DNA sequence of the corresponding fragment; importing the DNA sequenceof the corresponding fragment into a standard nucleic acid sequence database, carrying out sequence comparison, and carrying out bacterial strain identification, wherein the extraction and purification of the genomic DNA of the bacterial strain adopts lysozyme, sodium dodecyl sulfate and cetyltriethylammnonium bromide for bacterial crushing; nucleic acid is precipitated by phenol-chloroform-isoamyl alcohol and ethanol to obtain the genomic DNA which meets the quality control requirements. An objective and accurate judgment basis can be provided for the bacterial nucleic acid sequencing identification method, and rapid and integrated identification of bacterial pollutants is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST FOR FOOD & DRUG CONTROL
Liquid culture medium for detecting beta-galactosidase and application of liquid culture medium in bacterium identification
InactiveCN109355352ASolve solubilitySolve poisoningMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisSolventGalactoside
The invention discloses a liquid culture medium for detecting beta-galactosidase and application of the liquid culture medium in bacterium identification. Every 1,000 ml of the liquid culture medium for detecting beta-galactosidase is prepared from 5-50 g of nutrient substances, 2-10 g of sodium chloride, 50-250 ml of 0.2 mol / L PBS, 0.5-4 g of a specificity chromogenic substrate, 0.5-4 g of an enzyme induction agent, 0.1-10 ml of a cosolvent and 0.1-10 ml of a protection agent. According to the culture medium, 5-bromine-4-chlorine-3-indol-beta-D-galactoside is used as a substrate, the low-toxic cosolvent and the protection agent are adopted, and beta-galactosidase of living bacteria can be accurately and effectively detected through a liquid method; the culture medium can be applied to a commercial identification testing card, a drying substrate in a micro hole can be effectively redissolved, beta-galactosidase of the living bacteria is detected, the negative and positive results are clearer, and the identification accuracy for clinical common gram negative and positive bacteria is improved.
Owner:湖南迈瑞医疗科技有限公司
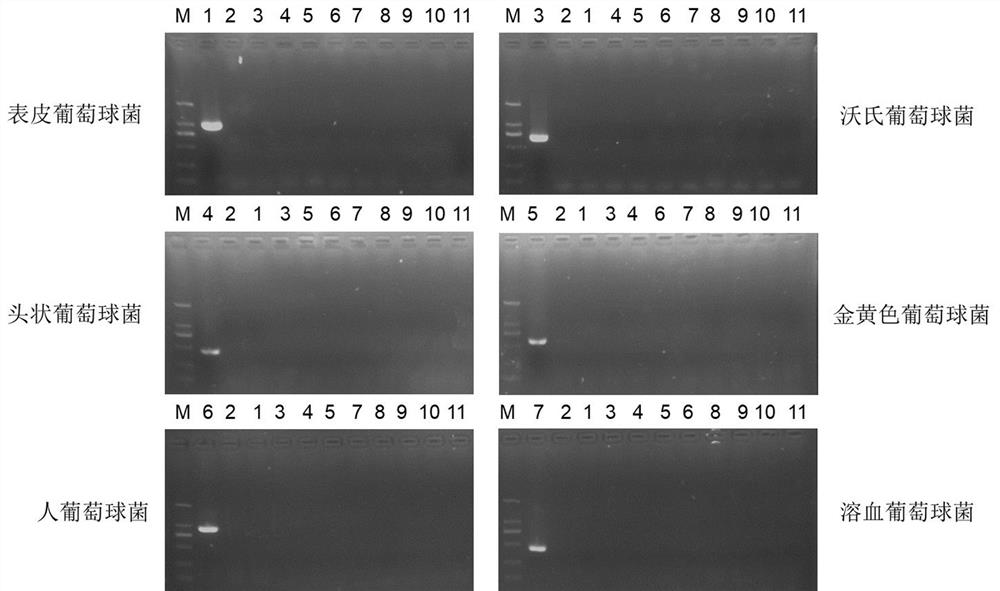
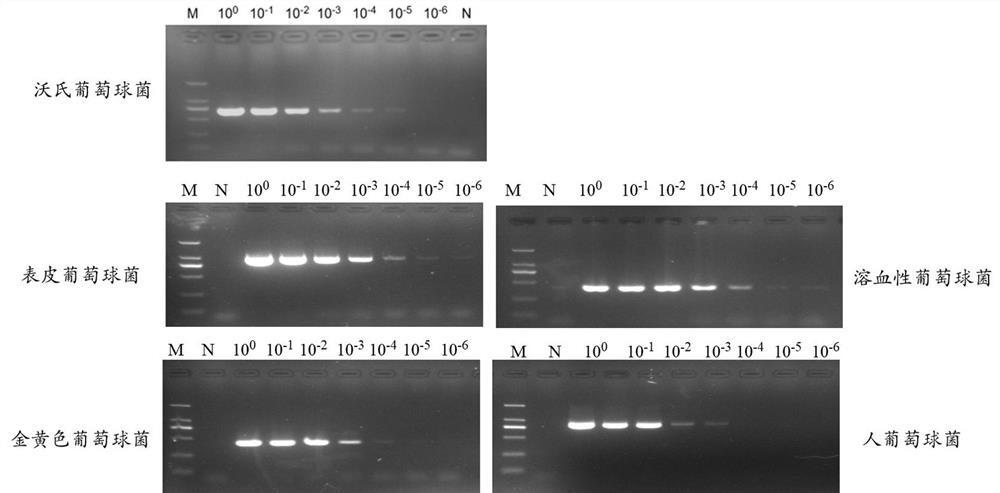
Primers and detection kit for identifying various staphylococci based on pheS gene and application of primers and detection kit
ActiveCN112980982AQuick checkRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBacteria identificationStaphylococcus haemolyticus
The invention provides primers and a detection kit for identifying various staphylococci based on a pheS gene and application of the primers and the detection kit, and belongs to the technical field of bacterial identification. The invention provides a primer group for identifying various staphylococci based on a pheS gene. The primer group comprises the following two or more primer pairs: a primer pair for specifically amplifying staphylococcus aureus, a primer pair for specifically amplifying staphylococcus warneri, a primer pair for specifically amplifying staphylococcus epidermidis, a primer pair for specifically amplifying staphylococcus hominis, a primer pair for specifically amplifying staphylococcus capitis, and a primer pair for specifically amplifying staphylococcus haemolyticus. The primer group has the characteristics of good amplification specificity, high detection sensitivity and simultaneous identification of various staphylococci. A method for detecting various staphylococci in the environment based on the primer group can realize simultaneous identification of various staphylococci, and has the characteristics of short detection time, low detection cost and an accurate and reliable detection result.
Owner:至微生物智能科技(厦门)有限公司
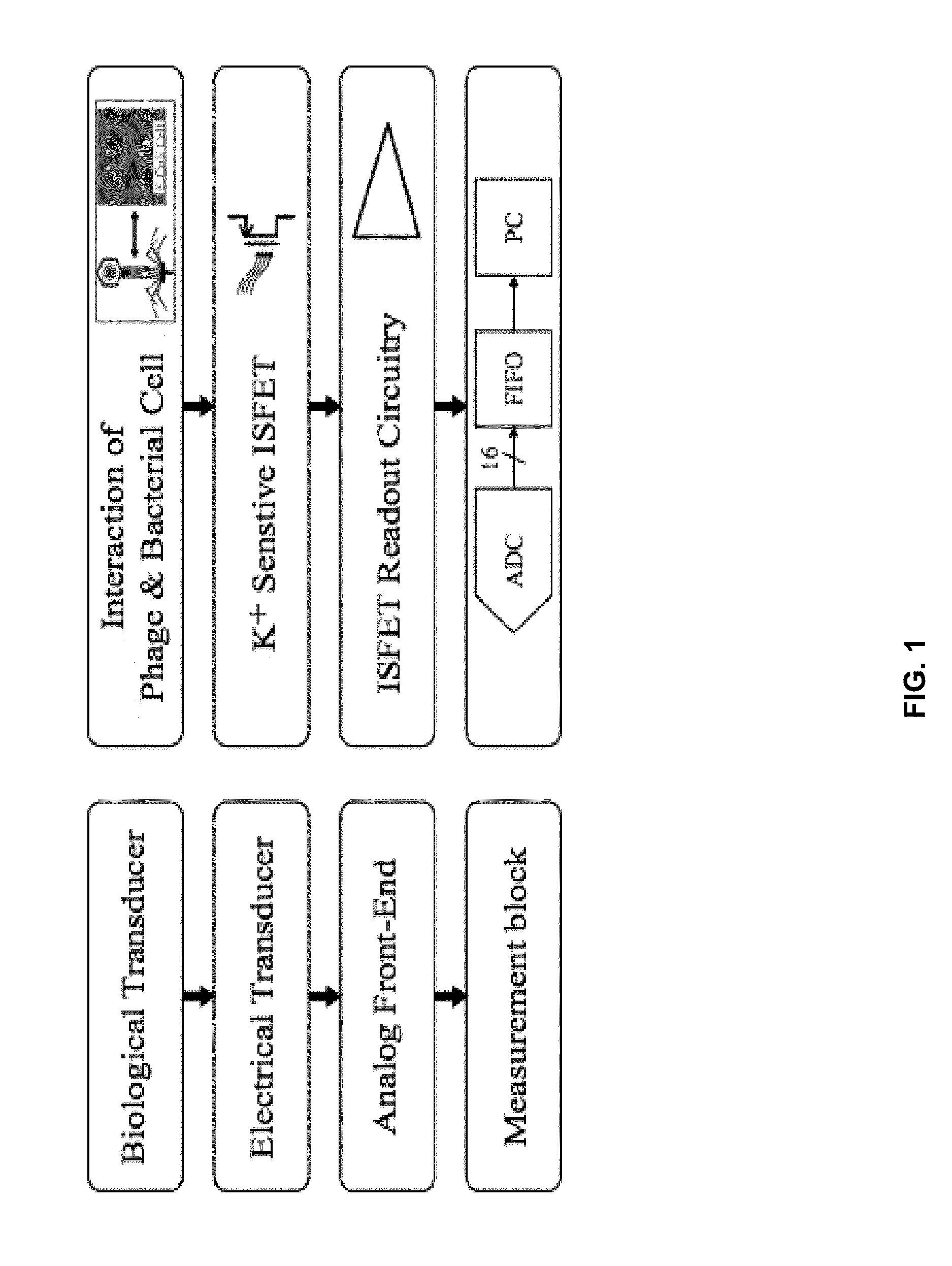
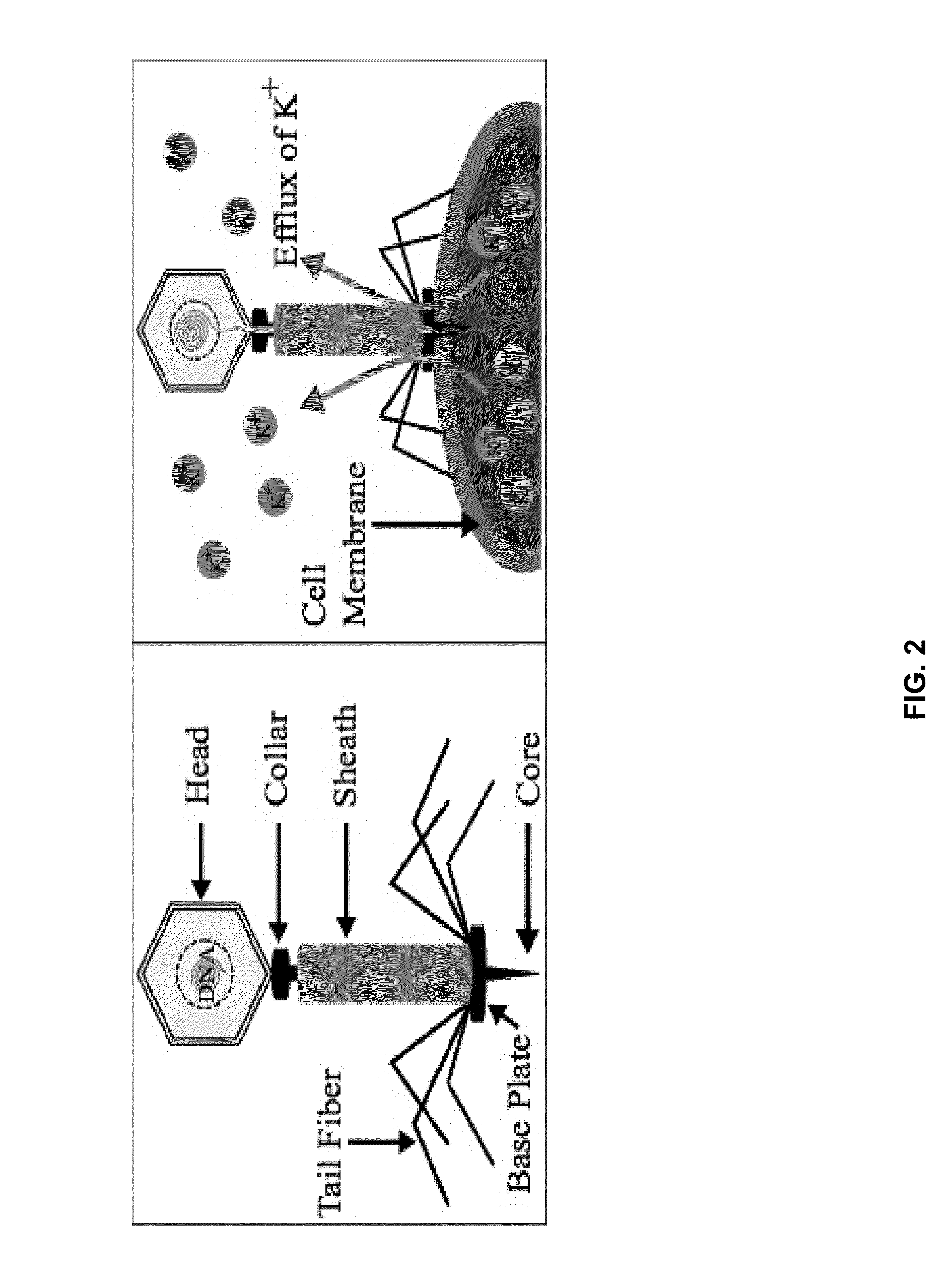
Integrated sensor for the rapid identification of bacteria using isfets
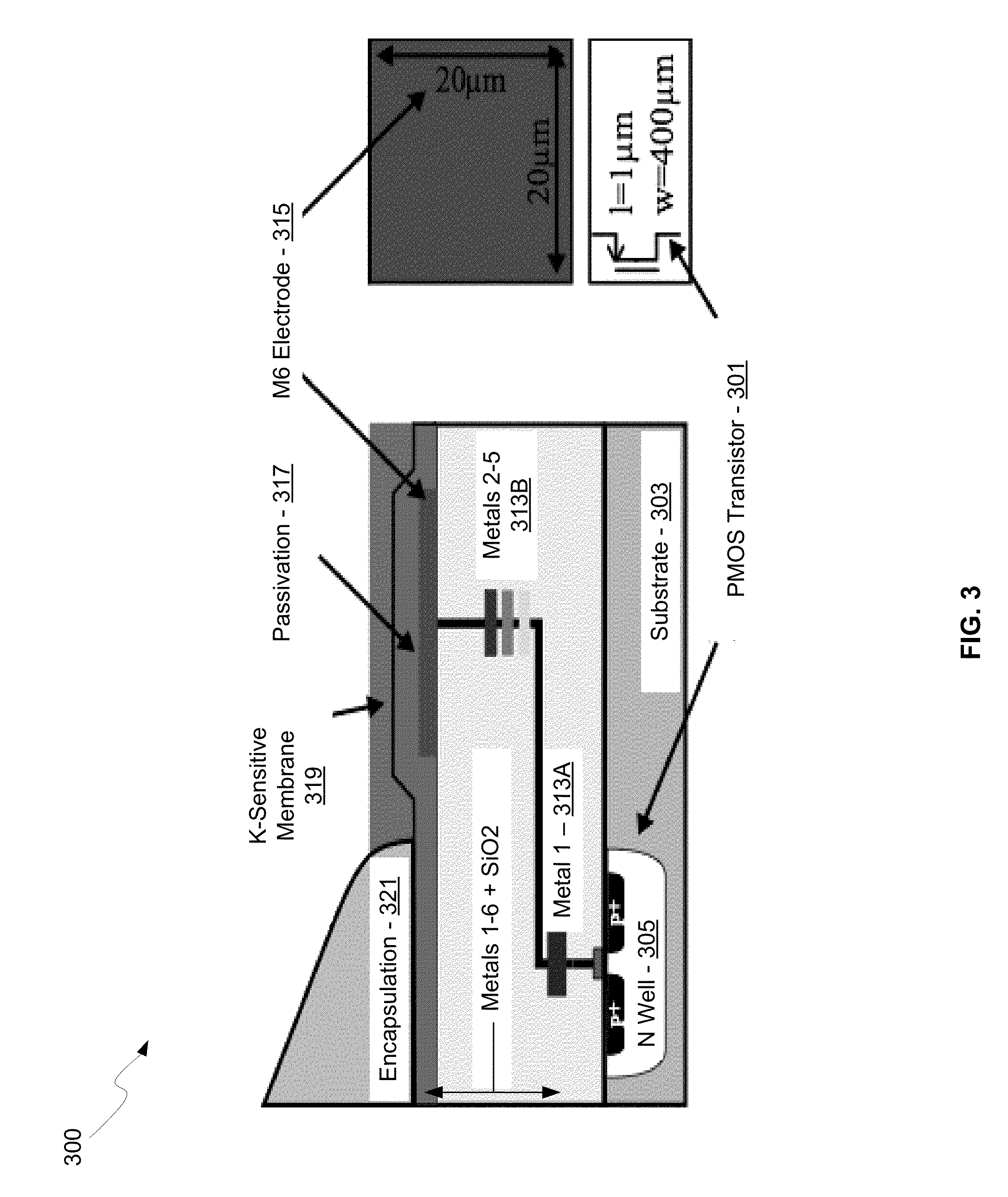
InactiveUS20140141408A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBacteria identificationPotassium ions
Disclosed are methods and systems for the detection of bacteria in a sample. The methods comprises contacting the sample with an antibacterial agent and a bacteria identification sensor, and involves the permeabilization of the bacteria by the antibacterial agent, and the subsequent detection of an efflux of potassium ions using a bacteria identification sensor comprising a potassium-sensitive ISFET. Also disclosed are bacteria identification sensor comprising a potassium-sensitive ISFET useful in the practice of the disclosed methods.
Owner:GULAK GLENN +2
Bacteria identification and typing analysis genome database and identification and typing analysis method
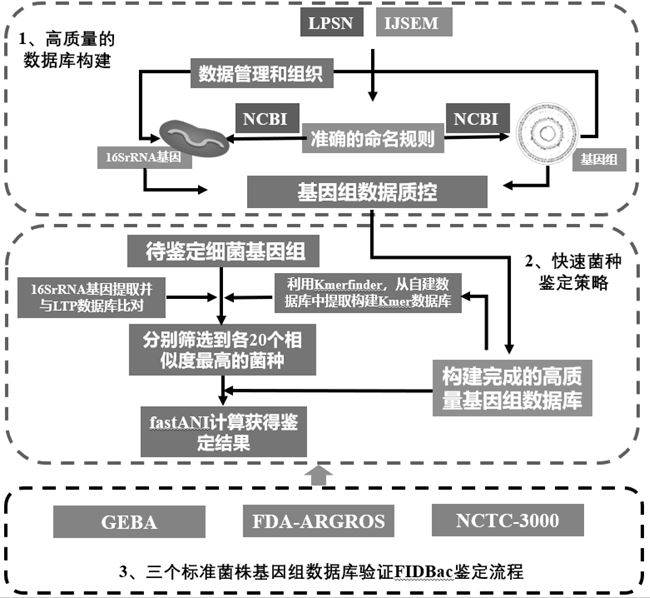
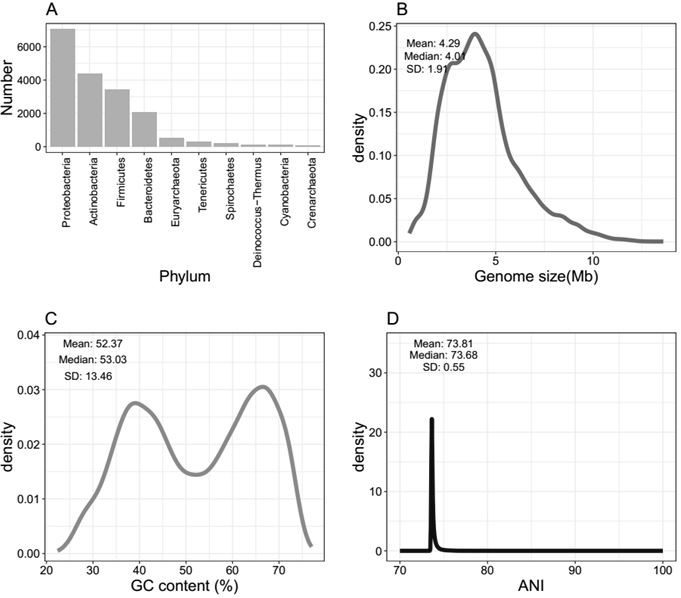
ActiveCN112863606AImprove accuracyRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBioinformaticsBacteria identificationFood industry
The invention discloses a bacterial identification and typing analysis genome database and an identification and typing analysis method. A high-quality bacterial identification and typing analysis genome database is created by deleting erroneous tags and assembling low-quality genomes. Based on the database, a bacterial identification and typing analysis method based on genome information is provided, and a set of rapid bacterial genome identification and identification platform (FIDBac) is developed. The accuracy rate of FIDBac identification reaches 97% or above, and is obviously higher than that of other identification systems or software of the same kind. The single, coherent and automatic bacterial genome identification working process has important significance in the fields of food industry, pharmaceutical industry, clinical diagnosis, microbial resource development and the like.
Owner:杭州微数生物科技有限公司
Spectroscopic means and methods for identifying microorganisms in culture
ActiveUS9365883B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismData set
A spectroscopic method for spectroscopic detection and identification of bacteria in culture is disclosed. The method incorporates construction of at least one data set, which may be a spectrum, interference pattern, or scattering pattern, from a cultured sample suspected of containing said bacteria. The data set is corrected for the presence of water in the sample, spectral features are extracted using a principal components analysis, and the features are classified using a learning algorithm. In some embodiments of the invention, for example, to differentiate MRSA from MSSA, a multimodal analysis is performed in which identification of the bacteria is made based on a spectrum of the sample, an interference pattern used to determine cell wall thickness, and a scattering pattern used to determine cell wall roughness. An apparatus for performing the method is also disclosed, one embodiment of which incorporates a multiple sample analyzer.
Owner:OPTICUL DIAGNOSTICS LTD +1
Bacterial identification
ActiveUS9185356B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsDielectrophoresisBacteria identificationBacteroides
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Screening method of salt-tolerant growth-promoting rhizosphere bacteria, strain and application of strain
PendingCN113736661AHigh outputImprove germination rateBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyBacteria identification
The invention provides a screening method of salt-tolerant growth-promoting rhizosphere bacteria, a strain and application of the strain. The screening method comprises the following steps: collecting soil attached to the surfaces of root systems of different types of saline-alkali soil plants as a separation source; diluting the obtained separation source, respectively placing the diluted separation source in LB solid culture media with different salinity concentrations for coating culture, and selecting monoclonal bacteria; carrying out secondary screening on the obtained multiple primary screening rhizosphere bacterial colonies to obtain rhizosphere bacterial single colonies; carrying out bacterial identification on the bacterial colonies to obtain various strains of different types; performing a germination rate test on multiple different types of bacteria, and screening out strains capable of improving the germination rate of the seeds; carrying out further salt tolerance screening on the screened strains, and selecting strains with good salt tolerance; and carrying out growth-promoting function screening on the strains with good salt tolerance, and finally screening out the strains with the growth-promoting function. According to the method, the salt-tolerant rhizosphere growth-promoting bacteria are screened out from the soil attached to the surfaces of the plant root systems of the saline-alkali soil, and the growth condition of crops in the saline-alkali soil can be improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Automatic bacteria identification device and method, automatic test equipment, urine analyzer
InactiveCN103789203AHigh precisionLow costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsImage enhancementBacteria identificationAutomatic test equipment
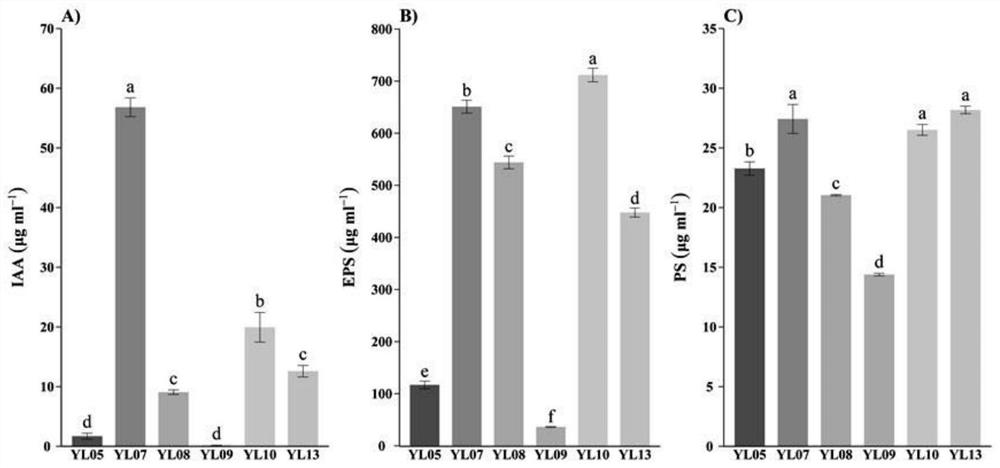
The embodiment of the invention provides an automatic bacteria identification device and method, automatic test equipment, as well as a urine analyzer. The automatic bacteria identification device includes a detection unit and a classification unit, the detection unit is used for detection of a regional part, in an input image, which may contain bacteria, so as to generate an output image containing the regional part, the classification unit is used for extracting a feature from the regional part detected by the detection unit, and identifies if the regional part is the bacteria on the basis of the feature; the feature is at least one from area, area ratio, cyclic shape, aspect ratio, contrast ratio and texture complexity of the regional part. According to the automatic bacteria recognition device and method of the embodiment of the invention, the bacteria can be automatically identified from the input image, and then a scheme, which is very effective in aspects of accuracy, cost and time, can be obtained.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Pit mud microorganism separation method
InactiveCN111321082AShorten activation timeRapid enrichmentFungiMicroorganism separationBiotechnologyBacteria identification
The preset invention belongs to the technical field of microorganism separation and discloses a pit mud microorganism separation method. The pit mud microorganism separation method comprises the following steps: step 1, collecting pit mud by a five-point sampling method; step 2, weighing 10 g of a pit mud sample to prepare a pit mud suspension; step 3, after water bath, inoculating the pit mud suspension into an enrichment culture medium, coating the enrichment culture medium into a separation culture medium by adopting a gradient dilution manner, placing the inoculated separation cultured medium into an anaerobic tank, performing separation culture, and performing plate streaking purification on microorganism colonies with various different characteristics to obtain single microorganism colonies; and step 4, streaking and separating the obtained single microorganism colonies and conducting caproic acid bacteria identification of the separated strain. Vinasse immersion liquid is used as the culture medium to simulate primary growth environment of microorganisms, so that the microorganisms in the pit mud can rapidly adapt to the new environment, activation time of the microorganismsis shortened, and microorganism separation efficiency can be improved.
Owner:HEBEI GUXIANGYANG WINE CO LTD
High-throughput separation culture method for crop root system microbiome
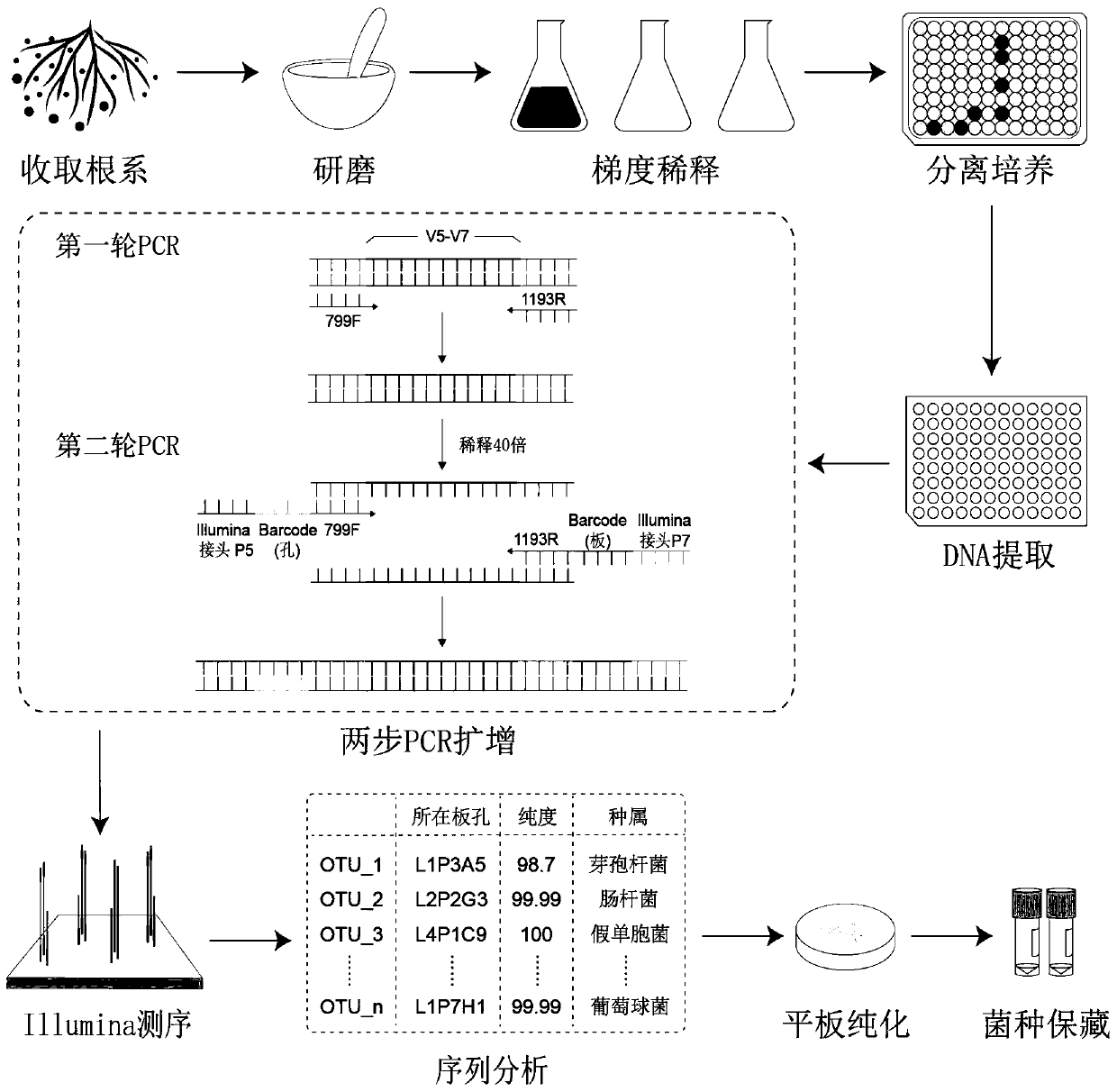
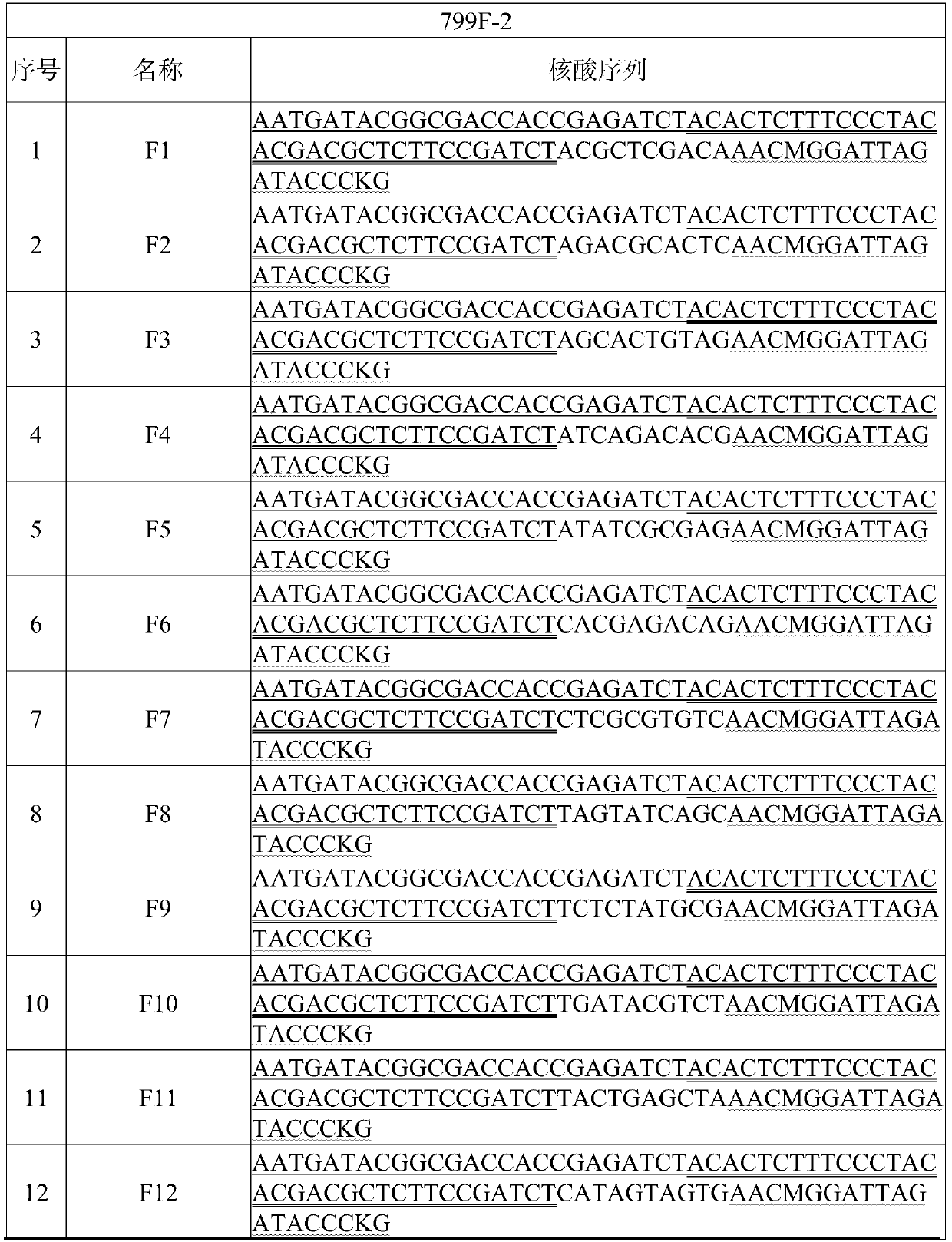
The invention discloses a high-throughput separation culture method for crop root system microbiome. The method comprises the following steps of S1, performing gradient dilution separation culture oncrop root system bacteria; S2, extracting DNA of cultured bacteria; S3, carrying out two-step PCR on DNA sub-holes, namely amplifying 16S variable regions V5-V7 by taking 799F and 1193R as primers inthe first step and taking 799F-2 containing hole barcode and 1193R-2 containing plate barcode as primers in the second step to obtain a bacterium identification library; S4, carrying out sequencing analysis; and S5, constructing the crop root system microbiome. By means of the method, a large number of bacteria can be separated and cultured in a short time with less manpower, the types of the bacteria can be rapidly identified through a one-key sequence analysis process, crop root microbiome can be assembled, and technical support is provided for obtaining more crop root microbial resources.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
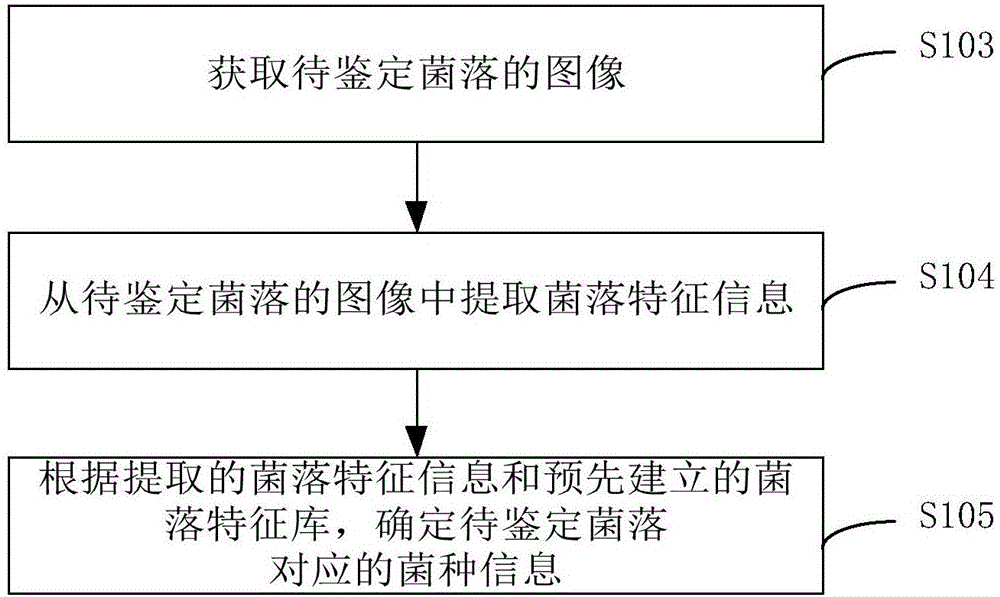
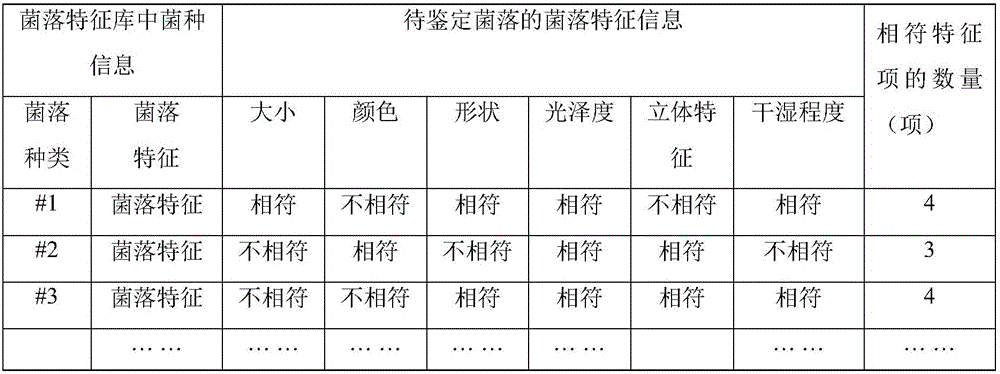
Bacteria identification method and device
InactiveCN106295572ALow costImprove securityMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymology/microbiology apparatusBacteria identificationInformation processing
The invention provides a bacteria identification method and a device. The method comprises steps that an image of a to-be-identified bacterium colony is acquired; the bacterium colony characteristic information is extracted from the to-be-identified bacterium colony; according to the extracted bacterium colony characteristic information and a pre-established bacterium colony characteristic database, the bacterial strain information corresponding to the to-be-identified bacterium colony is determined. Through a non-contact mode, the bacterial strain of the bacterium colony is identified, and safety of identification workers is improved; professional bacteria and medical requirements for the identification workers are quite low; an identification process can be rapidly accomplished through an automatic information processing process, an identification result can be further rapidly acquired, identification efficiency is greatly improved, and accuracy of the identification result is quite high; the image of the to-be-identified bacterium colony can be acquired through multiple modes, cost of the bacteria identification device is quite low, and identification cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:李辰
Bacteria identification and antimicrobial susceptibility test
ActiveUS20180245124A1Growth inhibitionMicrobiological testing/measurementTesting dairy productsBacteria identificationMicrobial Susceptibility
The present invention provides compositions, methods and kits for bacteria identification and anti-microbial susceptibility testing for the treatment of, for example, acute and chronic infections including infectious disease. The present invention is particularly useful in the identification of bacteria causing mastitis, and to antibiotic susceptibility testing to facilitate in the identification of an appropriate treatment for mastitis.
Owner:MASTAPLEX LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com