Bacterial nucleic acid sequencing identification method and bacterial identification kit based on DNA characteristic sequence
A bacterial nucleic acid and characteristic sequence technology, which is applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, bioreactors/fermenters for specific purposes, etc. The judgment basis is not standardized and unified, and the resolution is low
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] The establishment of the standard nucleic acid sequence database of embodiment 1-bacterial nucleic acid sequencing identification
[0066] (1) The screening of standard nucleic acid sequence fragments for bacterial DNA characteristic sequence identification was expanded on the basis of the inventor's prior patent (CN201610984864.0), and the scope of application of the sequence fragments screened in this example was wider.
[0067] The present invention uses Staphylococcus, Pseudomonas, Escherichia, Salmonella, Clostridium, Bacillus, Micrococcus, library Kocuria, Enterobacter, Pantoea, Klebsiella, Cronobacter, Citrobacter, Burkholderia ( Burkholderia), Enterococcus (Enterococcus), Streptococcus (Streptococcus), Acinetobacter (Acinetobacter), Legionella (Legionella) and other common bacterial pollutants in the production and inspection of pharmaceuticals are the research objects, and the sequences in the Genbank public nucleic acid database are screened , a total of 458 ...
Embodiment 2
[0117] Example 2-Validation of Escherichia DNA Characteristic Sequence Identification Method
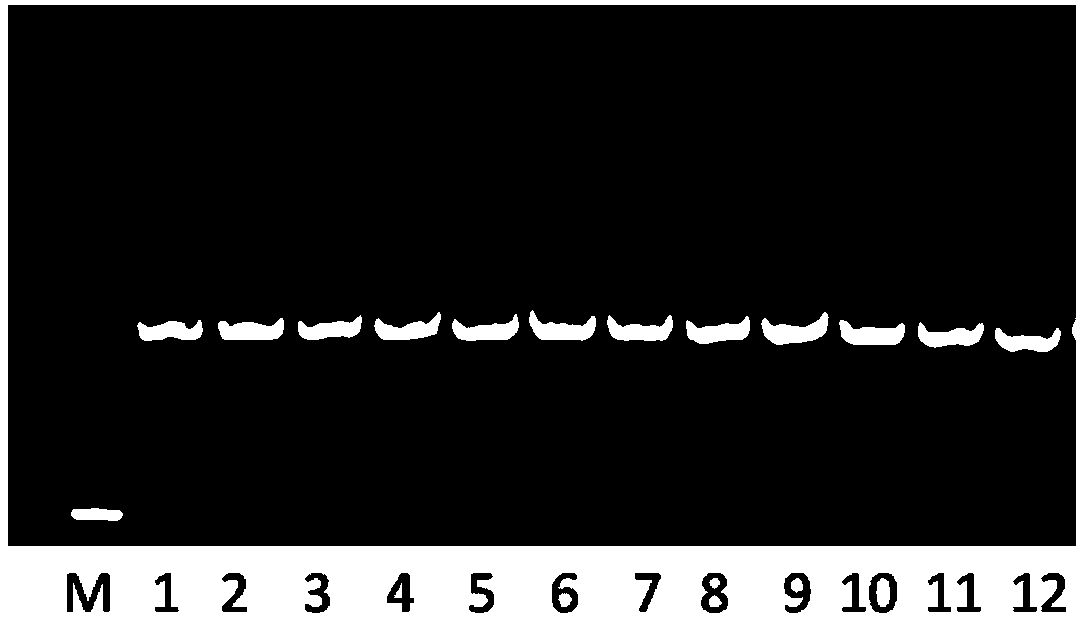
[0118] A total of 10 strains of Escherichia and other standard strains of Enterobacteriaceae were collected from microbial strain collection centers at home and abroad, including 2 strains from ATCC, 2 strains from CMCC, and 6 strains from CICC. Morphological identification and biochemical identification methods were used to confirm the genetic information of the strains; then, according to the optimized method steps in Example 1, genomic DNA was extracted, PCR, nucleic acid sequencing, nucleic acid sequencing of standard strains, and standard nucleic acid sequences were established.
[0119] The NJ phylogenetic tree was constructed by clustering the characteristic DNA sequences of Escherichia and other standard strains of Enterobacteriaceae confirmed by genetic information. The nucleic acid sequences of Escherichia coli clustered into one cluster, indicating that the "species" level...
Embodiment 3
[0120] Example 3-Validation of the Bacillus DNA Characteristic Sequence Identification Method
[0121] A total of 5 standard strains of Bacillus were collected from microbial strain collection centers at home and abroad, including 2 strains from ATCC and 3 strains from CICC. Morphological identification and biochemical identification methods were used to confirm the genetic information of the strains; then, according to the optimized method steps in Example 1, genomic DNA was extracted, PCR, nucleic acid sequencing, nucleic acid sequencing of standard strains, and standard nucleic acid sequences were established.
[0122] The identification result was confirmed as the DNA characteristic sequence of Bacillus for sequence comparison analysis, and Clostridium was used as the exogenous control group to construct the NJ phylogenetic tree. The results showed that the DNA characteristic sequence of Bacillus subtilis could be clearly distinguished from other species (see Figure 7 ). ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com