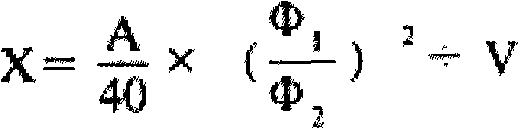Patents
Literature
296 results about "Micrococcus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Micrococcus (mi’ krō kŏk’ Əs) is a genus of bacteria in the Micrococcaceae family. Micrococcus occurs in a wide range of environments, including water, dust, and soil. Micrococci have Gram-positive spherical cells ranging from about 0.5 to 3 micrometers in diameter and typically appear in tetrads. They are catalase positive, oxidase positive, indole negative and citrate negative. Micrococcus has a substantial cell wall, which may comprise as much as 50% of the cell mass. The genome of Micrococcus is rich in guanine and cytosine (GC), typically exhibiting 65 to 75% GC-content. Micrococci often carry plasmids (ranging from 1 to 100 MDa in size) that provide the organism with useful traits.
Method for making fermented minced or cubed meat by utilizing fermenting agent
InactiveCN103704765AGood colorAdd flavorMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsFood ingredient for microbe protectionBiotechnologyFlavor
The invention provides a method for making fermented minced or cubed meat by utilizing a fermenting agent. The method comprises the steps of minced or cubed meat raw material pretreatment, preserving, fermenting, storing and the like, the above raw material selects cold meat or fresh meat, and a strain comprises one or more of lactic acid bacteria, Debaryomyces hansenii, Micrococcus Kristinae, Micrococcus varians and Staphylococcus xylosus. A fermented product obtained in the invention has the characteristics of fine texture, elasticity, rich and pure fragrance, possessing of the sour fragrance specially possessed by fermented meat products, good mouthfeel and unique flavor, and also has the advantages of high nutrition value, high safety, eating convenience, easy preservation, probiotic effect and the like.
Owner:胡永金
Erythro micrococcus Em and usage for generating biologic emulsifier as well as degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
InactiveCN1519312AStrong solubilizationPromotes the degradation of petroleum hydrocarbonsBacteriaFermentationSolubilityAlkane
A Rhodococcus ruber Em (CGMCC No.0868) features that its cells, cell suspension, or immobilized cells can degradate the paraffin and polycyclic arylhydrocarbon because the paraffin and polycyclic arylhydrocarbon are used as its only carbon source and energy source for growing to generate the bioemulsifier of ester. Said emulsifier can obviously decrease the surface tension of aqueous solution, has strong emulsifying power to ester substance, and can increase the solubility of paraffin and polycyclic arylhydrocarbon in water, so it can be used for treating the oil-contained sewage and repairing the petroleum polluted soil.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bioreactor for remediation of pollutants with butane utilizing bacteria
InactiveUS6051130AReduce and eliminate hydrocarbon pollutantEasy to transportGas treatmentBacteriaBacteroidesComamonas
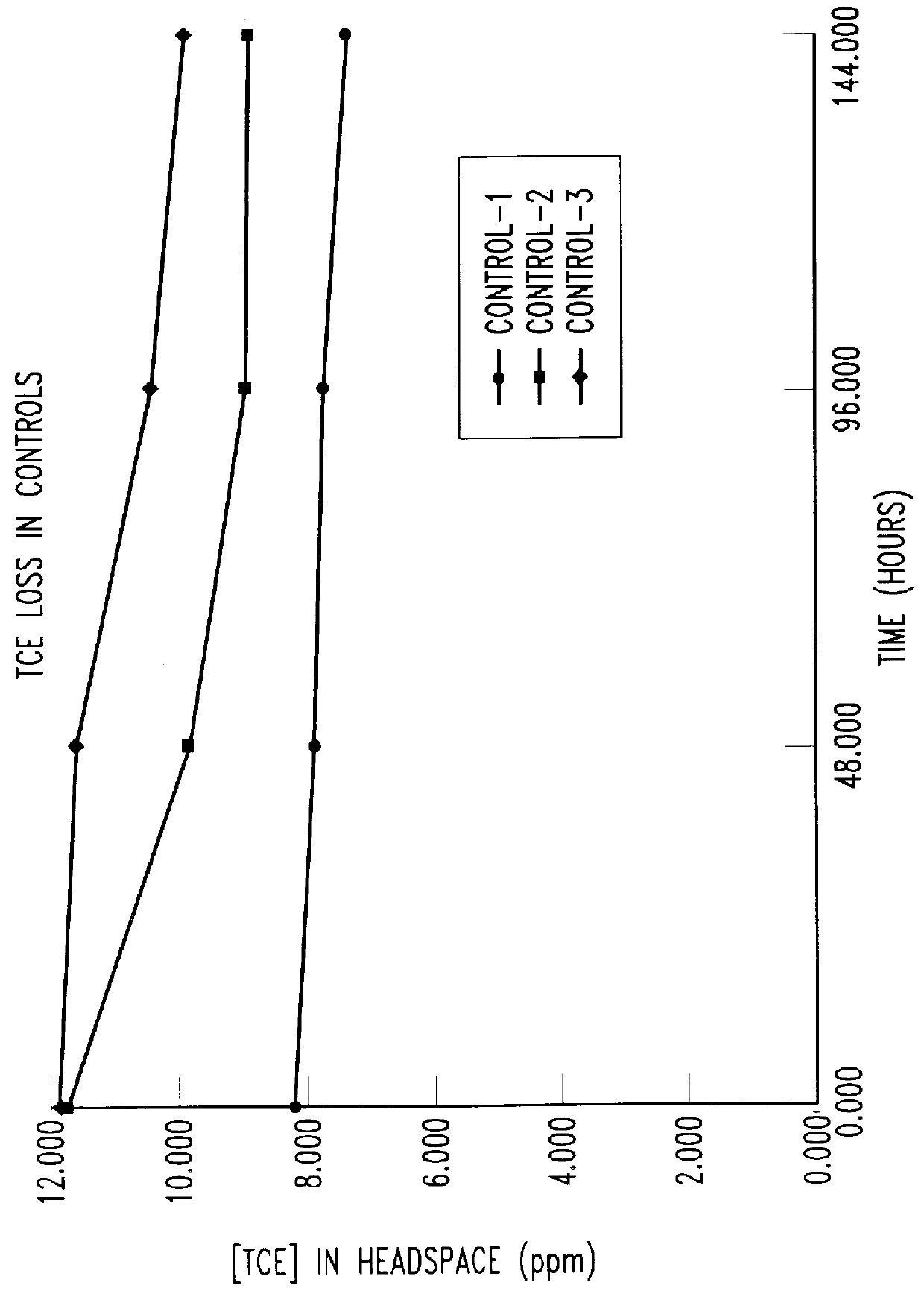
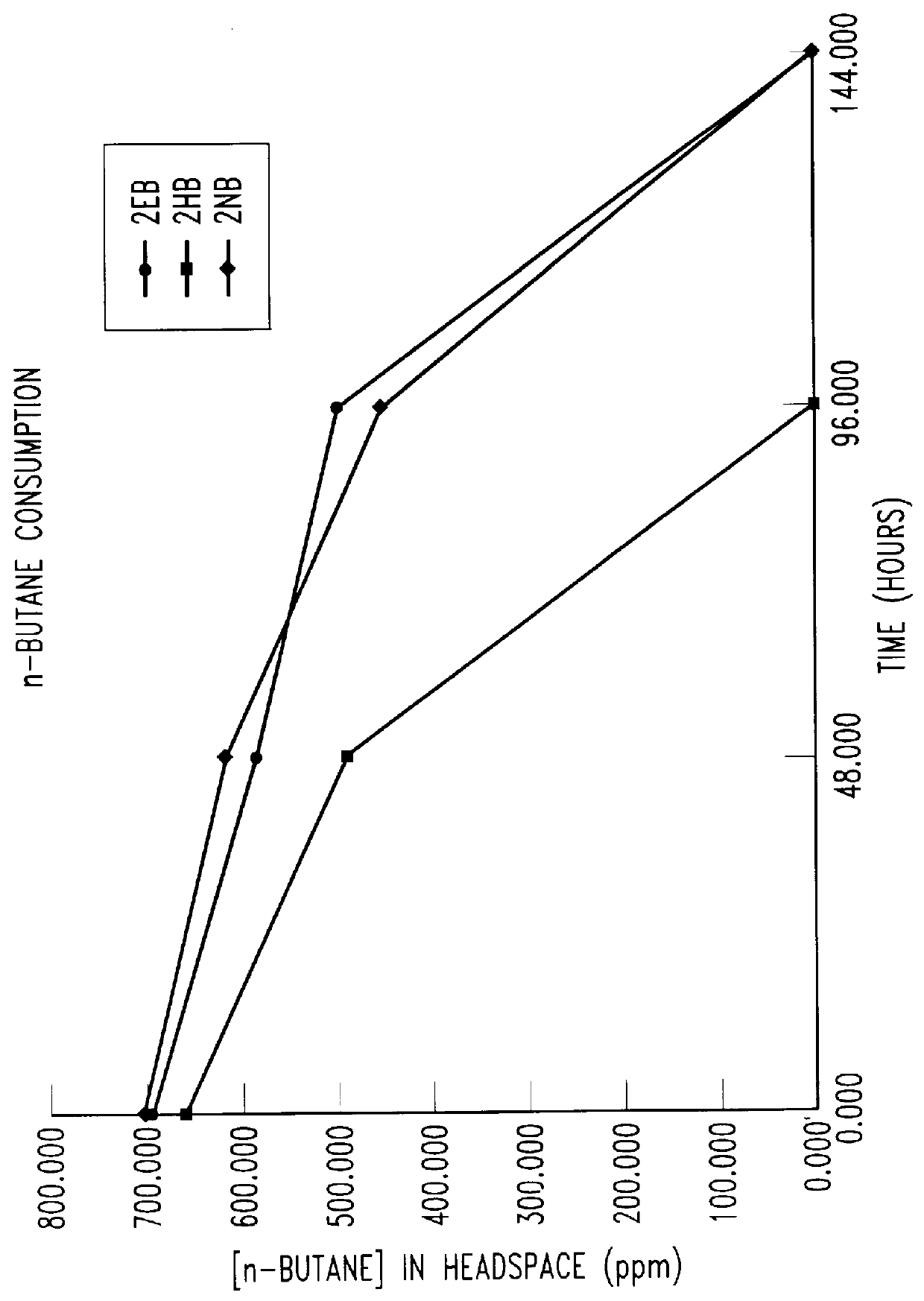
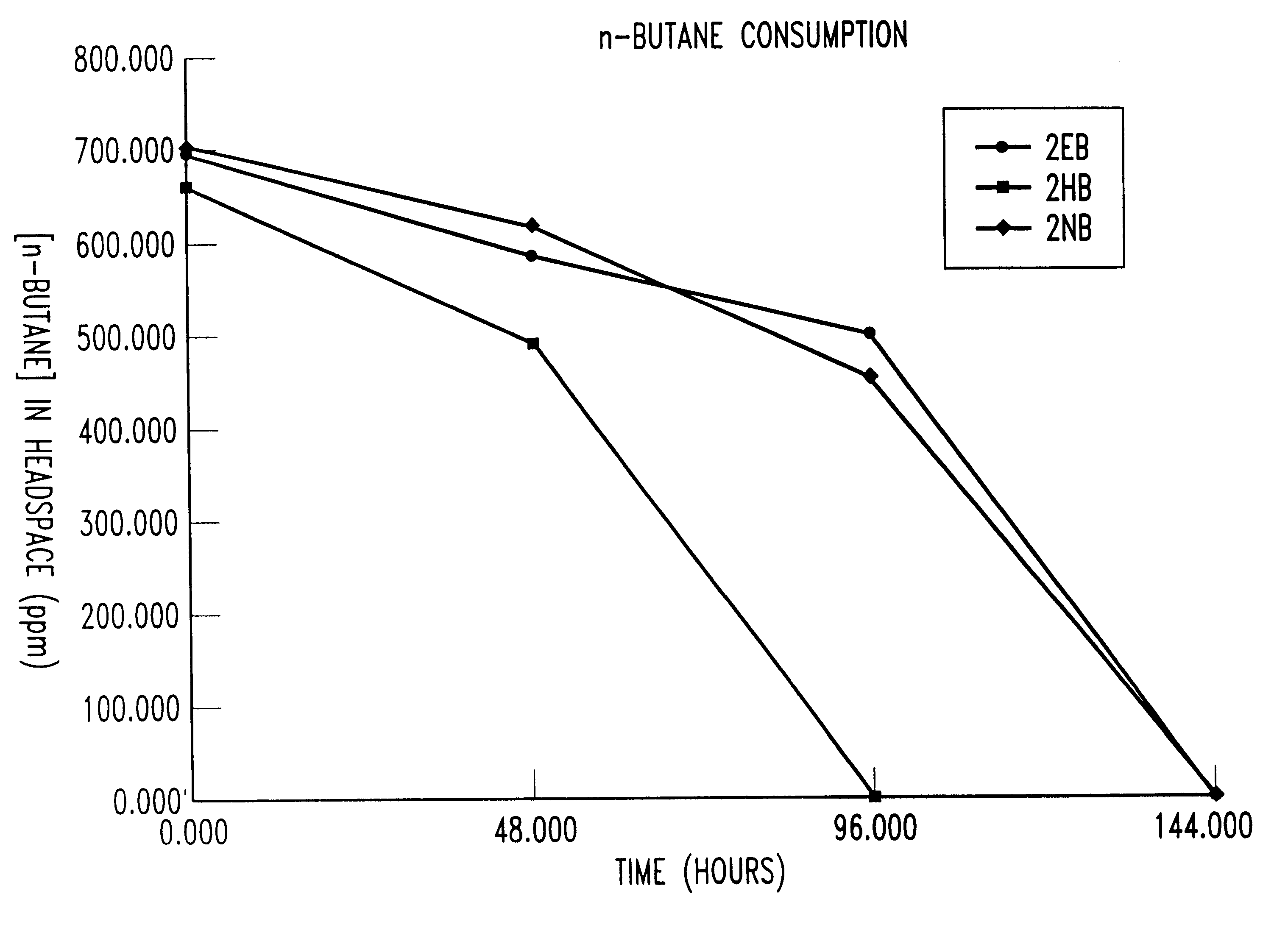
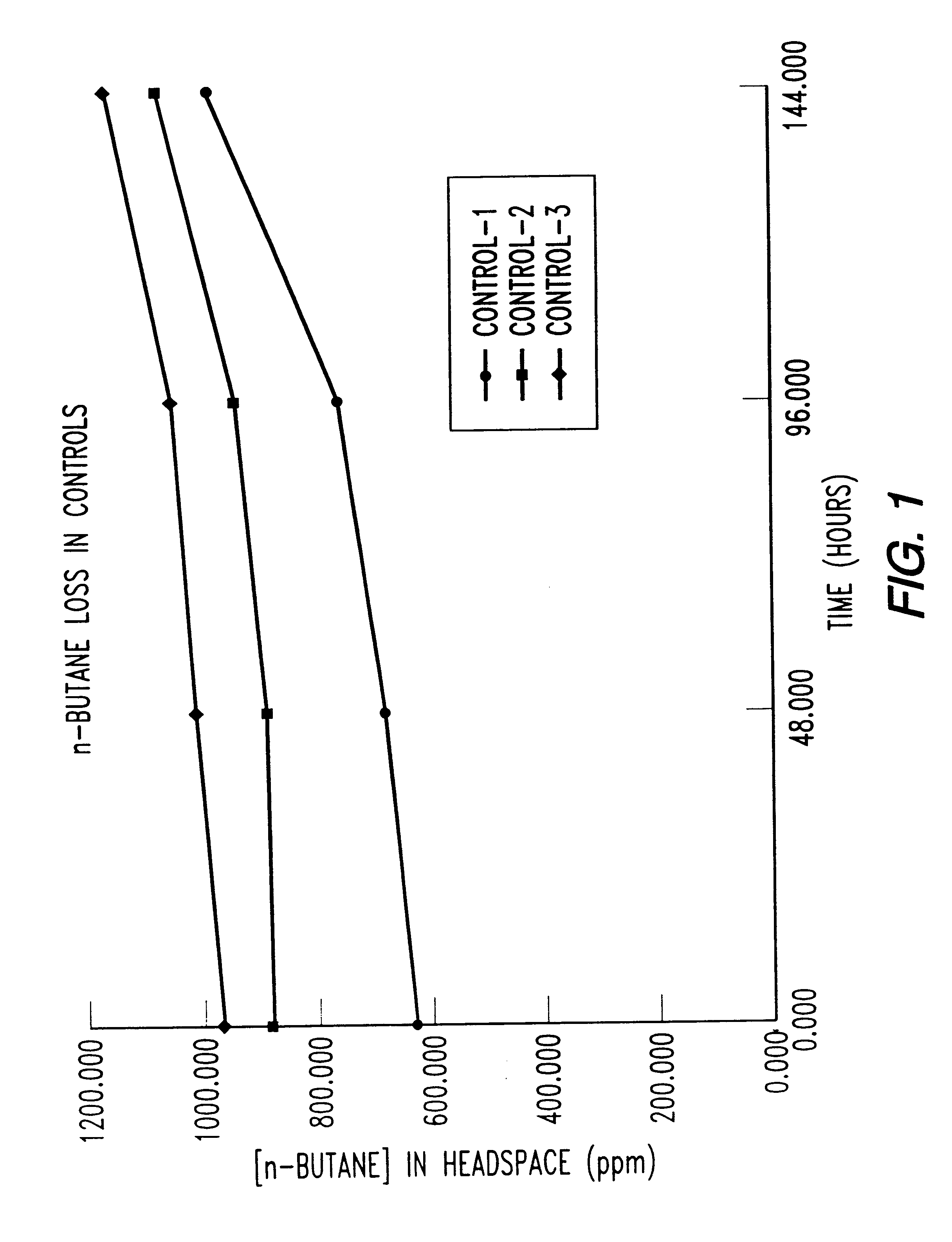
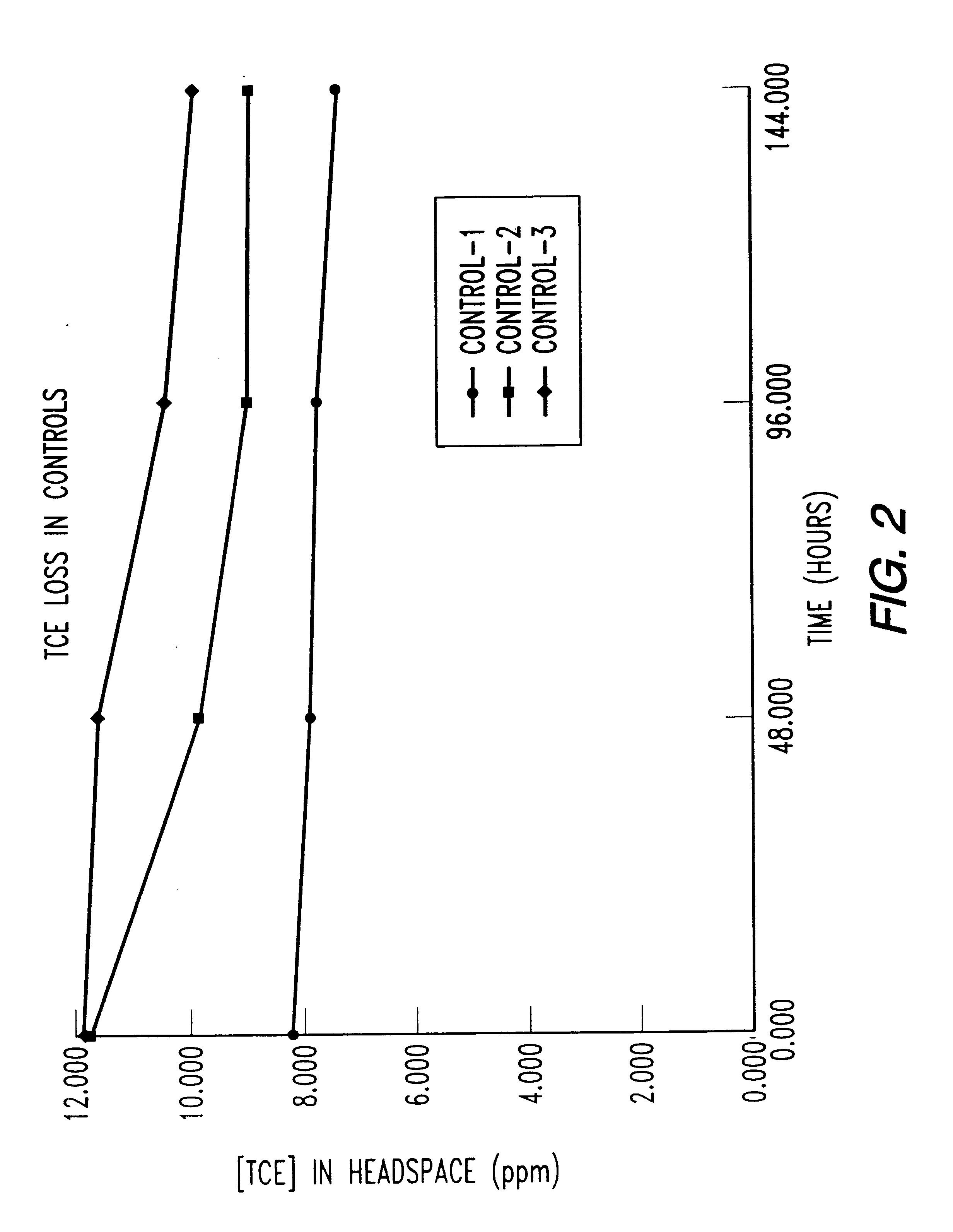
Butane-utilizing bacteria are used to degrade hydrocarbon pollutants such as trichloroethene (TCE). In-situ or ex-situ techniques may be used to reduce or eliminate hydrocarbon pollutants from liquid, gas and solid sources. In a preferred embodiment, TCE concentrations in various aqueous environments are reduced by contacting a contaminated water source with butane-utilizing bacteria in the presence of oxygen to degrade the TCE by cometabolism or direct metabolism. Suitable butane-utilizing bacteria include Pseudomonas, Variovorax, Nocardia, Chryseobacterium, Comamonas, Acidovorax, Rhodococcus, Aureobacterium, Micrococcus, Aeromonas, Stenotrophomonas, Sphingobacterium, Shewanella, Phyllobacterium, Clavibacter, Alcaligenes, Gordona, Corynebacterium and Cytophaga. The butane-utilizing bacteria have relatively low TCE toxicity in comparison with conventional methane-utilizing bacteria, and demonstrate an improved ability to degrade TCE.
Owner:GLOBAL BIOSCI
Bioremediation of pollutants with butane-utilizing bacteria
InactiveUS6210579B1Reduce and eliminate hydrocarbon pollutantEasy to transportGas treatmentTreatment using aerobic processesBacteroidesComamonas
Butane-utilizing bacteria are used to degrade hydrocarbon pollutants such as trichloroethene (TCE). In-situ or ex-situ techniques may be used to reduce or eliminate hydrocarbon pollutants from liquid, gas and solid sources. In a preferred embodiment, TCE concentrations in various aqueous environments are reduced by contacting a contaminated water source with butane-utilizing bacteria in the presence of oxygen to degrade the TCE by cometabolism or direct metabolism. Suitable butane-utilizing bacteria include Pseudomonas, Variovorax, Nocardia, Chryseobacterium, Comamonas, Acidovorax, Rhodococcus, Aureobacterium, Micrococcus, Aeromonas, Stenotrophomonas, Sphingobacterium, Shewanella, Phyllobacterium, Clavibacter, Alcaligenes, Gordona, Corynebacterium and Cytophaga. The butane-utilizing bacteria have relatively low TCE toxicity in comparison with conventional methane-utilizing bacteria, and demonstrate an improved ability to degrade TCE.
Owner:GLOBAL BIOSCI
Biological organic repairing agent for soil pollution and application and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105347884AReduce absorptionReduced enrichmentBio-organic fraction processingExcrement fertilisersBiotechnologyPollution
The invention relates to the field of soil fertilizer and provides a biological organic repairing agent for soil pollution and its application and preparation method. The biological organic repairing agent of the invention is composed of, by weight, 1.5-3 parts of eymogenic bacterium, 1-1.5 parts of wheat bran, 1.5-2 parts of molasses meal, 45-50 parts of ammonium humate, 45-50 parts of hydrolase dregs, 150-200 parts of soybean meal, 100-150 parts of humic acid powder, 80-100 parts of zeolite powder, 25-40 parts of a calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer, 150-200 parts of cattle and sheep manure, 150-204 parts of plant straw, 25-40 parts of potassium humate, 1.5-3 parts of bacillus mucilaginosus, 1-1.5 parts of Gliocladium roseum, 1.5-2 parts of Streptomycesvinaceus-drappus, 1-1.5 parts of trichoderma spp, 1-1.5 parts of Paecilomyces lilacinus, 1-1.5 parts of bacillus subtilis and 1-1.5 parts of micrococcus. According to the invention, soil pollution control, improvement and nutrition are integrated.
Owner:HEBEI CIXIN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Erythro micrococcus ZJB-064 and application thereof
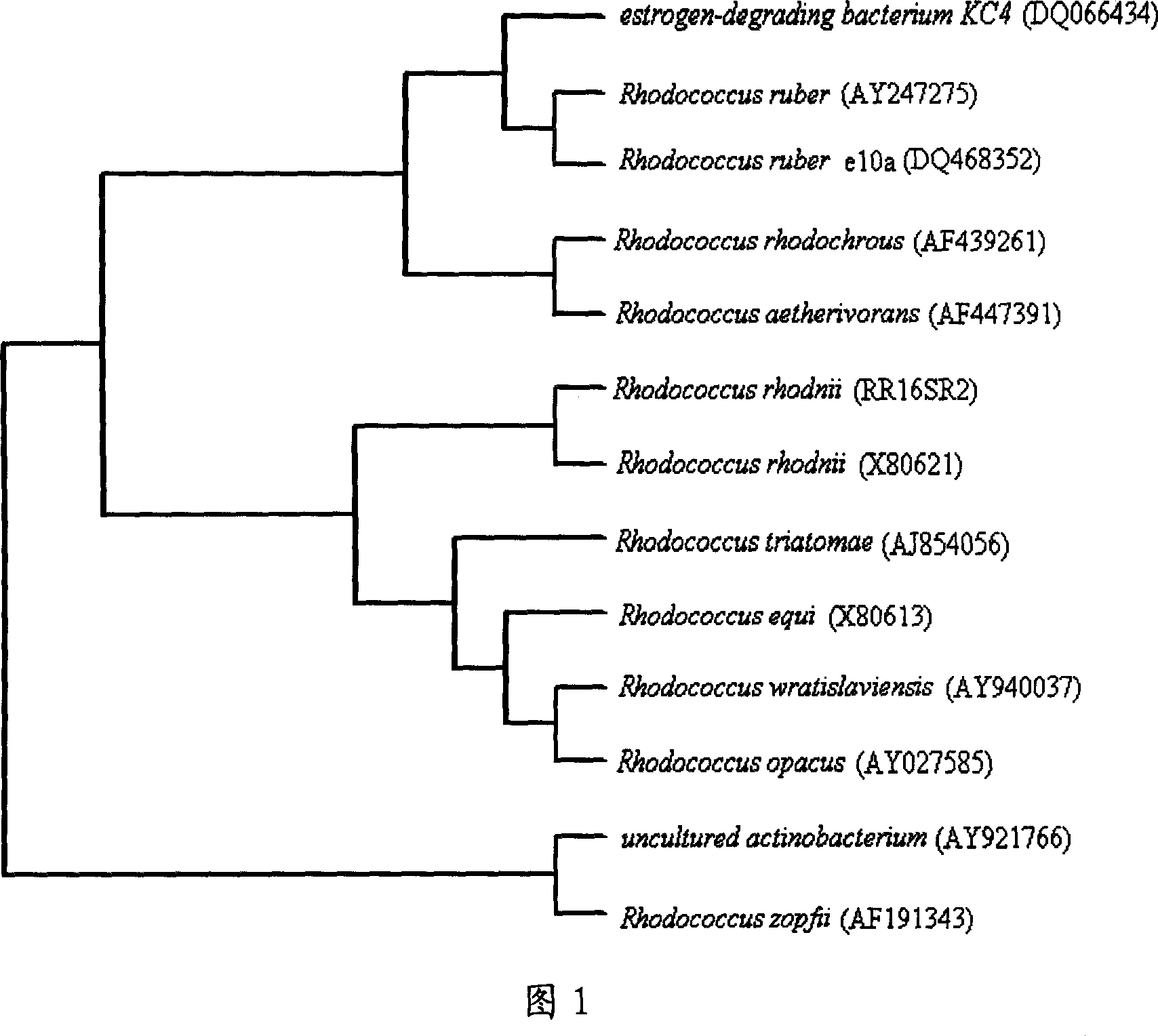
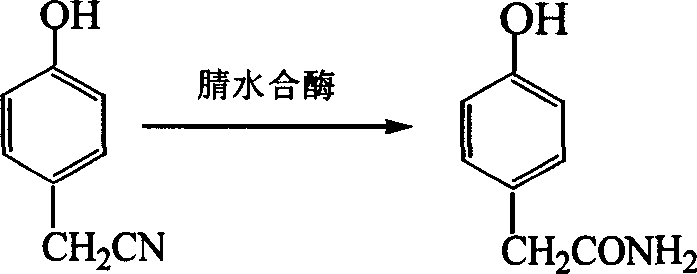
This invention provides ZJB-064(Rhodococcus rubber ZJB-064) of a new microbial strain selected from soil and its application in preparing p-hydroxyben acetamide, in which, said ZJB-064 was preserved in China tipical cultivated subject center in April 14, 2006 with the preservation number of CCTCCNo: M206040 and is used in sybthesizing p-hydroxyben acetamide.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A kind of Lactococcus lactis and the antibacterial peptide produced by the Lactococcus lactis and the application of the antibacterial peptide
InactiveCN102286393ANo inhibitionAntibacterialBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLactobacillusMicroorganism
The invention relates to lactococcus lactis subsp.lactis, antibacterial peptide produced by lactococcus lactis subsp.lactis and the application of antibacterial peptide. In the invention, the collection number of the lactococcus lactis subsp.lactis LLC518 in the General Microorganism Center of China Microorganism Culture Collection Management Committee is CGMCC No. 4584. In the invention, the antibacterial peptide produced by the lactococcus lactis subsp.lactis can restrain micrococcus tetragenus, Bacillus thuringiensis, lactococcus lactis and listeria innocua, particularly, has strong restraint function to L. monocytogenes which can cause serious food poisoning. Thus, the lactococcus lactis subsp.lactis and the antibacterial peptide thereof have active function in food fresh keeping.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of microbe immobilized particles for restoring pesticide contaminated soil
InactiveCN101701216AAvoid leachingGuaranteed quantityContaminated soil reclamationOn/in inorganic carrierCellulosePorous carbon
The invention relates to in-situ restoration of pesticide contaminated soil, in particular to a preparation method of microbe immobilized particles for restoring pesticide contaminated soil. Porous carbon is used as a main carrier material, and cellulose, chitosan and sodium alginate are used as auxiliary carriers to realize the purpose of immobilizing the microbes; and the obtained microbe immobilized particles are used for in-situ restoration of the pesticide contaminated soil. The carrier material used in the invention has cheap price, low cost, wide sources, good air permeability and no toxicity to organisms, and can not cause secondary pollution to the soil. The carrier and the immobilizing process thereof can be used for immobilizing multi-bacterium microbes, such as pseudomonas, bacillus, zoogloea, micrococcus and the like, and have certain broad-spectrum applicability; and the bacillus can reach more than 10 billions / gram. Compared with the prior immobilizing method, the invention is characterized by directly sowing the immobilized cell particles into the soil without destroying the original soil structure.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Solid microbial bacterium agent for petroleum degradation and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102839137AOptimize the microbial systemGood physical propertiesBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationBacillus cereusBacillus aryabhattai
The invention discloses a solid microbial bacterium agent for petroleum degradation. The agent is prepared by mixing of the following components by weight: 85-90 parts of a microbial bacterial fertilizer, and 10-15 parts of a mixed fermentation solution of Micrococcus luteus, Bacillus cereus and Bacillus pumilus. In addition, the invention also provides a preparation method of the solid microbialbacterium agent. The solid microbial bacterium agent provided in the invention can introduce beneficial microorganisms into the soil, optimize the soil microbial system, enhance physical properties of the soil, enhance soil biological activity, and restore hardened and degraded soil, thus being an eco-environment-friendly green bacterium agent. Application of the solid microbial bacterium agent provided in the invention in the soil can promote crop growth, degrade and transform petroleum pollutants in the soil, and also can enhance the stress resistance of crops, as well as improve crop yield.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Compound preservative
InactiveCN101999736AReduce dosageAvoid safety hazardsMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsSodium lactateBacillus cereus
The invention discloses a compound preservative which is characterized by comprising the raw materials in percent by weight: 1-10 percent of nisin, 1-10 percent of sodium dehydroacetate, 1-10 percent of tea polyphenol, 1-10 percent of potassium sorbate and 60-96 percent of sodium lactate. The compound preservative can remarkably inhibit multiple putrefying bacteria of bacillus subtilis, bacillus pumilus, bacillus cereous, pseudomonas aeruginosa, micrococcus, staphylococcus aureus and the like, is applied to meat products, can remarkably prolong the shelf life, and improve the food safety.
Owner:烟台喜力科技发展有限公司
High-concentration chemical sewage composite inocula and use thereof
ActiveCN105621626AThe method of treating sewage is simple and easyImprove survival rateBiological water/sewage treatmentSynechococcusBacillus cereus
The invention discloses high-concentration chemical sewage composite inocula. The high-concentration chemical sewage composite inocula comprise, by weight, 180-220 parts of bacillus cereus, 150-160 parts of bacillus circulans, 75-85 parts of Exiguobacterium acetylicum, 90-120 parts of bacillus coagulans, 150-170 parts of pseudomonas aeruginosa, 20-25 parts of micrococcus luteus, 120-140 parts of thiobacillus thiooxidans, 180-230 parts of rhodococci, 20-30 parts of lactobacillus brevis, 50-65 parts of paracoccus denitrificans, 95-112 parts of alcaligenes faecalis, 110-125 parts of pseudomonas putida, 100-130 parts of enterobacter aerogenes, 280-320 parts of beer yeast and 140-160 parts of lactobacillus fermenti. All strains of the composite inocula reasonably cooperate with each other, produce synergistic effects, do not produce antagonism, have a high survival rate, is suitable for one step addition and fast forms dominant bacterial community. The high-concentration chemical sewage composite inocula have unique treatment effects on high-concentration chemical sewage, have a COD clearance rate of 94.17%, reduce an operation cost and promote qualified discharge.
Owner:江苏元捷环境科技有限公司
Treatment process applicable to industrial wastewater and application of industrial wastewater in preparation of bacterial manure
InactiveCN104086001ASimple processEasy to handleBiological water/sewage treatmentFertilizer mixturesBacillus megateriumBacillus cereus
The invention belongs to the field of wastewater treatment and discloses a treatment process applicable to industrial wastewater. The treatment process applicable to the industrial wastewater comprises the following steps: 1) preparing complex microbial inoculant; 2) precipitating wastewater; 3) purifying the wastewater; 4) preparing bacterial manure. The prepared complex microbial inoculant comprises 5-6 parts of micrococcus luteus, 4-5 parts of bacillus mucilaginosus, 3-4 parts of paracoccus denitrificans, 2-3 parts of rhodococcus, 2-3 parts of acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, 1-2 parts of bacillus megaterium and 1-2 parts of bacillus cereus. The invention also discloses bacterial manure prepared by utilizing the treatment process applicable to the industrial wastewater. The treatment process applicable to the industrial wastewater is simple and feasible, the industrial wastewater can be effectively treated, and the bacterial manure is prepared by utilizing the treatment process applicable to the industrial wastewater.
Owner:东莞市统泉环保科技有限公司
Method for quickly detecting harmful bacteria in beer
InactiveCN102071243ADetectableMeet the requirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence in situ hybridizationFluorescence microscope
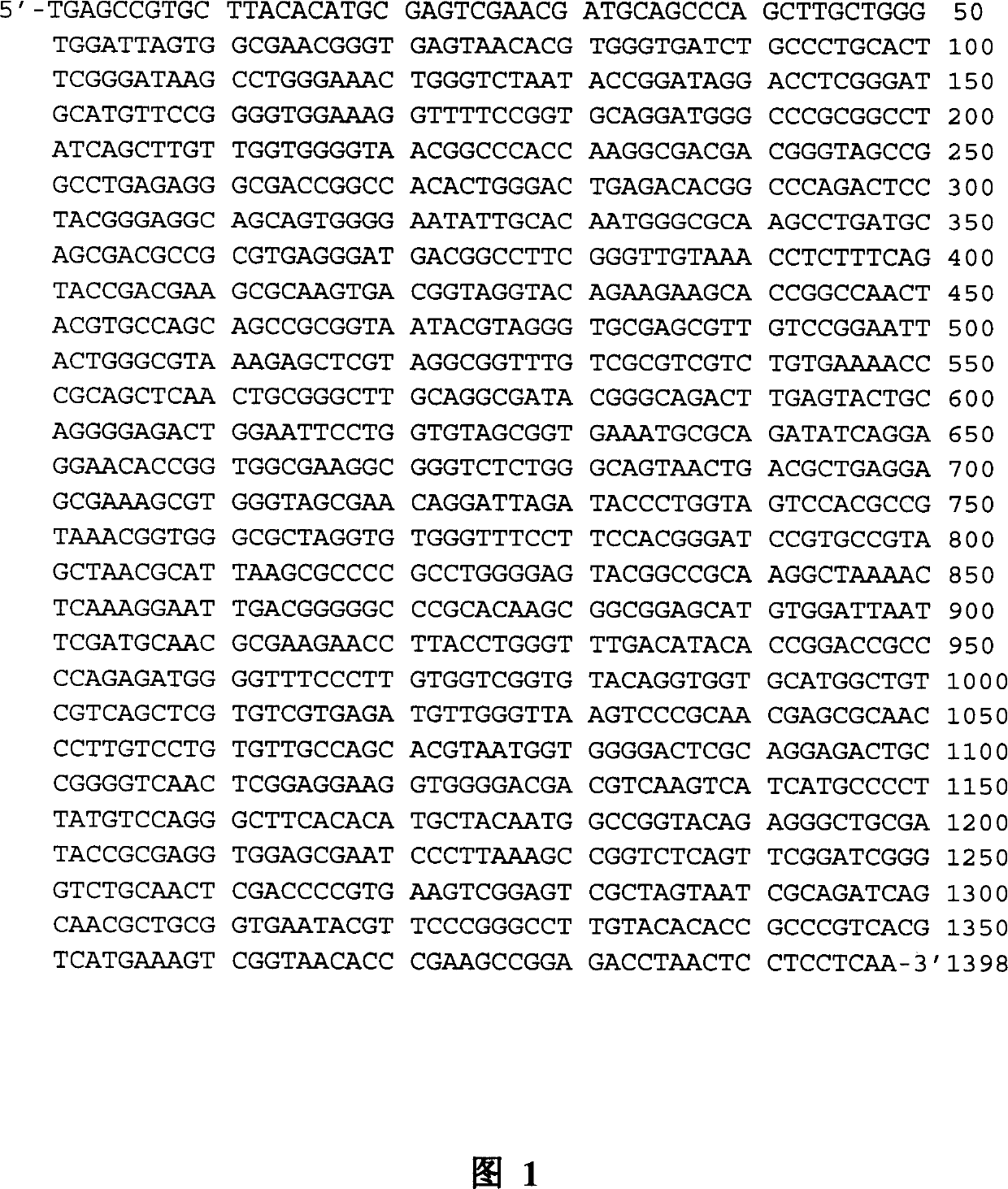
The invention discloses a method for quickly qualitatively and quantitatively detecting harmful bacteria in beer breweries by applying fluorescence in situ hybridization and fluorescent microcolony combined technology. The method comprises steps of: preparing sample solution and a culture medium; performing fluorescent microcolony and fluorescence in situ hybridization experimental operation; andobserving by using a fluorescence microscope, counting, and qualitatively and quantitatively analyzing the harmful bacteria in the production process of the beer breweries according to fluorescent probes and excited fluorescence with different colors of a carboxyfluorescein diacetate (CFDA) dye. The invention also discloses two specific probes, which are respectively a probe for detecting Lactobacillus brevis, namely 5'-TAGCCGGTGTAACCCTGACTCTG-3' of which one end is marked by Cy3, and a probe for detecting micrococcus tetragenus, namely 5'-GAGATTAGGAAGAACACCAGTGGCGAA-3' of which one end is marked by Cy3. By combining two methods, phenomena that the fluorescence in situ hybridization is difficult to quantitate bacteria and experimental results are easy to show false negative and false positive are avoided, and the problem that the fluorescent microcolony technology cannot qualitatively analyze the bacteria is also solved. Therefore, the requirement on quick detection and qualitative and quantitative requirements for the production of the beer breweries are met.
Owner:CHINA NAT RES INST OF FOOD & FERMENTATION IND CO LTD +1
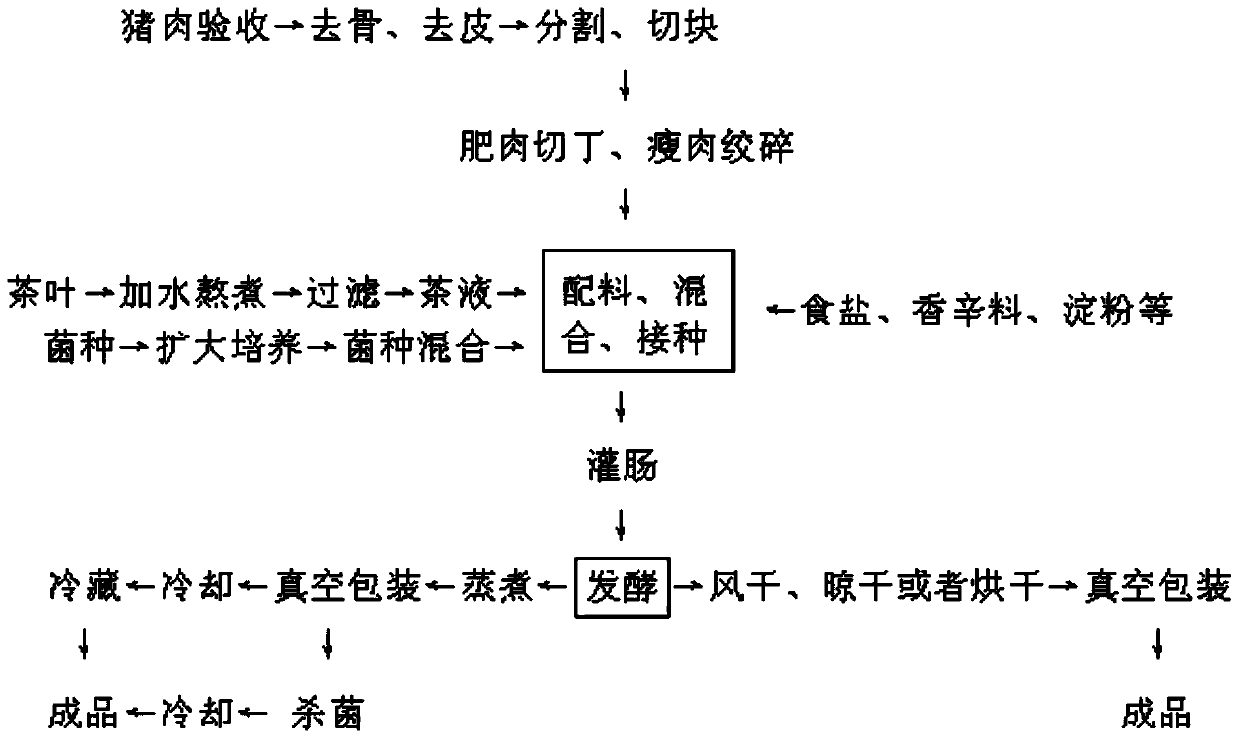
Fermented tea sausage and processing method thereof
ActiveCN103798831ADeliciousHigh nutritional valueFood freezingMeat/fish preservation by heatingNutritive valuesFood flavor
The invention discloses fermented tea sausage and processing methods thereof. The fermented tea sausage is produced by adopting tea liquid and pork as main raw materials to be fermented by a mixed strain consisting of lactobacillus, saccharomycetes and micrococcus. According to different product preservation methods, the invention provides the processing methods of three products such as dry-type fermented tea sausage, cold-stored cooked fermented tea sausage and normal-temperature-stored cooked fermented tea sausage. By adding the tea liquid and the mixed strain which is prepared from the purely-cultured lactobacillus, saccharomycetes and micrococcus into the processing flow of the sausage, the growth and propagation of inoculated microorganisms, such as the lactobacillus, which are beneficial to processing and cooking of the sausage can be effectively promoted, the production and accumulation of nitrite and biogenic amine in the sausage processing process can be suppressed by adequately utilizing tea polyphenol in the tea liquid; meanwhile, the sausage is unique in flavor, and the grease of the sausage can be reduced; the fermented tea sausage is delicious in taste, high in nutritional value, low inn nitrite and biogenic amine content, free from benzopyrene and high in food safety.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
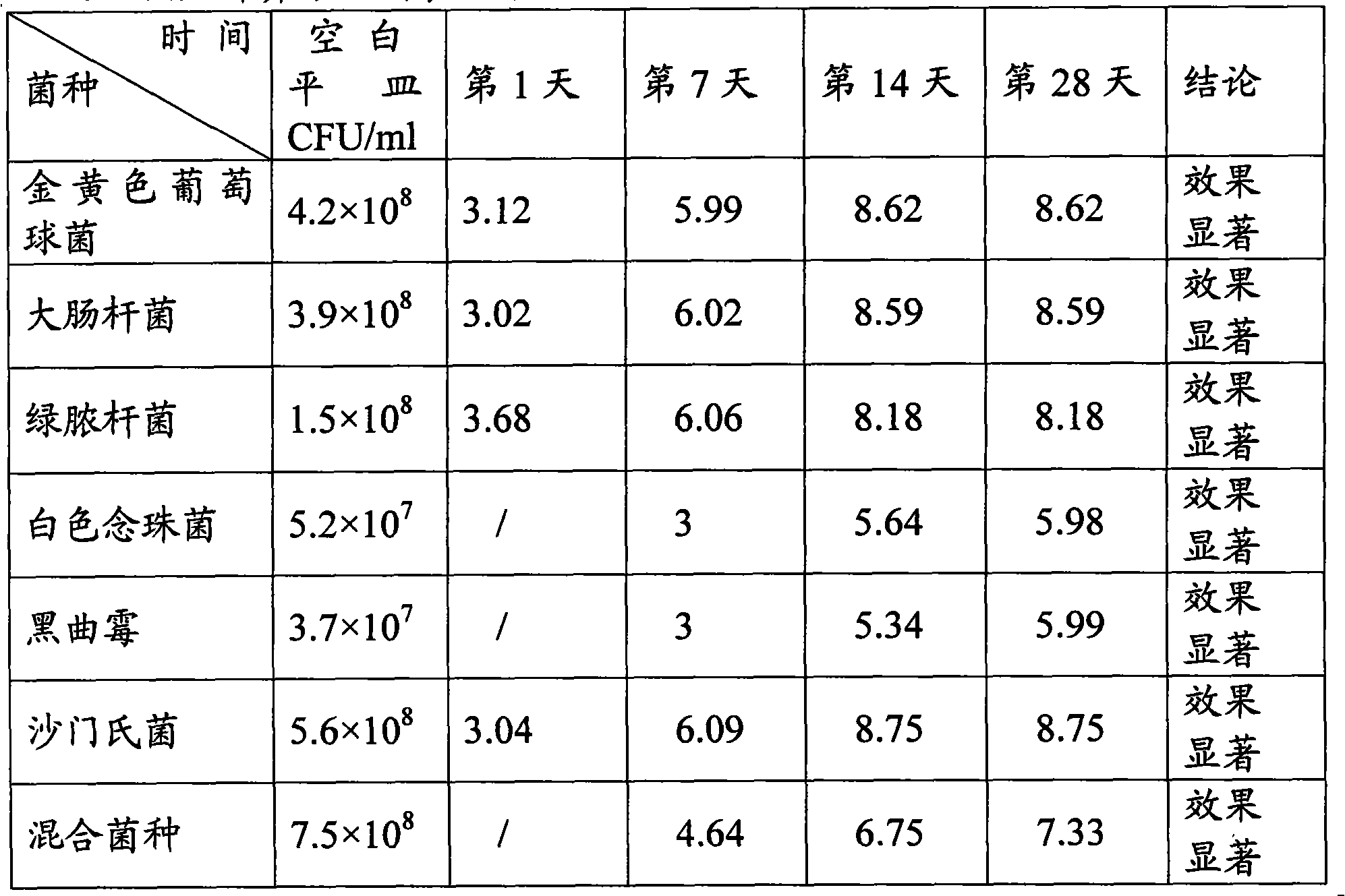
Method for testing and evaluating capacity of corrosion prevention system of cosmetic
InactiveCN101550438AReal life situationTrue response to living conditionsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBacillus pyocyaneus
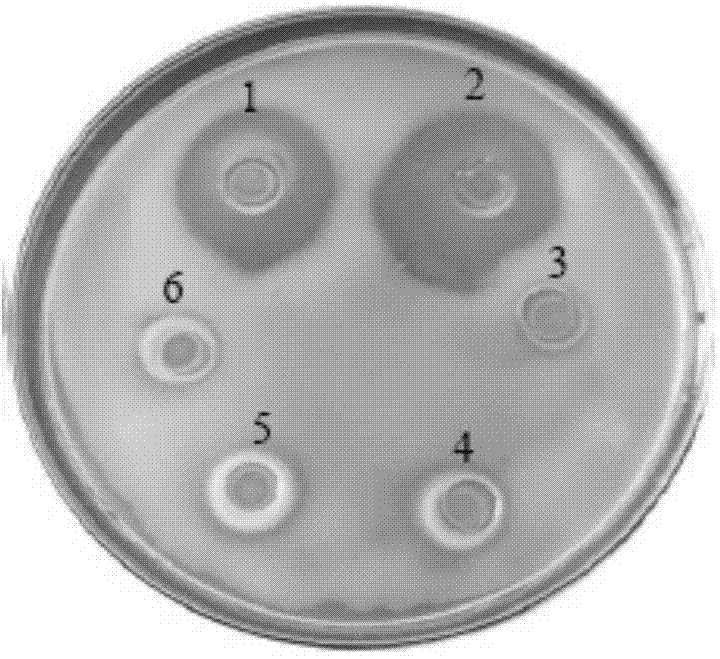
The present invention relates to a method for resting and evaluating capacity of corrosion prevention system of cosmetic. The invention selects micrococcus pyogenes, bacillus coil, bacillus pyocyaneus, candida albicans, aspergillus niger and salmonella as evaluating strain. The product is grafted into the cosmetic sample solution through the six pathogens and the mixed strains composed of the six pathogens for executing culture experiment. The corrosion prevention capacity of cosmetic is evaluated through comparing and identifying data. The risk resistance capacity of cosmetic for resisting the microbial pollution is effectively evaluated. As the six pathogens have wide representativeness and typical reference value, the six pathogens are used as the typical representative sample strains for evaluating. If the corrosion prevention capacity test is passed, the pollution of product by the microorganism can be effectively prevented, and the possibility of product pollution caused by the reproduction of microorganism can be effectively suppressed. The safety risk caused by product and the cost for frequently executing microbiological examination can be reduced through the basic product formula checked by the corrosion prevention capacity test or all products extended from the basic product formula. The effect is extraordinarily remarkable.
Owner:TIANJIN TIANSHI BIOLOGICAL DEV +2
Harmless biological comprehensive treatment method for oily sludge
InactiveCN106565066AReduce concentrationEasy to handleWater contaminantsSludge processingSludgePseudomonas
The invention discloses a harmless biological comprehensive treatment method for oily sludge. The method includes the following steps that (1), a crude oil deflocculation agent is added to deflocculate crude oil; (2), an auxiliary material is added for anaerobic compost; (3), microbial fungicide is added for aerobic fermentation; (4), plant auxiliary degradation is performed; the microbial fungicide comprises pseudomonas pseudomonas aeruginosa, micrococcus genera micrococcus luteus, bacillus bacillus subtilis, acinetobacter acinetobacter junii and acetobacter acetobacter aceti with the weight percentage being 1: 1.5: 1: 1.6: 2. The harmless biological comprehensive treatment method for the oily sludge aims to achieve the purposes of being economic, environmentally friendly and efficient.
Owner:湖北亦胜环保生物技术有限公司
Safe food preservative
InactiveCN105077511AImprove anti-corrosion performanceFruit and vegetables preservationNatural extract food ingredientsHalobacteriumBacilli
The invention belongs to the technical field of food processing, and particularly relates to safe food preservative. The safe food preservative comprises, by mass, 2-7 parts of gingko leaf extractives, 4-9 parts of lysozyme, 12-15 parts of chitosan, 3-7 parts of spice extractives, 4-10 parts of protamines and 80-100 parts of water. According to the safe food preservative, the main inhibiting objects are pseudomonades, micrococcus, bacilli, enterobacteriaceae, vibrios, halobacterium, mycete and the like, and the application range is wide in beverages, seasoning, cooked wheaten food, cakes, sausages, canned fruit, various melons and fruits, vegetables and the like.
Owner:SICHUAN HUIQUAN CANNED FOOD
Traditional Chinese medicine antibacteria composition for inhibiting micrococcus luteus
ActiveCN104013682AGood antibacterial effectReduce dosageAntibacterial agentsInorganic active ingredientsMicroorganismWater soluble
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine antibacteria composition for inhibiting micrococcus luteus, and belongs to the traditional Chinese medicine field. A rheum officinale extracting solution and water-soluble nano-silver are mixed in the antibacteria composition in proportion, two medicines are synthesized to play the synergistic effect to inhibit the micrococcus luteus. Compared with the prior art, the antibacteria composition containing the rheum officinale extract and the nano-silver can solve the problem that the dosage of the rheum officinale bacteriostatic agent in the conventional antibacteria method is great; and meanwhile, the microorganism medicine resistance generating rate is reduced by adopting two antibacterial substances in low dosage, the toxicity to the human body is lowered, and the composition is safer.
Owner:ANSON BIO-TECH(HUNAN) CO LTD
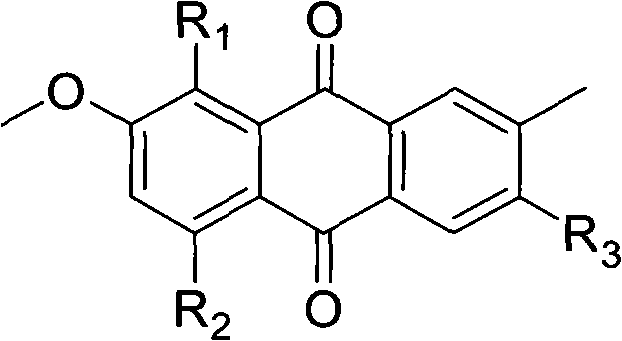
Quinones derivative as well as preparation method of quinones derivative and application of quinones derivative as antibacterial agent
ActiveCN102603524AStrong antibacterial activityHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsEscherichia coliBacillus cereus
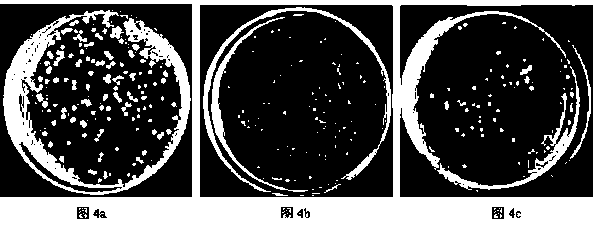
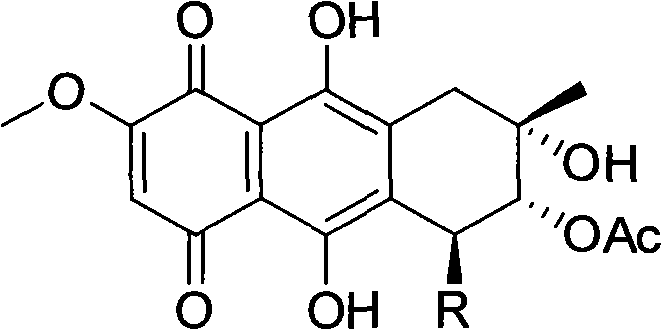
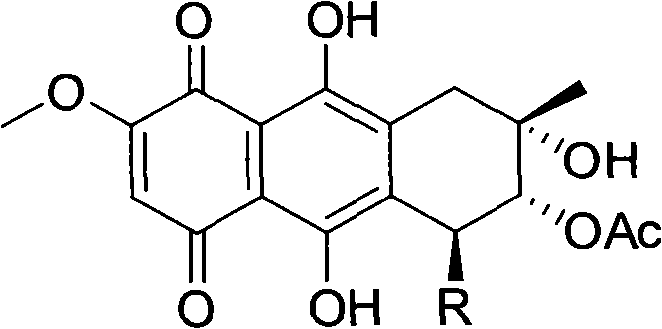
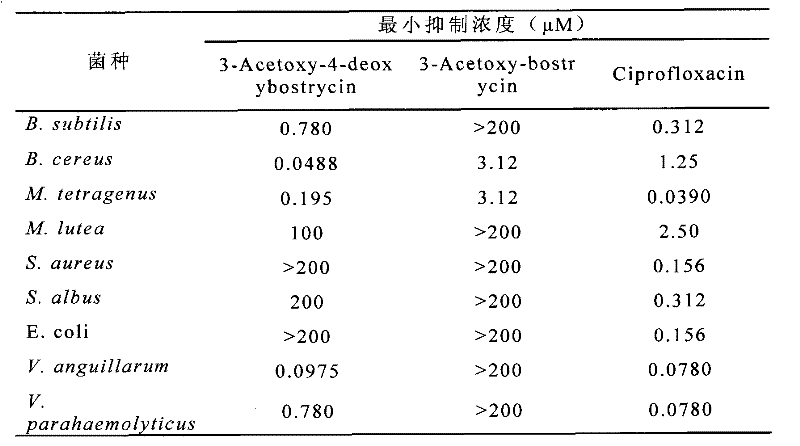
The invention relates to a quinones derivative as well as a preparation method of the quinones derivative and an application of the quinones derivative as an antibacterial agent. During the preparation, marine fungi Nigrospora sp.(HM565952) is subjected to strain culture in a culture medium, then, the marine fungi are subjected to fermentation culture in a fermentation culture medium, next, the obtained fermentation liquid is filtered, thalli are removed, and the fermentation liquid is extracted by ethyl acetate; after the extraction liquid is concentrated, chromatographic separation is carried out, and the obtained eluent is concentrated to obtain two red crystals which are respectively 4-Deoxybostrycin and Bostrycin; and acetyl oxide is added into solution in which the two compounds dissolve for reaction to obtain 3-Acetoxy-4-deoxybostrycin and 3-Acetoxy-bostrycin. The quinones derivative provided by the invention has the obvious antibacterial activity on Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus cereus, Micrococcus tetragenus, Micrococcus lutea, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus albus, Escherichia coli, Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio anguillarum and can be used for developing antibacterial agents, in addition, raw materials can be produced in large scales, and the resource limitation is avoided, so the application prospect is wide.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Temperature resistant quaternary ammonium type anion exchange resin phase transfer catalyst and preparation method thereof
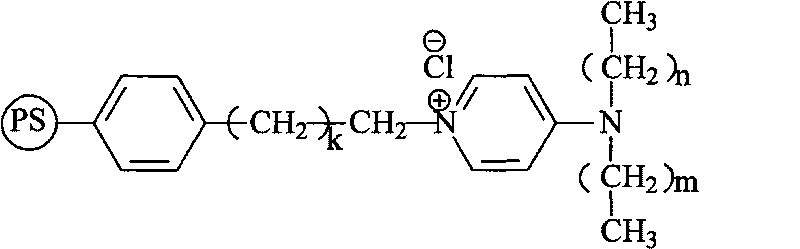
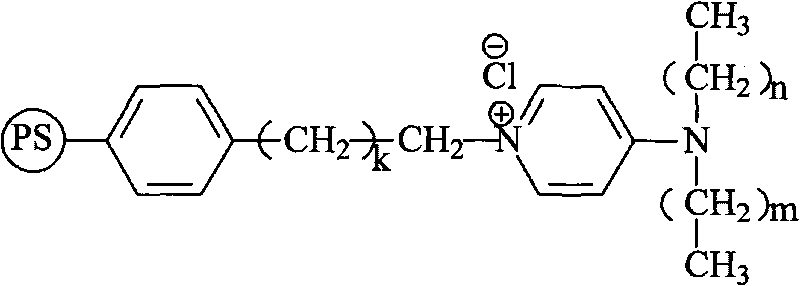
ActiveCN101703945AImprove thermal stabilityReduce organic contentOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPolystyreneIon-exchange resin
The invention discloses a temperature resistant quaternary ammonium type anion exchange resin phase transfer catalyst and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the synthesis field of anion exchange resin and phase transfer catalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: swelling polystyrene alkylated by macroporous chlorine and divinyl benzene copolymer bead body by solvents, adding a certain amount of N-alkyl aminopyridine, stirring and heating, preserving the temperature at 40-100 DEG C, carrying out salifying reaction at the temperature of 40-100 DEG C for 10-30h, filtering after reaction, washing with alcohol and drying to obtain the temperature resistant quaternary ammonium type anion exchange resin phase transfer catalyst, wherein, the amount of substance ratio of micrococcus chlorinus to N-alkyl aminopyridine is 1:1-3, and the amount of substance of micrococcus chlorines is expressed by chlorine element; the solvents used in swelling are as follows: methylene dichloride, tetrahydrofuran, N,N-dimethyl fomamide or n-butyl alcohol; the expressed polystyrene and divinyl benzene co-polymer framework is a repeat unit of the polystyrene and the divinyl benzene; and k, n, and m are respectively 0,1,2,3.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
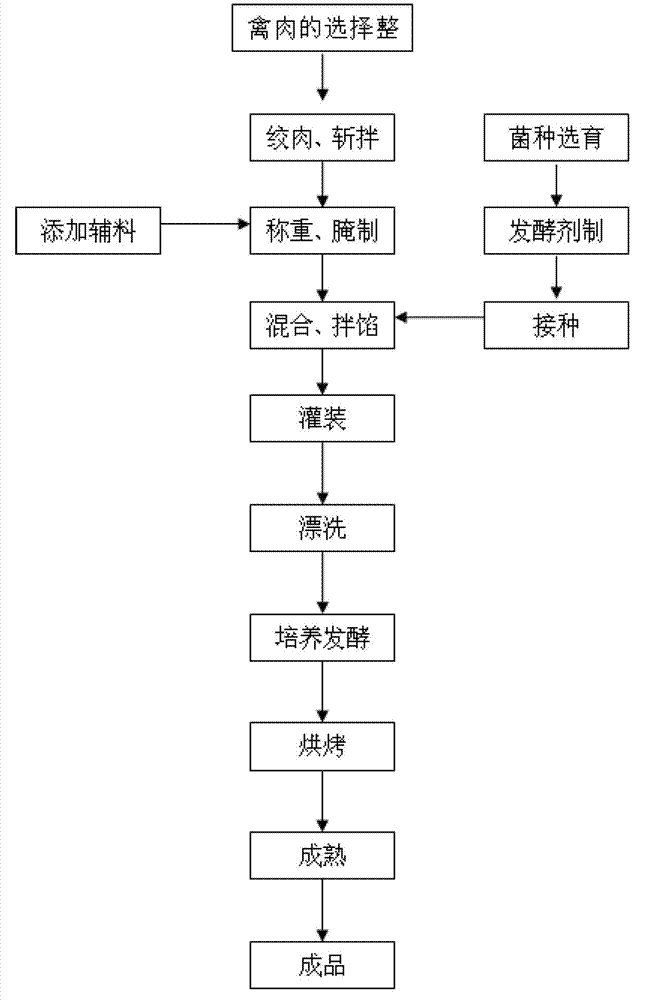
Manufacturing method of poultry bifidobacteria fermented sausage
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a poultry bifidobacteria fermented sausage, comprising the following steps of: selecting poultry meat, mincing and chopping, adding auxiliary materials, uniformly stirring, placing in an environment of 2-5 DEG C, preserving for 16-20 h, optimally selecting lactics, bifidobacteria, staphylococcus and micrococcus, separating, domesticating, culturing, choosing strong bacterial strains, inoculating mixed strains according to 0.3% of the total weight of the poultry meat, mixing stuffing, and carrying out technologies of filling, rinsing, cultivation fermentation, baking and maturation on poultry meat so as to obtain the finished product. The cultivation fermentation time is 2.5-4.5 hours, and the temperature is 35-37 DEG C. The poultry bifidobacteria fermented sausage provided by the invention is rich in nutrients, has a unique flavor, is suitable for the taste of countrymen and is easy to digest. By the adoption of the manufacturing method, shelf-life can be prolonged, conversion from a traditional technology of natural fermentation to a modern technology of pure fermentation is completed, and quality and security are guaranteed.
Owner:安徽康宏园食品有限公司
Histone-modified chromosome co-immunoprecipitation method applicable in tissue sample
InactiveCN104651506AEfficient acquisitionImprove sedimentation efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementWater bathsEnzyme digestion
The invention relates to a histone-modified chromosome co-immunoprecipitation method applicable in a tissue sample, which comprises the following steps: carrying out tissue sample pretreatment; grinding in an ice bath, filtering with sterile gauze, collecting cells in the filtrate, and treating the suspended cells in an enzyme digestion buffer solution under water-bath conditions; adding micrococcus nuclease into the cells with the enzyme digestion buffer solution, carrying out enzyme digestion, and adding an enzyme digestion termination solution with the same amount as the micrococcus nuclease; carrying out high-frequency ultrasonic treatment and centrifugation in an ice bath to obtain a pulverized chromatin solution; taking ProteinA / G, adding a BSA (bovine serum albumin)-containing PBS (phosphate buffer solution), adding an antibody, incubating, adding the pulverized chromatin solution, and incubating over night; and washing with a high salt solution many times on a magnetic rack, eluting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) on the magnetic bead with a TE solution, and purifying with a purification solution, extracting the DNA, and dissolving the DNA in ultrapure water. Compared with the prior art, the method can accurately position the combination site of the histone or transcription factor on the high flux level, thereby enhancing the detection effect of the clinic sample.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
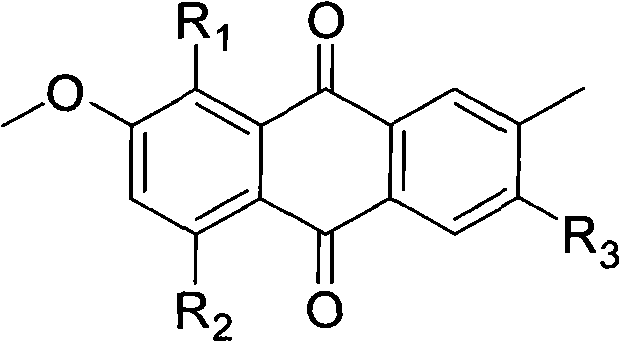
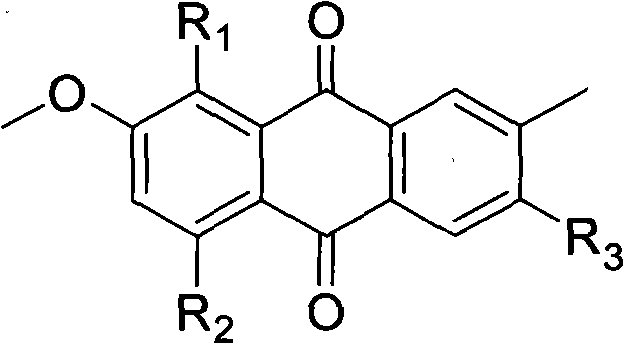
Anthraquinone derivative, as well as preparation method and application of anthraquinone derivative serving as antibacterial agent
InactiveCN102603525AHas selective inhibitory activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsEscherichia coliBacillus cereus
The invention provides an anthraquinone derivative, as well as a preparation method and application of the anthraquinone derivative serving as an antibacterial agent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: culturing a strain of Nigrospora sp. (HM565952) in a strain culture medium; fermenting the nigrospora sp. in a fermentation culture medium; filtering the fermentation broth, removing thallus, and extracting the fermentation broth with ethyl acetate; concentrating the extract, and performing chromatographic separation, and concentrating the eluent to obtain two types of yellow powder, namely 3,5,8-Trihydroxy-7-methoxy-2-methylanthracene-9,10-dione and austrocortirubin; and adding an acetic anhydride reagent in a solution dissolved with the compound, and reacting to obtain the anthraquinone derivative. The anthraquinone derivative obtained from the Nigrospora sp. (HM565952) has selective inhibitory activity to Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus cereus, Micrococcus tetragenus, Micrococcus lutea, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus albus, Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio anguillarum, and can be used for developing selective bacteriostatic agents; and the raw materials can be produced on a large scale, and not limited by resources. Therefore, the anthraquinone derivative has the advantage of wide application prospect.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Stichopus japonicas BPI gene, encoded protein, cloning method of stichopus japonicas BPI gene, and method for constructing recombinant stichopus japonicas BPI genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN104745595AEfficient killingAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBPI proteinVibrio parahaemolyticus
The invention discloses a stichopus japonicas BPI gene, an encoded protein, a cloning method of the stichopus japonicas BPI gene, and a method for constructing a recombinant stichopus japonicas BPI genetically engineered bacterium. The stichopus japonicas BPI gene is characterized in that a stichopus japonicas BPI gene sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1; the cloning method comprises the step of designing a nested primer of RACE according to an expressed sequence tag EST sequence which is homologous to the BPI gene; a full-length gene is expanded by employing an RACE technique; a stichopus japonicas BPI protein sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2; an N-terminal protein structure domain sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.3; an N-terminal structure domain of the stichopus japonicas BPI protein is amplified by employing primers which respectively comprise BamH I sites and Not I sites; the cloned target gene is inserted into a vector to obtain recombinant plasmids; and the recombinant plasmids are subjected to induced expression, and purification and renaturation, so as to obtain the genetically engineered bacterium. The stichopus japonicas BPI gene has the advantage of having obvious sterilization effect on vibrio parahaemolyticus, vibrio harveyi and micrococcus luteus.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Efficient repairing complex inoculant and application thereof
InactiveCN103484404AAchieve selectionImprove growing conditionsFungiBacteriaSaccharomycesEnergy conservation
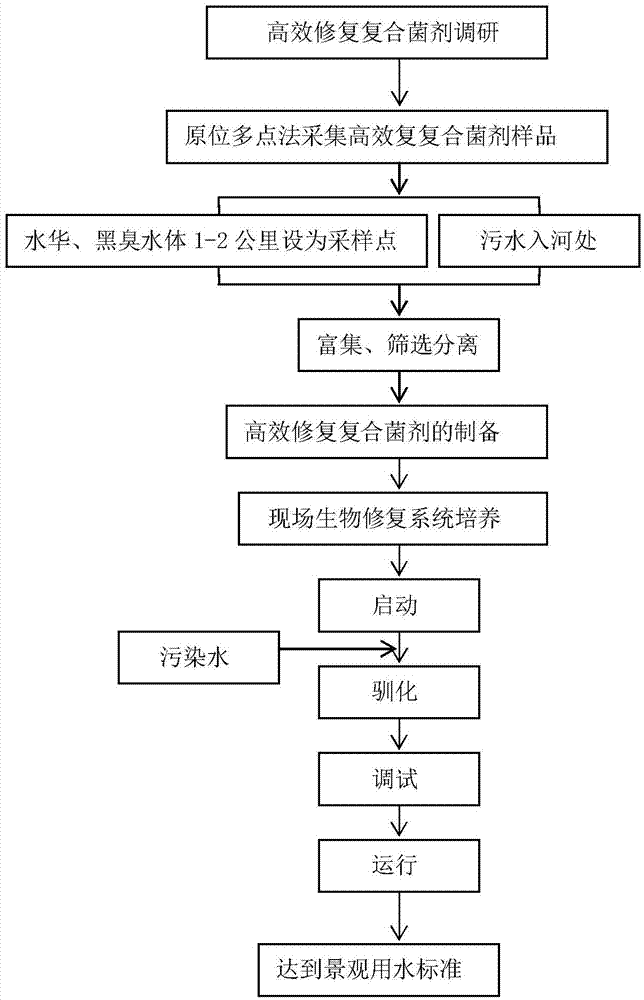
The invention relates to the field of biology and in particular to an efficient repairing complex inoculant and application thereof. The complex inoculant provided by the invention comprises strains of rhodococcus, pseudomonas, saccharomyces and micrococcus luteus, where the preservation number of the rhodococcus is CGMCC No.3276; the preservation number of the pseudomonas is CGMCC No.3277; the preservation number of the saccharomyces is CGMCC No.3278; the preservation number of the micrococcus luteus is CGMCC No.3903. The complex inoculant has remarkable effects of water ecosystem restoration, water bloom prevention and deodorization, in addition, the removal rate of the complex inoculant to all organic matters reach more than 70 percent, and national policies of circular economy and energy conservation and emission reduction are met better. By using the complex inoculant, a large amount of running cost for various water areas can be saved, and recycling treatment to wastewater is achieved.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Staphylococcus aureus fusion protein of fibronectin and bindin, its preparation method and uses
InactiveCN1884302AImprove protectionImproving immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsSkeletal disorderStaphylococcus cohniiMicrococcus pyogenes
The invention discloses a fusion protein for Micrococcus pyogenes surface protein, and also discloses the method for preparing the same as well as its usage. The fusion protein is fused by Micrococcus pyogenes fnb and thioredoxin Trx on expression carrier, and the process comprises preparation of Micrococcus pyogenes surface protein fnb coding gene, colony of fnb coding gene into expression carrier and protein fusion. The fusion protein is soluble protein and retains immunity of natural protein. It is detected that said fusion protein is characterized by good response for humoral immunity and cell immunity, enlargement of protection range of protein vaccine and prevention of infection caused by most of Micrococcus pyogenes.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
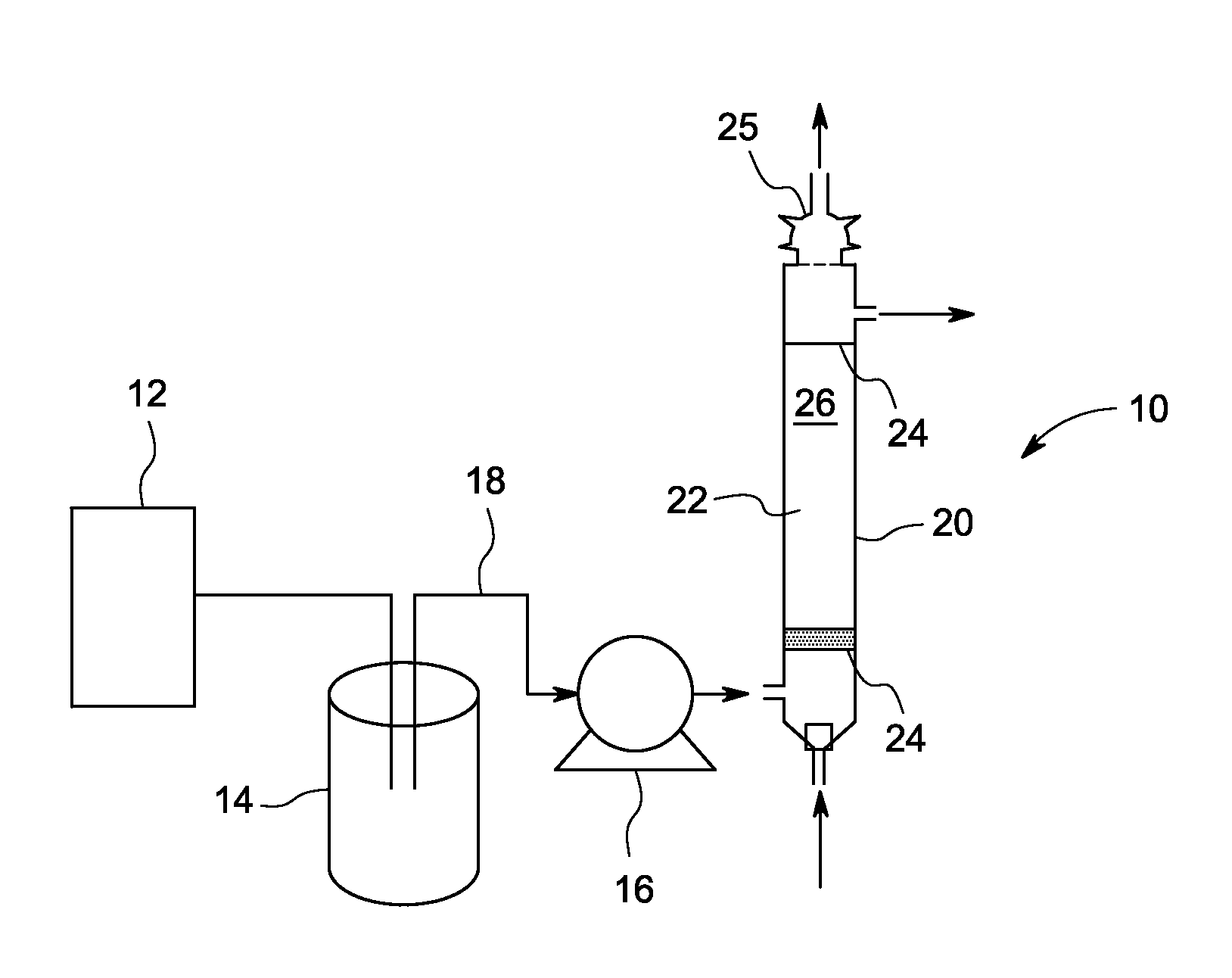
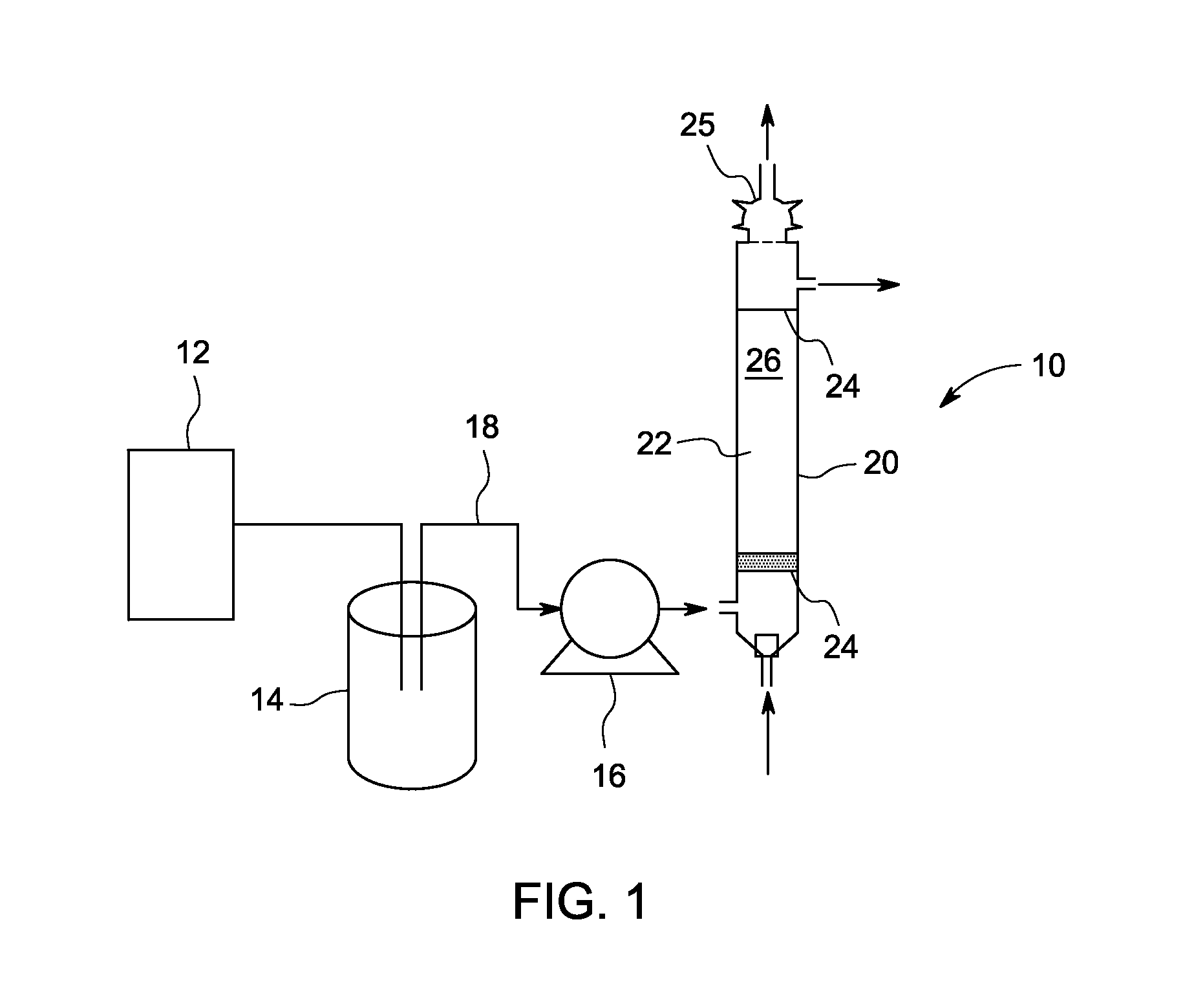
Method of removing recalcitrant organic pollutants
InactiveUS20130334135A1Efficient biodegradationReducing the recalcitrant chemical oxygen demand (COD)Treatment using aerobic processesBacteriaChemical oxygen demandComamonas
Recalcitrant chemical oxygen demand (COD) of a liquid is reduced in a water treatment system. The method includes pretreating the liquid in a pretreatment unit to remove indigenous bacteria or microbes to a population level below which the indigenous organisms can interfere with the screened and externally introduced microorganisms. The liquid is then provided to a reactor that has a filter bed formed with a carrier material. Special microbes are screened and used to colonize the carrier material to remove recalcitrant COD. A biofilm is cultured on the surface of the carrier material to immobilize the screened microbes in the reactor. The method further includes percolating the liquid from the pretreatment unit through the filter bed colonized with the screened microbes to degrade at least part of the recalcitrant COD under aerobic conditions. In one embodiment, the filter is formed with biological granular activated carbon (GAC) as the carrier material and the screened microbes comprise at least one microbial species selected from the group consisting of Bacillus, Comamonas, Arthrobacter, Micrococcus, Pseudomonas, Pediococcus, Achromobacter, Flavobacterium, Mycobacterium, Rhodanobacter, Stenotrophomonas and Yeast.
Owner:BL TECH INC
Low salt pickling and artificial fermentation process of Xuanwei ham
InactiveCN106937726AHigh hardnessIncrease elasticitySugar food ingredientsFood ingredient as flavour affecting agentDecompositionAmino acid
The invention discloses a low salt pickling and artificial fermentation process of Xuanwei ham, the technical proposal includes four steps of raw material selection, low salt pickling, fermentation fungi group cultivation and artificial fermentation, and a fermentation fungi group comprises Penicillium, lactic acid bacteria, Bacterium lacticum and Micrococcus in the ratio of 2.7:0.73:0.2:1. The advantages are that after raw material meat is inoculated with the lactic acid bacteria, the lactic acid bacteria uses carbohydrates such as glucose for fermentation to produce lactic acid, gelatinous tissues are formed by degeneration of muscle proteins under acidic conditions, bonding force among meat blocks is increased, and hardness and elasticity of meat products are improved, the lactic acid bacteria has high salt tolerance, can be used for fermentation of sugar to produce the lactic acid to play antibacterial and hypoglycemic effects and improve meat freshness; the Micrococcus has effects of decomposition of proteins and fat and reduction of nitrates, large amounts of amino acids are produced after the proteins are broken down, the amino acids are sources of a fresh taste, meanwhile by reduction of the cancerogenic substance nitrates, health of food customers can be protected.
Owner:XUANWEI HAIHUI FOOD CO LTD
Skin treatment compositions
ActiveUS20110189133A1Growth inhibitionEffective colonisationAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesSkin treatments
This invention relates to Micrococcus luteus containing compositions useful for controlling skin disorders in which bacteria are a causative component. The invention also provides for a new strain of Micrococcus luteus useful in these compositions.
Owner:BLIS TECHNOLOGIES LTD
Facial mask containing garlic extract product
InactiveCN107157886ARepair particlesRepair roughCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsLeupeptinHamamelis virginiana
The invention discloses a facial mask containing a garlic extract product. The facial mask comprises, by mass, 1 to 5% of propylene glycol, 3 to 7% of 1,3-butylene glycol, 0.1 to 0.2% of a thickening agent, 0.05 to 0.15% of formic ester, 50 to 70% of water, 0.02 to 0.06% of small molecular hyaluronic acid, 3 to 7% of propylene glycol, 0.1 to 0.3% of dipotassium glycyrrhizinate, 0.1 to 0.2% of triethanolamine, 1 to 5% of water, 0.5 to 1.5% of garlicin, 3 to 4% of a garlic extracted solution, 3 to 7% of a witch hazel extracted product, 1 to 5% of yeast extracted product, 0.5 to 1.5% of an epidermal stem cell activation factor, 1 to 3% of Sophora flavescens, 5 to 10% of water, and 2 to 3% of leupeptin. The facial mask is capable of inhibiting bacteria and diminishing inflammation, possesses inhibition and killing effect on a plurality of micrococcus, bacillus, fungus, and viruses, is capable of eliminating acne caused by skin inflammation and bacteria, supplying nutrients and trace elements, and improving immunity.
Owner:江苏天芳健康科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com