Patents
Literature
165 results about "Epidermal stem cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Epidermal stem cells are a subpopulation of keratinocytes. Epidermal stem cells give rise to interfollicular epidermis, hair follicles and sebaceous gland. Epidermal stem cells form clusters located in the upper hair follicle (bulge) and patches of basal keratinocytes at the tips of dermal papillae (between rete ridges)
Particulate acellular tissue matrix
A method of processing an acellular tissue matrix to give a particulate acellular tissue matrix includes: cutting sheets of dry acellular tissue matrix into strips; cryofracturing the dry acellular tissue matrix strips at cryogenic temperatures; separating the resulting particles by size at cryogenic temperatures; and freeze drying the fraction of particles desired size to remove any moisture that may have been absorbed to give a dry particulate acellular tissue matrix. Rehydration of the dry particulate acellular tissue matrix may take place just prior to use. The particulate acellular tissue may be applied to a recipient site, by way of injection, spraying, layering, packing, in-casing or combinations thereof. The particulate acellular tissue may further include growth and stimulating agents selected from epidermal growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, nerve growth factor, keratinocyte growth factor, platelet derived growth factor, vasoactive intestinal peptide, stem cell factor, bone morphogetic proteins, chondrocyte growth factor and combinations thereof. Other pharmaceutically active compounds may be combined with the rehydrated particulate material including: analgesic drugs; hemostatic drugs; antibiotic drugs; local anesthetics and the like to enhance the acceptance of the implanted particulate material. The particulate material product may also be combined with stem cells selected from mesenchymal stem cells, epidermal stem cells, cartilage stem cells, hematopoietic stem cells and combinations thereof.
Owner:LIFECELL
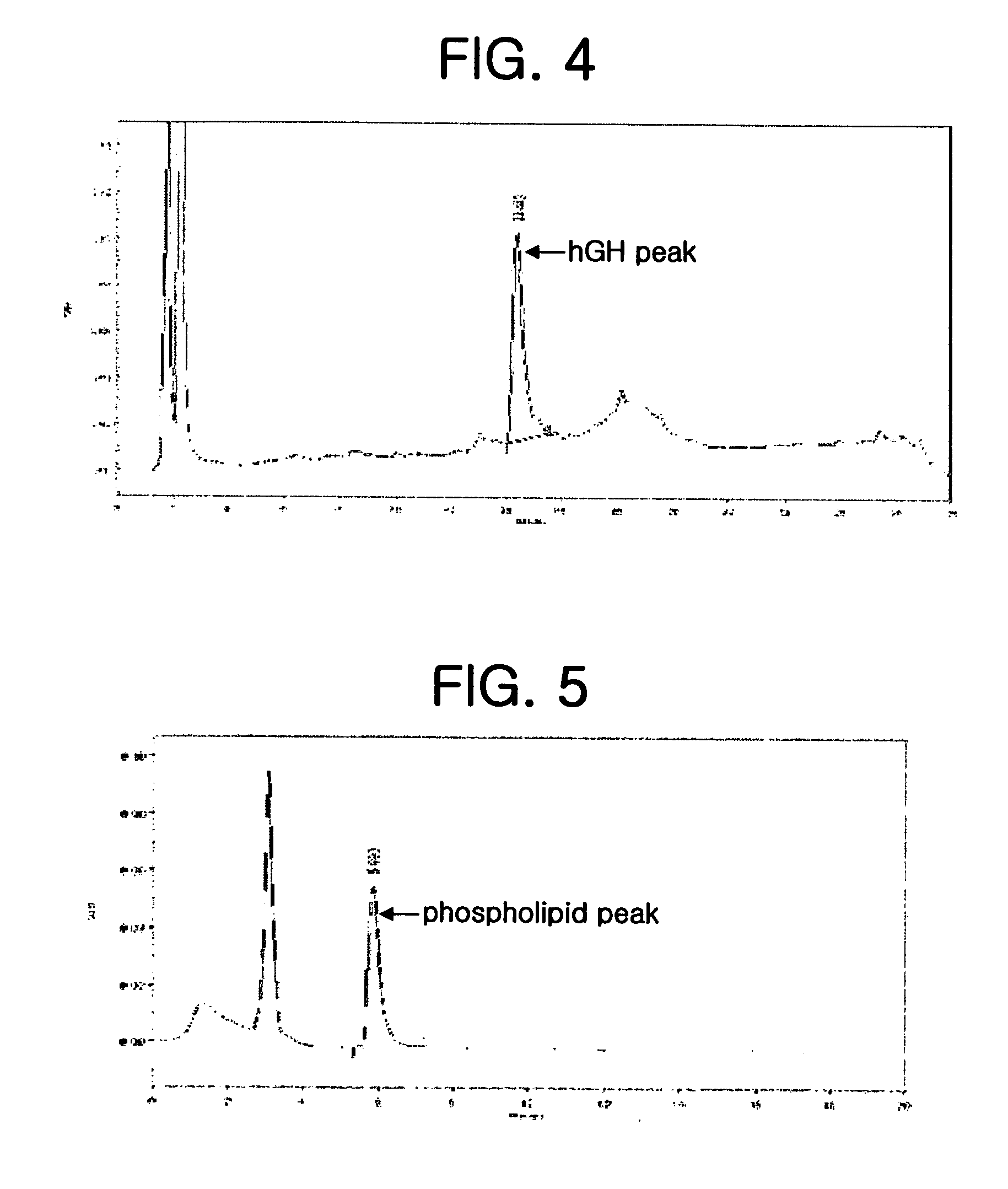
Composition for improving skin conditions comprising human growth hormone as an active ingredient
InactiveUS20070081963A1Improve skin conditionCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsWrinkle skinBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Disclosed herein is a skin condition-improving composition for topical application to the skin, comprising human growth hormone as an active ingredient, and a method for improving skin conditions using the same. The disclosed composition exhibits various skin conditioning effects, such as acne treatment, wrinkle improvement, dark spot removal, skin elasticity improvement, hair growth stimulation, skin aging prevention, skin moisturization and the proliferation of skin epidermal stem cells.
Owner:REGERON
Novel method for constructing tissue engineering skin
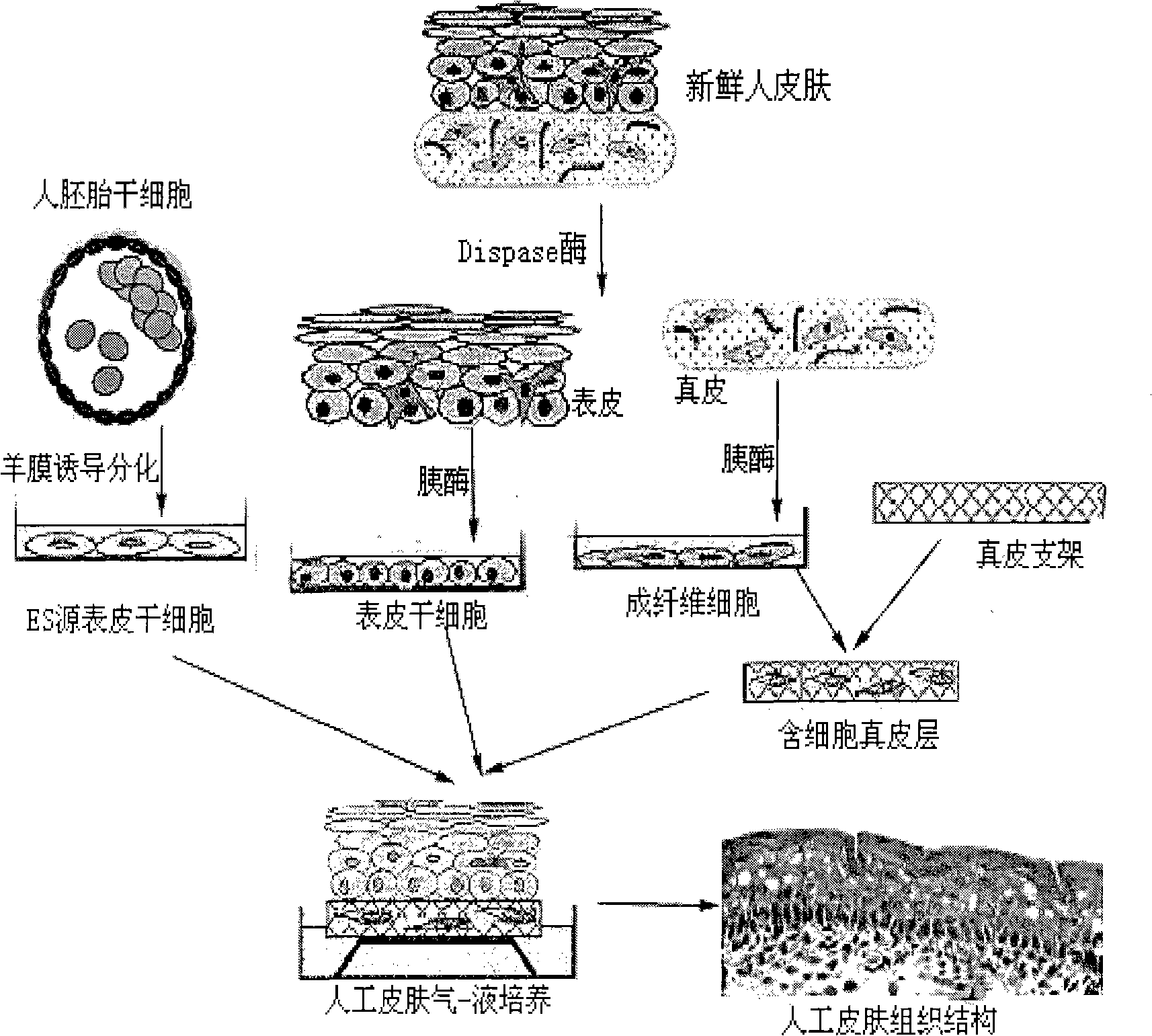
The invention provides a method for constructing tissue engineering skin. In the method, human epidermal stem cells and hypodermal fibroblasts are taken as seed cells, and a homologous acellular dermal matrix modified by a human placental type IV collagen is taken as a stent, so that active dual-layer engineering skin is compounded and constructed by using a gas-liquid interface separate culture method. The tissue engineering skin constructed by using the method is closer to the structure of natural skin; and as proved by histomorphology, the tissue engineering skin has an epidermal and hypodermal double-layer structure, wherein the hypodermal collagen stent has a complete structure, an epidermal layer is provided with a plurality of layers of cells of different differentiation degrees, and the morphological requirement of the tissue engineering skin is met.
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
Method using CRISPR-Cas system to perform GING2 gene knockout on epidermal stem cell
ActiveCN108715850AStrong knockout effectGood sgRNAGenetically modified cellsEpidermal cells/skin cellsPlasmidGenetic stability
The invention provides a method using a CRISPR-Cas system to perform GING2 gene editing on an epidermal stem cell and particularly relates to a method for building an epidermal stem cell line with theGING2 gene being knocked out. Two specific gRNAs are built and acquired, and the GINS2 gene editing efficiency of CRISPR / Cas9 in the epidermal stem cell can be increased evidently. An epidermal stemcell GINS2 knockout plasmid is good in hereditary stability and high in targeting efficiency.
Owner:GUANGDONG AIE BIOSCIENCE CO LTD
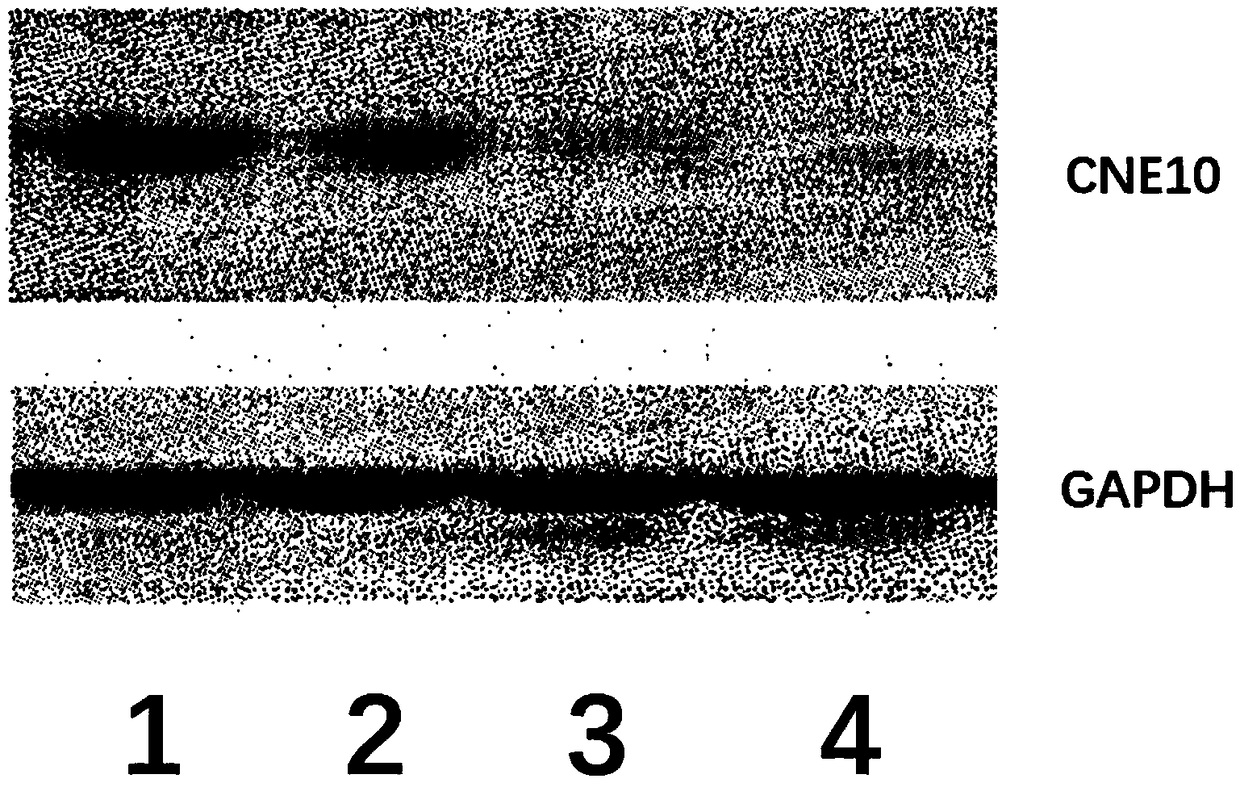
CNE10 gene knockout in epidermal stem cells by using CRISPR-Cas system
The invention provides CNE10 gene editing for epidermal stem cells by using a CRISPR-Cas system, and particularly relates to establishment of an epidermal stem cell system with GNE10 gene knocked out.Through the establishment, two specific gRNA (guide ribose nucleic acids) are obtained, editing efficiency of the CRISPR-Cas system aiming at the GNE10 gene in the epidermal stem cells can be increased remarkably. An obtained epidermal stem cell plasmid with CNE10 gene knockout is good in hereditary stability and high in targeting efficiency.
Owner:江西汉氏联合干细胞科技有限公司
Method for preparing full-thickness skin for toxicity test by stem cell raft type cultivation
InactiveCN101352586AStrong ability to divide and proliferateMorphological integrityArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsRaft cultureSerum free media
The invention relates to a method for preparing full-thickness skin used in toxicity testing by adopting stem cell raft culture, which comprises: 1. preparing and modifying a polymeric dermal scaffold; 2. preparing epidermal stem cells from embryonic stem cells and skin tissues; 3. preparing pancreatic islet cells; 4. preparing a special medium for the full-thickness skin; 5. and constructing the full-thickness skin. By utilizing the characteristics of strong differentiation and proliferation capacity of the epidermal stem cell, the skin morphology, organizational structure and functional activity of the constructed full-thickness skin of the invention can meet the demands of sub-chronic toxicity testing; the synthetic scaffold material has high degree of standardization and small batch-to-batch variation; as a serum free medium is adopted through the skin construction process, the factors influencing tissue construction are reduced, thus providing a foundation for the future use in toxicity testing. The all-thickness skin prepared by the method of the invention is closer to a natural skin, the application of which in the mode of toxicity testing and detection index agrees with practical situation better, thus being able to replace animals to be directly applied to the skin toxicity testing of chemicals, cosmetics, medicines and other health-related products.
Owner:程树军 +1
In-vitro inducing differentiation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into tissue engineering skin seed cells
The invention relates to in-vitro inducing differentiation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into skin tissue engineering seed cells. The invention discloses a new research direction for human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, i.e. in-vitro inducting differentiation into skin tissue engineering seed cells. The invention also discloses an experimental method thereof, which comprises the following steps: collecting the caesarean umbilical cords in aseptic environment; culturing original-generation umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (UCMSCs) by an enzyme digestion or tissue-piece adherent method; after purifying and subculturing to the third generation, inducing by using different in-vitro condition induction liquids to differentiate into epidermis stem cells and fibroblasts; and inducing and differentiating epidermis stem cells and fibroblasts into sudoriferous gland cells by using coculture mode with the normal sudoriferous cells. After the induced cells are digested, liquid nitrogen is stored for later use. The invention provides seed cells for skin tissue engineering, and has the advantages of strong multiplication capacity, easy inducing differentiation, low immunogenicity, abundant sources and easy obtainment.
Owner:FIRST HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Method for preparing corneal epithelium form epidermis stem cell through fabrication of tissue engineering, and application
InactiveCN1563366AWeakened immune memoryRich sourcesEye implantsTissue cultureSerum free mediaCulture mediums
Owner:陕西九州生物医药科技集团有限公司
In-vitro recombined human skin epidermis model and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105734009AMicrobiological testing/measurementEpidermal cells/skin cellsGranular cellMatrigel
The invention discloses an in-vitro recombined human skin epidermis model.A layer of hemidesmosome protein is arranged on the lower surface of a basal cell layer, the upper surface of the basal cell layer is covered with 6-8 spinous cell layers containing short protruding spinous cells, the upper surface of the spinous cell layers is covered with 3-4 granular cell layers containing transparent granular cells, the upper surface of the granular cell layers is covered with a keratinocyte layer, all the cell layers are obviously separated, and the overall barrier function of a lipid composition is approximate to that of human skin.A preparation method comprises the steps of preparation of matrigel particles, screening and amplification of epidermal stem cells, preparation of the basal cell layer, preparation of the spinous cell layers, preparation of the granular cell layers, and maturation and keratinization of the in-vitro recombined epidermis model.The model is applied to evaluation of cosmetics with the human skin barrier repair effect, screening of plant extract with the human skin barrier repair effect, evaluation and detection of irritation of medical apparatus materials on the human skin and detection of irritation of chemicals on the skin.
Owner:GUANGDONG BOXI BIO TECH CO LTD
Tissue-engineered skin containing blood vessels and hair follicle structures based on 3D printing and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108525021ASimple structureIncrease elasticityAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationMicrosphereVascular endothelium
The invention relates to tissue-engineered skin containing blood vessels and hair follicle structures based on 3D printing and a preparation method thereof. The tissue-engineered skin is composed of an epidermal layer, an acellular dermal scaffold and a dermis layer, wherein in the epidermal layer, epidermal stem cells are used seed cells, the seed cells are printed on the upper surface of the acellular dermal scaffold through a 3D printer after being compounded with a hydrogel carrier to differentiate and form a normal epidermal structure, in the dermis layer, mesenchymal stem cells, vascularendothelial cells, dermal papilla cells and adipose-derived stem cells are used as seed cells, the seed cells and a hydrogel carrier are compounded, through the 3D printer, gelatin slow-release micropheres compounded with cytokines are printed on the lower surface of the acellular dermal scaffold, and meanwhile, the hydrogel compound of the seed cells is printed in the gelatin slow-release micropheres to form a dermis structure with a three-dimensional spatial structure.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
Method for separating and culturing human epidermal stem cells
InactiveCN103865872AHigh activityStrong drynessArtificially induced pluripotent cellsNon-embryonic pluripotent stem cellsCuticleBiology
The invention belongs to the technical field of pathology, and in particular relates to a method for separating and culturing human epidermal stem cells. The technical problem to be solved by the method disclosed by the invention is to provide a new choice for separating and culturing the human epidermal stem cells. The technical scheme is that the method for separating and culturing the human epidermal stem cells comprises the steps of a, sterilizing; b, separating epidermis and dermis; c, collecting; d, culturing; e, sub-culturing. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the human epidermal stem cells at least can be sub-cultured to the eighth generation, so that the cell proliferation multiple is greatly increased.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Separation and culturing method of human epidermis stem cell
A process for separating and culturing human epidermal stem cells includes such steps as providing ectocytic matrix covering Petri dish, separating epidermal cells, preparing trophoblastic cells and screening and culturing epidermal stem cells.
Owner:陕西艾尔肤组织工程有限公司
Umbilical placental stem cell technology for cosmetic skin care product
InactiveCN103446029AStay flexibleKeep fighting diseaseCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSide effectGlycerol
Relating to the fields of biotechnologies and cosmetic science, the invention provides a technology for using the umbilical cords and placentas of volunteers to prepare a skin care product for skin rejuvenation. Specifically, the umbilical cords and placentas of term delivery volunteers are separated, blood vessels and envelopes therein are removed, a tissue homogenizing machine is employed to make the obtained tissue into homogenate, and then medical grade glycerin, preservative and the like are added to prepare the skin care product. Being rich in trophic factors, the skin care product has the efficacy of promoting the proliferation of epidermal stem cells and hair follicle stem cells, plays an important role in maintaining skin elasticity and health, and has the advantages of no toxic, side effect or adverse reactions, etc. The umbilical placental skin care product provides a good method for delaying aging and restoring skin elasticity.
Owner:孙勇
Separation and culturing method of human epidermis stem cell
Owner:陕西艾尔肤组织工程有限公司
Method for separating and purifying stem cell of skin epidemis
InactiveCN1563365AGrowth inhibitionAchieve purificationMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsMicrobiologyIntegrin
This invention discloses a method for separating and purifying skin caticular dry cells which adopts a self designed culture medium to suppress growth of fibrablasts and unform epithelioid cells grow around the tissue block to induce the cells to move out of the original micro-environment and gather again and grow on the new grown epithelioid cell layer. These clone grown cells are obviously different in morphology from its dependent trophocytes and can be selected with the help of dissection mirror and glass pins and nurtured for expansion independently. The acquired cells are tested by the generally acknowledged skin dry cells molecular label: ck19, integrin-beta1, P63, integrin-alpha 6 are positive which means the selected ones are purified skin dry cells.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Method of separating derma epidermis stem cell
InactiveCN1865436AGrowth inhibitionEffective and safe separation and purificationArtificial cell constructsArtificially induced pluripotent cellsEnzyme digestionBeta1 Integrin
The invention discloses a separation and purifying method of skin epiderm stem cell, which is characterized by the following: adopting self-designed culture medium to inhibit the growth of fiber cell to growing epithelial shaped cell around the tissue; inducing surface stem cell migrate original micro-environment; gathering to grow again on the new growing epithelial shaped cell. The cloned growth cell displays obvious shaped difference from epithelial shaped cell, which is defined purifying epiderm stem cell if the detection of epiderm stem cell molecular mark is CK19, beta1-integrin,P63, alpha-6-integrin, which is positive. The invention overcomes defect of traditional enzyme digestion method, which can separate and purify human and animal epiderm stem cell.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Facial mask containing garlic extract product
InactiveCN107157886ARepair particlesRepair roughCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsLeupeptinHamamelis virginiana
The invention discloses a facial mask containing a garlic extract product. The facial mask comprises, by mass, 1 to 5% of propylene glycol, 3 to 7% of 1,3-butylene glycol, 0.1 to 0.2% of a thickening agent, 0.05 to 0.15% of formic ester, 50 to 70% of water, 0.02 to 0.06% of small molecular hyaluronic acid, 3 to 7% of propylene glycol, 0.1 to 0.3% of dipotassium glycyrrhizinate, 0.1 to 0.2% of triethanolamine, 1 to 5% of water, 0.5 to 1.5% of garlicin, 3 to 4% of a garlic extracted solution, 3 to 7% of a witch hazel extracted product, 1 to 5% of yeast extracted product, 0.5 to 1.5% of an epidermal stem cell activation factor, 1 to 3% of Sophora flavescens, 5 to 10% of water, and 2 to 3% of leupeptin. The facial mask is capable of inhibiting bacteria and diminishing inflammation, possesses inhibition and killing effect on a plurality of micrococcus, bacillus, fungus, and viruses, is capable of eliminating acne caused by skin inflammation and bacteria, supplying nutrients and trace elements, and improving immunity.
Owner:江苏天芳健康科技有限公司
Thermo-sensitive hydrogel and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a thermo-sensitive hydrogel. The thermo-sensitive hydrogel comprises the following raw materials: a cytokine activity stabilizer, an epidermal stem cell conditioned culture medium and a collagen cross-linking solution. The cytokine activity stabilizer is added into the epidermal stem cell conditioned culture medium, so that multiple cytokines secreted by EpSCs are stabilized, the half-life period of each of the multiple cytokines is prolonged, the effect of each of the multiple cytokines on trauma repair is prolonged, and further, wound healing is promoted. In addition, the invention discloses a preparation method of the thermo-sensitive hydrogel, which has the characteristics of being simple to operate, random in molding and capable of in-situ gelling; the prepared hydrogel is slightly-viscous and clear liquid under the condition of 4-25 DEG C, is a solid gel when being put under the condition of 30-37 DEG C, has better mechanical strength and better biological compatibility and can promote fibroblast proliferation and facilitate fresh skin apparent and functional recovery, so that wounds are healed with high quality.
Owner:广东颜值科技有限公司
Emulsion capable of promoting skin to regenerate
InactiveCN105963239APromote regenerationPromote wound healingCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsEmulsionSkin Injury
The invention discloses an emulsion that can promote skin regeneration. It is made of moisturizing agent, penetrant, preservative, emulsifier, stem cell complex factor, cell liposome and allantoin. The ingredients used are safe and compatible with the skin. High in moisture content, has the function of moisturizing. Stem cell factors encapsulated in cell liposomes secreted by human umbilical cord or umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells are used for skin regeneration. Encapsulated by liposomes, stem cell factor can penetrate deeply into the basal layer of the epidermis and dermis where skin stem cells are located, increase the concentration of stem cell factor in skin stem cells, activate dormant and aging epidermal stem cells and dermal mesenchymal stem cells, and activate the skin Self-healing mechanism, reverses the aging process, and promotes the healing of skin damage.
Owner:深圳海悦生物科技有限公司
Method for inducing and acclimating epidermal stem cells into nerve cells
InactiveCN101760447AOvercome prejudicePotential for multilineage differentiationTissue cultureCuticleNerve cells
The invention discloses a method for inducing and acclimating epidermal stem cells into nerve cells, comprising the following steps of: mixing an eplife culture medium and an induction culture medium according to different proportions, and ensuring that the epidermal stem cells have enough time fit for the continuous reduction of the eplife culture medium and the gradual increase of the induction culture medium, which is beneficial to reducing the differentiation to the epidermis and increasing the transformational probability to targeted cells. The method is simple and very effective to directively induce and acclimate the epidermal stem cells into the nerve cells, overcomes the prejudice from technical personnel in the filed, subverts a judgment that the epidermal stem cells are unipotent stem cells for the first time, and proves that the epidermal stem cells have the multi-directional differentiation potential.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Application of combination of polypeptide conjugates and epidermal stem cell exosomes in medicine and cosmetics
ActiveCN111110699AInhibits the synthesis of melaninAnti-freckle and anti-acneCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsExosomeMelanin synthesis
The invention relates to application of a combination of polypeptide conjugates and epidermal stem cell exosomes in medicine and cosmetics. According to the present invention, exosomes are extracted and obtained from epidermal stem cells, the exosomes and polypeptide conjugates are prepared into a composition that inhibits melanin synthesis, and at the same time, skin experiments prove that the composition has the effects of removing freckles and preventing acne.
Owner:广州市新纪元化妆品有限公司
Recovery liquid and method for cryopreserved epidermal stem cells
PendingCN106520677APromote growthSuppression of aging gene expressionCulture processEpidermal cells/skin cellsRecovery methodGlial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor
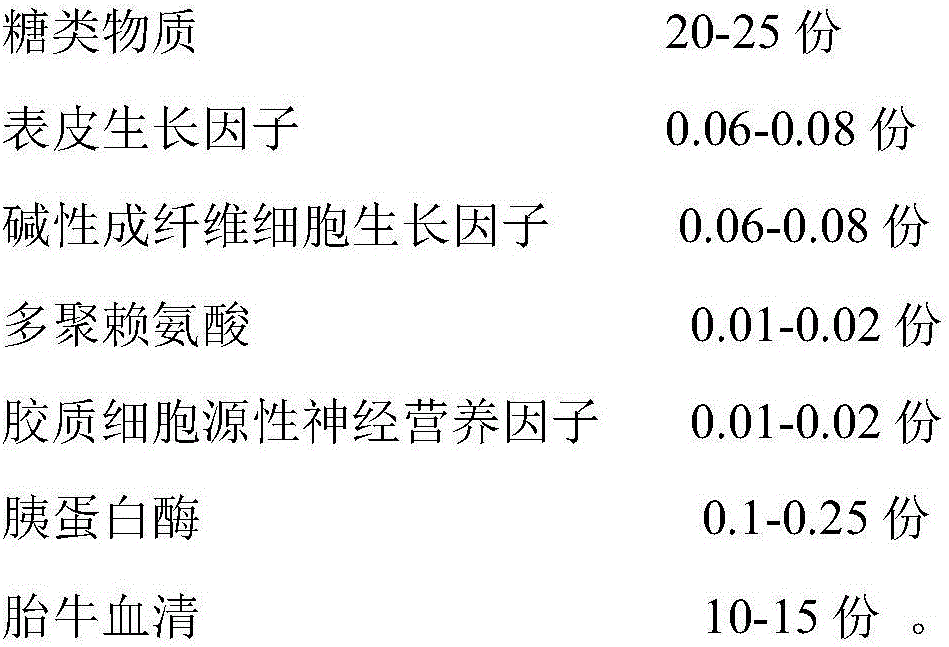
The invention discloses a recovery liquid and a recovery method for cryopreserved epidermal stem cells. According to the key point of the technical scheme, the recovery liquid is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 20-25 parts of carbohydrates, 0.06-0.08 part of epidermal growth factors, 0.06-0.08 part of alkaline fibroblast growth factors, 0.01-0.02 part of polylysine, 0.01-0.02 part of glial cell line derived neurotrophic factors, 0.1-0.25 part of trypsin and 10-15 parts of fetal calf serum. According to the technical scheme, good recovery effect of the epidermal stem cells is achieved, and the growth environment of the epidermal stem cells is relatively proper.
Owner:浙江译美生物科技有限公司
Method for producing tissue engineering skin outside of the body with scarifiskin stem cell
InactiveCN101152580AImprove proliferative abilityGuarantee normal developmentProsthesisDispaseBiology
The invention provides a method of manufacturing tissue engineering skin out of the body with epithelial stem cells. The method includes the following steps: (1) preparation of the epithelial stem cells: epithelial cells are made into cell suspension liquid, adhered and screened by IV collagen, and cultivated with epithelial stem cell media; (2) preparation of deepitheliarizing derma; (3) construction of the tissue engineering skin: epithelial stem cells for 2nd to 5th generation cultivation are selected, Dispase enzyme is adopted to digest the bossy cell patches in the size of rice to soya beam, the patches are inoculated to the deepitheliarizing derma, the tissue media is added, to cultivate the tissue engineering skin underwater or on the water. The tissue engineering skin constructed by the method of the invention is more suitable for the biological characteristics of human skin.
Owner:陆洪光
Prepn and application of epiderm or hair follicle stem cell from souce of human early embryo
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Skin cosmetic compositions comprising malus domestica extract and argania spinosa sprout extract for improving skin appearance
ActiveUS20150147360A1Slow onsetImprove skin appearanceCosmetic preparationsBiocideSkin appearanceDermatology
Owner:LEVY PHILLIP
Methods to prepare and use epidermal stem cells
InactiveUS6927060B2Low immunogenicityGenetically modified cellsPreparing sample for investigationCell basedCell biology
A method to prepare epidermal stem cells, and isolated epidermal stem cells, is provided. Also provided are methods of using epidermal stem cells, e.g., for cell based therapies.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Stretch mark repairing ointment containing epidermal stem cell extract
InactiveCN107753409AImprove antioxidant capacityAnti agingCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSkin InjuryMedicine
Owner:GUANGZHOU SALIAI STEMCELL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method for constructing composite tissue engineering skins
ActiveCN106620855AIdeal three-dimensional network structureMeet the requirements of morphologyProsthesisFiberReticular formation
The invention discloses a method for constructing composite tissue engineering skins. The method includes that human epidermal stem cells are used as seed cells, sheep accellular dermal matrixes are used as scaffold carriers, and the composite tissue engineering skins can be constructed by means of in-vitro culture by the aid of gas-liquid interface separation processes. The method has the advantages that the composite tissue engineering skins constructed by the aid of the method have perfect three-dimensional netted structures, and accordingly growth of cells and formation of new collagen fibers can be promoted; the composite tissue engineering skins are short in construction time and complete in histological structure and are similar to natural skins, and morphology requirements on tissue engineering skins can be met.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
Method for preparing culture medium without blood serum for epidermis stem cell of milch goat in the central Shanxi plain
InactiveCN1563360AMeet the nutritional needs of long-term expansion cultureMeeting nutritional needsArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsPenicillinFibroblast
An anserum culture medium for cuticular layer stem cells of ganzhong milch goat can be prepared according to formula of F12+1-1.2% BSA+20-25% GSMCM+20-25ng / EGF+5ug / ml insulin+15-20ng / ml IGF=1+0.4-0.6 microng / ml hydrocortisone+penicillin and streptomycin 100u / ml. The culture medium preparing process includes adding insulin growth factor based on only adding cuticular layer factor in traditional method, applying method of adding fibroblast condition culture medium in stead of method in using fibroblast for cocultivating.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Medicine for accelerating skin repair and regeneration, preparation method thereof and application thereof
ActiveCN102552323APromote repairEasily damagedUnknown materialsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsSkin repairOperability
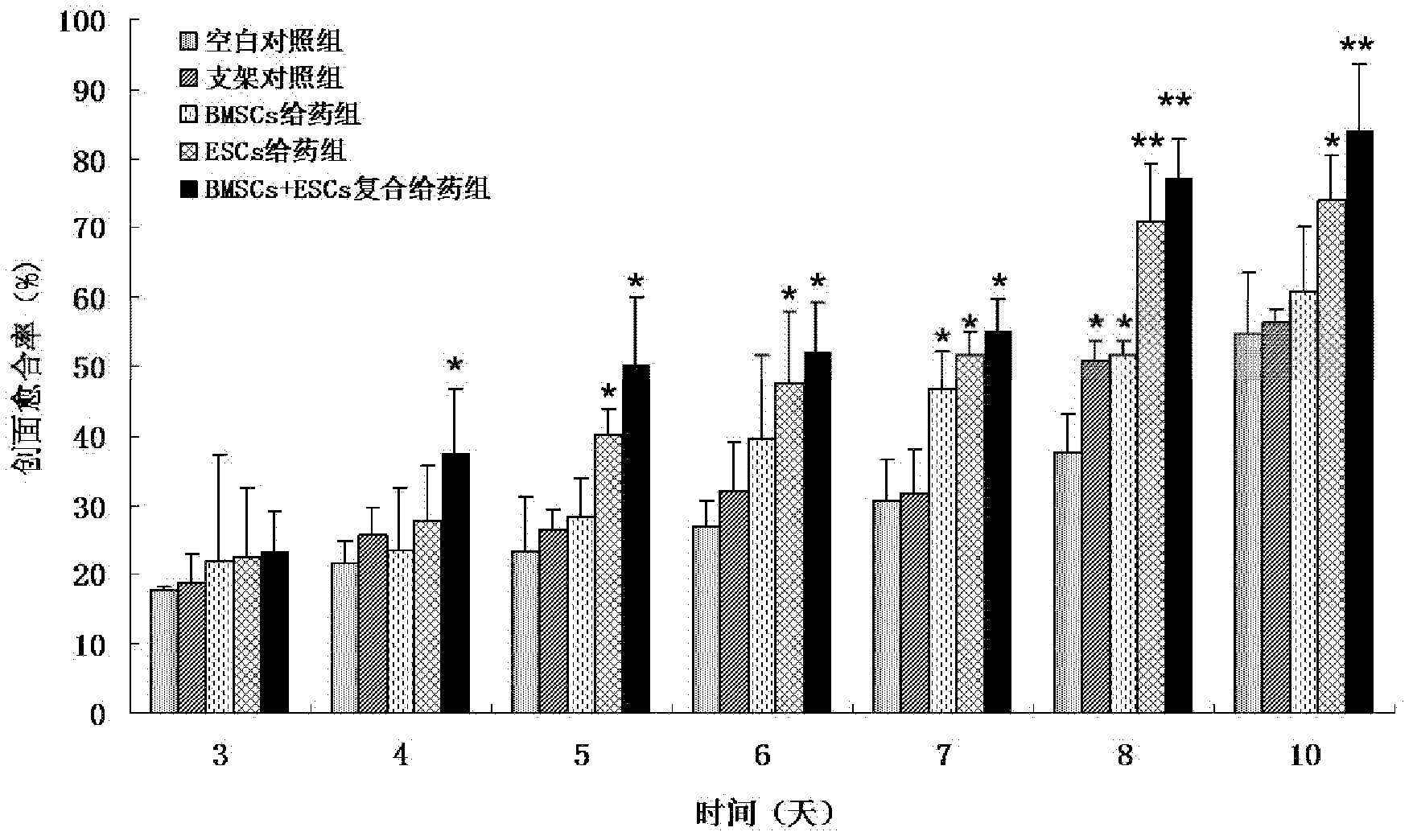
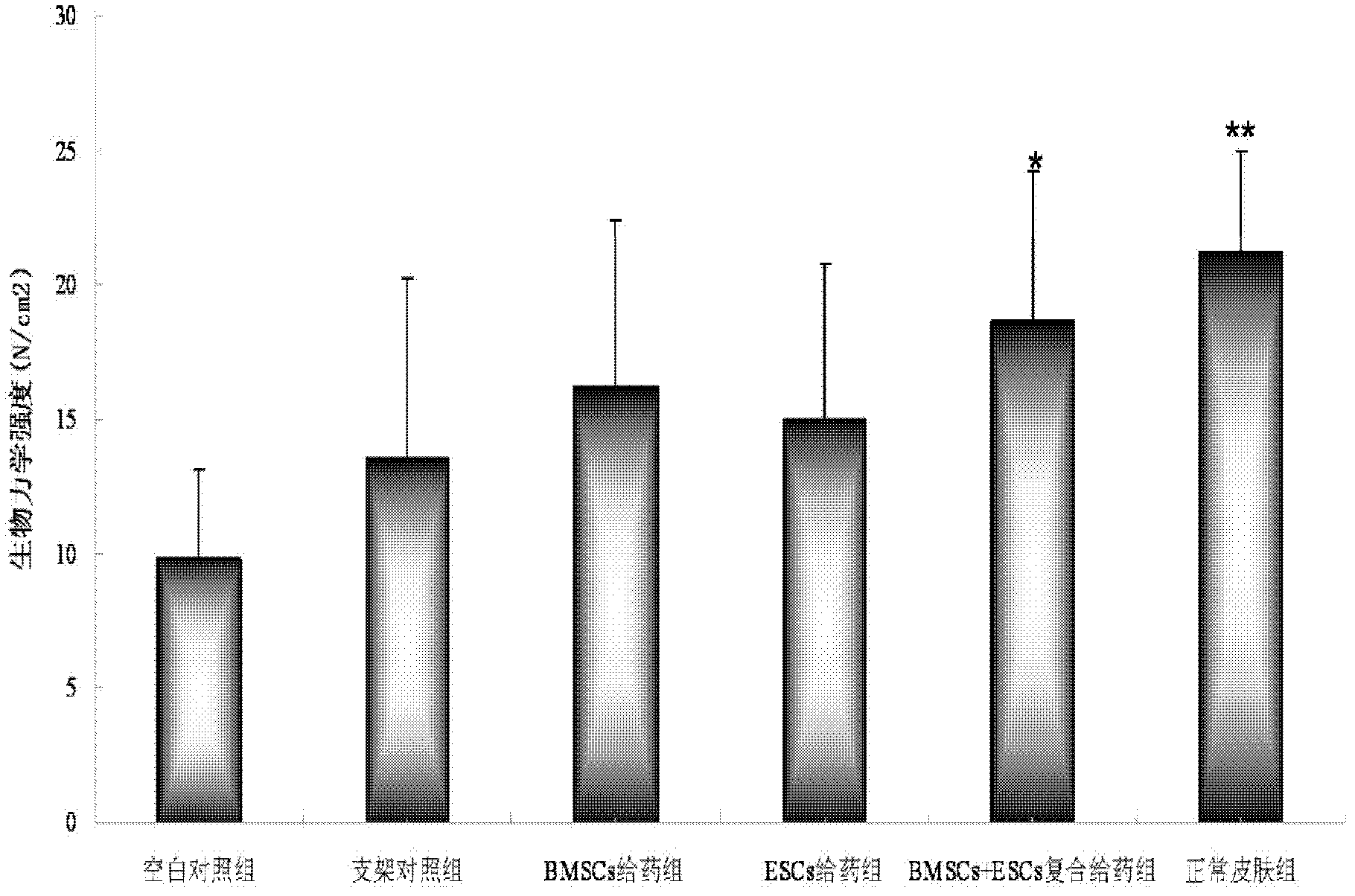
The invention discloses a medicine for accelerating the repair of stratum epidermis and the regeneration of skin appendages. The medicine consists of epidermal stem cells, bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and a medicine carrier, wherein the epidermal stem cells and the bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells are adhered to the medicine carrier, namely each cubic millimeter of the medicine carrier contains (0.3-1)*104 epidermal stem cells and (0.3-1)*104 bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. The medicine has an obvious effect in aspects of promoting the regeneration of the stratum epidermis, promoting the regeneration of dermis, enhancing the mechanical strength of regenerated skin, promoting the content of collagen of the regenerated skin, promoting revascularization, promoting the regeneration of hair follicles and the like, so that wounds can be repaired within a short time and the regeneration of the skin appendages can be accelerated. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the medicine for accelerating the repair of the stratum epidermis and the regeneration of the skin appendages, and the method is simple, high in controllability, high in operability and high in repeatability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com