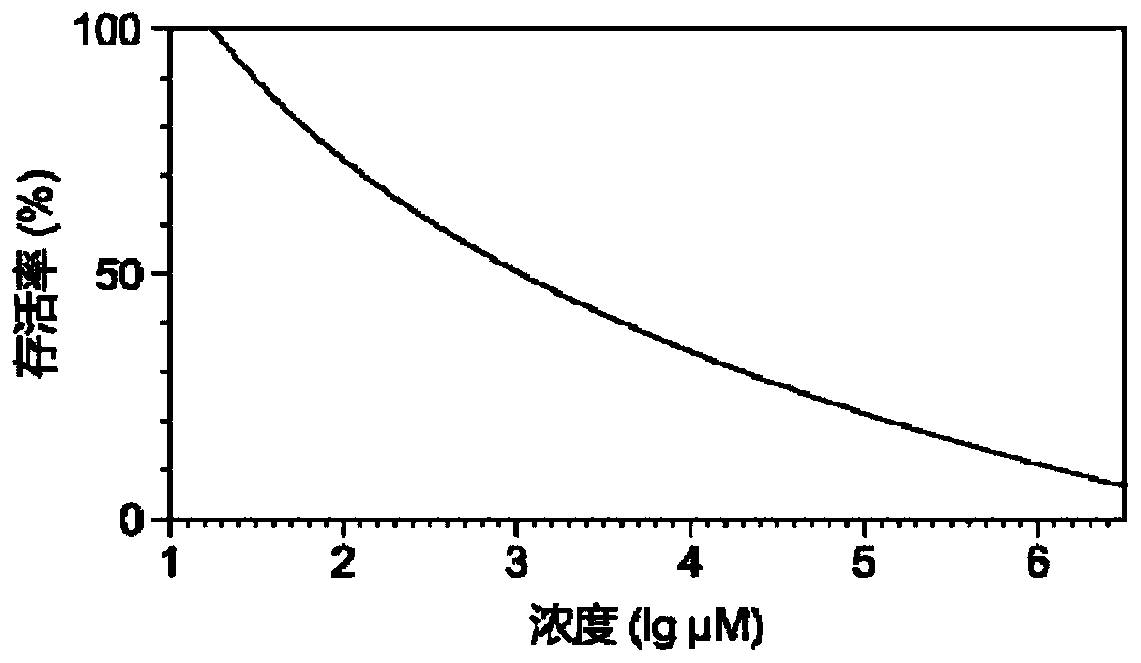
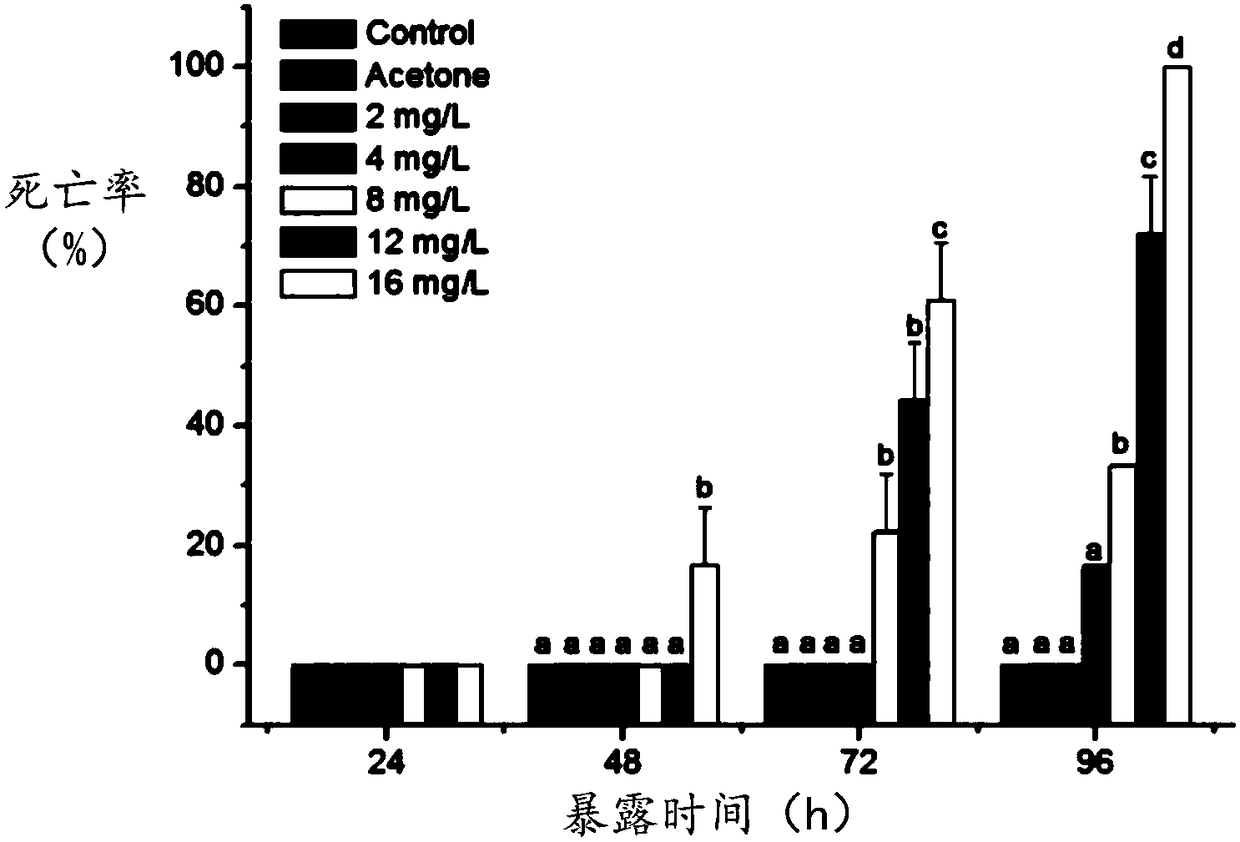
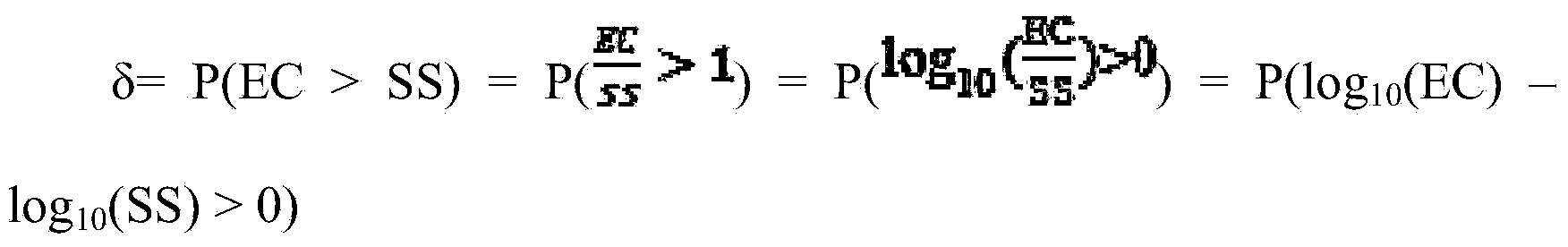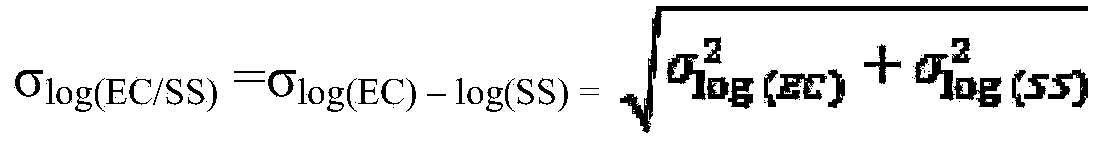Patents
Literature
45 results about "Chronic toxicity testing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chronic toxicity tests are performed to determine the long term toxicity potential of toxicants or other stressors, commonly to aquatic organisms. Examples of common aquatic chronic toxicity test organisms, durations, and endpoints include: Fathead minnow, Pimephales promelas, larval survival and growth.
Method for building model for collectively evaluating bioavailability and toxicity of cadmium accumulation in food for human body
InactiveCN102680654AAccurate evaluationThe result is accurateMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansTesting foodCell layerChronic toxicity testing
The invention relates to a method for building a model for collectively evaluating bioavailability and toxicity of cadmium accumulation in food for a human body, and the method comprises the following steps of (1) food sample digestion and determination liquid acquiring: a, grinding a food sample after the food sample is collected, and sequentially digesting the food sample by sequentially adopting gastric juice and intestinal juice; and b, centrifuging the digested mixed liquid, collecting supernate to be sterilized through high pressure; (2) independently culturing Caco-2 cells and 293T cells; (3) combined culture of Caco-2 cells and 293T cells: moving an insertion groove with the Caco-2 cells into a hexagonal-porous plate with the 293T cells to be continuously cultured for 24h; (4) evaluation of bioavailability and toxicity of cadmium: placing the food sample determination liquid on a Caco-2 cell layer of a combined culture model, simultaneously adding iso-osmotic incubation liquid on a 293T cell layer, and continuing the culture for 24h; in the chronic toxicity test, maximally collectively culturing the sample for 10d; and (5) detecting indexes. The method has characteristics of simpleness in operation, easiness in controlling test conditions, small pollution, economical efficiency, accurate result and the like, and also has the advantages for collectively evaluating the bioavailability and toxicity. The method is suitable for evaluating the safety of the cadmium accumulation in grains, vegetables and animal food.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
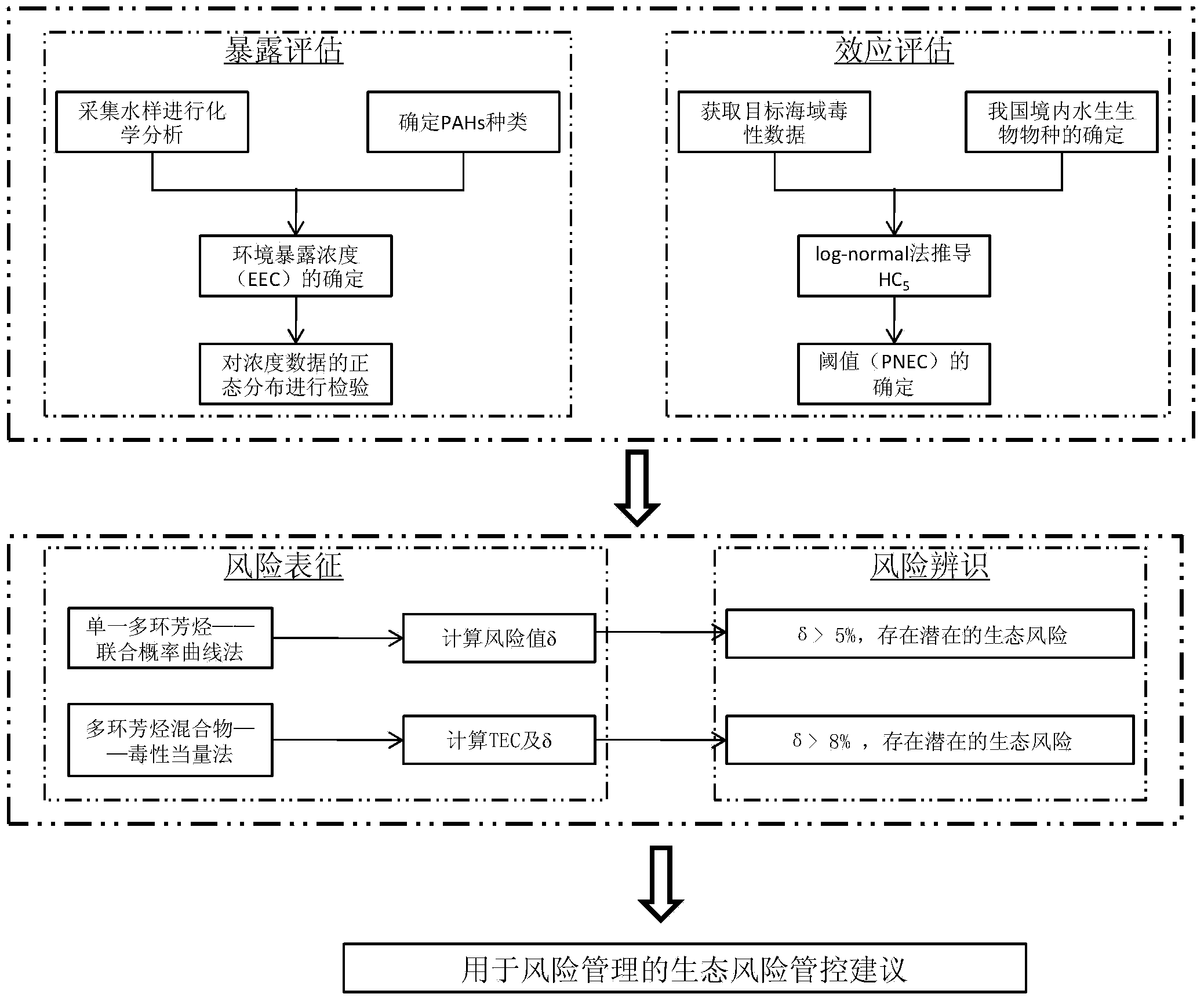
Ecological risk assessment method of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon compound and mixture thereof in marine water environment
InactiveCN103853931ASpecial data processing applicationsMaterial analysisPredicted no-effect concentrationFlora
The invention discloses an ecological risk assessment method of a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon compound and a mixture thereof in a marine water environment. The assessment method comprises the following steps of determining the type and concentration of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in the marine water environment; screening the representative biological species having the flora characteristics of the creatures of the China sea area; acquiring the chronic toxicity data of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in the water body of a target sea area; using a statistical extrapolation method to calculate the predicted no effect concentration of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon; using a joint probability curve method to calculate the level of the ecological risk of single polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in the water body of the target sea area; using a toxicity equivalent factor method to calculate the joint ecological risk of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon mixture in the water body of the target sea area; identifying the risk of the monomer and the mixture of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon according to the above results. The ecological risk assessment method of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon compound and the mixture thereof in the marine water environment provided by the invention realizes the ecological risk assessment of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon monomer and the mixture thereof in the China marine water environment by using the toxicity equivalent and the probability risk assessment method based on the species sensitivity distribution theory, and provides a decision basis for the marine ecological risk management of the China organic pollutants.
Owner:NATIONAL MARINE ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING CENTRE
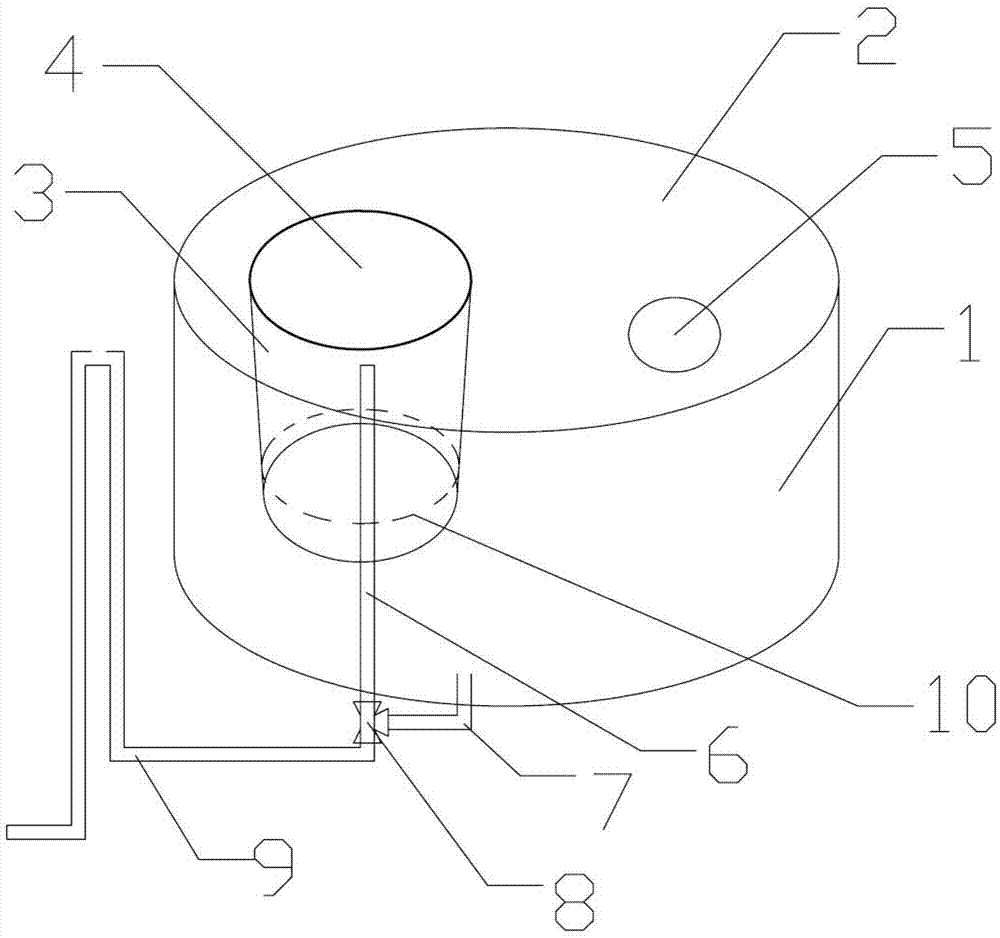
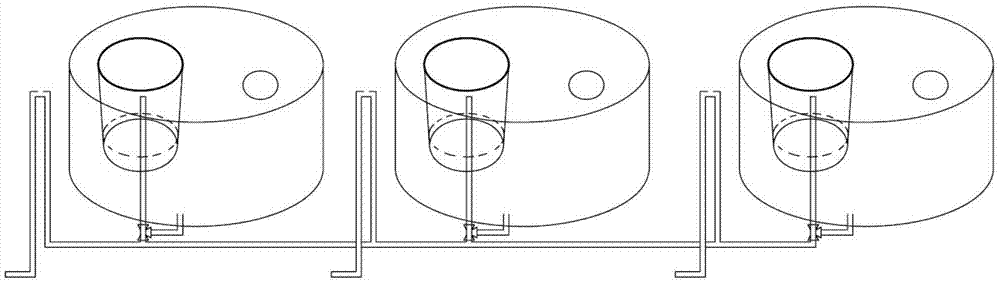
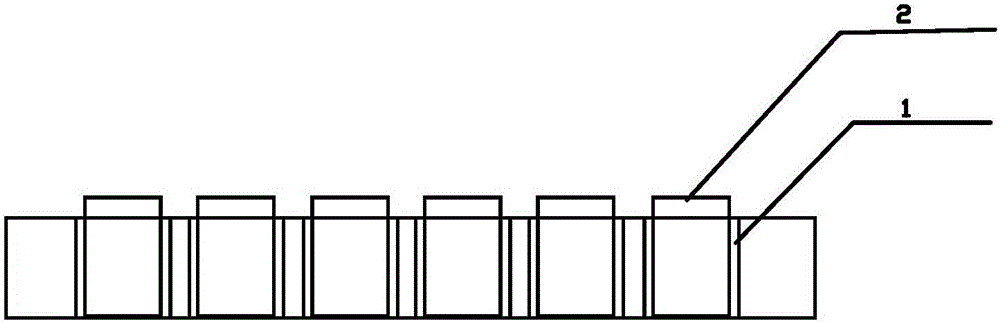
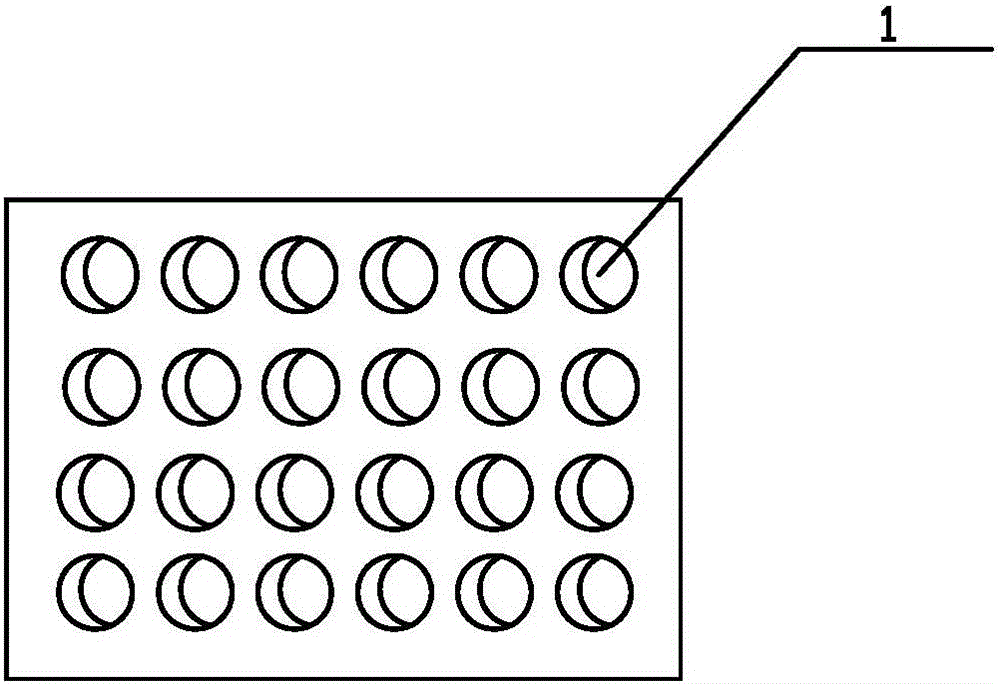
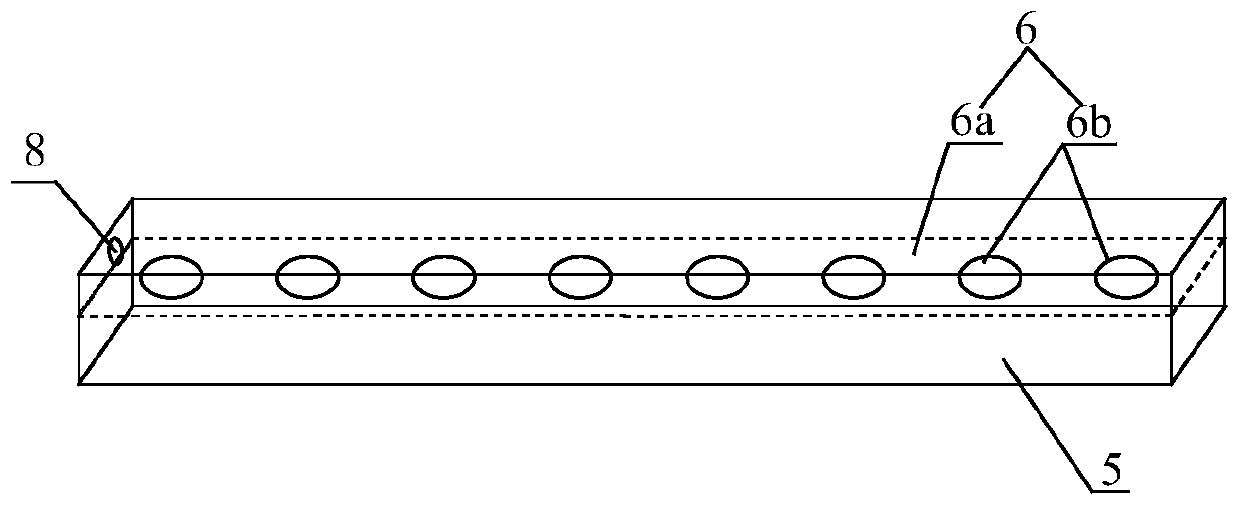
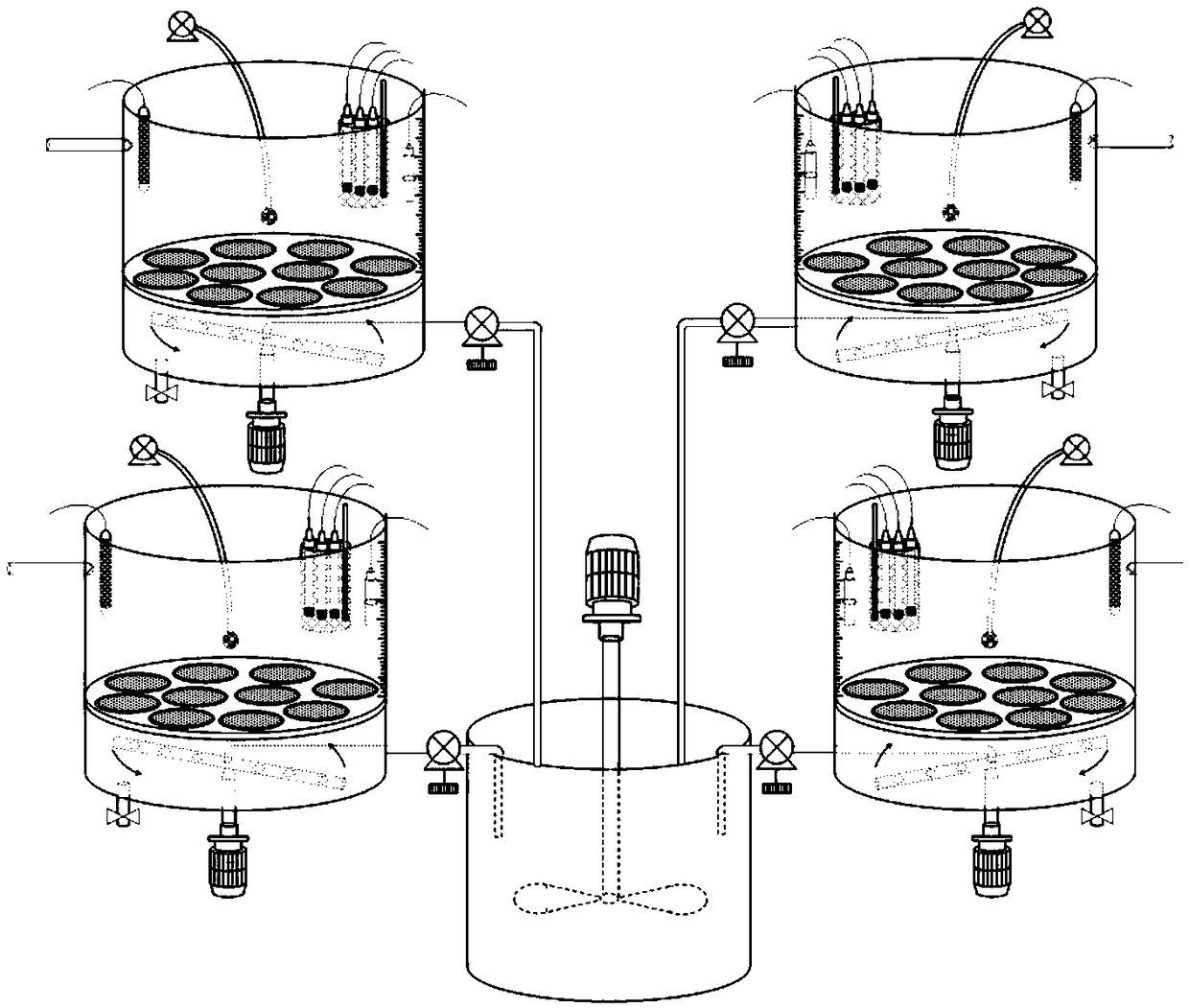
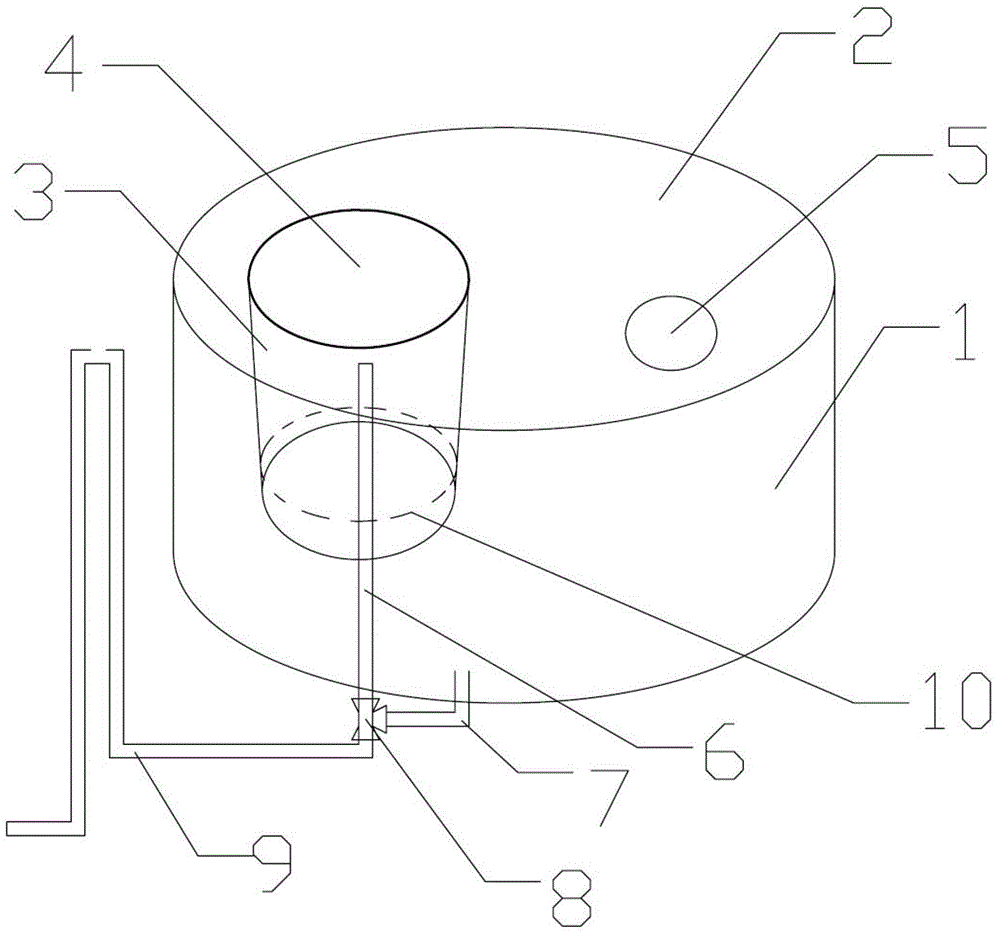
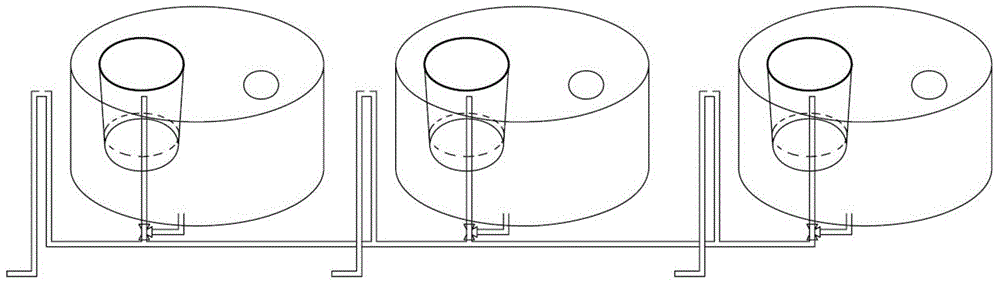
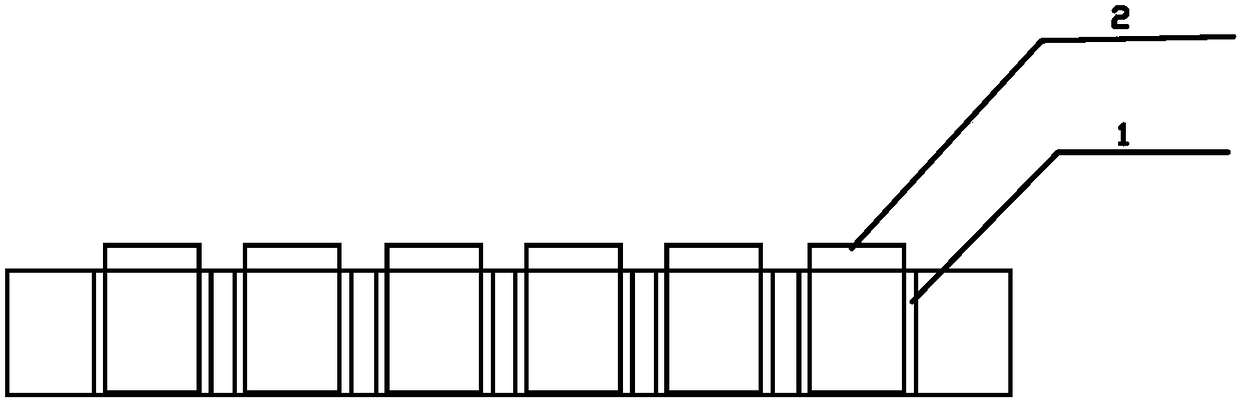
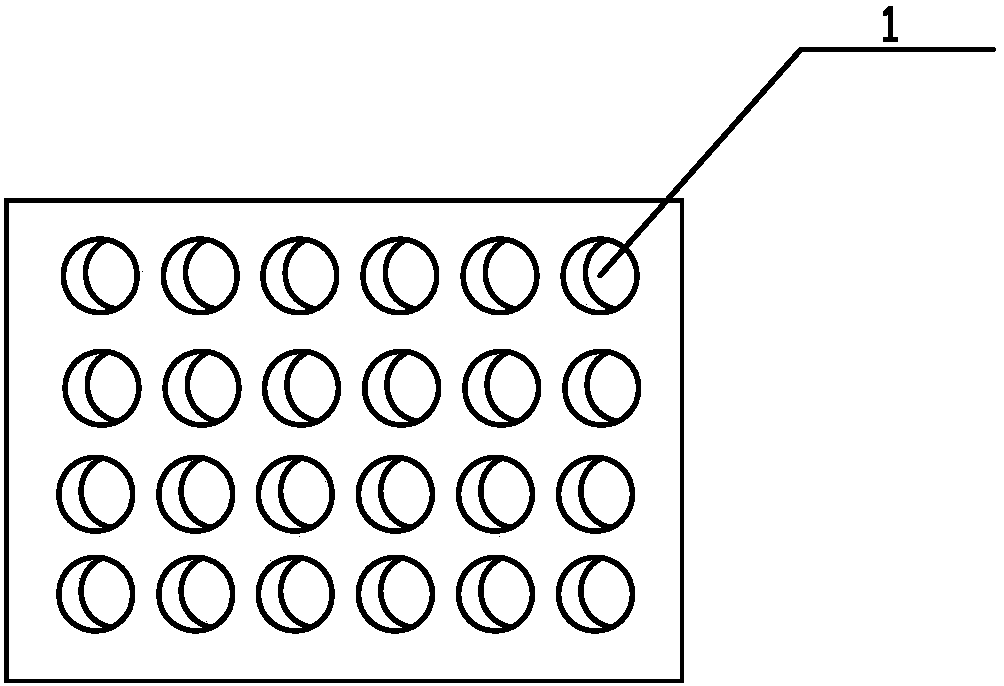
Exposure device for fish embryos and larva fish for long-term chronic toxicity tests
The invention discloses an exposure device for fish embryos and larva fish for long-term chronic toxicity tests. The exposure device comprises a tank and a tank cover which are arranged externally. The tank cover is provided with a plurality of small container ports. A small container is hung on each small container port so as to be allowed to extend into the inner space of the tank. The bottom of each small container keeps a certain distance from the bottom of the tank. An overflow pipe is arranged in each small container. Each overflow pipe penetrates out of the bottom wall of each small container and the bottom wall of the tank to be connected to a water inlet of a three-way valve. The other water inlet of each three-way valve is connected with a drain pipe, and each drain pipe penetrates out of the bottom wall of the tank and extends into the bottom of the tank. A water outlet of each three-way valve is connected with a protruding drain outlet, and the highest position of each protruding drain outlet is at the same level with an overflow pipe nozzle at the utmost top of each overflow pipe. The tank cover is further provided with a plurality of operating openings, and the lower periphery wall of each small container is provided with a narrow slit capable of leaking water and blocking the fish embryos and the larva fish from passing by.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
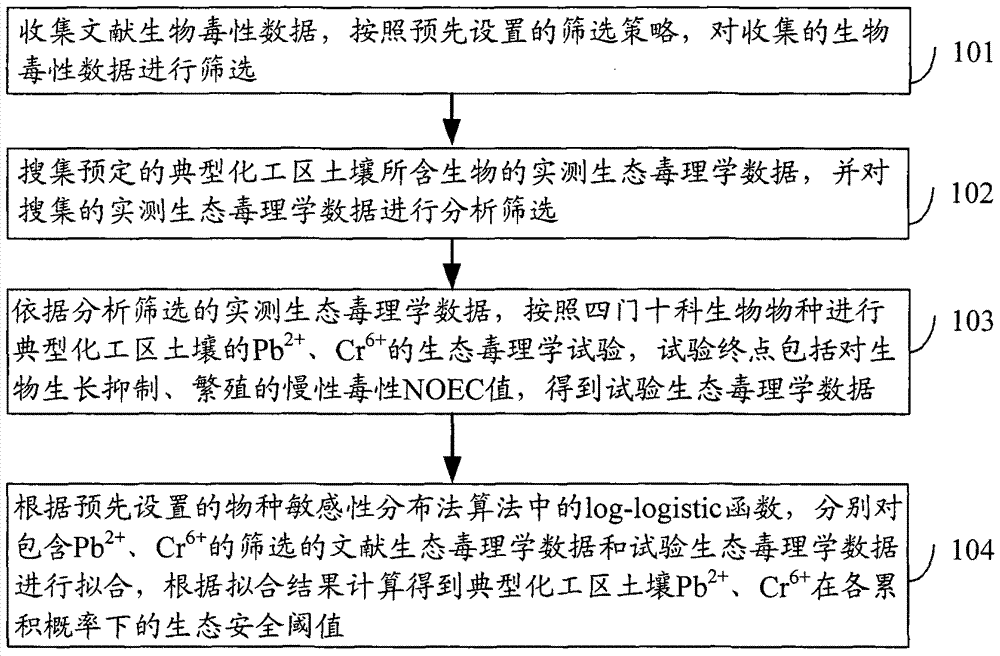
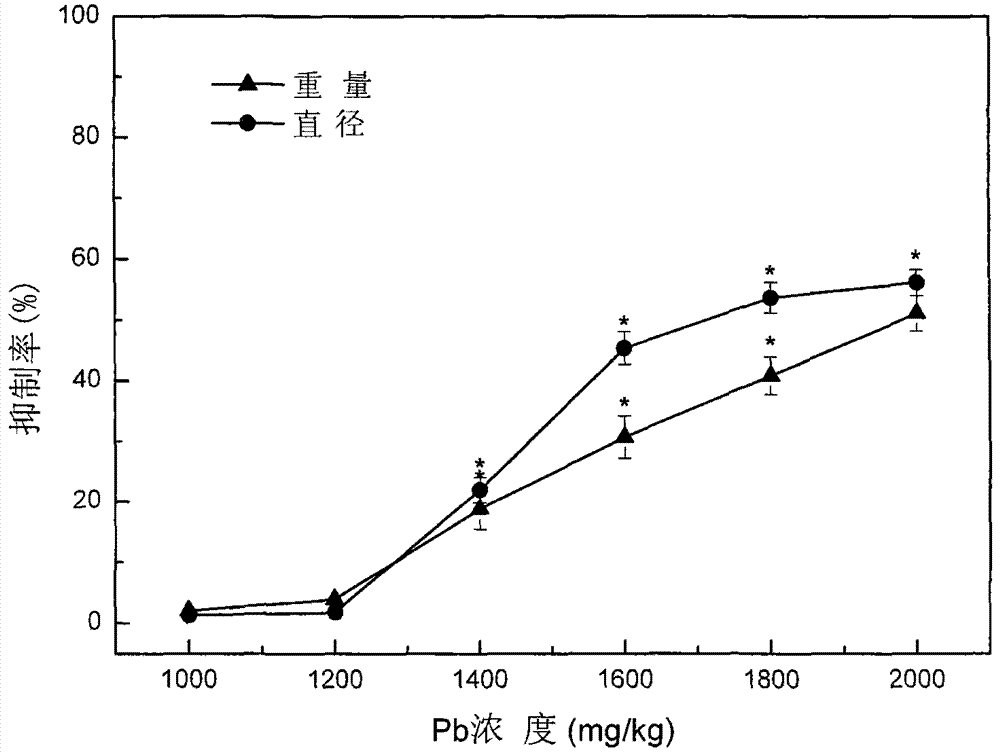
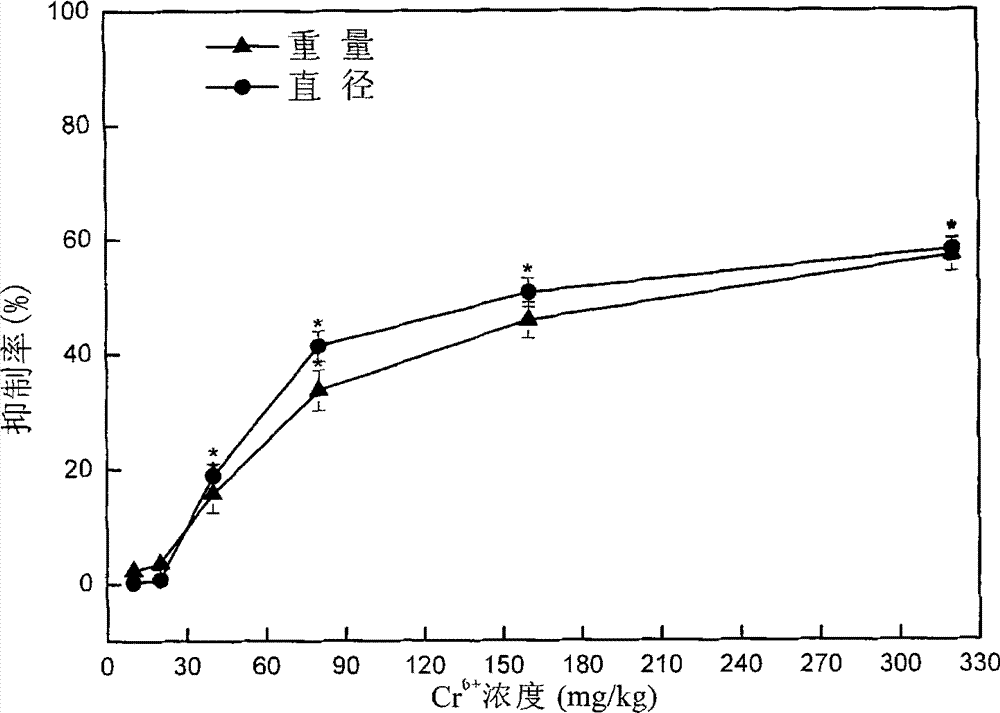
Four phyla and ten families based method for obtaining ecological safety thresholds of lead and chromium in soil
The invention discloses a four phyla and ten families based method for obtaining ecological safety thresholds of lead and chromium in soil. The method includes the steps of: screening the collected biological toxicity data; analyzing and screening the collected measured ecotoxicological data; according to the screened and analyzed measured ecotoxicological data, conducing ecotoxicological tests of Pb<2+> and Cr<6+> in the soil of a typical chemical industry zone and endpoints in accordance with four phyla and ten families, wherein test terminal points include chronic toxicity NOEC values on biological growth inhibition and reproduction; and according to a log-logistic function in a preset species sensitivity distribution method, respectively fitting the screened literature ecotoxicological data and ecotoxicological test data, and calculating the ecological safety threshold values of Pb<2+> and Cr<6+> in the soil of the typical chemical industry zone under each cumulative probability according to the fitting results. The method of the invention can effectively evaluate the soil ecological risk caused by heavy metal pollutants.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Early warning method for chronic toxicity of water quality substance to Daphnia magna
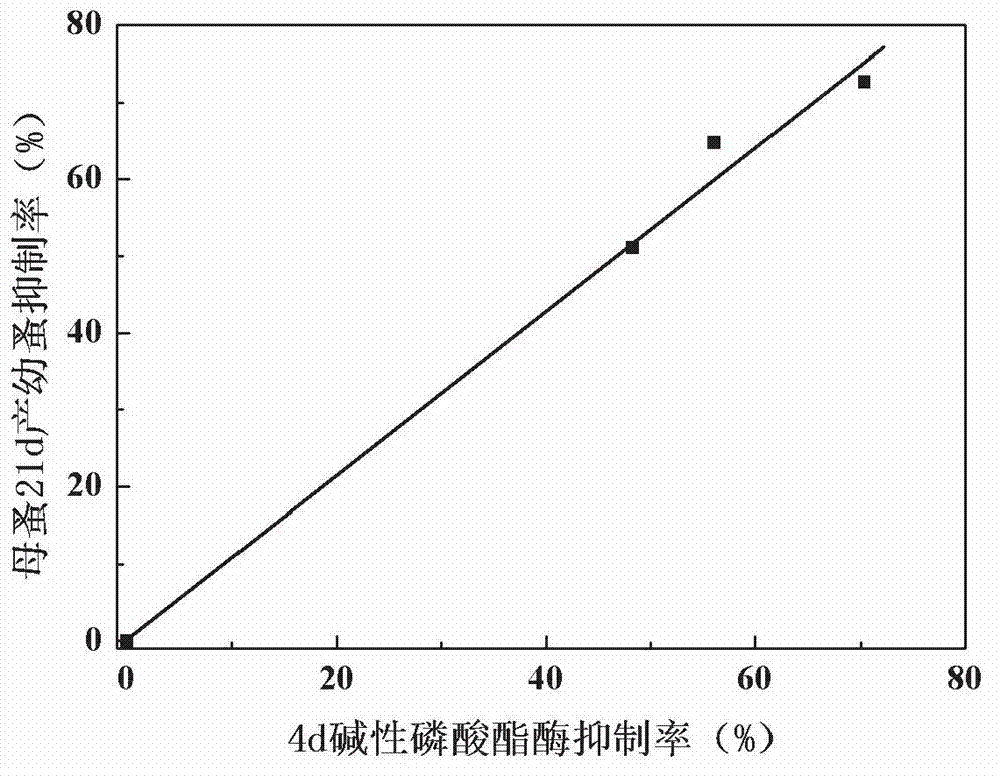
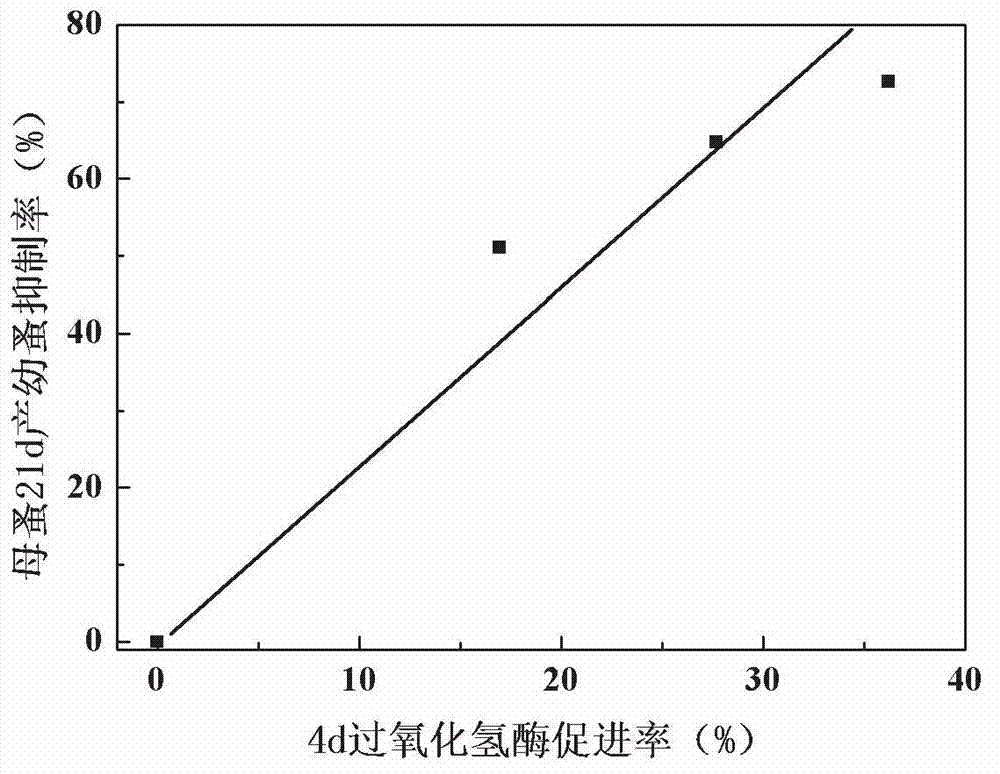
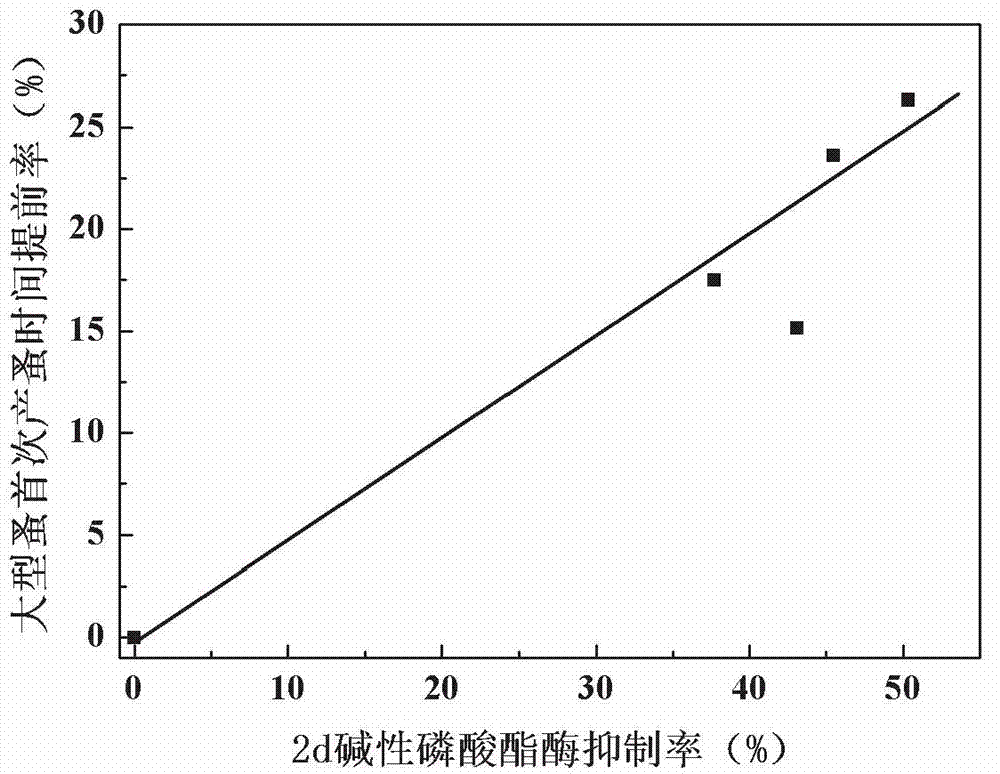
InactiveCN102827919AResolve detectionResolution cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementDaphnia magnaChronic toxicity testing
The invention discloses an early warning method for chronic toxicity of a water quality substance to Daphnia magna, which belongs to the technical field of water pollution control. According to the invention, directed at a low-toxicity water quality situation, marker enzyme having sensitive response to toxicity in Daphnia magna is screened out, and potential of chronic toxicity within 21 days is predicted based on results of detection on a change rate of the activity of the marker enzyme in a short period when Daphnia magna is tainted. There are standard methods or commercial kits for detection of the marker enzyme, detection is convenient, rapid and accurate, detection requirements of rapid early warning are met, and the method provided by the invention is applicable to a single-substance water sample with a low concentration or to a complex water sample like reclaimed water and surface water containing a variety of components and having low toxicity and can rapidly reflect the level of biotoxicity.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for predicting and evaluating toxicity of novel non-steroid anti-inflammatory agent pollutant based on daphnia magna toxicity
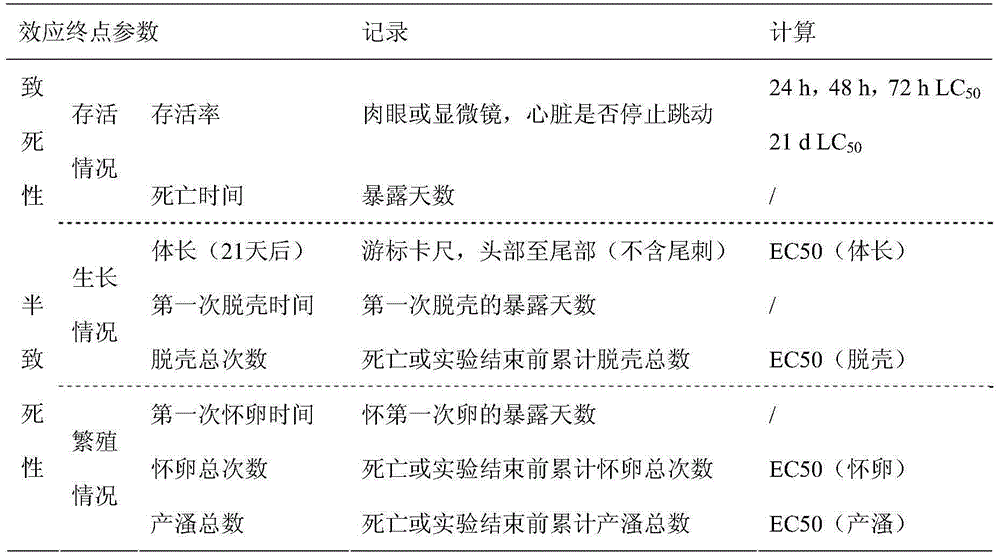
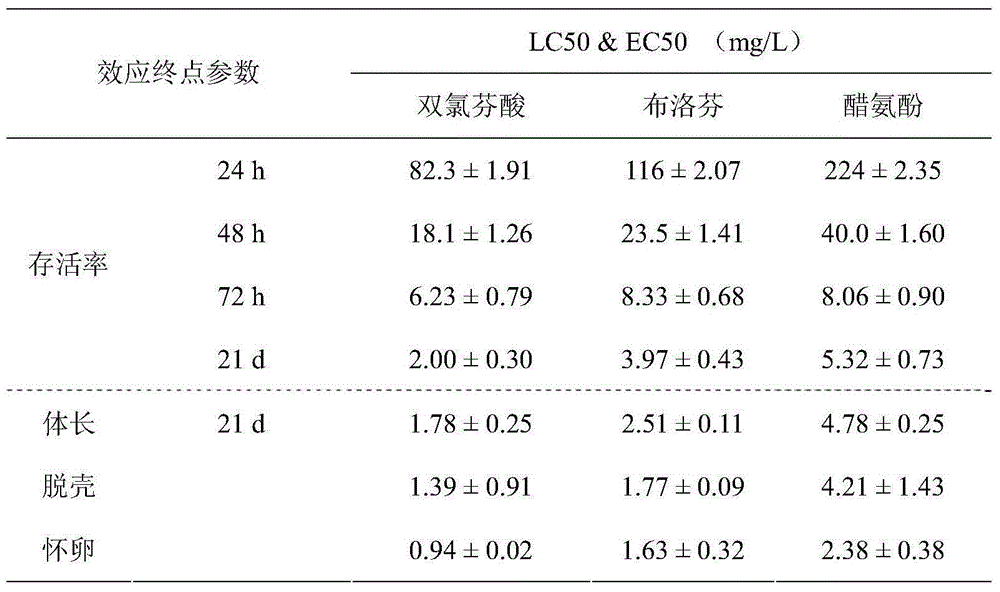
The invention discloses a method for predicting and evaluating toxicity of a novel non-steroid anti-inflammatory agent pollutant based on daphnia magna. According to the method, daphnia magna is exposed to the novel non-steroid anti-inflammatory agent pollutant with equal logarithm spacing concentration, the survival rates of daphnia magna generated when the daphnia magna is exposed for 24 h, 48 h and 72 h, and the survival rate, the body length, the total number of shelling and egg carrying times and the total daphnia magna producing amount of the daphnia magna exposed for 21 d are recorded respectively; corresponding 24 h LC50, 48 h LC50 and 72 h LC50 are obtained through calculation of SPSS software and used for evaluating acute toxicity, and corresponding 21 d LC50, body length EC50, shelling EC50, egg carrying EC 50 and daphnia magna producing EC50 are obtained and used for evaluating chronic toxicity; thus, the toxicity characteristic and the toxicity level of the novel non-steroid anti-inflammatory agent pollutant are analyzed, tested and quantitatively described, meanwhile can serve as indexes for monitoring and evaluating biotoxicity of non-steroid anti-inflammatory agent sewage, and can provide reference for predicting and evaluating potential ecotoxicity risks of the pollutant in water.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM
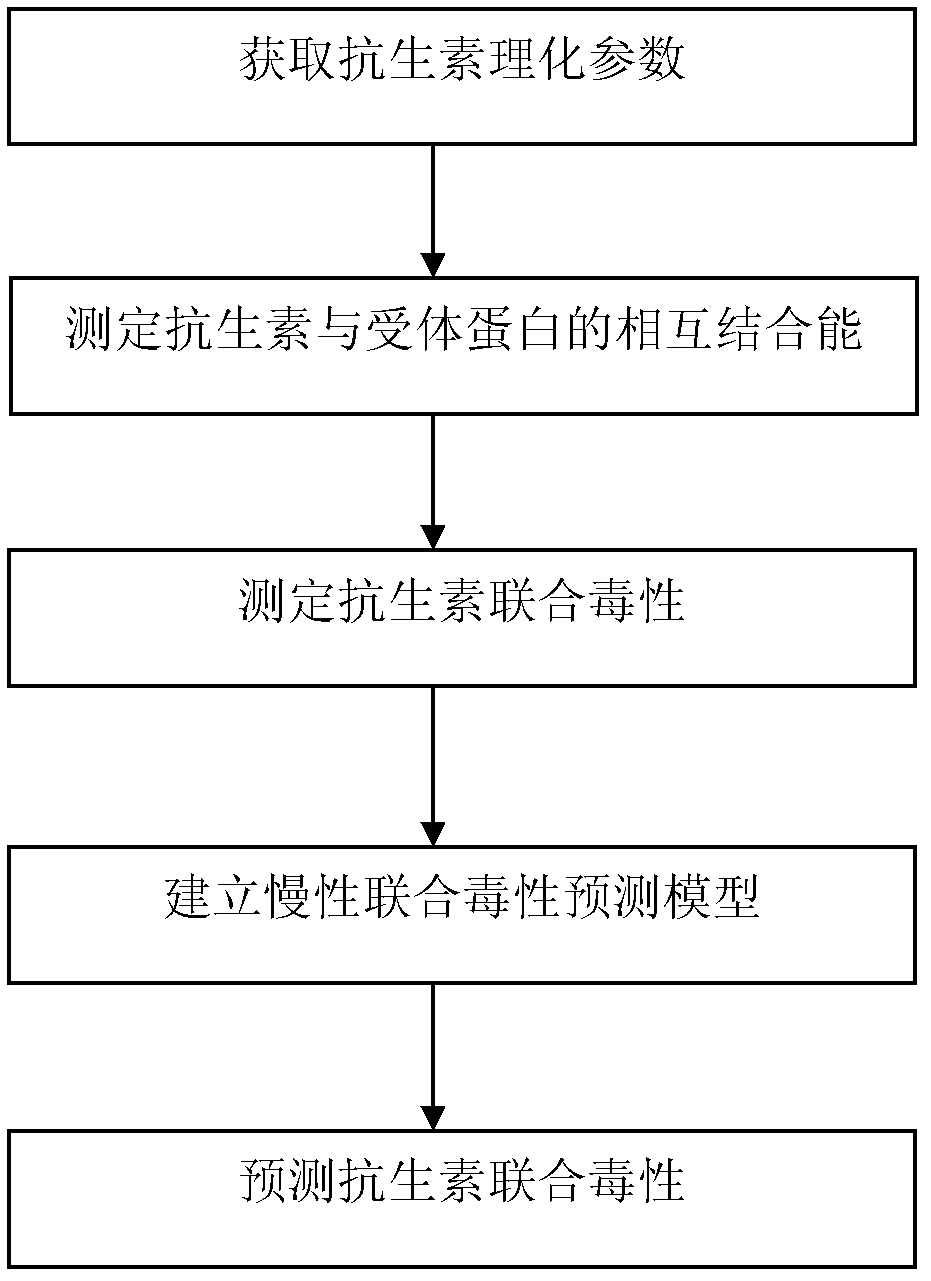
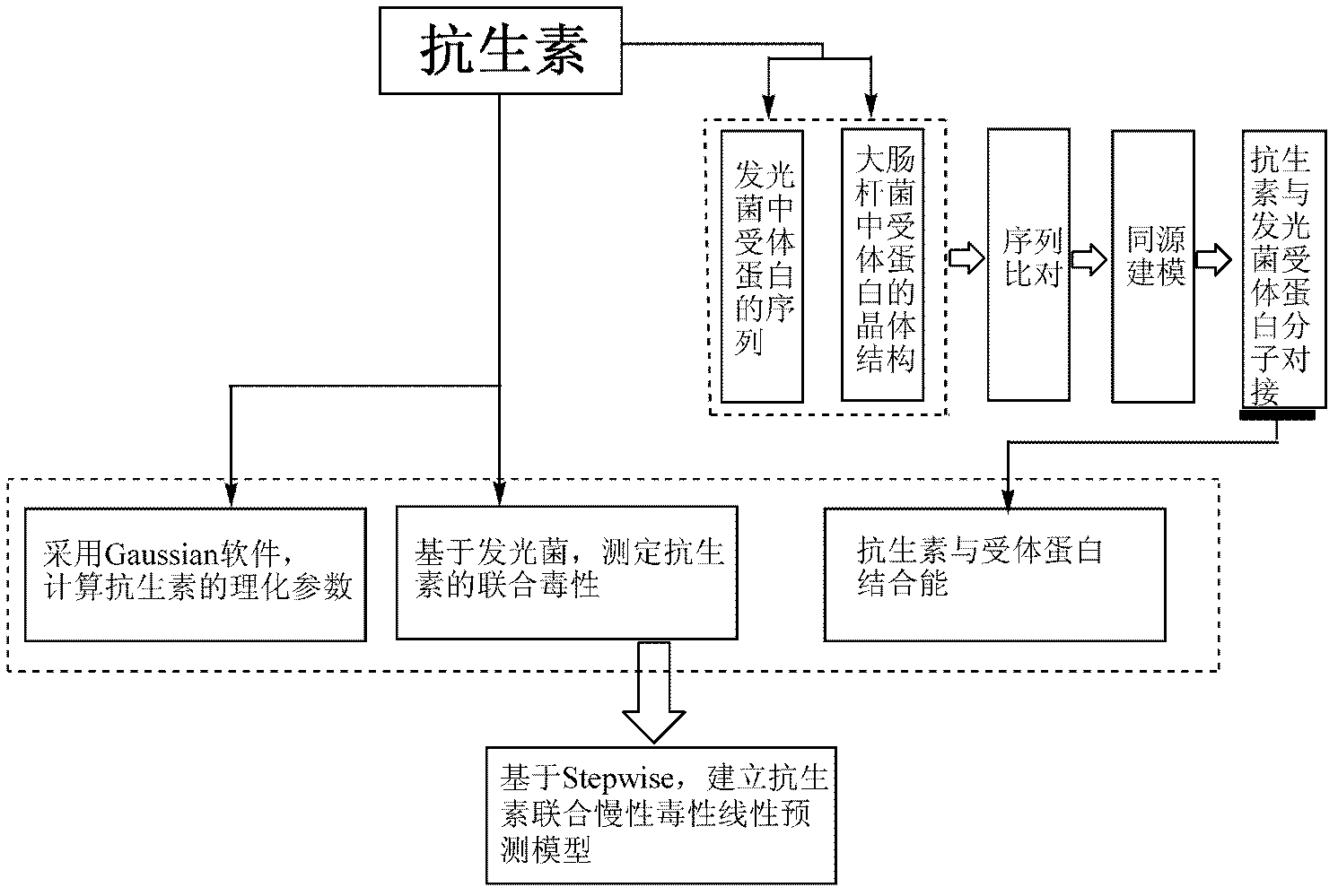
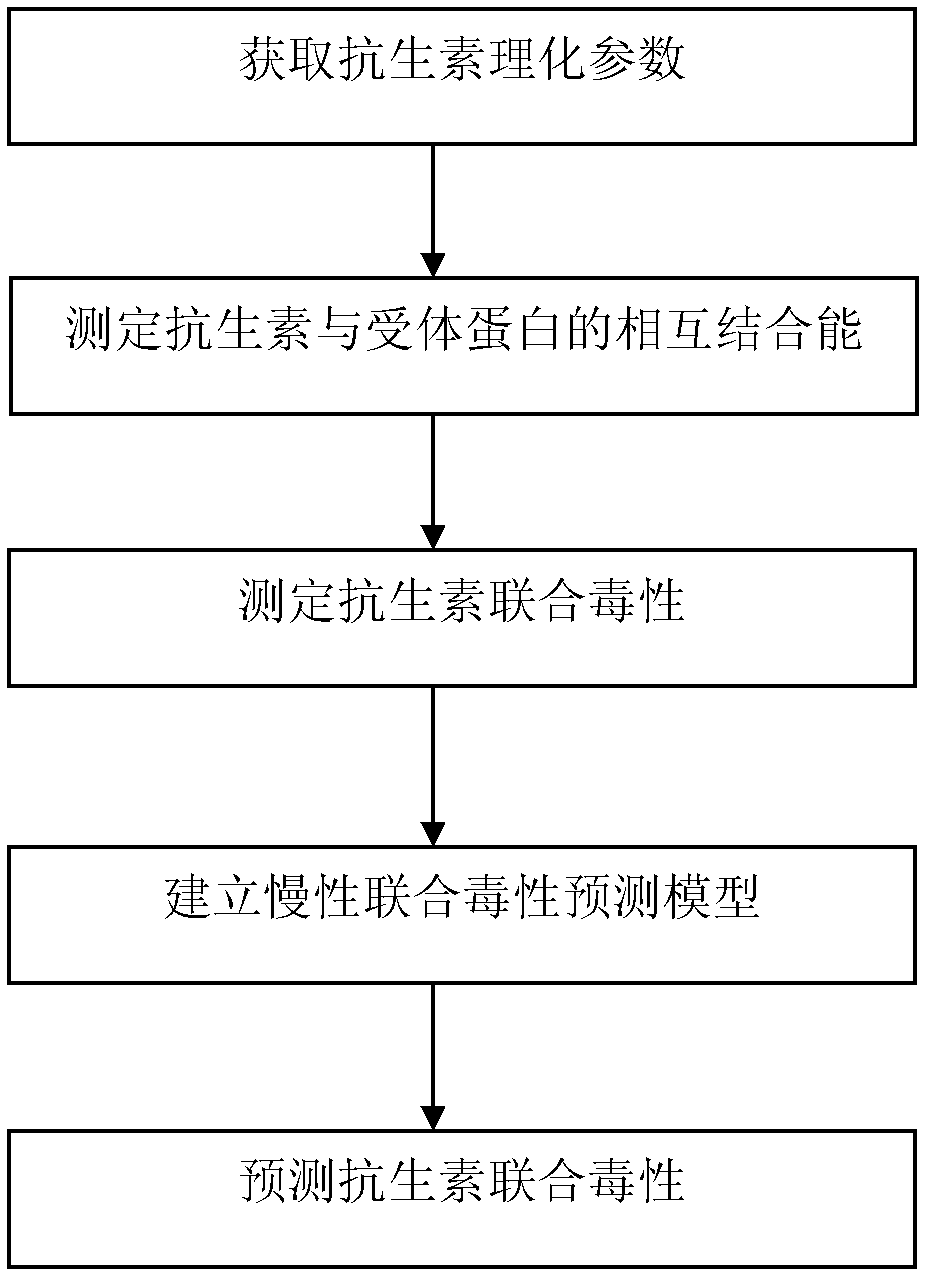
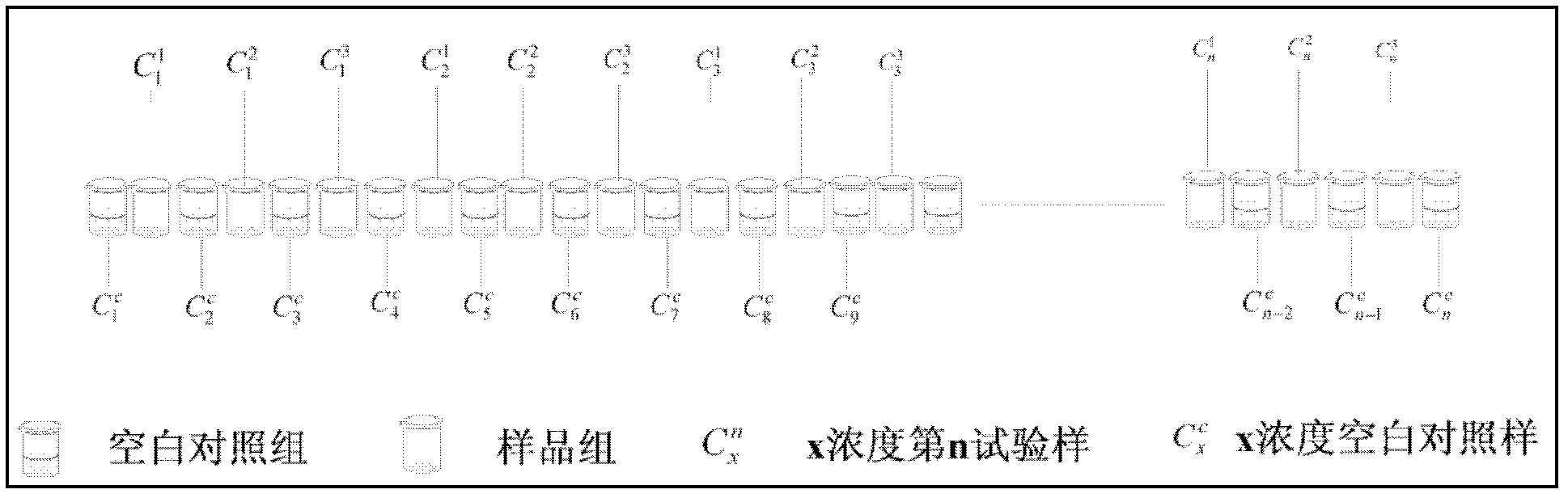
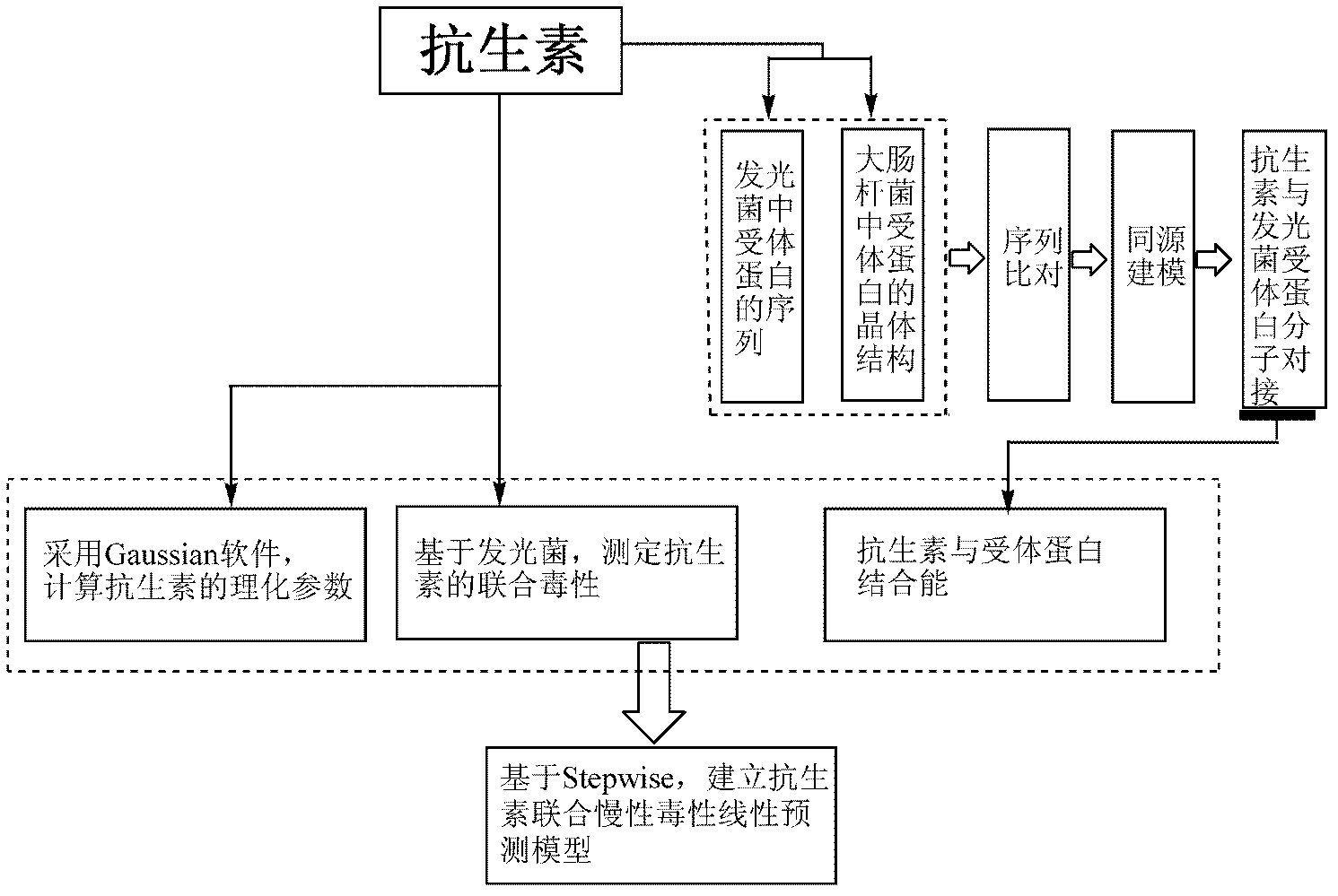
Method for predicting combined chronic toxicity of antibiotic pollutant
InactiveCN102435599ALarge predicted throughputReduce investmentChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceFluorescence/phosphorescenceBinding energyMedicine
The invention discloses a method for predicting the combined chronic toxicity of an antibiotic pollutant. The method comprises the following steps: 1, acquiring physical and chemical parameters of an antibiotic; 2, acquiring an acceptor protein, constructing a homologous model of the acceptor protein, and determining the mutual binding energy between the antibiotic and the acceptor protein; 3, determining the combined toxicity of the antibiotic; 4, establishing a prediction model for the chronic combined toxicity on the basis of the physical and chemical parameters of the antibiotic, the mutual binding energy between the antibiotic and the acceptor protein and the combined toxicity of the antibiotic; and 5, predicting the combined toxicity of the antibiotic through the model obtained in step 4. The method of the invention, which has the advantages of wide application range, no need of complex detection equipment, no test and environment pollution, and accurate prediction of the toxicity of the antibiotic composite pollutant, provides the scientific basis for the antibiotic pollutant discharge enforcement and the ecological risk evaluation.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Traditional Chinese medicine composition preventing and curing cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105012388AImprove hypoxia toleranceHas inhibitory effectCardiovascular disorderLeech/worm material medical ingredientsAcute toxicity testingMyocardial ischaemia
The invention relates to a traditional Chinese medicine composition preventing and curing cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. With milkvetch roots being principal herbs, the composition of salvia roots, ginkgo leaves and pseudo-ginseng in a specific proportion has the obvious effect of preventing and curing the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, can obviously reduce blood lipid of rats with hyperlipemia, has the obvious effect of restraining artery, vein and vein bypass thrombus and can improve hemorheology, restrain ear swelling caused by xylene and inflammatory reaction caused by cotton ball granuloma and obviously prolong survival time of the rats which are suffered from normal-pressure hypoxia tolerance, sodium nitrite poisoning and acute cerebral ischemic anoxia. In this way, the hypoxia tolerance capacity of organisms is improved, and the traditional Chinese medicine composition has a certain effect of protecting myocardial ischaemia injuries and cerebral injuries, and is free of acute toxicity, genetic toxicity and chronic toxicity and suitable for preventing and curing the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
Owner:张永煜
Method for measuring acute and chronic toxicity of drug against varroa jacobsoni
ActiveCN105850898ADetect realisticEasy to detectAnimal husbandryAcute toxicity testingMortality rate
The invention discloses a method for measuring acute and chronic toxicity of a drug against varroa jacobsoni. The method comprises the following steps: gently spraying the to-be-measured liquid onto the surfaces of healthy bee larvae; transferring the bee larvae from the inside of a larva culture plate into a bee pupa culture cup with the liquid-infiltrated filter paper piece at the bottom; collecting the to-be-measured varroa jacobsoni; introducing a varroa jacobsoni into the bee pupa culture cups of each treatment group and control group, and sealing the cup rims of the bee pupa culture cups with ventilated transparent films to prevent the introduced varroa jacobsoni from escaping the bee pupa culture cups; putting the bee pupa culture cups into an incubator for culturing, wherein the temperature is 34.5 DEG C, and the relative humidity is 75%; counting the deaths of varroa jacobsoni 48h or 72h later, calculating the death rate and analyzing the acute toxicity of the drug against varroa jacobsoni; or continuously recording the survival conditions of the varroa jacobsoni every day, counting the survival time of each varroa jacobsoni, and analyzing the chronic toxicity of the drug against varroa jacobsoni. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of controllable experiment conditions, high survival rate of the varroa jacobsoni, long survival time and accurate and credible result.
Owner:BEE RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
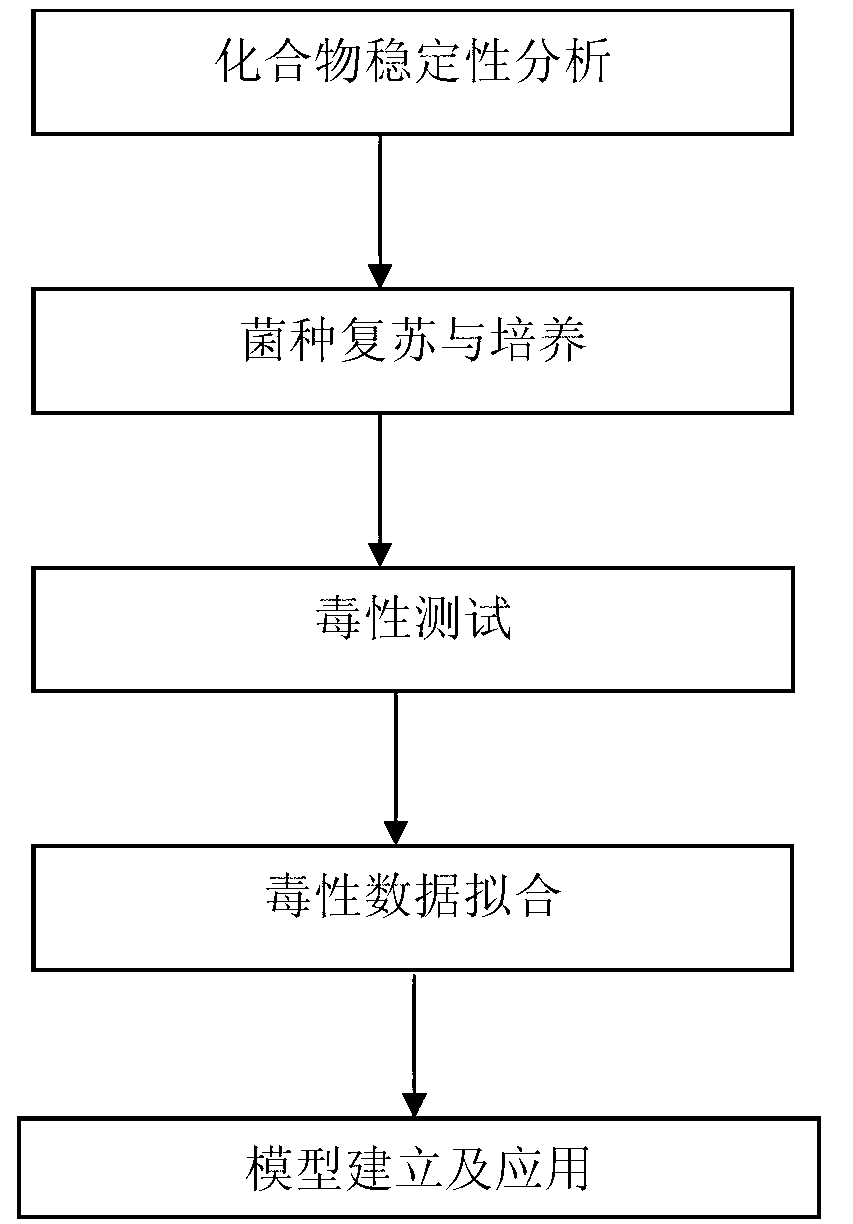
Method of establishing Hormesis dose-effect fitting model
InactiveCN103014116ASimple initializationEasy to initializeMicrobiological testing/measurementAcute toxicity testingHypothesis
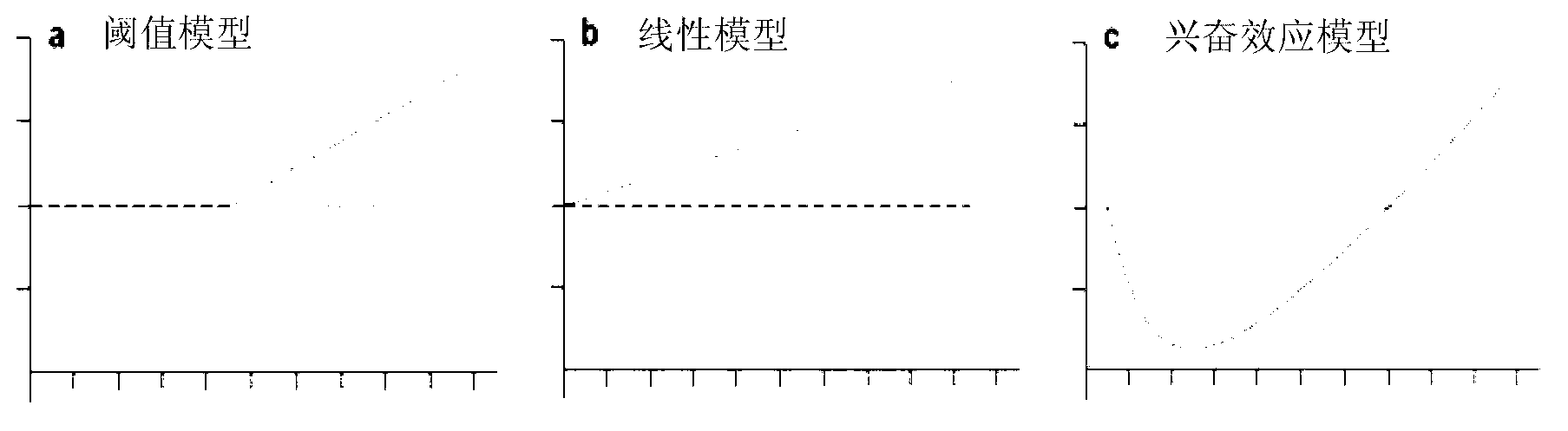
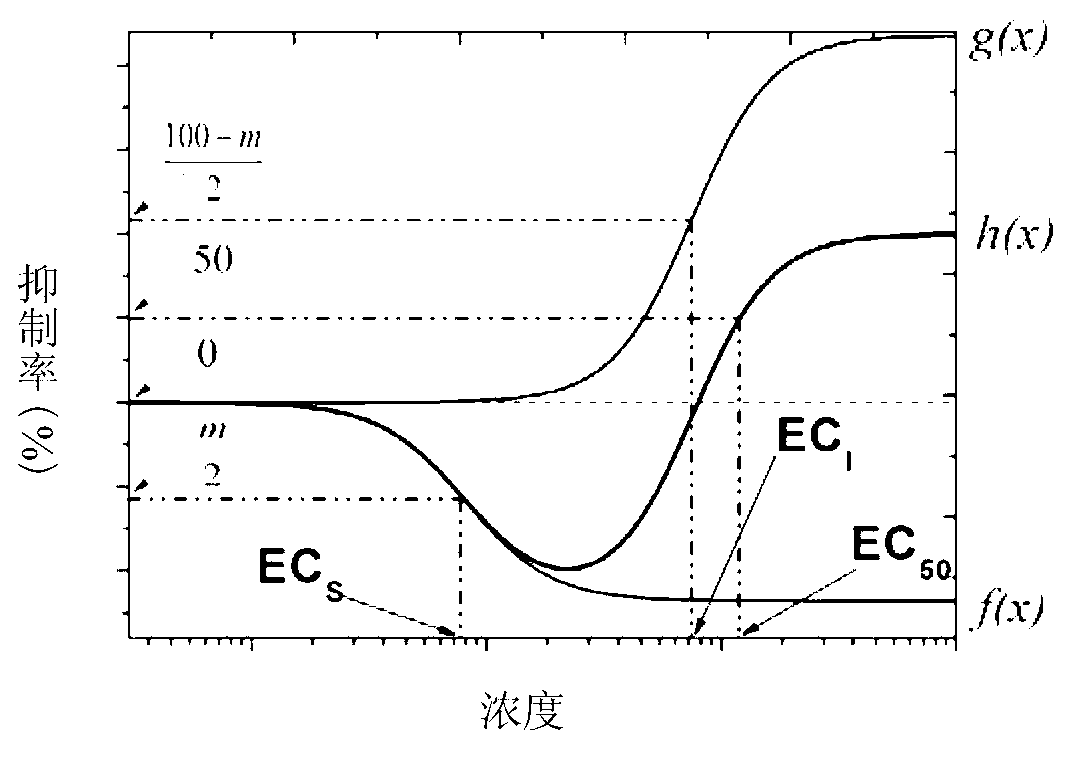
The invention belongs to the field of environment pollution detection technology and relates to a method of establishing a Hormesis dose-effect fitting model, namely a Bilogistic model. The method comprises the following steps: (1) analyzing the stability of a compound; (2) recovering and culturing strains; (3) conducting toxicity test including acute toxicity test and chronic toxicity test; (4) calculating the inhibition ratio of the compound analyzed in the step (1) to the strains recovered and cultured in the step (2) by applying the experiment result obtained in the step (3), and conducting toxicity representation by taking inhibition ratio as an index; and (5) fitting the toxicity data to obtain the Bilogistic model. The data fitting is more convenient through the model; parameters in the model are initialized simply; the model is established based on a receptor mechanism hypothesis, thereby having great biological significance; good fitting can be conducted under the condition of high stimulatory effect; the Hormesis effect can be effectively guided to the application in the drug design.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Growth effect and acute and chronic toxicity detection method of luminous bacteria
InactiveCN110441292AAvoiding Ignoring Delayed Toxicity of Test SubstancesThe detection effect is comprehensive and accurateChemiluminescene/bioluminescencePreparing sample for investigationBiotechnologyLuminescent bacteria
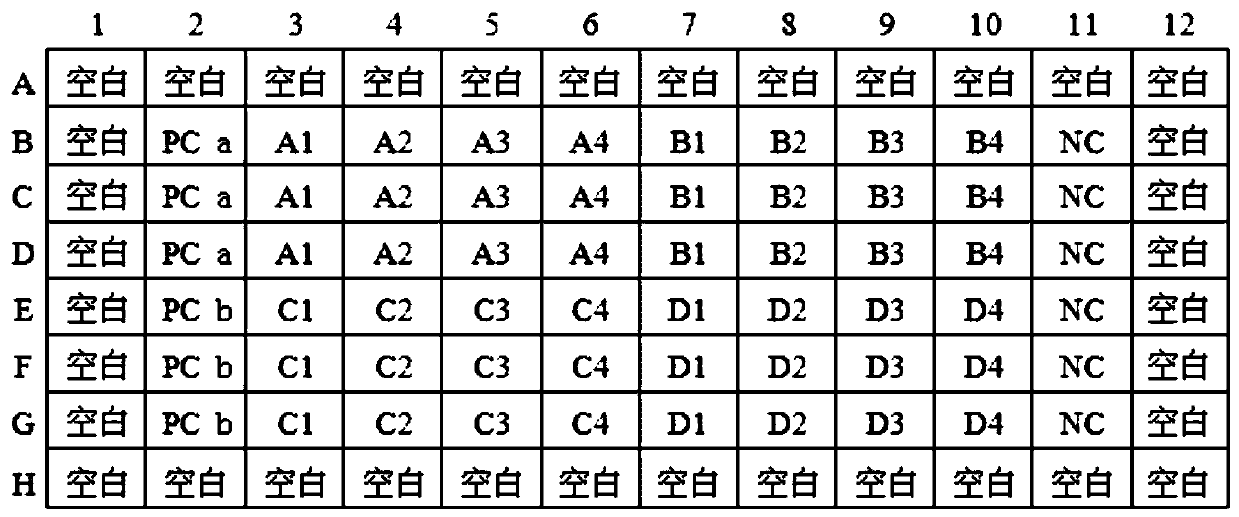
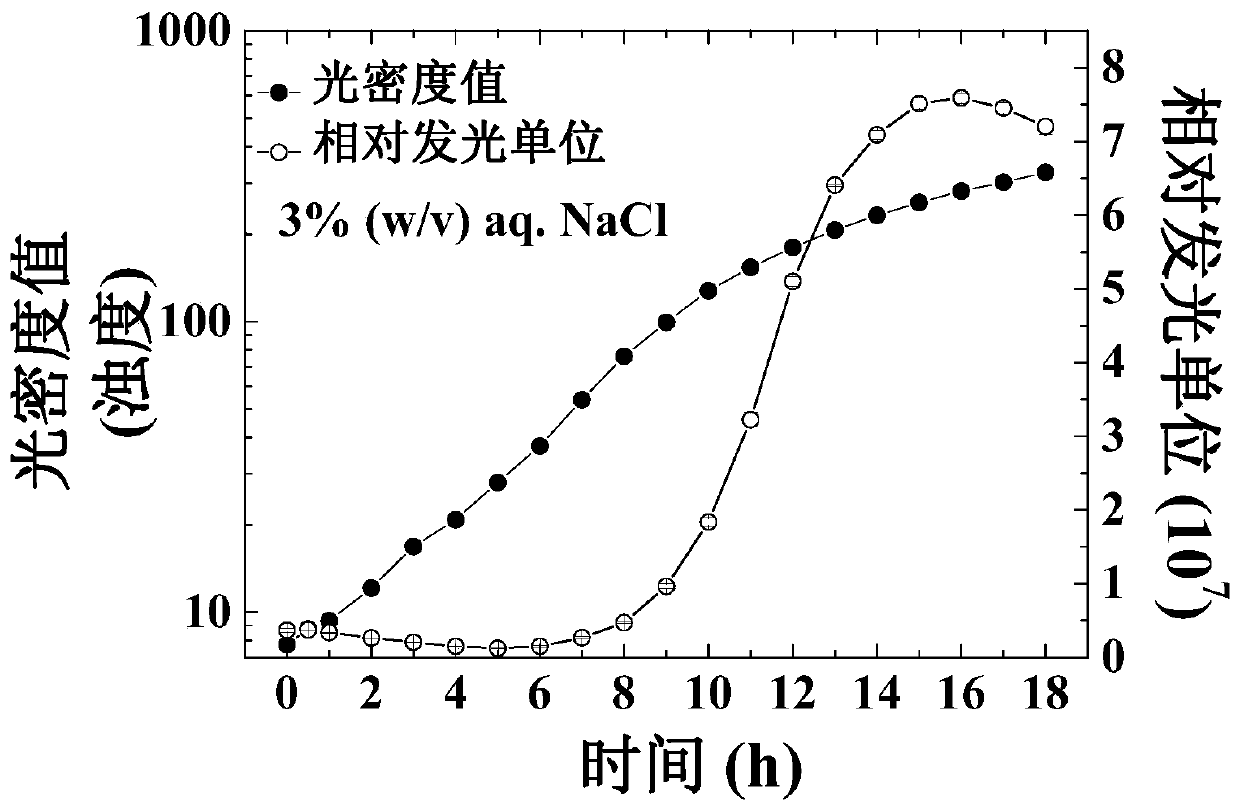
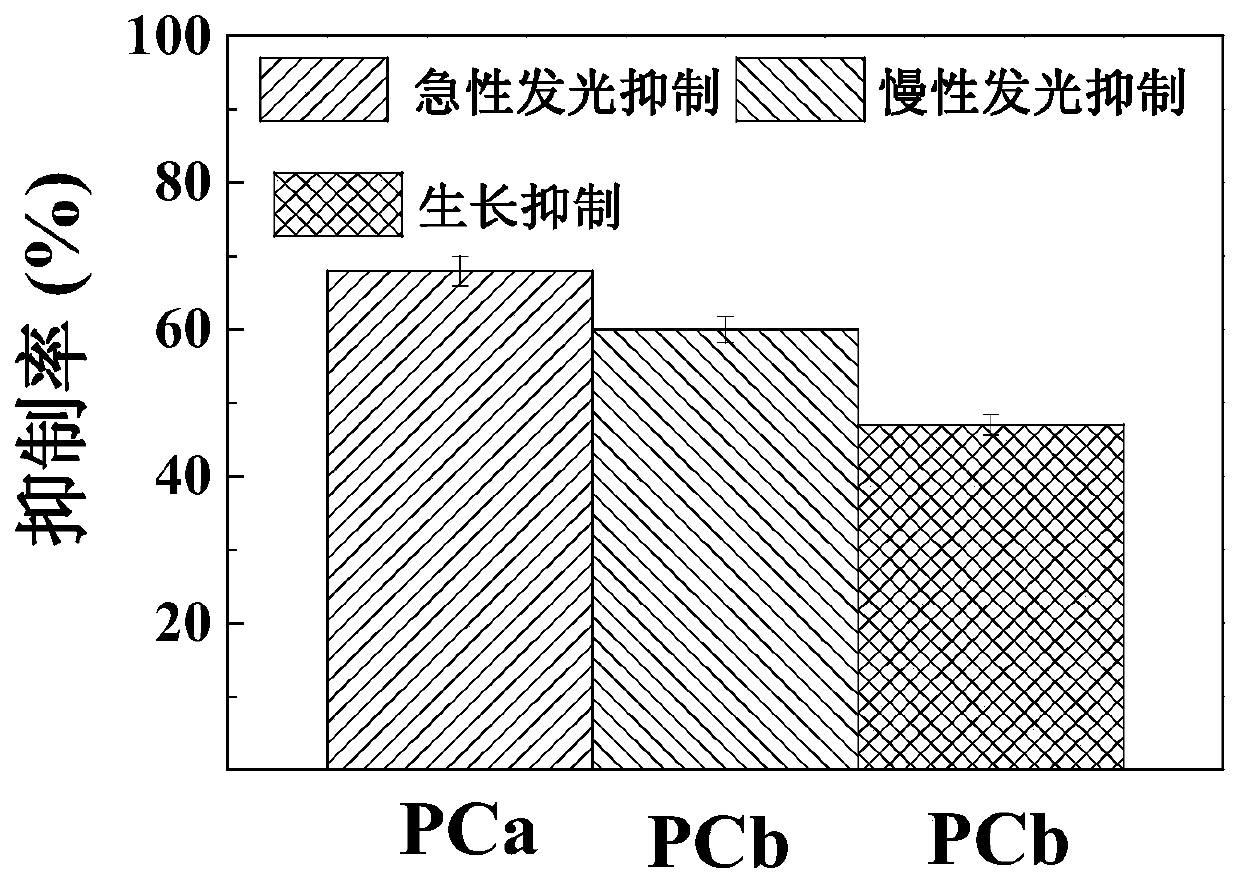
The invention discloses a growth effect and acute and chronic toxicity detection method of luminous bacteria. The method comprises the steps of: preparing an experiment sample, a negative control sample and a positive control sample; preparing a luminous bacteria solution; adding the luminous bacteria solution into a 96-pore cell culture board, then placing the 96-pore cell culture board on a microplate reader, and measuring an initial optical density value and an initial bioluminescence value 30 minutes later; adding the experiment sample, the negative control sample and the positive controlsample into the luminous bacteria solution, measuring the optical density value and the bioluminescence value every 30 minutes within the first 1 hour, and then measuring the optical density value and the bioluminescence value every 1h, and performing the test for not less than 24h; obtaining an optical density mutation time and a bioluminescence mutation time; and calculating an acute luminescence inhibition rate, a chronic luminescence inhibition rate and a growth inhibition rate. The growth effect and acute and chronic toxicity detection method disclosed by the invention can be used for simultaneously evaluating the growth effect, and acute and chronic toxic effects of a test substance on the luminous bacteria, the accuracy is high, high throughput of the toxicity test is achieved, andthe test efficiency is high.
Owner:NANJING COLLEGE OF INFORMATION TECH
Marine fish water ecology toxicity test method
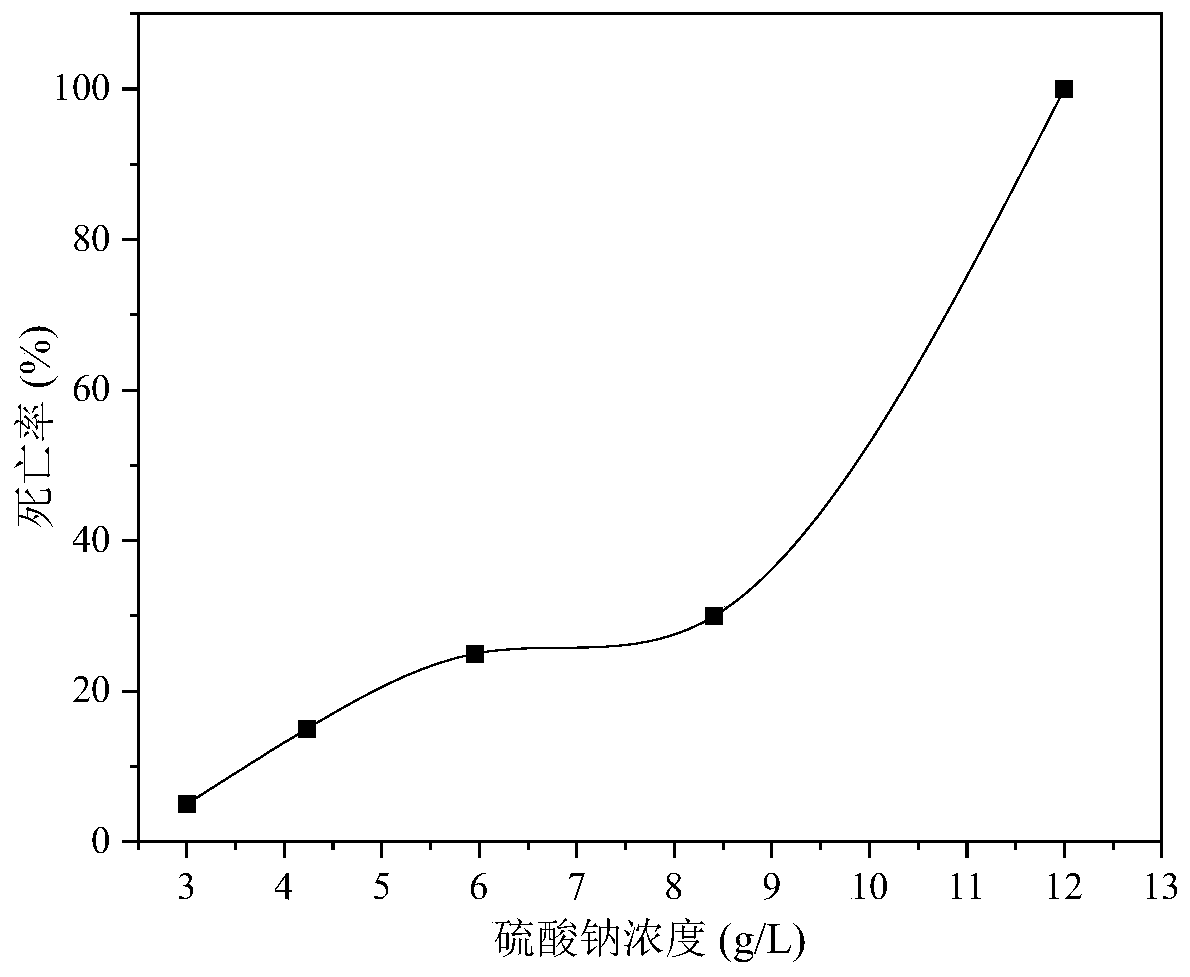
The invention discloses a marine fish water ecology toxicity test method. The method comprises the following steps of selecting gobies as tested fish species and domesticating in standard water which has a same water quality condition as a tested water sample; preparing a stock solution of the water sample to be tested; selecting a concentration gradient range through acute toxicity and chronic toxicity trial tests of the gobies, setting a concentration gradient with a small difference, taking sea water as a contrast group, and taking the water sample to be tested as a test group; simultaneously, carrying out acute toxicity and chronic toxicity tests of the gobies, recording changes in the gobies and the environment, carrying out variance analysis on data, and drawing a mortality curve of the gobies; and determining water quality toxicity through combining a physical condition of the gobies and water body index changes. Problems that current domestic research on a fish toxicity test is relatively simple, and there is aquatic ecotoxicity test method suitable for a salt-containing condition are solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
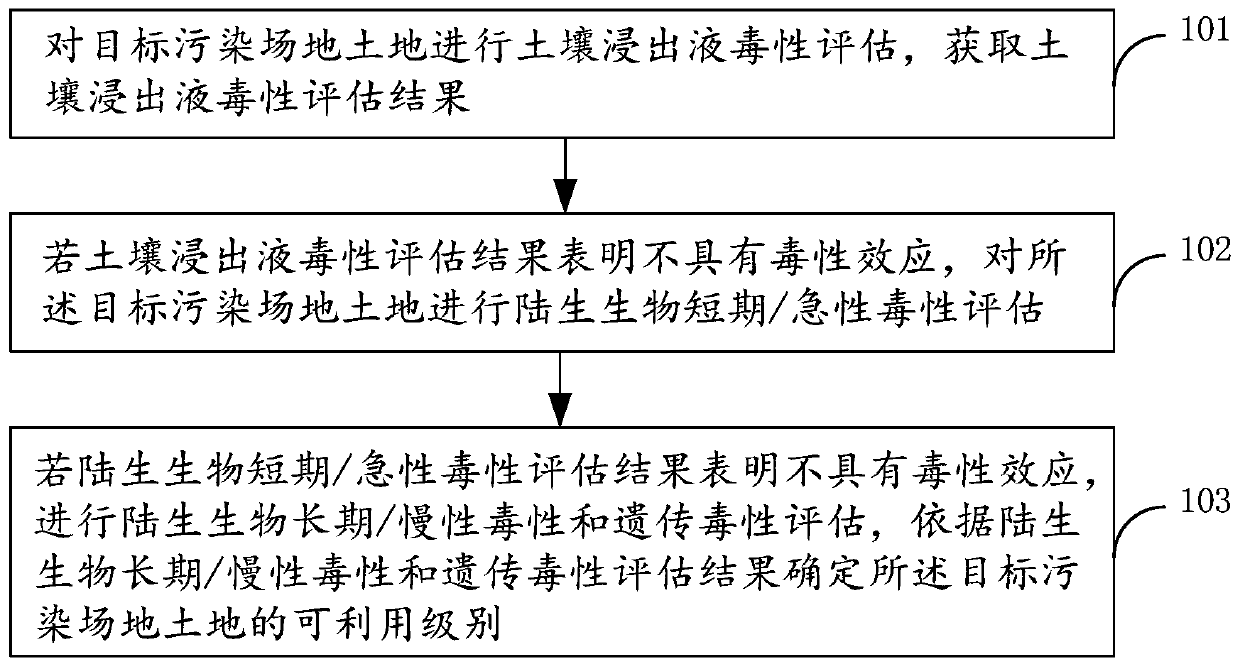
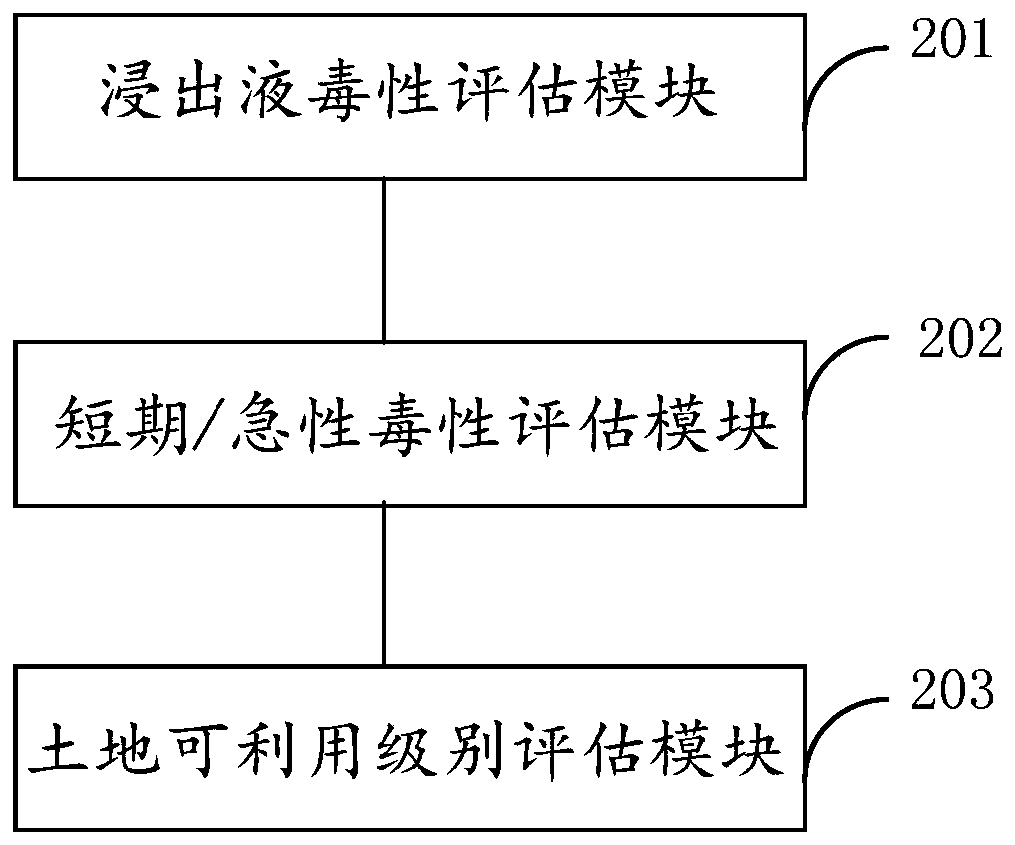
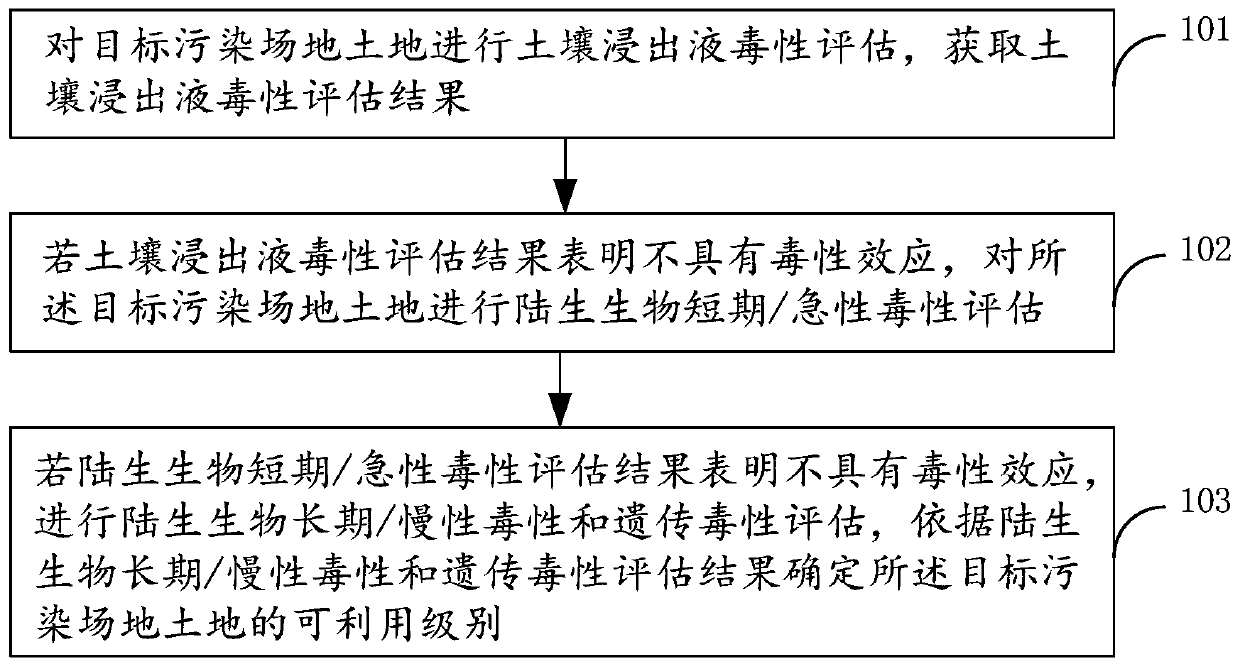
Method and apparatus for evaluating land reuse at contaminated site
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and apparatus for evaluating land reuse at a contaminated site. The method comprises the following steps that: the toxicity of soil leachate of the land at a target contaminated site is evaluated and a soil leachate toxicity evaluation result is obtained; if the soil leachate toxicity evaluation result shows that the land has no toxic effect, terrestrial organism short-term / acute toxicity evaluation is carried out on the land at the target contaminated site; and if the terrestrial organism short-term / acute toxicity evaluation result shows thatthe land has no toxic effect, terrestrial organism long-term / chronic toxicity and genotoxicity evaluation is carried out and an availability level of the land at the target contaminated site is determined based on the terrestrial organism long-term / chronic toxicity and genotoxicity evaluation results. Therefore, the accuracy of the reusable type of the land at the contaminated site is improved.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Marine crustacean water ecological toxicity test method
The present invention discloses a marine crustacean water ecological toxicity test method. The method comprises: selecting the mysis stage as a tested crustacean, and taming the mysis stage in standard water with the same water quality as a tested water sample; preparing to-be-tested water sample reserve liquid; by performing acute toxicity and chronic toxicity pre-tests of the mysis stage, respectively selecting a concentration gradient range, and setting the concentration gradient with a small gap; taking the seawater as a comparison group, and the to-be-tested water sample as a test group,and simultaneously performing acute toxicity and chronic toxicity tests of the mysis stage, recording the change of the mysis stage and the environment, performing variance analysis on the data, and drawing a mortality curve of the mysis stage; and in combination of the signs of the mysis stage and the change of water indicators, determining the water toxicity. According to the method provided bythe present invention, the defect that there is no water ecological toxicity test method applicable to salty conditions in the prior art is overcome, and formulating national standards for marine sewage discharge can be facilitated.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
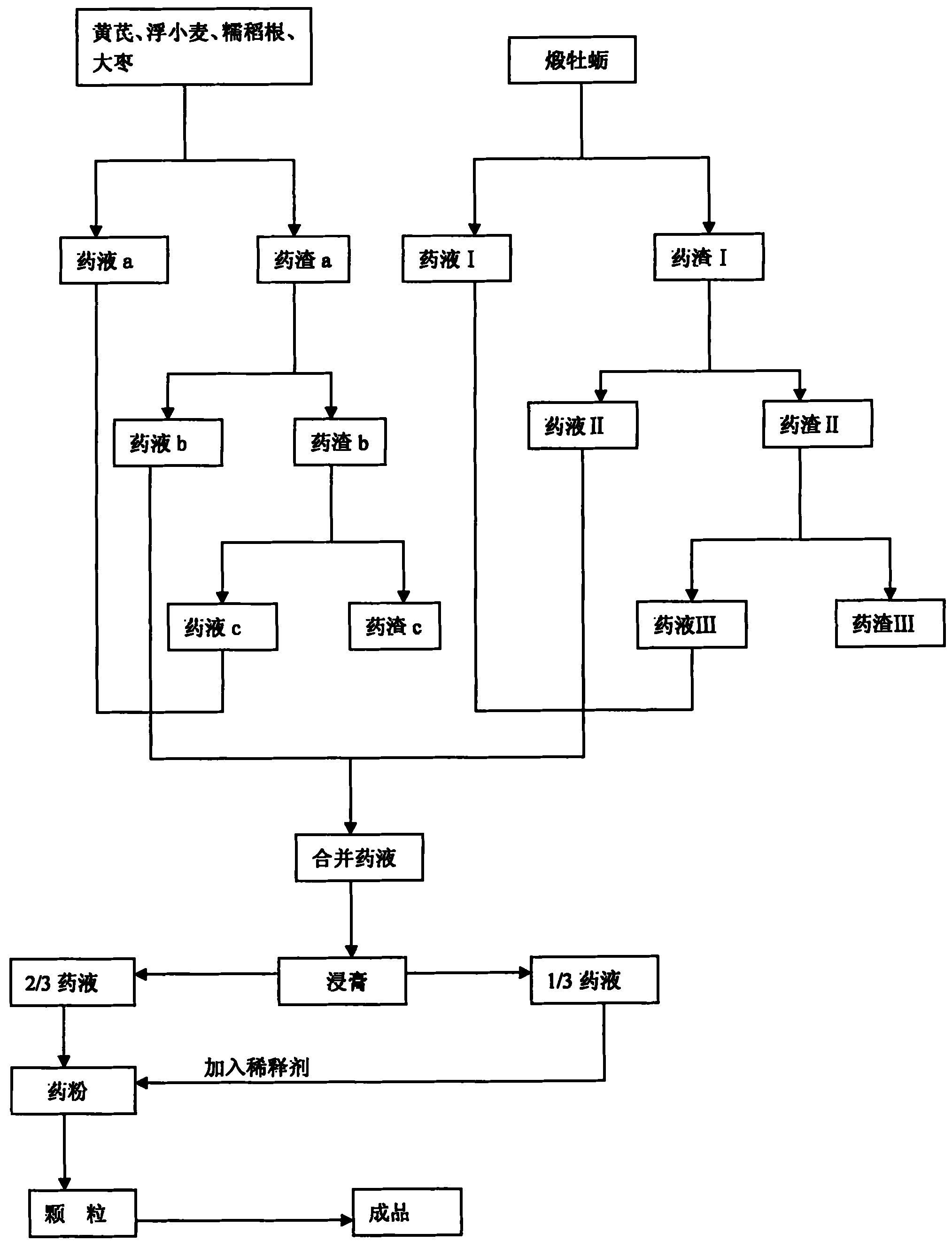
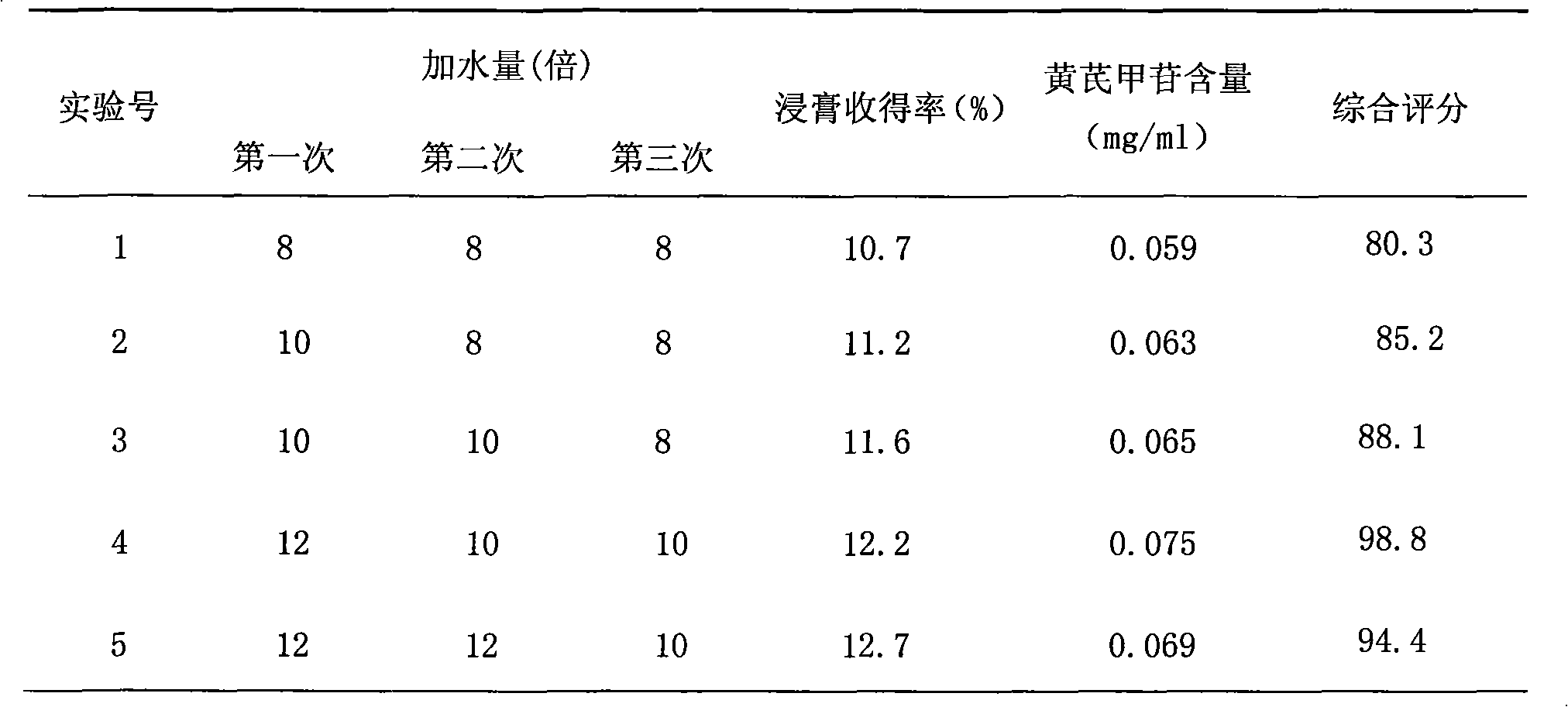
Chinese medicinal preparation for treating spontaneous sweating and night sweat
InactiveCN101884745AEffective treatmentEffective in treating spontaneous sweatingDrug compositionsCapsule deliveryOysterChronic toxicity testing
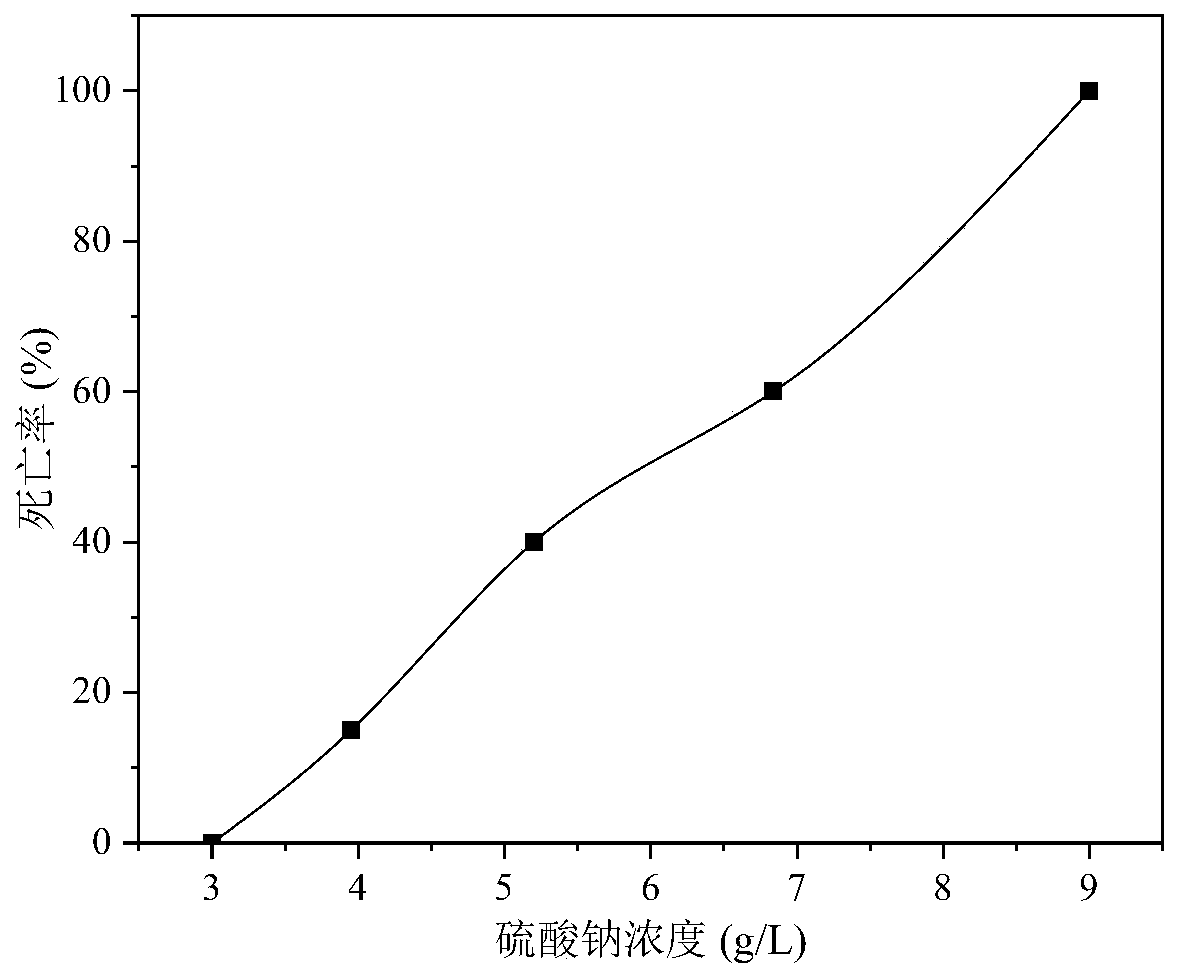
The invention discloses a Chinese medicinal preparation for treating spontaneous sweating and night sweat, which consists of the following raw material medicaments in part by weight: 9 to 15 parts of astragalus, 16 to 22 parts of blighted wheat, 9 to 15 parts of Chinese date, 16 to 22 parts of glutinosae rice root and 35 to 41 parts of calcined oyster shell. The Chinese medicinal preparation has the advantages that 1, Chinese medicinal raw materials selected by the invention accord with Provisions of Pharmaceutical Administration Law of the People's Republic of China, the Chinese medicinal preparation treats the spontaneous sweating and the night sweat by utilizing the synthetic effect of each traditional Chinese medicine, and has no toxicity and harm to human bodies; acute and chronic toxicity experiments of animals prove that experimental animals have no toxicity reactions, and the main visceral organs of the experimental animals are not changed obviously, and the Chinese medicinal preparation is safe and reliable; and 2, the Chinese medicinal preparation can effectively treat the spontaneous sweating and the night sweat, has the good function of preventing the spontaneous sweating and the night sweat, and is convenient to administrate.
Owner:王幺光
Method for predicting combined chronic toxicity of antibiotic pollutant
InactiveCN102435599BLarge predicted throughputReduce investmentChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceFluorescence/phosphorescenceBinding energyApplicability domain
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
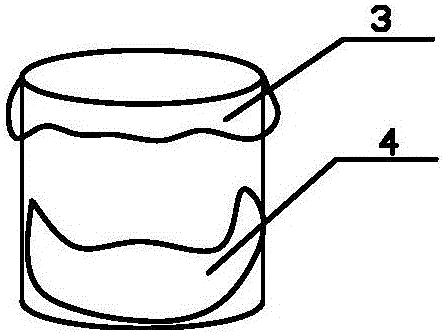
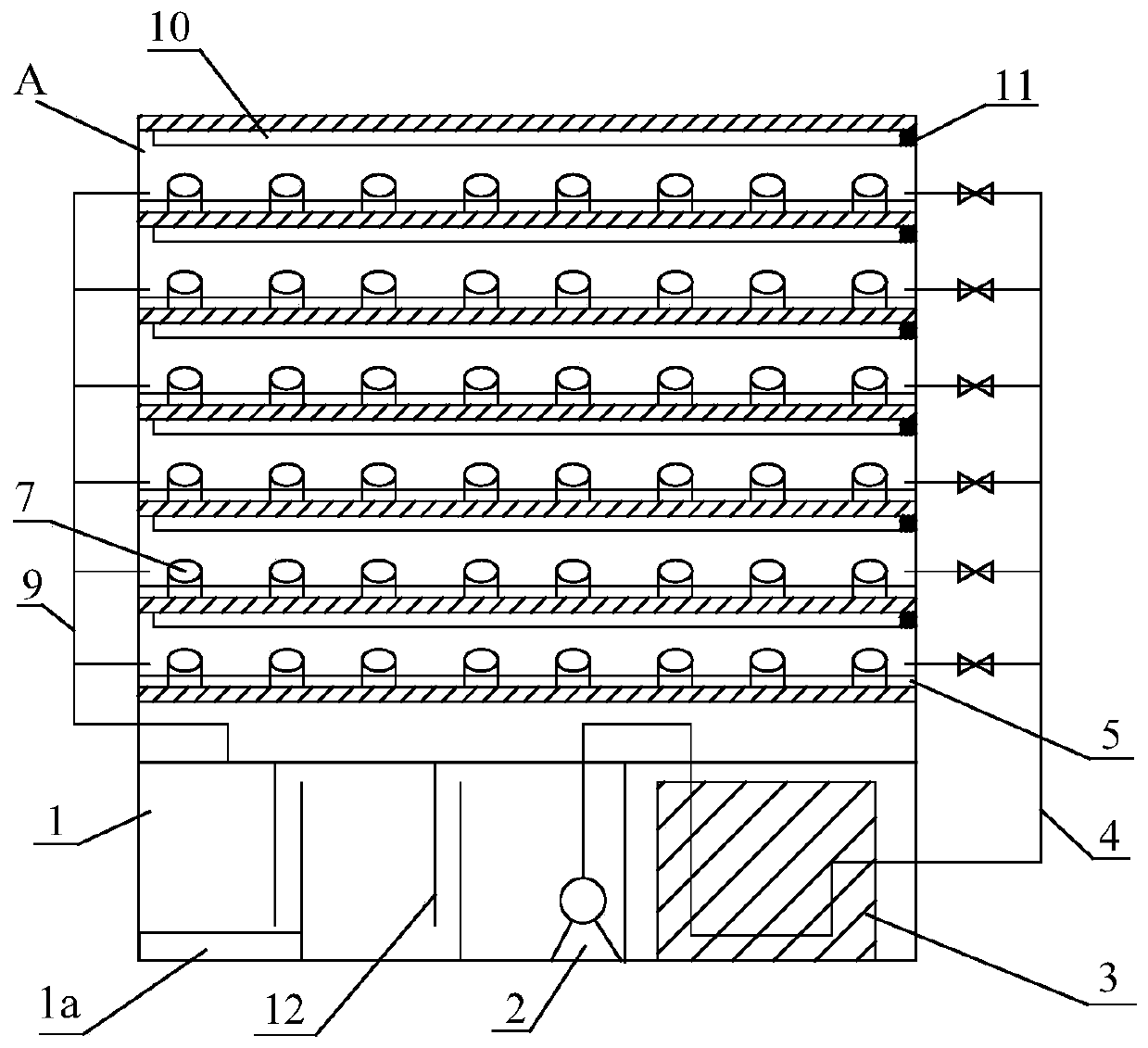
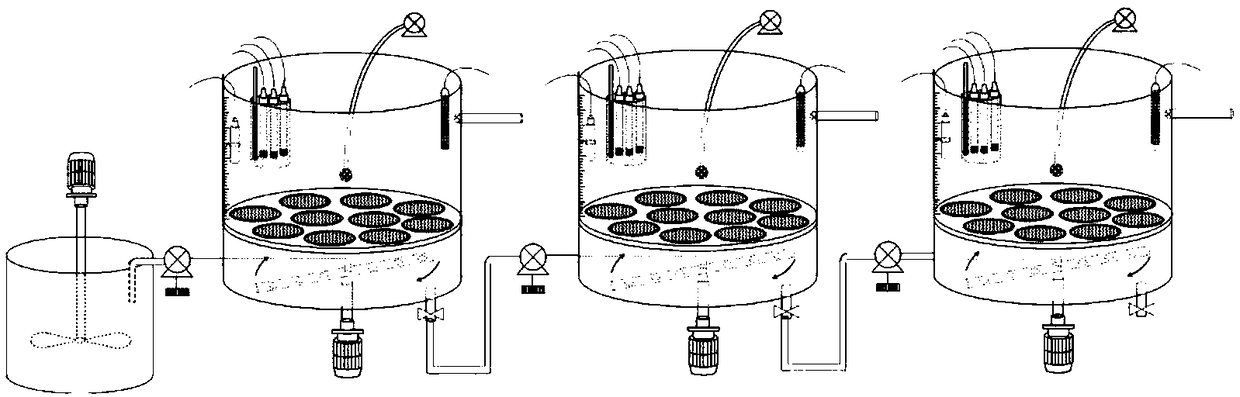
Temperature-controlled water ecological chronic toxicity testing device
InactiveCN110208517AAvoid errorsMeet various requirements of test temperatureBiological testingWater bathsTemperature control
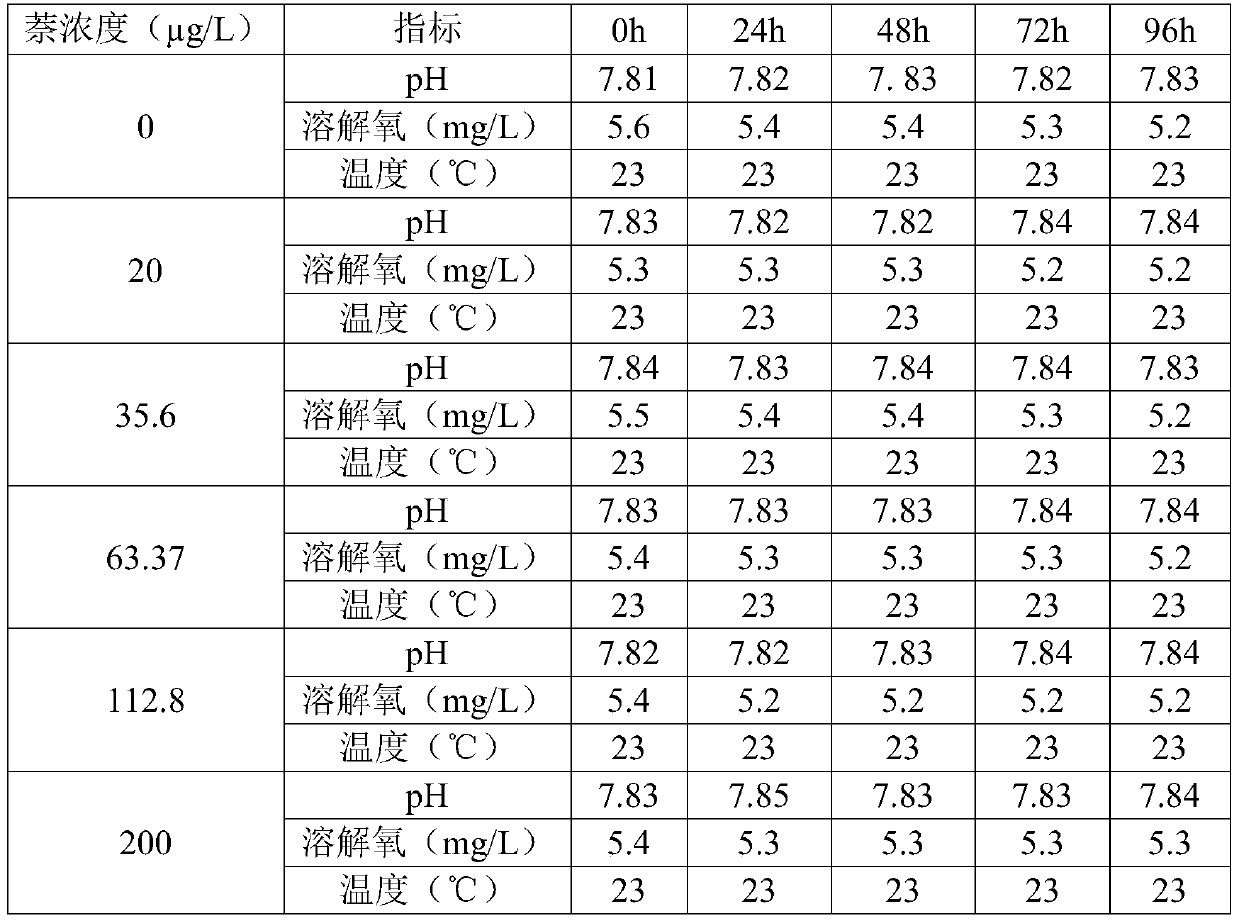
The invention relates to a temperature-controlled water ecological chronic toxicity testing device, which comprises a support. A water storage tank and a plurality of constant temperature water bath tanks are placed on the support from top to bottom; the water storage tank is internally provided with a water pump and a constant temperature water bath controller connected with the water pump; eachlayer of constant temperature water bath tank is internally provided with a plurality of testing cylinders; an upper water pipe is connected between one side of the constant temperature water bath tank and the constant temperature water bath controller; the other side of the constant temperature water bath tank is provided with an overflow port; a lower water pipe is connected between the overflowport and the water storage tank; an illumination pipe and an illumination adjuster are arranged above each row of test cylinders; a test cylinder fixing device is mounted in the constant temperaturewater bath tank; the test cylinder fixing device is composed of a horizontal plate and a plurality of round holes opened in the horizontal plate; and the test cylinder is placed in the round hole. Thetemperature of all test cylinders during the test process can be ensured to be completely the same, and errors brought to the test by external factors can be avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
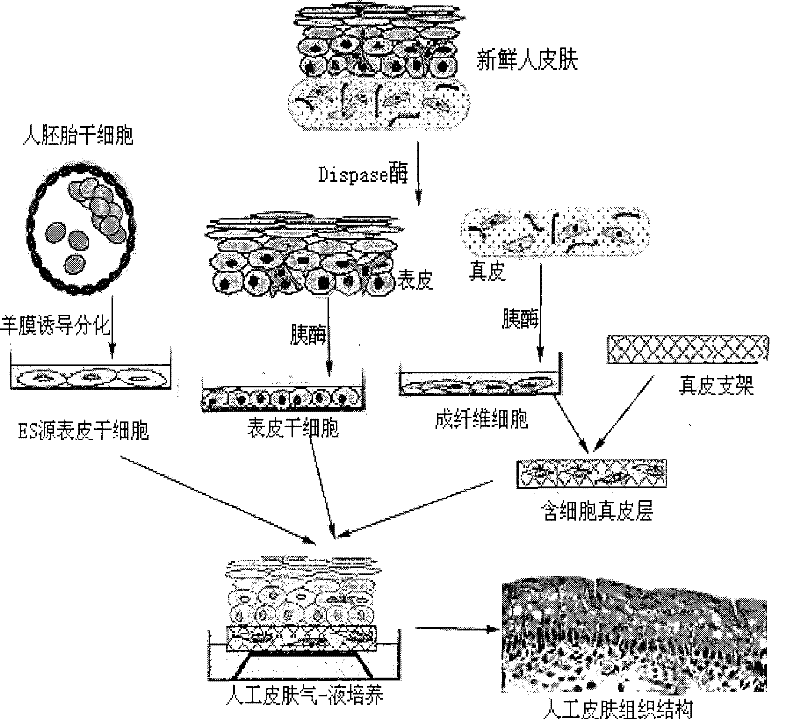
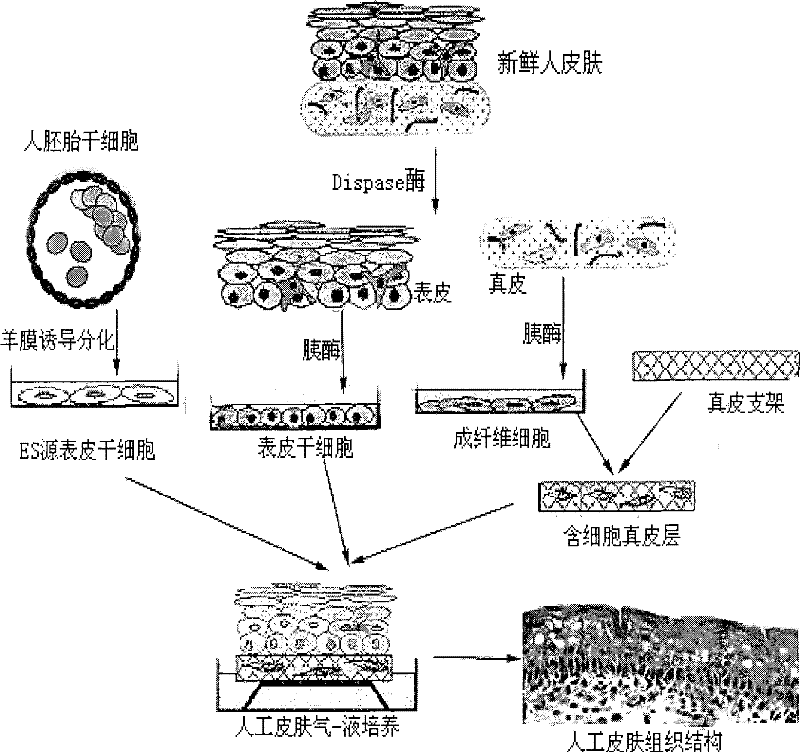
Method for preparing full-thickness skin for toxicity test by stem cell raft type cultivation
InactiveCN101352586BStrong ability to divide and proliferateMorphological integrityArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsChronic toxicity testingSkin toxicity
The invention relates to a method for preparing full-thickness skin used in toxicity testing by adopting stem cell raft culture, which comprises: 1. preparing and modifying a polymeric dermal scaffold; 2. preparing epidermal stem cells from embryonic stem cells and skin tissues; 3. preparing pancreatic islet cells; 4. preparing a special medium for the full-thickness skin; 5. and constructing the full-thickness skin. By utilizing the characteristics of strong differentiation and proliferation capacity of the epidermal stem cell, the skin morphology, organizational structure and functional activity of the constructed full-thickness skin of the invention can meet the demands of sub-chronic toxicity testing; the synthetic scaffold material has high degree of standardization and small batch-to-batch variation; as a serum free medium is adopted through the skin construction process, the factors influencing tissue construction are reduced, thus providing a foundation for the future use in toxicity testing. The all-thickness skin prepared by the method of the invention is closer to a natural skin, the application of which in the mode of toxicity testing and detection index agrees with practical situation better, thus being able to replace animals to be directly applied to the skin toxicity testing of chemicals, cosmetics, medicines and other health-related products.
Owner:程树军 +1
High-efficiency pesticide comprising bifenthrin, flubendiamide, dinotefuran and spinetoram
InactiveCN105519564ASynergistic effect is obviousReduce pollutionBiocideAnimal repellantsHomopteraFlubendiamide
The invention relates a high-efficiency pesticide composition used for killing agricultural pests. The high-efficiency pesticide composition is composed of the components of, by weigh, 10-40 parts of bifenthrin, 10-50 parts of flubendiamide, 20-40 parts of dinotefuran and 20-40 parts of spinetoram. The pesticide composition provided by the invention has a significant synergistic effect, such that a pesticidal spectrum is broad, effective component doses can be effectively reduced, and application cost can be reduced; with the pesticide, pest drug resistance can be retarded, and environmental pollution and pesticide residue can be effectively reduced. The pesticide causes no phytotoxicity, and has low toxicity and no chronic toxicity to human and mammals. The pesticide has significant effects against paddy rice stem borers and leaf rollers, and homoptera piercing-sucking mouthpart pests which are mainly plant hoppers, aphids and mites.
Owner:QINGDAO KANGHE FOOD
Method for efficiently and safely putting in deratting poison baits
The invention belongs to the technical field of deratting and discloses a method for efficiently and safely putting in deratting poison baits. The method comprises the following specific steps of filling the poison baits into a plastic bag; packaging the plastic bag; and after piercing the plastic bag to form small holes, directly putting in the plastic bag to use the deratting poison baits. According to the invention, the plastic bag is utilized to package the poison baits, so that freshness retaining time of the poison baits is prolonged, the poison baits are prevented from being flushed by rainwater, being lost and the like, and pollution of a rodenticide to the environment is reduced; storage time of the poison baits in the field is prolonged, mice can repeatedly eat poison baits for a small quantity, chronic toxicity of an anticoagulant is sufficiently played, prevention and treatment effects of efficiently and safely putting in the deratting poison baits is better than that of directly and nakedly putting in the baits, and killing efficiency is improved by 20 percent; the contact opportunity of nontarget organisms and the rodenticide is reduced and safety of the nontarget organisms is ensured; and odor of the poison baits in the bag can be emitted through the small holes, so that an attractive force for the mice is improved.
Owner:PLANT PROTECTION RES INST OF GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Hibiscus paste with anti-inflammatory effect
InactiveCN107029072ACompatibility with science and rigorUnique formulaAntibacterial agentsHydroxy compound active ingredientsDiseaseAcute toxicity testing
The invention discloses hibiscus paste with an anti-inflammatory effect and belongs to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicines. The hibiscus paste is prepared by the following materials in parts by weight: 10-20 part of cottonrose hibiscus, 10-20 parts of gamboge, 10-15 parts of arisaema erubescens, 6-12 parts of borneol, 5-12 parts of mint oil and 120-200 parts of vaseline. The hibiscus paste disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the compatibility is scientific and rigorous, the formula is unique, the manufacturing process is simple, convenient and easy, the advantage of 'multi-target action' of external use of traditional Chinese medicines is fully played, and the curative effect for multiple infectious and noninfectious diseases is unique; and the hibiscus paste can be applied to bacterial inflammations and non-bacterial inflammations, combination of acute inflammations and chronic inflammations, and symptoms such as acute toxicity and chronic toxicity, superficial infection and deep infection and local toxicity and general toxicity reaction.
Owner:江斌
Exposure device used for researching chronic toxicity of polluted sediments for fishes
PendingCN109307746AAchieve direct exposureAchieve indirect exposurePreparing sample for investigationGlass fiberAdsorption equilibrium
The invention discloses an exposure device used for researching the chronic toxicity of polluted sediments for fishes, and belongs to the field of aquatic organism toxicity detection. The device mainly comprises an exposure container and a sediment pre-balancing container, wherein sediments are fully mixed with a target pollutant in the pre-balancing container to achieve adsorption balance, then,the mixture is input into a sediment stabilization chamber on the lower part of the exposure container, and is evenly dispersed through a rotary hollow conduit, and then, the mixture enters a tested organism exposure chamber on the upper part of the exposure container along with a bottom-up hydraulic function. The sediment stabilization chamber and the exposure chamber are separated through a waterproof clapboard, the clapboard can be provided with glass fiber filter screens or filter membranes of different apertures through an annular clamping plate so as to control the form of pollutants which enter the tested organism exposure chamber, and the adsorption states of particular matters of different particle sizes under a dissolved state can be distinguished. A turbidimeter or a suspended particulate matter measurement probe is installed on a lantern ring capable of vertically moving on the inner wall of the exposure chamber so as to be convenient in monitoring the concentration of particulate matters of different depths in the exposure chamber in real time.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for testing ecotoxicity of disinfection by-products
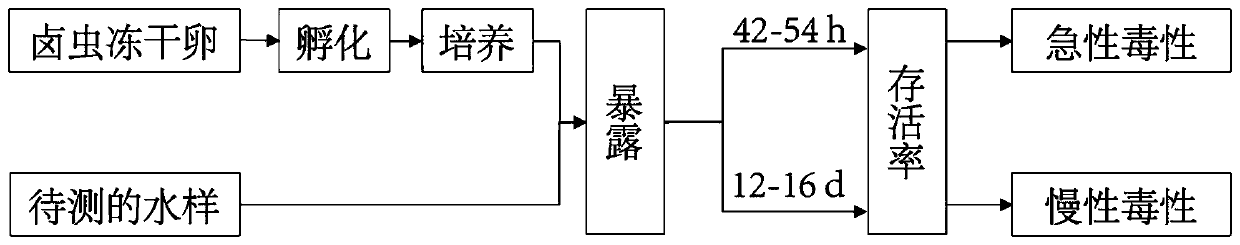
InactiveCN111289703AEasy to useImprove securityCompounds screening/testingTesting waterBiotechnologyArtemia sp.
The invention discloses a method for testing ecotoxicity of disinfection by-products, and the method comprises the following steps: incubating and culturing artemia to obtain second-instar artemia larvae; putting artemia larvae into a water sample containing disinfection by-products, and respectively obtaining the survival rate of the artemia larvae through acute toxicity and chronic toxicity exposure, so as to calculate the toxicity of the water sample to artemia. The method is wide in coverage and covers both acute toxicity and chronic toxicity, and a test water sample can be a single substance solution and an actual disinfection water sample; the used artemia is high in sensitivity, convenient to hatch and simple to culture; the raw materials are easy to obtain and low in price; the method has the advantages of low requirements on the culture environment, clear toxicity endpoint, and convenience in popularization in sewage and reuse water plants, and is a simple, sensitive and economic toxicity test method.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
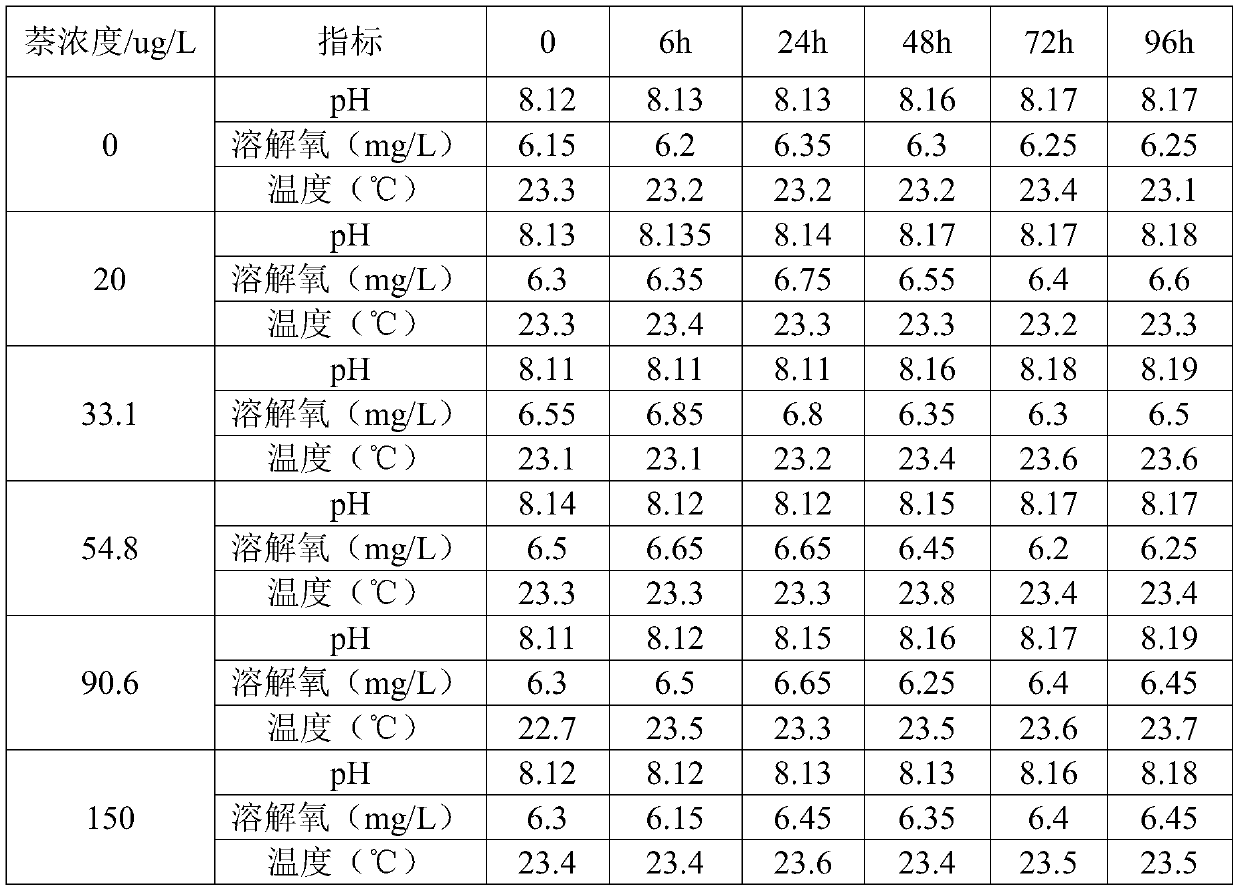
Method for detecting toxicity of 2,4-dinitrotoluene
ActiveCN108593397AEasy accessEasy to feedPreparing sample for investigationAcute toxicity testingMortality rate
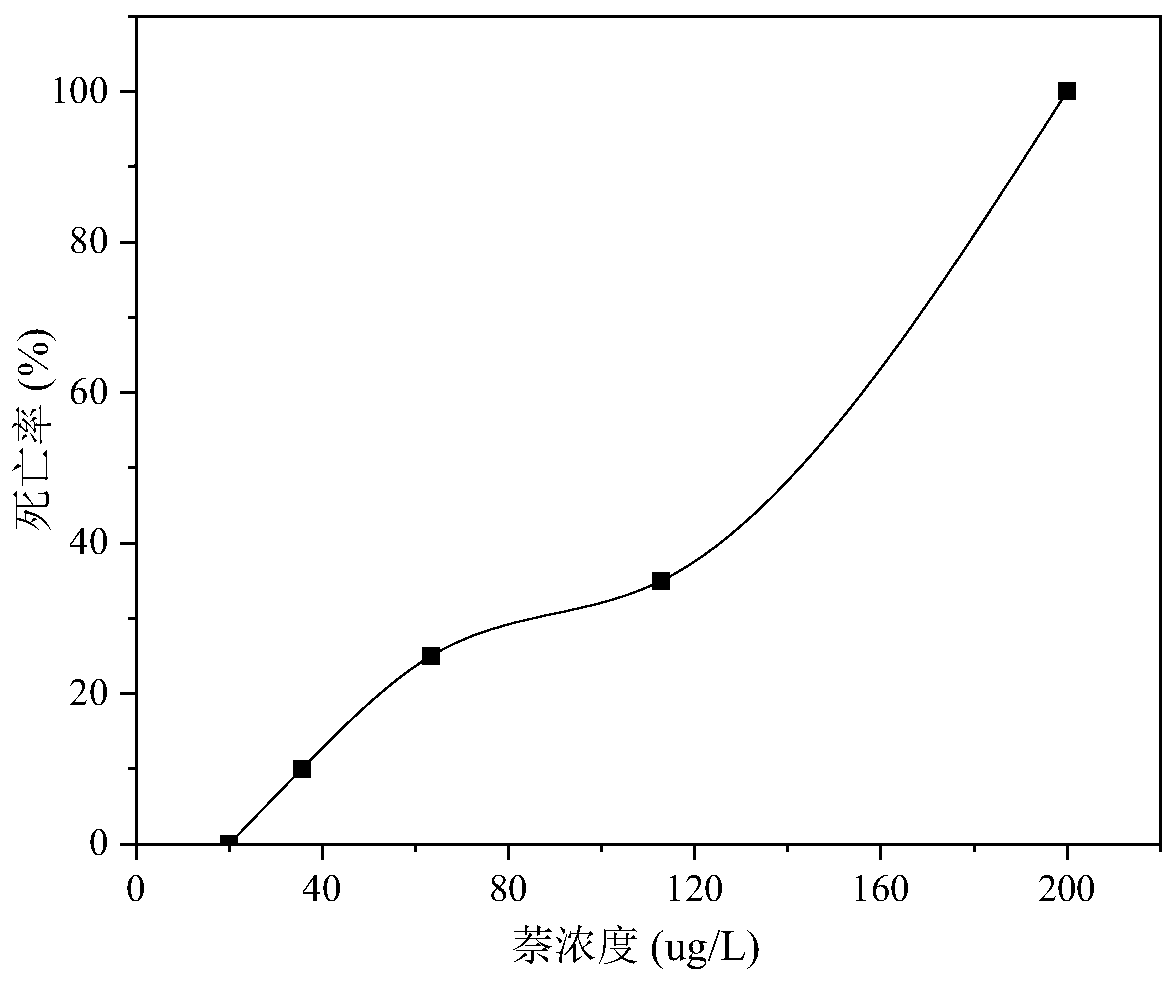
The invention discloses a method for detecting toxicity of 2,4-dinitrotoluene. The method comprises the following steps: preparing culture solutions containing different concentrations of 2,4-dinitrotoluene; respectively feeding the culture solutions containing different concentrations of 2,4-dinitrotoluene to zebrafish adult fish for 96 hours; carrying out multiple groups of acute exposure tests;recording death ratios of various groups of zebrafish and judging the acute toxicity effects of 2,4-dinitrotoluene on the zebrafish; respectively fishing the culture solutions containing the different concentrations of 2,4-dinitrotoluene to the zebrafish adult fish for 5 days; carrying out multiple groups of sublethal exposure tests; taking liver and ovary samples of the various groups of zebrafish and carrying out pathological observation; testing changes of lipid metabolism-related gene expression and oxygen respiratory regulation related gene expression of the various groups of zebrafish;and judging a chronic toxicity effect of 2,4-dinitrotoluene on the zebrafish. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the toxicity detection intuition property and accuracy of 2,4-dinitrotoluene are improved.
Owner:WUHAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
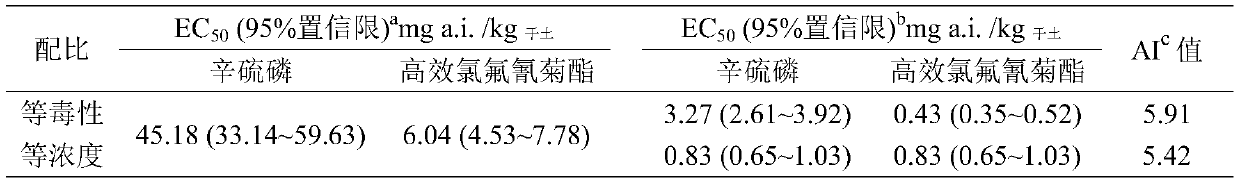
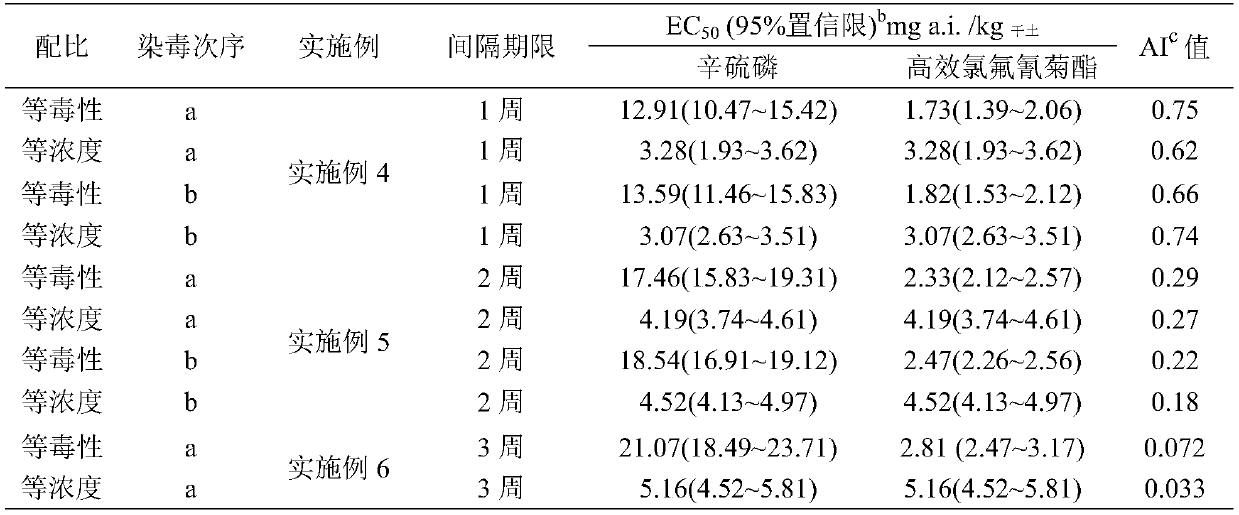
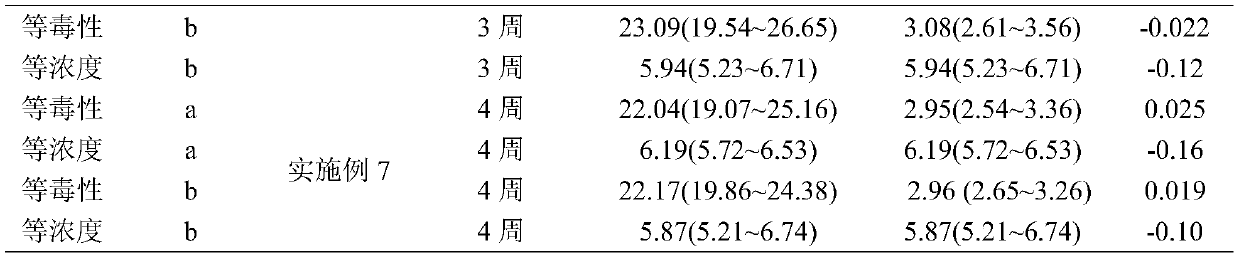
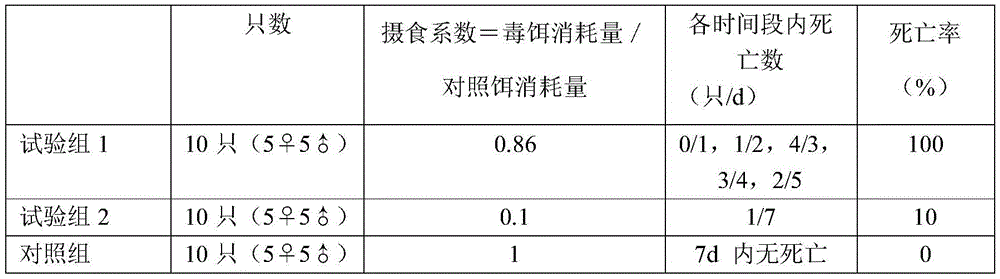
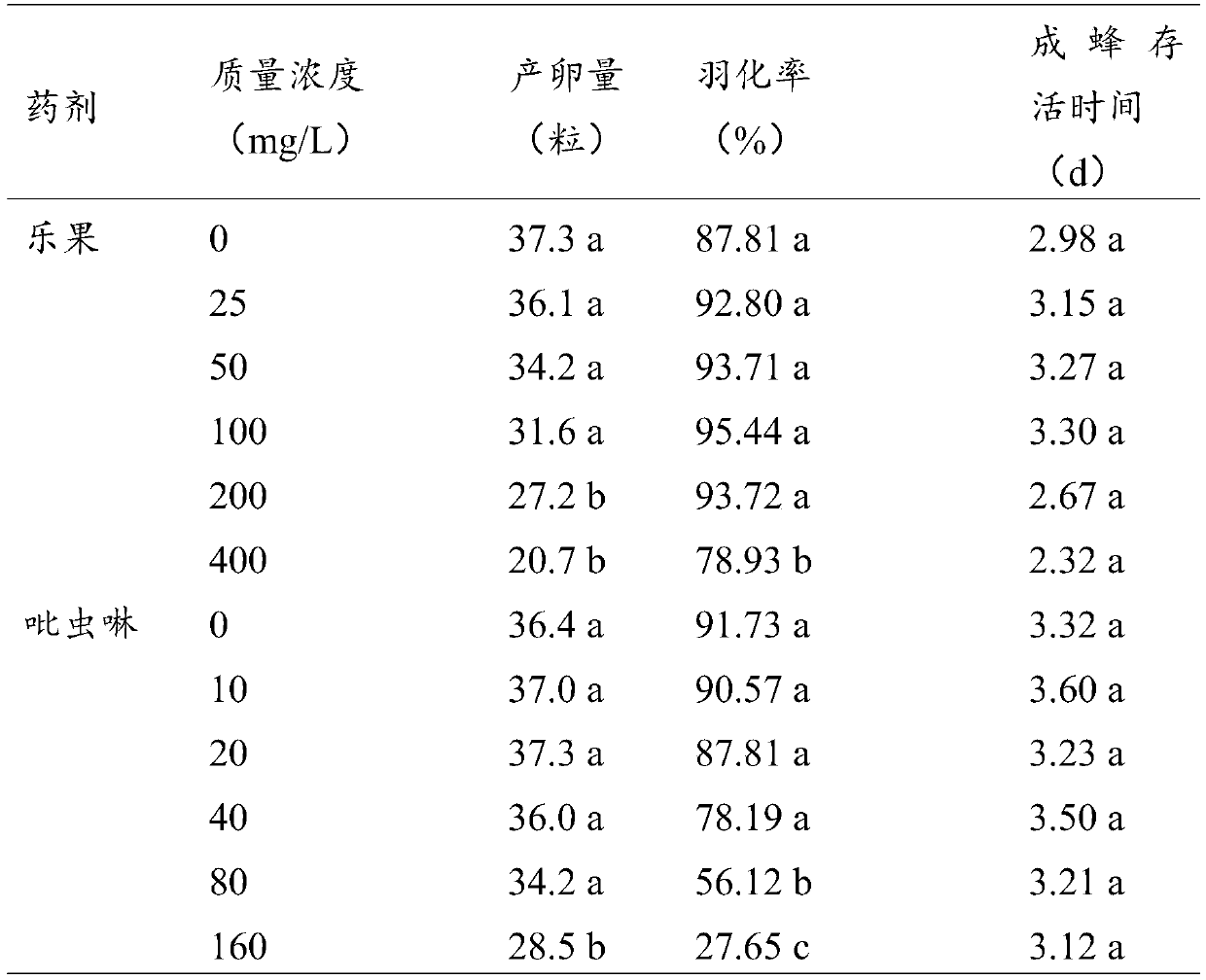
Application method of two insecticides
According to the invention, evaluation of earthworm propagation toxicity by combined exposure of phoxim and lambda-cyhalothrin is carried out; by researching the application isolation period, it is proposed that the two insecticides need to be applied in the same soil at intervals, the application dosage of phoxim is 1-50 g (effective components) / mu, the application dosage of lambda-cyhalothrin is0.1-20 g (effective components) / mu, and the application interval is not shorter than 1 week. Preferably, when phoxim is firstly applied to the same soil and then lambda-cyhalothrin is applied, the application interval is 3 weeks; when the lambda-cyhalothrin is applied firstly and then the phoxim is applied, the application interval is 2 weeks. According to the invention, a mixture of phoxim and lambda-cyhalothrin should be cautiously used in agricultural production; when phoxim and lambda-cyhalothrin are applied to the same soil, the application interval must be strictly carried out, andtherefore, adverse effects on the ecological environment are reduced, references are provided for research of combined exposure of other different kinds of pollutants on earthworm chronic toxicity tests and application intervals, and important scientific bases are also provided for monitoring, early warning and remediation treatment of soil combined pollution.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Medicament for preventing and controlling rodent damage and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104430324BReduced alertnessLow acute toxicityBiocideAnimal repellantsMonkshoodsAcute toxicity testing
The invention relates to a medicament capable of preventing and treating damages caused by rat and a preparation method of the medicament. The medicament comprises the following components in parts by weight: 1-10 parts of alkaloid microcapsules and 90-99 parts of auxiliary materials, wherein a capsule core of the alkaloid microcapsule comprises one or more of alkaloids extracted from wild aconite root, root of pendulous monkshood, datura stramonium, black false hellebore, lightyellow sophora root and nux vomica; and the capsule walls of the alkaloid microcapsules comprise polyurea prepared from polyamine and polyisocyanate. The alkaloid is covered by the alkaloid microcapsules so that the palatability is obviously improved and the speed of oxidizing and degrading the alkaloid in the environment is reduced. The swallowed alkaloid microcapsules can be slowly released in rats and the acute toxicity of the medicament is reduced; and the medicament mainly has chronic toxicity so that the alertness of the rats can be reduced and the damages to human and livestock, and rat natural enemies are alleviated.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
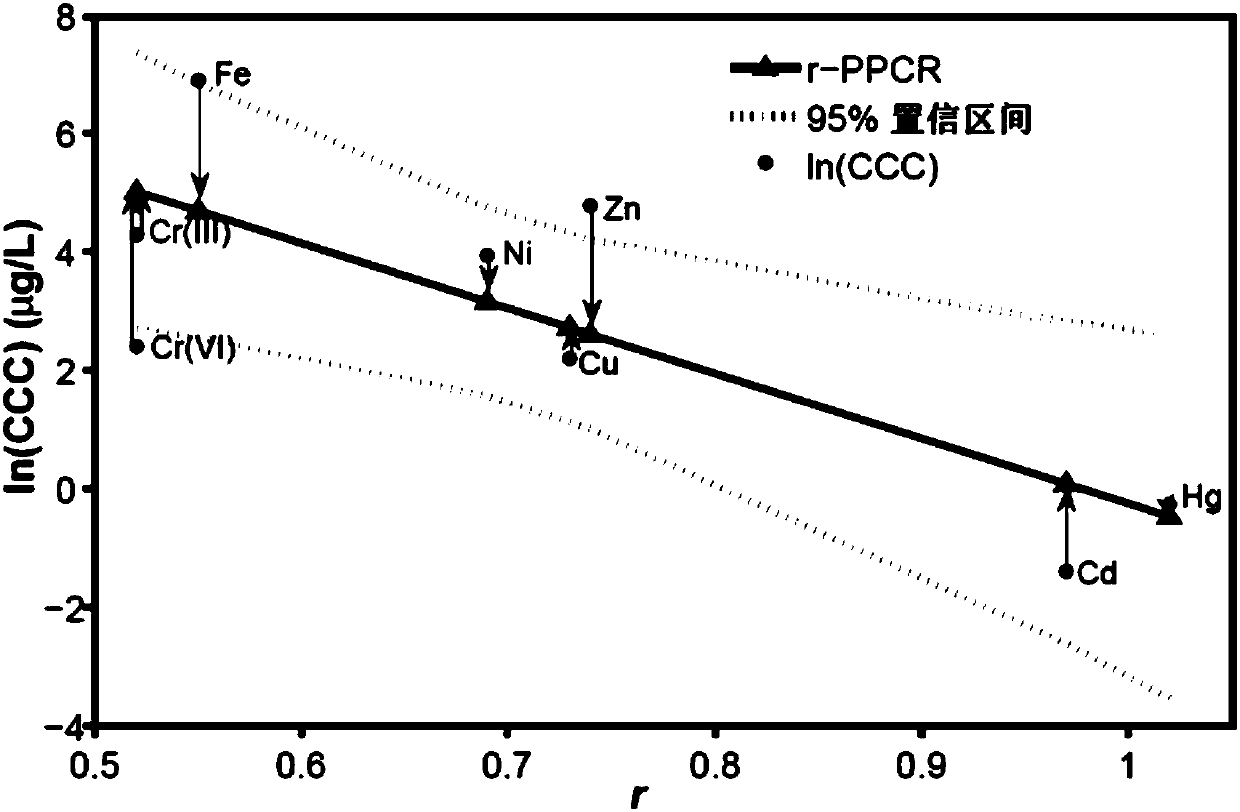
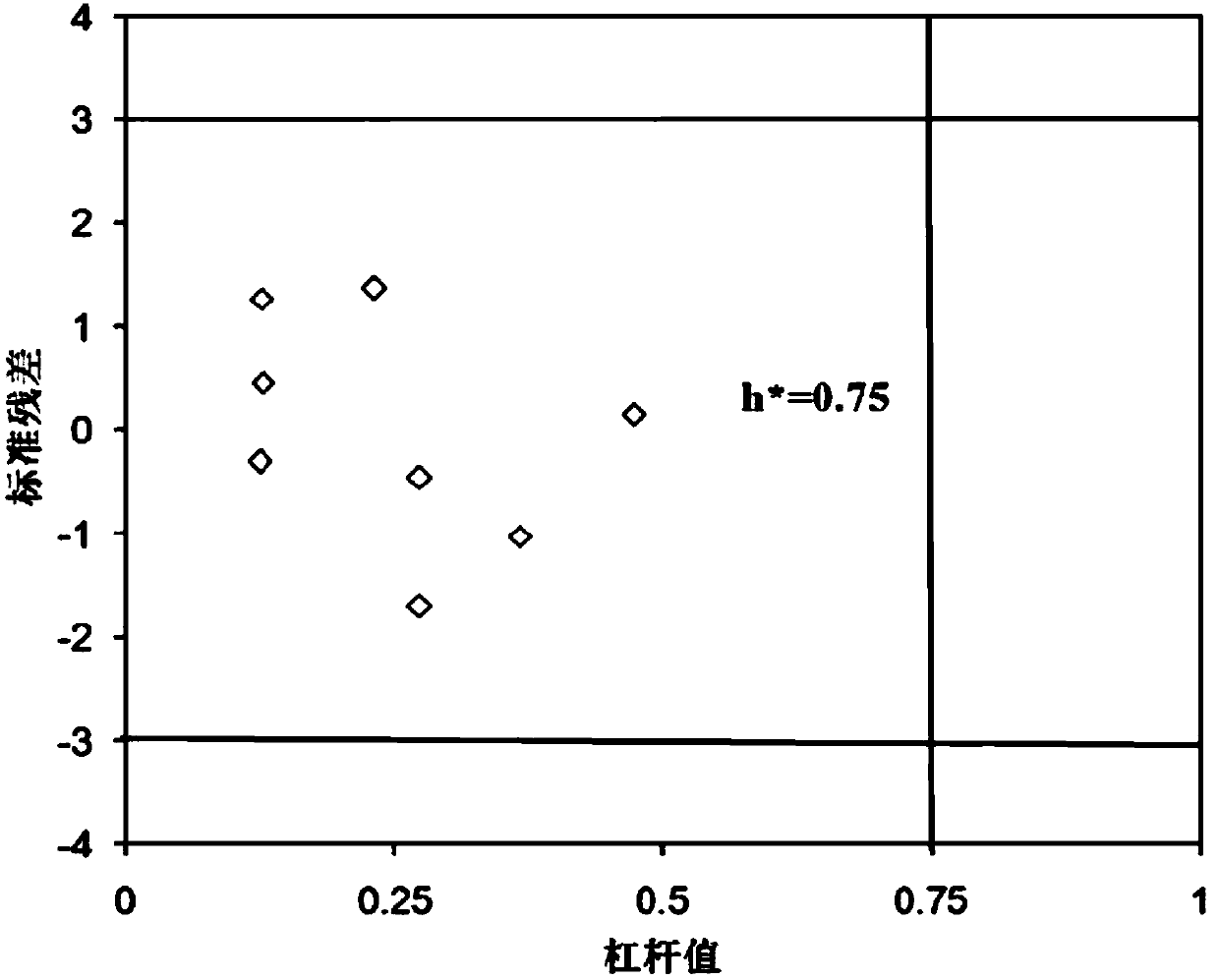
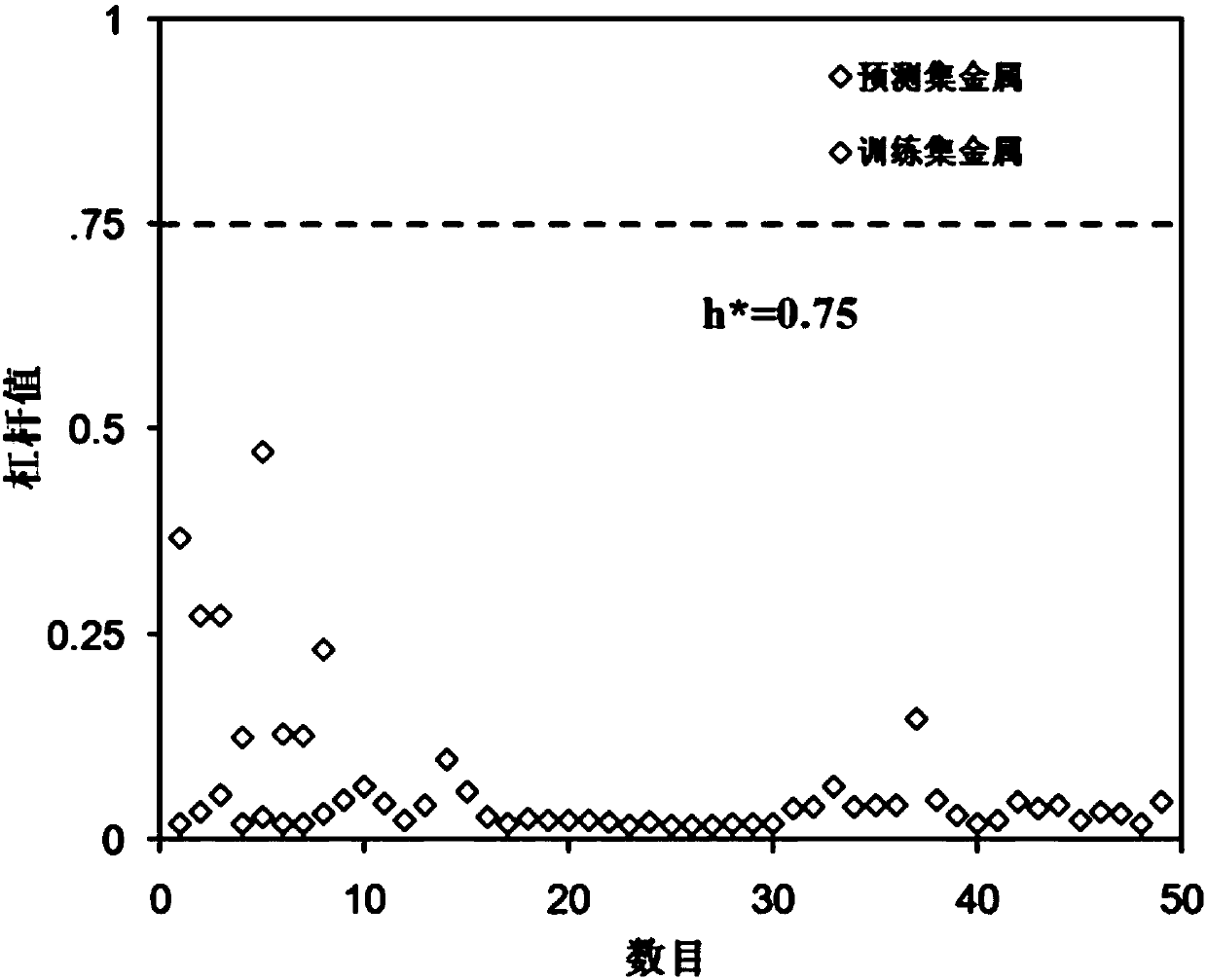
CCCs Prediction Method Based on Transition Metal Protection Aquatic Organism Water Quality Benchmark
ActiveCN107391960BAvoid manpowerComputational theoretical chemistrySpecial data processing applicationsWater qualityLanthanide
The invention relates to a criteria continuous concentrations prediction method, in particular to a CCCs (criteria continuous concentrations) prediction method for water quality criteria for aquatic life protection based on transition metals. The prediction method comprises: S1, selecting data; S2, building a PPCR model; S3, testing model goodness of fit and robustness; S4, evaluating an optimal prediction space; S5, predicting criteria continuous concentrations. The prediction method of the invention employs the PPCR method to predict the criteria continuous concentrations of transition metals in the periods IV, V and VI (including lanthanide and actinium series), mass manpower, material and financial resources consumed in chronic toxicity test are avoided, significant methodological advantages are manifested in the criteria deduction process, and reliable reference values are provided for the formulation of chronic water quality criteria for transition metals and the evaluation of risk.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
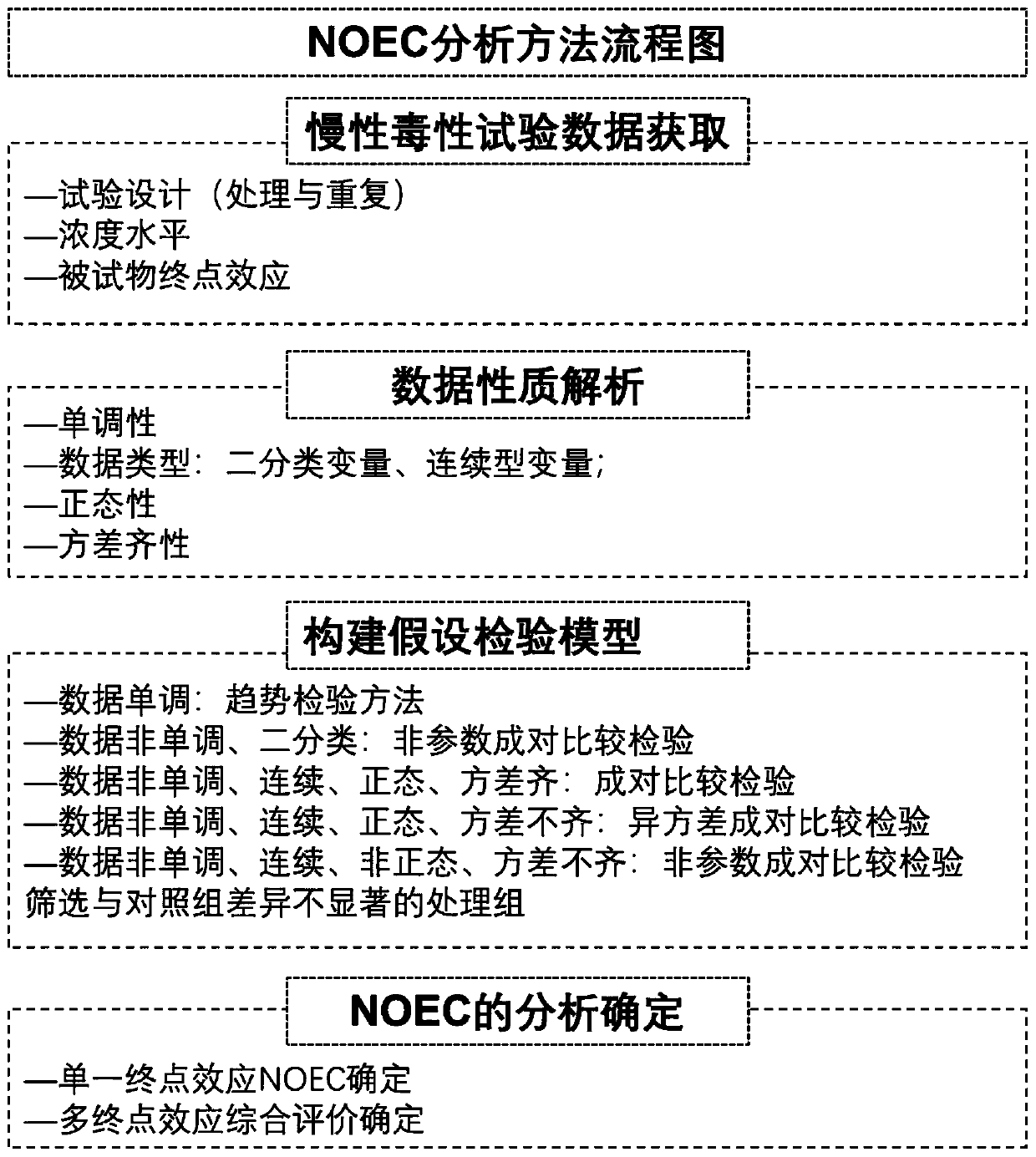
Method for analyzing maximum no-effect concentration of chemical acting on organisms
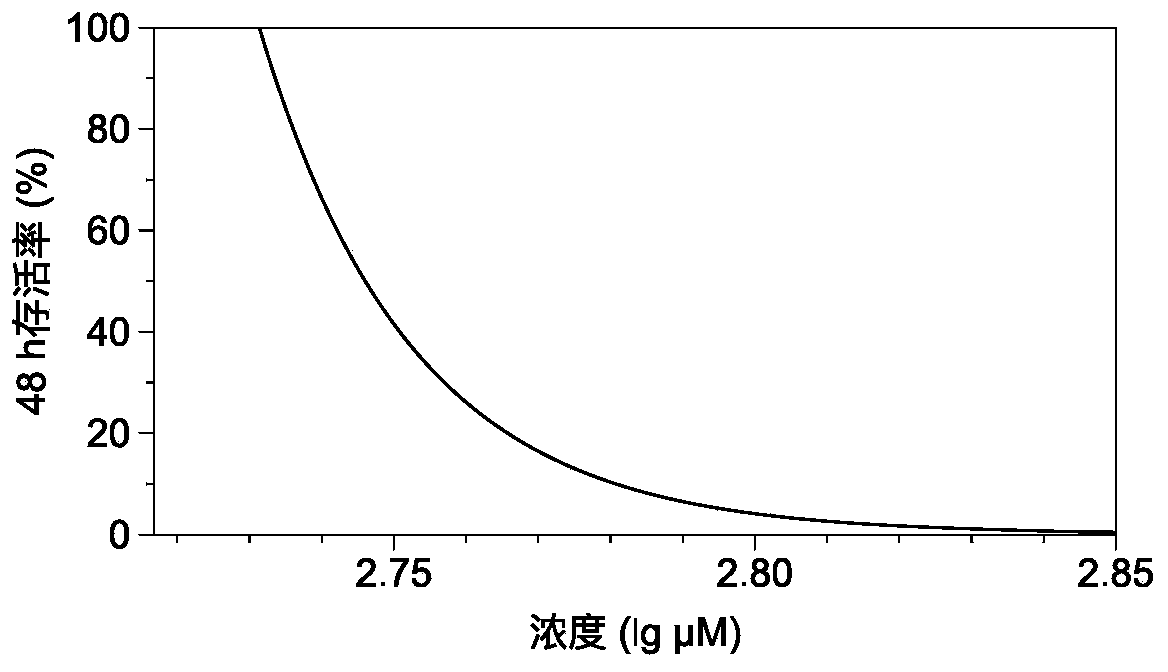
ActiveCN111524559AGuaranteed Analytical Energy EfficiencyGuaranteed accuracyCompounds screening/testingAnthropod material medical ingredientsTest organismChronic toxicity testing
The invention provides a method for analyzing the maximum no-effect concentration of a chemical acting on organisms, belonging to the field of pesticide data analysis techniques. The method comprisesthe following steps of: 1) allowing a tested chemical with different concentrations to act on tested organisms for chronic toxicity tests, and carrying out measuring to obtain a plurality of groups ofend effect data; 2) classifying the plurality of groups of end effect data obtained in the step 1); (3) constructing a hypothesis testing model by utilizing the data classified in the step (2), selecting the highest concentration of the tested chemical which does not generate significant effect from the same group of end effect data according to a significance value result in the statistics of the hypothesis testing model, determine the highest concentration of the tested chemical as NOEC in the group, and in different groups of the end effect data, selecting the NOEC of a group with a minimum NOEC value as the maximum no-effect concentration of the tested chemical acting on the tested organisms. The analysis method provided by the invention can ensure analysis efficiency and accuracy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Exposure device for fish embryos and larva fish for long-term chronic toxicity tests
The invention discloses an exposure device for fish embryos and larva fish for long-term chronic toxicity tests. The exposure device comprises a tank and a tank cover which are arranged externally. The tank cover is provided with a plurality of small container ports. A small container is hung on each small container port so as to be allowed to extend into the inner space of the tank. The bottom of each small container keeps a certain distance from the bottom of the tank. An overflow pipe is arranged in each small container. Each overflow pipe penetrates out of the bottom wall of each small container and the bottom wall of the tank to be connected to a water inlet of a three-way valve. The other water inlet of each three-way valve is connected with a drain pipe, and each drain pipe penetrates out of the bottom wall of the tank and extends into the bottom of the tank. A water outlet of each three-way valve is connected with a protruding drain outlet, and the highest position of each protruding drain outlet is at the same level with an overflow pipe nozzle at the utmost top of each overflow pipe. The tank cover is further provided with a plurality of operating openings, and the lower periphery wall of each small container is provided with a narrow slit capable of leaking water and blocking the fish embryos and the larva fish from passing by.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
A method for determining the acute and chronic toxicity of drugs to hornet mites
ActiveCN105850898BImprove survival rateProlong survival timeAnimal husbandryAcute toxicity testingMortality rate
Owner:BEE RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com