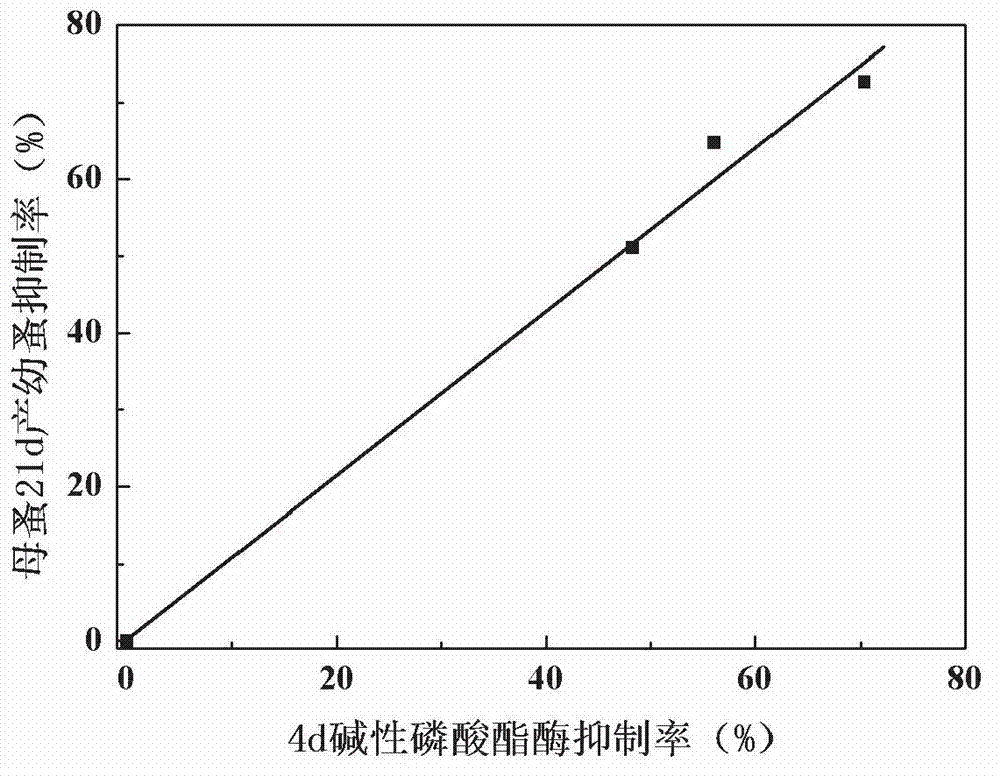
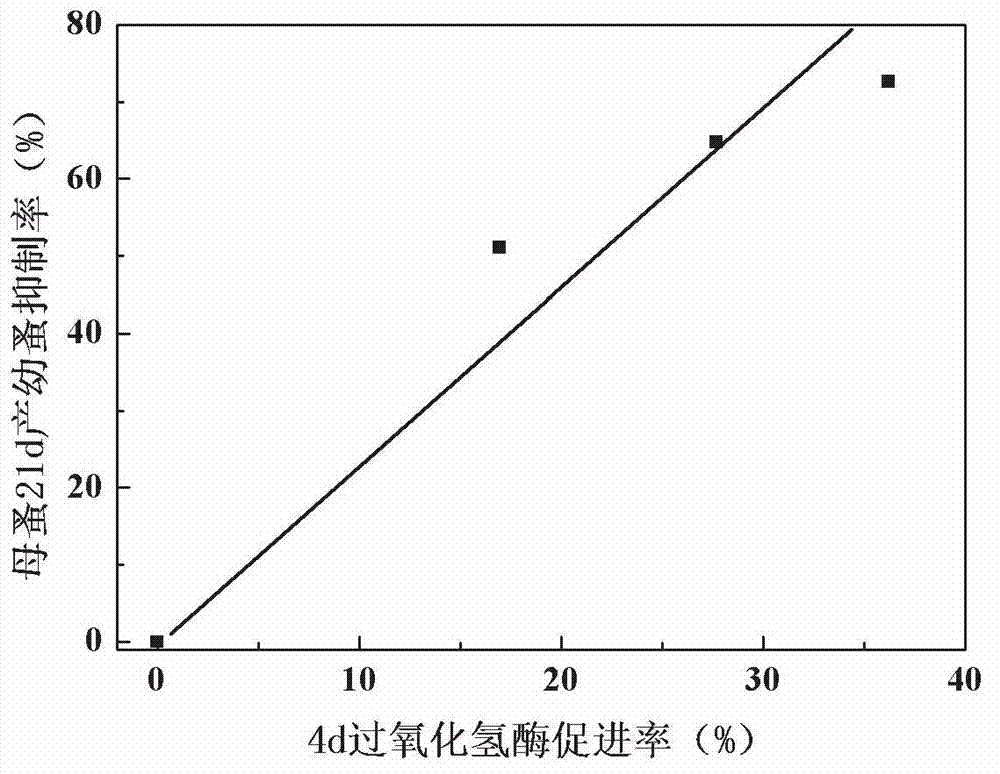
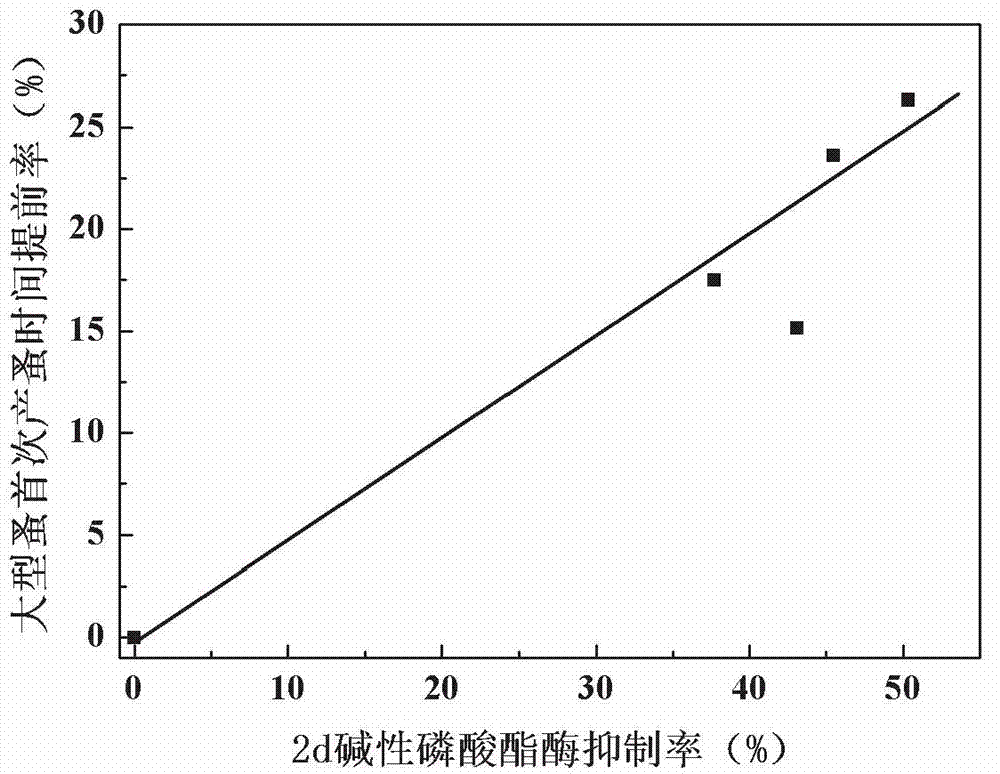
Early warning method for chronic toxicity of water quality substance to Daphnia magna
A technology for chronic toxicity and early warning, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of insensitivity, high detection limit of toxicity, long test time, etc., to solve the acute toxicity detection sensitivity Poor performance, rapid detection, and the effect of solving the long-term detection cycle of chronic toxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] The secondary effluent of sewage plant A was taken, filtered with qualitative filter paper to remove suspended particles, and then used as water samples for the acute toxicity, chronic toxicity and enzyme activity detection experiments of Daphnia magna.
[0020] Firstly, the acute toxicity test of Daphnia magna was carried out according to the OECD202 method. The acute lethality rate of the water sample to Daphnia magna was 30% at 1 times the concentration for 48 hours. Therefore, the secondary effluent test concentration of the chronic toxicity and enzyme activity detection experiment was selected as 50%. , 75% and 1 times, using aerated and dechlorinated tap water to dilute accordingly, set 10 parallels for each concentration, and set tap water as a control, OECD 211 method for 21-day Daphnia magna chronic toxicity test: in 20 mL water samples Or put 1 Daphnia magna into tap water, culture it continuously for 21 days in an incubator with a light-to-dark ratio of 16:8 a...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Take reclaimed water from sewage plant B, use qualitative filter paper to remove suspended particles, and then use solid phase extraction to concentrate organic matter in the water to obtain a concentrated water sample equivalent to 200 times the concentration of reclaimed water, which is used for acute toxicity, chronic toxicity and enzyme Activity detection experiment.
[0027] Firstly, the acute toxicity test of Daphnia magna was carried out according to the OECD202 method. The 48-hour LC50 of the water sample was 24 times that of Daphnia magna. Therefore, the test concentration of regenerated water for the chronic toxicity and enzyme activity detection experiments was selected as 1, 2, 5 and 10 times. The concentration was set to 10 parallels, and tap water was set as the control, and the OECD 211 method was used to conduct the 21-day Daphnia magna chronic toxicity test: put 1 Daphnia magna in 20 mL of water sample or tap water, and set the light-dark ratio at 16:8, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com