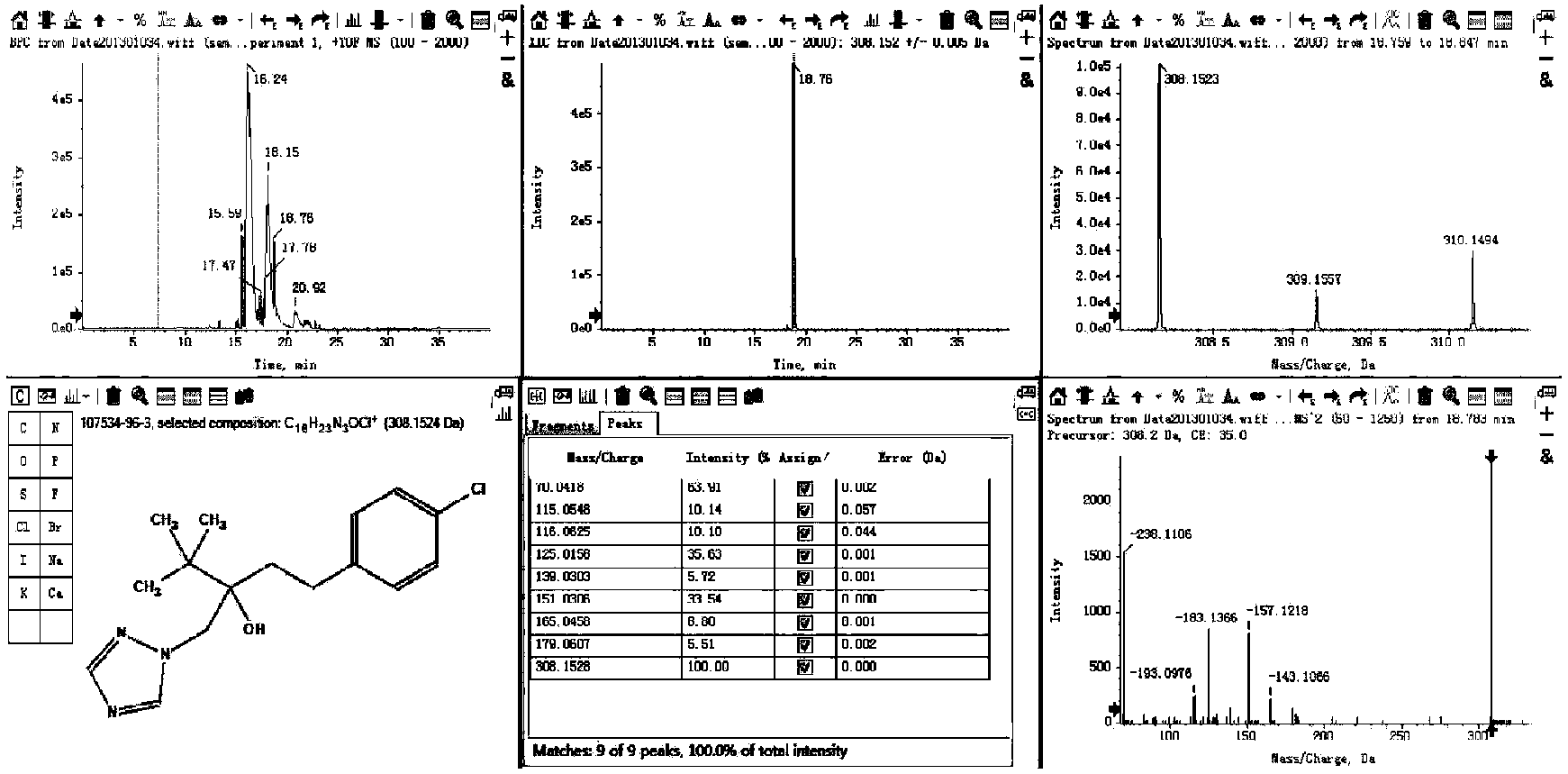
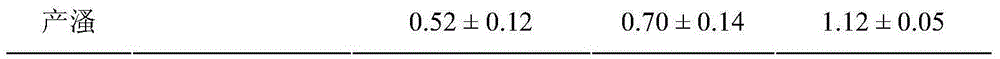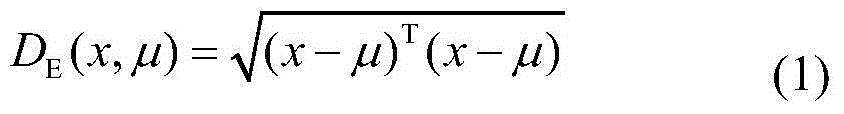Patents
Literature
75 results about "Daphnia magna" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
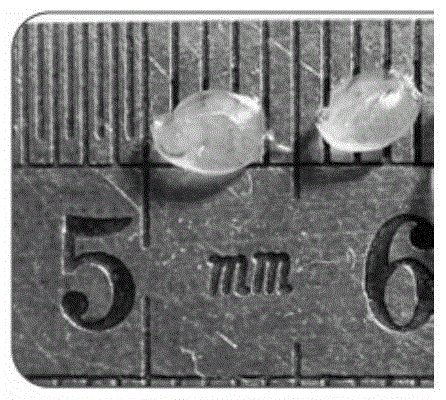
Daphnia magna is a small planktonic crustacean (adult length 1.5–5.0 mm) that belongs to the subclass Phyllopoda. It inhabits a variety of freshwater environments, ranging from acidic swamps to rivers made of snow runoff, and is broadly distributed throughout the Northern Hemisphere and South Africa.
Method of ecological restoration of water bodies containing excess nutrient
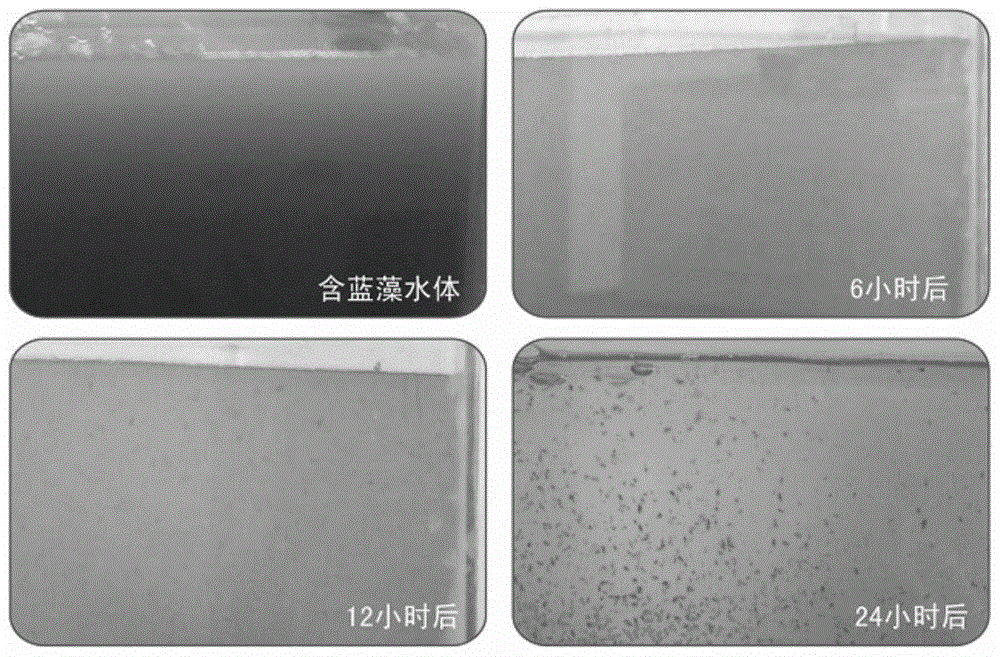
A method of ecological restoration of water bodies containing excess nutrient includes steps of: (a) taming Daphnia magna to be able to eat blue-green algae as an algae eating plankton with a taming composition fermented from spirulina powder, active yeast, and saccharide, so as to digest blue-green algae in the water bodies, and (b) putting the algae eating plankton in the water body polluted by the blue-green algae, wherein the algae eating plankton eats the blue-green algae, so that an eco-system of the water body containing excess nutrient can be restored. The method according to a preferred embodiment further includes a step of: (c) planting submerged plant in the water, wherein the submerged plant includes submerged forest and submerged turf.
Owner:SHANGHAI TAIHE WATER TECH DEV CO LTD
Method for establishing urban landscape water body ecological system
InactiveCN104310591AFast and efficient buildSelf-maintenanceSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentZooplanktonShrimp
The invention discloses a method for establishing an urban landscape water body ecological system. The method comprises the following steps: improving a water body substrate; planting submerged plants by using a method that upright posts are adopted to mark areas, so as to establish an underwater frost; planting layered emergent aquatic plants; putting zooplankton (daphnia magna) so as to improve the transparency of the water body; putting aquatic organisms such as fishes, shrimps and shells, so as to complete the water body ecological system; maintaining and managing the ecological system. Through the adoption of the method, the quality of the water body can be remarkably improved, the transparency can be greater than 2.0m, the quality can meet the III-type water quality standard for a long time, black, smell and dirty water bodies with blue-green algae can be thoroughly eliminated, and the water body is always kept clear completely.
Owner:广州太和水生态科技有限公司
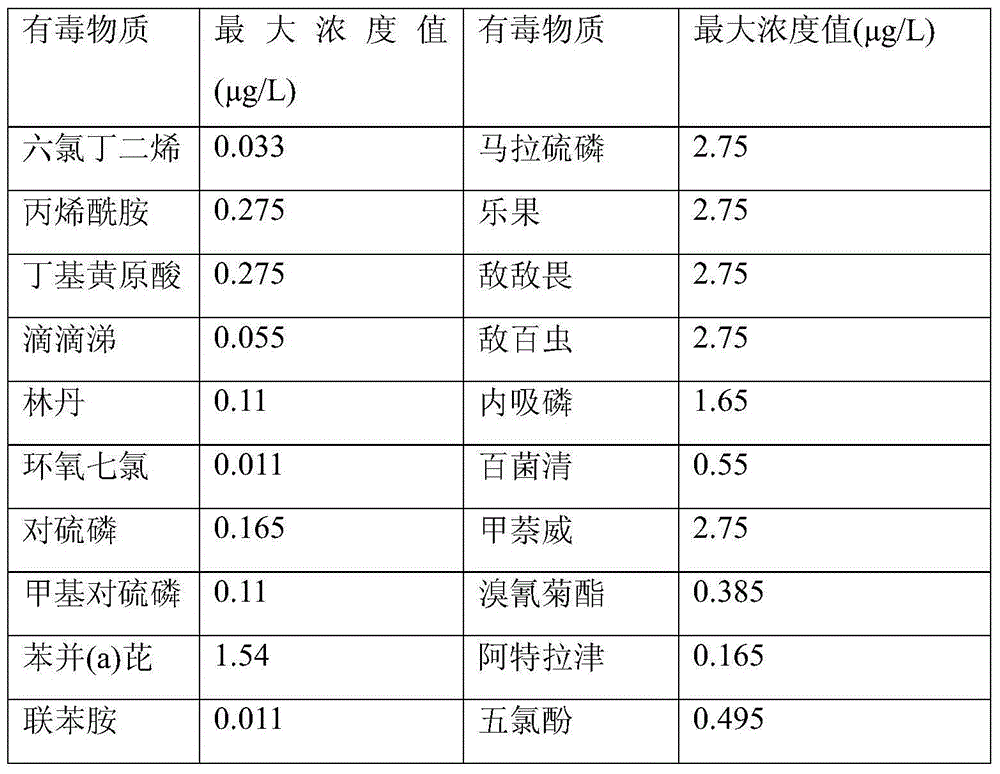
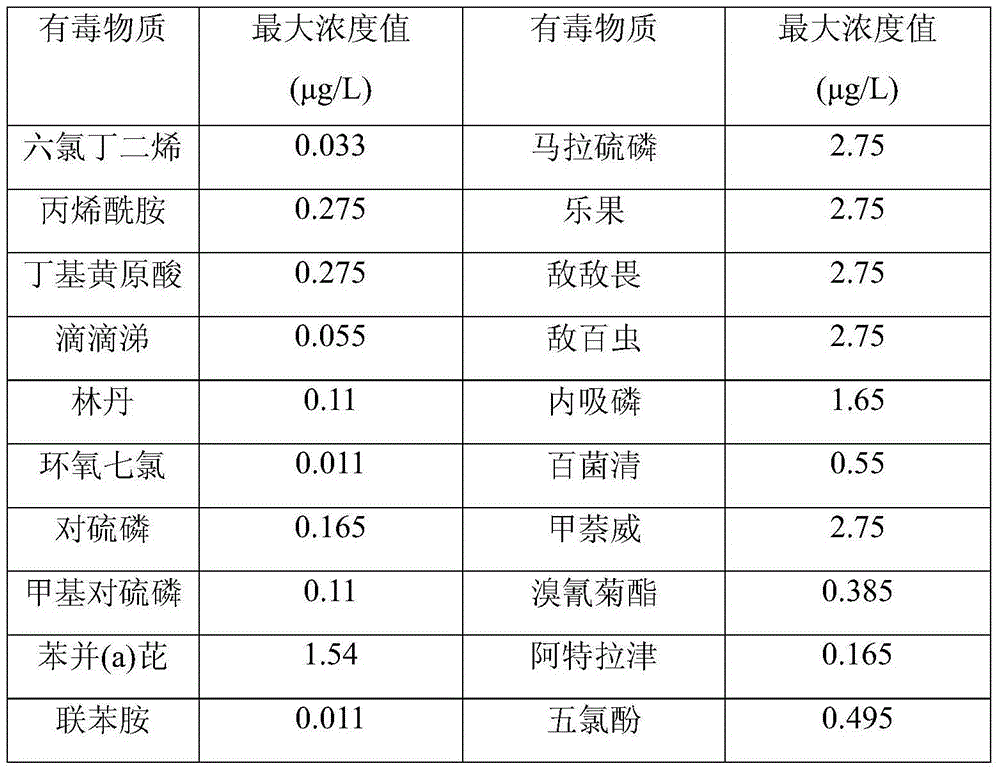
Method for identifying key toxic substances in pesticide wastewater by taking daphnia magna toxicity as guide
ActiveCN103983727AReduce complexityComprehensive screeningComponent separationSeparation technologyToxicant
The invention discloses a method for identifying key toxic substances in pesticide wastewater by taking daphnia magna toxicity as a precursor and belongs to the field of identification of non-target pollutants. The method comprises the following steps: performing enrichment on organic water sample extract; performing a daphnia magna toxicity experiment on an organic water sample extract; performing fractional separation on the organic water sample extract, and separating compounds of different polarities; performing the daphnia magna toxicity experiment on the separated components; and performing qualitative identification and quantitative determination on the compounds in toxic substances. The compounds of different polarities are separated by utilizing a fractional separation technology, the toxic substances are screened to reduce the complexity of a sample, the potential toxic substances are qualitatively identified through a high performance liquid chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry, suspicious toxic substances are quantitatively determined by utilizing a liquid chromatography mass spectrometry, and the defect that key toxic pollutants in a mixing system cannot be obtained by the traditional non-target chemical analysis is overcome. Meanwhile, due to fractional separation and feature object screening, the method is high in resolution ratio, high in accuracy and high in information amount, so that the identification of non-target key toxic substances is relatively convenient and reliable.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
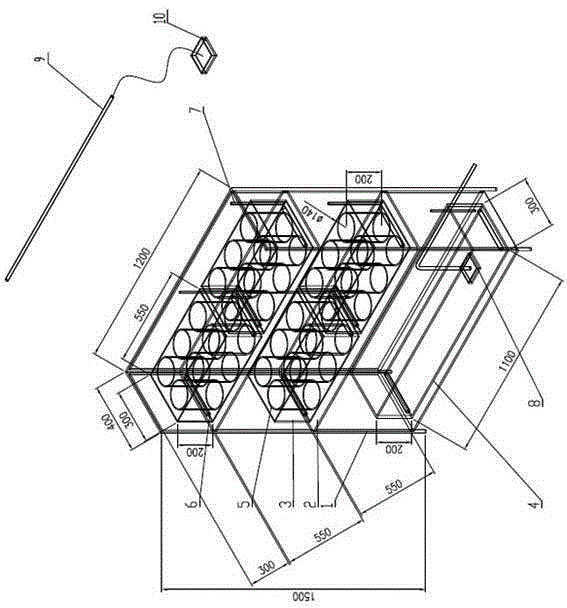
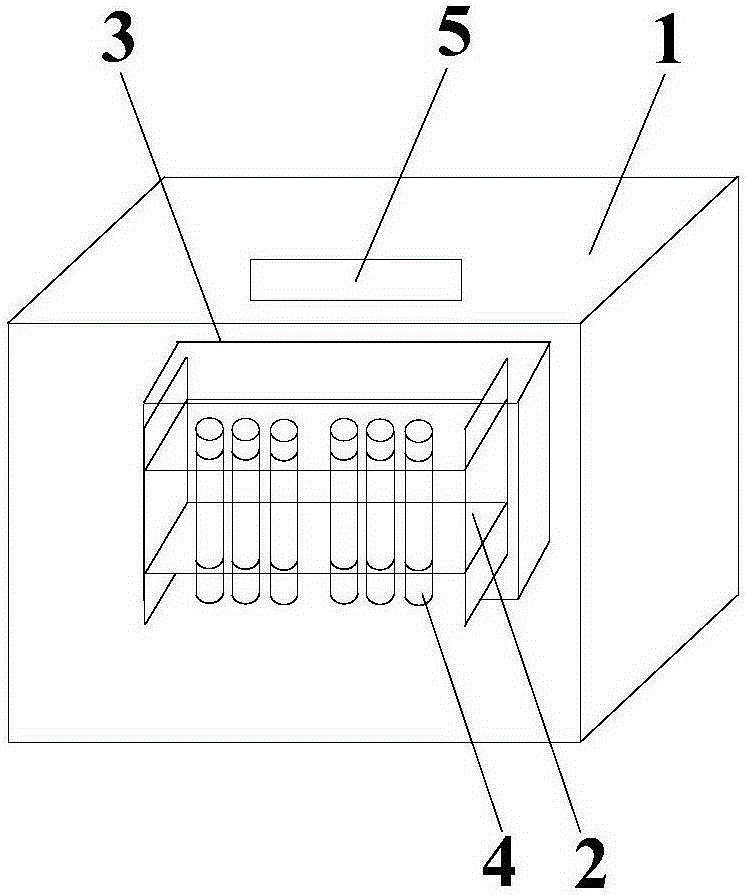
Rapid cultivation device and method of daphnia magna laboratory
The invention provides a rapid cultivation device and method of a daphnia magna laboratory and belongs to the field of cultivation of zooplankter. The rapid cultivation device comprises supports, base plates, water bath tanks, a water storage tank, cultivation cups, heating rods, thermometers, turbulence pumps, a fluorescent lamp and a time controller. Each base plate is arranged at the bottom of the corresponding support. The storage water tank is arranged on the base plate of the bottommost support. The water bath tanks are arranged on the base plates of the two upper supports. One thermometer, one turbulence pump and two heating rods are arranged in the water storage tank. Each water bath tank is provided with one thermometer, two heating rods and six cultivation cups. The fluorescent lamp is located above the portion deviating from the center of the support and is parallel to the support. The time controller is in contact with the fluorescent lamp. The rapid cultivation device is easy and convenient to operate, high in operability, easy to set up and free of a complicated device structure. Daphnia magna cultivated through the rapid cultivation device is rapid in reproduction and large in quantity, the life condition of the daphnia magna is stable, and the individual difference of the daphnia magna is small, so that results of toxic tests of fleas are stable and reliable, the test quality is guaranteed, and enough test materials can be provided for tests such as removal of zooplankter pollution to water in the industry of water treatment at the same time.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for domesticating daphnia magna and water ecological restoration method
ActiveCN104126550AImprove the immunityRestoration of water body ecologyEnergy based wastewater treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentRestoration methodSelf purification
The invention discloses a method for domesticating daphnia magna and a water ecological restoration method through the same inventive concept. According to the method for domesticating the daphnia magna, toxic substances are added to a culture pool, and the method for domesticating the daphnia magna is achieved through specific domesticating methods. According to the water ecological restoration method, the daphnia magna domesticated through the toxic substances is adopted and put into water rich in algae and toxic substances such pesticides, therefore, the water is purified, and underwater ecological balance is restored so as to achieve water ecology self-purification.
Owner:广东汇美生态科技有限公司
Method of ecological restoration of water bodies containing excess nutrient
A method of ecological restoration of water bodies containing excess nutrient includes steps of: (a) taming Daphnia magna to be able to eat blue-green algae as an algae eating plankton with a taming composition fermented from spirulina powder, active yeast, and saccharide, so as to digest blue-green algae in the water bodies, and (b) putting the algae eating plankton in the water body polluted by the blue-green algae, wherein the algae eating plankton eats the blue-green algae, so that an eco-system of the water body containing excess nutrient can be restored. The method according to a preferred embodiment further includes a step of: (c) planting submerged plant in the water, wherein the submerged plant includes submerged forest and submerged turf.
Owner:SHANGHAI TAIHE WATER TECH DEV CO LTD
Series method for removing algae by using zooplankton and filter-feeder fishes
InactiveCN101293709AGood removal effectAvoid monotonyBiological water/sewage treatmentFilter feederDensity ratio
The invention relates to a method for removing algae by series connection of zooplankton and filter-feeding fish, which relates to a method for controlling the removal of algae in eutrophic water. The invention can solve the problem that the algae in natural water can not be completely removed by utilizing aquatic organisms. The method of the invention is that first, at least two sluice facilities are connected with each other in series; then, the algae-containing water sequentially flows through every sluice facility; the hydraulic retention time of every sluice facility is one to three days; the zooplankton and the filter-feeding fish are alternatively stocked in the two neighboring sluice facilities; the stocked zooplankton are mainly daphnia magna which eats micro algae; at the same time, all the fishes in the sluice facility which stocks the zooplankton are completely cleaned out or predatory fishes are threw in; the stocked fishes in the sluice facility which stocks filter-feeding fishes are silver carp and bighead carp or only the silver carp is stocked. The stocking density of the silver carp is 40 to 200g / m<3>; every single silver carp weighs 60 to 500 grams; the stocking density ratio of the bighead carp and the silver carp is 1:3 to 1:5; every single bighead carp weighs 60 to 500 grams. The method of the invention can completely remove the algae in the natural water.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
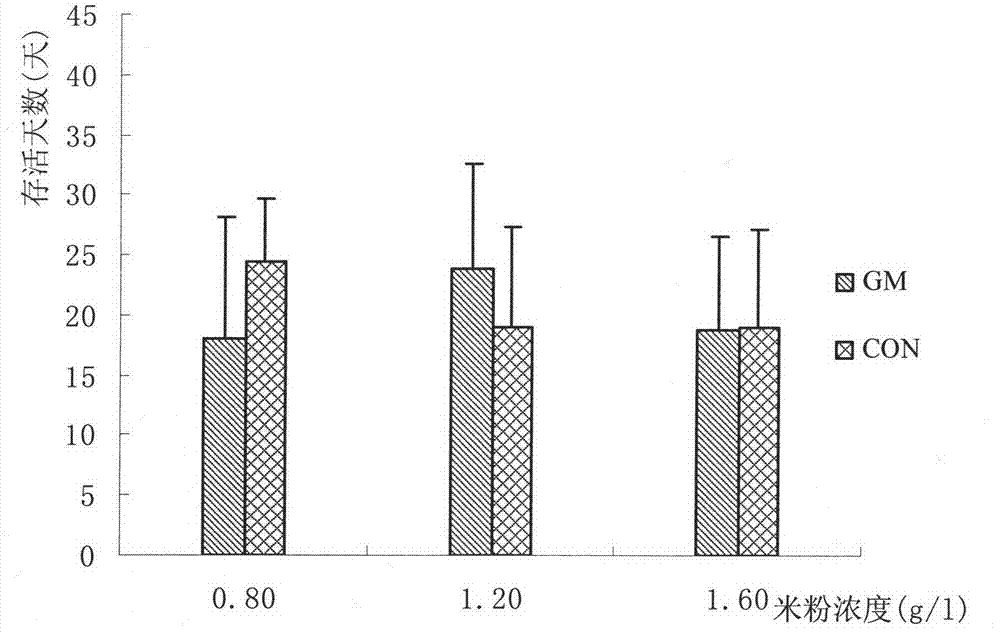
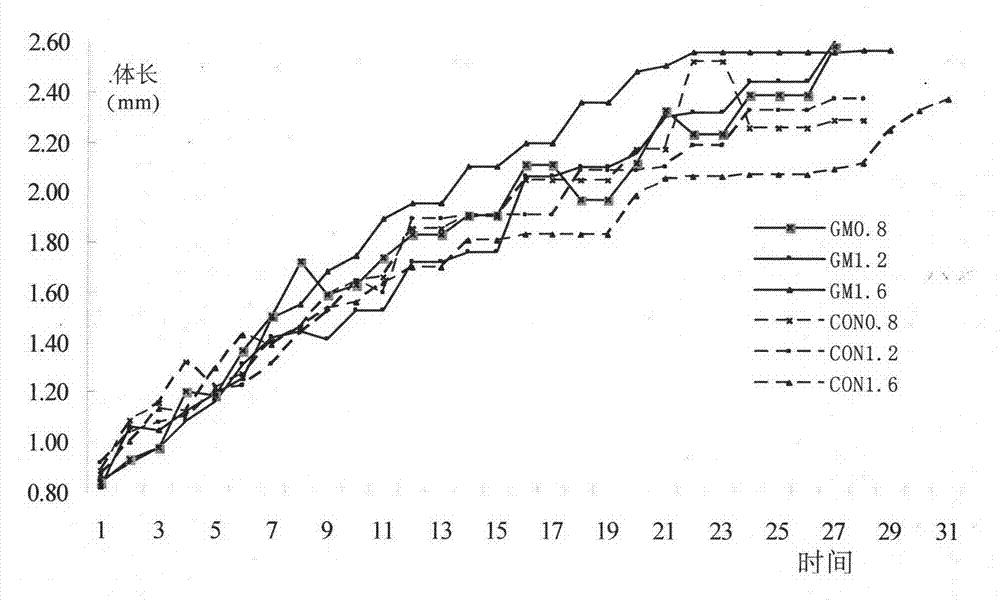
Daphnia magna breeding method for evaluating safety of transgenic rice
InactiveCN102948399AEliminate selectivityEliminate non-feedingAnimal husbandryGenetically modified riceAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a breeding method for an aquatic organism daphnia magna, and belongs to the technical field of insect breeding. The method is used for overcoming the defect in a traditional daphnia magna toxicity experiment technology, and the invention builds a method for breeding daphnia magna by utilizing rice. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a nutrient solution, preparing a rice flour solution, breeding and collecting young fleas. According to the daphnia magna breeding method disclosed by the invention, rice is used for breeding the daphnia magna, so that the defect that the daphnia magna in the conventional method selectively takes in natural goods such as green alga, but does not take in or take in a little rice is overcome. Moreover, an adverse factor that the experimental result is easily affected by uncertain nutritional ingredients of the green alga, and reliable experiment support is provided for evaluating the safety of transgenic rice.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MINIST OF ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT OF THE PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA
Preparation method of pyraclostrobin microcapsules
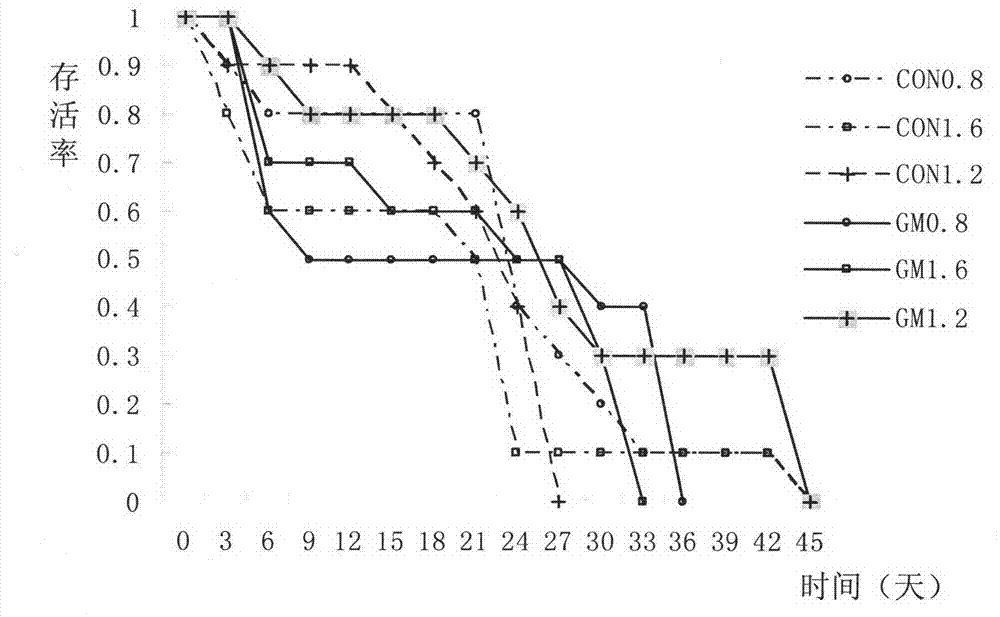
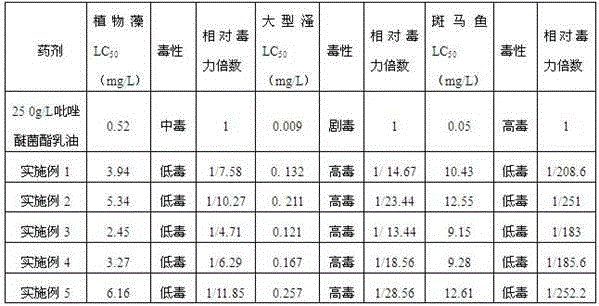
InactiveCN104823996AImprove securitySimple production processBiocideFungicidesPolyethylene glycolDaphnia magna
The invention discloses a preparation method of pyraclostrobin microcapsules and belongs to the technical field of agricultural pesticides. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving a crude drug at first, and then mixing the dissolved crude drug with isocyanate and polyethylene glycol; then dispersing the mixture in a water phase containing a surfactant and a colloid protecting agent, solidifying into capsules, and adjusting the pH value to obtain a microcapsule suspension; and on the basis of the suspension, adding a suspensions stabilizer to prepare a microcapsule suspension agent, or adding a solid auxiliary material to prepare microcapsule water dispersion granules. Diphenyl methane diisocyanate is particularly used as a material for preparing polyurethane capsule walls in the preparation method disclosed by the invention. The toxicity of the pyraclostrobin microcapsules prepared by the method disclosed by the invention to plant algae, daphnia magna and zebra fishes is obviously lower than that of pyraclostrobin missible oil, and the microcapsules can be used for preventing and treating plant leaf diseases of downy mildew, powdery mildew, late blight and the like of vegetables and can also be used for preventing and treating plant soil borne diseases of root rot, crown rot, southern blight and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Culture and separation device and culture and separation method for daphnia magna
InactiveCN102687709AGuaranteed not to leave the waterEasy accessAnimal husbandryDaphnia magnaOperability
The invention discloses a culture and separation device for daphnia magna, comprising an algae growth promoting device, a daphnia magna culture container arranged in the algae growth promoting device, a circulating water device arranged in the daphnia magna culture container, and a daphnia magna separation device. The invention also discloses a culture and separation method for daphnia magna by utilizing the device. The culture and separation device provided by the invention is simple and convenient for operation, and high in operability; the materials of the device are easy to be obtained; and the device is simple in structure, and convenient for manufacturing and maintenance. The culture container employed by the culture and separation device for daphnia magna is formed through one step and small in volume, thereby avoiding pollution of other substances and being easy for replacement, and also facilitating subculture; the flea food growth promoting device is advantageous for the growth and reproduction of flea food algae, thereby omitting the work of feeding each day; the circulating water device reduces the step of aeration needed in the flea culture process; and the separation device prevents fleas from leaving the water surface in the separation process to guarantee large-quantity quick separation of fleas. The application of the culture and separation device for daphnia magna can ensure the quality of flea toxicity tests.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MINIST OF ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT OF THE PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA
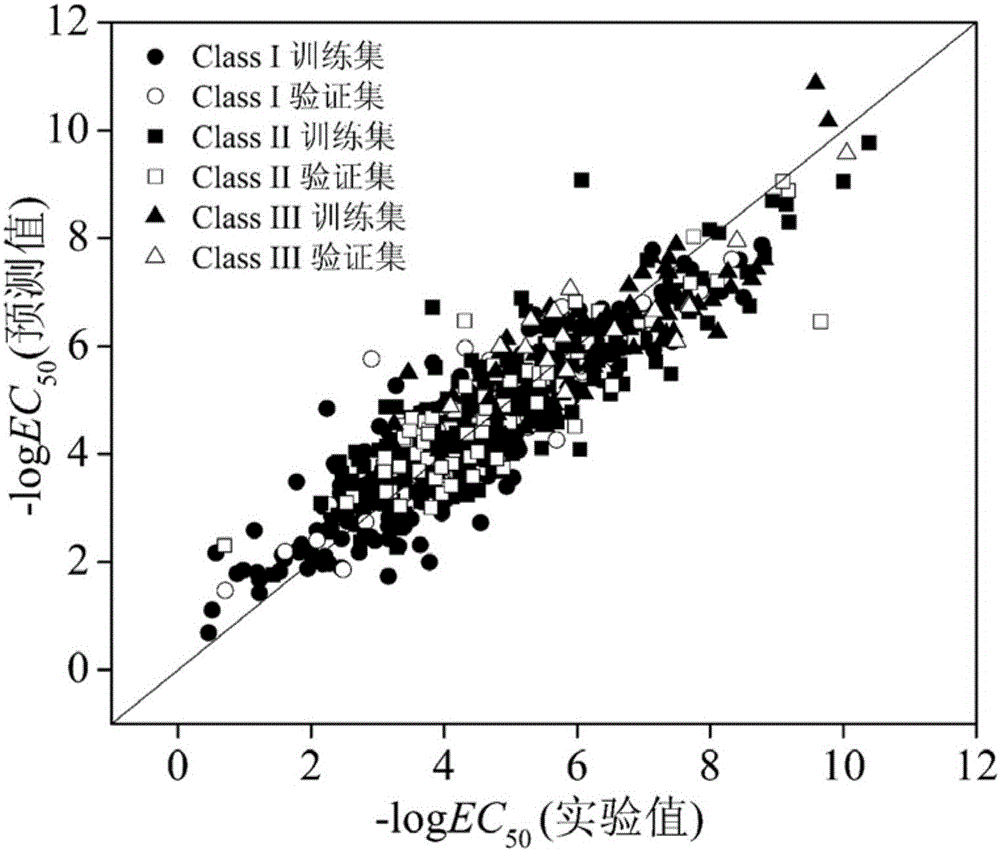
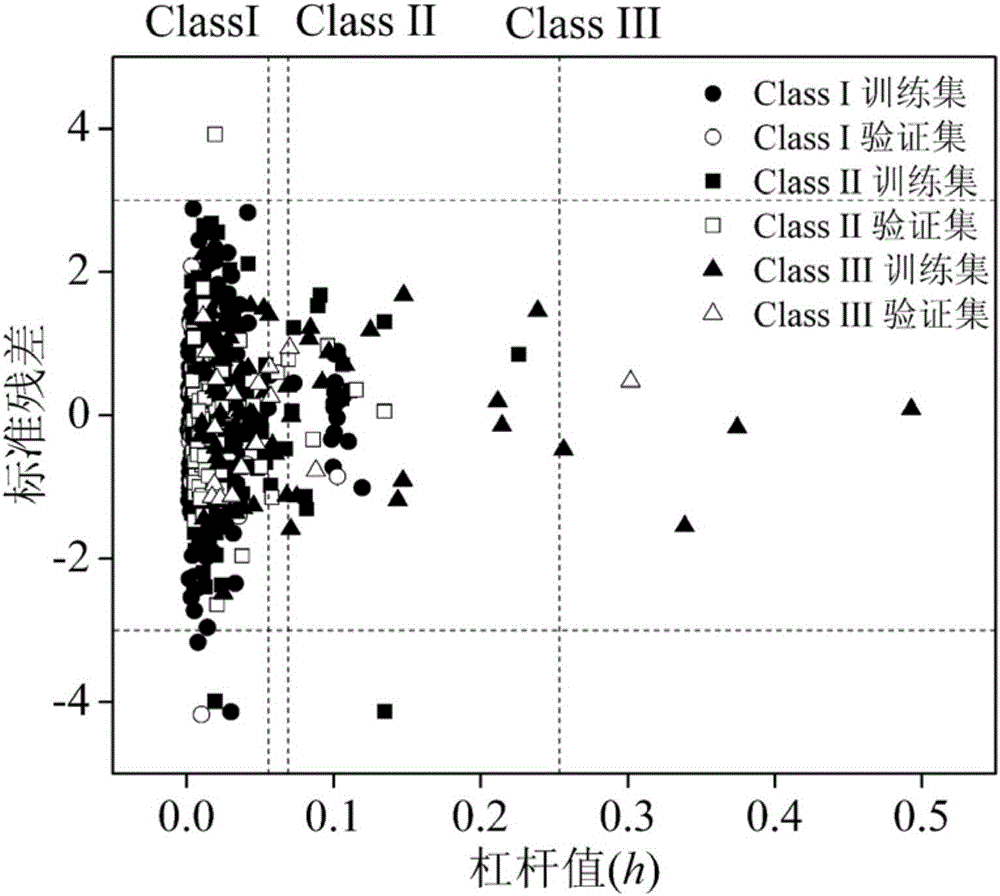
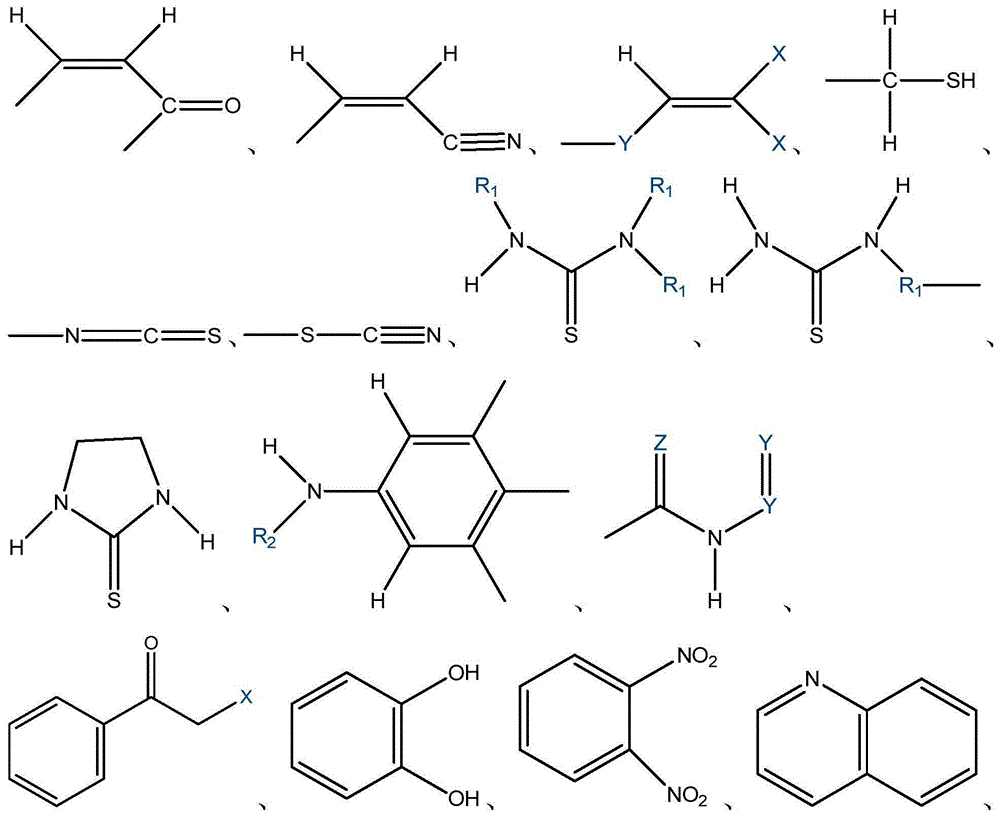
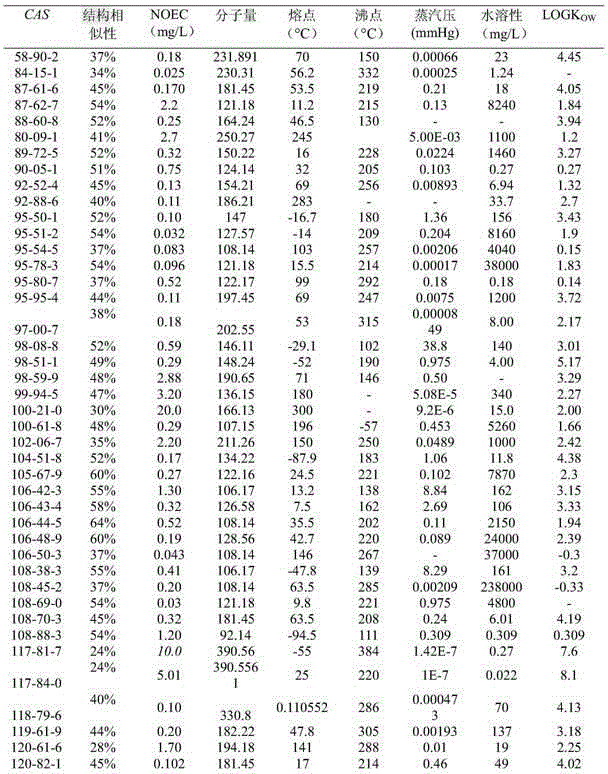
QSAR (Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships) model constructed based on comprehensive toxicity action mode classification for predicting acute toxicity of organic compound to daphnia magna
ActiveCN105005641ASave human effortSave moneyCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsGuidelineAcute toxicity testing
The invention discloses a QSAR (Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships) model constructed based on comprehensive toxicity action mode classification for predicting acute toxicity of an organic compound to a daphnia magna. At first, a comprehensive toxicity action mode classification method is developed, and the method is adopted to classify the compound based on structure characteristics. After the compound is classified according to the method, an EC50 model is constructed on the basis of a molecular structure descriptor of the compound through a multiple linear regression method, so that an EC50 value of acute effective toxicity of the organic compound to the daphnia magna can be quickly and effectively predicted; and the goodness of fit, the robustness and the predictive ability of the model are represented according to construction and verification guidelines of an organization for economic cooperation and development about the QSAR model; the model application domain is clear; the prediction model is simple and easy to be programmed, and an important data support is provided for acute toxicity assessment of organic chemicals.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
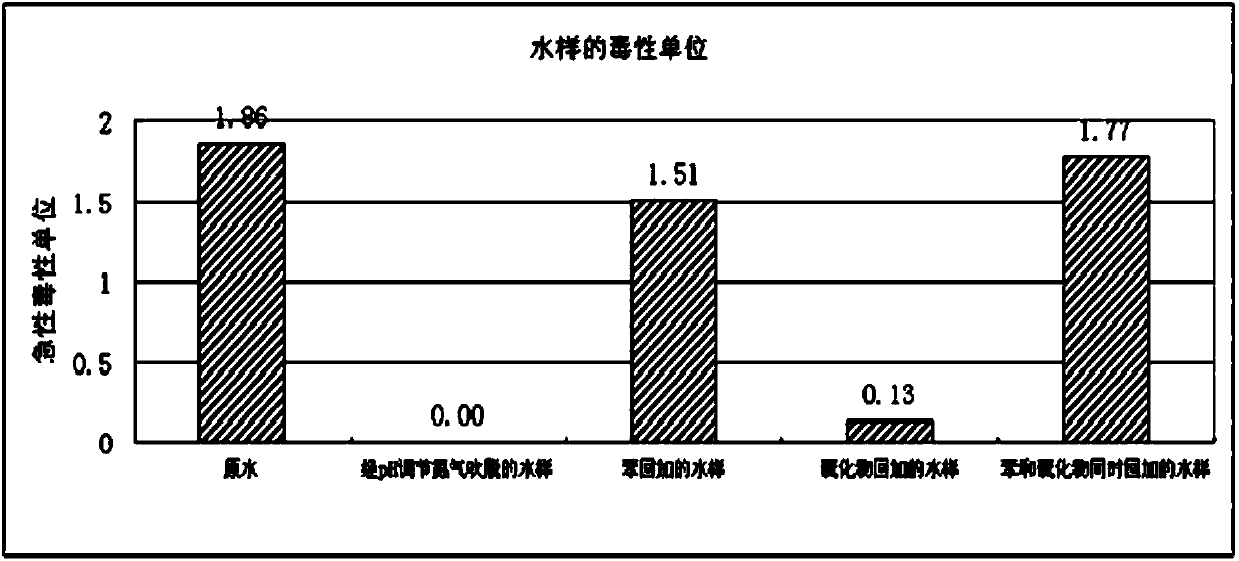
Identification method of poisonous substances in water from urban domestic wastewater treatment plant
InactiveCN103760315AShort life cycleBreed fastComponent separationTesting waterAcute toxicity testingOff Treatment
The invention discloses an identification method of poisonous substances in water from an urban domestic wastewater treatment plant, and belongs to the field of wastewater treatment. The identification method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of (1) carrying out acute toxicity biological detection by adopting daphnia magna so as to detect the toxicity of the wastewater; (2) detecting the suspected toxic substances in the wastewater; and (3) determining the main toxic substances in the wastewater, namely carrying out nitrogen blow-off treatment for 2h, carrying out nitrogen blow-off treatment for 2h after regulating the pH to 6, and regulating the pH to 6 for carrying out nitrogen blow-off treatment for 2h and then regulating the pH to 8.5, therefore, the main toxic substances, causing microbiological poisoning incidents of a biotreatment system, in the wastewater can be determined by detecting the change of the semilethal rate 24h-LC50 of the daphnia magna in a water sample after the three treating steps are performed and by adding the suspected toxic substances. The identification method of the poisonous substances in water from the urban domestic wastewater treatment plant provided by the invention has the advantages that the cost is low, and the period is short.
Owner:广州市净水有限公司
Water body eutrophication treatment technology based on daphnia magna domestication method
InactiveCN104743672ALower pHHigh transparencyEnergy based wastewater treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentFood chainDaphnia sinevi
The invention relates to a method for biologically eliminating and controlling the eutrophication of an open water body on the basis of a daphnia magna food chain relationship according to the principle of in-situ ecosystem remediation, and particularly relates to a daphnia magna domestication method. The method comprises the following steps: selecting a target water body to be treated; monitoring the water quality and pollution sources of the water body; according to the water quality and the pollution sources, domesticating and cultivating daphnia magna by stages with scenedesmus obliquus and eutrophic water mixed liquids until the daphnia magna is completely adapted to the environmental condition of the target water body to be treated, wherein the scenedesmus obliquus and eutrophic water mixed liquids have different scenedesmus obliquus concentrations; then continuously, regularly and uniformly putting the daphnia magna into the target water body according to a low concentration; and finally introducing specific fish, such as aristichthysnobilis, which feeds on the daphnia magna. Through the method, the problem of eutrophication of the open water body can be solved effectively, an original ecosystem is recovered, and in-situ remediation of the water body is realized.
Owner:潘力军 +3
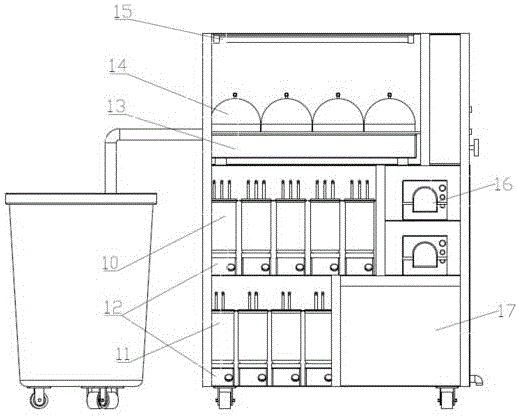
Automation running-water type cultivation device of daphnia magna
InactiveCN102845367ARealize dynamic trainingSave human effortAnimal husbandryDaphnia magnaAgricultural science
The invention relates to an automation running-water type cultivation device of daphnia magna. The device comprises six components including a feed culturing room, a cultivation ground substance storage room, a female daphnia feeding room, a young daphnia feeding room, a return room and a power system, wherein water outlet tubes at bottoms of the feed culturing room and the cultivation ground substance storage room are connected with the female daphnia feeding room through the power system; a water outlet tube at the bottom of the female daphnia feeding room is connected with the top of the young daphnia feeding room; a water outlet tube on the top of the young daphnia feeding room is connected with the top of the return room; and a water outlet tube at the bottom of the return room is connected with the cultivation ground substance storage room.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MINIST OF ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT OF THE PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA
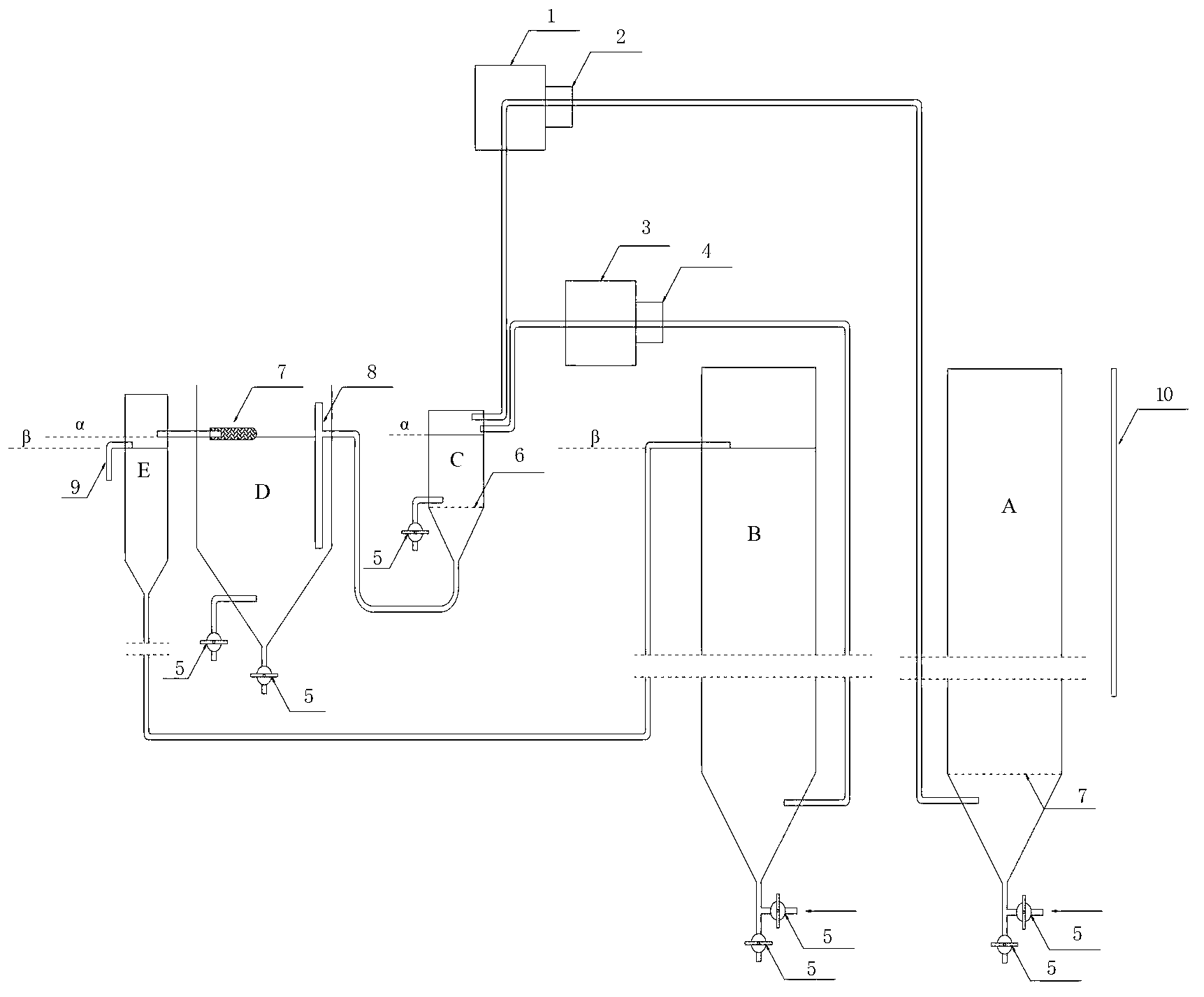
Running water type toxicity test device for daphnia magna
ActiveCN106442959ARealize automatic preparationRealize automatic update of water flowBiological material analysisBiological testingFiltrationDaphnia magna
The invention relates to a running water type toxicity test device for daphnia magna. The device comprises a solution preparation system, a temporary solution storage system, a toxicity exposure system, an automatic solution circulation and supplementation system and a waste liquid treatment system, wherein the solution preparation system is used for preparing a tested solution with the specific concentration for a daphnia magna toxicity test; the temporary solution storage system provides conditions for homogenization and temporary storage of the tested solution; the toxicity exposure system is used for providing appropriate space, temperatures and illumination for exposure of the daphnia magna in a test solution; the automatic solution circulation and supplementation system is connected between the solution preparation system and the temporary solution storage system and between the temporary solution storage system and the toxicity exposure system and can automatically supplement a solution from the preparation system to the temporary solution storage system and convey the solution from the temporary solution storage system to a toxicity test system; the waste liquid treatment system provides purification functions including filtration, adsorption and the like for a waste liquid produced by the toxicity exposure system.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MINIST OF ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT OF THE PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA
Early warning method for chronic toxicity of water quality substance to Daphnia magna
InactiveCN102827919AResolve detectionResolution cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementDaphnia magnaChronic toxicity testing
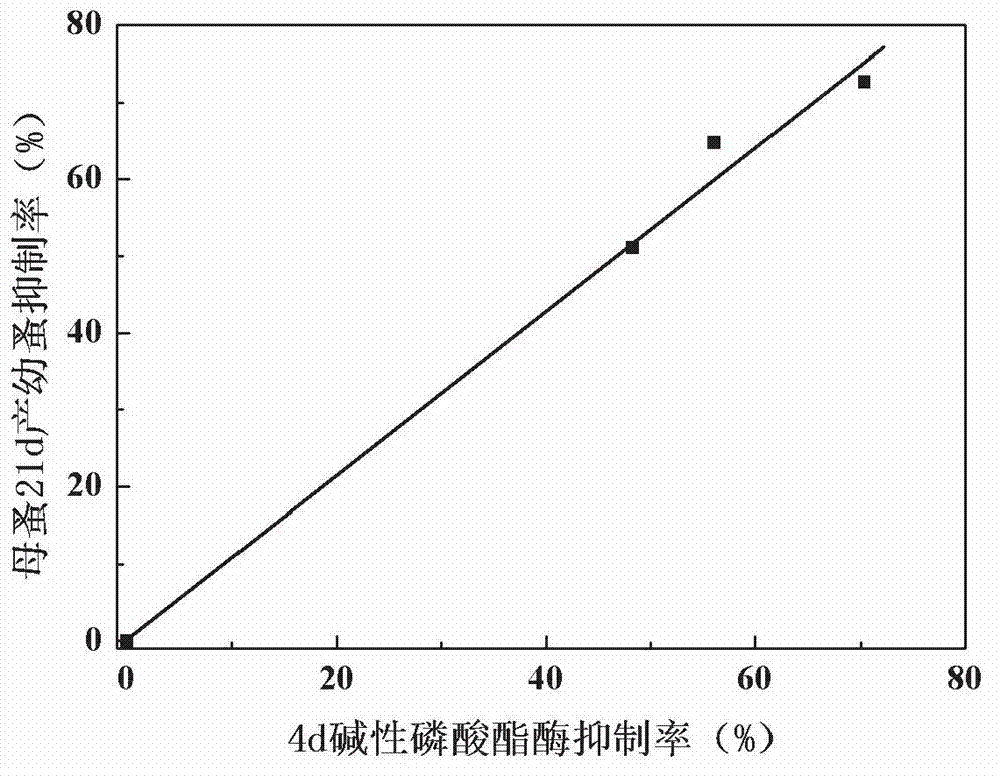
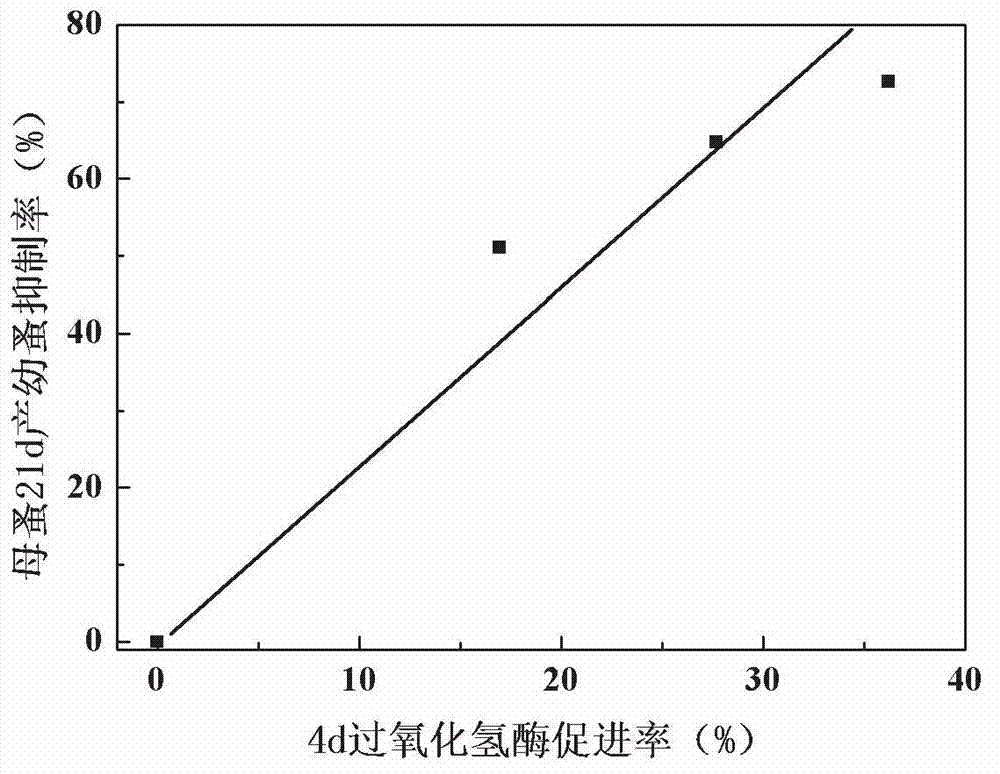
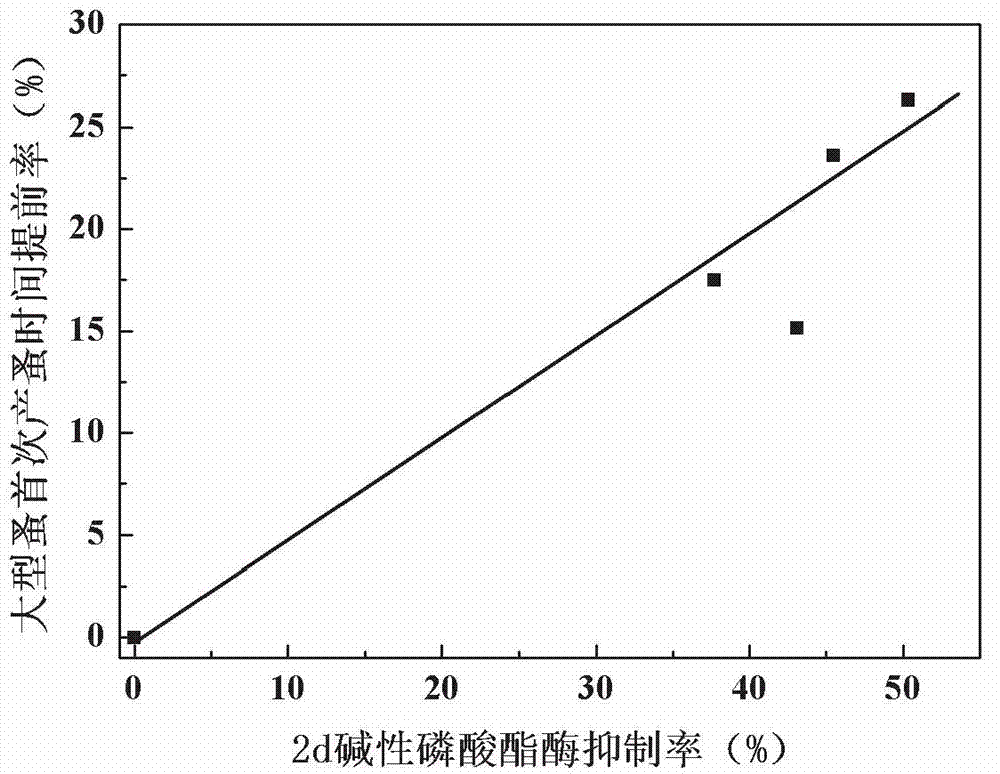
The invention discloses an early warning method for chronic toxicity of a water quality substance to Daphnia magna, which belongs to the technical field of water pollution control. According to the invention, directed at a low-toxicity water quality situation, marker enzyme having sensitive response to toxicity in Daphnia magna is screened out, and potential of chronic toxicity within 21 days is predicted based on results of detection on a change rate of the activity of the marker enzyme in a short period when Daphnia magna is tainted. There are standard methods or commercial kits for detection of the marker enzyme, detection is convenient, rapid and accurate, detection requirements of rapid early warning are met, and the method provided by the invention is applicable to a single-substance water sample with a low concentration or to a complex water sample like reclaimed water and surface water containing a variety of components and having low toxicity and can rapidly reflect the level of biotoxicity.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for predicting and evaluating toxicity of novel non-steroid anti-inflammatory agent pollutant based on daphnia magna toxicity
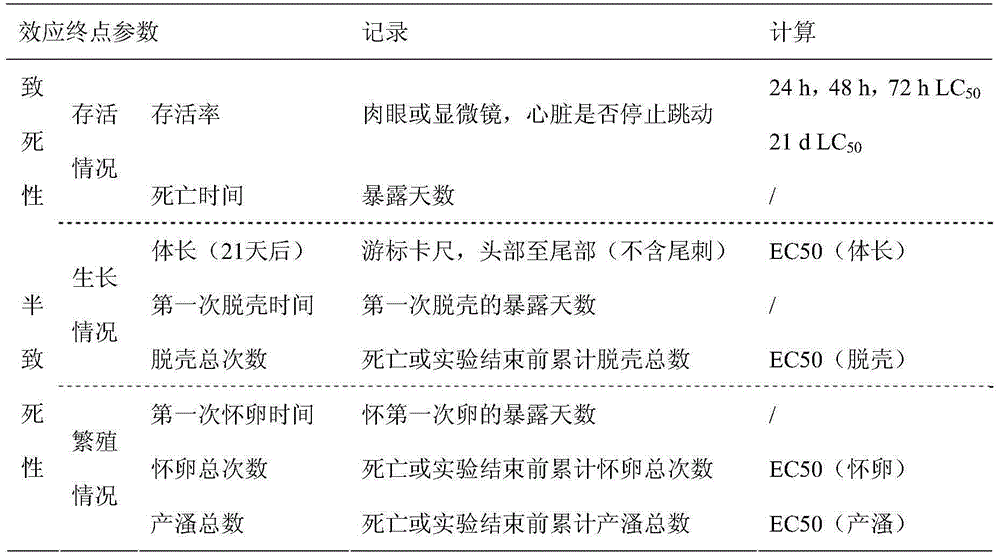
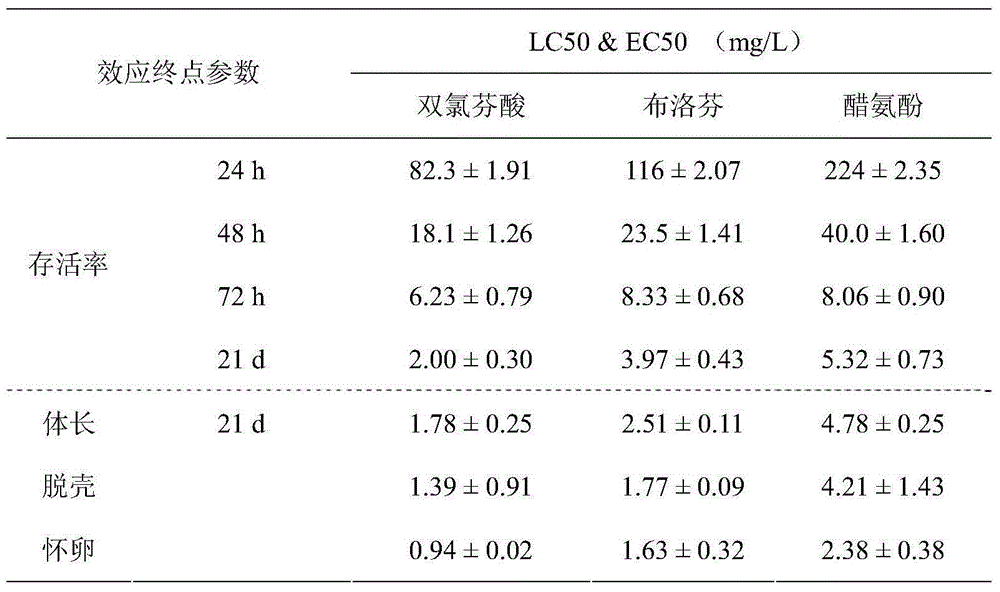
The invention discloses a method for predicting and evaluating toxicity of a novel non-steroid anti-inflammatory agent pollutant based on daphnia magna. According to the method, daphnia magna is exposed to the novel non-steroid anti-inflammatory agent pollutant with equal logarithm spacing concentration, the survival rates of daphnia magna generated when the daphnia magna is exposed for 24 h, 48 h and 72 h, and the survival rate, the body length, the total number of shelling and egg carrying times and the total daphnia magna producing amount of the daphnia magna exposed for 21 d are recorded respectively; corresponding 24 h LC50, 48 h LC50 and 72 h LC50 are obtained through calculation of SPSS software and used for evaluating acute toxicity, and corresponding 21 d LC50, body length EC50, shelling EC50, egg carrying EC 50 and daphnia magna producing EC50 are obtained and used for evaluating chronic toxicity; thus, the toxicity characteristic and the toxicity level of the novel non-steroid anti-inflammatory agent pollutant are analyzed, tested and quantitatively described, meanwhile can serve as indexes for monitoring and evaluating biotoxicity of non-steroid anti-inflammatory agent sewage, and can provide reference for predicting and evaluating potential ecotoxicity risks of the pollutant in water.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM
Coregonus ussuriensis fry culture method
ActiveCN107079843AImprove qualityImprove survival rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaDaphnia sineviDaphnia magna
The invention discloses a coregonus ussuriensis fry culture method, relates to a fish fry culture method, and aims to solve the technical problem of high death rate in a large-scale culture process of coregonus ussuriensis fries. The method comprises the following steps: 1, rupturing membranes of the coregonus ussuriensis fries; 2, after the coregonus ussuriensis fries float upwards, feeding the coregonus ussuriensis fries in a mouth opening stage with fairy shrimps serving as biological baits, then feeding the coregonus ussuriensis fries with daphnia magna (which is aquatic zooplankton belonging to cladocerans) for 5 to 10 days after the coregonus ussuriensis fries open mouths for 15 to 20 days, feeding the coregonus ussuriensis fries with a water earthworm-complete formula feed for 10 to 15 days, and finally enabling the coregonus ussuriensis fries to adapt to the acclimation of the complete formula feed till the fries are 8 to 10 g in weight, namely completing culture of the coregonus ussuriensis fries, wherein after the weights of the coregonus ussuriensis fries are greater than 0.3 g in the step 2, the culture density is 4,000 to 5,000 pieces / m<3>. The coregonus ussuriensis fries cultured by the coregonus ussuriensis fry culture method are high in quality, and the survival rate can be increased to 80 percent or above. The coregonus ussuriensis fry culture method belongs to the field of fish fry culture.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG RIVER FISHERY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF FISHERIES SCI
Device for separating mother daphnia magna and young daphnia magna for daphnia magna experiment and method of separating mother daphnia magna and young daphnia magna for daphnia magna experiment
InactiveCN103210880AEasy to separateSeparation and cleaningAnimal husbandryDaphnia magnaPore diameter
The invention discloses a device for separating mother daphnia magna and young daphnia magna for a daphnia magna experiment and a method of separating the mother daphnia magna and the young daphnia magna for the daphnia magna experiment. The device comprises a separating tank and separating screens, wherein the separating screens comprise a first separating screen and a second screen which are respectively stuck in the inner wall of the separating tank in a sealing way from top to bottom; the first separating screen is a nylon screen with the pore diameter of 1200 microns; and the second separating screen is a nylon screen with the pore diameter of 1000 microns. According to the device for separating the mother daphnia magna and the young daphnia magna for the daphnia magna experiment, the separating screens which are stuck in the separating tank in a sealing way are adopted, and optimal fineness is selected, so that the mother daphnia magna and the young daphnia magna for the daphnia magna experiment can be separated rapidly, conveniently and cleanly, and the mother daphnia magna and the young daphnia magna can be directly used in a laboratory or on the spot.
Owner:CHANGZHOU ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING CENT
Method for cooperative control of microcystis aeruginosa by using chub, bighead, silver xenocypris fish and daphnia magna
ActiveCN103880192ASustained growth inhibitionSolve stubborn problemsBiological water/sewage treatmentEutrophicationFood chain
The invention discloses a method for cooperative control of microcystis aeruginosa by using chub, bighead, silver xenocypris fish and daphnia magna, and belongs to the technical field of water treatment. The microcystis aeruginosa in water is controlled through a food chain relationship; the chub, the bighead, the silver xenocypris fish and the daphnia magna can directly eat the microcystis aeruginosa in a filtering manner; meanwhile, the chub, the bighead and the silver xenocypris fish also can intake the daphnia magna, so as to indirectly consume the microcystis aeruginosa in water; the fish, the daphnia magna and the microcystis aeruginosa form the food chain relationship. In addition, the upper, middle and lower microcystis aeruginosa and a microcystis aeruginosa resting body at the bottom can be controlled by fully utilizing the vertical spatial distribution difference of the three fishes in the water, the content of the microcystis aeruginosa in the water can be more effectively controlled, the eutrophication level is reduced, the balance of an ecological system of the water is facilitated, and meanwhile, certain economic value can be obtained by catching the chub, the bighead, the silver xenocypris fish. The method has the advantages of low cost, no secondary pollution and the like, and is simple and feasible.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MINIST OF ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT OF THE PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA
Breed conservation culture method of daphnia magna
The invention belongs to the field of cladocerous zooplankton culture, and relates to a laboratorial breed conservation culture method of daphnia magna. By the breed conservation culture method, long-term stable growth of the daphnia magna in a system can be ensured, and regular supplementation of evaporated water is needed, but addition of additional bait is not required. After adoption of a simple experimental system for breed conservation, the operation is simple, the cost is low, the daphnia magna can grow and propagate steadily, regular field seed collection is not required, troubles of frequent artificial water change, bait feeding and impurity and waste removal in ordinary culture are avoided, and thus a purpose of simple and convenient laboratorial long-term breed conservation is achieved.
Owner:广东中科英海科技有限公司 +2
Six-membered spiro rhodamine pH fluorescent indicator containing urea structure and application thereof
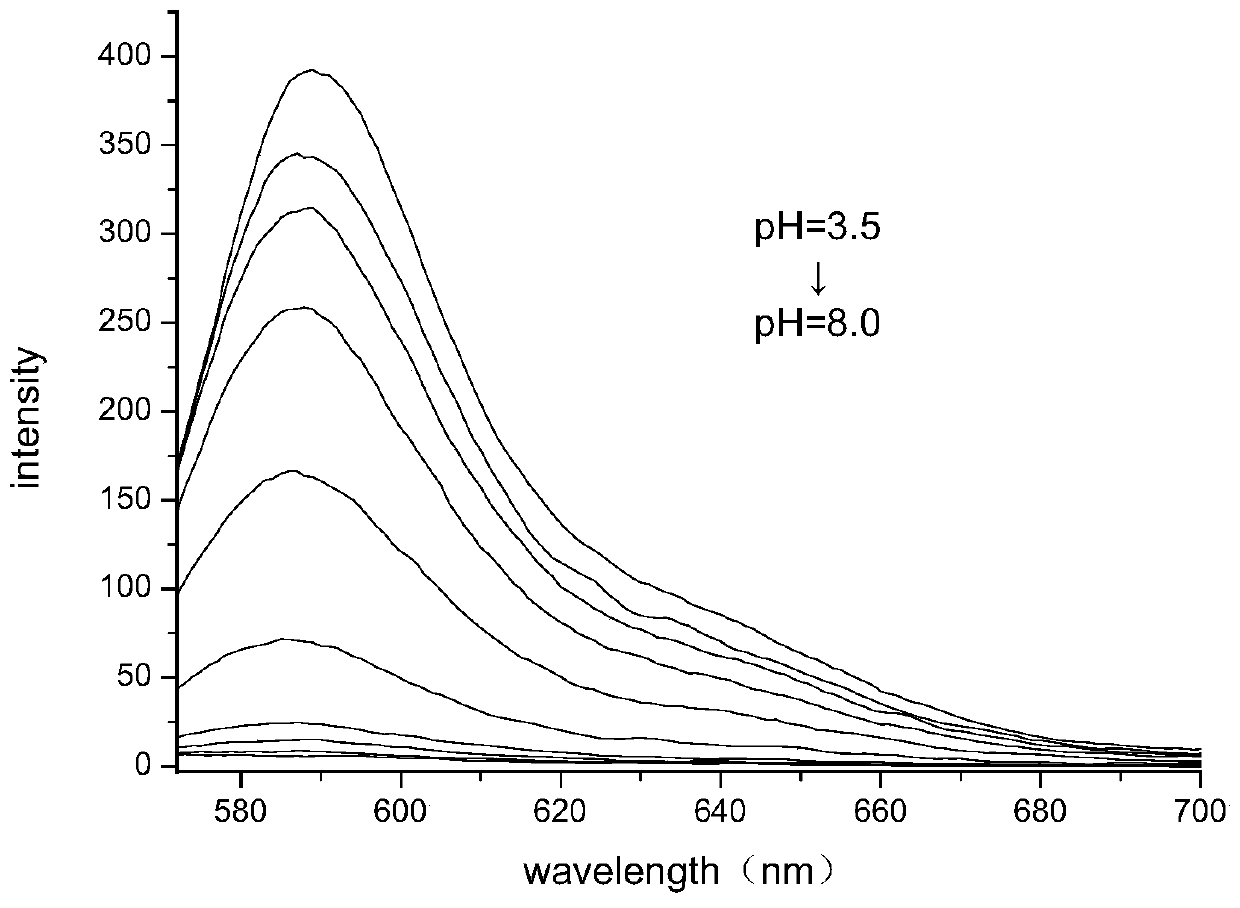
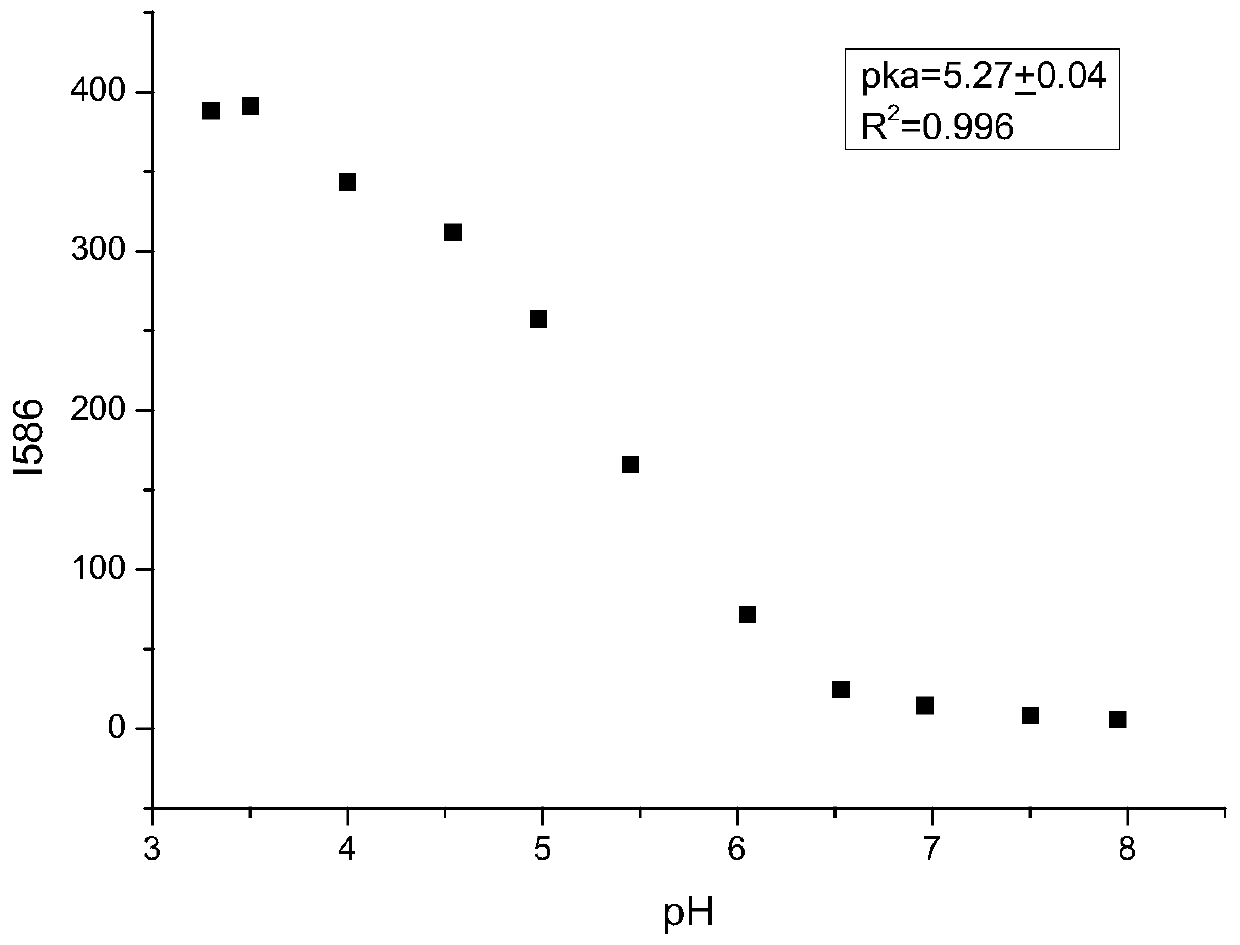
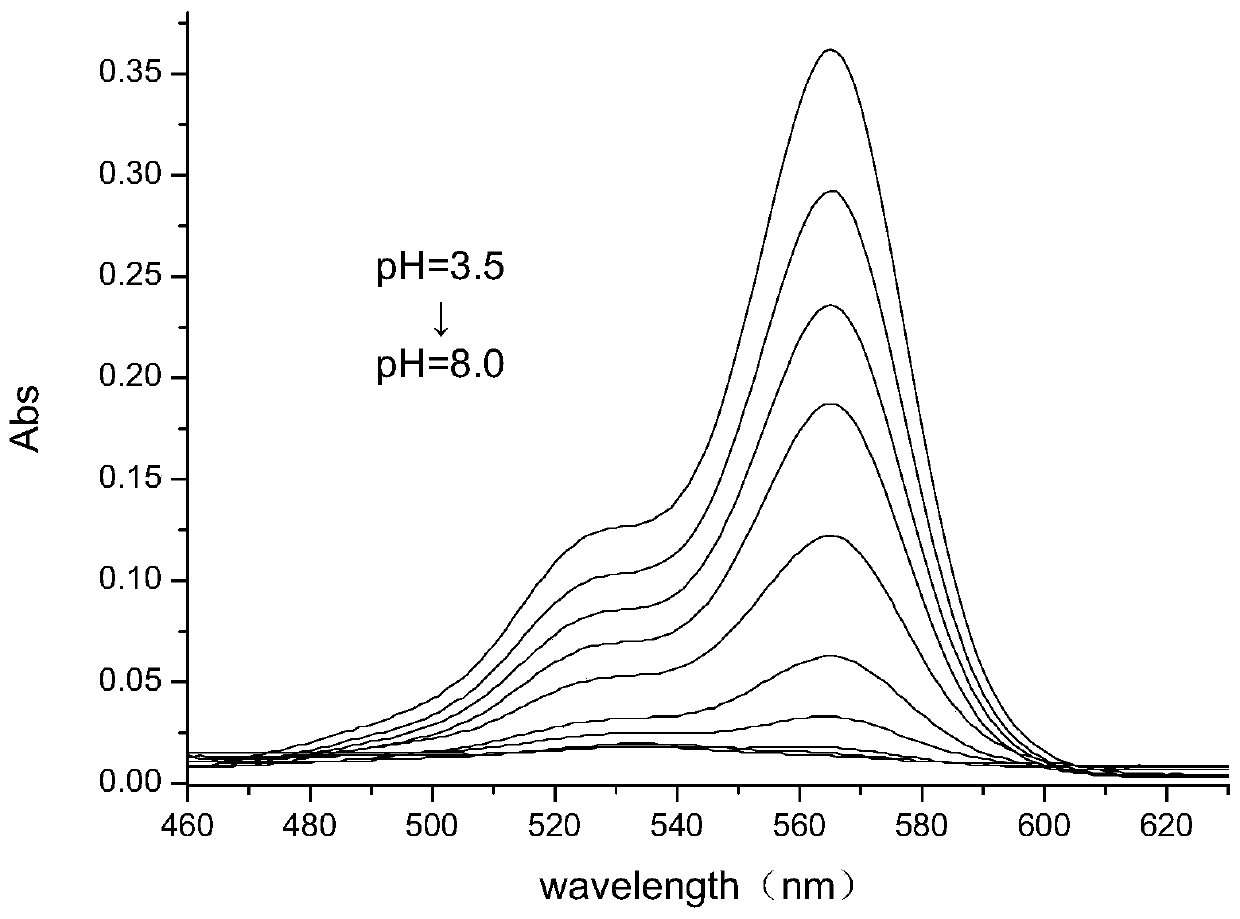
ActiveCN110330965AGood acid-base reversibilityQuick responseOrganic chemistryAzo dyesAqueous acetoneEvaporation
The invention relates to a six-membered spiro rhodamine pH fluorescent indicator containing a urea structure and application thereof. The fluorescent indicator has a structure as shown in a general formula (I). The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) adding a rhodamine compound and phosphorus oxychloride into 1,2-dichloroethane, carrying out heating reflux reaction, cooling the product to room temperature, and removing the solvent; 2) adding an acetone aqueous solution of sodium azide, stirring the mixture at room temperature, extracting the reaction solution with dichloromethane, drying the extract, and performing pressure reduced evaporation to remove the solvent; 3) dissolving the obtained reaction solution with dry acetonitrile, transferring into a reaction kettle, adding excessive ammonia water, and carrying out reaction in oil bath at 100 DEG C for 10 hours; and 4) extracting the obtained product with dichloromethane, drying the extract, and purifying the extractthrough silica gel column chromatography to obtain the target product Rh-NH. The indicator provided by the invention has good pH reversibility. After the indicator disclosed by the invention is usedfor dyeing the daphnia magna, the indicator Rh-NH1 can be positioned in the intestinal tract of the daphnia magna and indicates the acidity of the daphnia magna.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
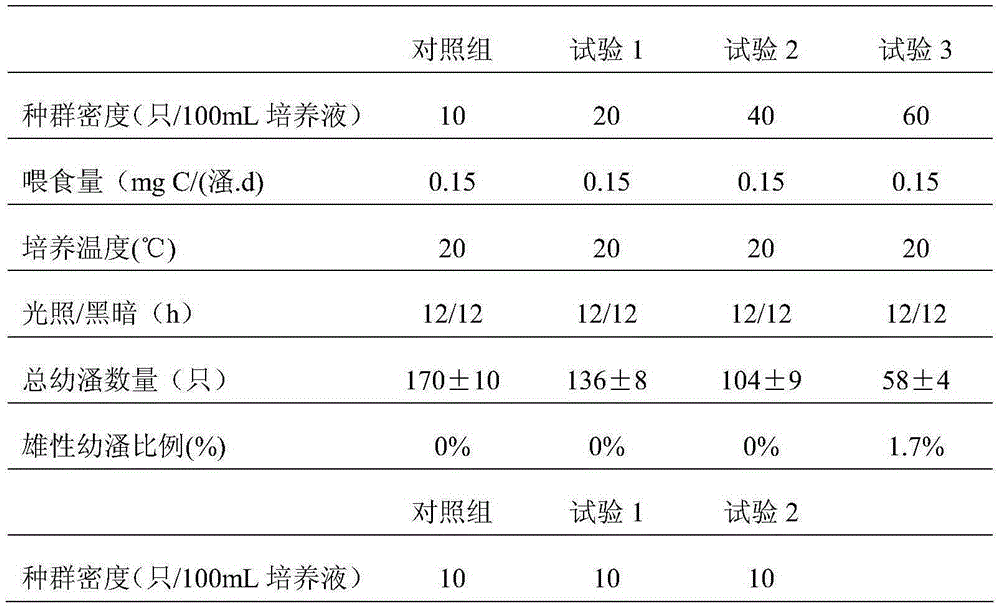
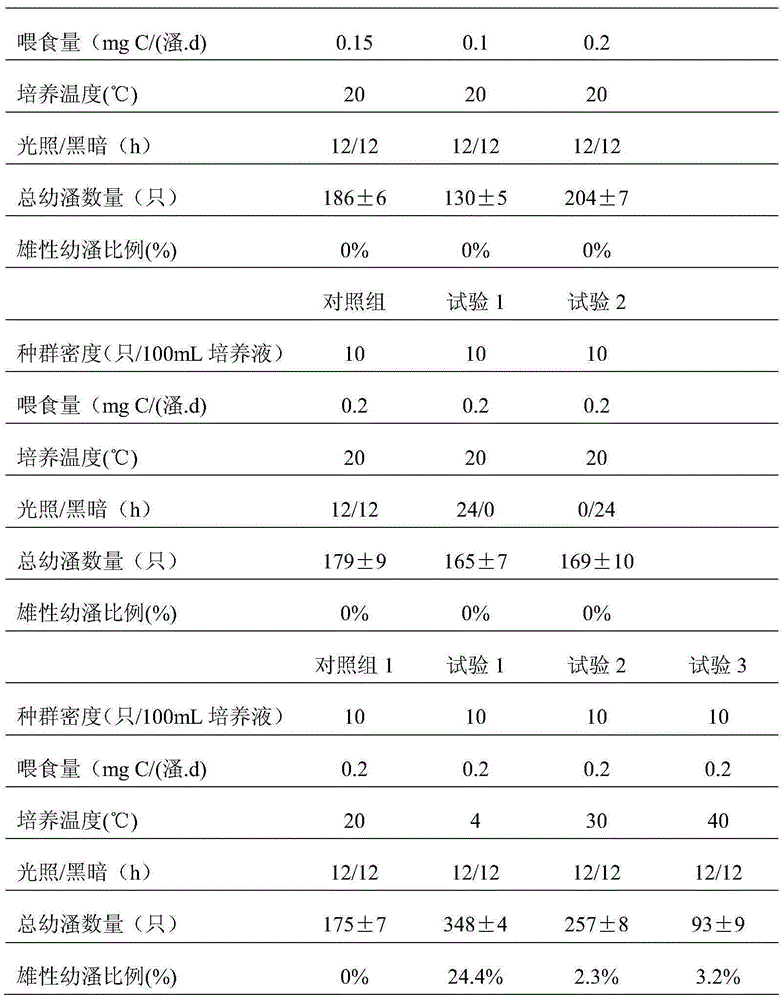
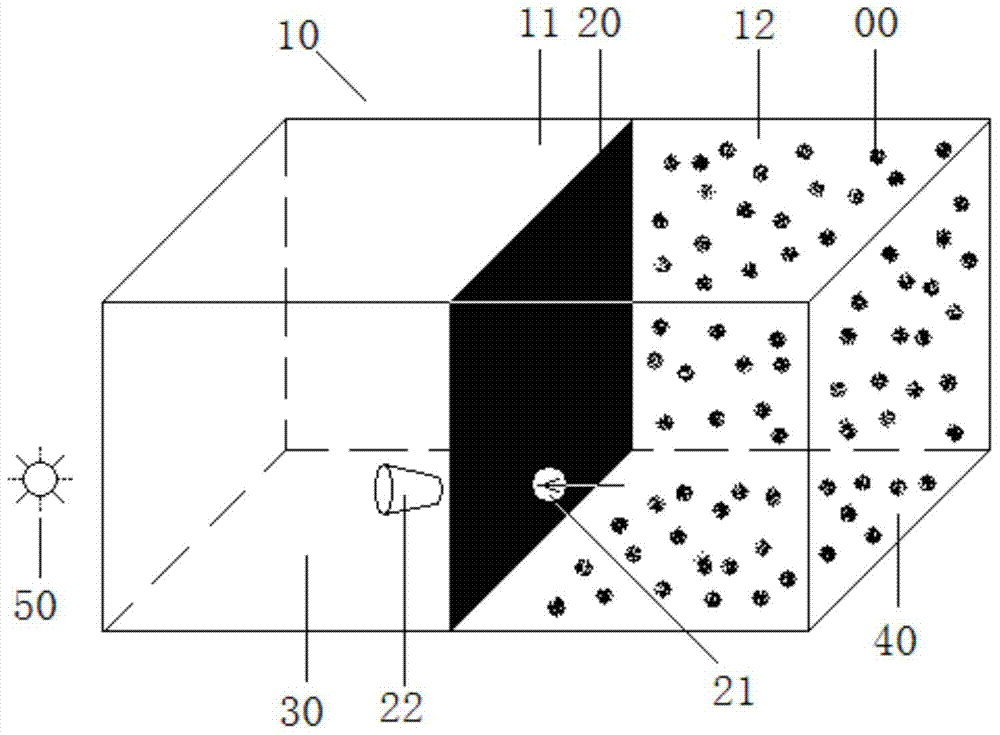
Method for quickly identifying sex of young daphnia of daphnia magna
InactiveCN105284740AEliminate the influence of identification resultsReduce manual workloadSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsDaphniaDaphnia magna
The invention discloses a method for quickly identifying sex of young daphnia of daphnia magna. The method comprises the steps of: putting newborn young daphnia in a test tube of a simple induction device; adding a GFID culture medium which is 16.5 cm high into the test tube, wherein the newborn young daphnia is adaptive in the GFID culture medium for 1 hour, the part which is 2.5 cm above the bottom of the test tube is called a system B, and the part which is 14 cm below a liquid level of the test tube is called a system A; and putting the induction simple device for 24 hours under the condition that the light density is 30 [Mu]E / (m2.s) and the temperature is 20 DEG C; after putting the device in a dark environment for 5 minutes, performing statistics on male daphnia and female daphnia entering into the system A or the system B at every 1 minute, respectively; and counting for 20 minutes and accumulating the quantity of the male daphnia and female daphnia entering into the system A or the system B in the time interval, wherein the result is that all the female daphnia enter into the system A while all the male daphnia enter into the system B. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for quickly identifying the sex of the newborn young daphnia and solves the problem that sex identification of newborn young daphnia is great in workload and overlong in consumed time.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY +1
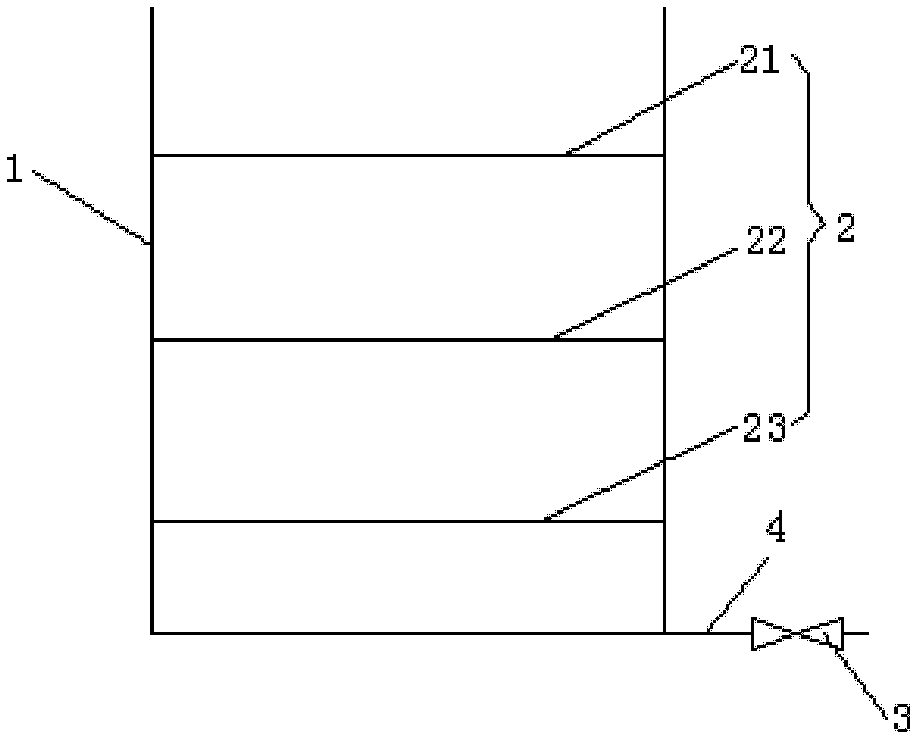
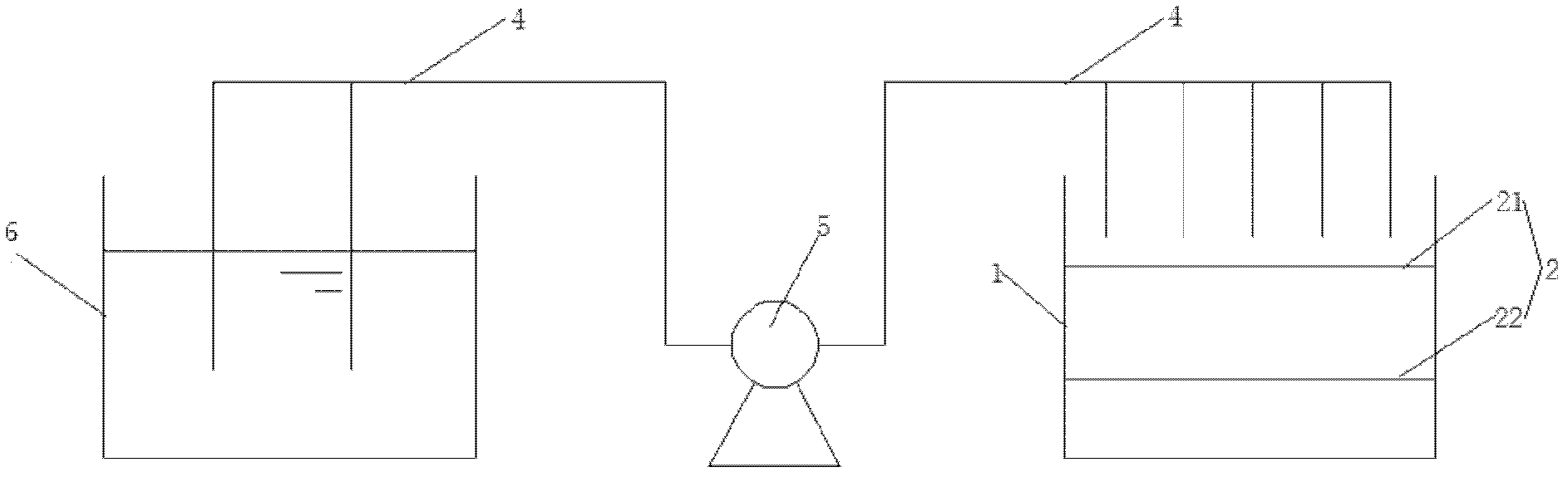
Device and method for replacing nutrient solution for indoor cultivation of daphnia magna
InactiveCN103563859AAvoid bodily harmImprove separation efficiencyAnimal husbandryDaphnia magnaEnvironmental engineering
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Algae removal and control method for low-speed small watershed
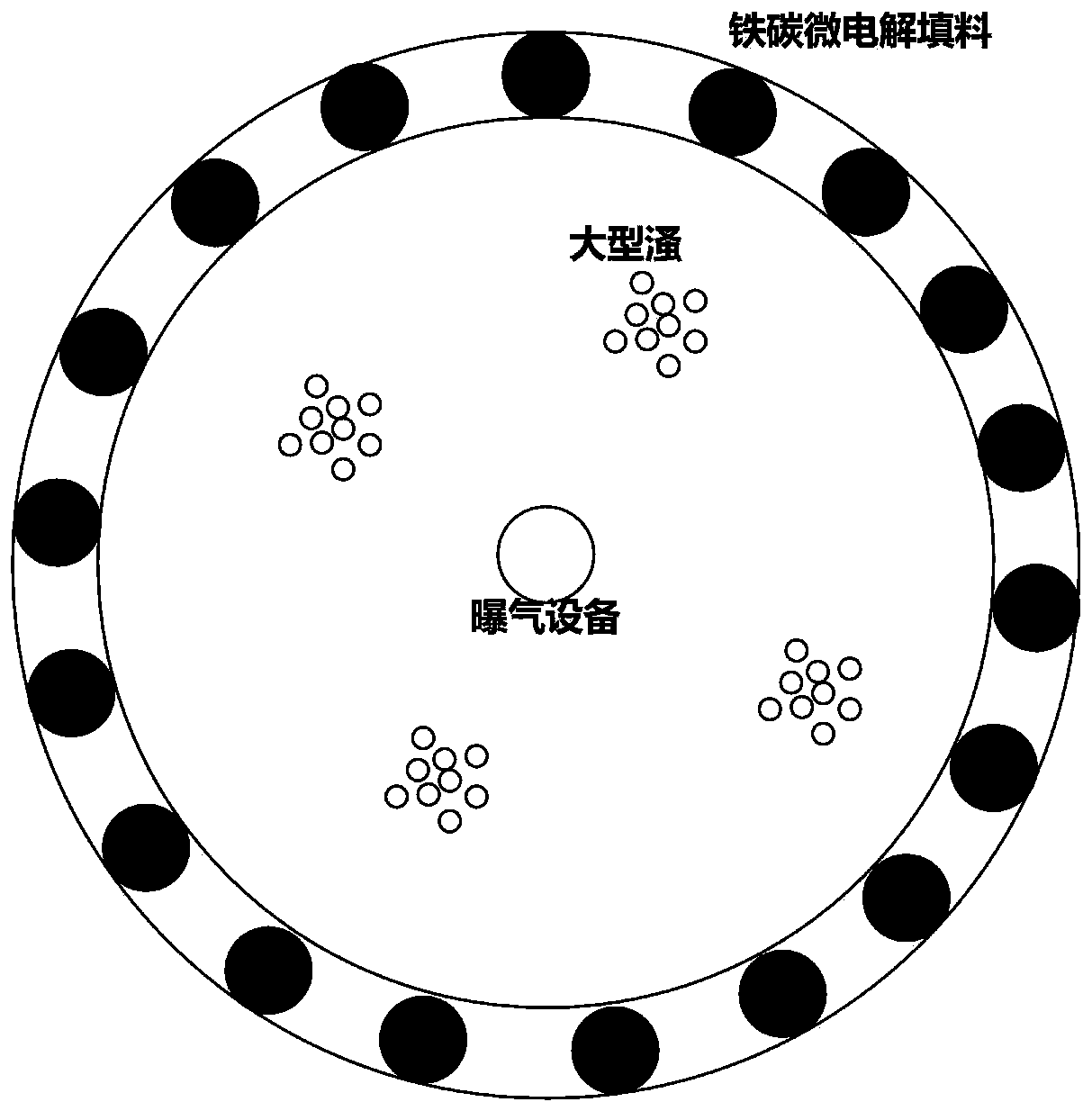
ActiveCN109851163ABring secondary pollutionIncrease dissolved oxygenWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentDaphnia magnaLow speed
The invention discloses an algae removal and control method for a low-speed small watershed. The method comprises the following steps: fishing at least 60% of algae in water; arranging a plurality ofgabion boxes filled with iron-carbon micro-electrolysis fillers along the periphery of the bank of the fished water area to remove phosphorus in the water; laying a sunshade net at 0.5 m above the water surface, and carrying out shading treatment for 10 days to inhibit growth of algae; mounting an aeration device so that aeration is started after shading is finished, and dissolved oxygen in wateris increased; uniformly throwing nitrifying bacteria into the water area for degrading ammonia nitrogen in the water by the nitrifying bacteria under an aerobic condition; uniformly spreading a phosphorus-accumulating bacterial agent to the water area for sucking phosphorus in the water into the body by the phosphorus-accumulating bacterium agent under the aerobic condition; by avoiding aeration positions, adding daphnia magna into a water area. Physical algae removal and biological algae removal methods are combined, so that the method is simple and easy to operate, takes effect quickly, doesnot bring secondary pollution to the environment and has few remaining problems.
Owner:SICHUAN QINGHE TECH
Method for removing water blue-green algae based on daphnia magna and method for purifying water area
InactiveCN109650546AReduced simplicityLow costBiological water/sewage treatmentAcute toxicity testingFood chain
The invention relates to a method for removing water blue-green algae based on daphnia magna, aims at the problem of blue-green algae outbreak in lakes, reservoirs and other natural water due to the acceptance of domestic sewage, industrial wastewater and the like containing a large amount of nitrogen and phosphorus, and develops a biological method taking ecosystem restoration as a principle based on a food chain relationship between the daphnia magna and blue-green algae to remove the water blue-green algae. The first technical problem to be solved by the invention is acute toxicity evaluation of blue-green algae enriched water, the second technical problem to be solved by the invention is screening and domestication of large and healthy daphnia magna. The acute toxicity evaluation is adopted to assess the feasibility of daphnia magna treatment, and then the cultivation domestication of laboratory and on-site two stages enables the daphnia magna to grow and reproduce in the blue-green algae outbreak. The daphnia magna is utilized to ingest the blue-green algae to increase the concentration of dissolved oxygen in water and promote the growth of submerged plants. Furthermore, fishes, shrimps, snails and other high-grade organisms are introduced and the daphnia magna are used as bait to form a closed cycle, thereby restoring an original water ecosystem and eliminating blue-greenalgae pollution.
Owner:中国疾病预防控制中心环境与健康相关产品安全所 +1
Puffing compound feed for culturing mandarin fish on circulating water runway and preparation method of puffing compound feed
InactiveCN110710618AImprove conversion rateImprove feeding capacityFood processingClimate change adaptationFeed conversion ratioAntioxidant
Owner:HUZHOU HAIHUANG BIOTECH
Method for forecasting reproduction toxicity of phenol compounds to daphnia magna
InactiveCN104408321AOvercome the shortcomings of poor generalization abilityImprove stabilitySpecial data processing applicationsData informationDaphnia magna
The invention relates to a method for using a cross-referencing method to forecast the reproduction toxicity of phenol compounds to daphnia magna and belongs to the risk evaluation and prediction technology. The method for forecasting the reproduction toxicity of the phenol compounds to the daphnia magna includes that building a data information set of the phenol compounds according to the common functional groups, physical and chemical properties, end point data and toxicity mechanism of the phenol compounds, and selecting the cross-referencing method to forecast the end point data of the reproduction toxicity of the phenol compounds to the daphnia magna according to the chemical substance similarity and end point change rule.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MINIST OF ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT OF THE PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA
Domestication method of a large flea and its application
ActiveCN104787893BPromote growthPromote photosynthesisWater treatment compoundsBiological treatment apparatusZooidCyanotoxin
The invention provides a daphnia magna domestication method and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: feeding daphnia magna into a domestication pool, cultivating the daphnia magna for a certain time period with specific domestication food, repeatedly domesticating and screening dominant species, and performing stabilization and rejuvenation to finally domesticate the daphnia magna into natural enemies of cyanophyta. The invention further discloses the domestication food for domesticating the daphnia magna and the application of the daphnia magna domestication method to the field of ecological water body remediation. The daphnia magna domesticated by the method has the characteristics of large individuals, high cyanophycean toxin conversion capability and high outdoor stability; when the domesticated daphnia magna is used for ecological remediation, underwater lighting conditions can be improved, the clarity of a water body can be rapidly improved, and quick response, environment friendliness, low carbon and high efficiency are achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI TAIHE WATER ENVIRONMENTAL TECH DEV CO LTD
Macrobrachium rosenbergii compound feed using daphnia magna dry powder for partially replacing fish meal
InactiveCN107232394AGood survival rateHigh in umami amino acidsClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffAntioxidative stressDaphnia magna
The invention discloses a macrobrachium rosenbergii compound feed using a daphnia magna dry powder for partially replacing fish meal. According to the macrobrachium rosenbergii feed, the daphnia magna dry powder is used for replacing 21.7 percent to 44.0 percent of fish meal. The optimum dosage of the daphnia magna dry powder is 5 percent to 20 percent, and the dosage of the fish meal is reduced to 16.8 percent to 26.7 percent from 30 percent. The experiment proves that compared with non-replaced fish meal control groups, macrobrachium rosenbergii hepatopancreas SOD, serum MDA, serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase, serum glutamic oxalacetic transaminase in replacement groups are lower than those in the control groups in different degrees, so that by using the daphnia magna dry powder for replacing the fish meal, the macrobrachium rosenbergii can have a better anti-oxidative stress capability, and is more beneficial for keeping the health of hepatopancreas.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com