Patents
Literature
138 results about "Fairy shrimps" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
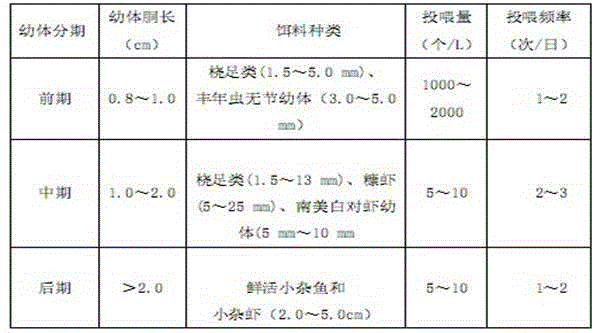
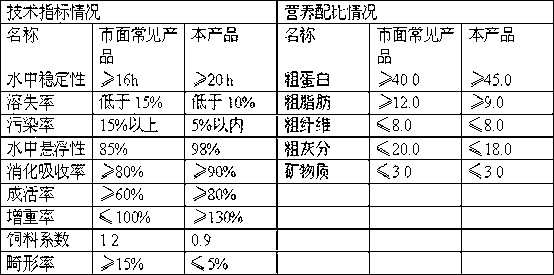
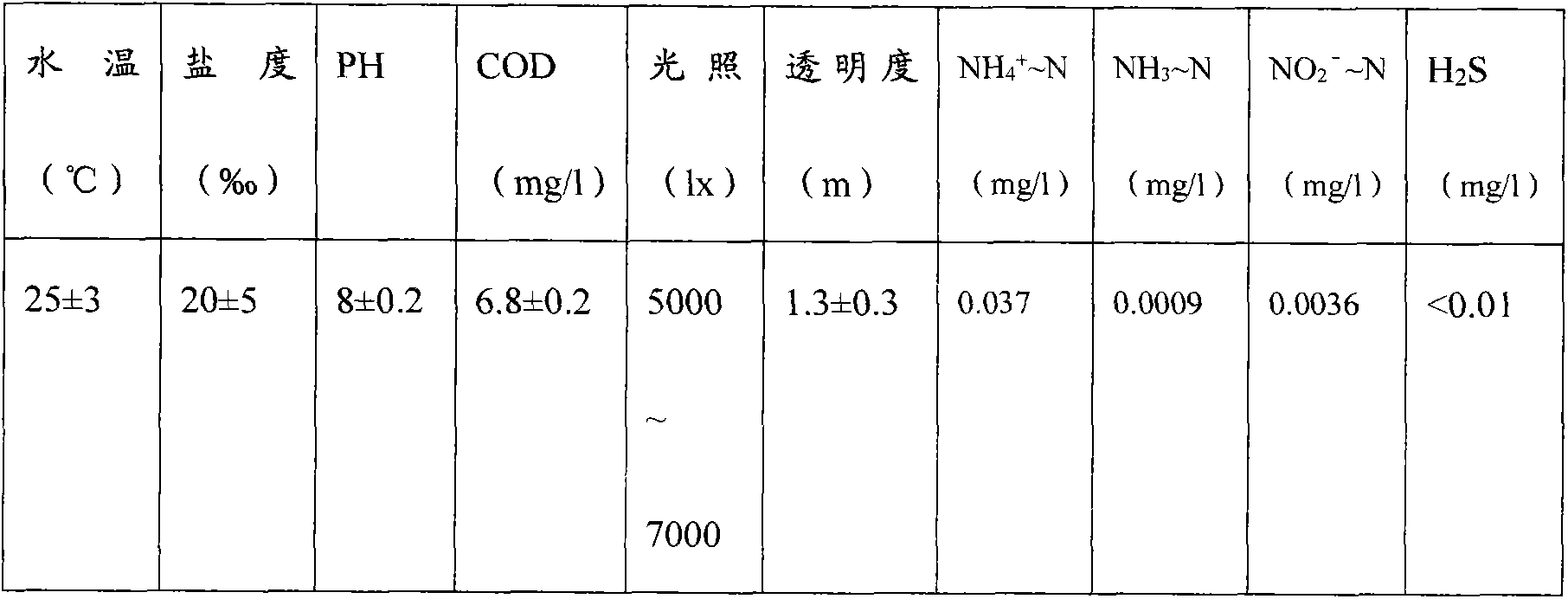
See text. Fairy shrimp is the common name for aquatic crustaceans in the branchiopod order Anostraca, characterized by elongated bodies, paired compound eyes on stalks, absence of a carapace, and an upside down swimming motion. Brine shrimp is the common name for some members of Anostraca.
Method for artificially breeding sepia lycidas gray
ActiveCN102939924AImprove hatchabilityImprove survival rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaOpossumAnimal science
The invention discloses a method for artificially breeding sepia lycidas gray, and the method is characterized by comprising the following steps of (1) parent breeding: selecting a harmless parent with complete body into a temporary culture cement tank to be temporarily cultivated, feeding the parent with chilled fishes twice a day, wherein the feeding quantity is 2 to 5 percent of the weight of the sepia lycidas gray; (2) artificial breeding: placing an egg attaching device inside the temporary culture cement tank, mating the male and the female parents to lay eggs, and then transferring the eggs into a hatching tank to be hatched; and (3) offspring breeding: transferring the hatched seedlings into a seedling tank, feeding fairy shrimp nauplius or copepoda in the early stage, feeding copepoda, opossum shrimp or larval prawn in the middle stage, and feeding fresh live fishes and small shrimps in the late stage, completing the breeding of the seedling when the length of the seedling is more than 2cm, the trunk length is more than 1.2cm, the trunk width is more than 0.9cm and the weight is more than 0.3g, and taking out the seedlings with water. The method has the advantages of high survival rate, easiness in cultivation, large cultivation specification, strong disease resistance and fast growth.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Percocypris scaled artificial propagation method
ActiveCN104663547ARealization of large-scale artificial reproductionIncreased labor induction rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaYarnBroodstock
The invention discloses a percocypris scaled artificial propagation method. The percocypris scaled artificial propagation method comprises the following steps of (1) culturing of parent fishes: using a flowing water pond as a parent fish culturing pond to culture; (2) distinguishing of male and female parent fishes: utilizing a B-ultrasonic scanner to check the abdomens of the parent fishes to distinguish the male and female parent fishes; (3) artificial maturation induction: injecting luteotropin into the distinguished female fishes to release hormone A2 to accelerate induction; (4) artificial spawning induction: performing artificial spawning induction on the selected male and female parent fishes; (5) artificial inseminating; (6) hatching: performing the flowing water and light shielding hatching on the fish spawns after artificial inseminating in a yarn silk hatching framework; (7) culturing of fish fries: when the hatching fish fries start to flatly swim, using the fairy shrimps or crushed water earthworms as an opening bait; after the fish fries are completely domesticated to eat an artificial matching feed, moving the fish fries to a fish fry culturing pond to culture. The method has the advantages that the implementation is easy, the operation is simple and convenient, and the distinguishing rate of the male and female parent fishes can reach more than 90%; the spawning induction rate of the matured parent fishes which are artificially cultured reaches 75%.
Owner:YANGTZE RIVER FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI +1
Perfect compound feed for groupers
ActiveCN103005183APromote digestion and absorptionImprove immunityAnimal feeding stuffDocosahexaenoic acidFish oil
The invention discloses a perfect compound feed for groupers, which is a compound feed suitable for the culture of grouper large-size fish seeds. The perfect compound feed is prepared by adopting imported fish meal, fermented soybean meal, alpha-starch, flour, squid meal, krill meal, yeast extracts, fairy shrimps, fish oil, soybean phospholipids, DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid), EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid), composite mineral salt, compound vitamins, compound enzyme preparations, compound immunopotentiators, hepatinica and compound microecologic preparations as raw materials. The perfect compound feed disclosed by the invention can promote the digestion and absorption of the groupers, regulate the stability of the intestinal flora of the groupers, enhance the immunity of the groupers and play a lipotropic role by sufficiently considering the digestion and physiology characteristics of the culture period of the groupers and adding various additives to the feed, has the advantages of balanced and complete nutrition without drugs, namely added antibiotics and the like, and no pollution on water bodies and belongs to a high-efficiency environment-friendly nuisanceless feed.
Owner:广东越群海洋生物科技股份有限公司
Ecological young shrimp culture method for macrobrachium rosenbergii
InactiveCN104938378AEasy to cleanReduce adhesionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsNutritionShrimp culture
The invention provides an ecological young shrimp culture method for macrobrachium rosenbergii. The method includes the steps of preparing a young shrimp culture pond, preparing water used for young shrimp culture, obtaining young shrimp larvas, feeding bait, managing water quality, transferring the young shrimps to another pond, desalting for young shrimp emergence and the like. In the bait feeding process, the young shrimps are fed on natural bait unit cell algae, fairy shrimp nauplii and artificial bait egg custard, the natural bait is environmentally friendly and healthy, the articical bait is rich in nourishment, and nutritional ingredients are not prone to running off; when the water quality is managed, nuisanceless water quality ameliorant and microbial preparations are adopted to adjust the water quality. Hormones and poisonous chemicals are not used in the young shrimp culture process, the young shrimps are high in survival rate and grow healthily and strongly, young shrimp emergence is fast, and the ecological young shrimp culture method is low in cost, high in efficiency and capable of effectively increasing economic benefits of an aquaculture farm.
Owner:GUANGXI ACADEMY OF FISHERY SCI
Hippocampus kelloggi ecological breeding method
ActiveCN103548722AImprove survival rateIncrease growth rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaShrimpJuvenile fish
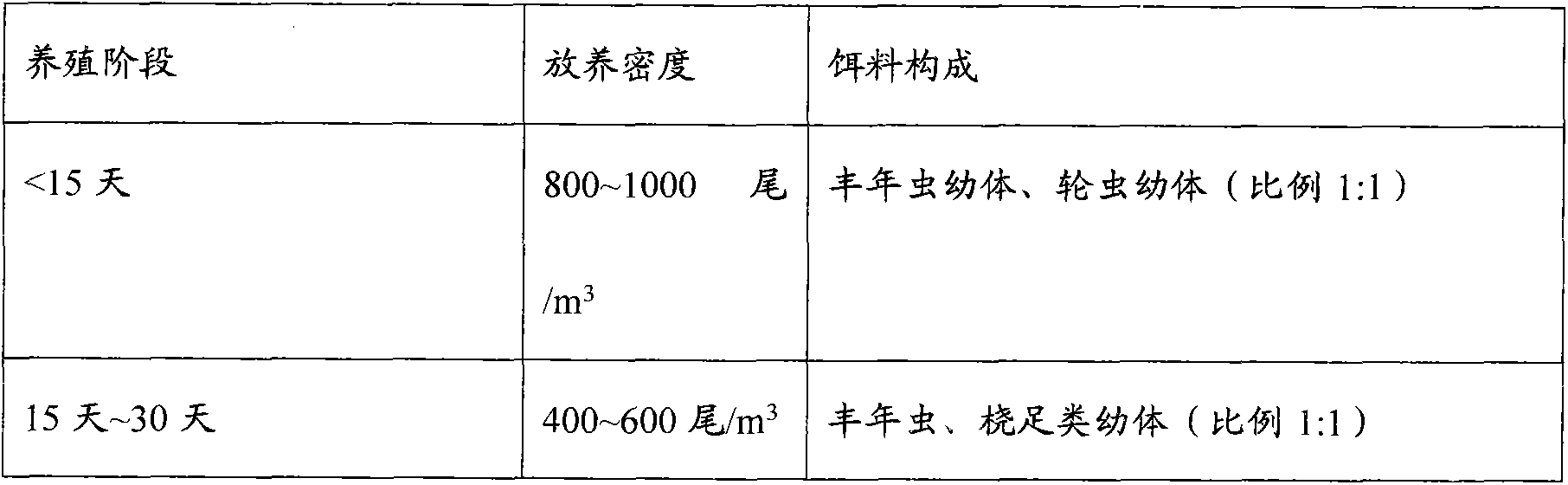
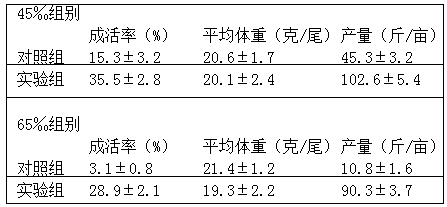
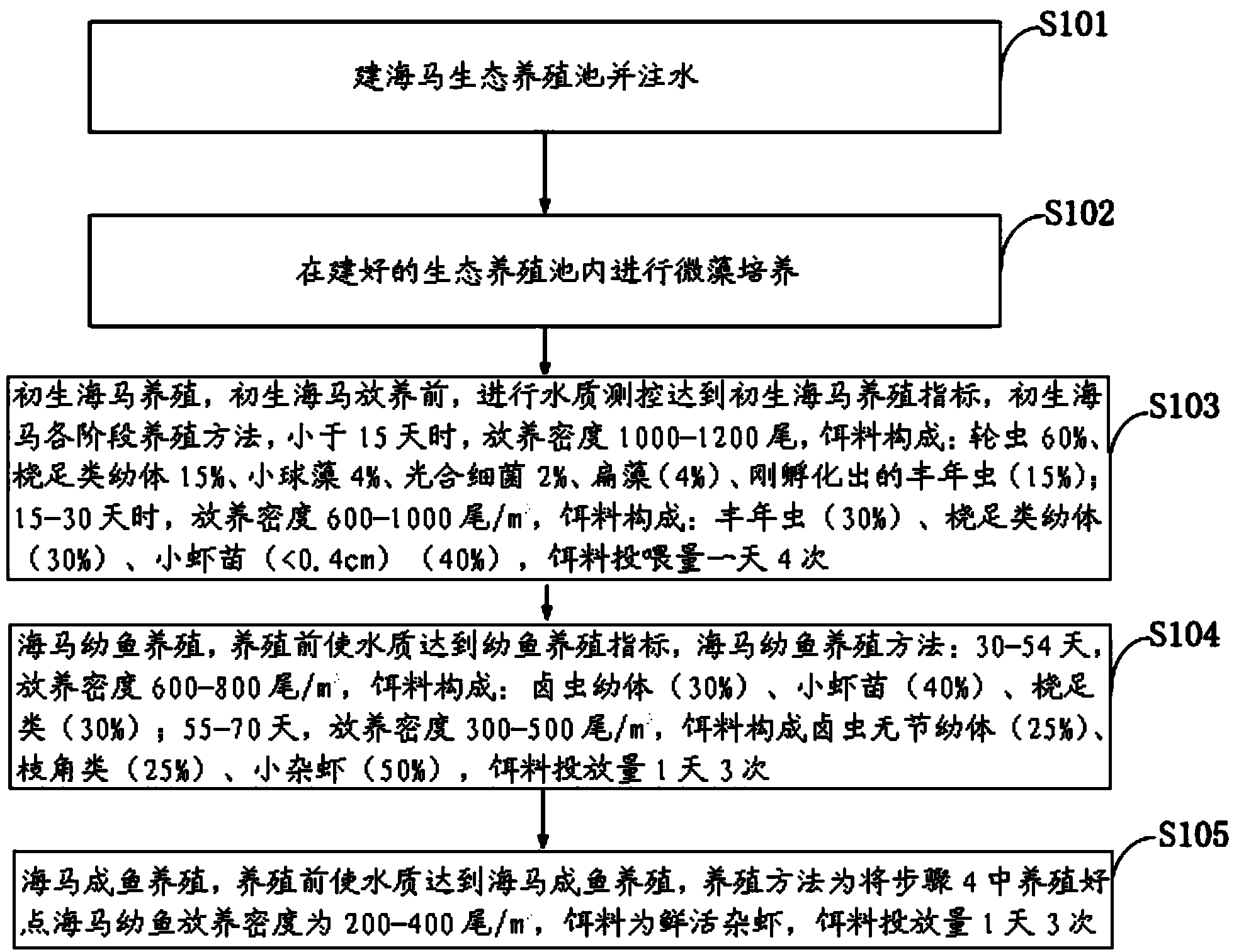
The invention discloses a Hippocampus kelloggi ecological breeding method. The Hippocampus kelloggi ecological breeding method comprises the steps of previous preparation, ecological breeding model establishment, newborn Hippocampus kelloggi breeding, Hippocampus kelloggi juvenile fish breeding and Hippocampus kelloggi adult fish breeding. The previous preparation includes reconstructing a shrimp seed breeding pond into a Hippocampus kelloggi breeding pond, and filling the pond with water after the pond is completely cleaned; ecological breeding model establishment includes in a microalgae cultivation stage, cultivating microalgae in water 3-5 days before Hippocampus kelloggi breeding, utilizing the microalgae as feedstuff of rotifers, artemia and fairy shrimps and improving water quality through photosynthetic bacteria; the newborn Hippocampus kelloggi breeding includes firstly measuring and controlling water quality, namely, detecting various indicators before stocking, then dividing the breeding stages into a breeding stage less than 15 days and a breeding stage between 15-30 days according to the duration of breeding days, and properly controlling the stocking density and feedstuff components of every breeding stage. The Hippocampus kelloggi ecological breeding method and artificial breeding method provide technical support and theoretical foundations for large-scale commercialized Hippocampus kelloggi breeding. By means of the Hippocampus kelloggi ecological breeding method, the breeding cost is reduced by 50%-60%, the quality of the breeding quality can be easily controlled by detecting various indicators before stocking, and high survival rate and growth rate of Hippocampus kelloggi can be guaranteed.
Owner:惠安港德海洋生物科技有限公司
Efficient health method for raising larvae of Litopenaeus vannamei
PendingCN106719206AStable algal phaseStable bacterial phaseClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffAir filtrationDisinfectant
The invention discloses an efficient health method for raising larvae of Litopenaeus vannamei, comprising the steps of (1) controlling the ambient in a raising shop, including air filtration, and humidity control via heat exchange; (2) controlling raising water quality, filtering raising water, inoculating single-celled algal liquid and probiotic under natural light intensity to carry out second water quality control, and culturing organisms as bait; (3) controlling larval quality, to be specific, treating the raising water body not with a disinfectant and antibiotics, raising larvae at the low temperature of 29 DEG C, performing low temperature resistant domestication on post-larvae, starting to feed with artificial formula feed from mysis stage which is mainly made with single-celled algae and fairy shrimp, performing mimic ecological desalination growing, and performing whole-course pathogen detection, including larvae raising water, feed, larvae and young shrimps. The method of the invention has the advantages that raising water quality and workshop ambient can be improved with no drug added, circulation of a raising pond is improved, success rate and growth rate in larval raising are increased, and the raised larvae have good quality and high adaptability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MARICULTURE RES INST
Intermediate culture method suitable for high-salinity mariculture of prawns
InactiveCN110250061AImprove survival rateImprove mu yieldClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaFairy shrimpsSeawater
The invention discloses an intermediate culture method suitable for high-salinity mariculture of prawns. The method comprises the steps of performing standardized seedling growing, and performing salinization intermediate culture after seedling growing, wherein according to standardized seedling growing, the seedling growing water temperature is 28-32 DEG C, the salinity is 26-32%., the culture density is 100,000-200,000 / m<3>, and all operations of feeding and water changing are consistent; in the zoea stage, adopting chaetoceros, wherein the quantity of chaetoceros is not smaller than 50,000 / mL; in the acanthosoma stage, adopting chaetoceros and skeletonema costatum, wherein the quantity is not smaller than 50,000 / mL; in the post larval, adopting fairy shrimps, wherein every 1,000,000 shrimp seeds are fed with not smaller than 0.75 kg of incubated fairy shrimps. According to the intermediate culture method suitable for high-salinity mariculture of prawns, standardized seedling growing is adopted at the early stage, salinization intermediate culture is performed at the later stage, the survival rate of South America white shrimps can be increased, and therefore the yield per mu and the total yield are greatly increased, and the culture area can be enlarged.
Owner:渤海水产股份有限公司 +2
Method for indoor low-cost high-density sustainable cultivation of artemia
ActiveCN105766810ASolve the costReduce the cost of farmingAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsWater qualityFairy shrimps
The invention relates to a method for indoor low-cost high-density sustainable cultivation of artemia. Filtered seawater at a suitable temperature is injected into a culture pond and then artificial water full of fertilizer is formed; artemia eggs are hatched in a container with the conical bottom, fairy shrimp larvae collected after the hatching for 12-16 h are placed in the culture pond to be cultured; artemia artificial composite feed are fed on the next day of inoculation to guarantee balanced nutrition of artemia in the growth and reproduction process; continuous aeration is performed in the culture process, and dissolved oxygen is maintained at 5 mg / L or above; after being cultivated for 9-15days, the artemia is collected as required; the self-reproduction and sustainable cultivation of the artemia can be performed in a timely pond division mode on the premise of not supplementing newly hatched artemia, and the cultivation scale is expanded continuously. The indoor low-cost high-density sustainable cultivation of the artemia is performed through optimization of artificial feed and timely pond division. Weather factor interference is effectively avoided, a good cultivation water environment is maintained, and the cultivation cost is reduced. Through water quality regulation and preparation and treatment of the artificial feed, the growth speed and yield of the artemia are effectively improved, the artemia quality is stabilized, and the industrial development of China's aquaculture is guaranteed.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Special feed for longsnout catfish in pond and preparation method of special feed
InactiveCN105394449APromote growthEasy to eatFood processingClimate change adaptationBetaineMortality rate
The invention discloses special feed for longsnout catfish in a pond. The special feed comprises raw materials in parts by weight as follows: 50-100 parts of fish meal, 5-10 parts of fairy shrimps, 10-20 parts of bean worm powder, 1-3 parts of fish oil, 0.5-1.5 parts of corn oil, 20-40 parts of bean pulp, 5-15 parts of rapeseed meal, 5-15 parts of high-gluten flour, 5-15 parts of corn flour, 10-30 parts of wheat bran, 5-14 parts of puffed sweet potato flour, 0.1-0.7 parts of glycine betaine, 15-30 parts of rice wine, 2-5 parts of soybean phospholipid and 5-15 parts of premix, wherein the premix comprises raw materials as follows: 0.01-0.4 parts of compound microelements, 1-2 parts of vitamins, 1-3 parts of mineral salt, 0.1-0.25 parts of lysine, 0.2-0.5 parts of methionine, 0.008-0.01 parts of bentonite and 2-3 parts of grape seed oil. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the special feed for the longsnout catfish in the pond. The special feed has balanced nutrition and can promote quick growth of the longsnout catfish, the death rate of the longsnout catfish is low, and a preparation method is simple and convenient to operate practically.
Owner:全椒县鮰鱼养殖专业合作社
Ecological Japanese sea horse breeding method
InactiveCN103960185ASuitable for artificial breedingClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaShrimpJuvenile fish
The invention discloses an ecological Japanese sea horse breeding method. The ecological Japanese sea horse breeding method comprises the steps of building an ecological sea horse breeding pond one week before breeding, cultivating microalgae in the built ecological breeding pond, and measuring and controlling water quality to reach newborn sea horse breeding indexes before newborn sea horses are bred. When the newborn sea horses is younger than 15 days, the released density is 1000-1200 tail / m<3>, and baits are composed of rotifer, copepods larvae, chlorella, photosynthetic bacteria, tetraselmis and fairy shrimps which are just incubated. During 15-30 days, the released density is 600-1000 tail / m<3>, baits are composed of fairy shrimps, copepods larvae and shrimp seeds, and the baits are fed into the breeding pond four times per day. A sea horse juvenile fish breeding stage comprises the step of enabling the water quality to reach juvenile fish breeding indexes before breeding. During 30-40 days, the released density is 600-800 tail / m<3>, and the baits are fed into the breeding pond three times per day. A sea horse adult fish breeding stage comprises the step of enabling the water quality to reach sea horse adult fish breeding indexes. The released density of sea horse adult fish is 200-400 tail / m<3>, baits are fresh and alive shrimps, and the baits are fed into the breeding pond three times per day. The ecological Japanese sea horse breeding method has the advantages of reducing production cost.
Owner:惠安港德海洋生物科技有限公司
Method for culturing and transplanting Scylla fries stage by stage
InactiveCN101990850ATo achieve the goal of stable and high productionReduce carnageClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaLive foodOrder copepoda
The invention provides a method for culturing and transplanting Scylla fries stage by stage, which relates to a Scylla culture method. The method comprises the following steps of: culturing zoeae in a culture pond for culturing for 12 to 18 days, and transferring the zoeae into a megalop culture pond with the area of 100 to 300 square meters for further culture; culturing live foods such as algae, fairy shrimps, copepods and the like in the megalop culture pond; transferring the fries at the last day of the fifth stage of the zoeae or at the first day of megalop, wherein the culture density of the megalop is controlled to be 1,000 to 2,000 fries per cubic meter; or culturing the zoeae at the fifth stage for 4 to 8 days, wherein the culture density is 2,000 to 4,000 fries per cubic meter; the water temperature of the megalop culture pond is between 24 and 32 DEG C; and the salinity is 1.5 to 2.6 percent; and transferring the megalop into a young Scylla culture pond, wherein the area ofthe young Scylla culture pond is 0.5 to 3 mu; the water temperature is between 26 and 33 DEG C; and the salinity is 1.0 to 2.0 percent.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Breeding technology for large-size parents of Eriocheir sinensis
ActiveCN103026989APromote steady developmentStable and sustainable useClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaMatingSarcocheilichthys sinensis
The invention relates to a breeding technology for large-size parents of Eriocheir sinensis. The breeding technology comprises the step of selecting the athletic parents of the Eriocheir sinensis, wherein the size of the female crab is above 150g and the size of the male crab is above 200g; the breeding technology is characterized by comprising the following steps: from the last ten-day of October to the first ten-day of November per year, soaking the selected parents of the Eriocheir sinensis into fresh water with tiny running water and sufficient oxygen for 2-3 minutes, and then taking out; after 3-5 minutes, disinfecting by using potassium permanganate; temporarily breeding in an indoor glass reinforced plastic over-wintering pool; starting the over-wintering breeding for the parents of the Eriocheir sinensis in the middle ten days of December; at the beginning of March per year, at a mating moment, controlling the water temperature at 9-12 DEG C, wherein the male and female ratio is (1.5-2):1 and the mating density is 7-13 pieces / m<2>; after oogenesis, continuously aerating and increasing the inflating volume, wherein the breeding temperature for the larva of the Eriocheir sinensis is at 24-25 DEG C and the breeding seawater salinity is 1.8%; and feeding rotifera, fairy shrimp larva and fresh water cladocerans biological baits.
Owner:上海市水产研究所(上海市水产技术推广站)
Microcapsule initial feed for prawn larva cultivation and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses microcapsule initial feed for prawn larva cultivation. The microcapsule initial feed for the prawn larva cultivation comprises, by weight, the following raw material components: 20-40% of enzymolysis barley pest thick liquid, 10-25% of fish meal, 5-10% of shrimp chaff, 10-25% of bean pulp, 1-5% of fairy shrimps, 1-6% of yeast powder, 0.5-2% of lecithin, 0.5-2% of fish oil, 0.4-1% of monocalcium phosphate, 1-20% of gelatin, 5-20% of maltodextrin, 0-2% of sodium carboxymethylcellulose, 0.1-2% of Chinese herbal medicine polysaccharide, and 1-10% of additive agent. The microcapsule initial feed for the prawn larva cultivation can greatly improve the growth speed, the metamorphosis rate and the immunocompetence of prawn larvae, and by means of a microcapsule manufacturing technique, the problem of water pollution caused by scattering of feed is solved.
Owner:中华全国供销合作总社天津再生资源研究所
Breeding method and device for improving survival rate of juvenile zebra fish
InactiveCN109089957AKeep healthyGuaranteed activityClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffYolkJuvenile fish
The invention discloses a breeding method and device for improving the survival rate of juvenile zebra fish. The breeding method comprises the steps that healthy adult zebra fish is selected as parents; male zebra fish and female zebra fish are taken and put in a breeding tank for breeding; the embryos in a lower layer of the breeding tank are collected and put in a breeding box and are blown awayby using a disposable dropper, and dead embryos in the breeding box are removed in time; the embryos are hatched, and all juvenile fish is fed with yolk water after being hatched; the yolk water is fed (for 7-10 days), and then the juvenile fish is fed with fresh hatched fairy shrimps. The breeding device is a breeding box and comprises a box body, an upper partition plate, a lower partition plate and a horn-shaped feeding port. The upper partition plate and the lower partition plate are parallelly placed on protrusions arranged on the inner wall of the breeding box body, and the box body isdivided into an upper portion, a middle portion and a lower portion. The feeding port is fixed to the upper partition plate. The upper partition plate and the lower partition plate are both provided with screen holes. By adopting the breeding method and the breeding device for breeding zebra fish, the survival rate of juvenile zebra fish can be remarkably improved, the cost is low, and the operation is simple and convenient.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Ecological feed special for promoting growth and enhancing immunity of lobsters
InactiveCN106616021APromote growthImprove qualityFood processingClimate change adaptationFairy shrimpsPhosphate
The invention discloses a special ecological feed for promoting the growth and enhancing the immunity of lobsters. The special ecological feed contains the following raw materials: wheat meal, broad beans, fried locust powder, fried puffing sweet potato powder, fried tenebrio molitor powder, bean worms, fairy shrimps, mulberries, folium eriobotryae, dragon fruit peels, spinach leaves, red dates, zeolite powder, L-carnitine, a microecological preparation, chitosan, vitamin C phosphate, beef tallow, anise oil, cerium citrate, taurine crystals, beta-glucan, a complex enzyme preparation and Chinese herbal medicines. The ecological feed special for promoting the growth and enhancing the immunity of the lobsters has the beneficial effects that the formula is reasonable, the nutrition is comprehensive, the growth of the lobsters can be promoted, and meanwhile, the immunity of the lobsters can be enhanced.
Owner:DINGYUAN PEIZHANG ECOLOGICAL GARDEN CO LTD
Method for preparing frozen sea horse feed
The invention discloses a method for preparing a frozen sea horse feed. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out temporary feeding on living fairy shrimps or acete chinensis until the polypides or shrimp bodies completely discharge baits in vivo; adding a nutrient supplement according or a use amount of 50-200mg in each liter of seawater, so as to reinforce the nutrition of the fairy shrimps or acete chinensis, wherein the nutrient supplement comprises 95-98wt% of microalgae dry powder and 2-5wt% of a concentrated nutrient solution, and the nutrient supplement is obtained by uniformly mixing the microalgae dry powder with the concentrated nutrient solution; sterilizing the fairy shrimps or acete chinensis by using hydrogen peroxide after being reinforced and flushing the fairy shrimps or acete chinensis with fresh water, and removing dead individuals after the sterilizing and cleaning operations; and detearing the living fairy shrimps or acete chinensis, and directly freezing the living fairy shrimps or acete chinensis in a cold storage to obtain the frozen sea horse feed. Compared with common frozen baits, the frozen sea horse feed disclosed by the invention has the advantages of few germs, convenience for storage and transportation, and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Killifish culture method
InactiveCN102440211AImprove hatchabilityImprove survival rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaKillifishOxygen content
The invention relates to a killifish culture method. The method includes the following steps: culture water, the pH of which is 6.5 to 8.0 and the oxygen content of which is 4mg / L to 8mg / L, is adopted to incubate spawns under 24 DEG C to 30 DEG C for 4 to 12 hours, incubated larvae are fed with brine shrimp larvae after 10 to 15 hours, water is changed every three days, and the amount of changed water is 1 / 10 to 1 / 5 each time; after 10 to 20 days, the larvae are grown into adult fishes, the adult fishes are transferred into a culture tank for raising and fed with fairy shrimps, water is changed every two days, and the amount of changed water is 1 / 8 to 1 / 4 each time. The culture method for culturing killifishes is easy to operate, and moreover, both the incubation rate and the survival rate of the killifishes are high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Method for labeling and culturing penaeus japonicus family in same pond of higher-place pond
ActiveCN104663549AOvercoming the difficulty of physically marking polycultureReduce the differenceClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaDisinfectantAntibiotic Y
The invention provides a method for labeling and culturing a penaeus japonicus family in the same pond of a higher-place pond and relates to the cultivation of young shrimps. Sand is paved in the higher-place pond and the higher-place pond is disinfected; a pipeline device for inflating and oxygenating is mounted, and seawater is filtered by the paved sand; the whole pond is disinfected, and a nutrition preparation and a bacillus viable bacterium preparation are sprayed; a fixed suspension net box is produced; the young shrimps are selected and transported; after the young shrimps are put into the pond, the water level is raised; the bacillus viable bacterium preparation and an organic fertilizer are sprayed, and povidone iodine is sprayed to disinfect a water body; after the young shrimps are put into the pond, fairy shrimp larvae which are manually incubated are fed in the morning and at night of each day within first 10 days; during a cultivation post-period, a young shrimp particle feed added with vitamins, amino acids and a lactobacillus viable bacterium preparation is fed; during the cultivation post-period, a water sample is taken every 5 days to observe the quantity of vibrio; when a lot of the vibrio is bred, a disinfectant is used for disinfecting the higher-place pond and antibiotics are added into a bait; when the young shrimps grow to be about 4cm, a fluorescent mark is injected to carry out family marking, and all the marked families are put into the same higher-place pond to be poly-cultured, and then the same pond property testing experiment is carried out.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Coregonus ussuriensis fry culture method
ActiveCN107079843AImprove qualityImprove survival rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaDaphnia sineviDaphnia magna
The invention discloses a coregonus ussuriensis fry culture method, relates to a fish fry culture method, and aims to solve the technical problem of high death rate in a large-scale culture process of coregonus ussuriensis fries. The method comprises the following steps: 1, rupturing membranes of the coregonus ussuriensis fries; 2, after the coregonus ussuriensis fries float upwards, feeding the coregonus ussuriensis fries in a mouth opening stage with fairy shrimps serving as biological baits, then feeding the coregonus ussuriensis fries with daphnia magna (which is aquatic zooplankton belonging to cladocerans) for 5 to 10 days after the coregonus ussuriensis fries open mouths for 15 to 20 days, feeding the coregonus ussuriensis fries with a water earthworm-complete formula feed for 10 to 15 days, and finally enabling the coregonus ussuriensis fries to adapt to the acclimation of the complete formula feed till the fries are 8 to 10 g in weight, namely completing culture of the coregonus ussuriensis fries, wherein after the weights of the coregonus ussuriensis fries are greater than 0.3 g in the step 2, the culture density is 4,000 to 5,000 pieces / m<3>. The coregonus ussuriensis fries cultured by the coregonus ussuriensis fry culture method are high in quality, and the survival rate can be increased to 80 percent or above. The coregonus ussuriensis fry culture method belongs to the field of fish fry culture.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG RIVER FISHERY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF FISHERIES SCI
Breeding method of released fry of schizothorax waltoni Regan
ActiveCN110537505AMeet growth needsEasy to operateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaGreenhouseCarp
The invention provides a breeding method of released fry of schizothorax waltoni Regan. The method comprises the following steps of breeding of the fry in the mouth opening period, wherein the fry arebred in parallel grooves, open mouths on the 18 day after hatching and are fed with microparticle compound feed 1-2 times every day with the daily feeding amount being 10% of the weight of the fishes and fed with fairy shrimps or chopped limnodrilus hoffmeisteri once every 4-6 days; breeding of the fry at the month age of 2 or older, wherein the fry at the month age of 2 which are bred in theparallel grooves are transferred into a greenhouse cement pond or an earthen pond cage, according to the breeding density, 100-300 fishes are put in per cubic meter of water, and the fry are fed withmicroparticle compound feed 1-2 times every day with the daily feeding amount being 5% of the weight of the fishes; breeding of the fry at the month age of 5-12 after hatching, wherein according to the breeding density, 20-50 fishes are put in per cubic meter of water, and the fry are fed with carp or pelteobagrus fulvidraco feed 1-2 times every day with the daily feeding amount being 3-5% of theweight of the fishes. The breeding method is easy to operate, meets the growth needs of schizothorax waltoni Regan, and can be used for large-scale production of the released fry of schizothorax waltoni Regan in Tibet.
Owner:西藏自治区农牧科学院水产科学研究所
Nutrient enhancing and producing method of fairy shrimp nauplius
ActiveCN105724828AEasy to trainEasy to getAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsArginineFairy shrimps
The invention belongs to the field of aquaculture, and discloses a nutrient enhancing and producing method of fairy shrimp nauplius. The method includes the step of adding L-arginine, butylated hydroxytoluene and chlorella to fairy shrimp nauplius for nutrient enhancing. By means of the method, the nutrient enhancing of fairy shrimp nauplius can be rapidly and easily improved, and the content of unsaturated fatty acid in fairy shrimp nauplius is increased.
Owner:阳江利洋苗种繁育有限公司
Method for improving breeding survival rate of Portunus trituberculatus larvae in northern areas
ActiveCN106035164ACultivate water environment safetySafe Seed Breeding ProcessClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaAntibiotic YFairy shrimps
A method for improving the breeding survival rate of Portunus trituberculatus larvae in northern areas belongs to the field of aquaculture. The method includes parent selection and breeding and larva breeding. The technical characteristics of the method are: performing disinfection treatment on parent crabs after gonad of the parent crabs matures; strictly controlling the feeding amount of nauplius of rotifer and fairy shrimp during a larva breeding stage after nutrient enrichment; evenly spraying the whole pool with zeolite powder during a megalops larva stage; and using a Bdellovbrio type product and viable bacteria degraded substrate improver to improve the larvae breeding water environment. Compared with the conventional breeding methods, in the same breeding scale, the method can decrease the water changing volume by more than 70%, can reduce the fire coal cost by more than 60%, can reduce the input cost by more than 50% after using the microorganism preparation to replace disinfection medicines and antibiotics medicines, can improve the average survival rate of the II stage larvae by 2-3 times, is safe, environment-friendly, efficient in a larvae breeding process, and has high promotion value and wide application prospect.
Owner:中国水产科学研究院下营增殖实验站
Method for supplying glyptosternon maculatum initial feed
ActiveCN107581110AEating wellWild and strongClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaAnimal scienceFairy shrimps
The invention provides a method for supplying glyptosternon maculatum initial feed. The method comprises the following steps: feeding hatched fairy shrimps after fry is hatched for 10 days and startsto come up; starting to feed rainbow trout initial feed after the fry is hatched for 20 days; starting to feed chopped tubificidae after the fry is hatched for 35 days; and starting to feed balls of mixture of rainbow trout initial feed, pig liver and tubificidae in the place with fries gathered after the fry is hatched for 60 days. The method can be used for successfully solving the problem of initial feed of glyptosternon maculatum fries, and the survival rate of fries can be remarkably increased.
Owner:西藏自治区农牧科学院水产科学研究所
Breeding method of hippocampus abdominalis family
ActiveCN113598092AIncrease mating rateIncrease exposureClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaOpossumAnimal science
The invention provides a breeding method of hippocampus abdominalis family, which comprises the following steps: S1, arranging a breeding pool with the daily water change amount of 100-300%; placing an inflatable stone and a breeding nest in the breeding pool; arranging an early-stage juvenile fish culture barrel and a later-stage juvenile fish culture barrel; placing the inflatable stone in the early-stage juvenile fish culture barrel, and placing the inflatable stone and an attachment frame in the later-stage juvenile fish culture barrel; S2, selecting healthy and mature parent male and female hippocampus abdominalis and putting the selected parent male and female hippocampus abdominalis into the breeding nest; S3, after the female and male hippocampus abdominalis lays fry, fishing out newborn hippocampus abdominalis fry and putting the fry into the early-stage juvenile fish culture barrel; S4, feeding the juvenile fishes with different birth day ages with fairy shrimp larvae and copepod with different densities, wherein the copepod is fed or opossum shrimps are fed. The breeding method of the hippocampus abdominalis family is easy to operate, and the survival rate of hippocampus abdominalis fry is high.
Owner:FISHERIES RES INST OF FUJIAN +1
Large-scale fingerling production technique for takifugu obscurus in brackish water
InactiveCN102860270AReduce disease infectionImprove survival rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaFresh water organismFairy shrimps
Disclosed is a large-scale fingerling production technique for takifugu obscurus in brackish water. The technique is characterized in that newly hatched takifugu obscurus larvae are transferred to a fingerling breeding pool after being temporarily fed for 2-3 days in a hatching pool, the density of the fingerlings is 5,000-10,000 per cubic meter, and the fingerlings are bred in fresh water; natural brackish water is gradually added until the salinity reaches 5-8 parts per thousand; water is added until the water level reaches 120cm on the third to fourth day after the fingerlings are put into the pool; bottom suction is carried out every day from the fourth to fifth day after the fingerlings are put into the pool and two thirds of water is changed every other day; two thirds of water is changed every day from the eighth to tenth day after the fingerlings are put into the pool; the fingerlings are separated and placed in different pools from the thirteenth to fourteenth day after the fingerlings are put into the pool and the salinity is gradually reduced until the brackish water is changed into fresh water; the density of air dispersion stones is 1.5 per square meter and is reduced to 1 per square meter in the later stage; the water temperature for fingerling placing is 21.5 plus or minus 0.5 DEG and is increased by 0.1 DEG every other 24 hours until being increased to 24.5 plus or minus 0.5 DEG; rotifers are fed to the fingerlings from the first to eighth day after the fingerlings are put into the pool; fairy shrimp larvae are fed to the fingerlings from the fifth to thirteenth day after the fingerlings are put into the pool; and freshwater cladocerans are fed to the fingerlings from the thirteenth to fourteenth day after the fingerlings are put into the pool.
Owner:SHANGHAI FISHERIES RES INST
Method for cultivating Australia lobster
InactiveCN106234281AImprove immunityNeat growth and developmentClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaFisheryOrganic matter
The invention belongs to a method for cultivating Australia lobster. The method comprises a first step of selecting a culture pond; a second step of decontaminating and sterilizing the culture pond; a third step of laying clean river sand with a thickness of 18 cm after the pond cleaning in the second step is over; a fourth step of starting to place shrimp larvae in 15 days after the third step is finished; a fifth step of placing no feed in first five days after the shrimp larvae are placed in culture pond water, and starting to place fairy shrimps and rice bran from the sixth day; a sixth step of using nuobiqing biological water-purifying agent and PondProtect once every other 12 days in the feeding process in the fifth step, and timely clearing organic matter at the bottom of the culture pond. The method has the advantages that the controllability is high, immunity of the Australia lobster can be enhanced, shrimp larvae grow and develop tidily, the survival rate is high, the culture speed is quick, and the quality and yield can be improved.
Owner:耿明生
Method for breeding young shrimps of macrobrachium rosenbergii
InactiveCN108782385AImprove survival rateImprove adaptabilityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaFresh waterSalinity
The invention relates to a method for breeding young shrimps of macrobrachium rosenbergii. The method comprises the following steps that (a) the salinity of water in a nursery pond is controlled, shrimp larvae fished by a filtering net are transferred to the nursery pond, and the density is controlled to be 80,000-120,000 ind / m<3>; the shrimp larvae are fed with fairy shrimp nauplii once every 4-8h; 7-10 days after the shrimp larvae are bred, the shrimp larvae are additionally fed with steamed egg custard before feeding of fairy shrimp nauplii; 15-18 days after the shrimp larvae are bred, theshrimp larvae are additionally fed with shrimp slices; the feeding amount of the fairy shrimp nauplii, the steamed egg custard and the shrimp slices accords with the standard that the shrimp larvae eat up the feed within 1 h; the salinity of the water in the nursery pond starts from 6-7 %o and is then reduced to 4-5 %o 6-7 days after breeding, reduced to 2.5-3 %o 12-13 days after breeding and reduced to 1-2 %o 18-19 days after breeding; (b) the young shrimps can be formed 20-22 days after the shrimp larvae are bred. In this way, the adaptability of the shrimp larvae to the fresh water can beimproved, and the survival rate of macrobrachium rosenbergii is increased accordingly; moreover, the cost can be reduced.
Owner:苏州市毛氏阳澄湖水产发展有限公司
Technology for cultivating takifugu flavidus summer fingerlings in cement pond of simple plastic greenhouse
ActiveCN103026990AShorten the timeTime stretchedClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaWater qualityOrder copepoda
The invention discloses a technology for cultivating takifugu flavidus summer fingerlings in a cement pond of a simple plastic greenhouse. The cement pond is adopted, and an arch-shaped ring top is formed above the cement pond. The technology is characterized in that: a dimmable shading film covers on the arch-shaped ring top; the air density in the cement pond is 1-1.5 pieces per square meter; the stocking sizes are 10-12 millimeters in full lengths per fingerling; the stocking density is 1,000-1,500 fingerlings per square meter; the water level is 70 centimeters during stocking; 20 centimeters of fresh water is injected every day from the second day, the cement pond is full of water four days later, and 50 percent of water is changed every other day from the fifth day; after 10-15 days of cultivation, bait scraps and fish excrement are cleared; the water quality indexes are that: the salinity of sea water is 0.8-1.2 percent, the water temperature is 25-28 DEG C, the dissolved oxygen is over 5 mg / L, and the pH is 7.5-8.5; medium-sized cladocerans and copepods are fed at an earlier stage, and large frozen fairy shrimps are fed at a middle stage; and after the full lengths of fingerlings are up to 30 millimeters, a compound feed is fed instead of the frozen fairy shrimps, and an eel feed is fed completely after 3-4 days of transition.
Owner:上海市水产研究所(上海市水产技术推广站)
Cultivation method for improving disease resistance and stress resistance of epinephelus spp. fries
ActiveCN111183932AImprove immunityImprove stress resistanceClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffAnimal scienceNutrition
The invention provides a cultivation method for improving disease resistance and stress resistance of epinephelus spp. fries. The cultivation method comprises the following steps of: 1) in two days before fries are added, introducing a variety of skeletonema costatum into a nursery pond; 2) within seven days after fries are added, adding SS type rotifers in each day; 3) during the 8th-15th day offry adding, adding fairy shrimp nauplius and LS type rotifers in each day; 4) during the 16th-25th days of the fry adding, adding the fairy shrimp nauplius in each day; and 5) during the 26th-35th days of the fry adding, adding the fairy shrimp nauplius and compound feed in each day. The nutrients of fingerlings during different periods can be regulated, fry immunity is improved, and the disease resistance and stress resistance of the epinephelus spp. fries can be improved. Through experiments, under a condition that salinity is 3.6%, a survival rate still can be above 68%, a survival rate still can be kept at about 30% under a condition that the salinity is 4.2%, and the survival rate is kept to be 70% or above after the epinephelus spp. fries are infected with vibrio alginnolyficus for two weeks.
Owner:HAINAN CHENHAI AQUATIC CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com