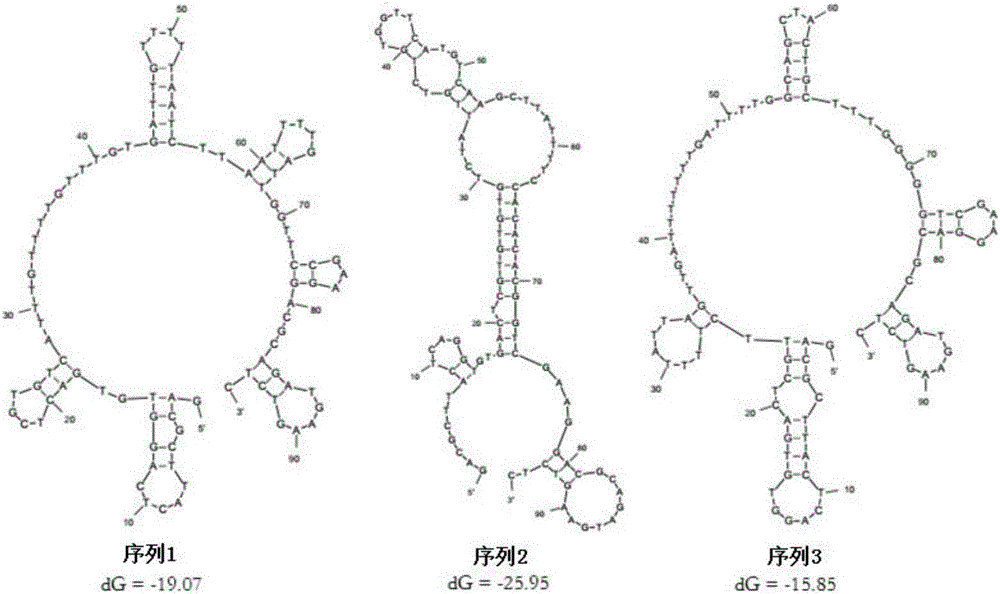
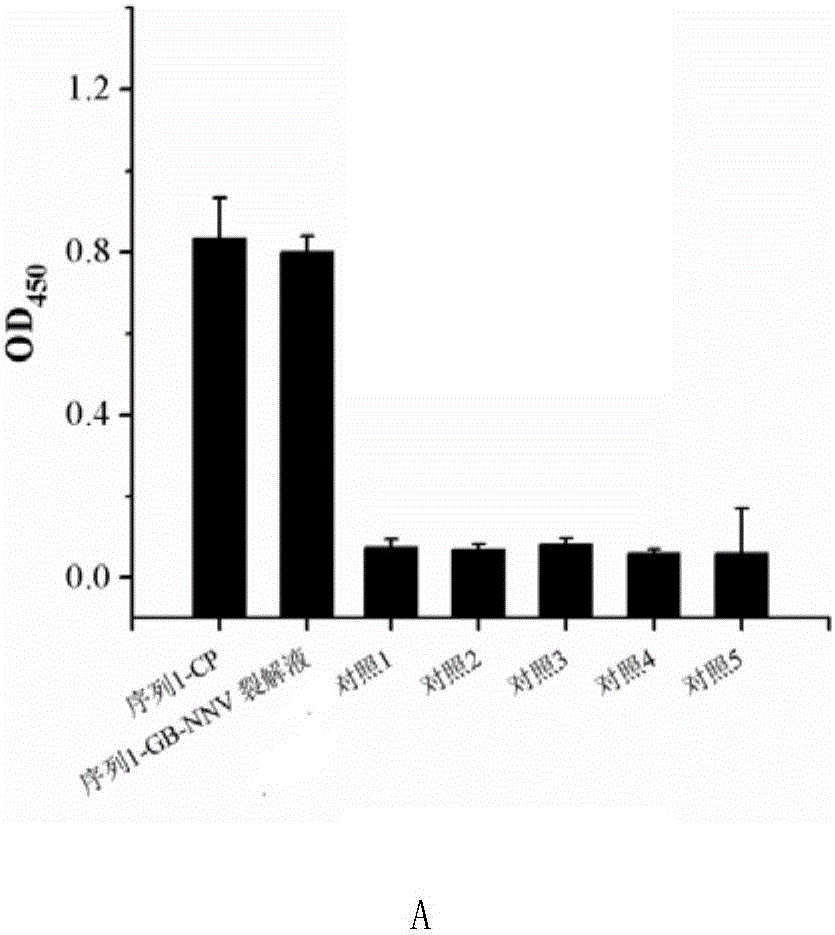
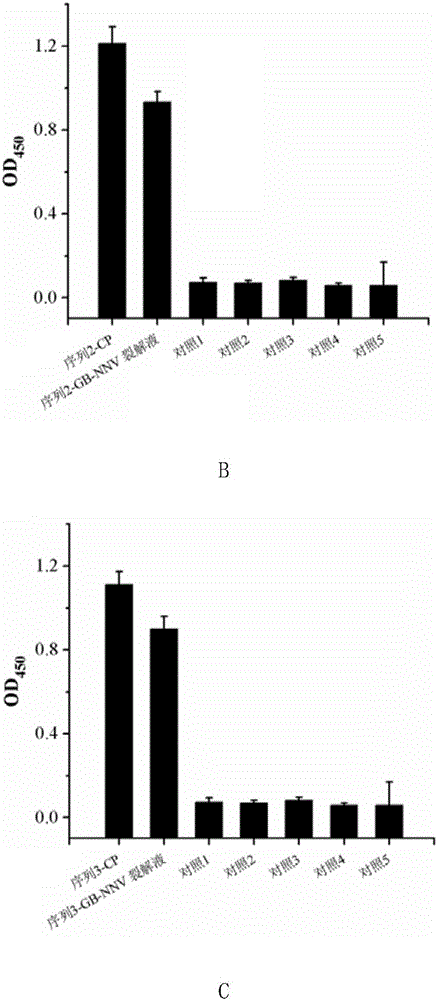
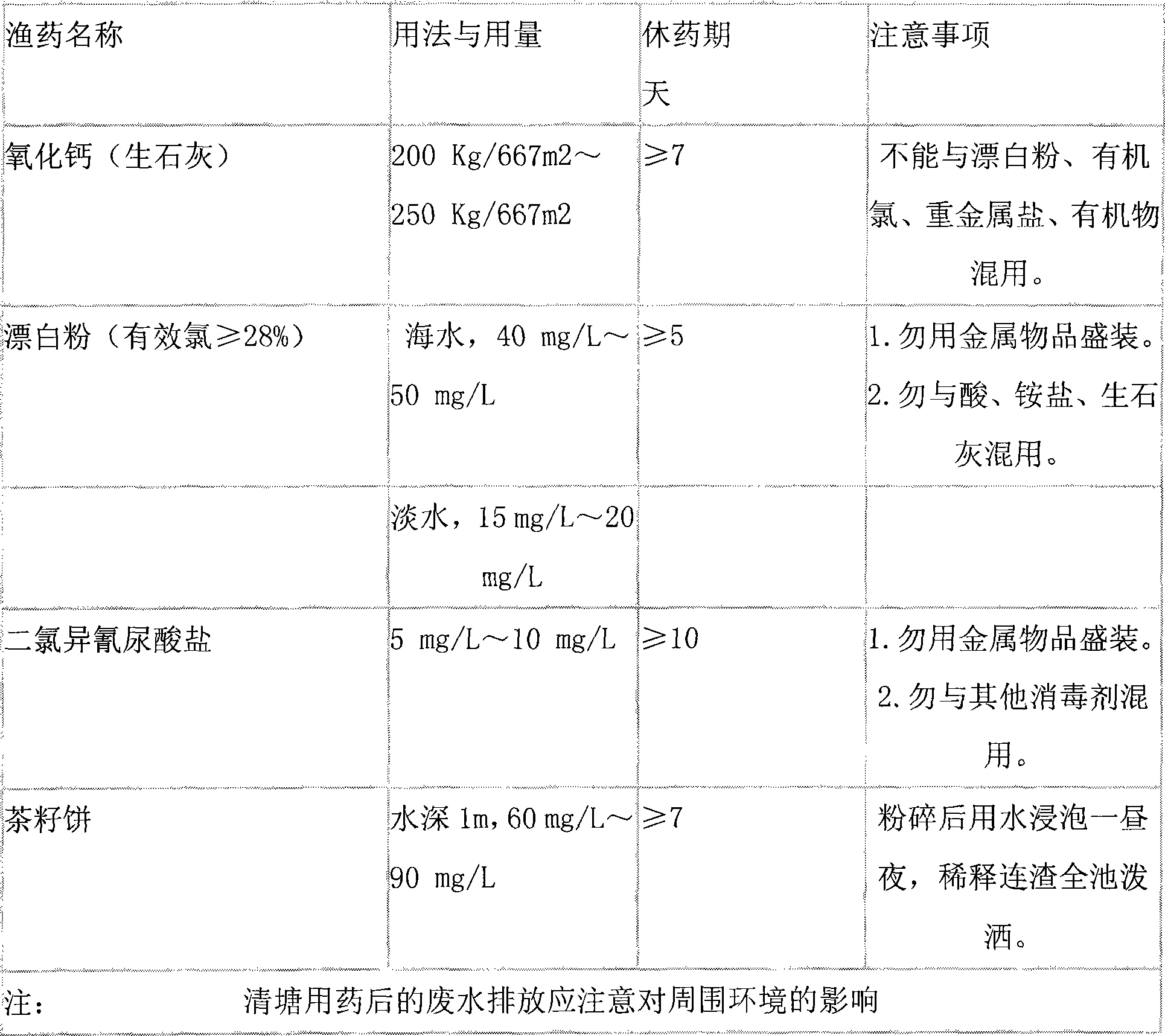Patents
Literature
314 results about "Grouper" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Groupers are fish of any of a number of genera in the subfamily Epinephelinae of the family Serranidae, in the order Perciformes. Not all serranids are called groupers; the family also includes the sea basses. The common name grouper is usually given to fish in one of two large genera: Epinephelus and Mycteroperca. In addition, the species classified in the small genera Anyperidon, Cromileptes, Dermatolepis, Gracila, Saloptia, and Triso are also called groupers. Fish in the genus Plectropomus are referred to as coralgroupers. These genera are all classified in the subfamily Epiphelinae. However, some of the hamlets (genus Alphestes), the hinds (genus Cephalopholis), the lyretails (genus Variola) and some other small genera (Gonioplectrus, Niphon, Paranthias) are also in this subfamily, and occasional species in other serranid genera have common names involving the word "grouper". Nonetheless, the word "grouper" on its own is usually taken as meaning the subfamily Epinephelinae.
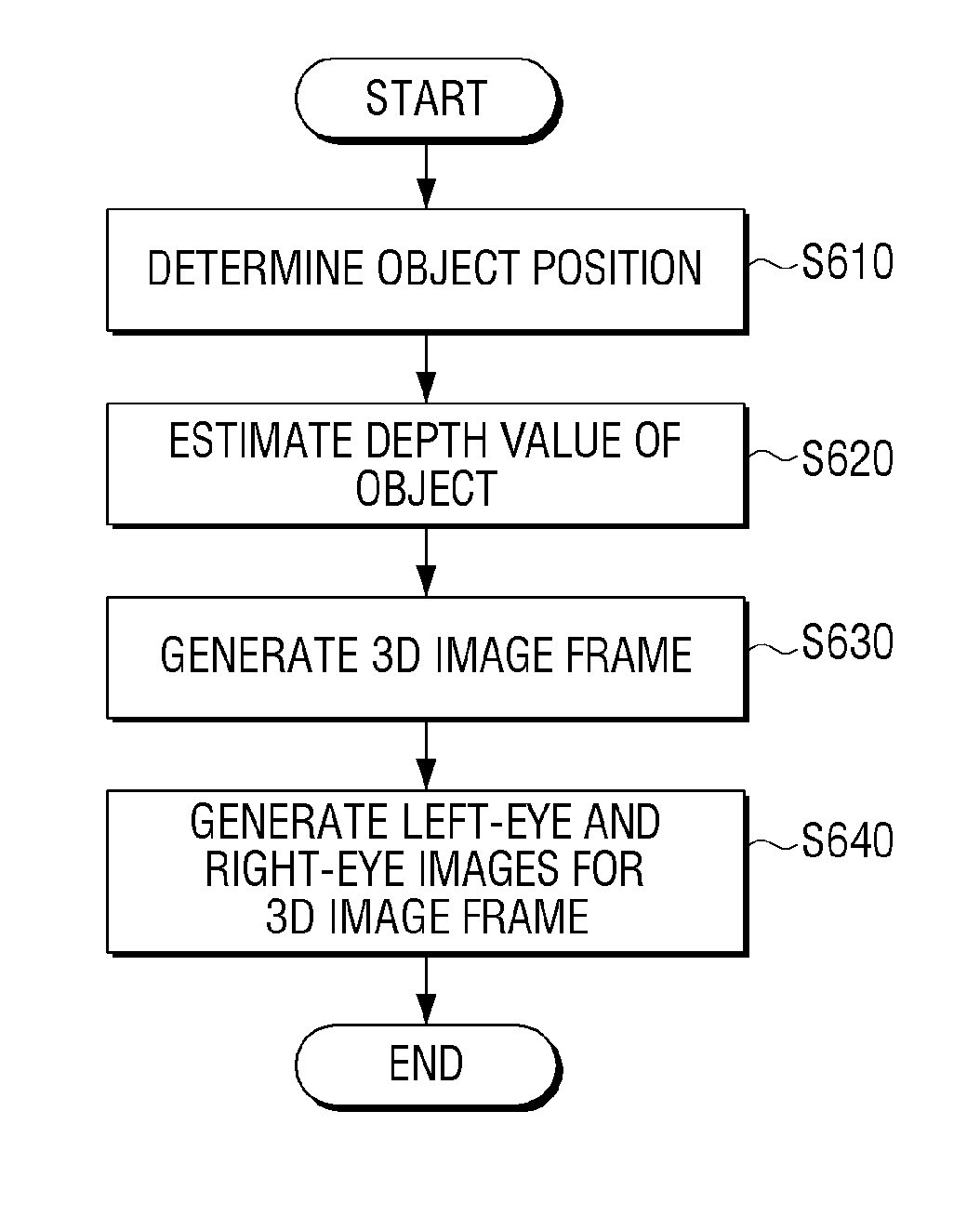
Apparatus and method for display
InactiveUS20140063005A1Minimize timeValid conversionSteroscopic systems3D-image rendering3d imageKey frame
Display apparatus and method are provided. The display apparatus may include a receiver for receiving an image; a grouper for analyzing the received image and grouping a plurality of frames of the received image based on the analysis; a depth allocator for determining at least two key frames from a plurality of frames grouped into at least one group, and allocating a depth per object in the determined key frames; and an image generator for generating a 3D image corresponding to other frames excluding the key frames based on a depth value allocated to the key frames. Hence, the display apparatus can allocate the depth value of a higher quality to the object in the frames of the received image.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
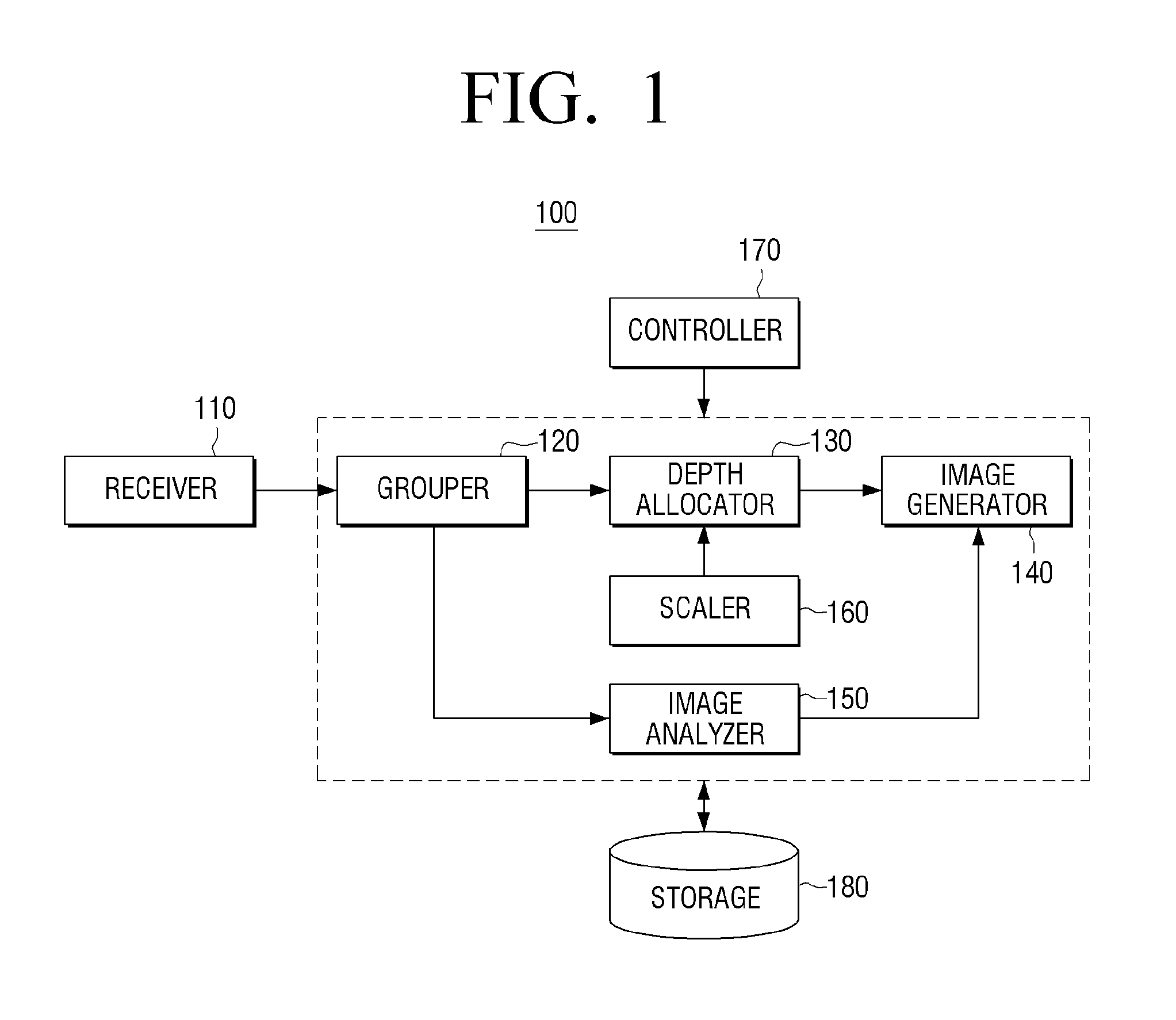
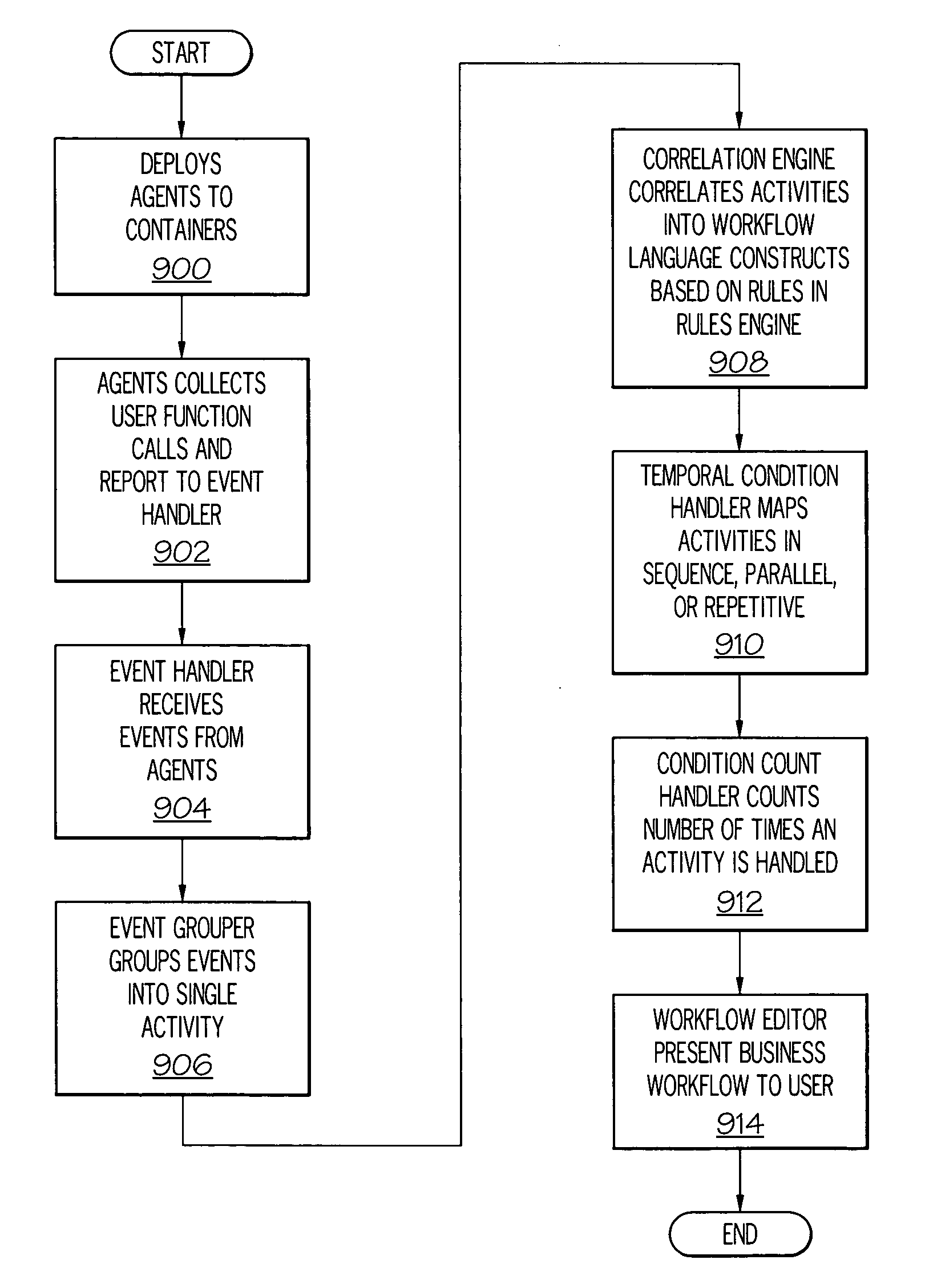
Automatic discovery and maintenance of business processes in web services and enterprise development environments
A method, an apparatus, and computer instructions are provided for automatic discovery and maintenance of business processes in Web services and enterprise development environments. A set of agents are deployed to a set of enterprise containers to collect user function calls and report events to a central business workflow language generator. An event handler collects the events reported and an event grouper groups the events into a single workflow activity. An event correlation engine correlates activities to business workflow language constructions by using a temporal condition handler and a collection counting handler. The temporal condition handler maps activities that are in sequence, in parallel, and are repetitive. The collection counting handler counts the number of times an event is handled. Events and Rules for these events are written on the system based on a variety of business constructs that are particular to given business process definition language. A business workflow language generator then generates a business workflow and a workflow presents the business workflow in a user interface.
Owner:IBM CORP
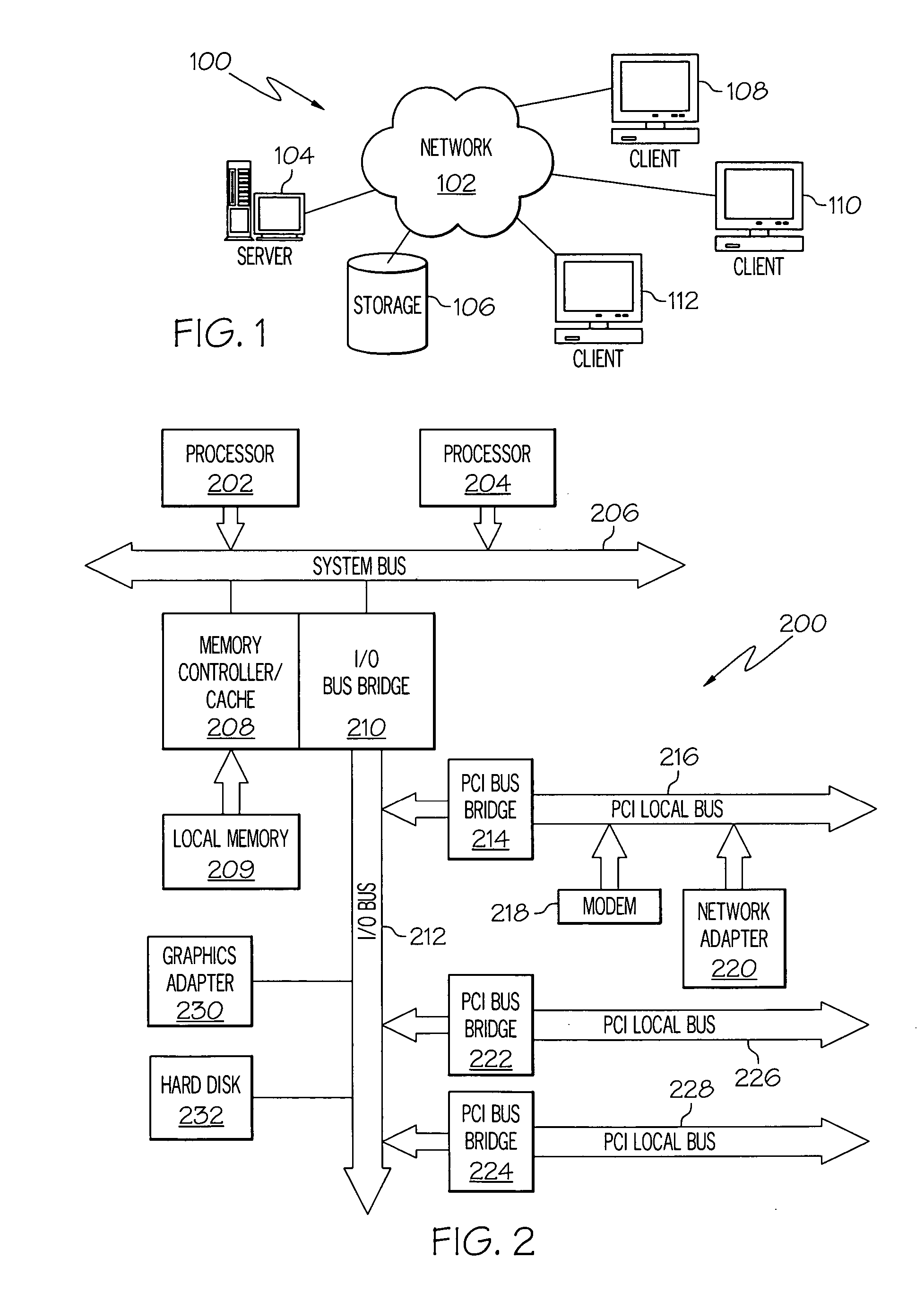
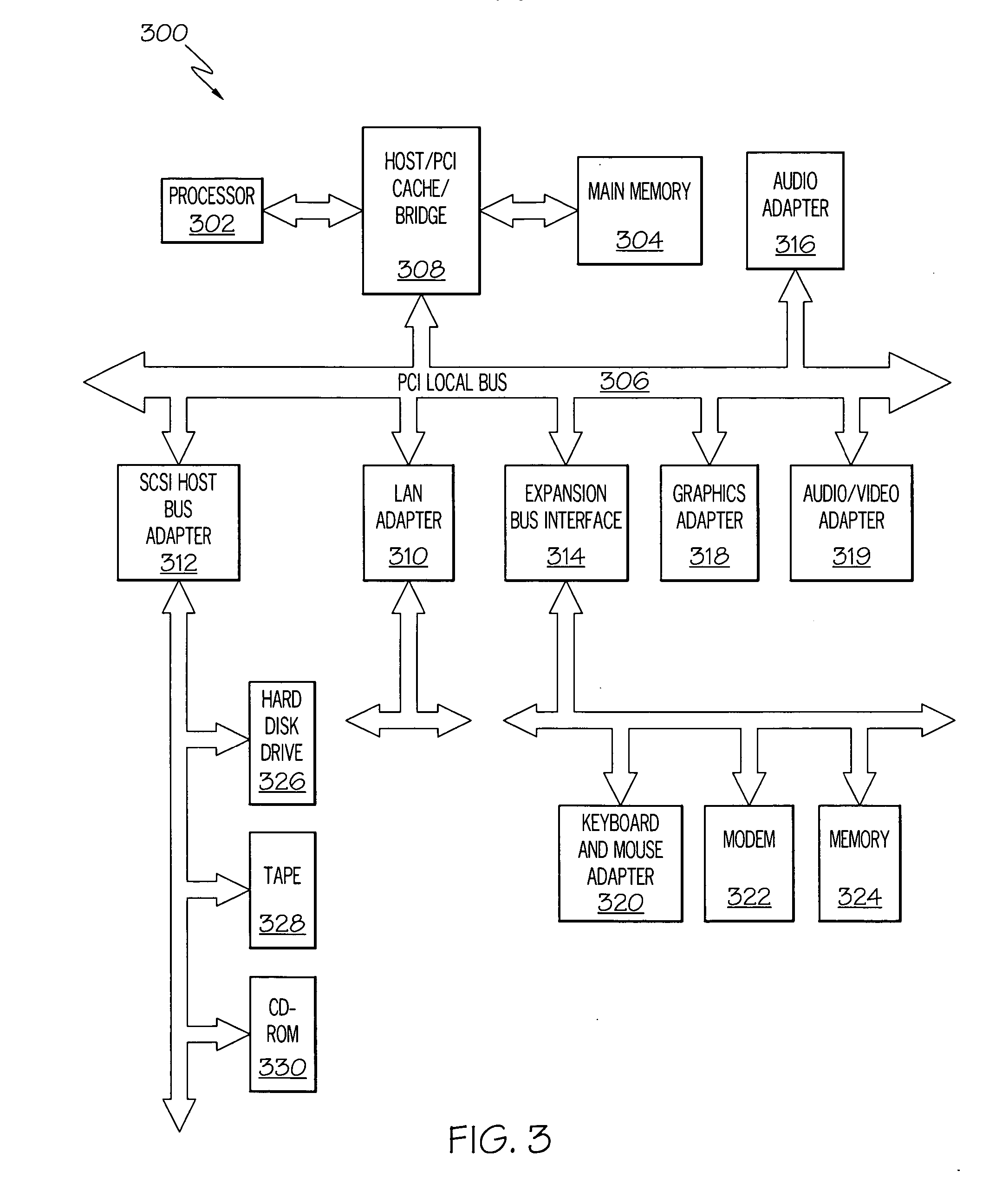
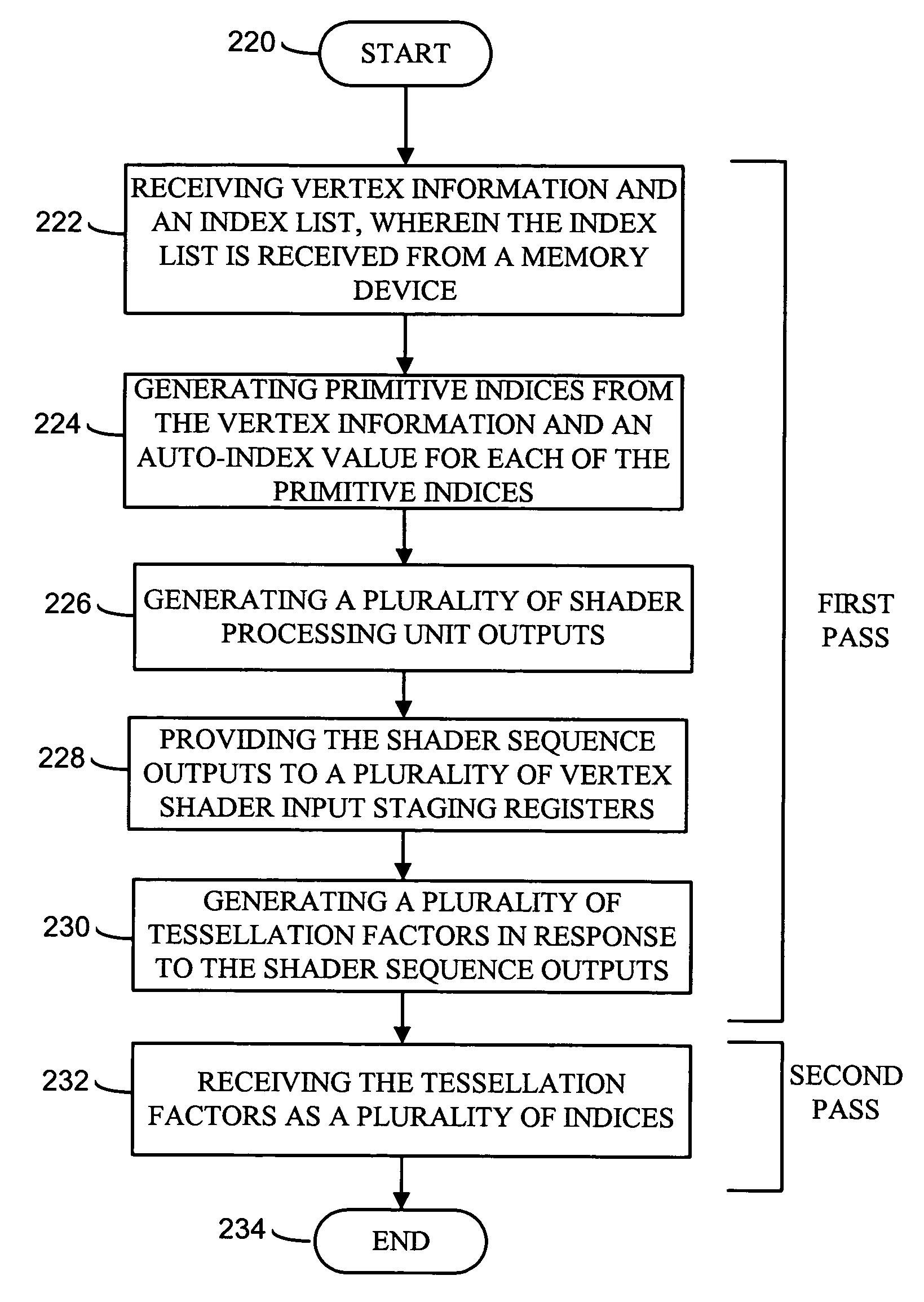
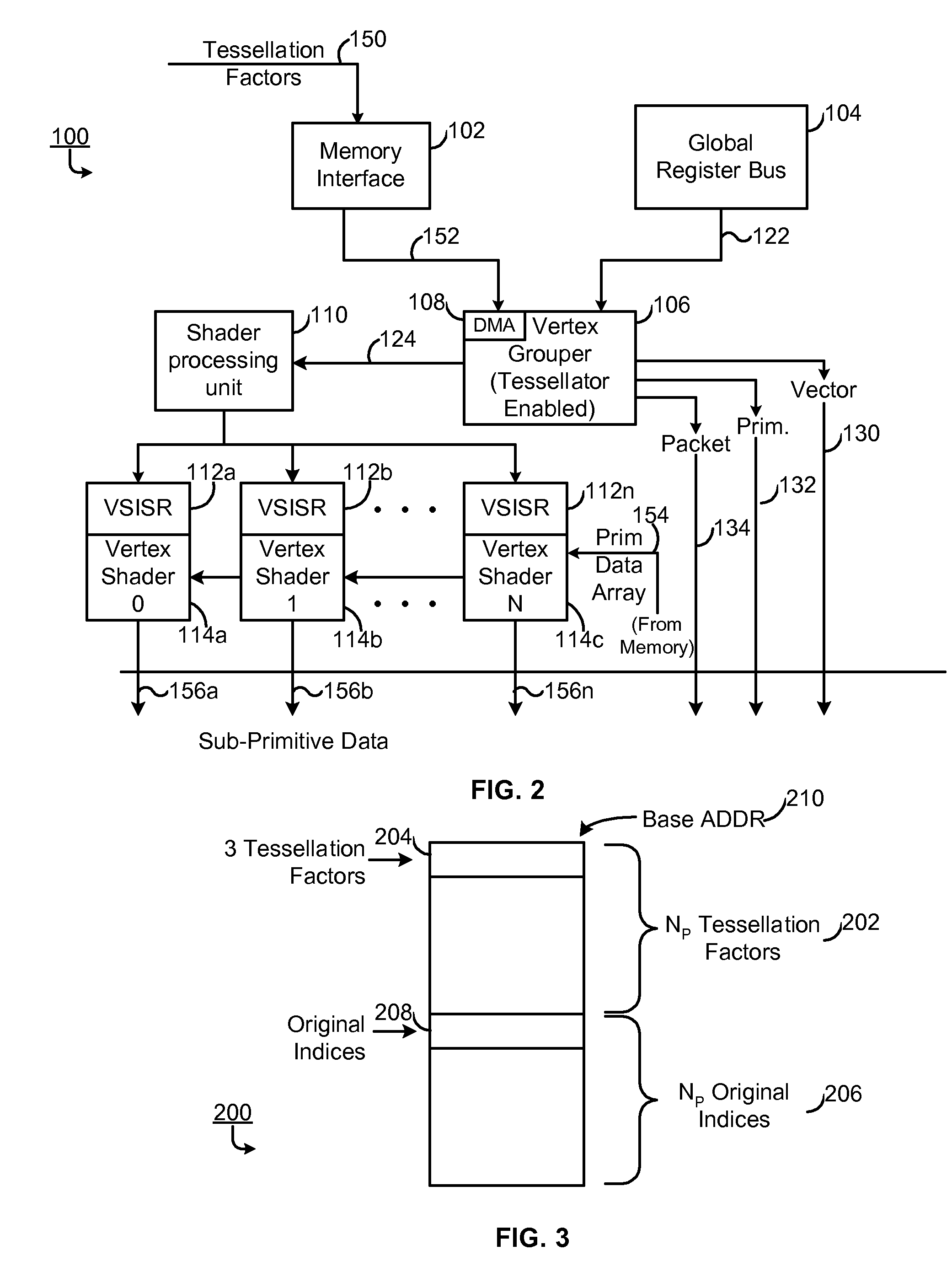
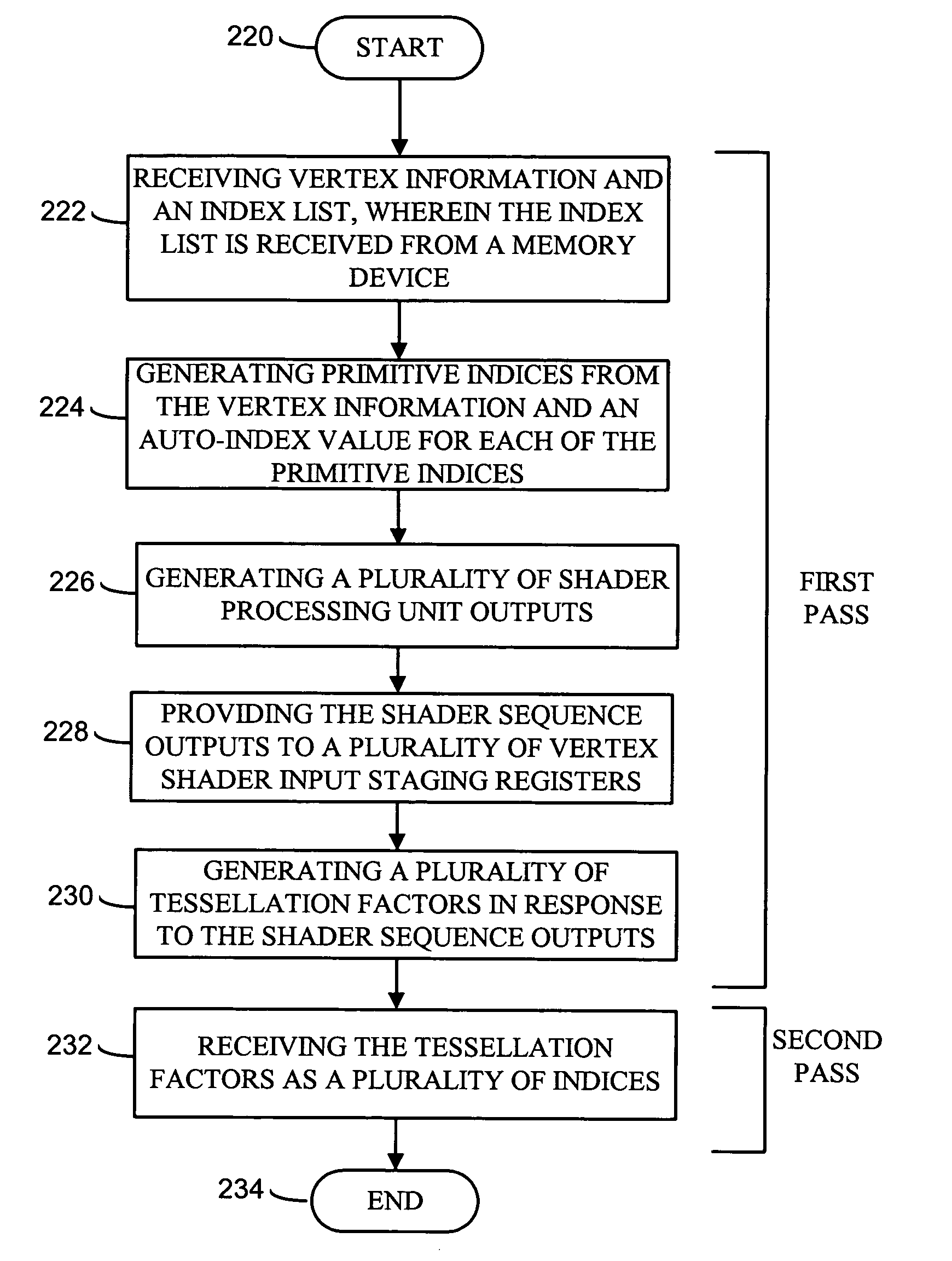
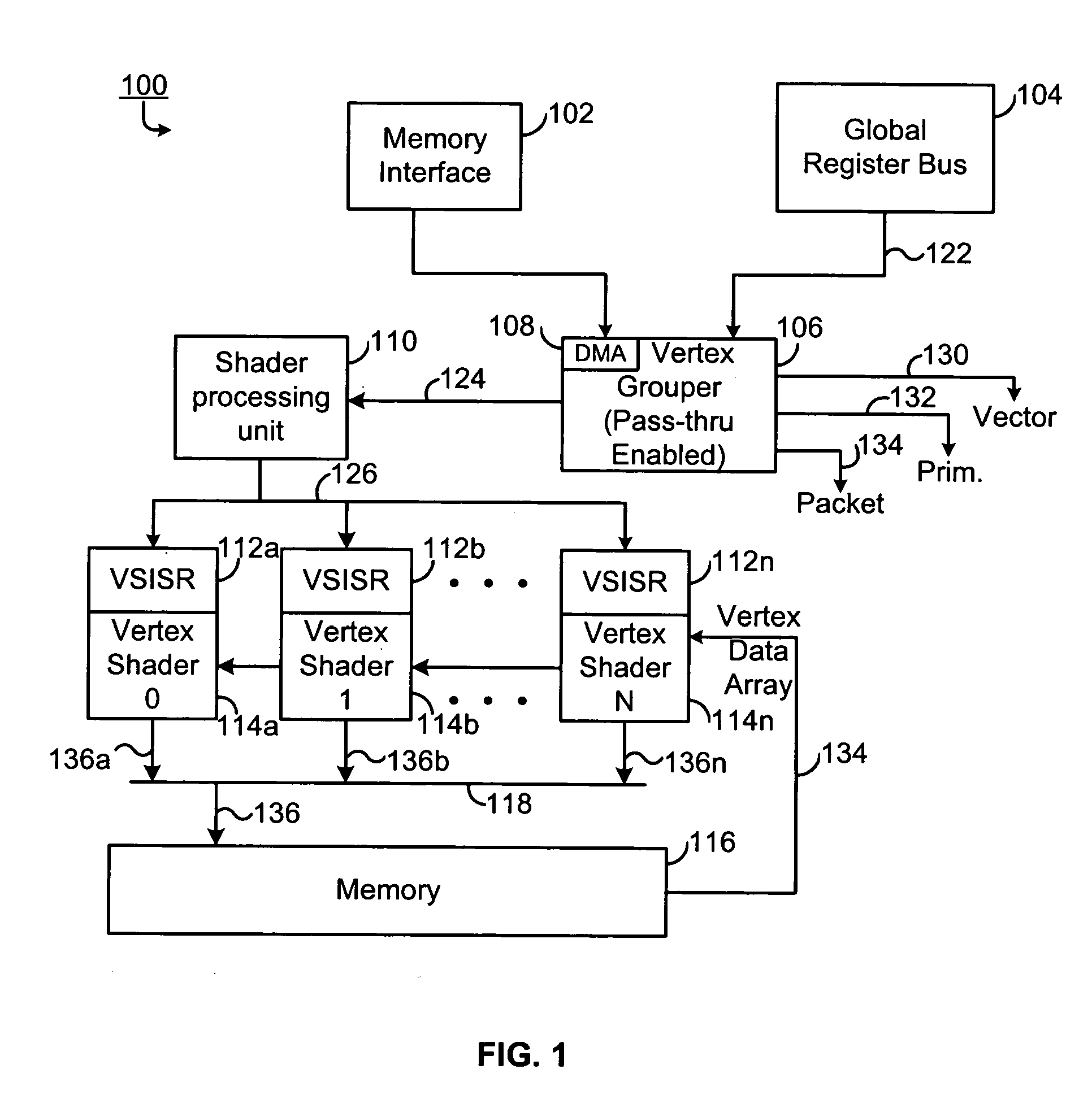
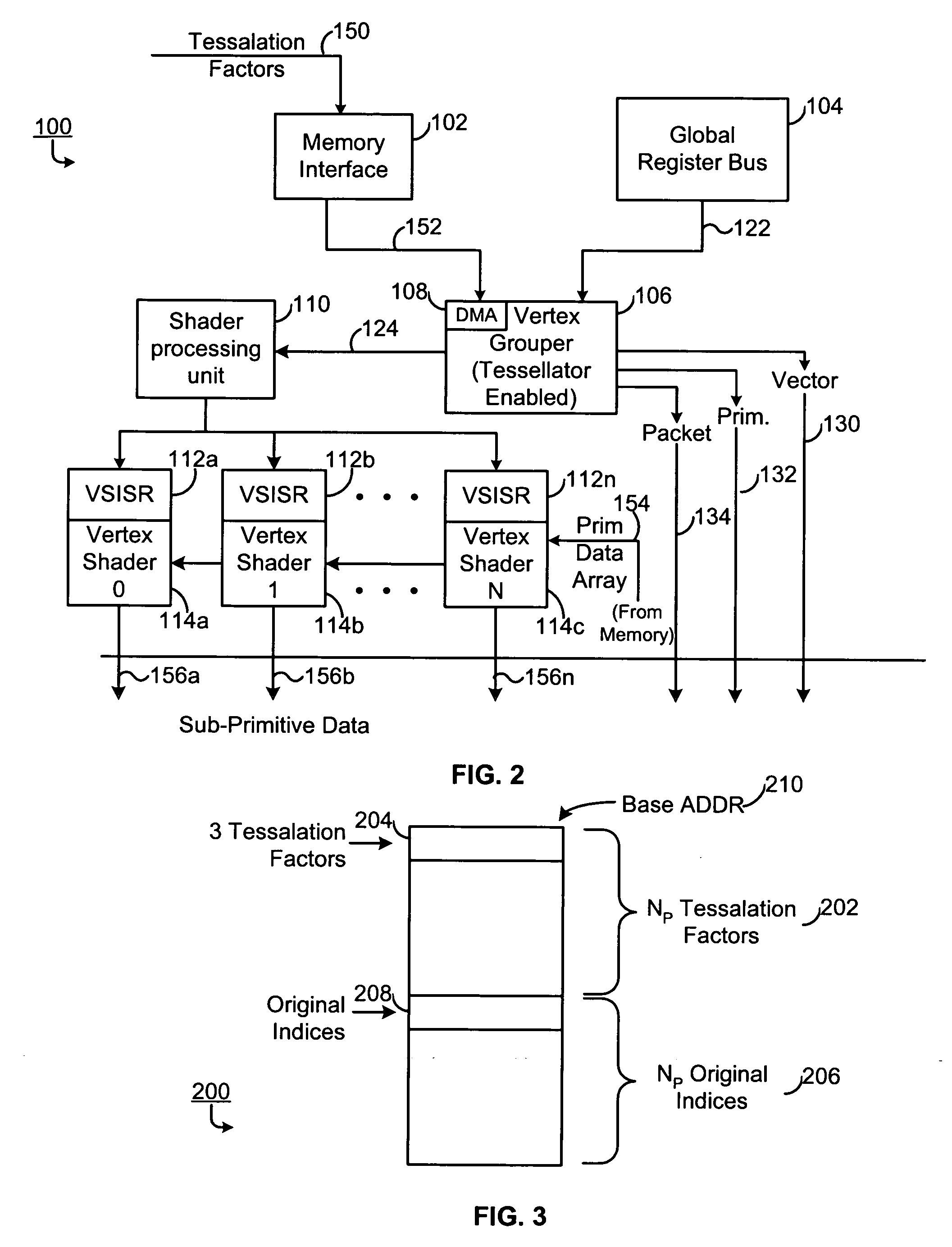
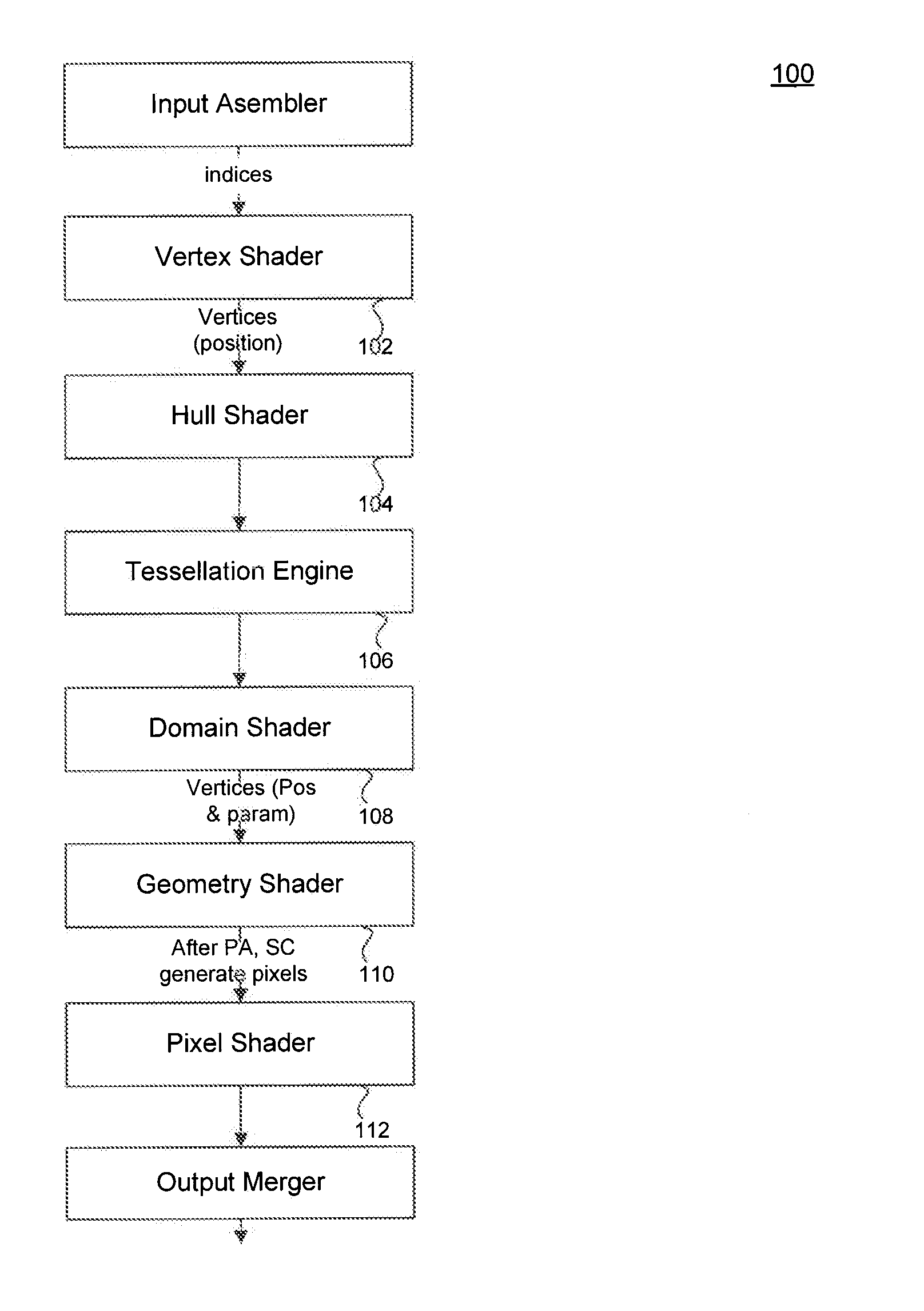
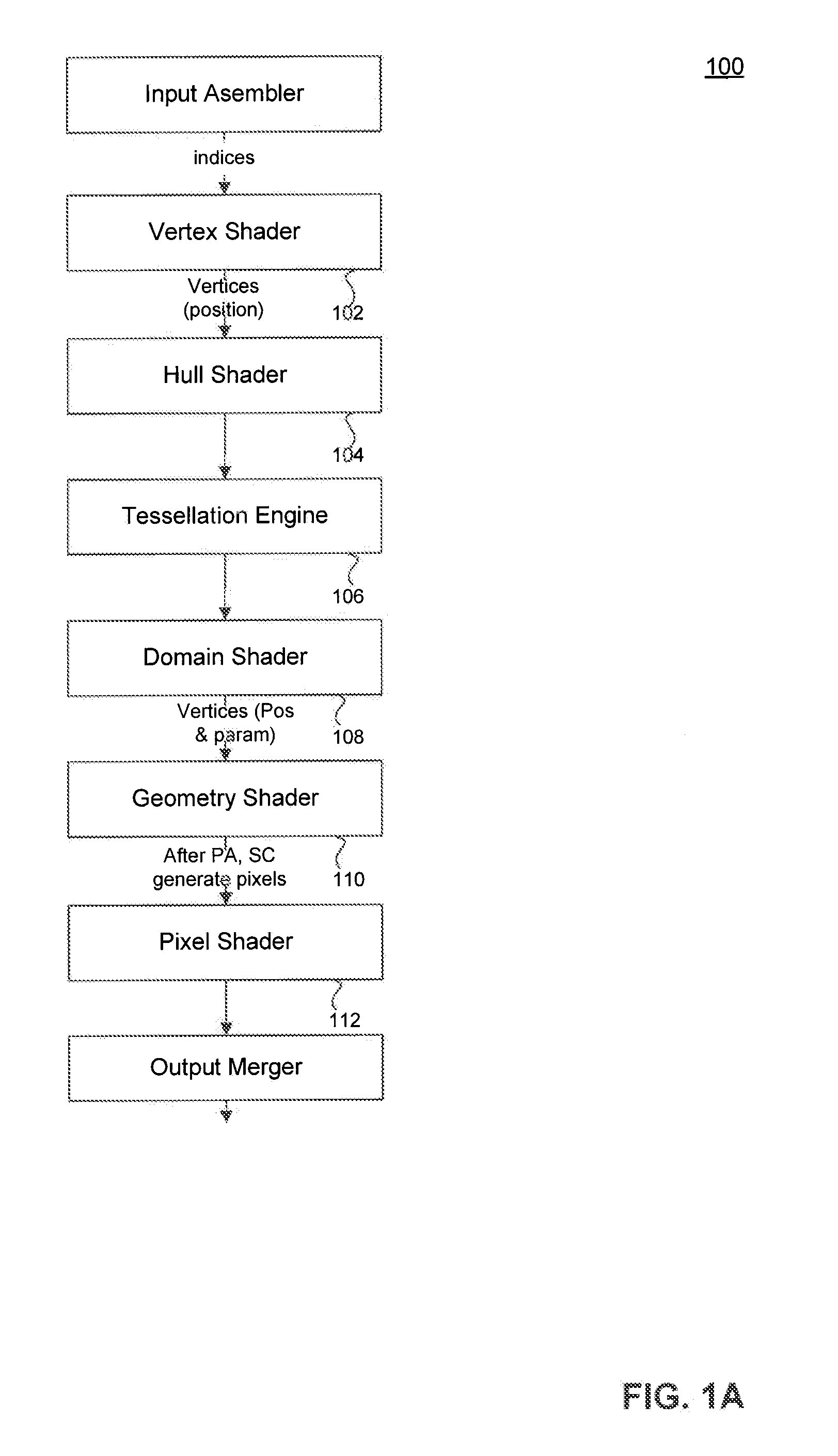
Method and apparatus for dual pass adaptive tessellation
ActiveUS7109987B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsProcessor registerComputer graphics (images)
A method and apparatus for dual pass adaptive tessellation includes a vertex grouper tessellator operably coupled to receive primitive information and an index list and a shader processing unit coupled to the vertex grouper tessellator. During a first pass, the shader processing unit receives primitive indices generated from the primitive information and an auto-index value for each of the plurality of primitive indices. The method and apparatus further includes a plurality of vertex shader input staging registers operably coupled to the shader sequence, wherein the plurality of vertex shader input staging registers are coupled to a plurality of vertex shaders such that in response to a shader sequence output, the vertex shaders generate tessellation factors. The tessellation factors are provided to the vertex grouper tessellator such that the vertex grouper tessellator generates a per-process vector output, a per primitive output and a per packet output during a second pass.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
Grouper environmentally-friendly soft granulated feed and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102178105ANutritional full priceBalanced nutritionFood processingClimate change adaptationEnvironmental resistanceEcological environment
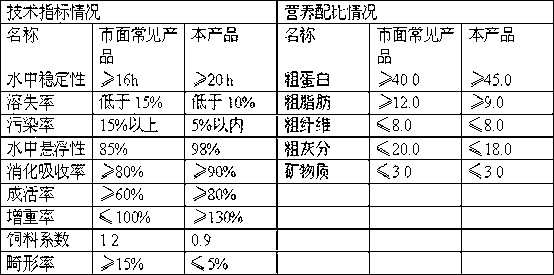
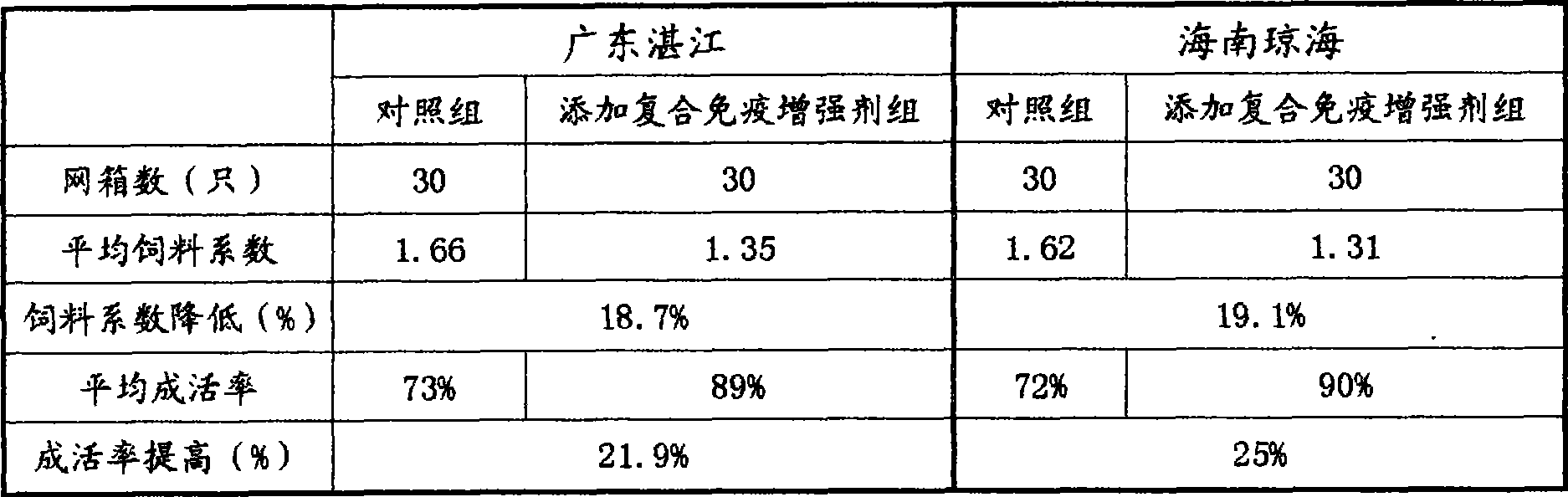
The invention provides a grouper environmentally-friendly soft granulated feed and a preparation method thereof. The grouper environmentally-friendly soft granulated feed comprises the following nutritional components in percentage by weight: 40 to 50 percent of crude protein, 6 to 12 percent of crude fat, 8 to 15 percent of crude ash, 22 to 28 percent of carbohydrate, and 6 to 10 percent of moisture. According to the invention, the high-quality grouper environmentally-friendly soft granulated feed is studied, popularized and applied, so that the nutrition of the launched feed goes to be complete and balanced, and the palatability of the feed is good, not only can the feed digestive absorption rate of grouper be improved, but also the survival rate and growing speed of the grouper are improved, and the fish quality is improved. Therefore, non-polluted fish products are produced, and the cultivation economical benefit is improved; and the feed has active and profound significance in reducing the usage of small trash fish, lightening the sea area pollution, protecting the marine eco-environment, and promoting the sustained stable and health development of the marine fish culture industry.
Owner:福建省淡水水产研究所
Method for rapidly detecting grouper irido virus
InactiveCN101173317AQuick checkHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementTranscriptional expressionReaction temperature
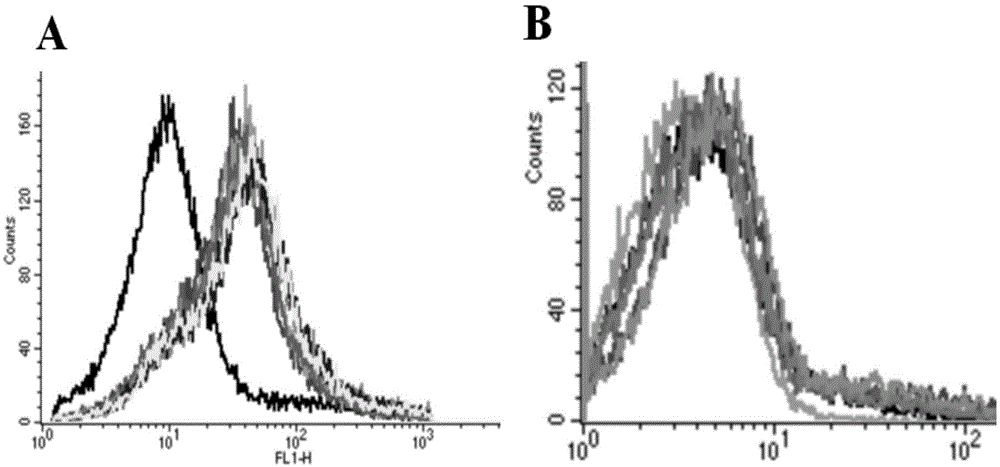
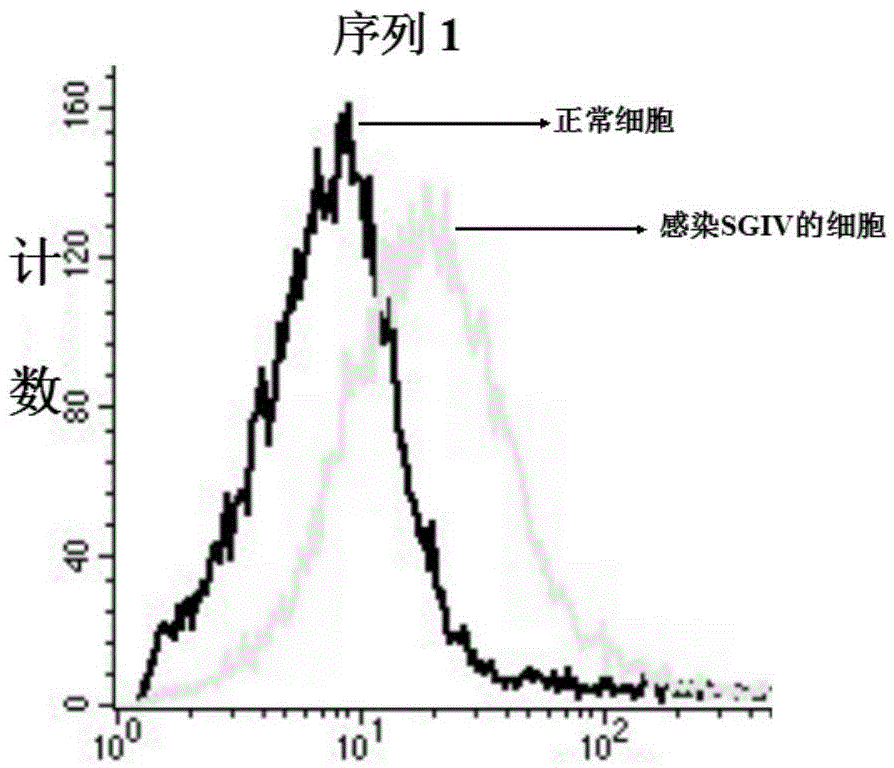
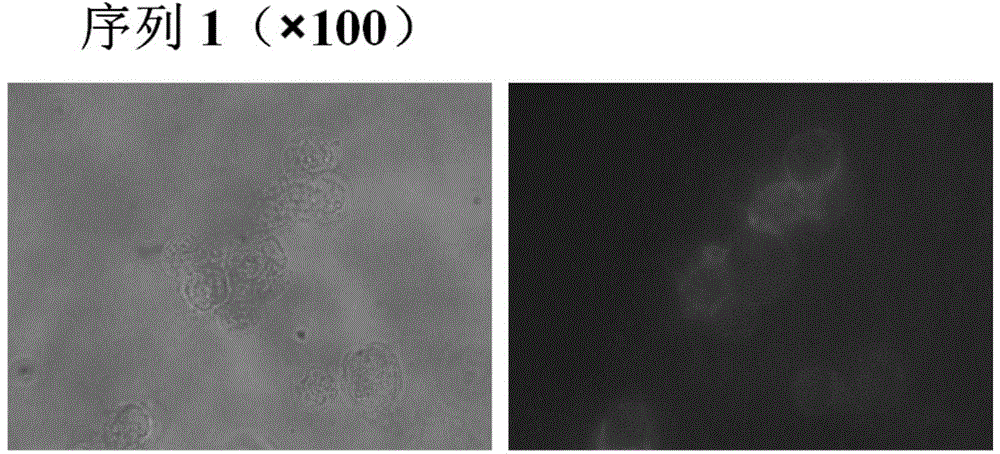
The invention discloses a fast detection method for grouper iridovirus, firstly proposing a loop-mediated isothermal nucleic acid amplifying detection applied for the detection of grouper iridovirus, which comprises the steps as follows: (1)a ORF-014L is cloned and a recombinant plasmid template containing ORF-014L is constructed; (2)primer design, primer sequence; (3)amplification, the reaction temperature is 63-65 DEG C, and the reaction time 20-60mins. The LAMP detection technique of the invention can rapidly detect SGIV, the transcriptional expression of SGV 014L in cells, the grouper tissue infected by SGIV, and the GP cells infected by SGIV; the sensitivity of the invention is three orders of magnitude higher than Nested PCR, reaching to six point six copies.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Grouper bait and method for making same
InactiveCN1602723AStrong attractant effectStrong physical stimulationAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsBiotechnologyBetaine
The invention pertains a kind of phagostimulant to rockfishes and other fishes, and its produce way. Materials by weight: animal protease 70-85%, nucleotide 2-10%, sulphocompound 0.4-3%, complex aminoacid 5-15%, betaine 2-20%, pigment 0.5-5%, oxidation preventive 0.1-0.5%. Production way: add animal protease after enzymolysis in oxidation preventive of 0.5-3% of fresh animal protease by weight; add by rate nucleotide, sulphocompound, complex aminoacid, betaine, pigment, oxidation preventive, mix and dry them, then the phagostimulant is made over. This phagostimulant can absorb sober of water animal effectually, promote growing, increase the ability of defeat disease, and increase the rate of living.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method and apparatus for dual pass adaptive tessellation
ActiveUS20050195188A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer graphics (images)Self adaptive
A method and apparatus for dual pass adaptive tessellation includes a vertex grouper tessellator operably coupled to receive primitive information and an index list and a shader processing unit coupled to the vertex grouper tessellator. During a first pass, the shader processing unit receives primitive indices generated from the primitive information and an auto-index value for each of the plurality of primitive indices. The method and apparatus further includes a plurality of vertex shader input staging registers operably coupled to the shader sequence, wherein the plurality of vertex shader input staging registers are coupled to a plurality of vertex shaders such that in response to a shader sequence output, the vertex shaders generate tessellation factors. The tessellation factors are provided to the vertex grouper tessellator such that the vertex grouper tessellator generates a per-process vector output, a per primitive output and a per packet output during a second pass.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
Perfect compound feed for groupers
ActiveCN103005183APromote digestion and absorptionImprove immunityAnimal feeding stuffDocosahexaenoic acidFish oil
The invention discloses a perfect compound feed for groupers, which is a compound feed suitable for the culture of grouper large-size fish seeds. The perfect compound feed is prepared by adopting imported fish meal, fermented soybean meal, alpha-starch, flour, squid meal, krill meal, yeast extracts, fairy shrimps, fish oil, soybean phospholipids, DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid), EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid), composite mineral salt, compound vitamins, compound enzyme preparations, compound immunopotentiators, hepatinica and compound microecologic preparations as raw materials. The perfect compound feed disclosed by the invention can promote the digestion and absorption of the groupers, regulate the stability of the intestinal flora of the groupers, enhance the immunity of the groupers and play a lipotropic role by sufficiently considering the digestion and physiology characteristics of the culture period of the groupers and adding various additives to the feed, has the advantages of balanced and complete nutrition without drugs, namely added antibiotics and the like, and no pollution on water bodies and belongs to a high-efficiency environment-friendly nuisanceless feed.
Owner:广东越群海洋生物科技股份有限公司
Facility fry-rearing method for grouper in large water body of outdoor cement pool
InactiveCN102657127AEasy to operateStable survival rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaWater useAnimal science
The invention relates to a facility fry-rearing method for grouper in a large water body of an outdoor cement pool. The facility fry-rearing method comprises the following steps of: fry-rearing facility building and water treatment, preparation before fry-rearing, incubation for fertilized eggs, feeding for bait, regulation and control for fry-rearing water body and the like, wherein fries can be caught when the whole lengths of the fries achieve 2.5 cm. The facility fry-rearing method disclosed by the invention is simple in operation, adopts a stable fry-rearing water body condition, has the advantages of being high in fry-rearing success rate, stable in survival rate, simple in operation and the like in case of no use of any antibacterial agent during the whole fry-rearing process, and is suitable for facility fry-rearing for many species of grouper in a large water body of an outdoor cement pool; and an effective way is provided for the formation of large-scale production in the aspect of artificial fry-rearing for grouper.
Owner:HAINAN PROVINCIAL FISHERIES RES INST
Aptamer-based Sandwich ELASA method for detecting nervous necrosis virus infection of groupers
InactiveCN105785023AFast specificityThe detection process is fastBiological testingTrue positive rateHorse radish peroxidase
The invention discloses an aptamer-based Sandwich ELASA method for detecting nervous necrosis virus infection of groupers. The method comprises the following steps: fixing a biotin-labeled aptamer onto a pore plate pre-coated with streptavidin; capturing CP proteins in a to-be-detected sample by the fixed aptamer, and combining the CP proteins by the biotin-labeled aptamer; adding horse radish peroxidase-streptavidin for incubating and combining, developing by a horse radish peroxidase developing kit, and analyzing whether NNV virus infection exists according to light absorption value change. According to the invention, by utilizing the characteristics of high affinity and high specificity of the aptamer, a Sandwich ELASA detection method based on aptamer detection is established and can be used for detecting nervous necrosis viruses during grouper culture. Compared with the traditional ELISA and other detection methods, the method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of high detection speed, high sensitivity and specificity, low cost and high simplicity in operation.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Amplification primer for grouper catostomidae mitochondrial genome complete sequence and design method thereof
InactiveCN101698842AEasy splicingNo mismatchMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGermplasmComplete sequence
The invention discloses an amplification primer for a grouper catostomidae mitochondrial genome complete sequence and a design method thereof, relates to groupers, and particularly relates to 16 pairs of amplification primers mainly used for specifically amplifying most grouper catostomidae mitochondrial genome complete sequences and a design method thereof. The invention provides an amplification primer for a grouper catostomidae mitochondrial genome complete sequence, a design method thereof and application thereof. The amplification primer for the grouper catostomidae mitochondrial genome complete sequence consists of 16 pairs of single-chain oligonucleotides, wherein each pair consists of one light-chain primer and one heavy-chain primer. The amplification primer for the grouper catostomidae mitochondrial genome complete sequence can be used in the aspects of variety authentication, geographical population authentication, germplasm resource evaluation and the like.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Grouper compound feed and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a fish feed and a preparation method thereof, in particular to a grouper compound feed and a preparation method thereof. The grouper compound feed consists of the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 30 to 40 percent of fish meal, 15 to 20 percent of bean pulp, 10 to 20 percent of wheat high protein flour, 20 to 30 percent of flour, 1 to 2 percent of yeast powder, 1 to 2 percent of compound vitamin, 0.1 to 1 percent of compound mineral matter, 0.5 to 1 percent of choline, 1 to 2 percent of monocalcium phosphate, 2 to 4 percent of isinglass, 0.1 to 0.5 percent of VC and 1 to 2 percent of dried small shrimp powder. The feed of the invention is prepared by refining according to the growth characteristic and nutritional requirement of the groupers, has comprehensive nutrition and strong food calling property, can furthest release the growth potential of the groupers, adds various mineral matters and vitamins and can improve the gut immunologic barrier and strengthen the immunologic function.
Owner:GUANGDONG EVERGREEN FEED INDAL
Factory culturing method for grouper
InactiveCN101053320AQuality improvementClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaWater qualityUv disinfection
The present invention discloses a grouper factory culturing method comprising the following steps: (1) Treatment water for culture: disinfecting and sterilizing culturation water by ozone and ultraviolet radiation, then filtering and detecting and controlling water quality; (2) Selection fry: selecting 12 to 15cm grouper fry without nervous necrosis virus; (3) Culturation for grouper: To discharge culturation water qualified by detected into culture pond, to stock the selected fry into pond, to control the content of dissolved oxygen, ammonia nitrogen, nitrite and bacterial in pond, and to control culture density and PH of culture water, to feed everyday; (4) During culturing procession to recycle treatment culture water, that is to separate protein for culture water, after disinfecting and sterilizing by ozone and ultraviolet radiation to process biological nitrification, and then filtering so as to renew culture water; (5) Pollution absorption, washing pond bottom and changing water each day, keeping pond wall and pond bottom cleaning. This method has high efficiency and environment protecting, using this method to produce grouper having good quality, high yield, health and high survival rate, lower feed coefficient.
Owner:广东省大亚湾水产试验中心
Pond culture method of grouper
InactiveCN101461337AImprove survival rateBreeding method is simpleClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaFish weightRockfish
A rockfishes pond culture method is disclosed, wherein young fish of rockfishes is released in a sea pond with water depth more than 80 cm and water temperature 13-38 DEG C, released density is 750-850 fish 667 m2, diet is feed at least twice a day in the release process, quantity of diet feeding is: 3-4% fish weight in the early breeding stage, 4-5% in the middle stage and 5-7% in the late stage; specification of the released fish is 6-8 per kg, the release pond is sand bottom, and water in the pond is more than 1.5 in depth, and provided with a separate inlet / discharge channel. The bottom of the pond is laid with a plurality of random rubbles or perforate junked tires or tile tunnels. The invention is characterized by simple breeding method, low breeding cost, high success ratio of the cultivated fish, healthy in water aquatic products with high quality and nuisance free and the like.
Owner:宁波海能渔业发展有限公司
Compound Chinese herbal medicine immunopotentiator for grouper
InactiveCN101480436ANo adverse effects on palatabilityPalatability without residueClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffAntibiotic YGLYCYRRHIZA EXTRACT
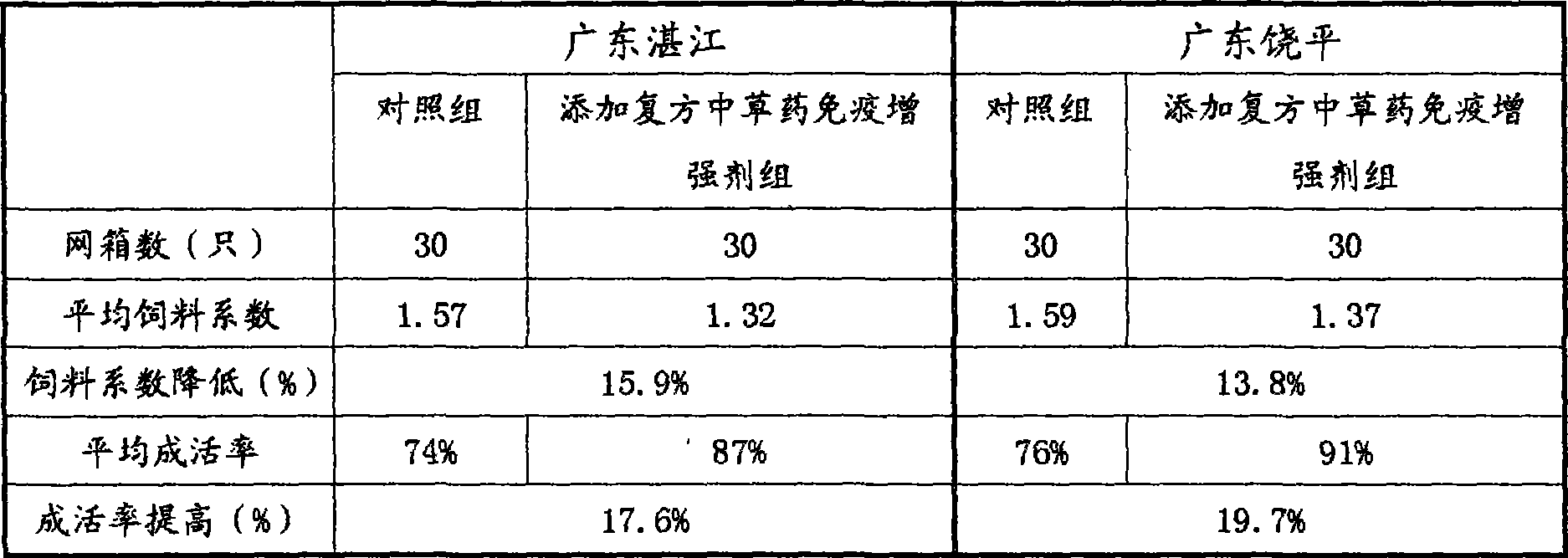
Compound Chinese medicinal herb immunopotentiator for rudd is prepared from the components by weight: 10 to 20 percent of radix astragali, 10 to 20 percent of honeysuckle, 10 to 15 percent of rhubarb, 10 to 15 percent of eucommia bark leaf powder, 10 to 15 percent of liquorice, 10 to 15 percent of hawthorn, 5 to 10 percent of Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae, and 5 to 10 percent of safflower. The invention has the following advantages that the compound Chinese medicinal herb immunopotentiator can be used as feed additive in rudd compound feed, and is added in to the rudd compound feed by only 0.1 to 0.2 percent, can remarkably increase the organism immunity and improve the survival rate of rudd, can completely replace antibiotics, has no adverse effect and no residue to the palatability of feed, and has a stable raw material resources, low cost and simple production technology.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
Rockfish viral nerve necrosis virogene diagnostic kit and detecting method thereof
InactiveCN1448520AEasy to detectSensitive and specificMicrobiological testing/measurementRockfishTiger frog
The present invention is rockfish viral nervous virus gene diagnosing kit and its usage. The kit and its usage is designed based on two pairs of primers for the conservation sequence of rockfish viral nervous virus gene. By means of PCR technology, the present invention detects qualitatively the specific DNA nucleic acid segment of tiger frog virus fast, simply, specifically and sensitively. The present invention may be used in the tracing detection of different stages of rockfish cultivation and environment monitoring.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Composite type intestinal-health regulating agent for groupers and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104323029AImprove growth performanceImprove efficiencyAnimal feeding stuffIntestinal structureGut flora
The invention discloses a composite type intestinal-health regulating agent for groupers. The composite type intestinal-health regulating agent comprises the following components in parts by weight: 5-10 parts of probiotic powder, 20-25 parts of fructooligosaccharide, 5-10 parts of tributyrin, 15-20 parts of glutamine, 10-20 parts of white carbon black and 15-45 parts of defatted rice bran. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the composite type intestinal-health regulating agent for the groupers. The composite type intestinal-health regulating agent has the advantages that the development of the intestines of the groups can be enhanced, the intestinal mucosal damage is restored, the immunologic function of the intestinal mucosa and the immunologic function of the system are activated, the balance of the intestinal flora is regulated, the health of the intestinal mucosa is maintained, and the morbidity of the enteritis is reduced. In addition, the activity of intestinal digestive enzyme can be improved, and the growth performance of the groupers and the feed utilization efficiency are improved.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Feed promoting agent for seawater cultured fishes
InactiveCN102067953ASafe and efficient for long-term useNo side effectsAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsL-AspartateTaurine
The invention relates to a feed additive, in particular to a feed promoting agent for seawater cultured fishes, which comprises the raw materials in weight ratio in the terms of addition per ton of feed: 300-1200g of crystal taurine, 300-1000g of L-glycine, 500-1000g of L-alanine, 500-1200g of L-glutamic acid, 800-1500g of L-aspartate, 500-3000g of betaine hydrochloride, 1000-2000g of dimethyl-beta-propiothetin (DMPT) crude powder and 1100-8000g of degreased condensed fish soluble protein powder. Proved by multiple culture tests in seawater fish feeds, such as Japanese sea bass, sciaenops ocellatus, trachinotus ovatus, garrupa and the like, the feed promoting agent for seawater cultured fishes is capable of remarkably enhancing the food intake of the seawater fishes to the composite feed by above 10 percent and quickening the intake speed as well as remarkably improving the stress-resisting capability of the cultured objects; and the cultured the seawater fishes have the advantages of high survival rate, bright color and strong stress resistance.
Owner:广西粤海饲料有限公司
Healthy and efficient method for cultivating giant groupers by deepwater anti-stormy waves cages
InactiveCN102823527AIncrease profitReduce investmentClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaFresh water organismFresh water
The invention discloses a healthy and efficient method for cultivating giant groupers by deepwater anti-stormy waves cages, which comprises the following steps: (1) selection of a cultivating sea area: the cultivating sea area is an opening sea area with reef island shields, smaller stormy waves, more smooth tide and above 15m of depth of water; (2) requirements of cage facilities: the cages have the capability of fighting against 12-level typhoon and the rough sea with a height of above 5 cm; (3) selection and stocking of the giant grouper fries: injury-free giant grouper fries with robust physique and consistent specifications are selected and then soaked and sterilized by fresh water before being fed; (4) feeding technique: after being hungered for 2 days, the giant grouper fries are recovered to feed for 2 days with the baits of iced and fresh trash fishes, and controlled to keep eight full at every time, and 0.1 to 0.3% of amino electrolytic polyvitamines and 0.02 to 0.04% of garlicin are added based on the weight of the baits in the baits; and (5) feeding and management. The method has the characteristics of being simple to cultivate and operate and less in bait investment, and the obtained nuisanceless cultivating giant groupers have the characteristics of high yield, good quality, low bait coefficient, high survival rate and fast growth speed and the like.
Owner:巫山天地农业开发有限公司
Microcapsule bait, bait feeding method and bait feeding device for grouper larvae
InactiveCN102934751AMeet the nutritional needs of growthMeeting nutritional needsClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffAnimal scienceNutrition
The invention provides a microcapsule bait, a bait feeding method and a bait feeding device for grouper larvae. The microcapsule bait comprises ingredients of maize meals, coconut cakes, rice bran, chicken bone powders, pea powders, silkworm chrysalis powders, sesame powders, sleeve-fish powders, and the like. According to the microcapsule bait, the bait feeding method and the bait feeding device for the grouper larvae, an innovative formula and a processing technology are utilized, the nutritional requirements for larva growth can be met, the nutrition is comprehensive, the palatability is good, the water stability is good, and the like; the bait can be produced in a batch mode, is convenient to store, transport and feed and applicable to factorial offspring seed production, simultaneously, the corresponding feeding method and feeding device are utilized, the growth and survival rate of the grouper larvae can be improved, and the microcapsule bait, the bait feeding method and the bait feeding device for the grouper larvae are applicable to large-scale popularization and usage.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
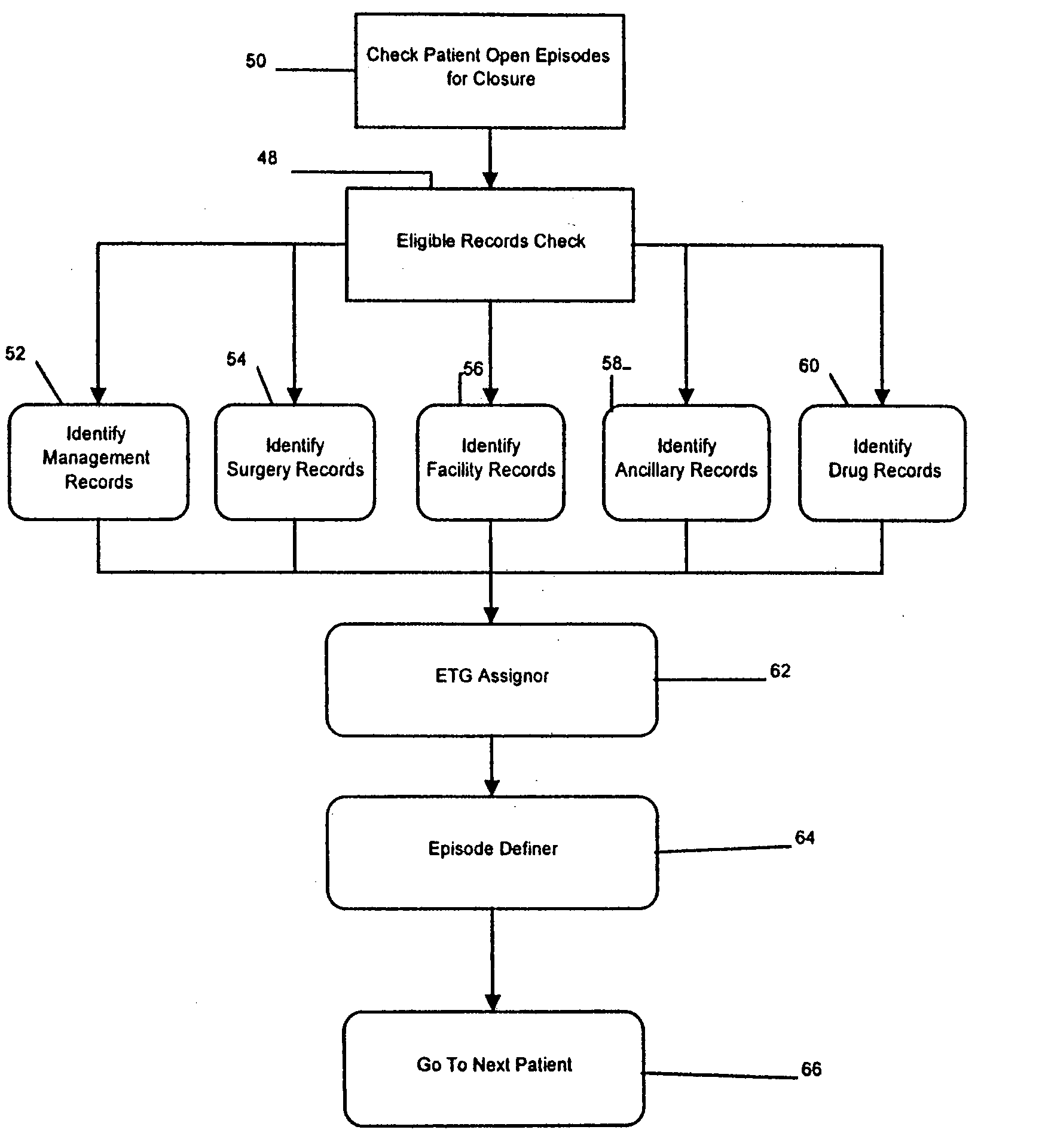
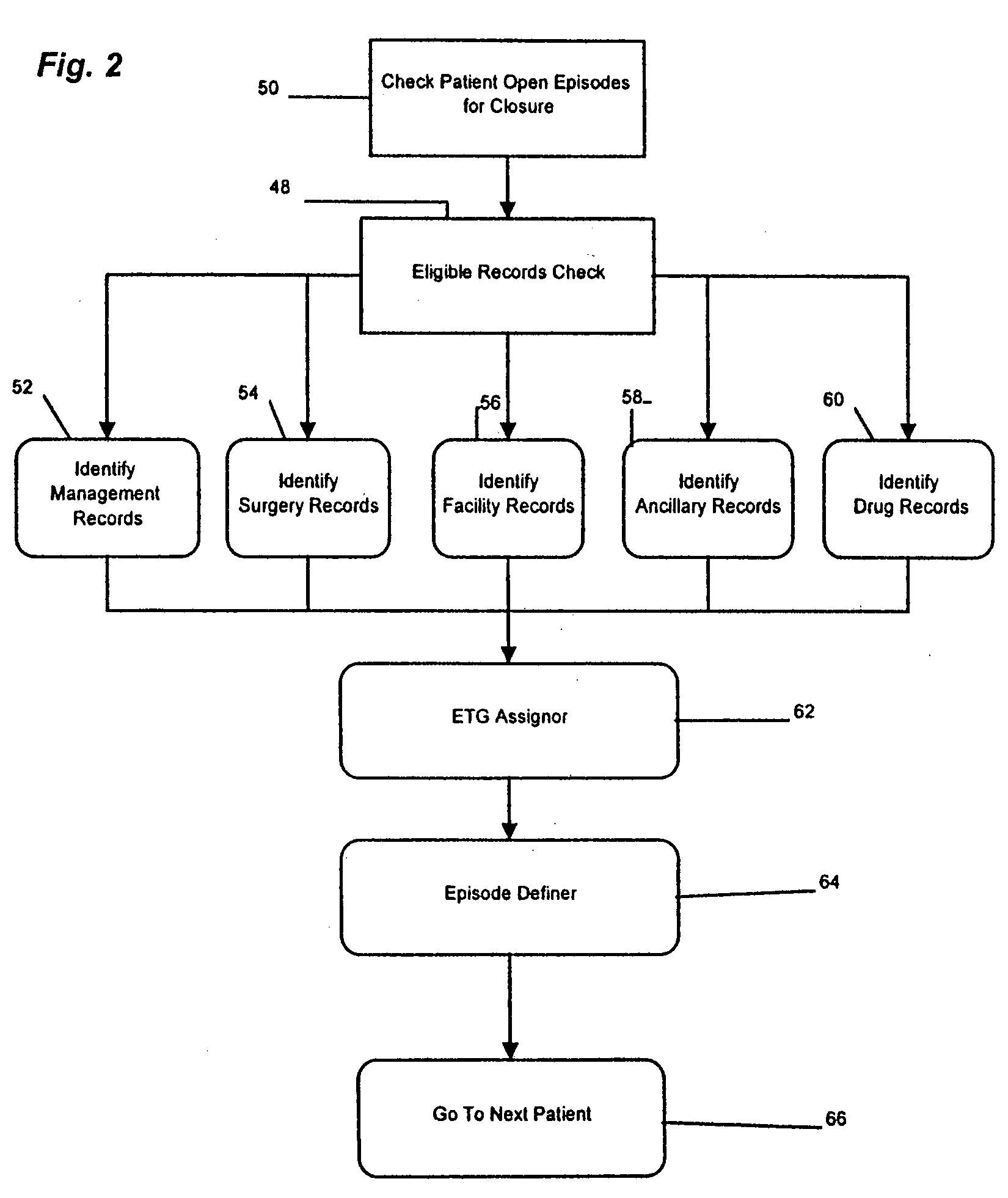
Episode treatment groups of correlated medical claims
InactiveUS20080021742A1FinanceComputer-assisted treatment prescription/deliveryDiseaseRecurrent episode
Owner:INGENIX INC
Complex immunopotentiator for grouper
InactiveCN101480488AOvercoming Negative Feedback Inhibition ProblemsImprove the body's immunityPeptide/protein ingredientsAnimal feeding stuffVitamin CLevamisole
The invention relates to a composite immunity intensifier for groupers, which comprises the following components according to weight percentage: 30 to 40 percent of Beta-dextran, 10 to 20 percent of A3 Alpha peptidoglycan, 10 to 20 percent of vitamin C-2- polyphosphate ester, 10 to 20 percent of levomisole, 5 to 10 percent of ginsenoside and 5 to 10 percent of vitamin E. The invention has the advantages that: firstly, the composite immunity intensifier effectively overcomes the problem that the body reverse feedback of the groupers is restrained and can be used in the whole culturing period of the groupers; secondly, the composite immunity intensifier as a feed additive is used in the compound feed of the groupers and only has 0.1 to 0.2 percent of addition amount; thirdly, the body immunity of the groupers is intensified obviously and the survival rate is improved; fourthly, the composite immunity intensifier has no bad effect on the palatability of feed; and fifthly, the raw material used by the composite immunity intensifier has stable source, low price and simple production process.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
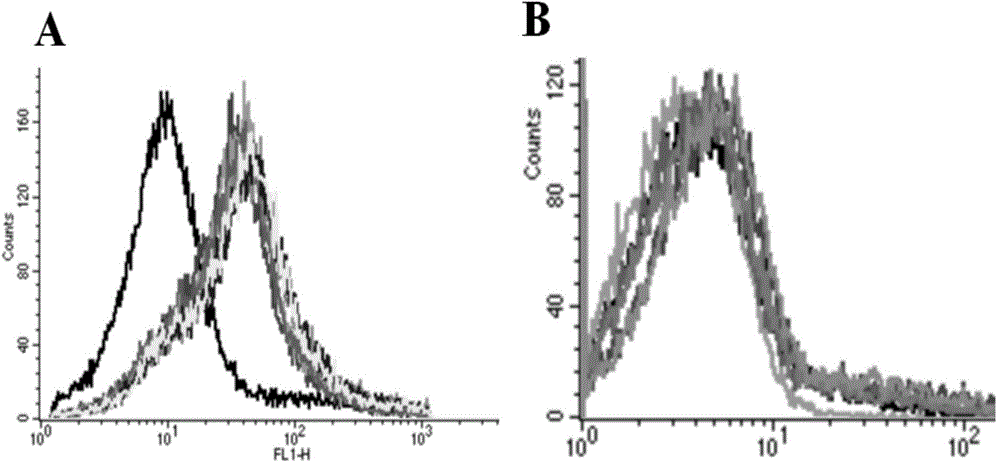
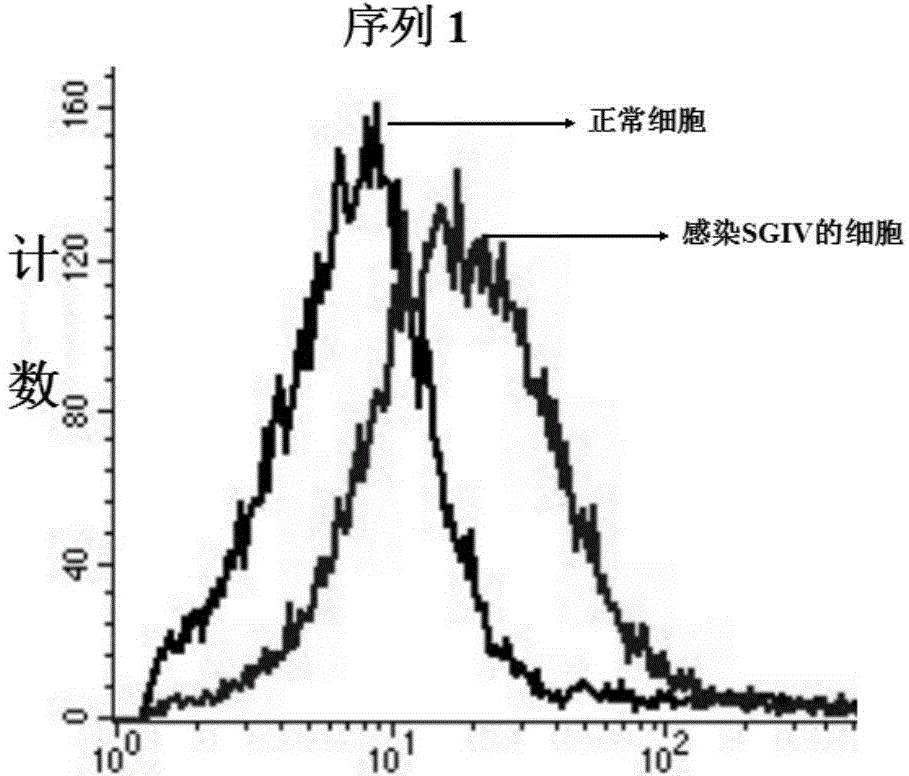
DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) aptamer for detecting grouper iridovirus infection, as well as screening method and application of DNA aptamer
ActiveCN104789696AHigh affinityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysis3-deoxyriboseDNA Aptamers
The invention discloses a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) aptamer for detecting grouper iridovirus infection, as well as a screening method and an application of the DNA aptamer. Two inverse screening steps are introduced in each screening process; first, a single-stranded DNA library of the former screening process is bound with normal cells to remove nonspecific ssDNA (single-stranded DNA) bound with the normal cells of a grouper; then, supernatant is bound with grouper iridovirus infected cells for screening; and ssDNA separated from the grouper iridovirus infected cells is bound with the normal cells for separation to obtain the supernatant. A PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification library prepares the single-stranded DNA library. The above screening flow is repeated; compared with the number of the normal cells in the first screening process, the number of the normal cells in the screening process is increased by 2-6 times; compared with binding time of the library and the cells in the first screening process, the binding time of the library and the cells in the subsequent screening process is increased to 1h from 0.5h; and the binding time of the library and the virus infected cells is shortened to 0.5h from 1h to improve the screening efficiency of each process.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) aptamer for detecting grouper iridovirus infection, as well as screening method and application of DNA aptamer
ActiveCN104789569AHigh affinityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processes3-deoxyriboseDNA Aptamers
The invention discloses a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) aptamer for detecting grouper iridovirus infection, as well as a screening method and an application of the DNA aptamer. Two inverse screening steps are introduced in each screening process; first, a single-stranded DNA library of the former screening process is bound with normal cells to remove nonspecific ssDNA (single-stranded DNA) bound with the normal cells of a grouper; then, supernatant is bound with grouper iridovirus infected cells for screening; and ssDNA separated from the grouper iridovirus infected cells is bound with the normal cells for separation to obtain the supernatant. A PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification library prepares the single-stranded DNA library. The above screening flow is repeated; compared with the number of the normal cells in the first screening process, the number of the normal cells in the screening process is increased by 2-6 times; compared with binding time of the library and the cells in the first screening process, the binding time of the library and the cells in the subsequent screening process is increased to 1h from 0.5h; and the binding time of the library and the virus infected cells is shortened to 0.5h from 1h to improve the screening efficiency of each process.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Germplasm identifying method of hybrid grouper
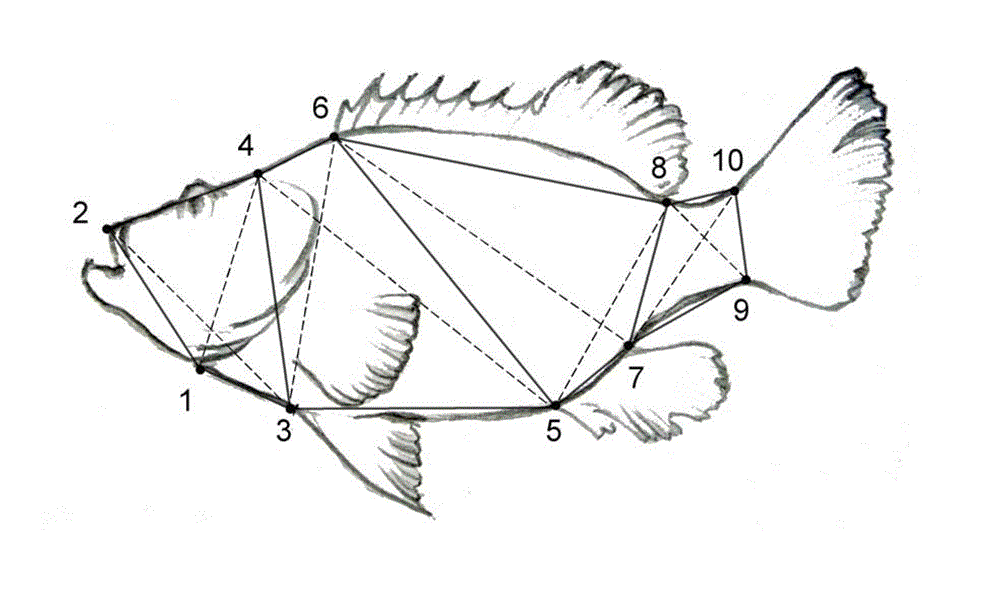
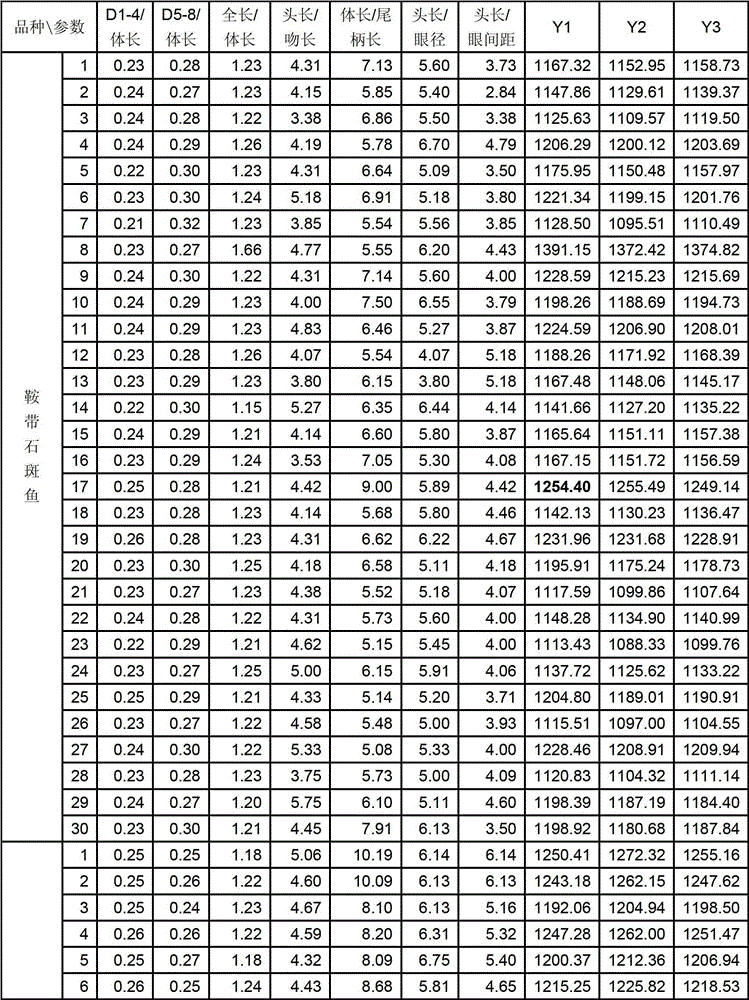
The invention discloses a germplasm identifying method of hybrid grouper, which comprises basic steps as follows: detecting morphological parameters including traditional measurable characters of the full length, the body length, the head length, the tail length, the snout length, the eye diameter, the interorbital distance as well as detecting framework measurement data D1-4 and D5-8 of a sample to be tested; preliminarily processing the obtained parameters to obtain the following characteristic parameters: D1-4 / body length, D5-8 / body length, the full length / body length, the head length / the snout length, the body length / the tail length, the head length / the eye diameter, and the head length / the interorbital distance; and processing the parameters and then substituting into a corresponding judgment function model, and judging the category of the sample according to the maximum Y value. The method provided by the invention is simple, feasible, precise and effective.
Owner:广东大麟洋海洋生物有限公司
DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) aptamer for detecting grouper iridovirus infection, as well as screening method and application of DNA aptamer
ActiveCN104789568AHigh affinityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processes3-deoxyriboseDNA Aptamers
The invention discloses a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) aptamer for detecting grouper iridovirus infection, as well as a screening method and an application of the DNA aptamer. Two inverse screening steps are introduced in each screening process; first, a single-stranded DNA library of the former screening process is bound with normal cells to remove nonspecific ssDNA (single-stranded DNA) bound with the normal cells of a grouper; then, supernatant is bound with grouper iridovirus infected cells for screening; and ssDNA separated from the grouper iridovirus infected cells is bound with the normal cells for separation to obtain the supernatant. A PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification library prepares the single-stranded DNA library. The above screening flow is repeated; compared with the number of the normal cells in the first screening process, the number of the normal cells in the screening process is increased by 2-6 times; compared with binding time of the library and the cells in the first screening process, the binding time of the library and the cells in the subsequent screening process is increased to 1h from 0.5h; and the binding time of the library and the virus infected cells is shortened to 0.5h from 1h to improve the screening efficiency of each process.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
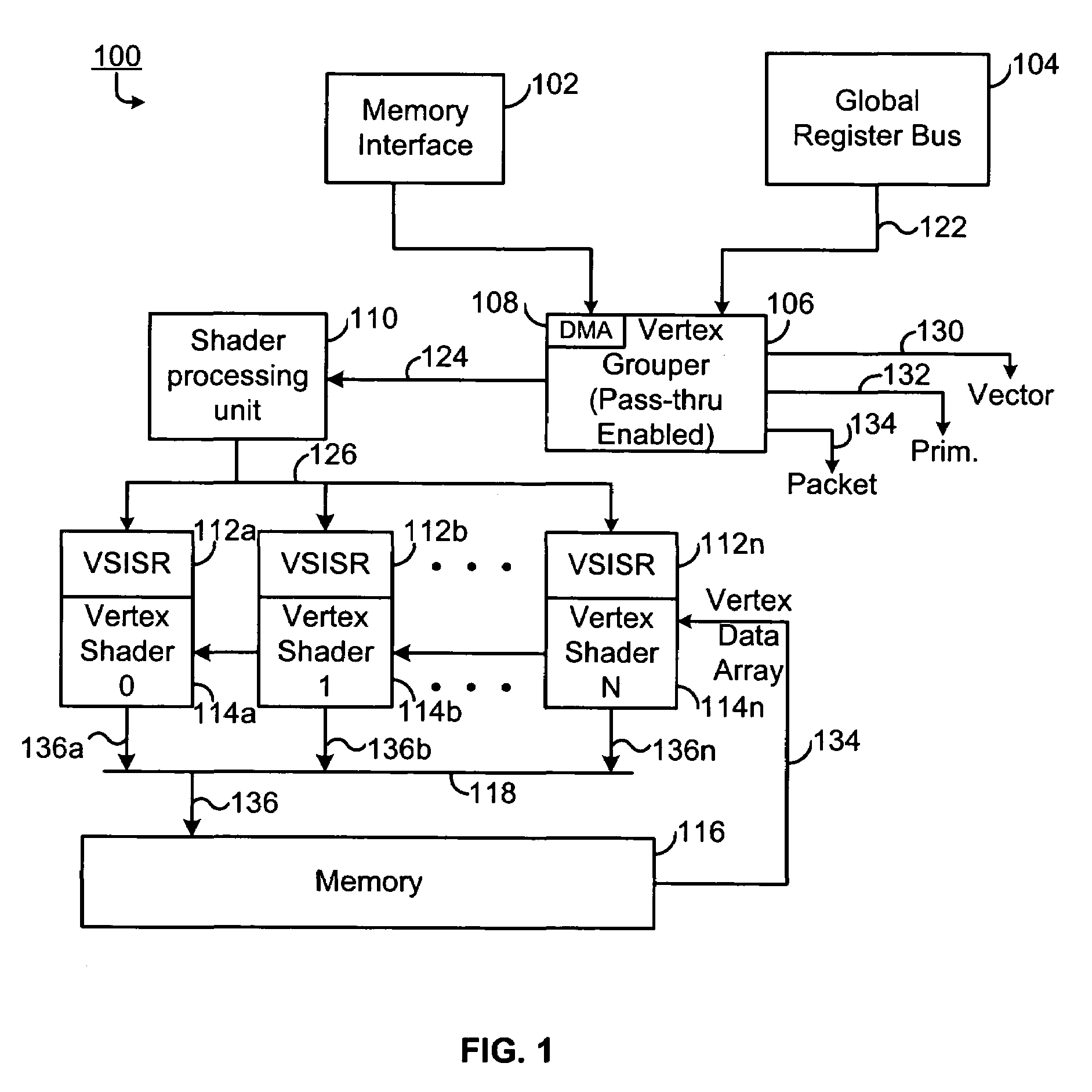
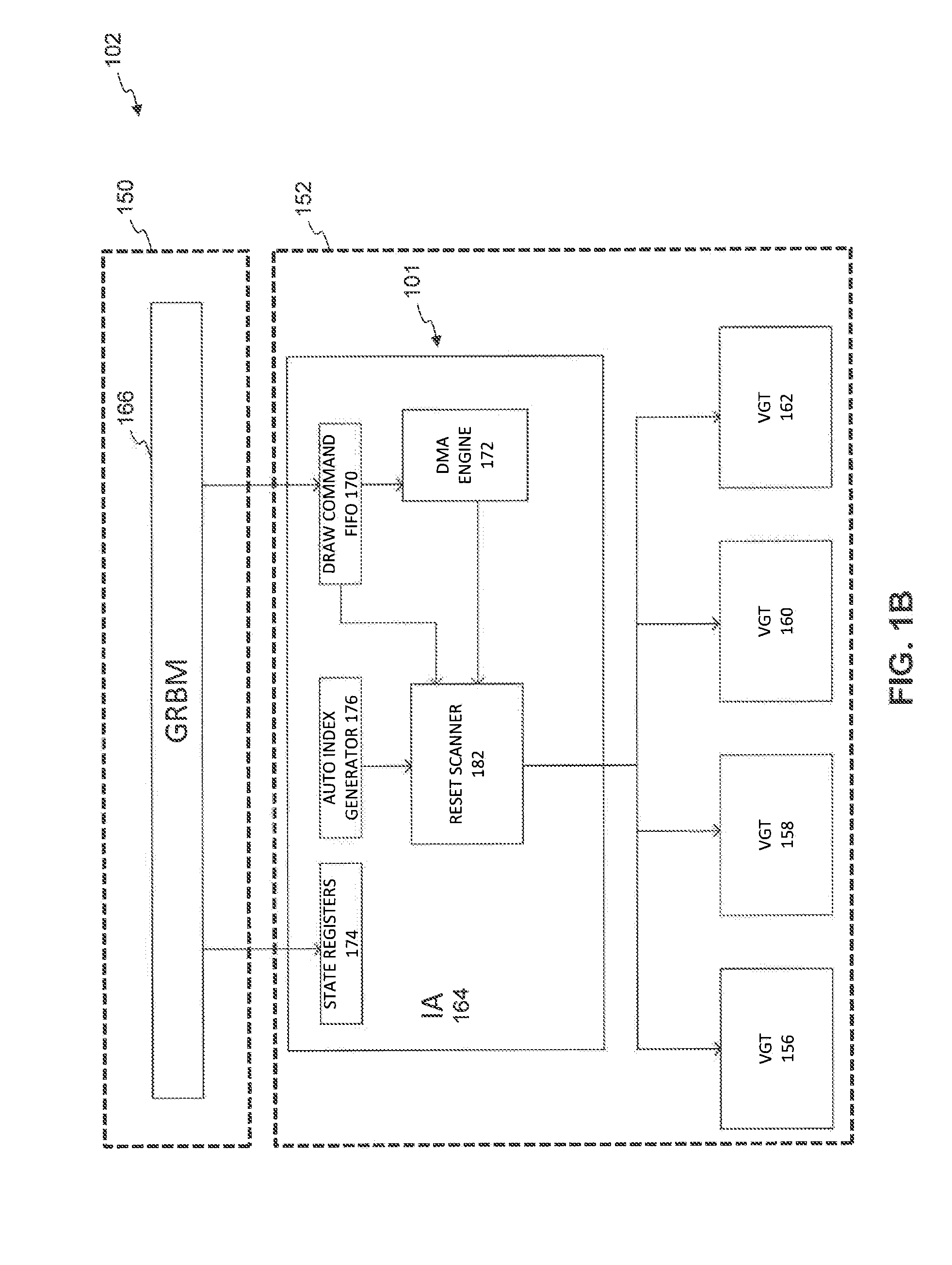
Scalable Multi-Primitive System
ActiveUS20130169635A1Efficient processingHigher primitive rateDrawing from basic elements3D-image renderingComputer graphics (images)Grouper
Disclosed herein is a vertex core. The vertex core includes a reset scanner configured to remove reset indices and partial primitives in an input stream and resolve draw calls into sub-draw calls at reset index boundaries; and provide the resolved sub-draw calls to a plurality of downstream vertex grouper tessellators.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Artificial propagation method for yellowfin groupers
ActiveCN110100768AImprove environmental adaptabilityIncrease food intakeClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffBroodstockRed mullet
The invention provides an artificial propagation method for yellowfin groupers. The artificial propagation method comprises the steps that (1) parents are selected; (2) a parent breeding pond is separated into a deep water area and a shallow water area with water flow communicated, wherein the water depth of the deep water area ranges from 4 m to 5.5 m, and the water depth of the shallow water area ranges from 3 m to 3.5 m; (3) parent fish breeding management is carried out, wherein a, in first 3 weeks during breeding, LED green light and yellow light alternately irradiate the water surface ofthe pond, and after the parent fishes are bred for 3 weeks or longer, the water surface of the pond is irradiated by the LED green light; b, feed is prepared from 3-5 parts of grouper compound feed and 1-2 parts of small fish and shrimp and artificial pellet feed, the parent fishes are fed with the first feed in the first 3 weeks during breeding, and the parent fishes are fed with the second feedafter being bred for 3 weeks or longer; c, the water temperature of the pond ranges from 21 DEG C to 26 DEG C, and water dissolved oxygen is larger than 4.8 mg / L; (4) breeding is enhanced before propagation is carried out; (5) artificial propagation is carried out; (6) zygotes are collected and hatched. According to the artificial propagation method for the yellowfin groupers, the adaptive capacity to environment of the parent fishes is enhanced, the activities of fish shoals are effectively promoted, the feeding rate is effectively increased, the fertility is high, and large-scale artificialbreeding of the yellowfin groupers can be effectively achieved.
Owner:HAINAN CHENHAI AQUATIC CO LTD
Desalination seedling method for seawater miniatus groupers
InactiveCN103651188AEnhance physical fitnessFast growthClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaGrouperSeawater
The invention discloses a desalination seedling method for seawater miniatus groupers. The desalination seedling method includes steps of 1, acquiring fertilized eggs of groupers; 2, incubating the fertilized eggs in nursery ponds to acquire seedlings, filling raw seawater in the nursery ponds and keeping the seawater temperature T to be higher than 28 DEG C and lower than 32 DEG C for 3-4 days; 3, gradually or directly reducing the salinity of water in the nursery ponds in the step 2 by 15%-25%, and keeping the salinity of the water unchanged for 6-10 days; 4, gradually or directly increasing the salinity of the water in the nursery ponds in the step 3 by 3%-7%, and keeping the salinity of the water unchanged for 3-5 days; 5, gradually reducing the salinity of the water in the nursery ponds until the salinity of the water is 0.4-0.8%, and keeping the salinity of the water unchanged for 15-30 days; 6, naturally cooling the water until the temperature of the water is equal to normal temperature, reducing the salinity of the water in the nursery ponds until the salinity of the water is 0.2-0.4%, and waiting for seedling emergence. The desalination seedling method has the advantages that the salinity of the water is changed according to a sequence of desalination, salinization and desalination, so that the adaptability of the grouper seedlings can be trained, and the seawater miniatus groupers can be cultivated in fresh water and become an aquaculture variety in fresh water regions.
Owner:郭明忠 +2
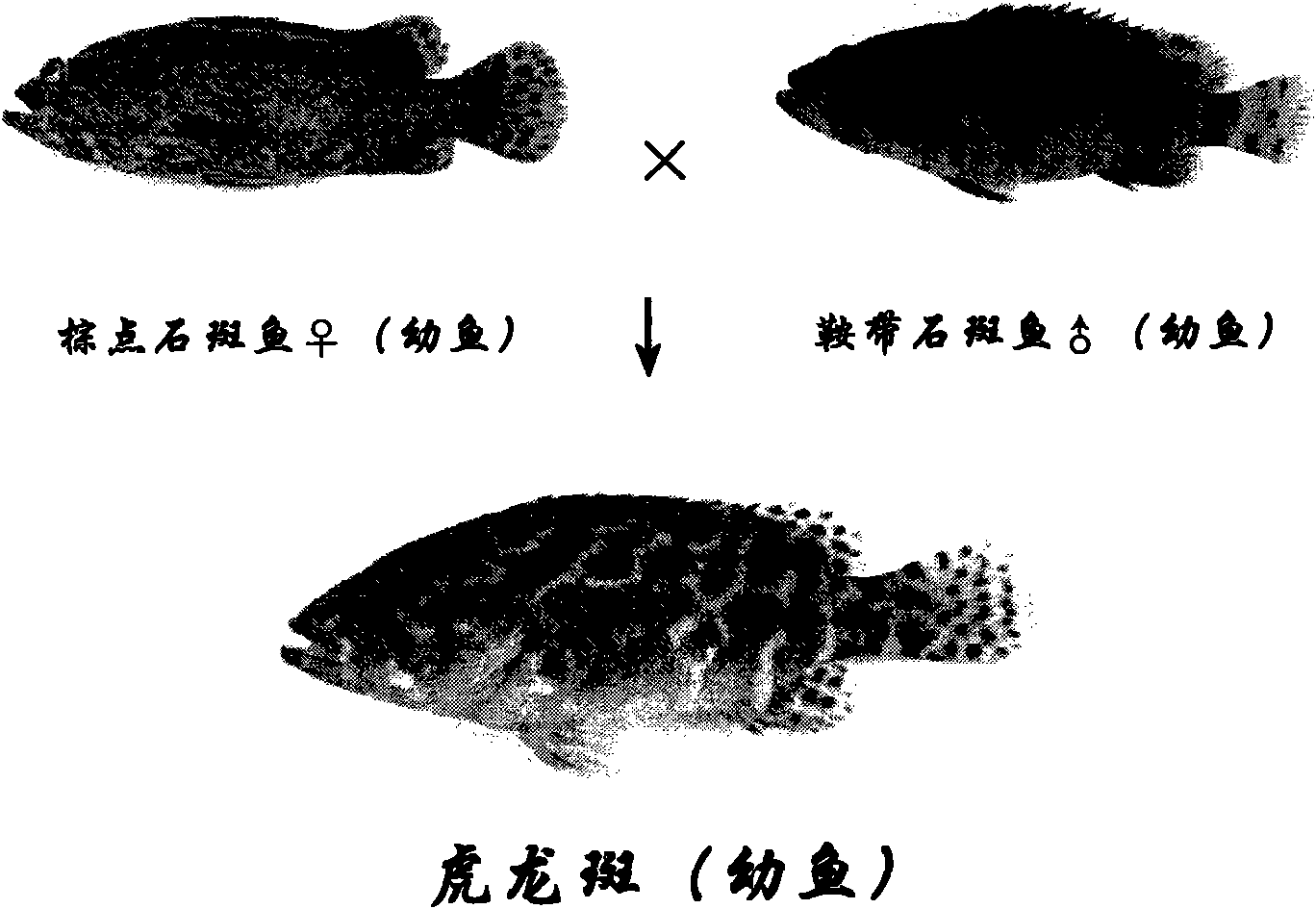
Method for breeding cross-bred 'Hulongban' fish
ActiveCN101933476AImprove fertilization rateImprove hatchabilityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaJuvenile fishMale individual
The invention discloses a method for breeding cross-bred 'Hulongban' fish fry. The method comprises: widely crossing blotchy rock cod male individuals serving as female parents and Epinephelus lanceolatus male individuals serving as male parents; and producing cross-bred 'Hulongban' fish fry by artificial induced spawning, insemination, incubation and juvenile fish culture. The method for breeding the 'Hulongban' fish of the invention is simple in operation and suitable for large-scale production; the survival rate of the cultured 'Hulongban' fish fry is 5 to 10 percent; the 'Hulongban' fish fry breeding survival rate is 5 to 10 percent; the culture survival rate is over 95 percent; the survival rates are much higher than those of common grouper; and thus, the method has a promising market prospect.
Owner:广东省大亚湾水产试验中心 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com