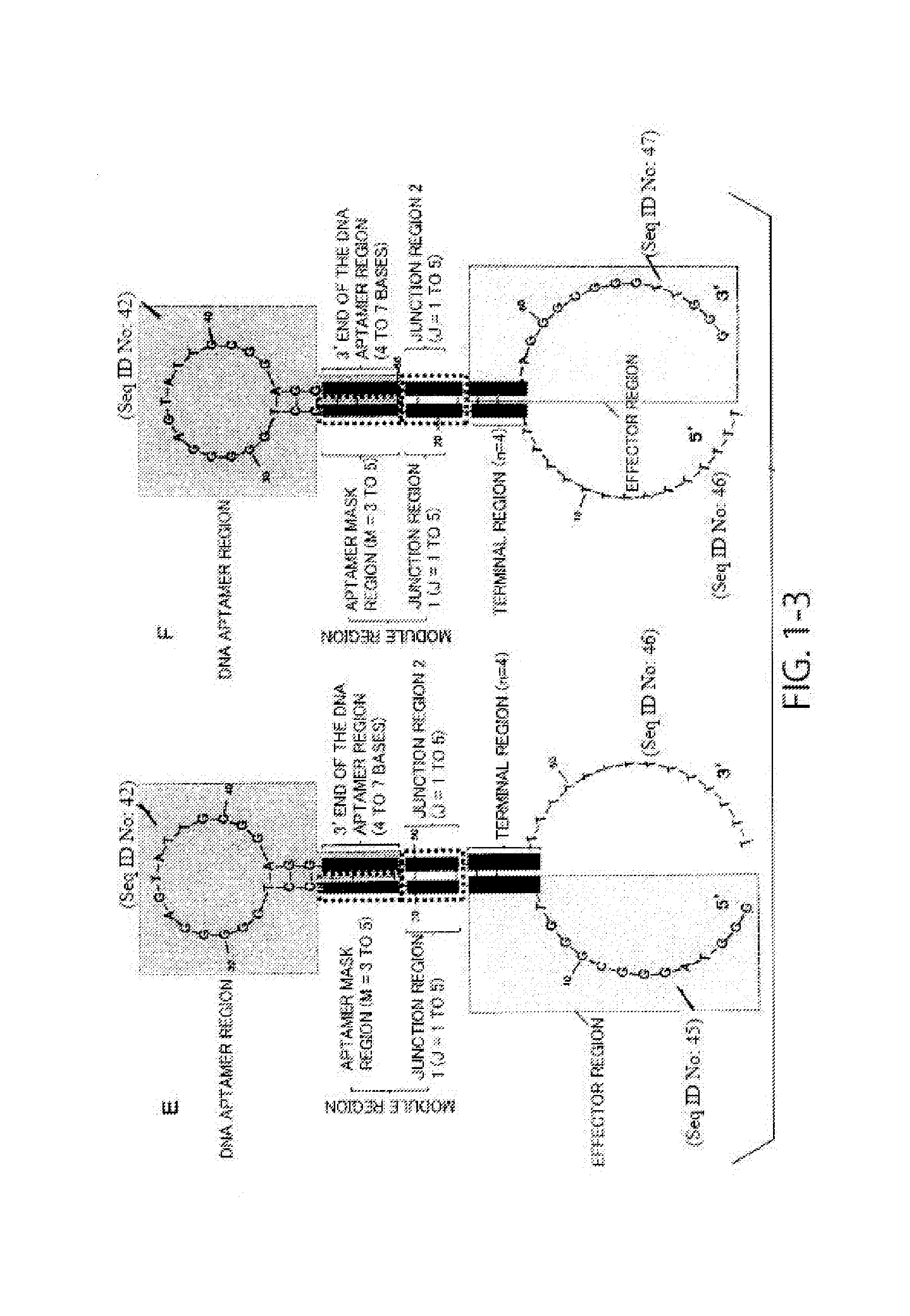
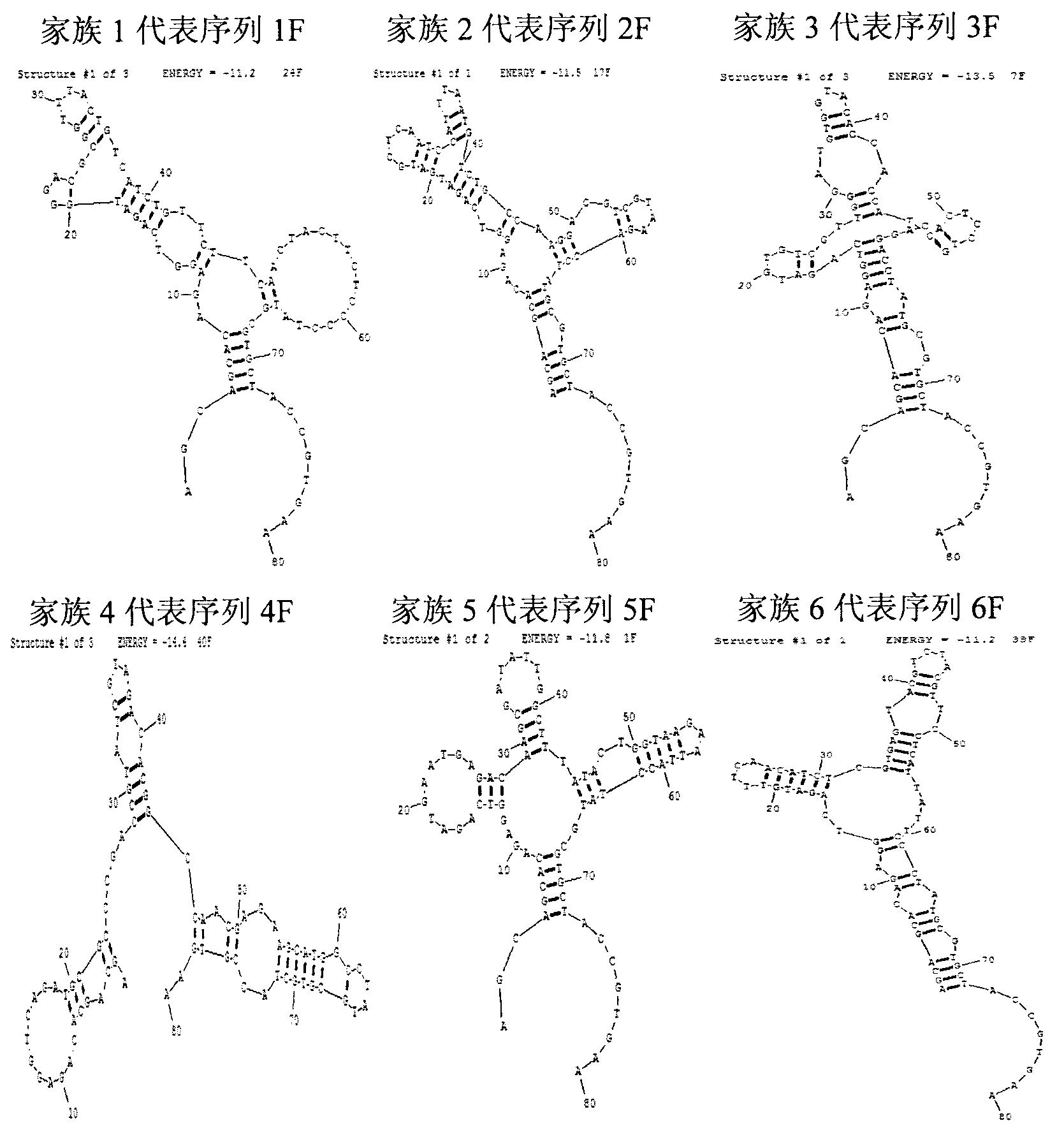
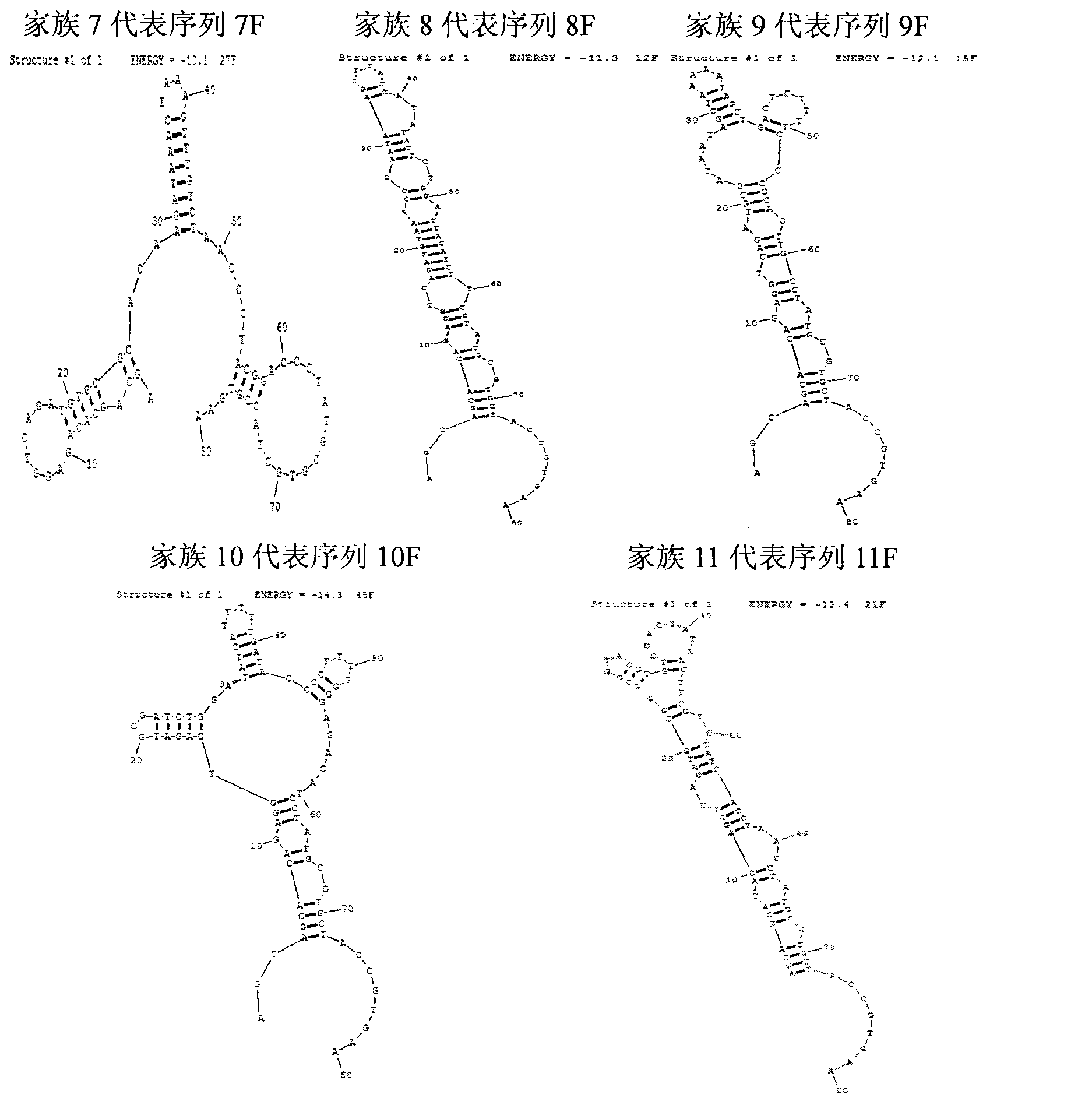
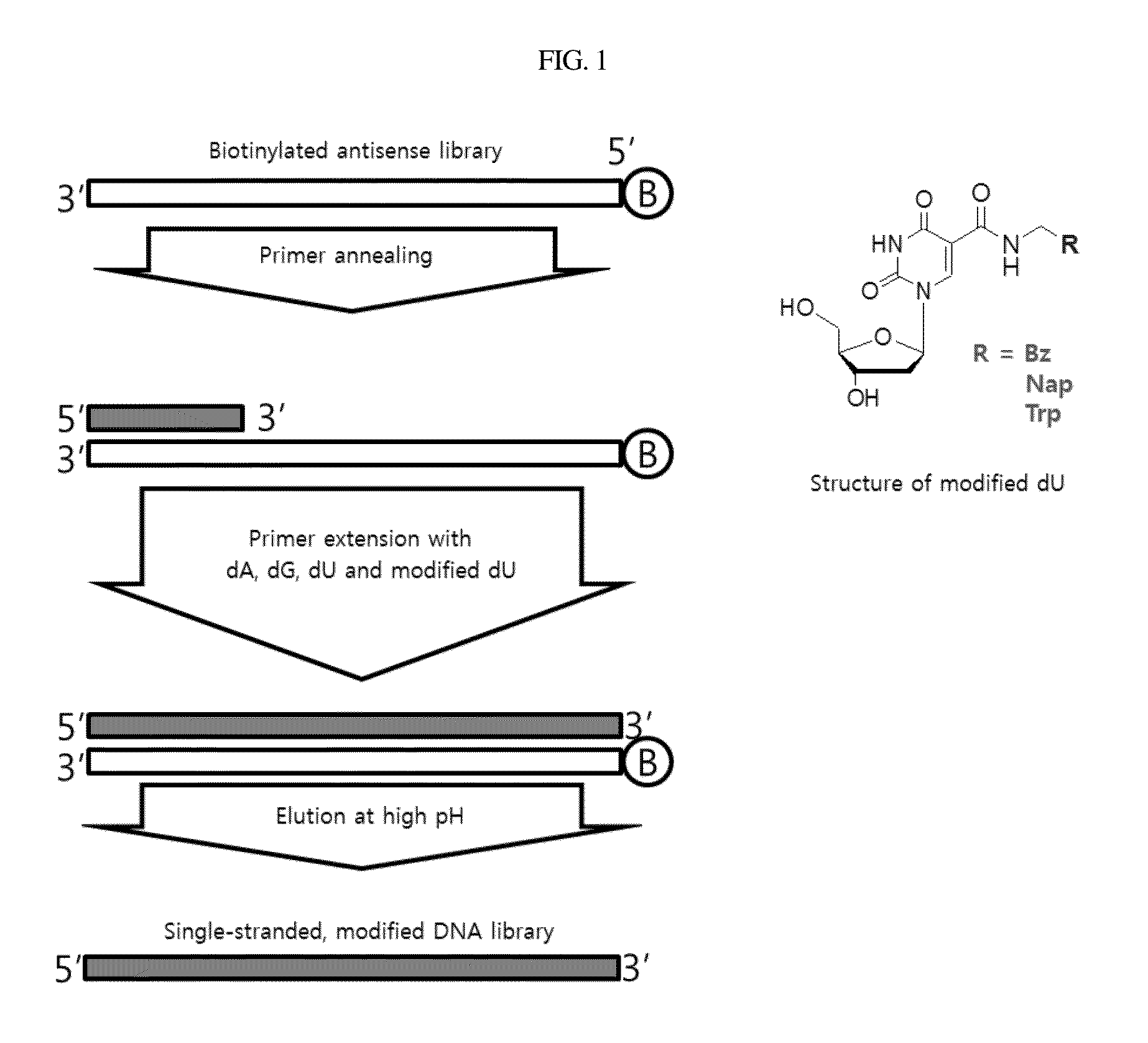
Patents
Literature
199 results about "DNA Aptamers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
DNA/Aptamer. Nucleic acid aptamers are single- or double-stranded DNA or RNA sequences than can bind specifically to molecular targets including but not limited to small molecules, proteins, and organims.
Combinatorial selection of phosphorothioate single-stranded DNA aptamers for TGF-beta-1 protein
InactiveUS20050239134A1Increased proliferationPrevent proliferationPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsDNA AptamersTgf β signalling
The present invention includes the selection and isolation of thioaptamers that target the signaling protein TGF-β1, compositions of such thioaptamers and the use of such thioaptamers to either block or enhance signal transduction of the TGF-β1 protein and thus function as, e.g., immunomodulatory agents. Thioaptamers may also be targeted alone or in combination with other thioaptamers against the ligand, the receptors, the ligand trap protein(s) and / or the co-receptors to modulate TGF-β signaling pathway.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
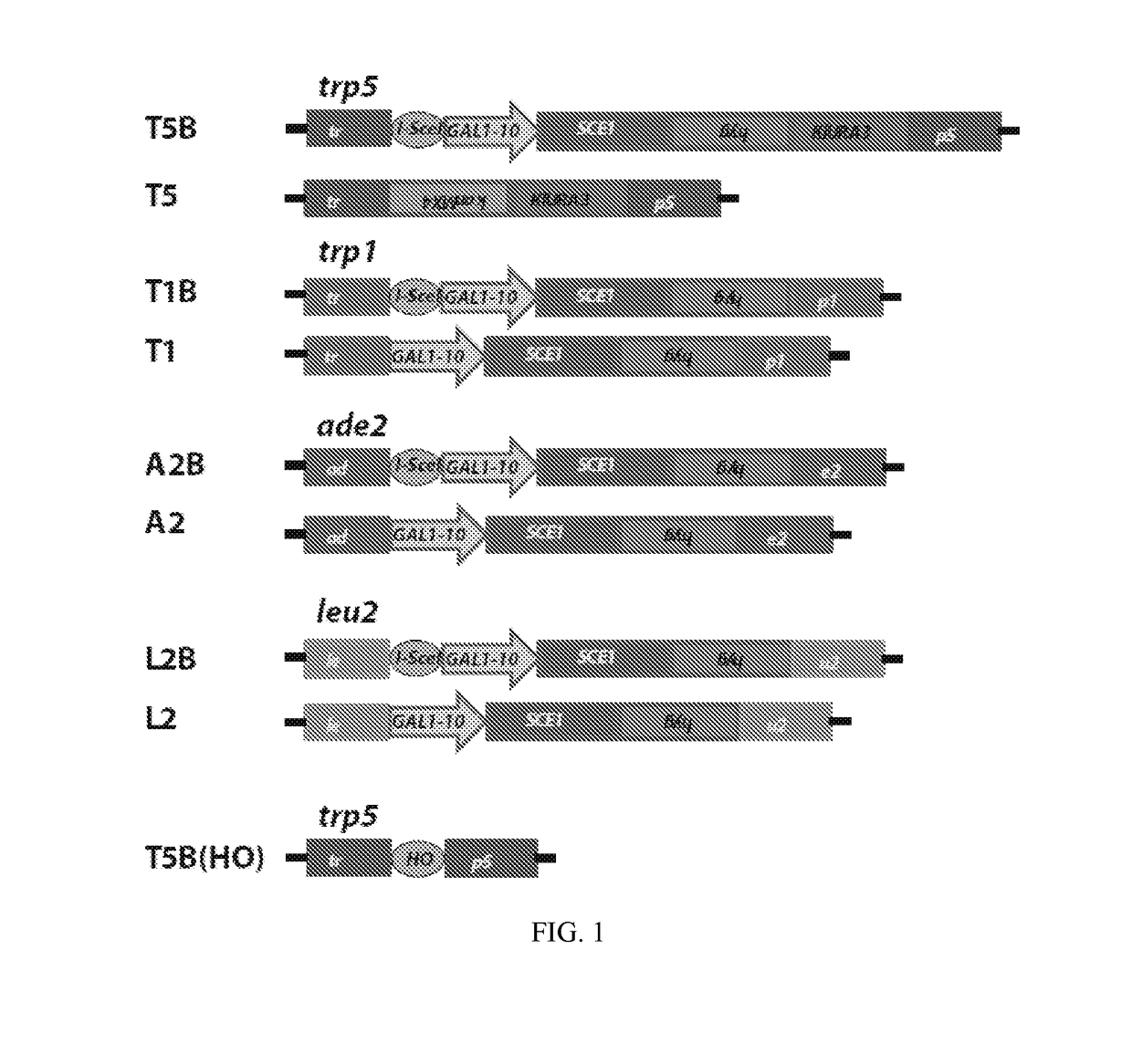
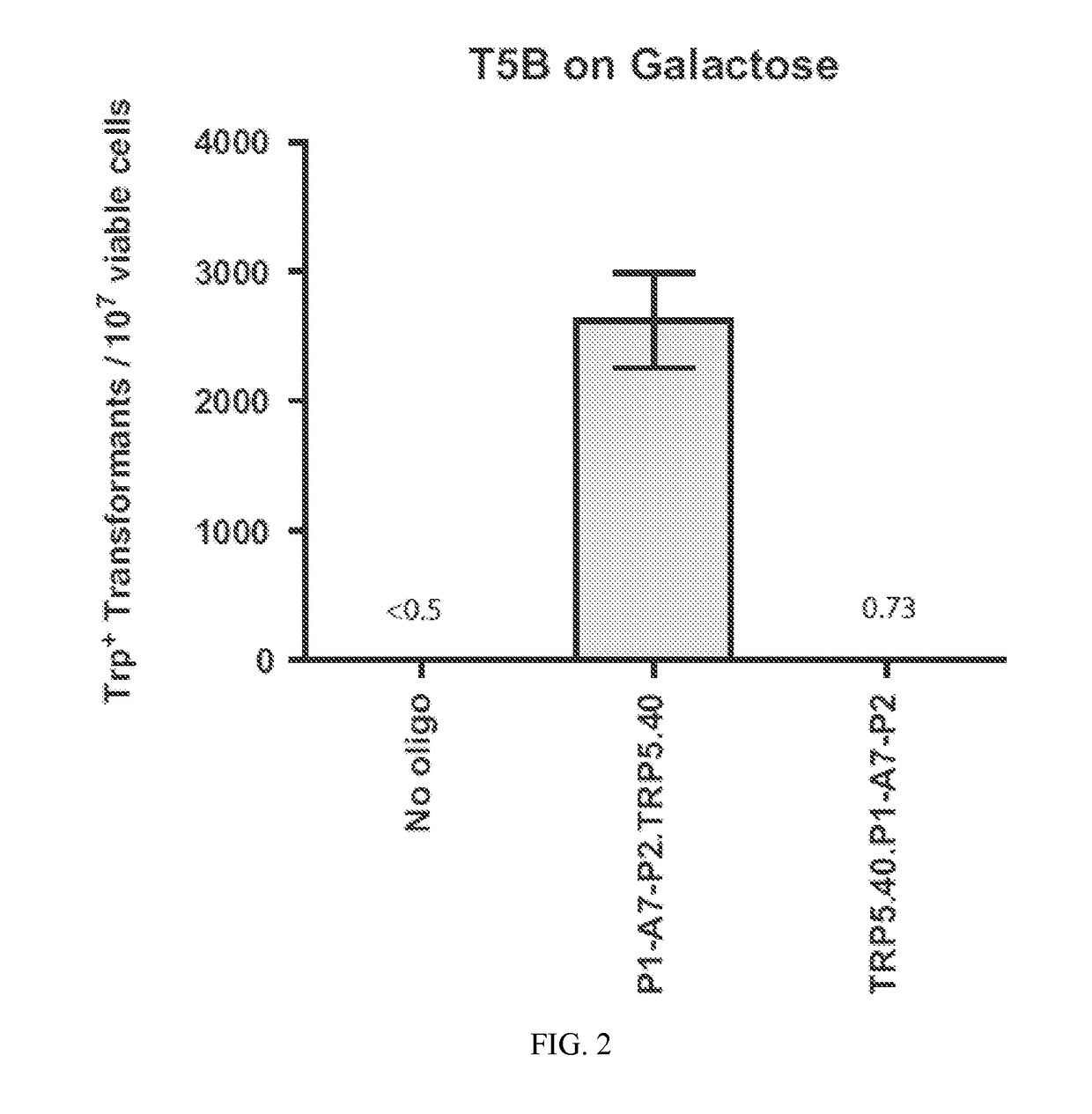
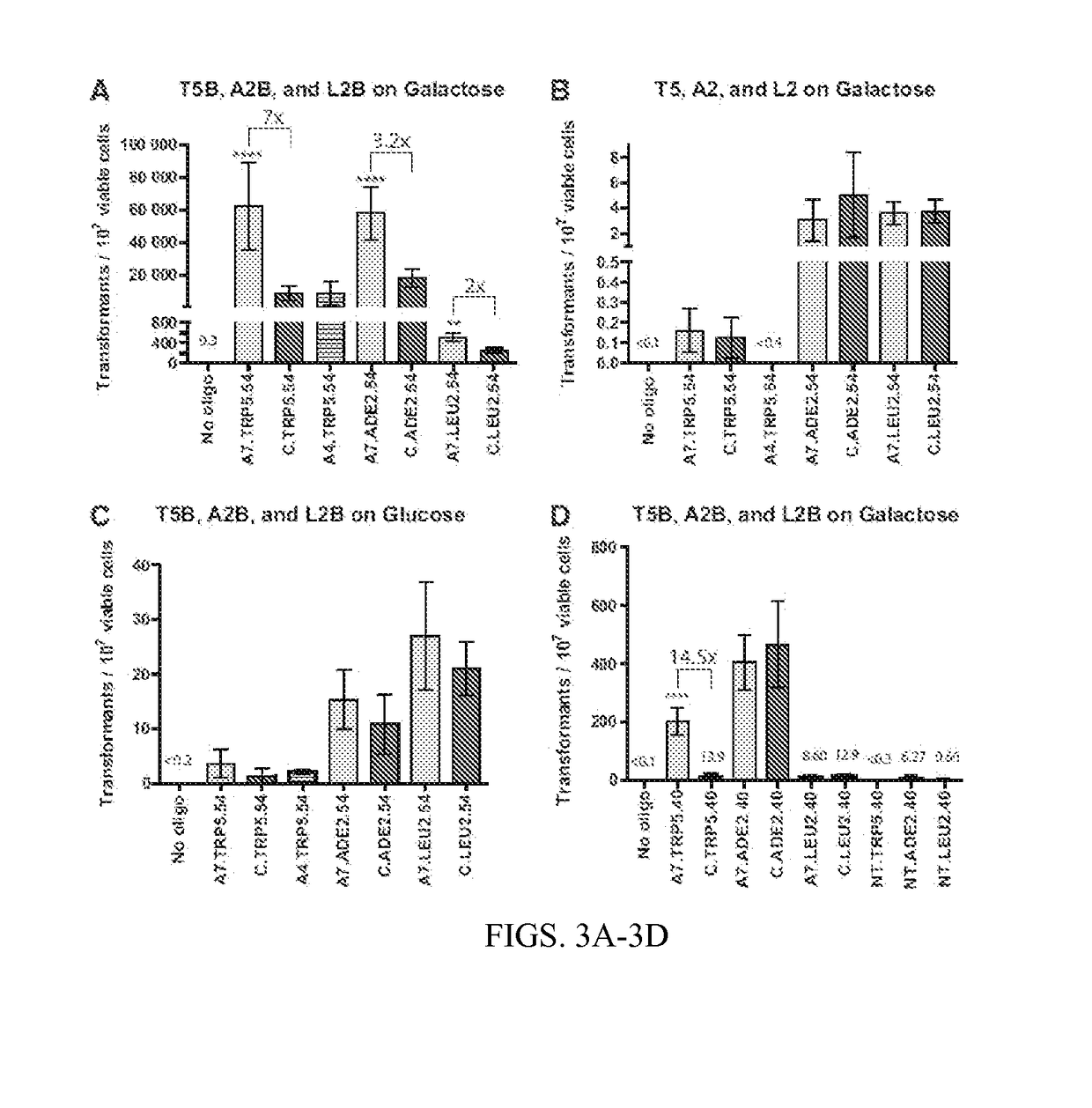
Aptamer-Guided Gene Targeting
Compositions and methods for modifying genetic material are provided. One embodiment provides aptamers capable of binding to a site-specific DNA binding moiety to facilitate the exchange of homologous genetic information between a donor molecule and the desired target locus (aptamer-guided gene targeting or AGT). One embodiment provides an oligonucleotide containing a aptamer, preferably a DNA aptamer at the 5′ end. The oligonucleotide also contains a region of homology, also referred to as donor DNA, to a desired nucleic acid, locus, or gene. The DNA binding moiety can be a nucleic acid, a protein, or a complex of proteins. In a preferred embodiment the DNA binding moiety is a homing endonuclease that cuts DNA to facilitate the modification of the DNA by the donor DNA.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Ophthalmic Device, and Method of Use Thereof, for Increasing Ocular Boundary Lubrication
ActiveUS20110142908A1Reduce lubricationPromote hyperosmolarityOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderLipid formationShear stress
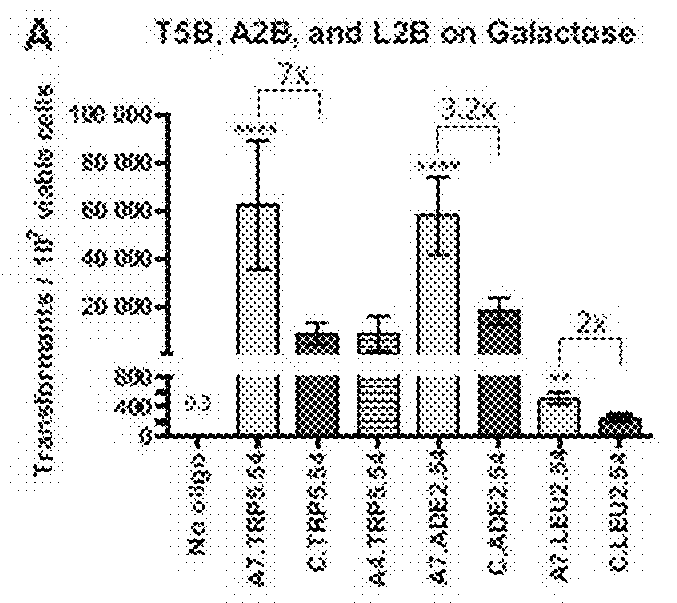
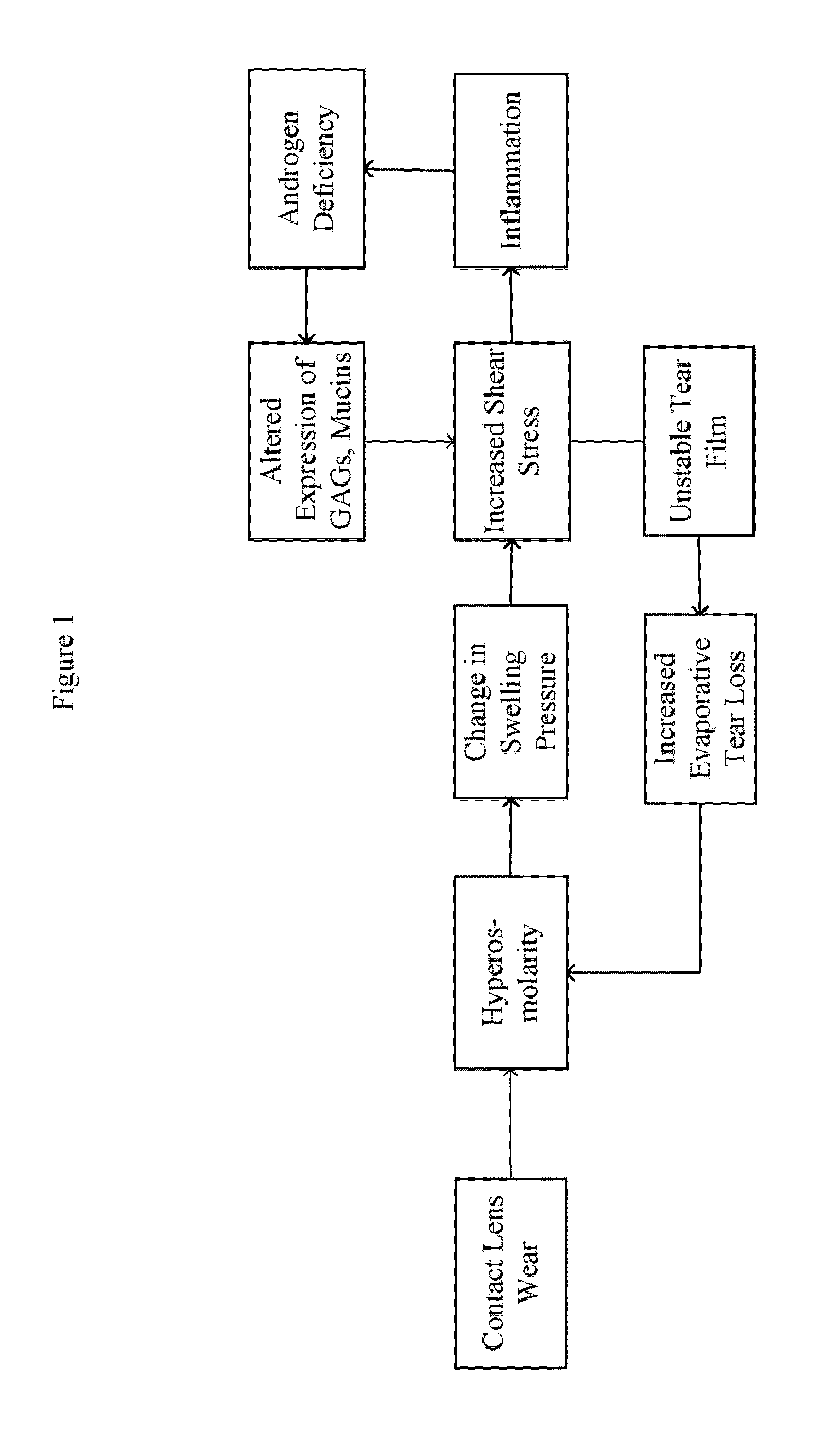
The present invention provides an ophthalmic device, and method of use thereof, for an individual wearing an ophthalmic lens to increase ocular surface boundary lubrication. The invention device comprises an ophthalmic lens and a sacrificial mechanism disposed on the ophthalmic lens, wherein the sacrificial mechanism comprises a plurality of surface bound receptors, such as PRG4, hyaluronic acid, and DNA aptamers, that reversibly bound to a lubricating composition comprising a gel forming agent, a surfactant, or a combination thereof, effectively inhibiting or preventing protein and lipid adsorption on the surface of the lens, and mitigate shear stress and reduce the friction between the lens and the ocular surface of the individual in need.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Aptamer-guided gene targeting
Compositions and methods for modifying genetic material are provided. One embodiment provides aptamers capable of binding to a site-specific DNA binding moiety to facilitate the exchange of homologous genetic information between a donor molecule and the desired target locus (aptamer-guided gene targeting or AGT). One embodiment provides an oligonucleotide containing a aptamer, preferably a DNA aptamer at the 5′ end. The oligonucleotide also contains a region of homology, also referred to as donor DNA, to a desired nucleic acid, locus, or gene. The DNA binding moiety can be a nucleic acid, a protein, or a complex of proteins. In a preferred embodiment the DNA binding moiety is a homing endonuclease that cuts DNA to facilitate the modification of the DNA by the donor DNA.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
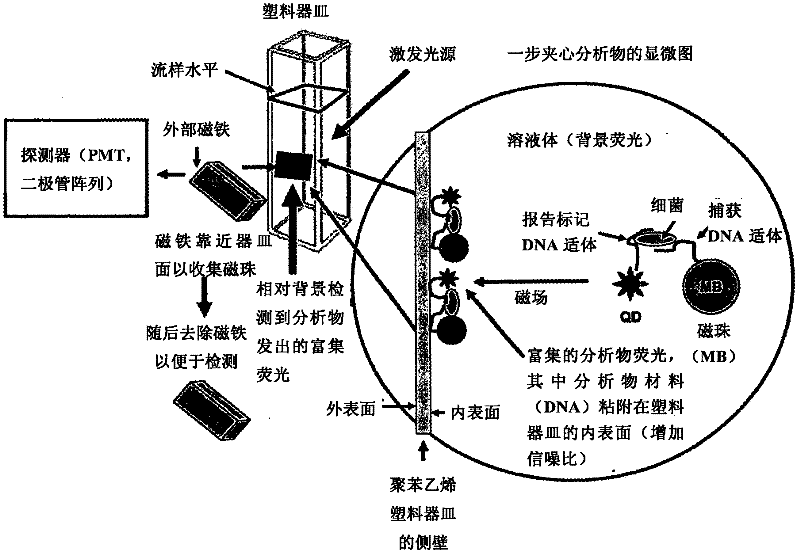
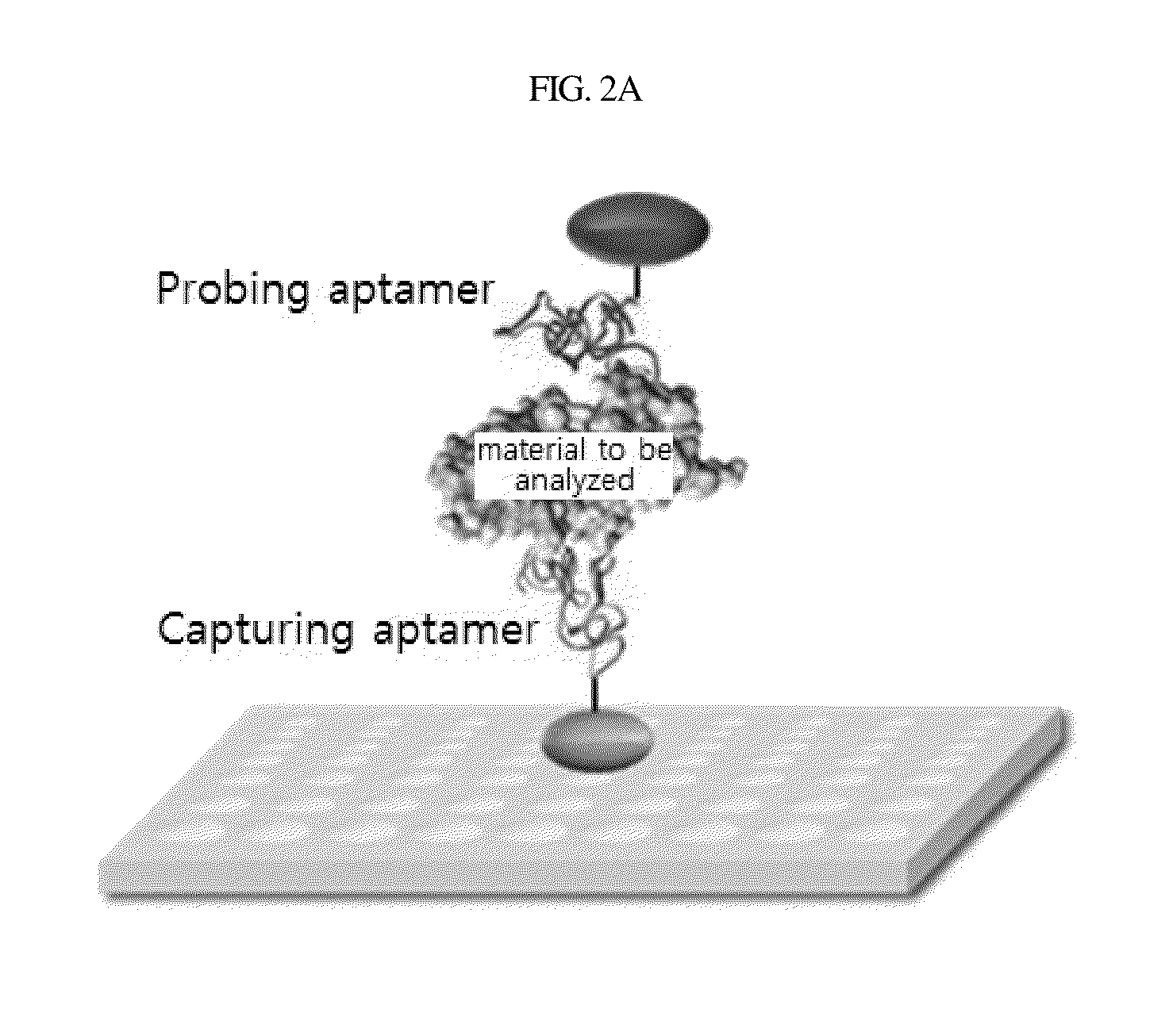
Methods of producing homogeneous plastic-adherent aptamer-magnetic bead-fluorophore and other sandwich assays
Methods are described for assembly of DNA aptamer-magnetic bead ('MB') conjugate plus aptamer-quantum dot ('QD') aptamer-fluorescent nanoparticle or other aptamer-fluorophore, aptamer-chemiluminescent reporter, aptamer-radioisotope or other aptamer-reporter conjugate sandwich assays that enable adherence to glass, polystyrene and other plastics. Adherence to glass or plastics enables detection of surface-concentrated partitioning of fluorescence versus background (bulk solution) fluorescence in one step (without a wash step) even when the external magnetic field for concentrating the assay is removed. This assay format enables rapid, one-step (homogeneous) assays for a variety of analytes without wash steps that do not sacrifice sensitivity.
Owner:OTC BIOTECH
Aptamer-guided gene targeting
Compositions and methods for modifying genetic material are provided. One embodiment provides aptamers capable of binding to a site-specific DNA binding moiety to facilitate the exchange of homologous genetic information between a donor molecule and the desired target locus (aptamer-guided gene targeting or AGT). One embodiment provides an oligonucleotide containing a aptamer, preferably a DNA aptamer at the 5′ end. The oligonucleotide also contains a region of homology, also referred to as donor DNA, to a desired nucleic acid, locus, or gene. The DNA binding moiety can be a nucleic acid, a protein, or a complex of proteins. In a preferred embodiment the DNA binding moiety is a homing endonuclease that cuts DNA to facilitate the modification of the DNA by the donor DNA.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
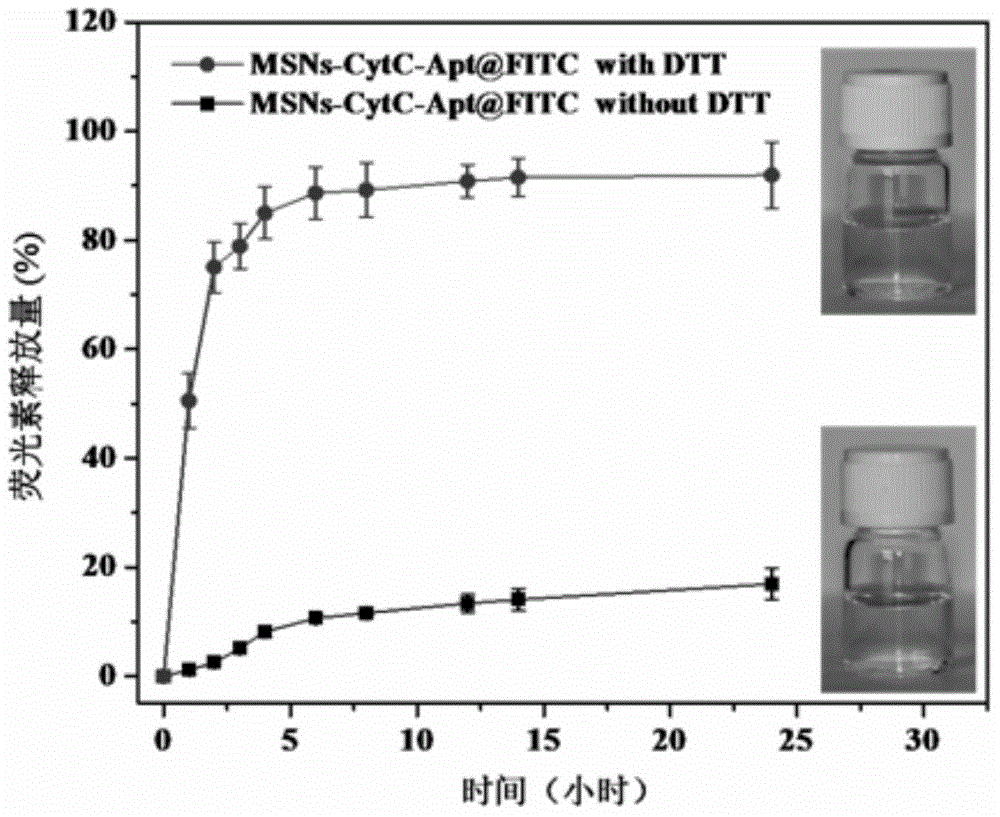
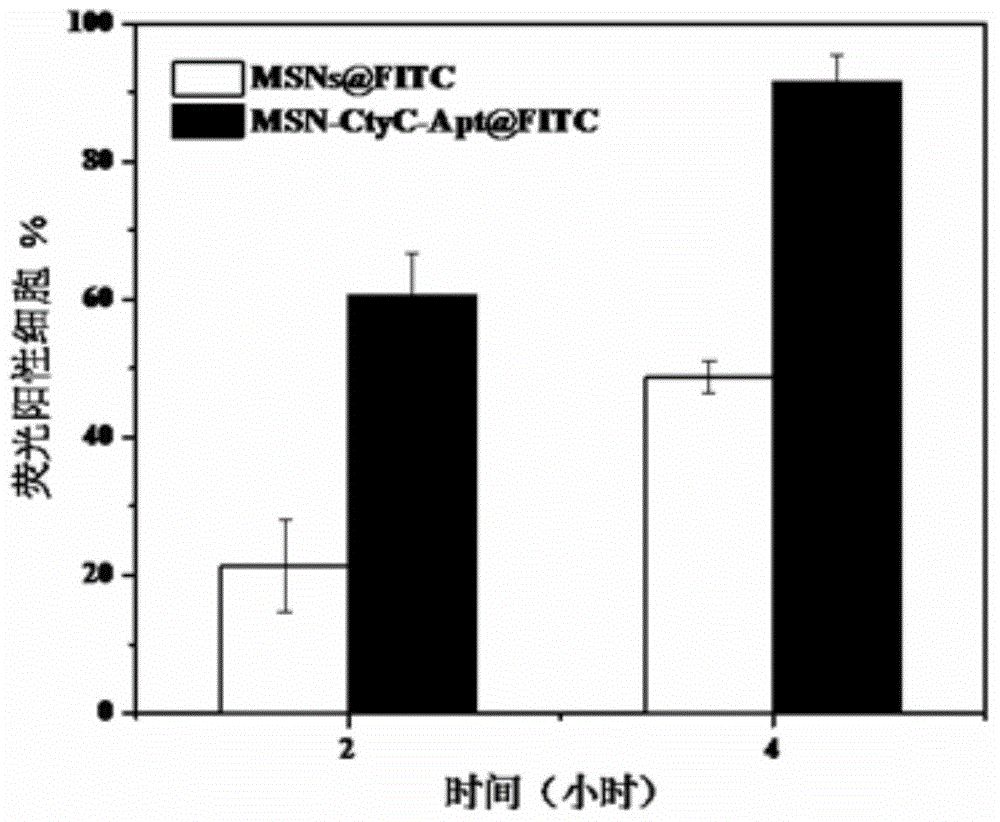
Method for preparing meso-porous silicon nano medicine carrier with cell specificity target, reduction responsiveness and triple anticancer treatment effects
InactiveCN104013965AOvercome toleranceEasy to operatePowder deliveryMacromolecular non-active ingredientsCell membraneCarrier system
The invention discloses a method for preparing a meso-porous silicon nano medicine carrier with cell specificity target, reduction responsiveness and triple anticancer treatment effects. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, synthesizing meso-porous silicon nano particles by using a gel dissolution method, subsequently, introducing a disulfide bond onto the surface of a meso-porous silicon nano reservoir by using a chemical modification method, innovatively fixing cytochrome C with an apoptosis-inducing function onto the surface of the meso-porous silicon nano reservoir, blocking meso-porous channels with medicines, finally modifying DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) aptamer single chain molecules (AS1411, with a cancer cell apoptosis-inducing function) onto the surface of a meso-porous silicon / cytochrome C nano composite system, and taking the system as specificity ligand of a receptor (nucleolin protein) which is overexpressed on the surface of liver cancer cytomembrane, thereby establishing a multifunctional composite type nano medicine carrier system for achieving triple anticancer treatment under combined action of medicines, blocking substances and target molecules inside meso-pores.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
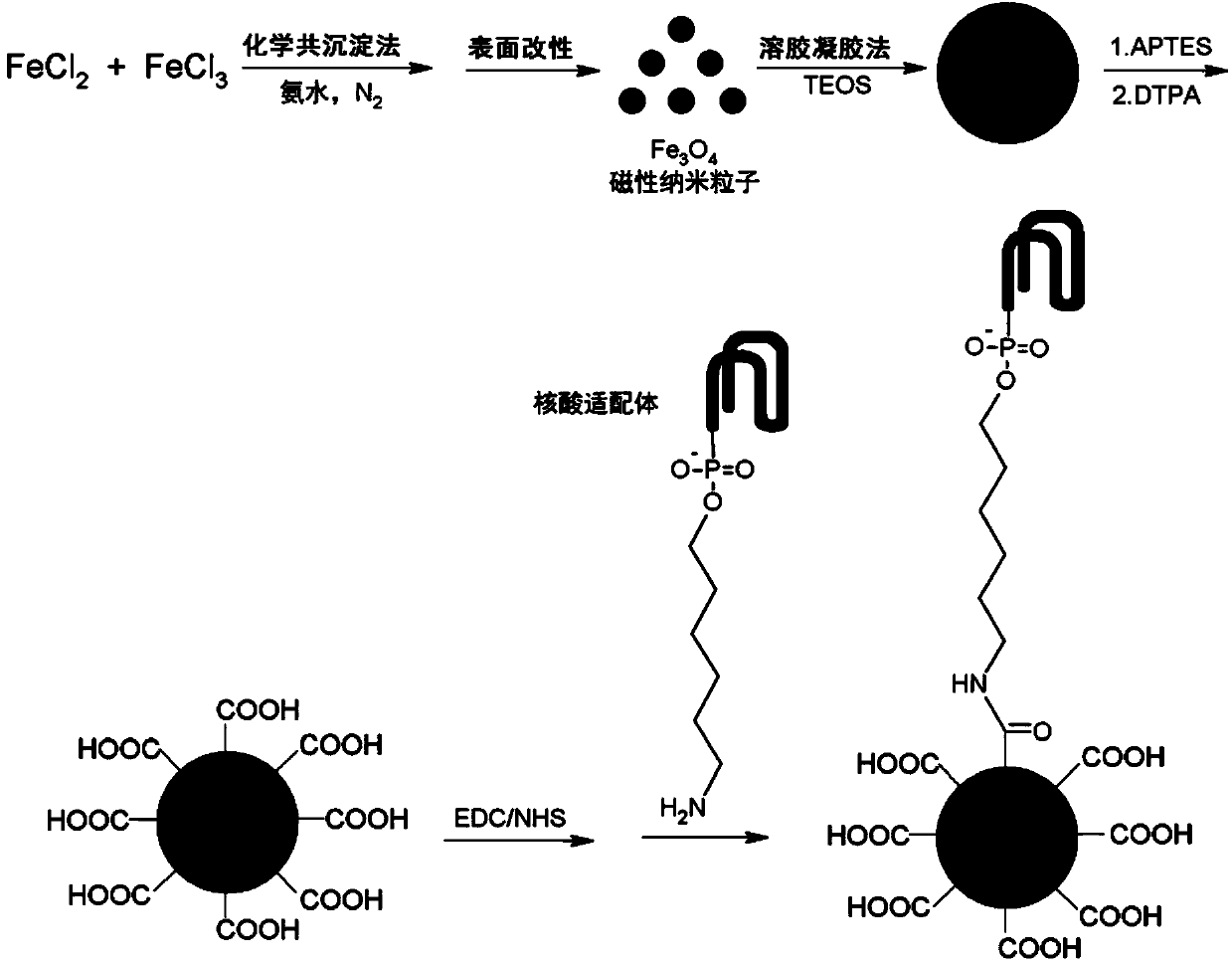
Single-stranded DNA aptamer modified SiO2/Fe3O4 magnetic microsphere preparation method
ActiveCN103990423AEasy to manufactureLarge specific surface areaOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesDNA AptamersMicrosphere
The present invention discloses a single-stranded DNA aptamer modified SiO2 / Fe3O4 magnetic microsphere preparation method, which comprises: (1) adopting a chemical co-precipitation method to obtain Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles; (2) adopting a sol-gel method to obtain SiO2 / Fe3O4 magnetic microspheres; (3) obtaining -NH2 modified SiO2 / Fe3O4 magnetic microspheres; (4) dispersing the -NH2 modified SiO2 / Fe3O4 magnetic microspheres in water to obtain -COOH modified SiO2 / Fe3O4 magnetic microspheres; and (5) dispersing the -COOH modified SiO2 / Fe3O4 magnetic microspheres in a Tris-HCl buffer solution to obtain the aptamer modified SiO2 / Fe3O4 magnetic microspheres.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
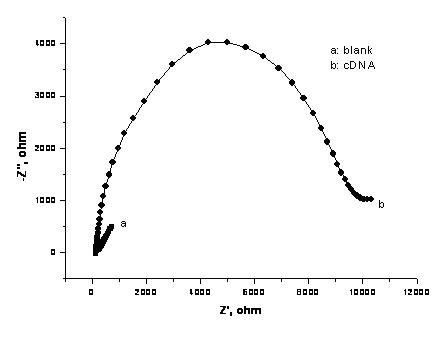
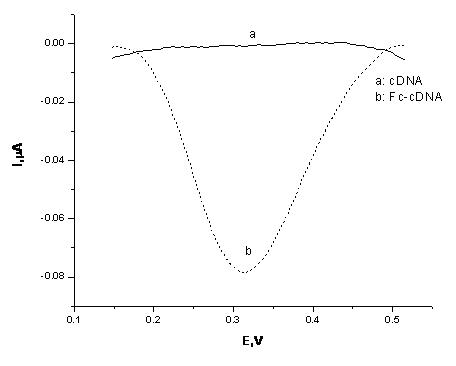
Bioelectrochemical sensor for detecting tumor markers and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102262118AMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDNA/RNA fragmentationProtein targetBioelectrochemistry
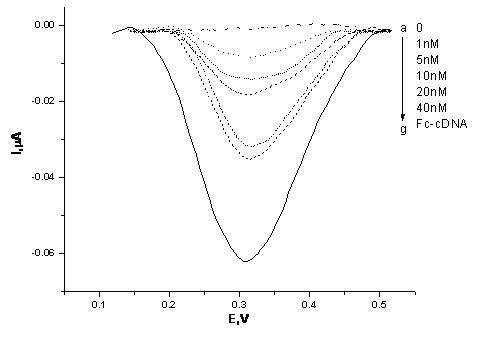
The invention relates to a bioelectrochemical sensor for detecting tumor markers and a preparation method thereof. It is a three-electrode system sensor, which is characterized in that the counter electrode in the three electrodes is a platinum electrode, the reference electrode is a saturated calomel electrode, and the working electrode is a gold electrode, and the gold electrode is decorated with two tumor markers The complementary DNA strand of the DNA aptamer, that is, the cDNA strand, is labeled with an electrochemical probe ferrocene molecule at the end of the cDNA strand. The novel bioelectrochemical sensor for detecting tumor markers of the present invention combines the characteristics of highly specific binding of DNA aptamers to target proteins and high sensitivity of electrochemical detection methods, making early diagnosis of cancer possible.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
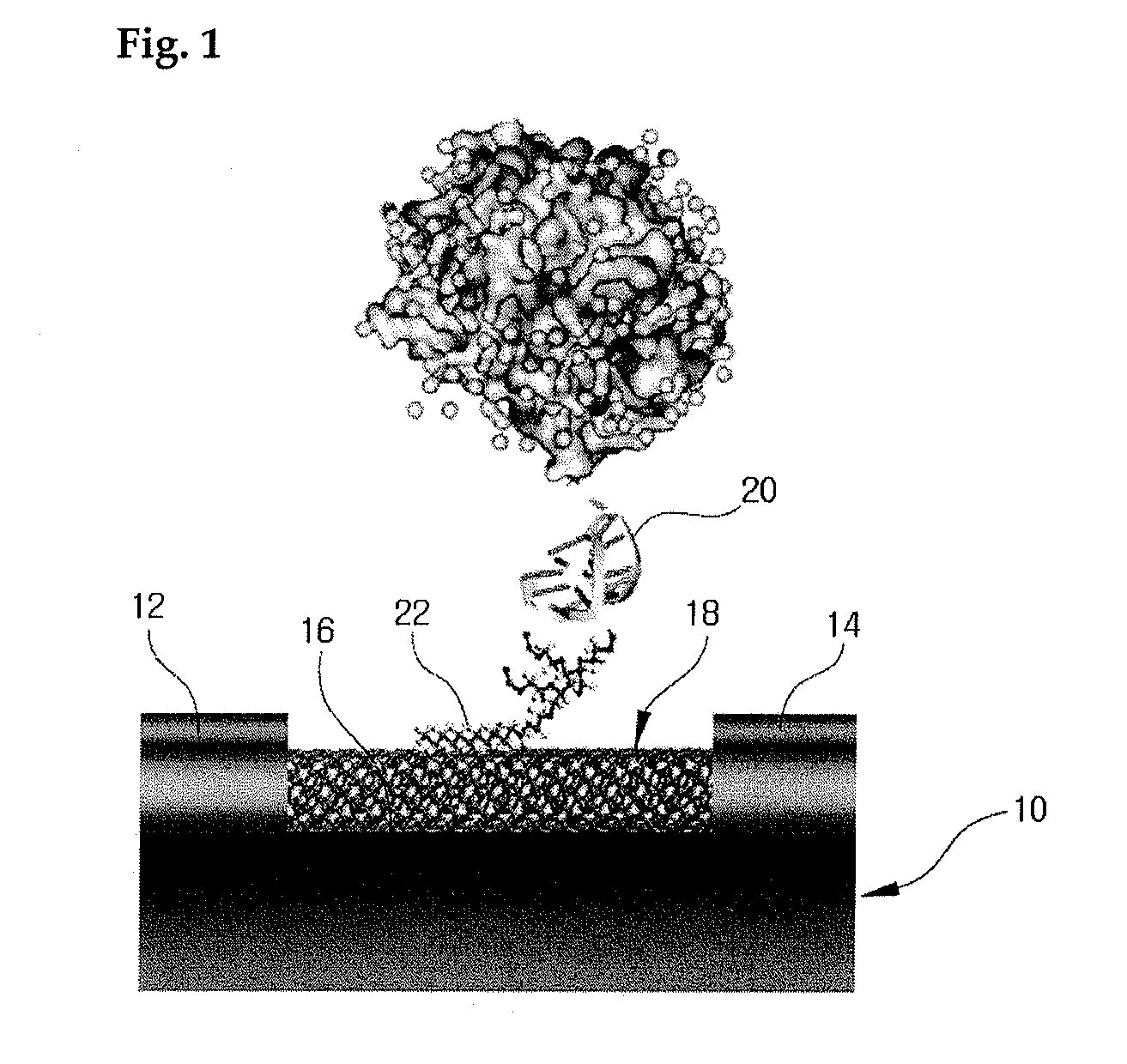
Carbon nanotube biosensors with aptamers as molecular recognition elements and method for sensing target material using the same
ActiveUS7854826B2Simple designHigh affinityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsDNA AptamersInorganic compound
The present invention relates to a carbon nanotube transistor biosensor with aptamers and a method for detecting a target material using the same, more particularly to a carbon nanotube transistor biosensor recognizing the target material, i.e., a specific molecule (such as a protein, a peptide, an amino acid, and an organic / inorganic compound) by using DNA aptamers and a method for screening a target material using the same. In the biosensor of the present invention, the aptamers binding specifically to a particular protein are adsorbed on a carbon nanotube constituting the channel domain of carbon nanotube transistor to easily detect / identify a particular protein via the electric conductivity of carbon nanotube that varies if the particular protein is exposed to corresponding aptamers.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF CHEM TECH
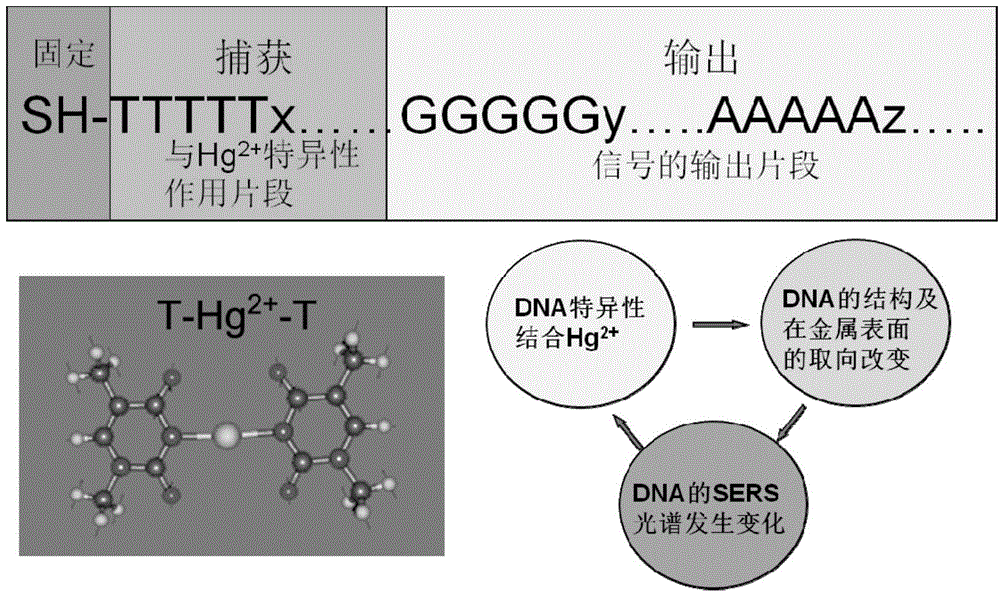
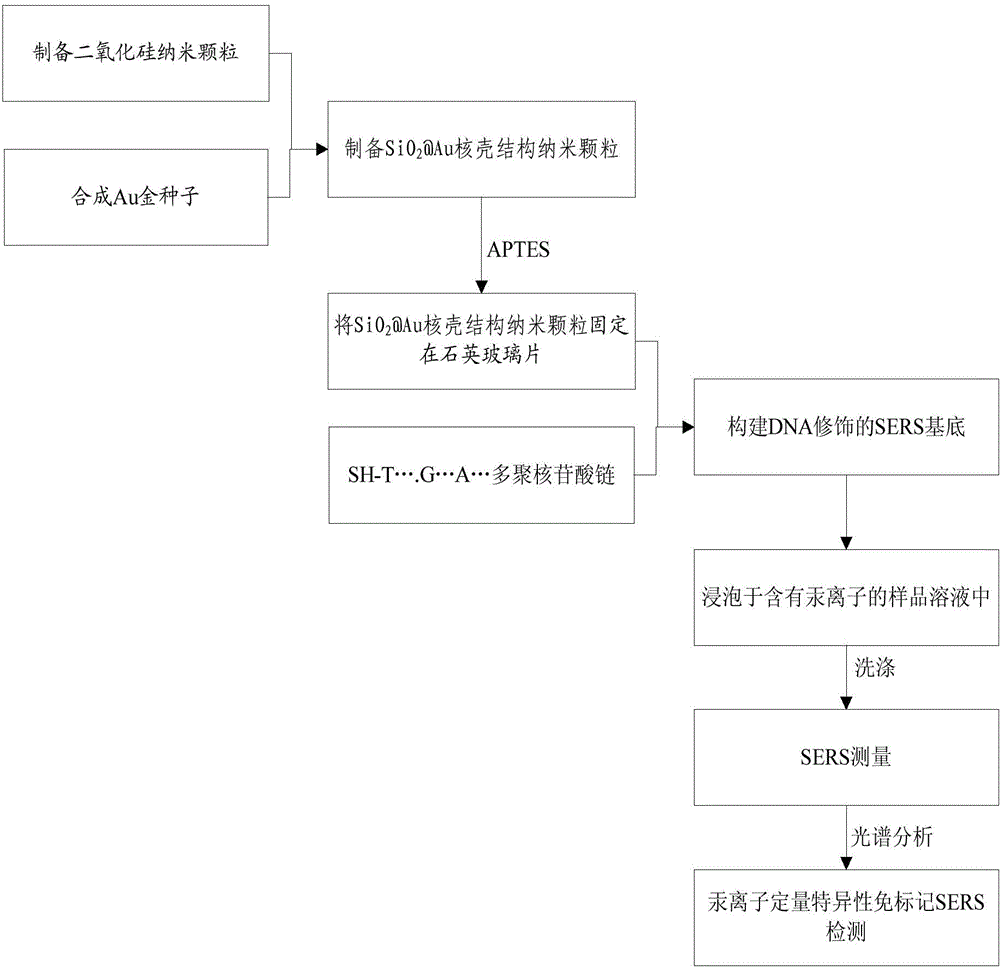
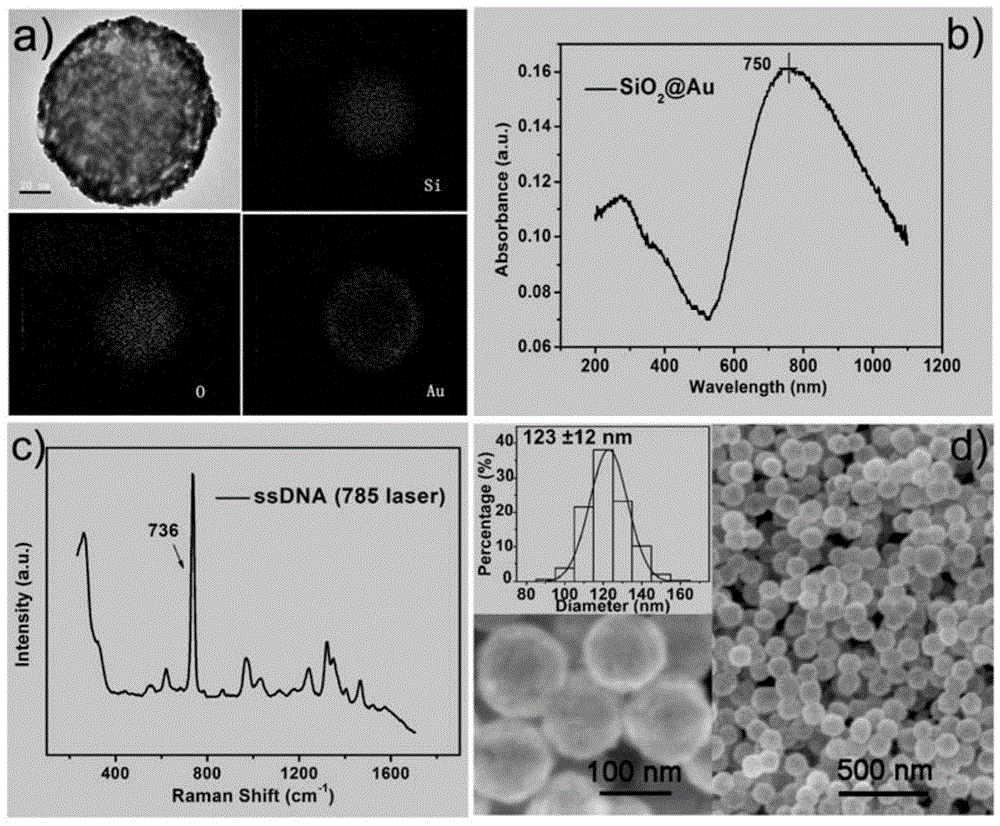
Method for detecting low-concentration mercury ions based on DNA modified SERS substrate
ActiveCN104458704AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityPreparing sample for investigationRaman scatteringDNA AptamersSilicon dioxide
The invention discloses a method for detecting low-concentration mercury ions based on a DNA modified SERS substrate. The method comprises the following steps: preparing uniform gold-covered silicon dioxide nano particles by a fractional step method and fixing nano particles with a core-shell structure on a quartz glass sheet by a coupling agent to construct an SERS substrate; modifying single-chain DNA molecules on the surfaces of gold shell layers of the gold-covered silicon dioxide nano particles through sulfydryls; immersing the prepared DNA aptamer modified SERS substrate into a solution containing the mercury ions; washing with de-ionized water; by taking an SERS signal specific value of a G basic group and an A basic group as spectrum standard measurement of DNA at a metal surface state, realizing quantitative and specific detection on the mercury ions by analyzing a characteristic Raman peak and the change of the specific value. Compared with the prior art, the method has the following advantages that the sensitivity of the method is high, the detection lower limit is about 50nM, the measurement operation is simple, the cost is low, and the real-time and rapid measurement can be realized.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
DNA aptamer specifically recognizing streptomycin and application of DNA aptamer
ActiveCN102703453AHigh affinityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationDNA AptamersMagnetic Bead Technology
The invention discloses a single-chain DNA aptamer specifically recognizing streptomycin and application of the DNA aptamer, belonging to the field of biochemistry and molecular biology, analytical chemistry and combinatorial chemistry. The invention provides a method for preferably selecting the streptomycin aptamer by using an improved magnetic bead SELEX technology and four single-chain DNA aptamers with high appetency with the streptomycin and sequences of A1, A3, A6 and A12, and provides a high-specificity detection recognition element with the advantages of better stability, high sensitivity, low cost, and easy preparation, modification and mark for the detection of residue of the streptomycin, especially streptomycin in foods.
Owner:苏州医疗器械产业发展集团有限公司
DNA aptamer modified bioelectrochemical sensor and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a novel DNA aptamer modified bioelectrochemical sensor and a preparation method thereof. The novel bioelectrochemical sensor is of a three-electrode system. The invention is characterized in that in the three electrodes, the counter electrode is a platinum electrode, the reference electrode is a saturated calomel electrode, and the working electrode is a gold electrode; and a DNA aptamer chain is modified on the gold electrode. The novel DNA aptamer modified bioelectrochemical sensor combines the characteristics of the high specificity of the DNA aptamer and the high sensitivity of an electrochemical detection method and ensures that the early diagnosis of cancer cells becomes possible.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
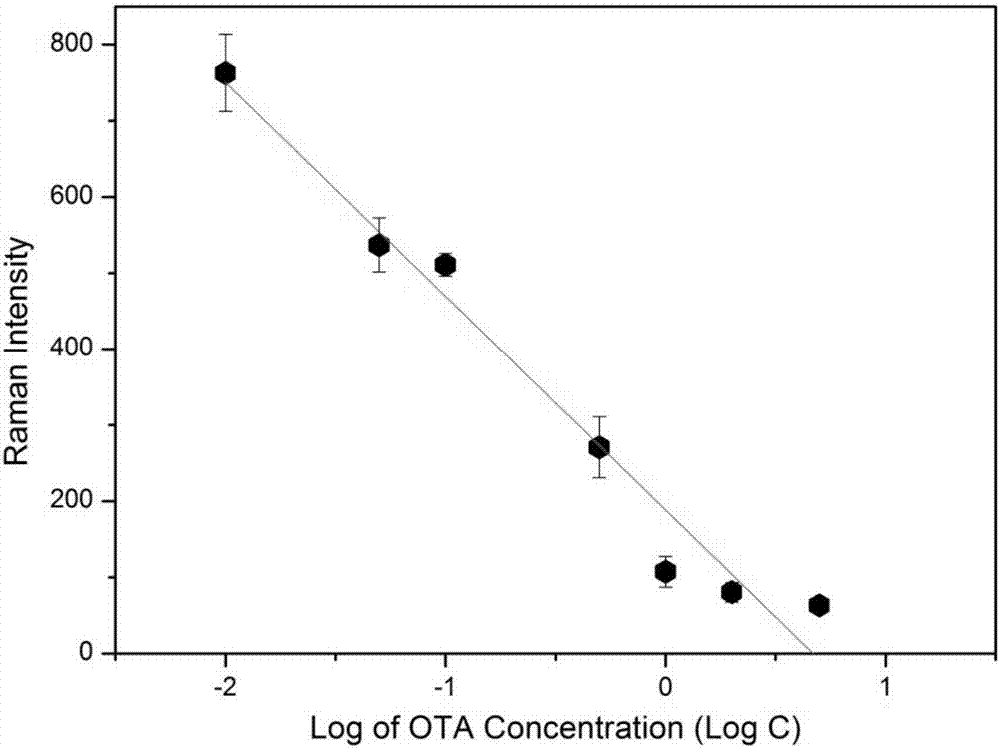
Construction method and application of SERS aptasensor based on nano-assembly structure
The invention discloses a construction method and application of SERS aptasensor based on nano-assembly structure. The method comprises the following steps: respectively modifying surfaces of gold nano-rod and gold nano-particle with two kinds of DNA complementary with an ochratoxin A aptamer segment part to form two nano-probes; then assembling an assembly nano-structure under complementary pairing connection of the two nano-probes and the DNA aptamer, and labeling a Raman beacon molecule on the assembly nano-structure; and adding a solution of a substance for detecting, and detecting the concentration of the assembly nano-structure by utilizing the fact that the SERS signal intensity of the assembly nano-structure is influenced by the substance for detecting. By adopting the method, reaction in a liquid environment is uniform, the detection has high sensitivity and high specificity, only one-step reaction is required, and the operation is simple.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Carbon nanotube biosensors with aptamers as molecular recognition elements and method for sensing target material using the same
ActiveUS20080094078A1Easily detect/identifyHigh selectivityImmobilised enzymesMaterial nanotechnologyDNA AptamersCarbon nanotube
The present invention relates to a carbon nanotube transistor biosensor with aptamers and a method for detecting a target material using the same, more particularly to a carbon nanotube transistor biosensor recognizing the target material, i.e., a specific molecule (such as a protein, a peptide, an amino acid, and an organic / inorganic compound) by using DNA aptamers and a method for screening a target material using the same. In the biosensor of the present invention, the aptamers binding specifically to a particular protein are adsorbed on a carbon nanotube constituting the channel domain of carbon nanotube transistor to easily detect / identify a particular protein via the electric conductivity of carbon nanotube that varies if the particular protein is exposed to corresponding aptamers.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF CHEM TECH
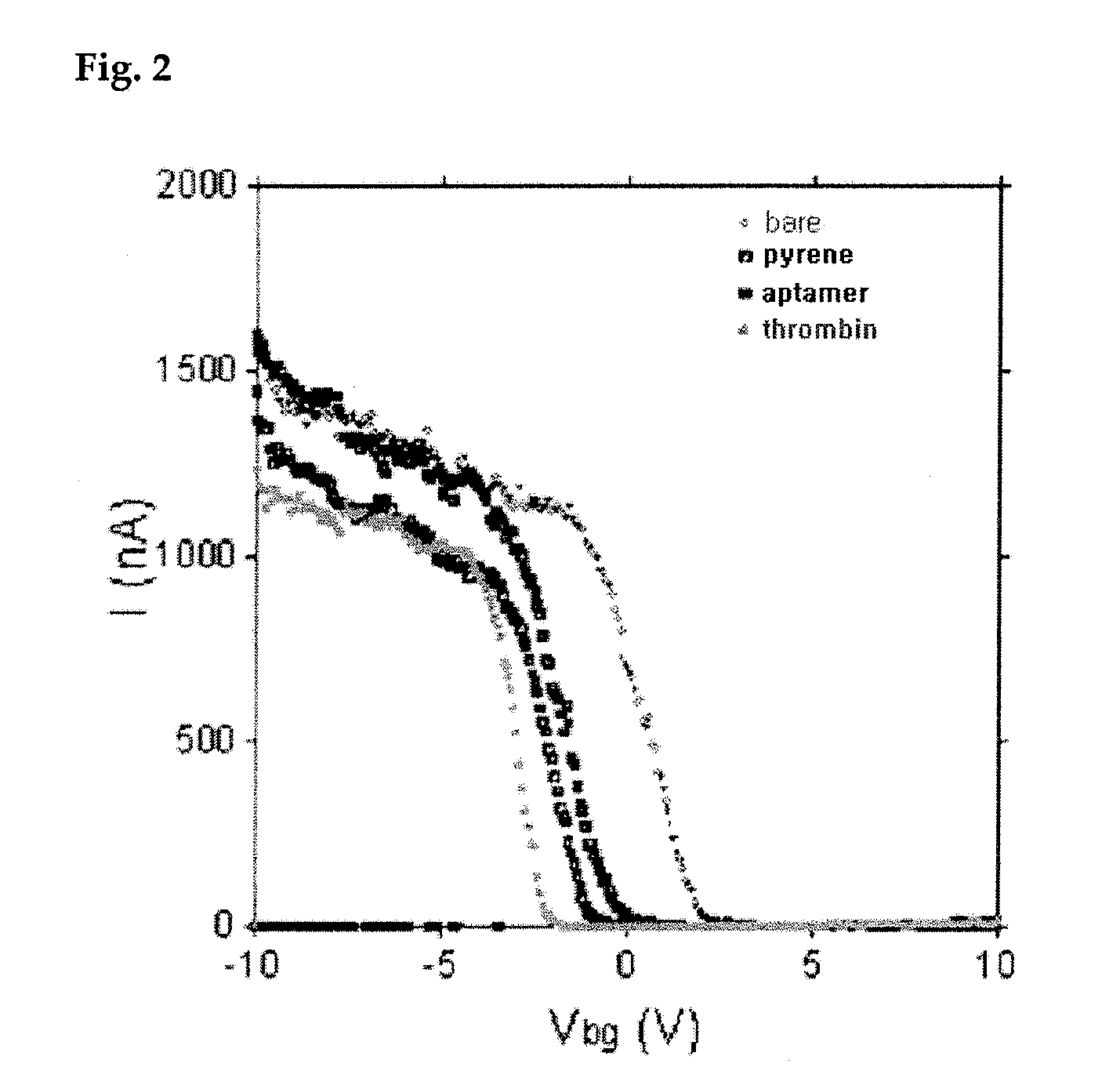
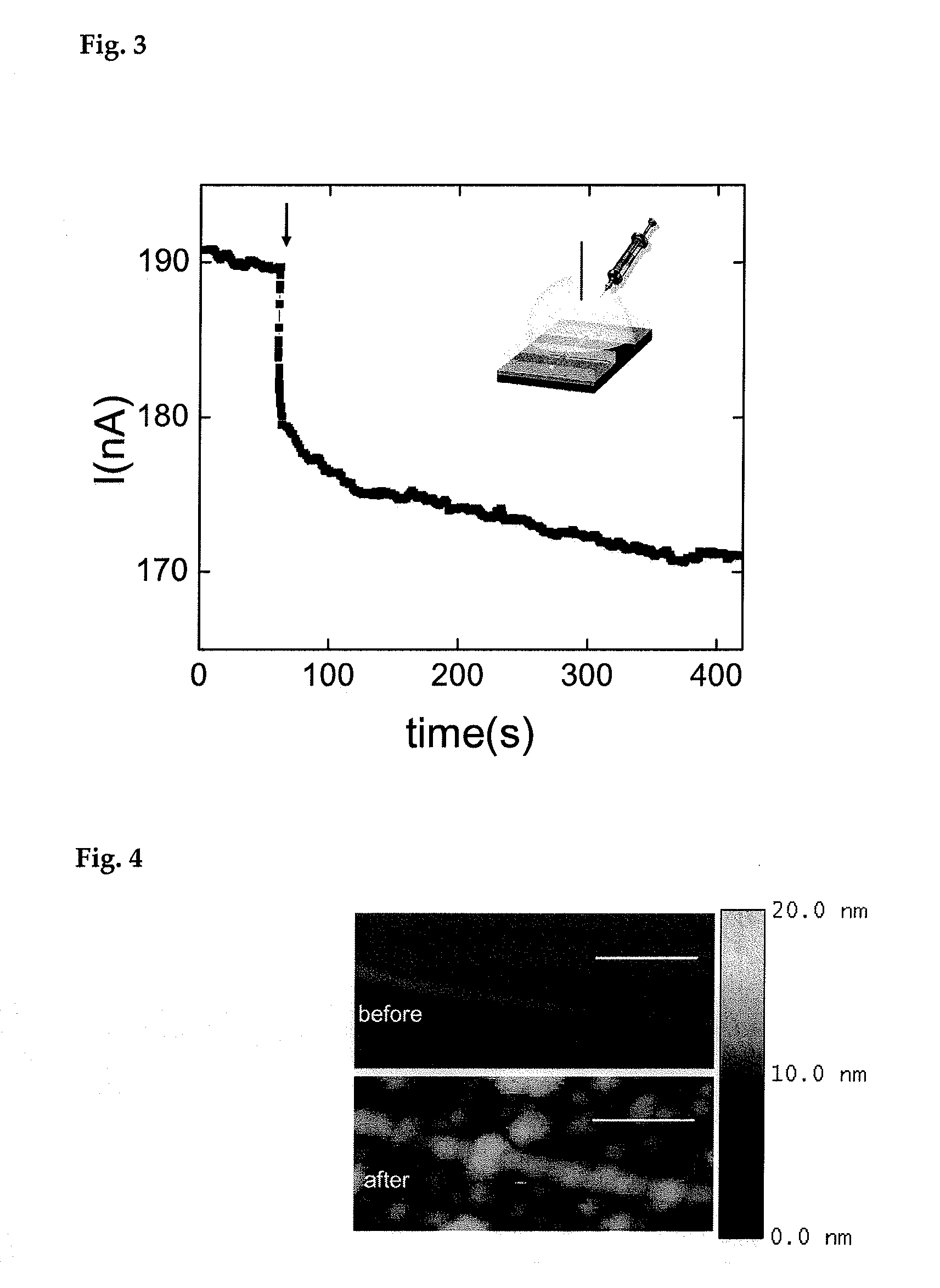
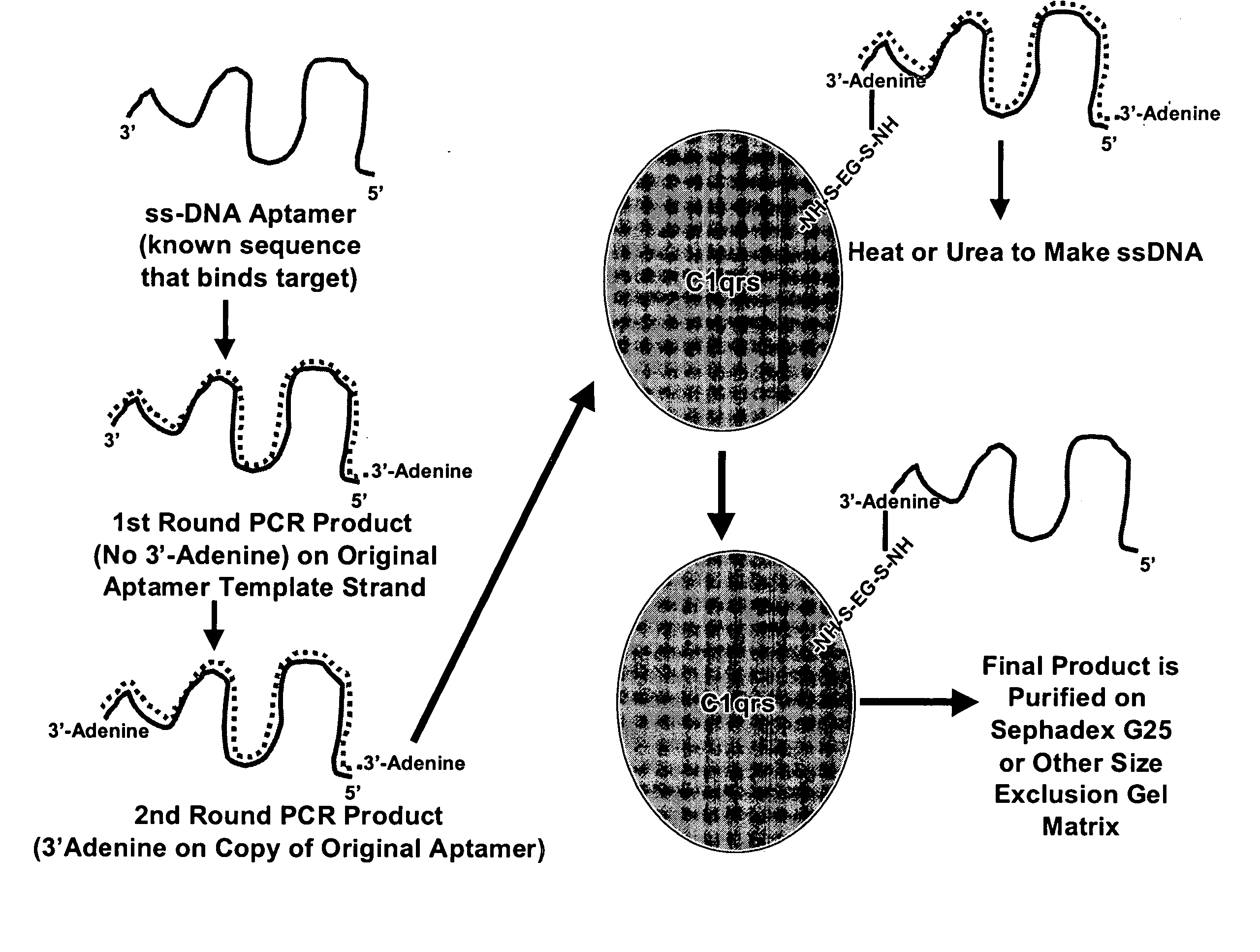
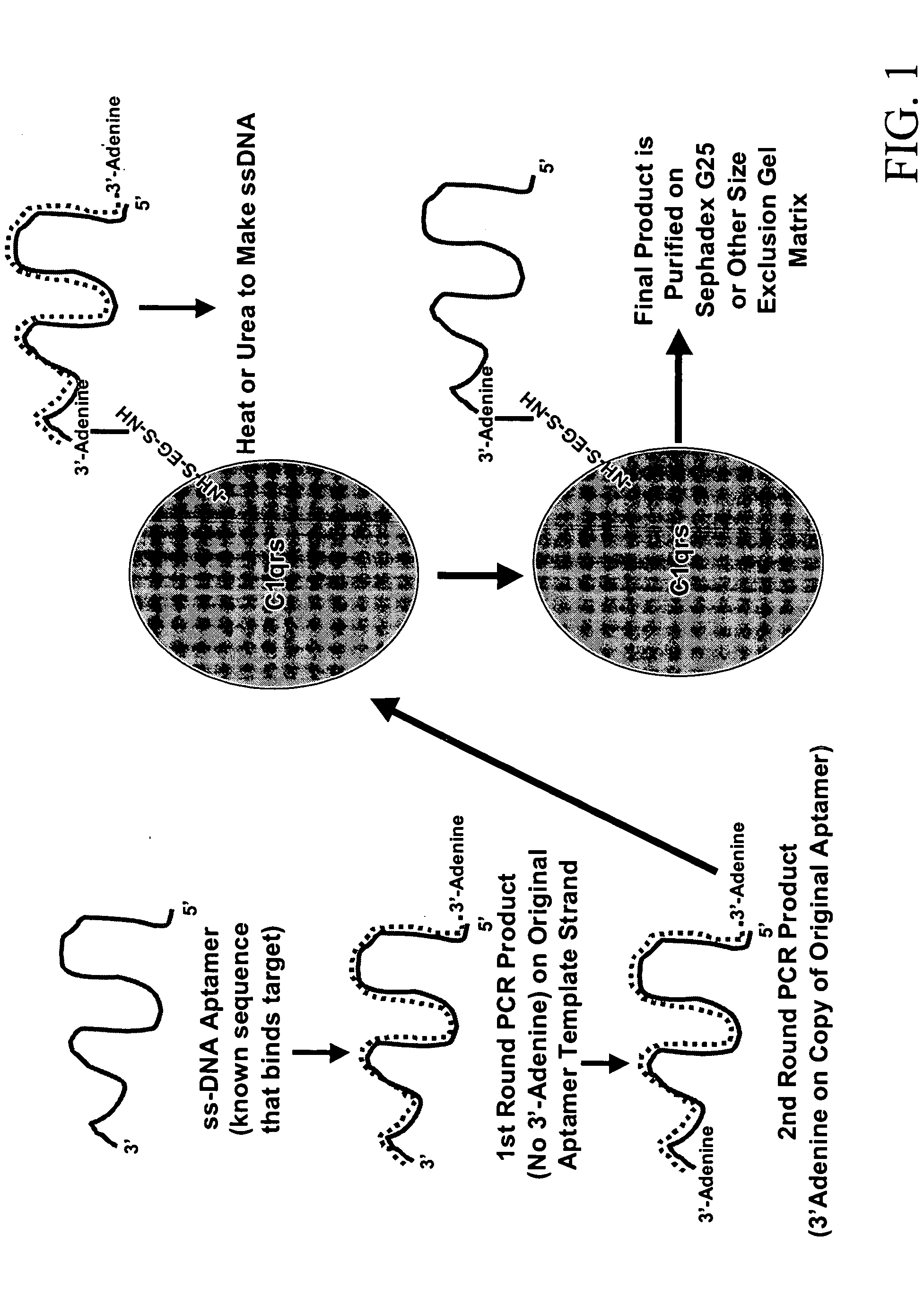
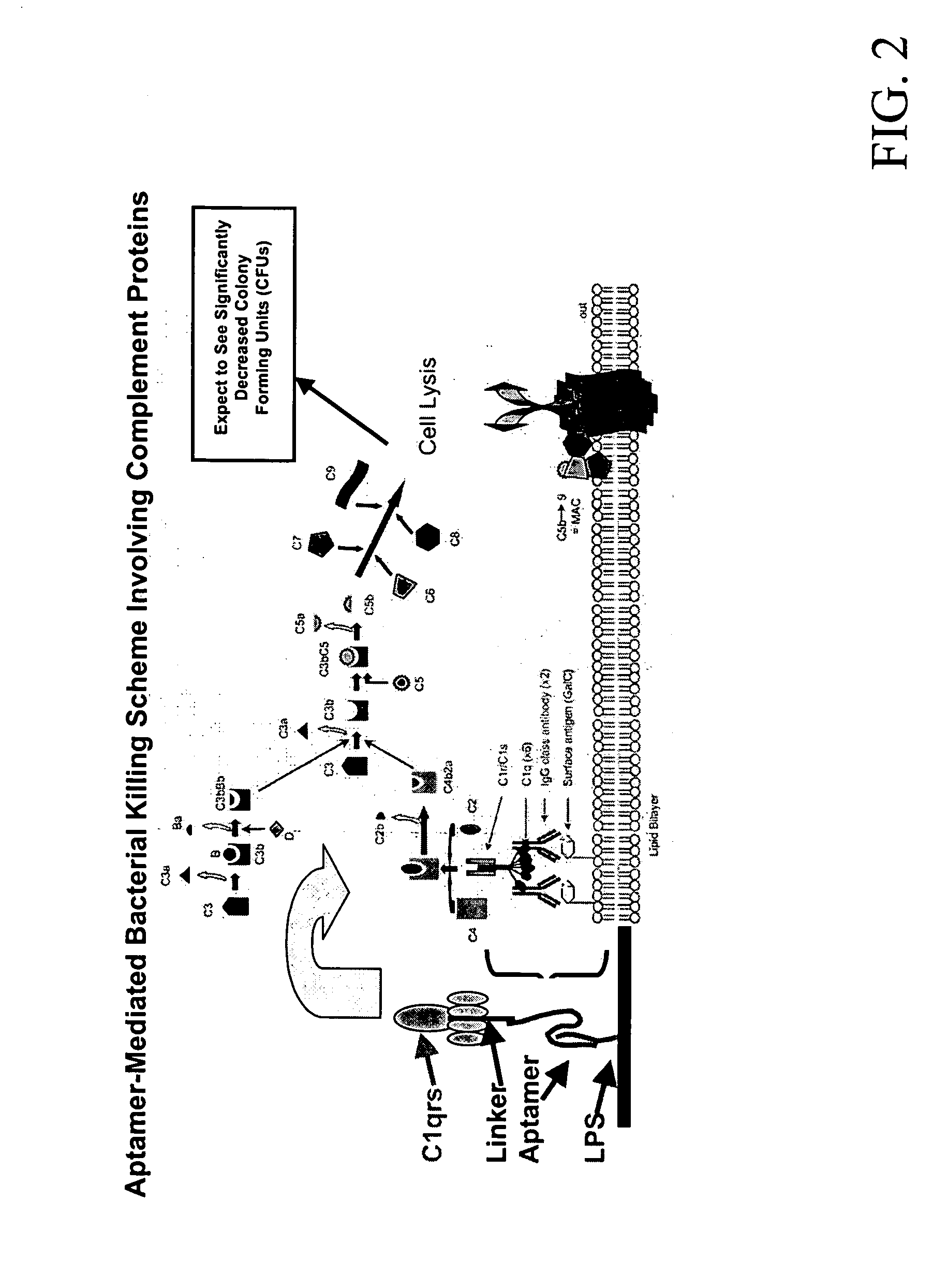
Therapeutic nucleic acid-3' -conjugates
InactiveUS20050191680A1Efficient killingPrevent breakdownMaterial nanotechnologyActivity regulationHalf-lifeWhite blood cell
Methods are described for improvement of the serum half life of therapeutic nucleic acids by 3′ conjugation to useful target proteins, or other large molecules with useful function. In one embodiment, a 3′ A, C or G overhang is added to ds-DNA and the primary amines conjugated using biocompatible bifunctional linkers to proteins. The resulting nucleic acid-3′-conjugates are serum nuclease-resistant and retained in vivo for long periods without rapid kidney clearance. Further, the choice of conjugate imparts additional functionality to the nucleic acid-3-conjugate. For example, if the protein in the DNA-protein conjugate is the first component of the complement cascade (Clq or Clqrs) and the DNA aptamer has been developed against surface components of a target cell, it can be used to treat bacterial or parasitic infections and cancers. If the protein is serum albumin or another common (nonimmunogenic) blood protein and the aptamer is directed against a toxin or venom, the aptamer-protein conjugate can be used as an antidote that binds and neutralizes the toxin or venom. Similar DNA (aptamer)-nanotube, -enzyme, and -toxin conjugates could also be used to target and selectively kill bacteria, parasites, and cancer cells in vivo. If the protein is an Fc antibody fragment or C3b protein from the complement system and the aptamer is developed against a bacterial cell capsular material, other cell surface component or viral cell surface component, then the aptamer-3′-protein conjugate can aid in opsonization of the target cells or viruses by phagocytic leukocytes.
Owner:OTC BIOTECH
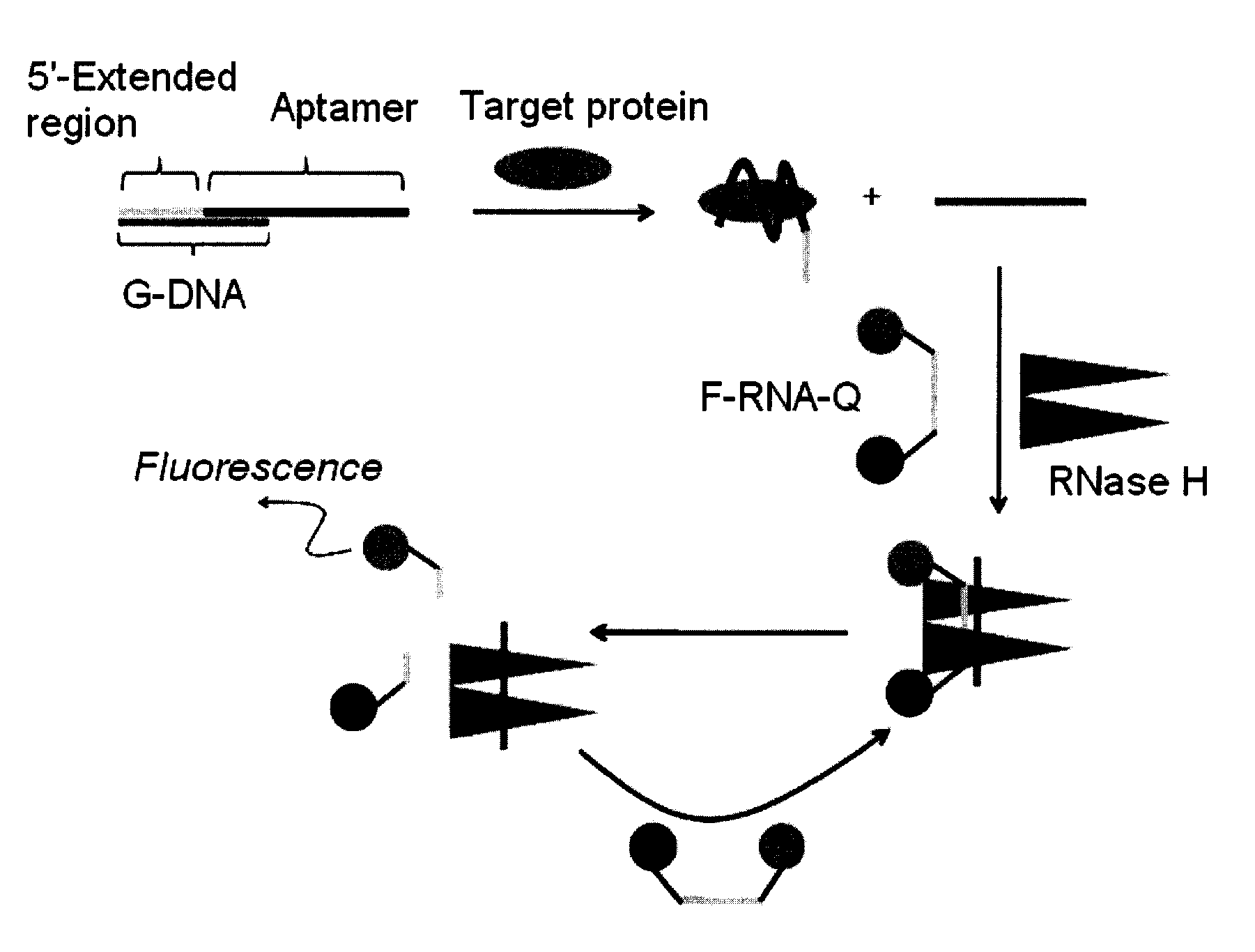
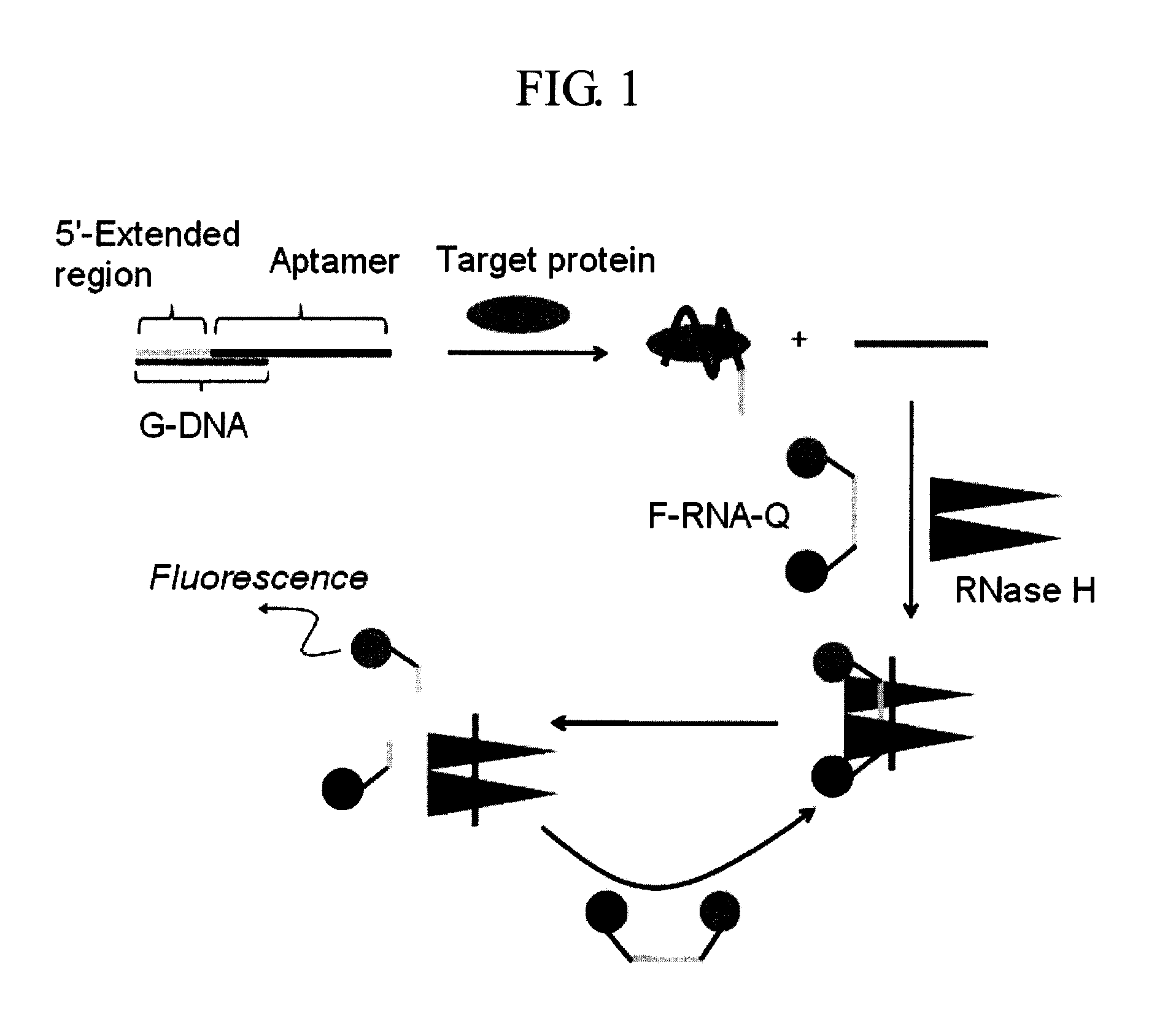
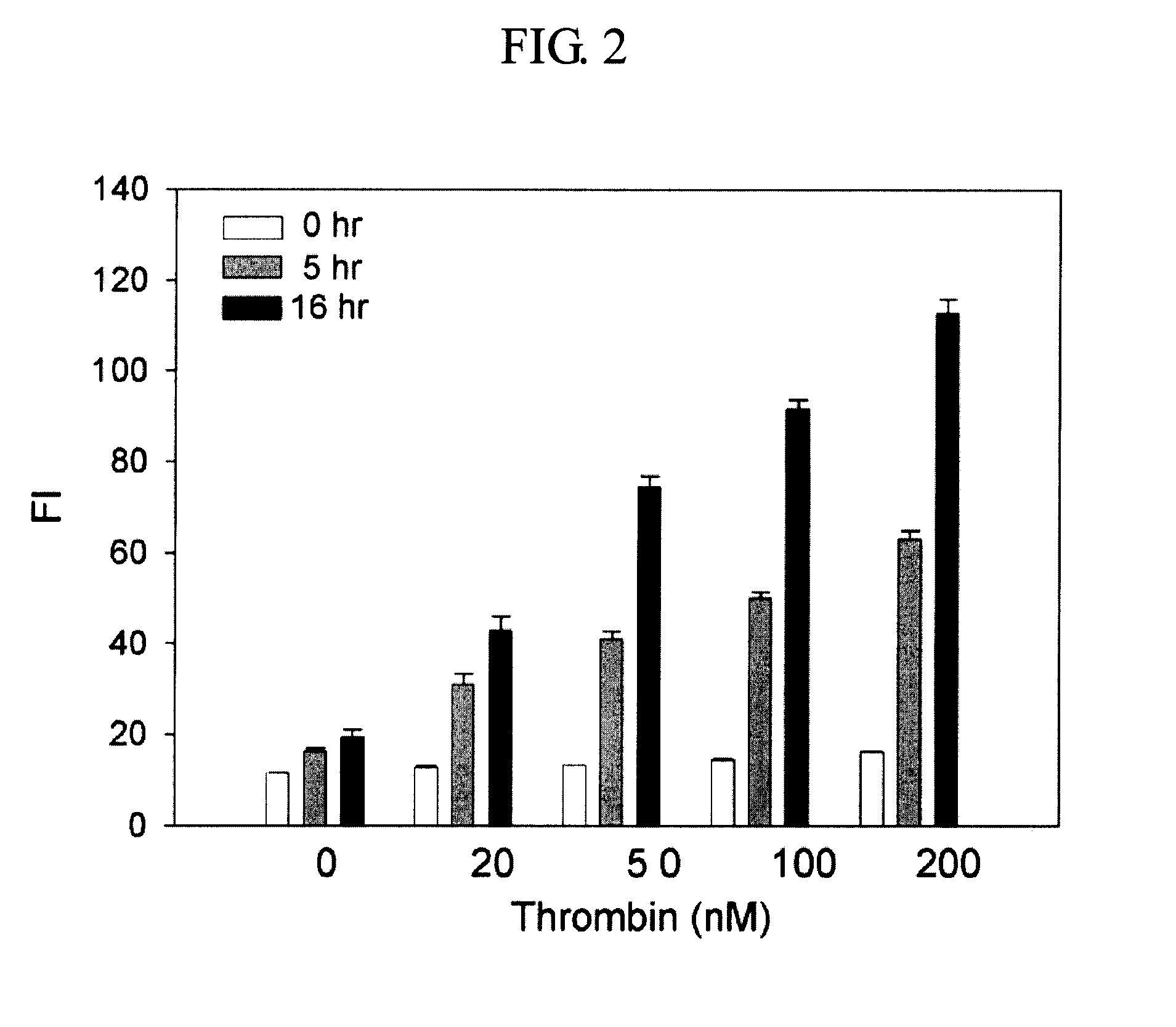
Method and kit for detecting a target protein using a DNA aptamer
A method and a kit for detecting a target protein in a sample with a signal amplification strategy are provided. The signal amplification strategy is established for the aptamer-based molecular recognition of a target protein with concomitant release of single-stranded DNA (G-DNA), which binds complementarily to a single-stranded RNA comprising a fluorophore and a quencher (“F-RNA-Q”). The fluorescence-quenched RNA is then degraded by RNase H to result in a fluorescence signal, and the undamaged G-DNA is recycled to yield fluorescence amplification.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
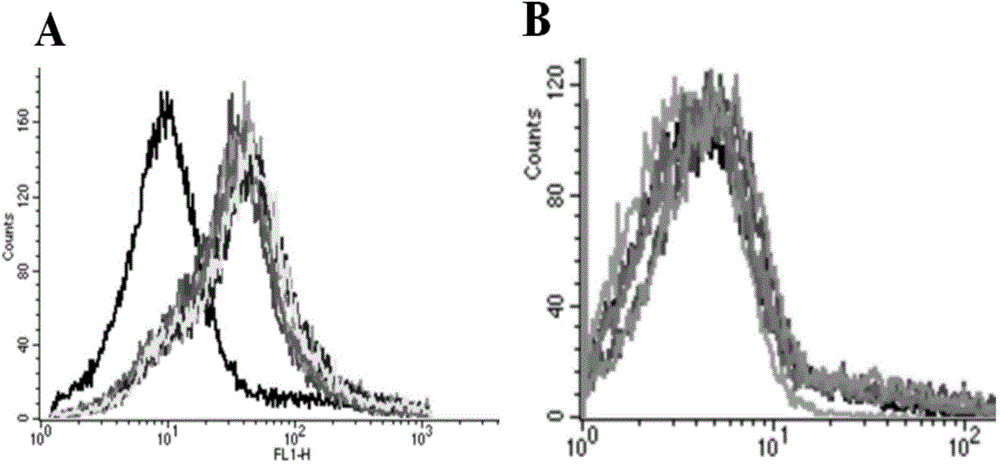
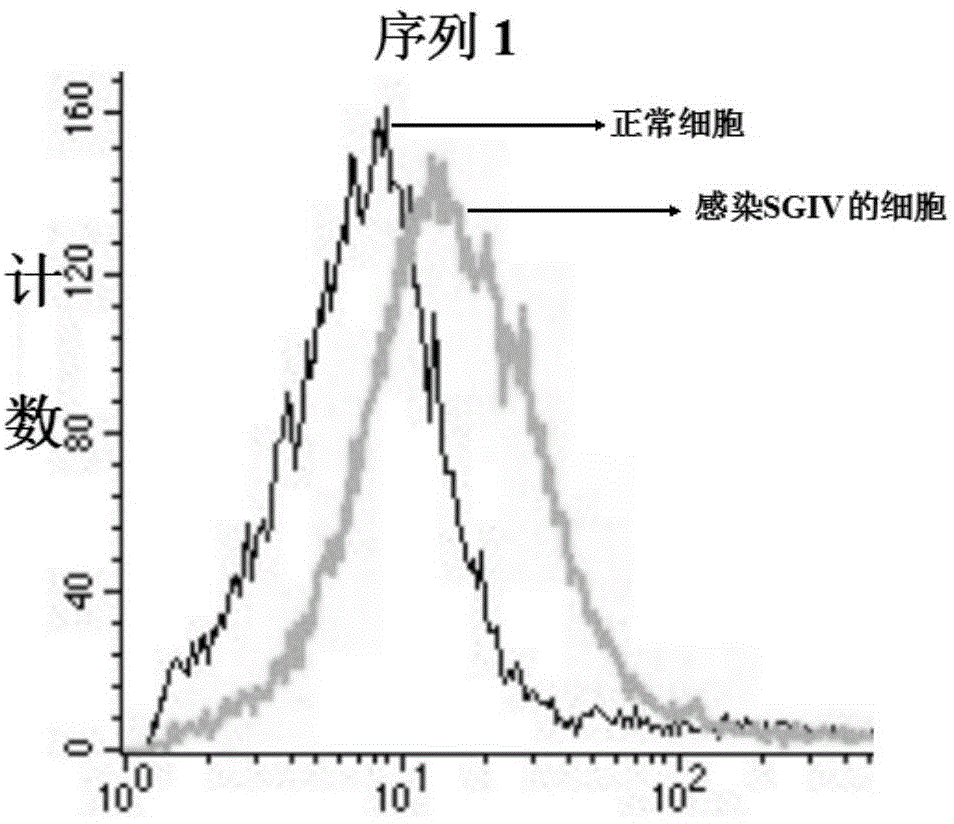
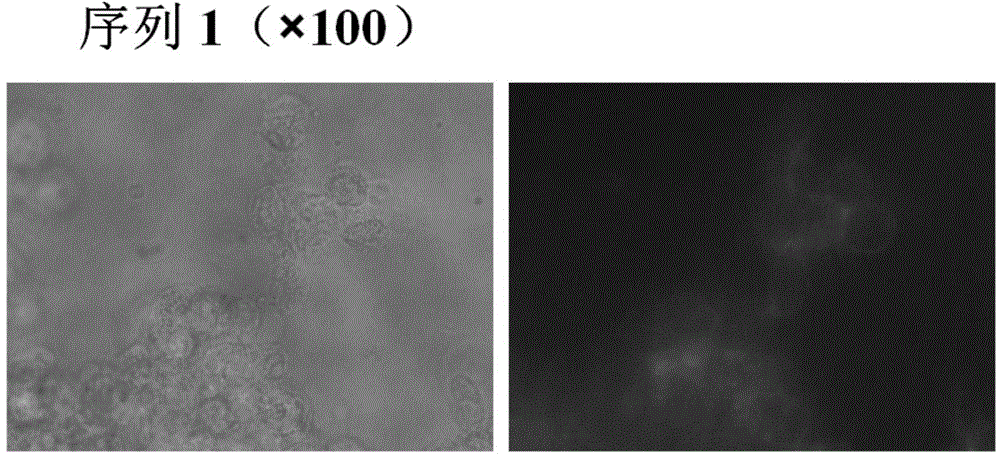
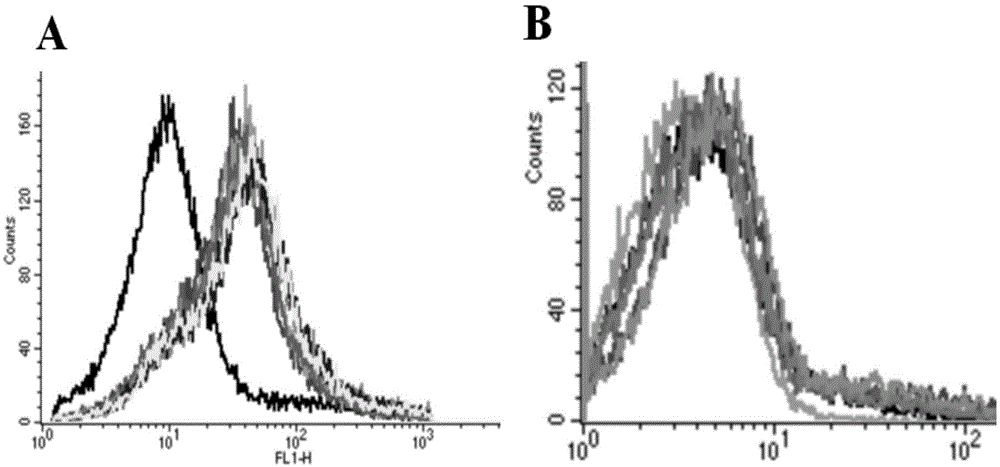
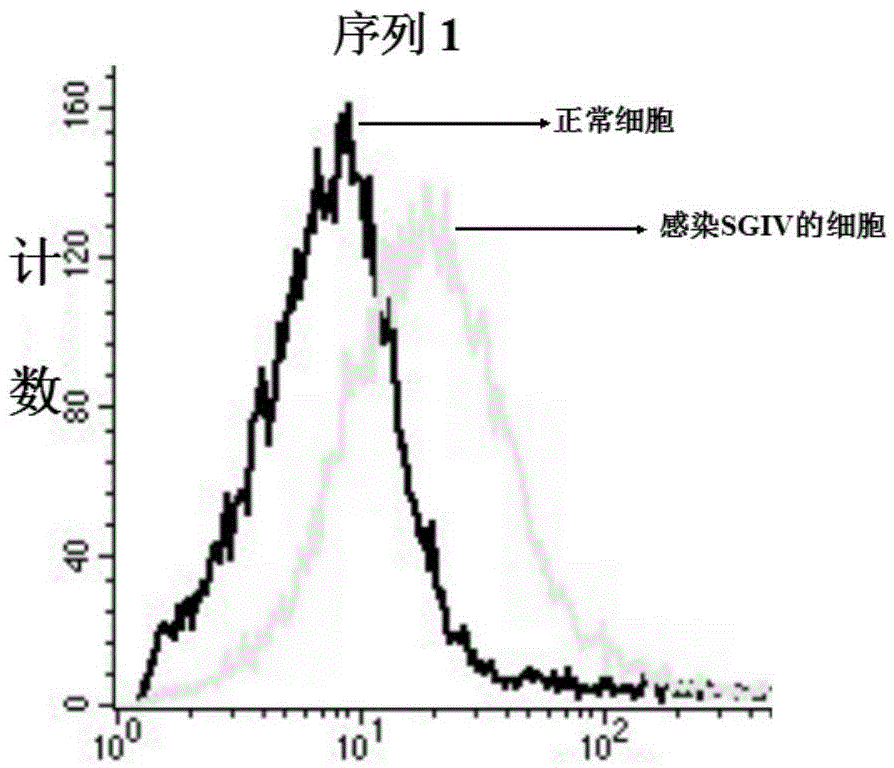
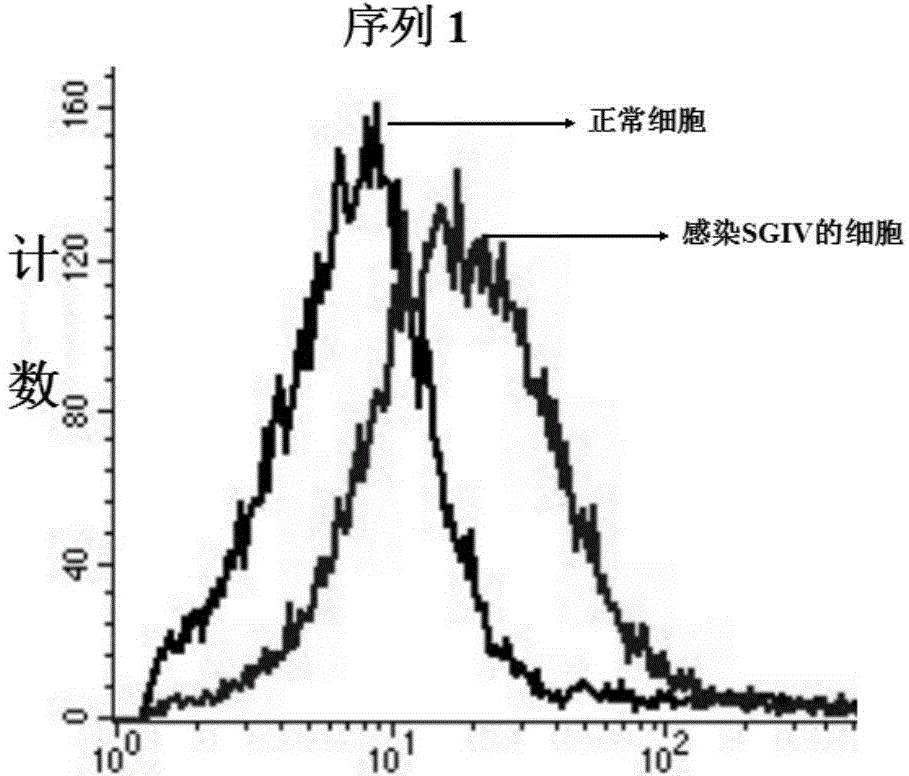
DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) aptamer for detecting grouper iridovirus infection, as well as screening method and application of DNA aptamer
ActiveCN104789696AHigh affinityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysis3-deoxyriboseDNA Aptamers
The invention discloses a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) aptamer for detecting grouper iridovirus infection, as well as a screening method and an application of the DNA aptamer. Two inverse screening steps are introduced in each screening process; first, a single-stranded DNA library of the former screening process is bound with normal cells to remove nonspecific ssDNA (single-stranded DNA) bound with the normal cells of a grouper; then, supernatant is bound with grouper iridovirus infected cells for screening; and ssDNA separated from the grouper iridovirus infected cells is bound with the normal cells for separation to obtain the supernatant. A PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification library prepares the single-stranded DNA library. The above screening flow is repeated; compared with the number of the normal cells in the first screening process, the number of the normal cells in the screening process is increased by 2-6 times; compared with binding time of the library and the cells in the first screening process, the binding time of the library and the cells in the subsequent screening process is increased to 1h from 0.5h; and the binding time of the library and the virus infected cells is shortened to 0.5h from 1h to improve the screening efficiency of each process.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) aptamer for detecting grouper iridovirus infection, as well as screening method and application of DNA aptamer
ActiveCN104789569AHigh affinityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processes3-deoxyriboseDNA Aptamers
The invention discloses a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) aptamer for detecting grouper iridovirus infection, as well as a screening method and an application of the DNA aptamer. Two inverse screening steps are introduced in each screening process; first, a single-stranded DNA library of the former screening process is bound with normal cells to remove nonspecific ssDNA (single-stranded DNA) bound with the normal cells of a grouper; then, supernatant is bound with grouper iridovirus infected cells for screening; and ssDNA separated from the grouper iridovirus infected cells is bound with the normal cells for separation to obtain the supernatant. A PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification library prepares the single-stranded DNA library. The above screening flow is repeated; compared with the number of the normal cells in the first screening process, the number of the normal cells in the screening process is increased by 2-6 times; compared with binding time of the library and the cells in the first screening process, the binding time of the library and the cells in the subsequent screening process is increased to 1h from 0.5h; and the binding time of the library and the virus infected cells is shortened to 0.5h from 1h to improve the screening efficiency of each process.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) aptamer for detecting grouper iridovirus infection, as well as screening method and application of DNA aptamer
ActiveCN104789568AHigh affinityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processes3-deoxyriboseDNA Aptamers
The invention discloses a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) aptamer for detecting grouper iridovirus infection, as well as a screening method and an application of the DNA aptamer. Two inverse screening steps are introduced in each screening process; first, a single-stranded DNA library of the former screening process is bound with normal cells to remove nonspecific ssDNA (single-stranded DNA) bound with the normal cells of a grouper; then, supernatant is bound with grouper iridovirus infected cells for screening; and ssDNA separated from the grouper iridovirus infected cells is bound with the normal cells for separation to obtain the supernatant. A PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification library prepares the single-stranded DNA library. The above screening flow is repeated; compared with the number of the normal cells in the first screening process, the number of the normal cells in the screening process is increased by 2-6 times; compared with binding time of the library and the cells in the first screening process, the binding time of the library and the cells in the subsequent screening process is increased to 1h from 0.5h; and the binding time of the library and the virus infected cells is shortened to 0.5h from 1h to improve the screening efficiency of each process.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nucleic acid aptamers specifically combined with beta-amyloid precursor protein lyase 1 and application of aptamers
ActiveCN104293794AInhibition of in vitro activityNervous disorderGenetic material ingredientsDNA AptamersNucleotide
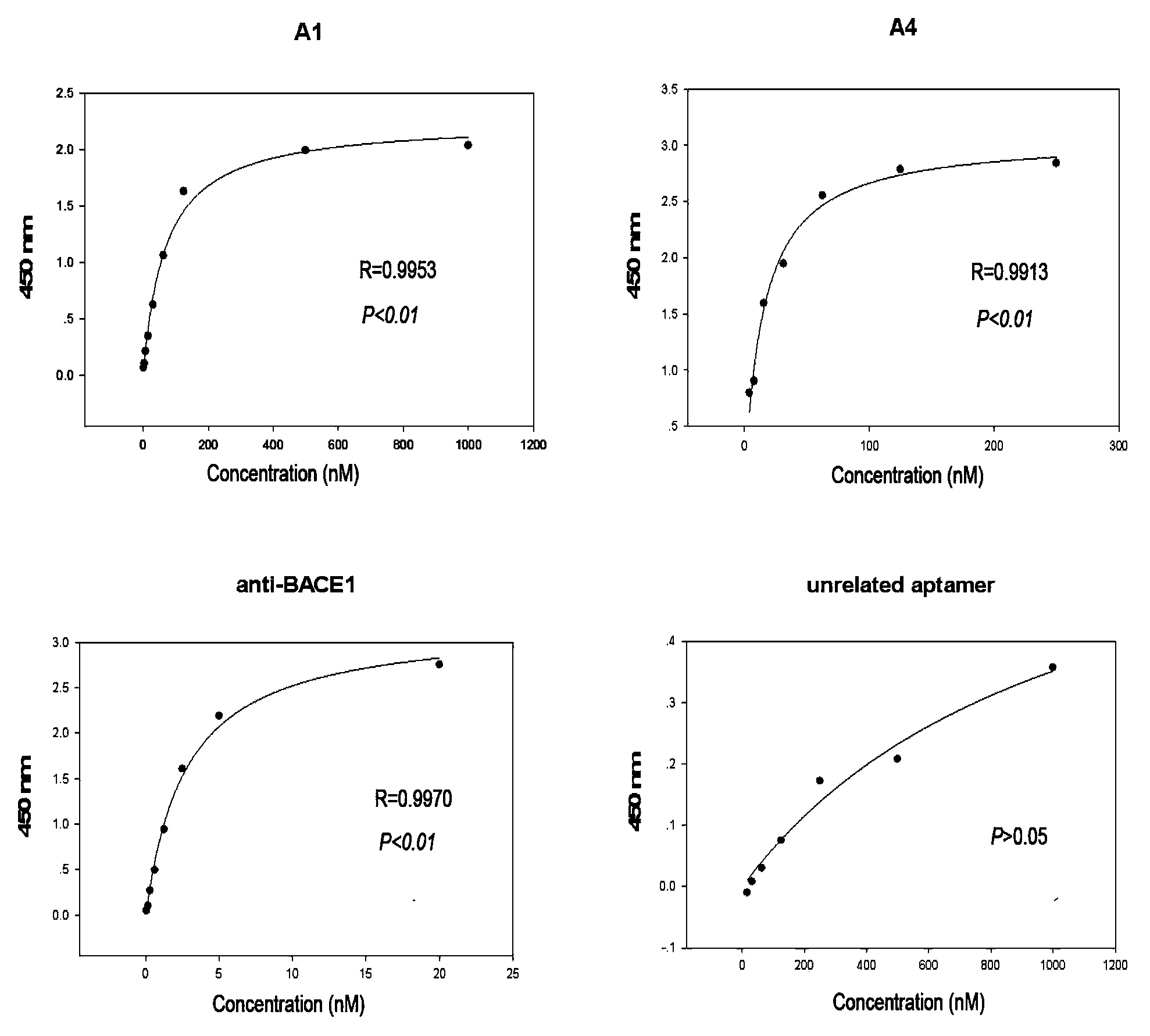
The invention discloses nucleic acid aptamers specifically combined with beta-amyloid precursor protein lyase 1 and an application of the nucleic acid aptamers. The nucleotide sequences of the nucleic acid aptamers are any one of SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO: 2. The nucleic acid aptamers or chemical modifiers of the nucleic acid aptamers serving as BACE1 inhibitors can be applied to preparing drugs for treating Alzheimer's disease. The DNA aptamers A1 and A4 which can be combined with BACE1 with high affinity are successfully screened by virtue of an SELEX technology in the research, and the aptamers have the effect of inhibiting the in vitro activity of the BACE1. The nucleic acid aptamers are used for providing a research basis on development of novel potent and specific BACE1 inhibitors and providing novel methods and concepts to treatment of AD.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation of two-color fluorescent gold bearing carbon dot and application of two-color fluorescent gold bearing carbon dot in visual inspection
ActiveCN105352919AObvious phenomenonRealize visual detectionFluorescence/phosphorescencePeroxidaseProstate cancer
The present invention discloses the preparation of a two-color fluorescent gold bearing carbon dot and application of the two-color fluorescent gold bearing carbon dot in visual inspection. The preparation of the gold bearing carbon dot is mainly as follows: a chloroauric acid solution and a glutathione solution are mixed and diluted with pure water; the mixed solution is heated while stirring for 1.5-2h in an oil bath at 80-100 DEG C, the mixed solution is hotly transferred into a conical flask containing glucose for heating for 20-25min at high fire in a domestic microwave oven; the resulting yellowish-brown product is dissolved with purified water, and centrifuged, the supernatant is dialyzed for 24hto obtain the product. Based on the nature of mimetic enzyme of peroxidase of the gold bearing carbon dot, the content of prostate cancer antigen in serum of patients with prostate cancer antigen can be detected by covering of two-color fluorescent gold bearing carbon dot catalytic surface sites by DNA aptamer and prostate cancer antigen specific effects, and fast visual detection of the prostate cancer antigen can be achieved. The method is simple, easy in operation, high in sensitivity, and has important significance in clinical medicine.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Nucleic acid molecules for highly sensitive detection of ligands, screening method for nucleic acid molecules, and optimization method for sensitivity of nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS20150292005A1High sensitivity detectionTall in constructionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDNA AptamersScreening method
It is an object of the present invention to provide nucleic acid molecules that enable highly sensitive detection of ligands (e.g., patulin). It is another object of the present invention to provide a screening method for nucleic acid molecules that enable highly sensitive detection of ligands (e.g., patulin), and a method for screening for nucleic acid molecules used for the optimization of nucleic acid molecules that enable highly sensitive detection of ligands (e.g., patulin). It is a further object of the present invention to provide a method for effectively removing ligands from samples containing ligands (e.g., patulin). According to the present invention, there is provided a loop-structured nucleic acid molecule for detection of ligands (e.g., patulin) having a DNA aptamer and a DNAzyme, wherein the sequence is modified between the DNA aptamer region and the DNAzyme.
Owner:KIRIN COMPANY
Oligonucleotides aptamer special for distinguishing fumonisin B1
ActiveCN103013999AHigh purityImprove efficiencyOrganic compound preparationMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical synthesisMagnetic bead
The invention provides a group of single-stranded DNA nucleic acid aptamers of fumonisin B1. Each aptamer is obtained by carrying out screening, amplification, sequencing, and analysis on affinity and specificity on a random original single-stranded DNA library with the combination of an SELEX (systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment) technology and a magnetic bead with fumonisin B fixed on the surface. As a special efficient distinguishing aptamer of fumonisin B, the group of DNA aptamers provides a new choice for developing a method for replacing the existing methods which are used for detecting fumonisin B by depending on an antibody, and can be used for analyzing and detecting or separating the fumonisin B in the environment of enriched food. The nucleic acid aptamer is small in molecular weight, low in chemical synthesis cost, easy to mark, strong in affinity and specificity, reversible in degeneration renaturation, high in speed, and suitable for repeated use, room-temperature transportation and long-term storage.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
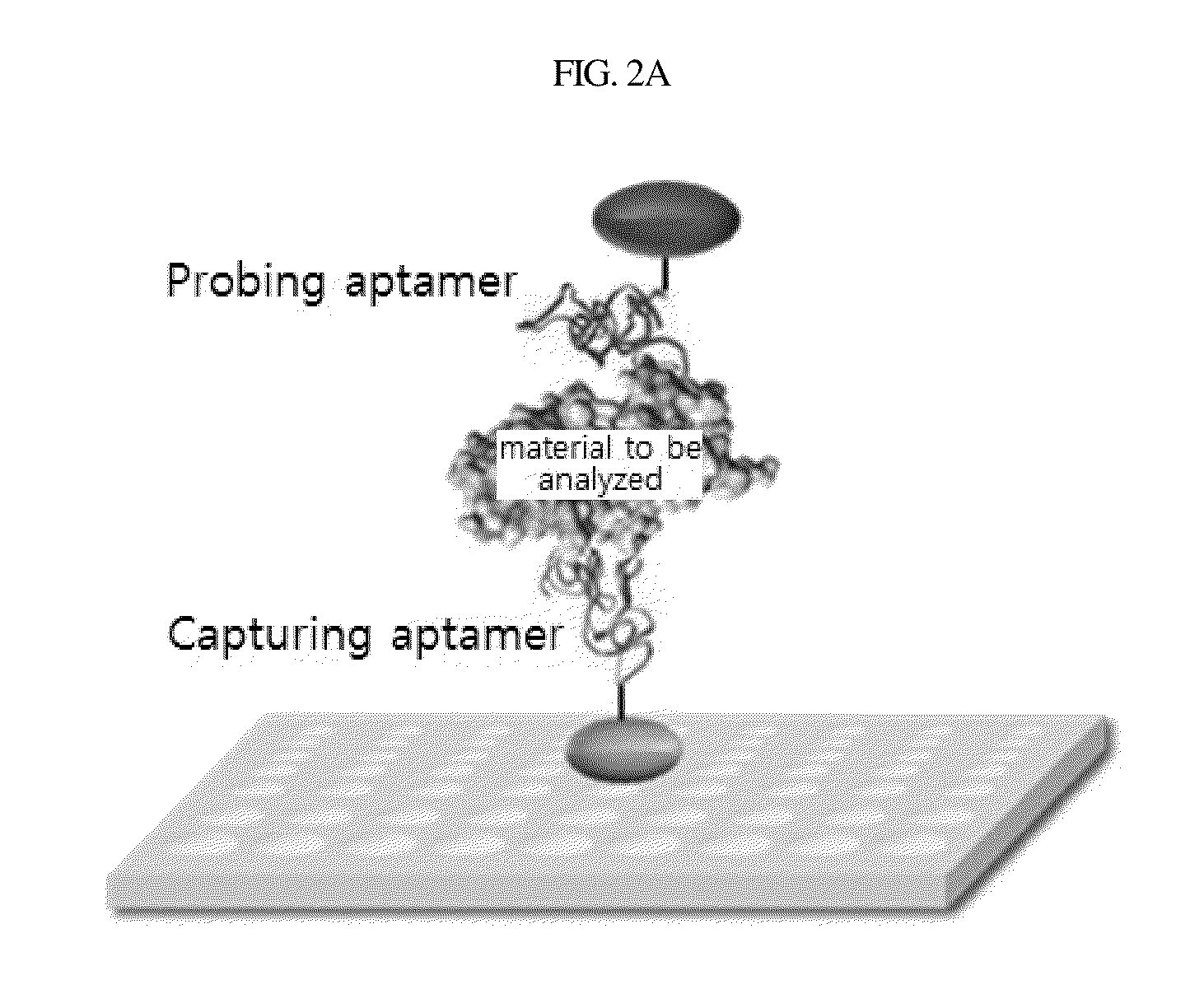
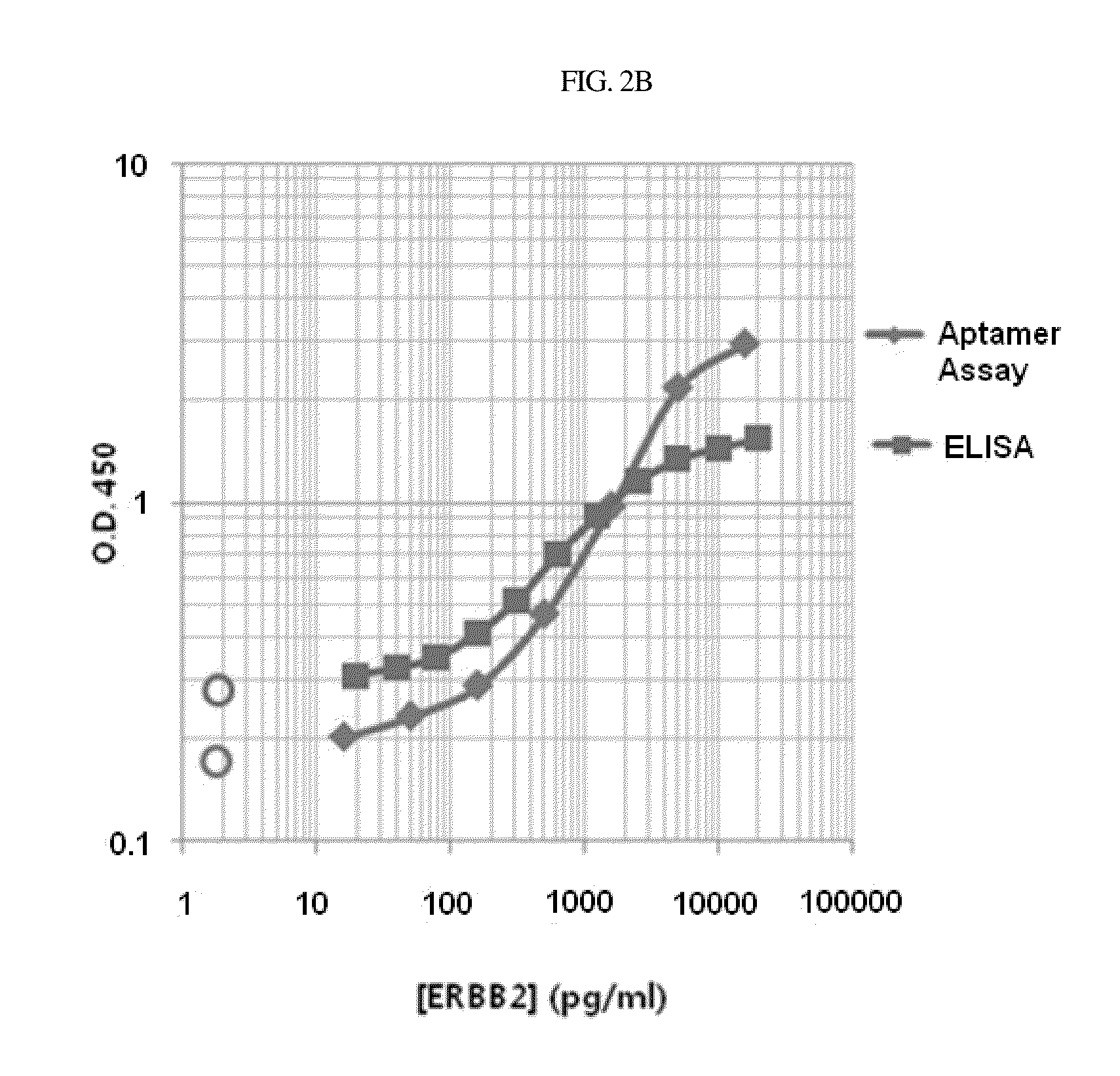
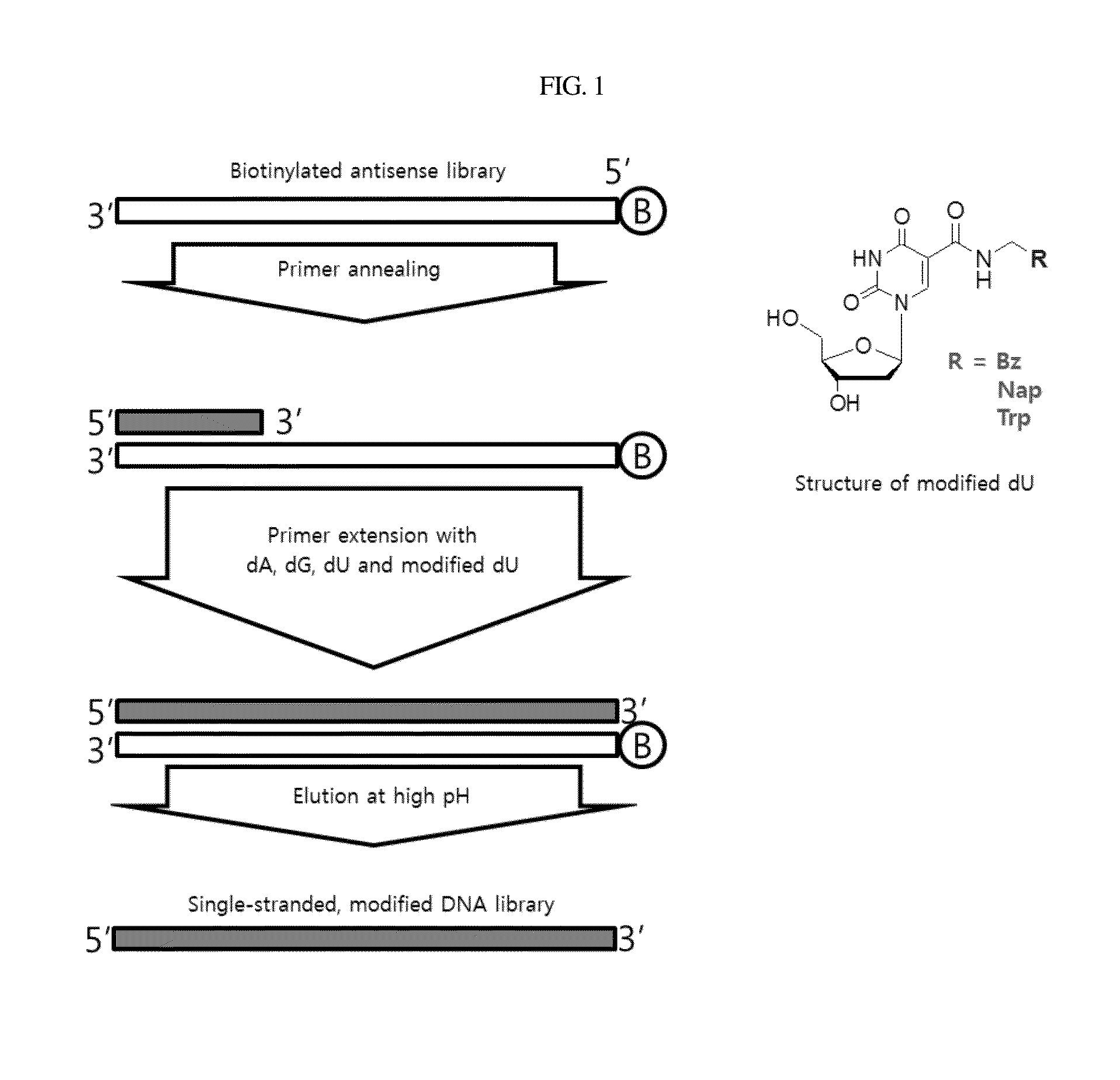
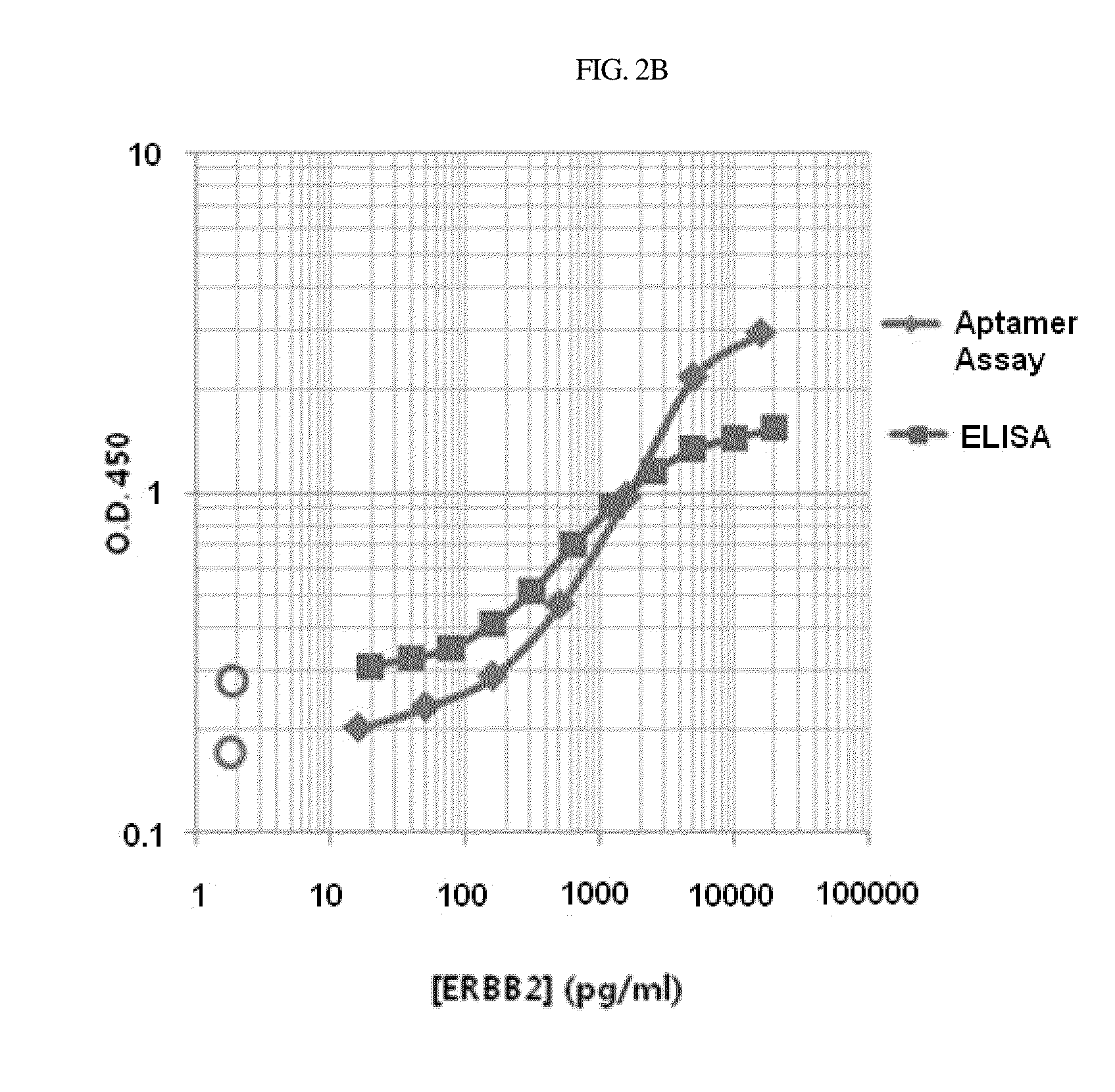
Aptamer which selectively binds to ERBB2 receptor and uses thereof
Disclosed are a DNA aptamer specifically binding to the Her2 (ERBB2) receptor involved in the onset of breast cancer, a composition for the suppression of cancer metastasis comprising the same as an active ingredient, and a composition for the diagnosis of cancer comprising the same as an active ingredient. Due to its binding mechanism being different from that of the conventional antibody, the aptamer can be effectively used for suppressing cancer metastasis and diagnosing cancer.
Owner:INTEROLIGO CORP +1
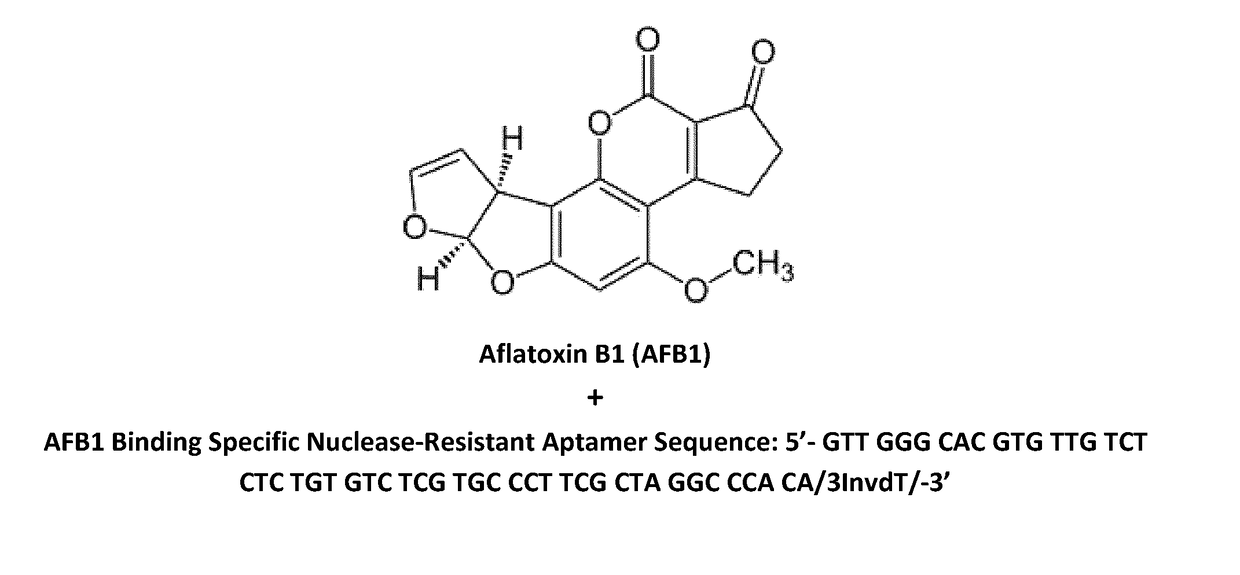
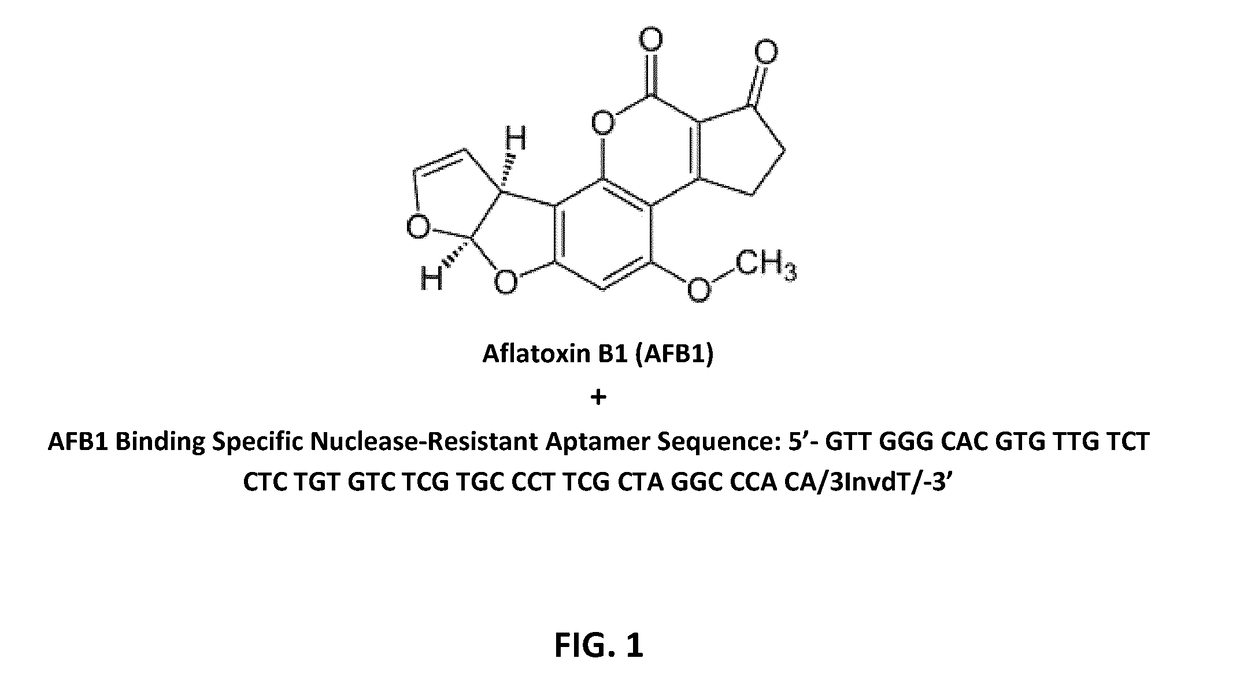
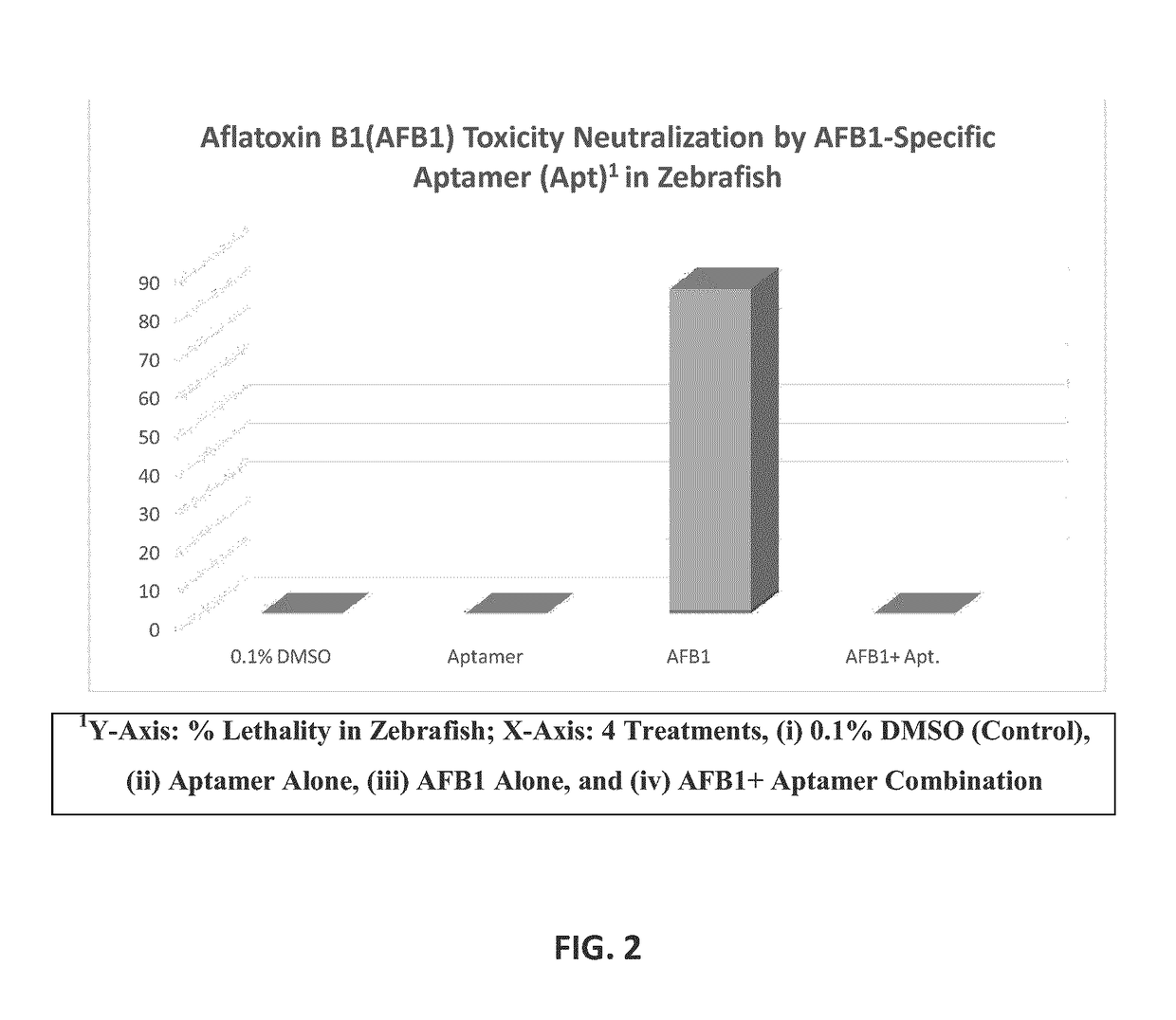
Aptamers for mycotoxin detoxification
ActiveUS20180325936A1Increased mycotoxin-deactivating abilityReduce absorptionOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsAdditive ingredientAntioxidant
Mycotoxin-deactivating aptamers, especially DNA aptamers, bind to mycotoxins in feed and feed ingredients resulting in the reduction or elimination of toxic and carcinogenic effects of mycotoxins. The invention also discloses a composition comprising a mycotoxin-deactivating aptamer, a binding agent, a biotransforming agent and an antioxidant for detoxifying mycotoxins in feeds. In addition, the invention teaches the methods of preparing said mycotoxin-deactivating aptamer-based composition and also the methods of using it as a feed additive. Furthermore, the invention relates to the use of said mycotoxin-deactivator / s alone, or in a composition comprising said aptamers and other mycotoxin-detoxifying agents, in feeds and feed ingredients for detoxifying the major mycotoxins such as aflatoxins, deoxynivalenol, zearalenone, fumonisins and ochratoxin A.
Owner:MYCOTOX SOLUTIONS INC
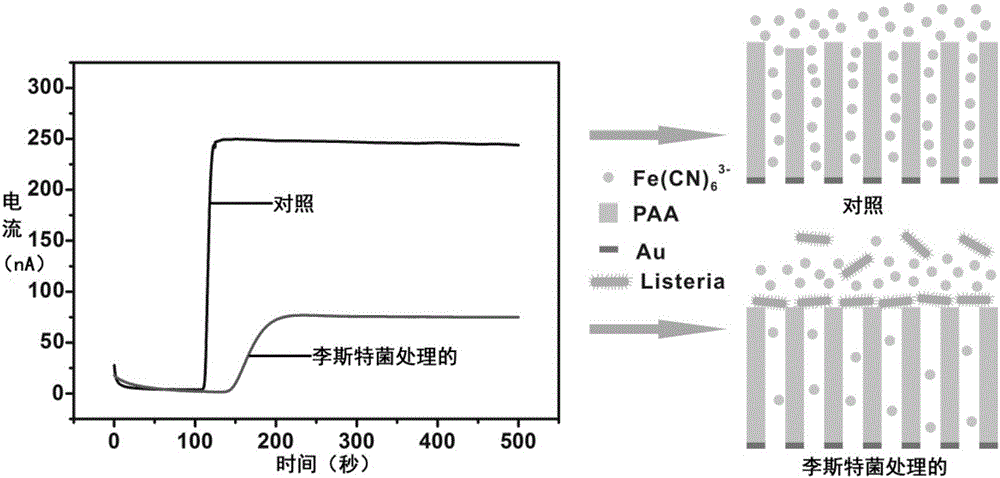
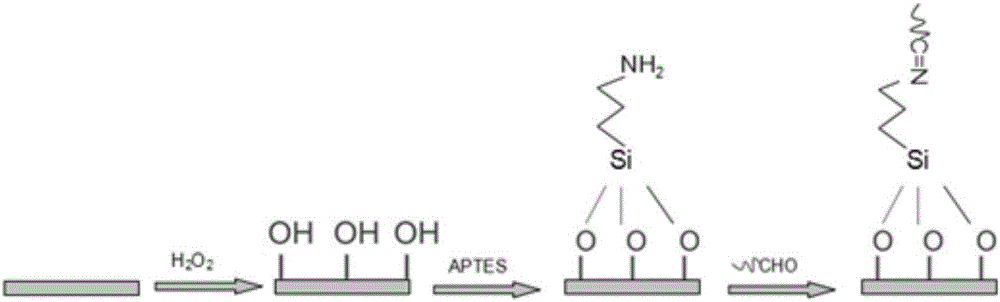
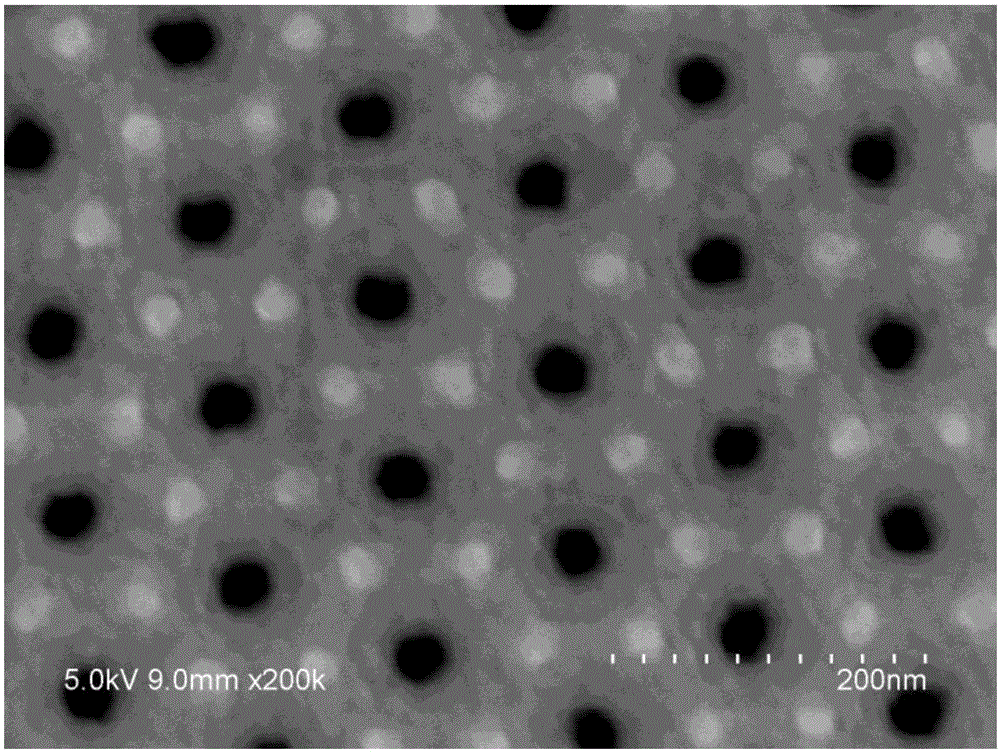
Novel high-sensitivity LM (listeria monocytogene) detection method based on aptamer modified porous alumina membrane
InactiveCN106018508ADetection has no effectHigh selectivityMaterial electrochemical variablesEscherichia coliPotassium ferricyanide
The invention relates to a fast ultra-sensitive LM (listeria monocytogene) detector based on nanochannel confinement characteristics and constructed according to the nature of specific identification between a target molecule and an aptamer of the target molecules. The invention further relates to a method for detecting the LM by taking potassium ferricyanide ions as probe ions and taking an LM DNA modified porous alumina membrane as an electrode for assembling a self-made electrolytic tank. When LM is present and the concentration is lower, a current increasing value is remarkably reduced with the increase of the concentration; a current change value is reduced with increase of the LM concentration; when the LM concentration is in a range of 100-1,250 CFU / mL, a linear relation is formed between the LM concentration and the current increasing value; when the LM concentration is higher than 1,500 CFU / mL, the current change value becomes stable. Therefore, the lowest detection limit of the detection method for the LM can reach 100 CFU / mL, the linear range is 100-1,250 CFU / mL, and the detection can be completed within 10 min; a 108 CFU / mL of escherichia coli and staphylococcus aureus control experiment indicates that the method has high selectivity on the LM.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
Aptamer which selectively binds to erbb2 receptor and uses thereof
Disclosed are a DNA aptamer specifically binding to the Her2 (ERBB2) receptor involved in the onset of breast cancer, a composition for the suppression of cancer metastasis comprising the same as an active ingredient, and a composition for the diagnosis of cancer comprising the same as an active ingredient. Due to its binding mechanism being different from that of the conventional antibody, the aptamer can be effectively used for suppressing cancer metastasis and diagnosing cancer.
Owner:INTEROLIGO CORP +1
DNA APTAMER SPECIFICALLY BINDING TO pLDH (PLASMODIUM LACTATE DEHYDROGENASE)
ActiveUS20120316325A1High sensitivityImprove accuracyOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesLactate dehydrogenaseDiagnosis of malaria
Disclosed herein are a DNA aptamer specifically binding to pLDH (Plasmodium Lactate Dehydrogenase), a composition for the diagnosis of malaria, comprising the same, and a diagnostic kit for malaria using the same. Superior in specificity and stability to antibodies which are conventionally used to diagnose malaria, the DNA aptamers specifically binding to pLDH (Plasmodium Lactate Dehydrogenase) in accordance with the present invention can be developed into biosensors which determine pLDH levels with high sensitivity and accuracy, greatly contributing to the diagnostic accuracy of malaria.
Owner:MD APTUS INC
Nucleic acid medicine loading system for targeted therapy and preparation method of nucleic acid medicine loading system
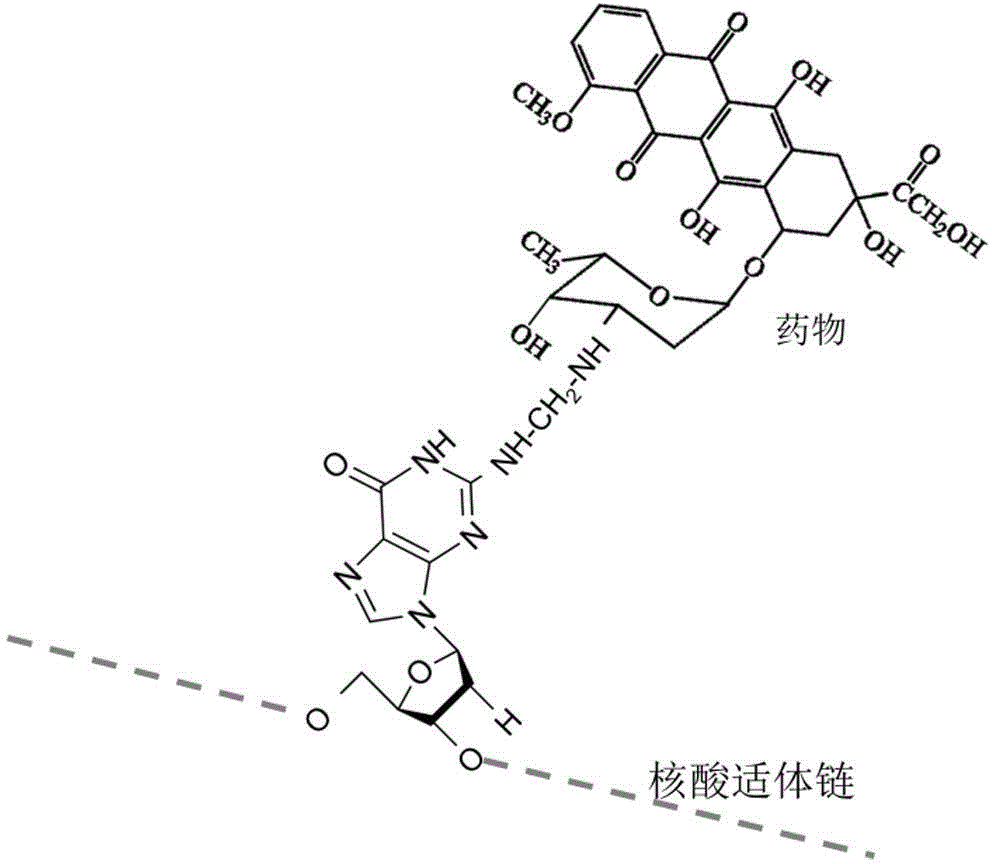
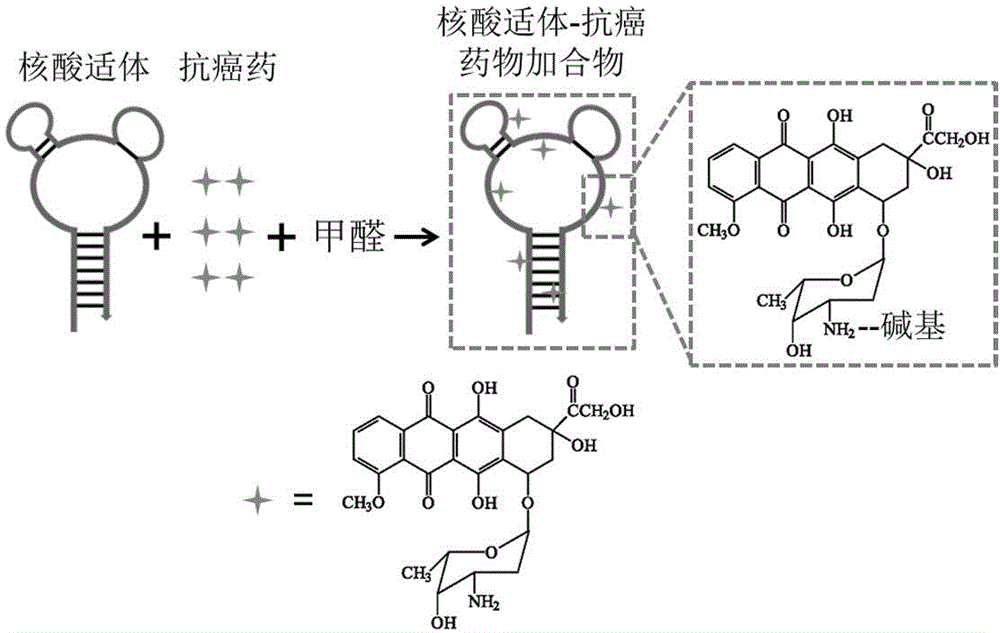
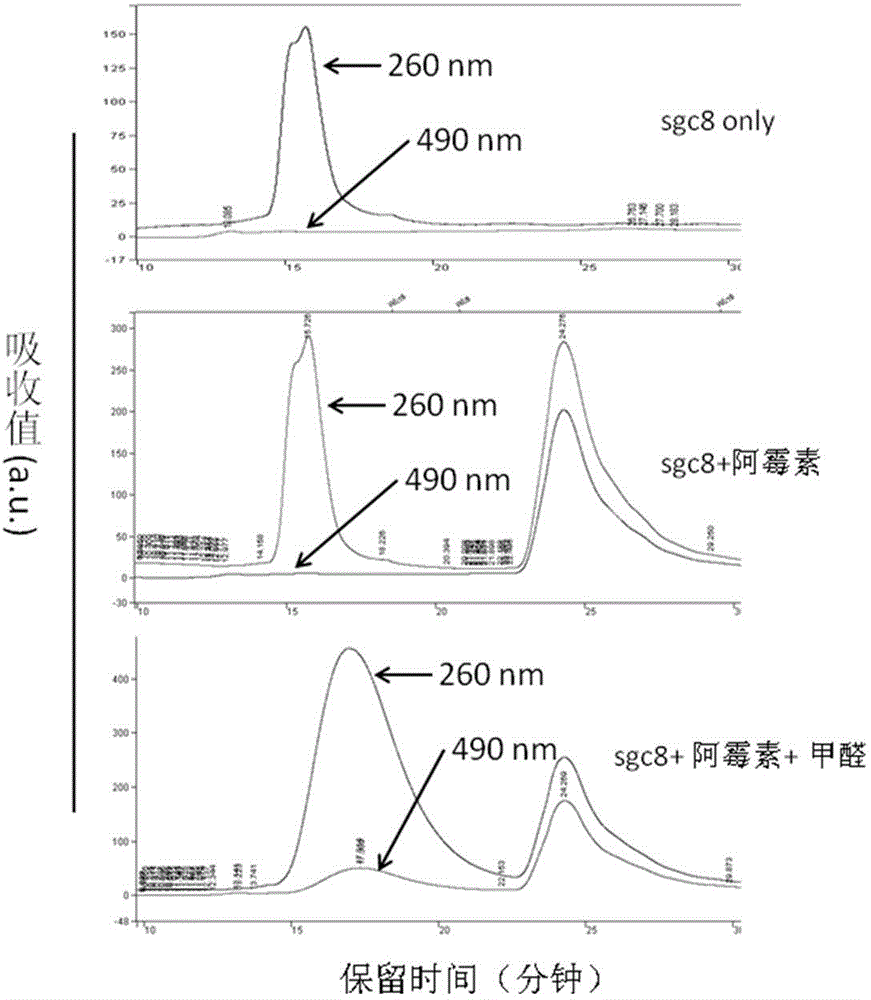
ActiveCN102716494AEasy to makeSimple preparation processOrganic active ingredientsAntiinfectivesAptamerCancer cell
The invention discloses a nucleic acid medicine loading system for targeted therapy and a preparation method of the nucleic acid medicine loading system. The system is adduct consisting of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) aptamers as medicine carriers and targeted probes and anticancer medicine loaded onto the DNA aptamers. The targeted identification specificity, high stability and easy modification of the DNA aptamers are utilized, and the DNA aptamer-anticancer medicine adduct is prepared, so small molecule medicine is modified onto the DNA aptamers. The DNA aptamers are very stable at the solid state or low temperature liquid state (such as the temperature below 10 DEG C) and is suitable for being stored for a long time. The adduct maintains the identification specificity of the original DNA aptamers to targeted cancer cells, medicine can be conveyed to cancer cells in a targeted way and can be gradually released at the physiological temperature, the special killing and injury effect on the targeted cancer cells is generated, the side effect is reduced, and the curative effect is improved. The nucleic acid medicine loading system and the preparation method have the advantages that the preparation process is simple, economy is realized, the efficiency is high, and the preparation process is suitable for mass production and is particularly suitable for being used for preparing the targeted medication anticancer medicine.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com