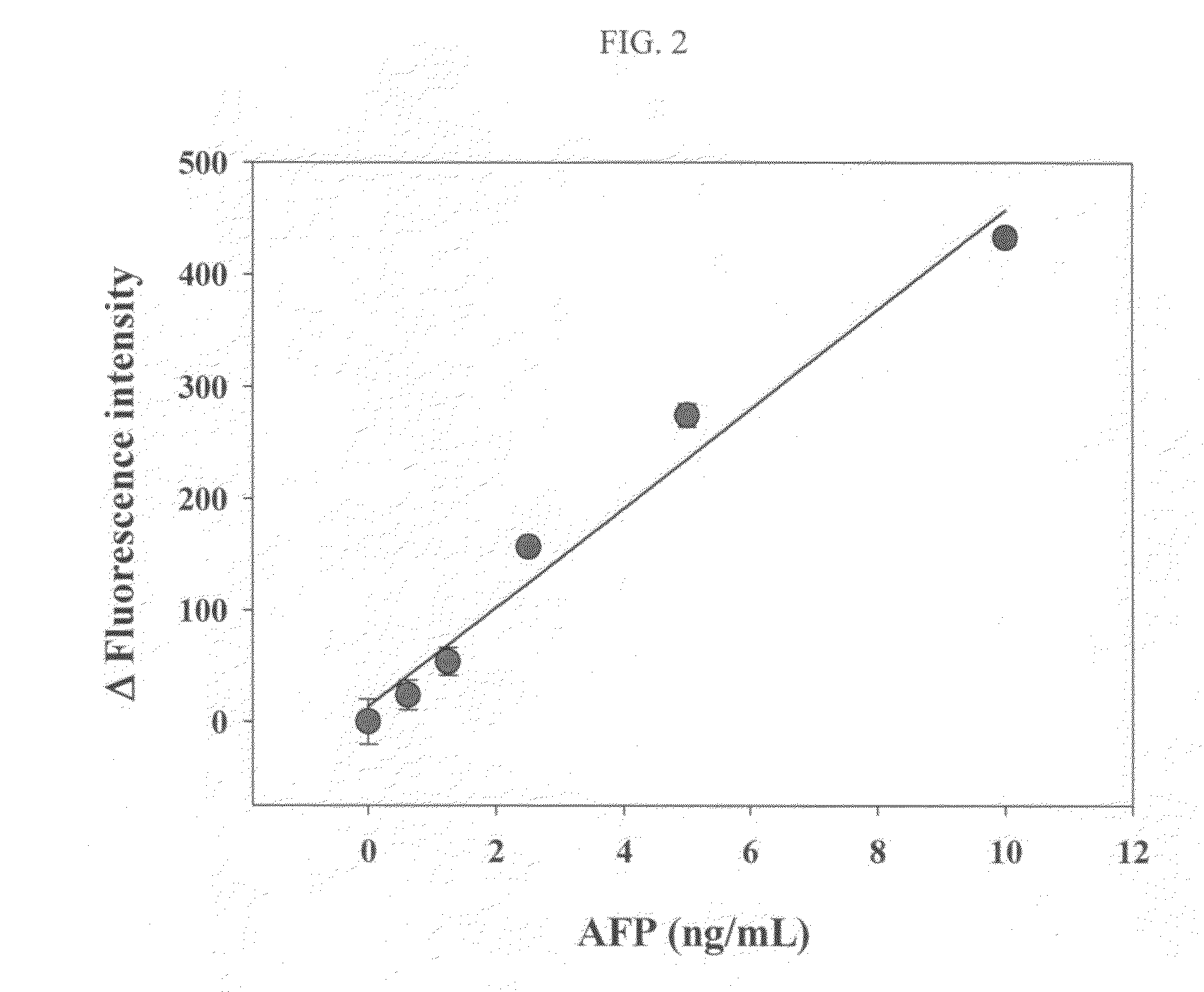
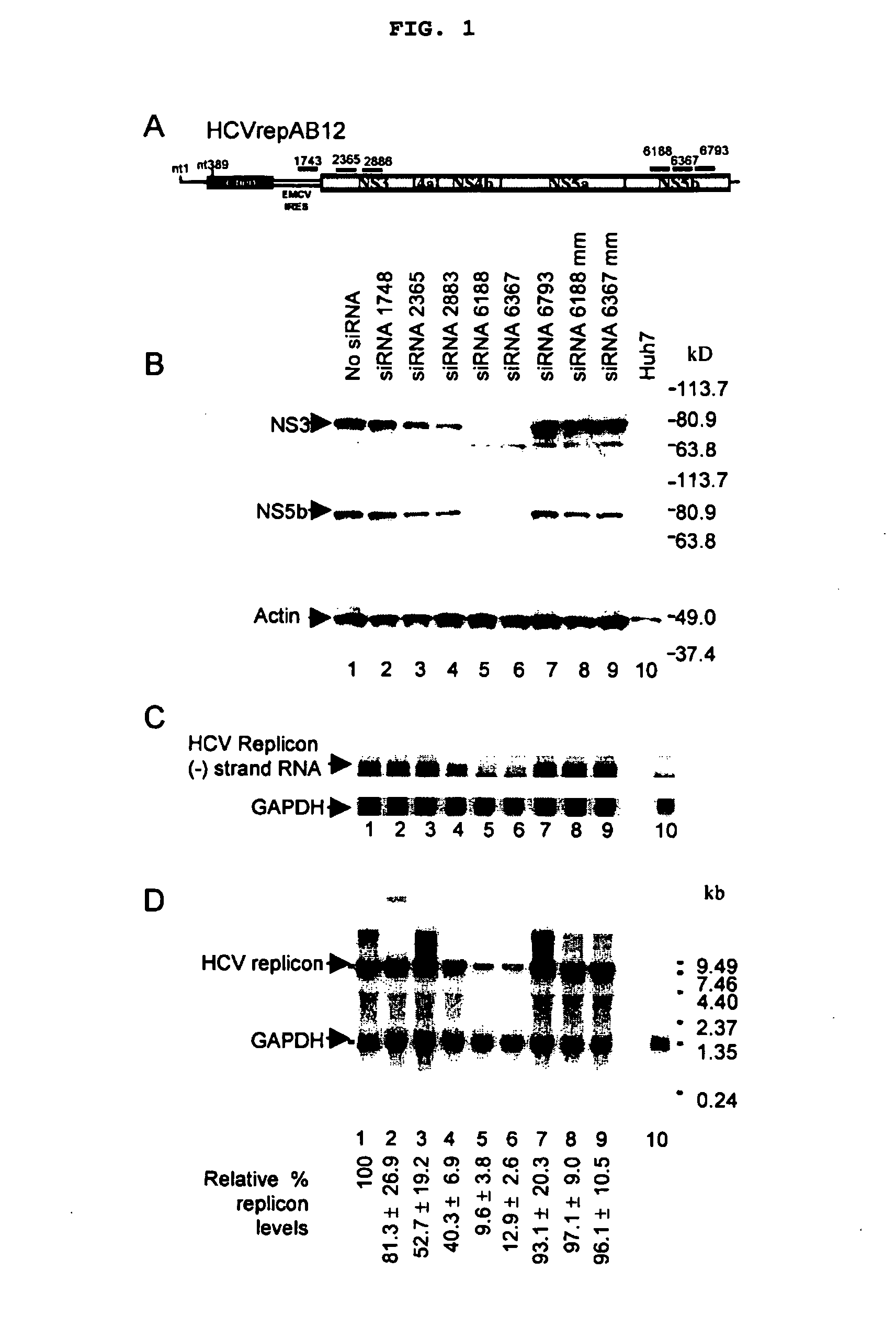
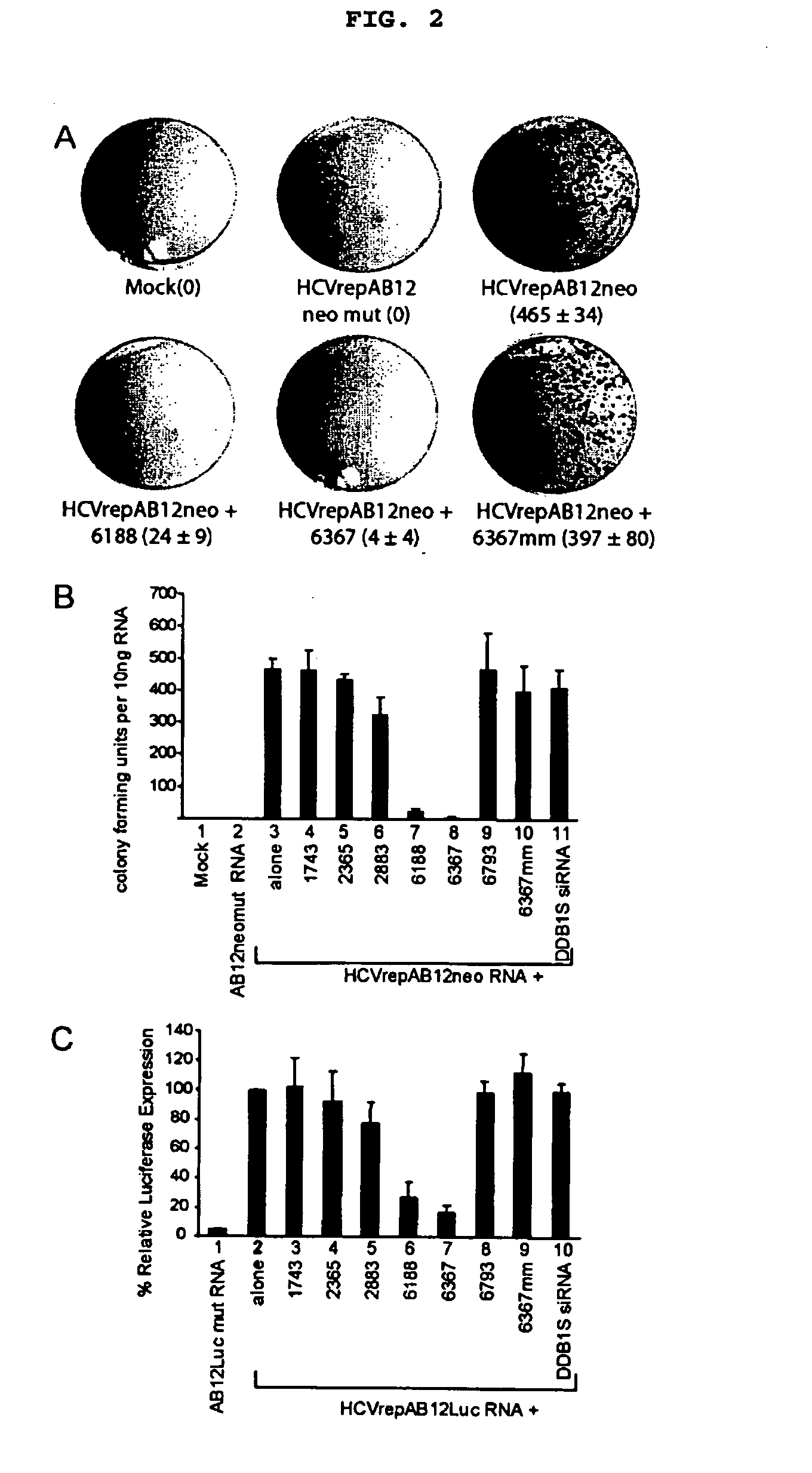
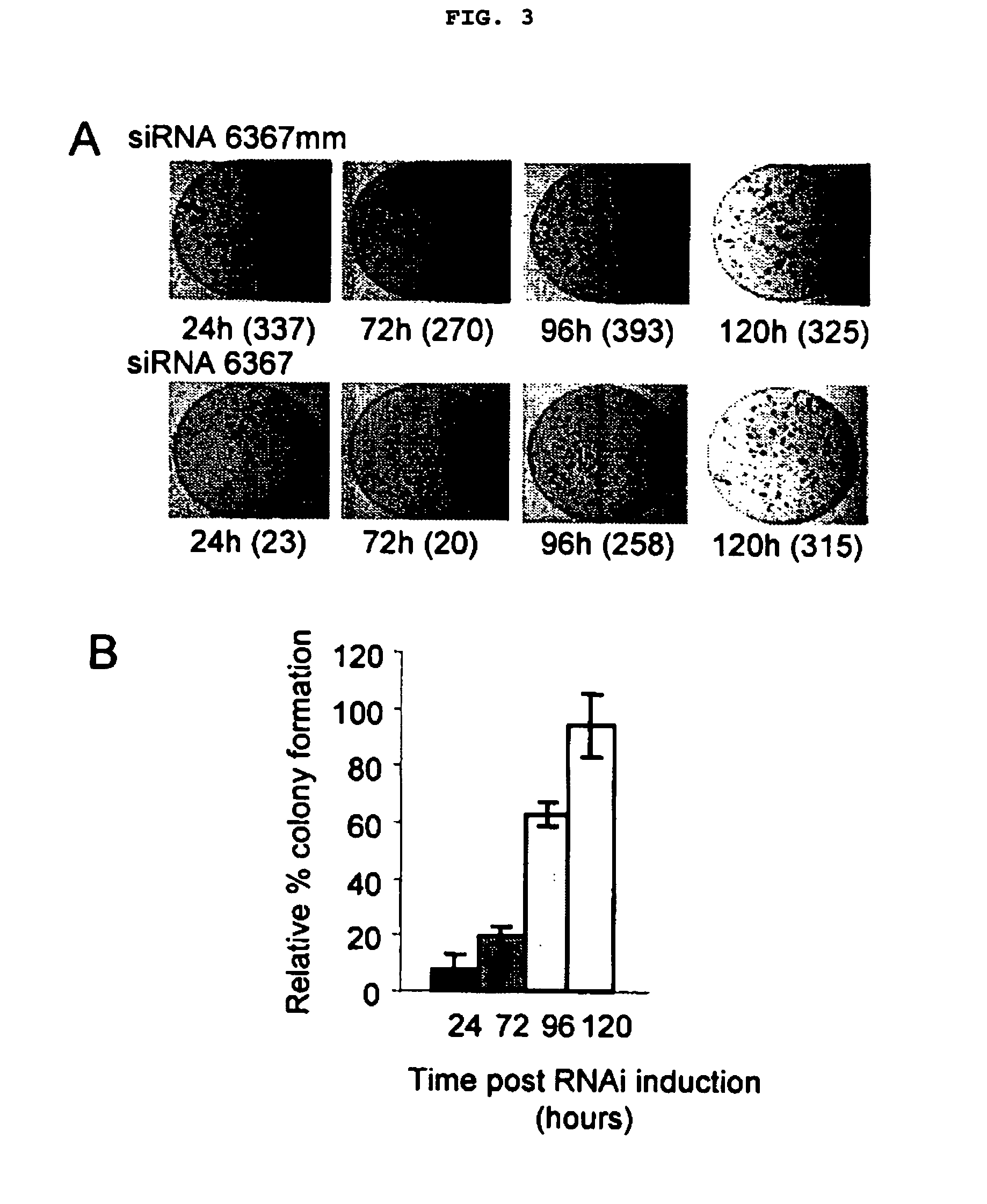
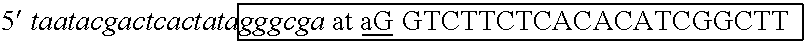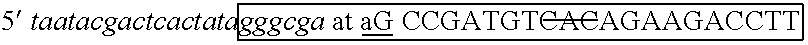Patents
Literature
147 results about "Single-Stranded RNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An RNA that consists of a single strand of ribonucleotides. Because it lacks a complementary strand this form of RNA can adopt unique tertiary structures.
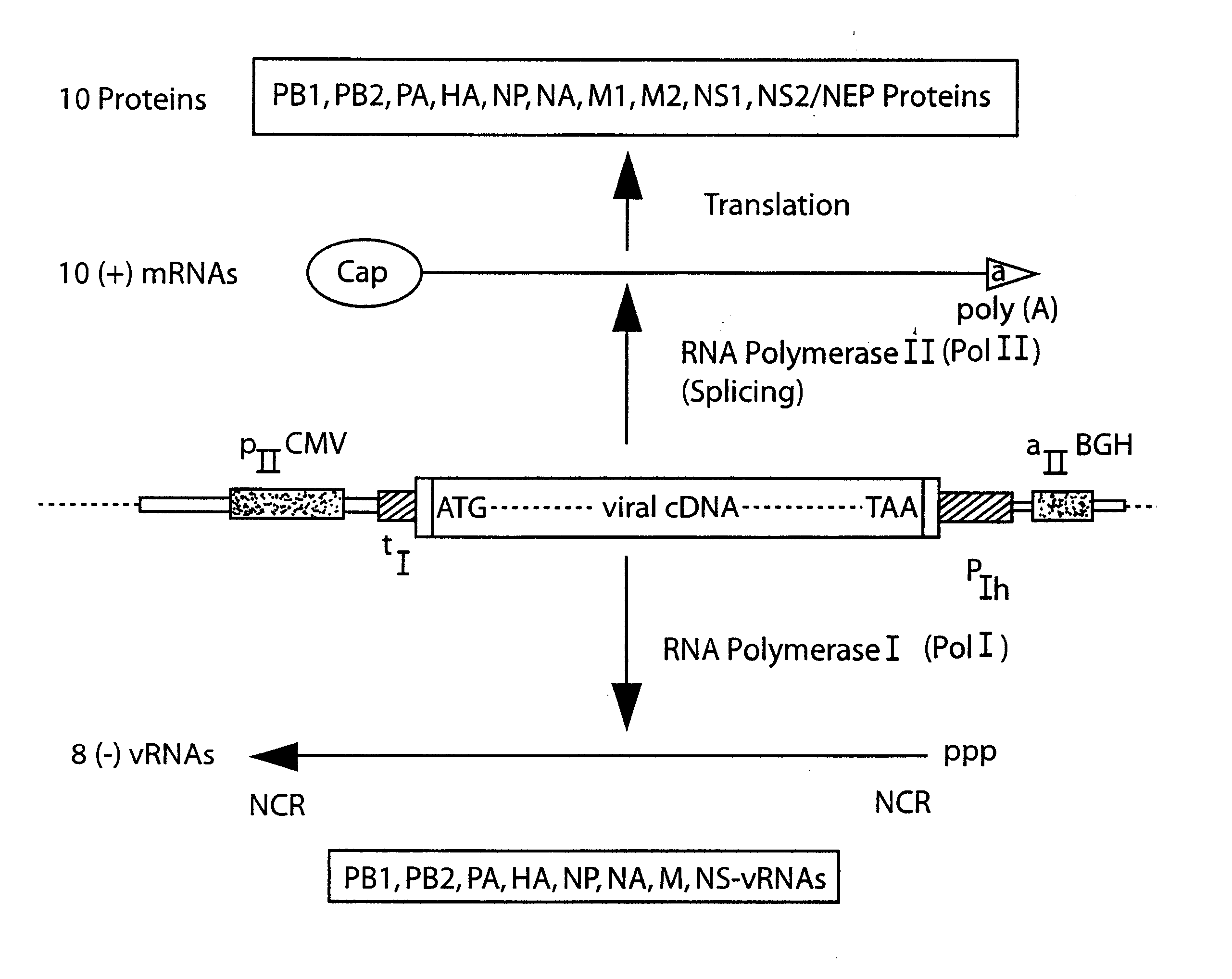
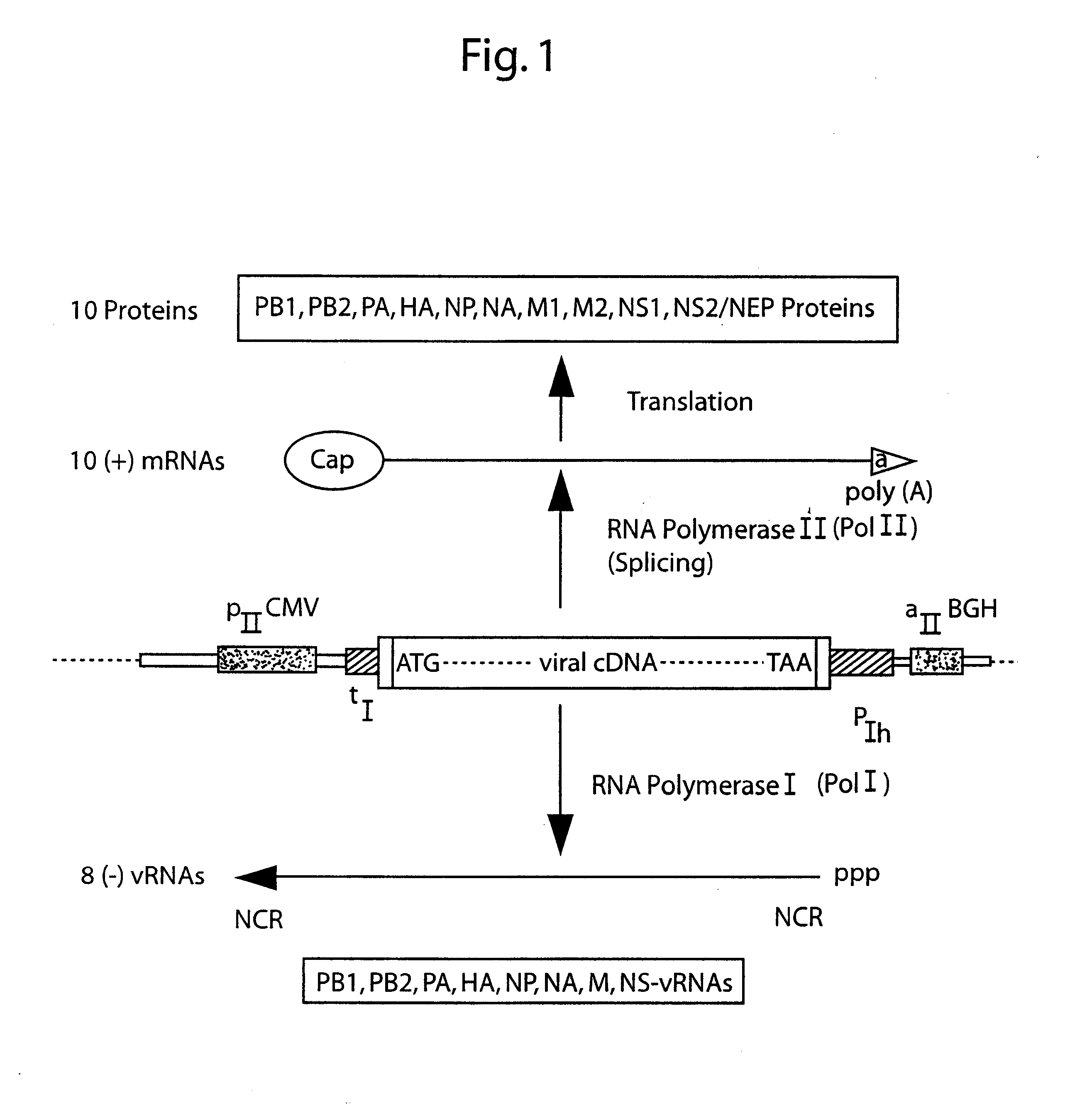
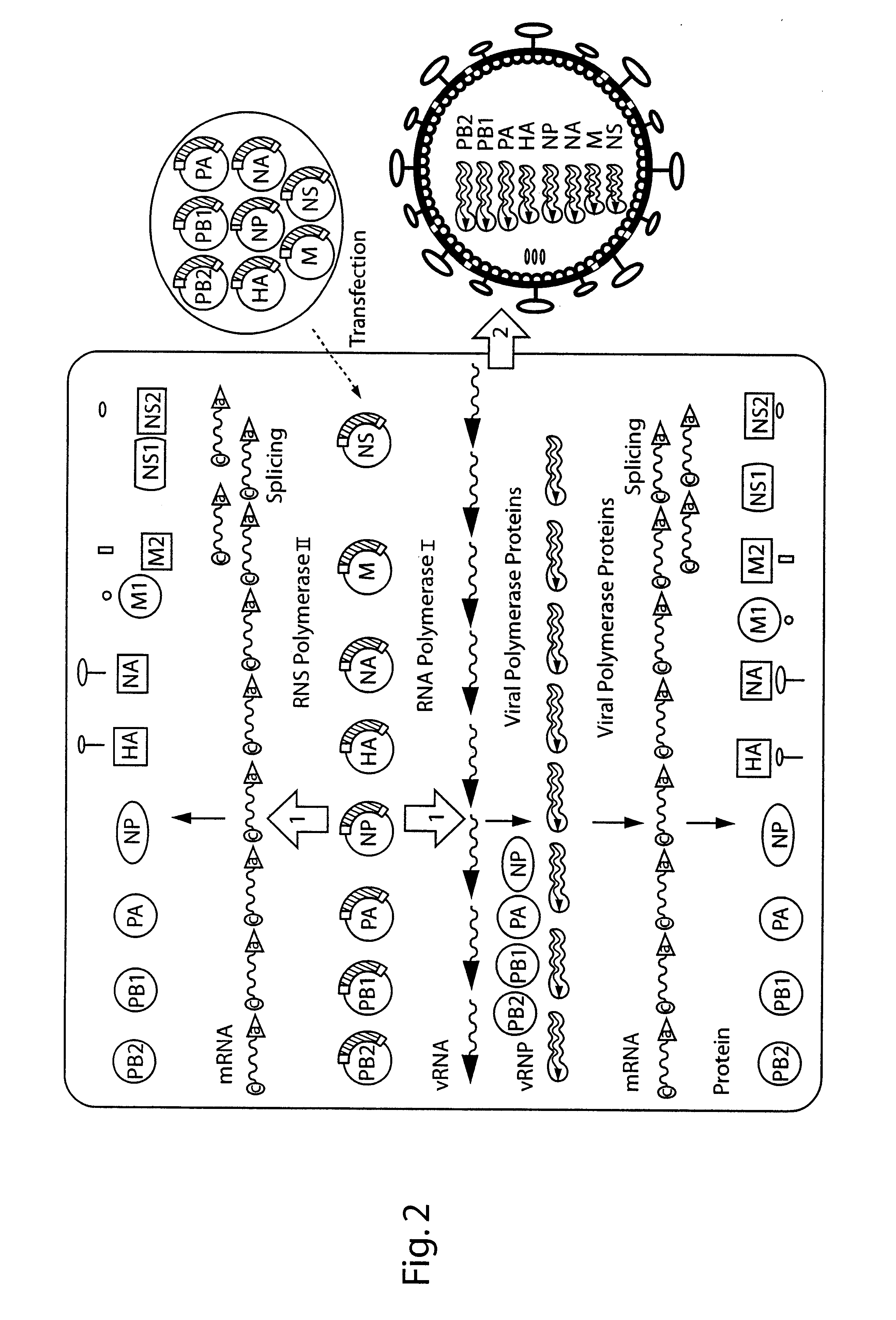
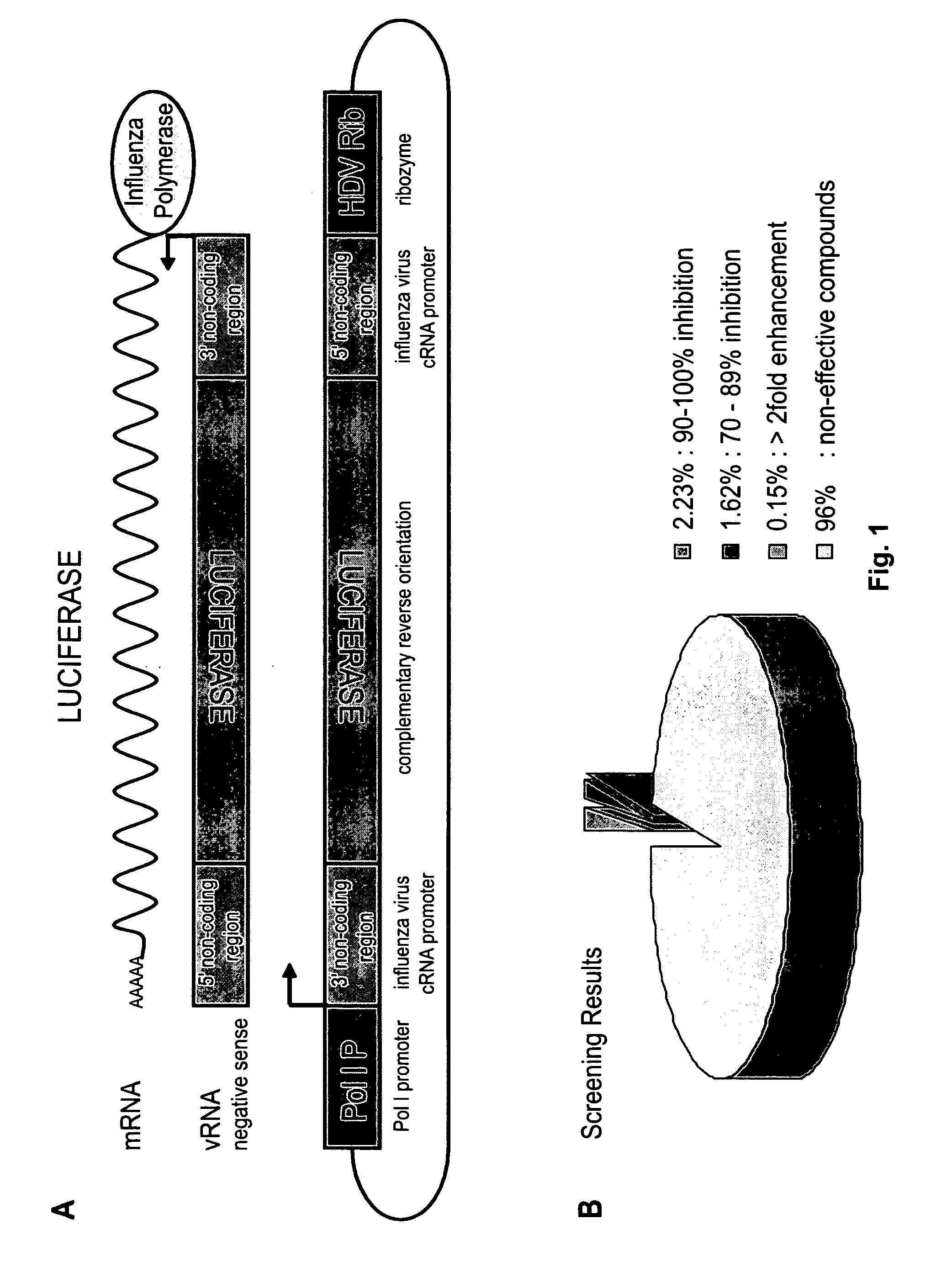
DNA transfection system for the generation of infectious influenza virus
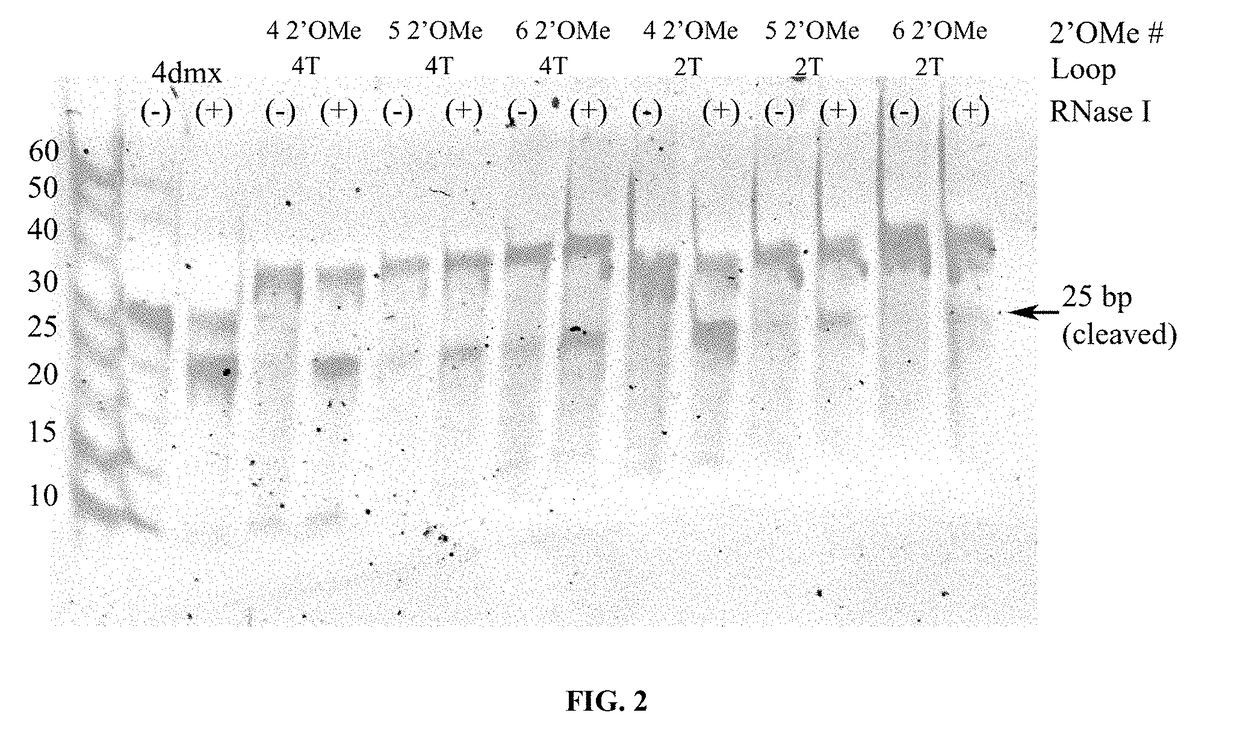
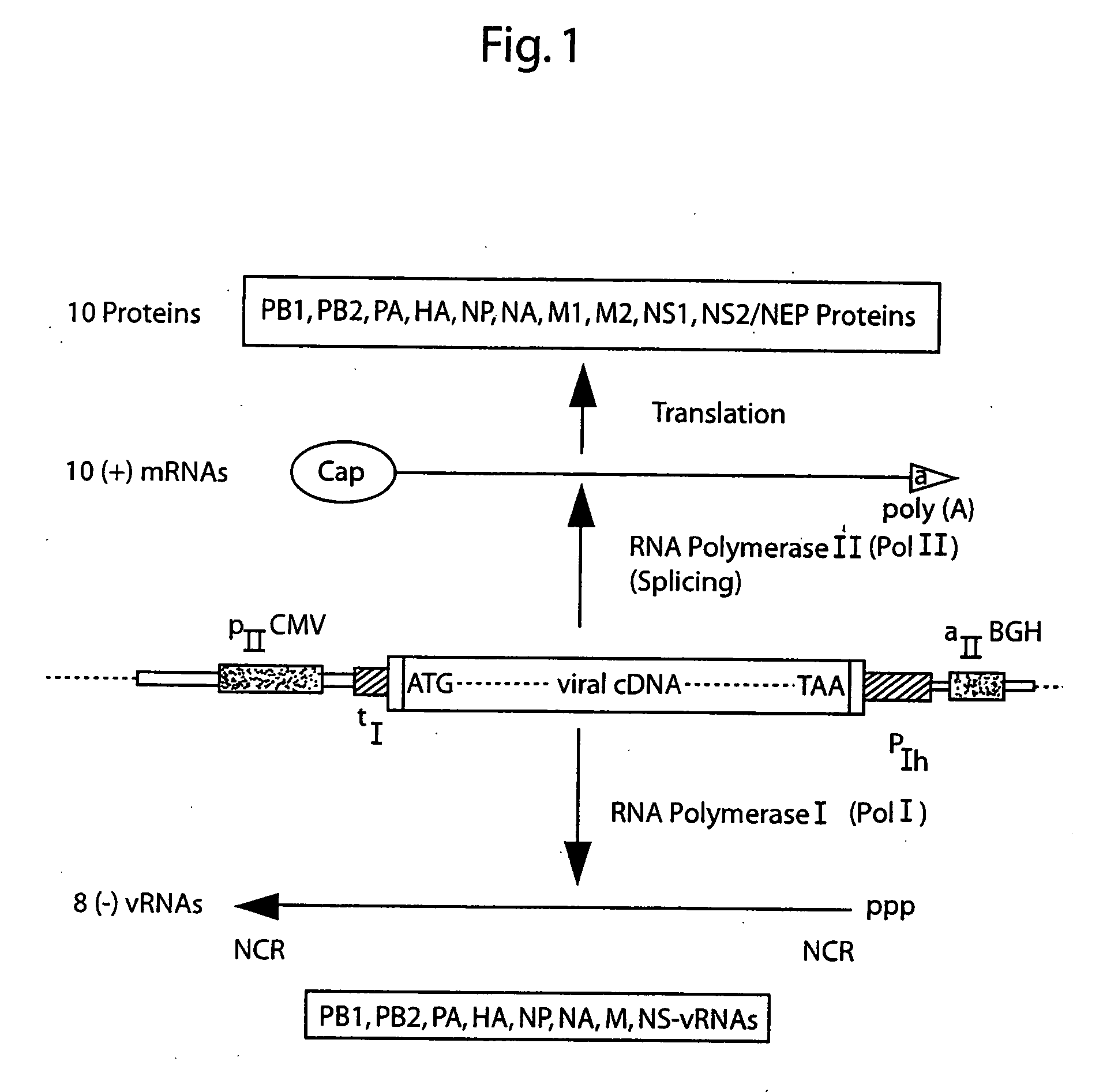
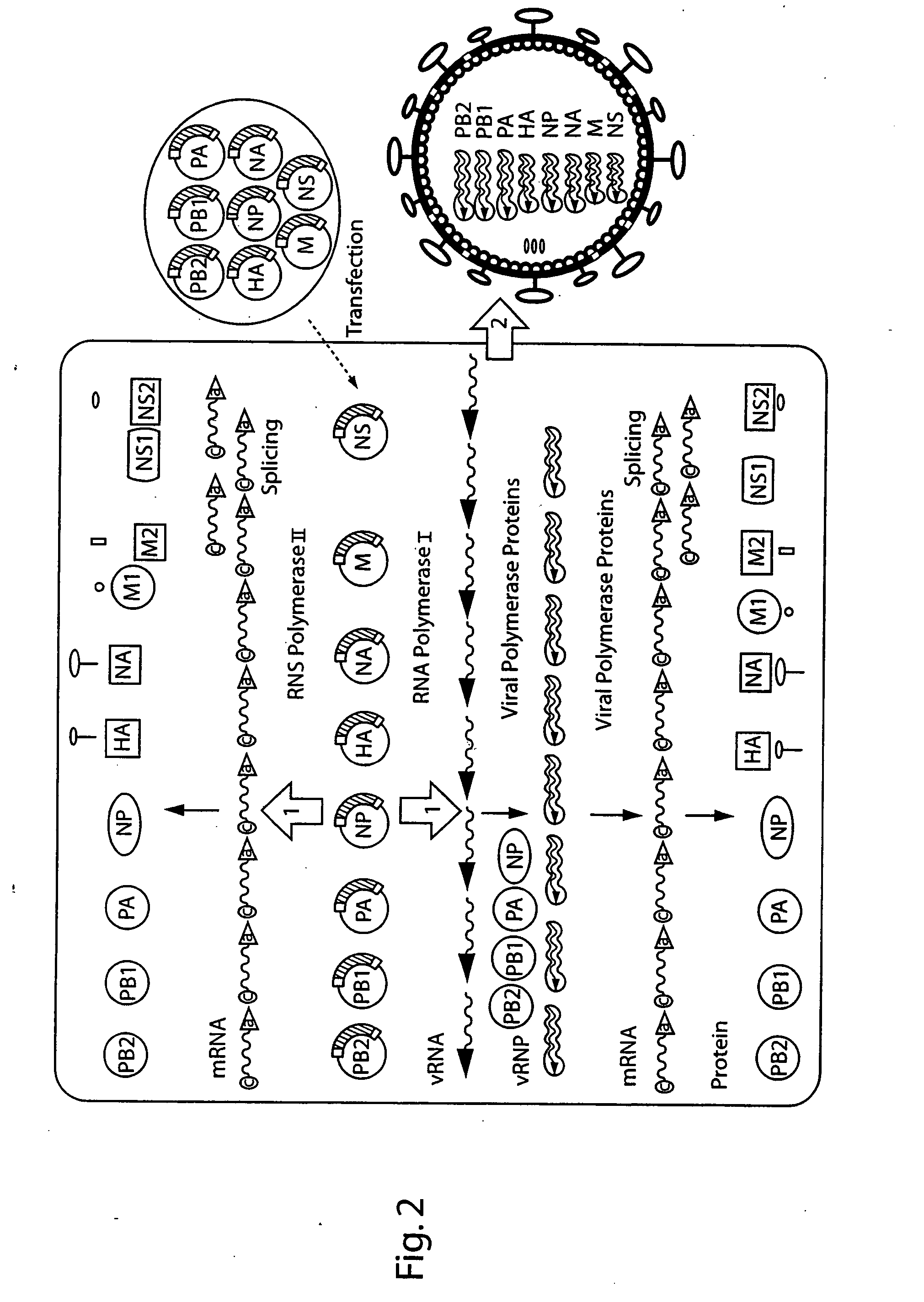
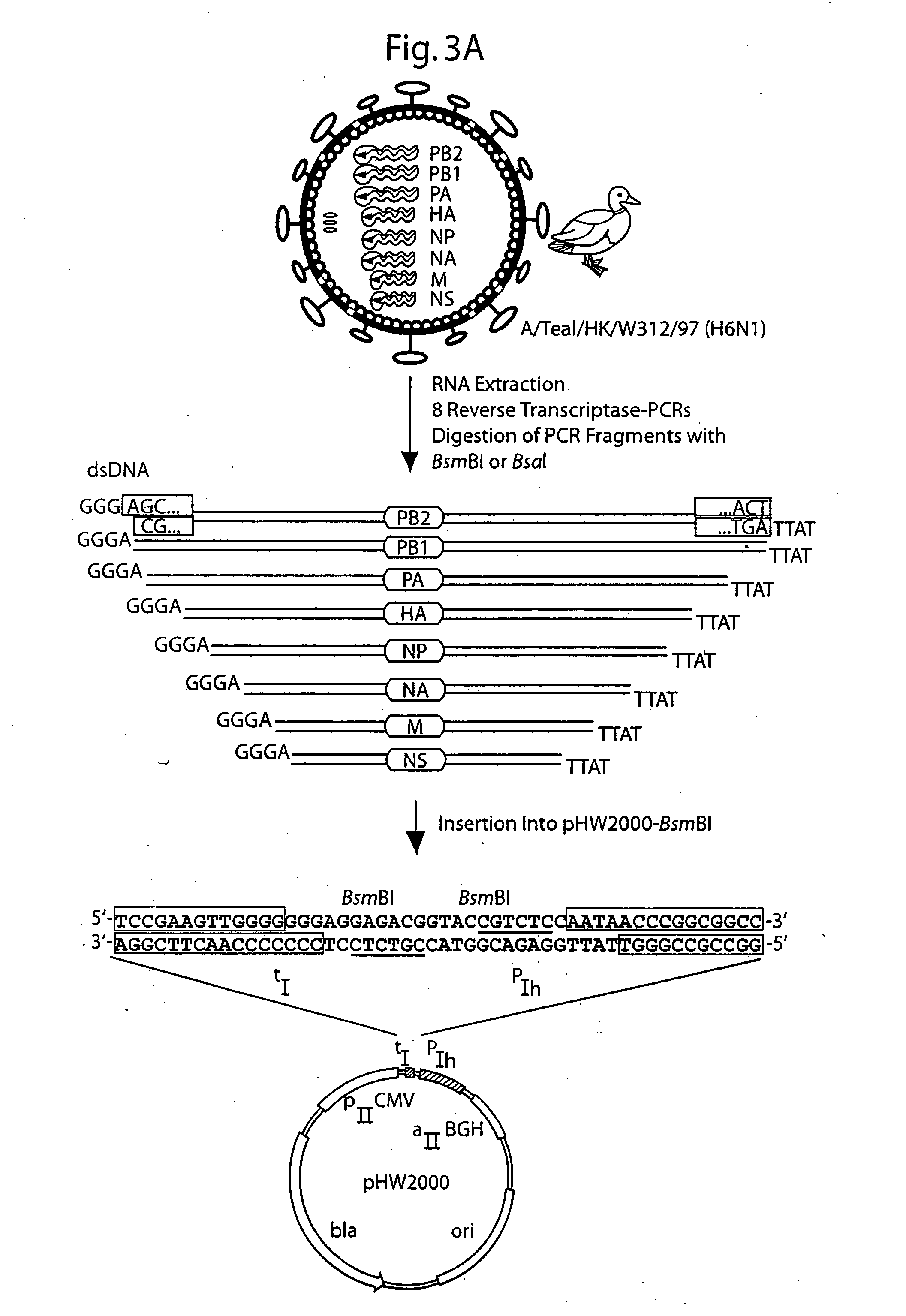
The present invention is based on the development of a dual promoter system (preferably a RNA pol I-pol II system) for the efficient intracellular synthesis of viral RNA. The resultant minimal plasmid-based system may be used to synthesize any RNA virus, preferably viruses with a negative single stranded RNA genome. The viral product of the system is produced when the plasmids of the system are introduced into a suitable host cell. One application of the system is production of attenuated, reassortant influenza viruses for use as antigens in vaccines. The reassortant viruses generated by cotransfection of plasmids may comprise genes encoding the surface glycoproteins hemagglutinin and neuramimidase from an influenza virus currently infecting the population and the internal genes from an attenuated influenza virus. An advantageous property of the present invention is its versatility; the system may be quickly and easily adapted to synthesize an attenuated version of any RNA virus. Attenuated or inactivated RNA viruses produced by the present invention may be administered to a patient in need of vaccination by any of several routes including intranasally or intramuscularly.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
Compositions and methods for treatment of viral diseases
InactiveUS20080161324A1Slow and stop replicationReduce loadBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-Stranded RNADisease
The present invention features compositions, methods, and kits useful in the treatment of viral diseases. In certain embodiments, the viral disease is caused by a single stranded RNA virus, a flaviviridae virus, or a hepatic virus. In particular embodiments, the viral disease is viral hepatitis (e.g., hepatitis A, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, hepatitis D, hepatitis E). Also featured are screening methods for identification of novel compounds that may be used to treat a viral disease.
Owner:EXCRX SINGAPORE PTE +1
Compositions and methods for treatment of viral diseases
InactiveUS20100009970A1Slow and stop replicationReduce loadBiocideNervous disorderSingle-Stranded RNADisease
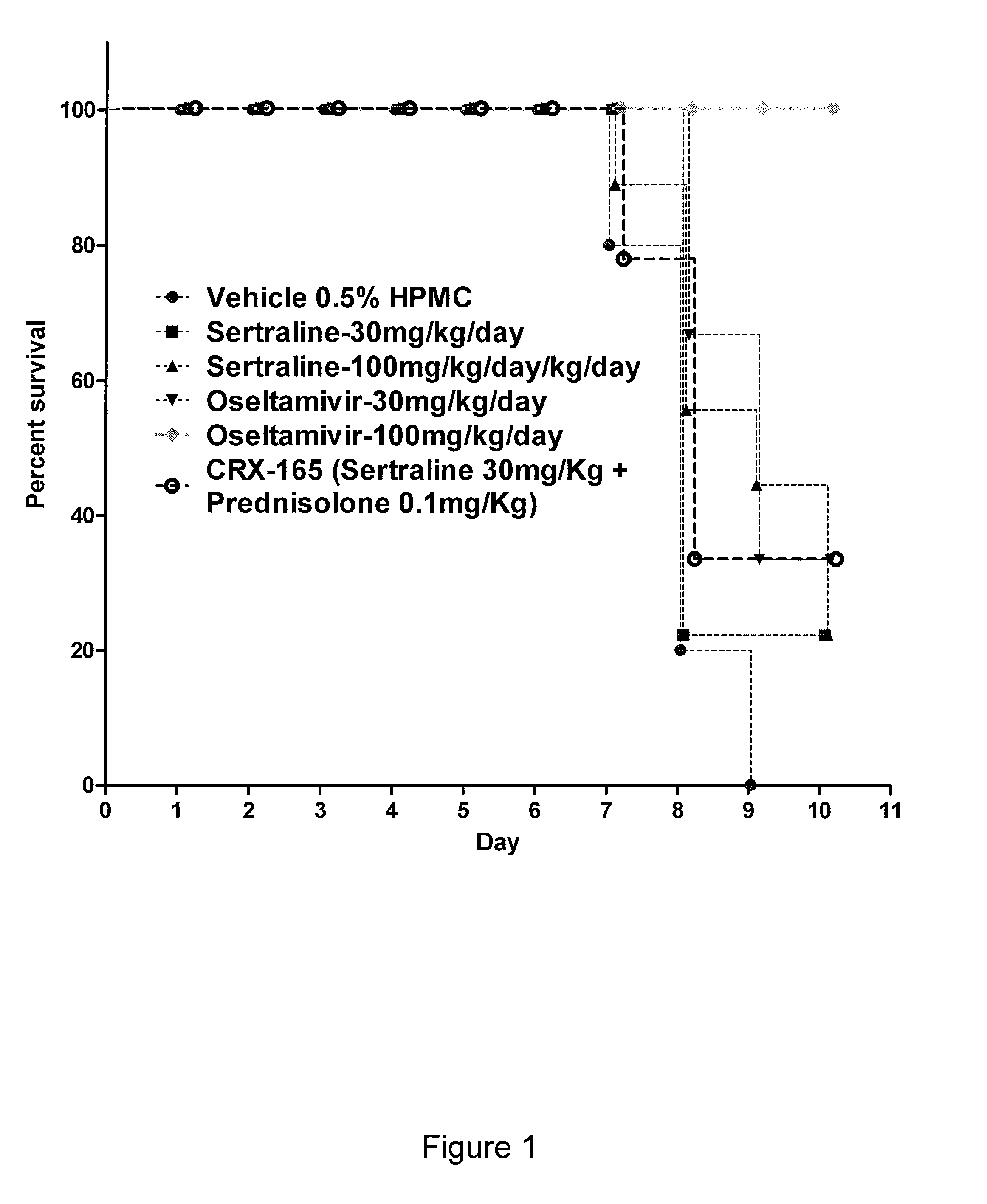
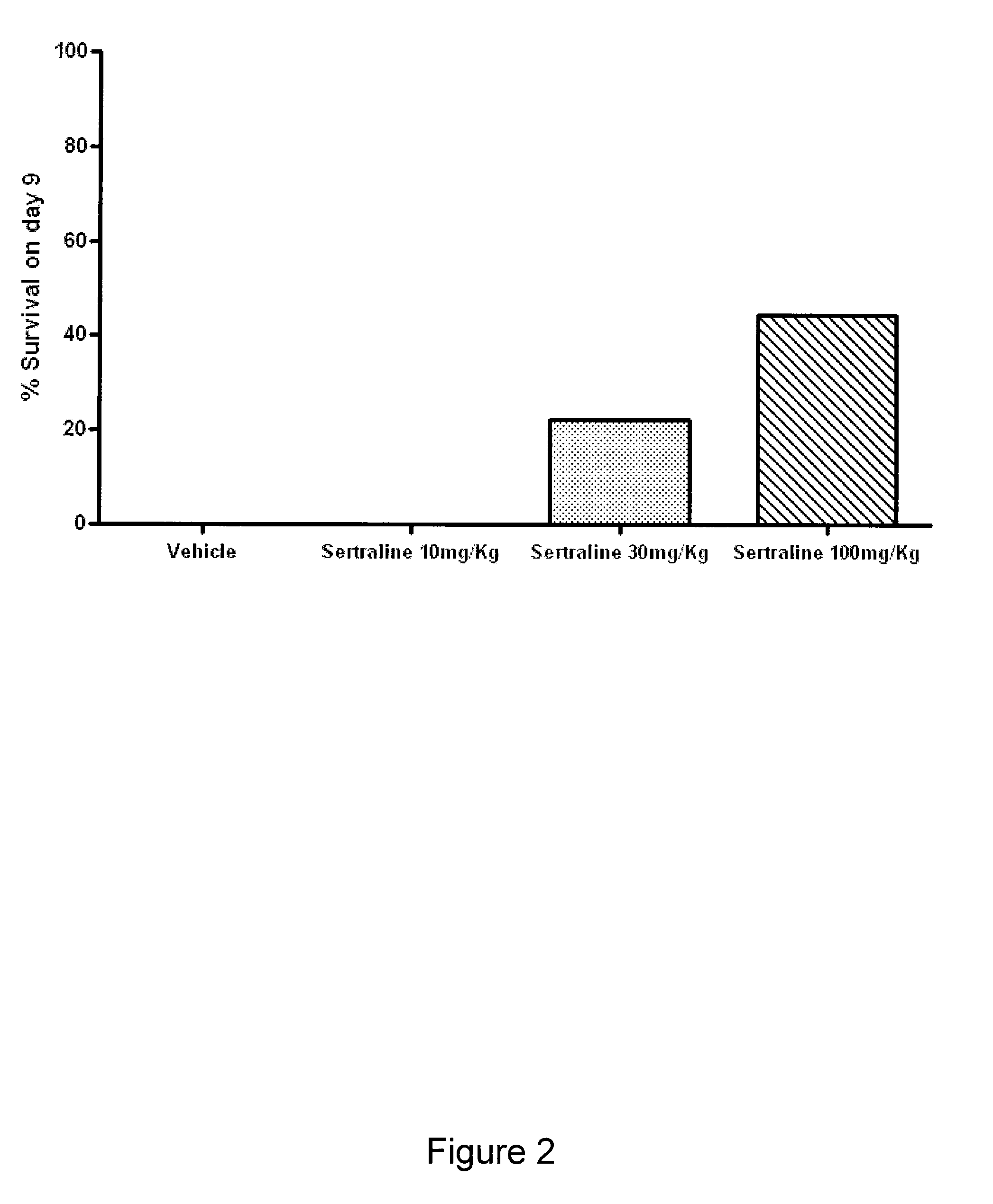
The present invention features compositions, methods, and kits useful in the treatment of viral diseases. In certain embodiments, the viral disease is caused by a single stranded RNA virus, a flaviviridae virus, or a hepatic virus. In particular embodiments, the viral disease is viral hepatitis (e.g., hepatitis A, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, hepatitis D, hepatitis E) and the agent or combination of agents includes sertraline, a sertraline analog, UK-416244, or a UK-416244 analog. Also featured are screening methods for identification of novel compounds that may be used to treat a viral disease.
Owner:EXCRX SINGAPORE PTE +1
Double-stranded and single-stranded RNA molecules with 5 ' triphosphates and their use for inducing interferon
InactiveUS20060178334A1Strong responseInhibits and prevents viral infectionSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsSingle-Stranded RNADouble stranded
Double-stranded and single-stranded RNA molecules, and their use in methods for inducing interferon are provided. The interferon induction provides anti-viral and other medically useful effects, such as anti-cancer effects. Also provided are methods for reducing or inhibiting interferon induction exhibited by such molecules, particularly siRNA and shRNA molecules produced in vitro.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
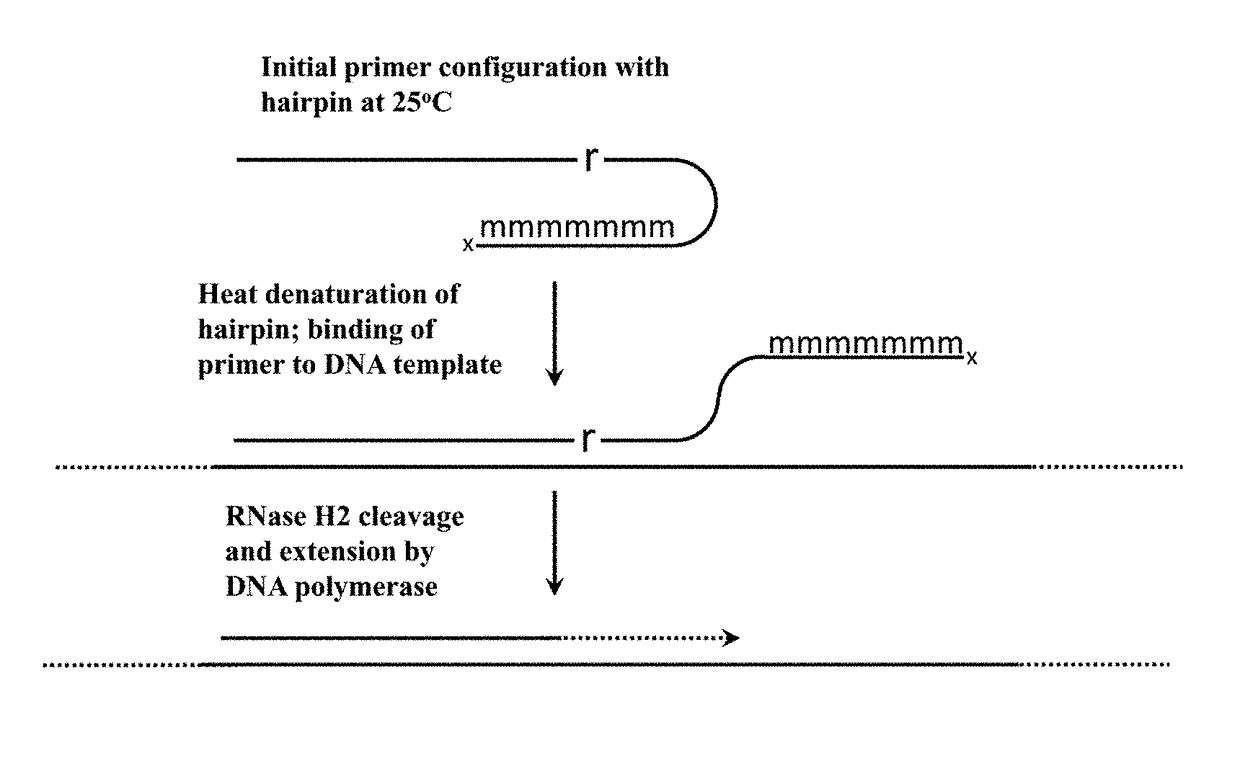
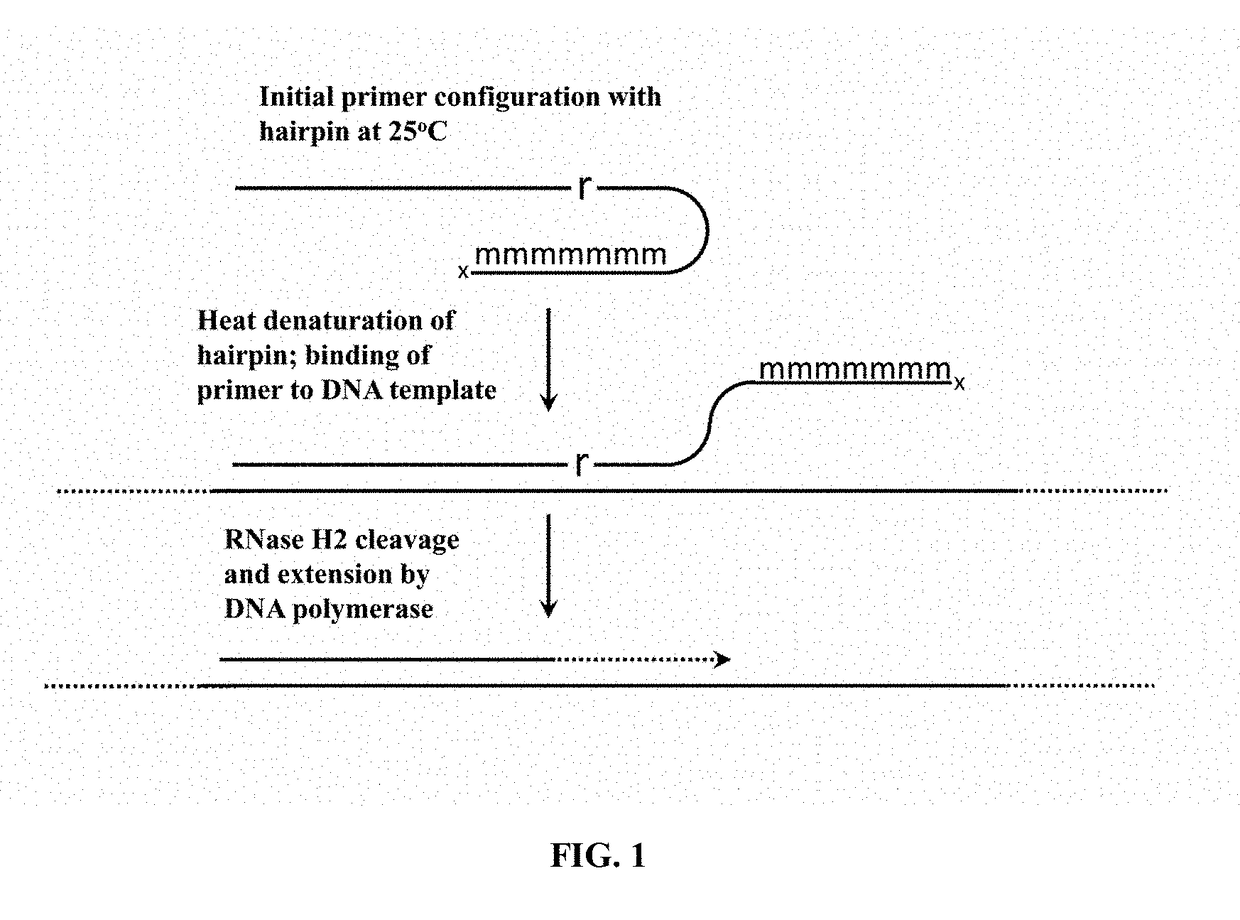
Cleavable hairpin primers
ActiveUS20180057868A1Improve reaction efficiencyStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringSingle-Stranded RNASingle strand
The invention describes composition and methods of use for novel hairpin blocked-cleavable primers. In one embodiment unblocking occurs through action of RNase H2. The method improves the specificity of PCR and reduces primer dimer events, enabling higher level multiplex reactions. Additionally, the invention protects RNA-containing primers from attack by single-strand RNases.
Owner:INTEGRATED DNA TECHNOLOGIES
DNA transfection system for the generation of infectious influenza virus
InactiveUS20050186563A1Improve effectivenessElicit protective immunitySsRNA viruses negative-senseFungiDual promoterSingle-Stranded RNA
The present invention is based on the development of a dual promoter system (preferably a RNA pol I-pol II system) for the efficient intracellular synthesis of viral RNA. The resultant minimal plasmid-based system may be used to synthesize any RNA virus, preferably viruses with a negative single stranded RNA genome. The viral product of the system is produced when the plasmids of the system are introduced into a suitable host cell. One application of the system is production of attenuated, reassortant influenza viruses for use as antigens in vaccines. The reassortant viruses generated by cotransfection of plasmids may comprise genes encoding the surface glycoproteins hemagglutinin and neuraminidase from an influenza virus currently infecting the population and the internal genes from an attenuated influenza virus. An advantageous property of the present invention is its versatility; the system may be quickly and easily adapted to synthesize an attenuated version of any RNA virus. Attenuated or inactivated RNA viruses produced by the present invention may be administered to a patient in need of vaccination by any of several routes including intranasally or intramuscularly.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
Methods and reagents to detect and characterize norwalk and related viruses
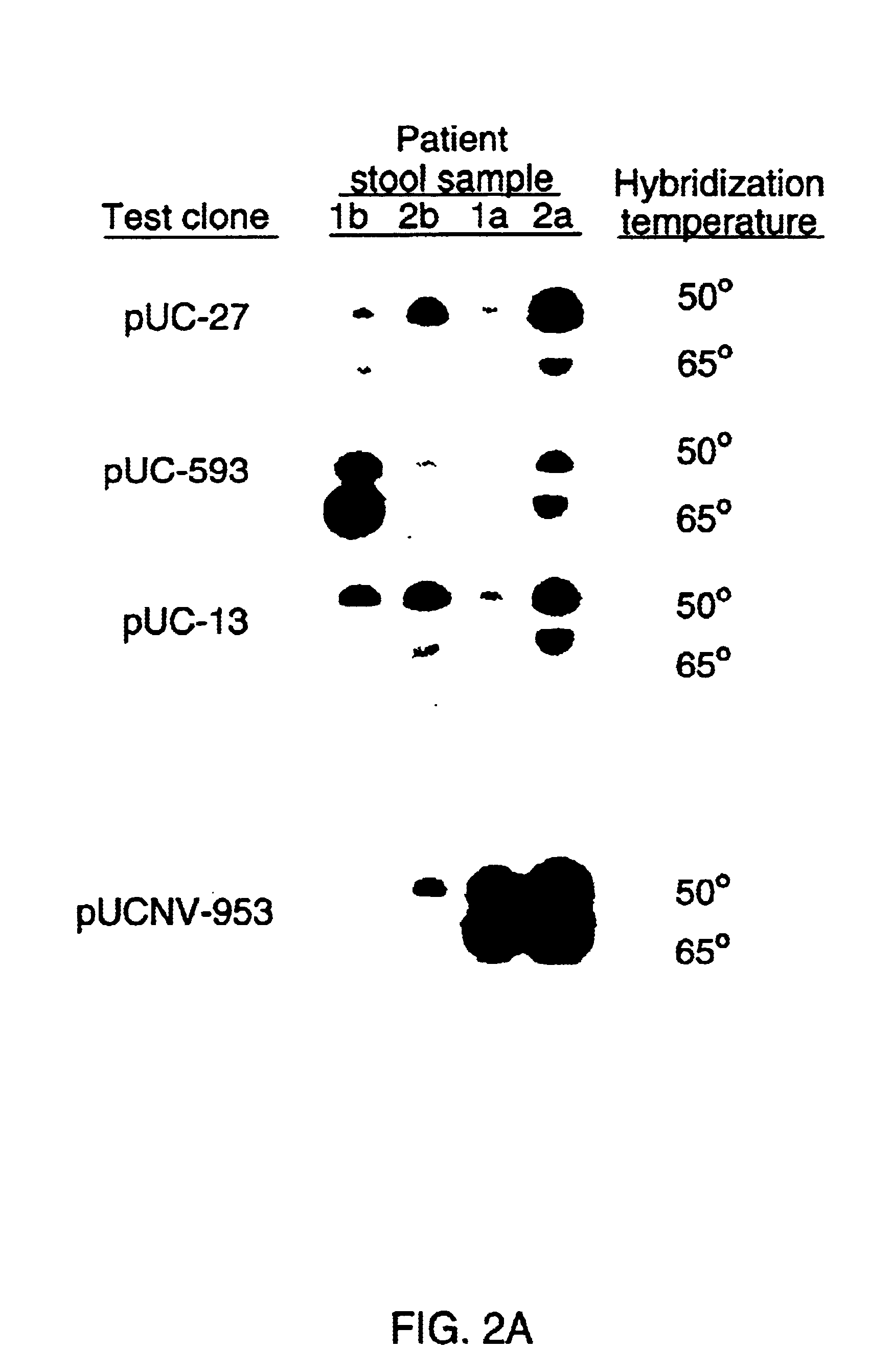
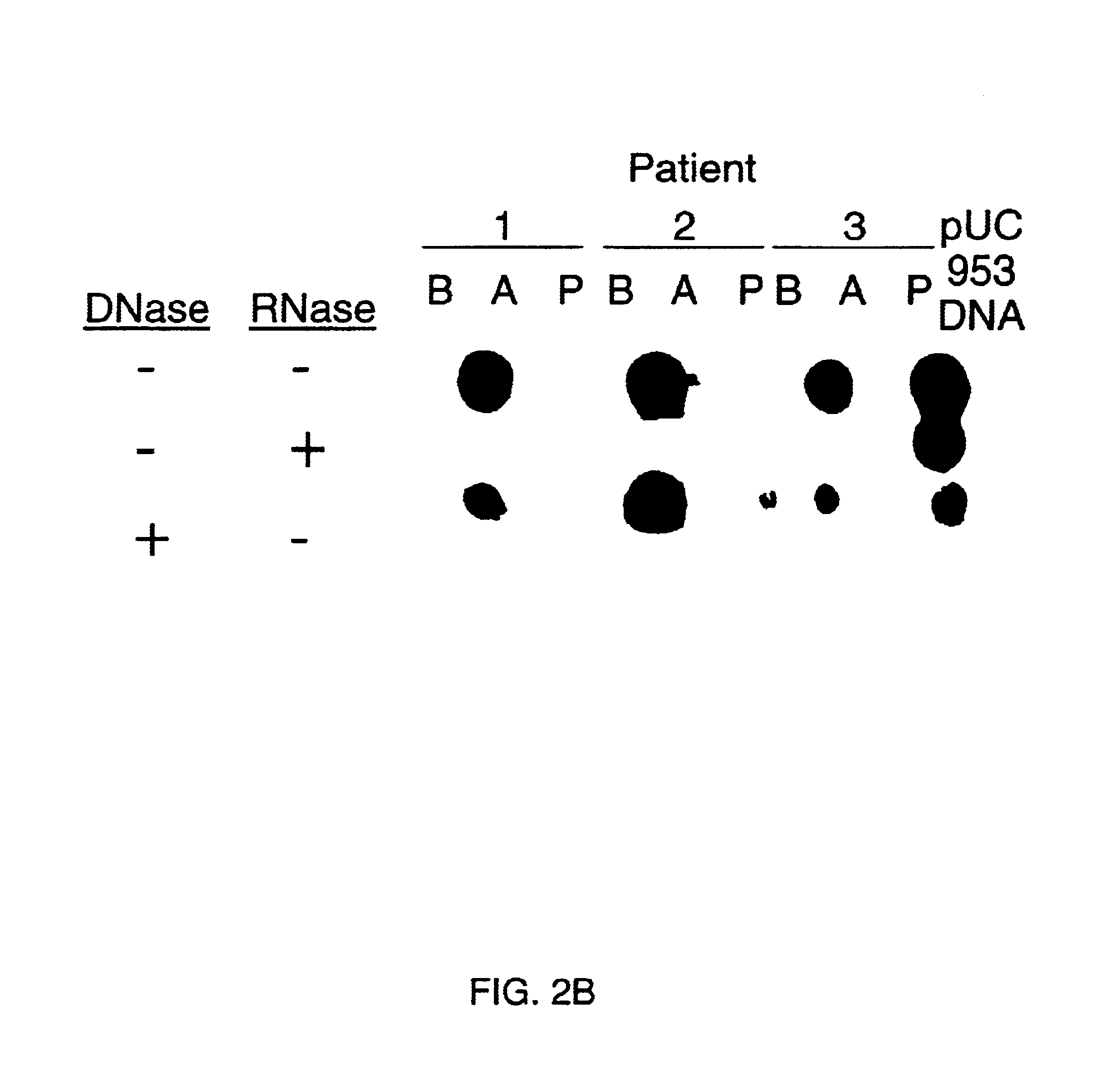
Double-stranded cDNA was synthesized from nucleic acid extracted from Norwalk virus purified from stool specimens of volunteers. One clone was isolated from a cDNA library constructed in a pUC-13 vector after amplification of the cDNA. The specificity of this cDNA (pUCNV-953) was shown by hybridization assays. The cDNA reacted with post (but not pre-) infection stool samples from Norwalk volunteers and with highly purified Norwalk virus, but not with other common enteric viruses such as hepatitis A virus and rotavirus. Finally, the probe detected virus in the same fractions of CsCl gradients in which viral antigen was detected using a specific Norwalk virus radioimmunoassay, and particles were detected by immune electron microscopy. Single-stranded RNA probes derived from the DNA clone after subcloning into an in vitro transcription vector were also used to show that the Norwalk virus contains a ssRNA genome of about 8 kb in size. The original clone was also used to detect additional cDNAs which represent at least 7 kb of nucleic acid of the Norwalk genome. The availability of a Norwalk-specific cDNA and the first partial genome sequence information allow rapid cloning of the entire genome and of establishment of sensitive diagnostic assays. Such assays can be based on detection of Norwalk virus nucleic acid or Norwalk viral antigen using polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies to proteins expressed from the cDNA or to synthetic peptides made based on the knowledge of the genome sequence. Assays using proteins deduced from the Norwlk virus genome and produced in expression systmes can measure antibody responses. Vaccines made by recombinant DNA technology are now feasible.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Antigen Detection Kit and Method
InactiveUS20110027772A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSingle-Stranded RNAAntigen
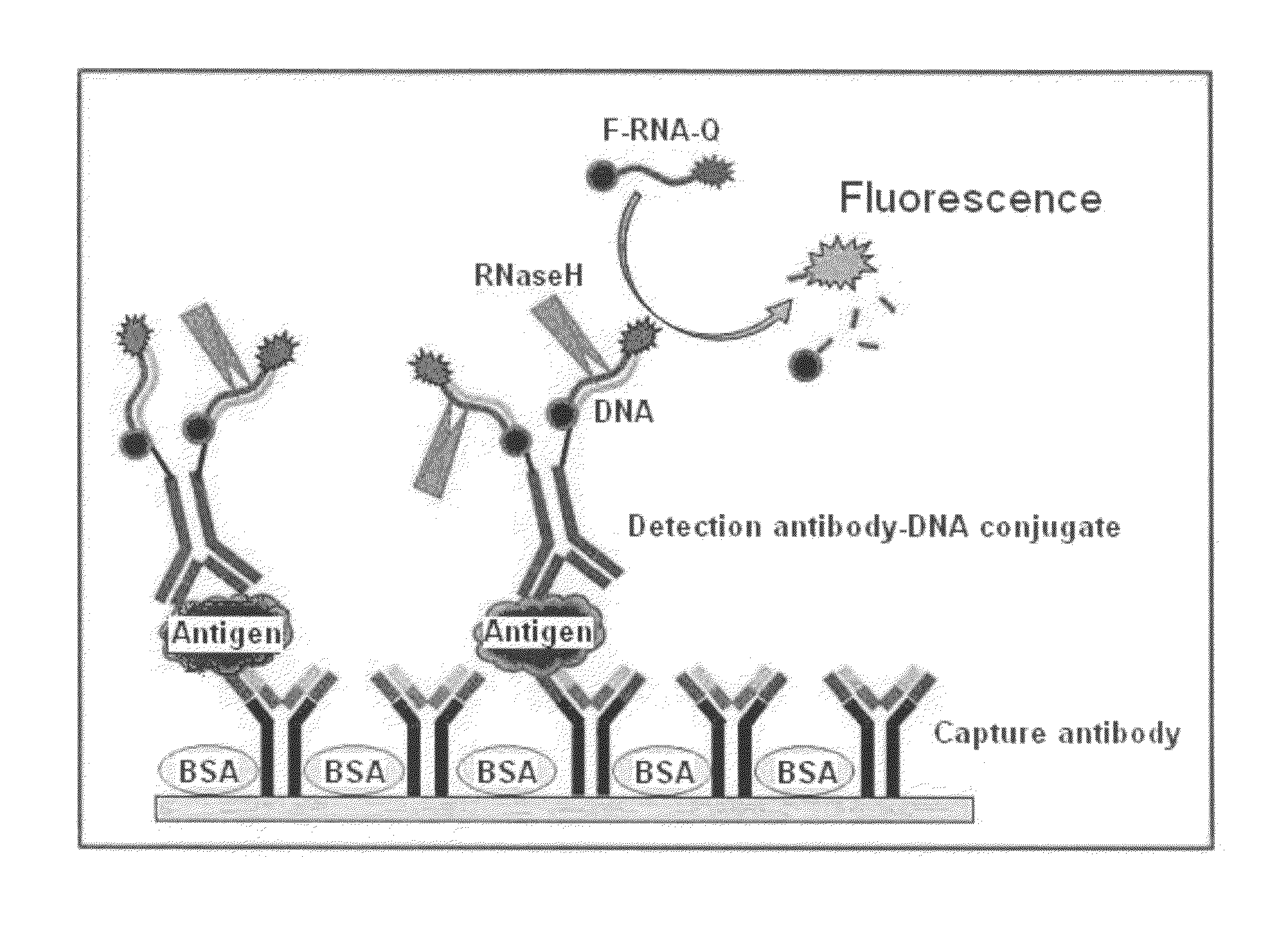
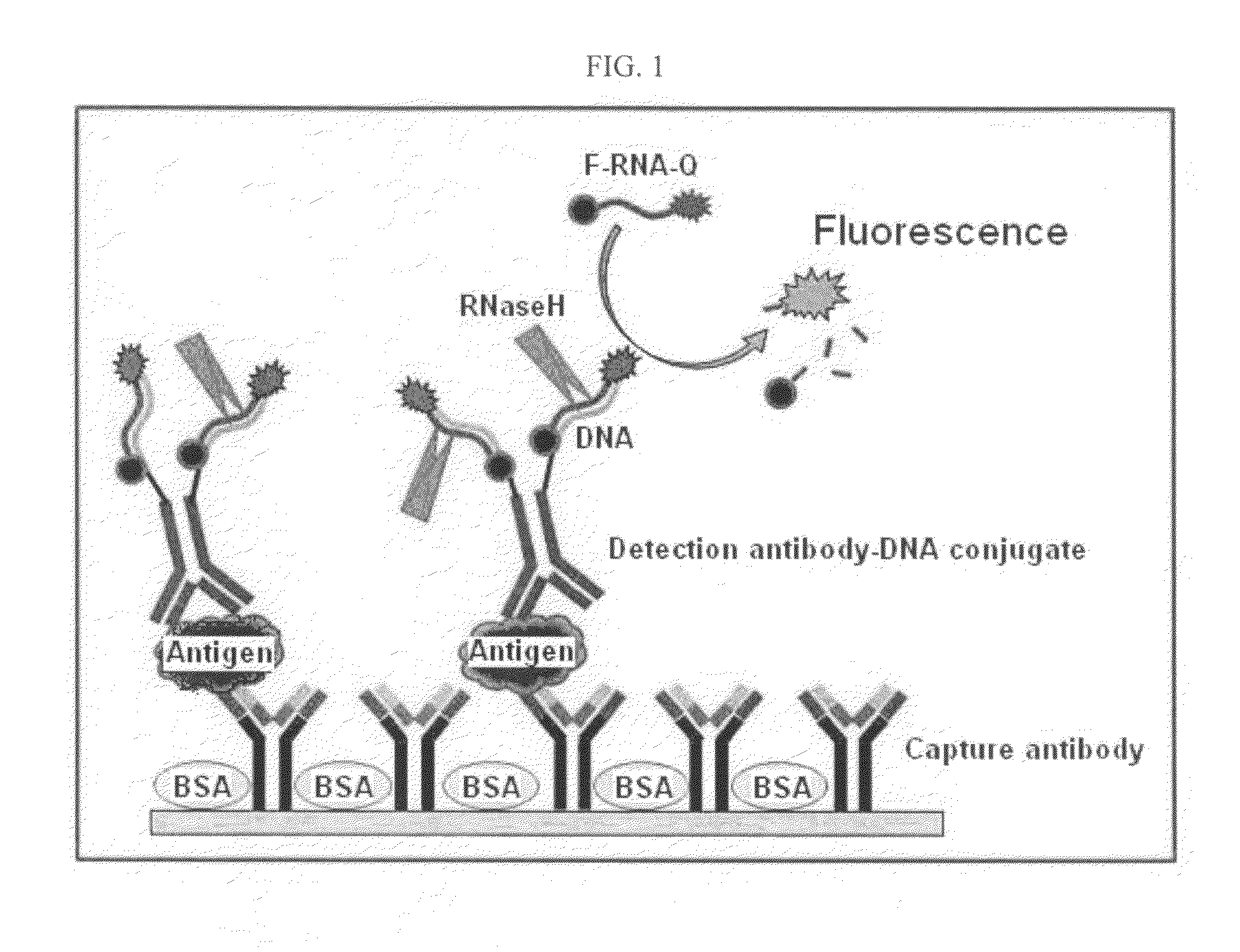
An antigen detection kit and an antigen detection method using the same are provided. The antigen detection kit comprises a capture antibody, a detection antibody bound to a single stranded DNA oligonucleotide, a single stranded RNA oligonucleotide complementary sequence to the DNA oligonucleotide, and an RNase.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
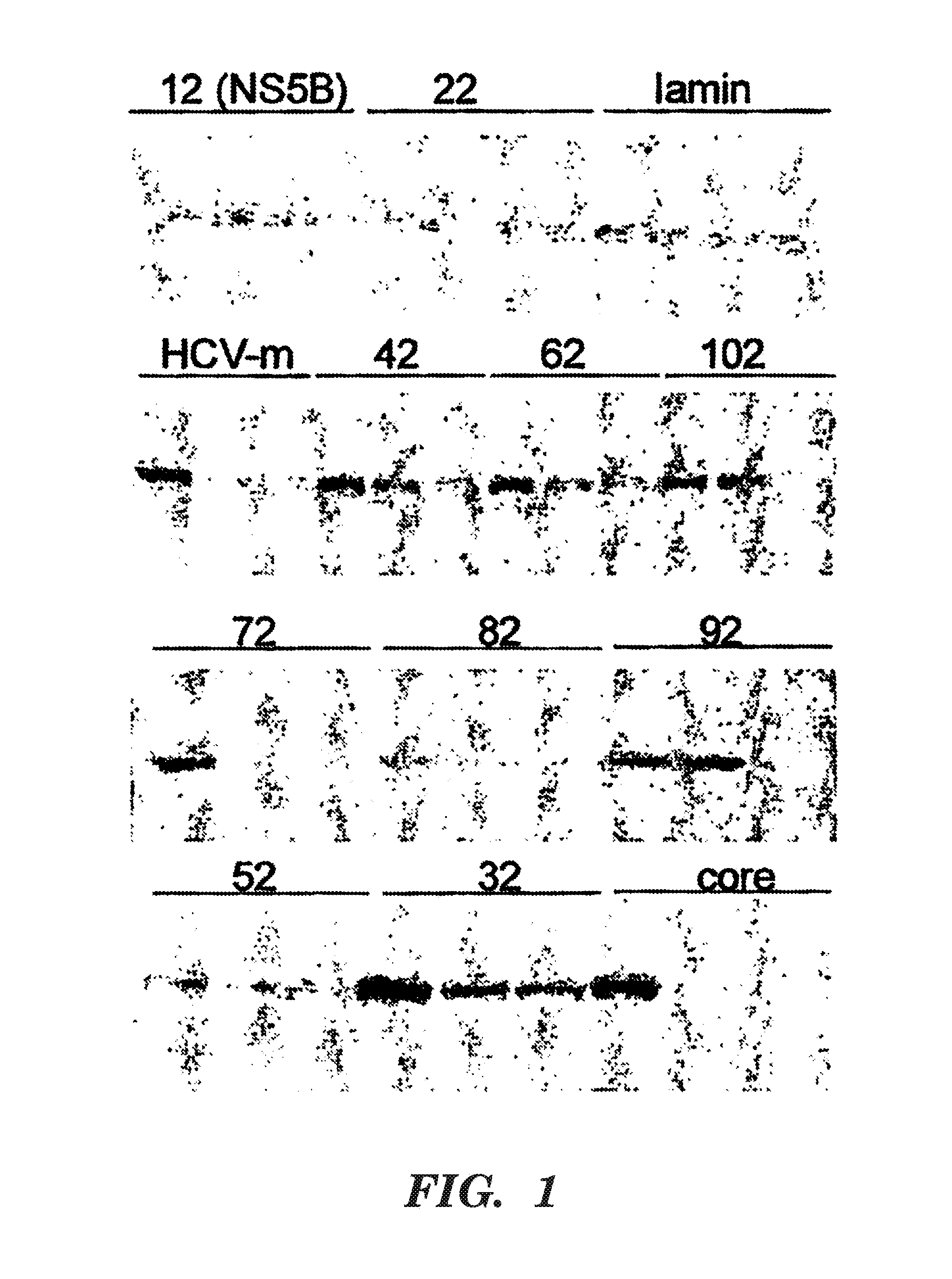
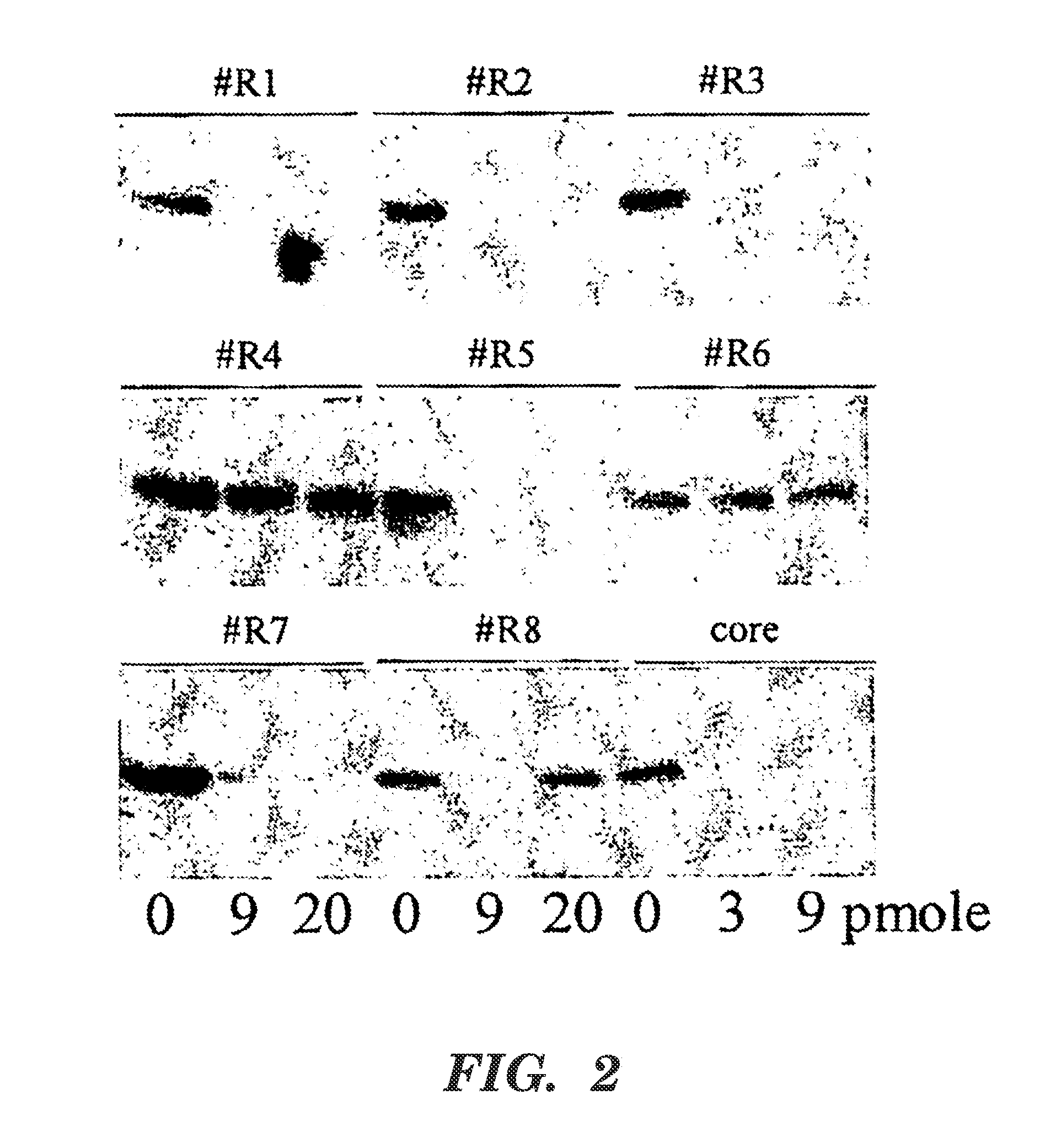
Short interfering RNA as an antiviral agent for hepatitis C
InactiveUS20050043266A1Useful in treatmentSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsSingle-Stranded RNAMessenger RNA
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a major cause of chronic liver disease and affects over 270 million individuals worldwide. The HCV genome is a single-stranded RNA that functions as both a messenger RNA and replication template, making it an attractive target for the study of RNA interference. Double-stranded short interfering RNA (siRNA) molecules designed to target the HCV genome are disclosed herein.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Virus causing respiratory tract illness in susceptible mammals
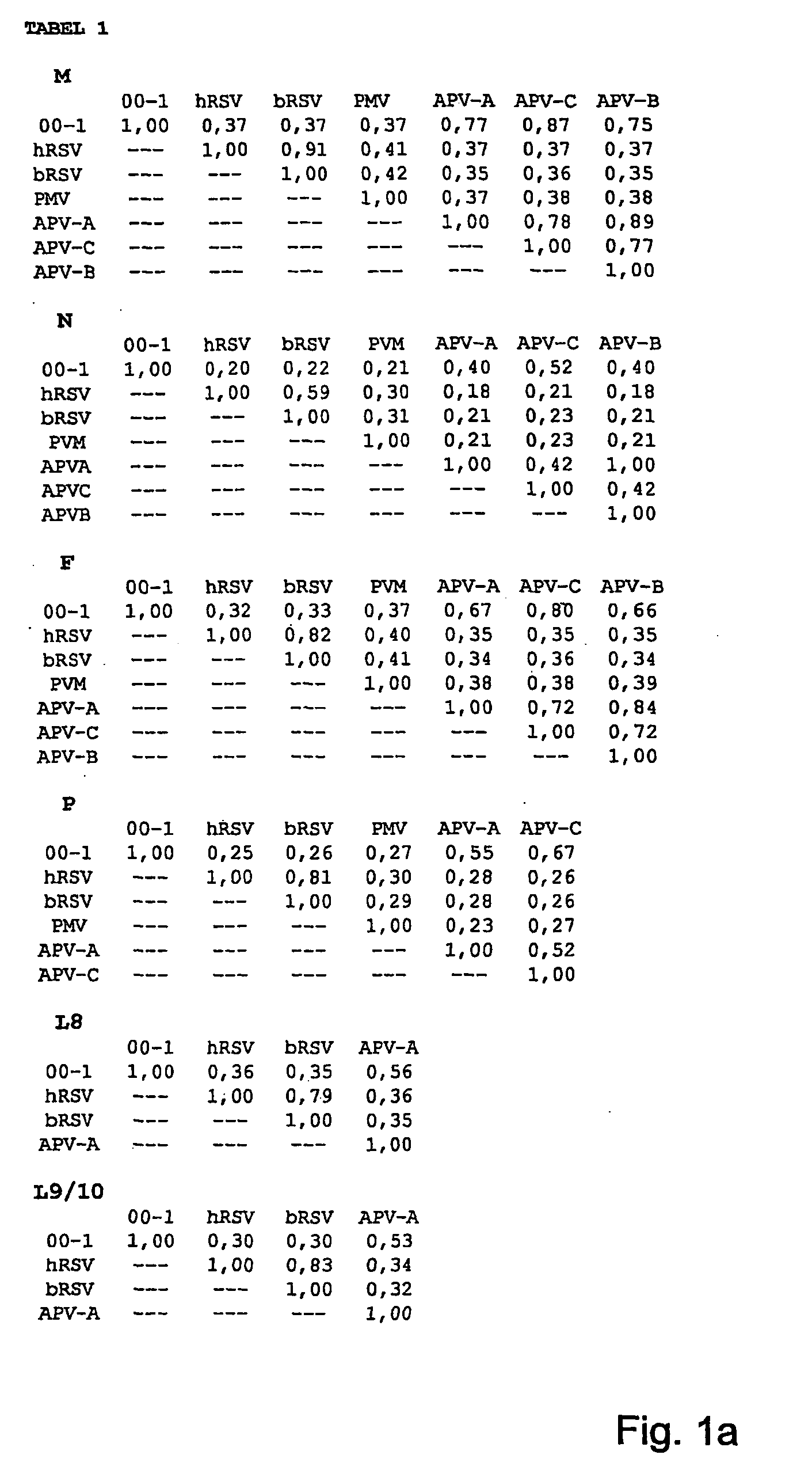
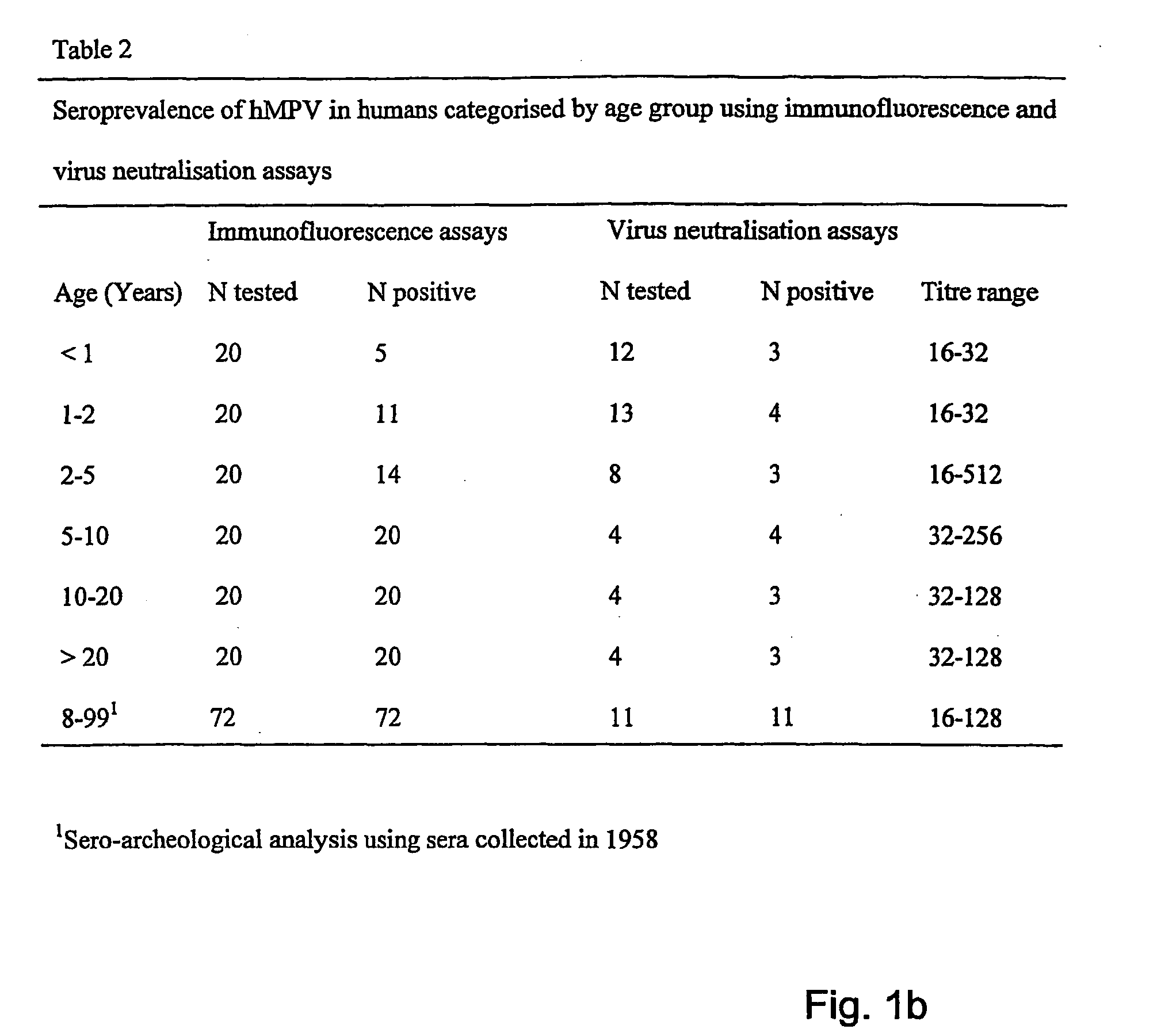
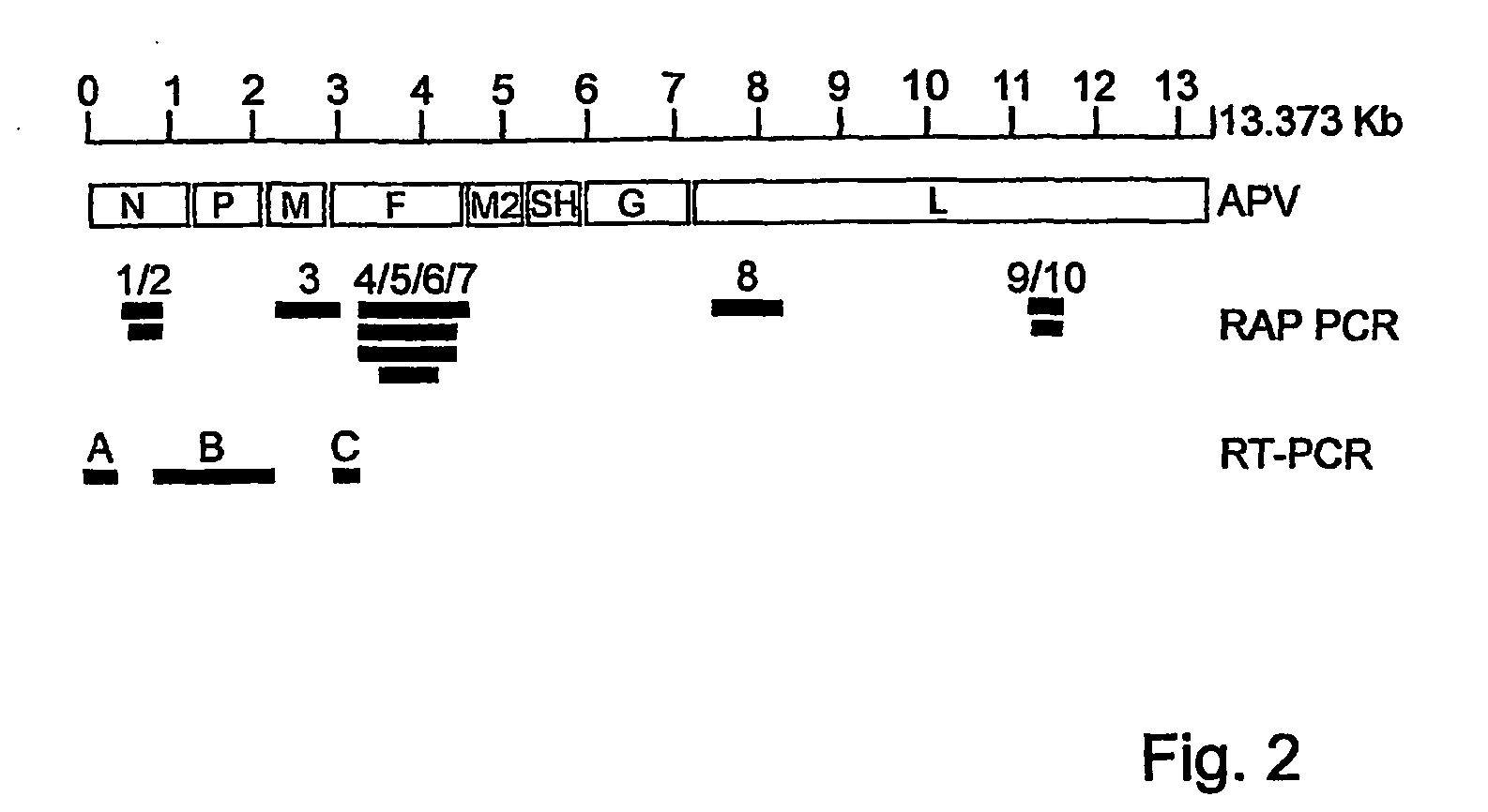
The invention relates to the field of virology. The invention provides an isolated essentially mammalian negative-sense single stranded RNA virus (MPV) within the sub-family Pneumovirinae of the family Paramyxoviridae and identifiable as phylogenetically corresponding to the genus Metapneumovirus and components thereof.
Owner:ERASMUS UNIV MEDICAL CENT ROTTERDAM ERASMUS MC
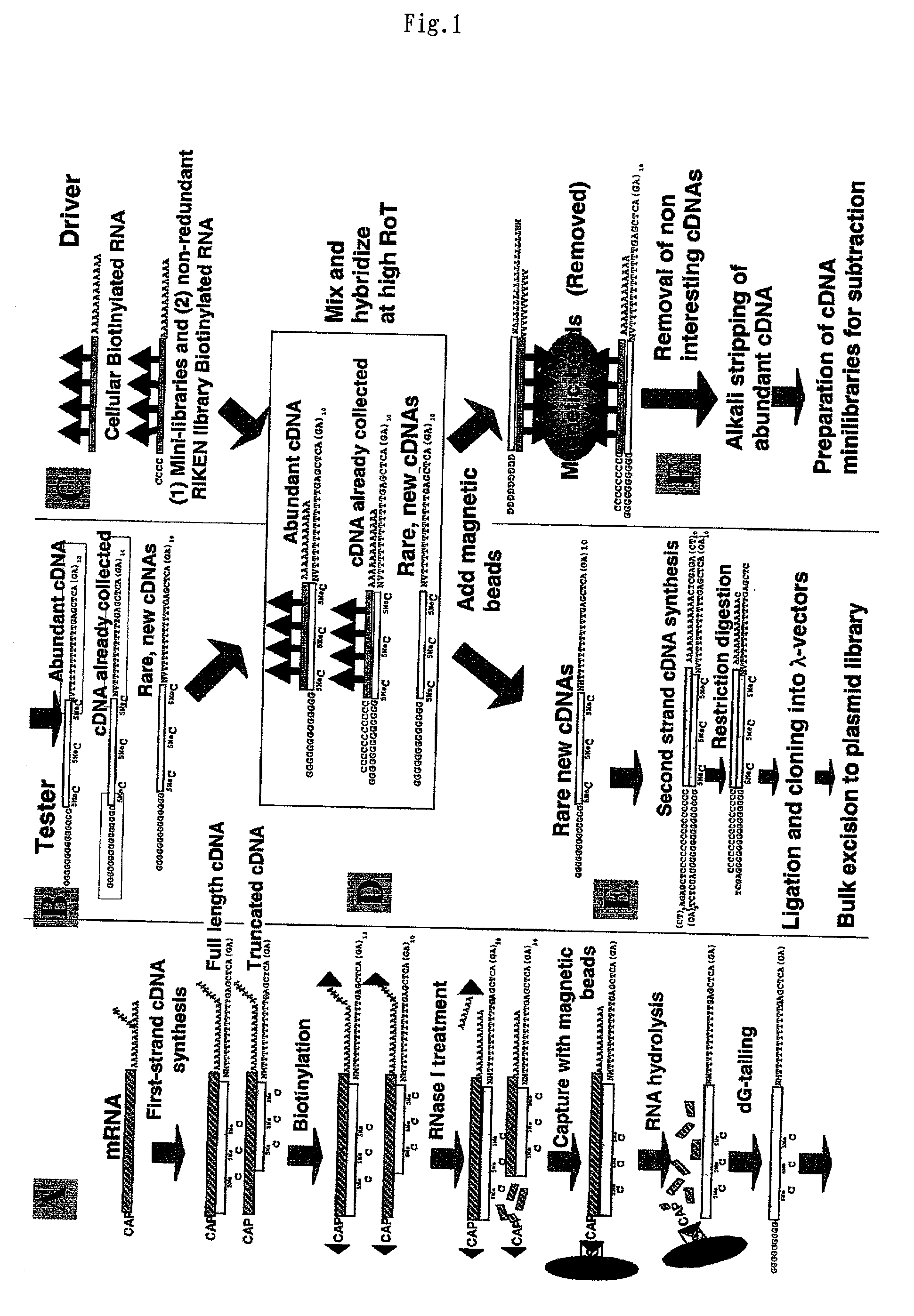
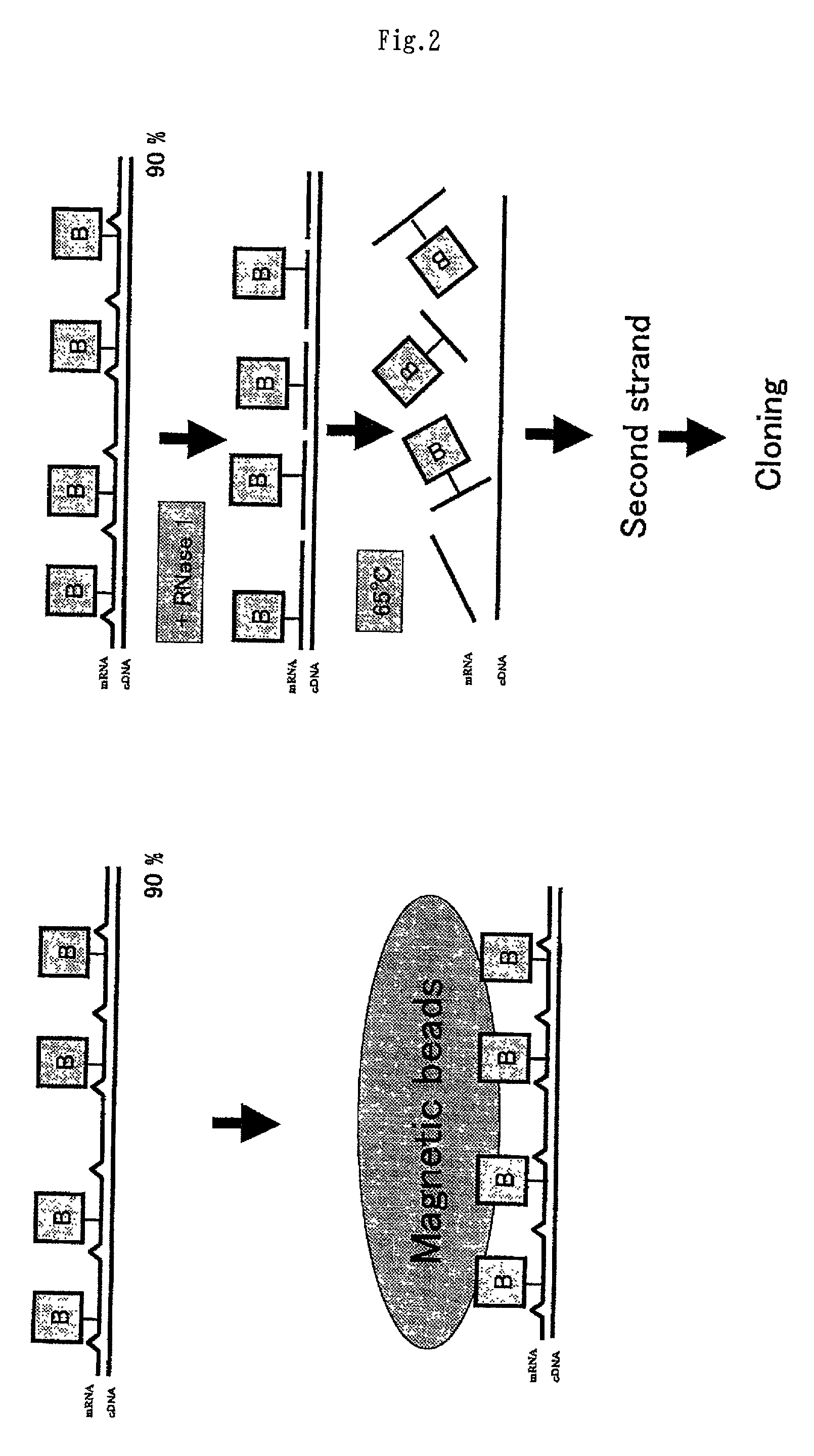
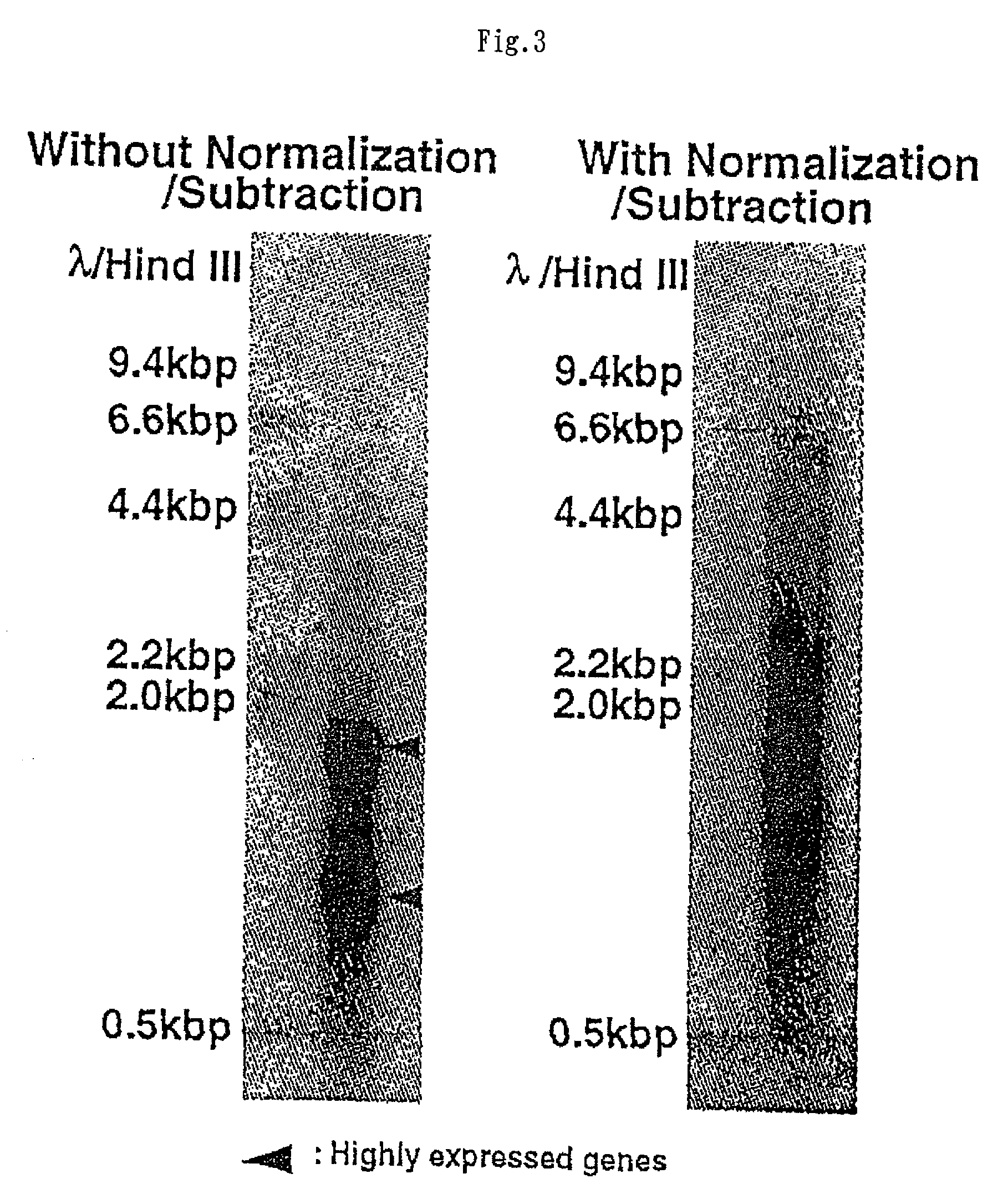
Method of preparing normalized and/or subtracted cDNA
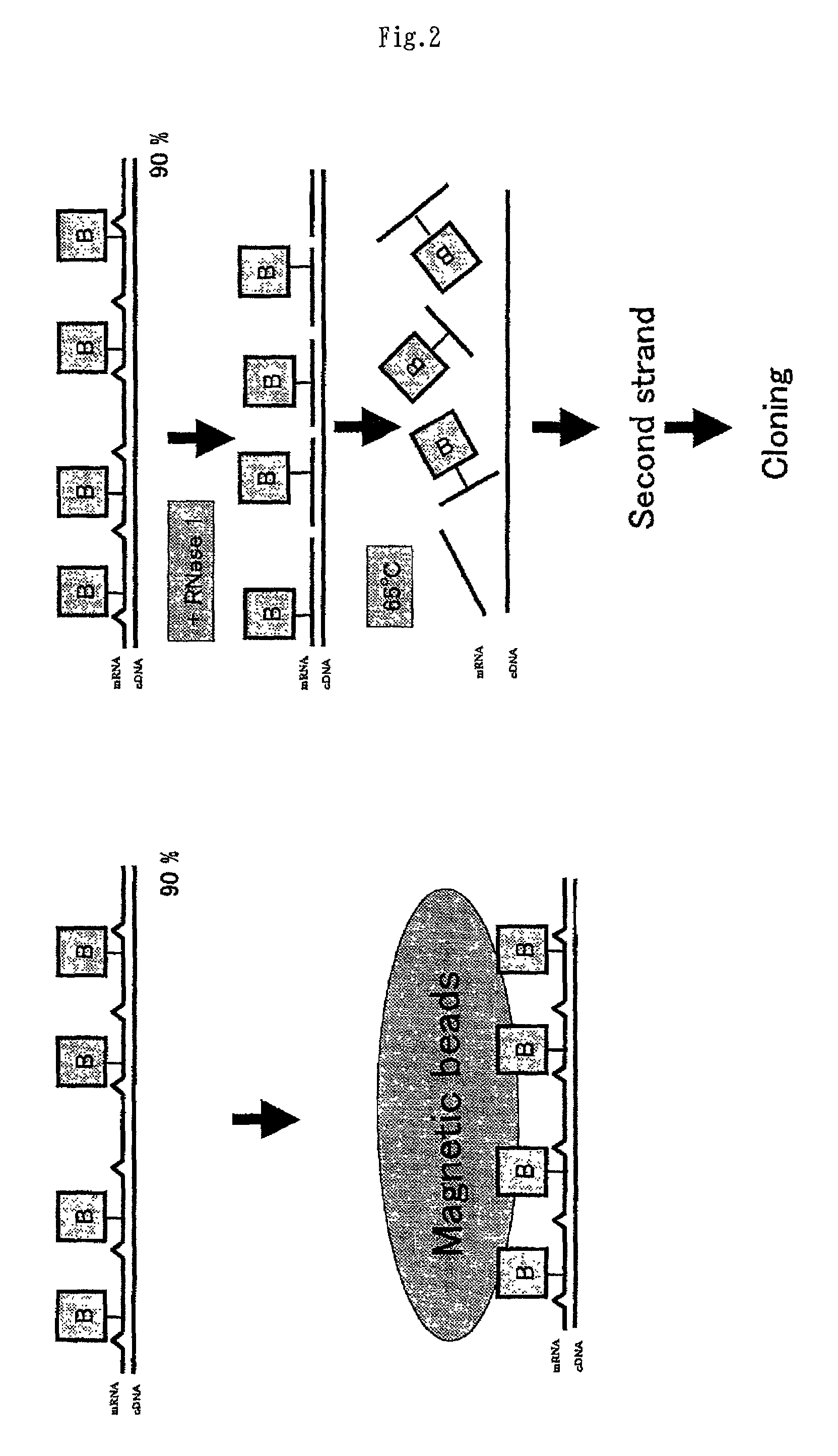
InactiveUS20020106666A1Avoid disadvantagesImproving and subtractionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-Stranded RNAFull length cdna
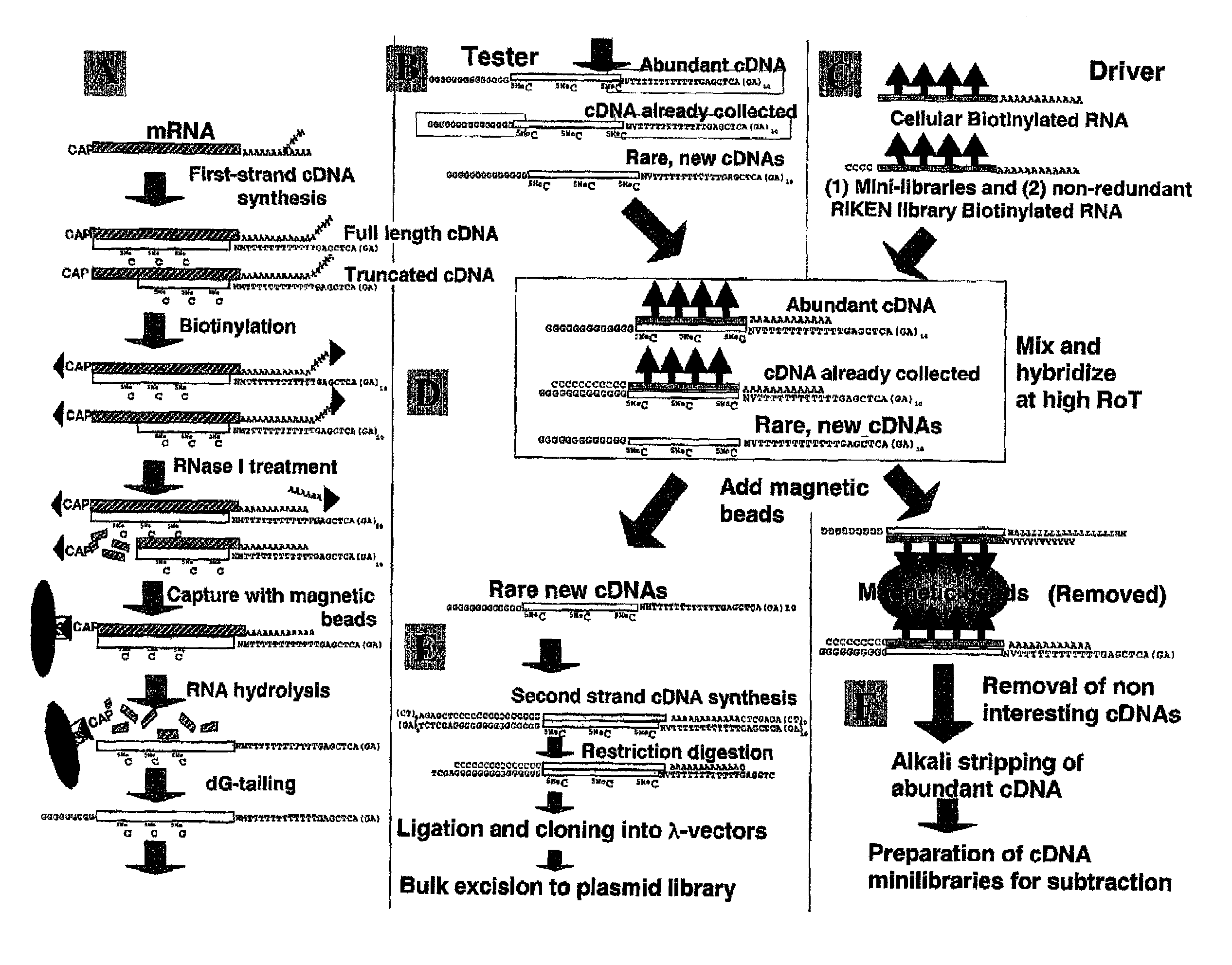
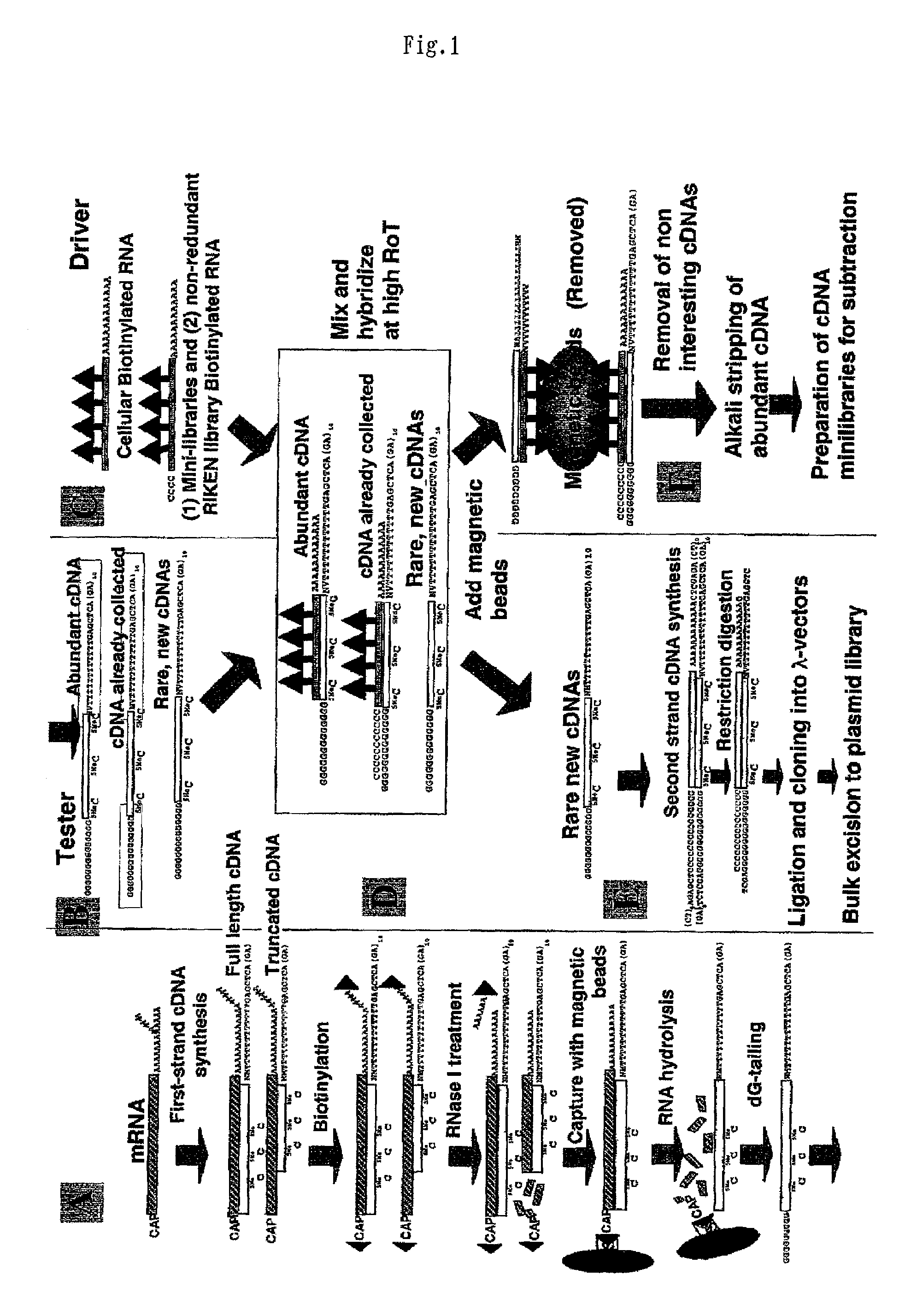
A method of preparing normalized and / or subtracted cDNA; a method in which the cDNA that is normalized and / or subtracted is in the form of uncloned cDNA (cDNA tester); a method of preparing normalized and / or subtracted cDNA comprising the steps of: (a) preparing cDNA tester; (b) preparing normalization and / or subtraction RNA driver; (c) conducting normalization and / or subtraction in two steps in any order, or conducting normalization / subtraction as a single step and mixing the normalization / subtraction RNA driver with said cDNA tester; (d) adding an enzyme capable of cleaving single strand sites on RNA drivers nonspecifically bound to cDNA tester; (e) removing said single strand RNA driver cleaved in step d) from the tester and removing tester / driver hybrids; and (f) recovering the normalized and / or subtracted cDNA; and a method of efficiently preparing normalized and / or subtracted long-chain, full-coding, and full-length cDNA libraries are provided.
Owner:YOSHIHIDE HAYASHIZAKI +2
Antigen detection kit and method
InactiveCN101988920AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingSingle-Stranded RNACapture antibody
An antigen detection kit and an antigen detection method using the same are provided. The antigen detection kit comprises a capture antibody, a detection antibody bound to a single stranded DNA oligonucleotide, a single stranded RNA oligonucleotide complementary sequence to the DNA oligonucleotide, and an RNase.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Methods for cleaving DNA with nucleotide integrases
The present invention provides new methods, employing a nucleotide integrase, for cleaving single-stranded RNA substrates, single-stranded DNA substrates, and double- stranded DNA substrates at specific sites and for inserting a nucleic acid molecule into the cleaved substrate. One method uses a nucleotide integrase to cleave one strand of a double-stranded DNA substrate. The method comprises the steps of: providing a nucleotide integrase comprising a group II intron RNA having two hybridizing sequences that are capable of hybridizing with two intron RNA binding sequences on the one strand of the DNA substrate, and a group II-intron encoded protein which binds to a first sequence element of the substrate; and reacting the nucleotide integrase with the double-stranded DNA substrate under conditions that permit the nucleotide integrase to cleave the one strand of the DNA substrate and to insert the group II intron RNA into the cleavage site. The method of cleaving both strands of a double-stranded DNA substrate comprises the steps of: providing a nucleotide integrase comprising a group II intron RNA having two hybridizing sequences that are capable of hybridizing with two intron RNA binding sequences on one strand of the substrate, and a group II-intron encoded protein that is capable of binding to a first sequence element and to a second sequence element in the recognition site of the substrate; and reacting the nucleotide integrase with the double-stranded DNA substrate such that the nucleotide integrase cleaves both strands of the DNA substrate and inserts the group II intron RNA into the cleavage site of the one strand. The method for cleaving a single-stranded nucleic acid substrate comprises the steps of: providing a nucleotide integrase having two hybridizing sequences that are capable of hybridizing with two intron RNA-binding sequences on the single-stranded substrate, and a group II intron encoded protein; and reacting the nucleotide integrase with the single stranded nucleic acid substrate for a time and at a temperature sufficient to allow the nucleotide integrase to cleave the substrate and to attach the group II intron RNA molecule thereto.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
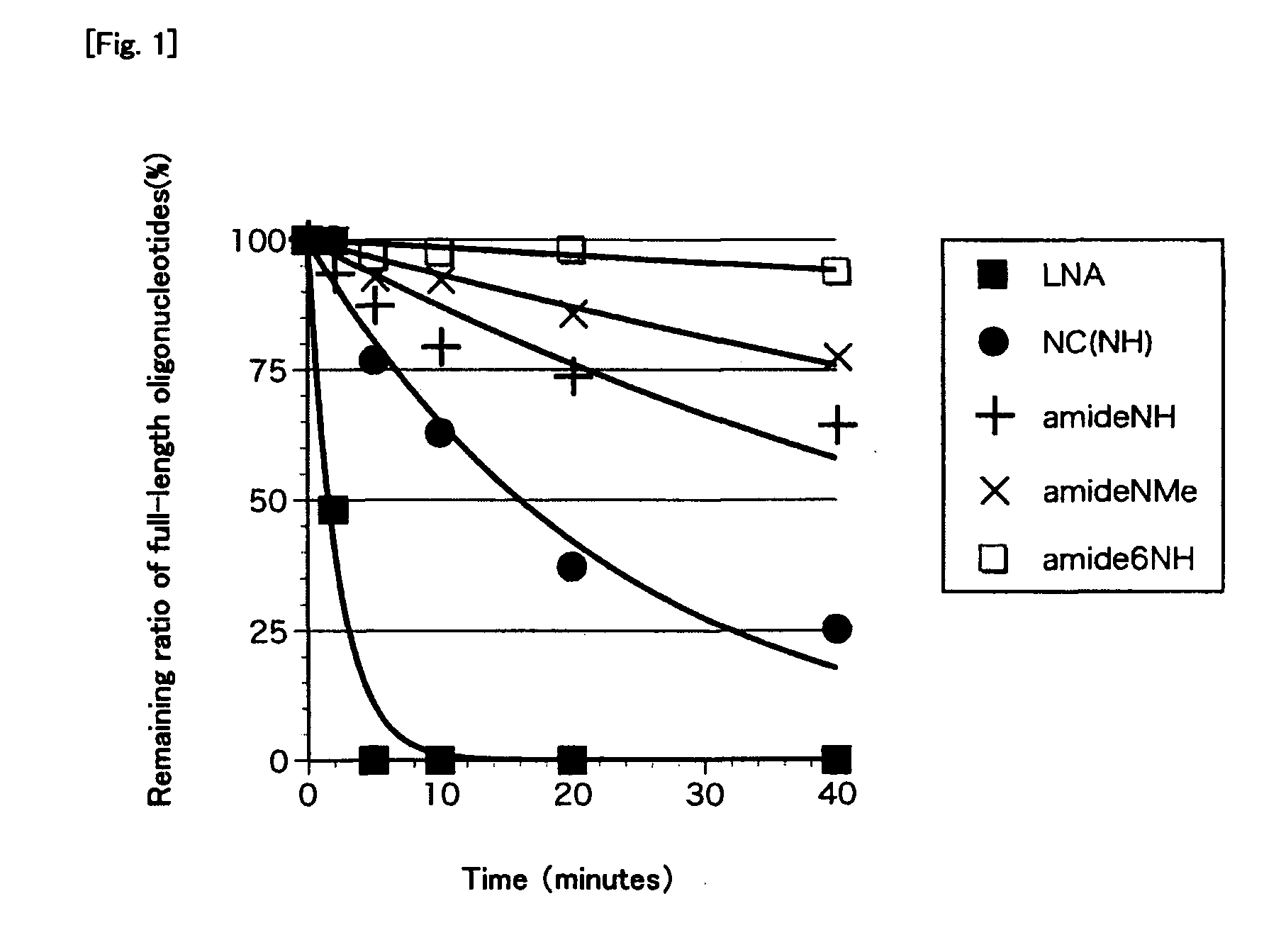
Bridged artificial nucleoside and nucleotide
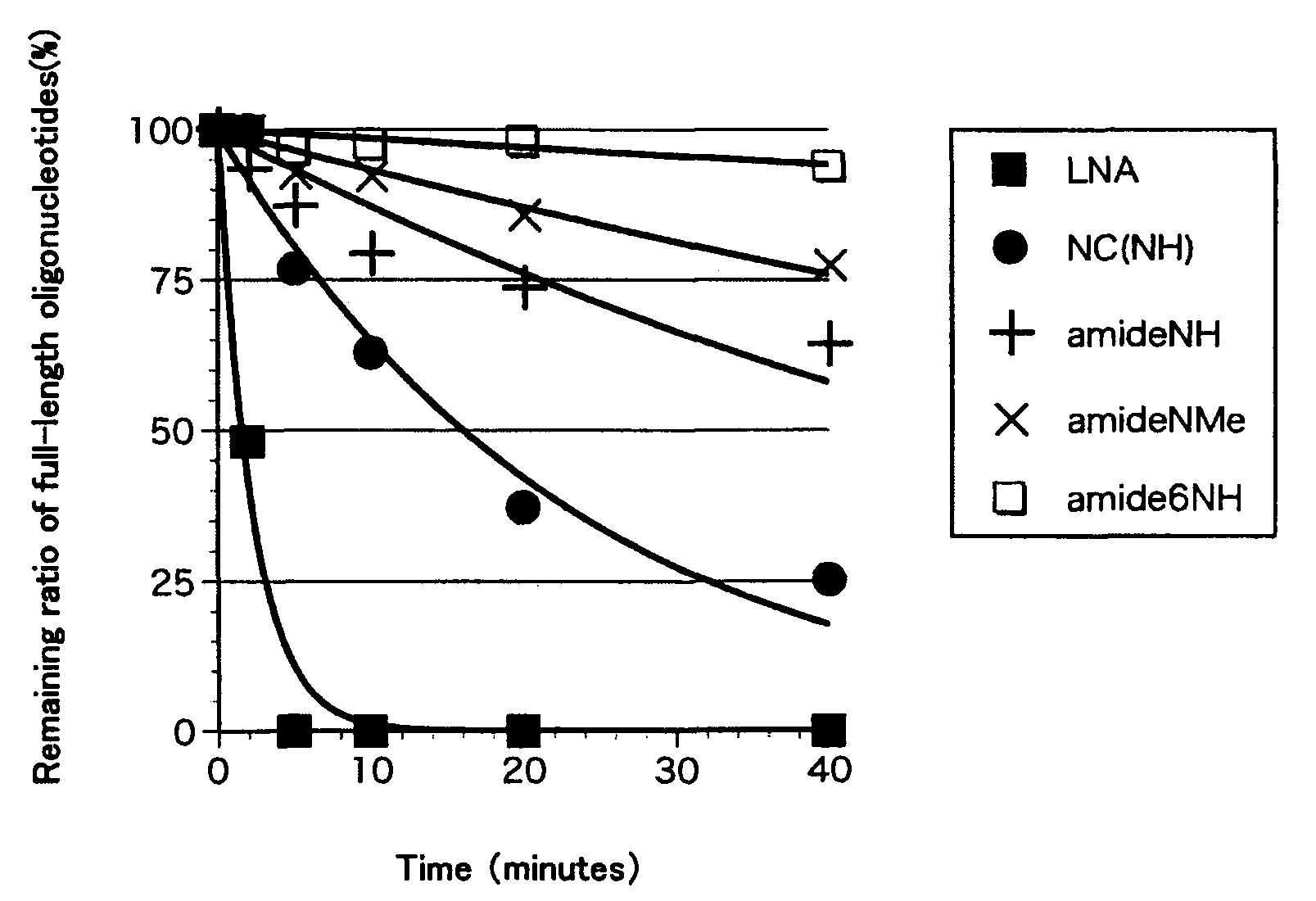
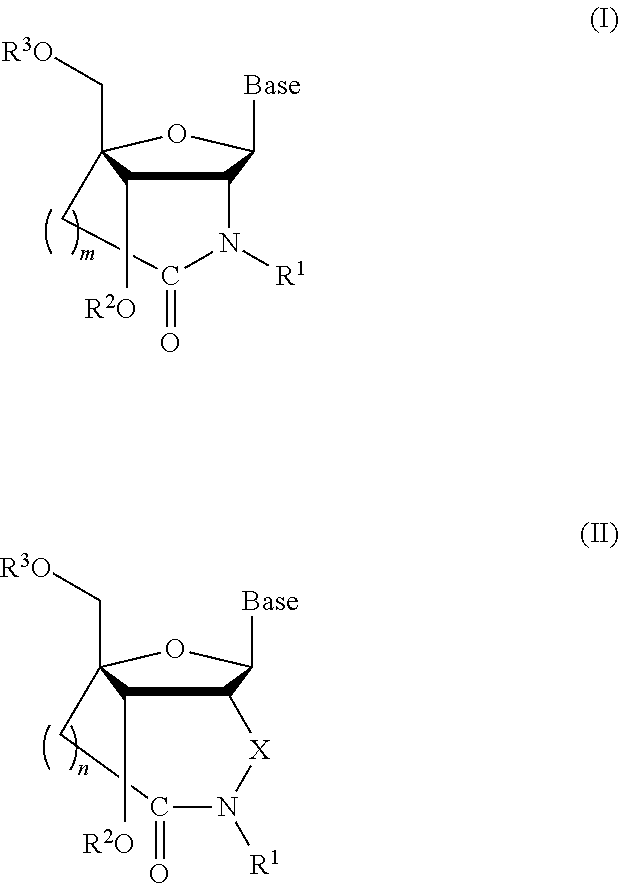
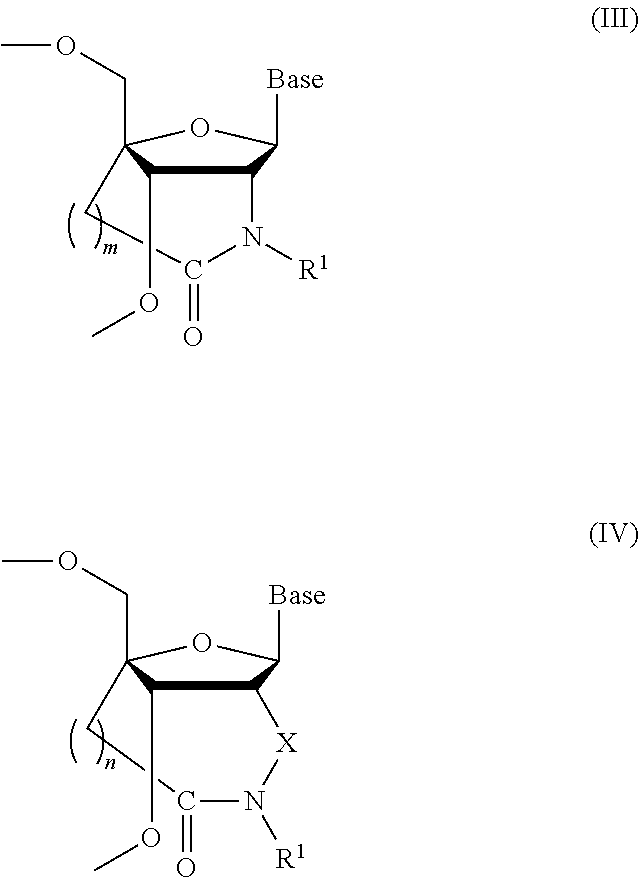
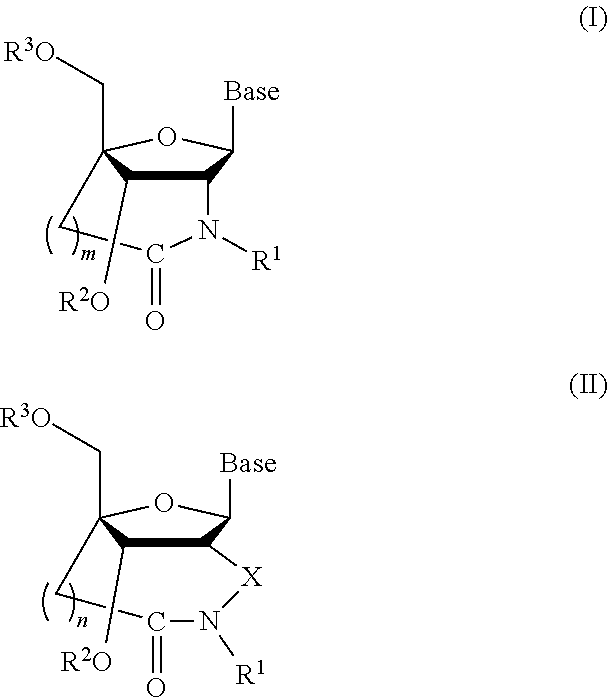
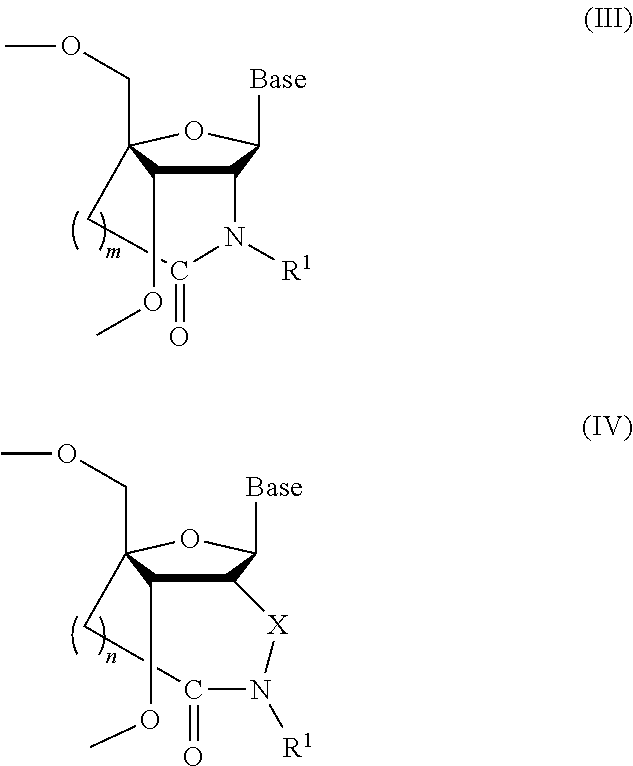
ActiveUS8541562B2Increase resistanceSugar derivativesActivity regulationSingle-Stranded RNANucleotide
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
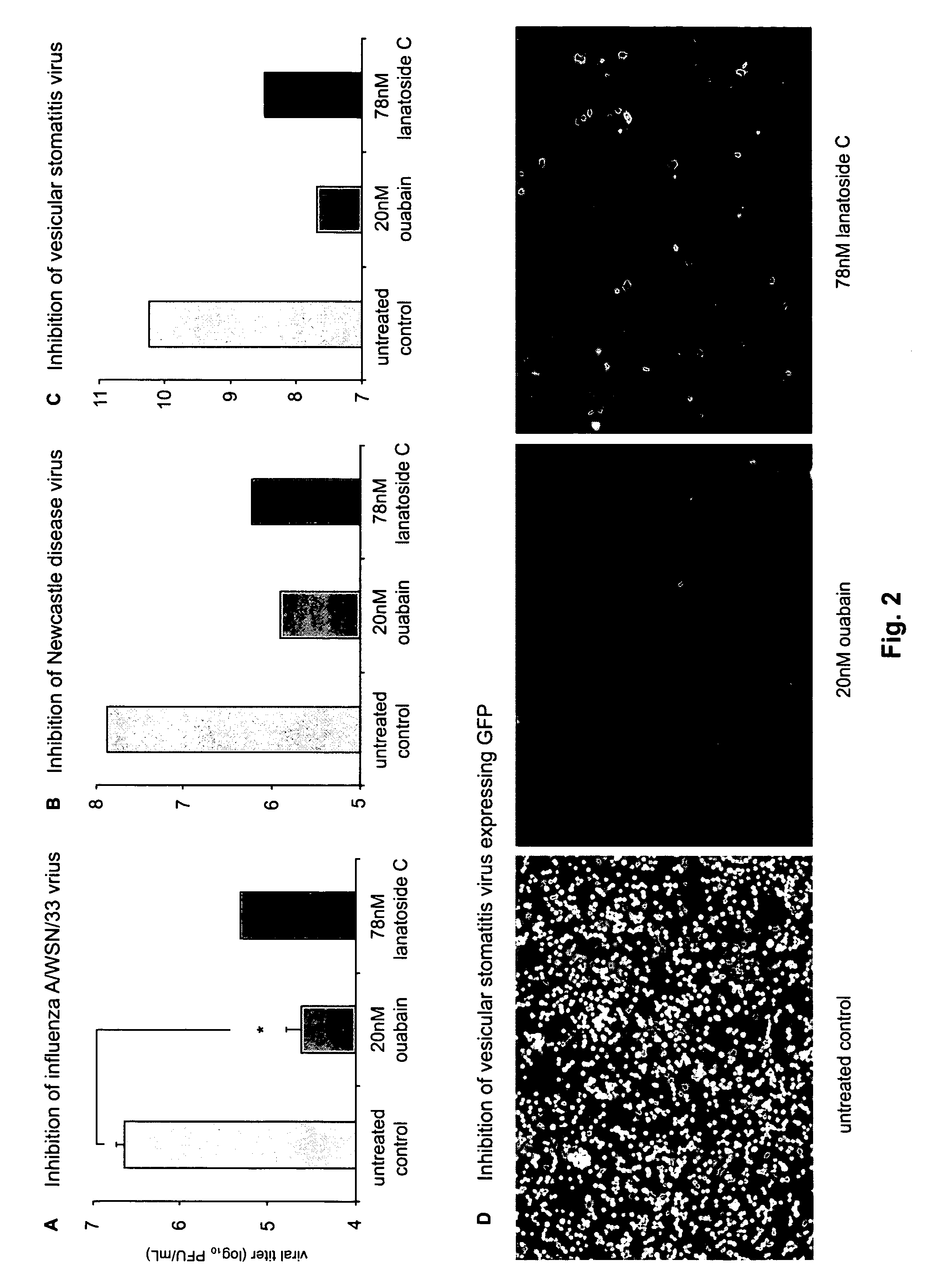
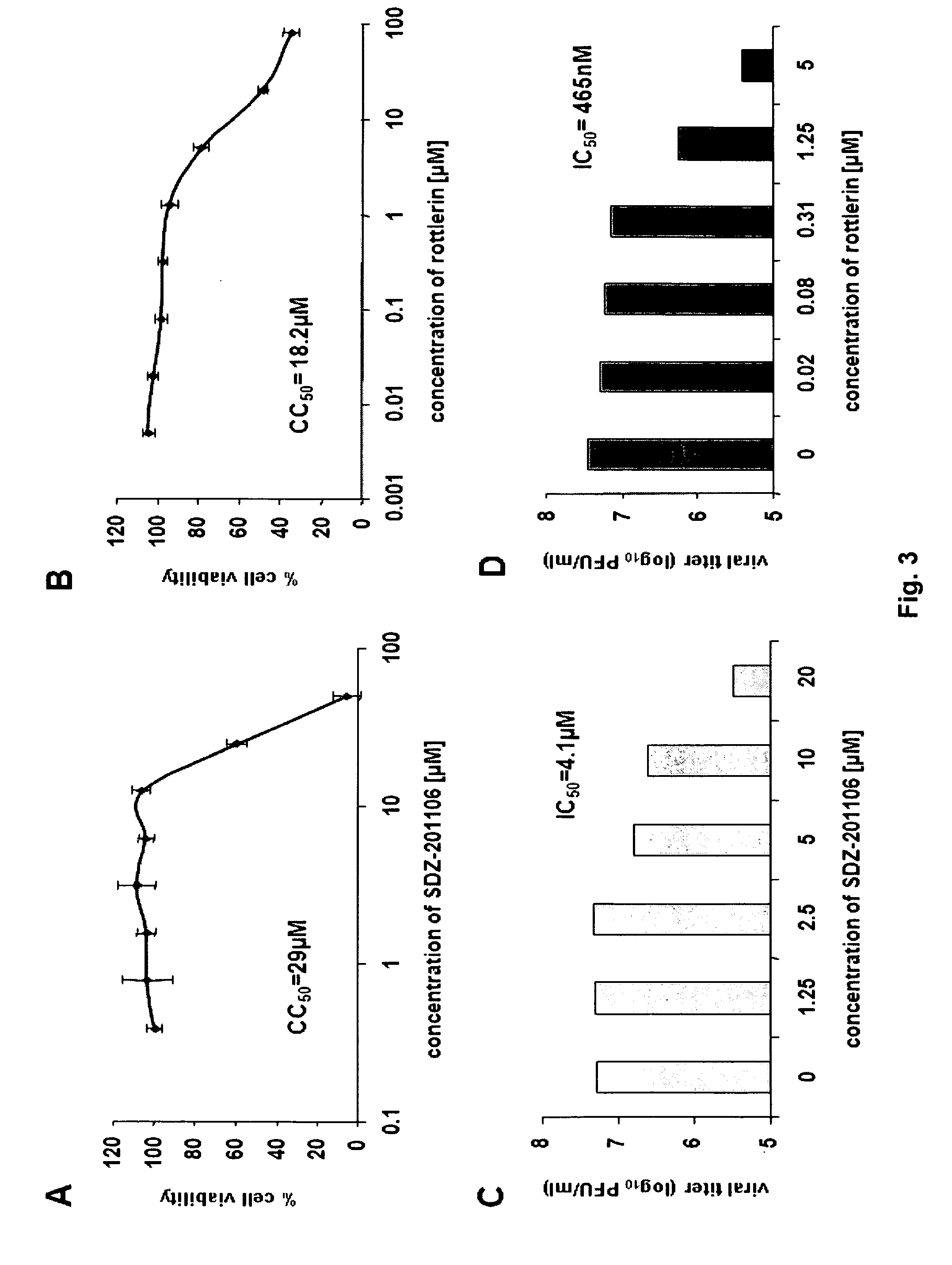
Compounds that modulate negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus replication and uses thereof
ActiveUS20110105423A1Easy to copyUtility in propagationBiocideOrganic chemistrySingle-Stranded RNAVirus multiplication
The present invention relates to compounds that modulate the replication of negative-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses, such as influenza virus, and the use of such compounds. The invention relates to methods for increasing the titer of negative-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses, such as influenza virus, in substrates for virus propagation (e.g., tissue culture). The invention also relates to the use of compounds that decrease virus replication as antiviral agents. The invention further relates to methods for identifying compounds that modulate the replication of negative-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses, in particular, influenza virus.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Novel crispr-associated (CAS) protein
ActiveUS20180282715A1Facilitates target knockdownHydrolasesClimate change adaptationSingle-Stranded RNANucleotide
A new CRISPR-associated (Cas) protein, termed “CasM,” is described, as well as polynucleotides encoding the same and methods of using CasM for site-specific genome engineering. CasM proteins are capable of targeting and cleaving single-stranded RNA.
Owner:LOCANABIO INC
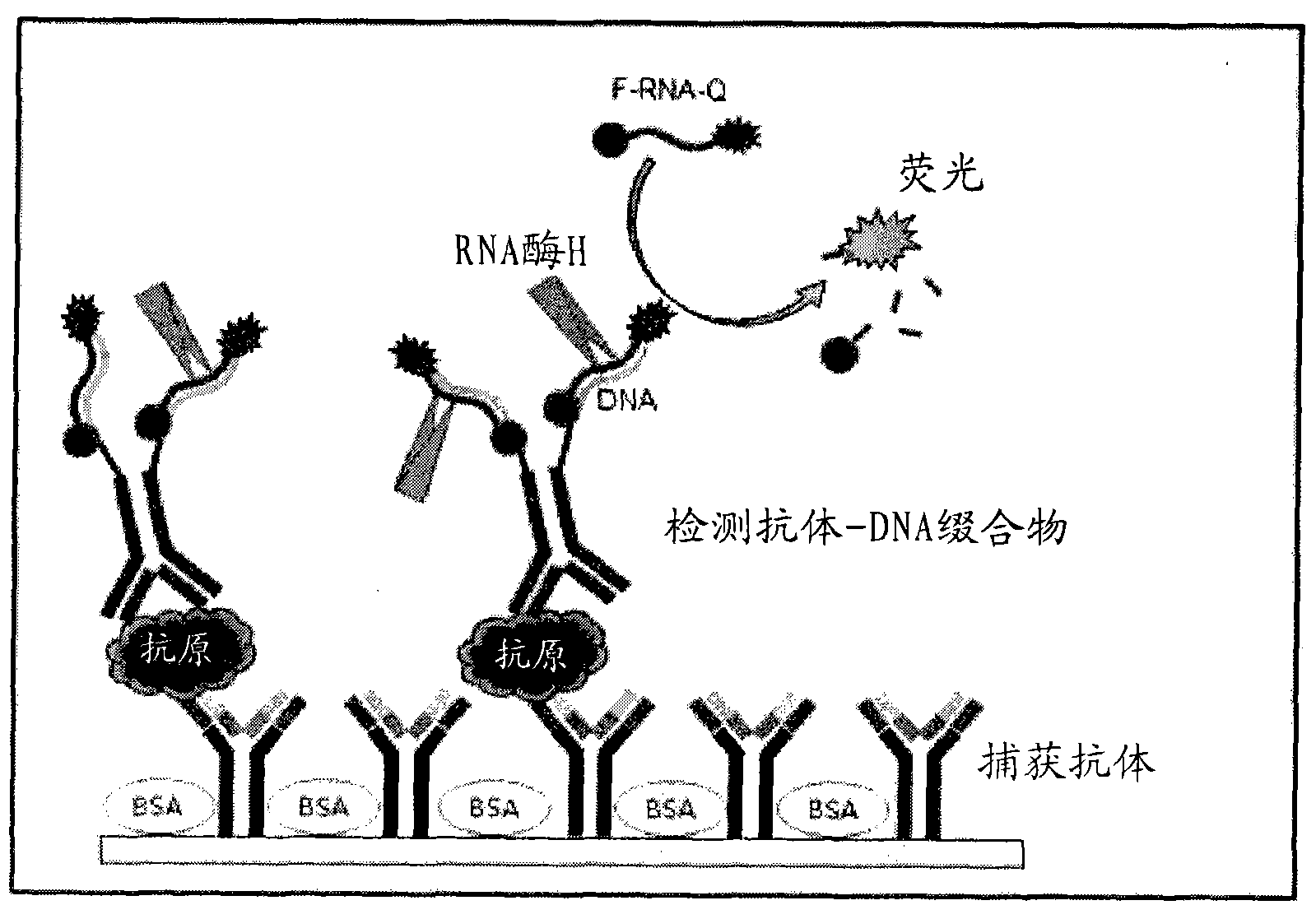
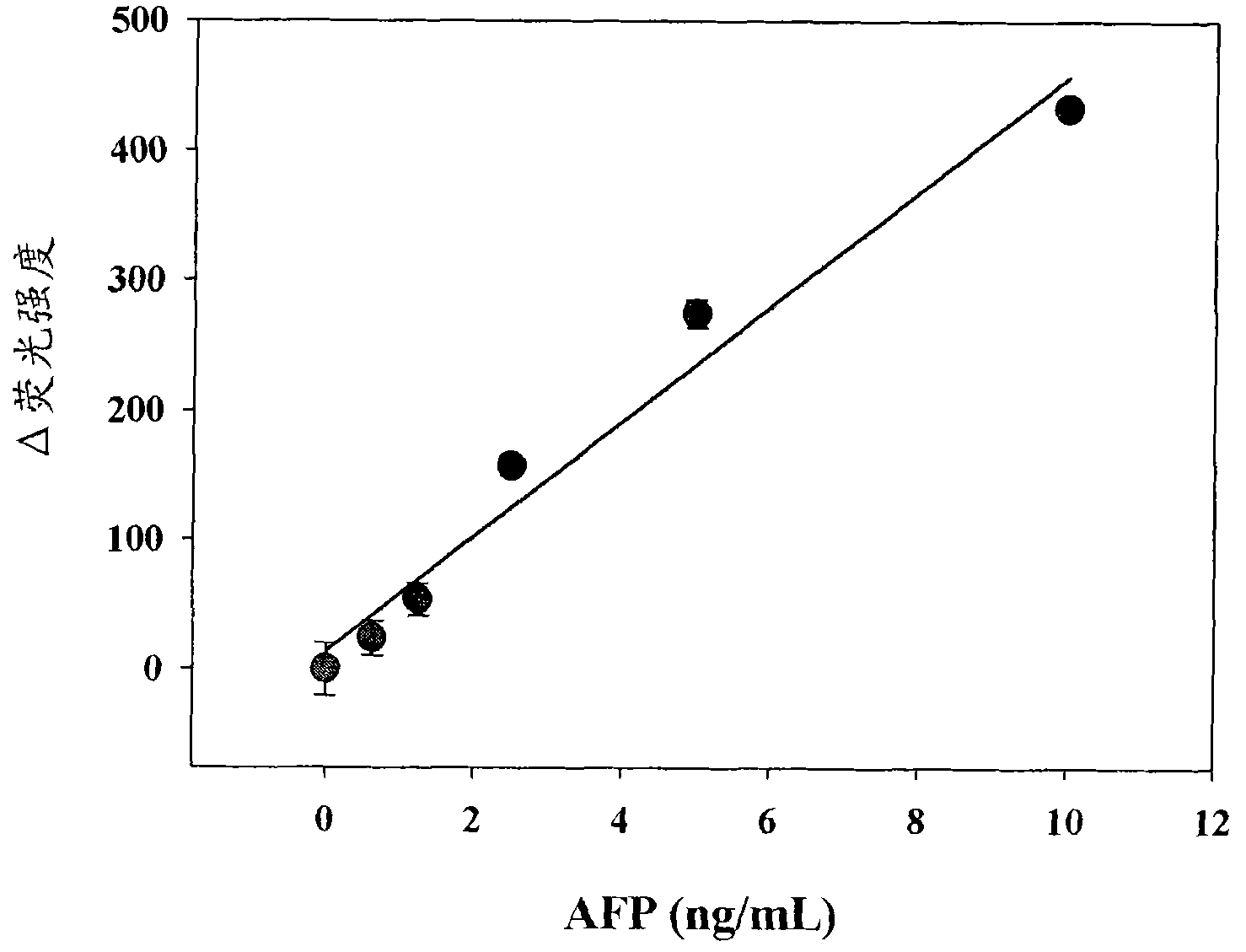
Method and kit for detecting a target protein using a DNA aptamer
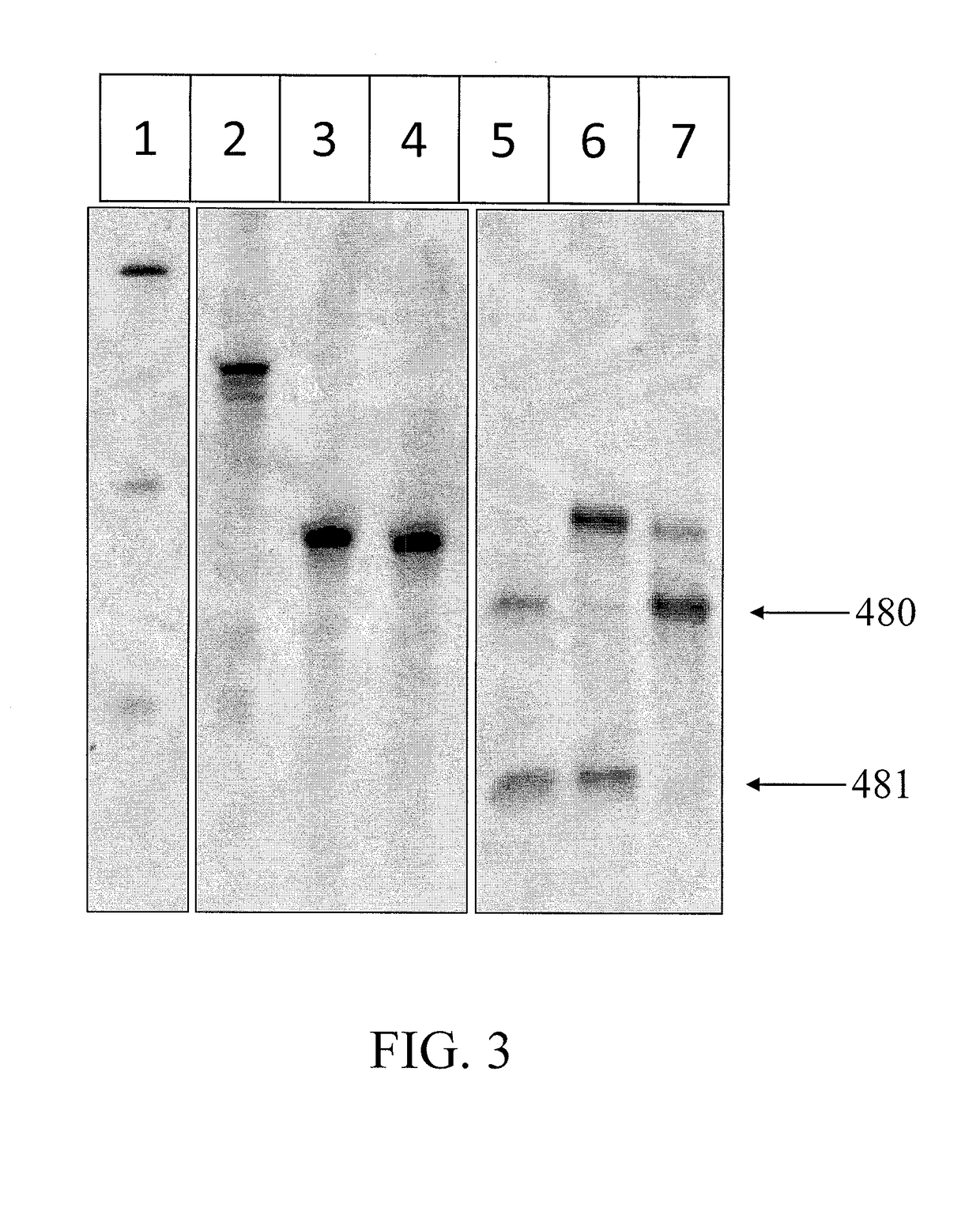
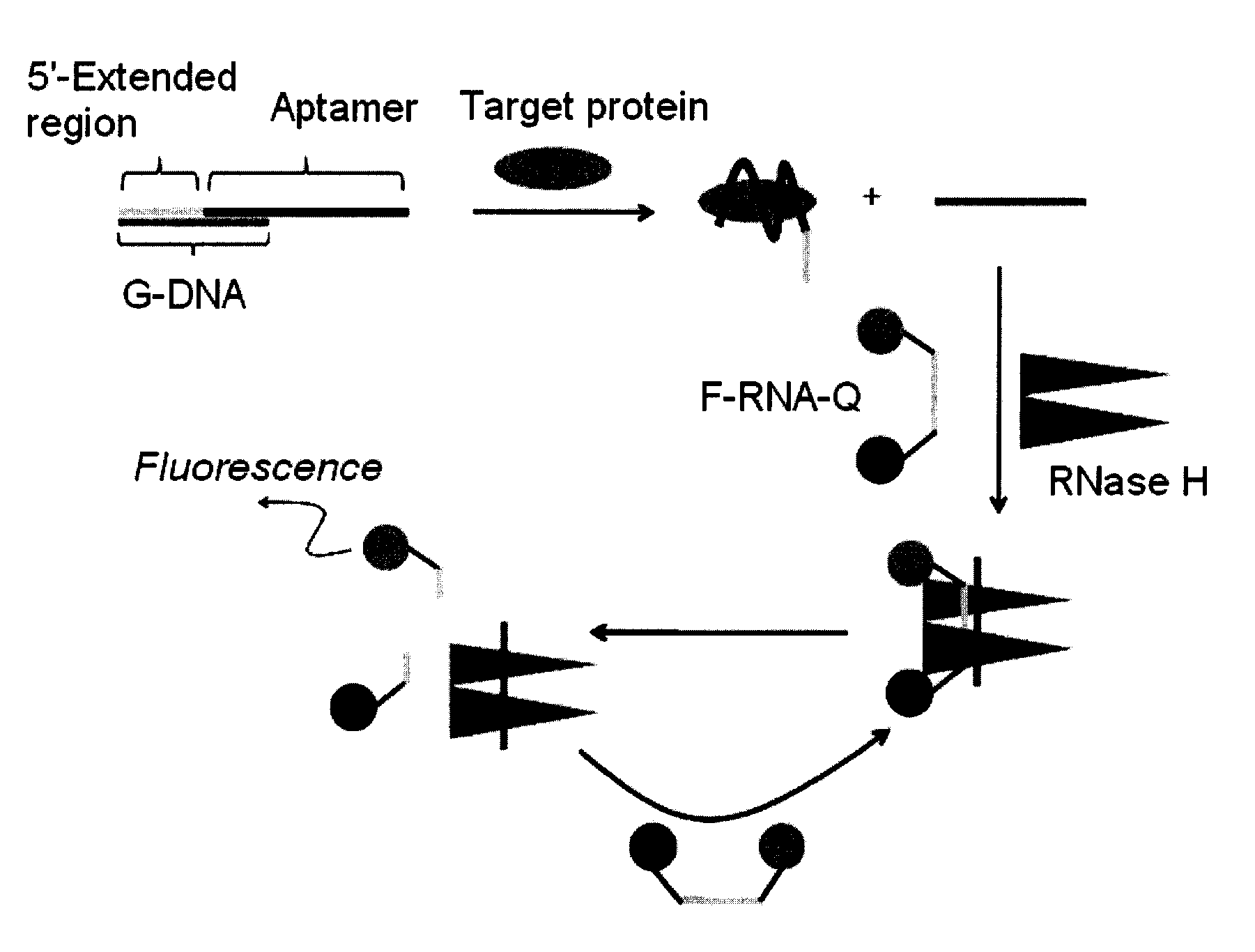
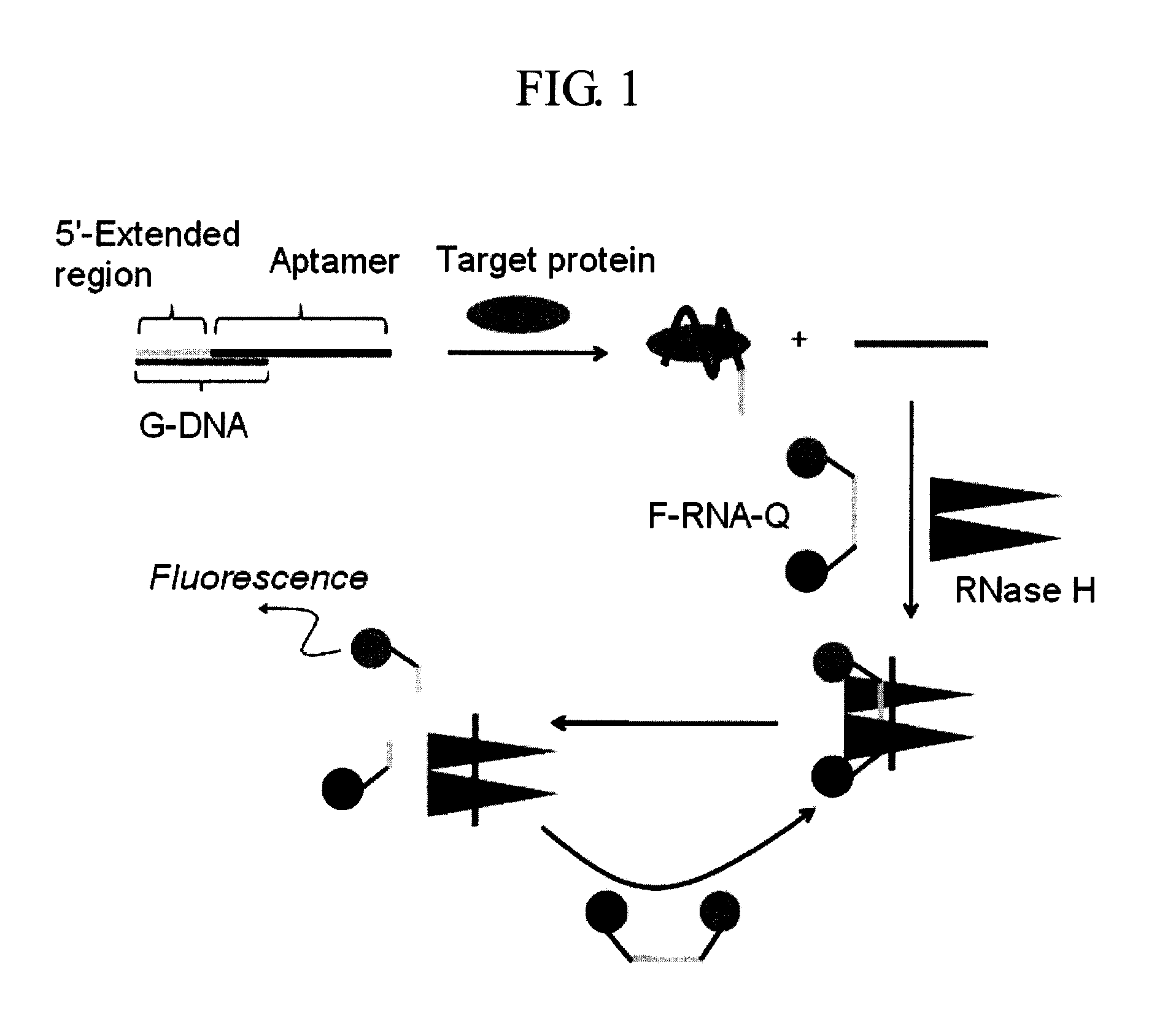
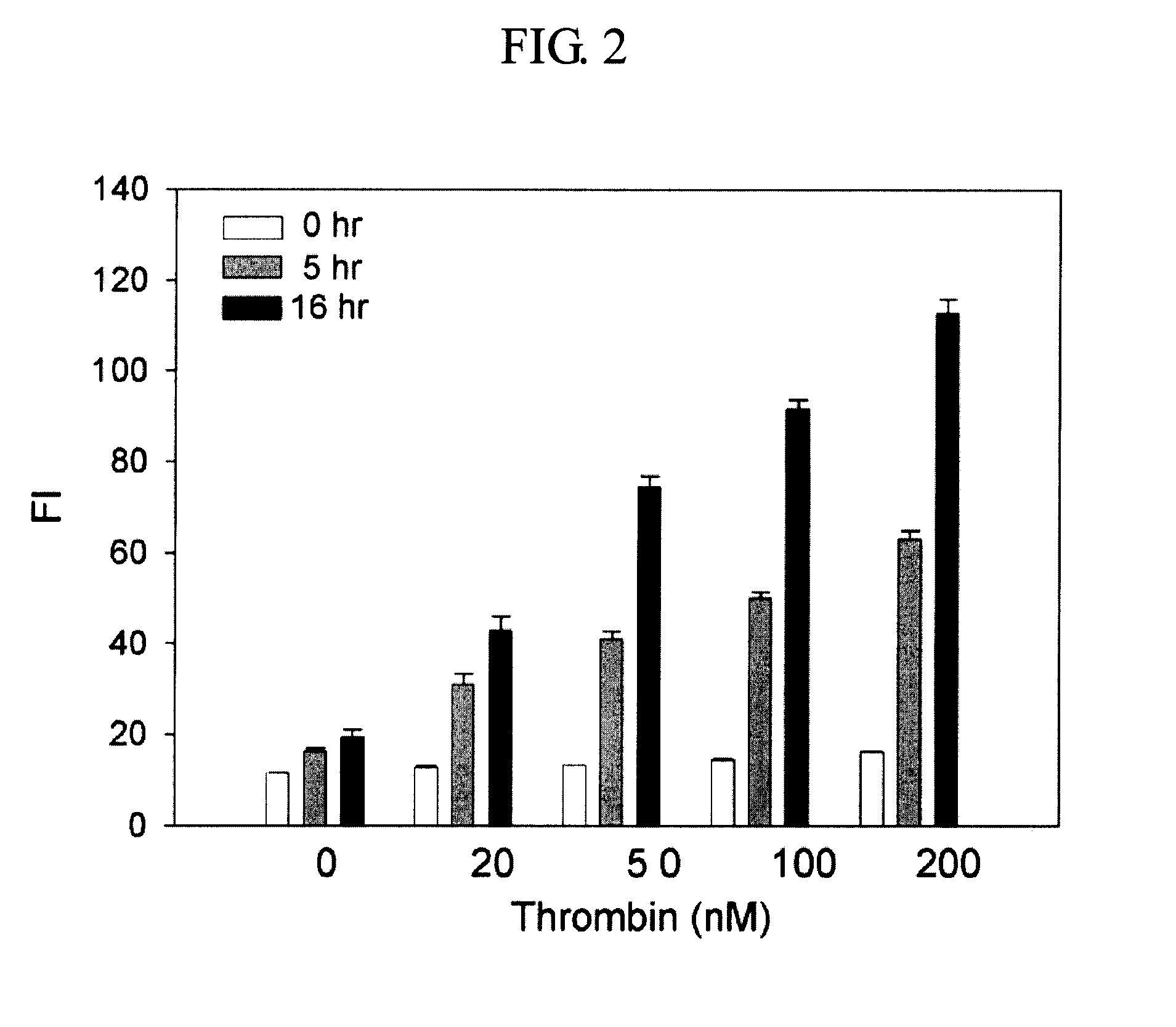
A method and a kit for detecting a target protein in a sample with a signal amplification strategy are provided. The signal amplification strategy is established for the aptamer-based molecular recognition of a target protein with concomitant release of single-stranded DNA (G-DNA), which binds complementarily to a single-stranded RNA comprising a fluorophore and a quencher (“F-RNA-Q”). The fluorescence-quenched RNA is then degraded by RNase H to result in a fluorescence signal, and the undamaged G-DNA is recycled to yield fluorescence amplification.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
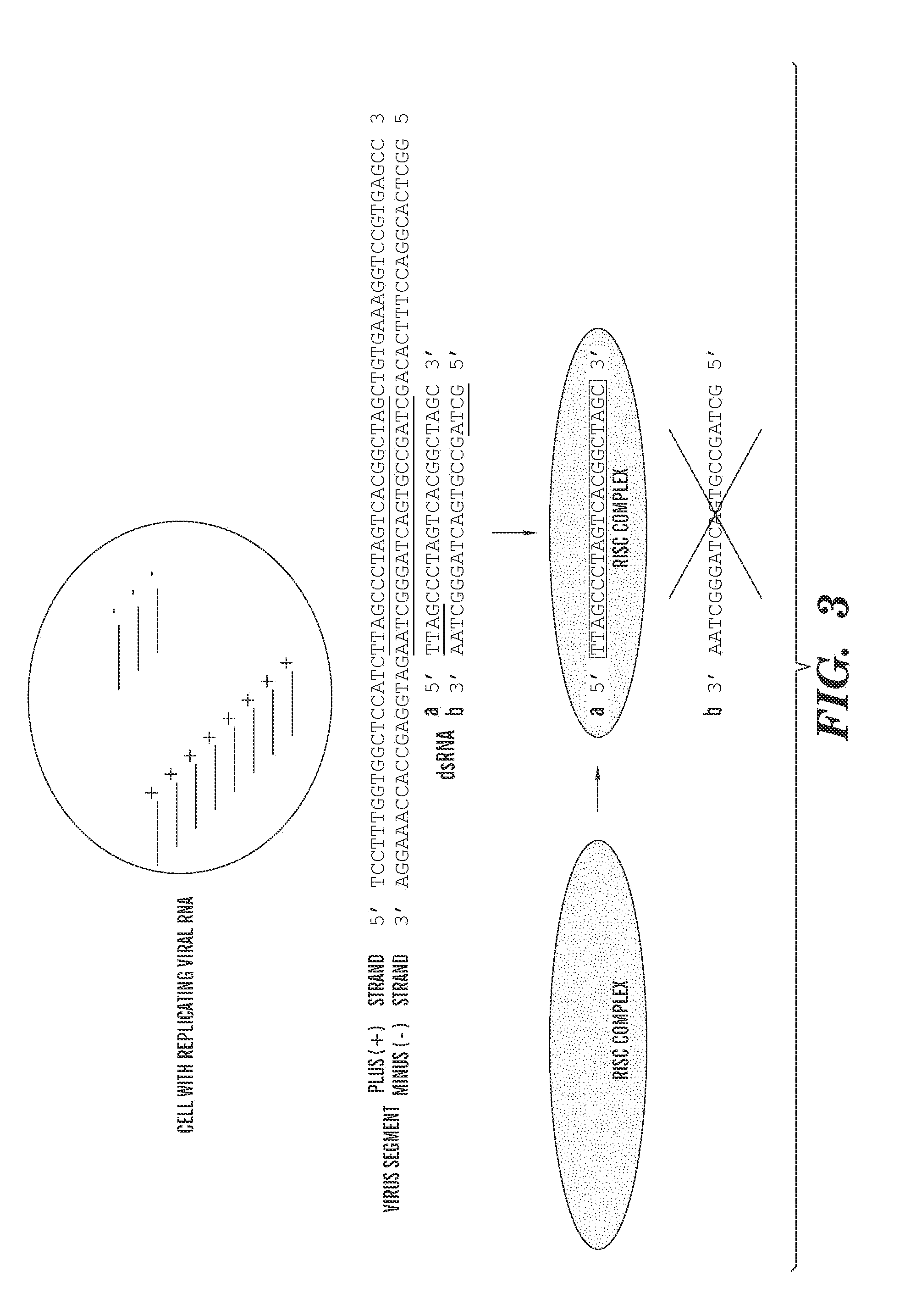
Targeting opposite strand replication intermediates of single-stranded viruses by rnai
ActiveUS20100267805A1High activityReduce eliminateOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsSingle-Stranded RNASingle strand
The invention relates to methods and compositions for modulating viral replication through double-stranded RNA-mediated gene silencing (RNAi), wherein the antiviral methods and compositions preferentially target opposite strand replication intermediates of single-stranded RNA viruses.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARMA INC
Bridged artificial nucleoside and nucleotide
ActiveUS20120208991A1Increased nuclease resistanceIncrease resistanceSugar derivativesActivity regulationSingle-Stranded RNANucleotide
It is an object of the present invention to provide a novel molecule for antisense therapies which is not susceptible to nuclease degradation in vivo and has a high binding affinity and specificity for the target mRNAs and which can efficiently regulate expression of specific genes. The novel artificial nucleoside of the present invention has an amide bond introduced into a bridge structure of 2′,4′-BNA / LNA. The oligonucleotide containing the 2′,4′-bridged artificial nucleotide has a binding affinity for a single-stranded RNA comparable to known 2′,4′-BNA / LNA and has an increased nuclease resistance over LNA. Particularly, it is expected to be applied to nucleic acid drugs because of its much stronger binding affinity for single-stranded RNAs than S-oligo's affinity
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
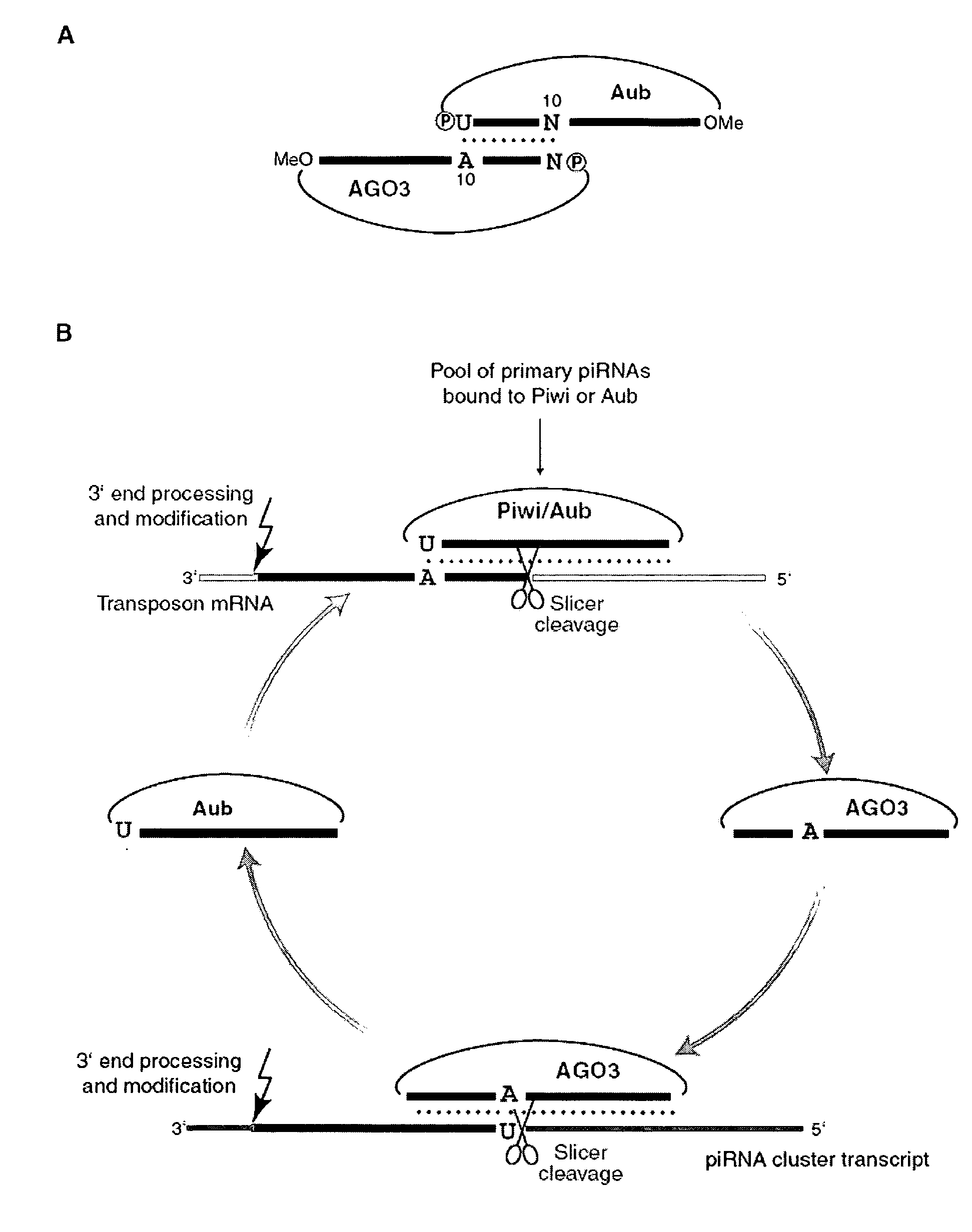
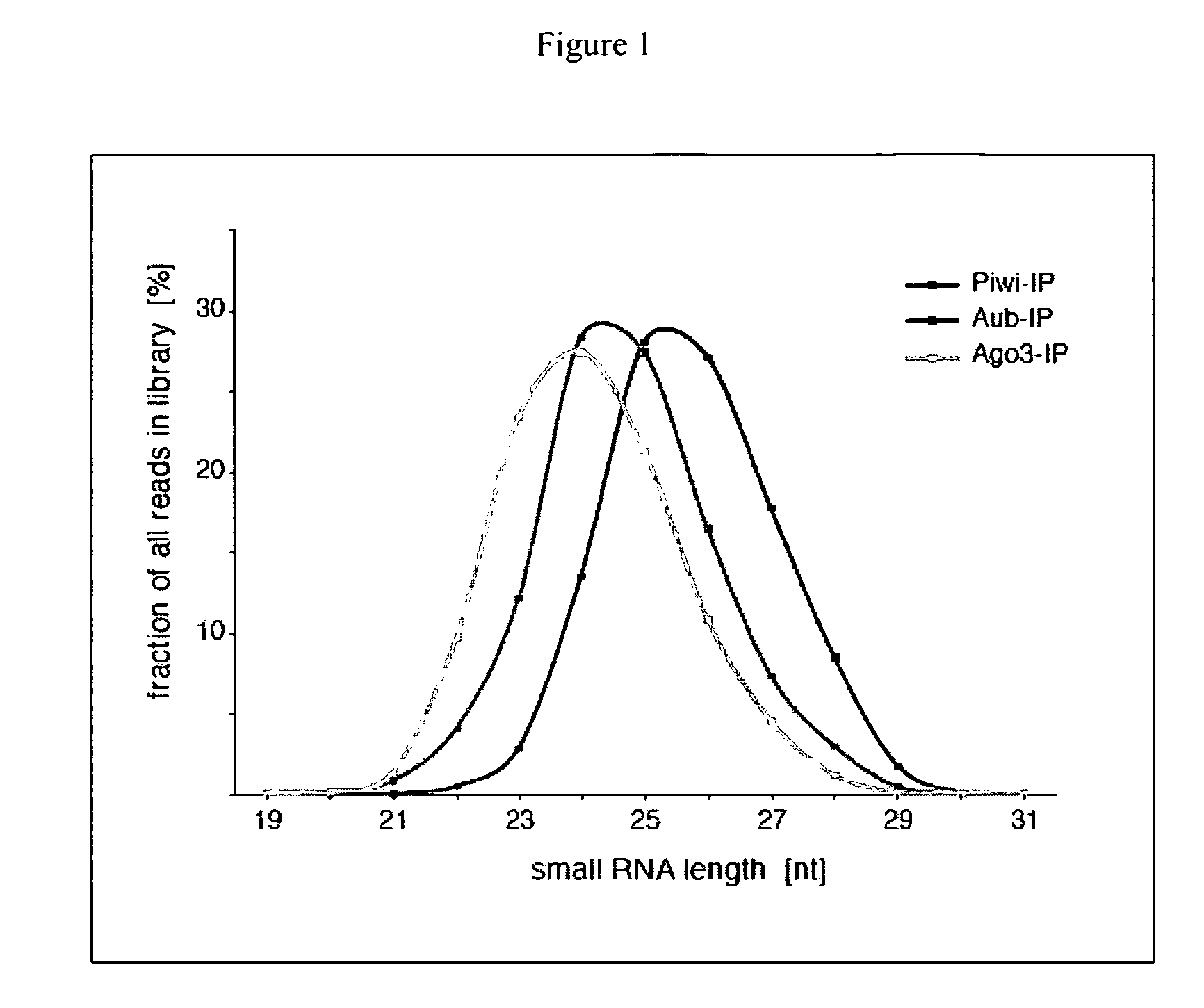
piRNA and uses related thereto
The invention relates to small single stranded RNAs and analogs thereof (collectively “piRNA” herein), compositions comprising such piRNAs, and their uses in regulating target gene expression or as markers for certain disease states.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC
Fast detection method of nucleic acid of A H1N1 influenza virus and kit thereof
InactiveCN101845517AIncreased sensitivitySolve pollutionMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceSingle-Stranded RNAReverse transcriptase
The invention relates to a fast detection method of nucleic acid of A H1N1 influenza virus, and a kit thereof, belonging to the technical field biotechnology. The invention provides a fast and synthermal RNA amplification method of A H1N1 influenza virus, and the accomplishment of the entire reaction depends on the cooperation of the AMV reverse transcriptase, the T7RNA polymerase and nuclease H (RNaseH), without the needs of the special instruments and the temperature cycling, the amplification efficiency is larger than or equal to that of the PCR, and the reaction product is single stranded RNA. The invention has the advantages of having equal or higher sensibility than that of the RT-PCR detection method, avoiding the pollution problem of the RT-PCR amplification product due to that the amplification product is RNA, finishing the reaction in one hour, and simple and convenient operation. The reaction can be monitored in real time and detected by the end-point method, can be used as the important tool in the detection of A H1N1 influenza virus.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCIAL CENT FOR DISEASE PREVENTION & CONTROL
Methods of producing RNAs of defined length and sequence
Methods of making RNA duplexes and single-stranded RNAs of a desired length and sequence based on cleavage of RNA molecules at a defined position, most preferably with the use of deoxyribozymes. Novel deoxyribozymes capable of cleaving RNAs including a leader sequence at a site 3' to the leader sequence are also described.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
Method of preparing normalized and/or subtracted cDNA
InactiveUS7049065B2Avoid disadvantagesImproving and subtractionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-Stranded RNAFull length cdna
Owner:YOSHIHIDE HAYASHIZAKI +2
Two-Component Rna Virus-Derived Plant Expression System
ActiveUS20070300330A1Improve efficiencyProvide efficiencySugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesSingle-Stranded RNAWhole body
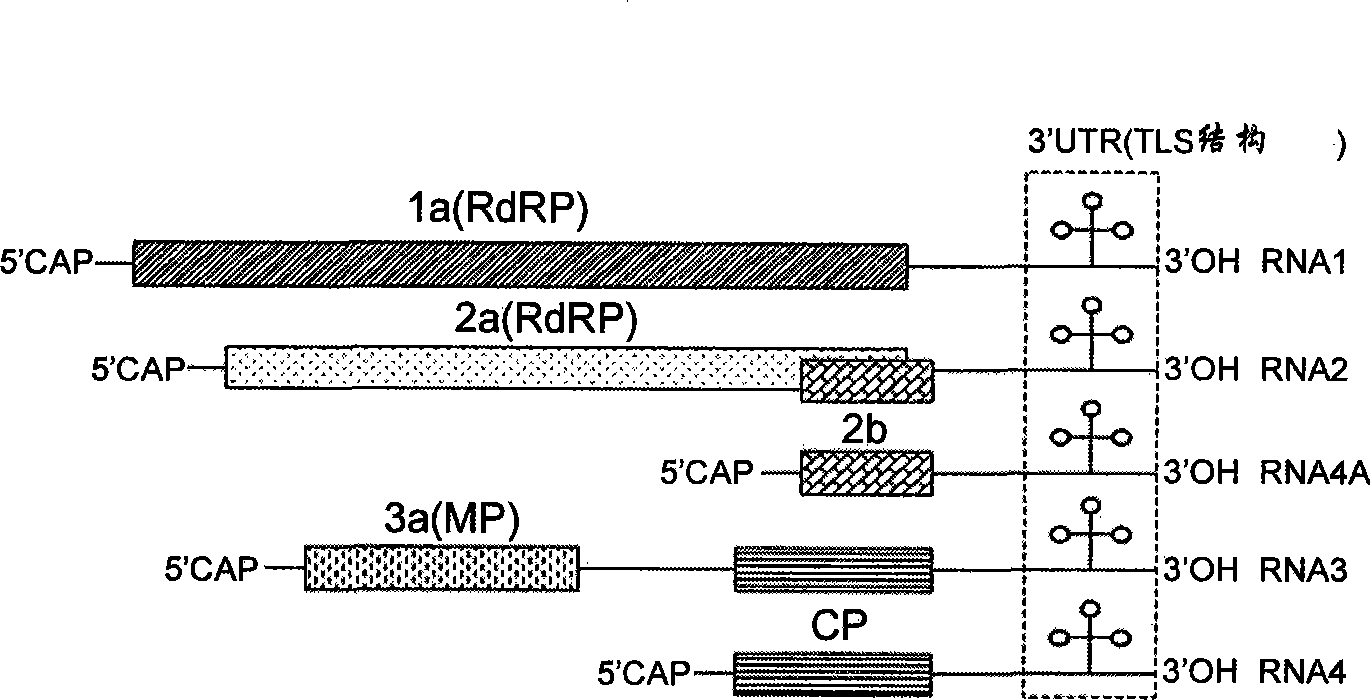
A process for replicating or for replicating and expressing a sequence of interest in a plant, comprising: (i) an RNA replicon or a precursor thereof, said RNA replicon being derived from a plus-sense single stranded RNA virus and comprising at least one sequence of interest; and (ii) a helper replicon, or a precursor thereof, wherein said helper replicon is (a) incapable of systemic movement in said plant both in the presence and in the absence of said RNA replicon (i) and (b) capable of expressing in a plant one or more proteins necessary for systemic movement of said RNA replicon (i), whereby said RNA replicon (i) is capable of replicating or replicating and expressing said sequence of interest in said plant, but unable to move systemically in said plant in the absence of said one or more proteins expressed by said helper replicon (ii).
Owner:ICON GENETICS
Application package to automatically identify some single stranded RNA viruses from characteristic residues of capsid protein or nucleotide sequences
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
RNA aptamer of targeting hepatocyte and nucleotide sequence thereof
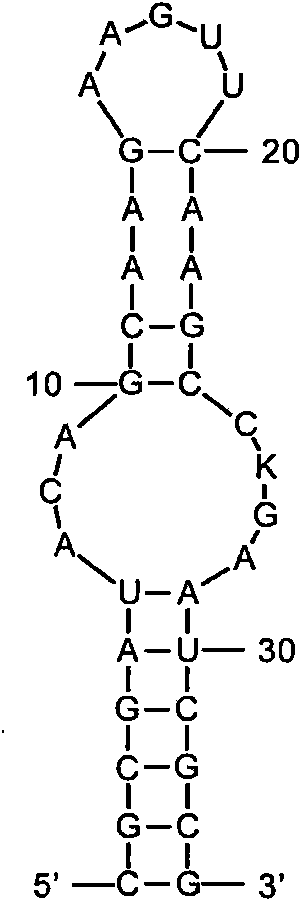
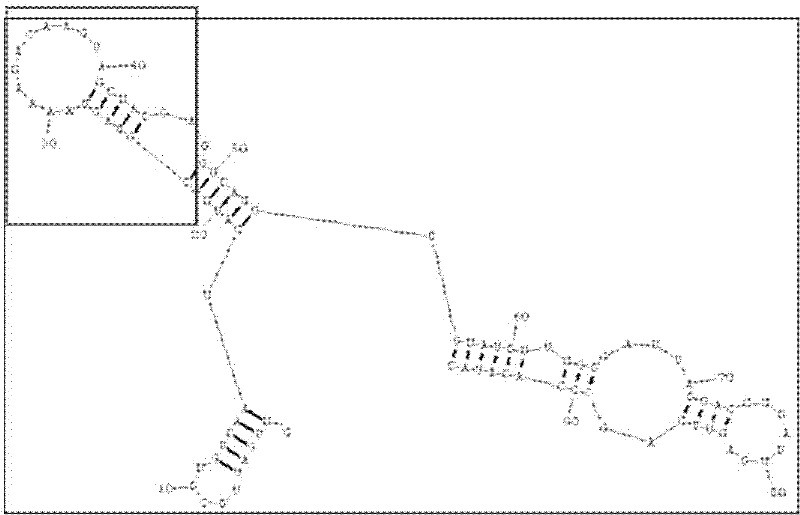
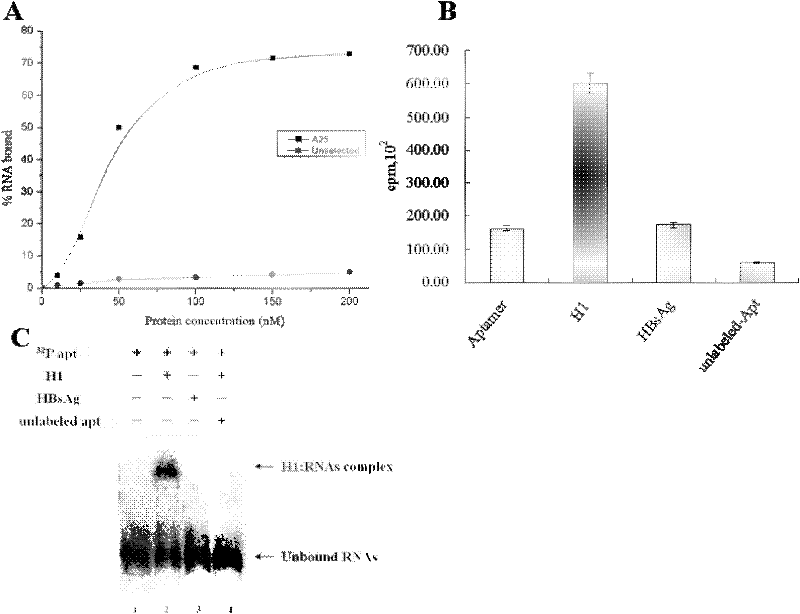
The invention discloses a RNA aptamer of a targeting hepatocyte and a nucleotide sequence thereof, and relates to the field of hepatic disease diagnosis and treatment. The RNA aptamer provides a novel specific and efficient molecule of a targeting hepatocyte for the field of hepatic disease diagnosis and treatment. In the invention, through using the new combinatorial chemical technology SELEX, and taking hepatic ASGPR (asialoglycoprotein receptor) large subunits as target proteins, an RNA aptamer which can specify the ASGPR is screened from a single-stranded RNA random library. The aptamer can be formed into a special stemloop structure in a random sequence region thereof, combines with big liver ASGP receptor subunit H1 protein with high specific affinity and can combine to liver cells in a targeted mode by high specific affinity. The RNA aptamer provides a new choice for developing a liver disease targeted diagnostic reagent and treatment drug.
Owner:TONGJI HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI TECH
Structure assisted directed evolution of multivalent aptamers
ActiveUS20180044663A1High affinityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening processSingle-Stranded RNASingle strand dna
Provided herein are methods and systems for structure-assisted evolution of multivalent aptamers using a single stranded DNA or single-stranded RNA nanostructure as a structural support. Also provided herein are methods for constructing ssDNA or ssRNA nanostructures as structural supports suitable for structure-assisted evolution of multivalent aptamers.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Chemically modified single-stranded rna-editing oligonucleotides
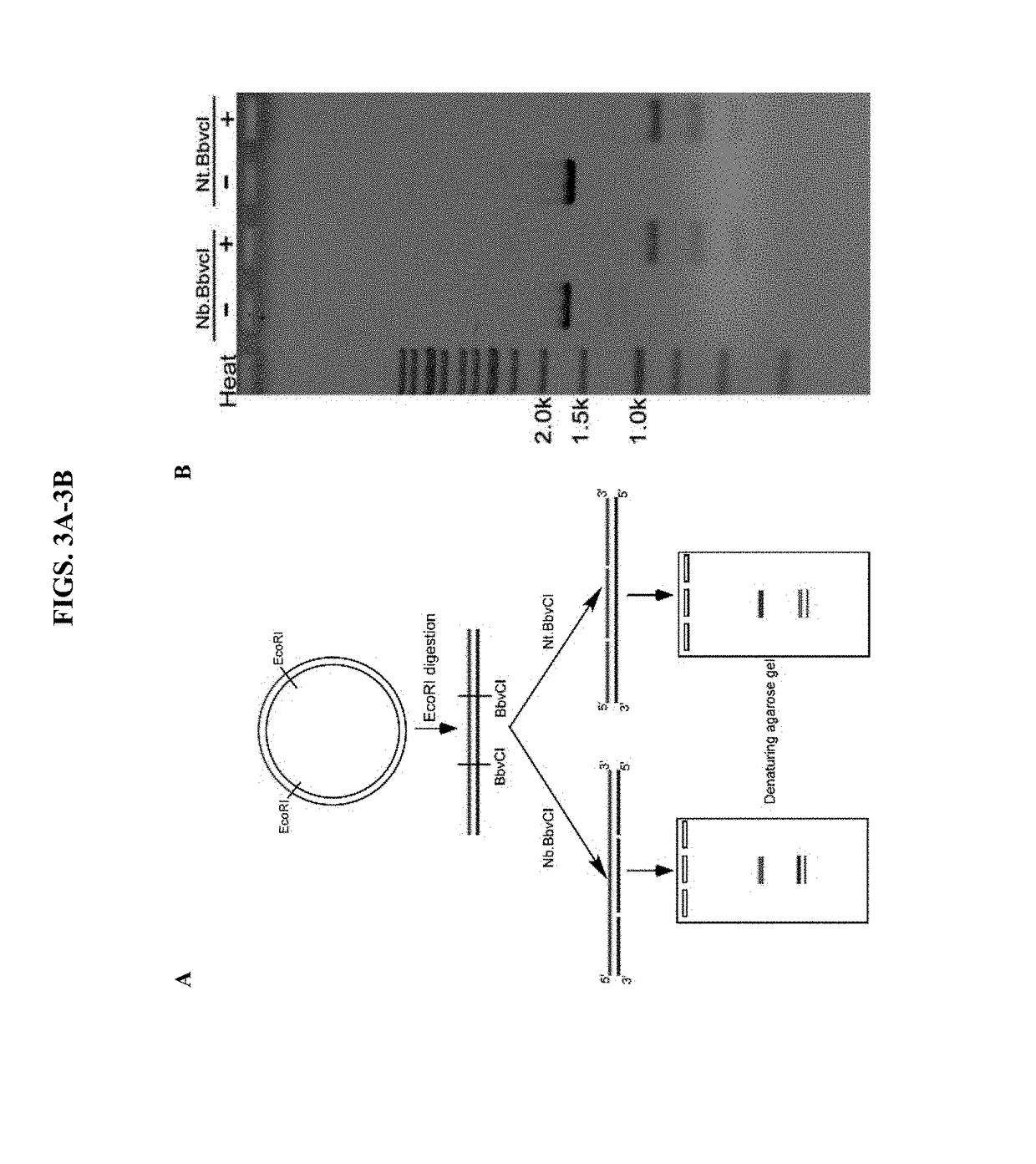
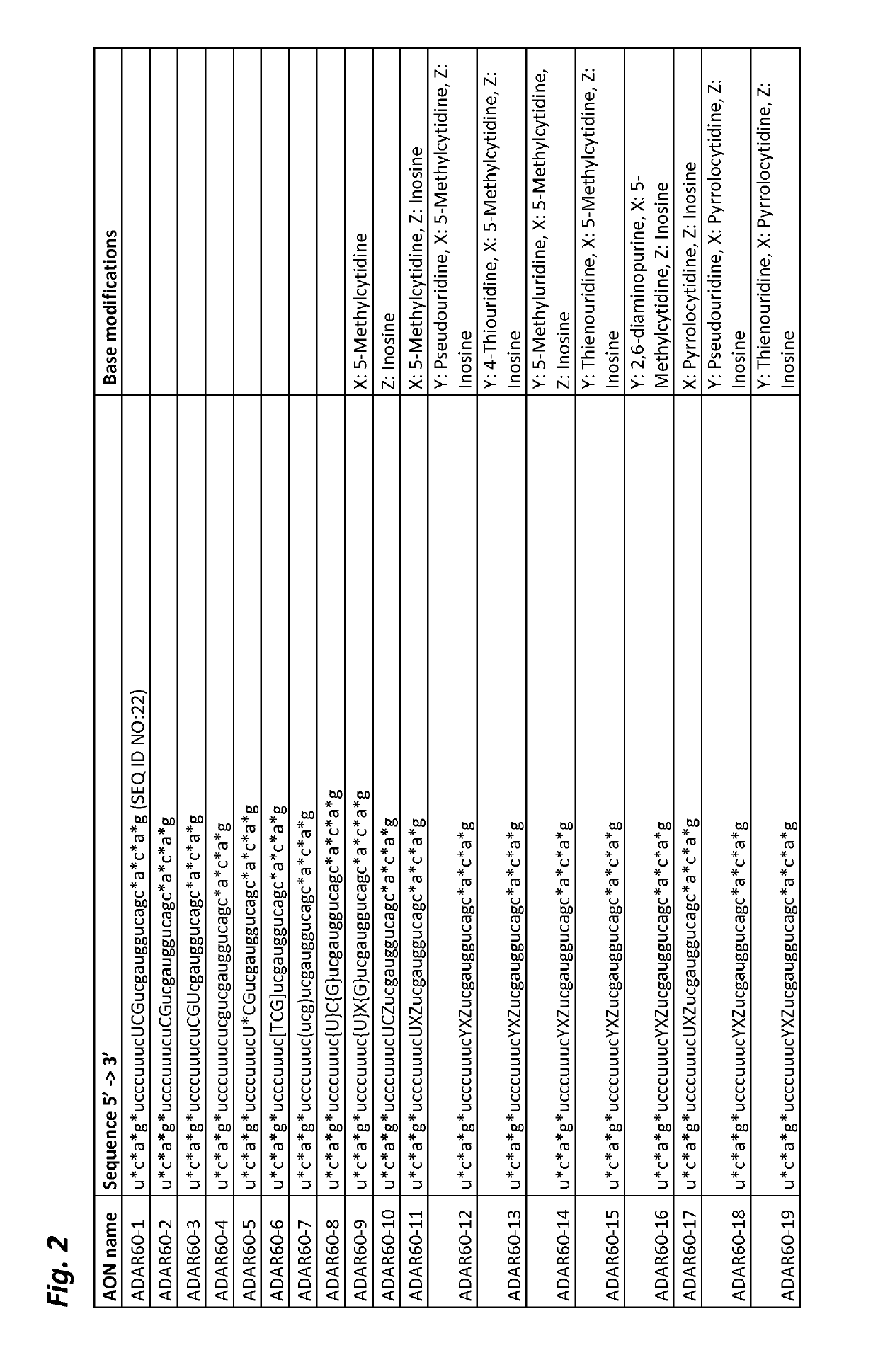
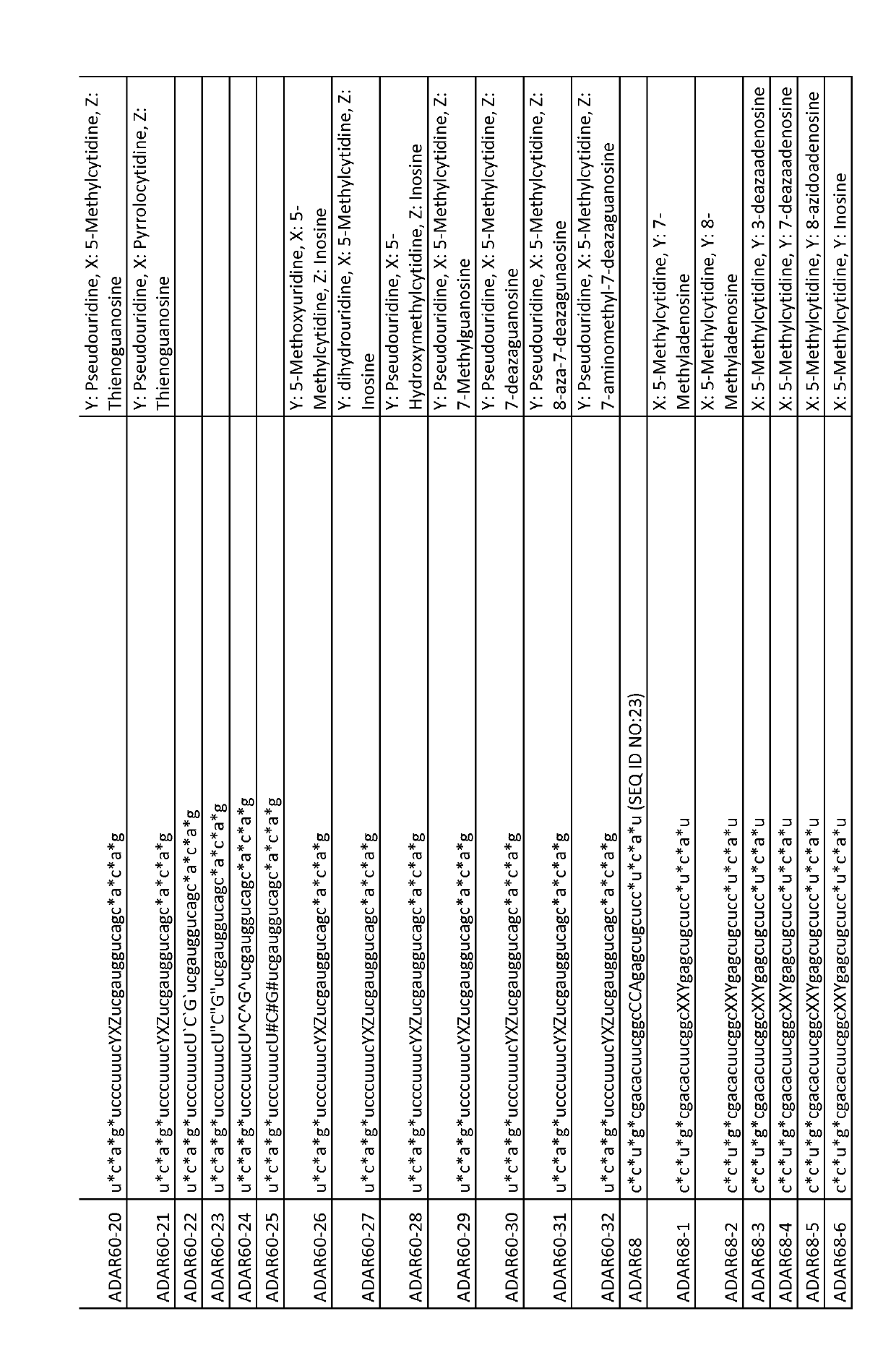
ActiveUS20190218552A1Ameliorate organ function.Disease reliefSenses disorderNervous disorderSingle-Stranded RNAAdenosine
The invention relates to antisense oligonucleotides that are capable of bringing about specific editing of a target nucleotide (adenosine) in a target RNA sequence in a eukaryotic cell, wherein said oligonucleotide does not, in itself, form an intramolecular hairpin or stem-loop structure, and wherein said oligonucleotide comprises a non-complementary nucleotide in a position opposite to the nucleotide to be edited in the target RNA sequence.
Owner:PROQR THERAPEUTICS II BV
RNA induced silencing complex mediated shearing site and uses thereof
InactiveCN101429513AEfficient virus resistanceResist infectionFungiBacteriaSingle-Stranded RNARNA-induced silencing complex
The invention discloses a shear locus mediated by RNA induced silencing complex and application thereof. The locus can be applied in designing a factitial tiny RNA. In a DNA molecule coding a factitial tiny RNA precursor, the factitial tiny RNA precursor is a single-chain RNA capable of generating a tiny RNA in plant; the single-chain RNA forms a stem-loop structure; a nucleotide sequence containing sequence 1 in a sequence list is arranged in a fragment of the stem part of the stem-loop structure; two base pairs which are not complementary are arranged on the stem part of the stem-loop structure; and the two uncomplementary base pairs correspond to the ninth position and the tenth position from tail end of 5' in the sequence 1. The invention also discloses a method for culturing plant resisting cucumber mosaic virus. With the DNA molecule coding the factitial tiny RNA precursor, the plant with high efficient virus resistance can be obtained, so that the method is a biological engineering method with economy and efficiency.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Double-labelling fluorescence activation type probe and method for detecting DNA by adopting same
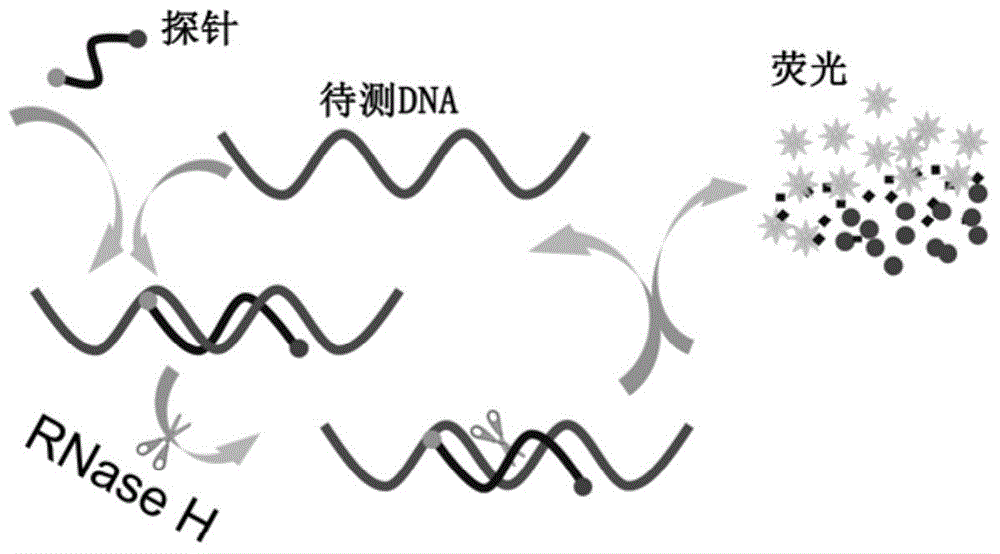
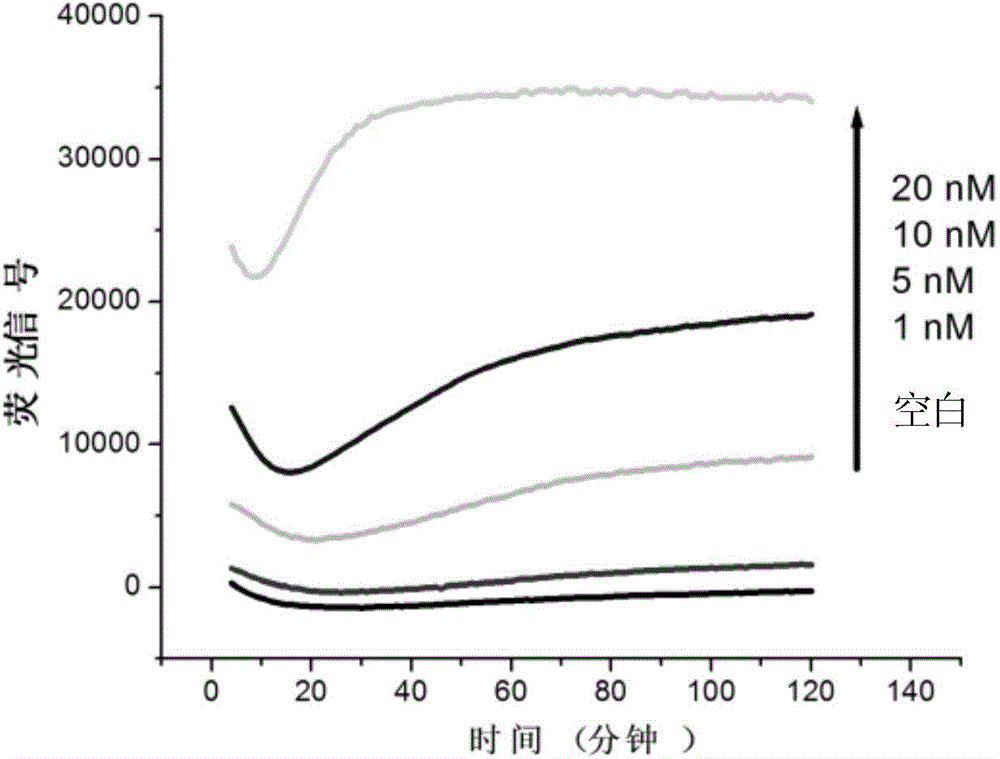
InactiveCN104946634ASimple structureEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSingle-Stranded RNAHeteroduplex
The invention discloses a double-labelling fluorescence activation type probe and a method for detecting DNA by adopting the same. The probe is a single stranded RNA which is complementary with a basic group of to-be-detected DNA and has the length of 5-40 basic groups or is a single stranded DNA which is complementary with a basic group of to-be-detected DNA and has the length of 5-40 basic groups; 1 / 5-4 / 5 of basic groups in the DNA sequence are RNA basic groups; The two ends of the probe are labeled with a fluorophore and a quenching group. The probe is simple in structure and fluorescence is completely quenched; when the probe hybridizes with the to-be-detected DNA to form DNA / RNA heteroduplex, RNase H hydrolyzes an RNA chain in a DNA / RNA structure in a specificity manner to enable the fluorophore to be away from the quenching group and enable a fluorescence signal to be recovered; simultaneously, the dissociative probe further hybridizes with the to-be-detected DNA, is hydrolyzed by RNase H and generates the fluorescence signal; circulation is performed in such a way, so that the system fluorescence signal is remarkably amplified to realize rapid and high-sensitive detection of the to-be-detected DNA. The probe can be used for quantitative detection of DNA in an amplification product.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com