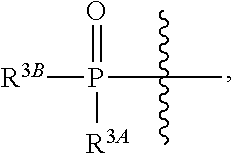Patents
Literature
36 results about "Paramyxoviridae" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
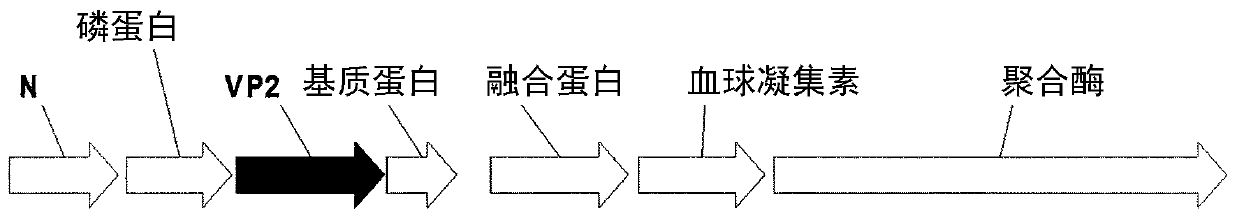
Paramyxoviridae is a family of viruses in the order Mononegavirales. Vertebrates serve as natural hosts; no known plants serve as vectors. Currently, 72 species are placed in this family, divided among 14 genera. Diseases associated with this negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus family include measles, mumps, and respiratory tract infections.
Anti-viral treatment and assay to screenfor Anti-viral agent
InactiveUS20130085133A1Improve palatabilityImprove stabilityBiocideSugar derivativesCytopathic effectAntiviral drug
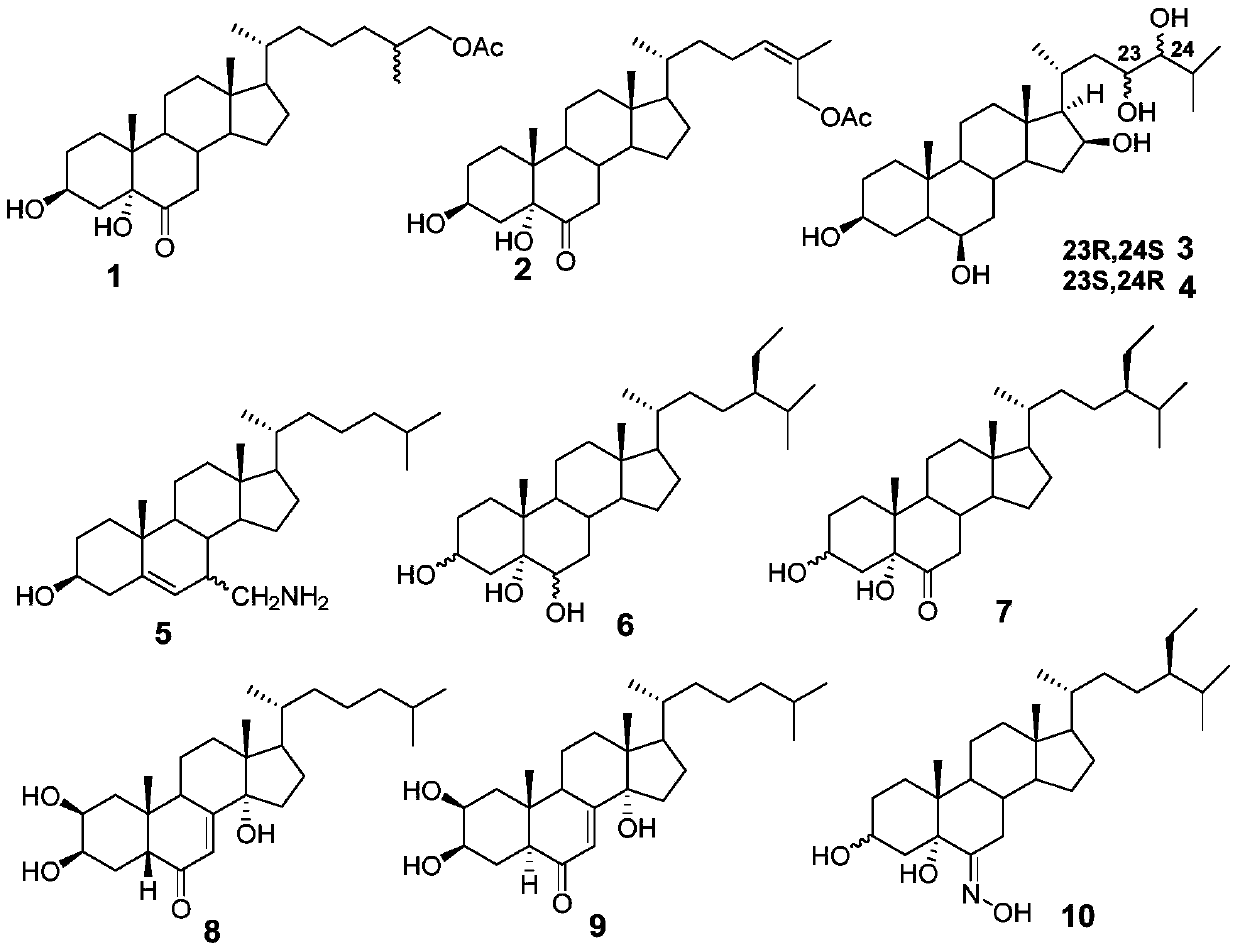
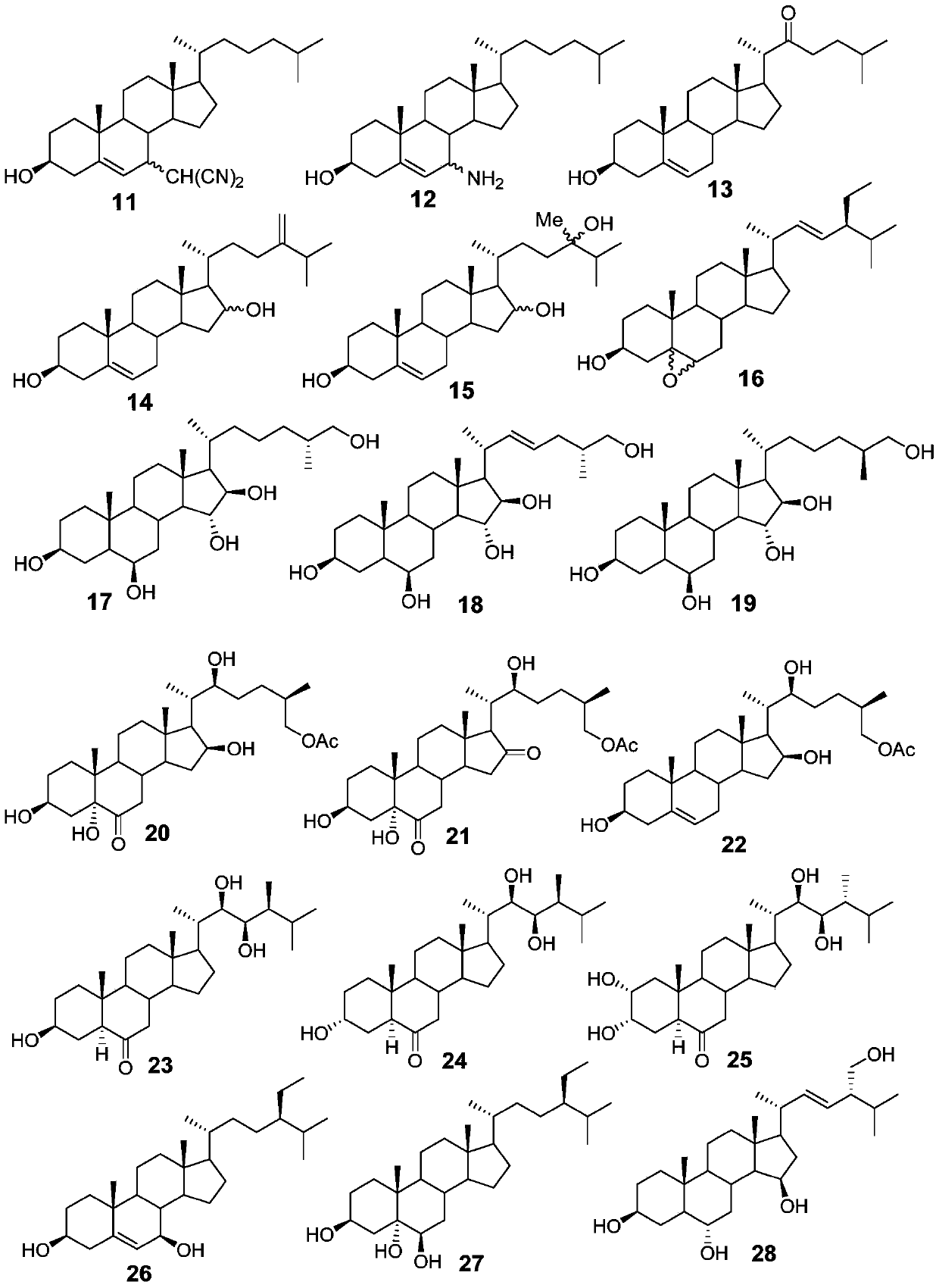
The present disclosure relates to novel compounds of formulas (1) through (19) and to a method for treating humans infected with a virus including various respiratory viruses such as members of the Paramyxoviridae family (respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), human metapneumovirus (HMPV), human parainfluenza virus (HPIV), measles virus, and mumps virus) with a compound of formulas (1) through (19). The present disclosure also relates to a cytopathic effect (CPE)-based assay that will assess virus-induced CPE for screening of compounds for treating viral diseases or inhibiting a virus.
Owner:SOUTHERN RES INST & IP
Antiviral Compounds and Methods of Using Thereof
InactiveUS20090012107A1Prolongs mean time to deathBiocideOrganic chemistryArenaviridaeParamyxoviridae
Disclosed herein are compounds which exhibit antiviral activity against a plurality of viruses belonging to different families such as Bornaviridae, Filoviridae, Paramyxoviridae, Rhabdoviridae, Arenaviridae, Bunyaviridae, Orthomyxoviridae, and Poxviridae. Thus, methods of preventing, inhibiting, or reducing the viral activity of various viruses are provided as well as methods of treating viral infections.
Owner:US ARMY MEDICAL RES MATERIEL COMMAND USAMRMC
Production of virus and purification of viral envelope proteins for vaccine use
Immunogenic envelope glycoproteins are produced from enveloped virus, such as of the paramyxoviridae family, particularly PIV-3 and RSV, by culturing the virus in the substantial absence of exogenous serum proteins, isolating the virus from the tissue culture, solubilizing the envelope glycoproteins and isolating the solubilized envelope glycoproteins by chromatography.
Owner:CONNAUGHT LAB
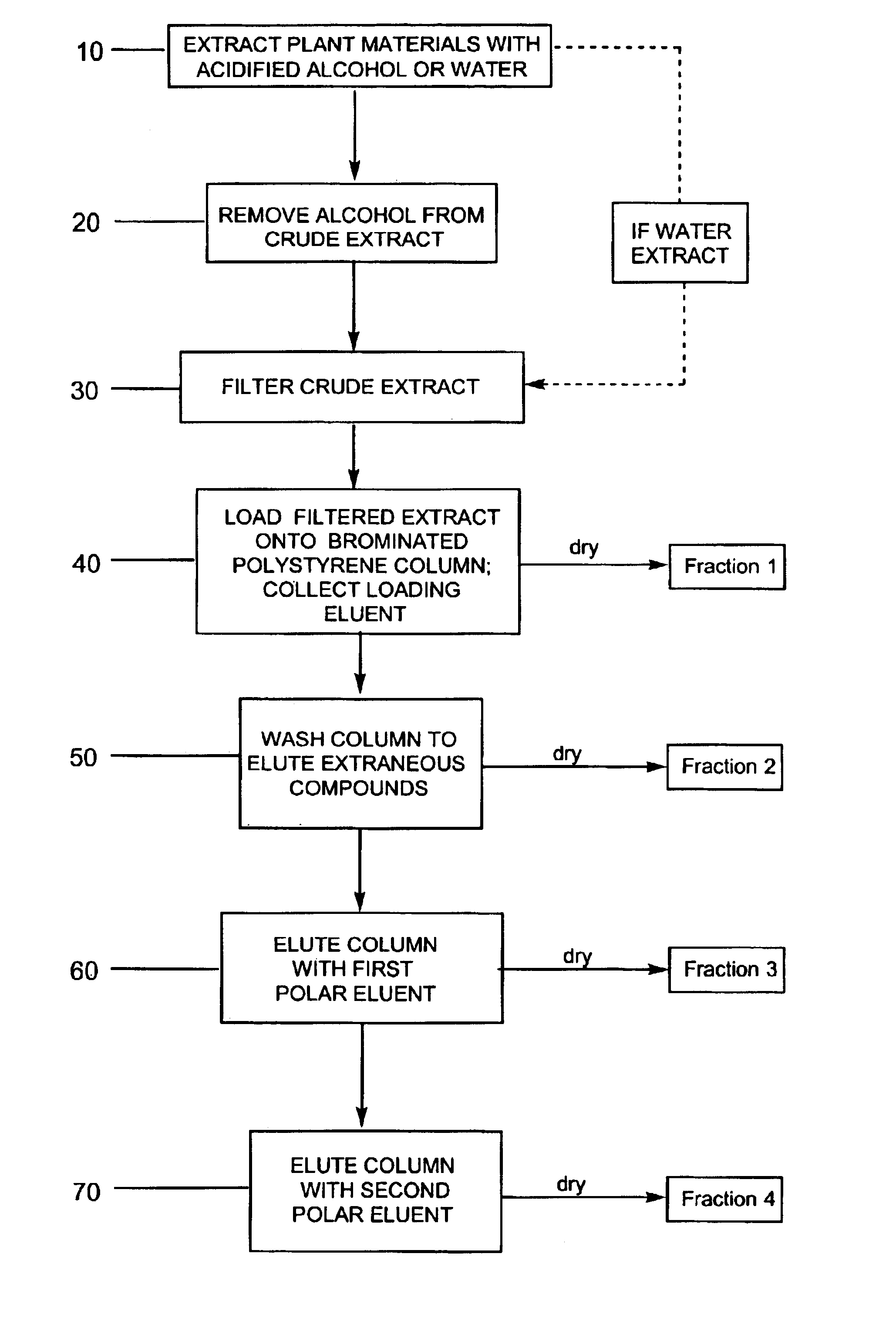
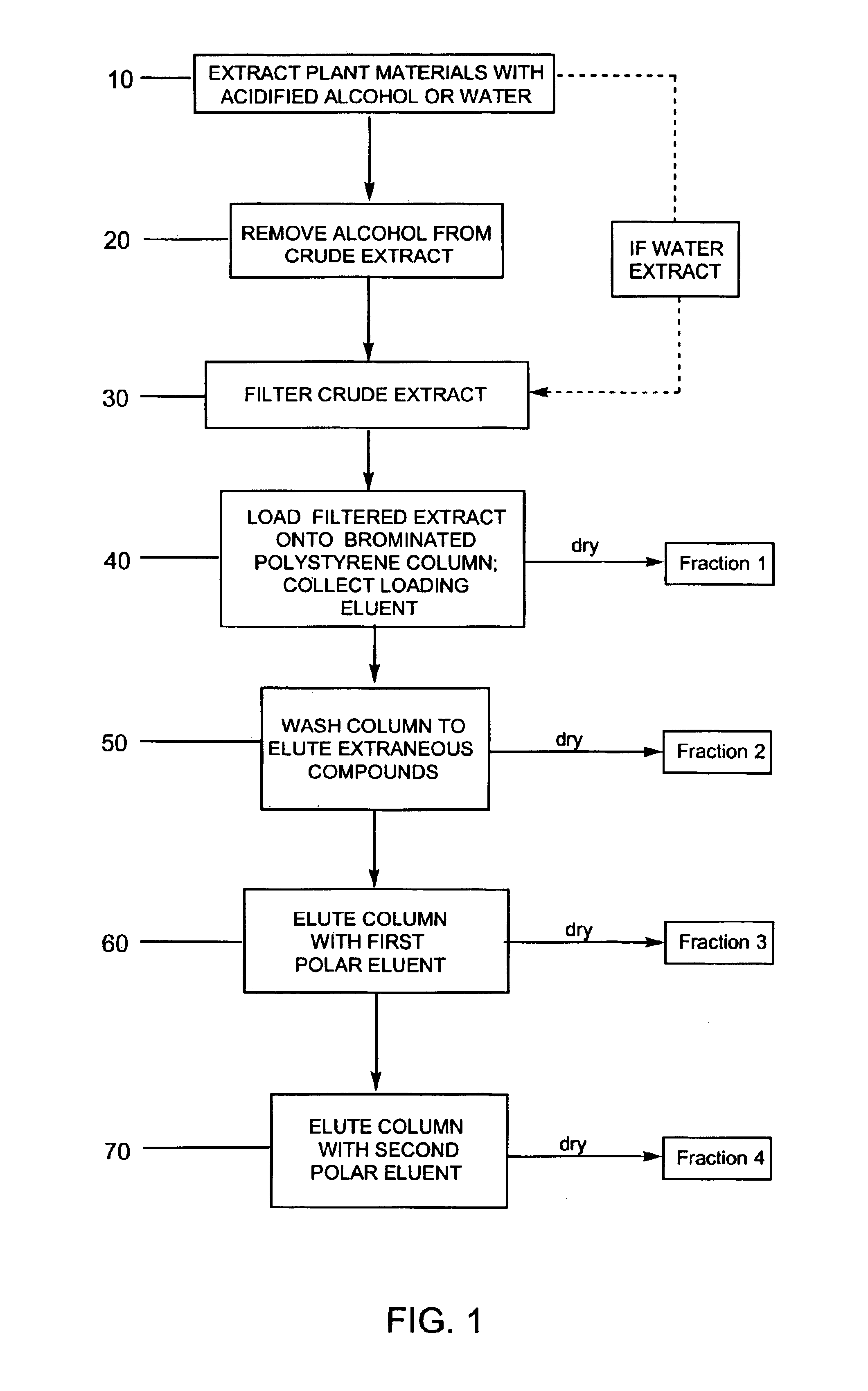
Compositions enriched in phenolic compounds and methods for producing the same
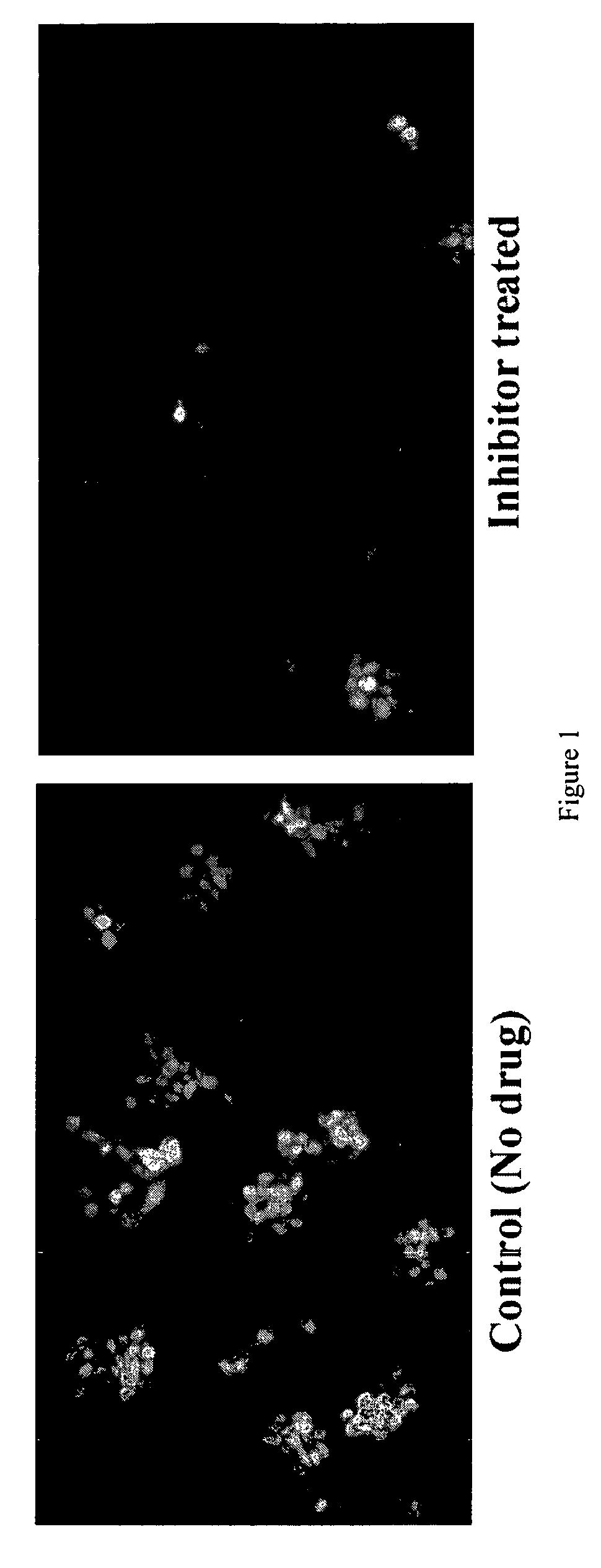
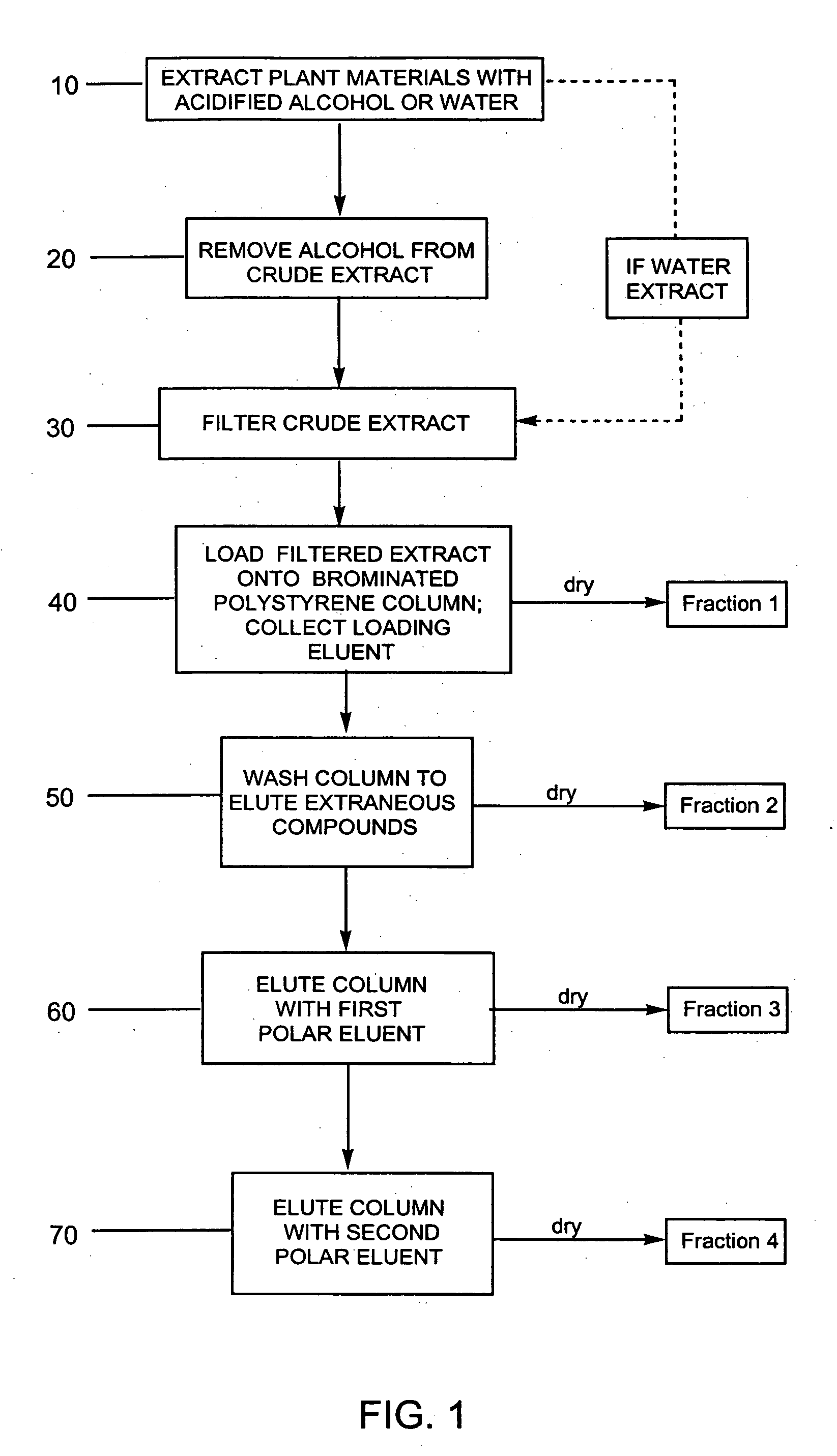
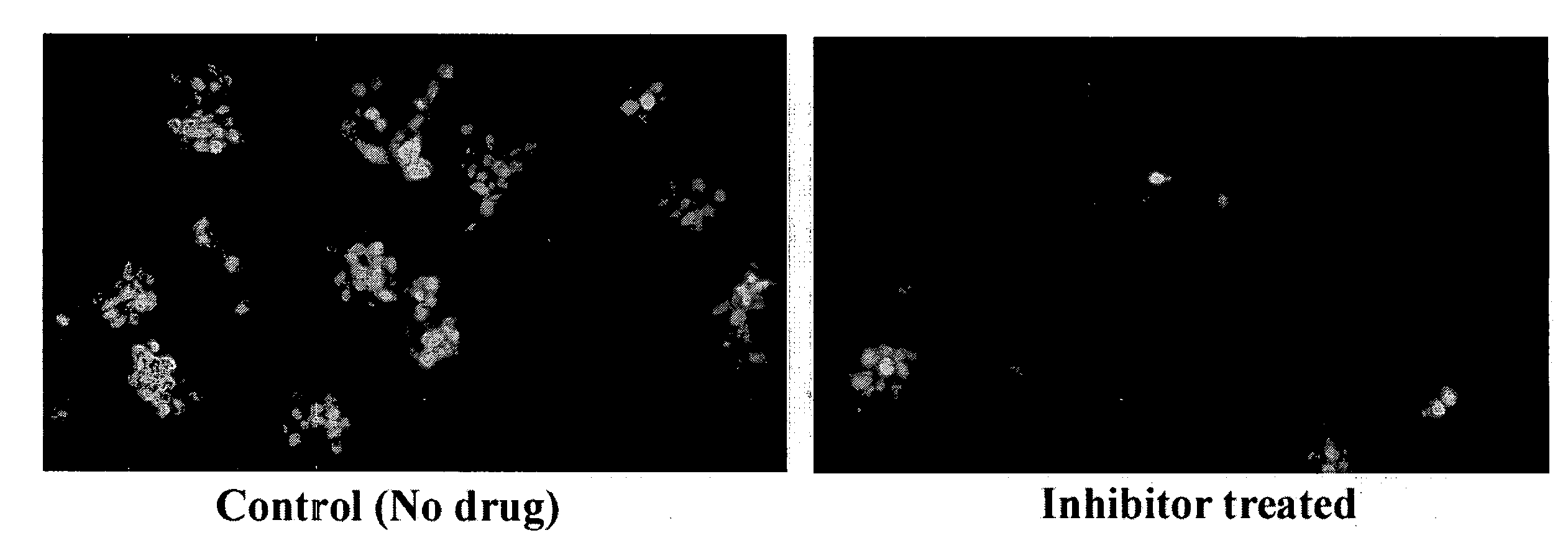
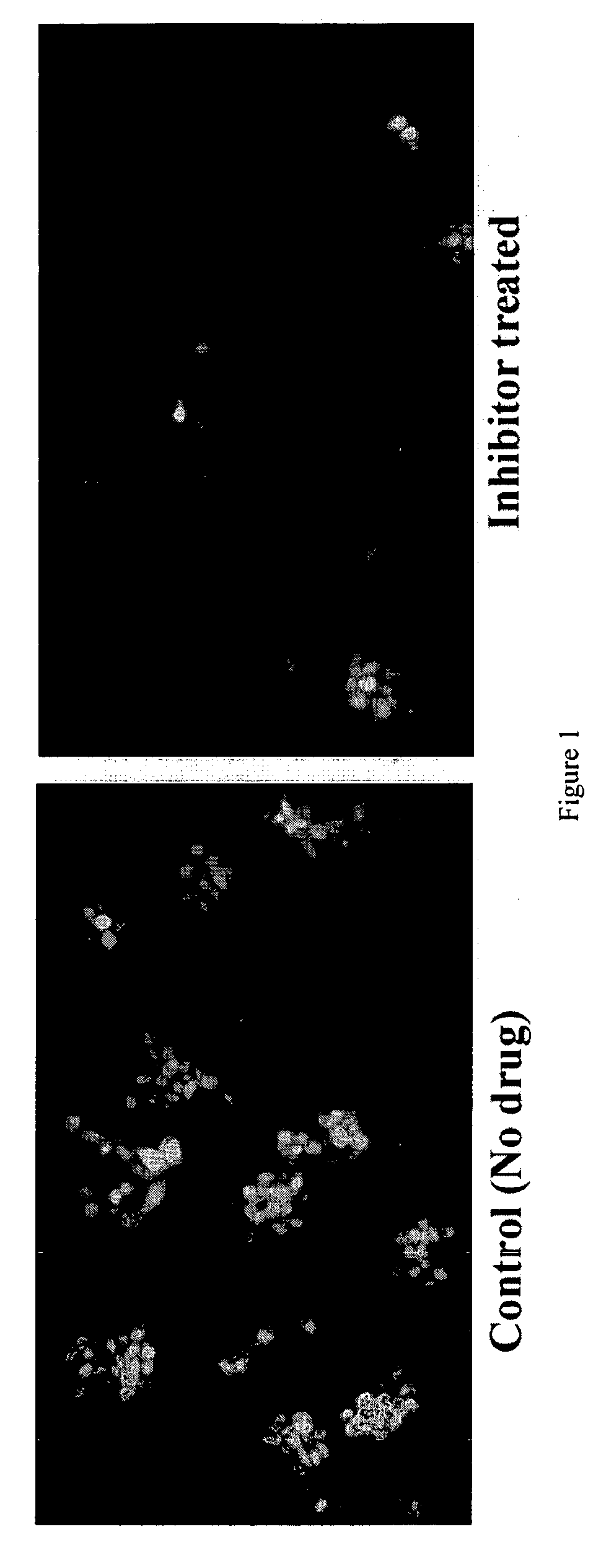
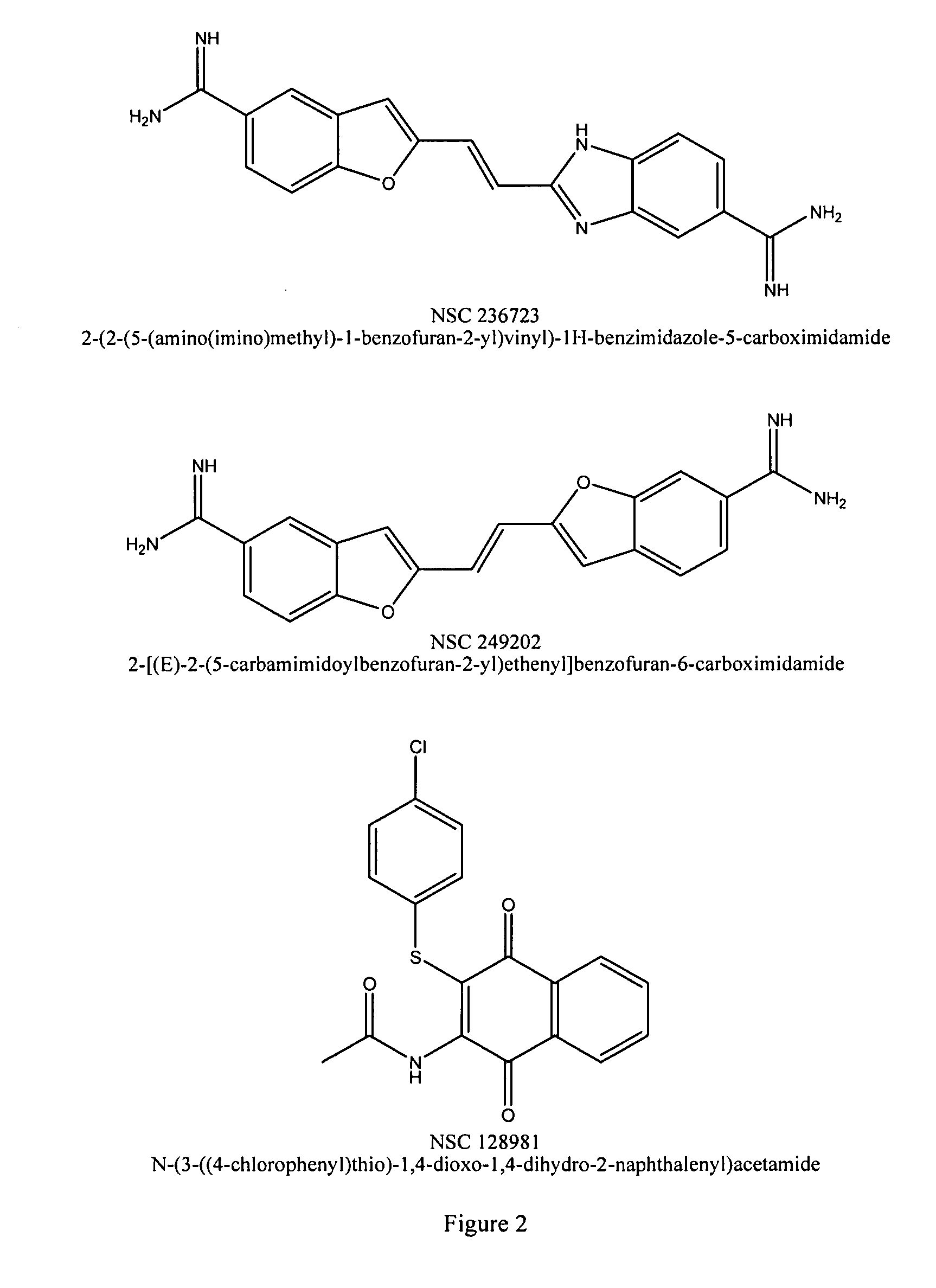
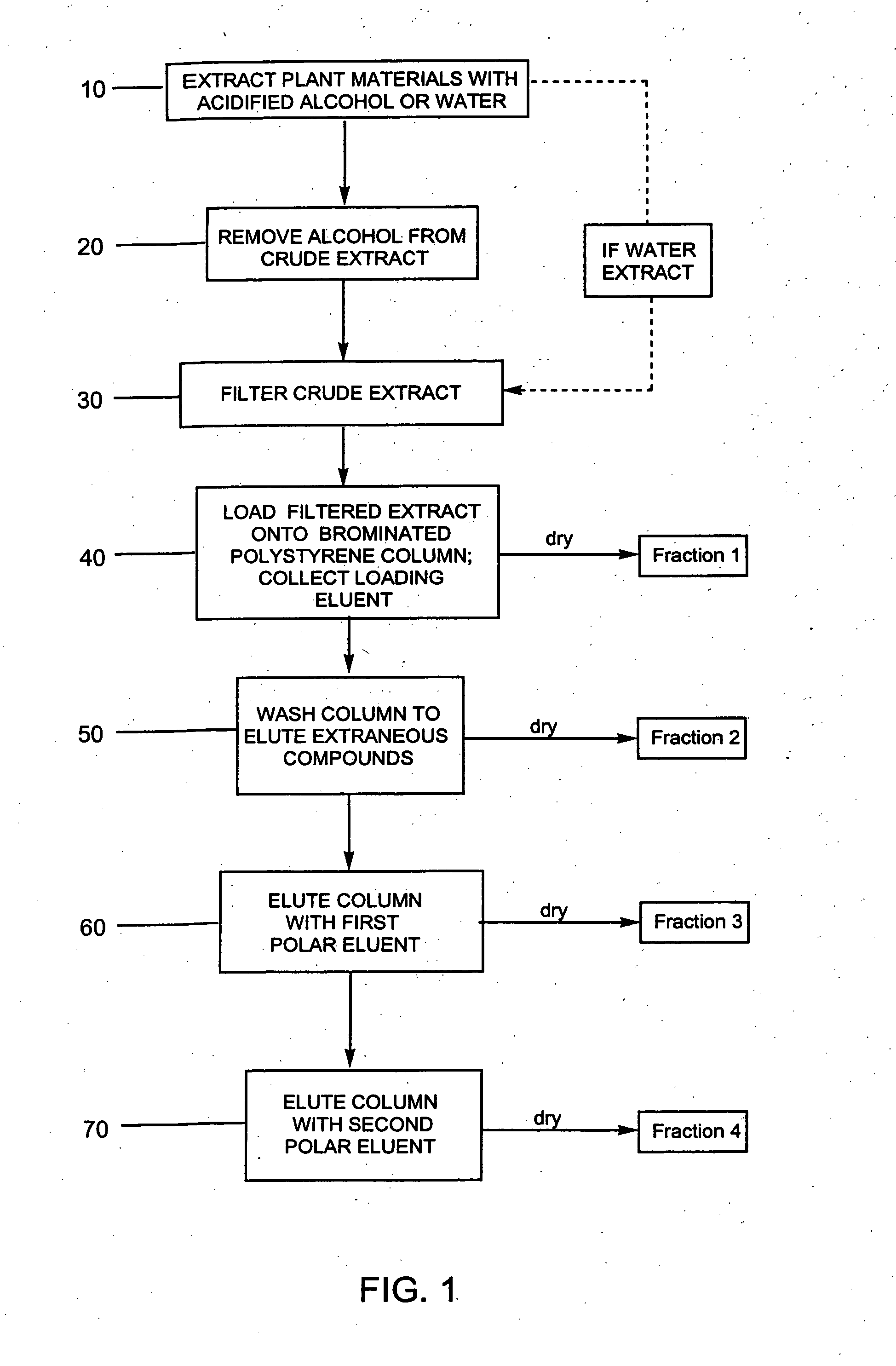
Provided are processes for the preparation of compositions enriched in phenolic compounds from a crude plant extract. One process includes a novel column purification step using a polymer resin that releasably adsorbs the phenolic compounds but does not retain polar non-phenolic compounds, wherein the resin comprises aromatic rings substituted with one or more electron-withdrawing groups. This invention also includes compositions enriched in phenolic compounds. This invention encompasses methods of using the phenolic-enriched compositions for treating warm-blooded animals, including humans, infected with paramyxovaridae such as respiratory syncytial virus, orthomyoxovaridae such as influenza A, B, and C, parainfluenza, Herpes viruses such as HSV-1 and HSV-2, and Flaviviruses such as West Nile Virus, and for treating inflammation such as caused by arthritis, stress and digestive disease. The compositions are also useful as meat additives to inhibit food-borne pathogens.
Owner:PHENOLICS LLC
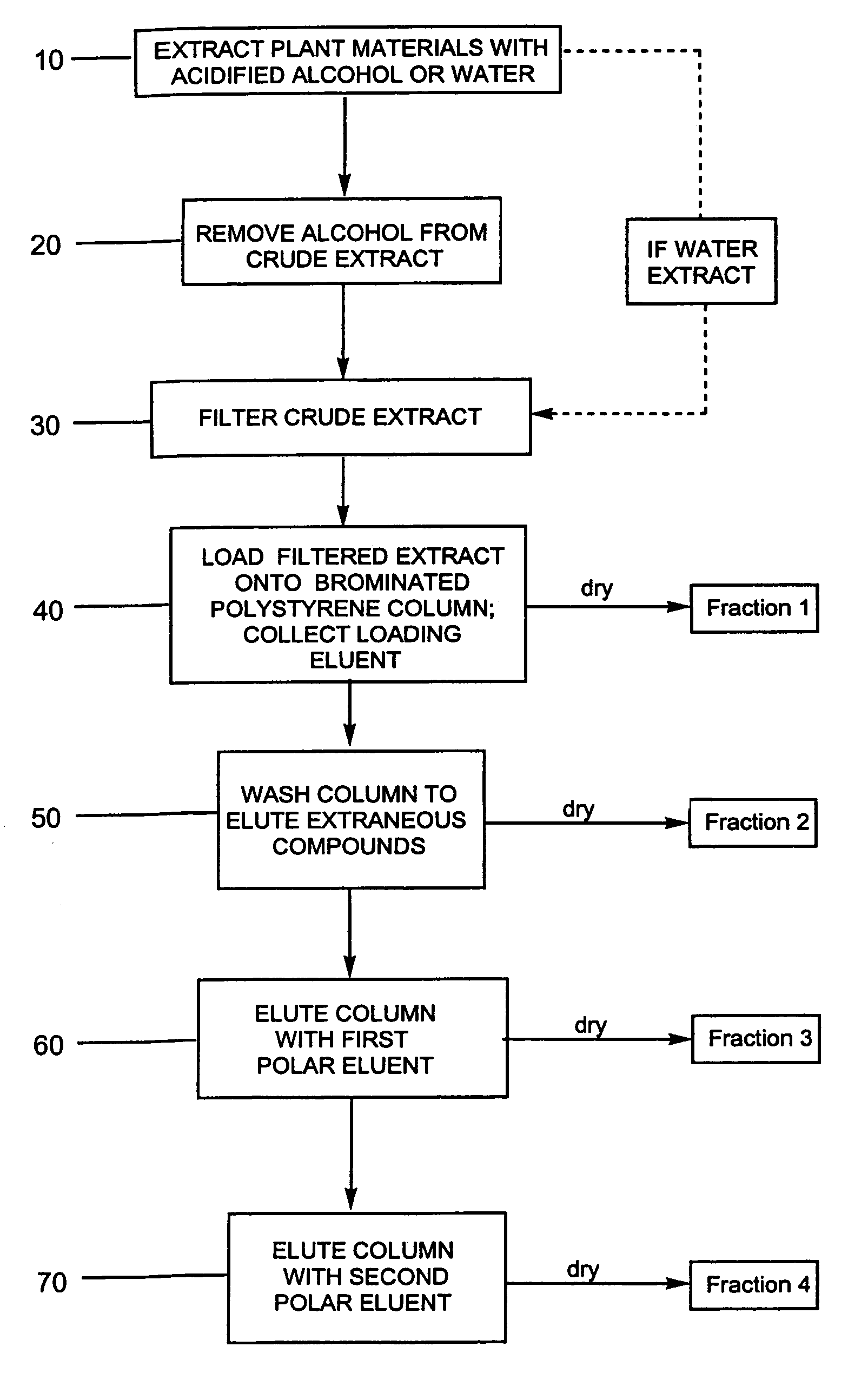
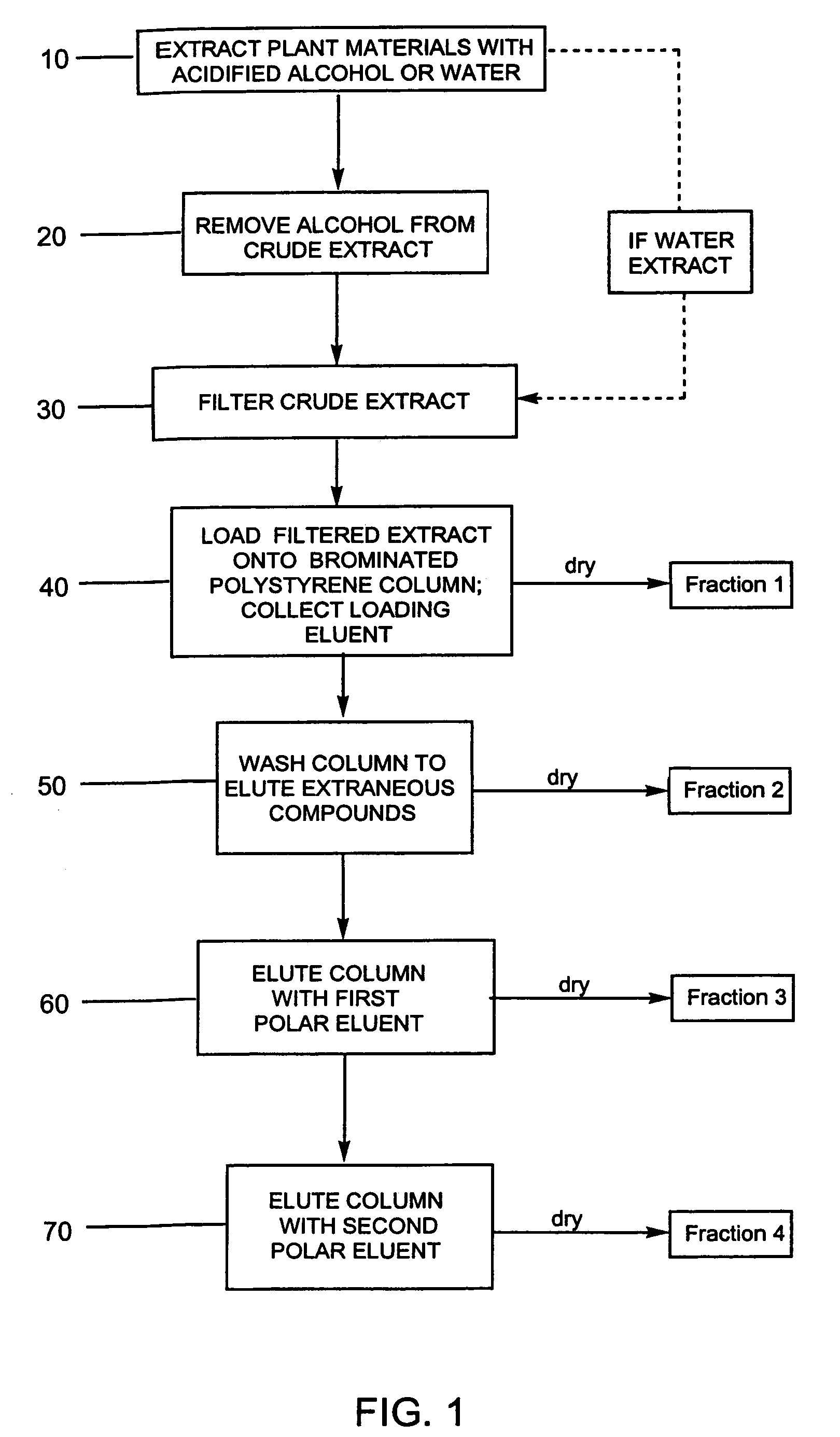
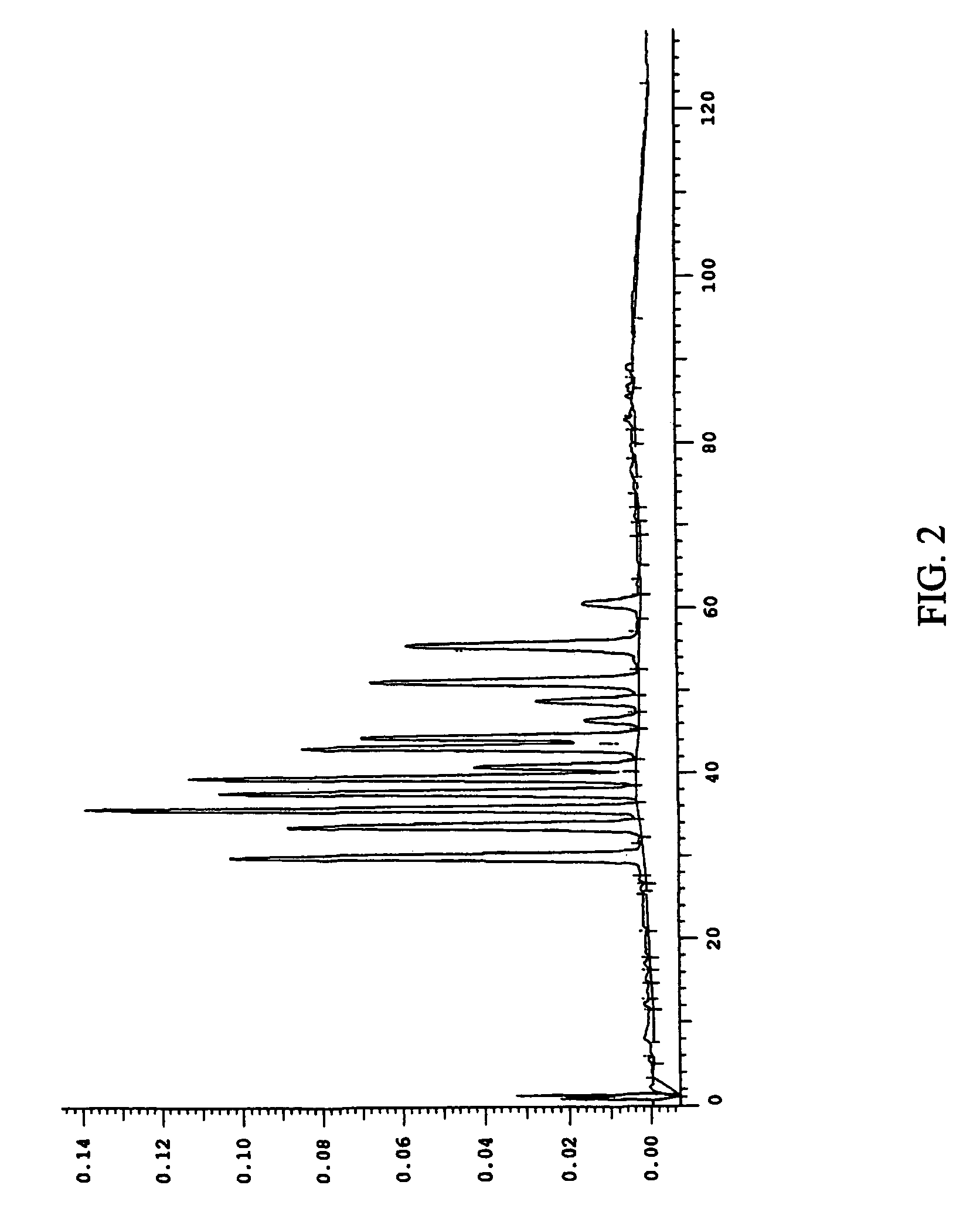
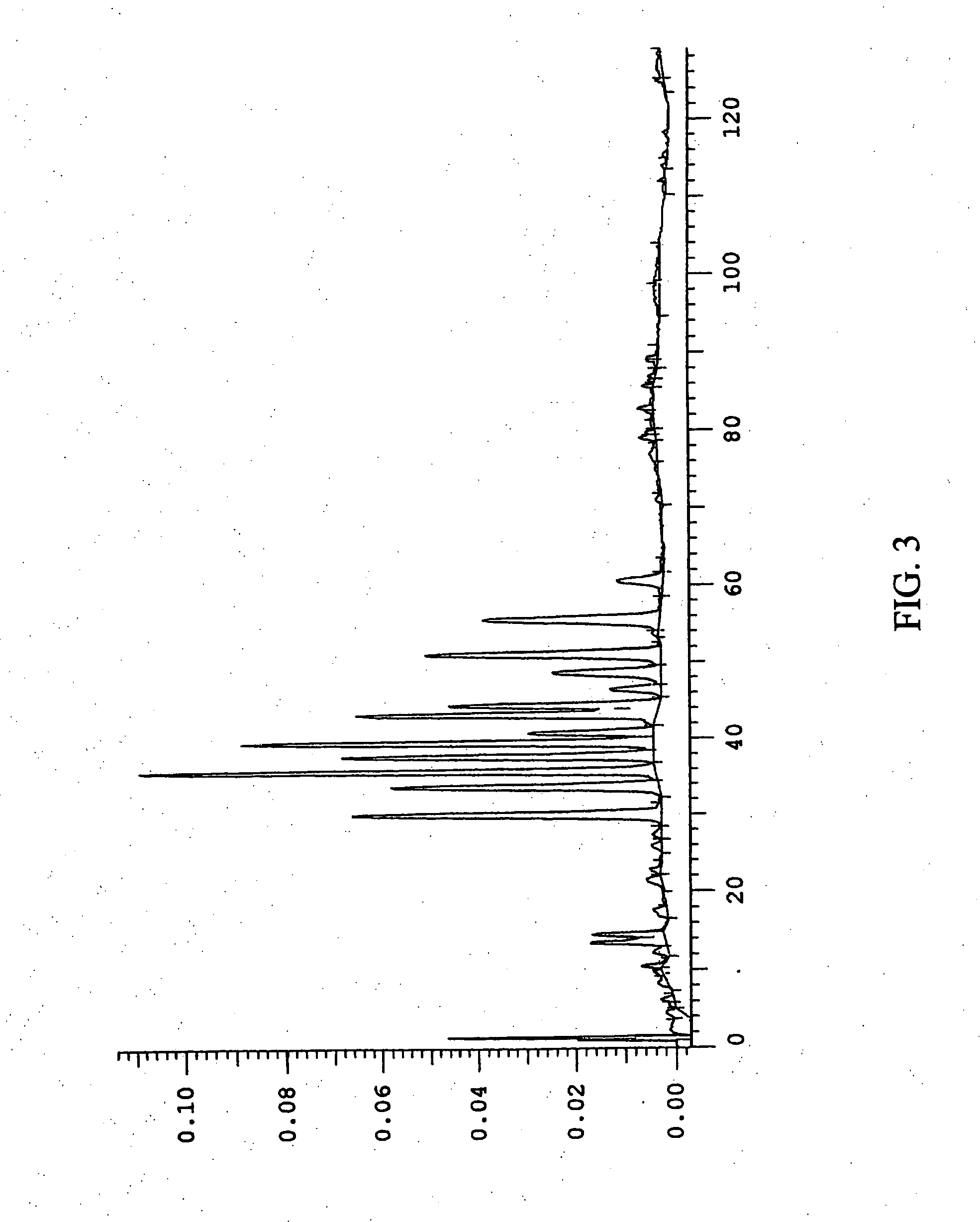
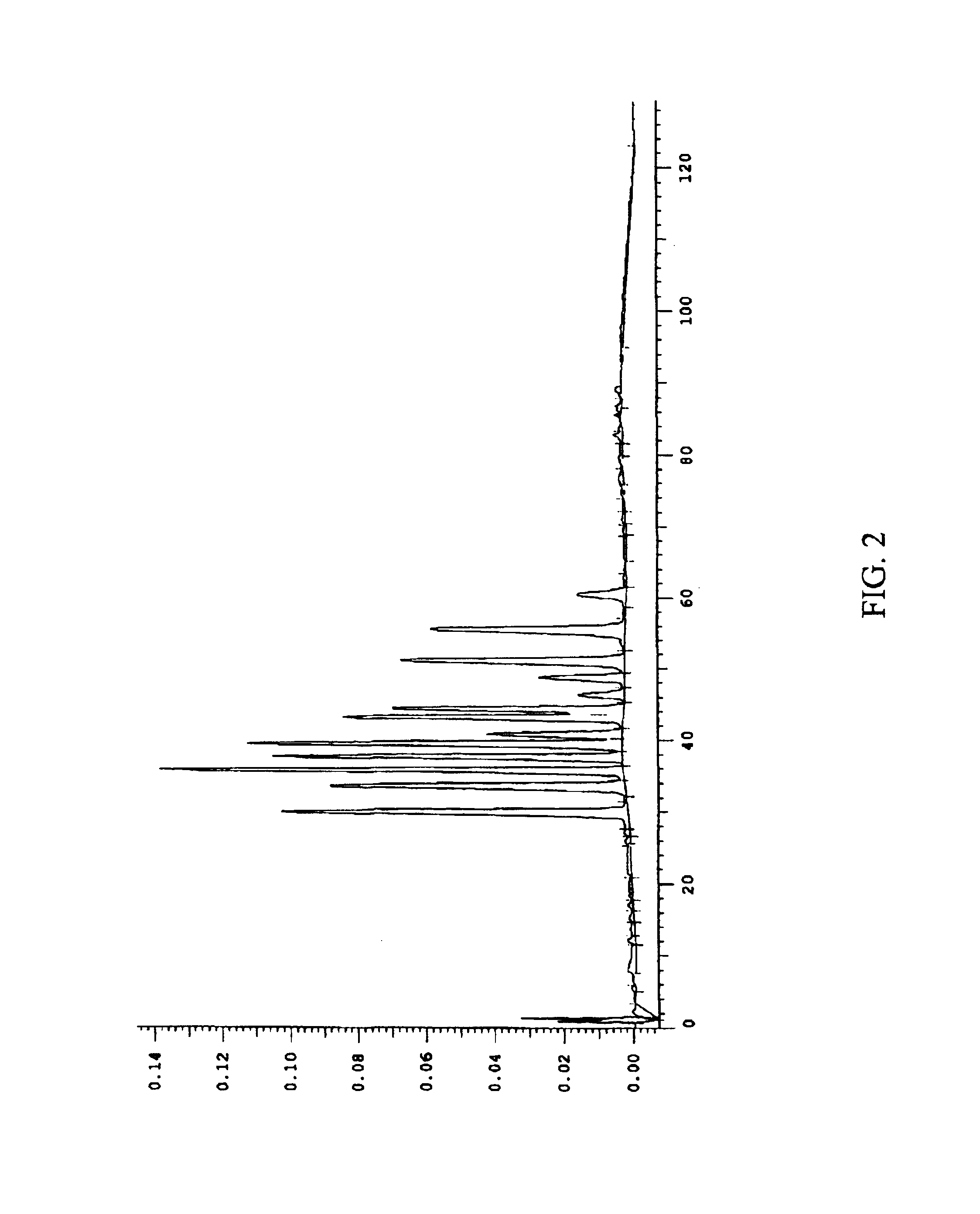
Efficient method for producing compositions enriched in total phenols
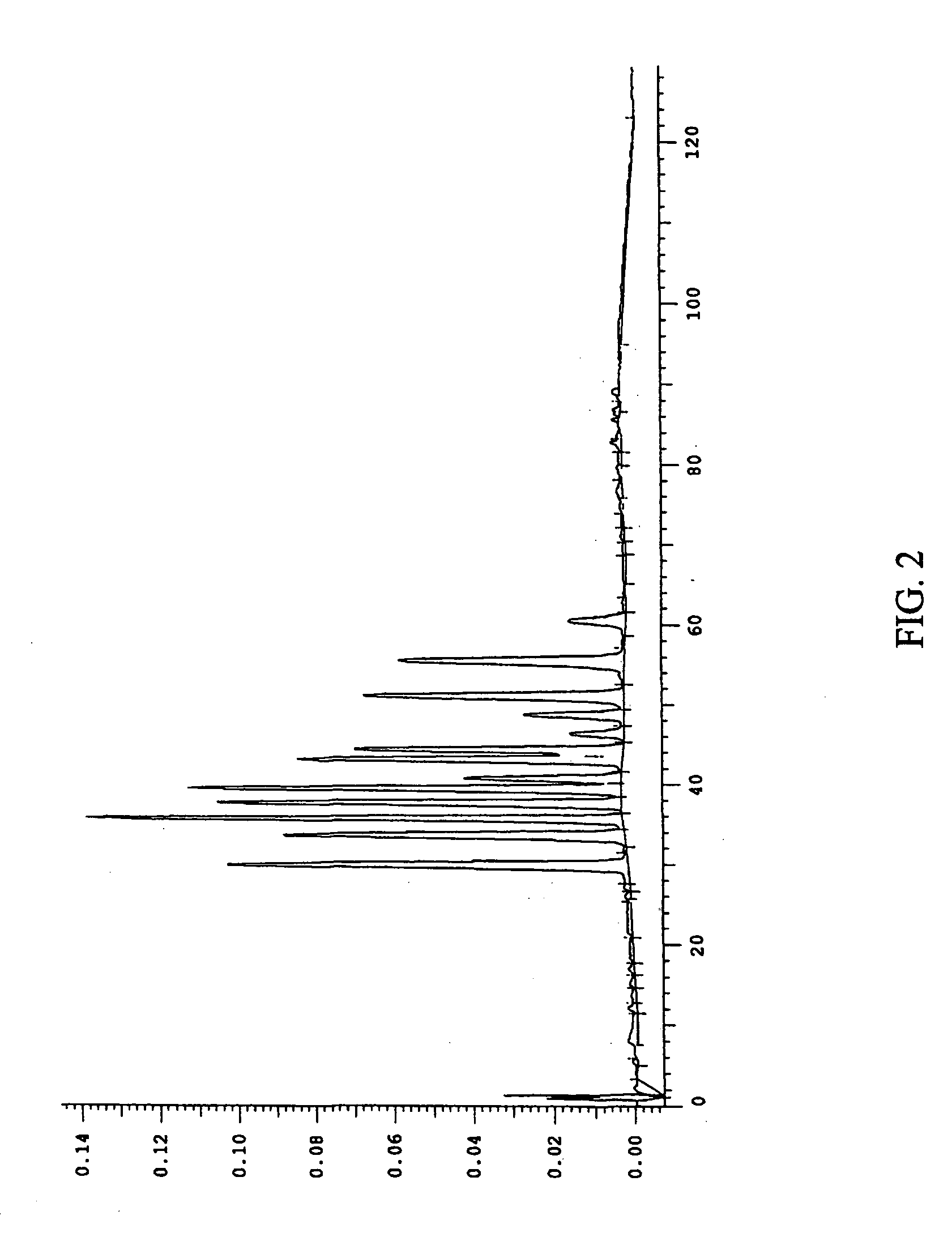
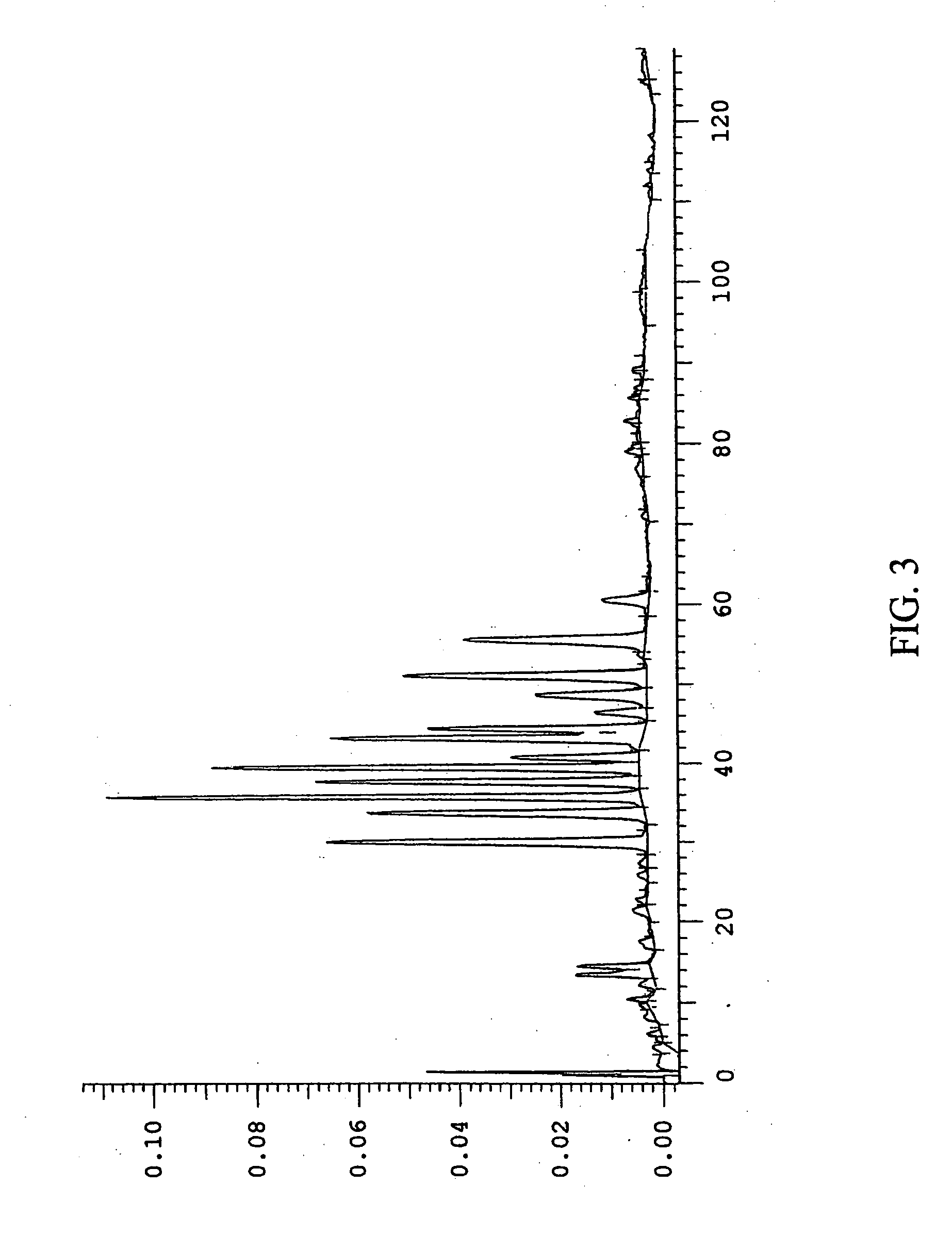
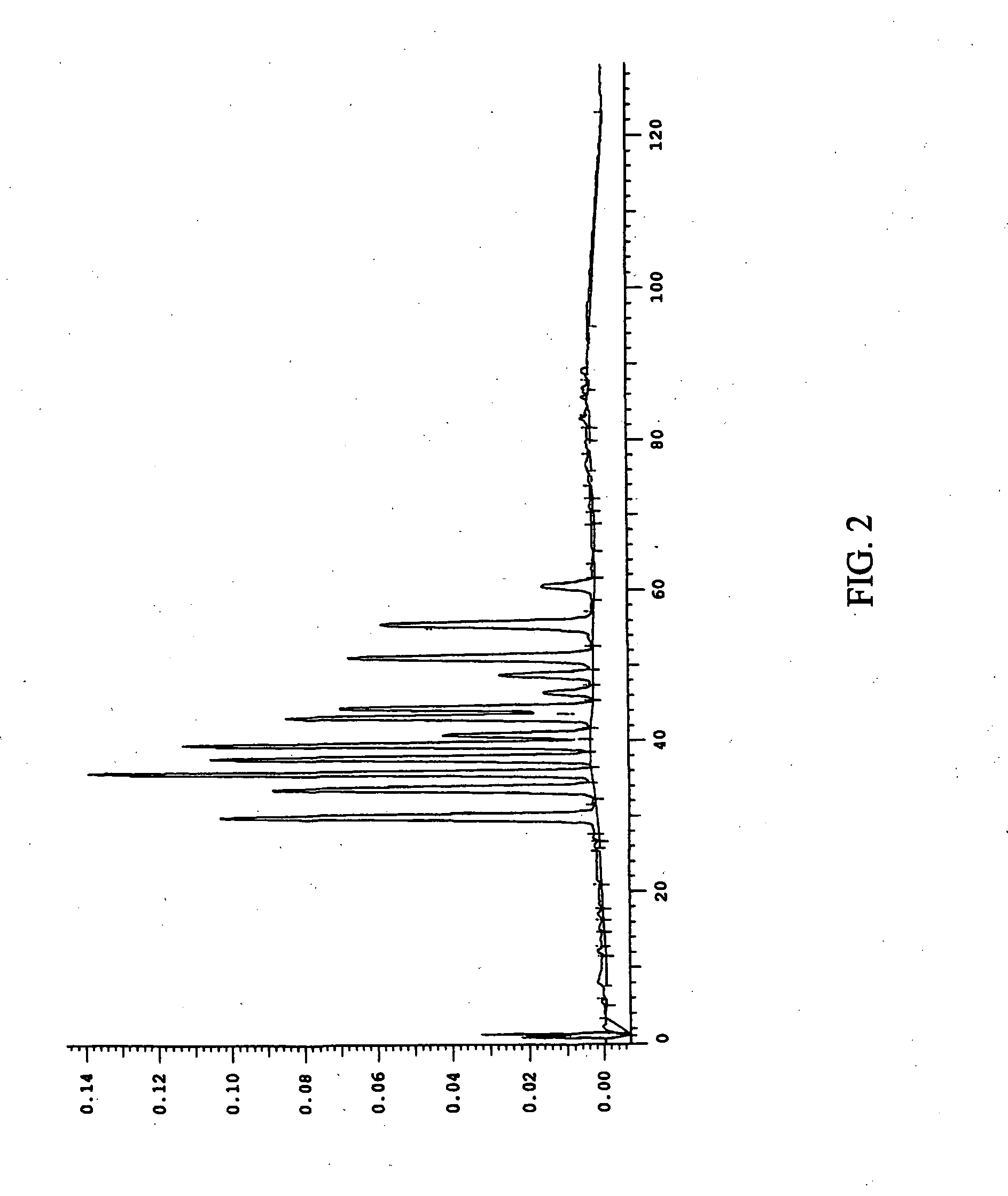
This invention provides a process for the preparation of compositions enriched in total phenols from a crude plant extract. The process includes a novel column purification step using a brominated polystyrene resin. This invention also includes compositions enriched in total phenols. The enriched compositions are characterized as containing monomeric, oligomeric and polymeric phenols and having HPLC chromatograms substantially as set forth in FIGS. 10-13. This invention encompasses methods of using the total phenol-enriched compositions for treating warm-blooded animals, including humans, infected with paramyxovaridae such as respiratory syncytial virus, orthomyoxovaridae such as influenza A, B, and C, parainfluenza, Herpes viruses such as HSV-1 and HSV-2, and Flaviviruses such as West Nile Virus, and for treating inflammation such as caused by arthritis, stress and digestive disease.
Owner:PHENOLICS LLC
Crystalline forms of (S)-2-ethylbutyl 2-(((S)-(((2R,3S,4R,5R)-5- (4-aminopyrrolo[2,1-f] [1,2,4]triazin-7-yl)-5-cyano-3,4-dihydroxytetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methoxy)(phenoxy) phosphoryl)amino)propanoate
The present invention relates to novel salts and crystalline forms of (S)-2-ethylbutyl 2-(((S)-(((2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(4-aminopyrrolo[2,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-7-yl)-5-cyano-3,4-dihydroxytetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methoxy)(phenoxy)phosphoryl)amino)propanoate having the structure:for use in treating viral infections. One crystalline form of the compound can be characterized by an X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD) pattern having peaks at 22.3°, 16.9°, and 16.2° 2-θ±0.2° 2-θ. In some embodiments, the viral infection is caused by a virus selected from the group consisting of Arenaviridae, Coronaviridae, Filoviridae, Flaviviridae, and Paramyxoviridae.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Compositions enriched in phenolic compounds and methods for producing the same
Provided are processes for the preparation of compositions enriched in phenolic compounds from a crude plant extract. One process includes a novel column purification step using a polymer resin that releasably adsorbs the phenolic compounds but does not retain polar non-phenolic compounds, wherein the resin comprises aromatic rings substituted with one or more electron-withdrawing groups. This invention also includes compositions enriched in phenolic compounds. This invention encompasses methods of using the phenolic-enriched compositions for treating warm-blooded animals, including humans, infected with paramyxovaridae such as respiratory syncytial virus, orthomyoxovaridae such as influenza A, B, and C, parainfluenza, Herpes viruses such as HSV-1 and HSV-2, and Flaviviruses such as West Nile Virus, and for treating inflammation such as caused by arthritis, stress and digestive disease. The compositions are also useful as meat additives to inhibit food-borne pathogens.
Owner:PHENOLICS LLC
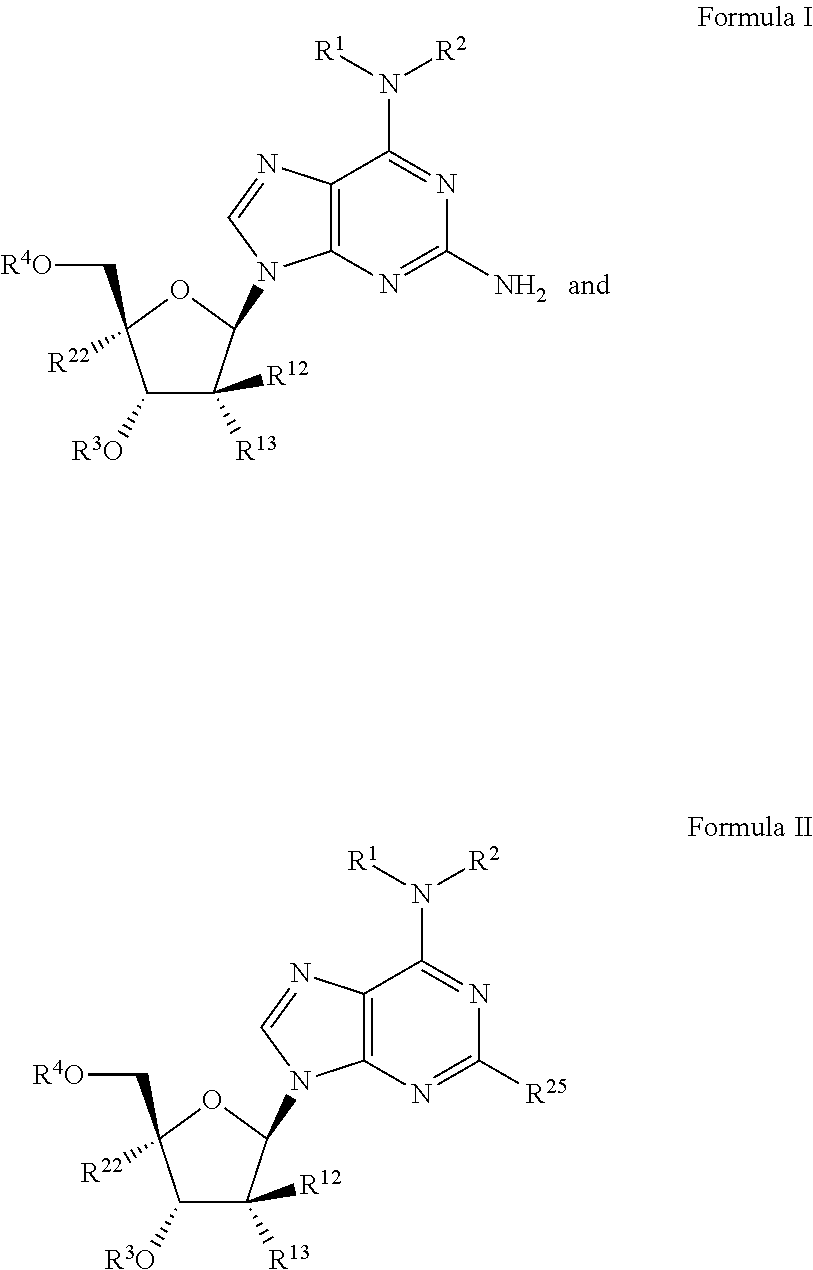
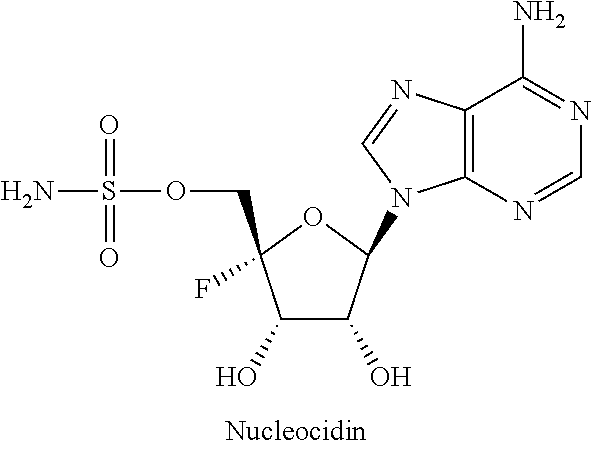
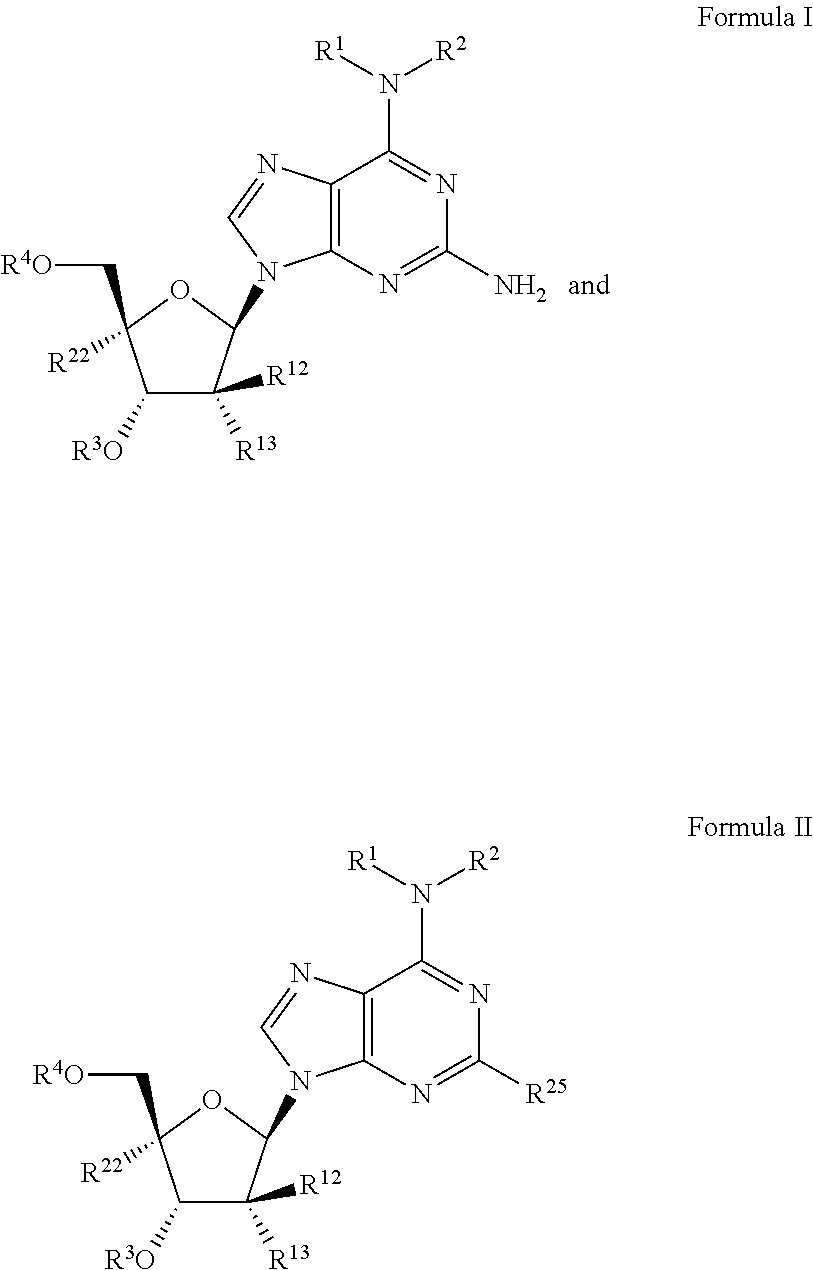
Beta-d-2'-deoxy-2'-substituted-4'-substituted-2-substituted-n6-substituted-6-aminopurinenucleotides for the treatment of paramyxovirus and orthomyxovirus infections
ActiveUS20180009836A1Improve lipophilicityStrong specificitySugar derivativesAntiviralsDiseaseNucleotide
A compound or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or composition thereof for the treatment of a host infected with or exposed to a virus of the Paramyxoviridae or Orthomyxoviridae family, or other disorders, in particular respiratory syncytial virus, more fully described herein.
Owner:ATEA PHARMA INC
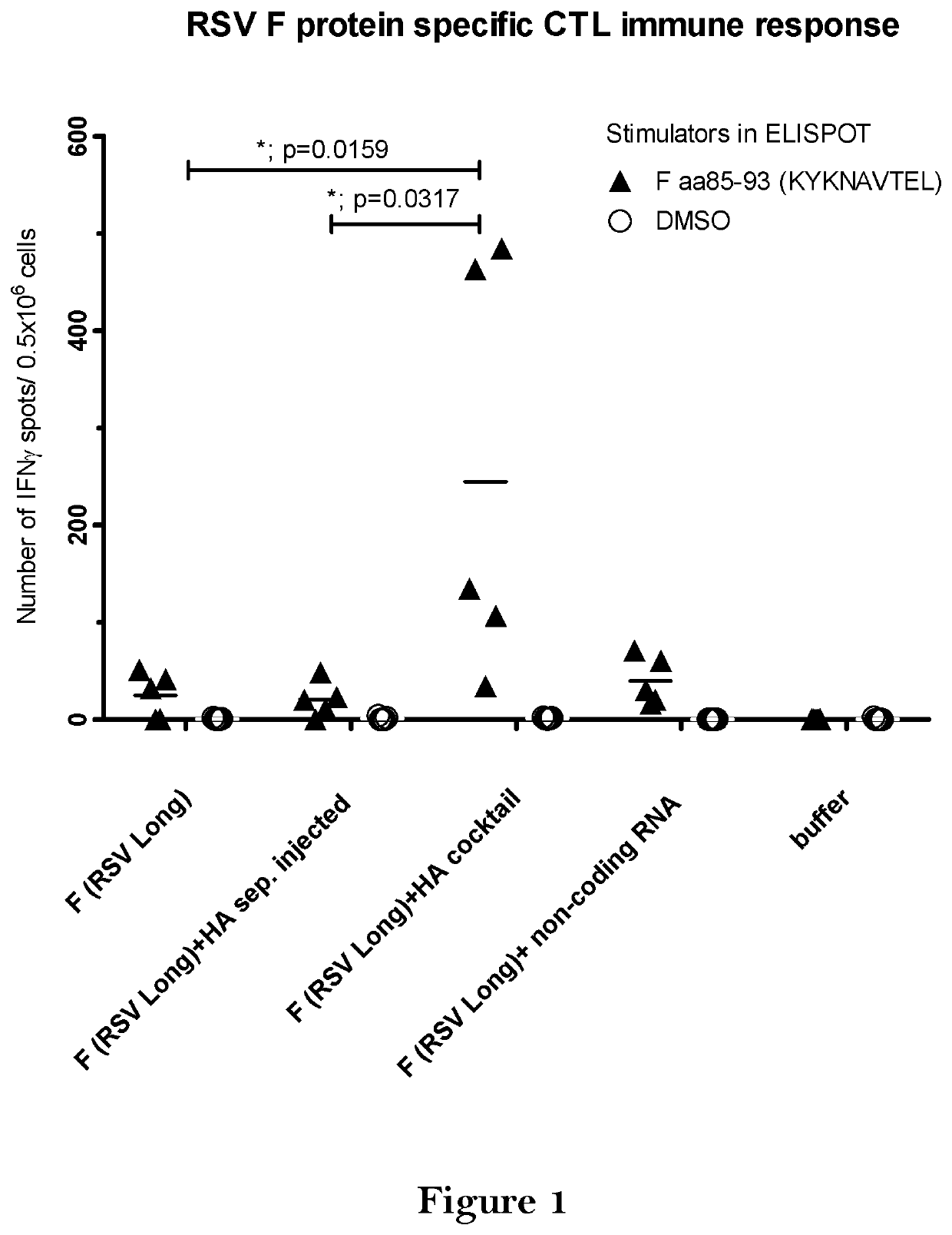
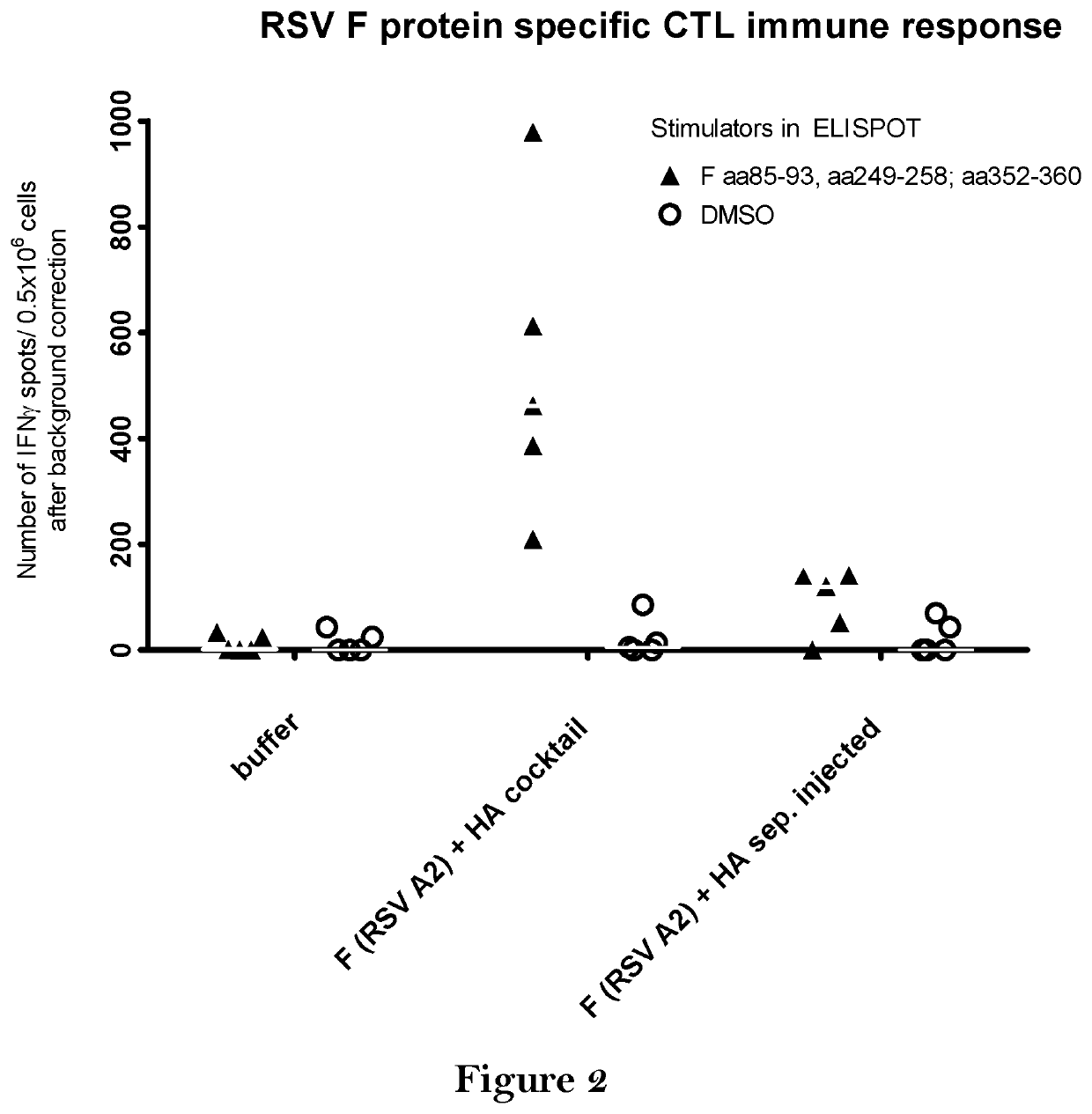
Combination vaccine
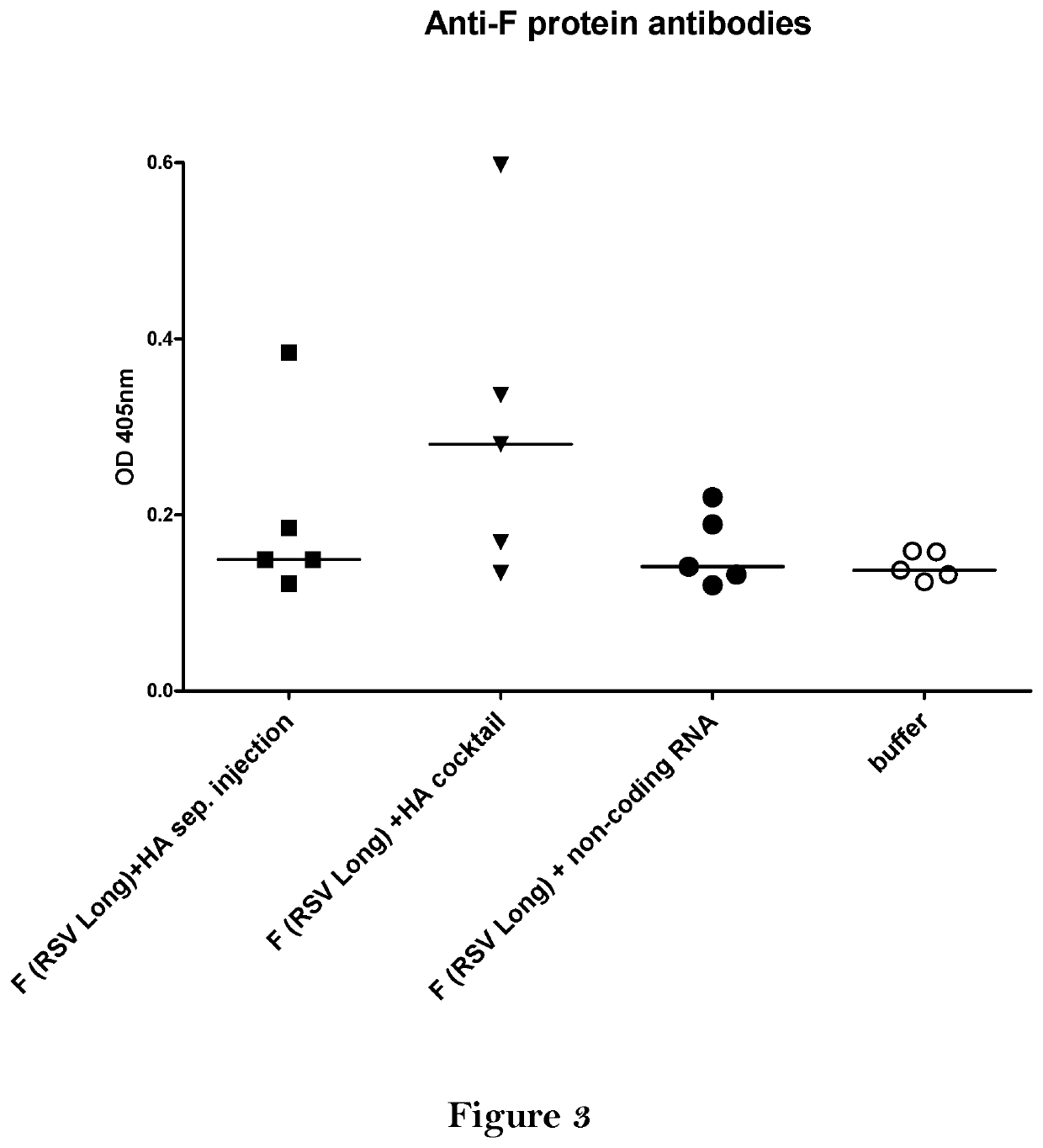
The present invention relates to a vaccine, especially a combination vaccine providing at least a first and a second antigenic function, the combination vaccine comprising at least one RNA encoding at least one or more proteins or fragments, variants or derivatives of proteins awarding antigenic function, wherein the first antigenic function being a Fusion (F) protein or a fragment, variant or derivative of a Fusion (F) protein derived from the virus family Paramyxoviridae and the second antigenic function being an Hemagglutinin (HA) protein or a fragment, variant or derivative of an Hemagglutinin (HA) protein derived from the virus family Orthomyxoviridae. Furthermore, the present invention is directed to a kit or kit of parts comprising the components of said combination vaccine and to said combination vaccine for use in a method of prophylactic or therapeutic treatment of diseases, particularly in the prevention or treatment of infectious diseases like RSV and influenza.
Owner:CUREVAC SE
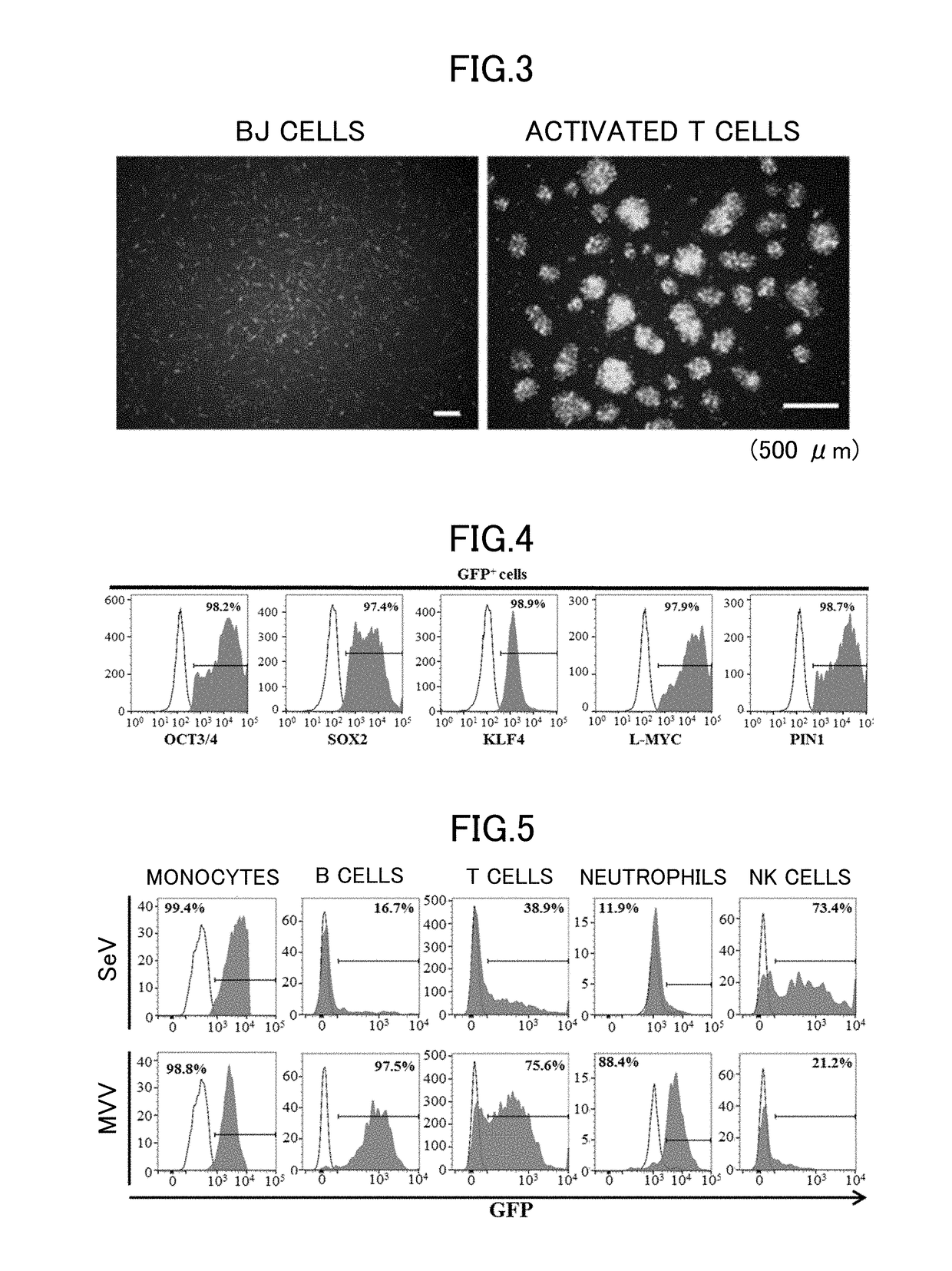
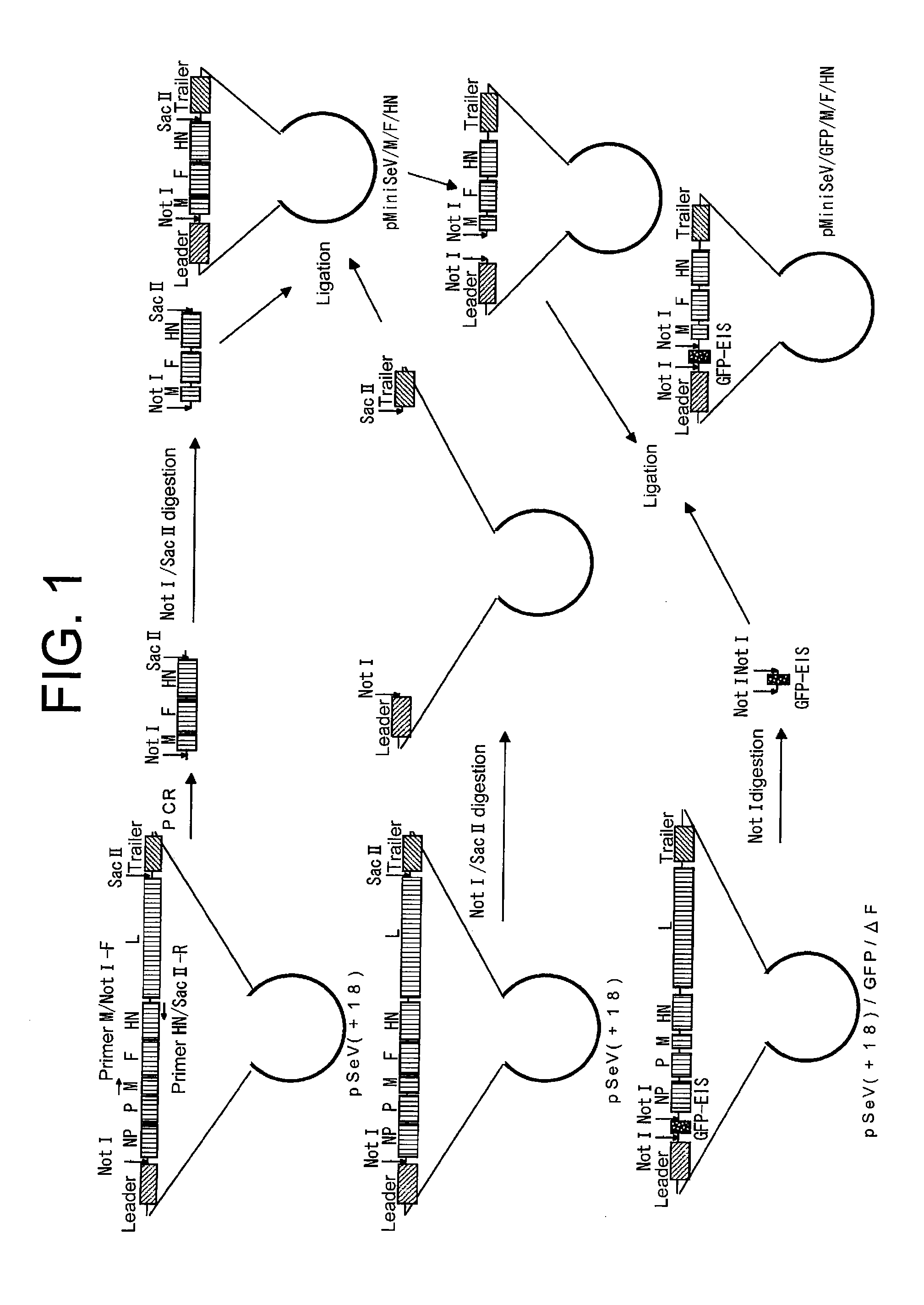
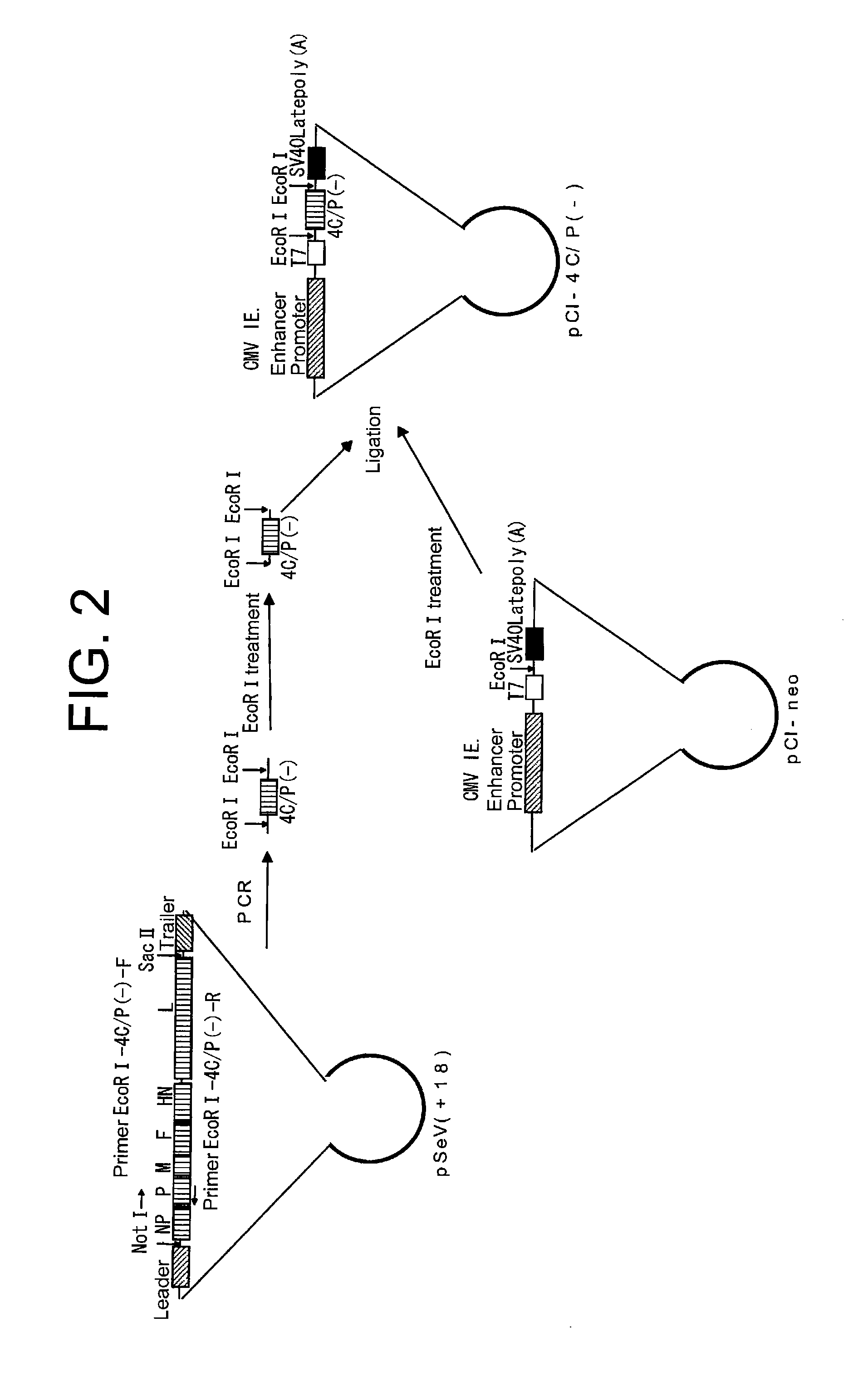
Paramyxorividae virus vector defective in envelope gene
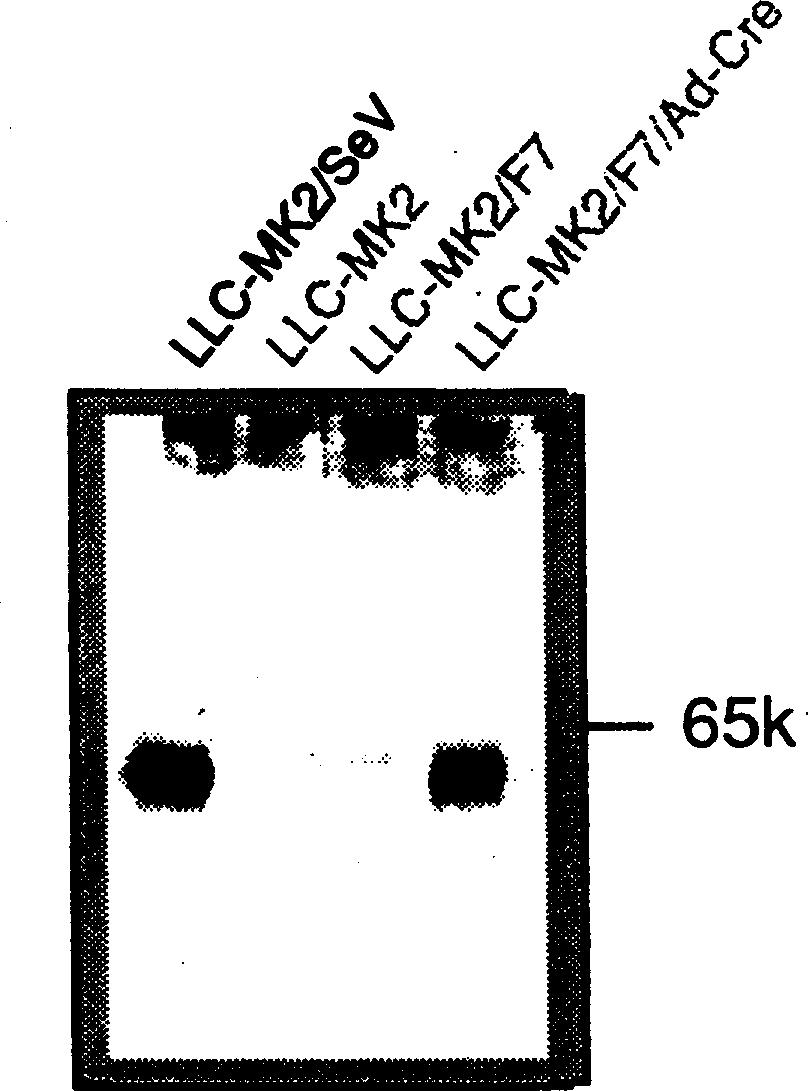
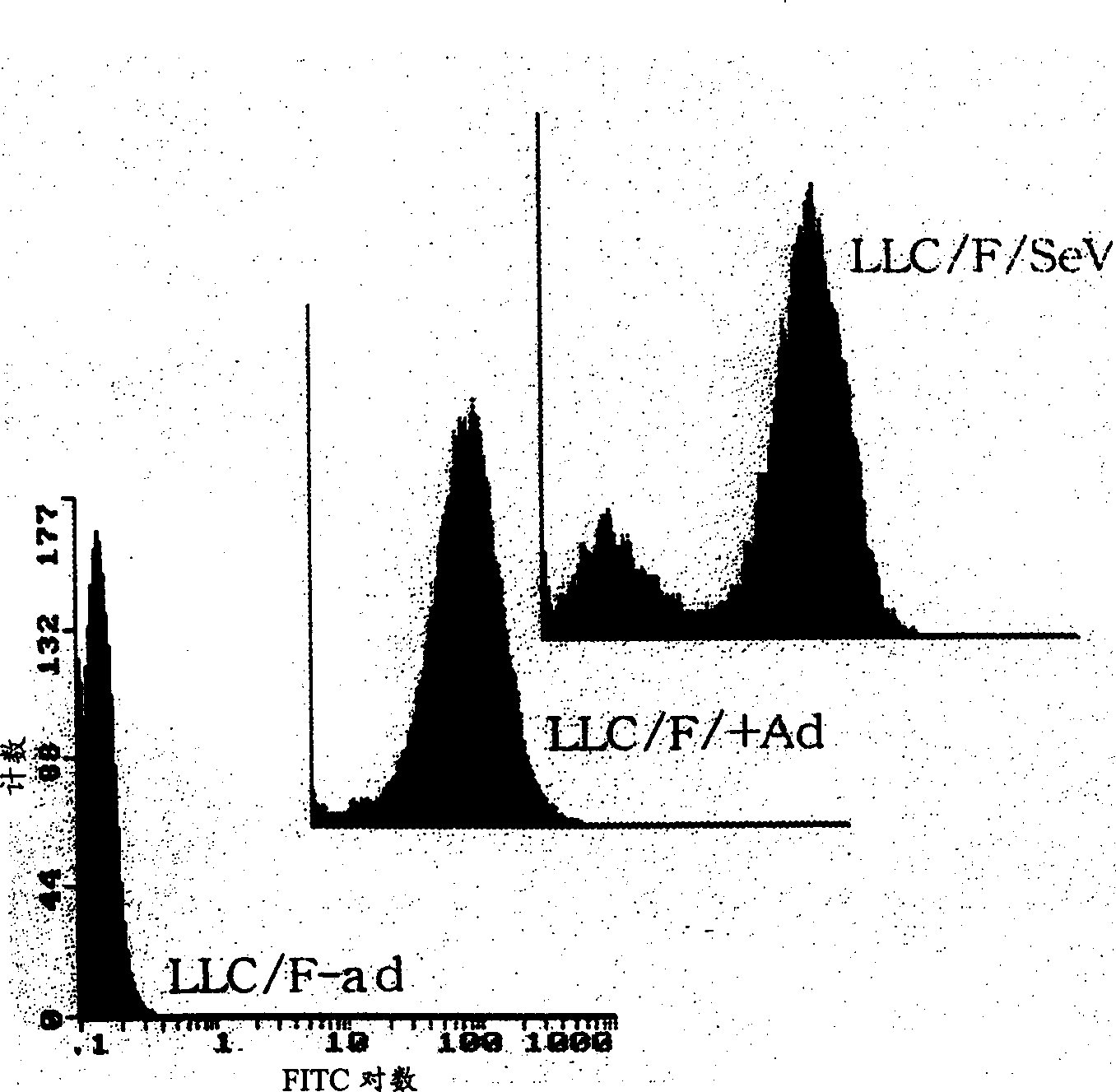
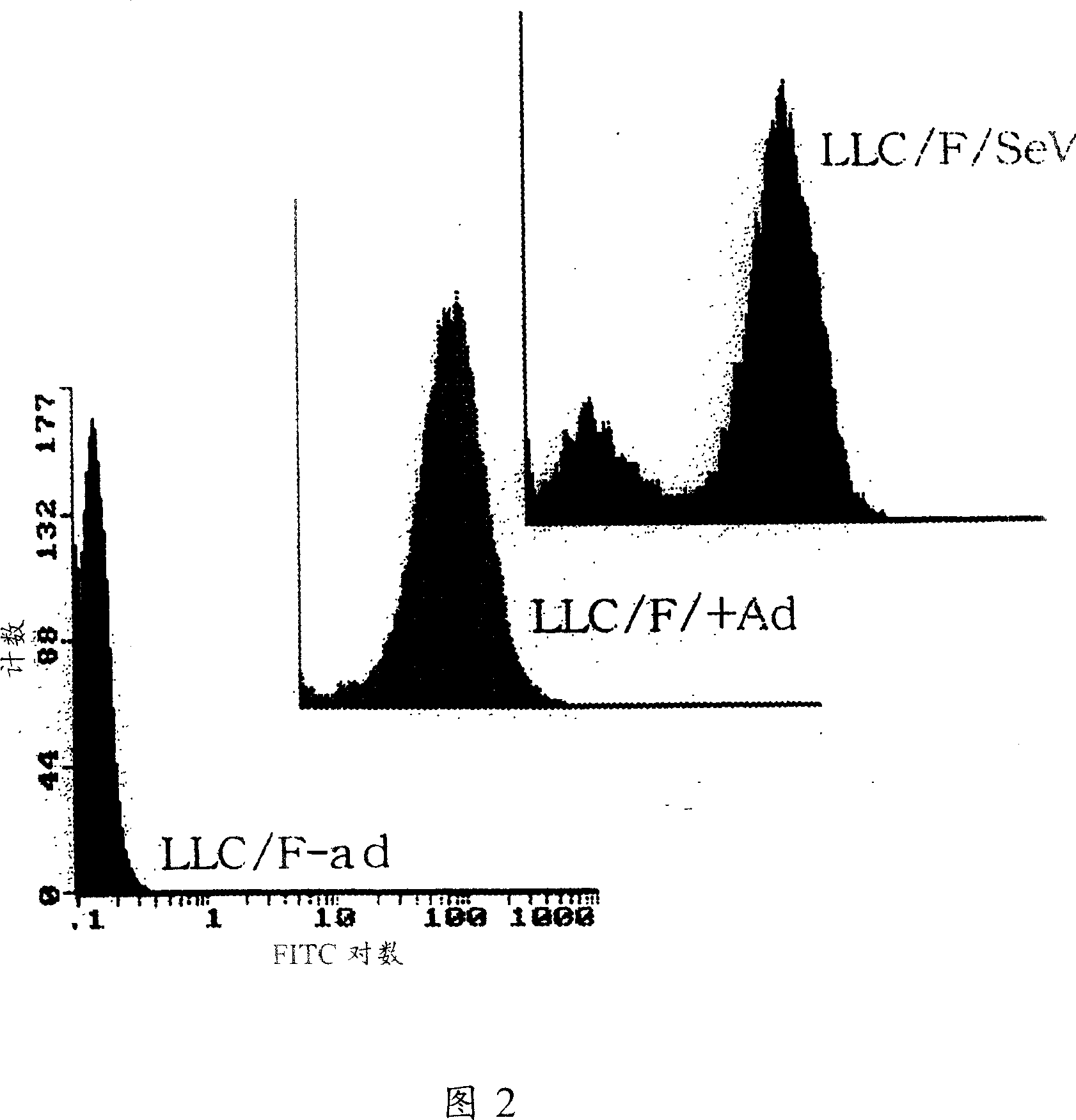
InactiveCN1355851AHigh gene transfer efficiencyImprove securitySsRNA viruses negative-senseGenetic material ingredientsF proteinParamyxoviridae
Virus virions defective in F gene are successfully collected by using a Sendai virus genomic cDNA with deletion of F gene. Further, infectious viral particles defective in F gene are successfully constructed by using F-expression cells as helper cells. Also, virus virions defective in F gene and HN gene are successfully collected by using a virus genomic cDNA with deletion of both of F gene and HN gene. Further, infectious viral particles defective in F gene and HN gene are successfully produced by using F- and HN-expression cells as helper cells. A virus being defective in F gene and HN gene and having F protein is constructed by using F-expression cells as helper cells. Further, a VSV-G pseudo type virus is successfully constructed by using VSV-G-expression cells. Techniques for constructing these defective viruses contribute to the development of vectors of Paramyxoviridae usable in gene therapy.
Owner:DNAVEC RES
Adapter-based retroviral vector system for the selective transduction of target cells
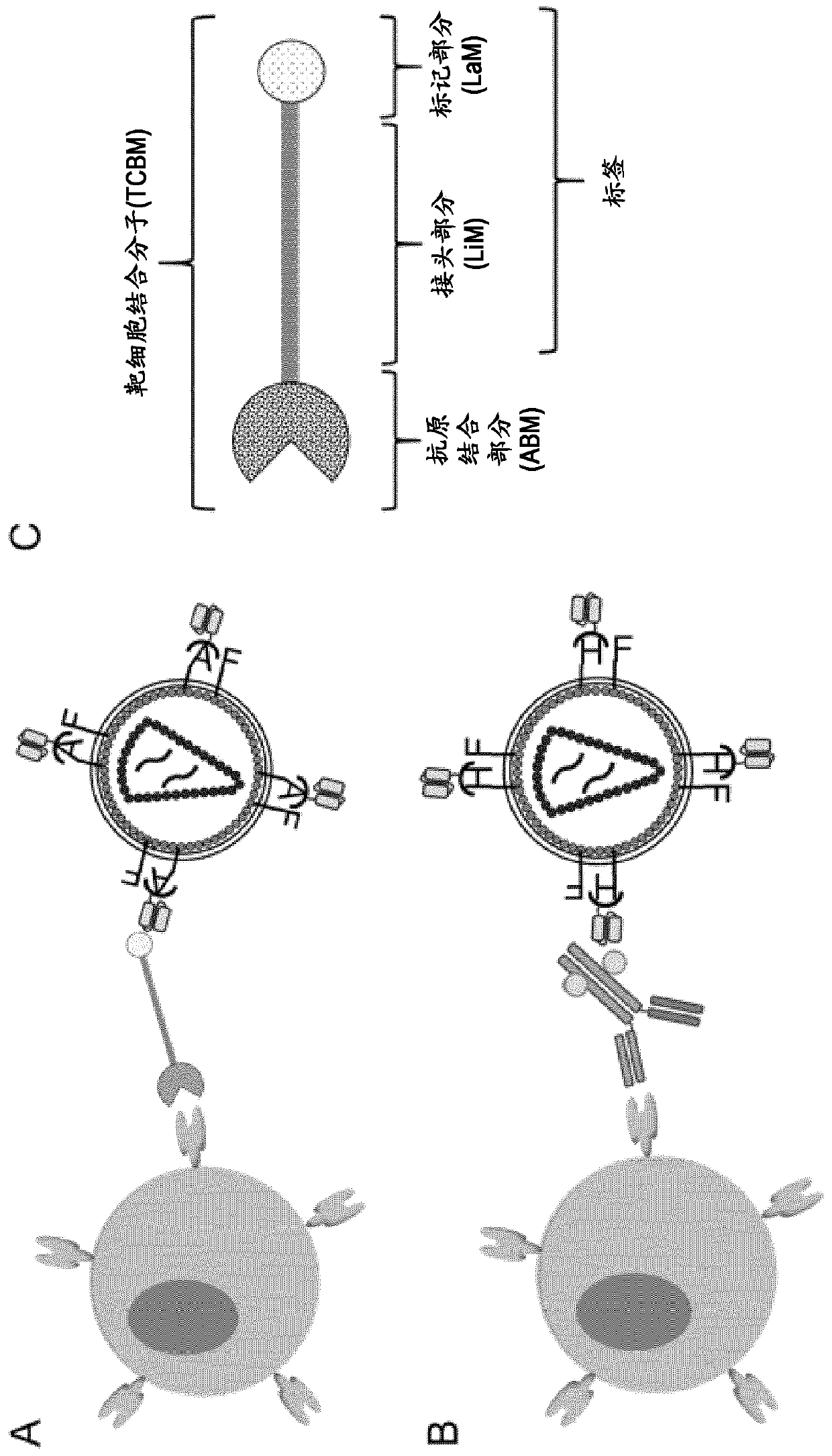
PendingCN111315761ASsRNA viruses negative-sensePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAntigen bindingEctodomain
The present invention provides a composition comprising i) a pseudotyped retroviral vector particle or virus-like particle thereof comprising a) one envelope protein with antigen-binding activity, wherein said envelope protein is a recombinant protein that does not interact with at least one of its native receptor(s) and is fused at its ectodomain to a polypeptide comprising an antigen binding domain specific for a tag of a tagged polypeptide, and wherein said envelope protein is protein G, HN or H derived from the Paramyxoviridae family, and b) one envelope protein with fusion activity derived from the Paramyxoviridae family, and ii) said tagged polypeptide, wherein said tagged polypeptide binds specifically to an antigen expressed on the surface of a target cell, thereby transducing thetarget cell with said retroviral vector particle or thereby inducing uptake of the virus-like particle into the target cell. A pharmaceutical composition thereof and an in vitro method for transduction of targets cells with said vector particle are also disclosed.
Owner:ミルテニイビオテックベーファーウントコーカーゲー
Antiviral compounds and methods of using thereof
Disclosed herein are compounds which exhibit antiviral activity against a plurality of viruses belonging to different families such as Bornaviridae, Filoviridae, Paramyxoviridae, Rhabdoviridae, Arenaviridae, Bunyaviridae, Orthomyxoviridae, and Poxviridae. Thus, methods of preventing, inhibiting, or reducing the viral activity of various viruses are provided as well as methods of treating viral infections.
Owner:US ARMY MEDICAL RES MATERIEL COMMAND USAMRMC
Efficient method for producing compositions enriched in total phenols
This invention provides a process for the preparation of compositions enriched in total phenols from a crude plant extract. The process includes a novel column purification step using a brominated polystyrene resin. This invention also includes compositions enriched in total phenols. The enriched compositions are characterized as containing monomeric, oligomeric and polymeric phenols and having HPLC chromatograms substantially as set forth in FIGS. 10-13. This invention encompasses methods of using the total phenol-enriched compositions for treating warm-blooded animals, including humans, infected with paramyxovaridae such as respiratory syncytial virus, orthomyoxovaridae such as influenza A, B, and C, parainfluenza, Herpes viruses such as HSV-1 and HSV-2, and Flaviviruses such as West Nile Virus, and for treating inflammation such as caused by arthritis, stress and digestive disease.
Owner:PHENOLICS LLC
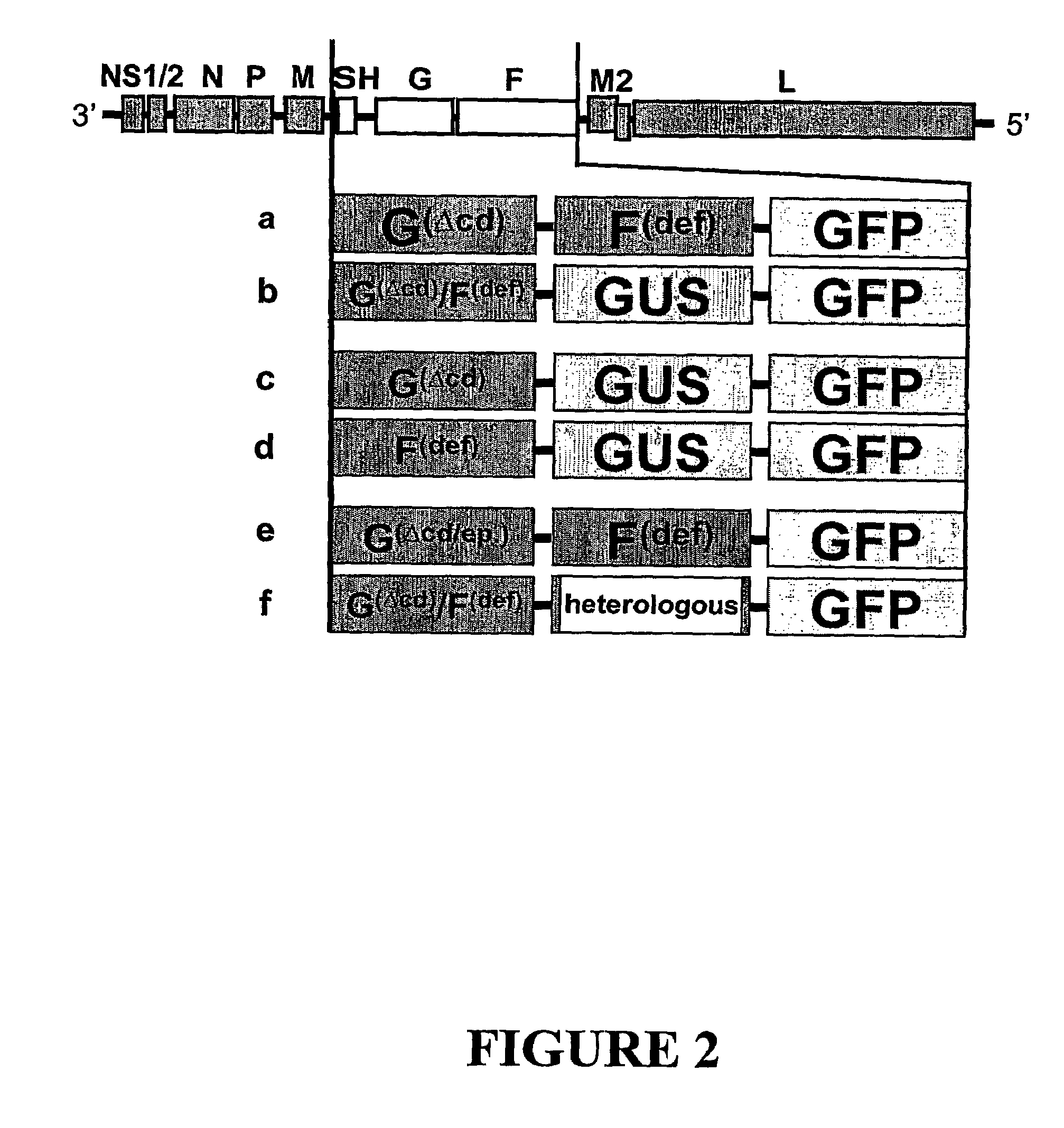
Recombinant viruses of the paramyxoviridae family with heterologous envelope glycoproteins
InactiveUS7588770B2Increase infectivityImproved potency and effectivenessSsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsHeterologousDisease
The invention provides recombinant viruses comprising heterologous envelope proteins capable of mediating entry of the recombinant viruses into host cells. In one embodiment, a recombinant virus of the invention is a member of the Paramyx-ovirzdae family (e.g., a respiratory syncytial virus), and the heterologous envelope protein includes the ectodomain of a baculovirus envelope protein (e.g., the GP64 protein). In some cases, the heterologous envelope protein is provided in addition to homologous envelope proteins) which may or may not be functional. The heterologous protein can provide the recombinant virus with enhanced stability (e.g., at 4° C., 22° C., or 37° C.), and allows production of high-titer virus stocks. The heterologous protein can also impart temperature sensitivity to the replication of the recombinant virus. In addition, the recombinant virus can be designed to be infectious but incapable of spreading between host cells by providing the heterologous protein by complementation in trans. These features attenuate the disease-causing potential of the recombinant virus, therefore increasing its safety of use as vaccines.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
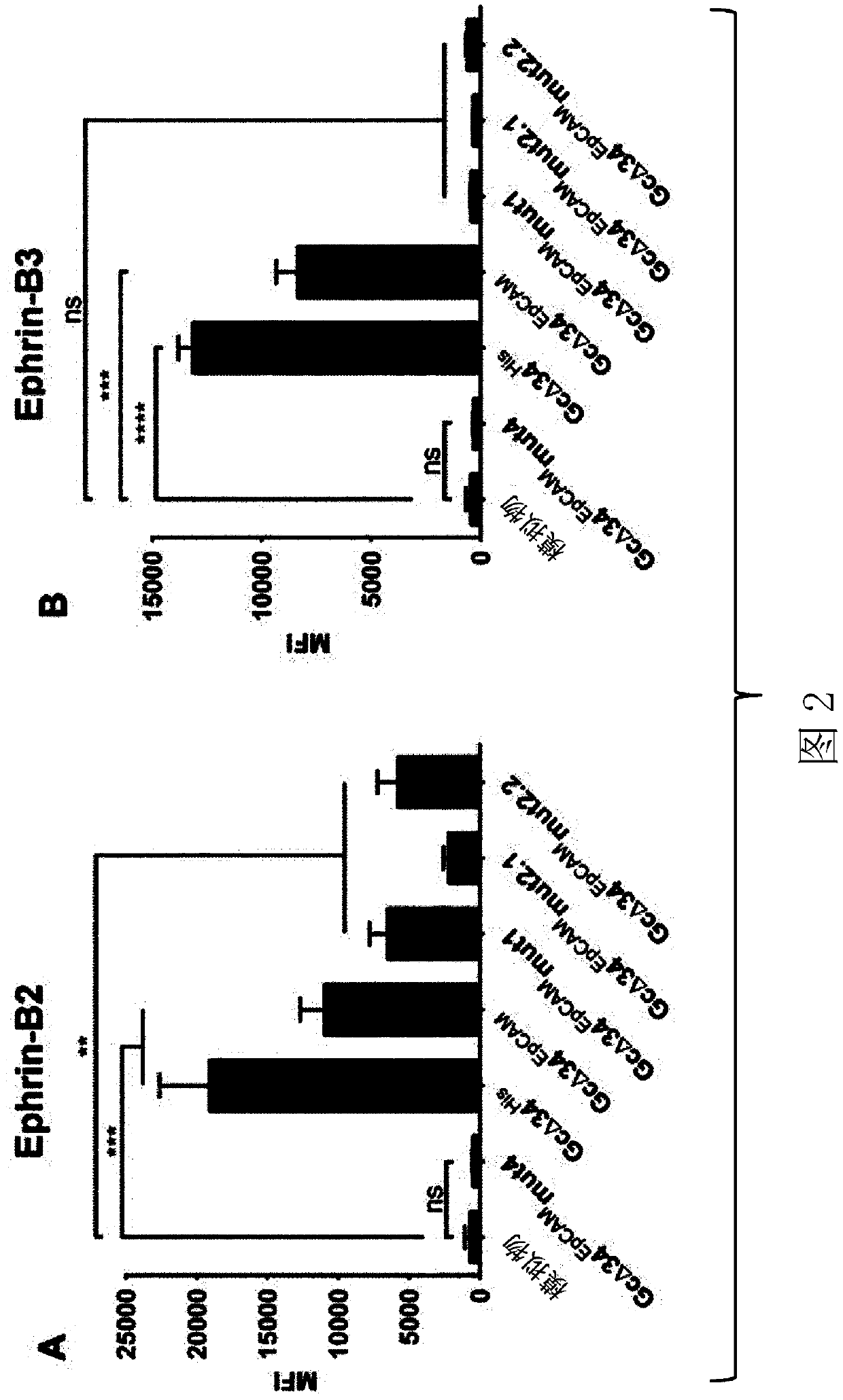
Use of ephrinb2 directed agents for the treatment or prevention of viral infections
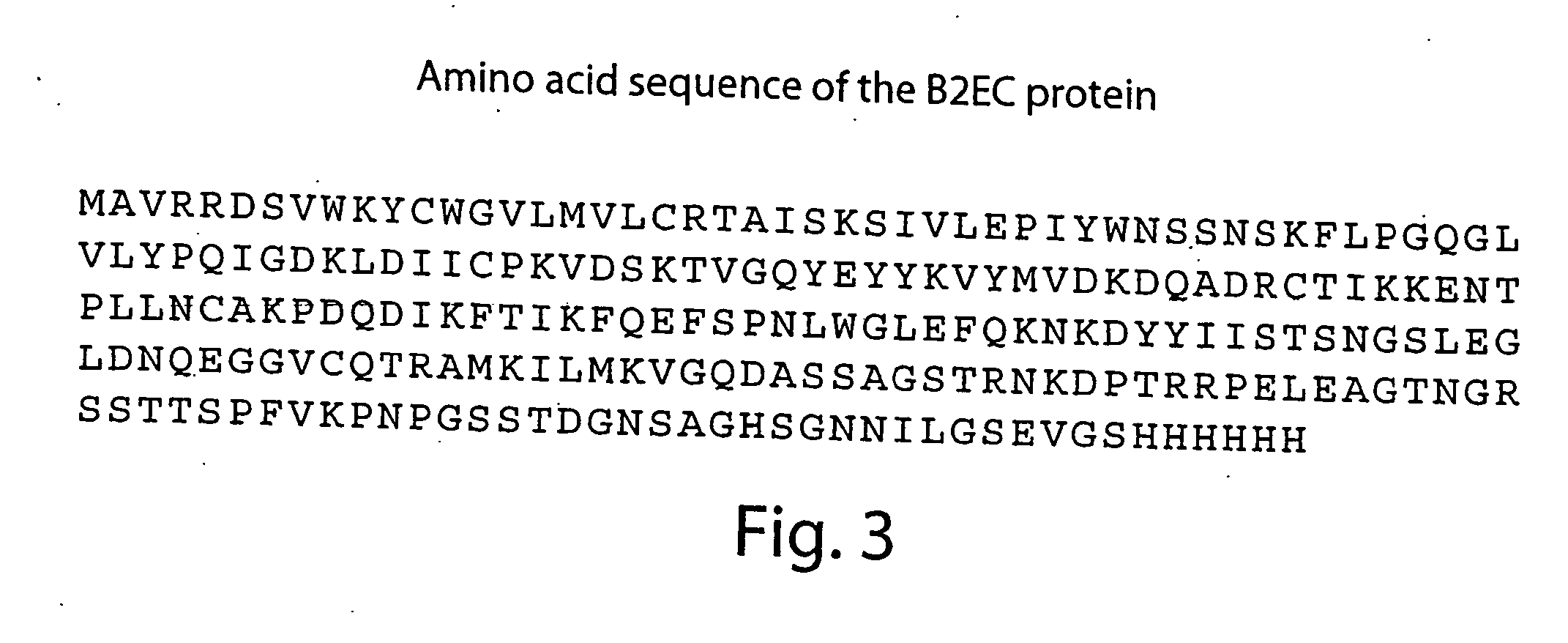
InactiveUS20070218061A1Decrease expressionImprove characteristicSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocidePolypeptide compositionFamily Paramyxoviridae
In certain embodiments, this present invention provides EphrinB2-targeted agents, including polypeptide compositions and nucleic acid compositions for the treatment or prevention of infections by viruses of the family Paramyxoviridae.
Owner:VASGENE THERAPEUTICS INC
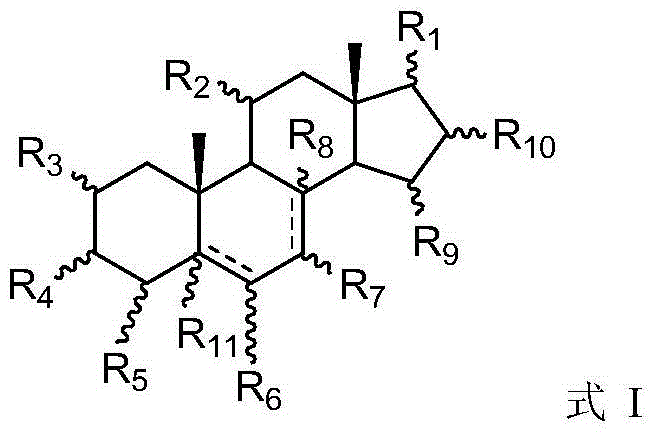
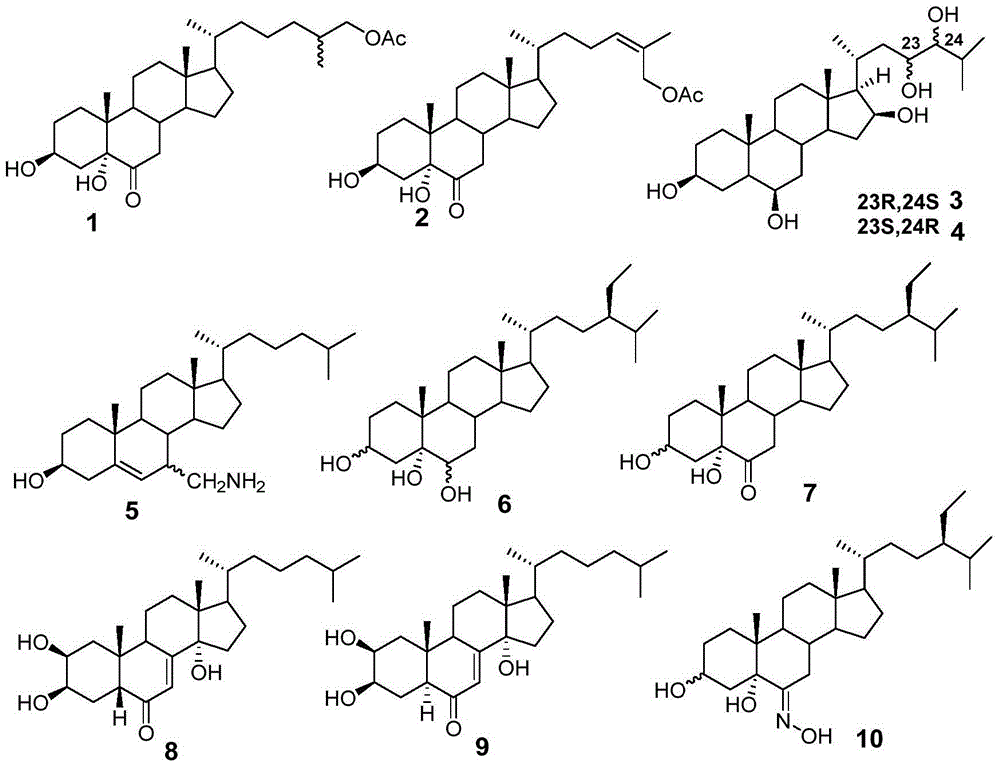
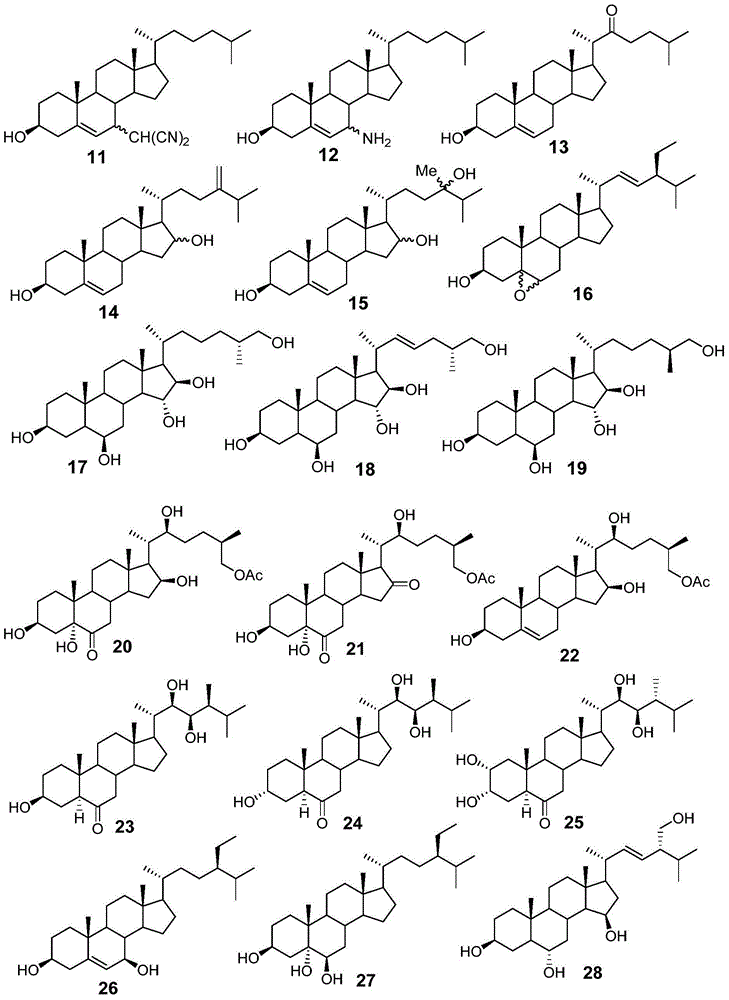
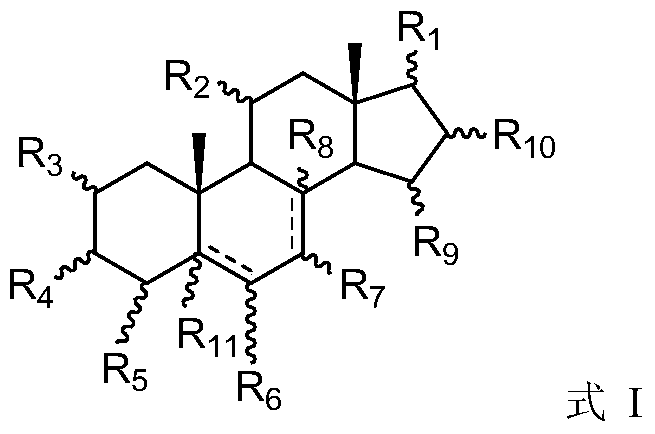
Steroid antiviral agent
The invention relates to a steroid antiviral agent, wherein a steroid compound has a structure as the formula I. The antiviral agent includes one or more of the compound as the formula I, or a stereoisomer, a geometric isomer, a tautomer, a solvate, a pre-drug or a pharmaceutically-acceptable salt of the compound I as effective components. The compound I has quite strong inhibition activity on respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in paramyxoviridae, and can be used as an antiviral medicine or a lead compound of the antiviral medicine.
Owner:YANGZHOU BLUE BIOMEDICAL TECH CO LTD
β-D-2′-deoxy-2′-substituted-4′-substituted-2-substituted-N6-substituted-6-aminopurinenucleotides for the treatment of paramyxovirus and orthomyxovirus infections
ActiveUS10202412B2Improve lipophilicityStrong specificitySugar derivativesAntiviralsDiseaseFamily Orthomyxoviridae
Owner:ATEA PHARMA INC
Methods for selectively modulating the activity of distinct subtypes of cells
PendingCN109642243AStable and constant stimulusImprove efficiencyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSsRNA viruses negative-senseVaccinationImmune therapy
The present invention relates to pseudotyped retrovirus-like particles or retroviral vectors comprising both engineered envelope glycoproteins derived from a virus of the Paramyxoviridae family fusedto a cell targeting domain and fused to a functional domain. The present invention also relates to the use of said pseudotyped retrovirus-like particles or retroviral vectors to selectively modulate the activity of specific subsets of cells, in particular of specific immune cells. These pseudotyped retrovirus-like particles or retroviral vectors are particularly useful for gene therapy, immune therapy and / or vaccination.
Owner:ECOLE NORMALE SUPERIEURE DE LYON +3
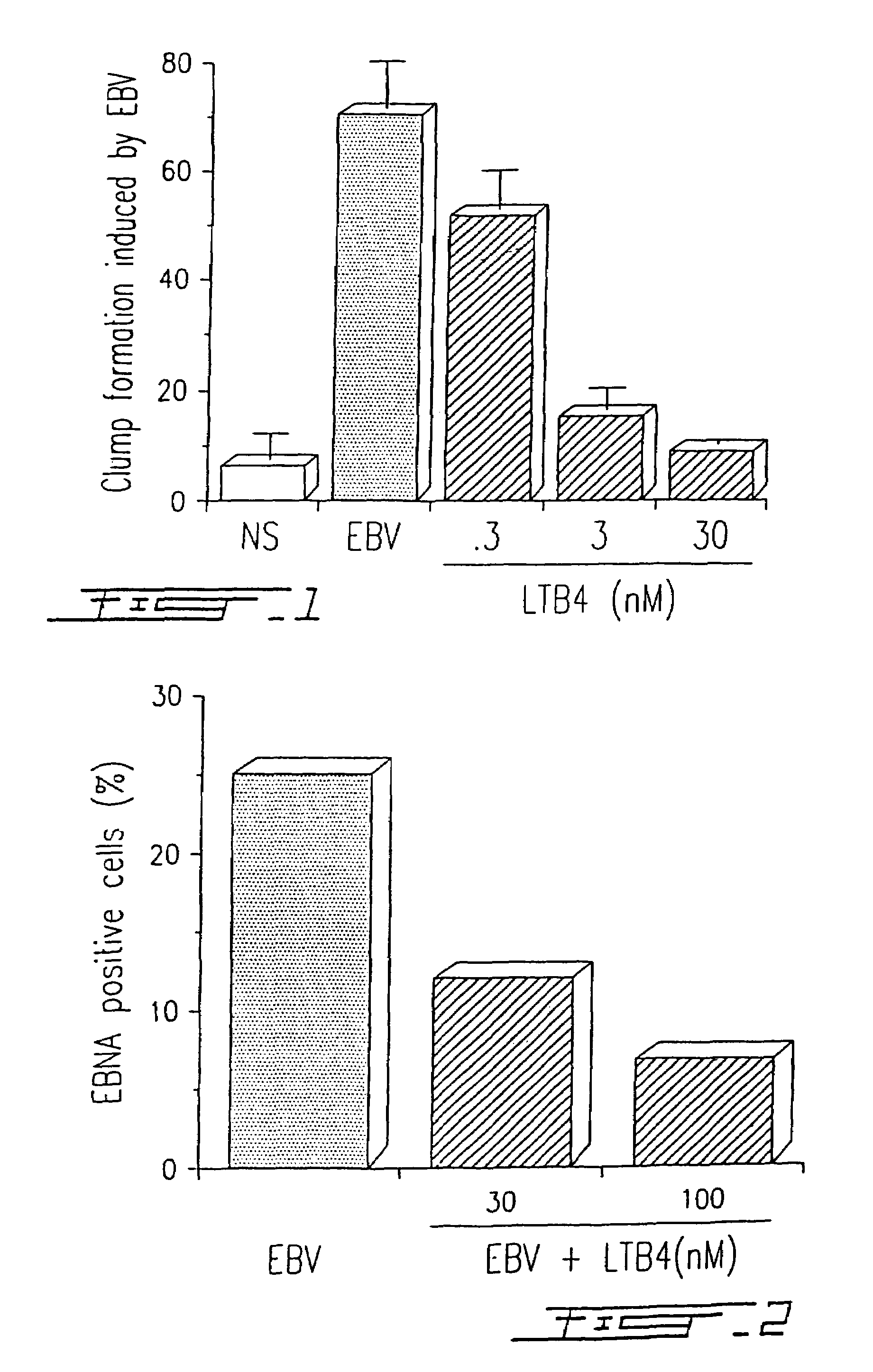
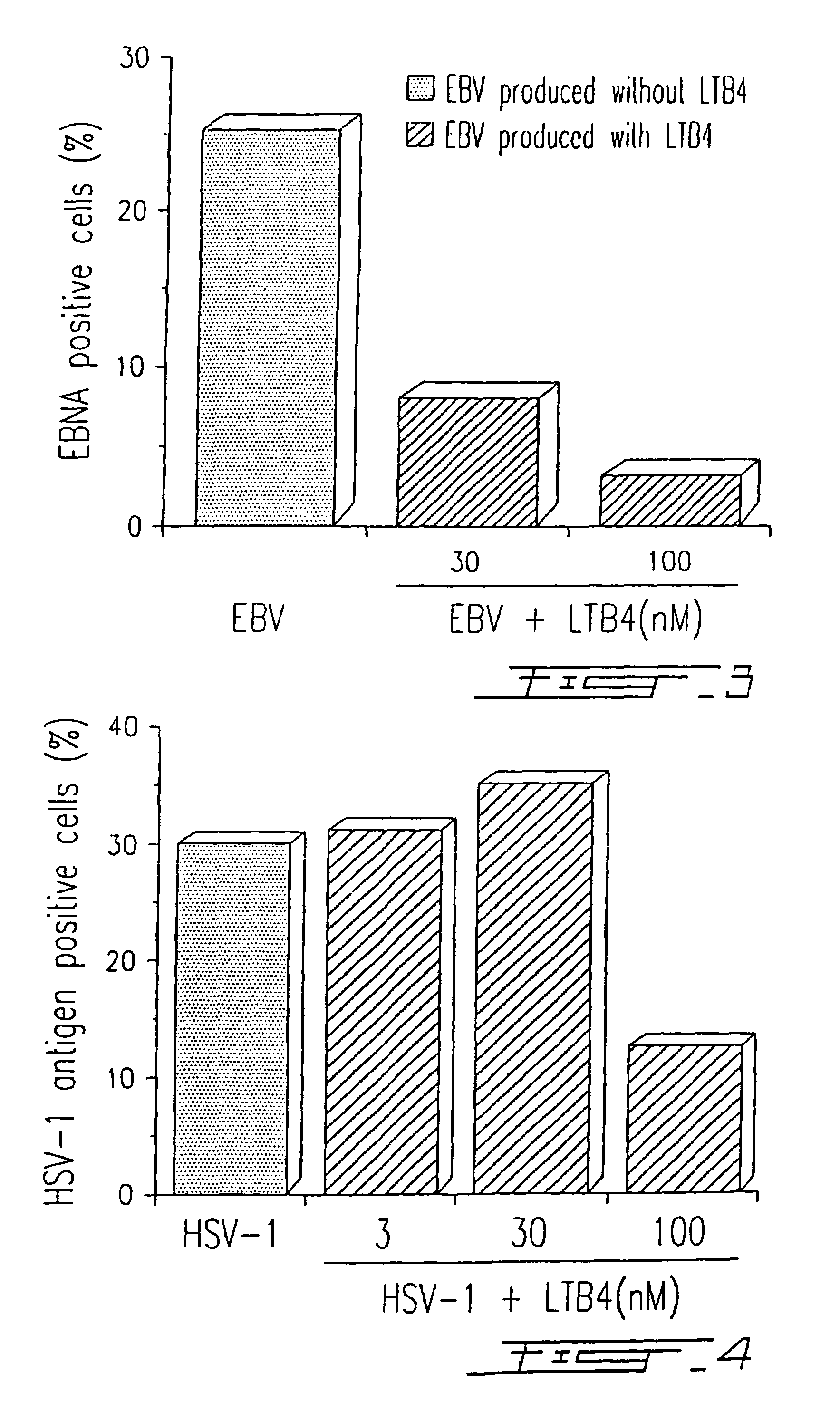
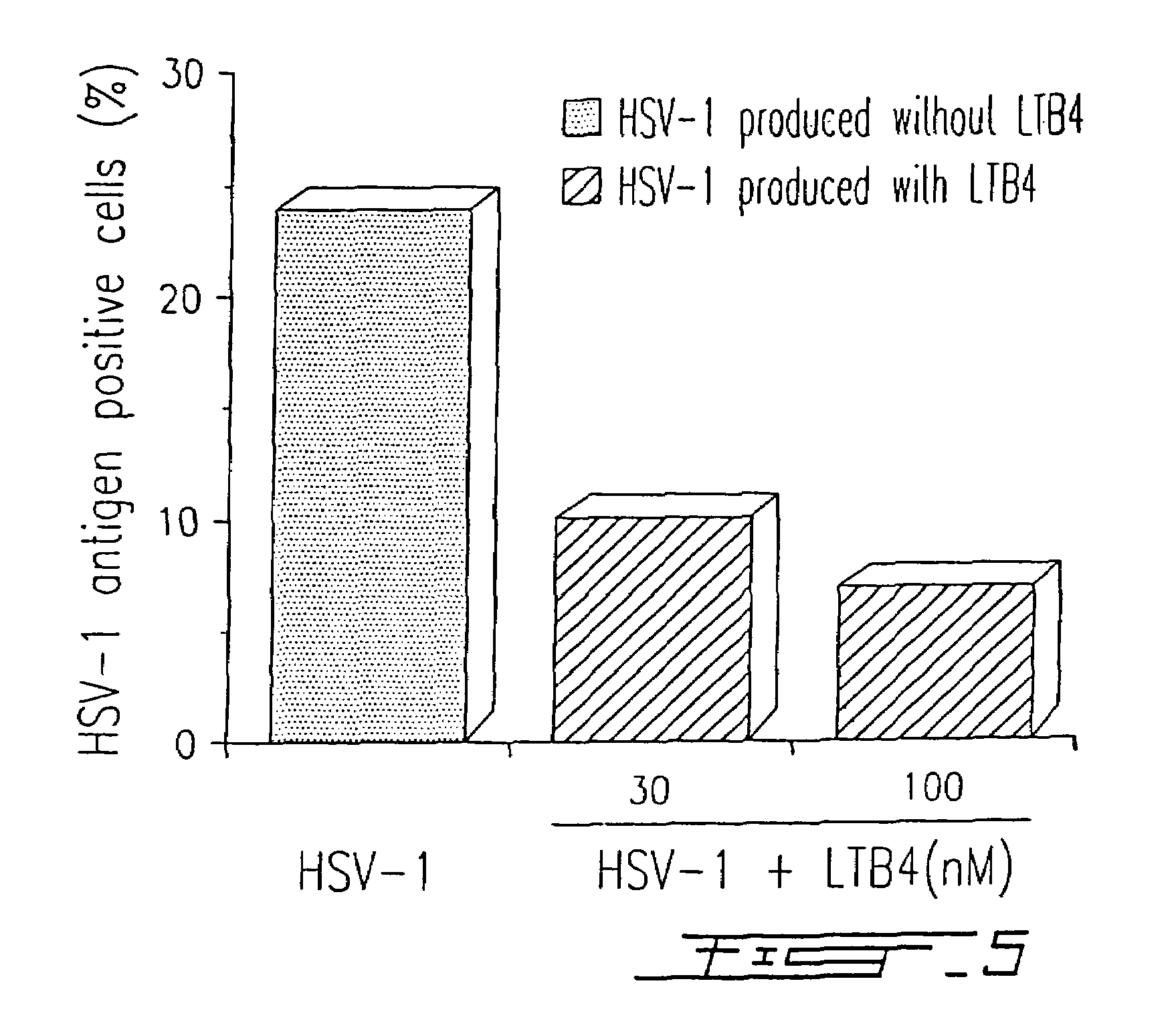
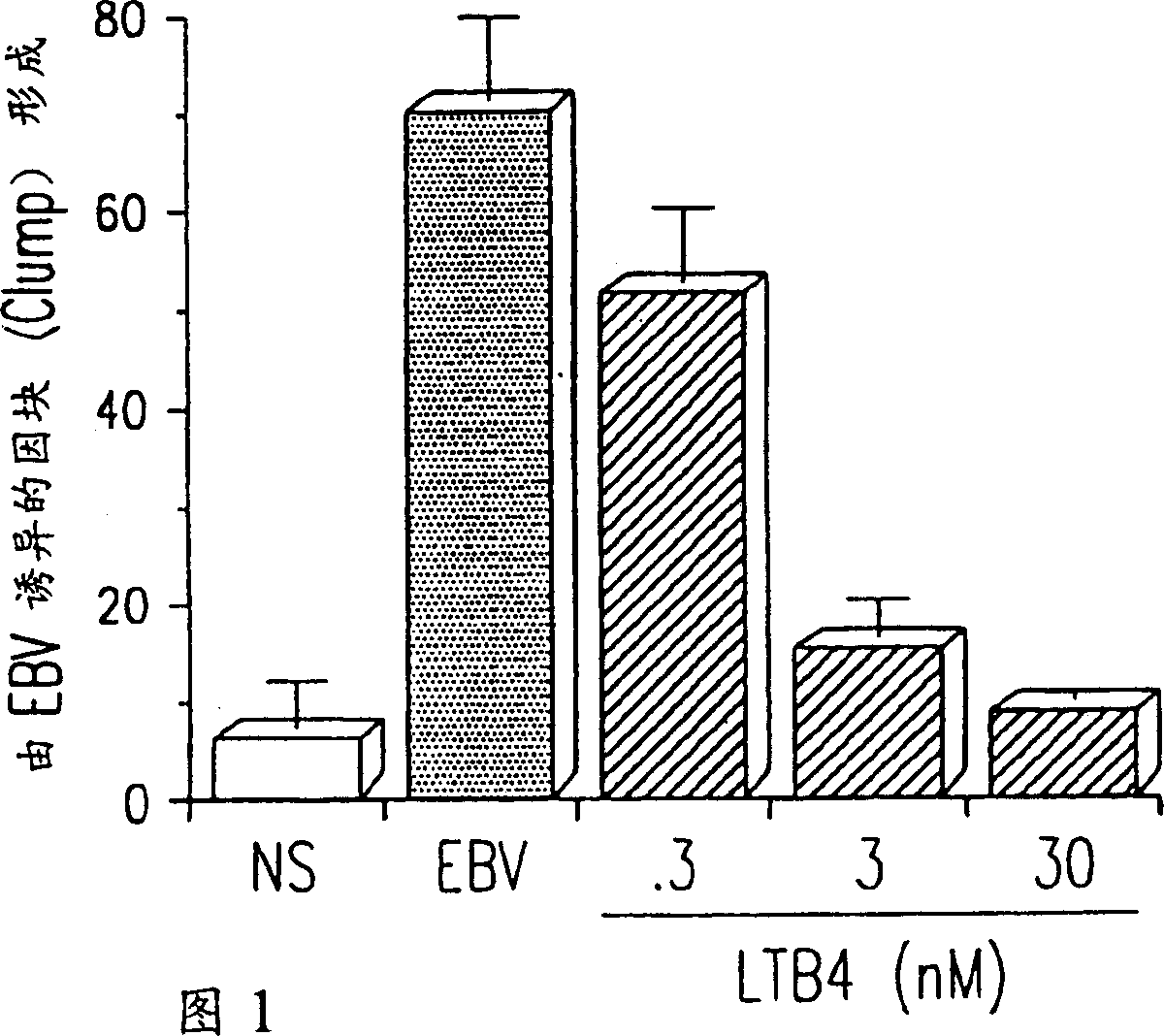
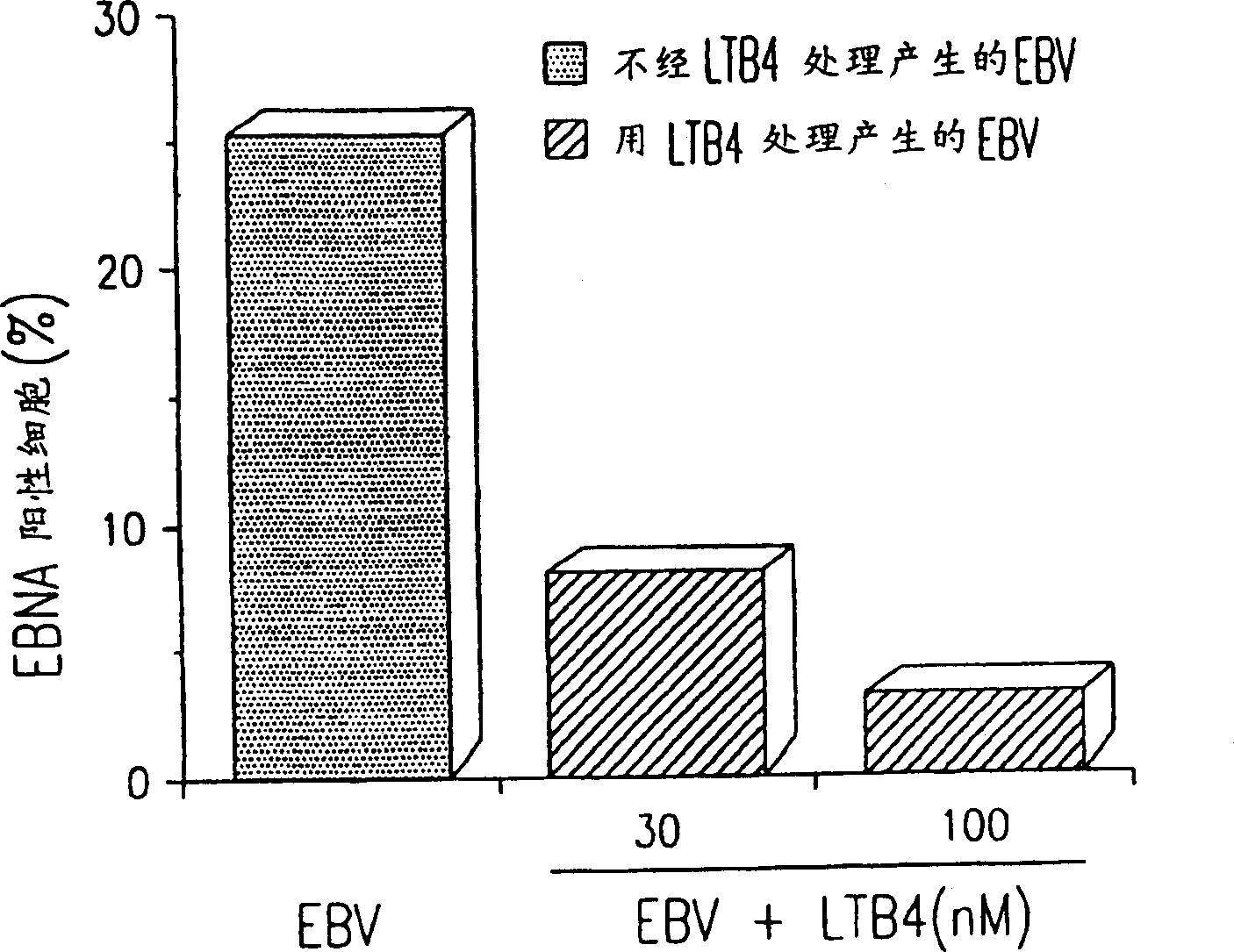
Agents with leukotriene B4-like antiviral (enveloped RNA) activities
The present invention relates to the use of the antiviral activity of exogenous leukotriene B4 (LTB4), variants and derivatives thereof as a therapeutic agent in viral infections caused by human and animal enveloped RNA viruses. The human and animal enveloped RNA viruses are RNA viruses, such as togaviridae, orthomyxoviridae, paramyxoviridae, coronaviridae, filoviridae, arenaviridae, bunyaviridae, rhabdoviridae and flaviviridae in general, and Retroviridae such as HIV-1 and HIV-2.
Owner:LTBE4 SWEDEN
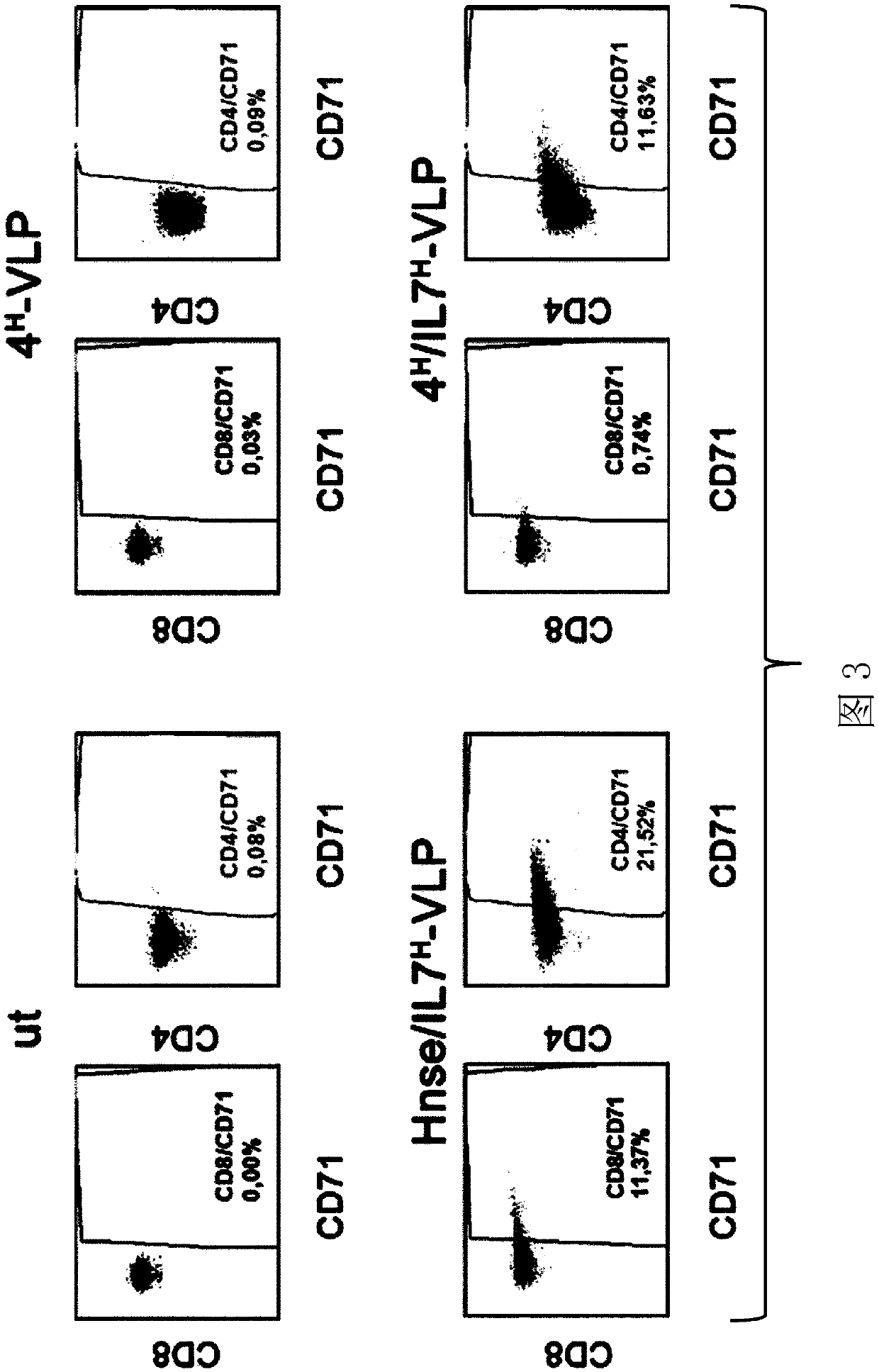
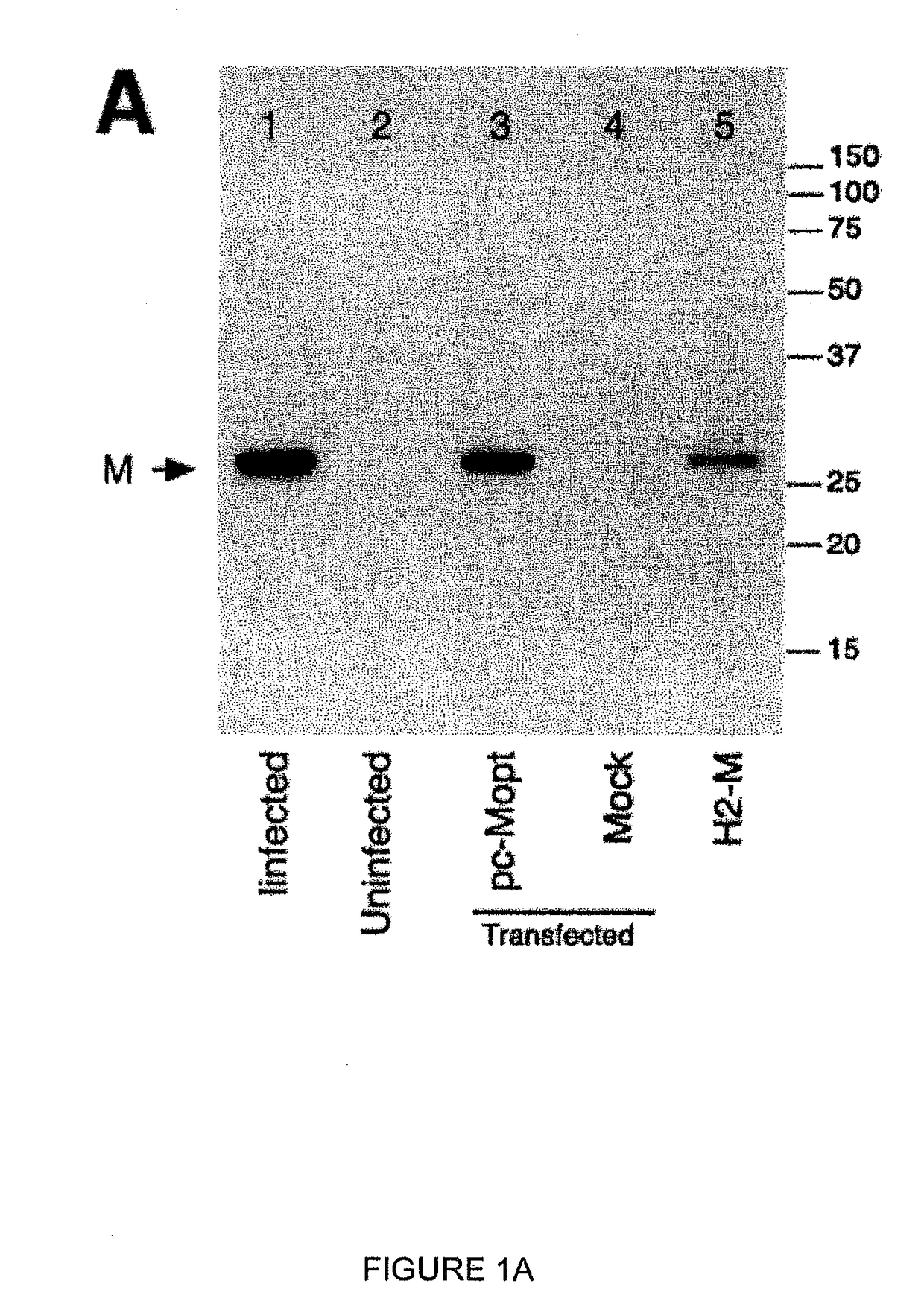
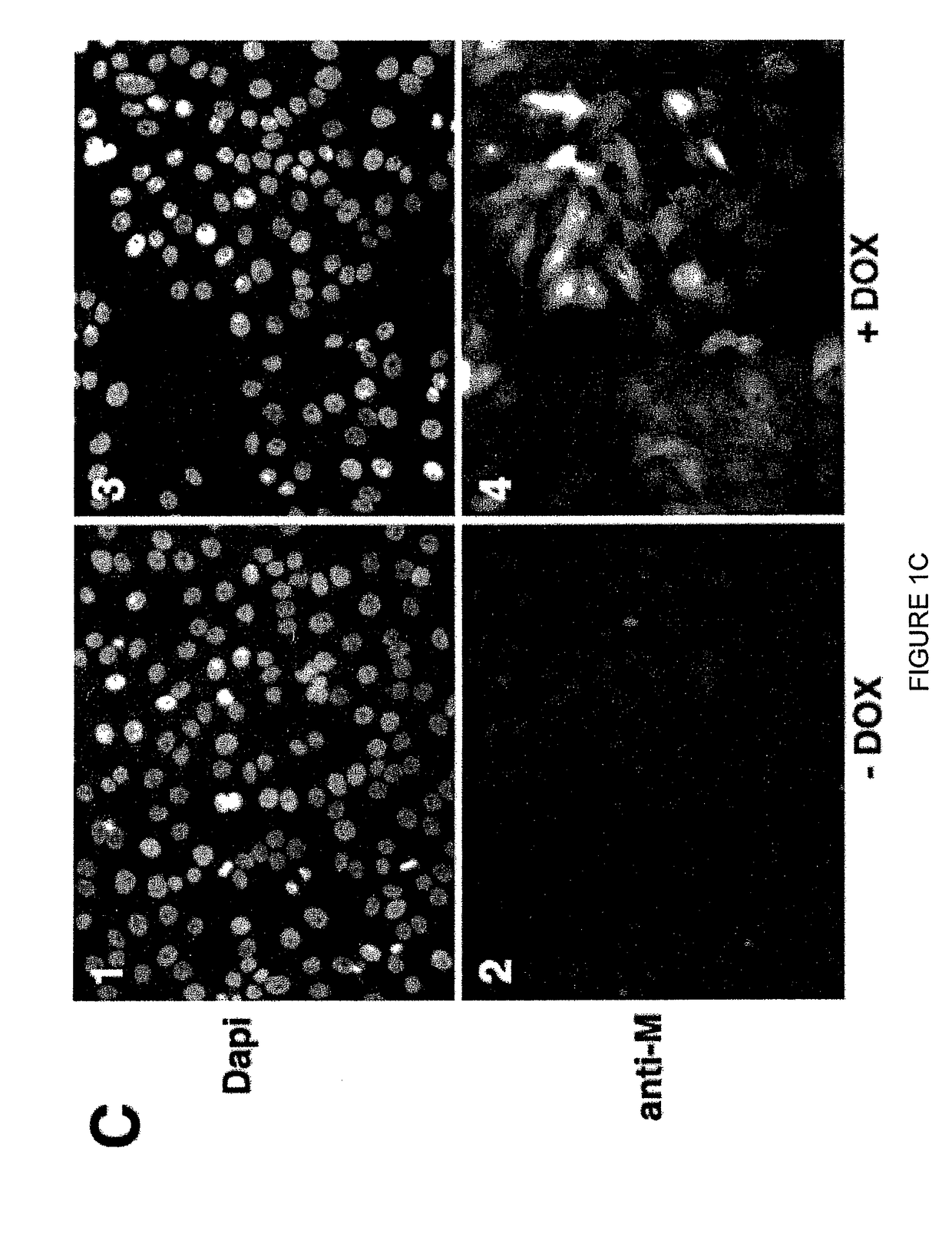
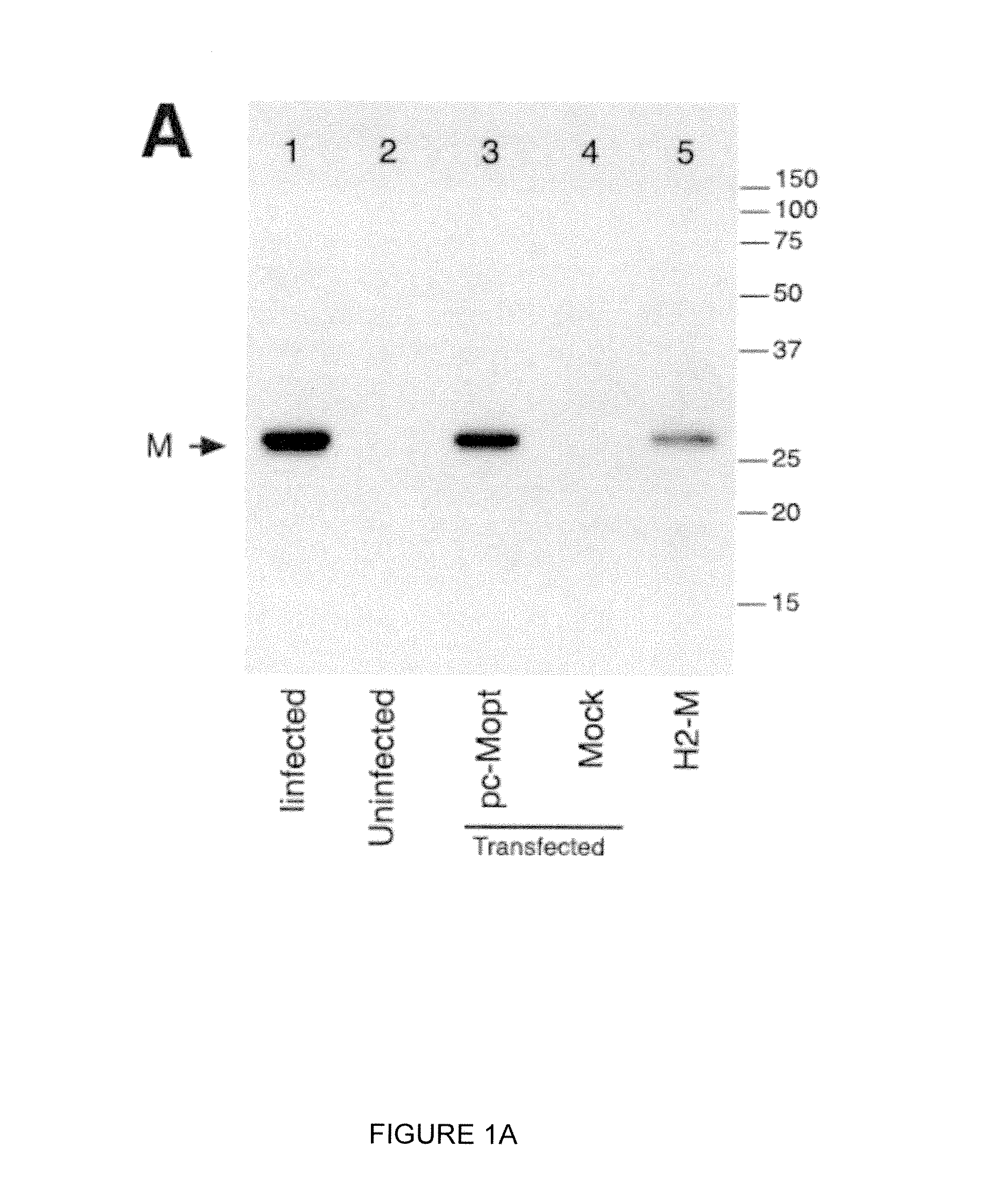
Engineered respiratory syncytial viruses with control of cell-to-cell virus transmission for enhanced safety of live virus vaccines
ActiveUS20180320146A1Improve the level ofReduce productionSsRNA viruses negative-senseCompound screeningCell to cell transmissionAttenuated vaccine
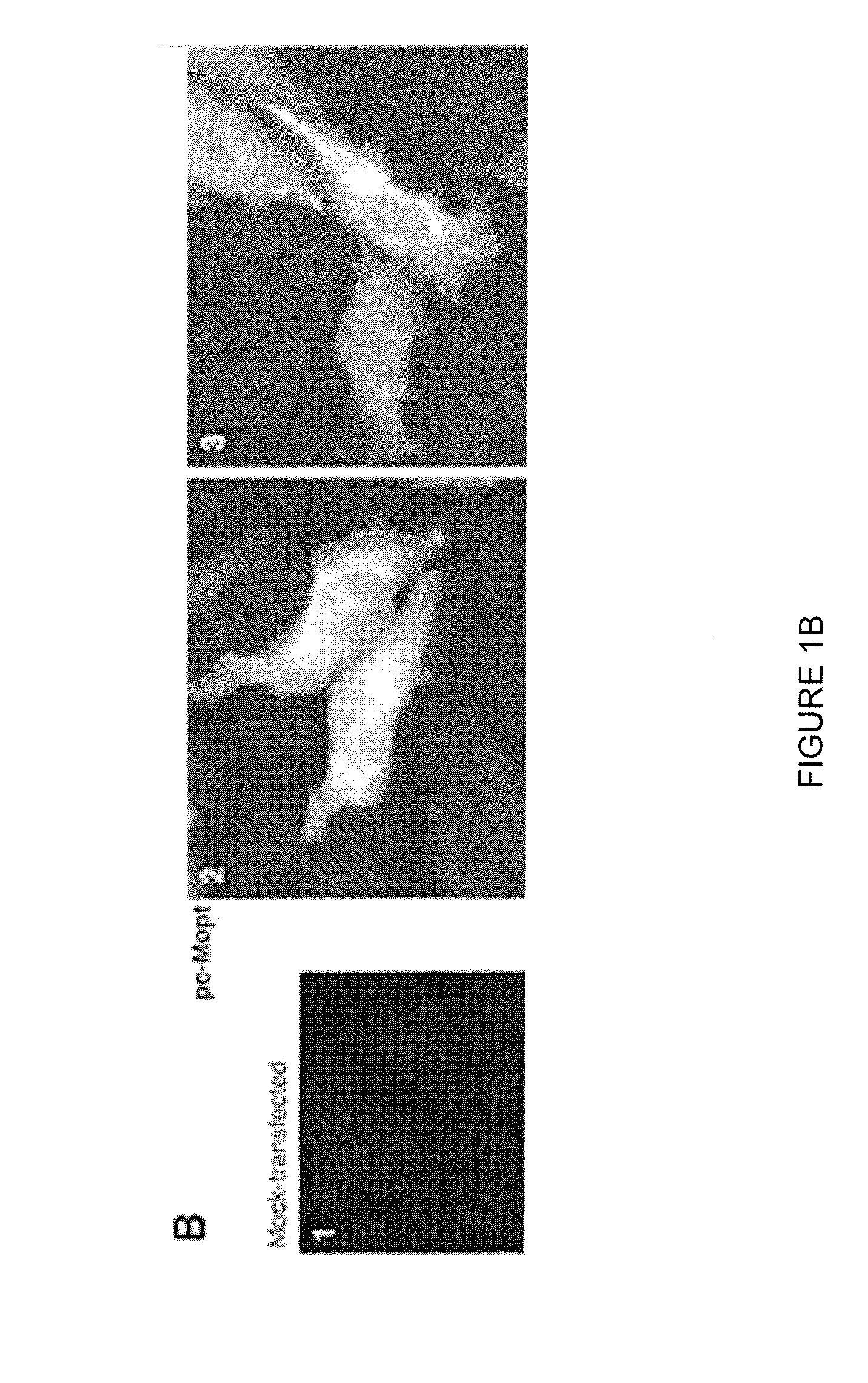
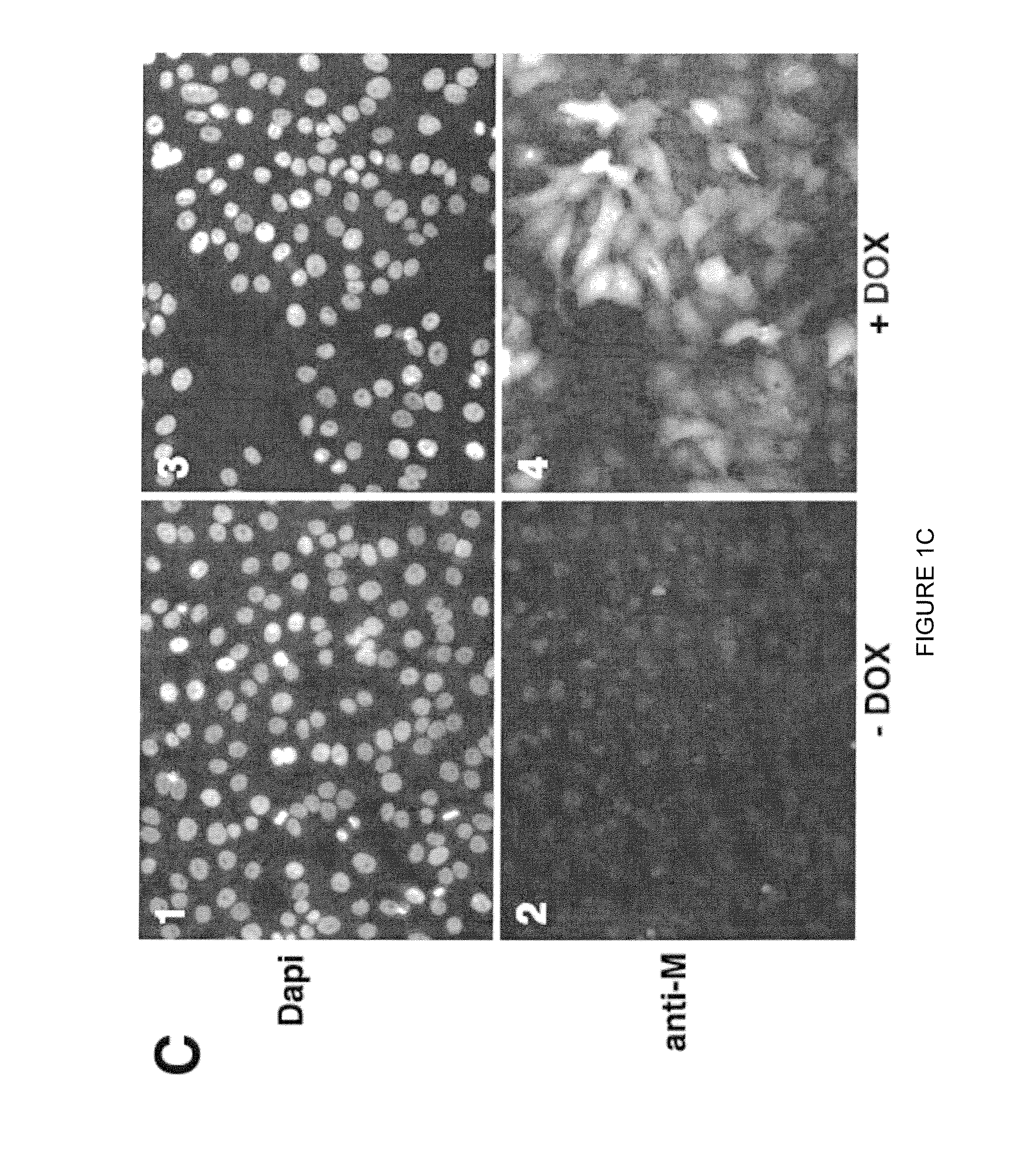
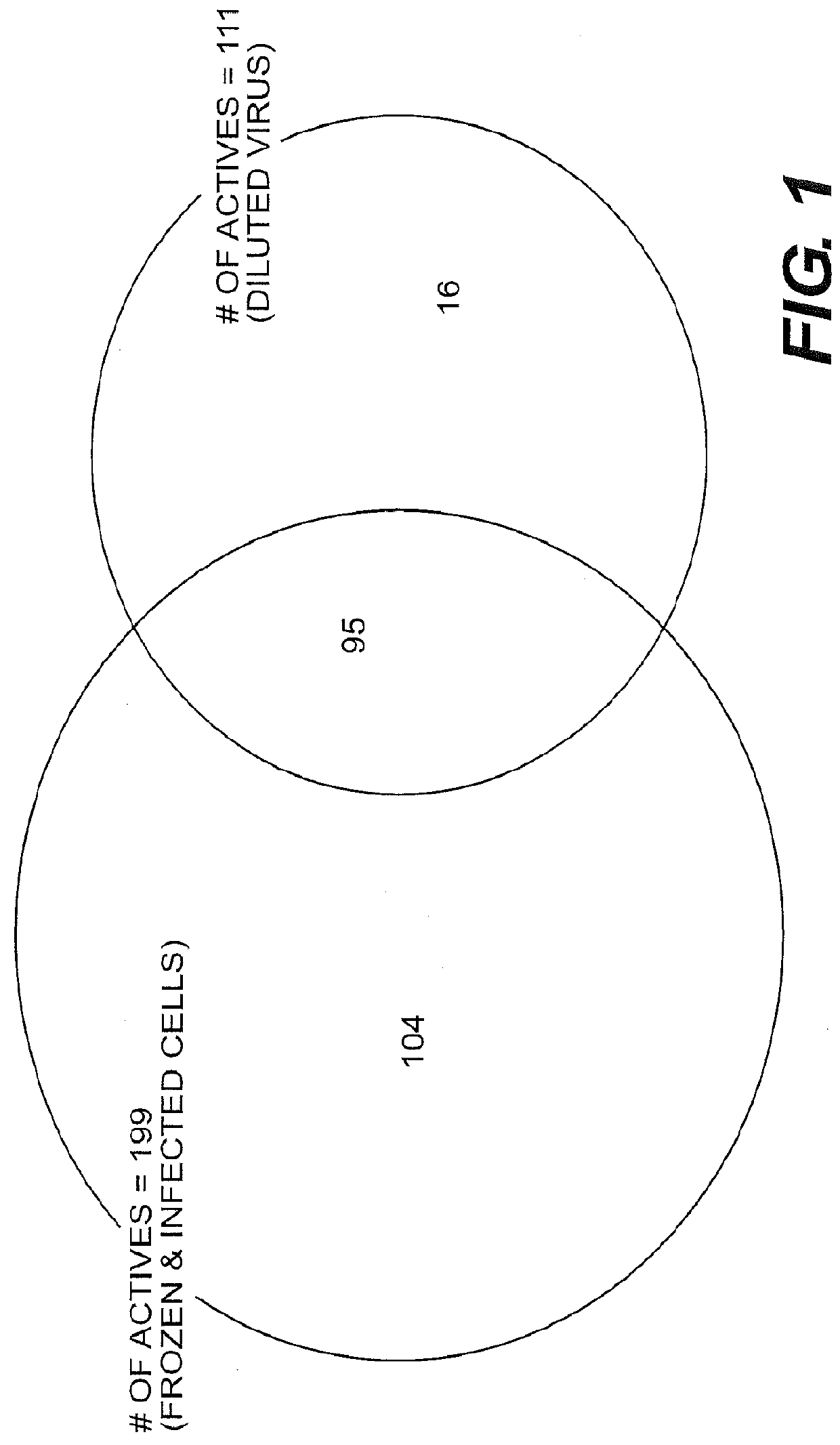
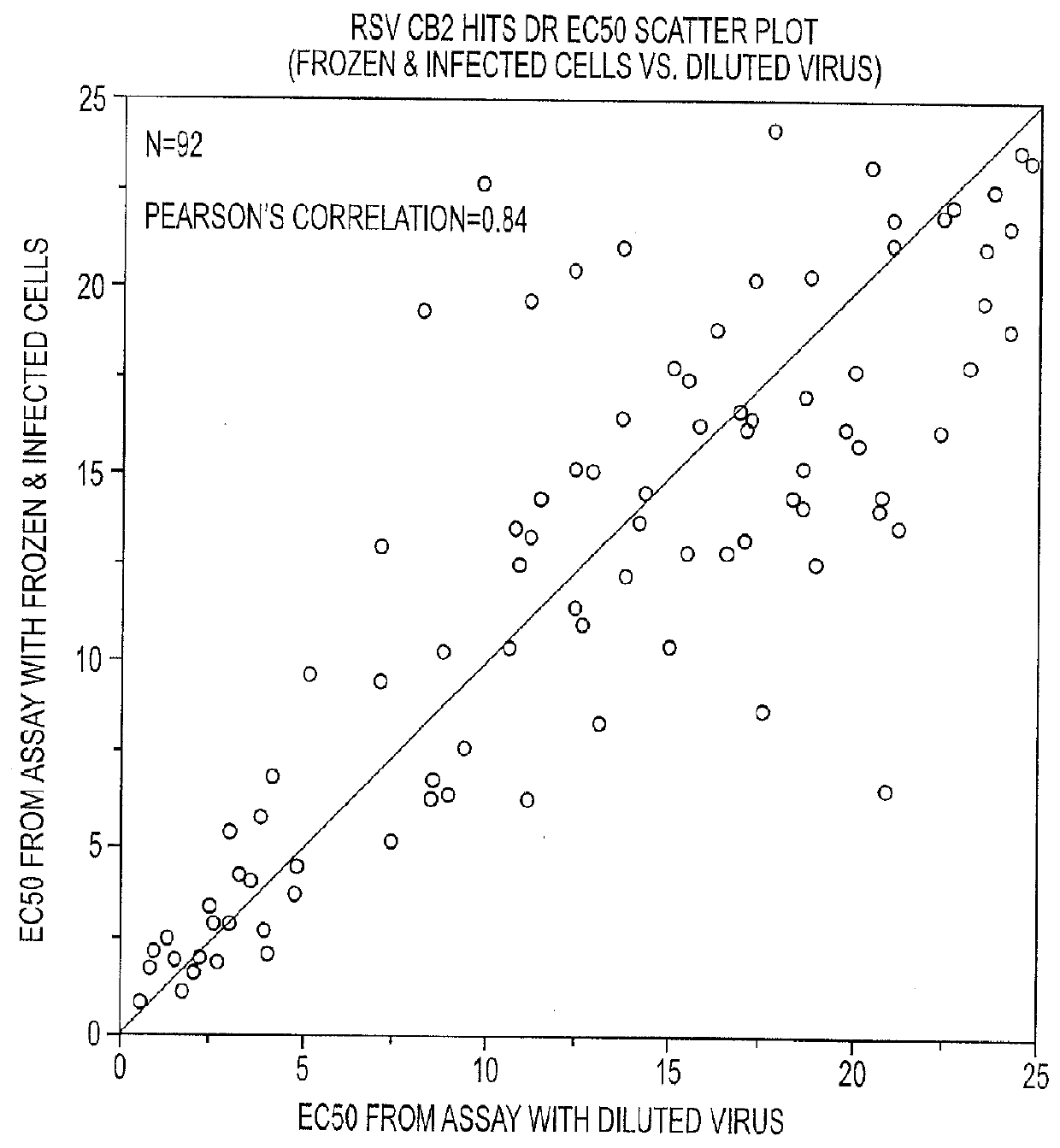
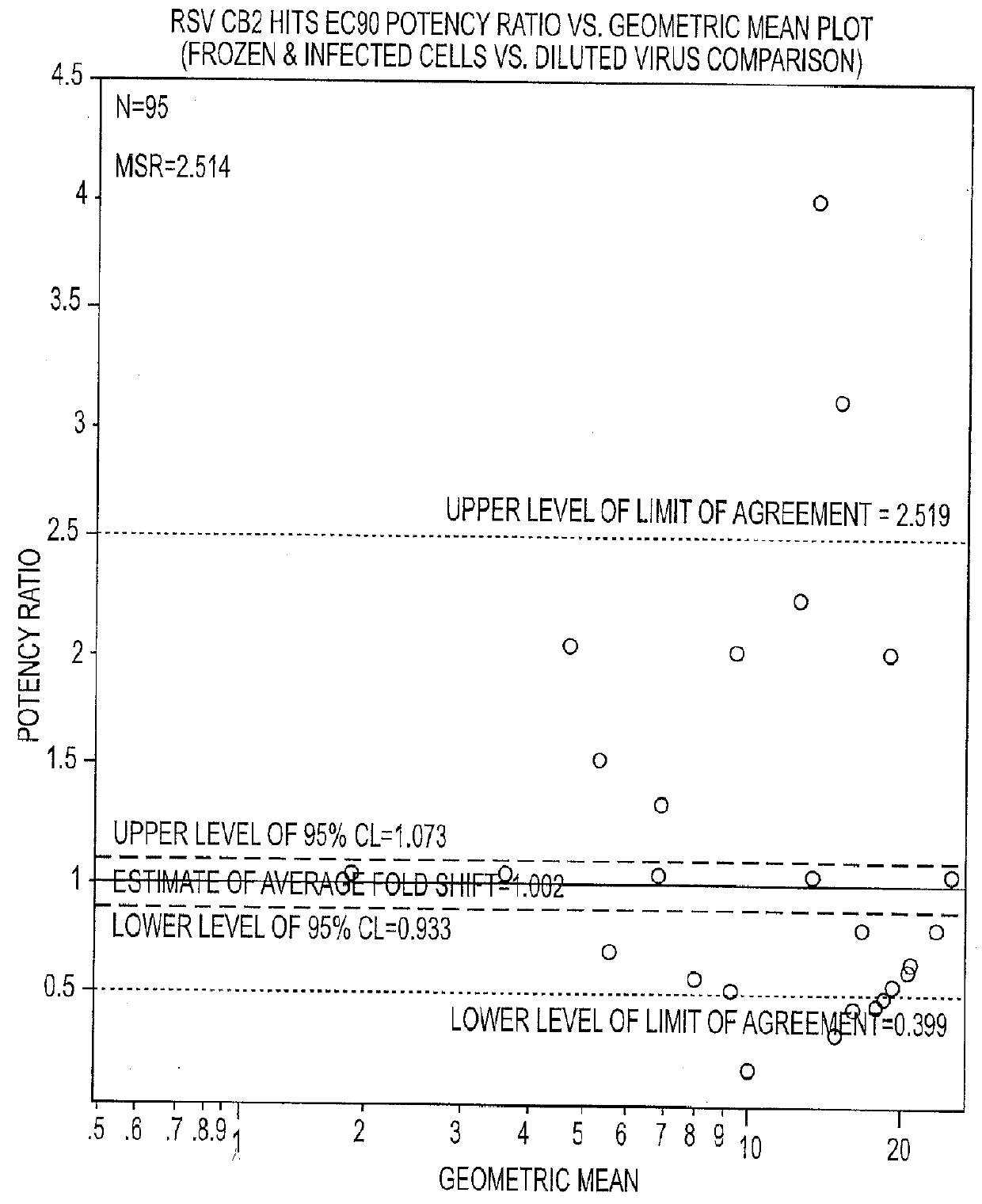
Highly antigenic yet safe vaccines against diseases caused by Paramyxoviridae viruses such as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are provided. The vaccines comprise attenuated Paramyxoviridae viruses with high antigenicity but which display impaired cell-to-cell transmission as a result of genetic manipulation of the gene encoding the matrix (M) protein. In the viruses, the M protein is absent or mutated to a less active form. Screening or assay systems and methods for evaluating the infectivity of mutant M proteins anf for identifying suitable M candidates for live-attenuated vaccine virus and VLP production, are also provided.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY
Method for optimized preparation of inactivated vaccine and/or attenuated live vaccine
InactiveCN105349498AOptimizing Viral TitersHigh potencyMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesCandidate Gene Association StudyViral Vaccine
The present invention provides a method for optimized preparation of an inactivated vaccine and / or an attenuated live vaccine, wherein in host cells, the cancer inhibition candidate gene 2 of glioma is subjected to over-expression to optimize the inside-host-cell replication environment for preparing the inactivated vaccine and / or attenuated live vaccine so as to improve the titers of 4 categories of viruses (including coronavirus, Paramyxoviridae, Orthomyxoviridae and herpes virus) by 1-3 lg unit. According to the present invention, the new strategy and the feasible basis are provided for the optimization of the whole virus vaccine virus titer, and important application prospects and innovative significance are provided in the biomedical field.
Owner:王晓佳
Virus vector, cell, and construct
InactiveUS20170304430A1Efficient introductionImprove security levelSsRNA viruses negative-senseGenetic material ingredientsF proteinParamyxoviridae
A virus vector contains a genome that is derived from a virus belonging to the family Paramyxoviridae, and has a gene encoding a modified H protein, a gene encoding a modified F protein, and foreign genes. The genome may be segmented into multiple segments, and each genome segment may have a leader sequence and a trailer sequence.
Owner:KYUSHU UNIV
Production of virus and purification of viral envelope proteins for vaccine use
Immunogenic envelope glycoproteins are produced from enveloped virus, such as of the paramyxoviridae family, particularly PIV-3 and RSV, by culturing the virus in the substantial absence of exogenous serum proteins, isolating the virus from the tissue culture, solubilizing the envelope glycoproteins and isolating the solubilized envelope glycoproteins by chromatography.
Owner:CONNAUGHT LAB
Use of leukotriene B4 or its analogues as antiviral and antineoplastic agents
InactiveCN1113653CEliminate side effectsElcosanoid active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAnimal virus
The present invention relates to the use of leukotriene B4 (LTB4), variants and derivatives thereof as a therapeutic agent in the treatment or prophylaxis of viral infections caused by human and animal viruses. The present invention also relates to the use of LTB4, variants and derivatives thereof as an anti-neoplastic agent in the prophylaxis and treatment of cancers induced by tumor viruses and in other neoplastic diseases. The human and animal viruses are DNA viruses, such as parvoviridae, papovaviridae, adenoviridae, herpesviridae, poxviridae and hepadnaviridae; RNA viruses, such as picornaviridae, togaviridae, orthomyxoviridae, paramyxoviridae, coronaviridae, reoviridae, oncornaviridae and filoviridae in general, and Retroviridae such as HIV-1 and HIV-2.
Owner:LTB4 SWEDAN AB
Non-replicating paramyxoviridae virus vector
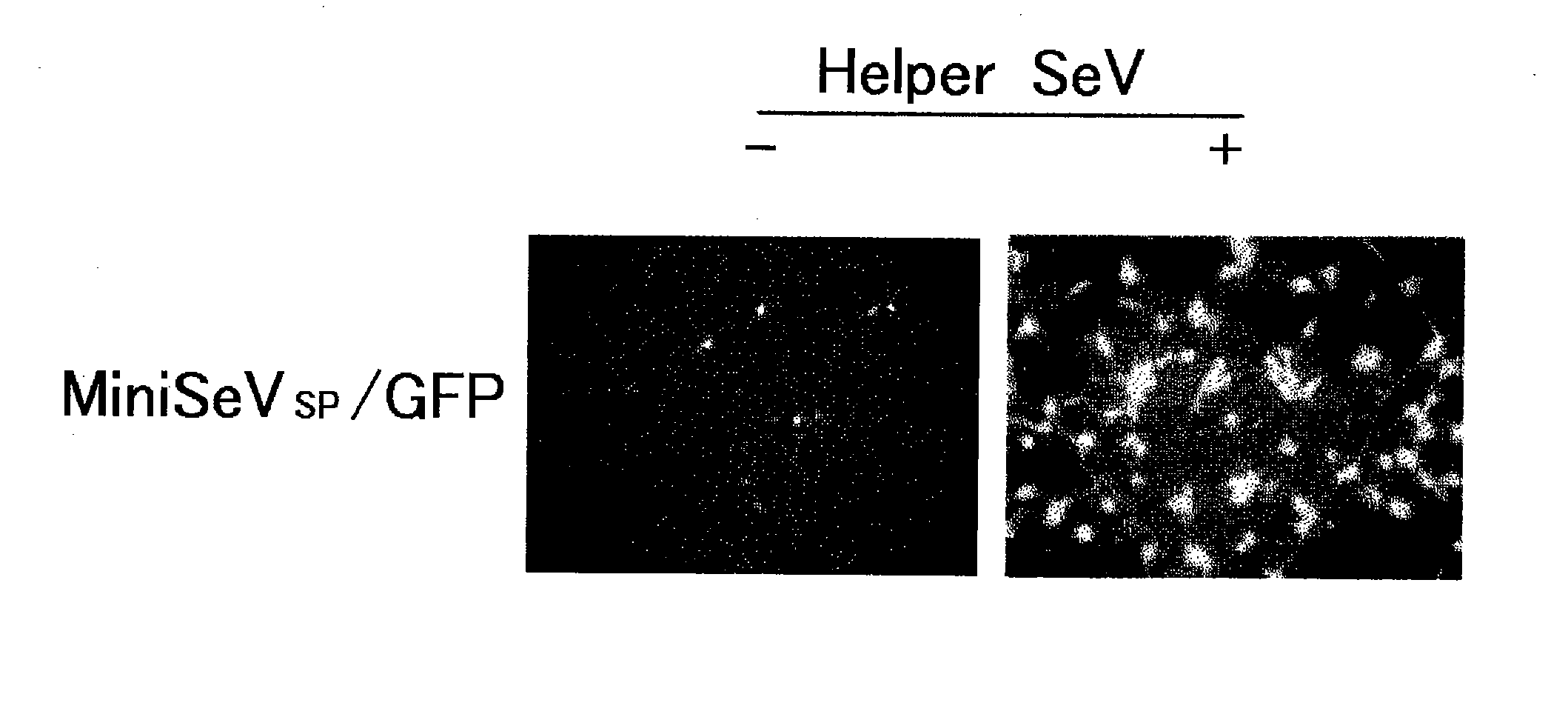
InactiveUS20100209974A1Good effectImprove versatilitySsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsIn vivoGenomic rna
The present inventors succeeded in producing non-replicating SeV vectors whose genomic RNAs lack all genes for the NP, P, and L proteins, which are RNP-constituting proteins. The present inventors confirmed that the NP / P / L-deficient SeV vectors carrying a marker gene such as GFP provide high productivity, and high transfer and expression efficiencies of foreign genes (high MOI infection is essential for achieving high expression levels). By lacking the L gene or two or more of the NP, P, and L genes, the vectors of the present invention enable lowering the level of virus-derived proteins expressed in host cells, thereby reducing the immunogenicity upon in vivo administration.
Owner:DNAVEC CORP
Engineered respiratory syncytial viruses with control of cell-to-cell virus transmission for enhanced safety of live virus vaccines
InactiveUS20140205620A1Improve the level ofTransmission limitSsRNA viruses negative-senseCompound screeningCell to cell transmissionAttenuated vaccine
Highly antigenic yet safe vaccines against diseases caused by Paramyxoviridae viruses such as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are provided. The vaccines comprise attenuated Paramyxoviridae viruses with high antigenicity but which display impaired cell-to-cell transmission as a result of genetic manipulation of the gene encoding the matrix (M) protein. In the viruses, the M protein is absent or mutated to a less active form. Screening or assay systems and methods for evaluating the infectivity of mutant M proteins and for identifying suitable M candidates for live-attenuated vaccine virus and VLP production, are also provided.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY
Paramyxoviridae expression system
PendingCN111093698ASsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The present invention relates to the field of (vector) vaccines, and especially to an enhanced arrangement of nucleotide sequences for expressing a Paramyxoviridae virus containing an exogenous gene of interest. The present invention further concerns related expression cassettes and vectors, which are suitable to express genes of interest, especially antigen encoding sequences. The viral vectors of the present invention are useful for producing an immunogenic composition or vaccine.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM VETMEDICA GMBH
A method for optimizing the preparation of inactivated vaccines and/or live attenuated vaccines
InactiveCN105349498BOptimizing Viral TitersHigh potencyMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesCandidate Gene Association StudyTGE VACCINE
The present invention provides a method for optimized preparation of an inactivated vaccine and / or an attenuated live vaccine, wherein in host cells, the cancer inhibition candidate gene 2 of glioma is subjected to over-expression to optimize the inside-host-cell replication environment for preparing the inactivated vaccine and / or attenuated live vaccine so as to improve the titers of 4 categories of viruses (including coronavirus, Paramyxoviridae, Orthomyxoviridae and herpes virus) by 1-3 lg unit. According to the present invention, the new strategy and the feasible basis are provided for the optimization of the whole virus vaccine virus titer, and important application prospects and innovative significance are provided in the biomedical field.
Owner:王晓佳
A steroidal antiviral agent
Owner:YANGZHOU BLUE BIOMEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Paramyxorividae virus vector defective in envelope gene
Virus virions defective in F gene are successfully collected by using a Sendai virus genomic cDNA with deletion of F gene. Further, infectious viral particles defective in F gene are successfully constructed by using F-expression cells as helper cells. Also, virus virions defective in F gene and HN gene are successfully collected by using a virus genomic cDNA with deletion of both of F gene and HN gene. Further, infectious viral particles defective in F gene and HN gene are successfully produced by using F- and HN-expression cells as helper cells. A virus being defective in F gene and HN gene and having F protein is constructed by using F-expression cells as helper cells. Further, a VSV-G pseudo type virus is successfully constructed by using VSV-G-expression cells. Techniques for constructing these defective viruses contribute to the development of vectors of Paramyxoviridae usable in gene therapy.
Owner:DNAVEC RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

![Crystalline forms of (S)-2-ethylbutyl 2-(((S)-(((2R,3S,4R,5R)-5- (4-aminopyrrolo[2,1-f] [1,2,4]triazin-7-yl)-5-cyano-3,4-dihydroxytetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methoxy)(phenoxy) phosphoryl)amino)propanoate Crystalline forms of (S)-2-ethylbutyl 2-(((S)-(((2R,3S,4R,5R)-5- (4-aminopyrrolo[2,1-f] [1,2,4]triazin-7-yl)-5-cyano-3,4-dihydroxytetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methoxy)(phenoxy) phosphoryl)amino)propanoate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/ff2b4087-9dcd-48db-bfe0-8cbe99326db5/US10836787-D00001.png)
![Crystalline forms of (S)-2-ethylbutyl 2-(((S)-(((2R,3S,4R,5R)-5- (4-aminopyrrolo[2,1-f] [1,2,4]triazin-7-yl)-5-cyano-3,4-dihydroxytetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methoxy)(phenoxy) phosphoryl)amino)propanoate Crystalline forms of (S)-2-ethylbutyl 2-(((S)-(((2R,3S,4R,5R)-5- (4-aminopyrrolo[2,1-f] [1,2,4]triazin-7-yl)-5-cyano-3,4-dihydroxytetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methoxy)(phenoxy) phosphoryl)amino)propanoate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/ff2b4087-9dcd-48db-bfe0-8cbe99326db5/US10836787-D00002.png)
![Crystalline forms of (S)-2-ethylbutyl 2-(((S)-(((2R,3S,4R,5R)-5- (4-aminopyrrolo[2,1-f] [1,2,4]triazin-7-yl)-5-cyano-3,4-dihydroxytetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methoxy)(phenoxy) phosphoryl)amino)propanoate Crystalline forms of (S)-2-ethylbutyl 2-(((S)-(((2R,3S,4R,5R)-5- (4-aminopyrrolo[2,1-f] [1,2,4]triazin-7-yl)-5-cyano-3,4-dihydroxytetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methoxy)(phenoxy) phosphoryl)amino)propanoate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/ff2b4087-9dcd-48db-bfe0-8cbe99326db5/US10836787-D00003.png)