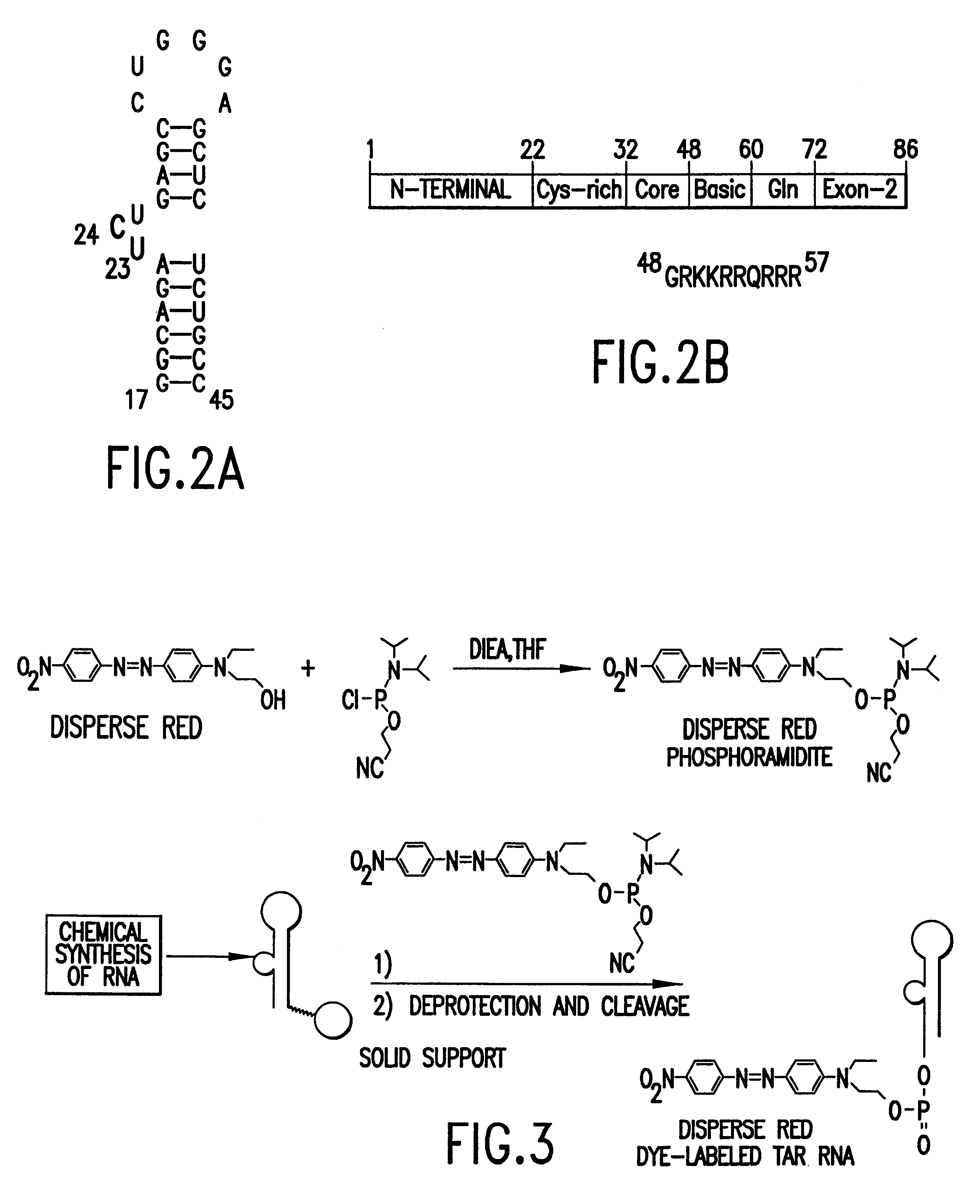
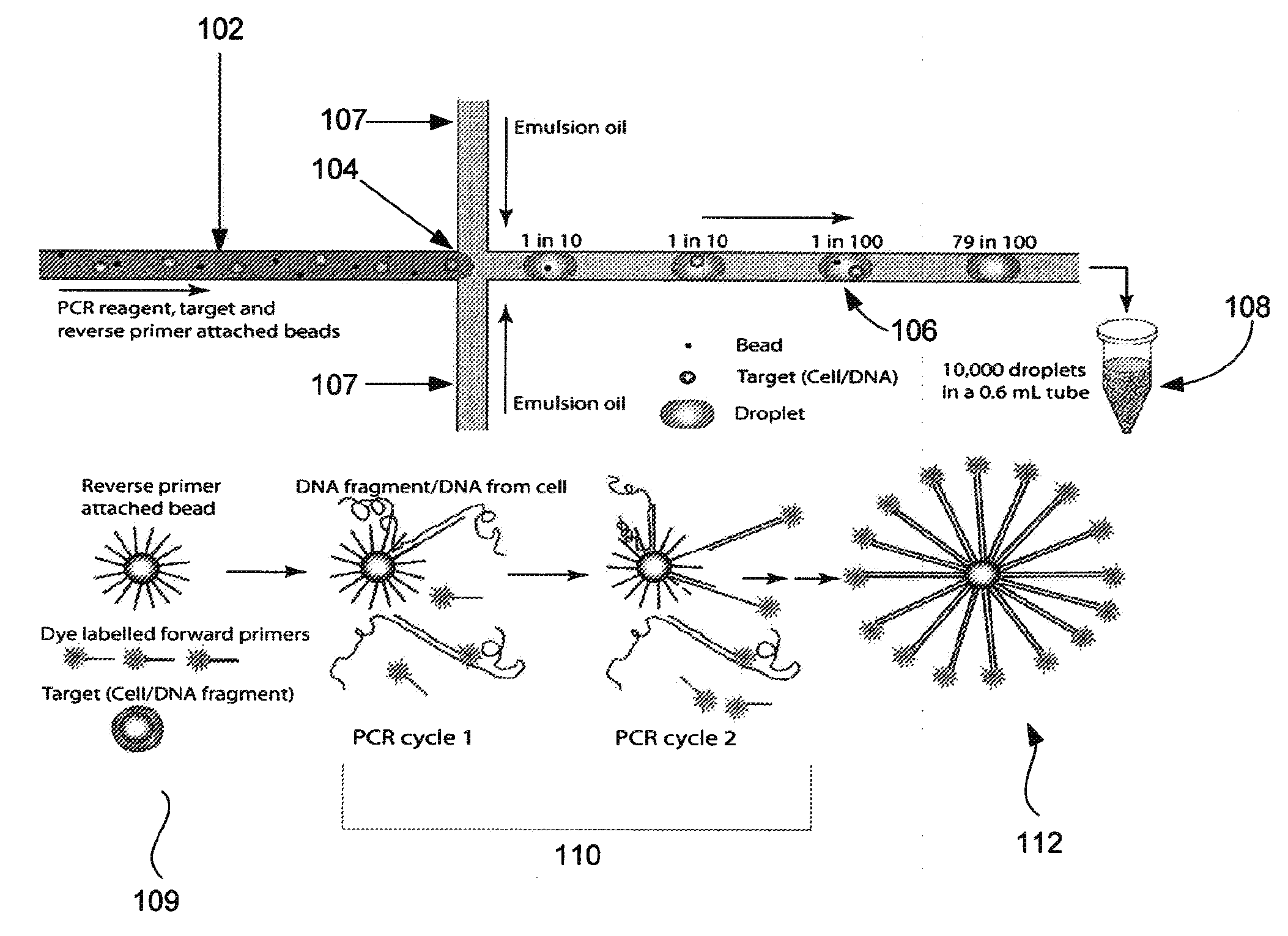
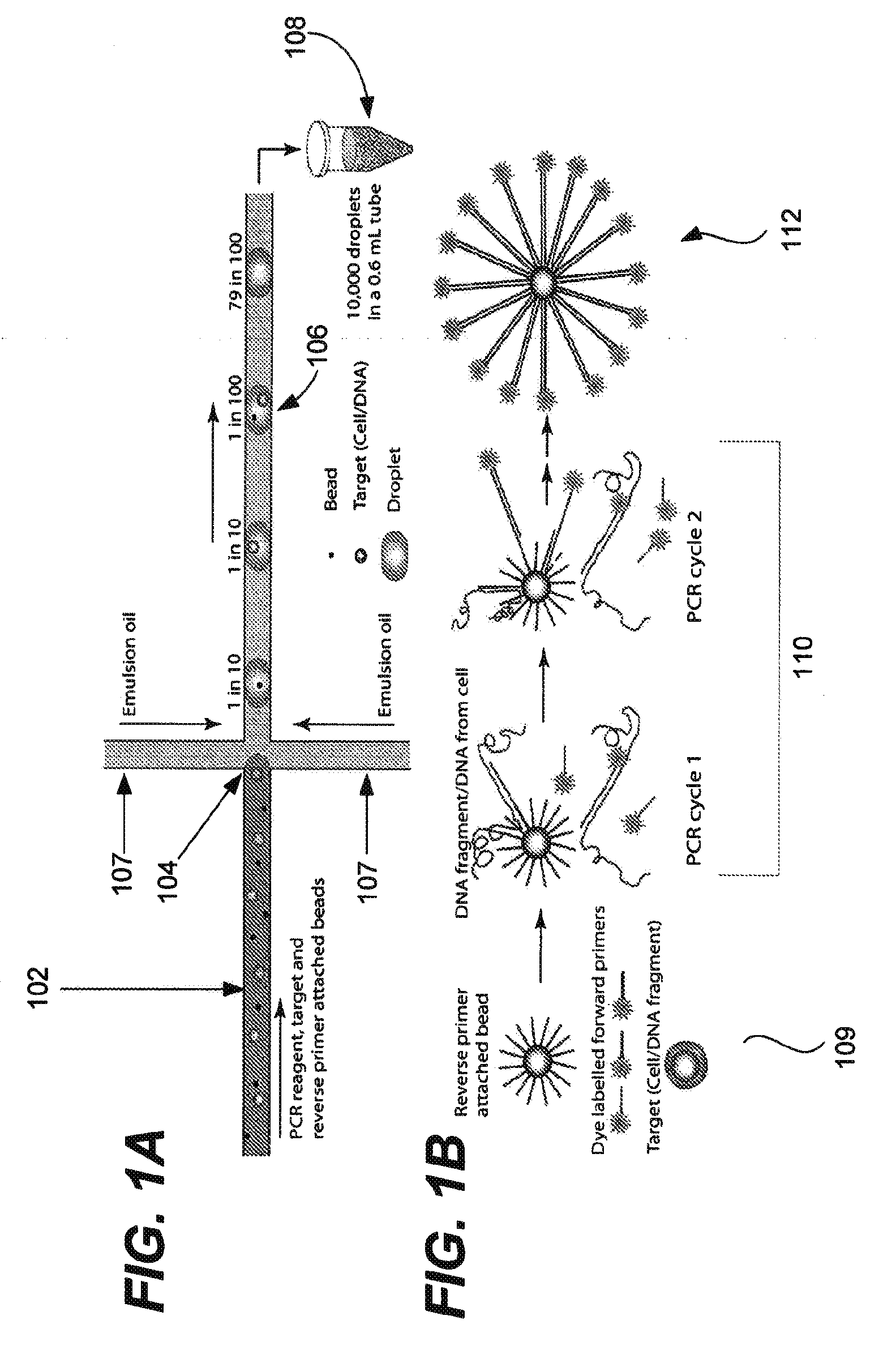
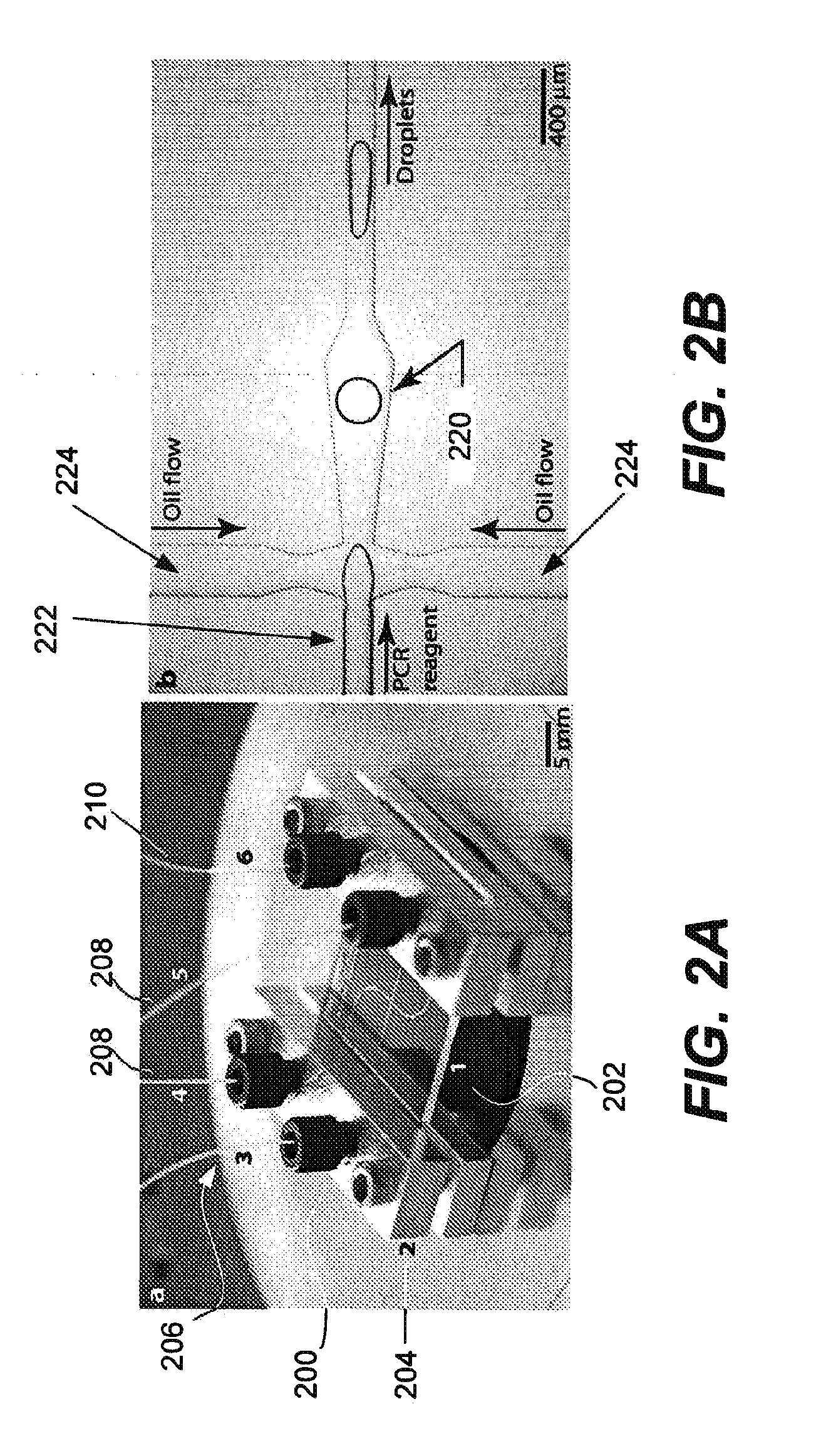
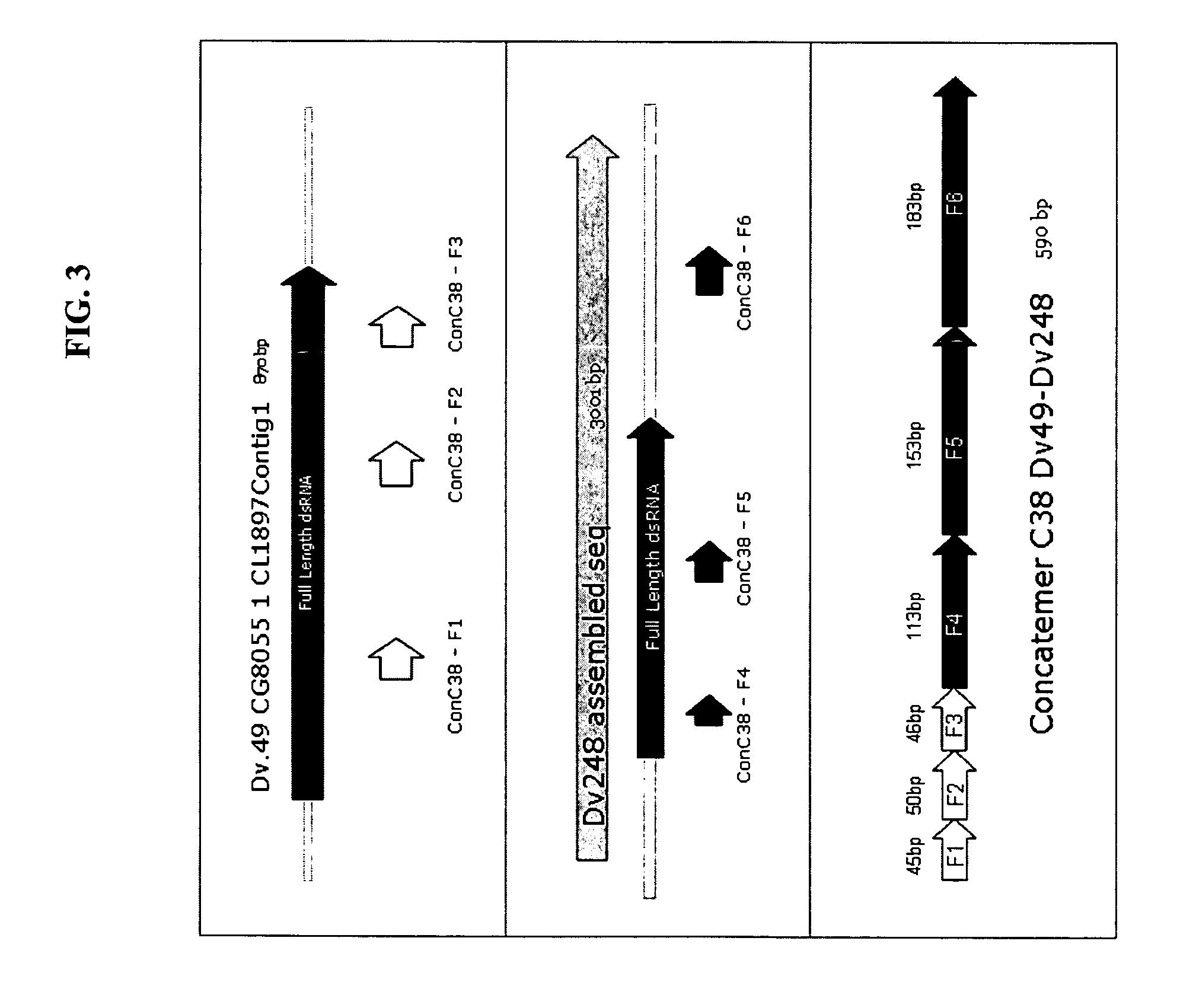
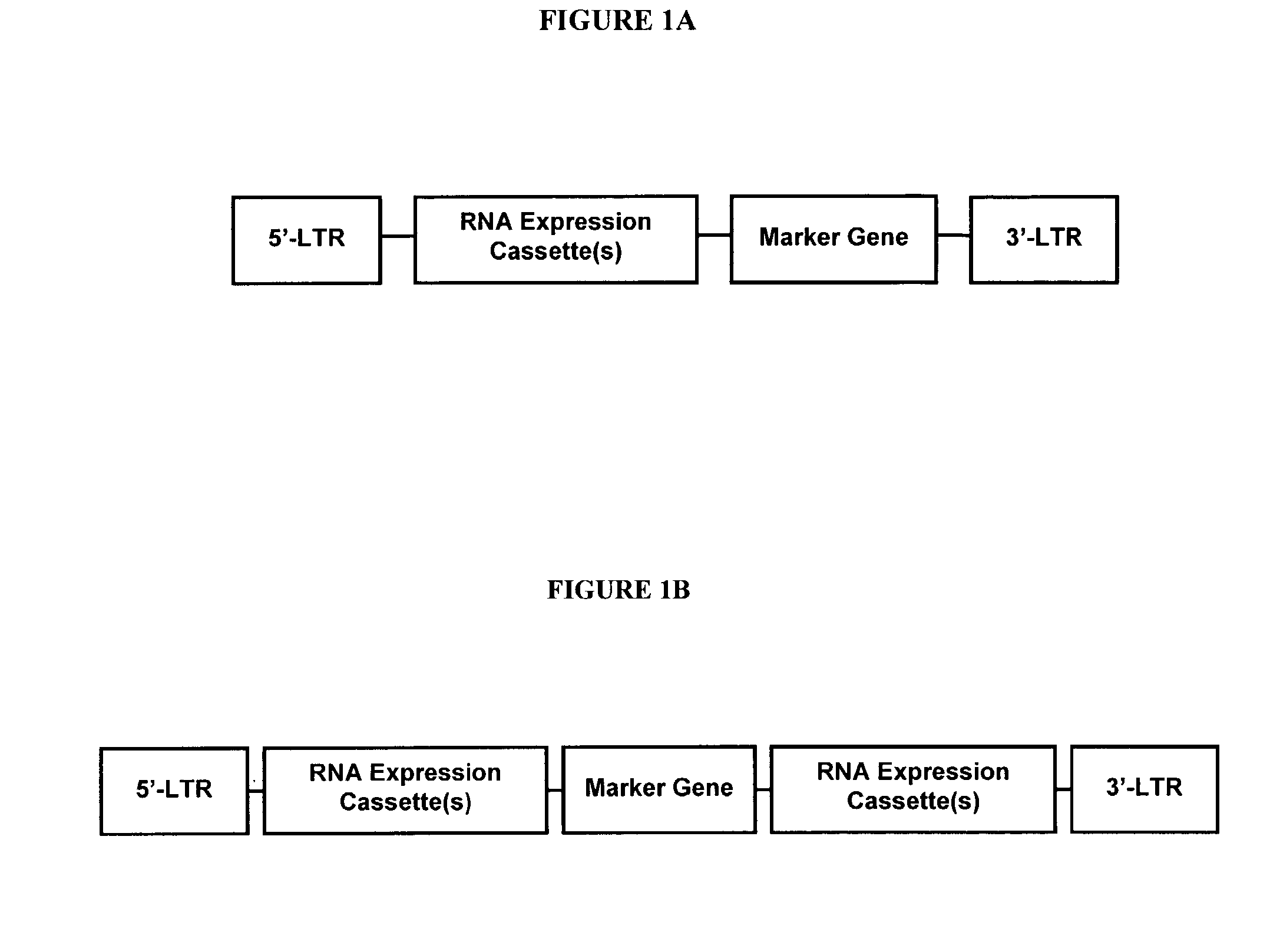
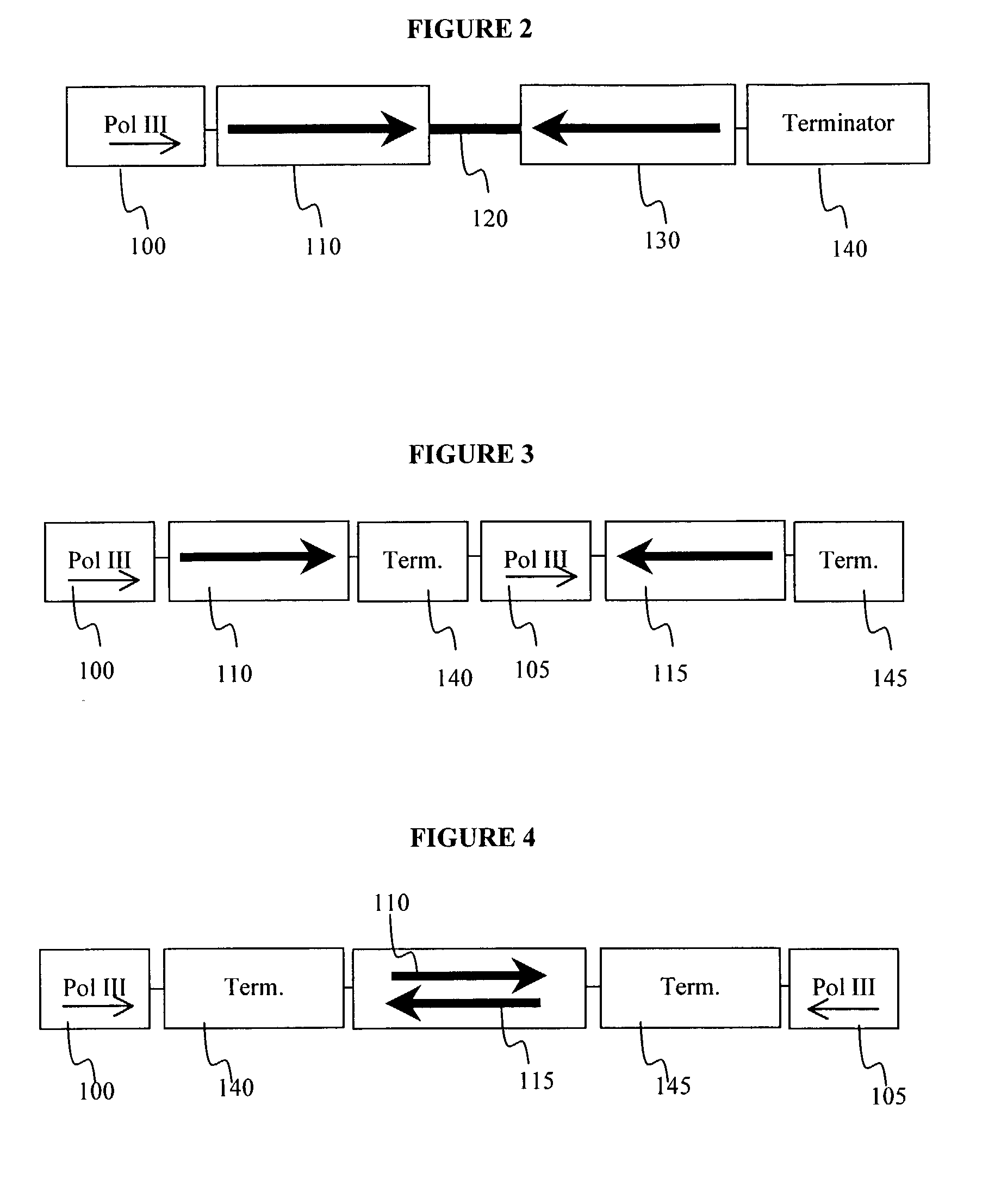
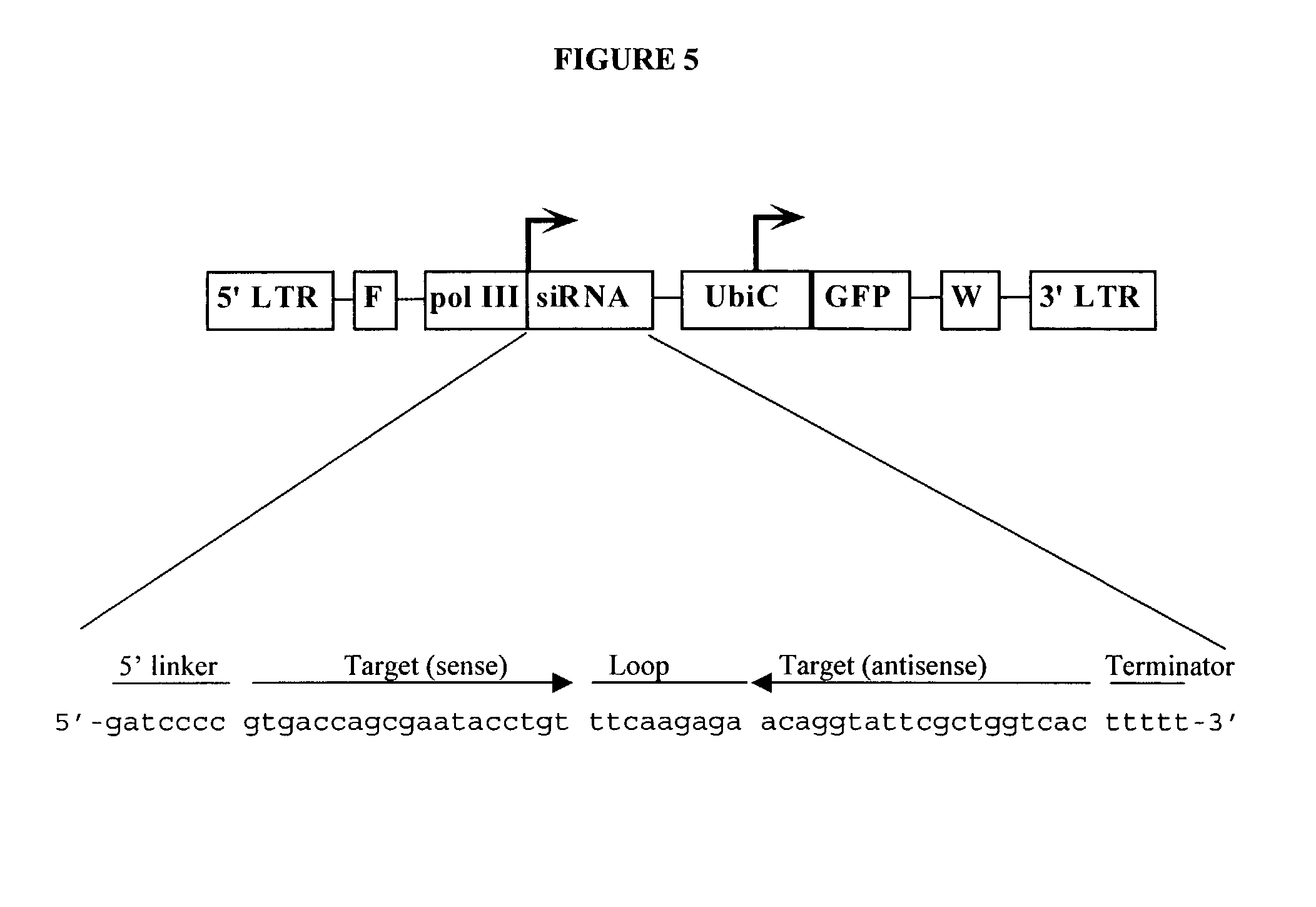
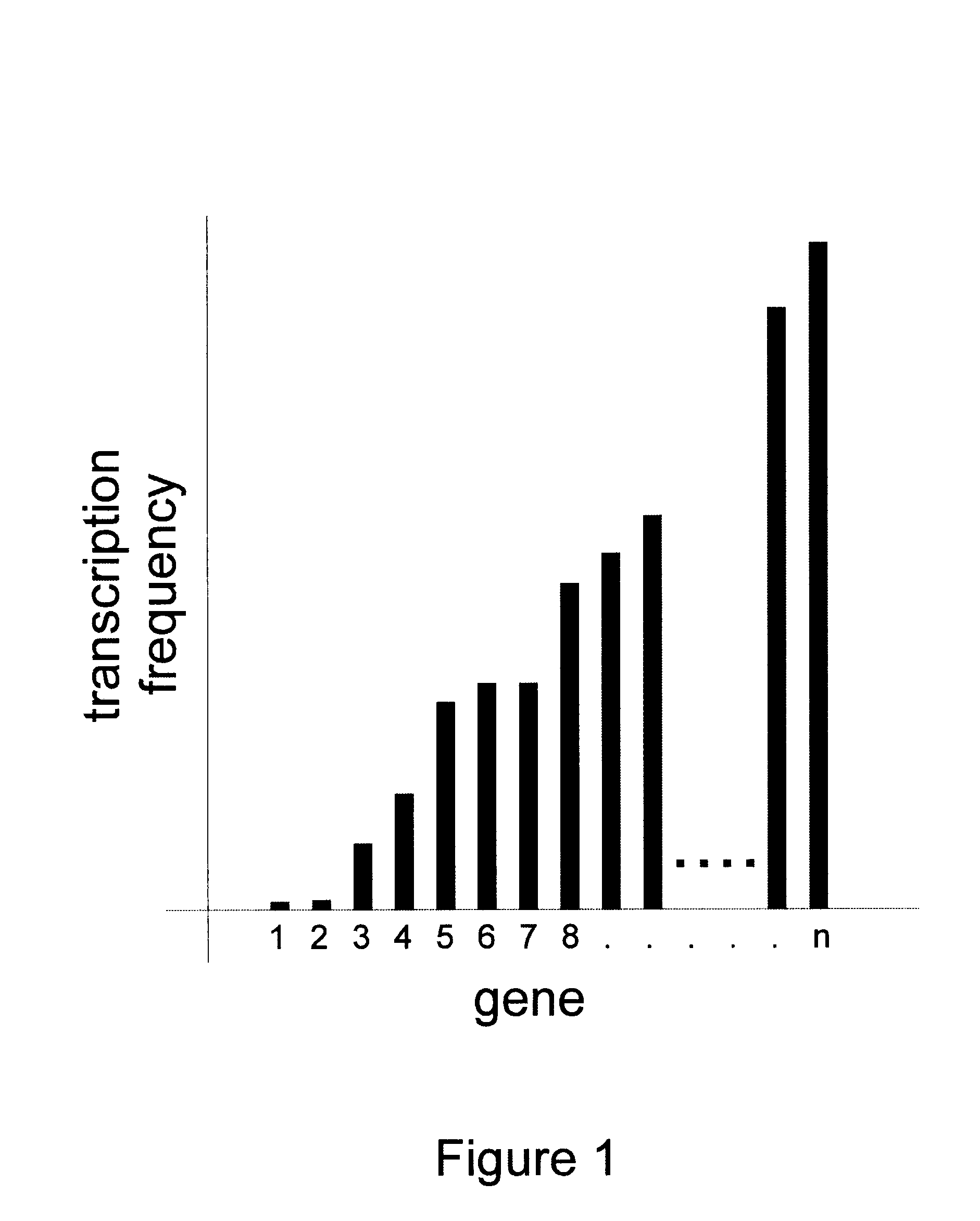
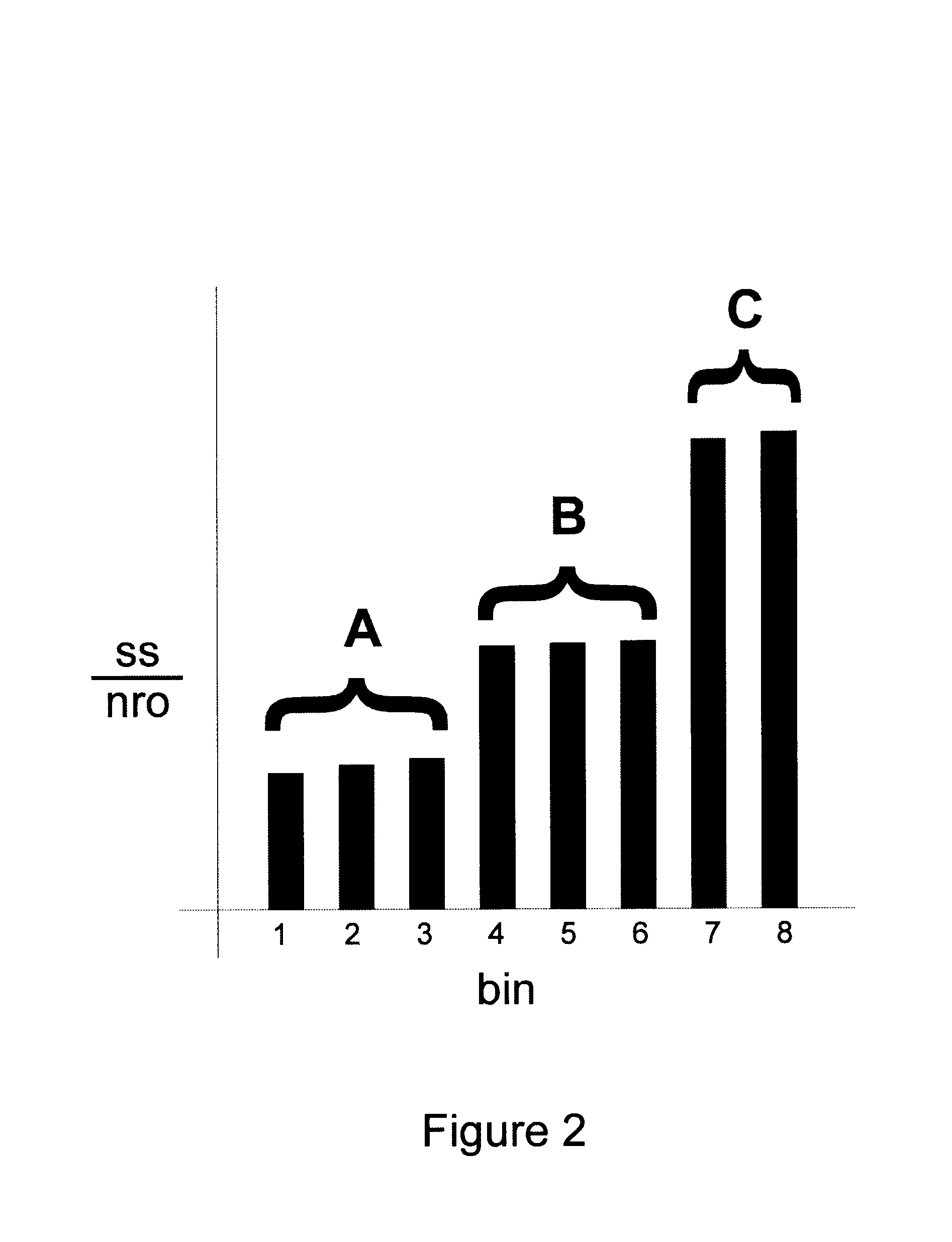
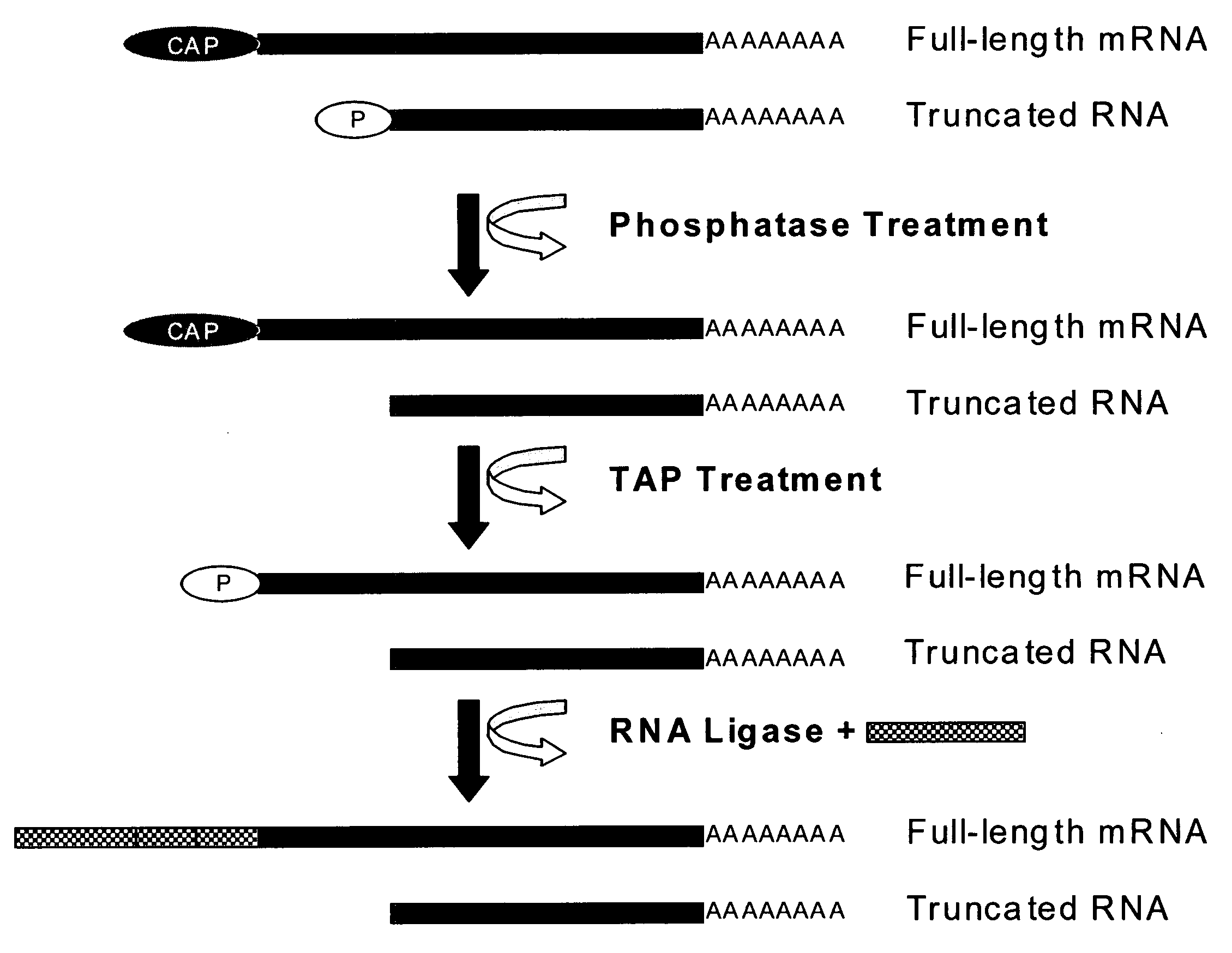
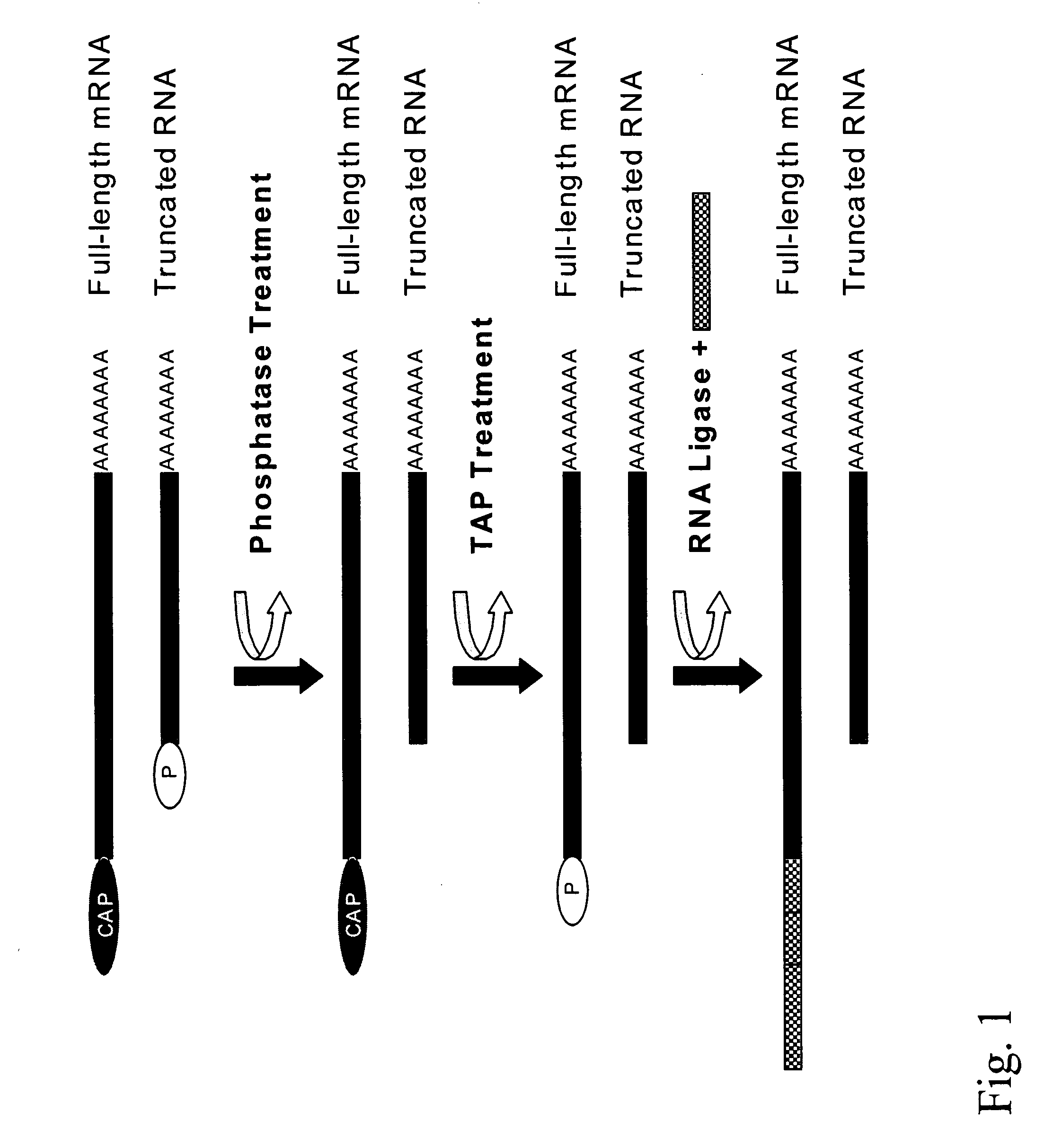
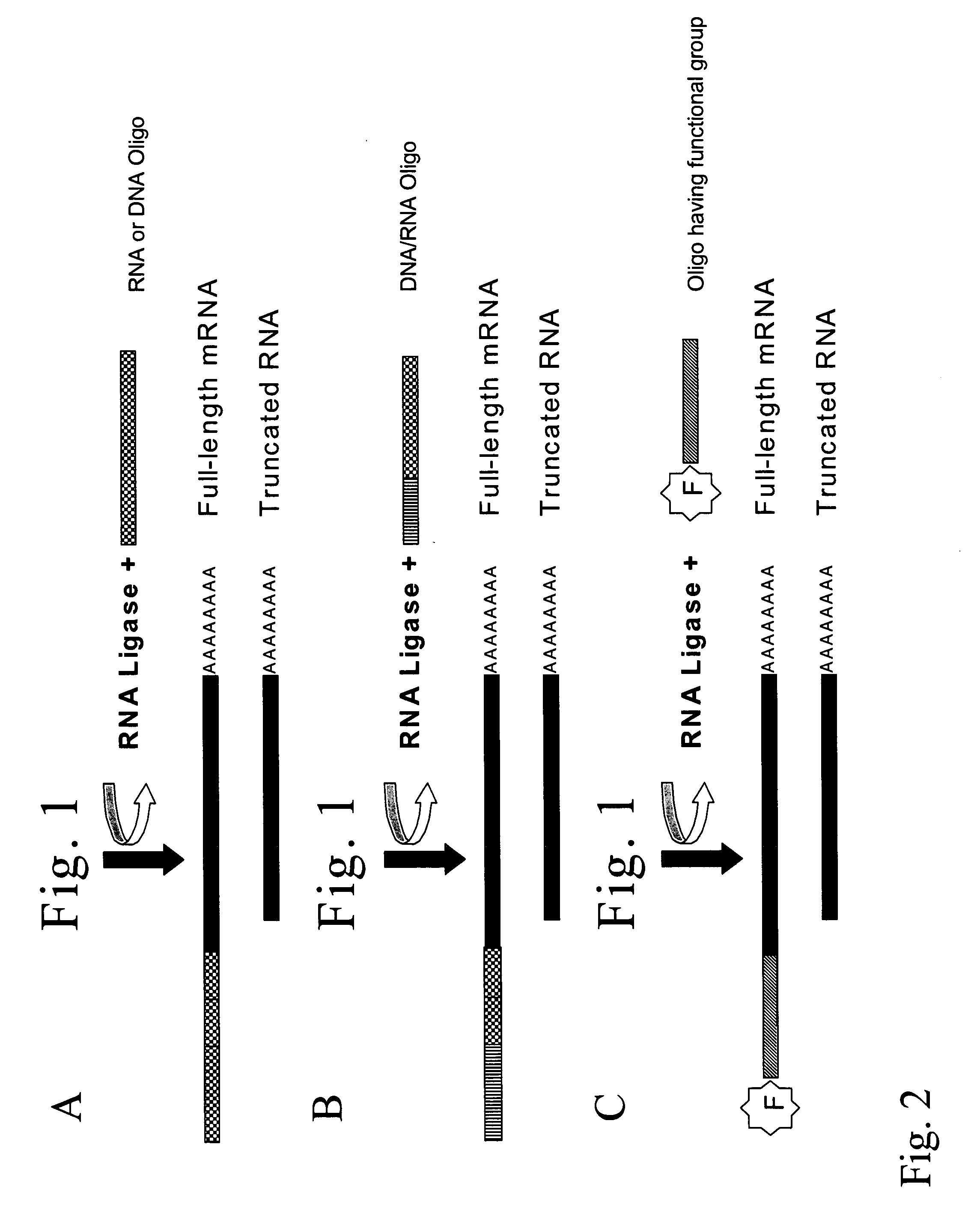
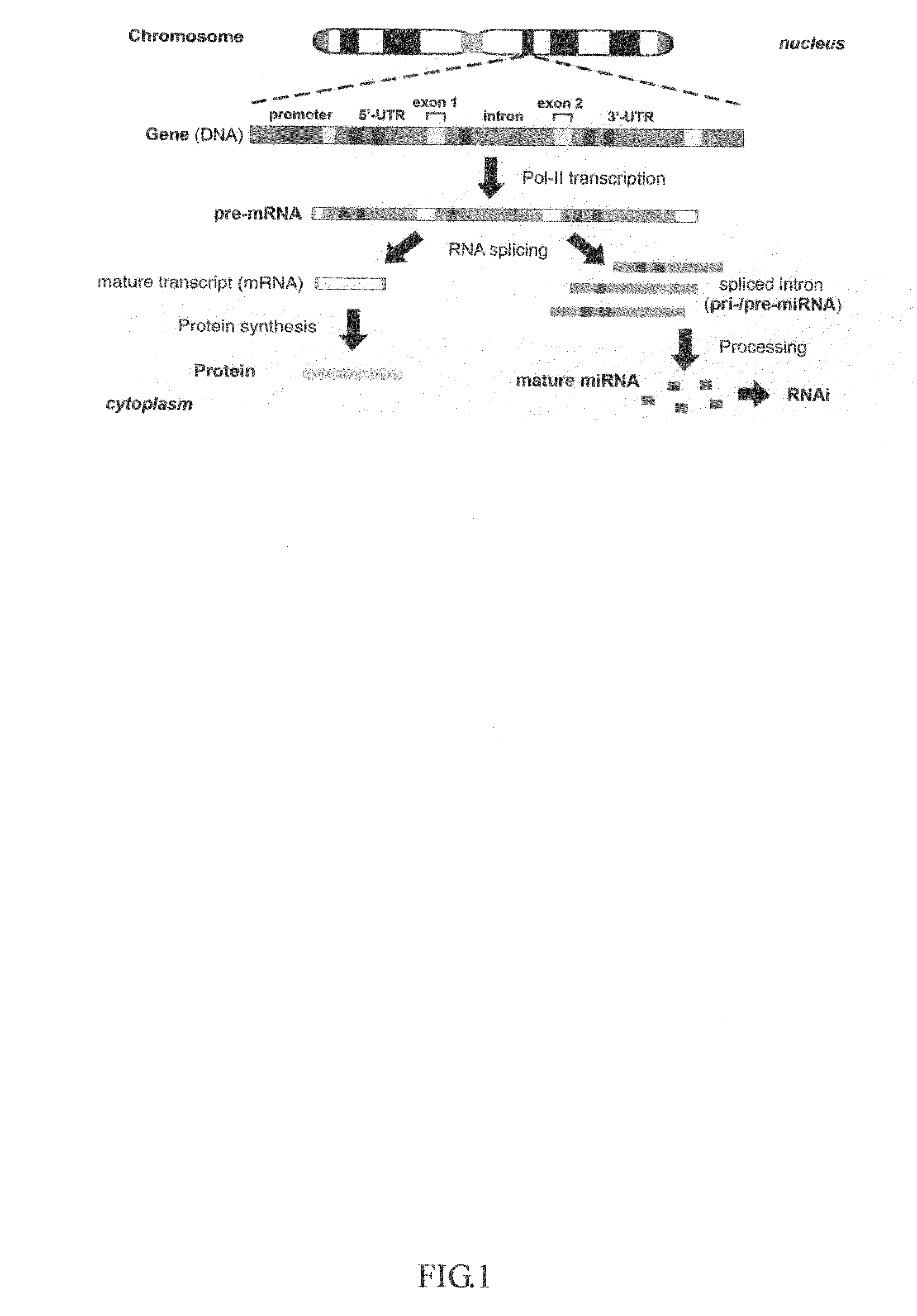
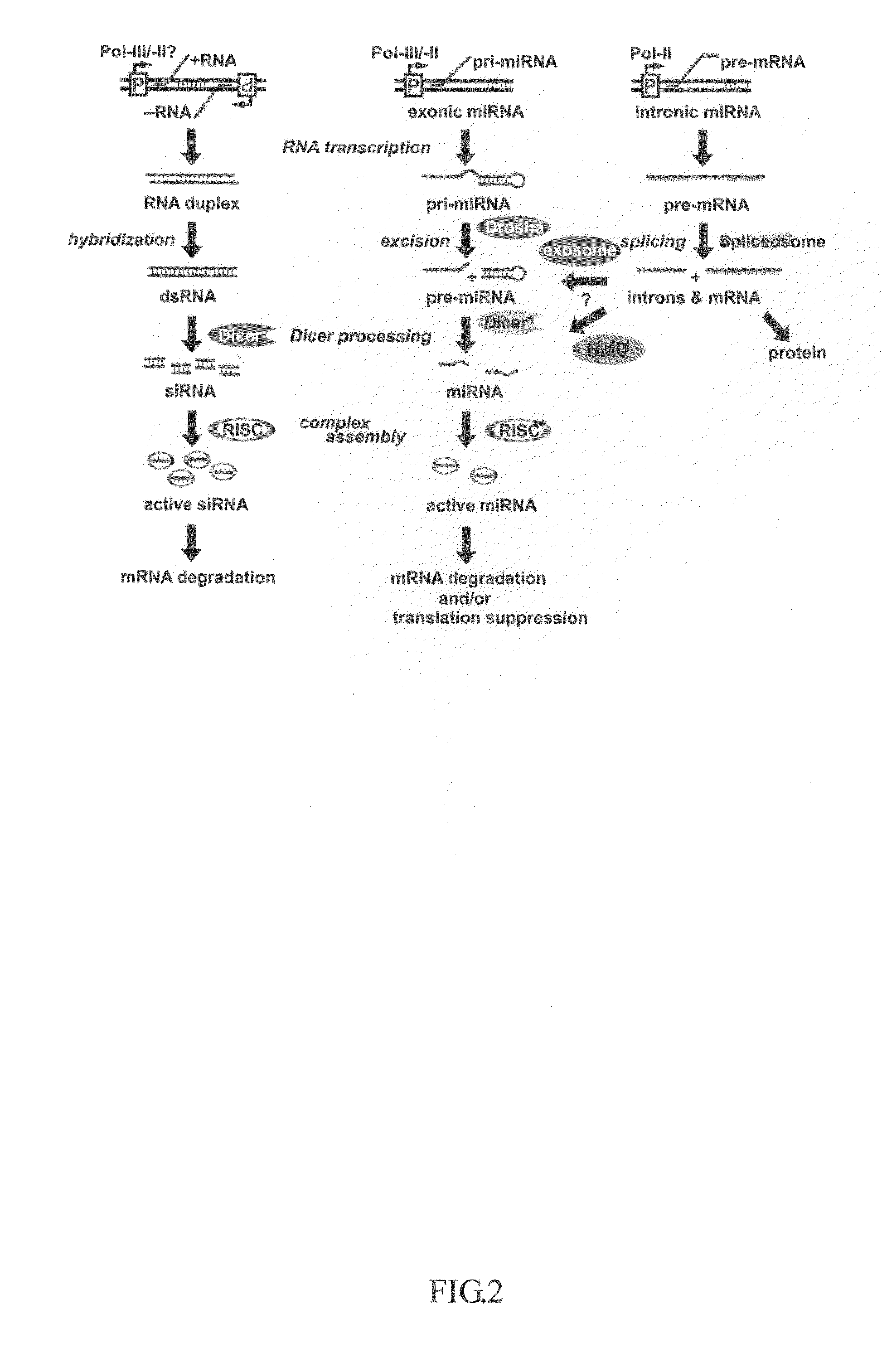
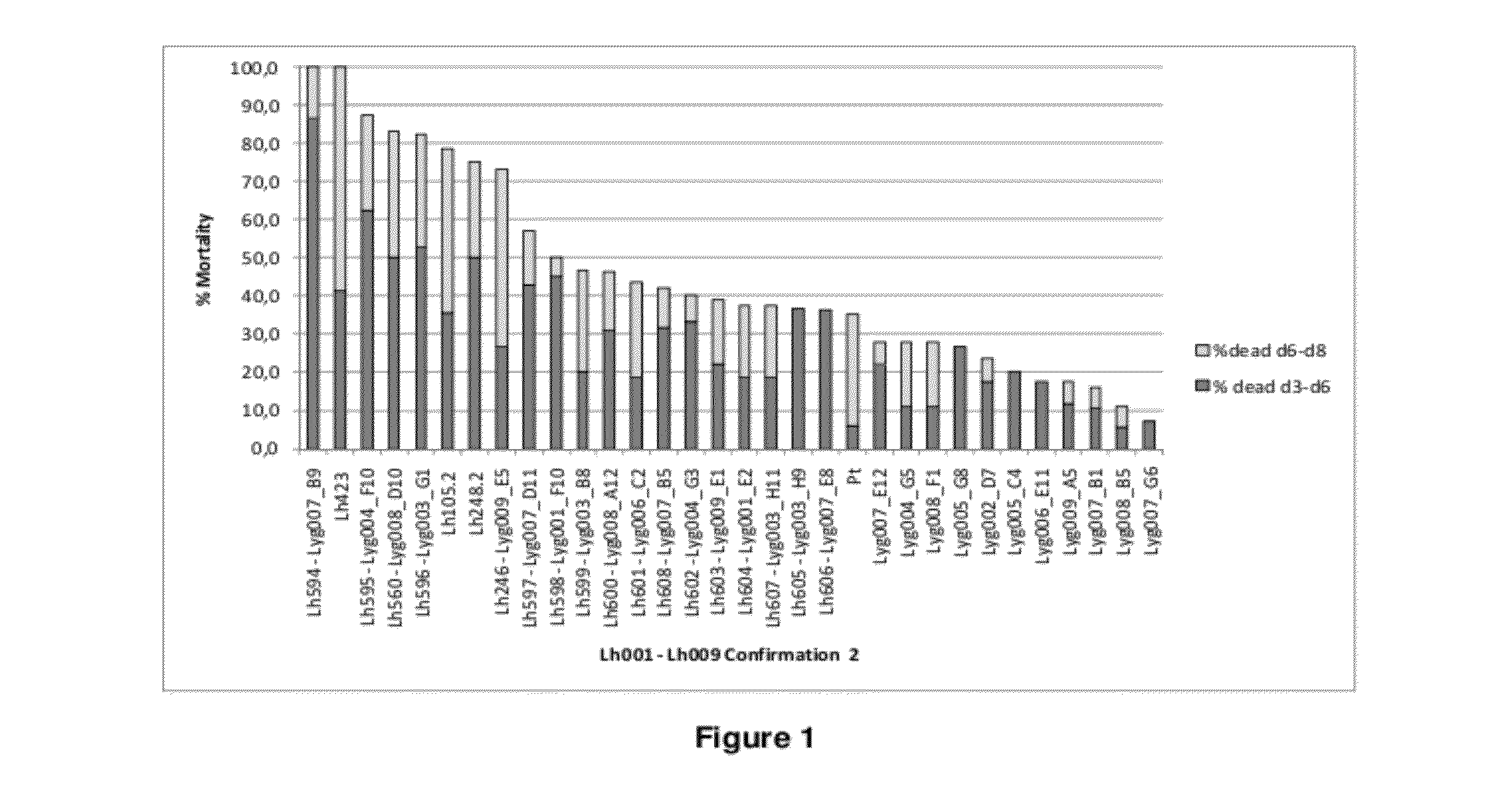
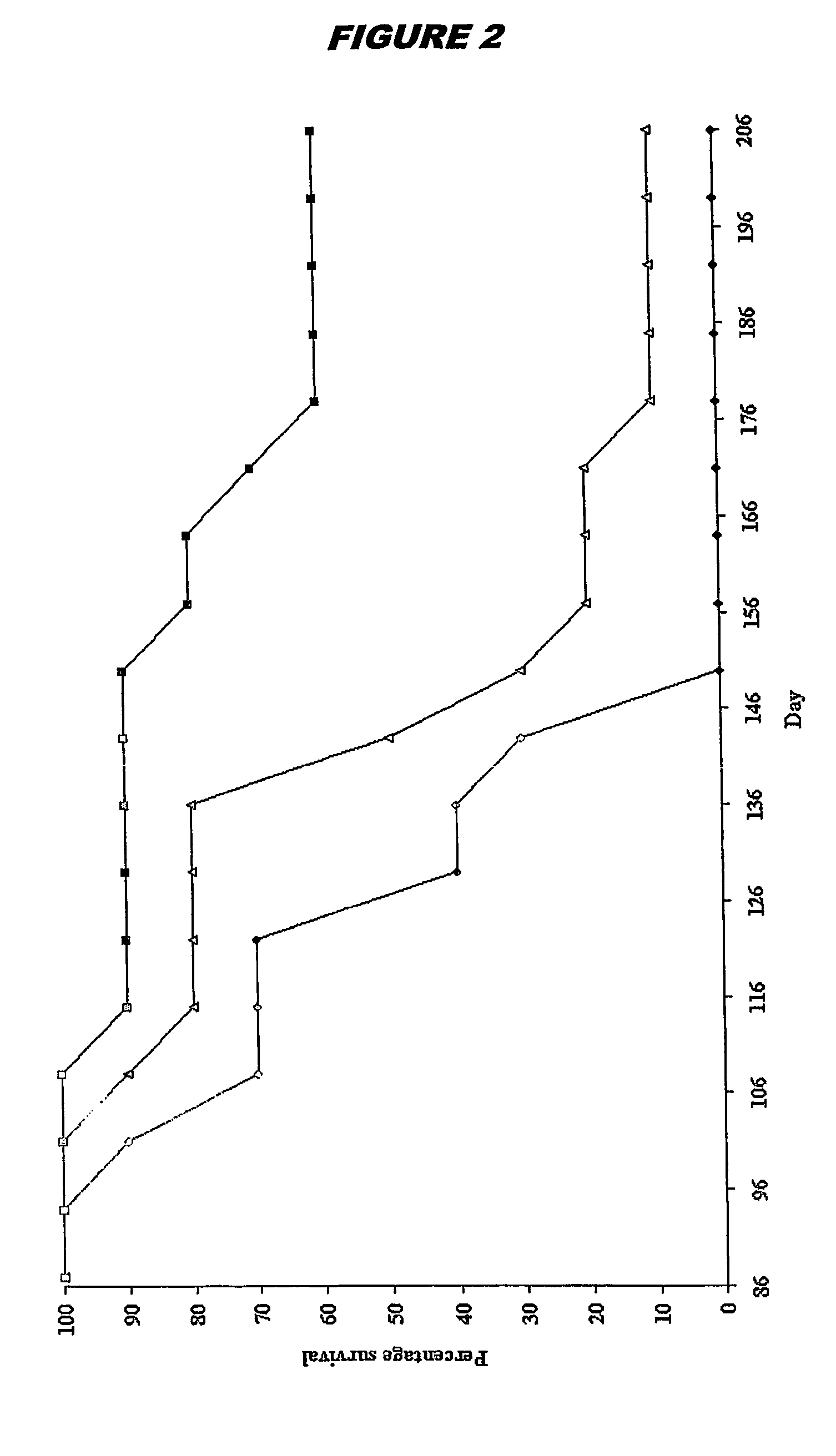
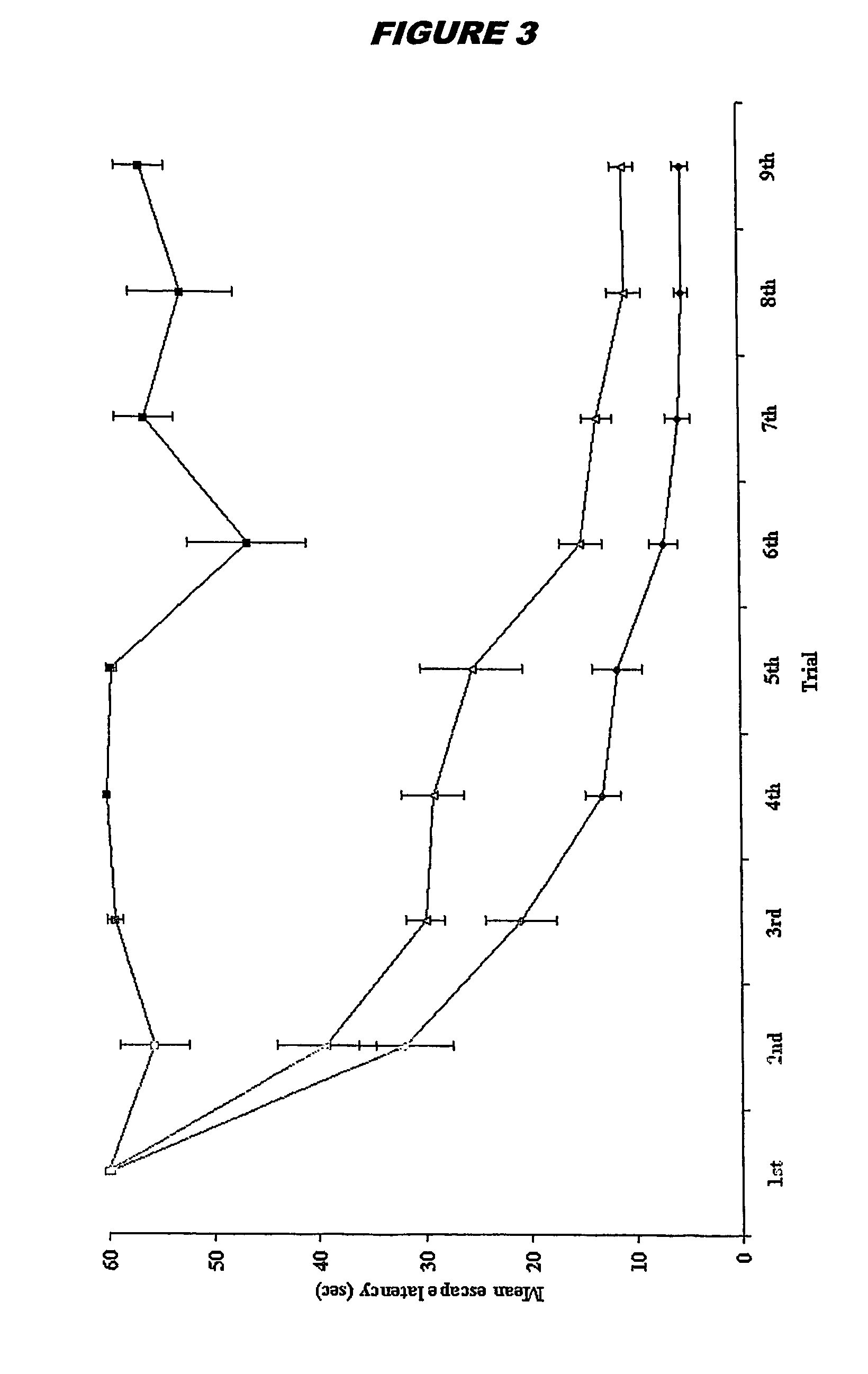
Patents
Literature
881 results about "RNA molecule" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
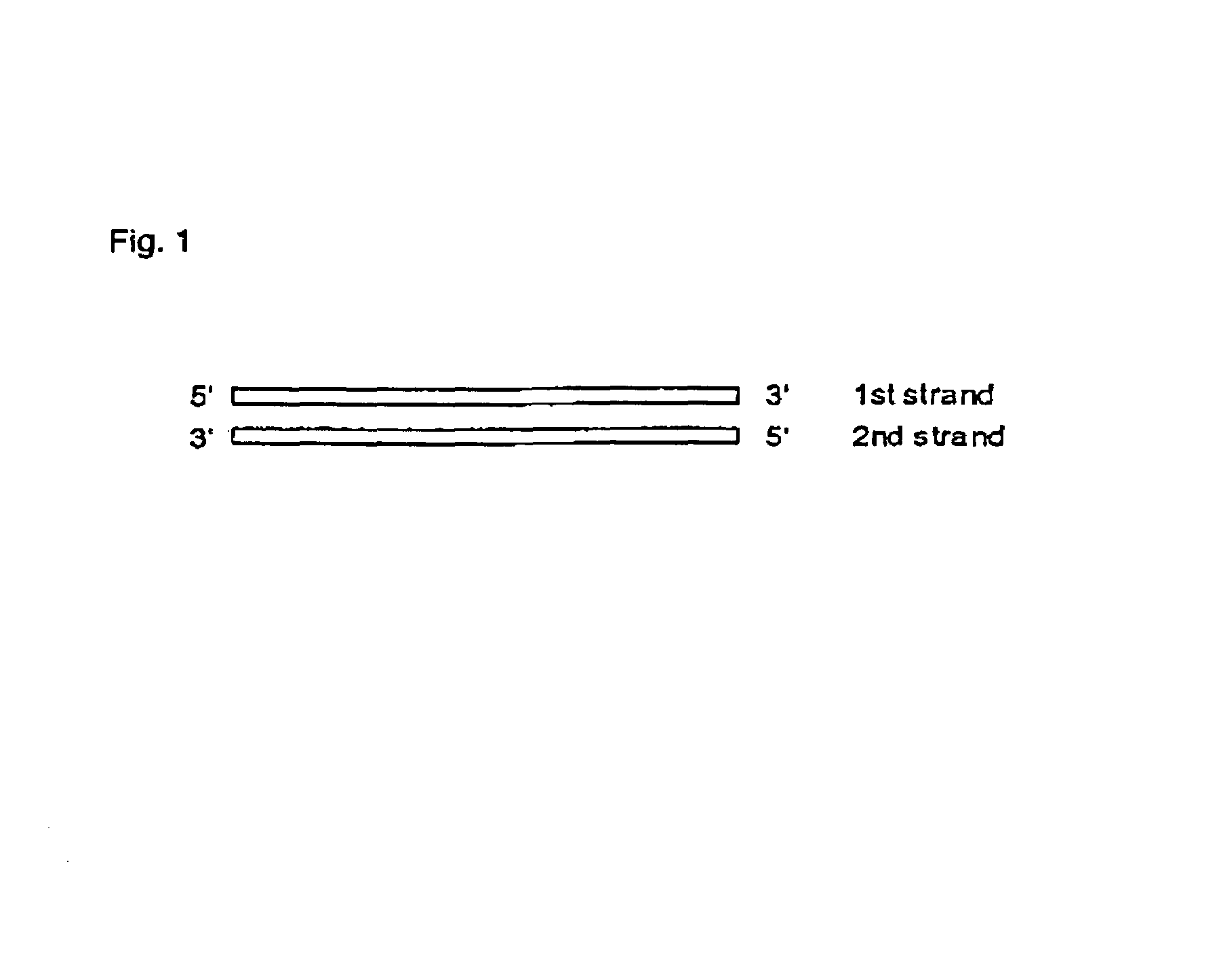
RNA nitrogenous bases include adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and uracil (U). The five-carbon (pentose) sugar in RNA is ribose. RNA molecules are polymers of nucleotides joined to one another by covalent bonds between the phosphate of one nucleotide and the sugar of another.
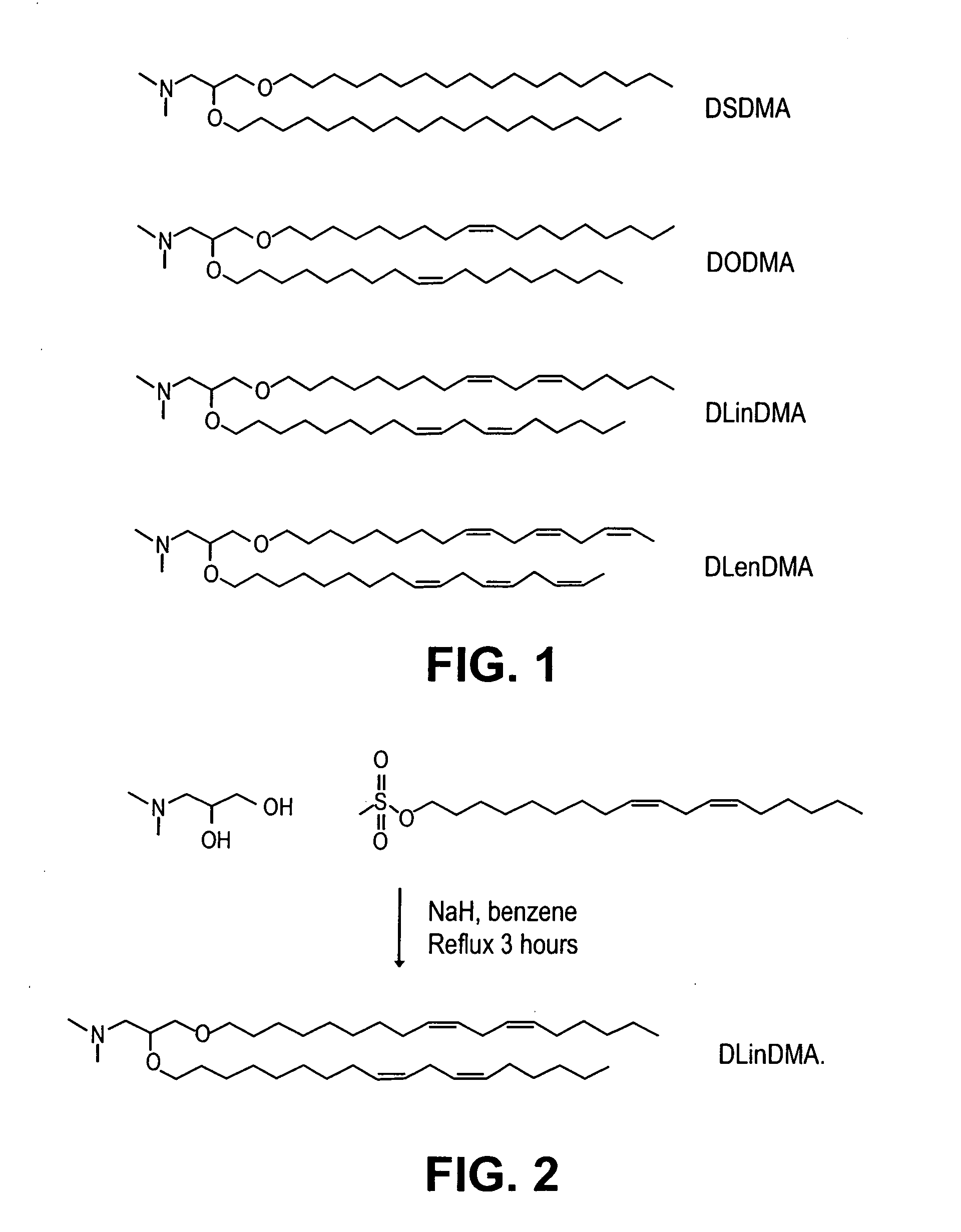
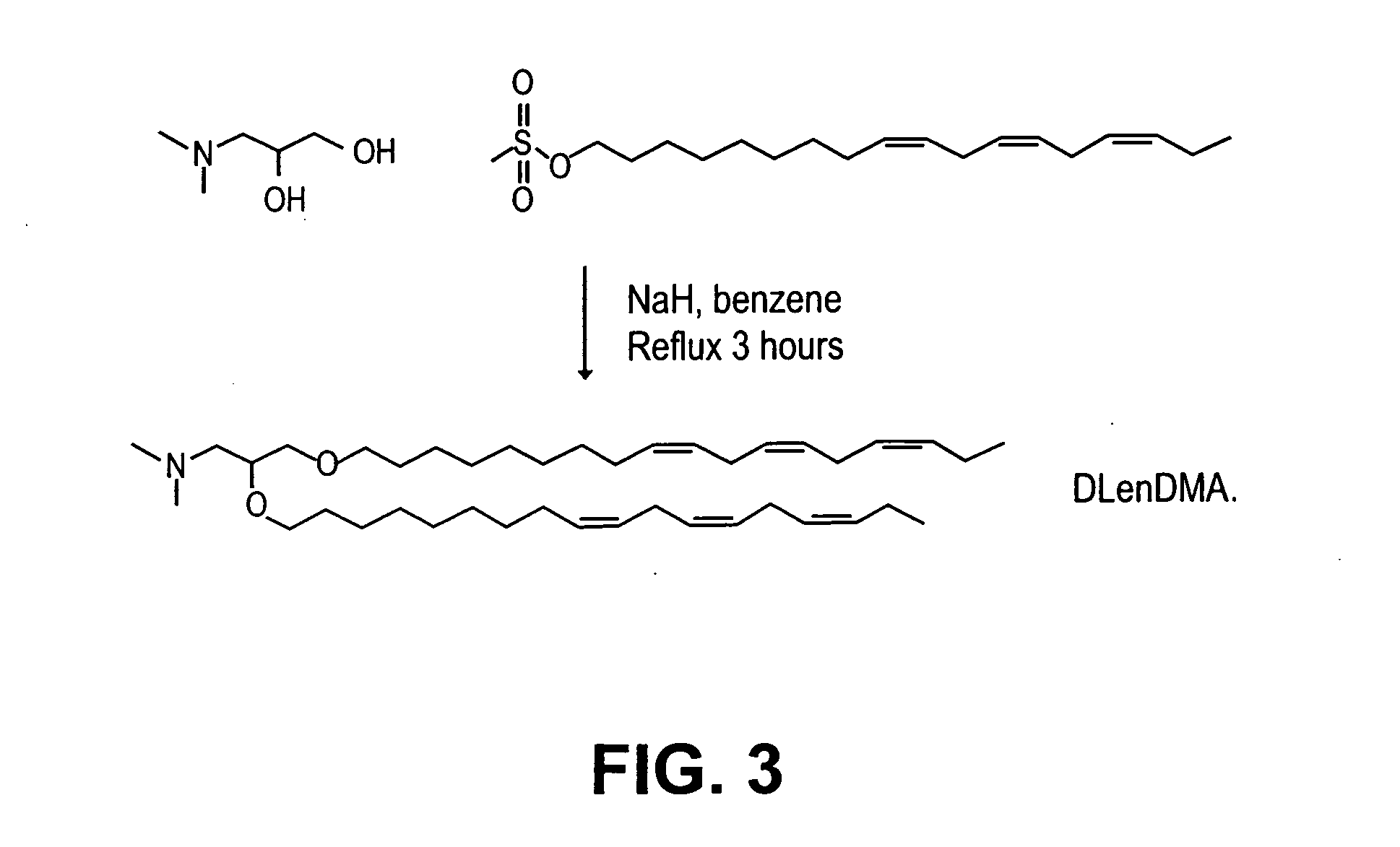
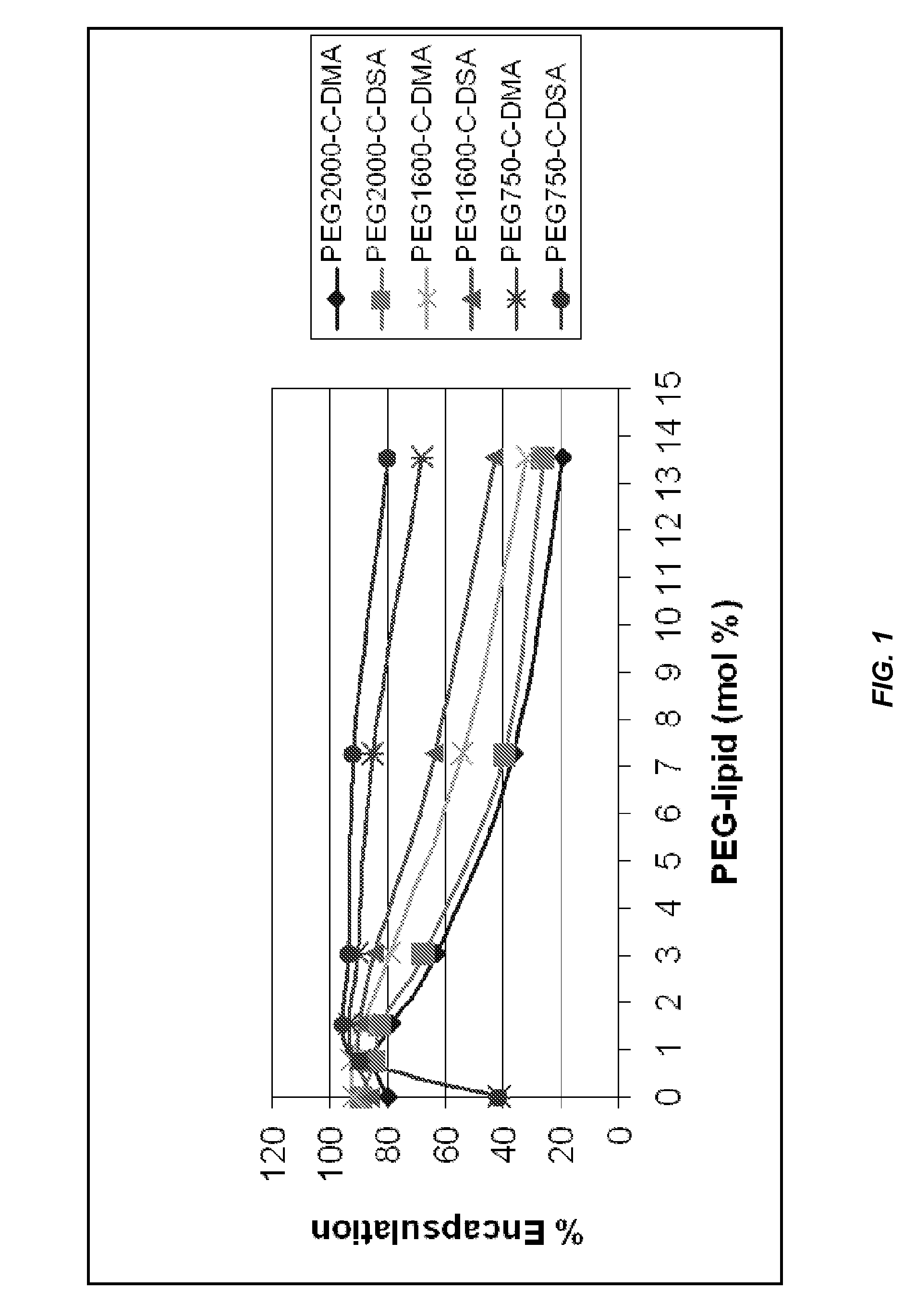
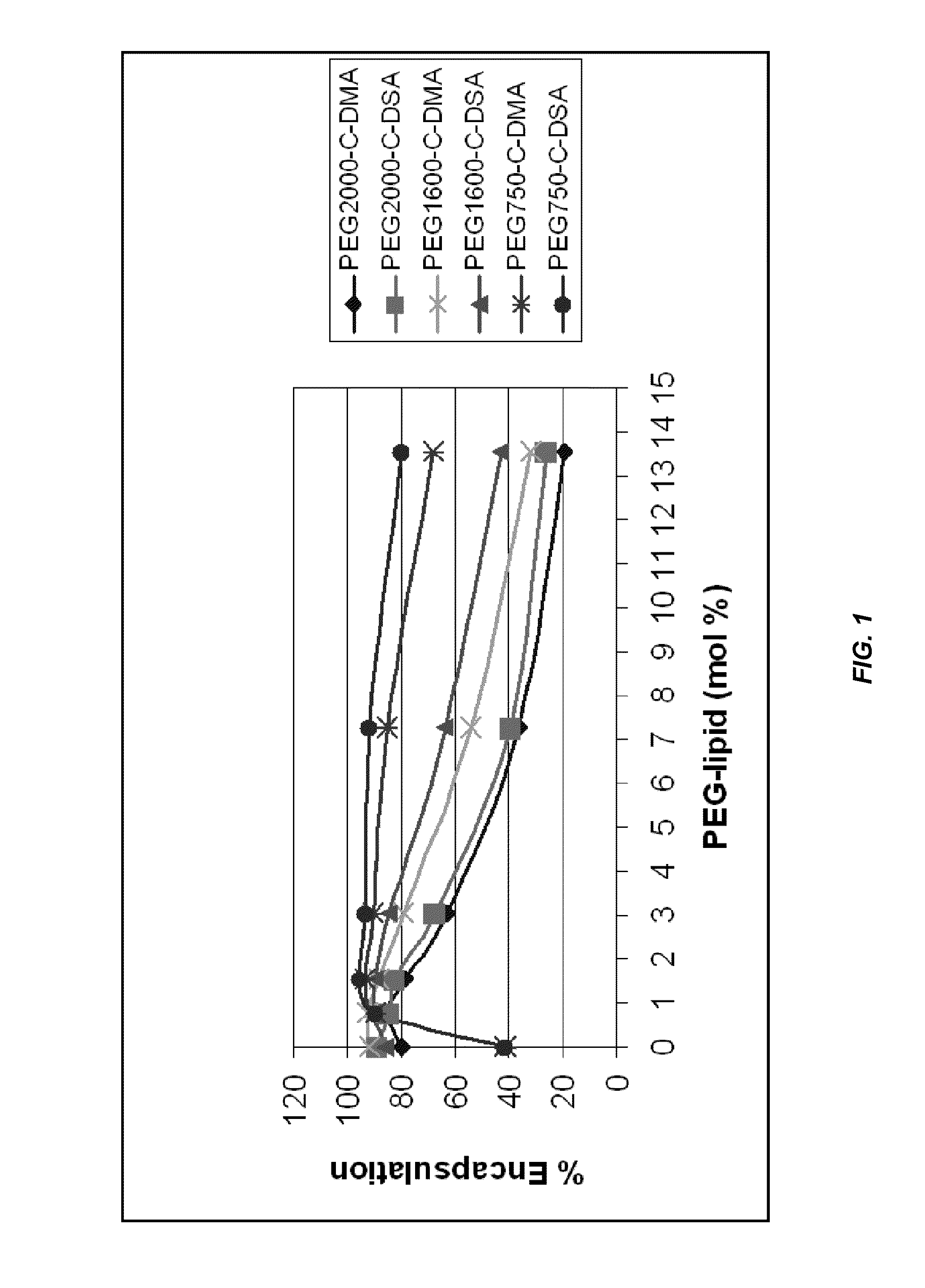
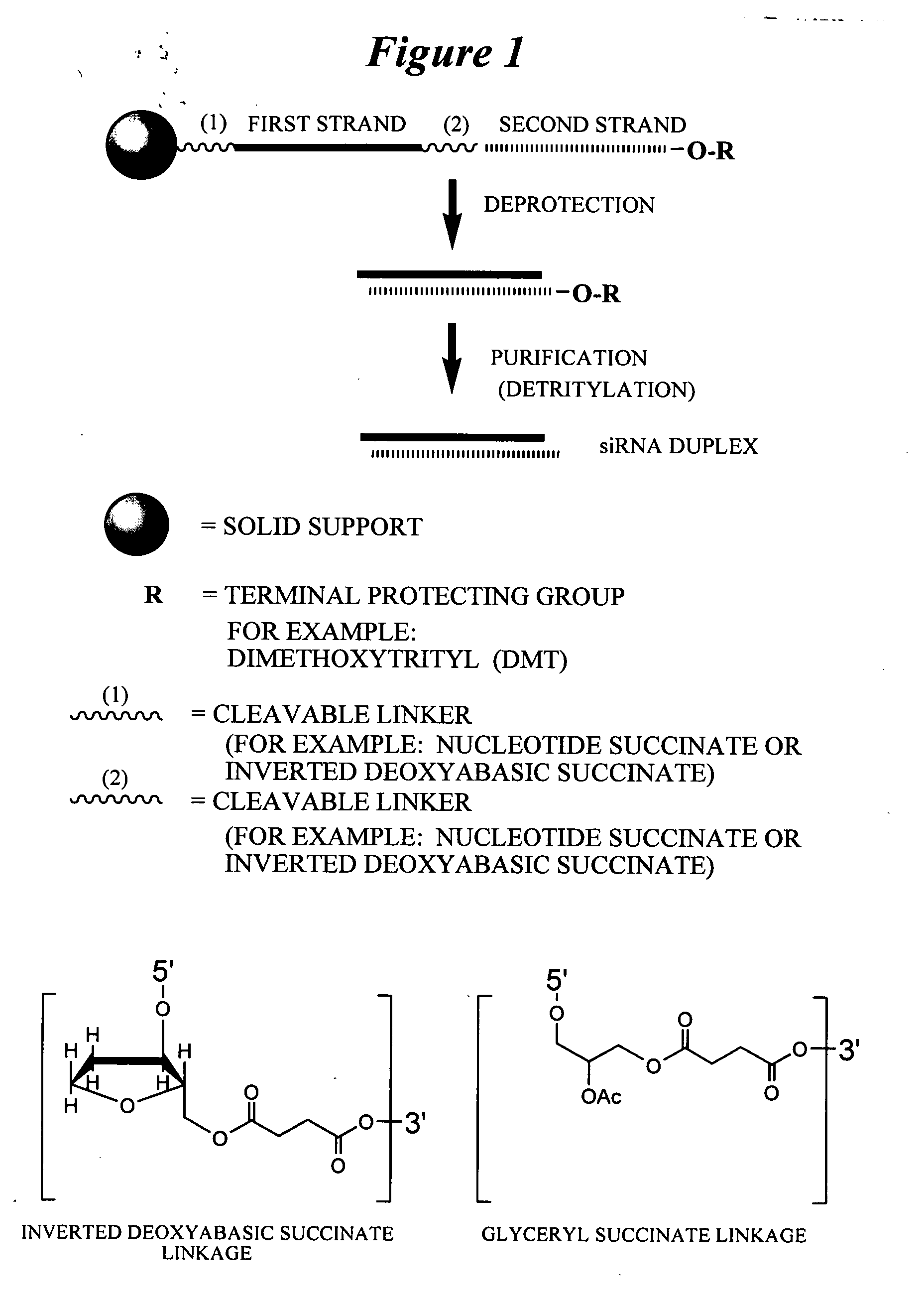
Lipid encapsulated interfering RNA
InactiveUS20060008910A1Inhibit aggregationReduce overexpressionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsLipid formationLipid particle
The present invention provides lipid-based formulations for delivering, e.g., introducing, nucleic acid-lipid particles comprising an interference RNA molecule to a cell, and assays for optimizing the delivery efficiency of such lipid-based formulations.
Owner:ARBUTUS BIOPHARMA CORPORAT ION
RNA preparations comprising purified modified RNA for reprogramming cells
ActiveUS20110143397A1Promote growthArtificial cell constructsCell culture active agentsSingle strandSomatic cell
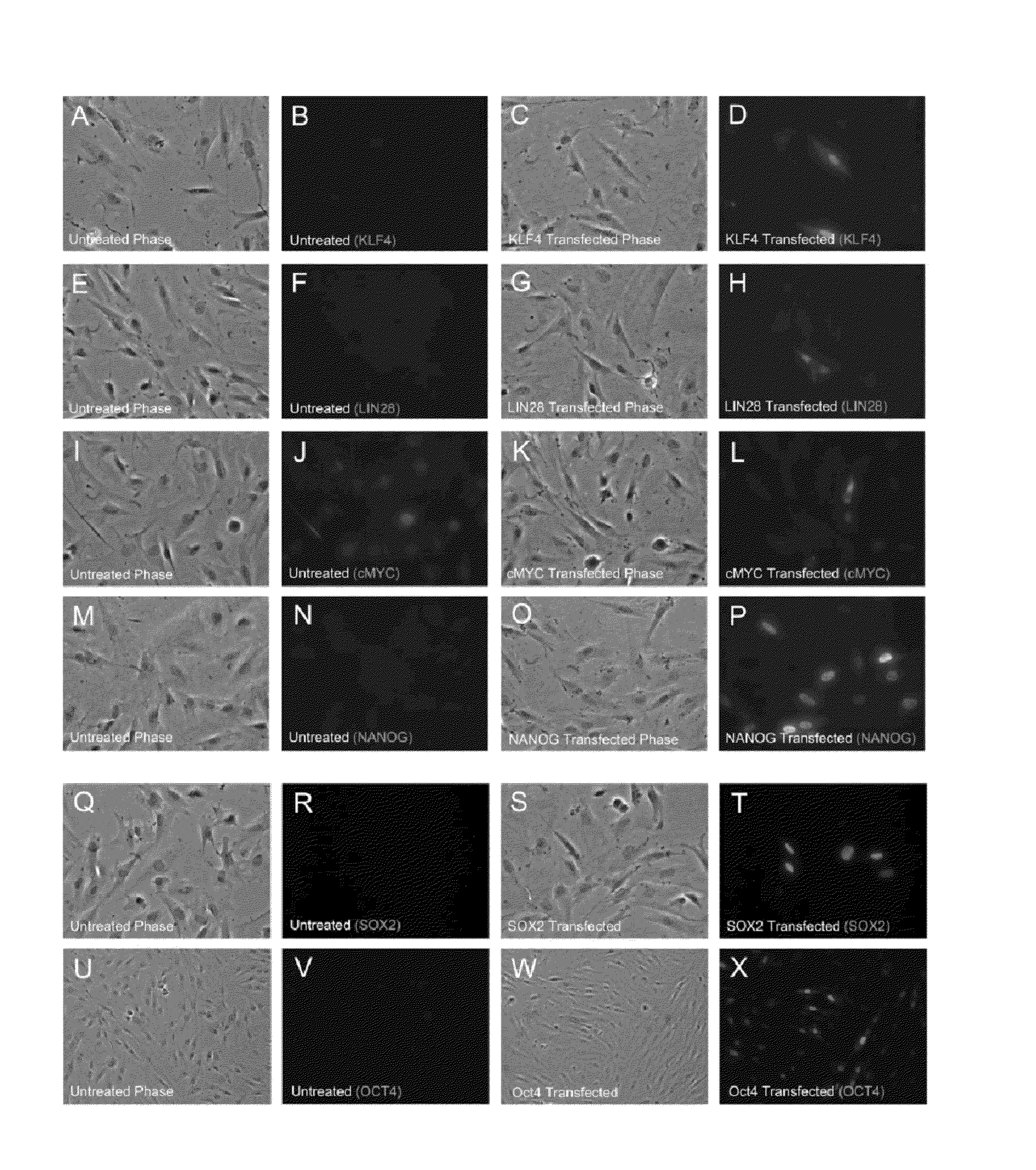
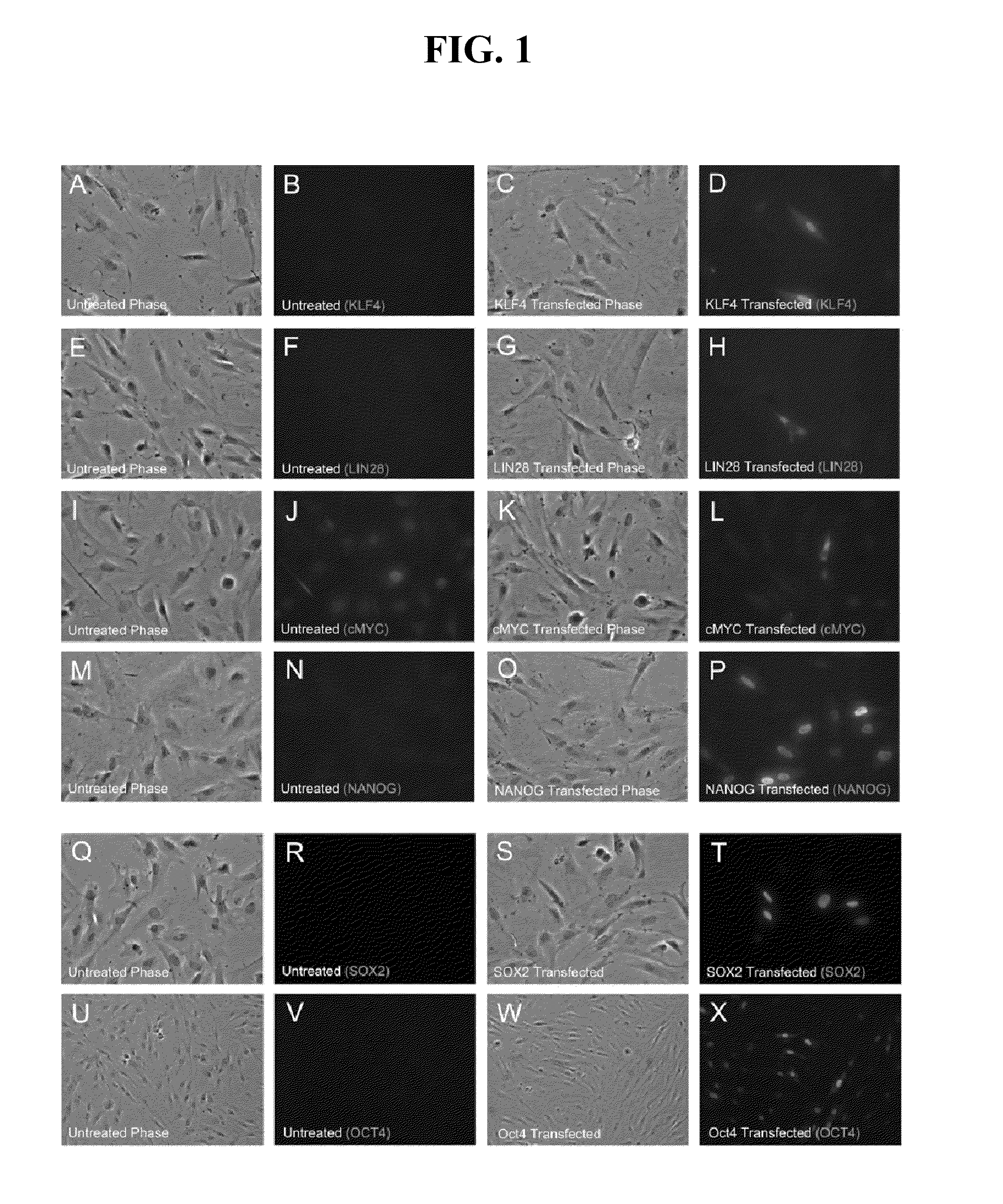
The present invention provides compositions and methods for reprogramming somatic cells using purified RNA preparations comprising single-strand mRNA encoding an iPS cell induction factor. The purified RNA preparations are preferably substantially free of RNA contaminant molecules that: i) would activate an immune response in the somatic cells, ii) would decrease expression of the single-stranded mRNA in the somatic cells, and / or iii) active RNA sensors in the somatic cells. In certain embodiments, the purified RNA preparations are substantially free of partial mRNAs, double-stranded RNAs, un-capped RNA molecules, and / or single-stranded run-on mRNAs.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
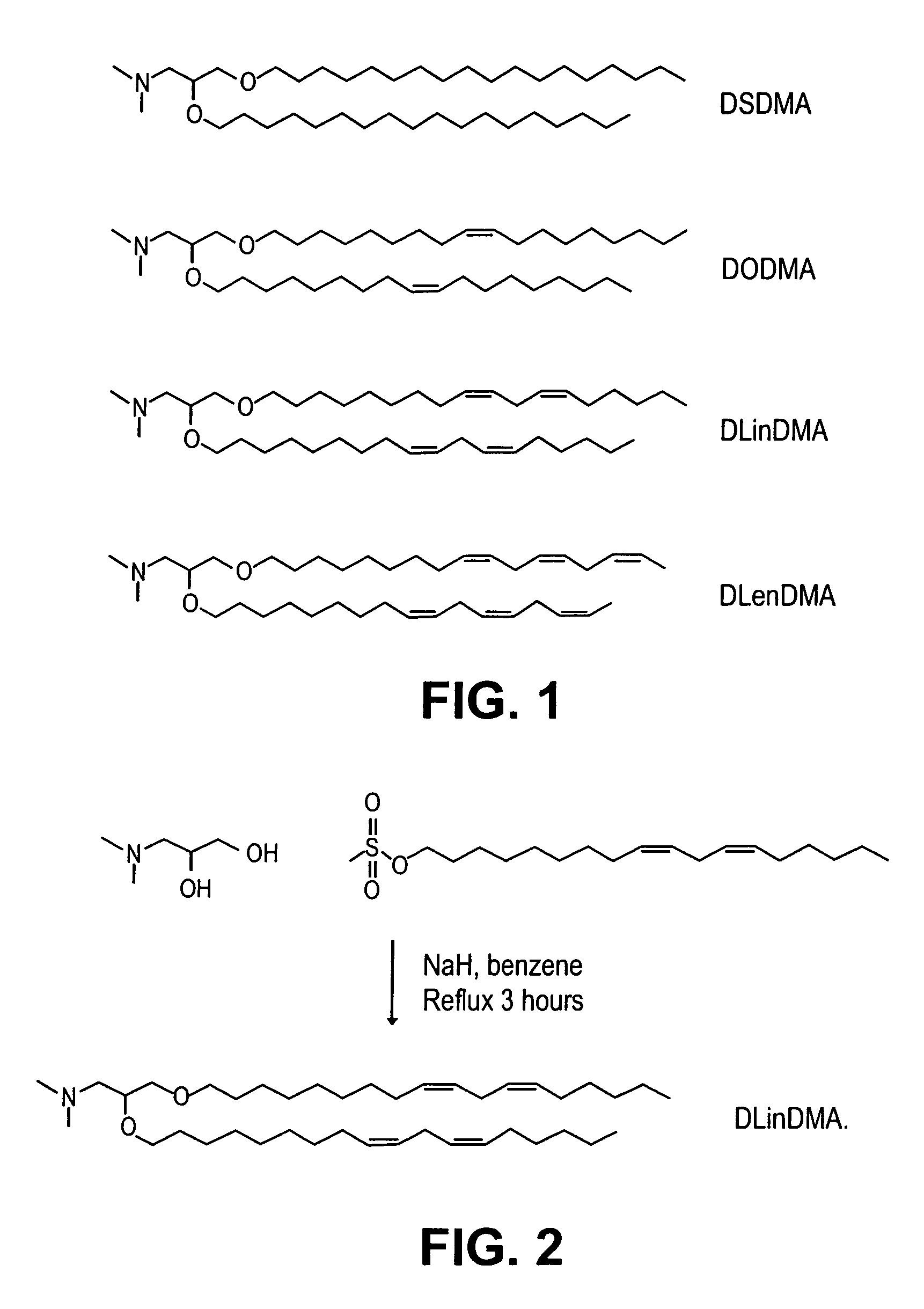
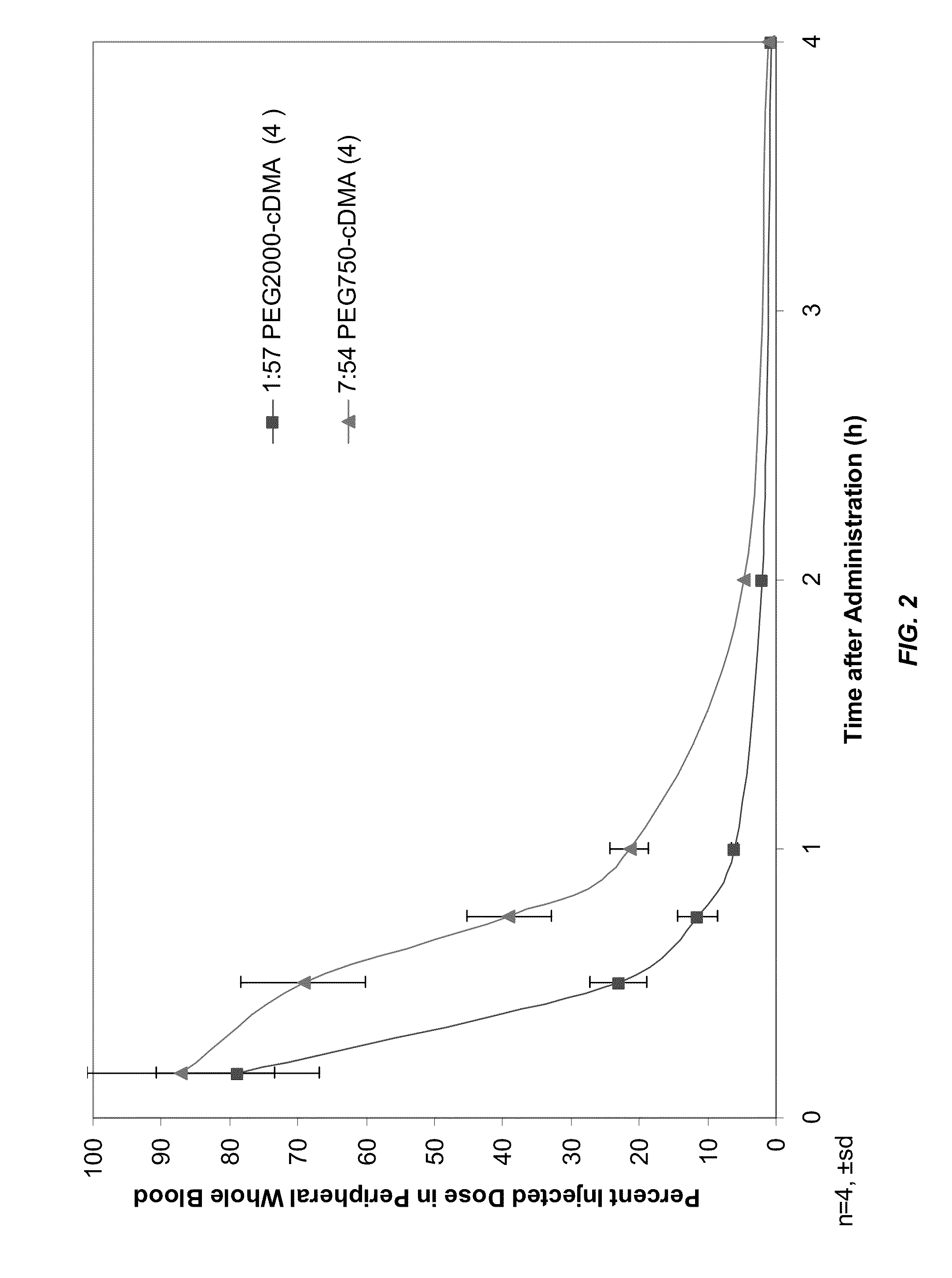
Lipid formulations for nucleic acid delivery
ActiveUS8283333B2Improve effectivenessHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesLipid particleActive agent
The present invention provides novel, serum-stable lipid particles comprising one or more active agents or therapeutic agents, methods of making the lipid particles, and methods of delivering and / or administering the lipid particles. More particularly, the present invention provides serum-stable nucleic acid-lipid particles (SNALP) comprising a nucleic acid (e.g., one or more interfering RNA molecules), methods of making the SNALP, and methods of delivering and / or administering the SNALP (e.g., for the treatment of cancer). In particular embodiments, the present invention provides tumor-directed lipid particles that preferentially target solid tumors. The tumor-directed formulations of the present invention are capable of preferentially delivering a payload such as a nucleic acid to cells of solid tumors compared to non-cancerous cells.
Owner:ARBUTUS BIOPHARMA CORPORAT ION
Lipid encapsulated interfering RNA
The present invention provides lipid-based formulations for delivering, e.g., introducing, nucleic acid-lipid particles comprising an interference RNA molecule to a cell, and assays for optimizing the delivery efficiency of such lipid-based formulations.
Owner:ARBUTUS BIOPHARMA CORPORAT ION
Method for facilitating pathogen resistance
InactiveUS20030150017A1Convenient researchImprove developmentClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesDNA constructNucleotide
Methods are provided for the genetic control of pathogen infestation in host organisms such as plants, vertebrate animals and fungi. Such methods utilize the host as a delivery system for the delivery of genetic agents, preferably in the form of RNA molecules, to a pathogen, which agents cause directly or indirectly an impairment in the ability of the pathogen to maintain itself, grow or otherwise infest a host plant, vertebrate animal or fungus. Also provided are DNA constructs and novel nematode nucleotide sequences for use in same, that facilitate pathogen resistance when expressed in a genetically-modified host. Such constructs direct the expression of RNA molecules substantially homologous and / or complementary to an RNA molecule encoded by a nucleotide sequence within the genome of a pathogen and / or of the cells of a host to effect down-regulation of the nucleotide sequence. Particular hosts contemplated are plants, such as pineapple plants, and particular pathogens are nematodes.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND +1
Compositions and methods for control of insect infestations in plants
InactiveUS20060021087A1Limiting and eliminating invertebrateInhibit expressionBiocideSugar derivativesInvertebrateOrganism
The present invention is directed to controlling pest infestation by inhibiting one or more biological functions in an invertebrate pest. The invention discloses methods and compositions for use in controlling pest infestation by feeding one or more different recombinant double stranded RNA molecules to the pest in order to achieve a reduction in pest infestation through suppression of gene expression. The invention is also directed to methods for making transgenic plants that express the double stranded RNA molecules, and to particular combinations of transgenic pesticidal agents for use in protecting plants from pest infestation.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Methods for identifying RNA binding compounds
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Microfabricated droplet generator for single molecule/cell genetic analysis in engineered monodispersed emulsions
ActiveUS20100285975A1Efficient routingEfficient single-molecule amplificationTransportation and packagingLibrary screeningEmulsionMicroparticle
Provided are microfluidic designs and methods for rapid generation of monodisperse nanoliter volume droplets of reagent / target (e.g., molecule or cell) mix in emulsion oil. The designs and methods enable high-throughput encapsulation of a single target (e.g., DNA / RNA molecules or cells) in controlled size droplets of reagent mix. According to various embodiments, a microfabricated, 3-valve pump is used to precisely meter the volume of reagent / target mix in each droplet and also to effectively route microparticles such as beads and cells into the device, which are encapsulated within droplets at the intersection of the reagent channel and an oil channel. The pulsatile flow profile of the microfabricated pumps provides active control over droplet generation, thereby enabling droplet formation with oils that are compatible with biological reactions but are otherwise difficult to form emulsions with.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
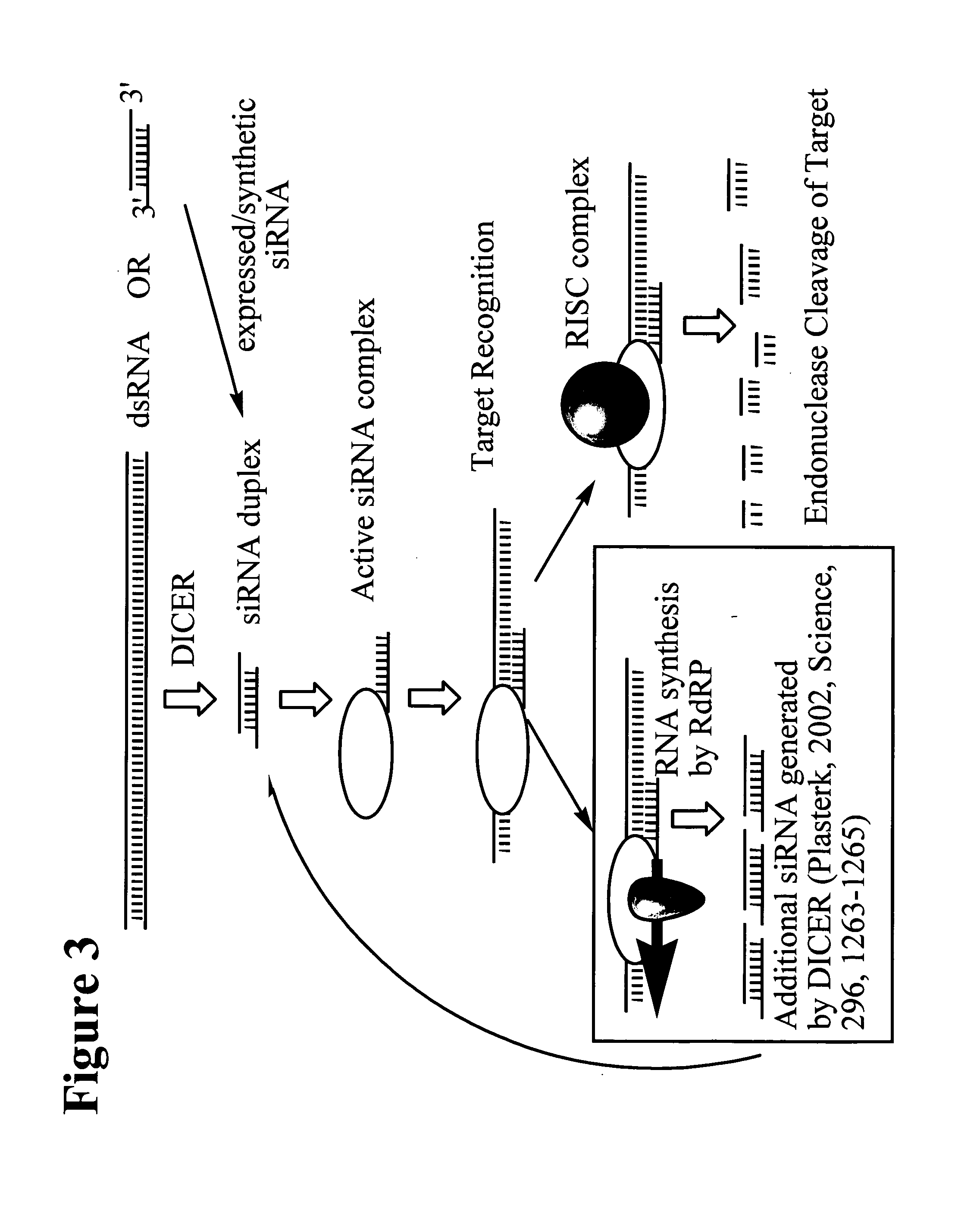
Interfering RNA molecules
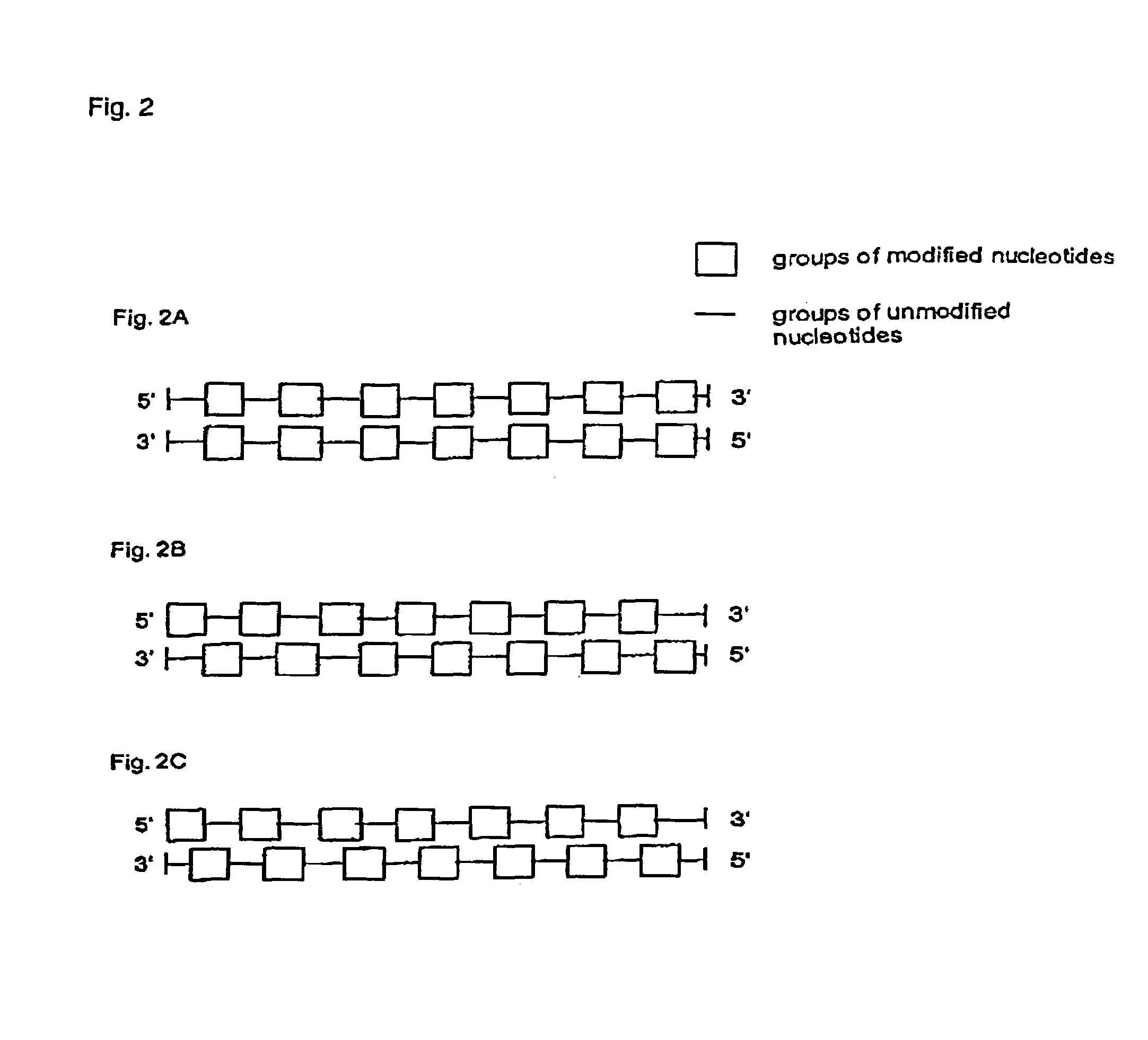
The present invention is related to a ribonucleic acid comprising a double stranded structure whereby the double-stranded structure comprises a first strand and a second strand, whereby the first strand comprises a first stretch of contiguous nucleotides and whereby said first stretch is at least partially complementary to a target nucleic acid, and the second strand comprises a second stretch of contiguous nucleotides whereby said second stretch is at least partially identical to a target nucleic acid, and whereby the double stranded structure is blunt ended.
Owner:SILENCE THERAPEUTIC AG
New sequencing method for sequencing rna molecules
InactiveUS20060166203A1Reduce decreaseMicrobiological testing/measurementReverse transcriptaseNucleotide
The present invention provides a method for determination of the identity of at least one nucleotide in a RNA-molecule comprising the steps of: (i) providing the RNA-molecule, an oligonucleotide primer binding to a predetermined position of the RNA molecule, a reverse transcriptase, deoxynucleotides and other necessary reagents, in a reaction vessel; (ii) performing a primer extension reaction, whereby the oligonucleotide primer is extended on the RNA-molecule through incorporation of at least one deoxynucleotide by the action of a reverse transcriptase, resulting in the release of a PPi molecule only upon incorporation of a deoxynucleotide; and (iii) detecting the presence or absence of incorporation, thereby indicating the nucleotide identity of the RNA molecule in the relevant position. In a preferred embodiment, the sequencing of the invention is coupled to the Pyrosequencing™ reaction. A variant of the method employs incorporation of modified nucleotides, with an optionally cleavable linker arm to which is attached a label.
Owner:TOOKE NIGEL
Methods for genetic control of insect infestations in plants and compositions thereof
ActiveUS7943819B2Reduced expression levelLow effective doseSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationGMO PlantsDouble stranded rna
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
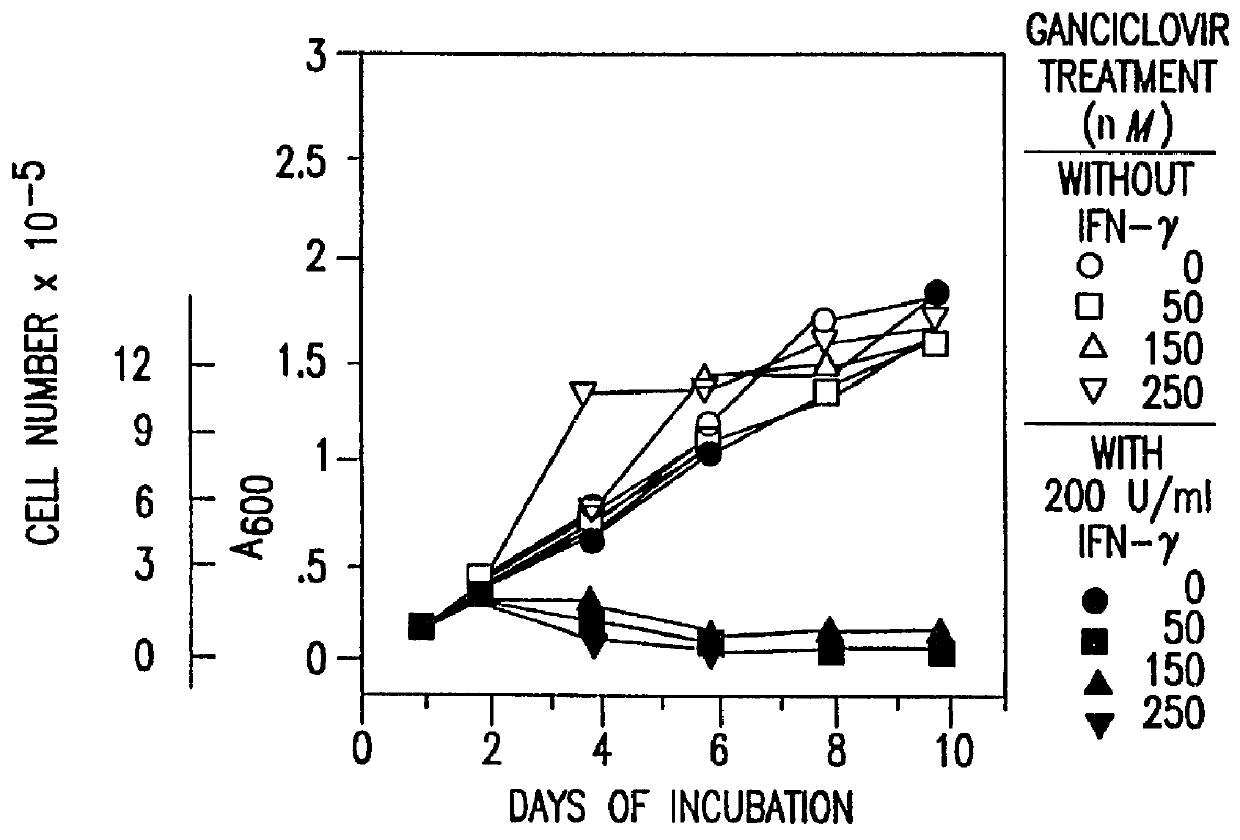
Method for expression of small antiviral RNA molecules within a cell
ActiveUS20030059944A1Prevents sequenceHigh expressionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsGeneticsViral life cycle
In one aspect, the invention provides methods and compositions for the expression of small RNA molecules within a cell using a retroviral vector. The methods can be used to express double stranded RNA complexes. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) can be expressed using the methods of the invention within a cell, that interfere with a viral life cycle by down regulating either the viral genome, a viral genome transcript, or a host cell that. In another aspect the invention provides methods for treating patients having suffering from infection, particularly infection with HIV.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method for modifying genetic characteristics of an organism
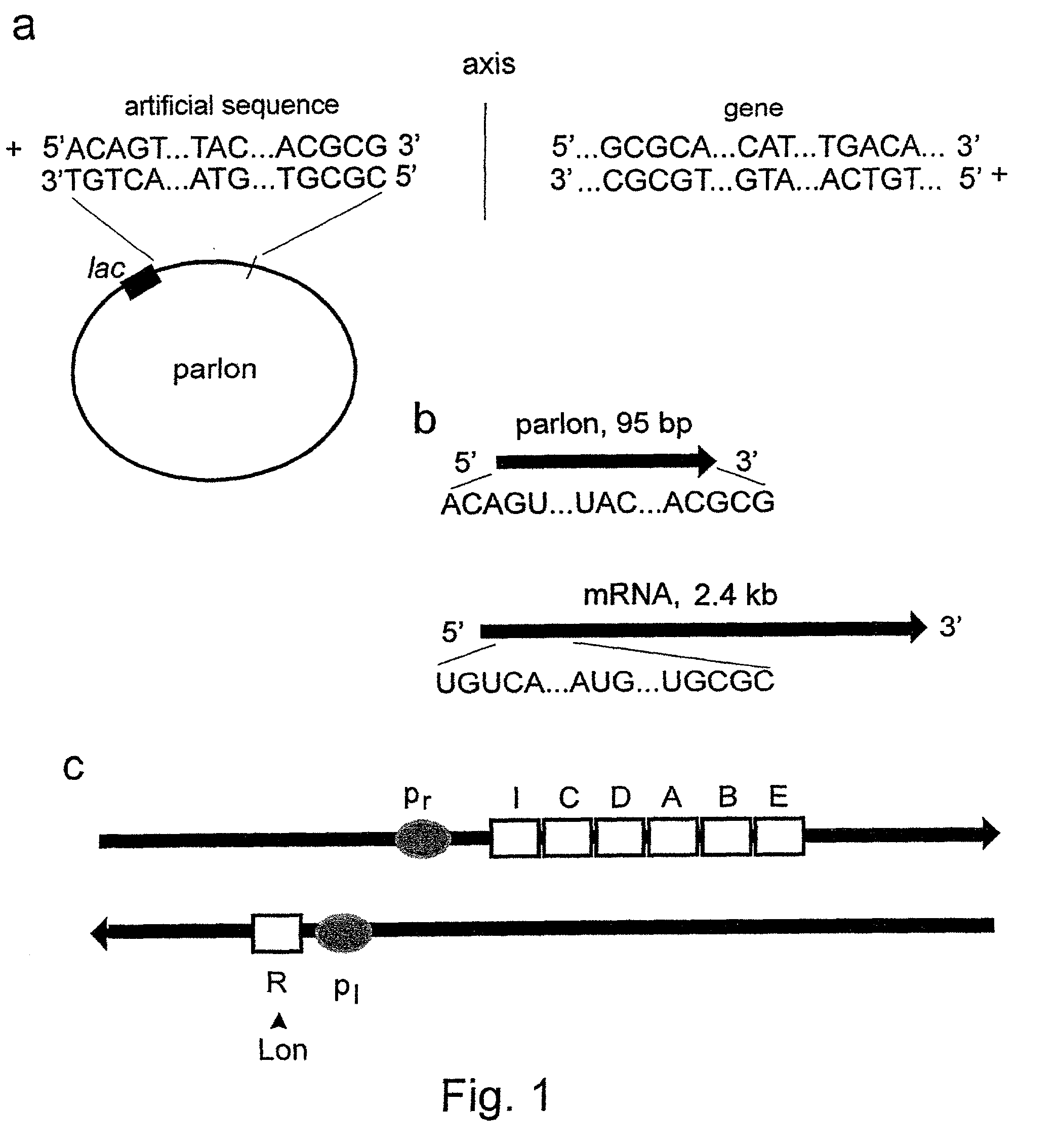
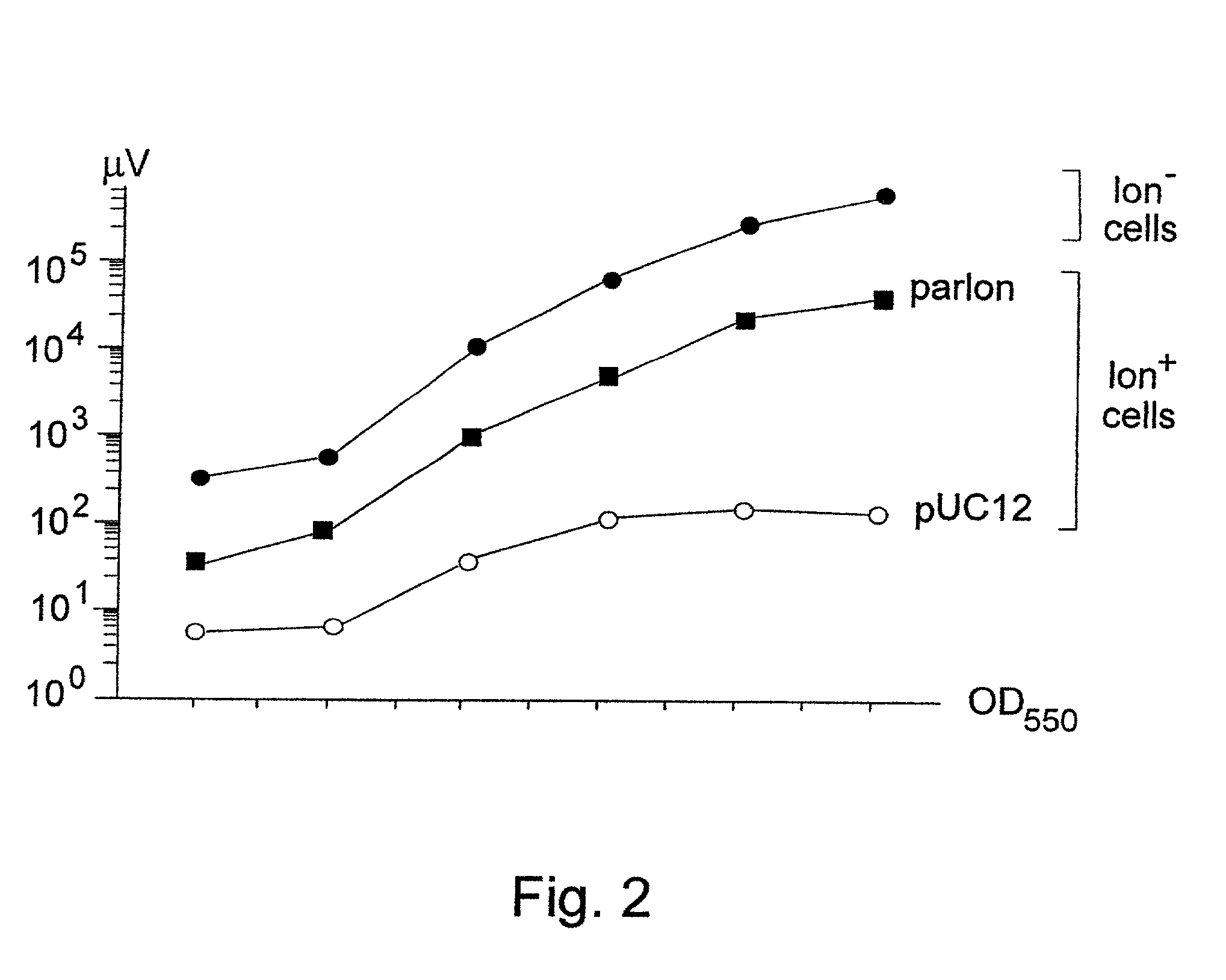
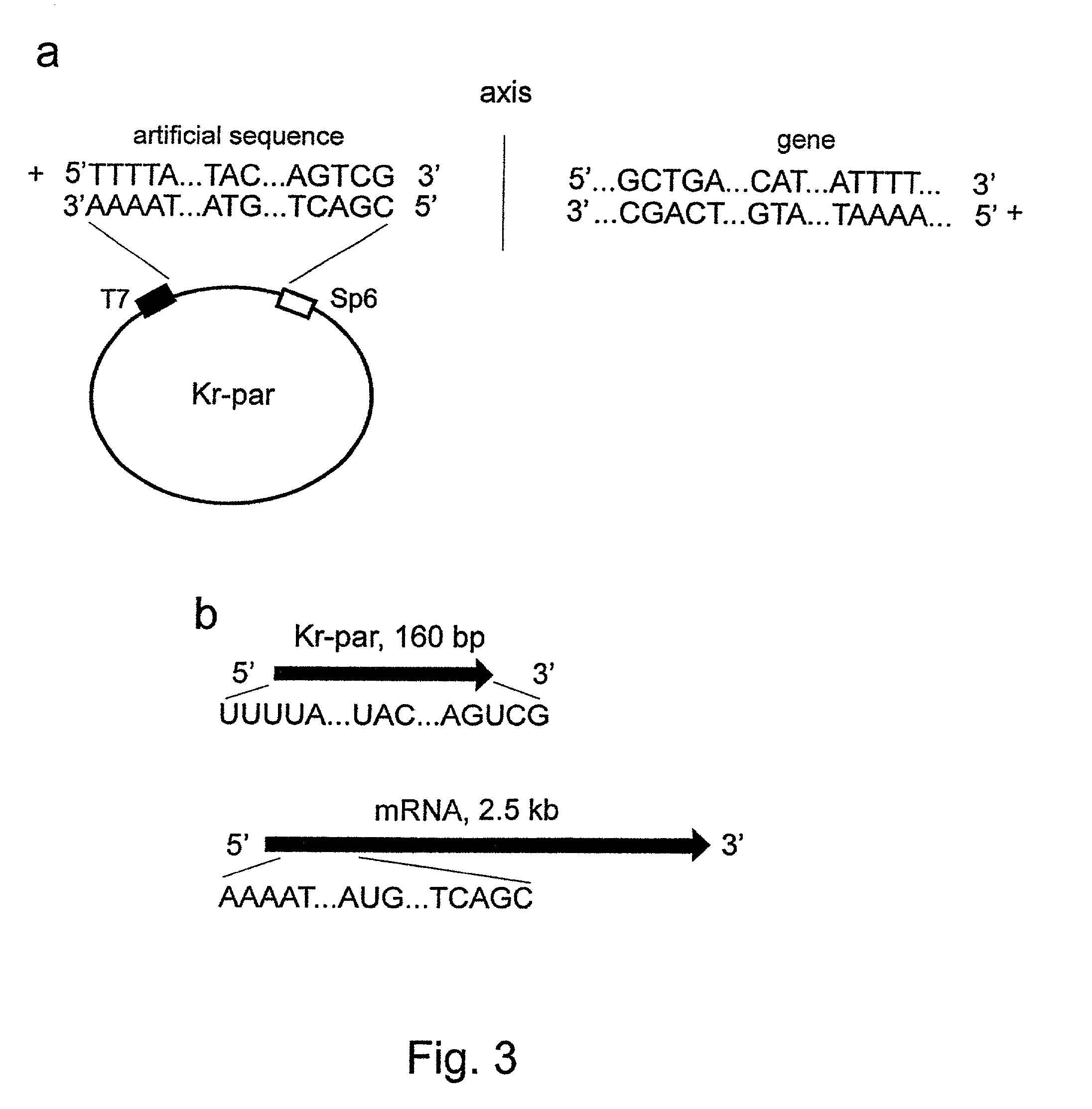
The invention concerns with the molecular biology, molecular genetics and biotechnology and can be used in the gene-therapy in the medicine and the agriculture or in the industrial biotechnology for a gene-specific silencing of the disease-related genes or the genes interfering a buildup of a product, respectively. The approach is suggested for changing of genetic properties of an organism by RNA interference leading to gene-specific silencing of a selected gene by RNA molecules, that are complementary in a parallel orientation (pcRNA) to mRNA of the selected gene; pcRNA are synthesized in vivo or in vitro on the artificial DNA sequence possessing symmetrical nucleotide ordering (mirror inversion) in respect to the nucleotide sequence of the gene. The invention suggests the general approach for changing of genetic properties of an organism and is based on the biological properties of mirror inversions of nucleotide sequences that are realized in RNA interference and gene-specific silencing.
Owner:INST MOLEKULJARNOJ BIOLOGII IM V A EHNGELGARDTA RAN
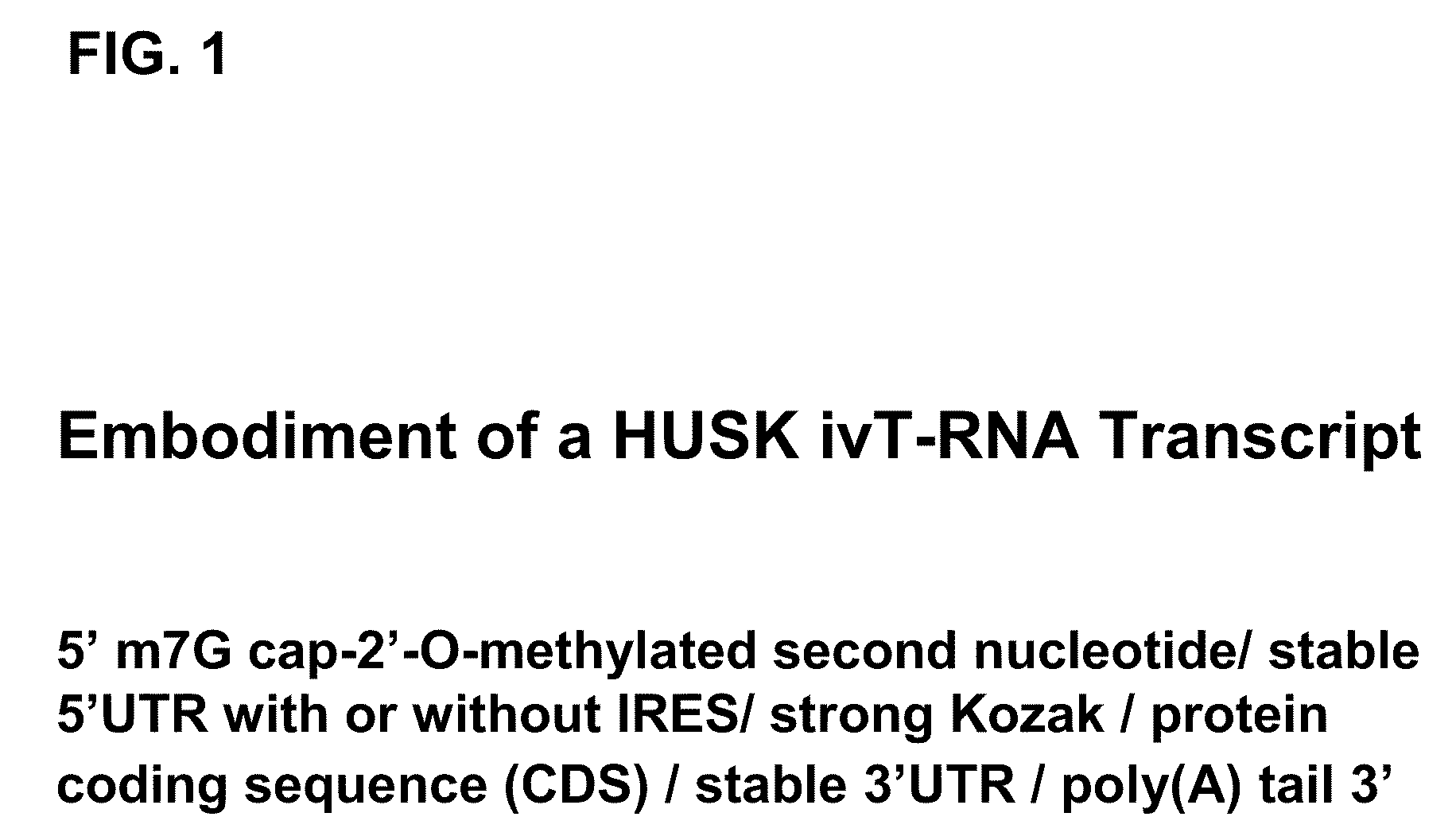
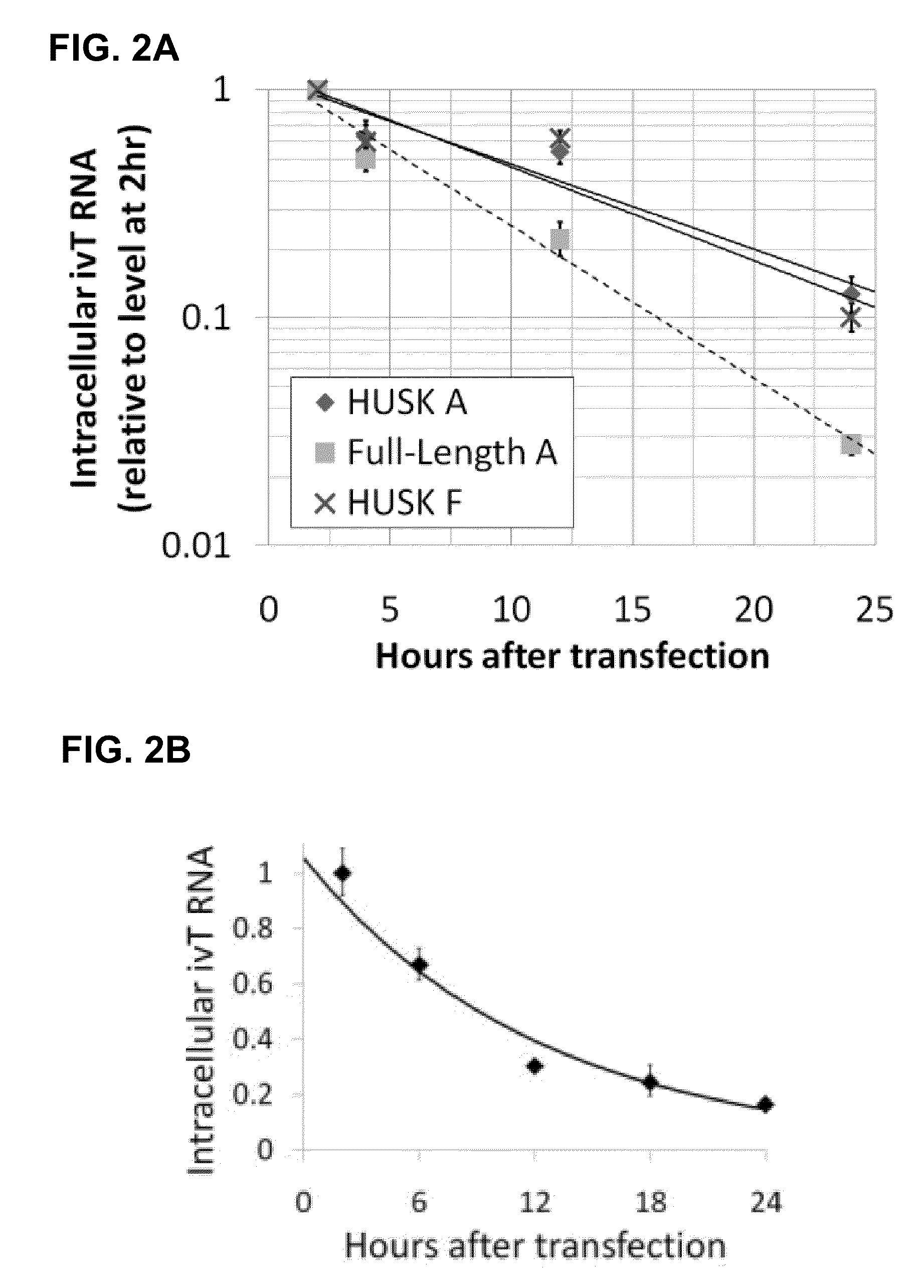
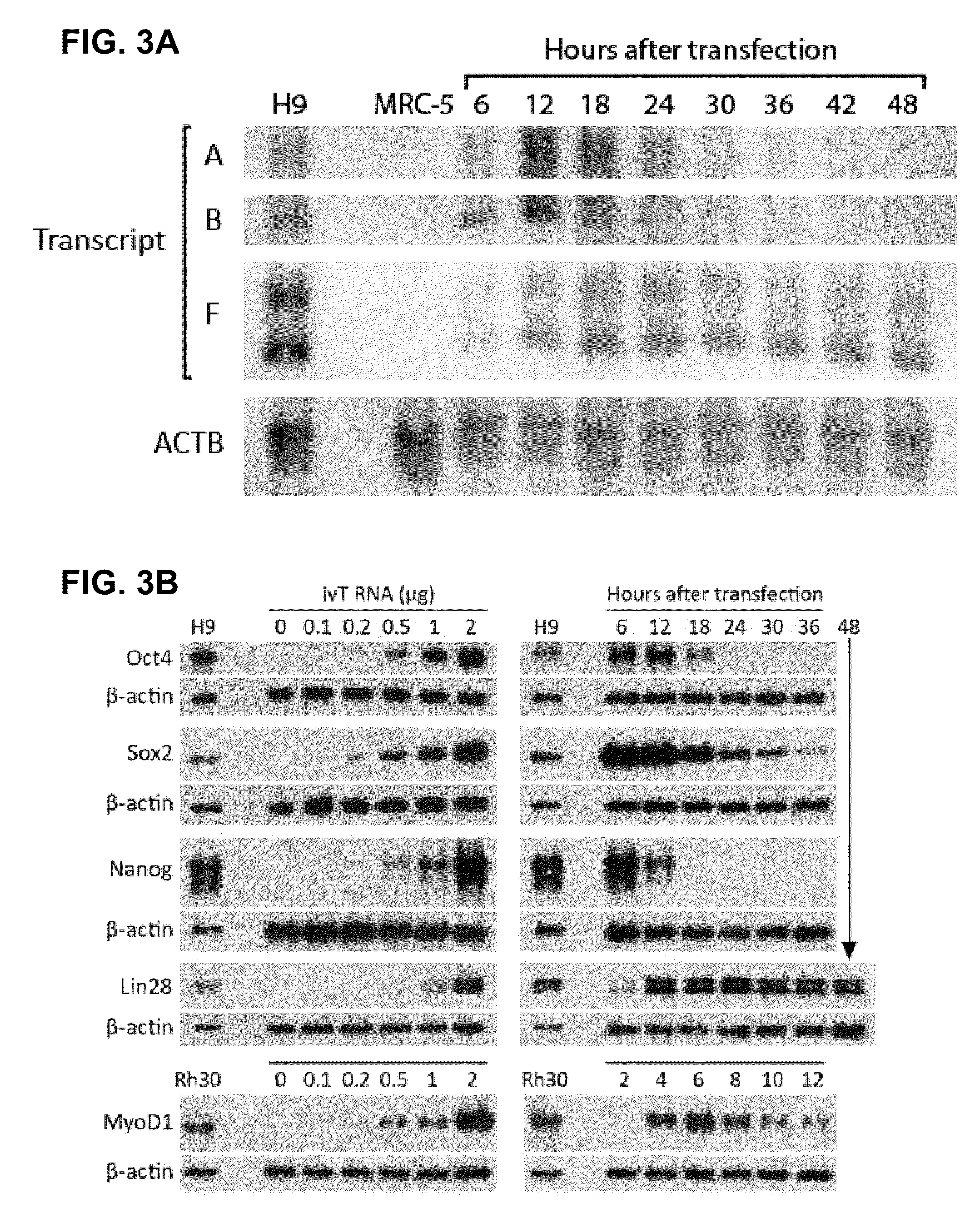
Innate immune suppression enables repeated delivery of long RNA molecules
InactiveUS20100273220A1Suppressing innate immune responseReduce expressionSugar derivativesArtificial cell constructsENCODETransient transfection
The present invention relates in part to methods for suppressing the innate immune response of a cell to transfection with an exogenous nucleic acid, to methods for increasing expression of a protein encoded by an exogenous nucleic acid by repeated delivery of the exogenous nucleic acid to a cell, and to methods of changing the phenotype of a cell by differentiating, transdifferentiating or dedifferentiating cells by repeatedly delivering one or more nucleic acids that encode defined proteins. A method is provided for extended transient transfection by repeated delivery of an in vitro-transcribed RNA (“ivT-RNA”) to a cell to achieve a high and sustained level of expression of a protein encoded by an ivT-RNA transcripts.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Insect resistance using inhibition of gene expression
The current invention provides methods to silence insect genes by using unpackaged dsRNA or siRNA, in one embodiment such dsRNA or siRNA is present in plant vascular tissue, preferably phloem, more particularly phloem sap, and the insect is a plant sap-sucking insect. Also provided are DNA sequences which when transcribed yield a double-stranded RNA molecule capable of reducing the expression of an essential gene of a plant sap-sucking insect, methods of using such DNA sequences and plants or plant cells transformed with such DNA sequences. Also provided is the use of cationic oligopeptides that facilitate the entry of dsRNA or siRNA molecules in insect cells, such as plant sap-sucking insect cells.
Owner:BASF AG
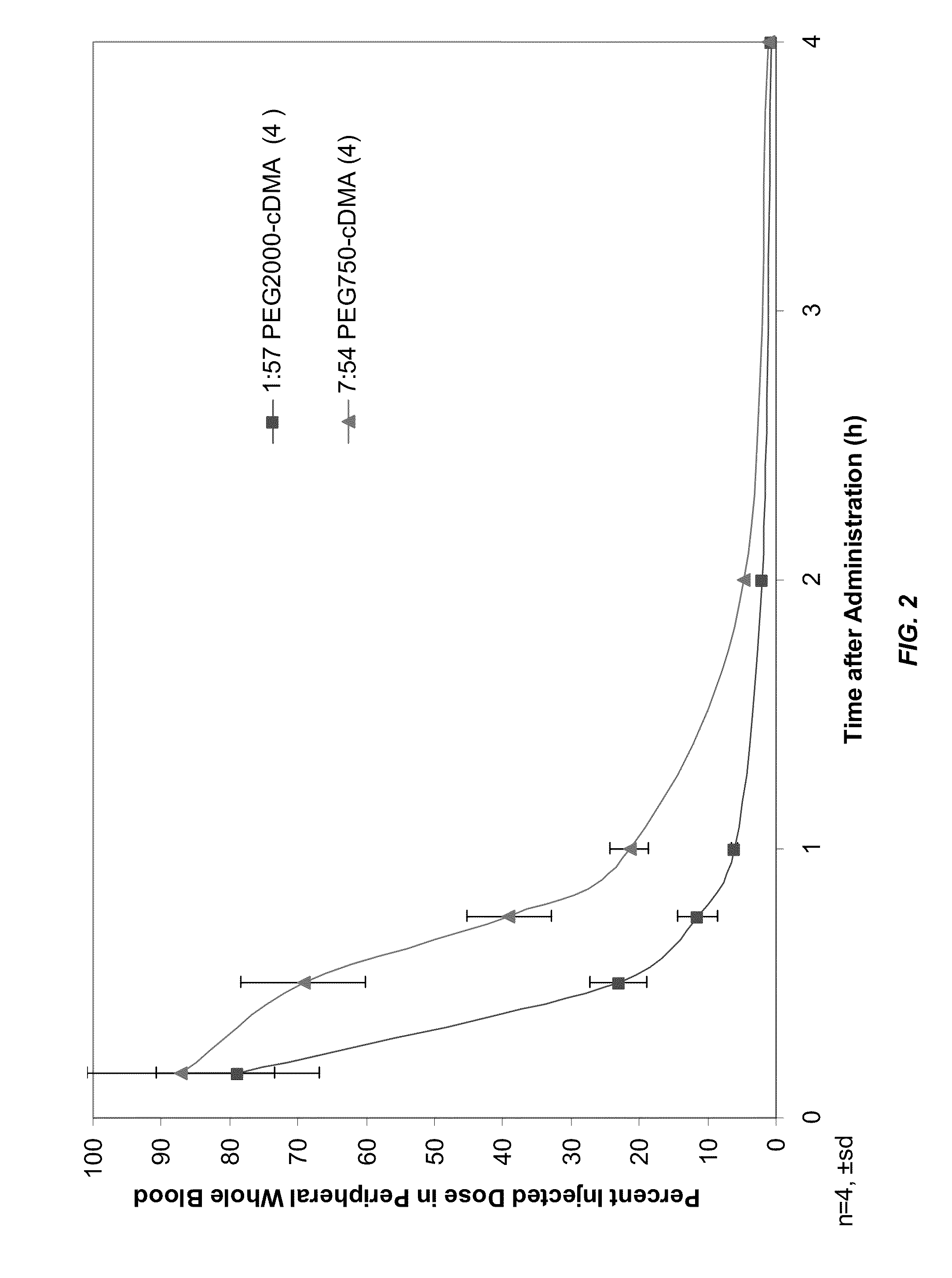
Novel lipid formulations for delivery of therapeutic agents to solid tumors
ActiveUS20110076335A1Improve effectivenessFavorable toxicity profileOrganic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryLipid formationLipid particle
The present invention provides novel, serum-stable lipid particles comprising one or more active agents or therapeutic agents, methods of making the lipid particles, and methods of delivering and / or administering the lipid particles. More particularly, the present invention provides serum-stable nucleic acid-lipid particles (SNALP) comprising a nucleic acid (e.g., one or more interfering RNA molecules), methods of making the SNALP, and methods of delivering and / or administering the SNALP (e.g., for the treatment of cancer). In particular embodiments, the present invention provides tumor-directed lipid particles that preferentially target solid tumors. The tumor-directed formulations of the present invention are capable of preferentially delivering a payload such as a nucleic acid to cells of solid tumors compared to non-cancerous cells.
Owner:ARBUTUS BIOPHARMA CORPORAT ION
Regulation of gene expression
InactiveUS6022863APrevention of fetal rejectionSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsMHC class IDisease
The present invention relates to utrons, RNA molecules which contain promoter regulatory motif(s) and DNA analogs thereof and DNA molecules that can be transcribed to produce the foregoing. In particular, the invention provides gene promoter suppressing nucleic acids which suppress transcription from a promoter of interest. In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides the TSU gene, nucleotide sequences of the TSU gene and RNA, as well as fragments, homologs and derivatives thereof. Methods of isolating TSU genes are also provided. Therapeutic and diagnostic methods and pharmaceutical compositions are also provided. In particular, the invention relates to methods for cell replacement therapy, gene therapy or organ transplantation wherein TSU nucleic acids suppress MHC class I and II gene expression, thus preventing immuno-rejection of non-autologous cells or organs. The invention also provides methods for treatment of diseases or disorders by suppression of MHC class I, MHC class II, ICAM-1, B7-1, B7-2, and / or Fc gamma R expression by provision of TSU function.
Owner:YALE UNIV
RNA interference in respiratory epitheial cells
InactiveUS7297786B2Speed up the processAvoid insufficient lengthPowder deliveryBacteriaRespiratory epitheliumSmall interfering RNA
The present invention is directed to small interfering RNA molecules targeted against a gene of interest in respiratory epithelial cells, and methods of using these RNA molecules.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
RNA sequencing and analysis using solid support
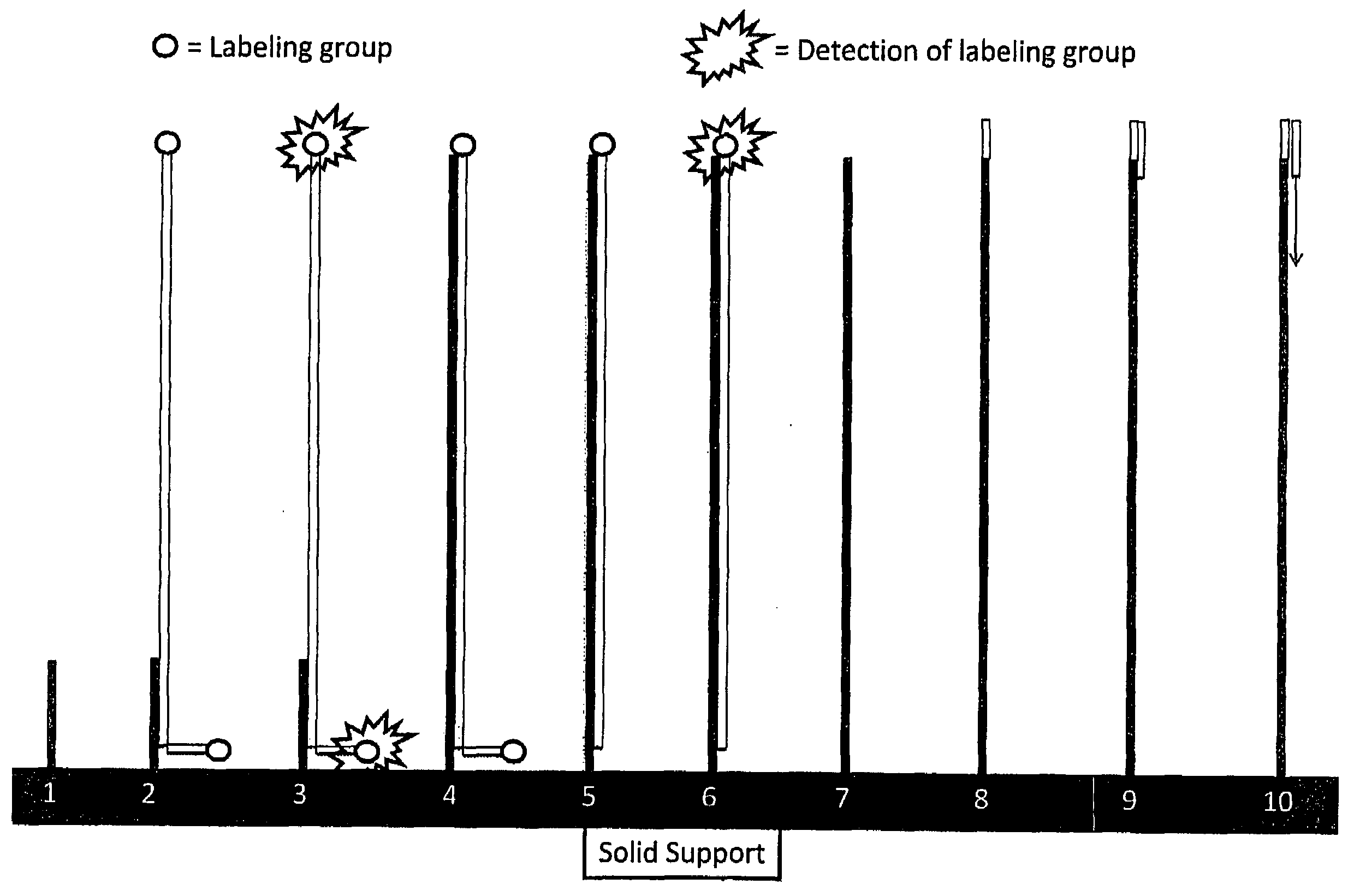
InactiveUS20100035249A1Facilitate direct bindingReduce lossesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological bodyGenomic information
The present invention provides methods for the sequencing of all RNA species within an RNA sample, such as the RNA content obtained from a cell, a tissue, a living organism, or from an artificial source. RNA molecules within the samples are labeled in a RNA-specific manner prior to immobilization on a solid support. One label is used to mark the location of the RNA molecule on the solid support, whereas the second label is used to mark selectively the S′ end of full-length mRNA molecules. RNA molecules are sequenced while being bound to the solid support in one or more sequencing reactions, and sequences of individual RNA molecules can be forwarded to computational analysis for assembling sequence information from individual sequencing reads obtained from the same location on the solid support. Not only unsupervised expression profiling on a genome-wide scale, but also the direct analysis of RNA-RNA interactions become possible as revealed by the analysis of the sequencing information obtained along with genomic information.
Owner:DNAFORM +1
Methods for gene array analysis of nuclear runoff transcripts
InactiveUS6617112B2Rapid and efficient and extensive analysisAccurate predictionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementStructure functionOrganism
Methods for determining transcription rate of mRNA in eukaryotic cells using nuclear runoff transcription where labeled RNA molecules are hybridized against an array of at least 500 nucleic acid molecule probes representing at least part of the genome of the native eukaryotic organism to identify the quantity of nascent mRNA transcripts in said cells. The method can be used to simultaneously identify the quantity of a large number of mRNA transcripts. A rate of degradation for distinct mRNA in a eukaryotic cell rate is determined by comparing a steady state mRNA with nuclear runoff mRNA. Steady state to nuclear runoff ratios are used to determine gene and mRNA structure function relations that leads to gene expression and mRNA stability, predict structural determinants for mRNA stability and predict regulatory motifs for transcription rates. Methods of constructing recombinant organisms with enhanced stability for mRNA expressed from a gene of interest comprise introducing into the genome of an organism a gene containing one or more sequence elements that confer structural stability on mRNA transcribed from said gene.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
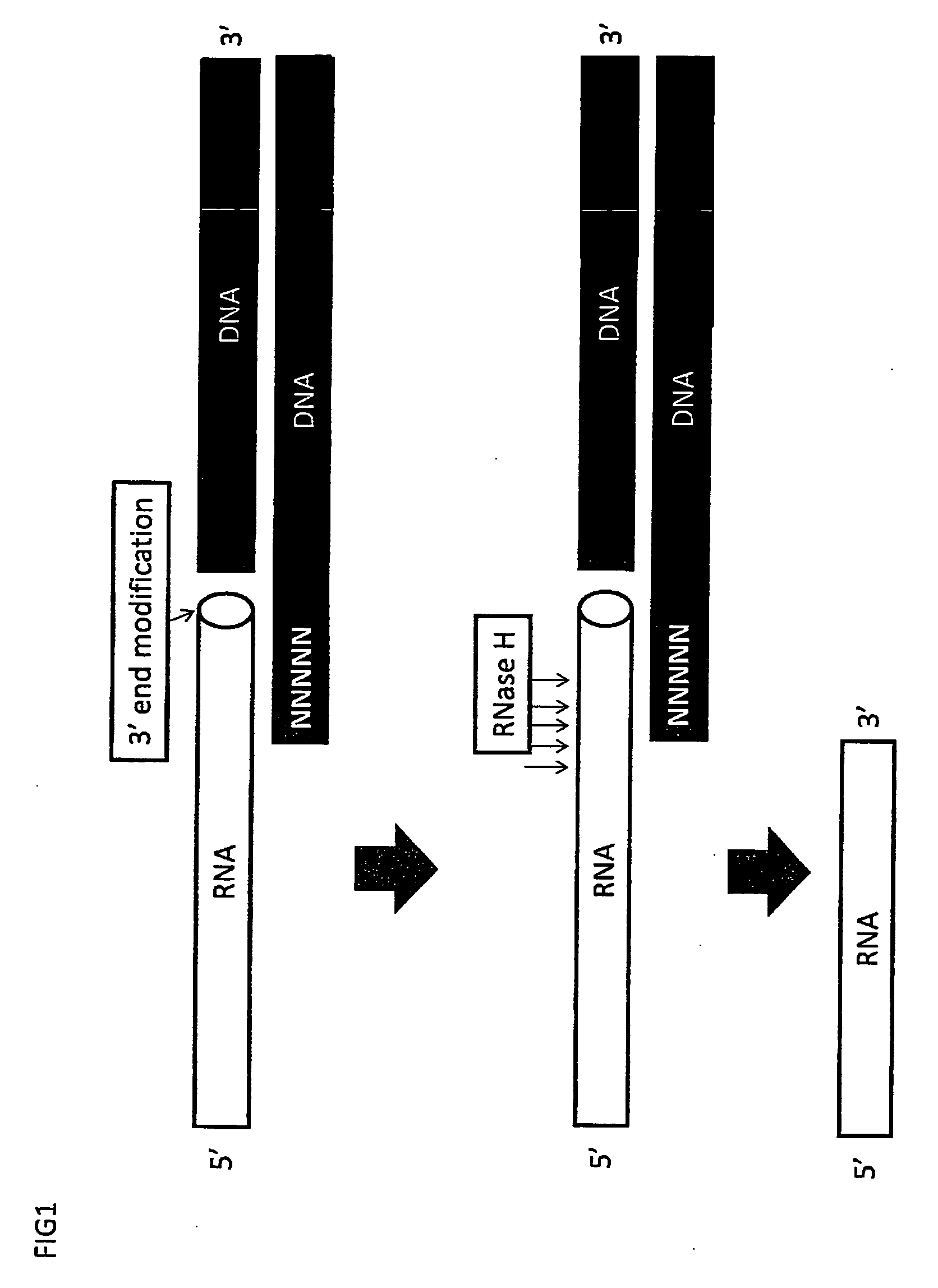
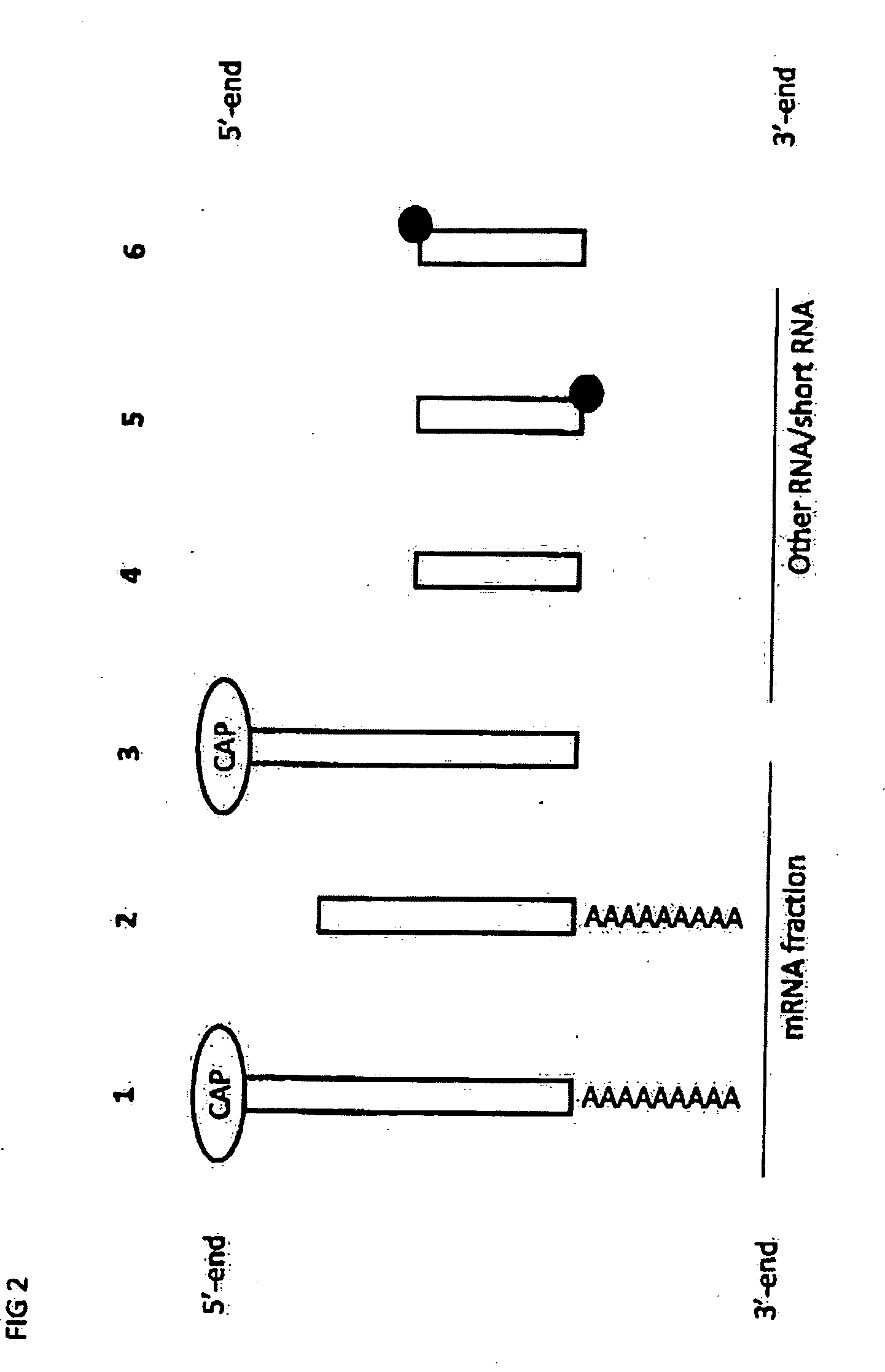
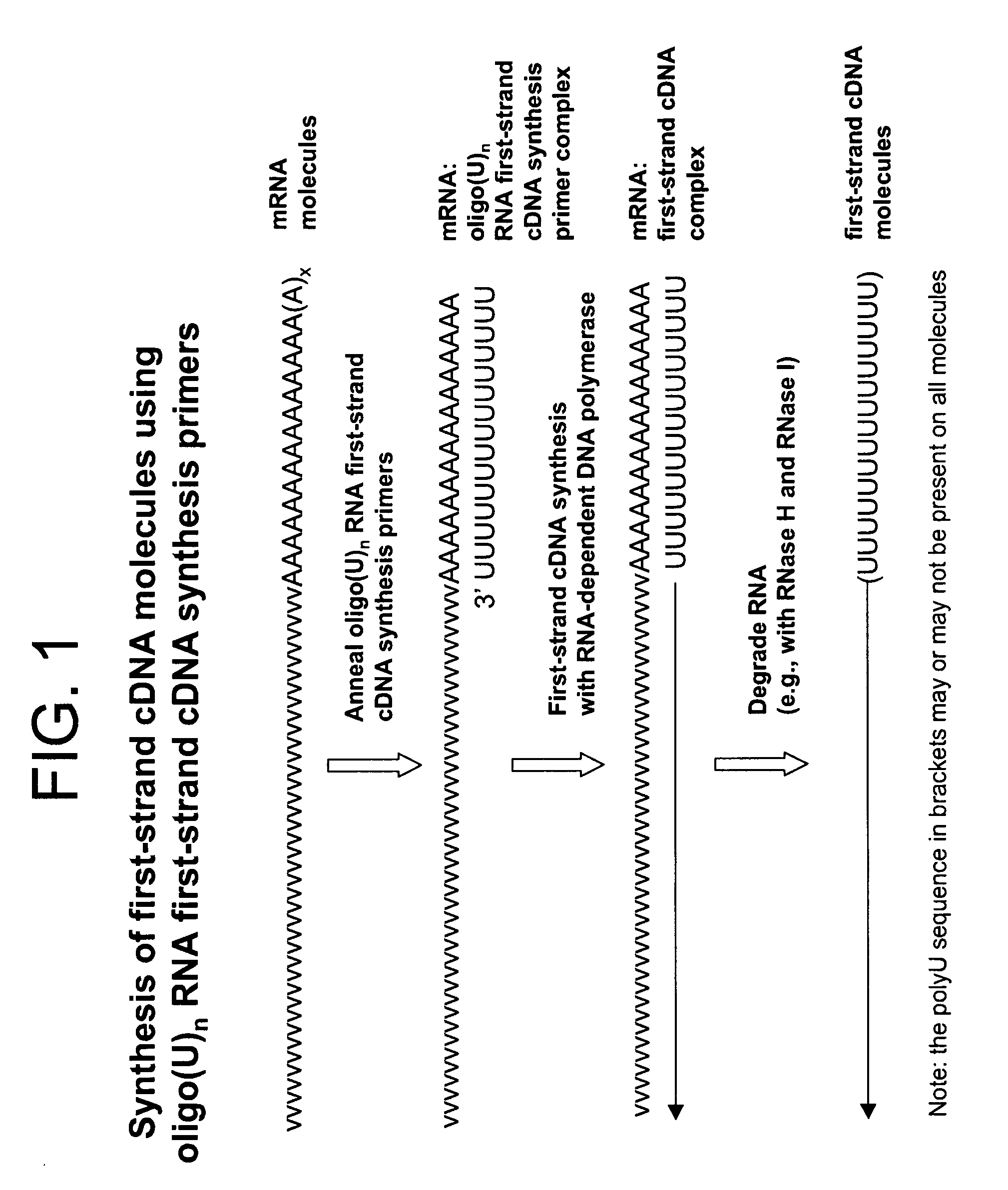
Method for modifying RNAS and preparing DNAS from RNAS
InactiveUS20080108804A1Fast and effective manipulationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPooled SampleDNA
A method is disclosed for the modification of an end of RNA molecules and the use of such modified RNA molecules in cDNA synthesis for the purpose of cloning, detection, sequencing, and amplification of parts of the RNAs, the entire RNAs, or any cDNAs derived from such modified RNAs. The invention relates further to the amplification and the identification of nucleic acid molecules for the purpose of single molecule detection and / or high-throughput sequencing. In addition, a method is provided for the preparation of pooled samples that contains molecules each of which is marked by an “Identifier Sequence” for its origin. The invention facilitates studies on biological systems and analysis of genes expressed therein.
Owner:DNAFORM
Generation of human embryonc stem-like cells using intronic RNA
ActiveUS20080293143A1Stable and relatively long-term effectDelivery stabilityOther foreign material introduction processesElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentReprogrammingMammal
This invention generally relates to a method for developing, generating and selecting human embryonic stem (hES)-like pluripotent cells using transgenic expression of intronic microRNA-like RNA agents. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method and composition for generating a non-naturally occurring intron and its intronic components capable of being processed into mir-302-like RNA molecules in mammalian cells and thus inducing certain specific gene silencing effects on differentiation-related and fate-determinant genes of the cells, resulting in reprogramming the cells into a pluripotent embryonic stem (ES)-cell-like state. The ES-like cells so obtained are strongly express hES cell markers, such as Oct3 / 4, SSEA-3 and SSEA-4, and can be guided into various tissue cell types by treating certain hormones and / or growth factors under a feeder-free cell culture condition in vitro, which may be used for transplantation and gene therapies. Therefore, the present invention offers a simple, effective and safe gene manipulation approach for not only reprogramming somatic cells into ES-like pluripotent cells but also facilitating the maintenance of pluripotent and renewal properties of ES cells under a feeder-free cell culture condition, preventing the tedious retroviral insertion of four large transcription factor genes into one single cell as used in the previous iPS methods.
Owner:MELLO BIOTECH +1
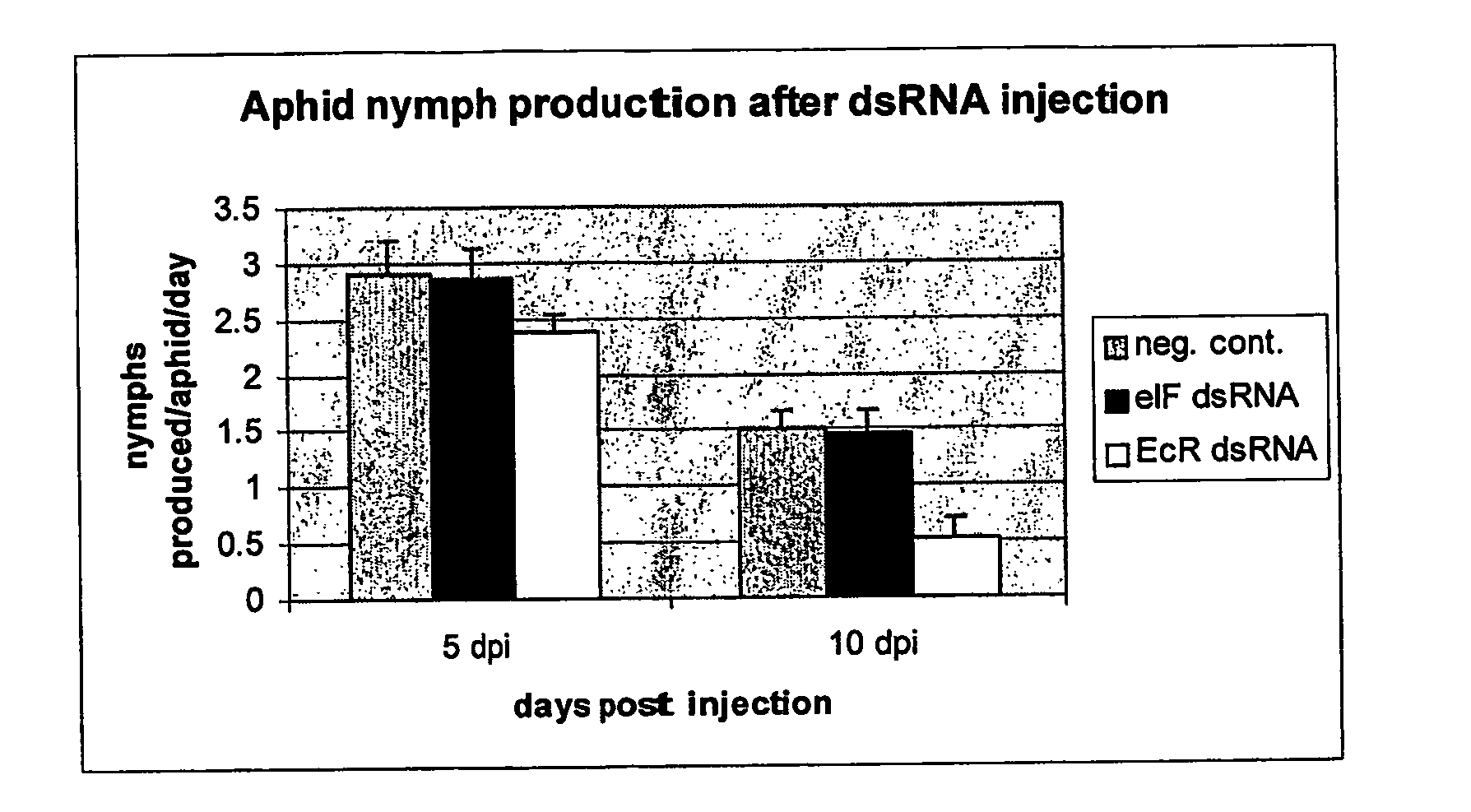
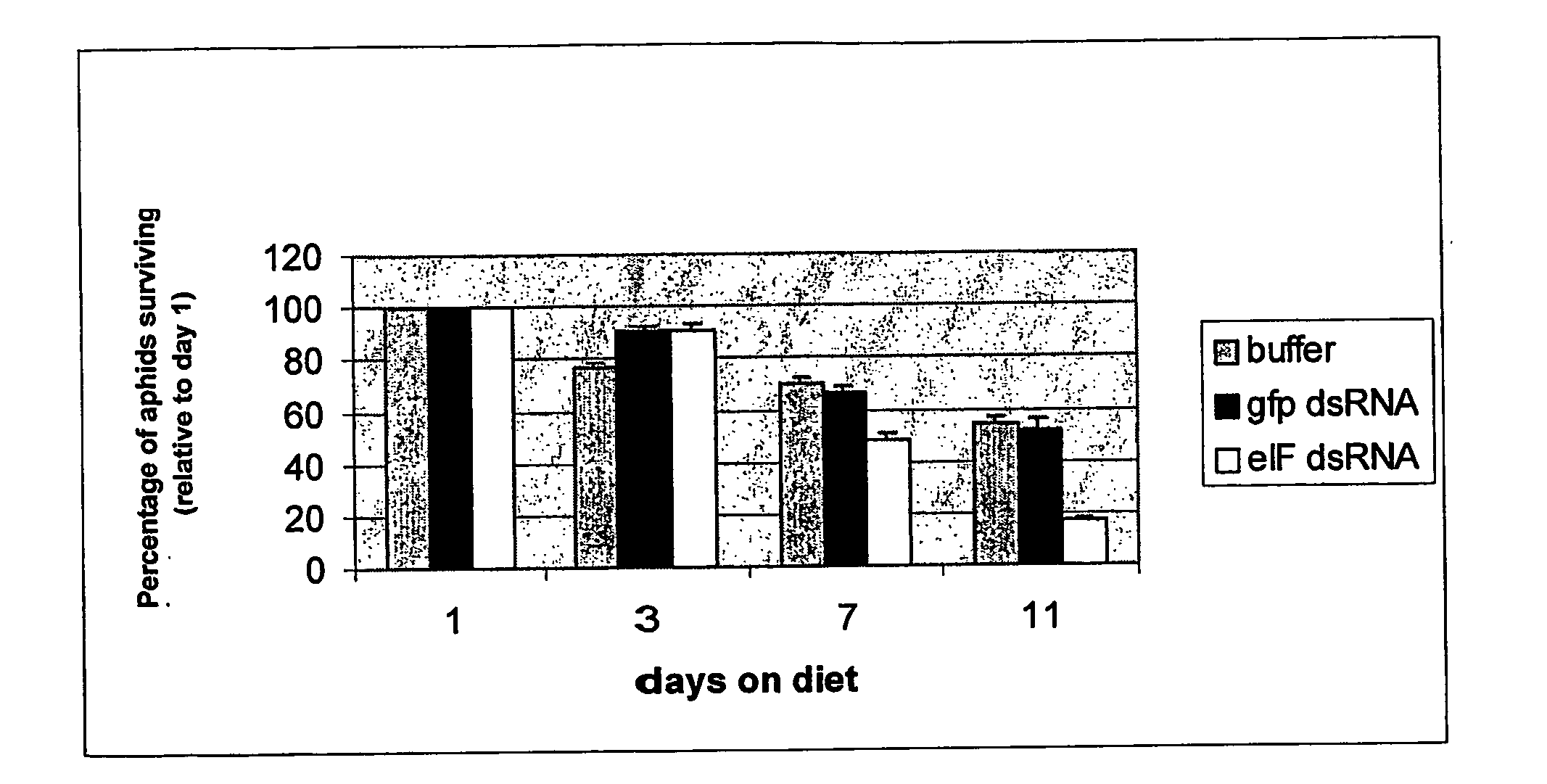
Down-regulating gene expression in insect pests
The present invention relates to genetic control of infestation by insect pest species, particularly prevention and / or control of pest infestation of plants, using interfering ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules. Compositions and combinations containing the interfering RNA molecules of the invention for use in topical applications, for example in the form of insecticides.
Owner:DEVGEN NV
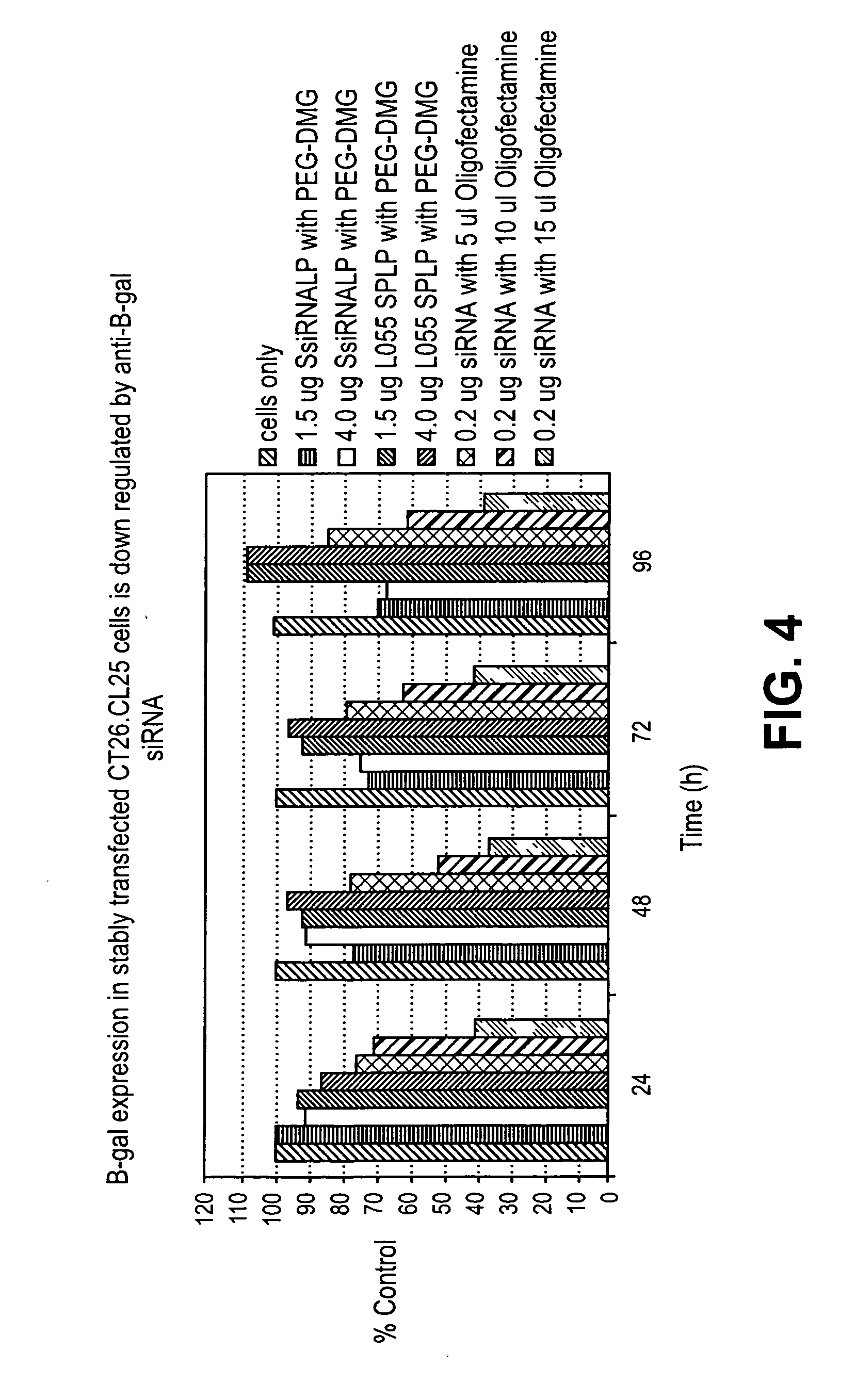
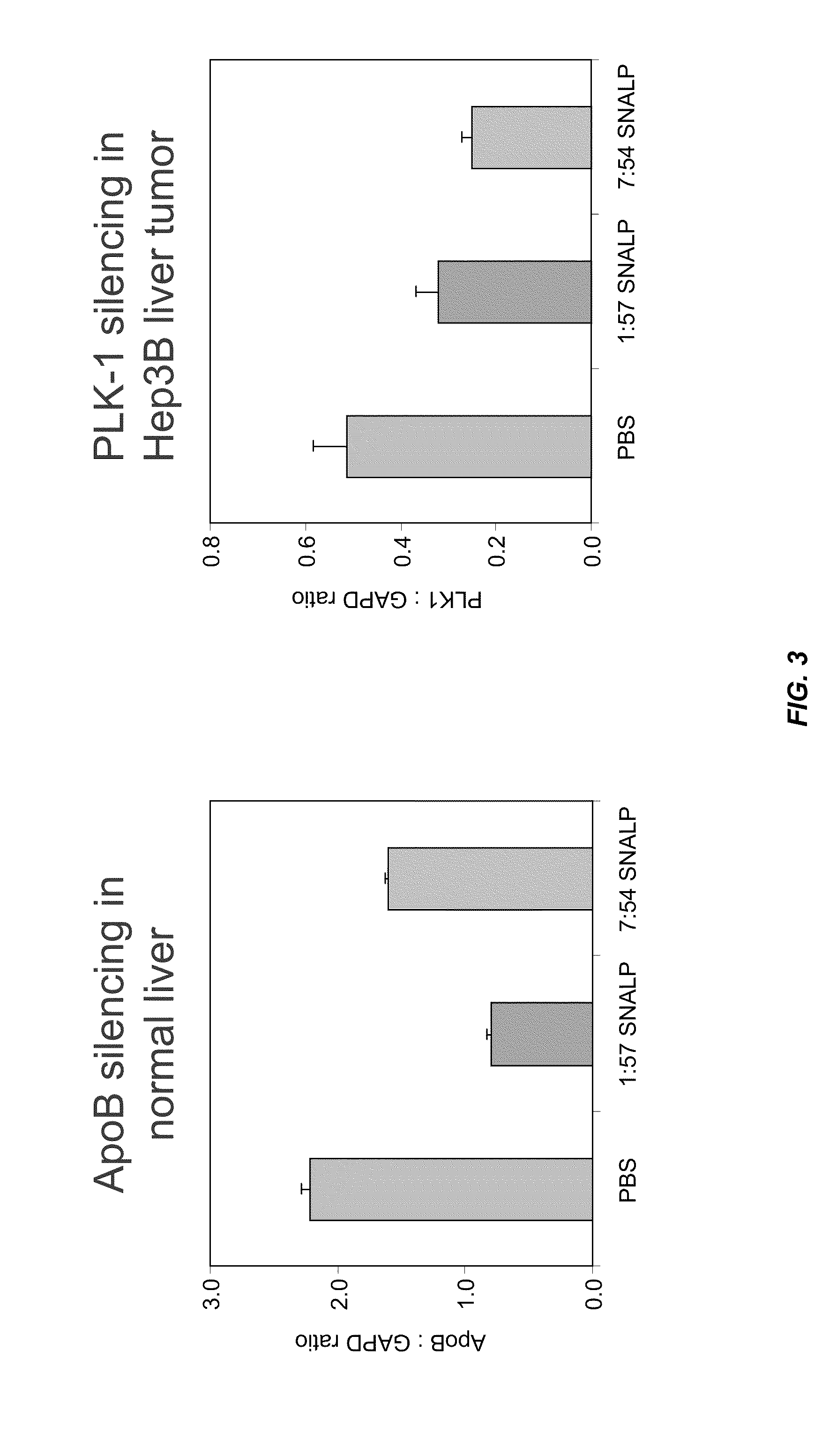
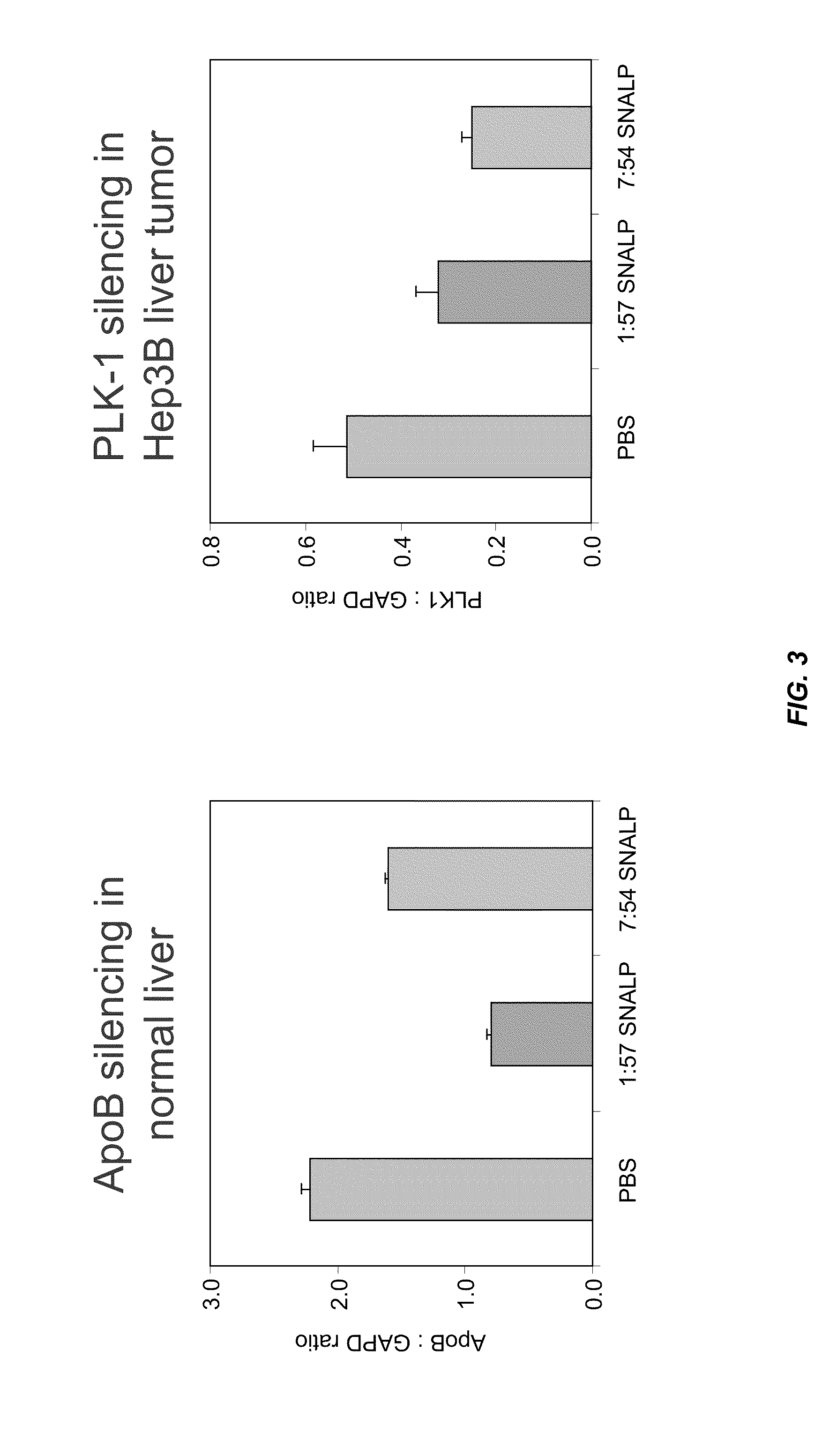
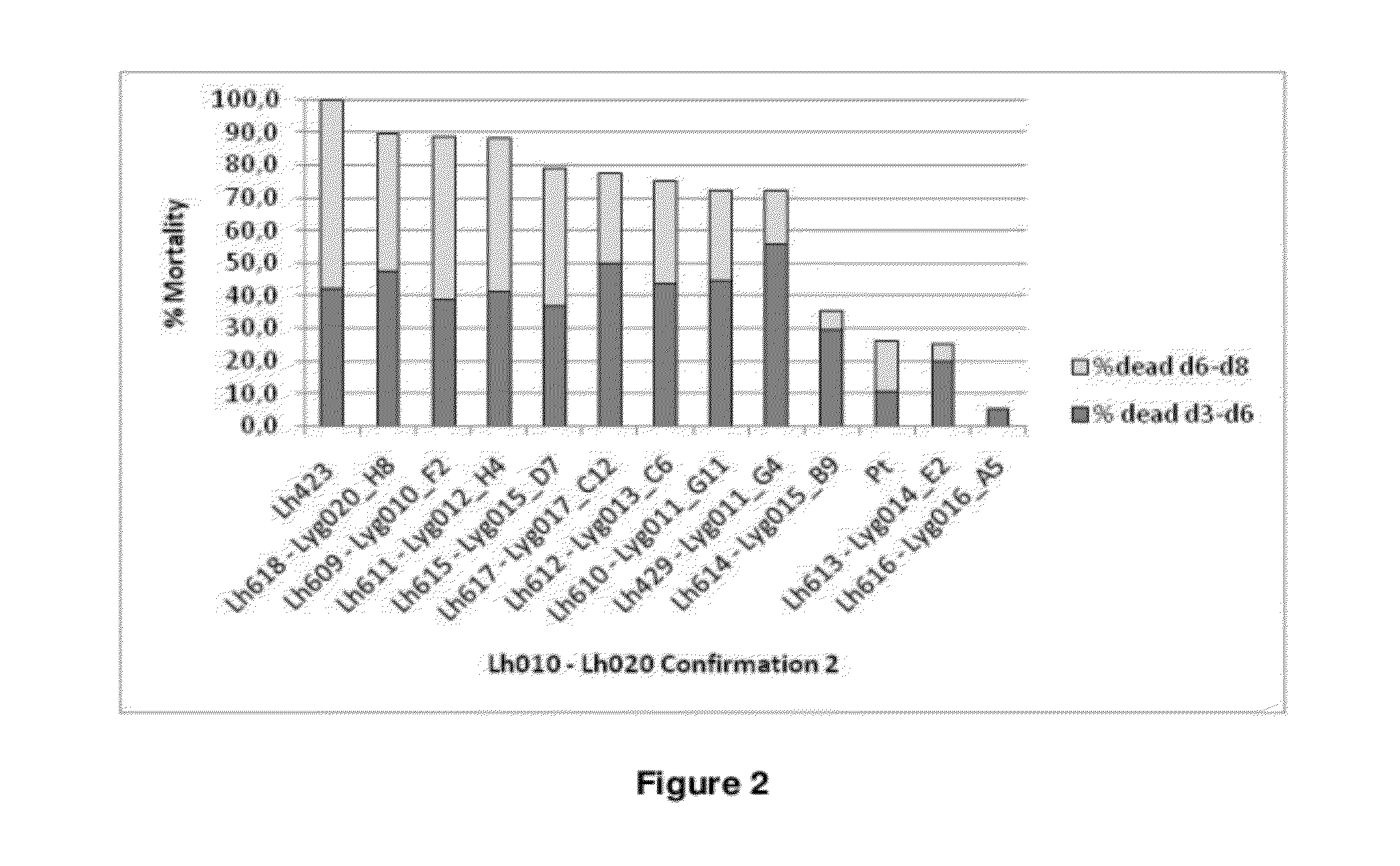
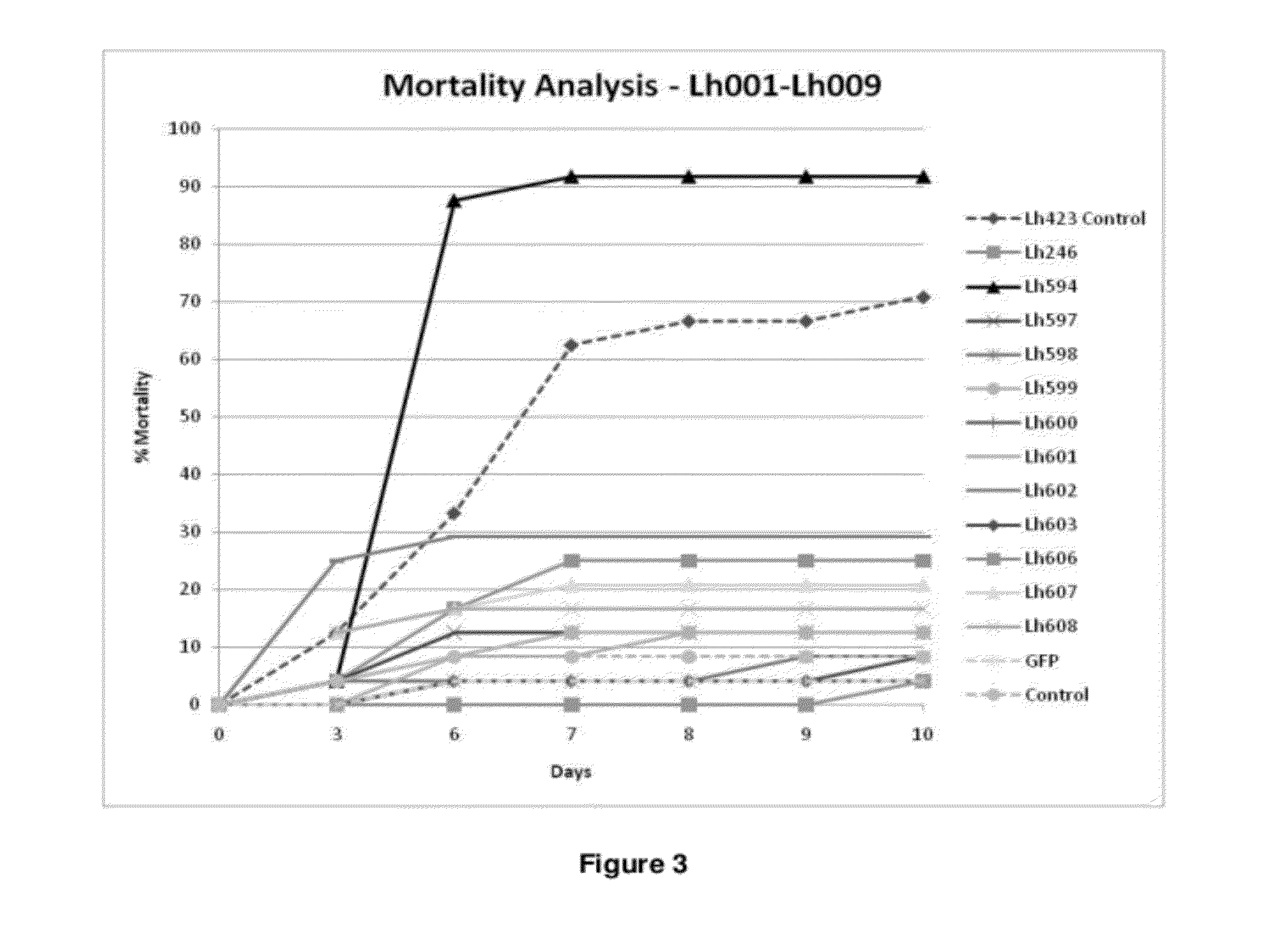
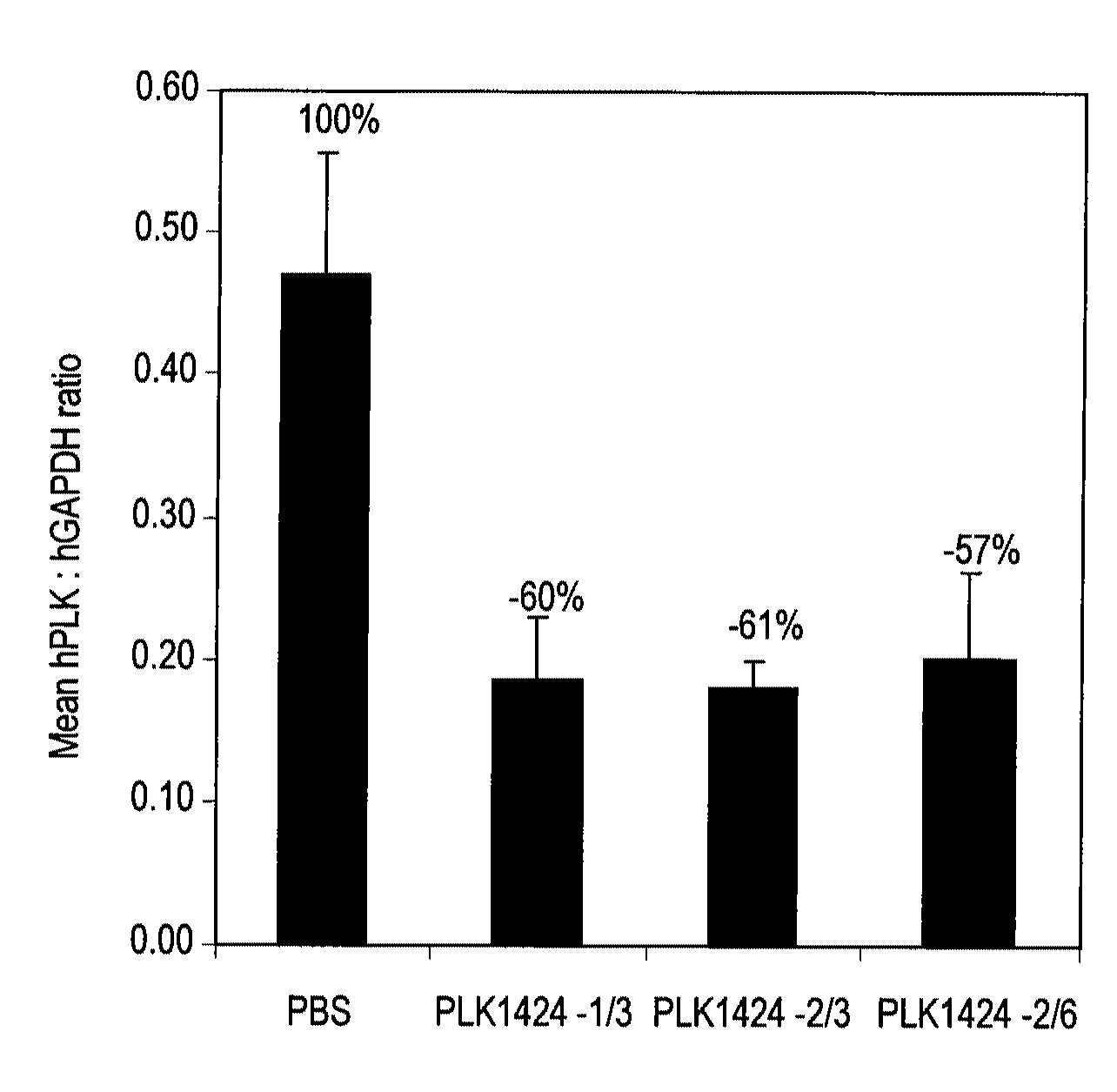
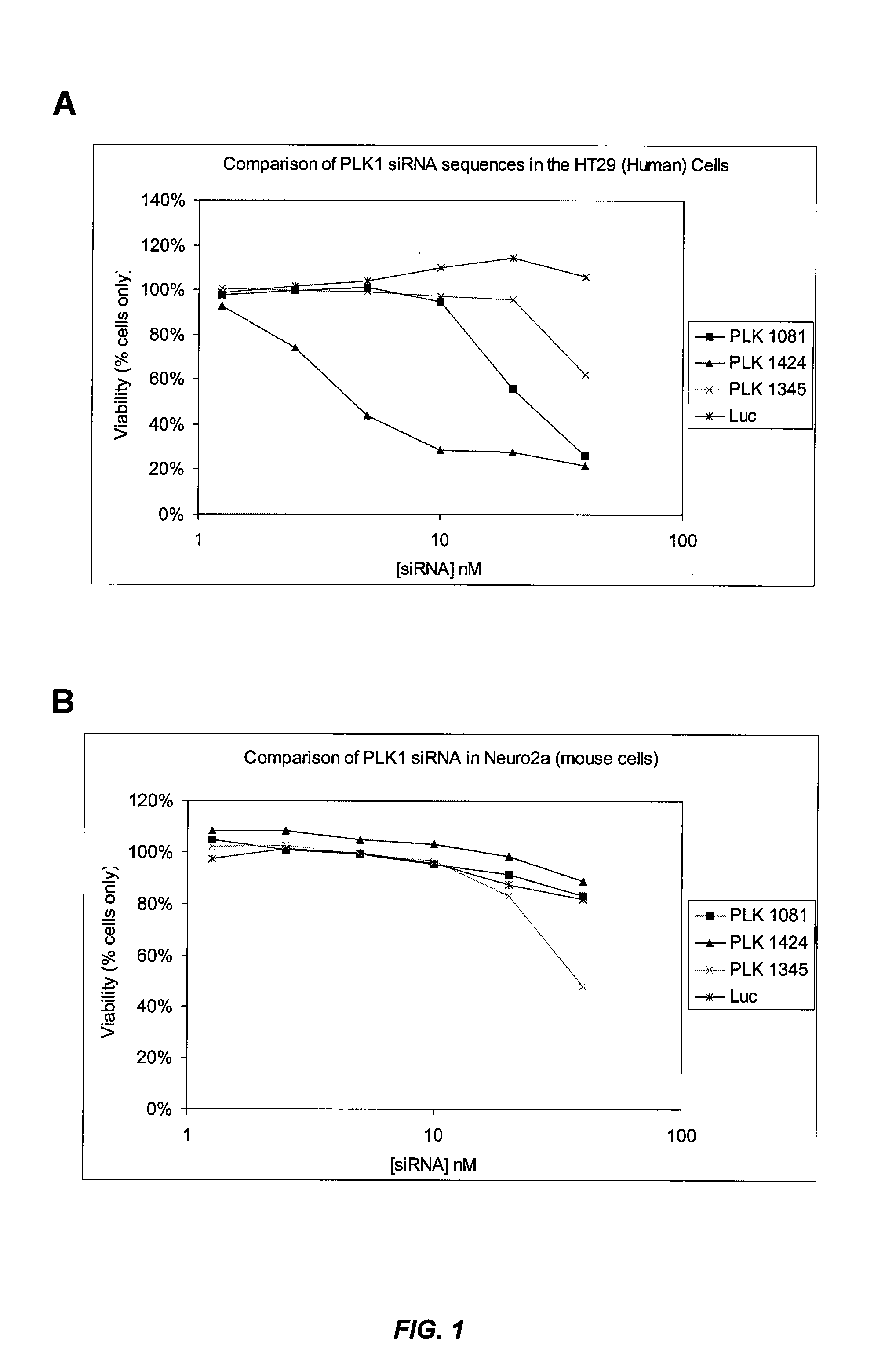
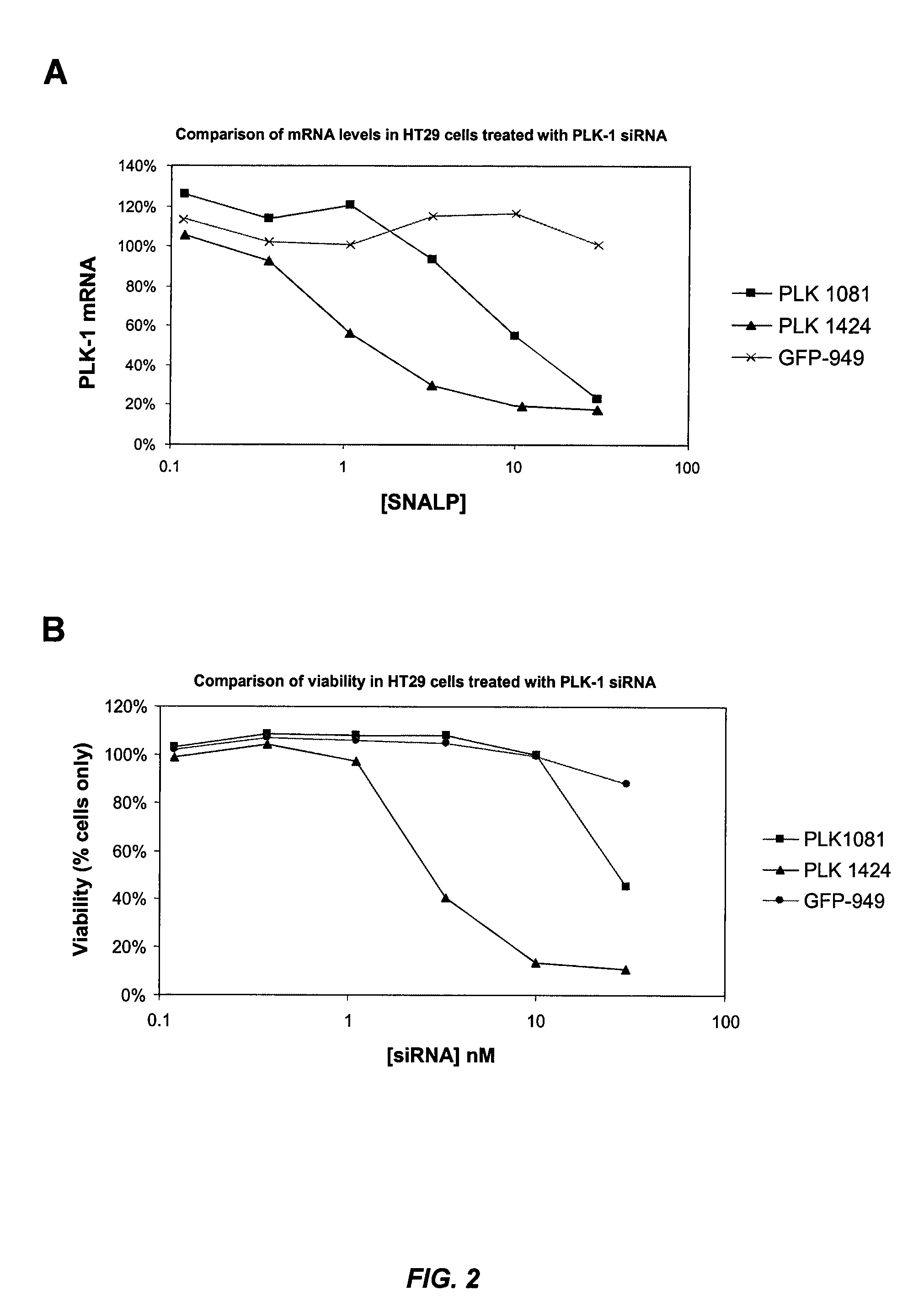
Silencing of polo-like kinase expression using interfering RNA
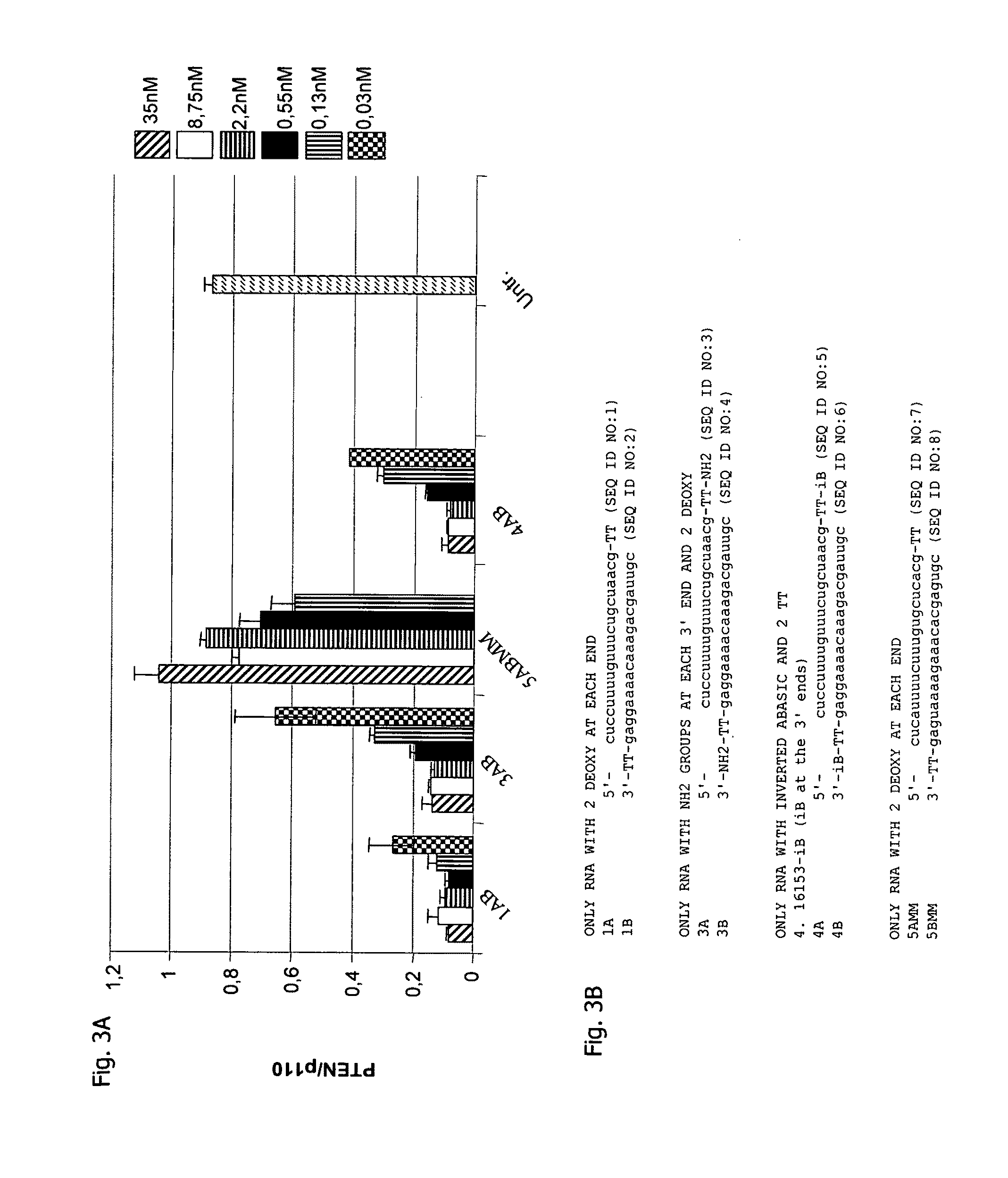
The present invention provides compositions comprising interfering RNA (e.g., siRNA, aiRNA, miRNA) that target polo-like kinase 1 (PLK-1) expression and methods of using such compositions to silence PLK-1 expression. More particularly, the present invention provides unmodified and chemically modified interfering RNA molecules which silence PLK-1 expression and methods of use thereof. The present invention also provides serum-stable nucleic acid-lipid particles (e.g., SNALP) comprising an interfering RNA molecule described herein, a cationic lipid, and a non-cationic lipid, which can further comprise a conjugated lipid that inhibits aggregation of particles. The present invention further provides methods of silencing PLK-1 gene expression by administering an interfering RNA molecule described herein to a mammalian subject. The present invention additionally provides methods of identifying and / or modifying PLK-1 interfering RNA having immunostimulatory properties. Methods for sensitizing a cell such as a cancer cell to the effects of a chemotherapy drug comprising sequentially delivering PLK-1 interfering RNA followed by the chemotherapy drug are also provided.
Owner:ARBUTUS BIOPHARMA CORPORAT ION
Device for immobilizing chemical and biochemical species and methods of using same
InactiveUS20060172408A1Improve throughputEasy to checkBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsA-DNARNA molecule
A substrate is provided that facilitates immobilization of nucleic acid molecules, including DNA molecules and RNA molecules. Also provided is a device that includes the substrate, which, for example, can be a chip. In addition, methods of using the substrate are provided, including, for example, methods of sequencing a DNA molecule anchored to the substrate, and methods for conducting the process of sequencing using such devices.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
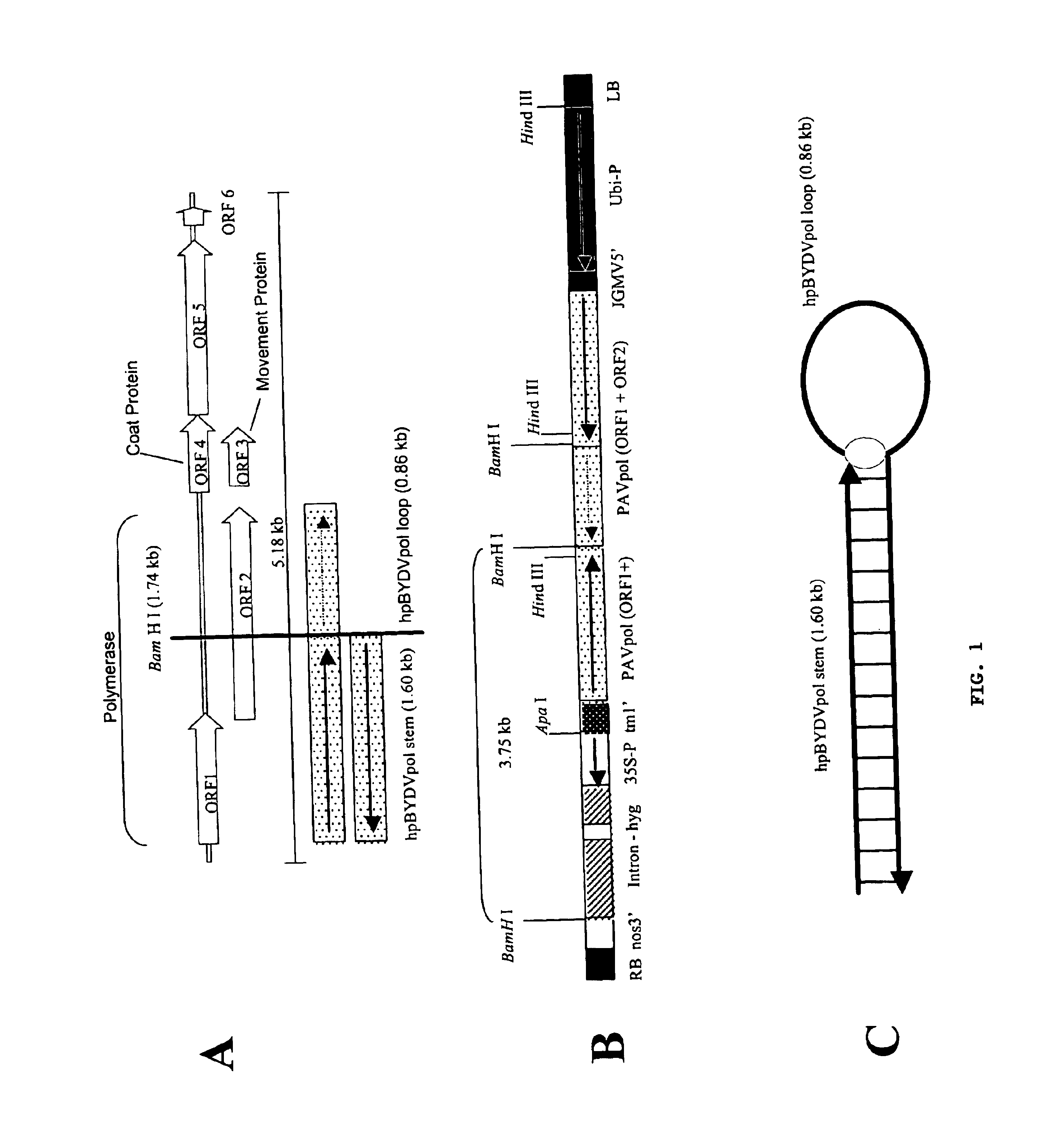
Methods and means for producing barley yellow dwarf virus resistant cereal plants
The invention relates to methods for producing transgenic cereal plants resistant to Barley Yellow Dwarf Virus, particularly in the presence of co-infecting Cereal Yellow Dwarf Virus, by stably integrating into the cells of the transgenic plant a chimeric gene comprising a DNA region operably linked to plant expressible promoter in such a way that the RNA molecule may be transcribed from the DNA region, the RNA molecule comprising both sense and antisense RNA capable of pairing and forming a double stranded RNA molecule or hairpin RNA.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
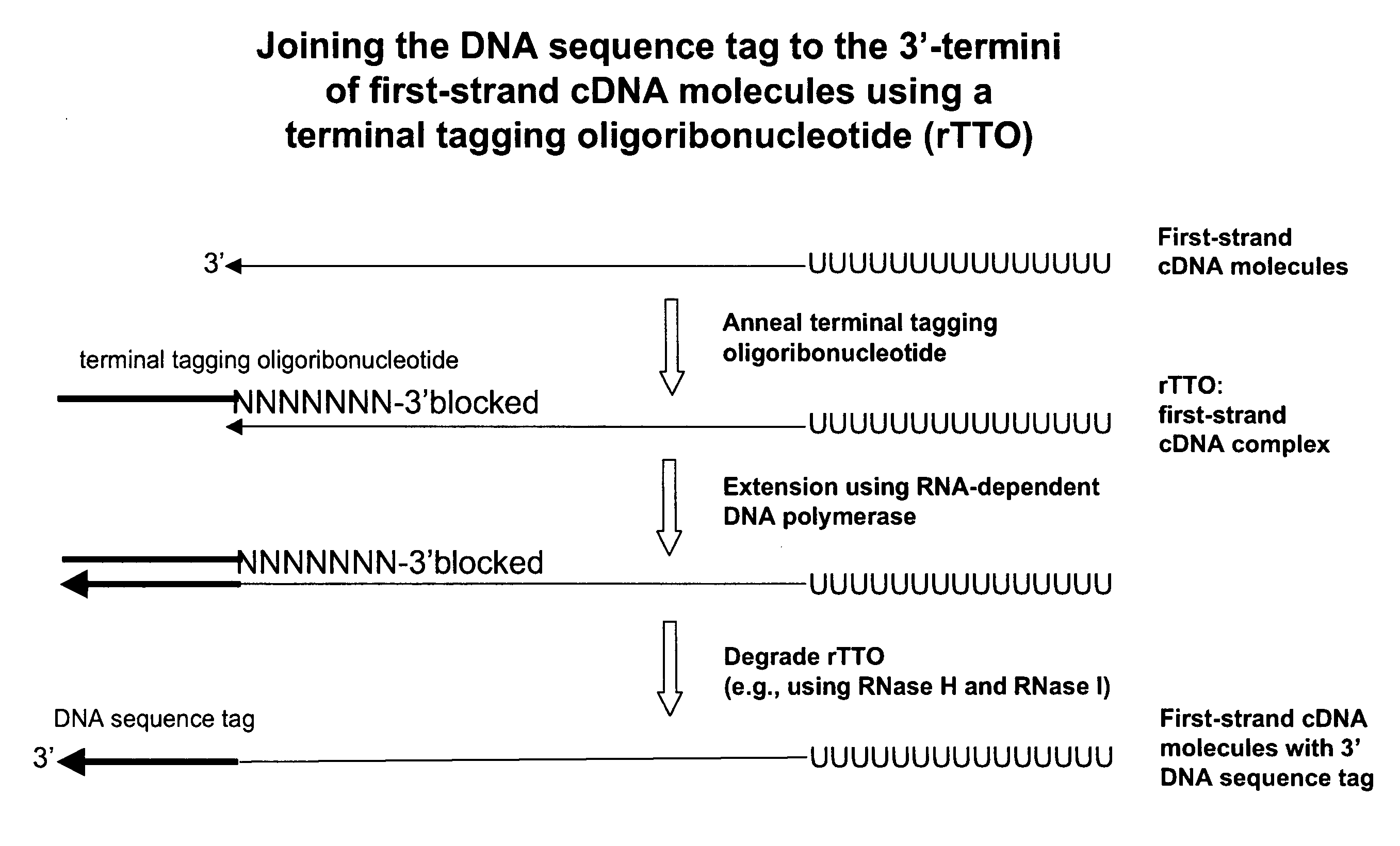
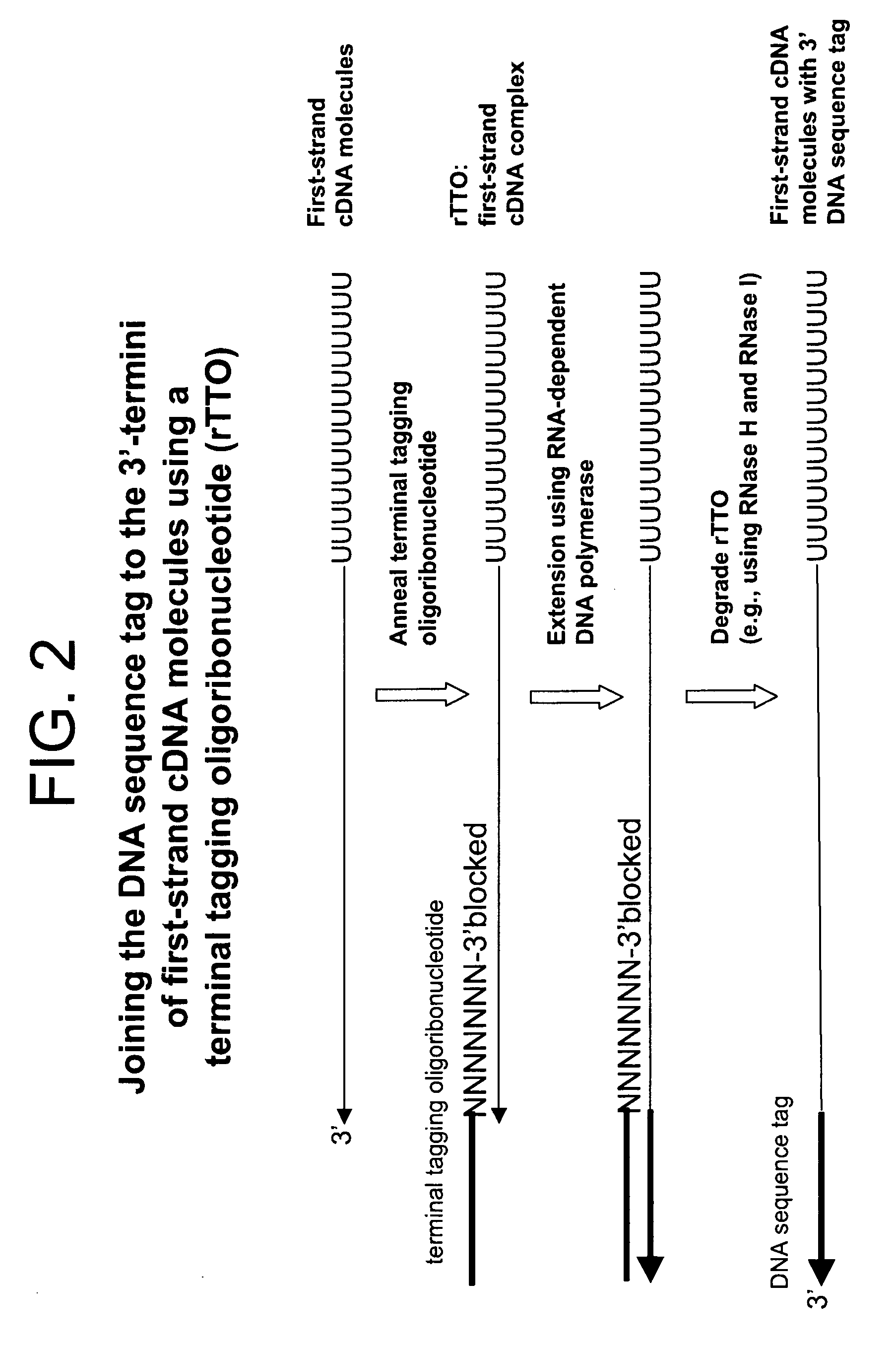
Synthesis of tagged nucleic acids
ActiveUS8039214B2Reduce in quantityGood removal effectMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesOligoribonucleotidesRibonucleotide synthesis
The present invention relates generally to methods, compositions and kits for synthesizing sense RNA molecules from one or more RNA molecules of interest in a sample. In exemplary embodiments, the methods use a terminal tagging oligoribonucleotide (rTTO) to join a DNA sequence tag to the 3′-termini of first-strand cDNA molecules. The use of an rTTO comprising ribonucleotides results in decreased oligonucleotide-derived background synthesis of RNA in the absence of sample RNA and, surprisingly and unexpectedly, also results in significantly increased yields of sense RNA molecules that exhibit sequences that are substantially identical to those of the RNA molecules of interest in the sample. The sense RNA molecules also have an RNA sequence tag on their 5′-termini that is useful for fixing the lengths of sense RNA molecules that are synthesized in a second or subsequent round.
Owner:CELLSCRIPT
RNA interference mediated inhibition of proprotein convertase subtilisin Kexin 9 (PCSK9) gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20070173473A1Improve stabilityModulating RNAi activitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementLipid formationProprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin 9
The present invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin Kexin 9 (PCSK9) gene expression and / or activity. The present invention is also directed to compounds, compositions, and methods relating to traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of expression and / or activity of genes involved in Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin Kexin 9 (PCSK9) gene expression pathways or other cellular processes that mediate the maintenance or development of such traits, diseases and conditions. Specifically, the invention relates to double stranded nucleic acid molecules including small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules capable of mediating RNA interference (RNAi) against Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin Kexin 9 (PCSK9) gene expression, including cocktails of such small nucleic acid molecules and lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations of such small nucleic acid molecules. The present invention also relates to small nucleic acid molecules, such as siNA, siRNA, and others that can inhibit the function of endogenous RNA molecules, such as endogenous micro-RNA (miRNA) (e.g, miRNA inhibitors) or endogenous short interfering RNA (siRNA), (e.g., siRNA inhibitors) or that can inhibit the function of RISC (e.g., RISC inhibitors), to modulate PCSK9 gene expression by interfering with the regulatory function of such endogenous RNAs or proteins associated with such endogenous RNAs (e.g., RISC), including cocktails of such small nucleic acid molecules and lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations of such small nucleic acid molecules. Such small nucleic acid molecules and are useful, for example, in providing compositions to prevent, inhibit, or reduce metabolic diseases traits and conditions, including but not limited to hyperlipidemia, hypercholesterolemia, cardiovascular disease, atherosclerosis, hypertension, diabetis (e.g., type I and / or type II diabetis), insulin resistance, obesity and / or other disease states, conditions, or traits associated with PCSK9 gene expression or activity in a subject or organism.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
DNA and RNA sequencing by nanoscale reading through programmable electrophoresis and nanoelectrode-gated tunneling and dielectric detection
An apparatus and method for performing nucleic acid (DNA and / or RNA) sequencing on a single molecule. The genetic sequence information is obtained by probing through a DNA or RNA molecule base by base at nanometer scale as though looking through a strip of movie film. This DNA sequencing nanotechnology has the theoretical capability of performing DNA sequencing at a maximal rate of about 1,000,000 bases per second. This enhanced performance is made possible by a series of innovations including: novel applications of a fine-tuned nanometer gap for passage of a single DNA or RNA molecule; thin layer microfluidics for sample loading and delivery; and programmable electric fields for precise control of DNA or RNA movement. Detection methods include nanoelectrode-gated tunneling current measurements, dielectric molecular characterization, and atomic force microscopy / electrostatic force microscopy (AFM / EFM) probing for nanoscale reading of the nucleic acid sequences.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Method of altering cell properties by administering rna
InactiveUS20060247195A1Less activeMinimise and prevent riskCell differentiationGenetic material ingredientsRNA SequenceIn vivo
The invention relates to the alteration of cell properties using RNA molecules. In particular, it relates to the alteration of the ability of cells to mobilise, migrate, integrate, proliferate and / or differentiate. For example, it relates to the induction of differentiation of stem cells, including the acquisition of the ability to migrate, integrate, and proliferate. It also relates to the induction of in vivo stem cell mobilisation, migration, integration, proliferation and / or differentiation. Accordingly, it relates to the promotion of stem cell-mediated functional repair. The invention also relates to the reversal of differentiation of differentiated cells. All these effects may be effected by providing isolated RNA comprising a RNA sequence extractable from cells comprising the desired cell type(s) to a population of cells under conditions whereby the alteration of the cell property is achieved.
Owner:RIBOSTEM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com