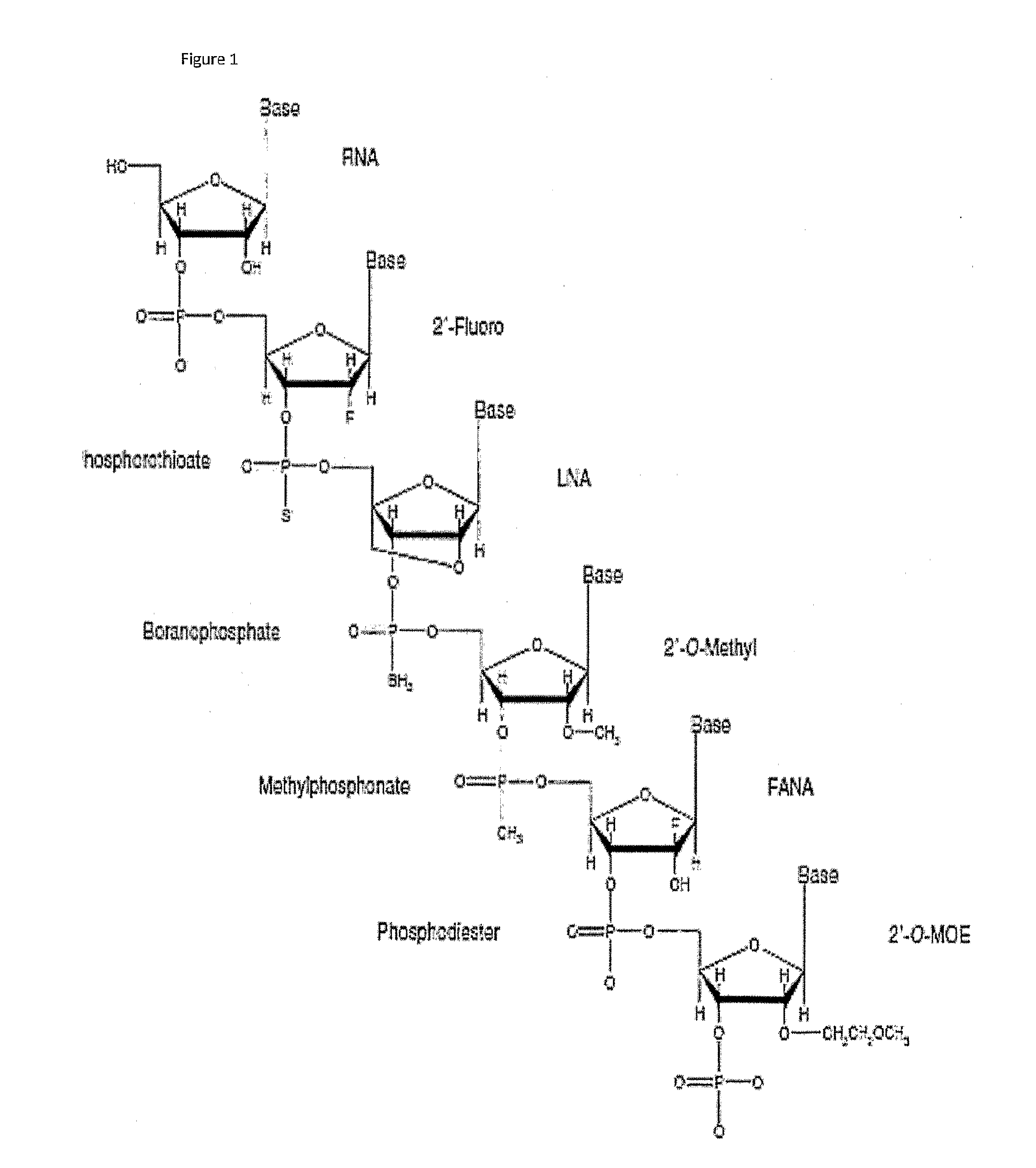
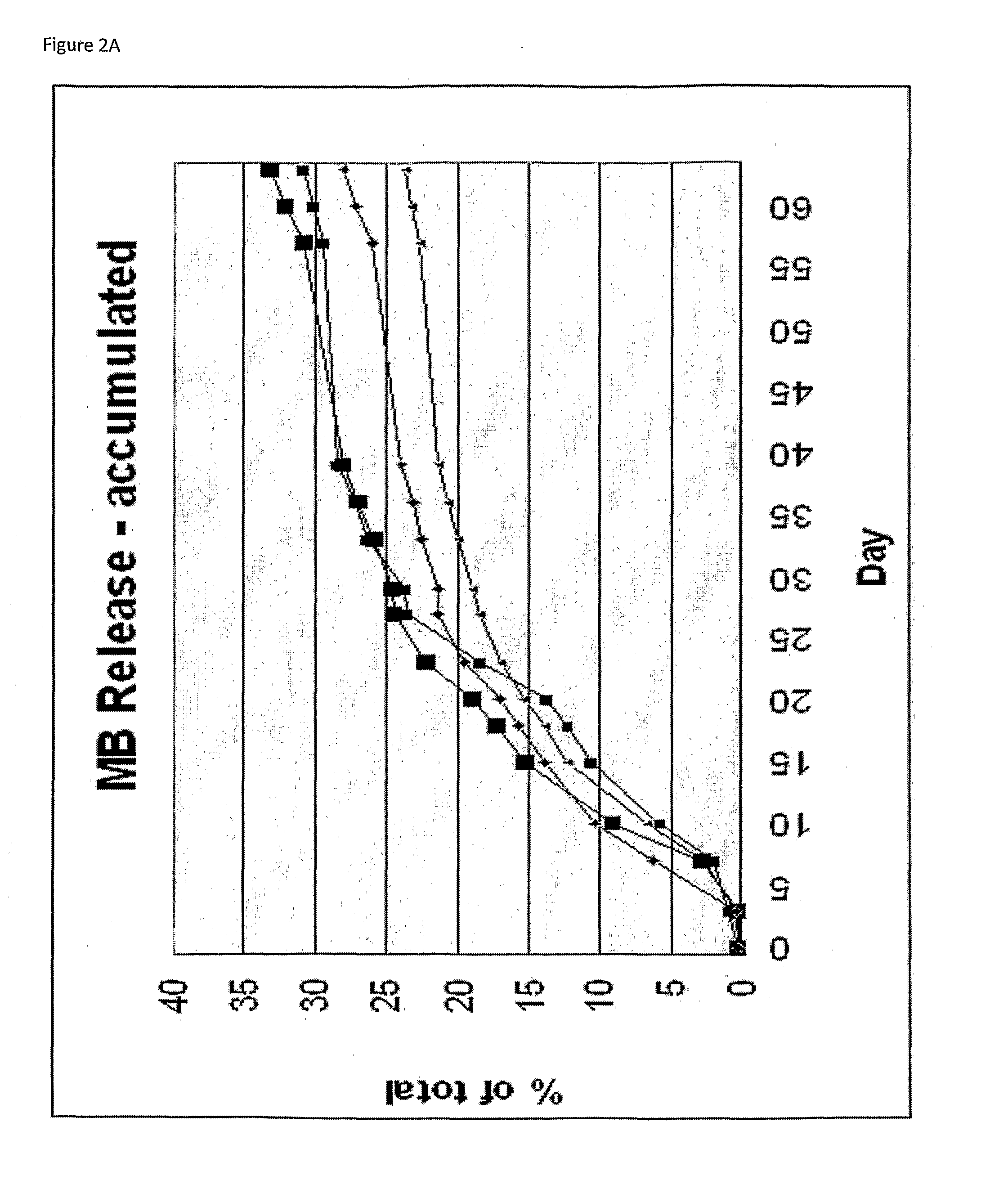
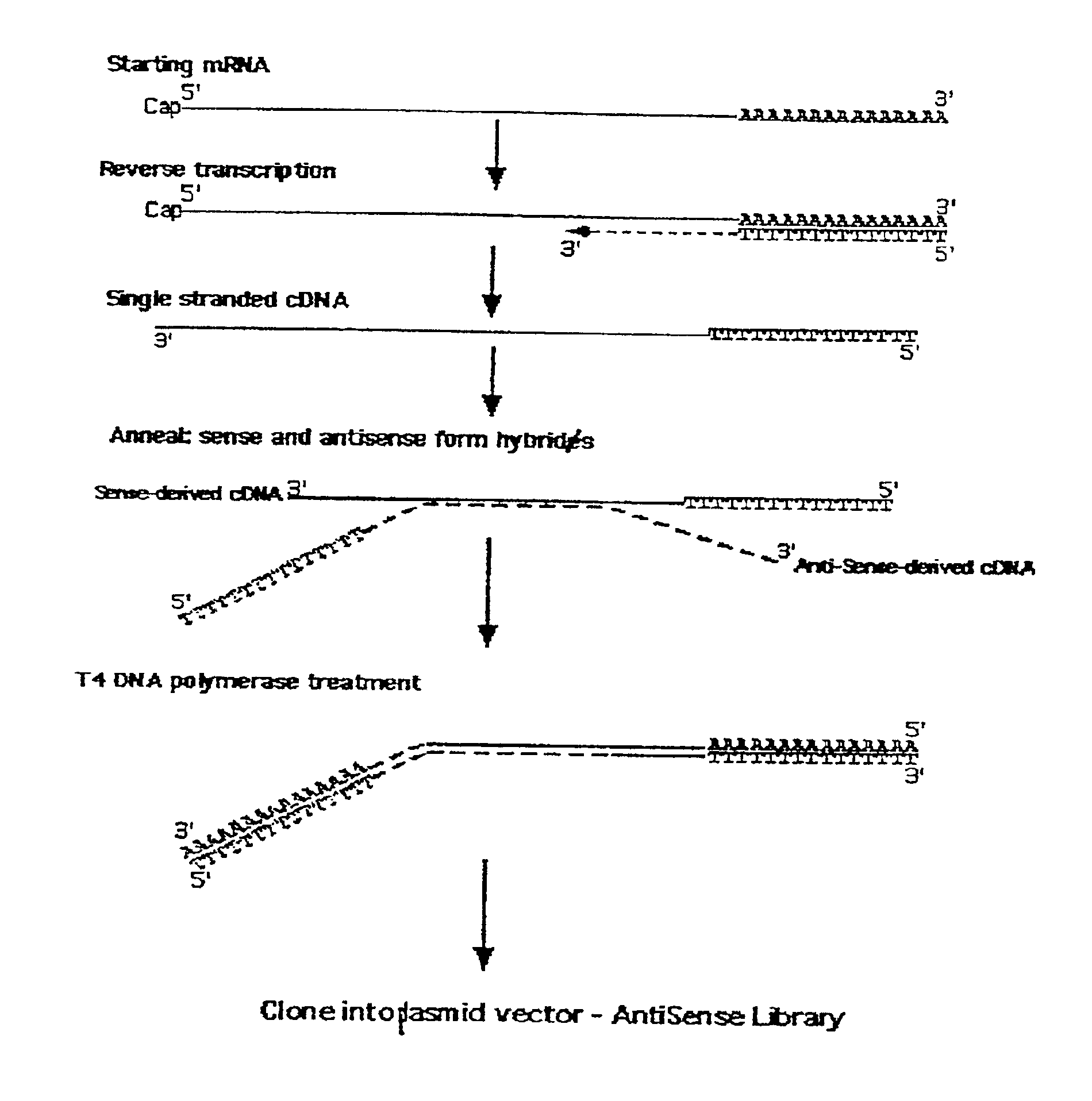
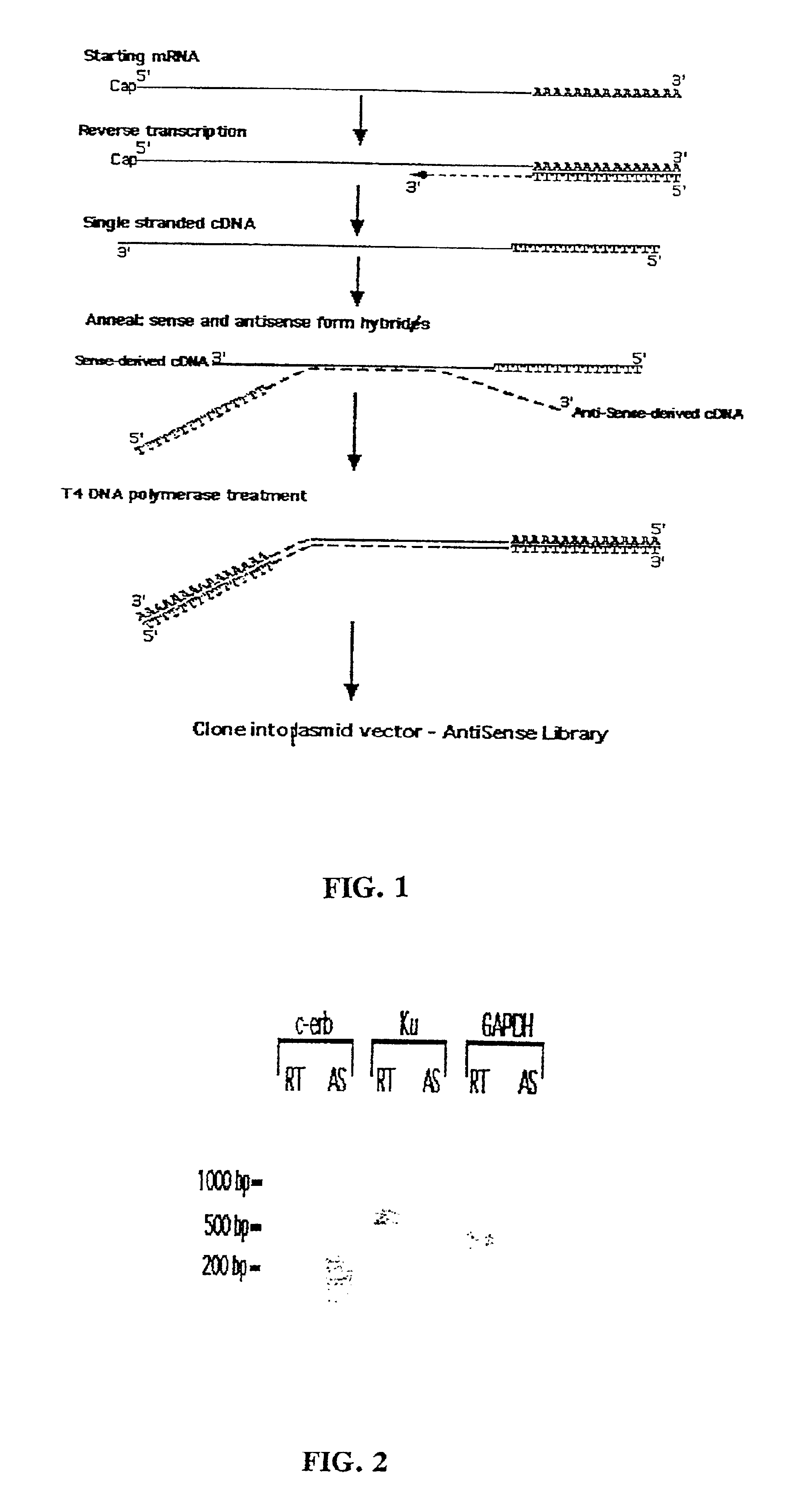
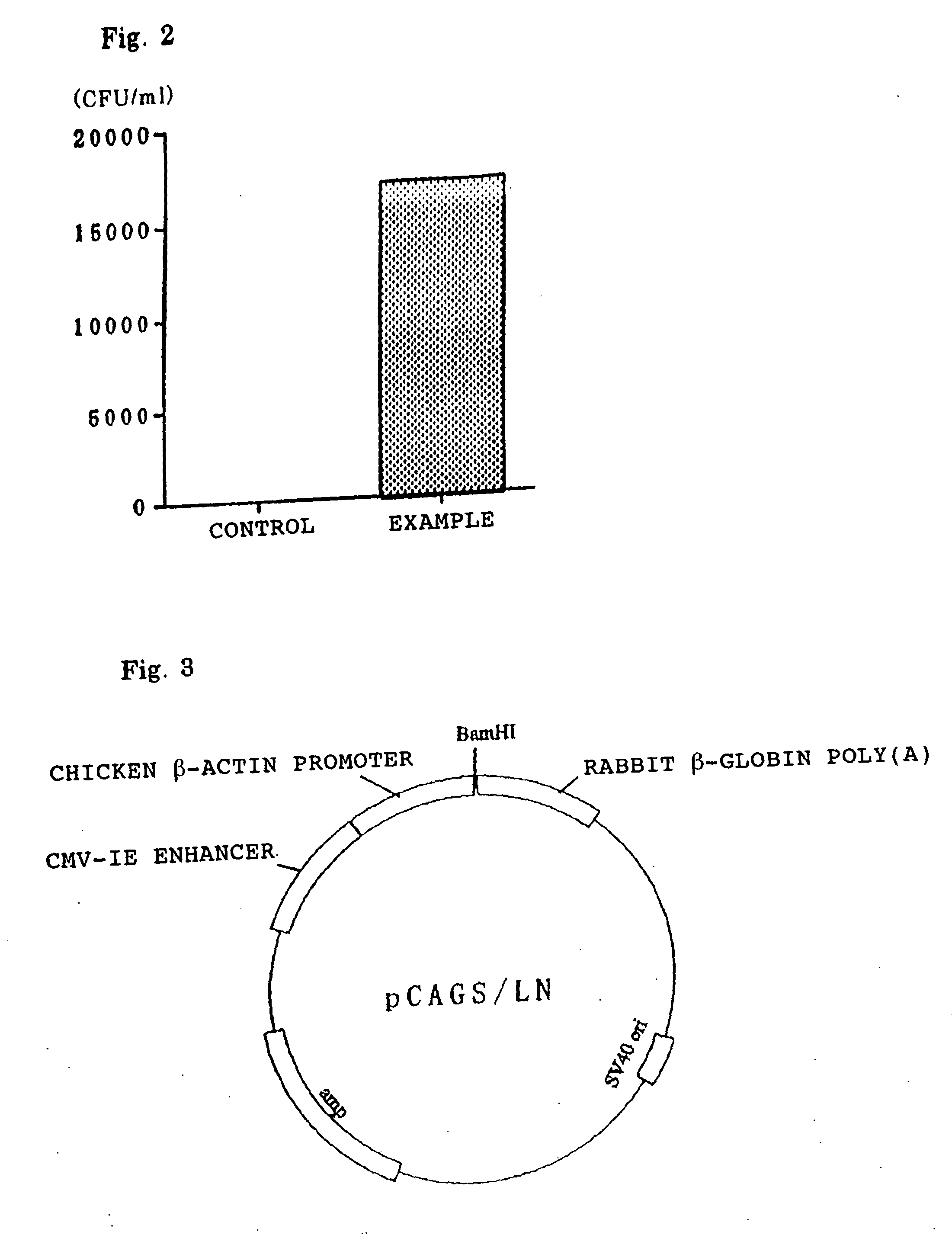
Patents
Literature
189 results about "Antisense RNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
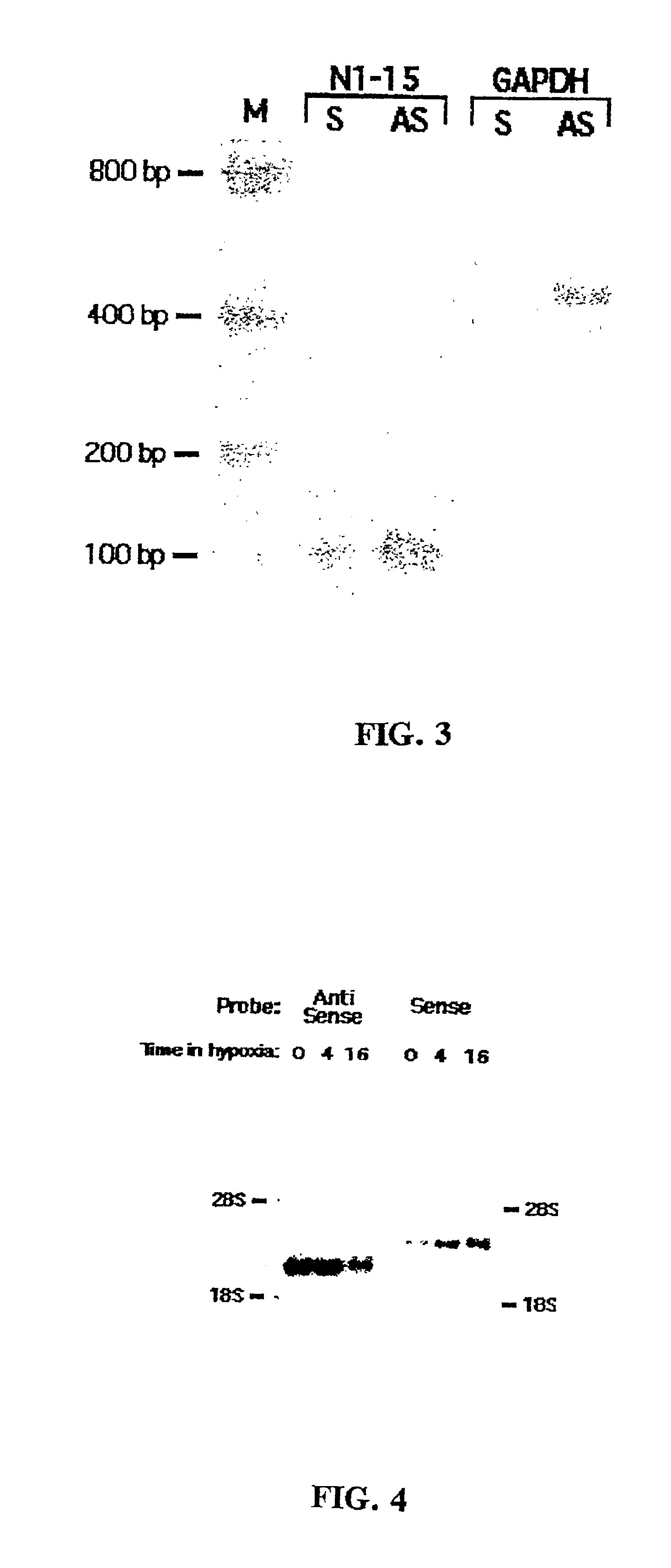
Antisense RNA (asRNA), also referred to as antisense transcript, natural antisense transcript (NAT) or antisense oligonucleotide, is a single stranded RNA that is complementary to a protein coding messenger RNA (mRNA) with which it hybridizes, and thereby blocks its translation into protein. asRNAs (which occur naturally) have been found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, antisense transcripts can be classified into short (<200 nucleotides) and long (>200 nucleotides) non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). The primary function of asRNA is regulating gene expression. asRNAs may also be produced synthetically and have found wide spread use as research tools for gene knockdown. They may also have therapeutic applications.
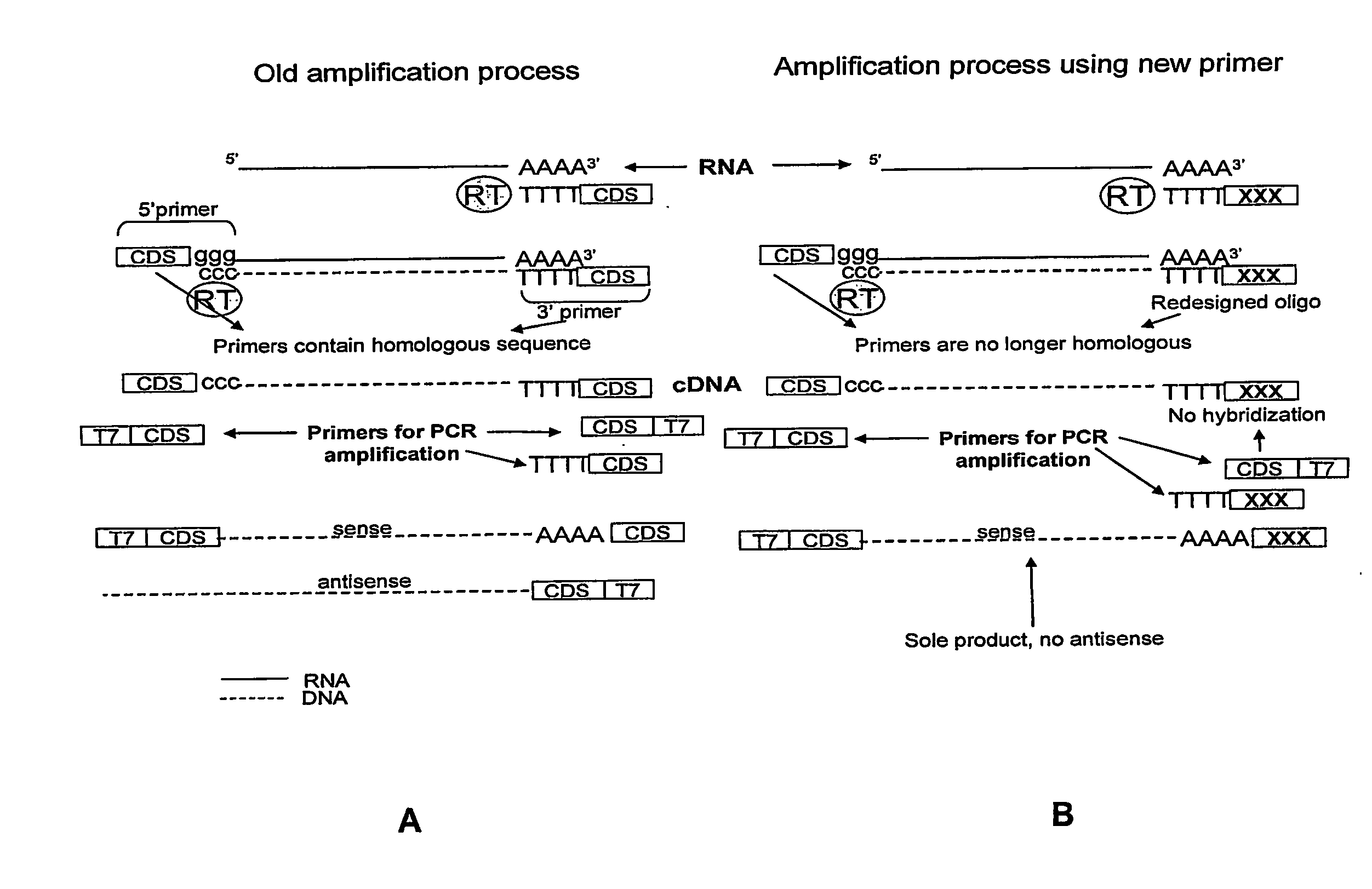
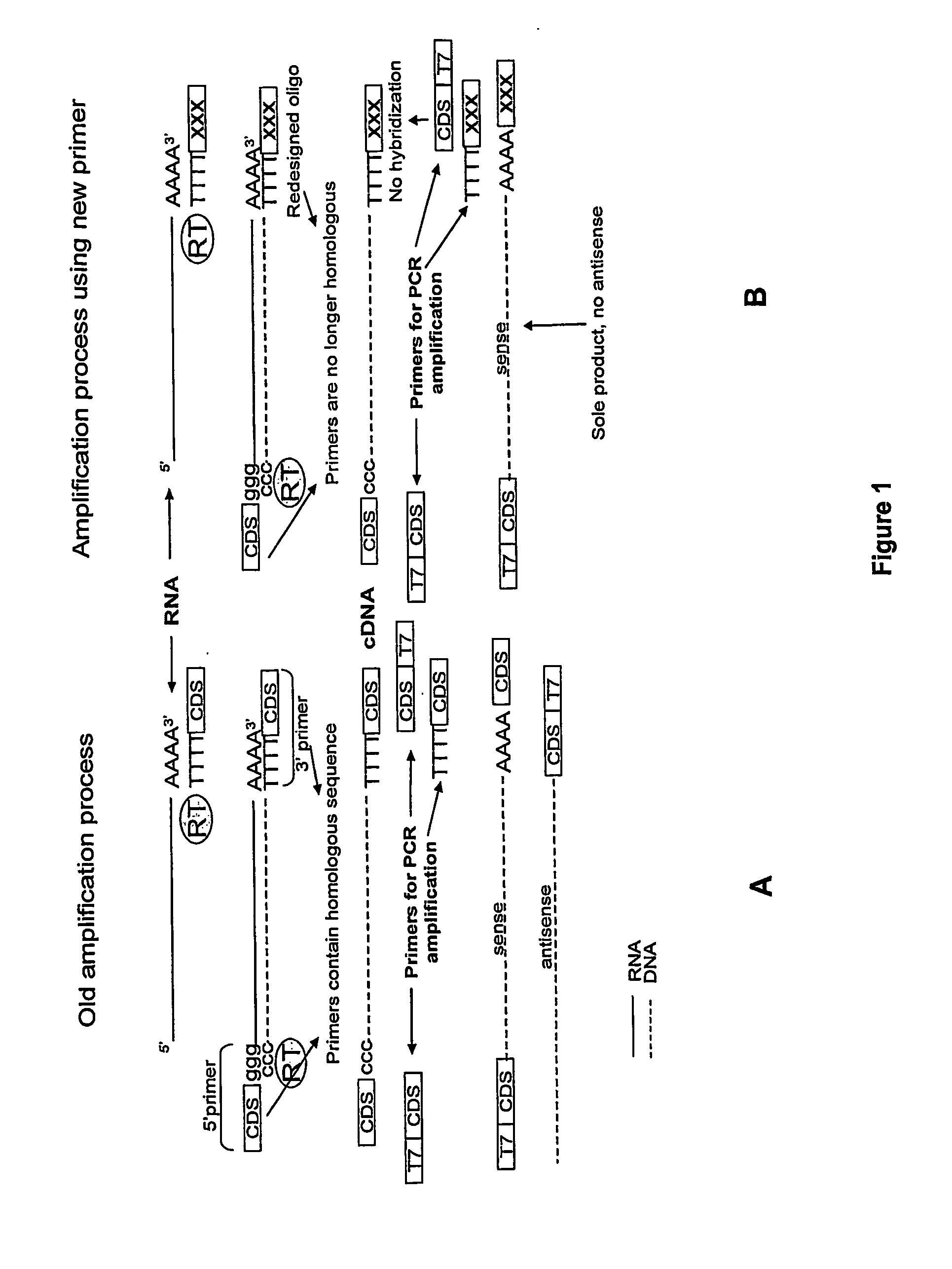
Method for linear mRNA amplification
InactiveUS6132997ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAntisense RNAReverse transcriptase
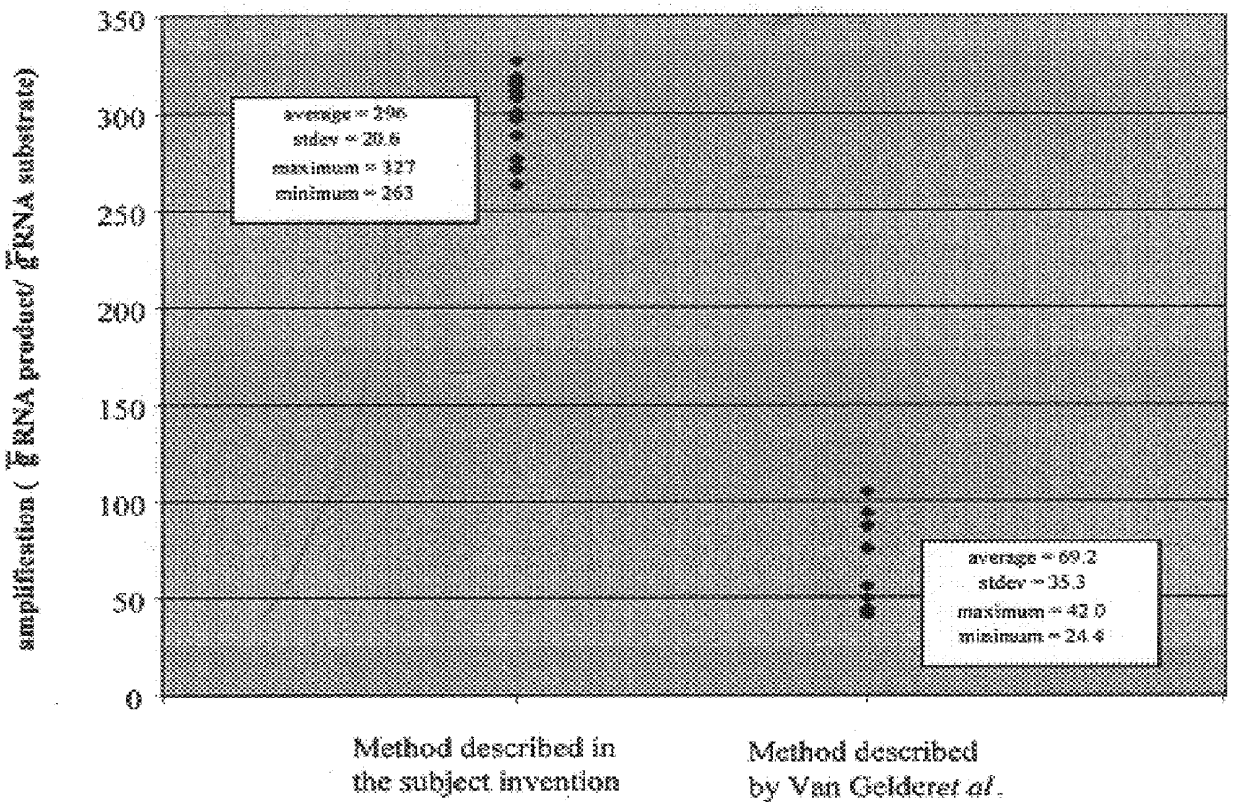
Methods for linearly amplifying mRNA to produce antisense RNA are provided. In the subject methods, mRNA is converted to double-stranded cDNA using a promoter-primer having a poly-dT primer site linked to a promoter sequence so that the resulting double-stranded cDNA is recognized by an RNA polymerase. The resultant double-stranded cDNA is then transcribed into antisense RNA in the presence of a reverse transcriptase that is rendered incapable of RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity during this transcription step. The subject methods find use a variety of different applications in which the preparation of linearly amplified amounts of antisense RNA is desired. Also provided are kits for practicing the subject methods.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
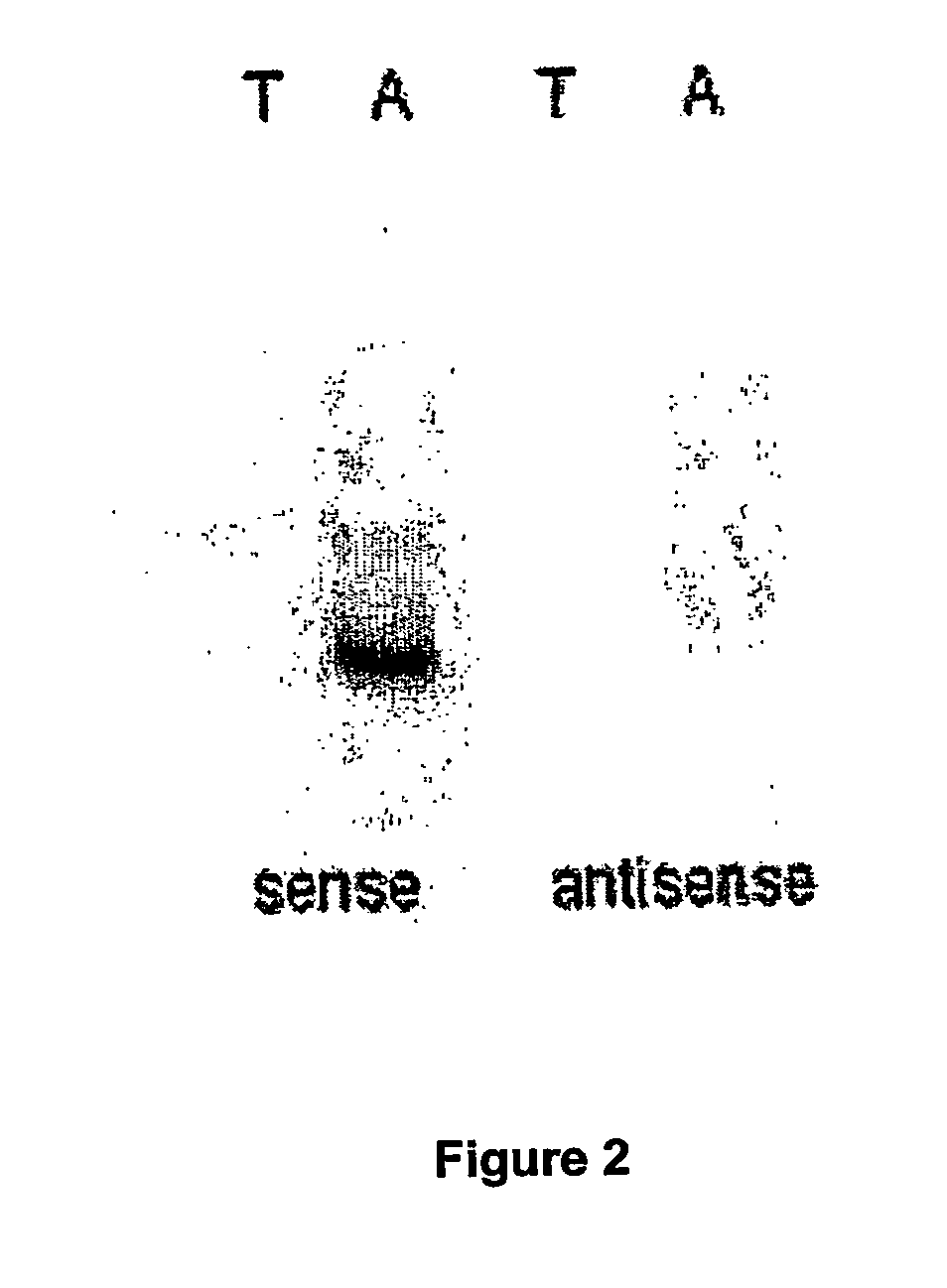
Method for enrichment of natural antisense messenger RNA
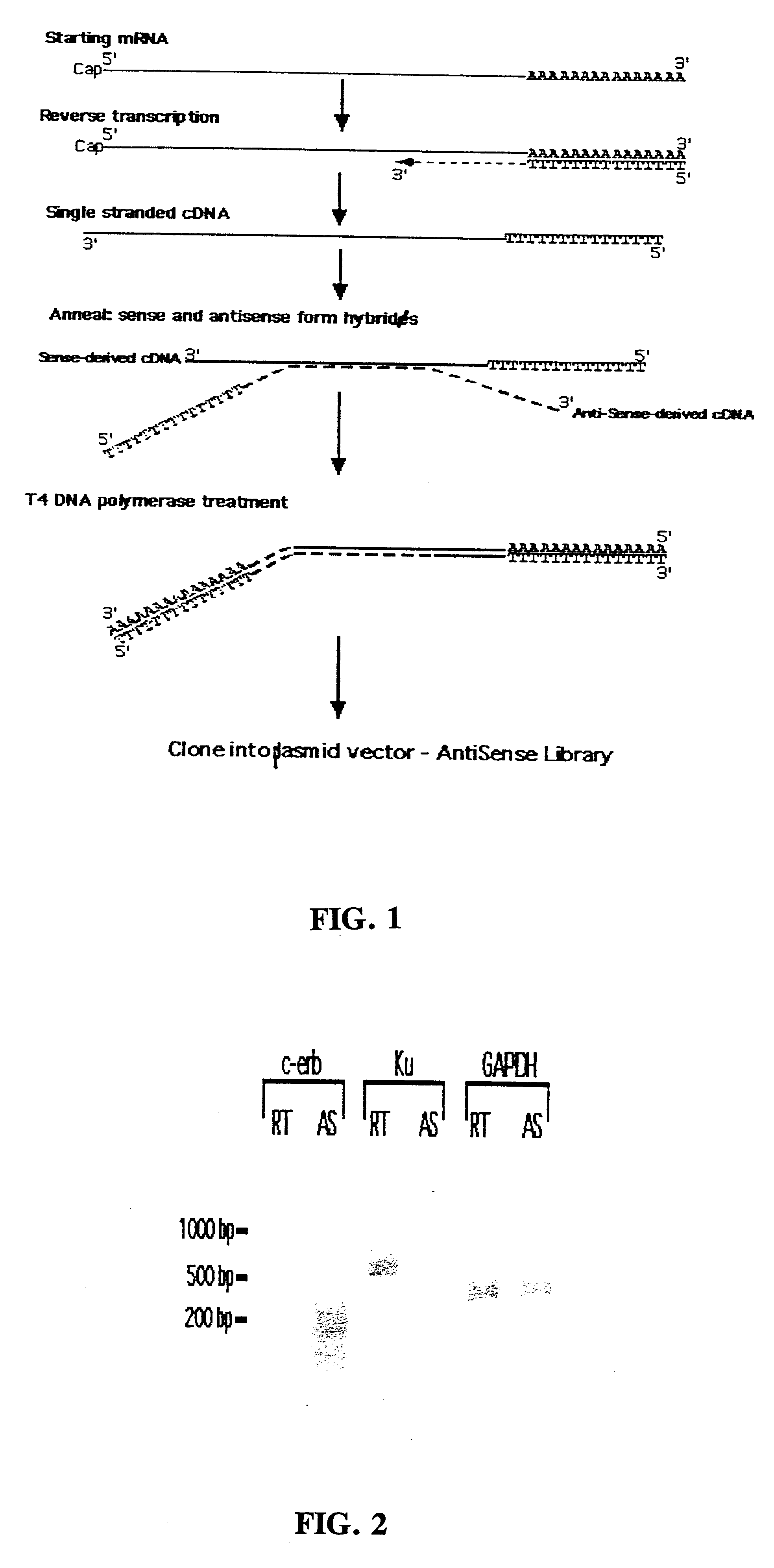
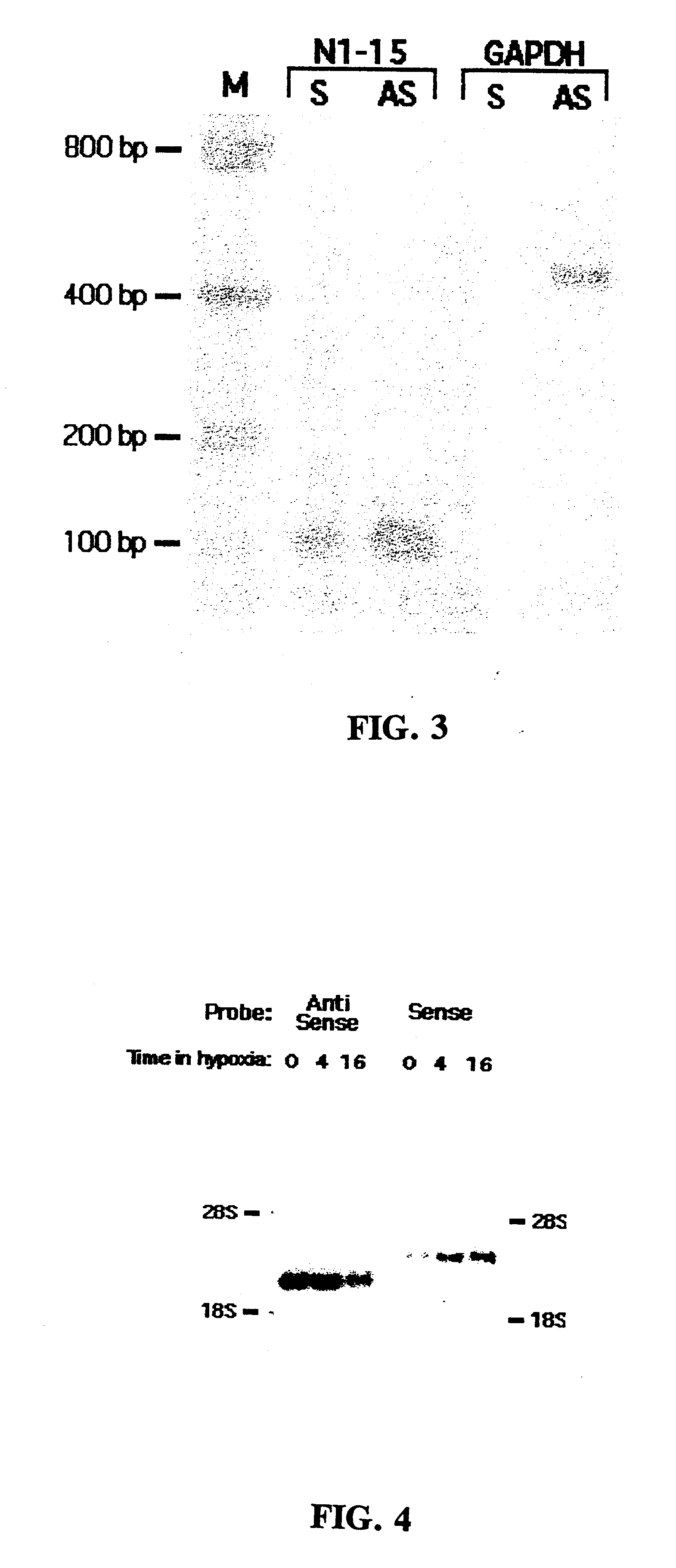
A method for enrichment of natural antisense mRNA which involves hybridization of cDNA obtained from sense RNA with cDNA obtained from antisense RNA, followed by DNA polymerase treatment of the sense-antisense hybrid DNA molecule. A natural antisense library can be generated by cloning of sense-antisense hybrid DNA molecules in a vector.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
Methods, compositions and systems for local delivery of drugs
ActiveUS20110195123A1Reduce degradationImprove permeabilityBiocidePowder deliveryCell-Extracellular MatrixBrachytherapy
Implantable medical device eluting drug locally and in prolonged period is provided, including several types of such a device, the treatment modes of implementation and methods of implantation. The device comprising of polymeric substrate, such as a matrix for example, that is used as the device body, and drugs, and in some cases additional scaffolding materials, such as metals or additional polymers, and materials to enhance visibility and imaging. The selection of drug is based on the advantageous of releasing drug locally and in prolonged period, where drug is released directly to the extracellular matrix (ECM) of the diseased area such as tumor, inflammation, degeneration or for symptomatic objectives, or to injured smooth muscle cells, or for prevention. One kind of drug is the gene silencing drugs based on RNA interference (RNAi), including but not limited to si RNA, sh RNA, or antisense RNA / DNA, ribozyme and nucleoside analogs. The modes of implantation in some embodiments are existing implantation procedures that are developed and used today for other treatments, including brachytherapy and needle biopsy. In such cases the dimensions of the new implant described in this invention are similar to the original implant. Typically a few devices are implanted during the same treatment procedure.
Owner:SILENSEED LTD
Method for enrichment of natural antisense messenger RNA
A method for enrichment of natural antisense mRNA which involves hybridization of cDNA obtained from sense RNA with cDNA obtained from antisense RNA, followed by DNA polymerase treatment of the sense-antisense hybrid DNA molecule. A natural antisense library can be generated by cloning of sense-antisense hybrid DNA molecules in a vector.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
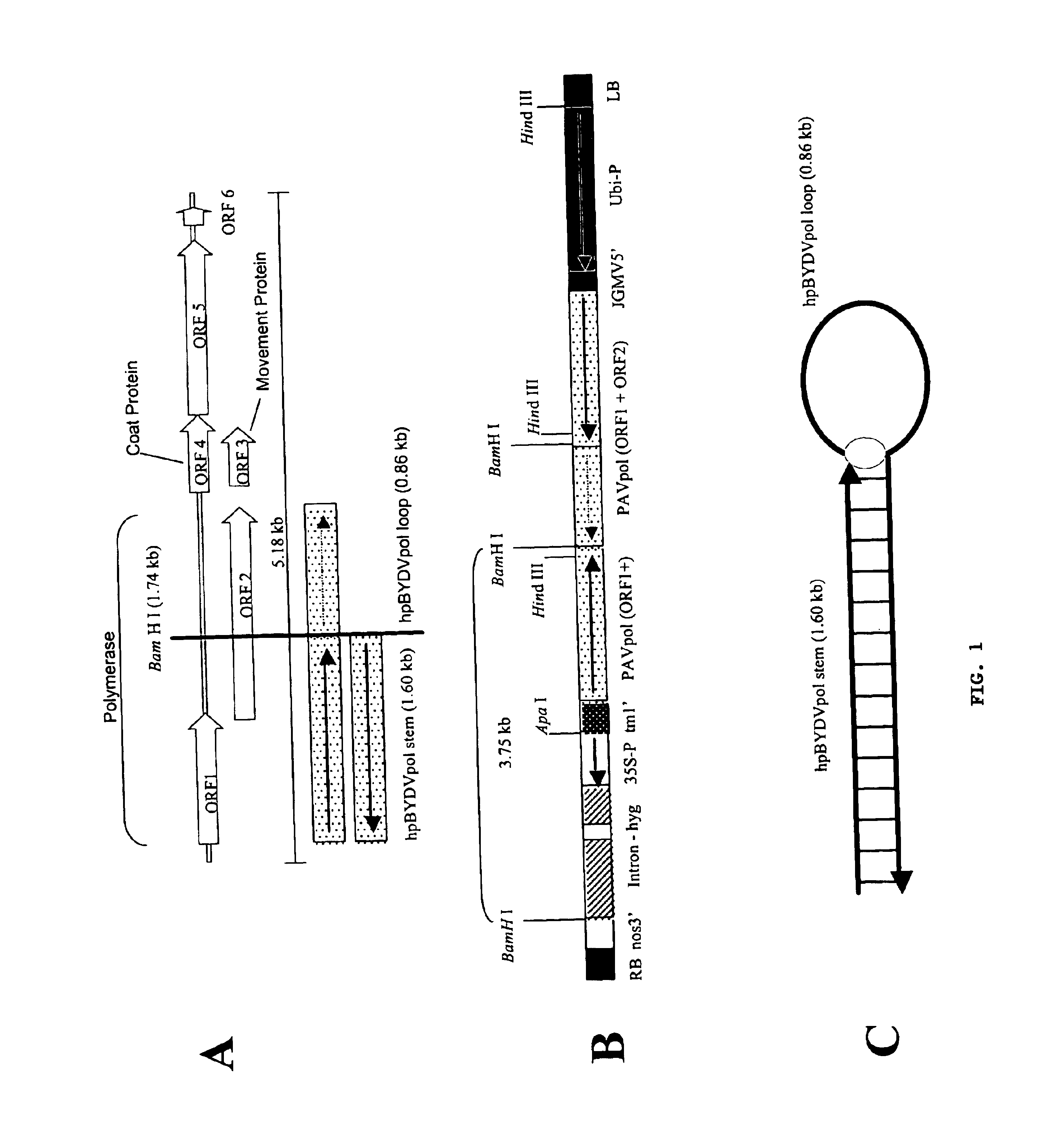
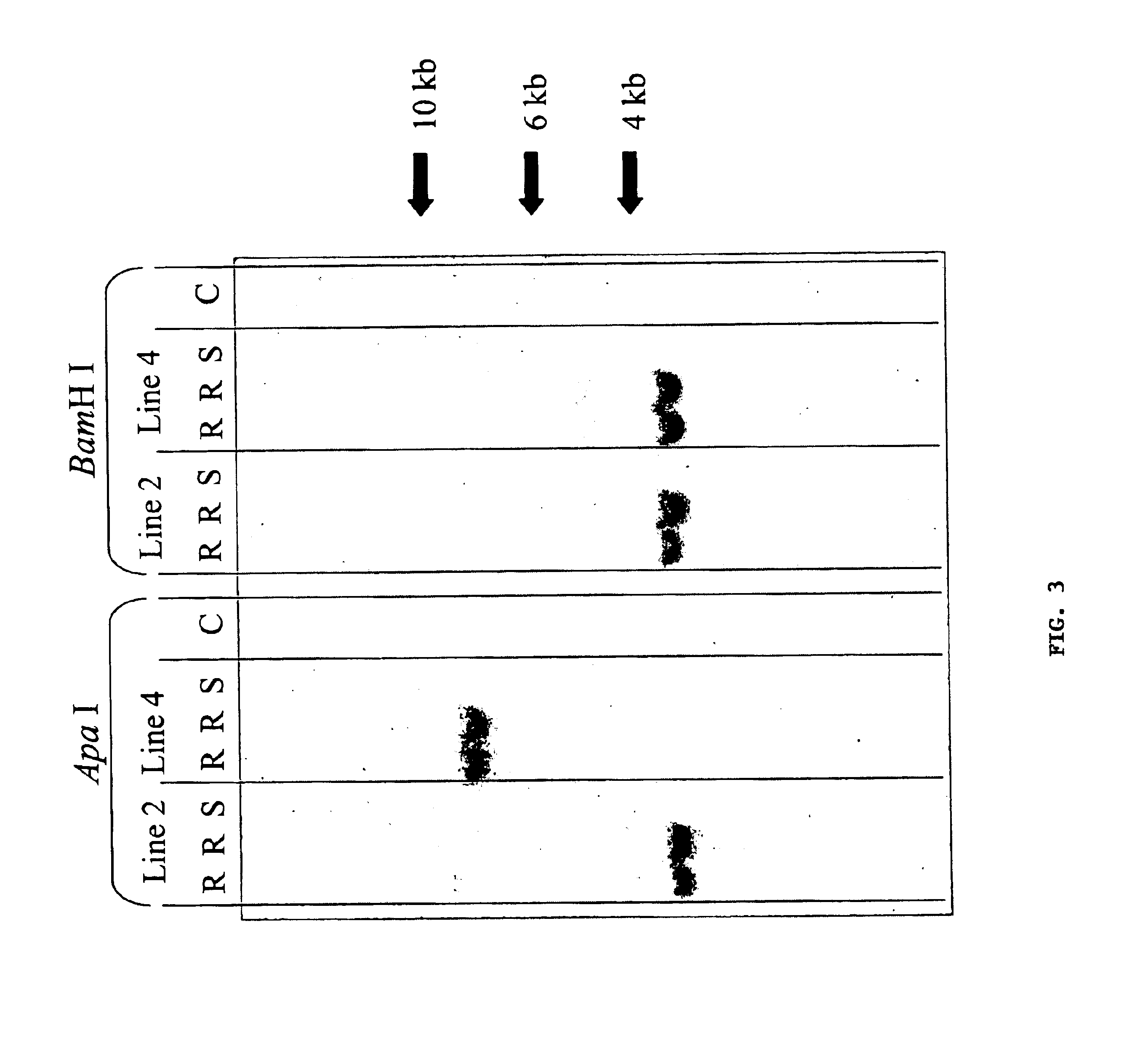
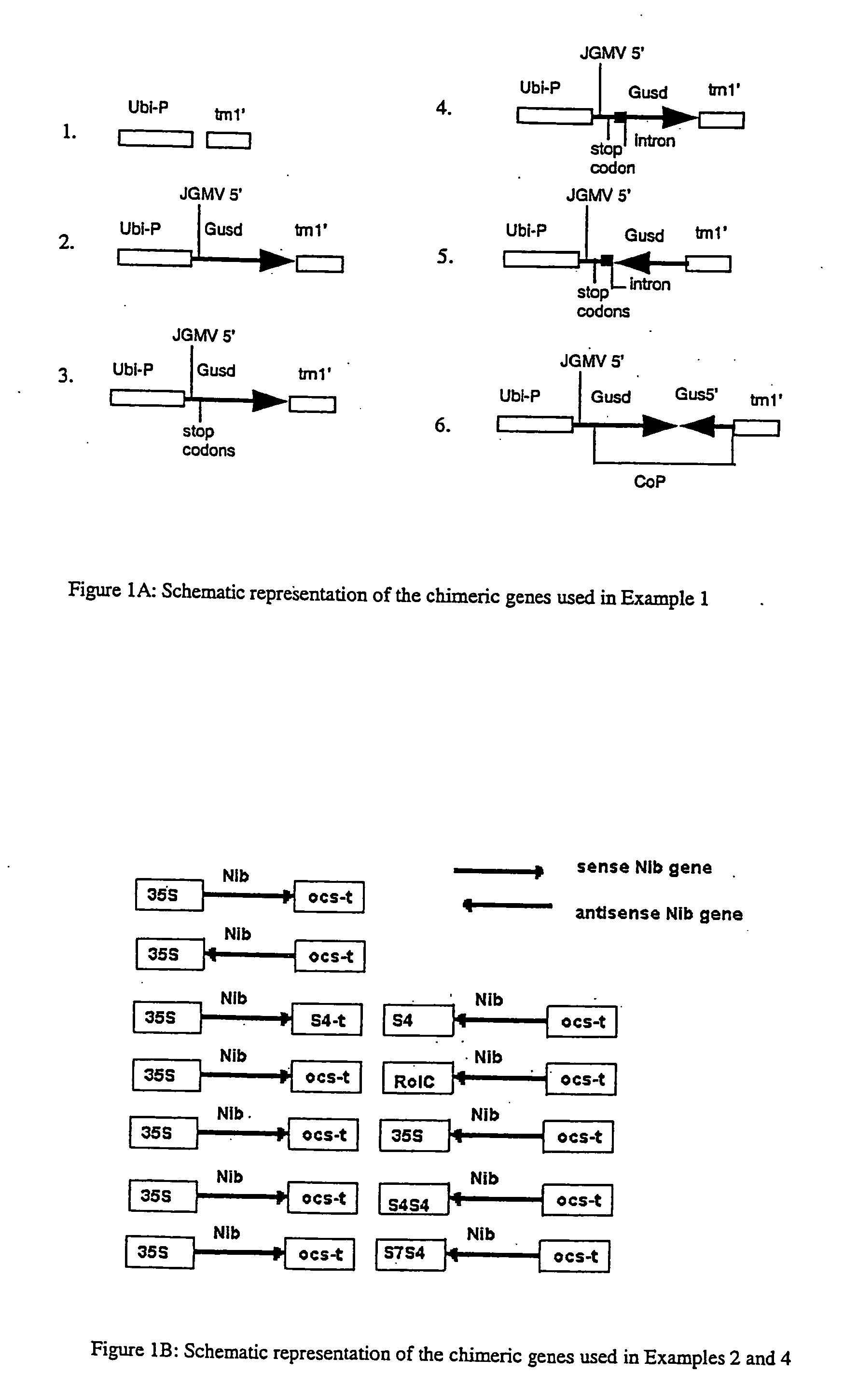
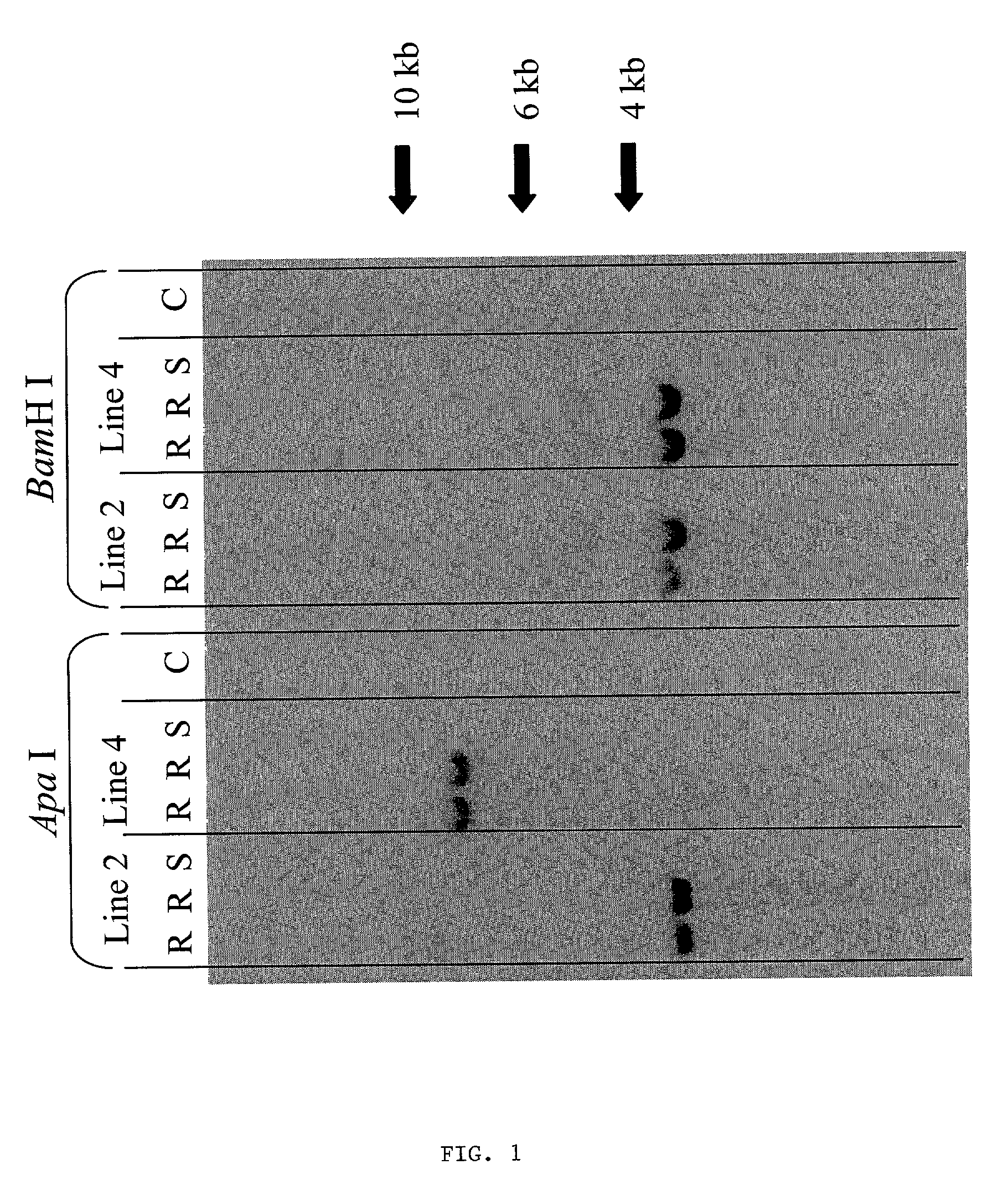
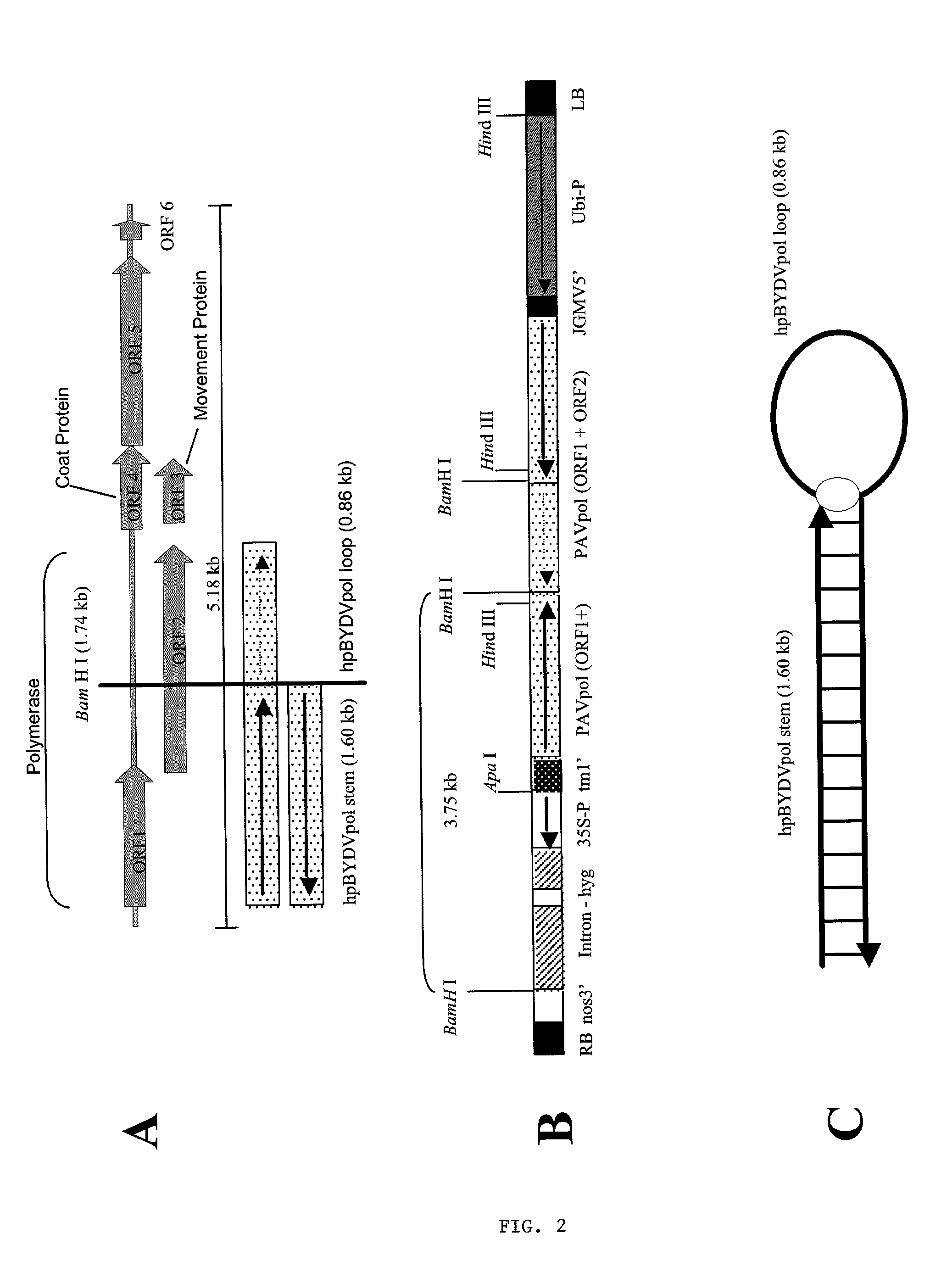
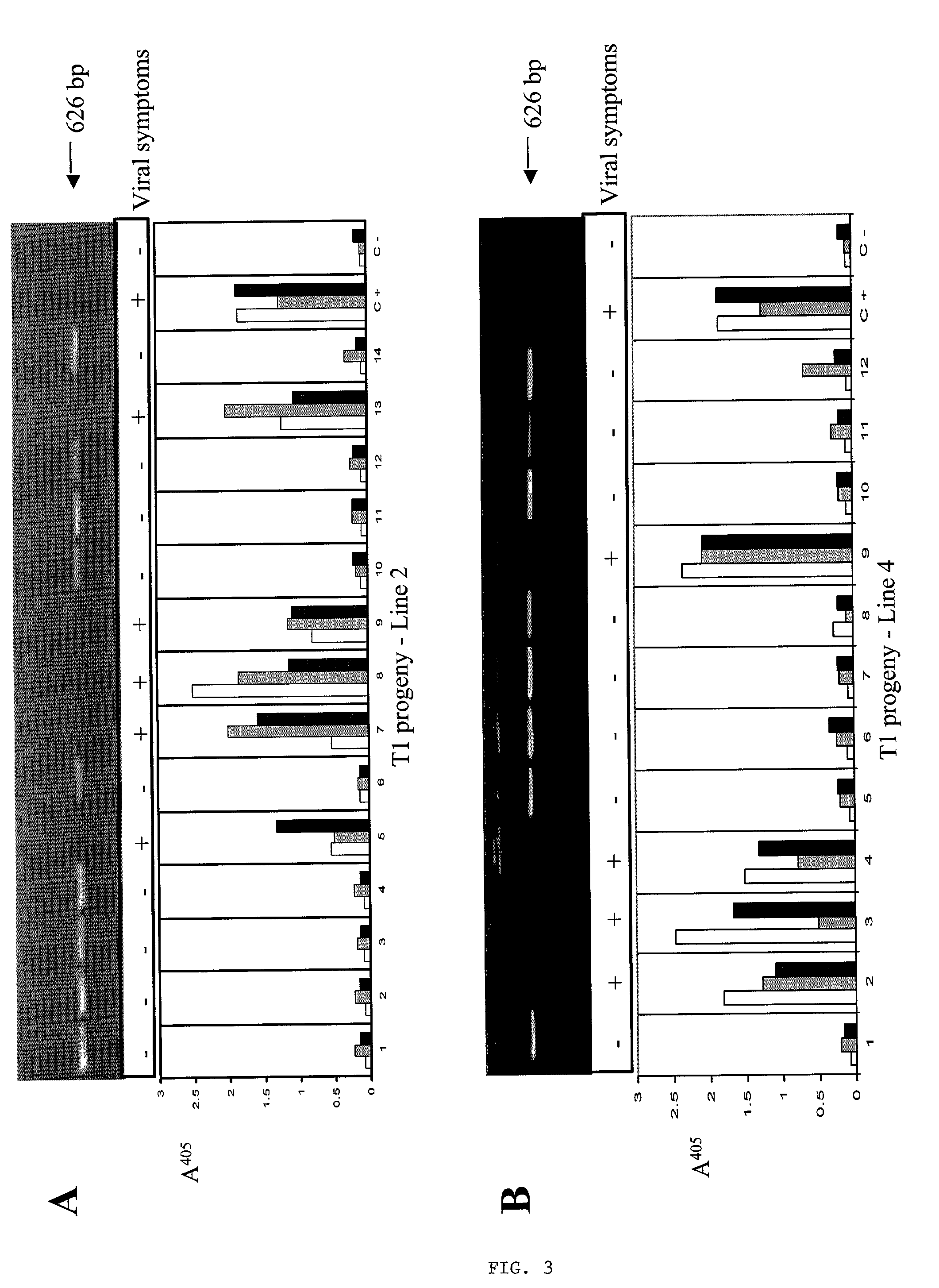
Methods and means for producing barley yellow dwarf virus resistant cereal plants
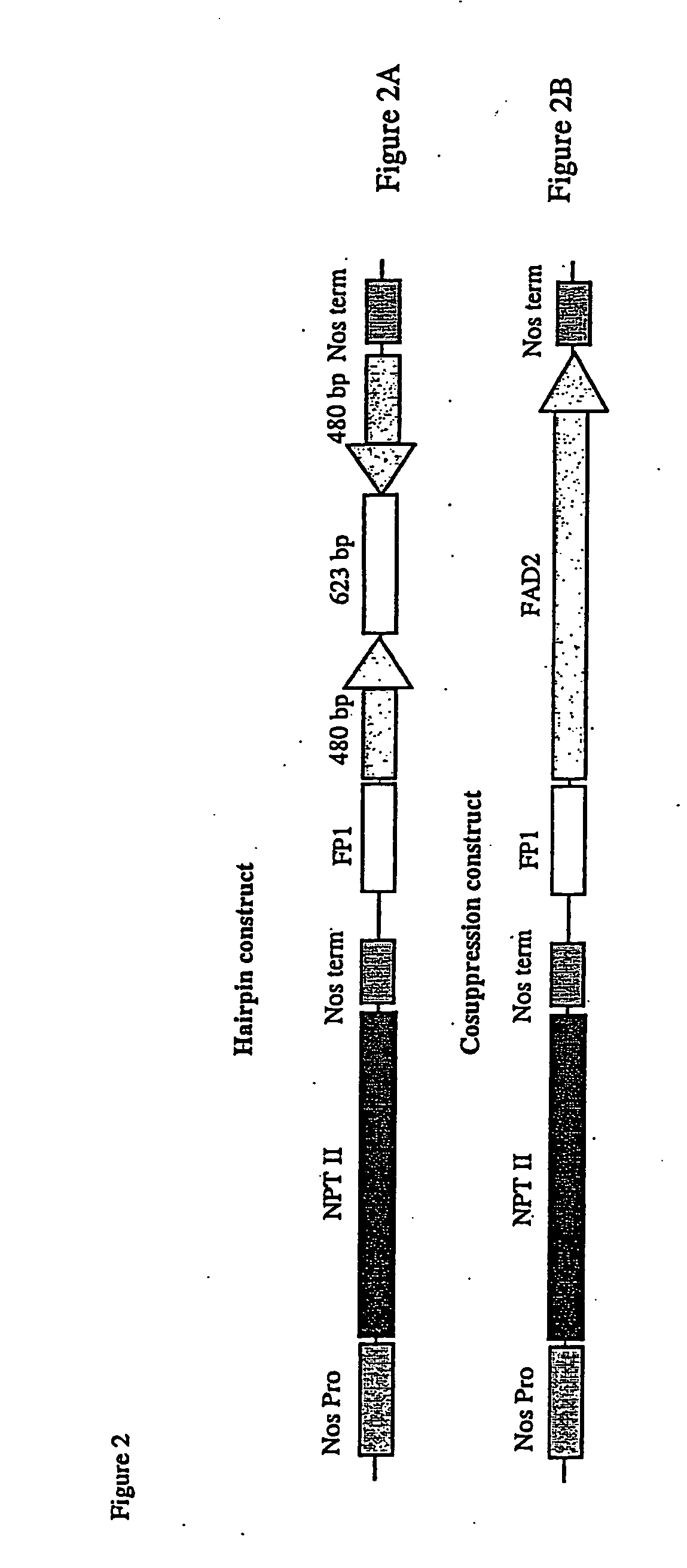
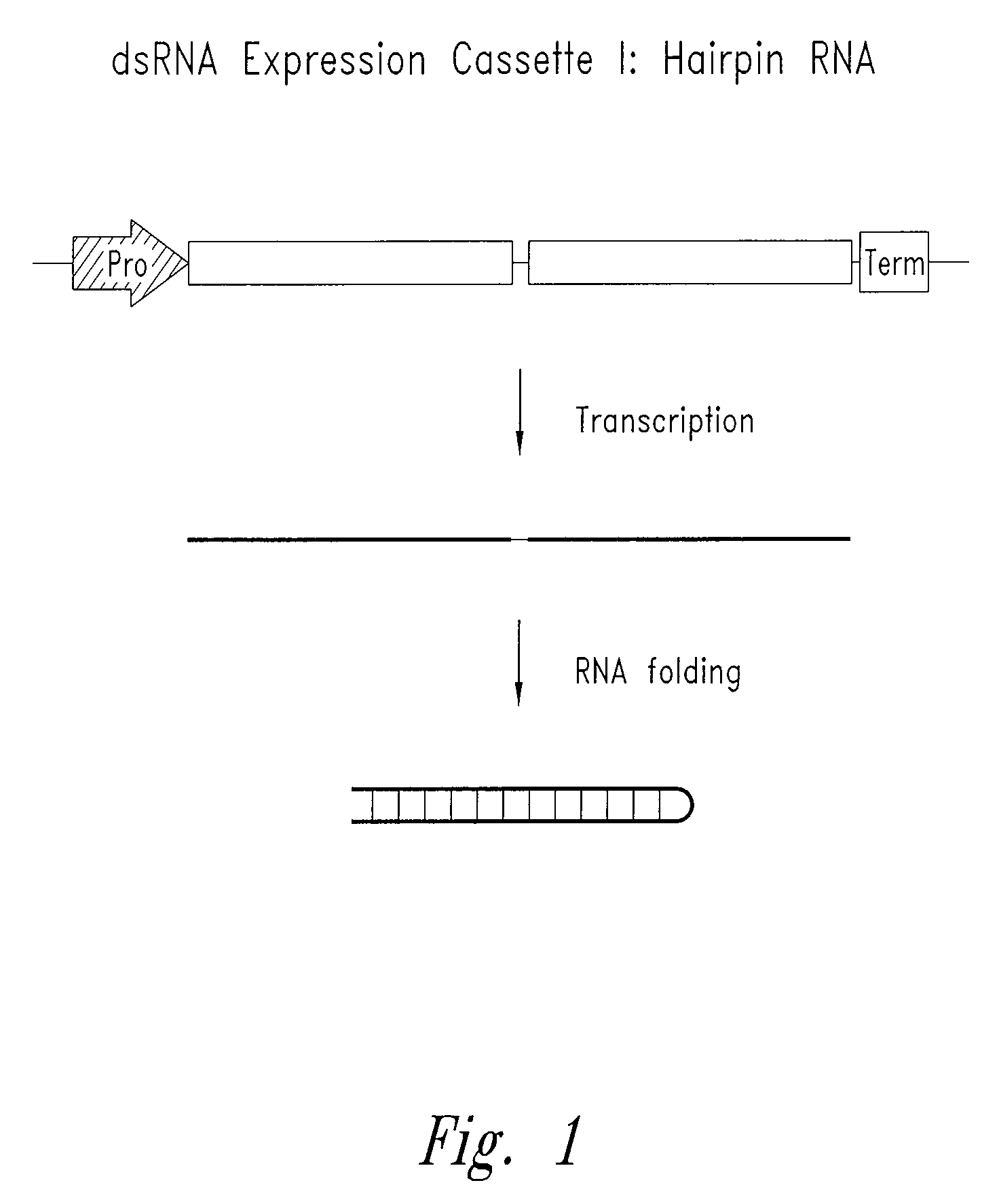
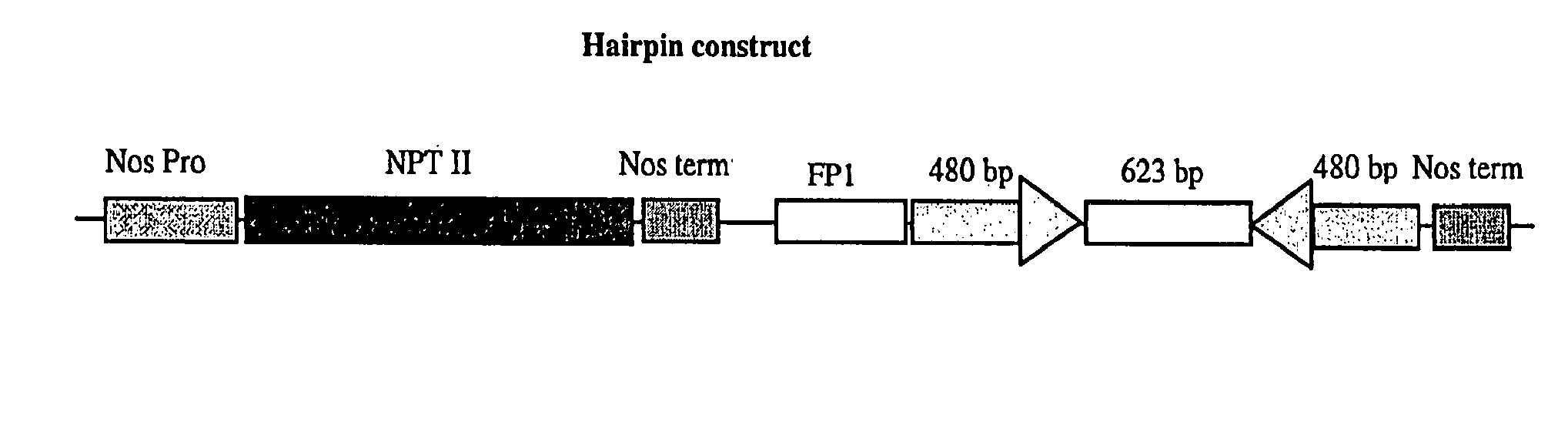
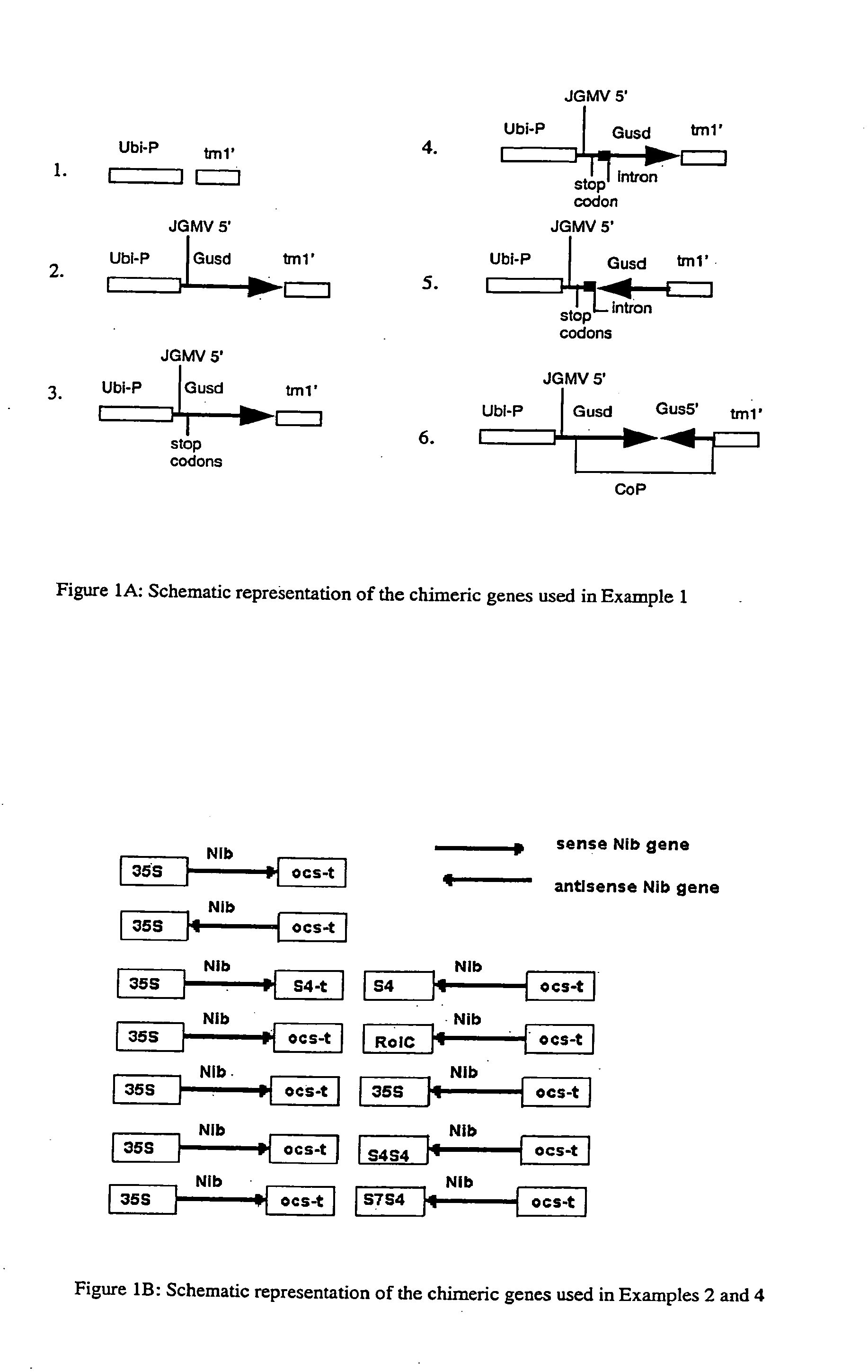
The invention relates to methods for producing transgenic cereal plants resistant to Barley Yellow Dwarf Virus, particularly in the presence of co-infecting Cereal Yellow Dwarf Virus, by stably integrating into the cells of the transgenic plant a chimeric gene comprising a DNA region operably linked to plant expressible promoter in such a way that the RNA molecule may be transcribed from the DNA region, the RNA molecule comprising both sense and antisense RNA capable of pairing and forming a double stranded RNA molecule or hairpin RNA.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Intranasal delivery of nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS20050265927A1Suppress gene expressionInhibit expressionPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsViral vectorExcipient
Aerosol delivery of nucleic acids to the lungs using viral vectors, polymers, surfactants, or excipients has been described. Compositions for intranasal administration are described that contain nucleic acids without viral or plasmid vectors and with little to no polymers, surfactants, or excipients. In one embodiment, the composition for intranasal delivery consists essentially of at least one nucleic acid and an aqueous solution. Suitable nucleic acids for intranasal delivery include, but are not limited to, dsDNA, dsRNA, ssDNA, ssRNA, short interfering RNA, micro-RNA, and antisense RNA. Methods for treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of at least one symptom or manifestation of a lung disease are also described consisting of administration by intranasal delivery an effective amount of a composition containing a nucleic acid. The composition may be formulated as a liquid or aerosol or other acceptable formulation for intranasal administration.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Method for linear mRNA amplification
InactiveUS6916633B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAntisense RNAReverse transcriptase
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Culturing method of auxilliary bud less tobacco after topping
The present invention discloses a tobacco cultivation method. Said method is characterized by that it adopts a molecular biological technique to identify key gene capable of promoting axillary bud germination and growth after the tip is pruned, then uses nocuity inducible promoter to drive antisense RNA and make it promptly express after the tip is pruned so as to inhibit the expression of said key gene capable of promoting axillary bud germination and growth and make the axillary bud can not be germinated or grown.
Owner:贾朝钧
Temperature sensing male fertile gene and use thereof
ActiveCN101333533AImprove selection efficiencyBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyMicroorganism
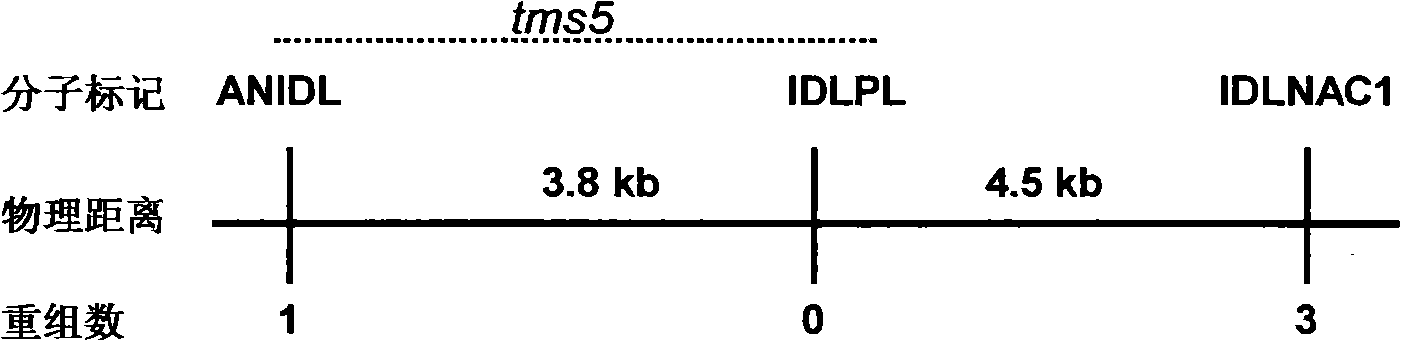
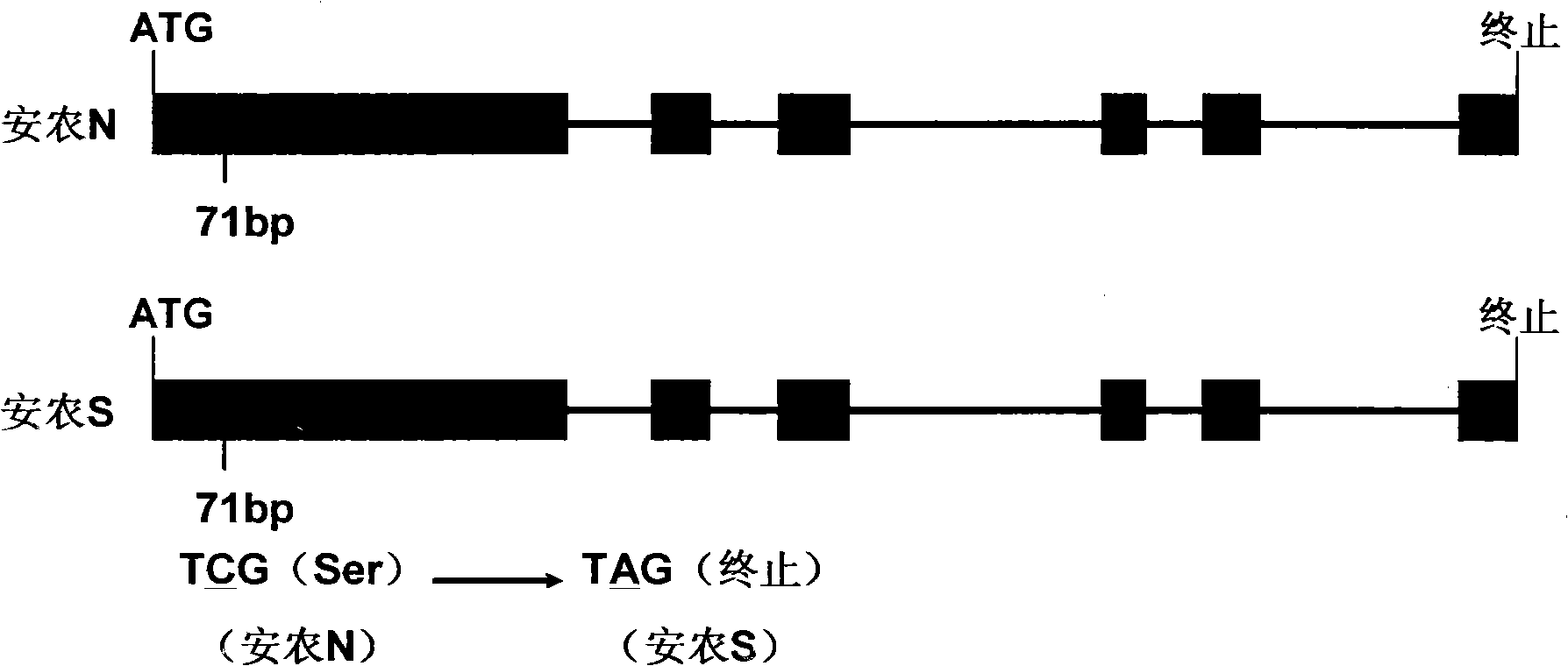
The invention discloses a thermo-sensitive male fertility gene and an application thereof and also discloses a genetic marker of the thermo-sensitive male fertility gene, and provides a protein coded by the thermo-sensitive male fertility gene and a carrier containing the thermo-sensitive male fertility gene and a recombinant microorganism. The invention also discloses the application of the thermo-sensitive male fertility gene in cultivating a thermo-sensitive male sterile line and an application of the genetic marker in rice breeding. The thermo-sensitive fertility gene TSSNR is acquired through the map-based cloning technique of Annong S-1 thermo-sensitive sterility gene locus tms5, functions of the gene are validated through transgene experiments, and the transgene technique of RNAi or antisense RNA or the over-expression dominant negative principle is provided, functions of the TSSRZ gene in normal rice varieties are incapable, so as to cultivate the thermo-sensitive male sterile line, and the application value is significant.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
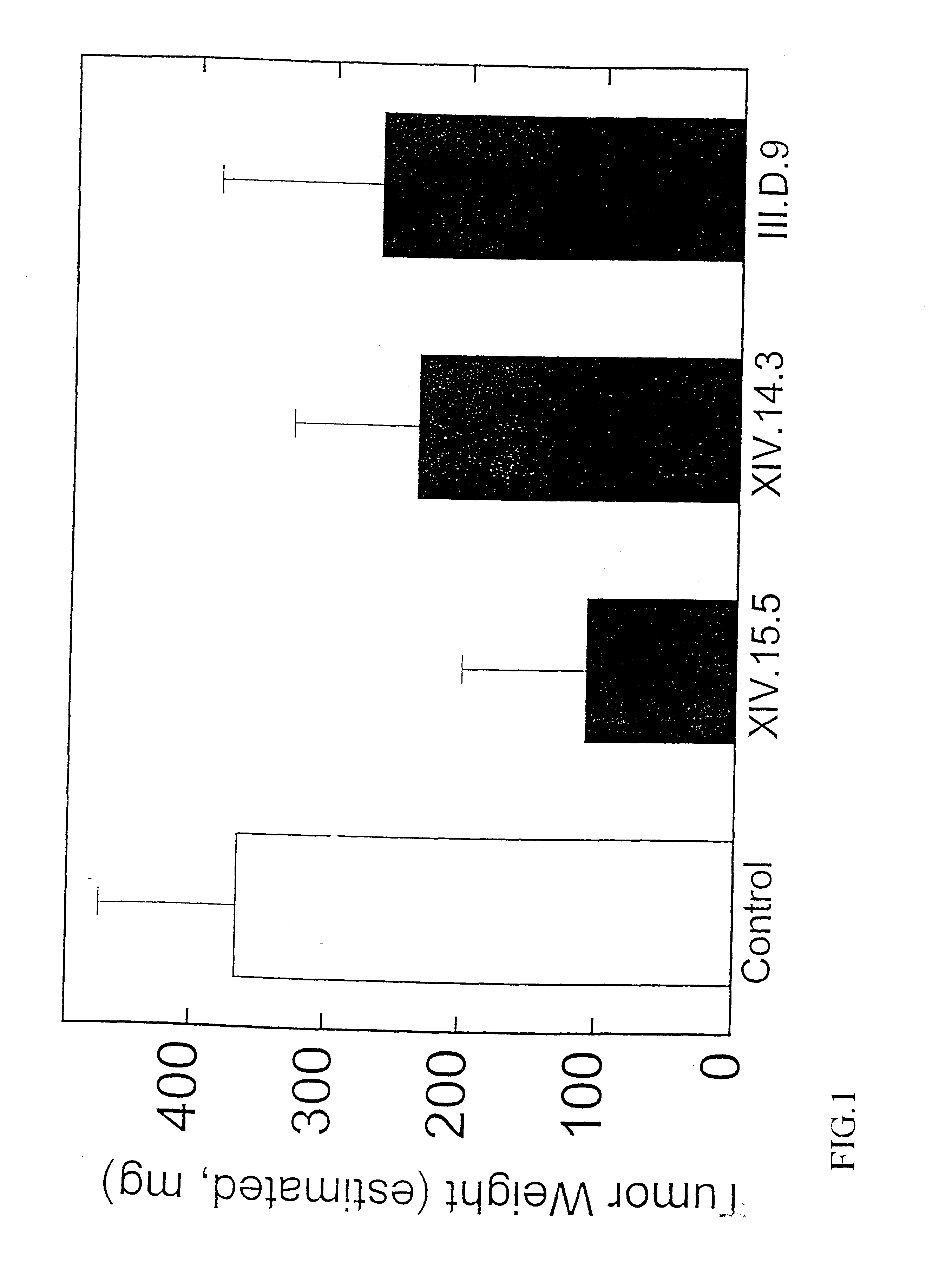
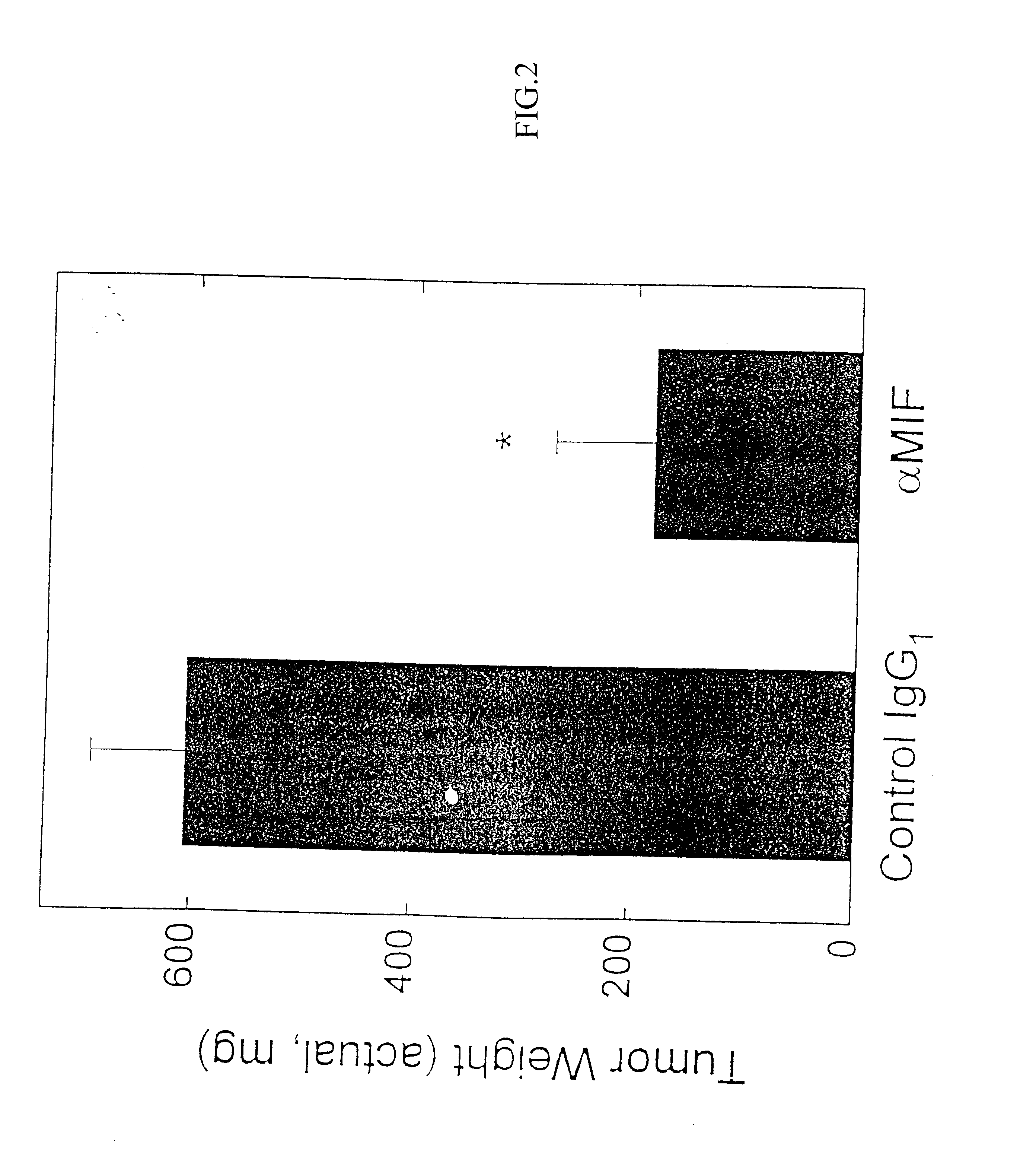
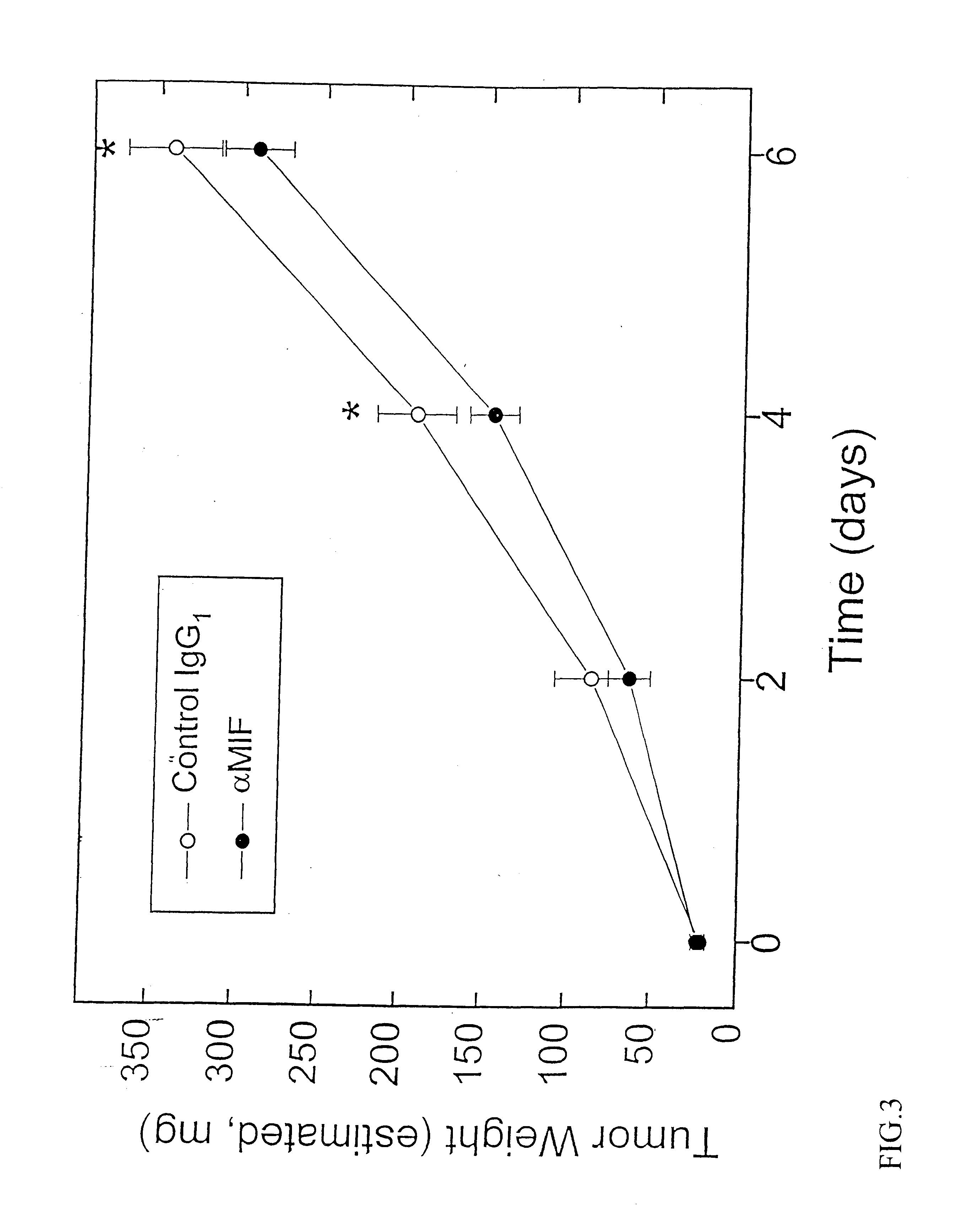
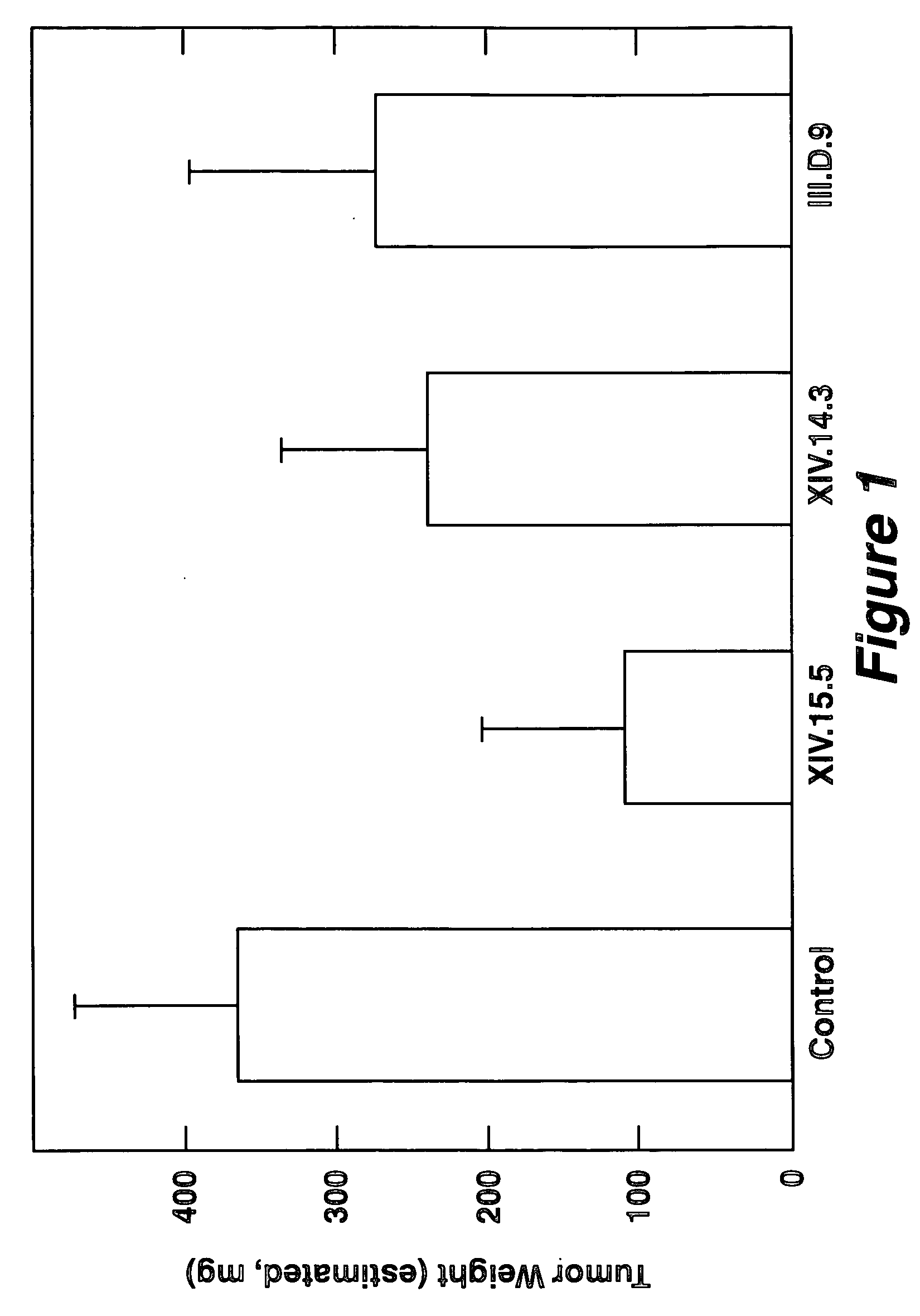
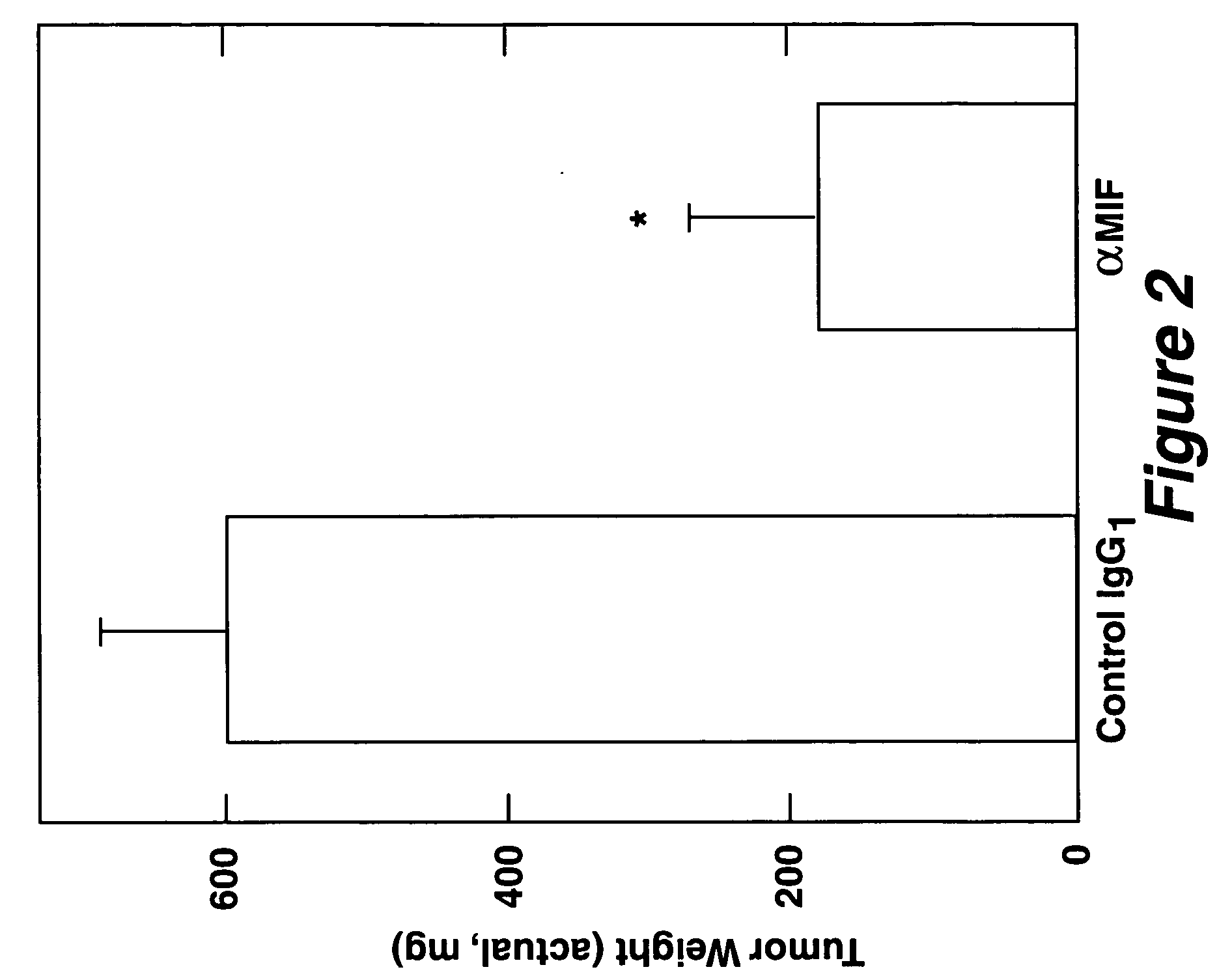
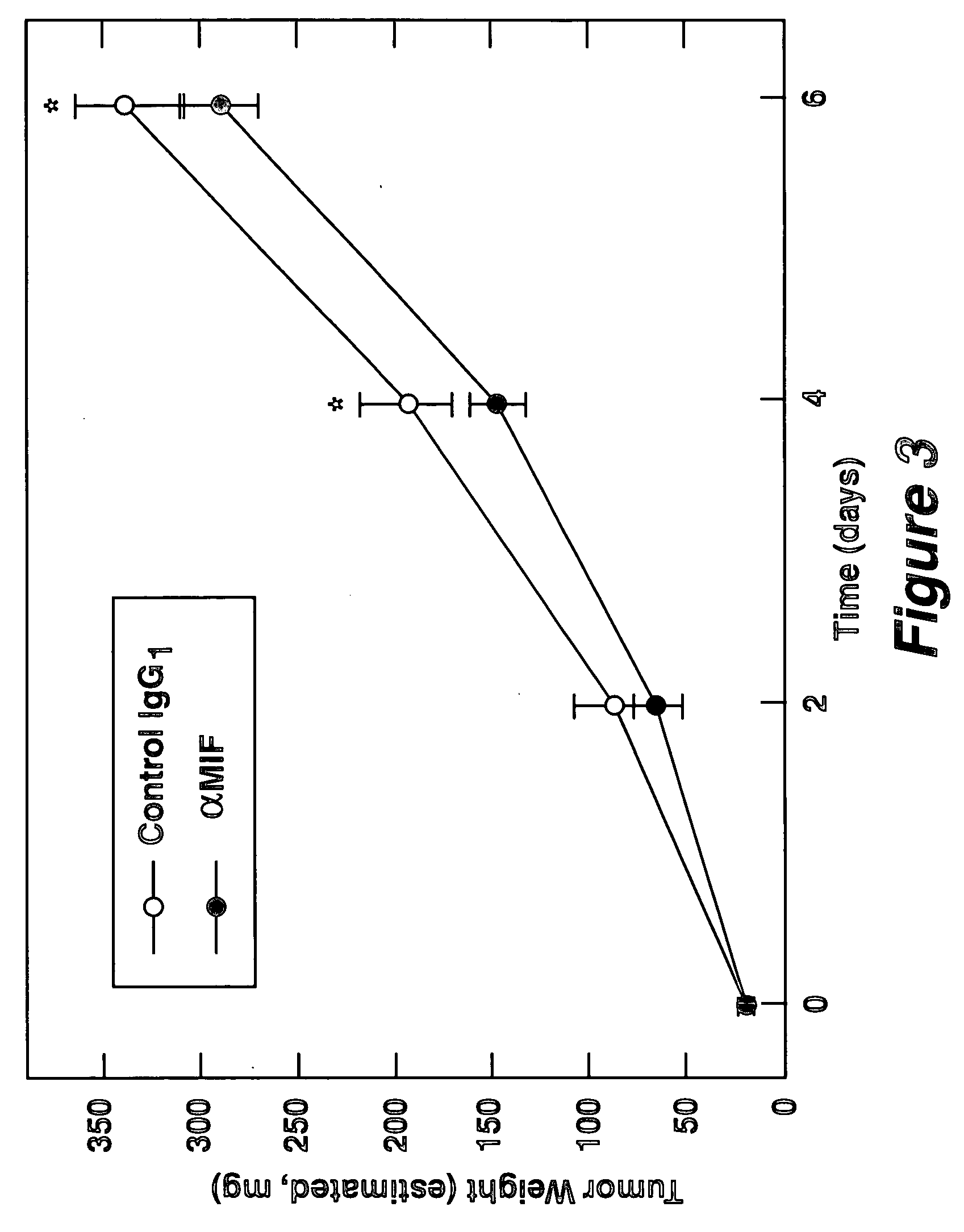
Therapeutic uses of factors which inhibit or neutralize MIF activity
InactiveUS6774227B1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntisense RNAMonoclonal antibody
The present invention relates to methods of treating disorders related to cellular overproliferation comprising neutralizing the production or activity of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF). The invention also relates to therapeutic compositions comprising factors which inhibit or neutralize MIF activity, such as, MIF antisense RNA molecules and MIF monoclonal antibodies and derivatives or analogs thereof. The invention further relates to the uses of such compositions and methods for the treatment of malignancies, including, but not limited to, B and T cell lymphomas.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
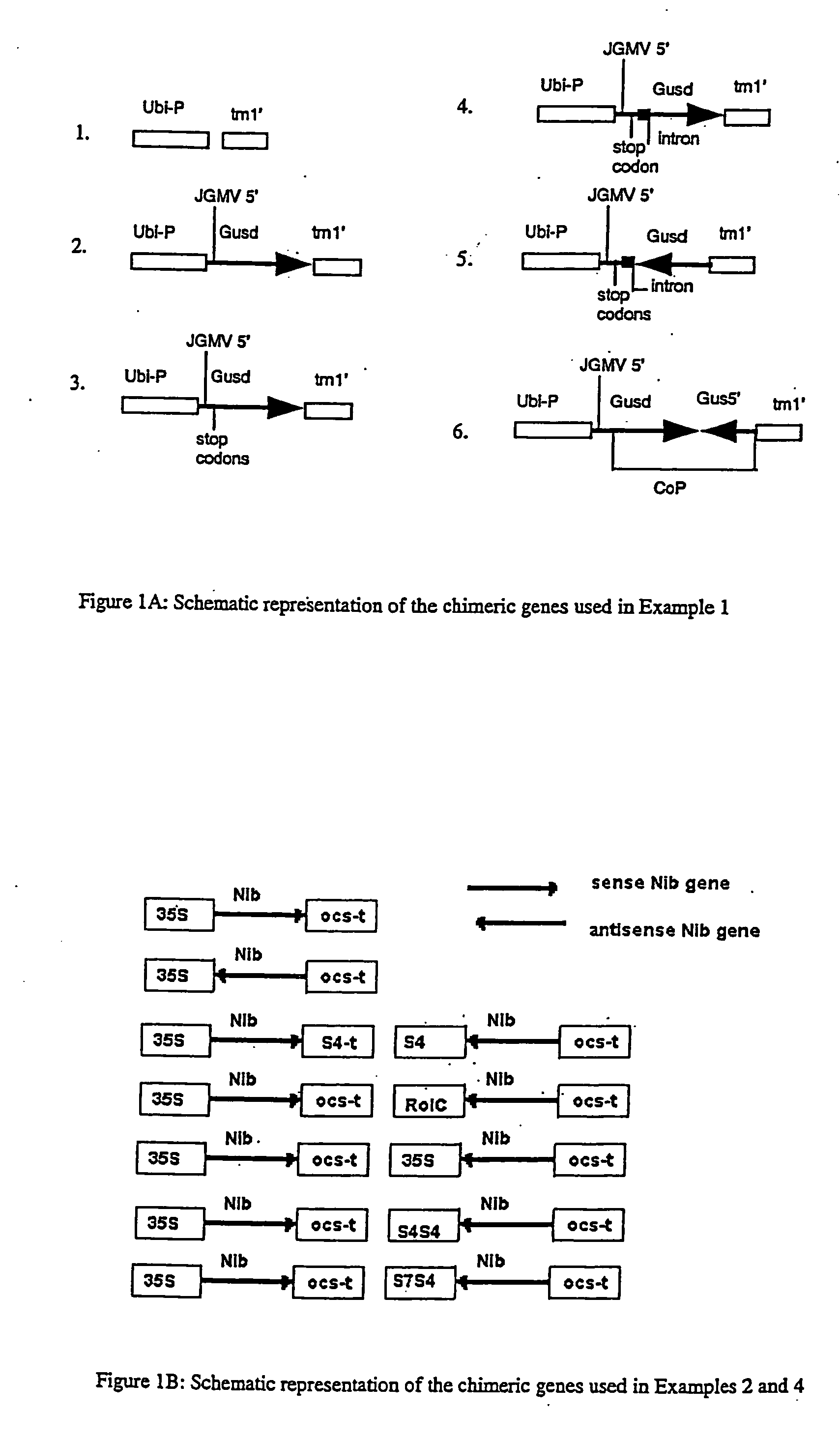
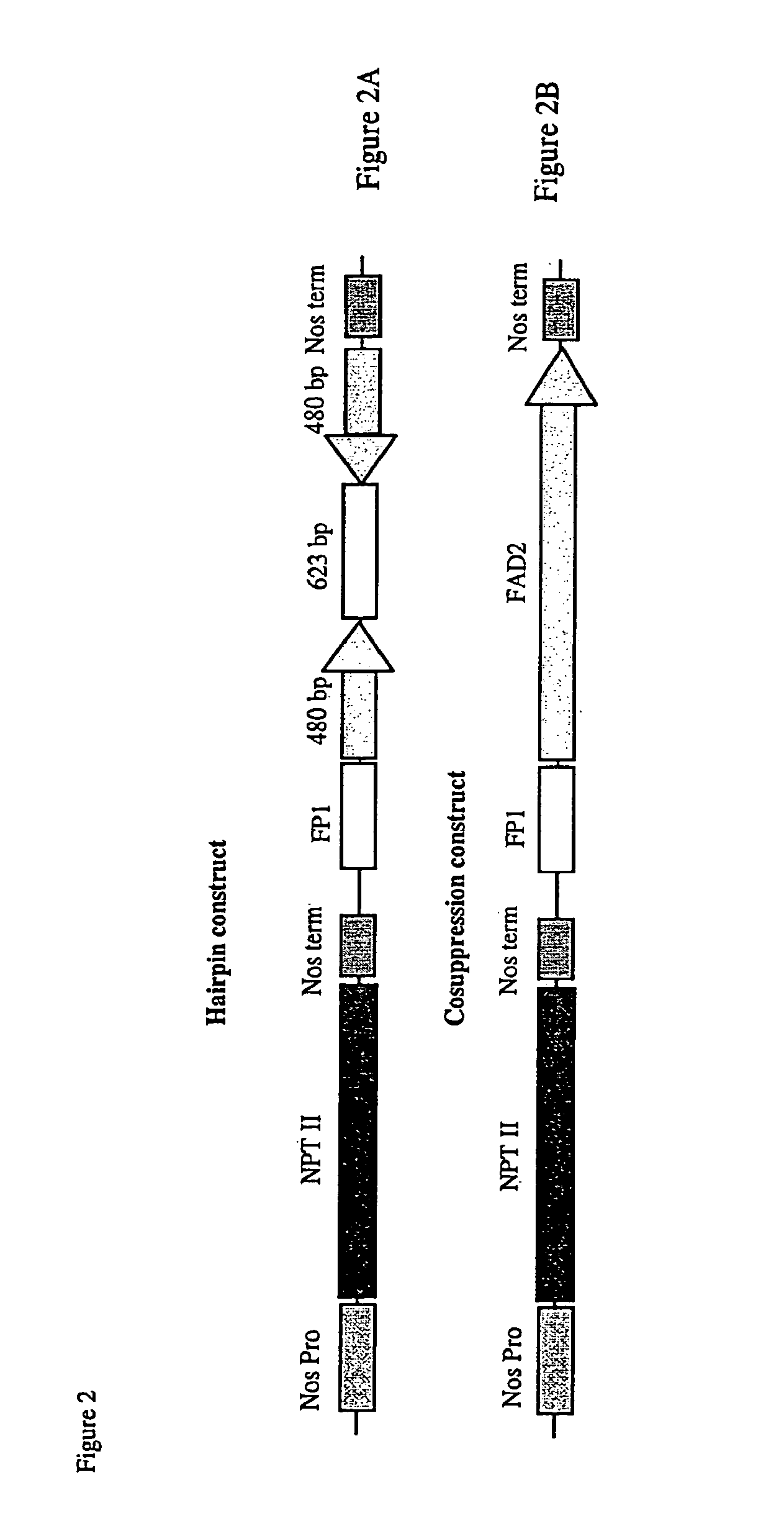
Methods and means for obtaining modified phenotypes
InactiveUS20060178335A1Reducing phenotypic expressionGenetic material ingredientsVector-based foreign material introductionEucaryotic cellAntisense RNA
Methods and means are provided for reducing the phenotypic expression of a nucleic acid of interest in eucaryotic cells, particularly in plant cells, by introducing chimeric genes encoding sense and antisense RNA molecules directed towards the target nucleic acid, which are capable of forming a double stranded RNA region by base-pairing between the regions with sense and antisense nucleotide sequence or by introducing the RNA molecules themselves. Preferably, the RNA molecules comprises simultaneously both sense and antisense nucleotide sequence.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Compositions and methods for therapeutic use
The present invention is directed to compositions and methods of treating cancer by gene therapy using a therapeutic gene formulated in a buffer comprising a delivery-enhancing agent. The delivery-enhancing agents of the invention can be used to formulate therapeutic or diagnostic agents, such as proteins, nucleic acids, antisense RNA, small molecules, etc., for administration to any tissue or organ having an epithelial membrane. The delivery-enhancing agents include detergents, alcohols, surfactants and other molecules.
Owner:CANJI +1
Cells to be used in producing virus vector, process for producing the same, and process for producing virus vector with the use of the cells
InactiveUS20040043490A1High potencySolve the complicated productionGenetically modified cellsClimate change adaptationAntisense RNAAntisense gene
It is intended to establish a novel cell line for efficiently producing a virus vector without resort to any troublesome operations and provide a process for producing a virus vector having a high titer with the use of the cell line. Namely, cells to be used in producing a virus vector having an antisense gene been transferred thereinto are provided, wherein the gene expresses an antisense RNA against the whole or partial sequence of a sense RNA expressed by a gene encoding a cytotoxic polypeptide.
Owner:HISAMITSU PHARM CO INC
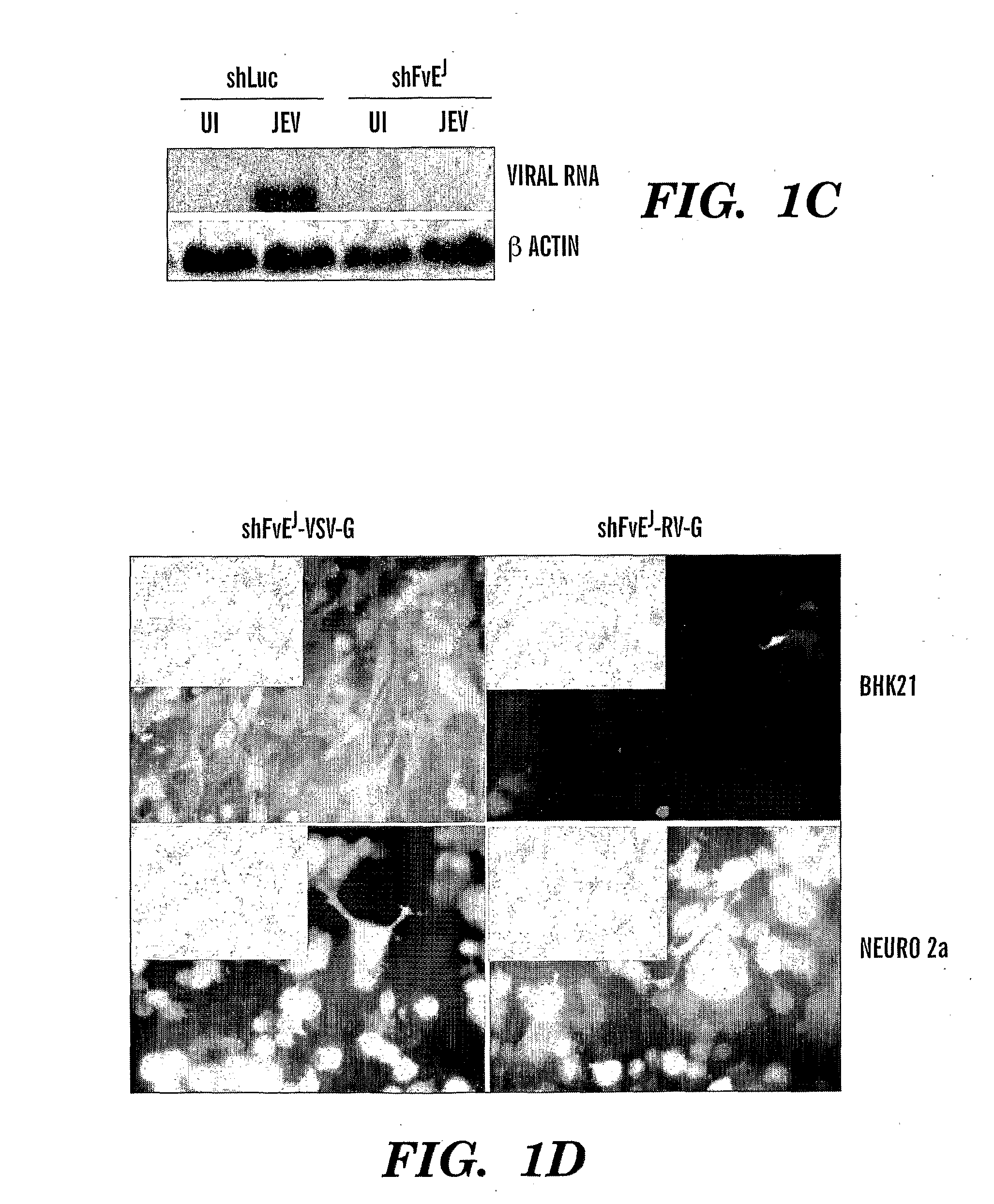
Method to Treat Flavivirus Infection with siRNA
InactiveUS20090047338A1Avoid infectionInhibit expressionOrganic active ingredientsSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntisense RNADisease
The present invention is directed to methods of treating flavivirus mediated diseases using siRNAs. The invention is based upon our findings in a mouse model that siRNAs directed against sequences conserved among multiple flaviviruses prevents and treats flavivirus infections. Accordingly, the present invention provides an isolated siRNA comprising a sense RNA and an antisense RNA strand or a single strand. The sense and the antisense RNA strands, or the single RNA strand, form an RNA duplex, and wherein the RNA strand comprises a nucleotide sequence identical to a target sequence of about 15 to about 30 contiguous nucleotides in flavivirus mRNA or mutant or variant thereof.
Owner:IMMUNE DISEASE INST INC
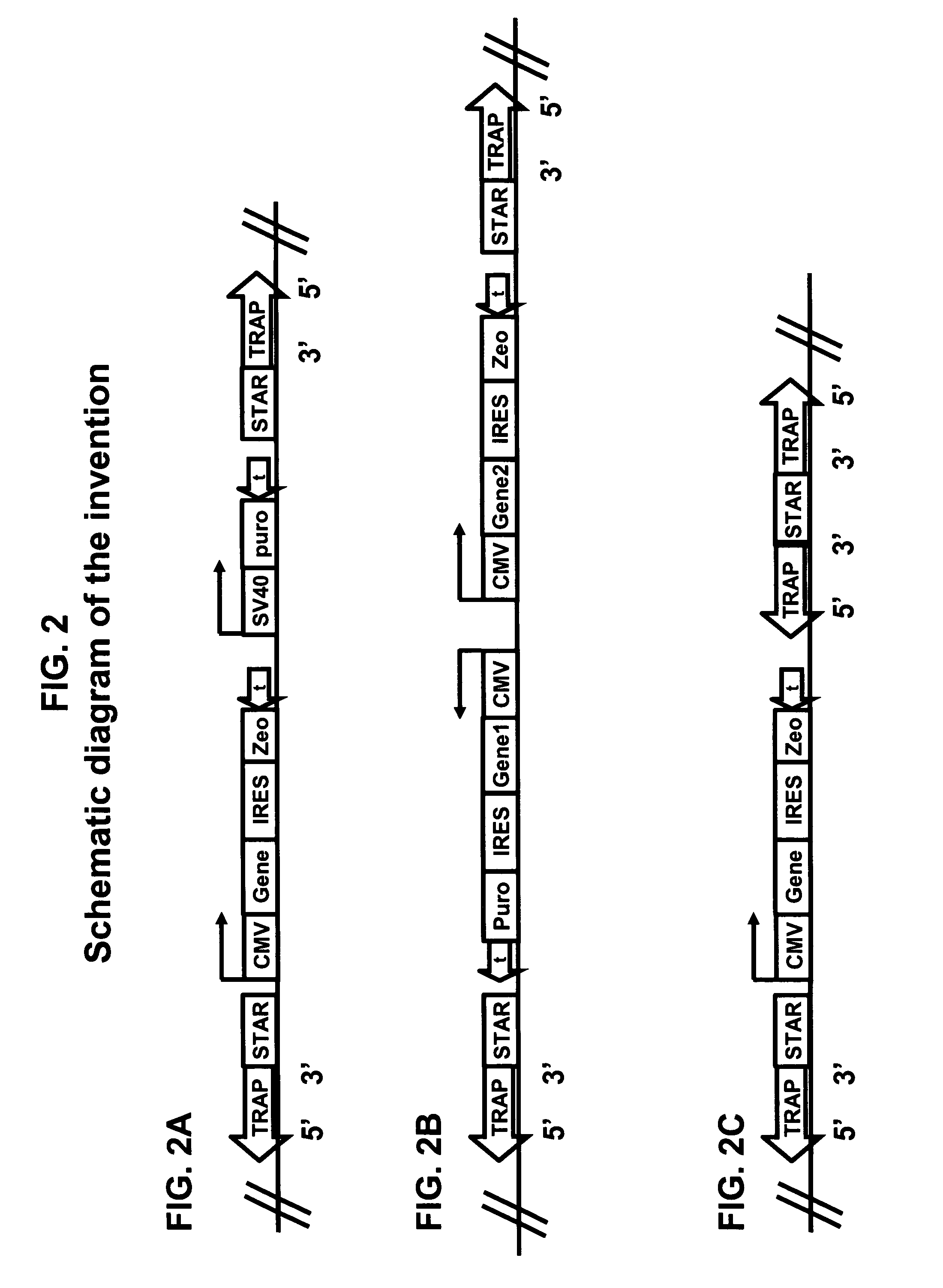
Method for improving protein production
ActiveUS20060010506A1Improve featuresStable transcriptionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAntisense RNAOpen reading frame
The present invention relates to the production of proteins in a cell or host cell. The invention uses a TRAnscription Pause (TRAP) sequence to enhance a protein expression characteristic of a protein expression unit. The TRAP sequence is thought to prevent, at least in part, formation of antisense RNA or to, at least in part, prevent transcription to enter the protein expression unit. In one embodiment, the invention provides a method for expression of at least one protein of interest in a cell comprising providing the cell with at least one protein expression unit that comprises a promoter functionally linked to an open reading frame encoding at least one protein of interest, characterized in that the protein expression unit further comprises at least one TRAP sequence and wherein the TRAP sequence is functionally located downstream of the open reading frame and at least in part prevents formation of antisense RNA. In another embodiment, the TRAP sequence is functionally located upstream of the promoter and at least in part prevents transcription to enter the expression unit. Preferably, the expression protein unit further comprises at least one STabilizing Anti-Repressor sequence.
Owner:CHROMAGENICS BV
Methods and means for obtaining modified phenotypes
InactiveUS20070078105A1Reducing phenotypic expressionGenetic material ingredientsGenetic engineeringEucaryotic cellAntisense RNA
Methods and means are provided for reducing the phenotypic expression of a nucleic acid of interest in eucaryotic cells, particularly in plant cells, by introducing chimeric genes encoding sense and antisense RNA molecules directed towards the target nucleic acid, which are capable of forming a double stranded RNA region by base-pairing between the regions with sense and antisense nucleotide sequence or by introducing the RNA molecules themselves. Preferably, the RNA molecules comprises simultaneously both sense and antisense nucleotide sequence.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Enhancement of the immune response for vaccine and gene therapy applications
Expression cassettes are provided comprising a promoter operably linked to a nucleic acid molecule which, when transcribed in vivo, forms double-stranded RNA that induces the production of interferon. Expression cassettes also are provided comprising a promoter operably linked to a ribozyme or antisense nucleic acid molecule which, when transcribed in vivo, forms a ribozyme or antisense RNA molecule that stimulates an immune response. In addition, expression cassettes are provided comprising a promoter operably linked to a ribozyme or antisense nucleic acid molecule which, when transcribed in vivo, stimulates apoptosis. Finally, gene delivery vectors are provided which contain such expression cassettes, host cells containing the gene delivery vectors, and methods of utilizing the expression cassettes, gene delivery vectors, and host cells.
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
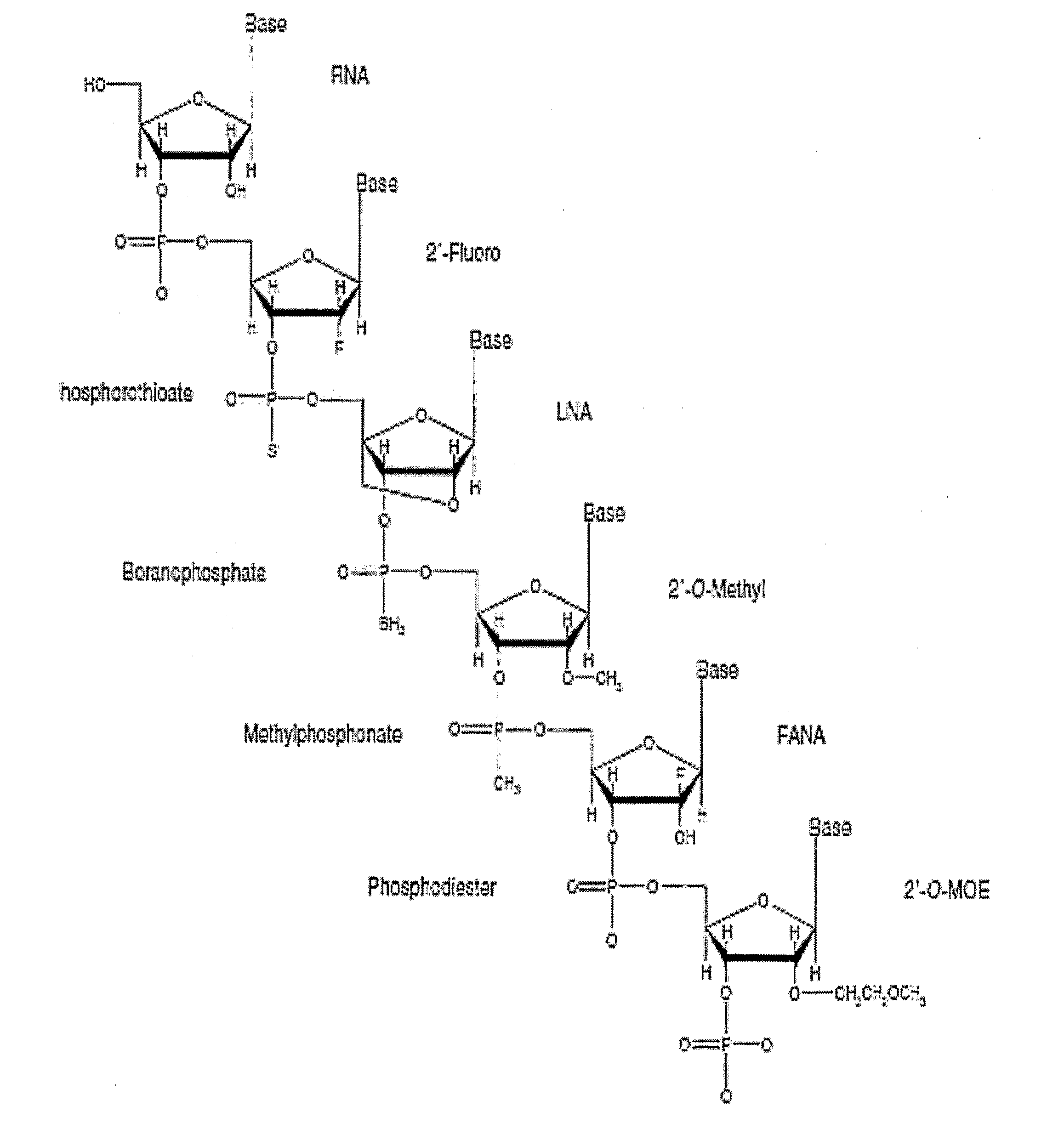
Nucleic acid molecules inducing RNA interference, and uses thereof
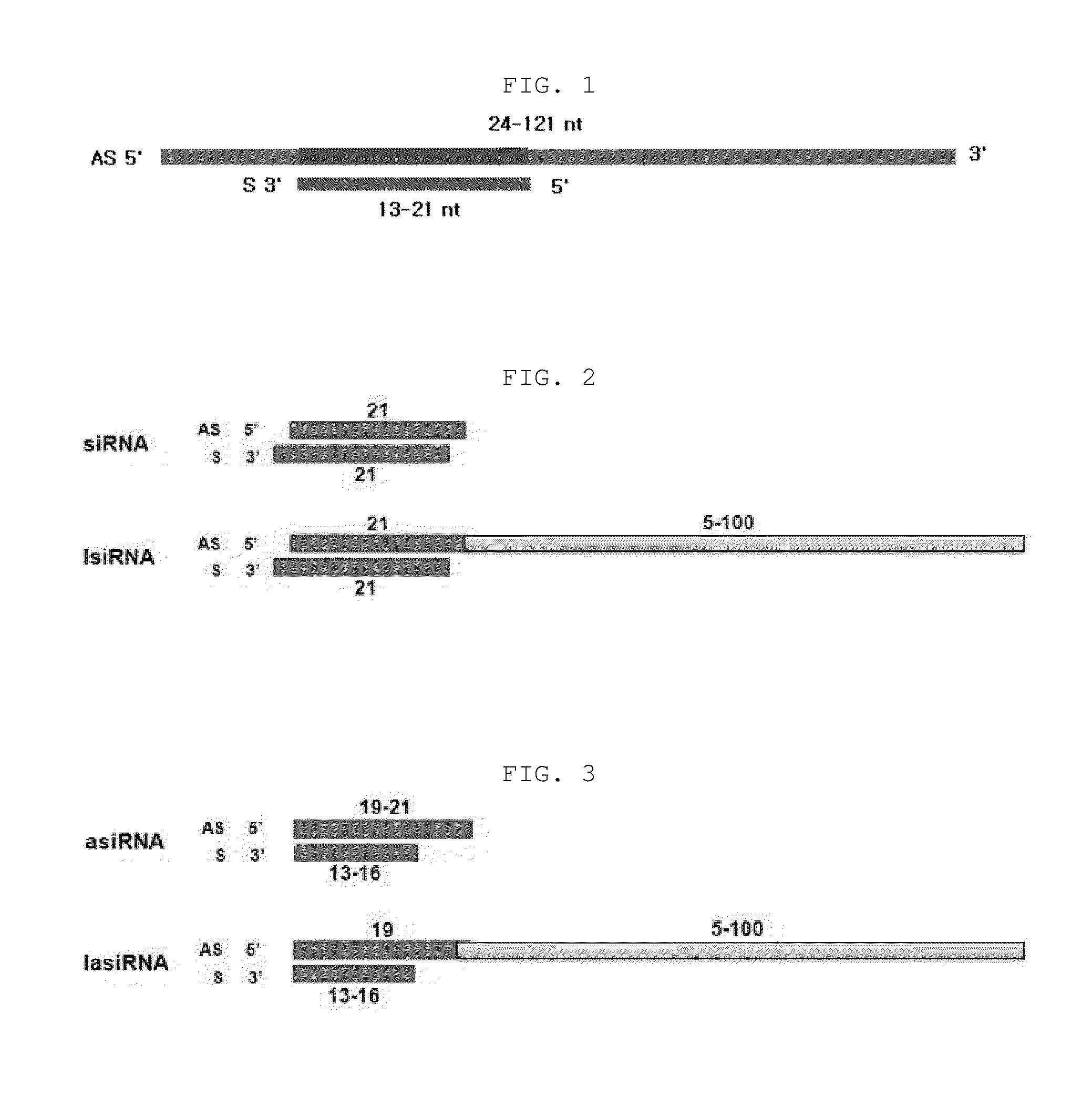
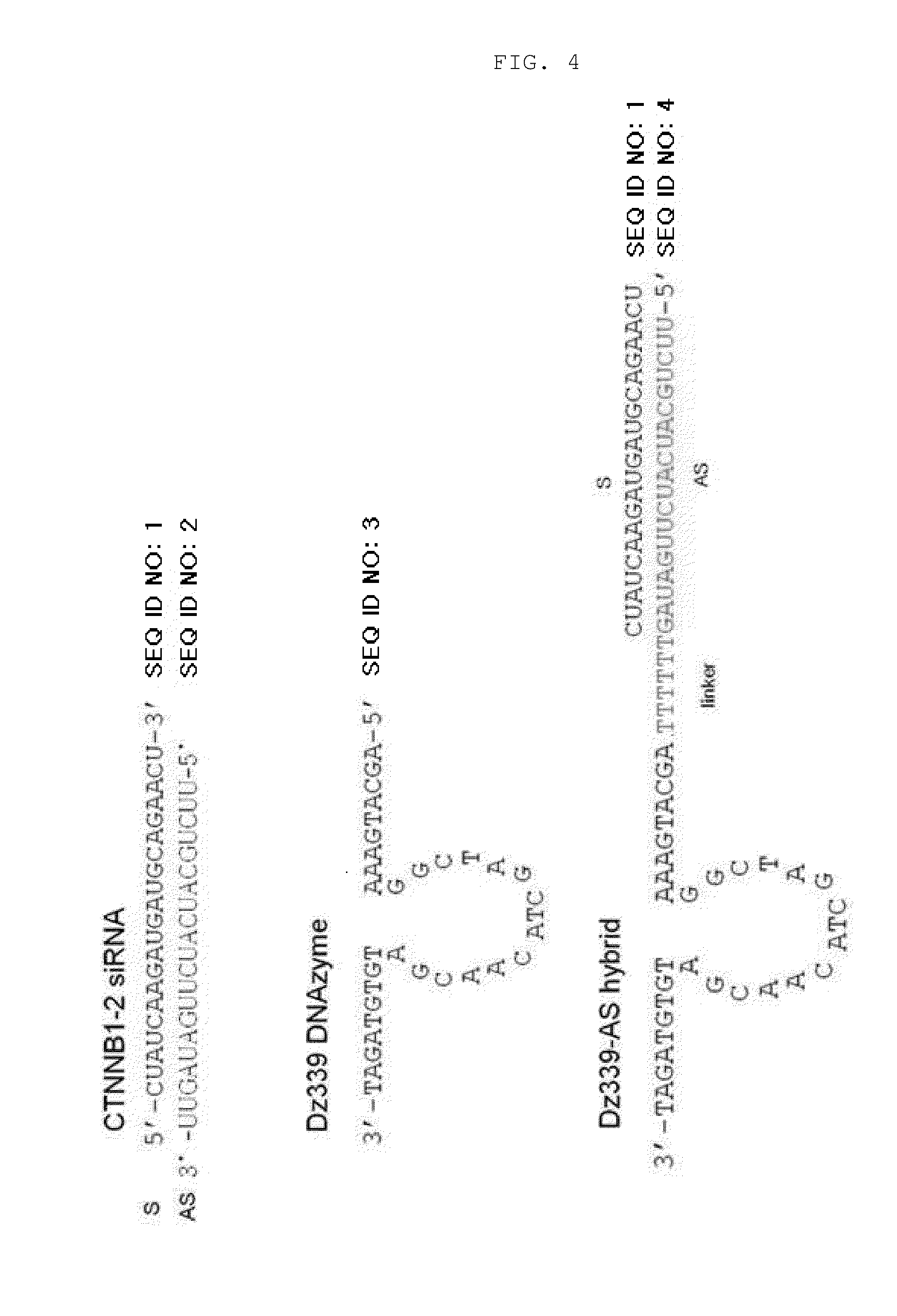
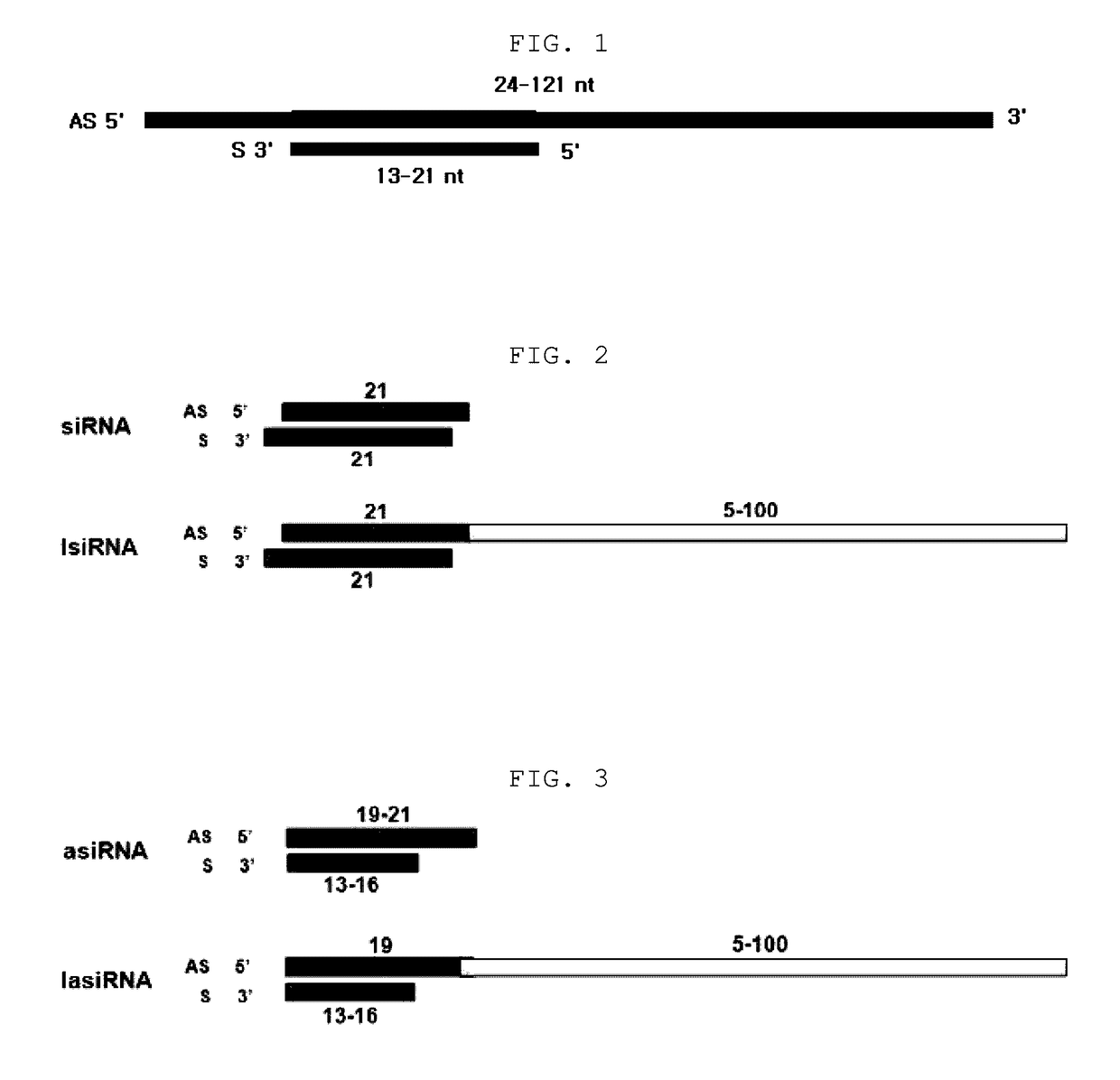
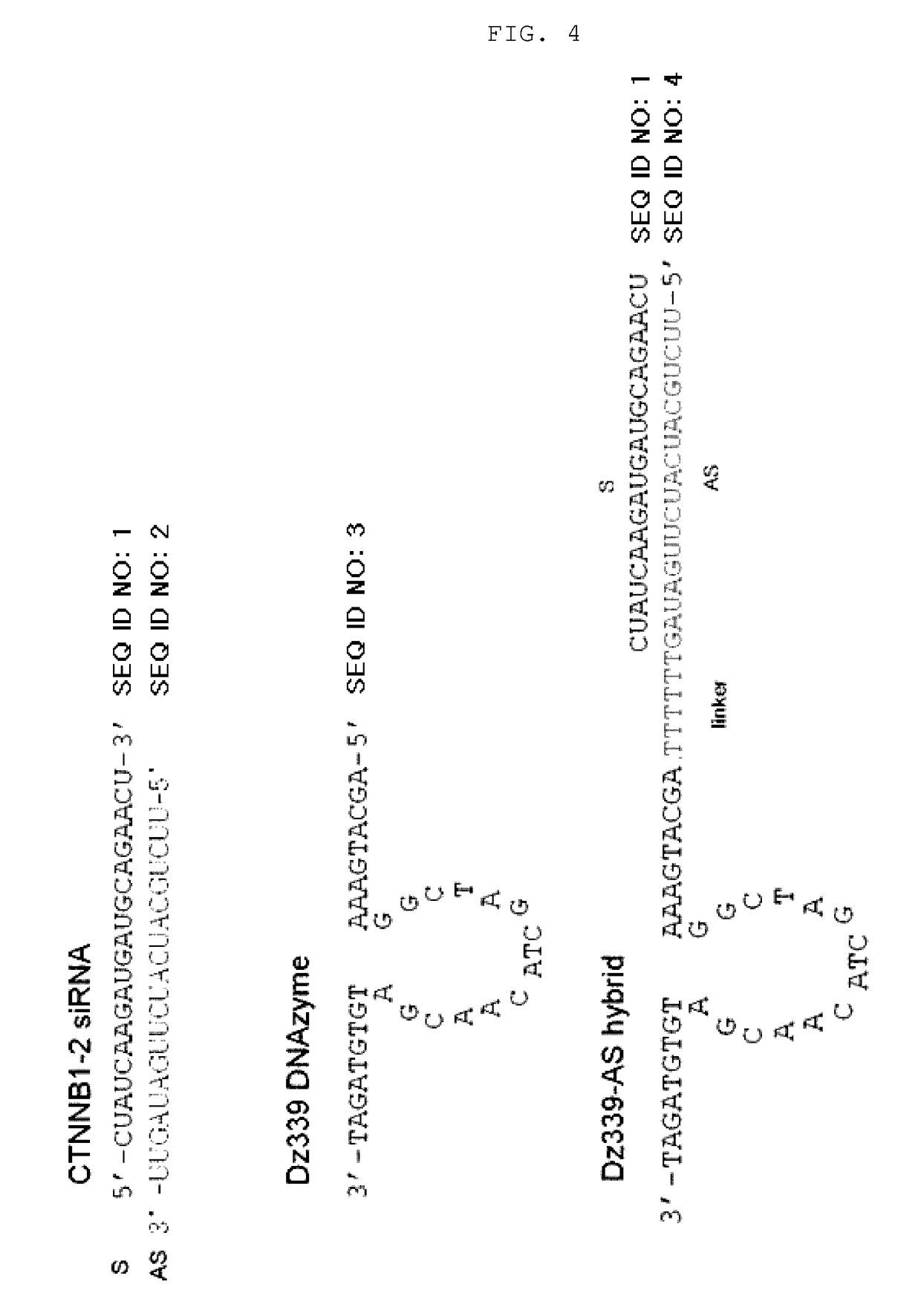
ActiveUS20130273657A1Novel structureGood effectOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAntisense RNAAntisense DNA
The present invention relates to an RNAi-inducing nucleic acid molecule having a new structure and the use thereof, and more particularly to a novel nucleic acid molecule having a structure comprising a first strand, which is 24-121 nt in length and comprises a region complementary to a target nucleic acid, and a second strand which is 13-21 nt in length and has a region that binds complementarily to the region of the first strand, which is complementary to the target nucleic acid, so that the nucleic acid molecule inhibits the expression of a target gene with increased efficiency, and to a method of inhibiting the expression of a target gene using the nucleic acid molecule. The nucleic acid molecule structure of the present invention increases the efficiency with which the nucleic acid molecule inhibits the target gene. Alternatively, the nucleic acid molecule of the present invention can either increase the ability of the siRNA to bind to the target gene or cause synergistic cleavage, by introduction of antisense DNA, antisense RNA, ribozyme or DNAzyme, thereby increasing the efficiency with which the nucleic acid molecule inhibits the target gene. In addition, when the nucleic acid molecule according to the present invention is used, the efficiency with which the target gene is inhibited can be maintained for an extended period of time. Accordingly, the RNAi-inducing nucleic acid molecule of the present invention can be effectively used for the treatment of cancer or viral infection in place of conventional siRNA molecules.
Owner:OLIX PHARMA
Methods and means for obtaining modified phenotypes
InactiveUS20080104732A1Microbiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesEucaryotic cellAntisense RNA
Methods and means are provided for reducing the phenotypic expression of a nucleic acid of interest in eucaryotic cells, particularly in plant cells, by introducing chimeric genes encoding sense and antisense RNA molecules directed towards the target nucleic acid, which are capable of forming a double stranded RNA region by base-pairing between the regions with sense and antisense nucleotide sequence or by introducing the RNA molecules themselves. Preferably, the RNA molecules comprises simultaneously both sense and antisense nucleotide sequence.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Method for conferring resistance or tolerance aganist furovirus, potyvirus, tospovirus, and cucomovirus to plant cells
InactiveUS7019195B1Reduce sensitivityAccumulation and reduced and preventedStable introduction of DNAFermentationAntisense RNAPotyvirus
The present invention relates to a method to confer resistance or tolerance to more than one virus from the group consisting of furovirus, potyvirus, tospovirus, and cucomovirus, using sense and antisense RNA fragments of a sequence from their genomes. The sense and antisense RNA fragments are capable of pairing and forming a double-stranded RNA molecule, thereby reducing expression of the viral genome.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Method for acquiring transgenic gramineae farm crop capable of being selectively eliminated
InactiveCN101205537AAvoid spreadingAvoid mixingClimate change adaptationVector-based foreign material introductionAntisense RNASulfonylurea
The invention provides an acquisition method for transgenic gramineous crops capable of being selectively perished, comprising the following steps: when target genes are expressed, expression of genes participating in herbicide detoxification in the transgenic gramineous crops is inhibited by utilization of antisense RNA or RNAi means, and the transgenic gramineous crops capable of being selectively perished are obtained. The invention mainly has the advantages that: the transgenic gramineous crops acquired by utilization of the method can be selectively perished by Bentazon or sulphuryl carbamide herbicide as required, thereby transmission of the transgenic gramineous crops and interfusion to non-transgenic gramineous crops are prevented, and the method has great significance in transgenic crop research later on.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Cellulose digesting enzyme gene and utilization of the gene
InactiveUS20050181485A1Controlling in paper strengthReduce yieldFungiOxidoreductasesCelluloseAntisense RNA
A method for treating woodchips, comprising the steps of: preparing a DNA encoding an antisense RNA substantially complementary to the whole or a part of a transcription product of a cellulolytic enzyme gene derived from Basidiomycete; preparing a vector comprising (a) the above DNA, or (b) a recombinant DNA comprising the above DNA and a DNA fragment having a promoter activity, wherein the above DNA binds to the above DNA fragment such that an antisense RNA of the cellulolytic enzyme gene is generated as a result of transcription; transforming host cells with the above vector, so as to prepare the host cells having a suppressed cellulolytic enzyme activity; and inoculating the above host cells having a suppressed cellulolytic enzyme activity into woodchips to treat them.
Owner:OJI PAPER CO LTD
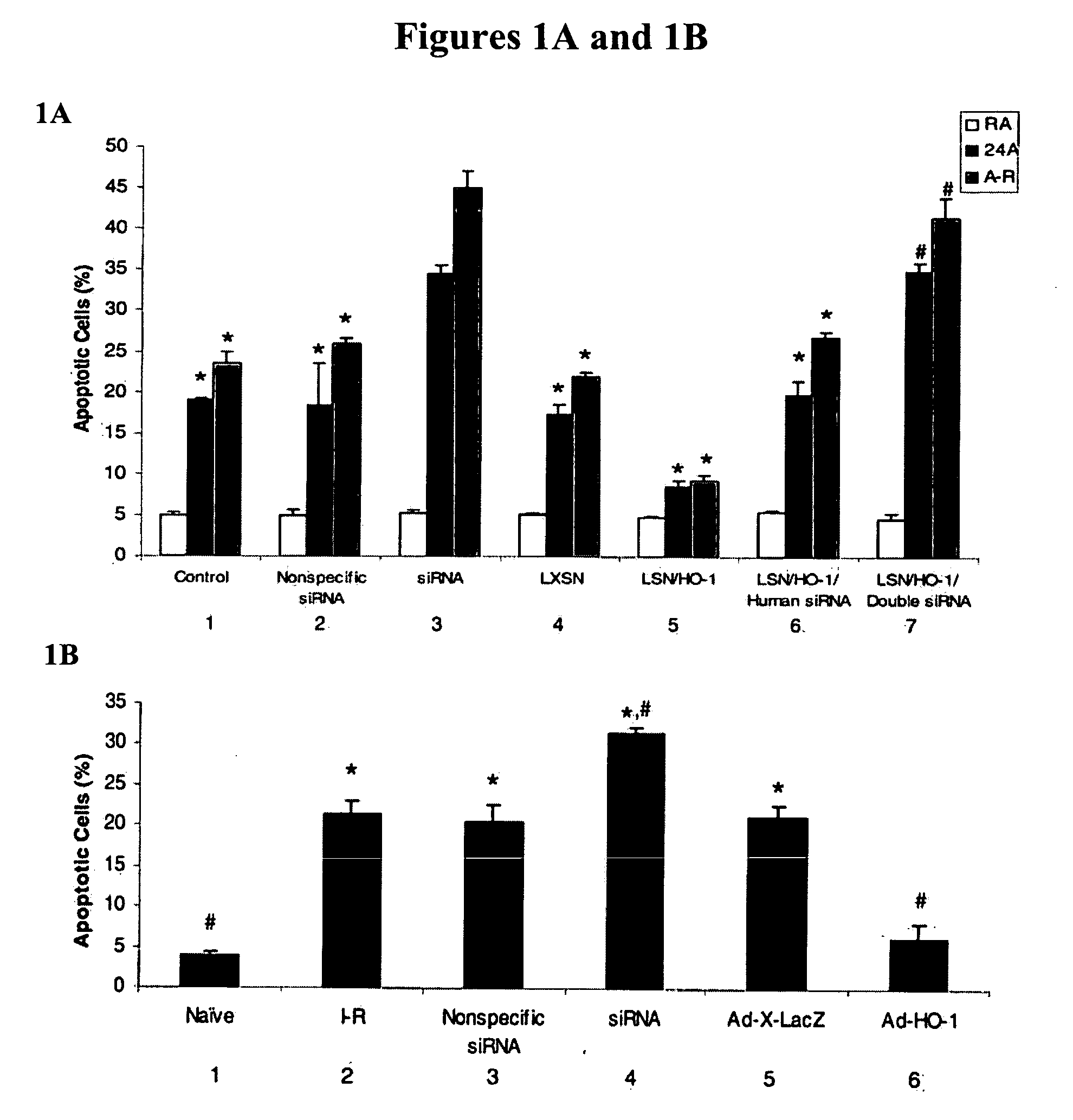
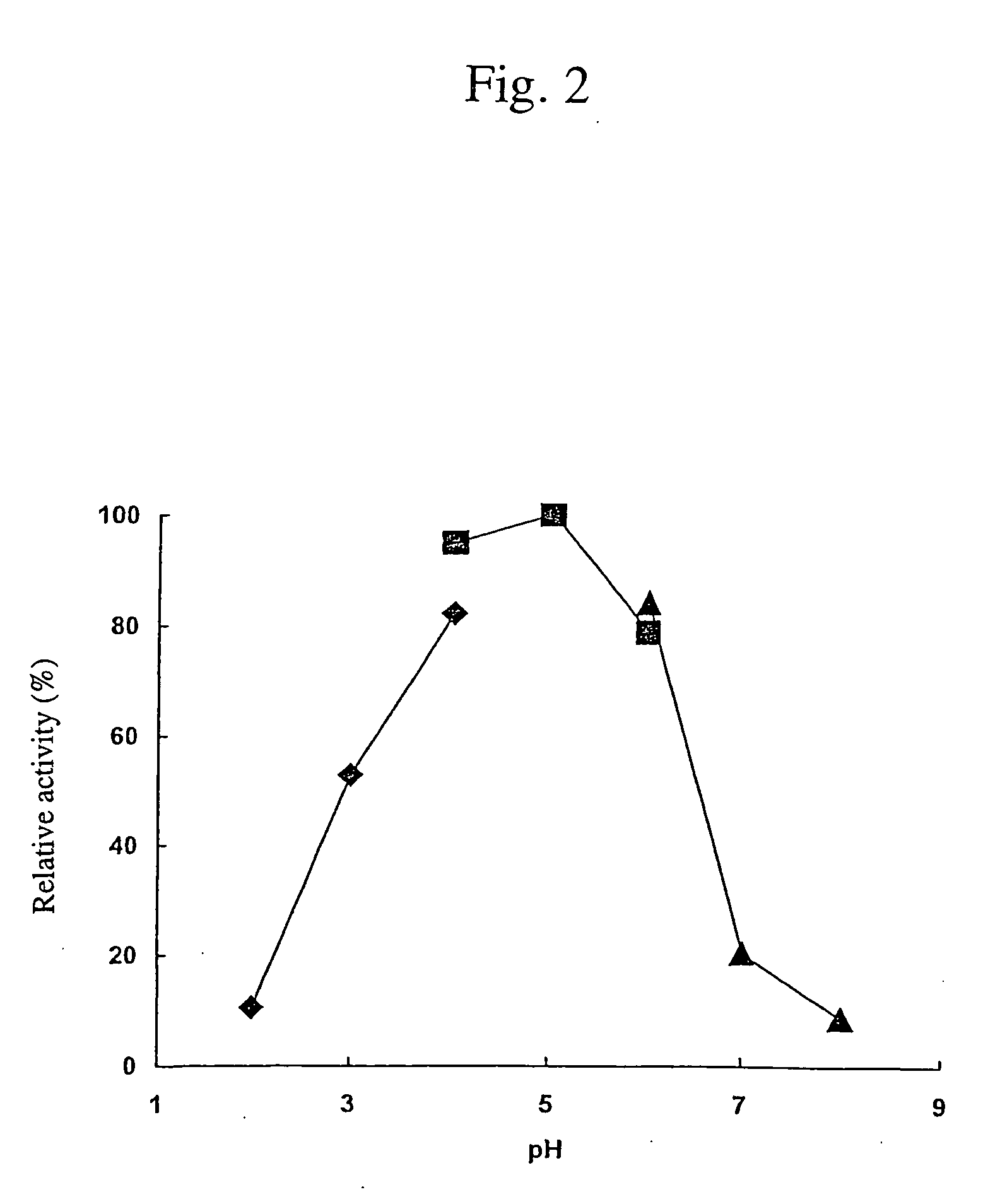
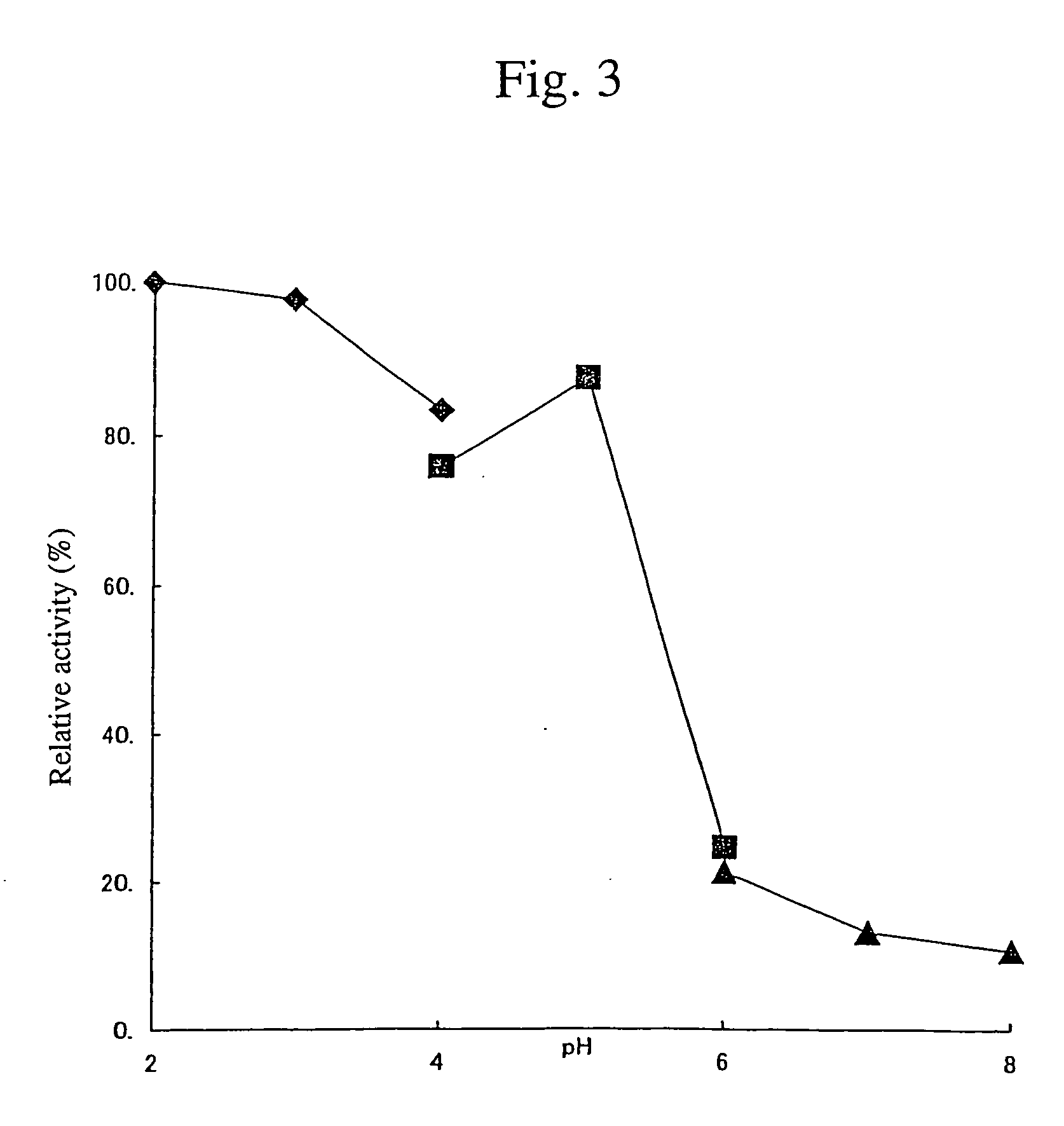
Use of miRNA-34a
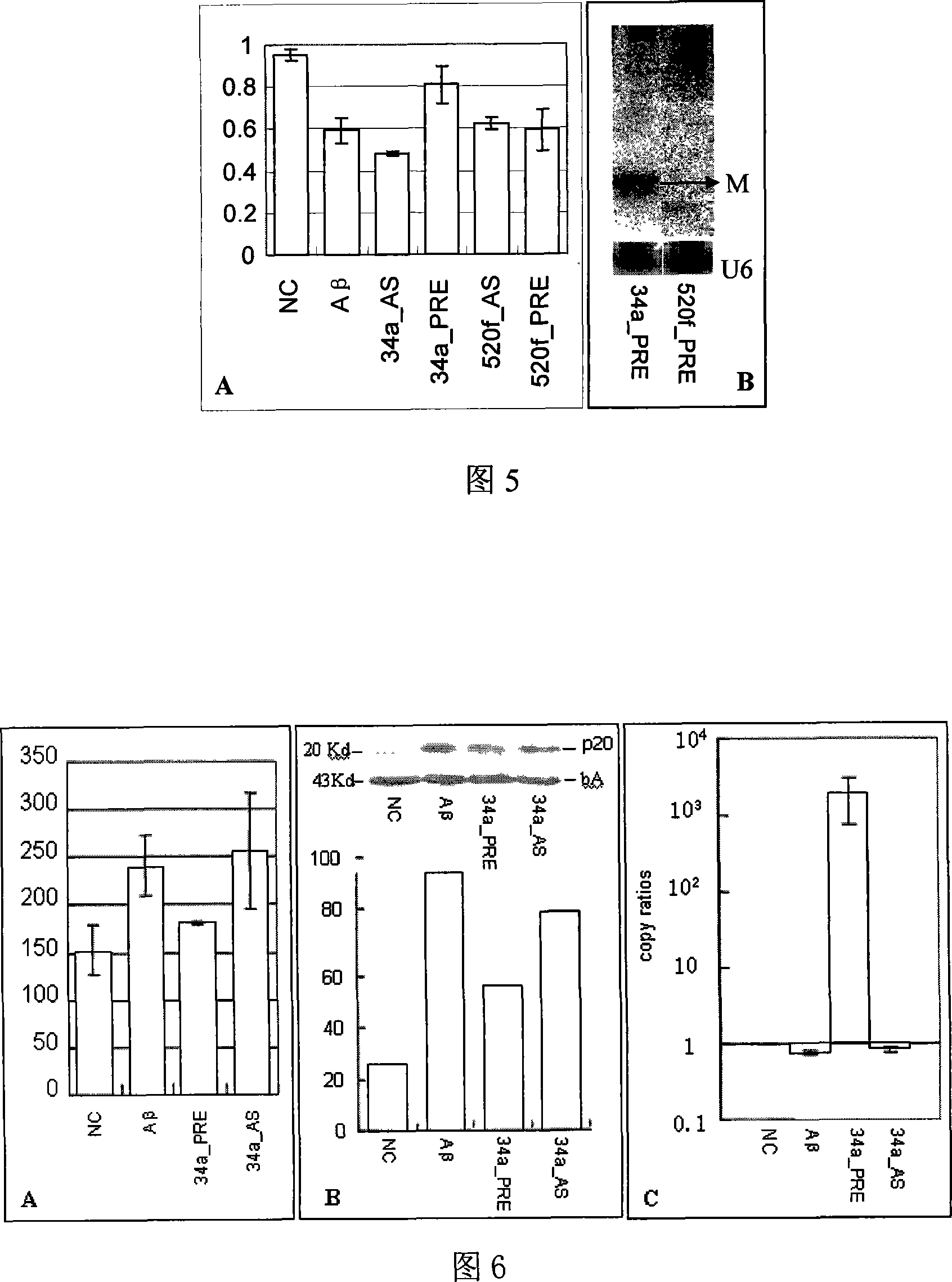
The present invention relates to use of small RNA molecule, is especially use of miRNA-34a, and belongs to the field of biomedicine material technology. By means of Northern process and other process, miRNA-34a is determined to be the age related expression, and by means of the contrast to the prefrontal lobe cortical tissue miRNA' s of rats in different age sections, it is found that the expression of miRNA-34a in the pallium of rhesus and the prefrontal lobe cortex of rat exhibits age dependent change. The present invention establishes a rat neuron AD cell model for the research of possible action mechanism of miRNA-34a. By means of further transfecting miRNA-34a precursor, miRNA-34a antisense RNA and other contrasts, it is found that miRNA-34a possesses neuron apoptosis effect of antagonizing A-beta induction.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV +1
Methods and means for producing barley yellow dwarf virus resistant cereal plants
InactiveUS20020169298A1Easy to identifySsRNA viruses positive-senseSugar derivativesAntisense RNAA-DNA
The invention relates to methods for producing transgenic cereal plants resistant to Barley Yellow Dwarf Virus, particularly in the presence of co-infecting Cereal Yellow Dwarf Virus, by stably integrating into the cells of the transgenic plant a chimeric gene comprising a DNA region operably linked to plant expressible promoter in such a way that the RNA molecule may be transcribed from the DNA region, the RNA molecule comprising both sense and antisense RNA capable of pairing and forming a double stranded RNA molecule or hairpin RNA.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Therapeutic uses of factors which inhibit or neutralize MIF activity
InactiveUS20040156848A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntisense RNAMonoclonal antibody
The present invention relates to methods of treating disorders related to cellular overproliferation comprising neutralizing the production or activity of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF). The invention also relates to therapeutic compositions comprising factors which inhibit or neutralize MIF activity, such as, MIF antisense RNA molecules and MIF monoclonal antibodies and derivatives or analogs thereof. The invention further relates to the uses of such compositions and methods for the treatment of malignancies, including, but not limited to, B and T cell lymphomas.
Owner:CYTOKINE PHARMASCI
Mrna Transfected Antigen Presenting Cells
A method of amplifying RNA to obtain RNA molecules that are predominantly in the sense orientation and essentially devoid of RNA molecules that are in the anti-sense orientation. A method of transfecting antigen presenting cells with a composition comprising sense RNA encoding immunogenic antigens and essentially devoid of antisense RNA and dsRNA is also provided as well as dendritic cells prepared according to the method.
Owner:ARGOS THERAPEUTICS INC
Nucleic acid molecules inducing RNA interference, and uses thereof
ActiveUS9637742B2Good effectNovel structureOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAntisense DNAAntisense RNA
The present invention relates to an RNAi-inducing nucleic acid molecule having a new structure and the use thereof, and more particularly to a novel nucleic acid molecule having a structure comprising a first strand, which is 24-121 nt in length and comprises a region complementary to a target nucleic acid, and a second strand which is 13-21 nt in length and has a region that binds complementarily to the region of the first strand, which is complementary to the target nucleic acid, so that the nucleic acid molecule inhibits the expression of a target gene with increased efficiency, and to a method of inhibiting the expression of a target gene using the nucleic acid molecule. The nucleic acid molecule structure of the present invention increases the efficiency with which the nucleic acid molecule inhibits the target gene. Alternatively, the nucleic acid molecule of the present invention can either increase the ability of the siRNA to bind to the target gene or cause synergistic cleavage, by introduction of antisense DNA, antisense RNA, ribozyme or DNAzyme, thereby increasing the efficiency with which the nucleic acid molecule inhibits the target gene. In addition, when the nucleic acid molecule according to the present invention is used, the efficiency with which the target gene is inhibited can be maintained for an extended period of time. Accordingly, the RNAi-inducing nucleic acid molecule of the present invention can be effectively used for the treatment of cancer or viral infection in place of conventional siRNA molecules.
Owner:OLIX PHARMA
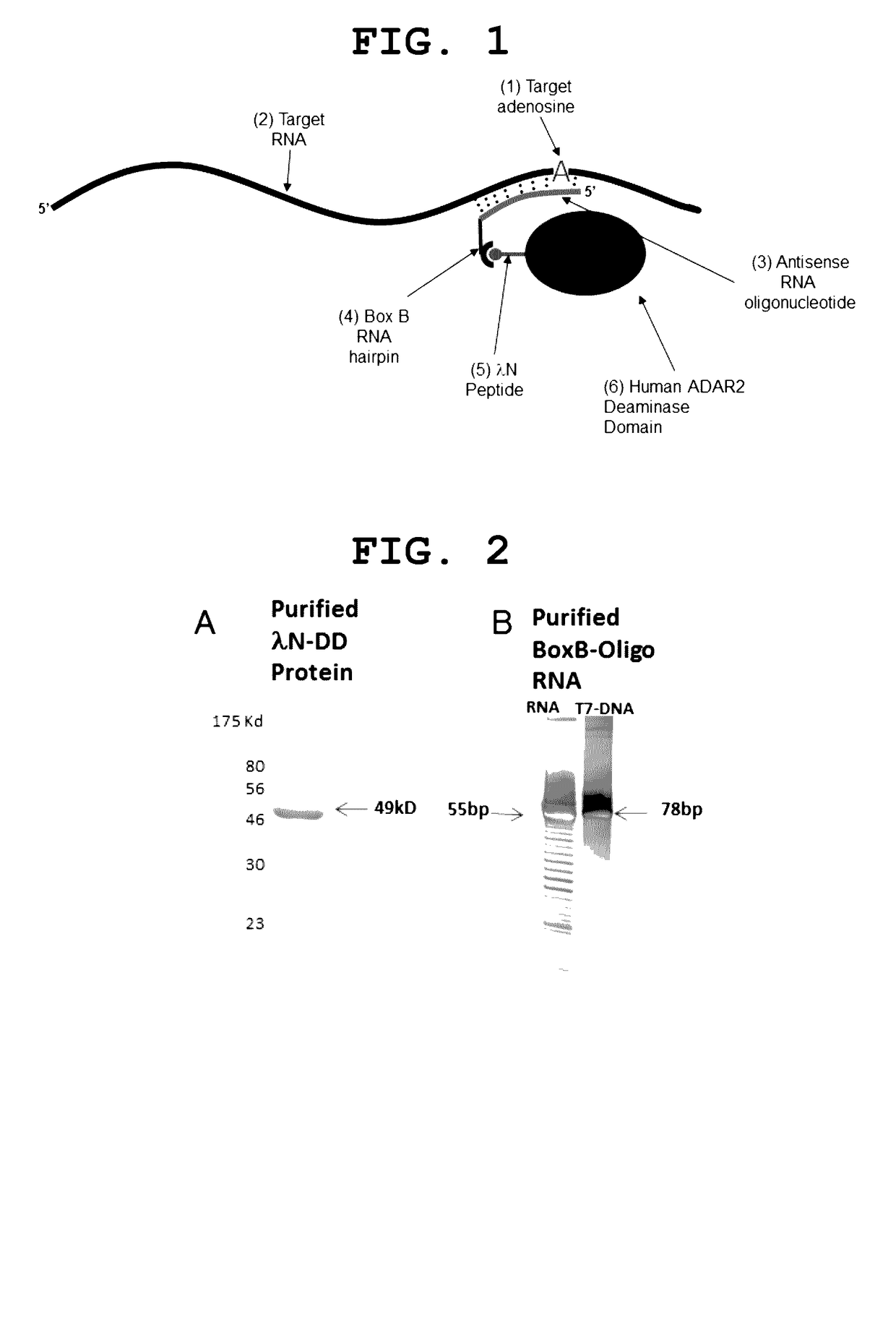
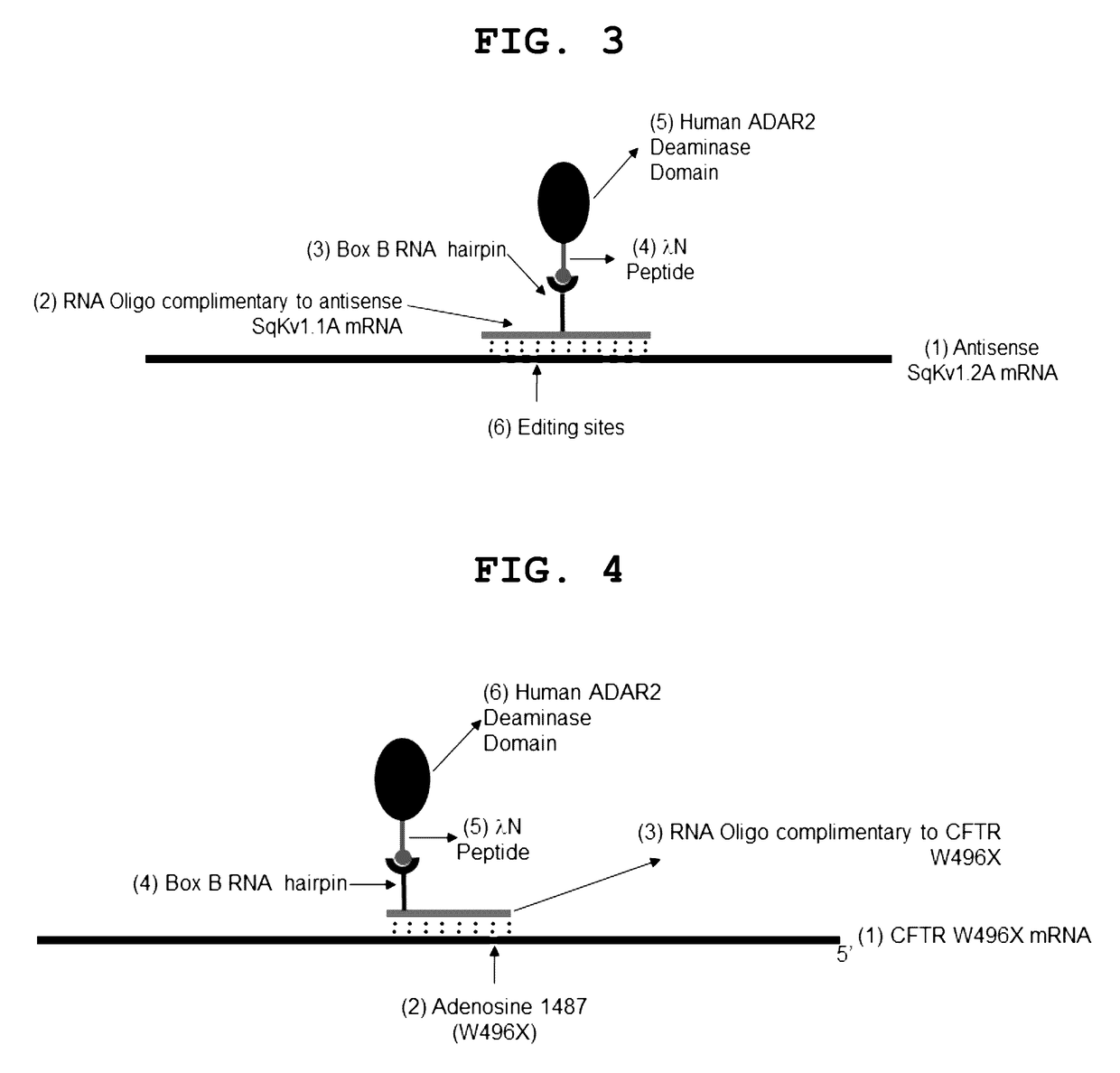
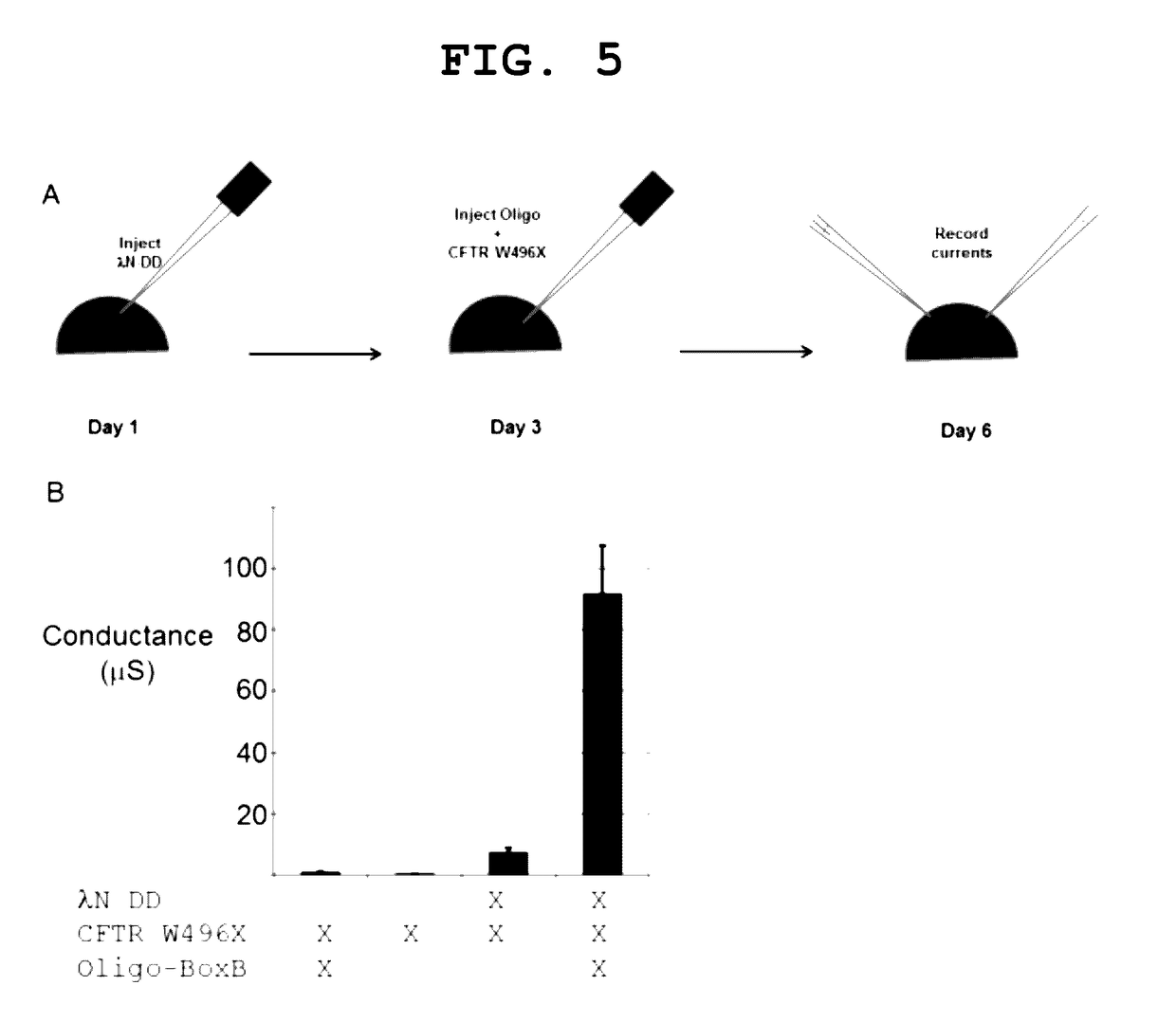
Site-directed RNA editing
The invention provides a way to target RNA editing by adenosine deamination to a chosen adenosine within RNA. An antisense RNA oligonucleotide is used for targeting the entire complex to a specific address on the RNA molecule. A Box B RNA and a λ N-peptide are used as a linkage between the antisense RNA oligonucleotide and a deaminase domain of human ADAR2 used to catalyze the deamination of the specific adenosine residue. These elements make up two molecules: the antisense RNA Oligo Box B RNA hairpin forms a single unit, as does the λ N-peptide-deaminase domain of human ADAR2.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PUERTO RICO
Selective 5' Ligation Tagging of RNA
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
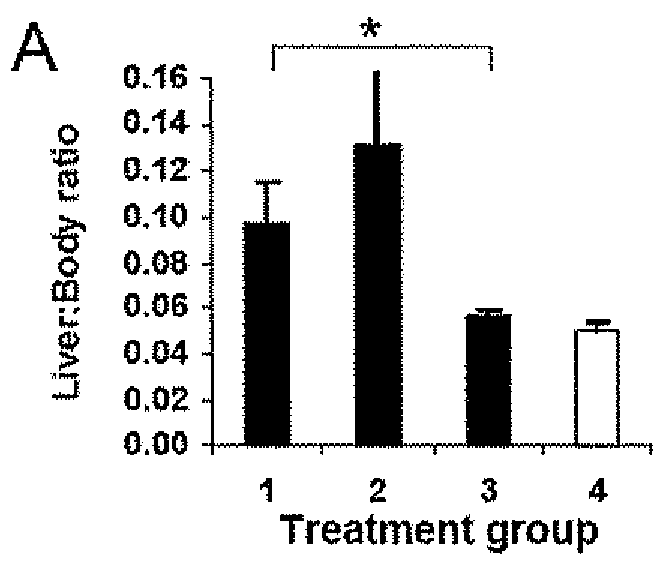
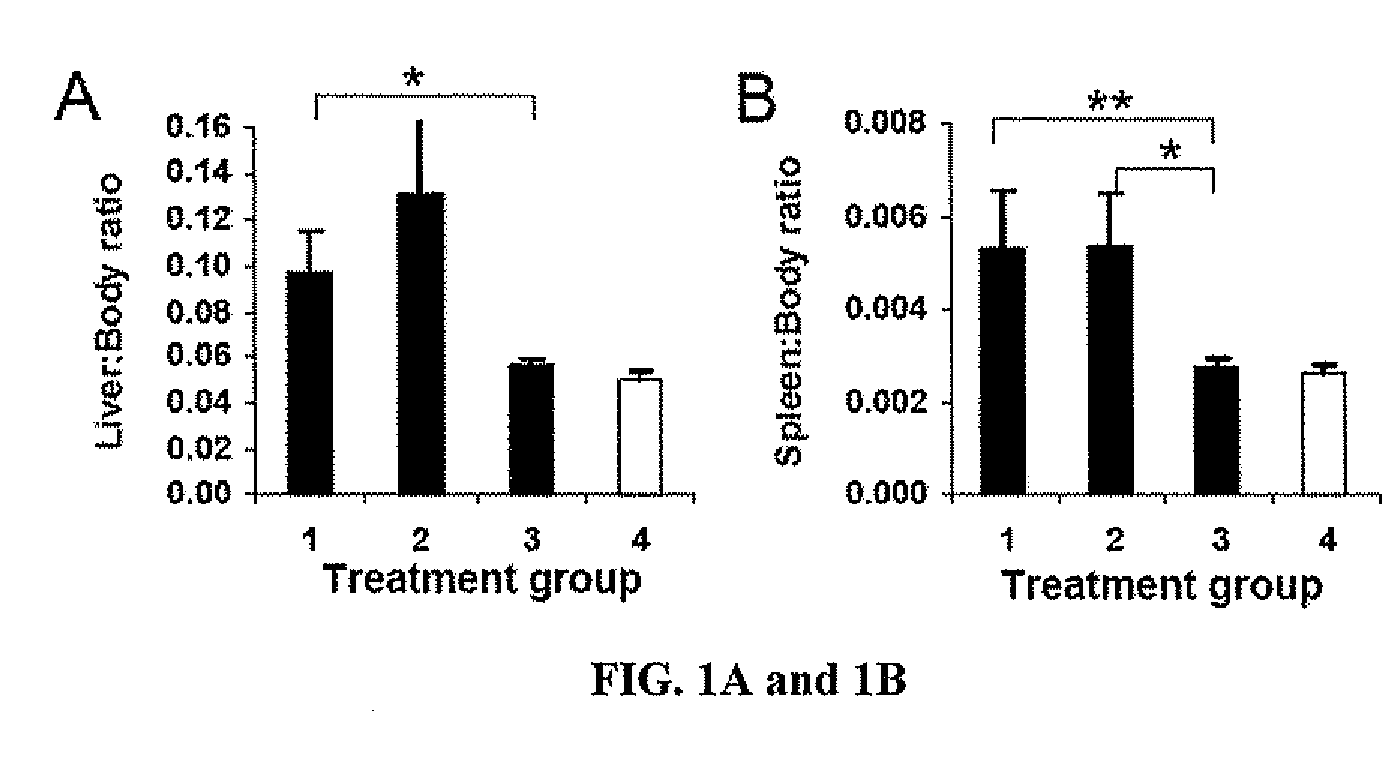
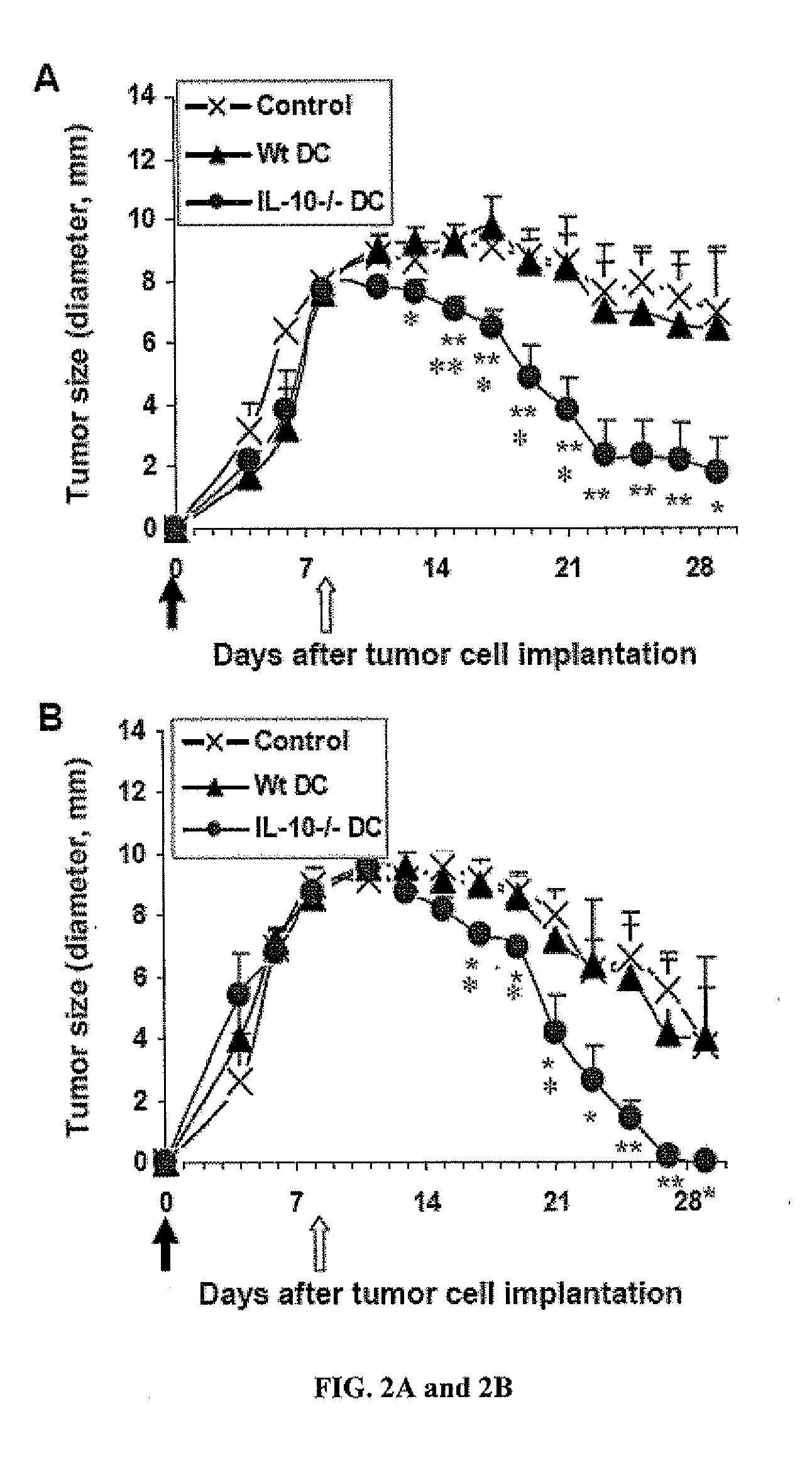
Anti-tumor vaccines delivered by dendritic cells devoid of interleukin-10
InactiveUS20090010948A1Highly effectiveBiocideGenetic material ingredientsDendritic cellInterleukin 10
It has been discovered that reducing, inhibiting or preventing the expression of immunosuppressive cytokines or tolergenic agents in antigen presenting cells improves the ability of the antigen presenting cell to promote an immune response. One embodiment provides a genetically engineered antigen presenting cell that has reduced or no expression of IL-10. Preferred antigen presenting cells are dendritic cells. Expression of IL-10 can be inhibited or blocked by genetically engineering the antigen presenting cell to express inhibitory nucleic acids that inhibit or prevent the expression mRNA encoding immunosuppressive cytokines. Inhibitory nucleic acids include siRNA, antisense RNA, antisense DNA, microRNA, and enzymatic nucleic acids that target mRNA encoding immunosuppressive cytokines. Immunosuppressive cytokines include, but are not limited to IL-10, TGF-β, IL-27, IL-35, or combinations thereof. Tolerogenic agents include but are not limited to indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com