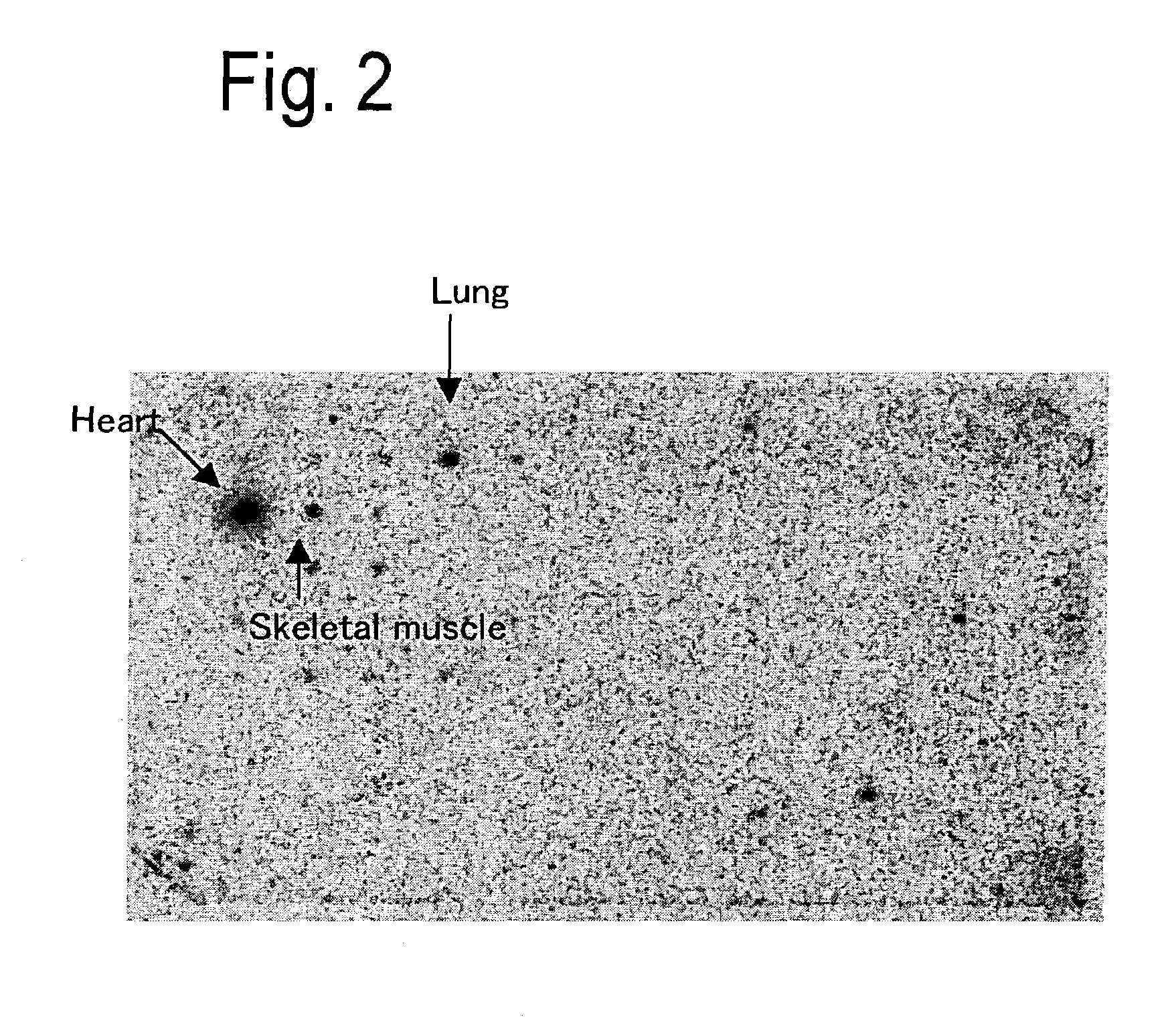
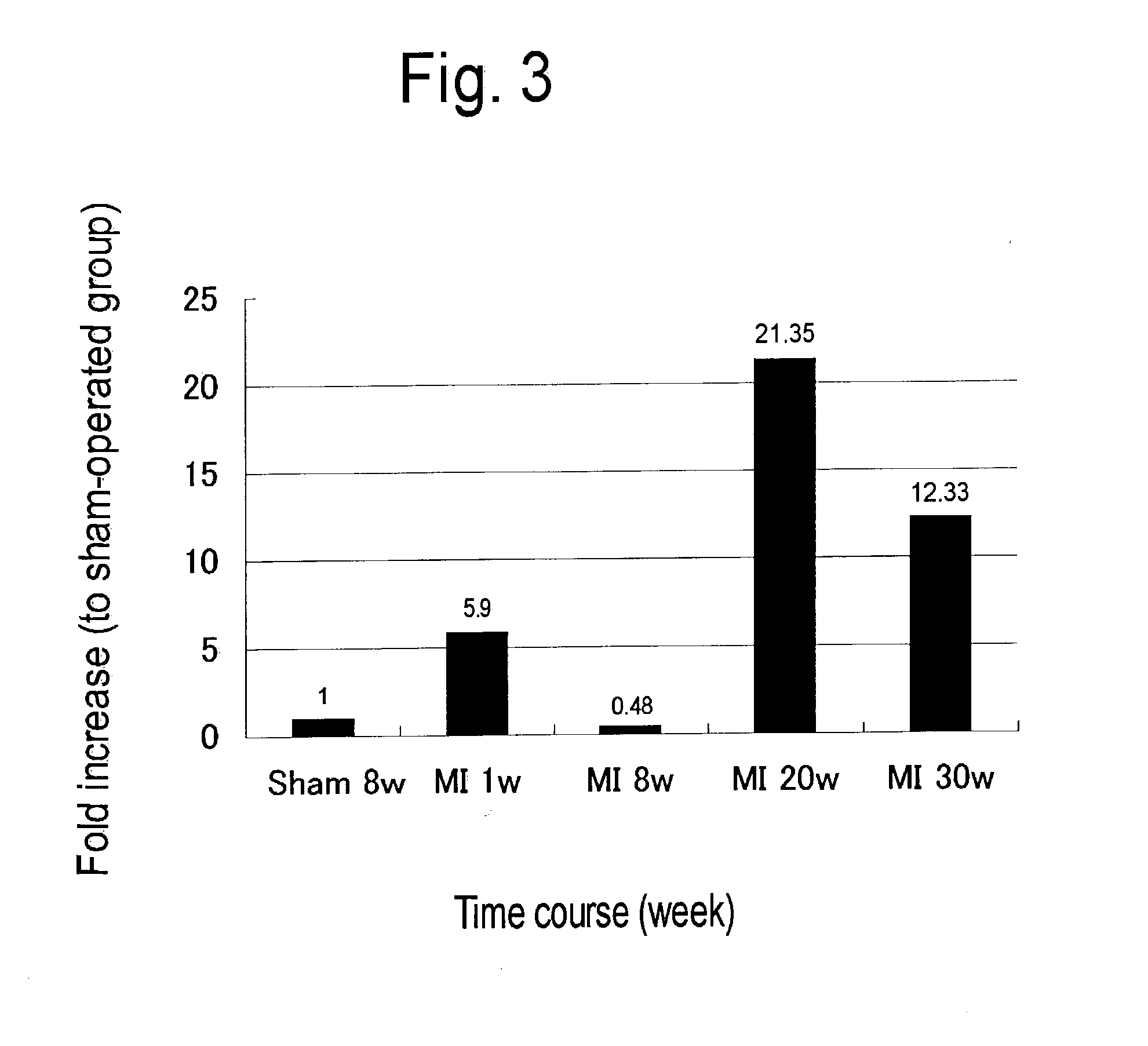
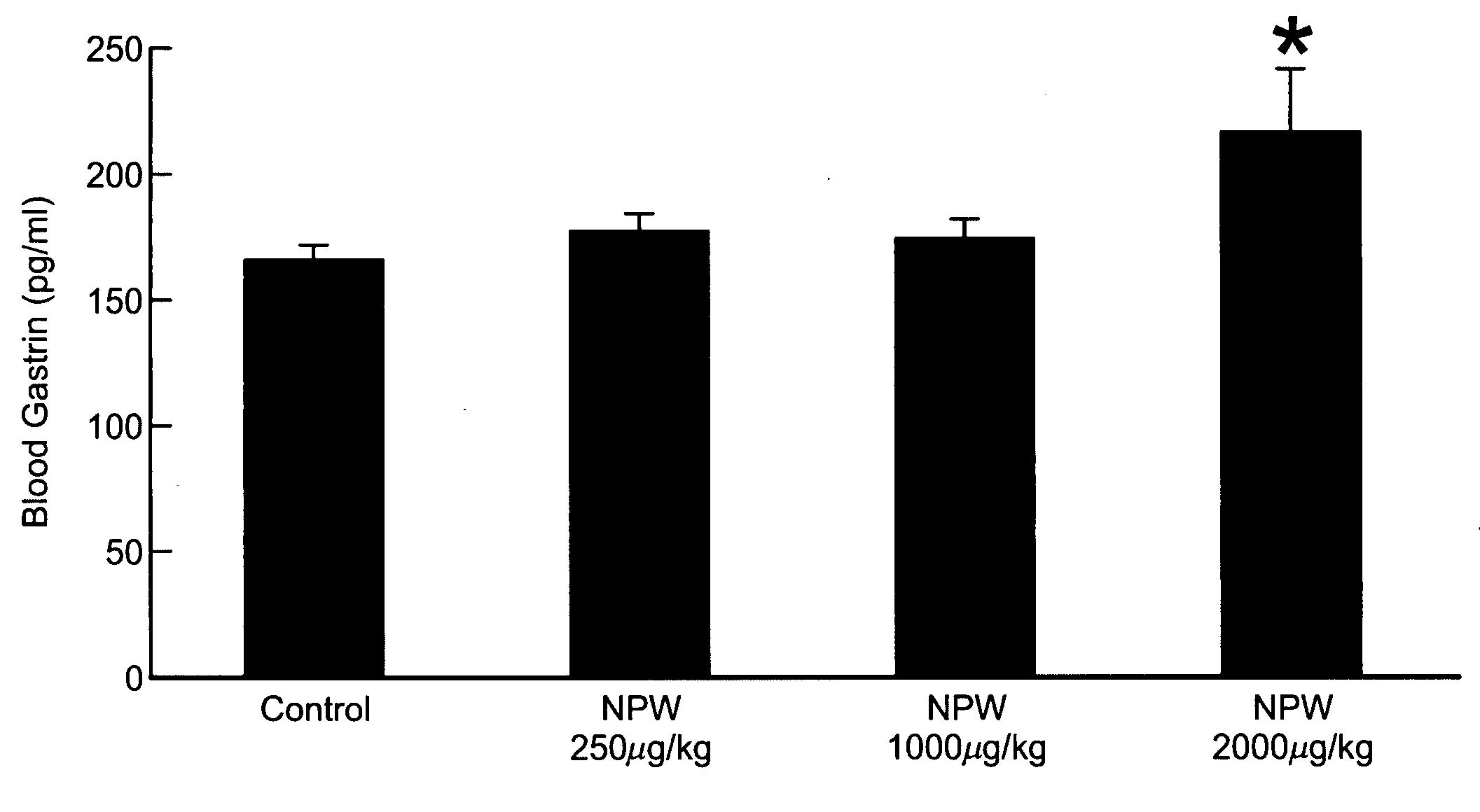
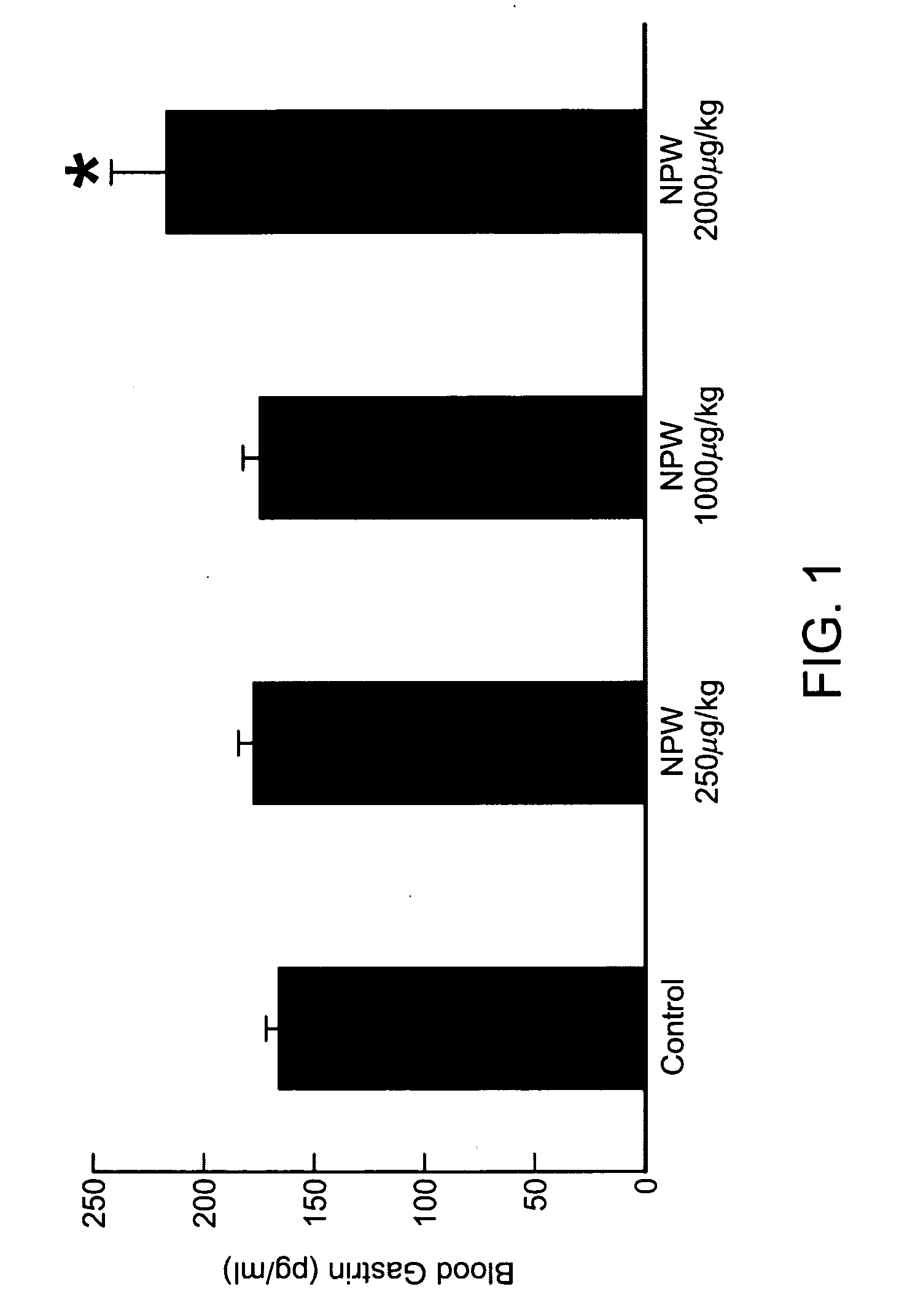
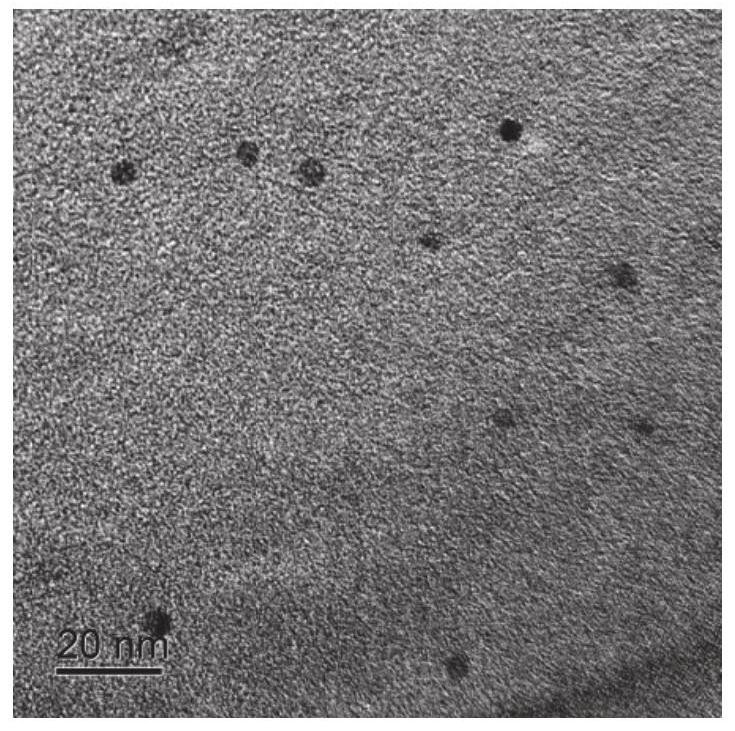
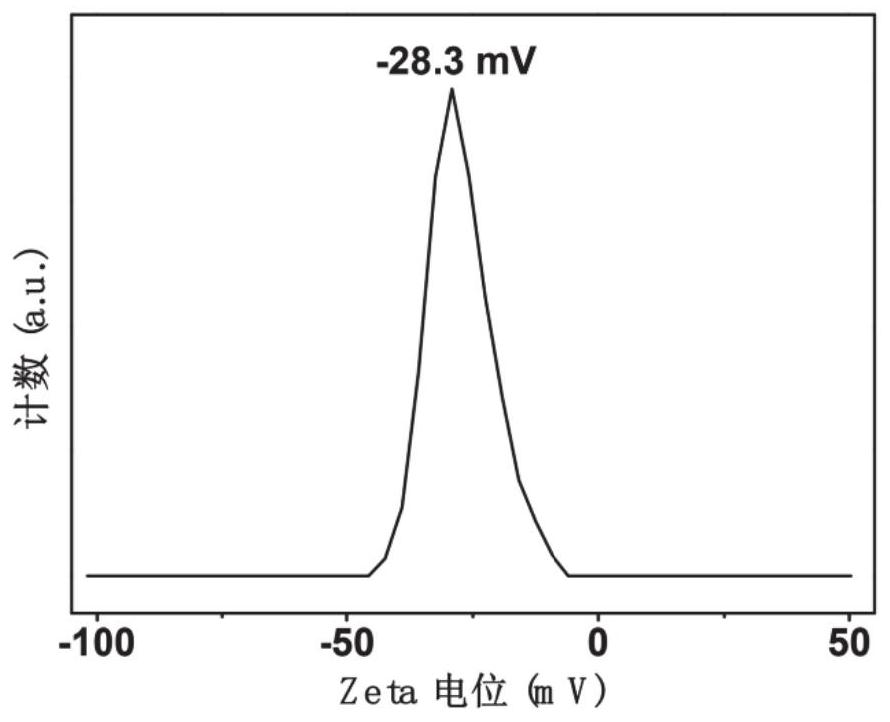
Patents
Literature
37 results about "Antisense DNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
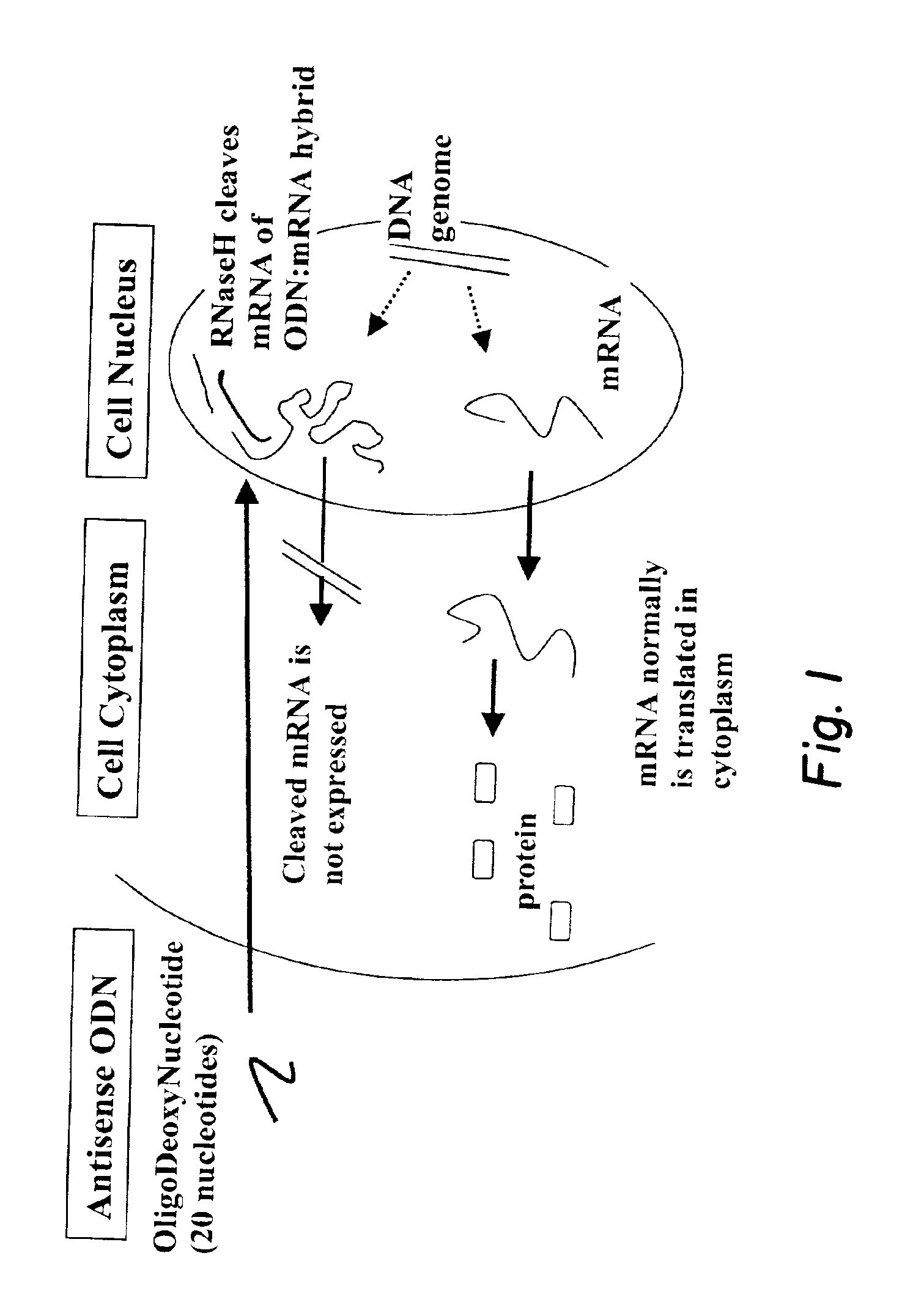
Antisense DNA: DNA normally has two strands, i.e., the sense strand and the antisense strand. In double-stranded DNA, only one strand codes for the RNA that is translated into protein. This DNA strand is referred to as the antisense strand.
Antisense gene systems of pollination control for hybrid seed production
A process is described for producing hybrid seed using male-sterile plants created by employing molecular techniques to manipulate antisense DNA and other genes that are capable of controlling the production of fertile pollen in plants. Transformation techniques are used to introduce constructs containing antisense DNA and other genes into plants. Said plants are functionally male-sterile and are useful for the production of hybrid seed by the crossing of said male-sterile plants with pollen from male-fertile plants. Hybrid seed production is simplified and improved by this invention and can be extended to plant crop species for which commercially acceptable hybrid seed production methods are not currently available.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Nucleic acid molecules inducing RNA interference, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20130273657A1Novel structureGood effectOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAntisense RNAAntisense DNA
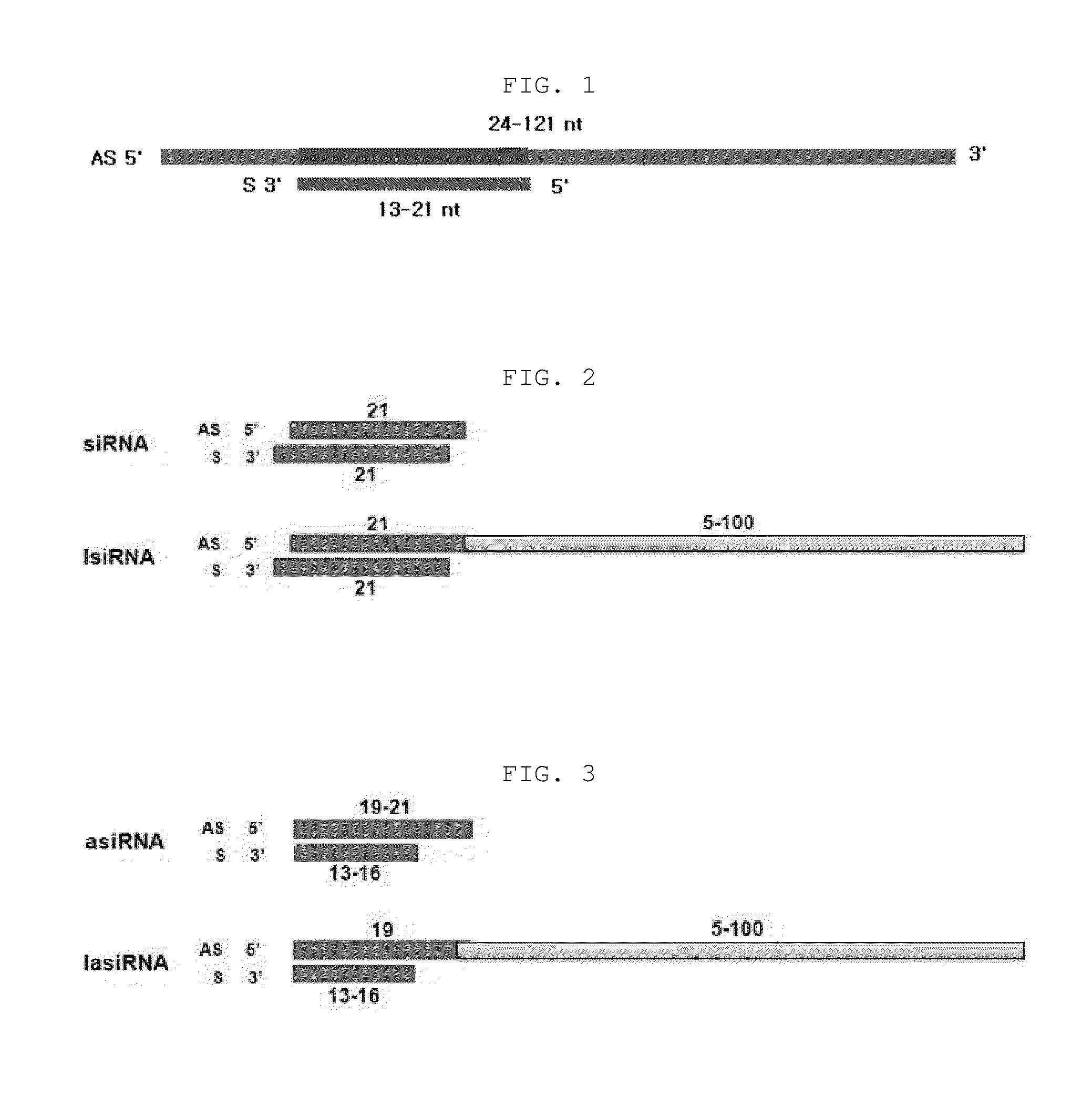
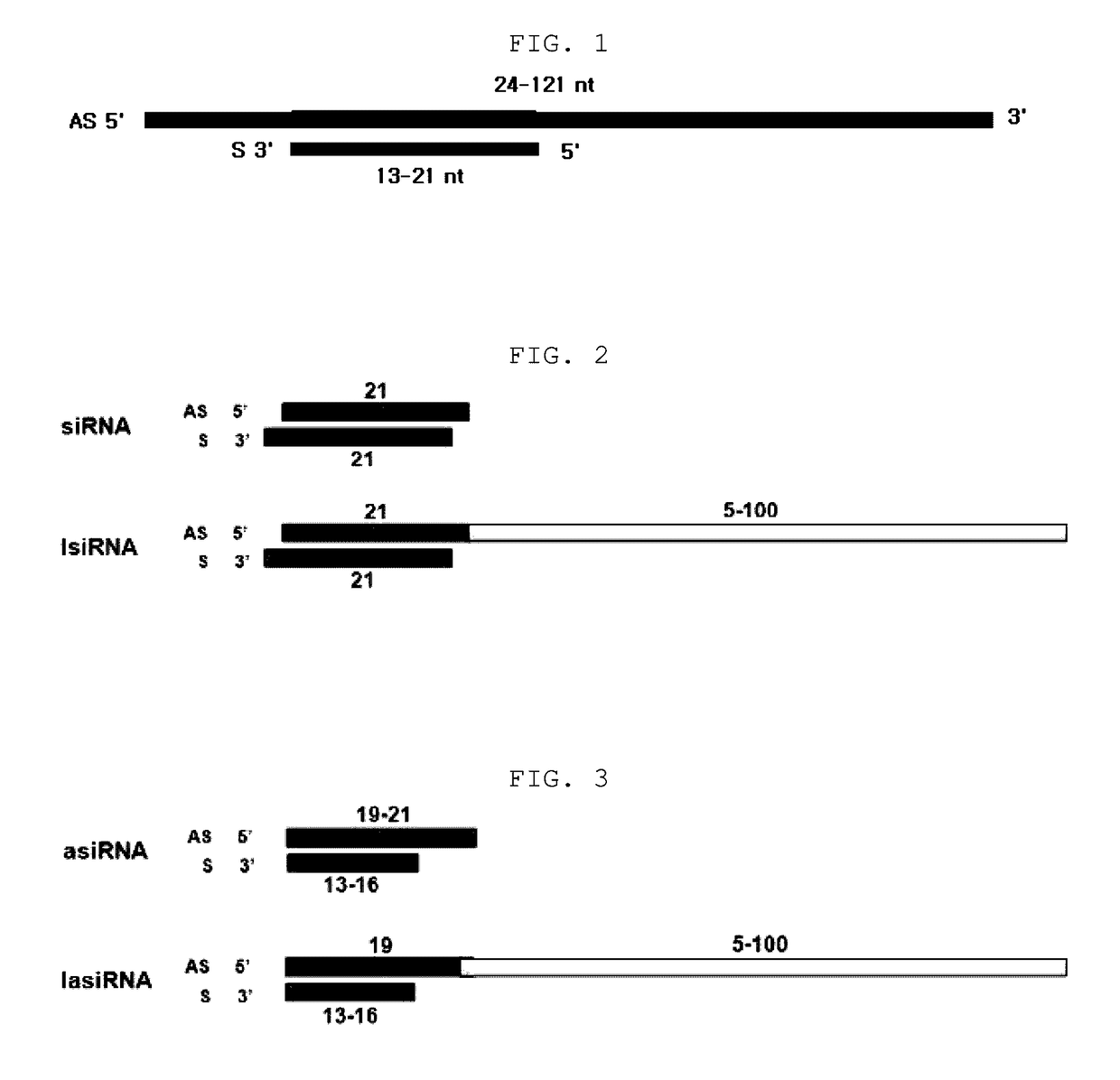
The present invention relates to an RNAi-inducing nucleic acid molecule having a new structure and the use thereof, and more particularly to a novel nucleic acid molecule having a structure comprising a first strand, which is 24-121 nt in length and comprises a region complementary to a target nucleic acid, and a second strand which is 13-21 nt in length and has a region that binds complementarily to the region of the first strand, which is complementary to the target nucleic acid, so that the nucleic acid molecule inhibits the expression of a target gene with increased efficiency, and to a method of inhibiting the expression of a target gene using the nucleic acid molecule. The nucleic acid molecule structure of the present invention increases the efficiency with which the nucleic acid molecule inhibits the target gene. Alternatively, the nucleic acid molecule of the present invention can either increase the ability of the siRNA to bind to the target gene or cause synergistic cleavage, by introduction of antisense DNA, antisense RNA, ribozyme or DNAzyme, thereby increasing the efficiency with which the nucleic acid molecule inhibits the target gene. In addition, when the nucleic acid molecule according to the present invention is used, the efficiency with which the target gene is inhibited can be maintained for an extended period of time. Accordingly, the RNAi-inducing nucleic acid molecule of the present invention can be effectively used for the treatment of cancer or viral infection in place of conventional siRNA molecules.
Owner:OLIX PHARMA
Nucleic acid molecules inducing RNA interference, and uses thereof
ActiveUS9637742B2Good effectNovel structureOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAntisense DNAAntisense RNA
The present invention relates to an RNAi-inducing nucleic acid molecule having a new structure and the use thereof, and more particularly to a novel nucleic acid molecule having a structure comprising a first strand, which is 24-121 nt in length and comprises a region complementary to a target nucleic acid, and a second strand which is 13-21 nt in length and has a region that binds complementarily to the region of the first strand, which is complementary to the target nucleic acid, so that the nucleic acid molecule inhibits the expression of a target gene with increased efficiency, and to a method of inhibiting the expression of a target gene using the nucleic acid molecule. The nucleic acid molecule structure of the present invention increases the efficiency with which the nucleic acid molecule inhibits the target gene. Alternatively, the nucleic acid molecule of the present invention can either increase the ability of the siRNA to bind to the target gene or cause synergistic cleavage, by introduction of antisense DNA, antisense RNA, ribozyme or DNAzyme, thereby increasing the efficiency with which the nucleic acid molecule inhibits the target gene. In addition, when the nucleic acid molecule according to the present invention is used, the efficiency with which the target gene is inhibited can be maintained for an extended period of time. Accordingly, the RNAi-inducing nucleic acid molecule of the present invention can be effectively used for the treatment of cancer or viral infection in place of conventional siRNA molecules.
Owner:OLIX PHARMA
Anti-tumor vaccines delivered by dendritic cells devoid of interleukin-10
InactiveUS20090010948A1Highly effectiveBiocideGenetic material ingredientsDendritic cellInterleukin 10
It has been discovered that reducing, inhibiting or preventing the expression of immunosuppressive cytokines or tolergenic agents in antigen presenting cells improves the ability of the antigen presenting cell to promote an immune response. One embodiment provides a genetically engineered antigen presenting cell that has reduced or no expression of IL-10. Preferred antigen presenting cells are dendritic cells. Expression of IL-10 can be inhibited or blocked by genetically engineering the antigen presenting cell to express inhibitory nucleic acids that inhibit or prevent the expression mRNA encoding immunosuppressive cytokines. Inhibitory nucleic acids include siRNA, antisense RNA, antisense DNA, microRNA, and enzymatic nucleic acids that target mRNA encoding immunosuppressive cytokines. Immunosuppressive cytokines include, but are not limited to IL-10, TGF-β, IL-27, IL-35, or combinations thereof. Tolerogenic agents include but are not limited to indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
STAT function-regulatory protein
Disclosed is a protein having the ability to inhibit the function of a STAT in a mammalian JAK / STAT signal transduction pathway, which is induced by STAT3 or STAT6, which has the ability to inhibit tyrosine phosphorylation of gp130 or STAT3 and which comprises an SH2 domain; and also disclosed is a DNA coding for the same. Further disclosed is a method for screening a substance having the capability to regulate cytokine activity, in which the protein of the present invention is used. Still further disclosed are an antisense DNA and an antisense RNA capable of inhibiting the biosynthesis of the above-mentioned protein; a monoclonal antibody capable of binding to the above-mentioned protein; and a DNA probe and an RNA probe capable of hybridizing to the above-mentioned DNA. Still further disclosed are a replicable recombinant DNA molecule comprising a replicable expression vector and, operably inserted therein, the DNA of the present invention; a cell of a microorganism or cell culture, transformed with the replicable recombinant DNA molecule; and a method for screening a substance having the capability to regulate cytokine activity in which the transformant is used.
Owner:NAT INST OF BIOMEDICAL INNOVATION HEALTH & NUTRITION
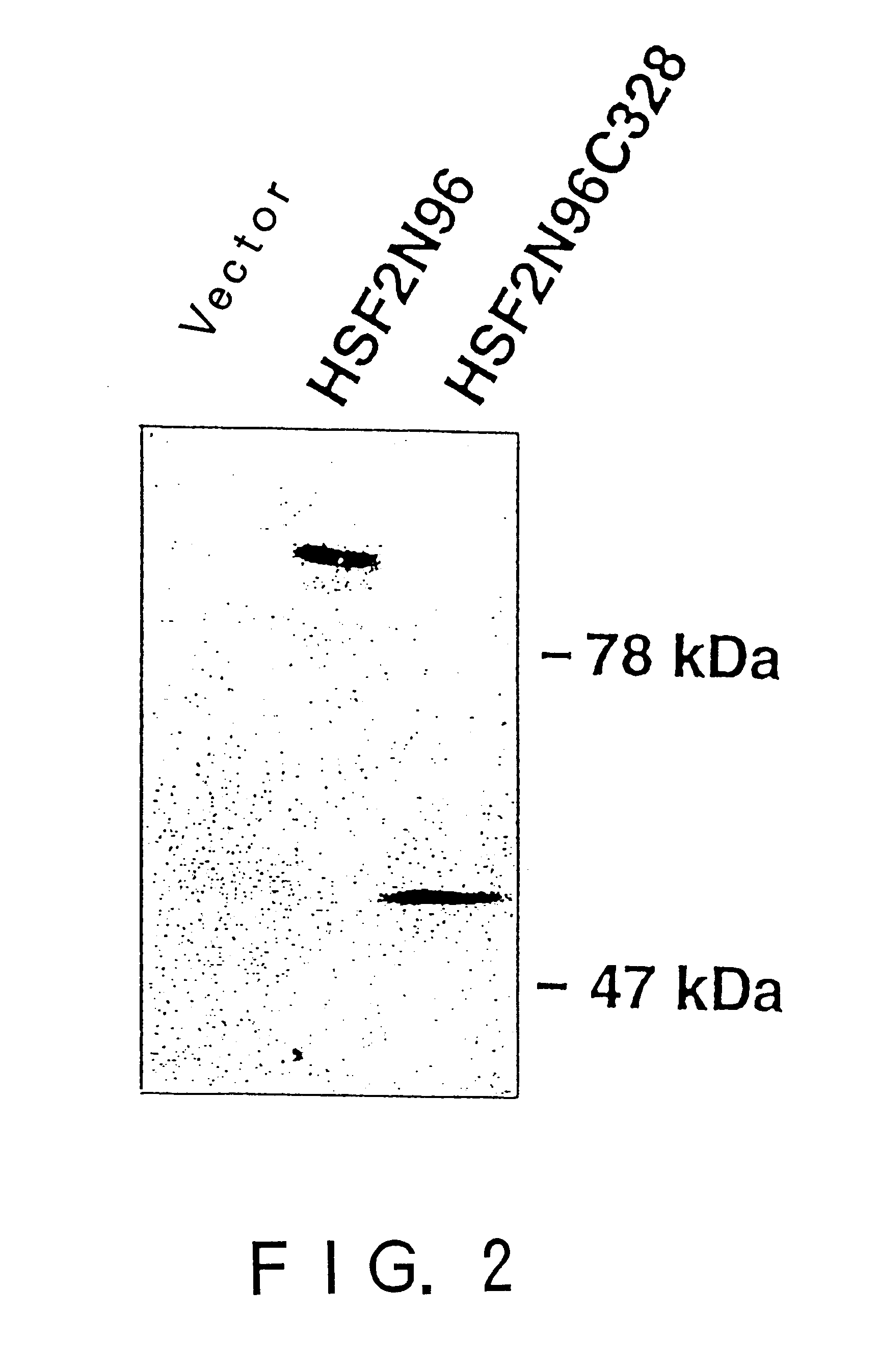
Heat shock transcription factor-binding protein
InactiveUS6485936B1Rule out the possibilityImprove purification effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesA-DNAHsp70
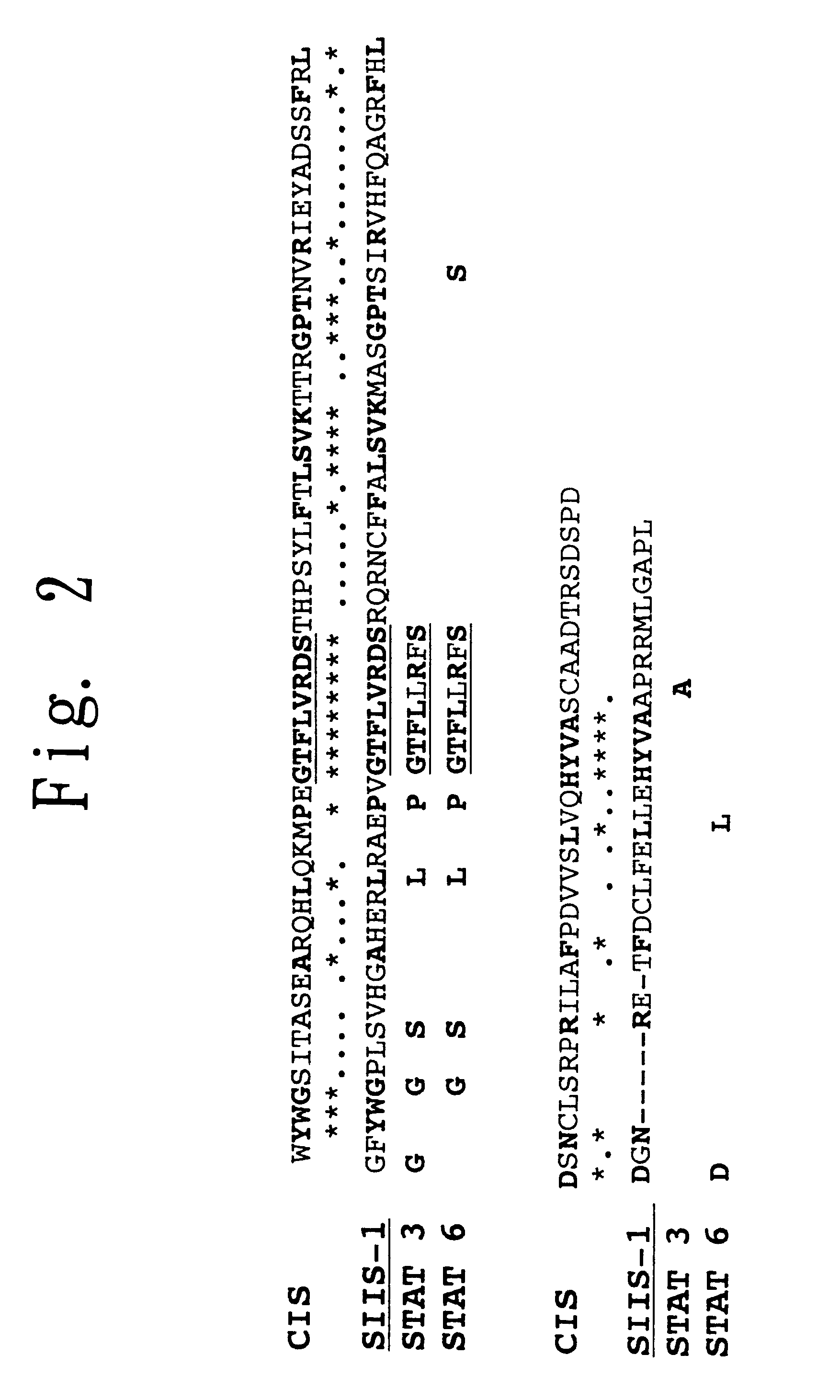
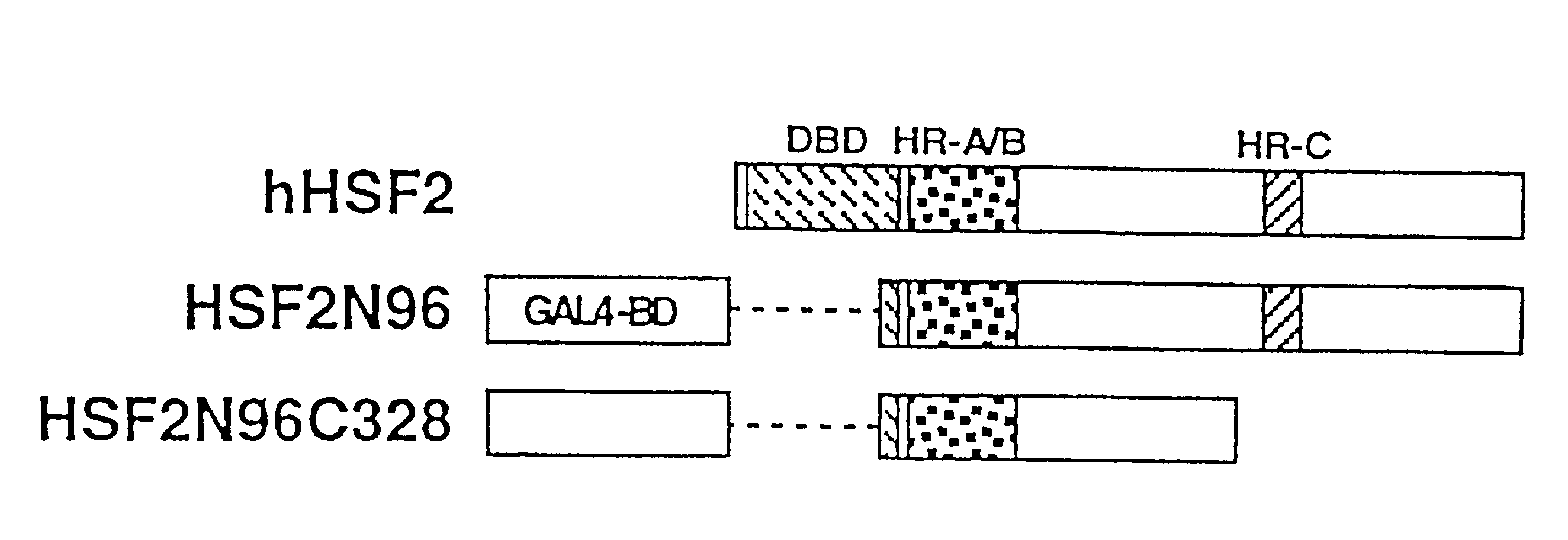
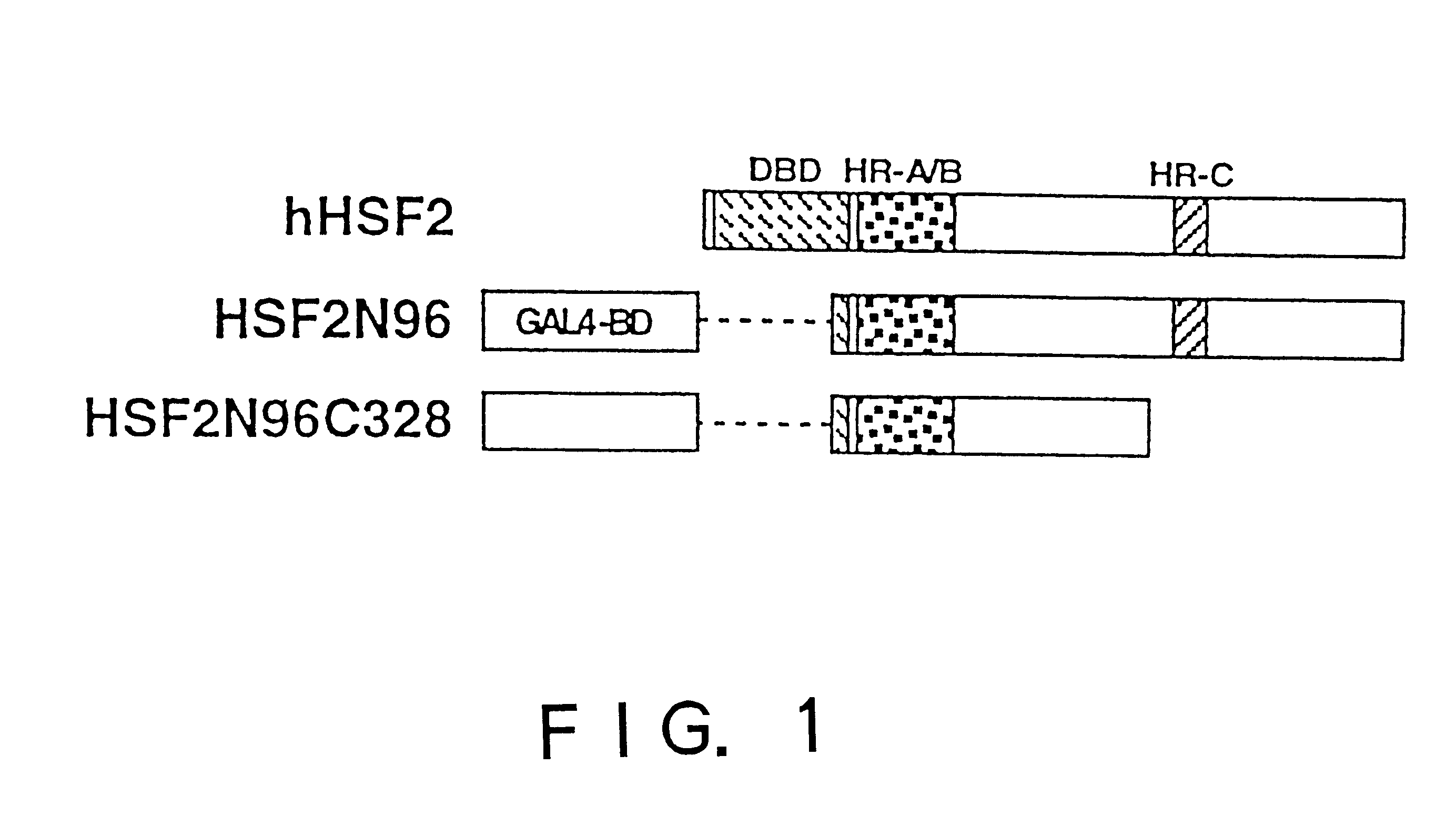
To provide a heat shock transcription factor (HSF) 2 binding factor, which can be involved in the transcriptional regulation of HSP70.2 playing an essential role in spermatogenesis; a DNA encoding the binding factor; an expression vector carrying the DNA; a transformant harboring the expression vector; a process for preparing a recombinant protein comprising the step of culturing the transformant; an antibody or a fragment thereof capable of specifically binding to the binding factor; an antisense DNA or antisense RNA complementary to the DNA; and an oligonudeotide probe or primer capable of specifically hybridizing to the DNA.
Owner:HSP RES INST
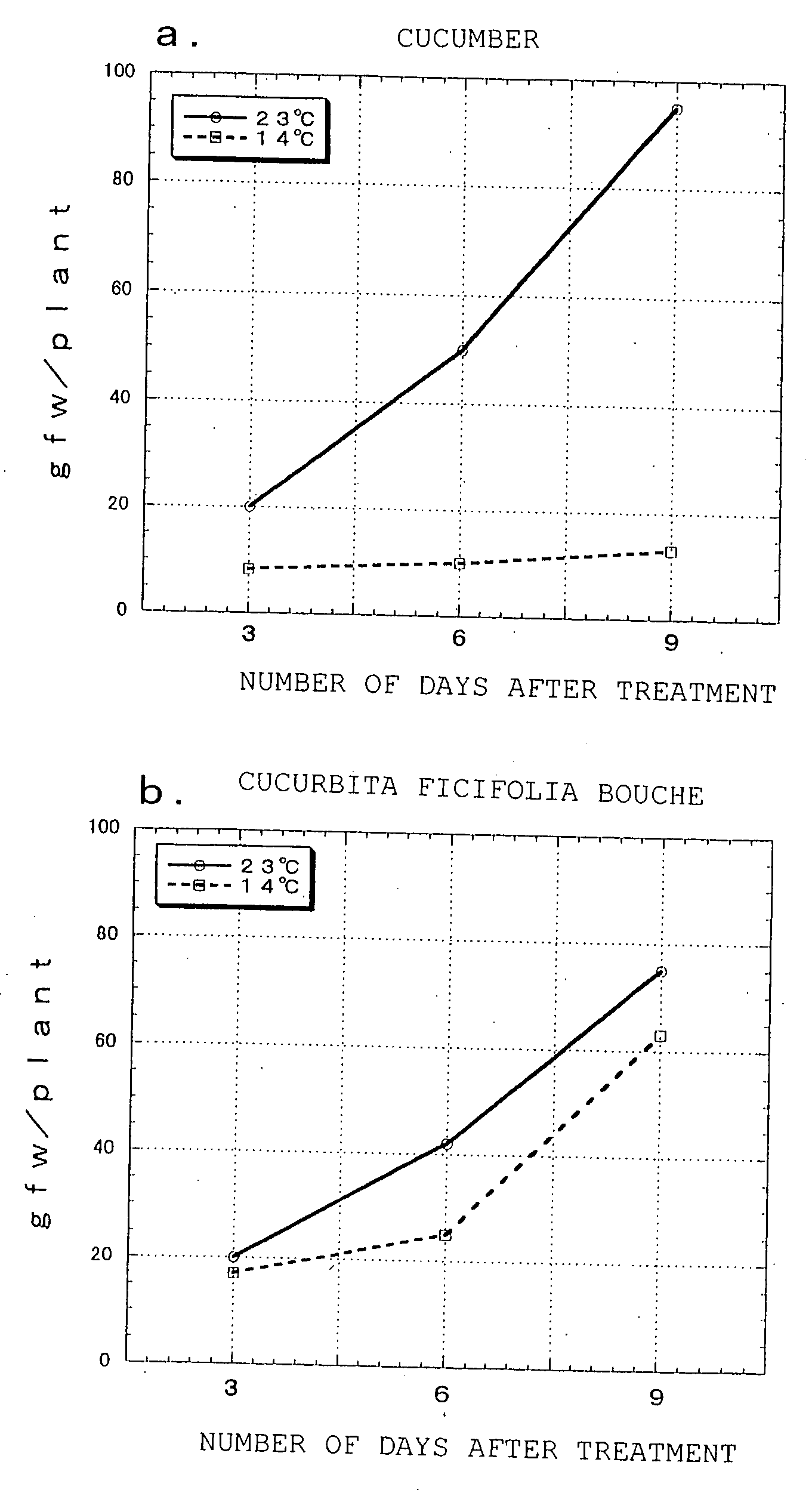
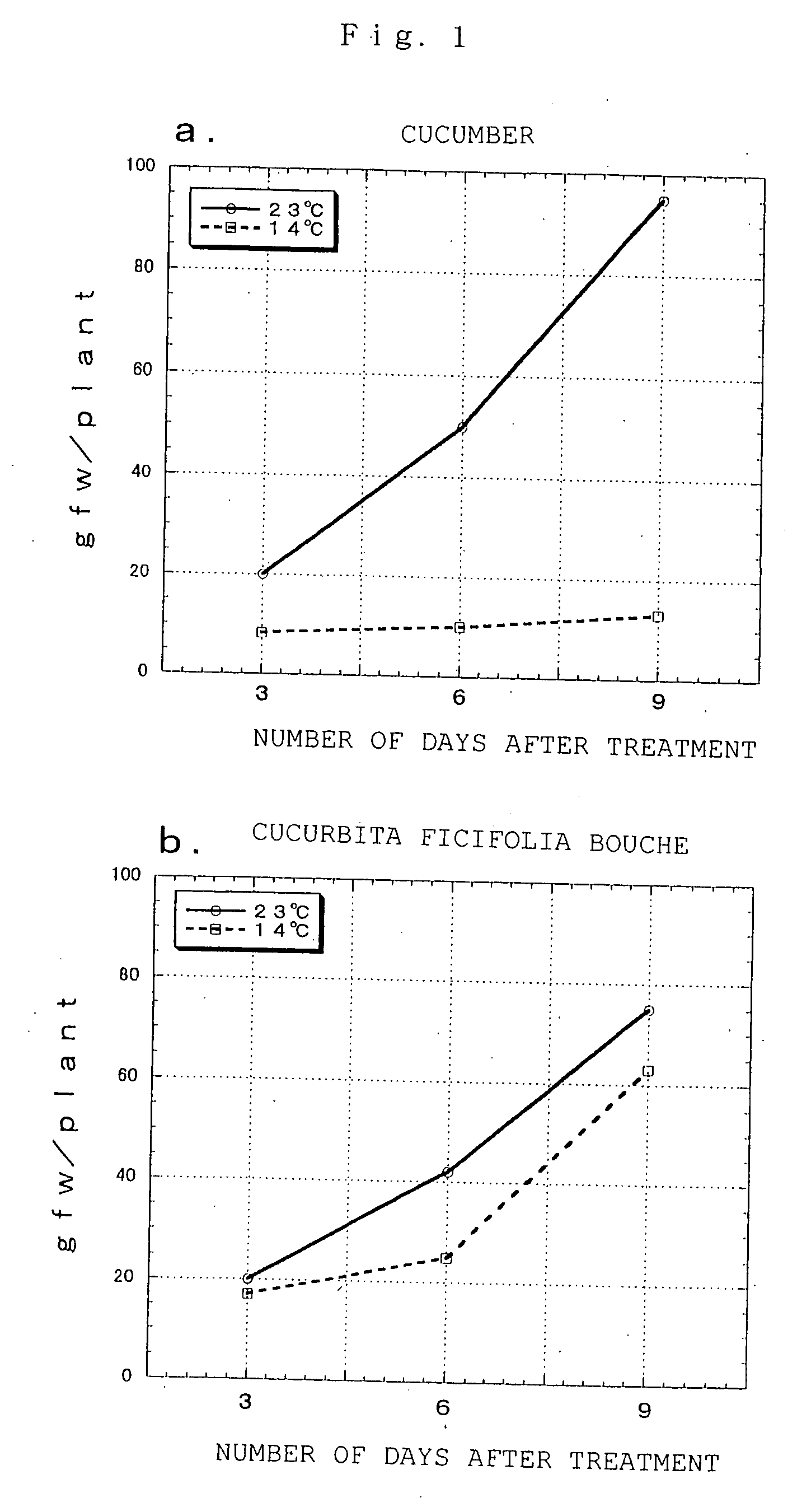
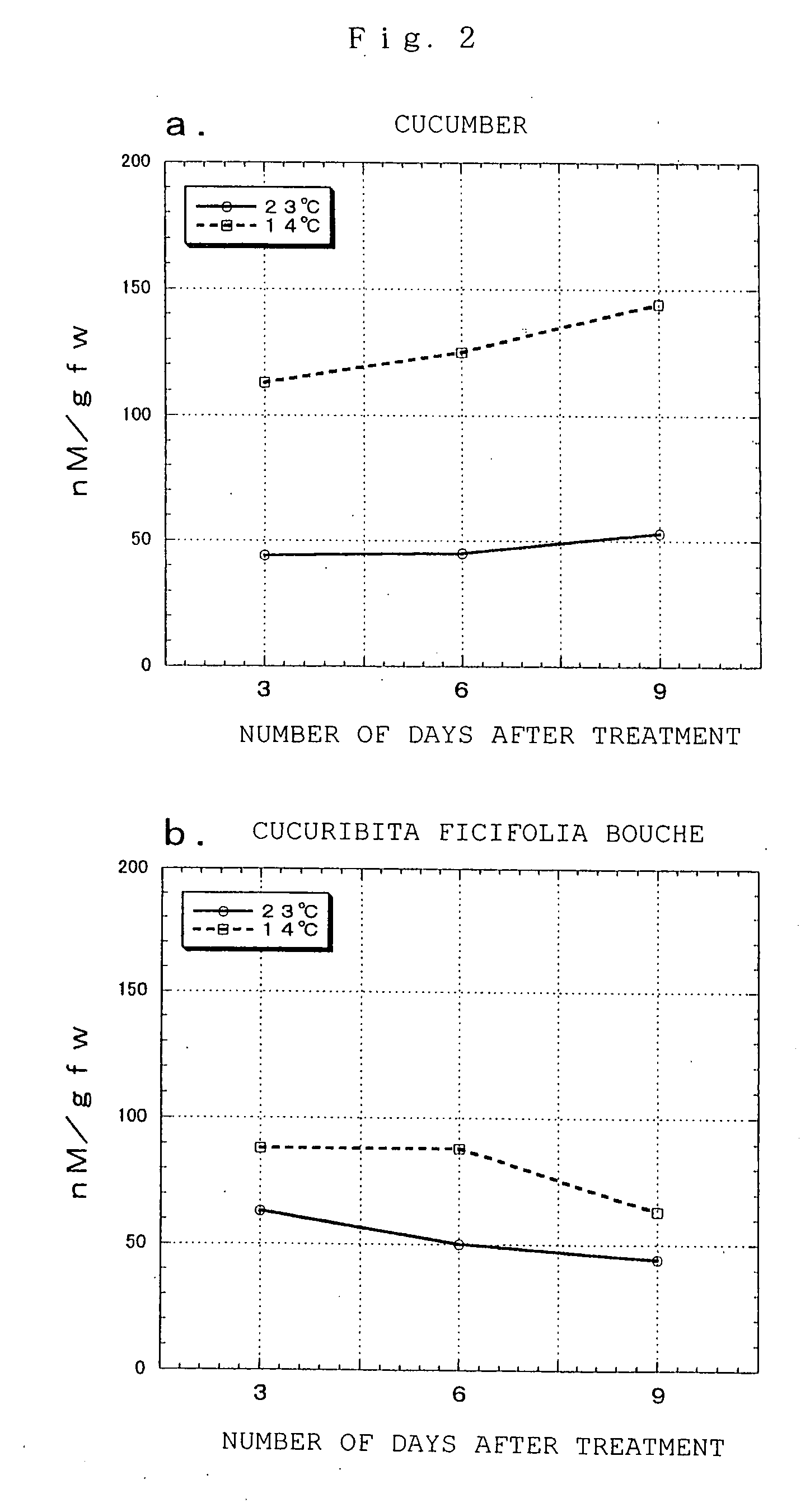
Plants having improved tolerance to various types of environmental stress, their production, and polyamine metabolism-related enzyme gene
InactiveUS20080010702A1Improve stress resistanceIncrease typeFungiBacteriaAntisense RNAMicroorganism
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
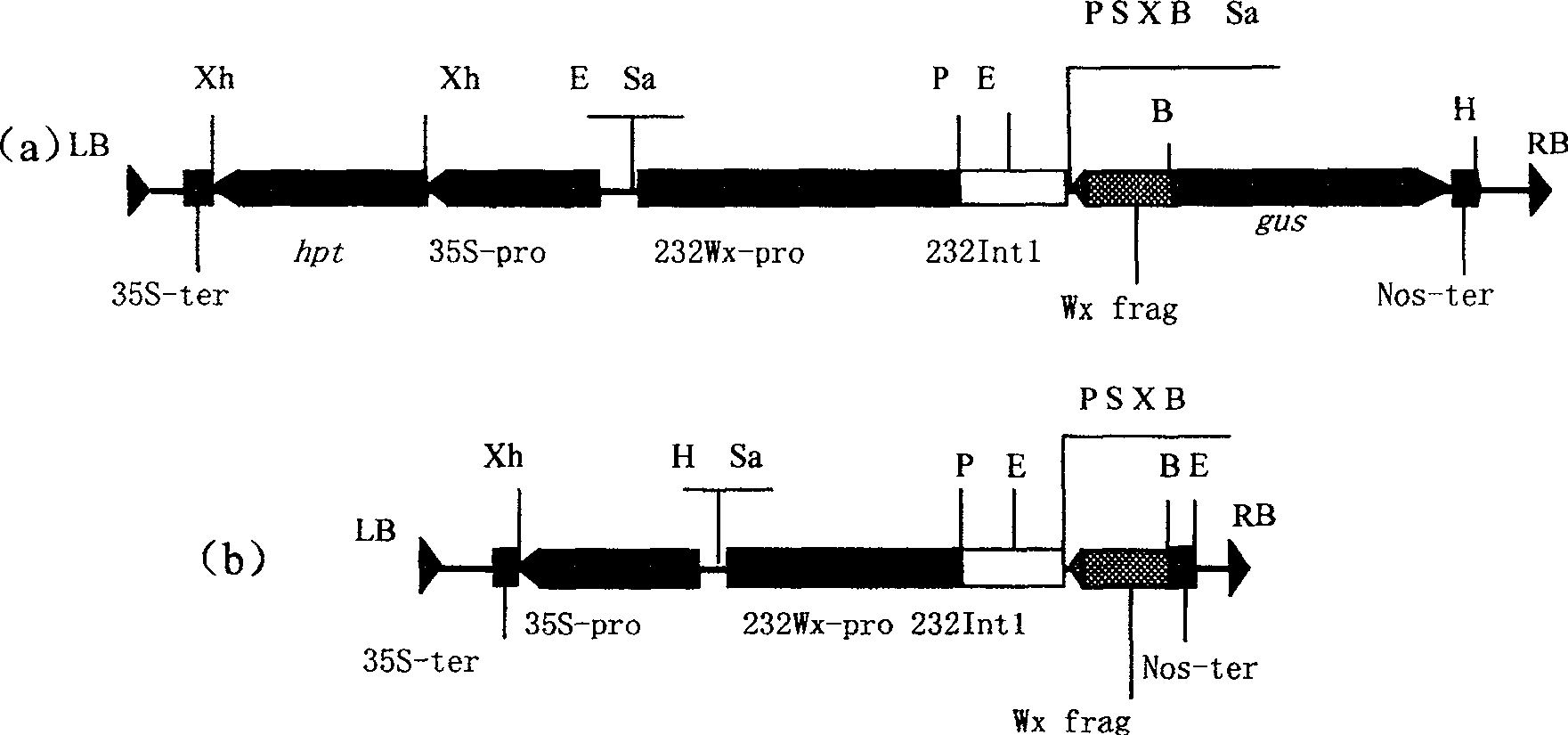
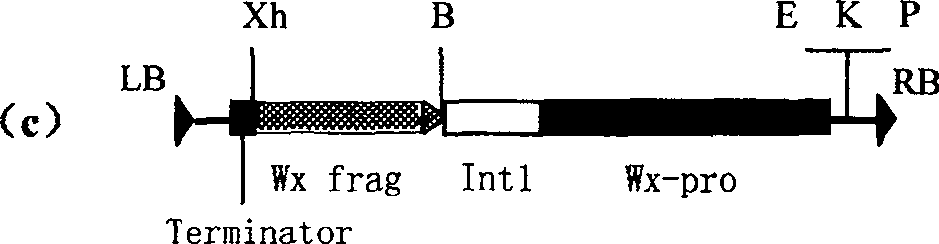
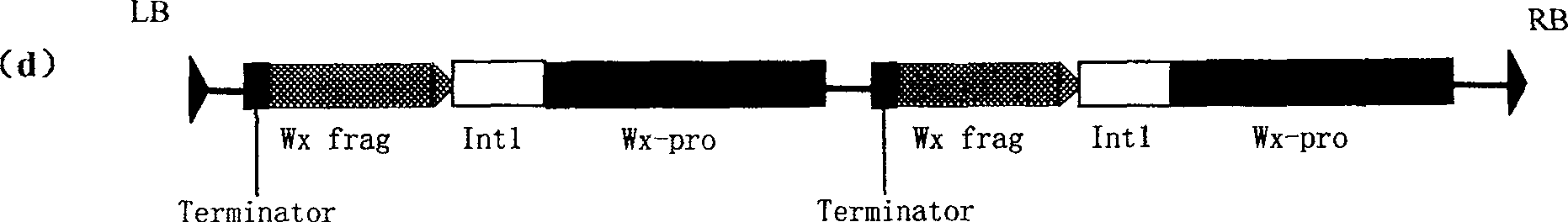
Expression vector of duplicate inverted waxy gene, preparation method, and application
InactiveCN1958799AReduce amylose contentReduce expressionVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationAntisense DNAAgricultural science
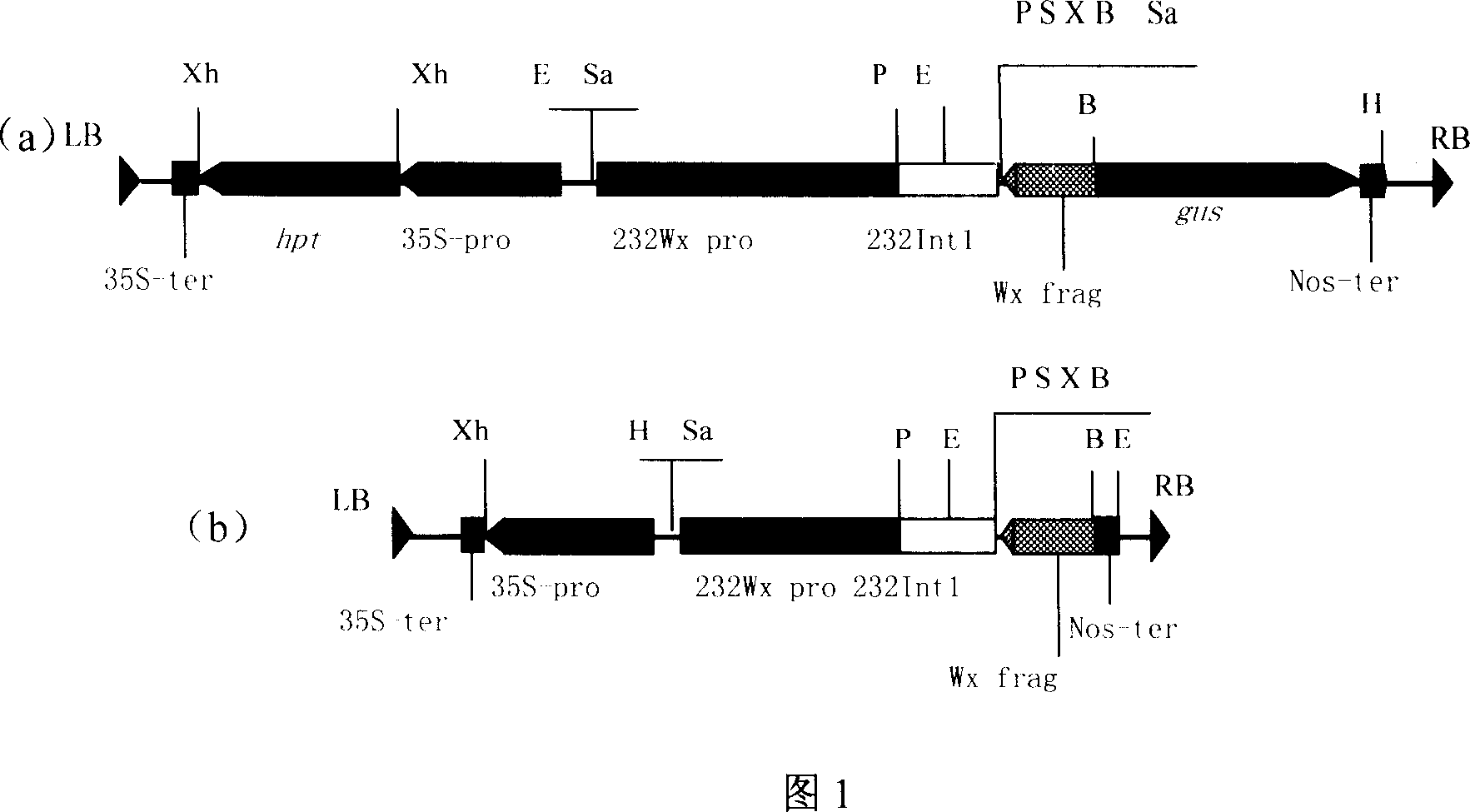
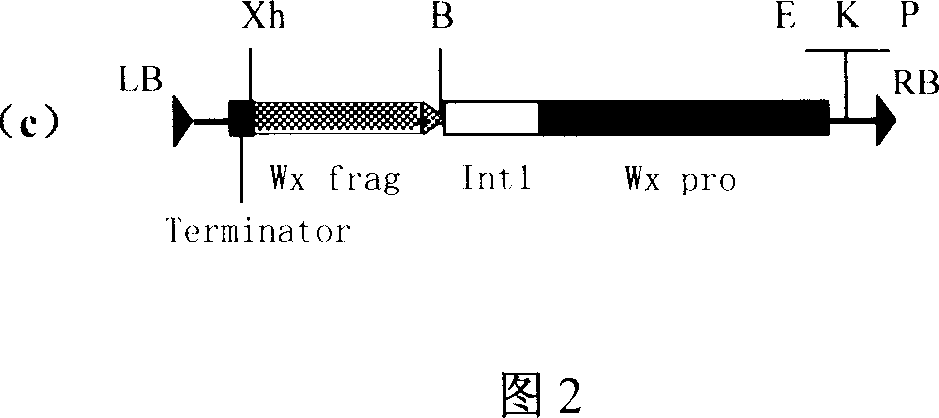
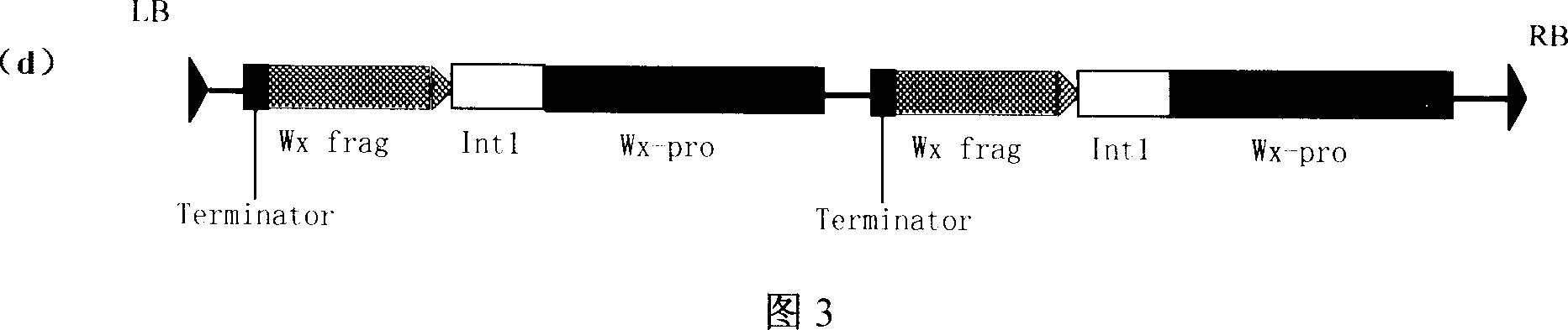
This invention discloses a method for preparing an expression vector containing double antisense waxy genes and its application. The structure and characteristics of the expression vector are shown in figure (d). The expression vector comprises promoter sequence, antisense DNA fragment of the target gene, terminator sequence, and endonuclease-sensitive sequence or marker gene sequence. All the sequences are doubled along the same direction. The expression vector can be used for breeding Gramineae plants such as rice without resistance-screening gene and with low amylase content.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
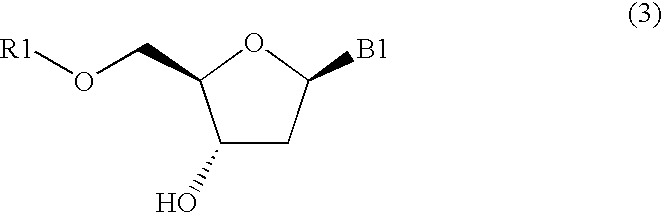
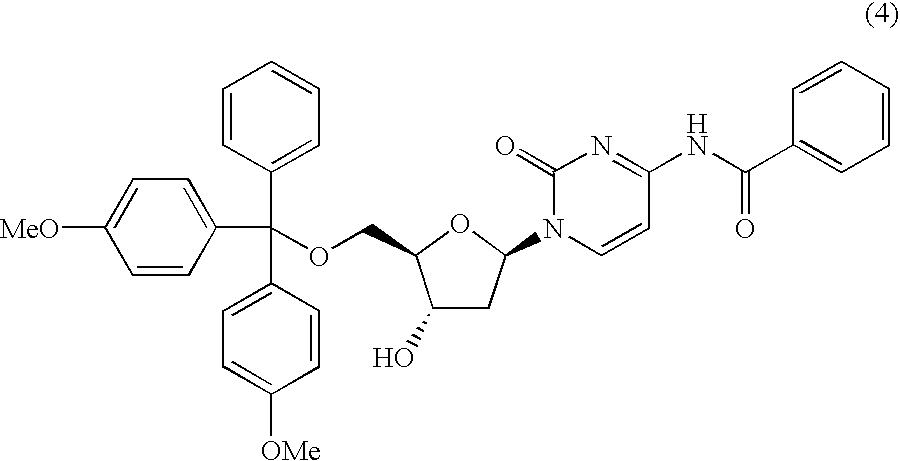
Method for purifying protected 2'-deoxycytidines and hydrated crystals thereof
InactiveUS6936709B2Efficient manufacturingEfficient preparationOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAntisense DNACytosine
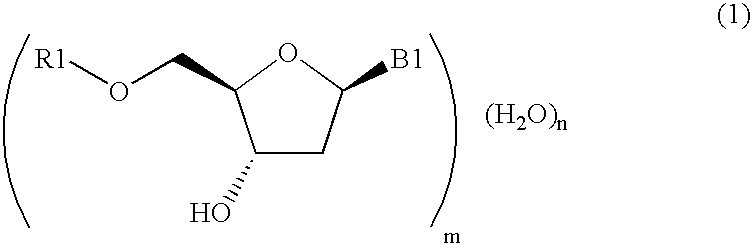
A protected 2′-deoxycytidine is purified by precipitating the protected 2′-deoxycytidine represented by general formula (3) in the form of a hydrated crystal from a solution containing the protected 2′-deoxycytidine and water, and by recovering the protected 2′-deoxycytidine: wherein R1 represents a 4-methoxytrityl, 4, 4′-dimethoxytrityl, or triphenylmethyl group; and B1 represents a cytosine group having a protected amino group. The compound represented by general formula (3) is, in particular, a protected 2′-deoxycytidine represented by formula (4): The 2′-deoxycytidine is used as a raw material for antisense DNA.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Compositions and methods for inhibiting HIV infections by inhibiting lerepo4 and glipr
InactiveUS20090233985A1Reduces infective potentialHigh expressionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAntisense DNAIn vivo
The present invention relates to inhibitor molecules of LEREPO4 or GliPR or respective functional homologues thereof including siRNAs, shRNAs, antisense RNAs, antisense DNA and dominant negative proteinaceous mutants of LEREPO4 or functional homologues thereof. The present invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions and methods for preventing and / or inhibiting HIV infections by inhibiting the function of LEREPO4 or GliPR or respective functional ho mo logues thereof in vivo. Furthermore, the present invention relates to methods of treating, preventing or diagnosing AIDS and / or HIV infections in an individual. Moreover, the present invention relates to diagnostic methods to determine the susceptibility of HIV strains and isolates for such LEREPO4 or GliPR directed treatment.
Owner:SCHEURING URBAN
Method for identifying accessible binding sites on RNA
A method for identifying sites on a target RNA which are accessible to pairing by antisense DNA, ribozymes or DNAzymes. Native or in vitro-synthesized target RNA is incubated with defined ODNs and RNase H, or with a random or semi-random ODN library and RNase H, or with defined ribozymes or DNAzymes, or with a semi-random ribozyme or DNAzyme library, in a cell extract containing endogenous RNA-binding proteins, or in a medium which mimics a cell extract due to presence of one or more RNA-binding proteins. Any antisense ODN, ribozyme or DNAzyme which is complementary to an accessisble site in the target RNA hybridizes to that site and the RNA is cleaved at that site. Reverse transcription can be used to generate a first strand DNA from the RNA cleavage product, and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-dependent polymerase chain reaction (TDPCR) can be used to identify sites on target RNA to which antisense ODNs, ribozymes or DNAzymes have bound and cleavage has occurred.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Use of diseases-associated gene
InactiveUS20030108951A1Low toxicEfficient activationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseHeart disease
The present invention relates to a method of screening a drug by using a disease-associated gene product, an antibody to the disease-associated gene product, an antisense DNA that suppresses the expression of the disease-associated gene, etc. A compound regulating the activity of a protein having an amino acid sequence which is the same or substantially the same amino acid sequence as the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1, or its salt, a neutralizing antibody regulating the activity of the above protein, an antisense DNA, etc. can regulate the expression of the protein having an amino acid sequence which is the same or substantially the same amino acid sequence as the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1 and, therefore, are usable as preventive / therapeutic agents for diseases, e.g., heart diseases, etc.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
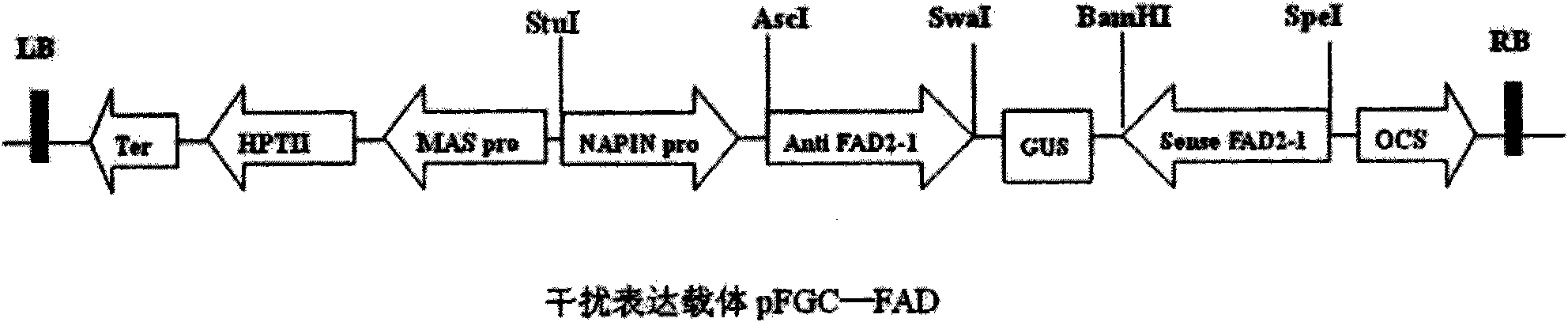
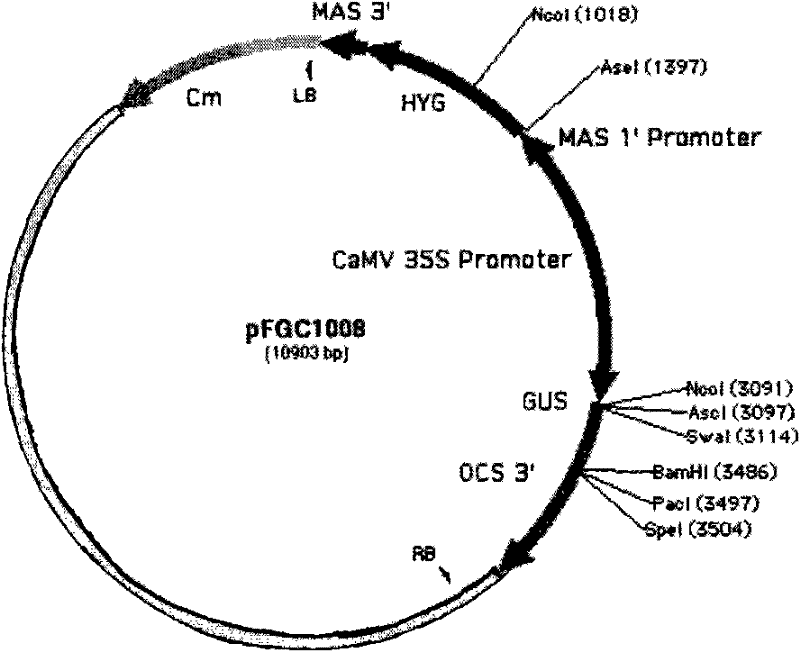
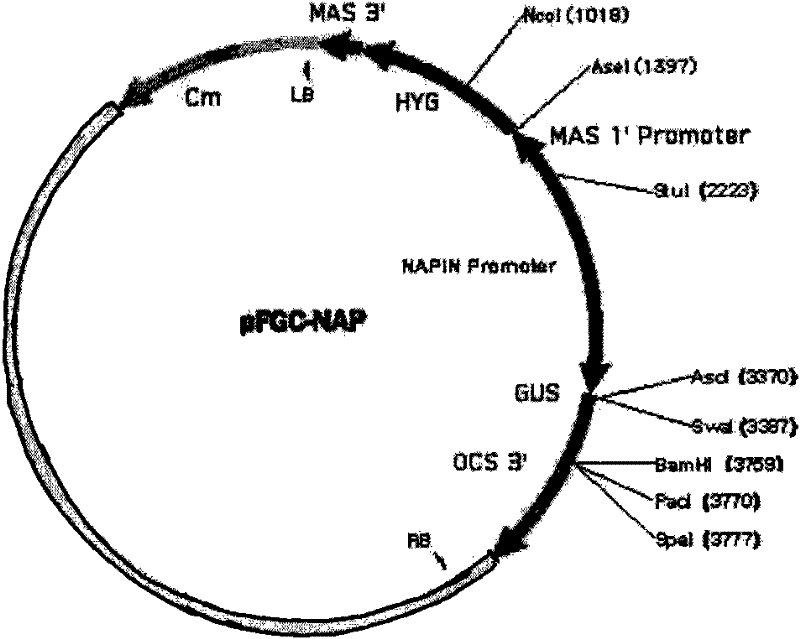
Plasmid for constructing interference vector and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN101880683AImprove qualityHigh interference efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsInverted Repeat SequencesA-DNA
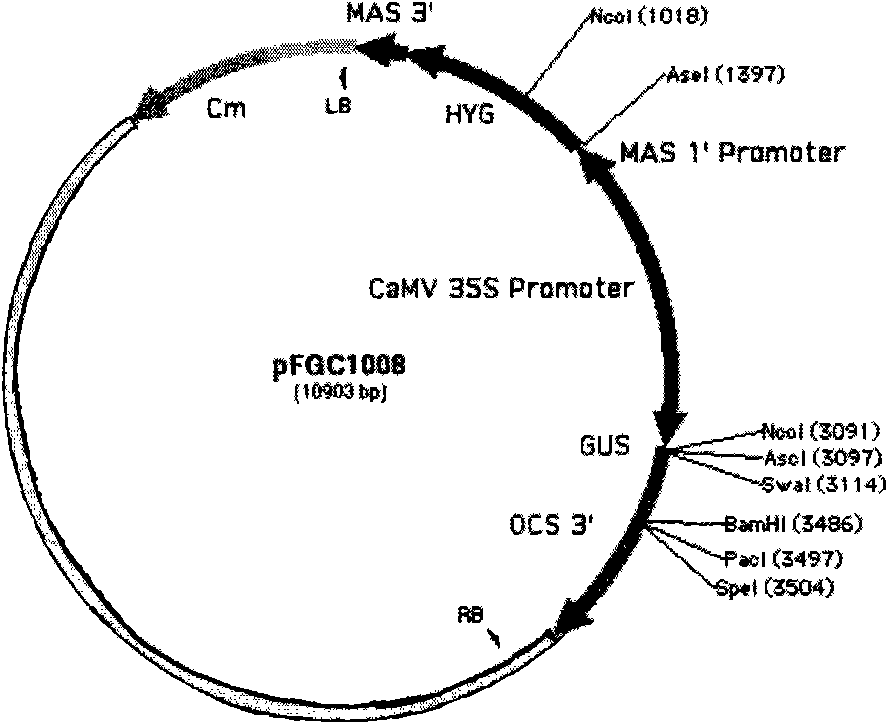
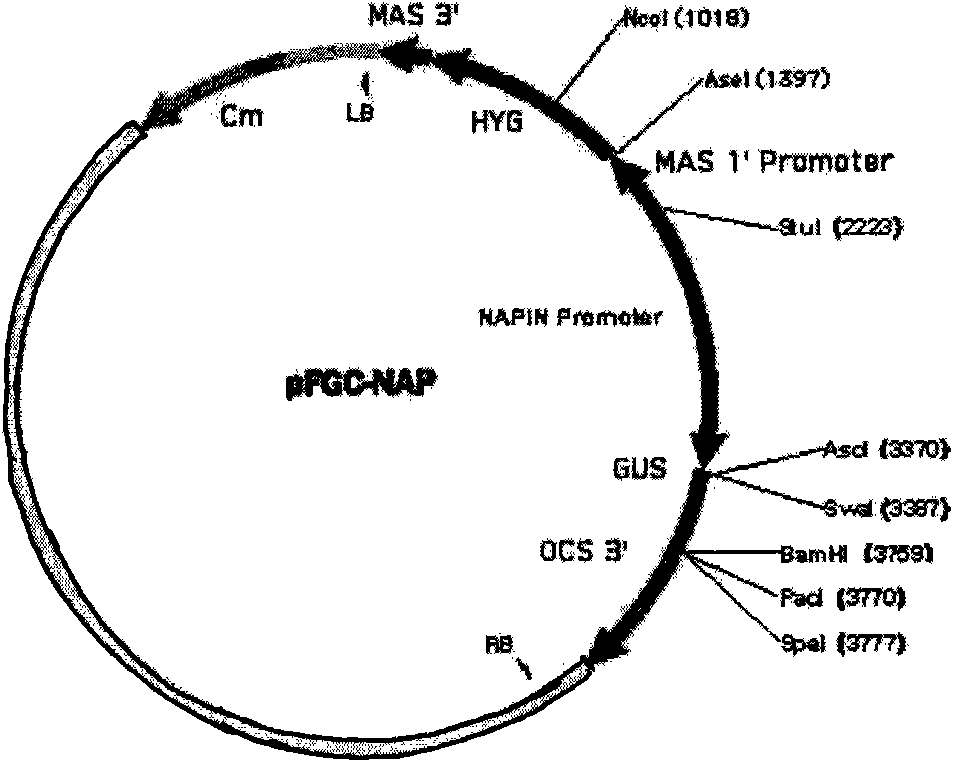
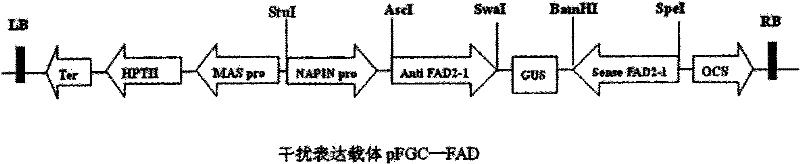
The invention discloses a plasmid for constructing an interference vector, a construction method thereof and application thereof. The invention provides a plasmid pFGC-NAP obtained by inserting a DNA presented by sequence 1 in a sequence list between an Stu I enzyme cutting site and an Asc I enzyme cutting site of a plasmid pFGC1008. The interference vector can be obtained by respectively inserting a plus-sense DNA fragment and an anti-sense DNA fragment into a multiple cloning site of the plasmid pFGC-NAP, wherein the plus-sense DNA fragment and the anti-sense DNA fragment are inverted repeat sequences designed for a target gene to be interfered and expressed. The plasmid constructs the interference vector capable of specially expressing a promoter during a seed development period, has high interference efficiency, can control a spatial temporal specificity expression, can be used for a specific gene expressed in silent plant seeds, and improves quality of oil crop seeds or other plant seeds.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
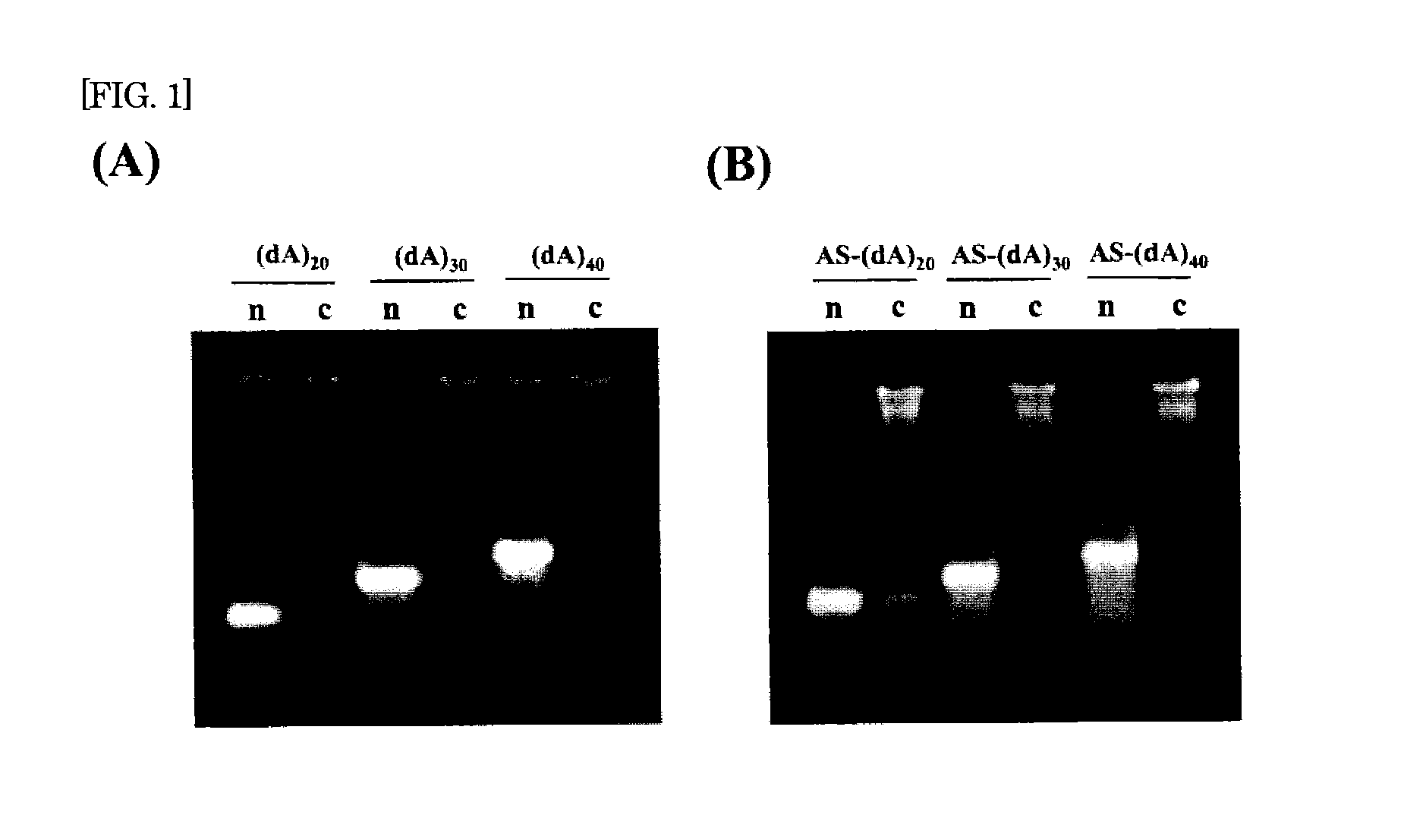
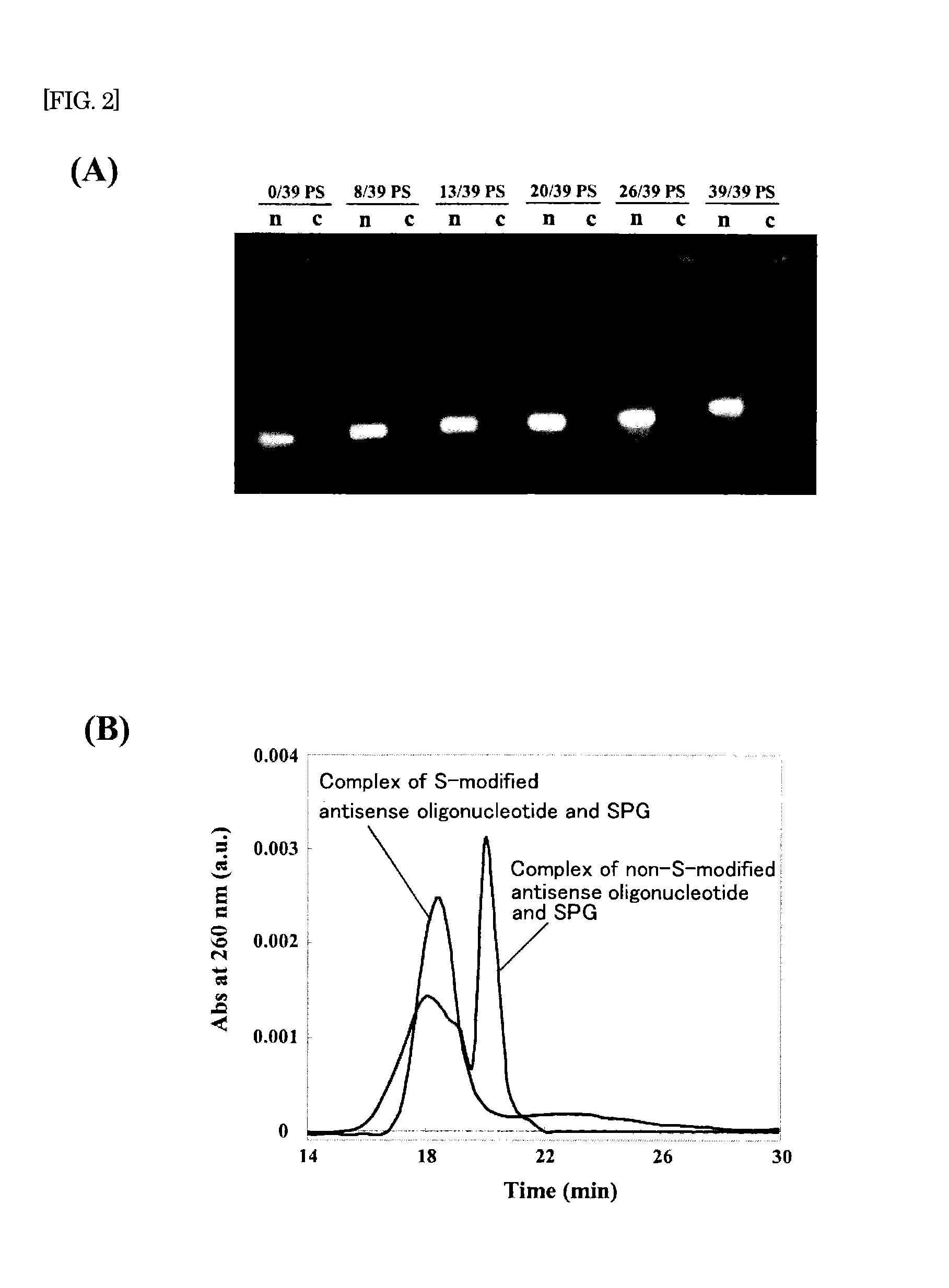
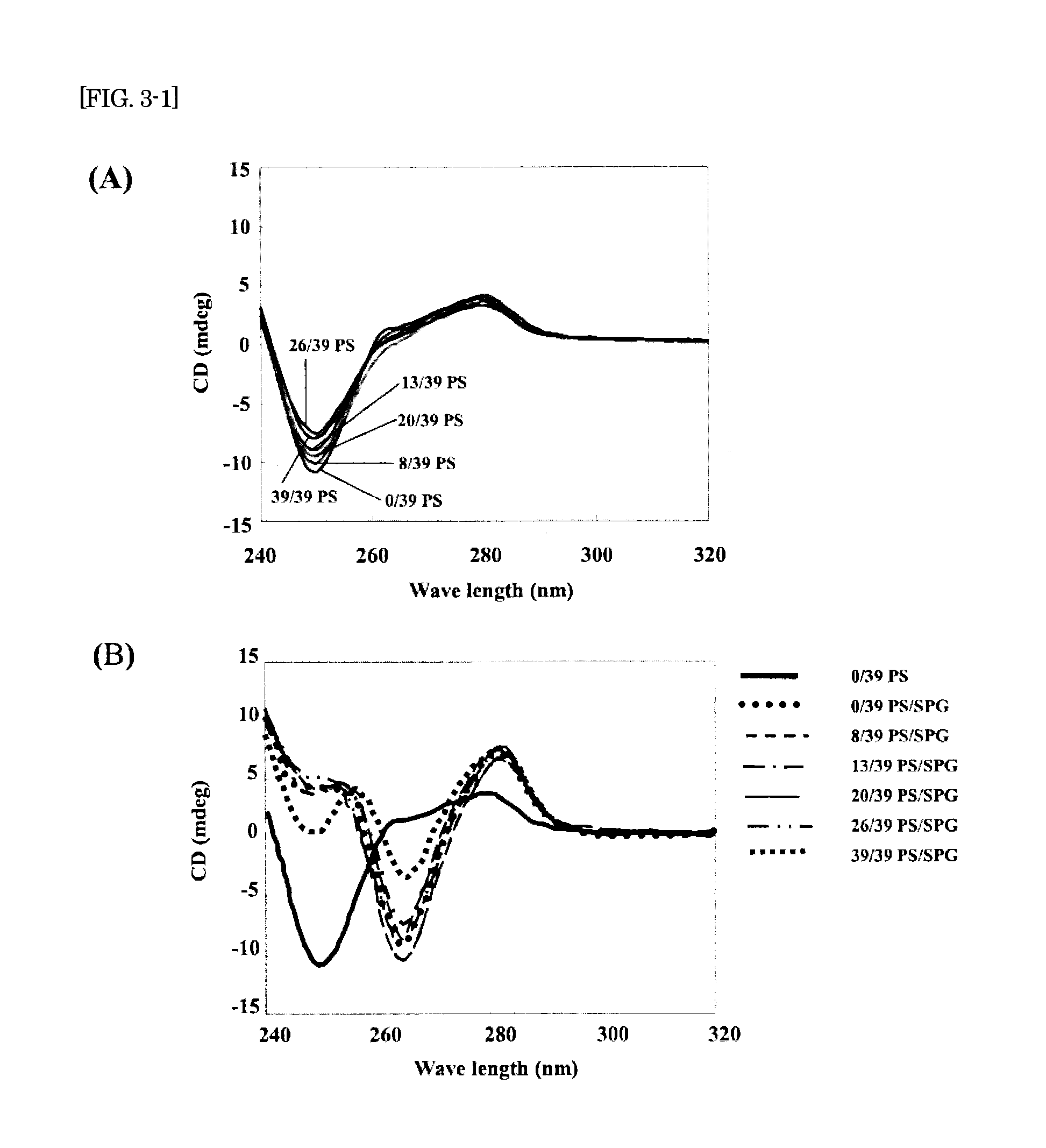
(nucleic acid)-polysaccharide complex
InactiveUS20130267576A1Improve stabilityLow cytotoxicityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAntisense DNAPolysaccharide binding
The present invention provides a nucleic acid-polysaccharide complex that is highly stable and has reduced cytotoxicity in a high yield. That is, the present invention provides a nucleic acid-polysaccharide complex of an antisense DNA having polydeoxyadenine (dA) as a polysaccharide binding site and a polysaccharide having a β-1,3-glucan skeleton wherein at least part of phosphodiester links of the polydeoxyadenine is phosphorothioated (provided that the phosphodiester links of the antisense DNA and the polydeoxyadenine are not entirely phosphorothioated).
Owner:NAPAJEN PHARMA
Agents for preventing and/or treating upper digestive tract disorders
A compound or its salts that inhibit the activity of the polypeptide or receptor of the present invention and the antibody of the present invention as well as the antisense DNA of the present invention are useful as, e.g., gastric acid secretion inhibitors, mucosa protectants, mineral absorption promoters, etc., which are less toxic and safe, and can be used as, e.g., agents for preventing / treating upper digestive tract disorders, antibacterial agents to Helicobacter pylori, etc. A compound or its salts that promote the activity of the polypeptide or receptor of the present invention, the polypeptide or receptor of the present invention and the DNA of the present invention can be used as, e.g., gastric acid secretion promoters and can be used as, e.g., agents for preventing / treating dyspepsia, bone metabolism disorders, anemia, etc. A compound or its salts that promote the activity of the polypeptide or receptor of the present invention, the polypeptide of the present invention, etc. can also be used as test agents for gastric secretory function. Furthermore, the polypeptide or receptor of the present invention and the DNA of the present invention are also useful for screening the agents for the prevention / treatment described above.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
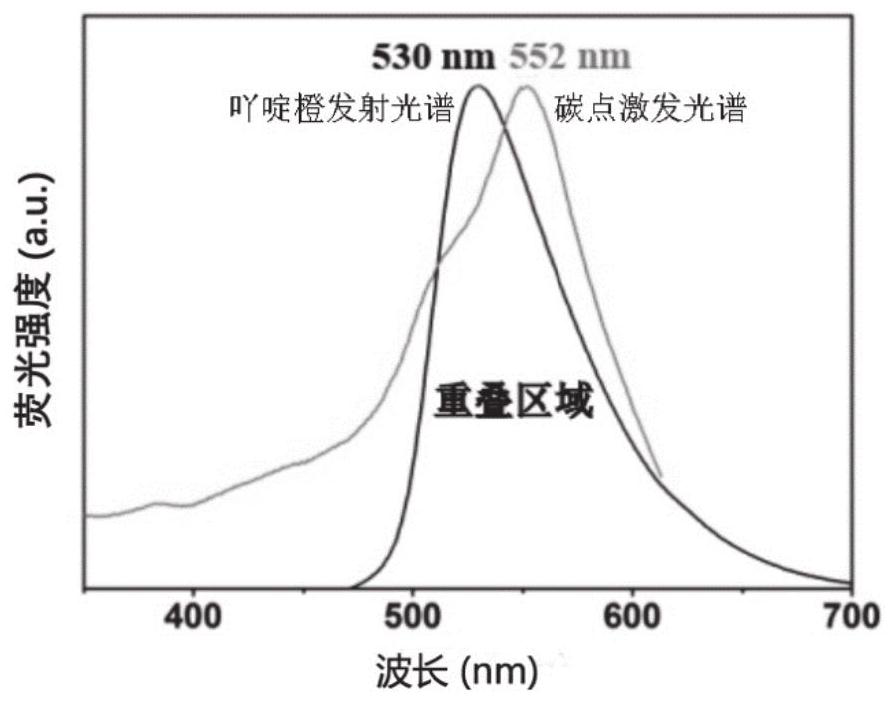
Method for in-vitro detection of miRNA based on ratio fluorescence of acridine orange and carbon dots
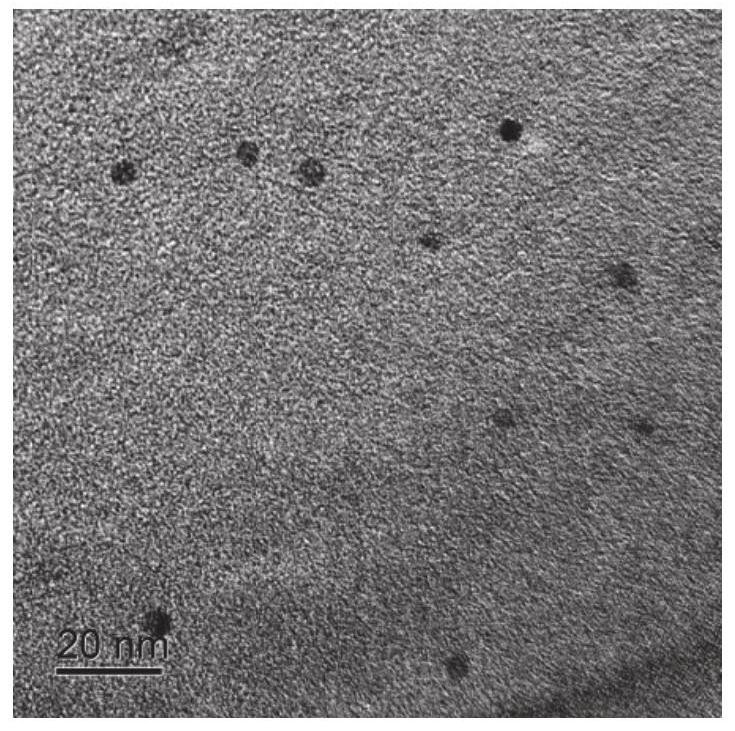
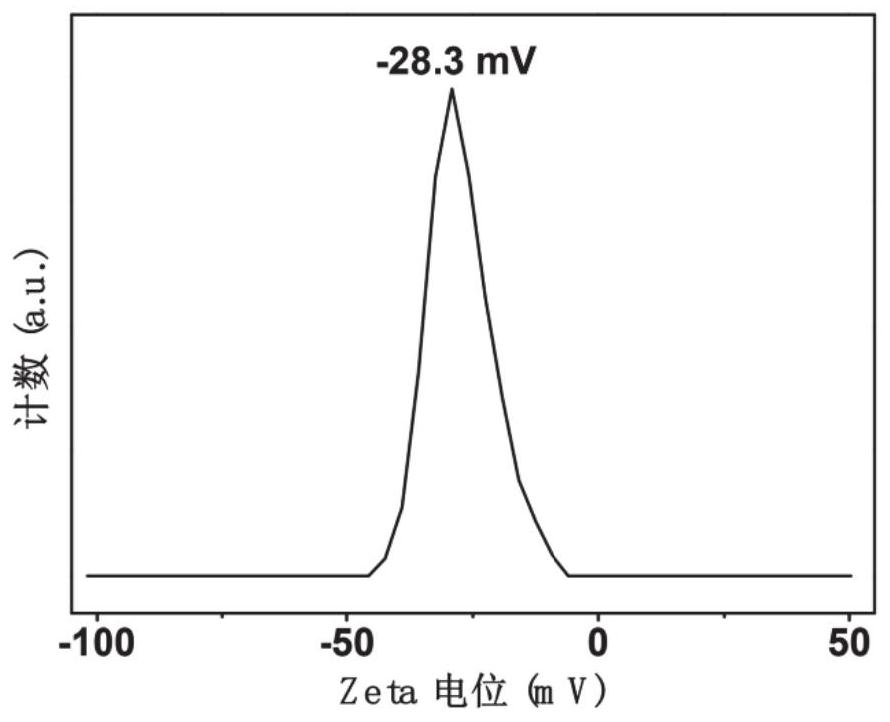
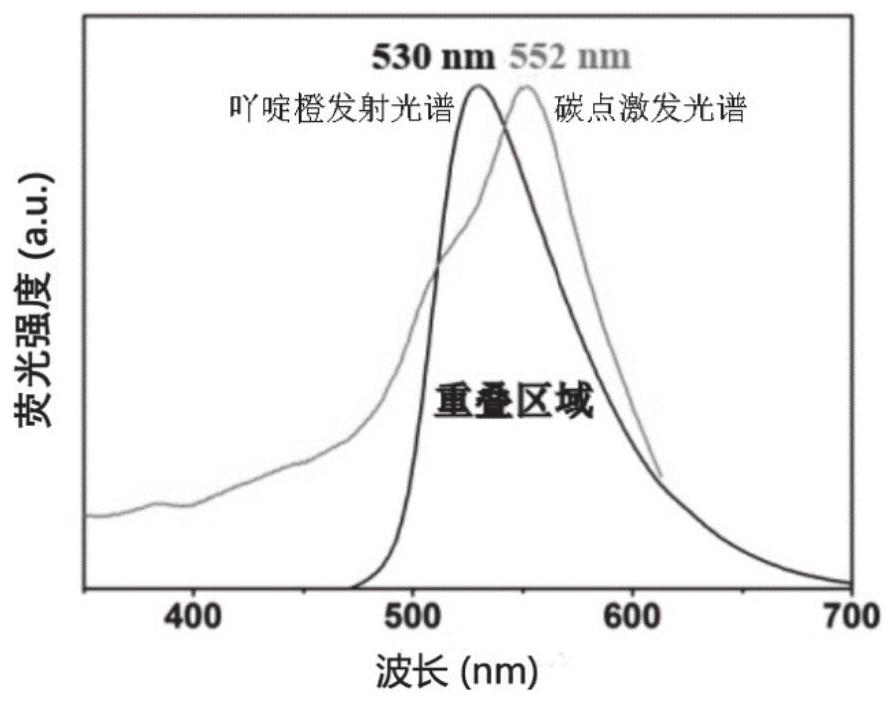
ActiveCN112798567AGood repeatabilitySimple Ratiometric Fluorescence DetectionFluorescence/phosphorescenceAntisense DNAReceptor
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological detection and relates to a method for in-vitro detection of miRNA based on ratiometric fluorescence of acridine orange and carbon dots. The method comprises the following steps of preparing a carbon dot which is subjected to fluorescence resonance energy transfer with acridine orange, taking the acridine orange as a donor, taking the carbon dot as a receptor, and taking an antisense DNA chain of miRNA to be detected as a probe; adding a to-be-detected miRNA solution into a DNA probe solution with a certain concentration, incubating at 37 DEG C for 90 minutes, adding an acridine orange solution, adsorbing for 10 minutes, adding a carbon dot solution, and standing for 10 minutes; and testing fluorescence intensity of the mixed solution by using a fluorospectro photometer and calculating the concentration of the miRNA to be detected. The method is simple and convenient to operate, high in sensitivity and good in repeatability and specificity, and is a reliable method for miRNA in-vitro detection.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for identifying drug-sensitizing antisense DNA fragments and use thereof
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
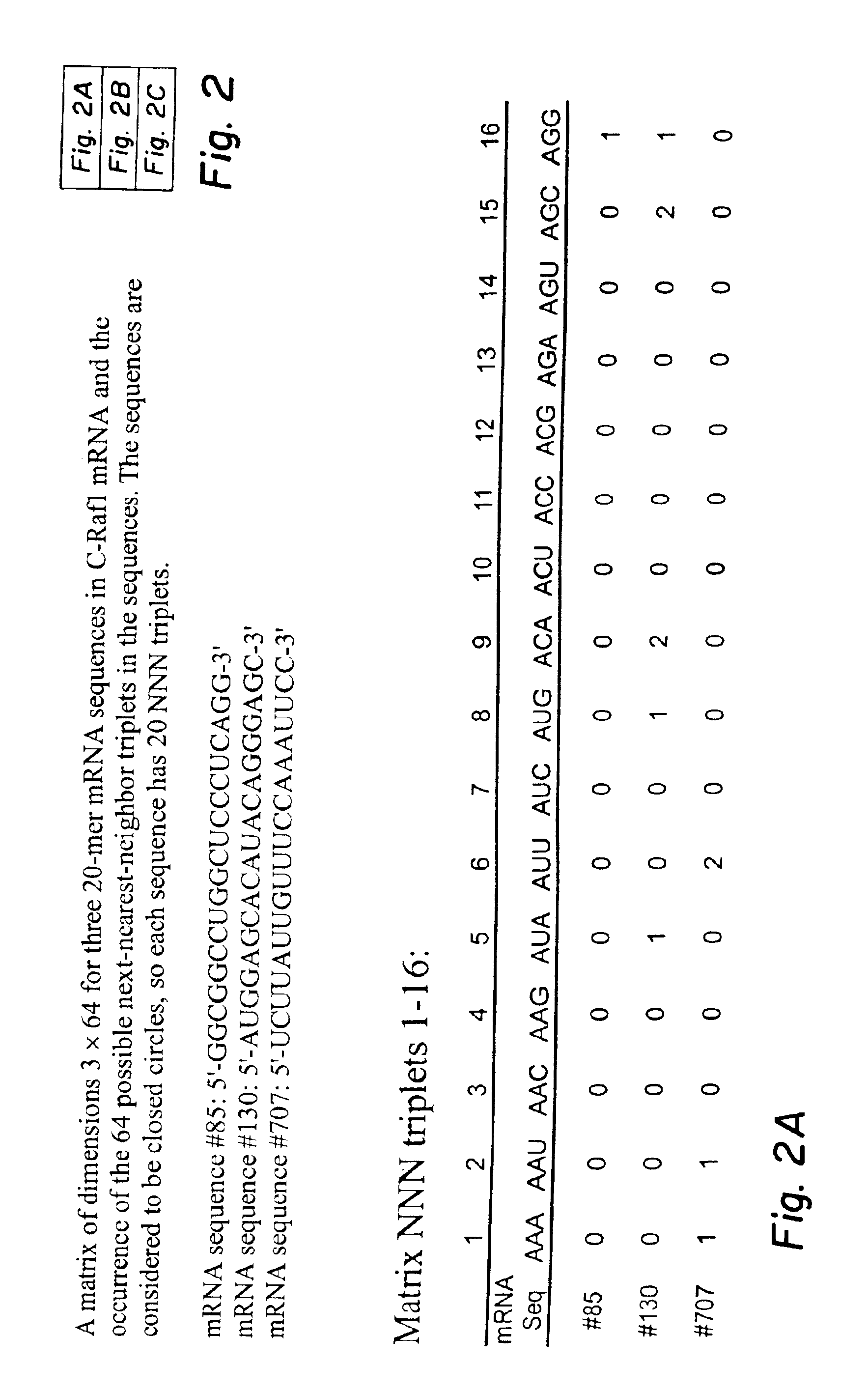
Next-nearest-neighbor sequence determinants of antisense DNA
InactiveUS6957148B2Positively correlatedImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingBinding siteNucleotide
The use of antisense oligodeoxyribonucleotides (ODNs) to inhibit translation of mRNAs promises to be an important means of controlling gene expression and disease processes. ODNs are about 20 nucleotides long, so hundreds of possible targets are available in a given mRNA. An elusive goal has been to efficiently predict the best in vivo antisense target without having to study a large pool of possible ODN sequences for each mRNA. It would be a breakthrough if ODN selection could be accurately guided by the application of sequence specific parameters to an mRNA sequence. The selection of the best ODN sequence is complicated since cellular uptake, conditions at the mRNA target site, non-sequence-specific effects, sequence redundancy, and mRNA secondary structures are difficult to predict. Thermodynamic parameters for nearest-neighbor (dimer) duplex stabilities, from in vitro studies, have not been adequate predictors of in vivo hybridization. The methodology of this application shows that it is possible to obtain parameters for in vivo motifs, which are defined as combinations of next-nearest-neighbors, that are correlated with efficient antisense targeting. These parameters can be used to identify mRNA sequences that are binding sites for effective antisense ODNs. Next-nearest-neighbor nucleotide parameters can be derived directly from cell culture inhibition data so that in vivo conditions are taken into account.
Owner:BOARD OF REAGENTS
Expression vector of duplicate inverted waxy gene, preparation method, and application
InactiveCN100489103CReduce amylose contentReduce expressionVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationAntisense DNAAgricultural science
This invention discloses a method for preparing an expression vector containing double antisense waxy genes and its application. The structure and characteristics of the expression vector are shown in figure (d). The expression vector comprises promoter sequence, antisense DNA fragment of the target gene, terminator sequence, and endonuclease-sensitive sequence or marker gene sequence. All the sequences are doubled along the same direction. The expression vector can be used for breeding Gramineae plants such as rice without resistance-screening gene and with low amylase content.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A method based on ratiometric fluorescence of acridine orange and carbon dots for miRNA detection in vitro
ActiveCN112798567BGood repeatabilitySimple Ratiometric Fluorescence DetectionFluorescence/phosphorescenceAntisense DNARatiometric fluorescence
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological detection, and relates to a method for in vitro detection of miRNA based on the ratio fluorescence of acridine orange and carbon dots. The method comprises the following steps: preparing carbon dots that undergo fluorescence resonance energy transfer with acridine orange, acridine orange as a donor and carbon dots as acceptors, using the antisense DNA strand of the miRNA to be tested as a probe; Add the solution to a certain concentration of DNA probe solution and incubate at 37°C for 90 minutes, add acridine orange solution and absorb for 10 minutes, add carbon dot solution and let it stand for 10 minutes; use a fluorescence spectrophotometer to test the fluorescence of the above mixed solution Intensity and calculate the concentration of miRNA to be tested. The invention has the advantages of simple operation, high sensitivity, good repeatability and specificity, and is a reliable method for in vitro detection of miRNA.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
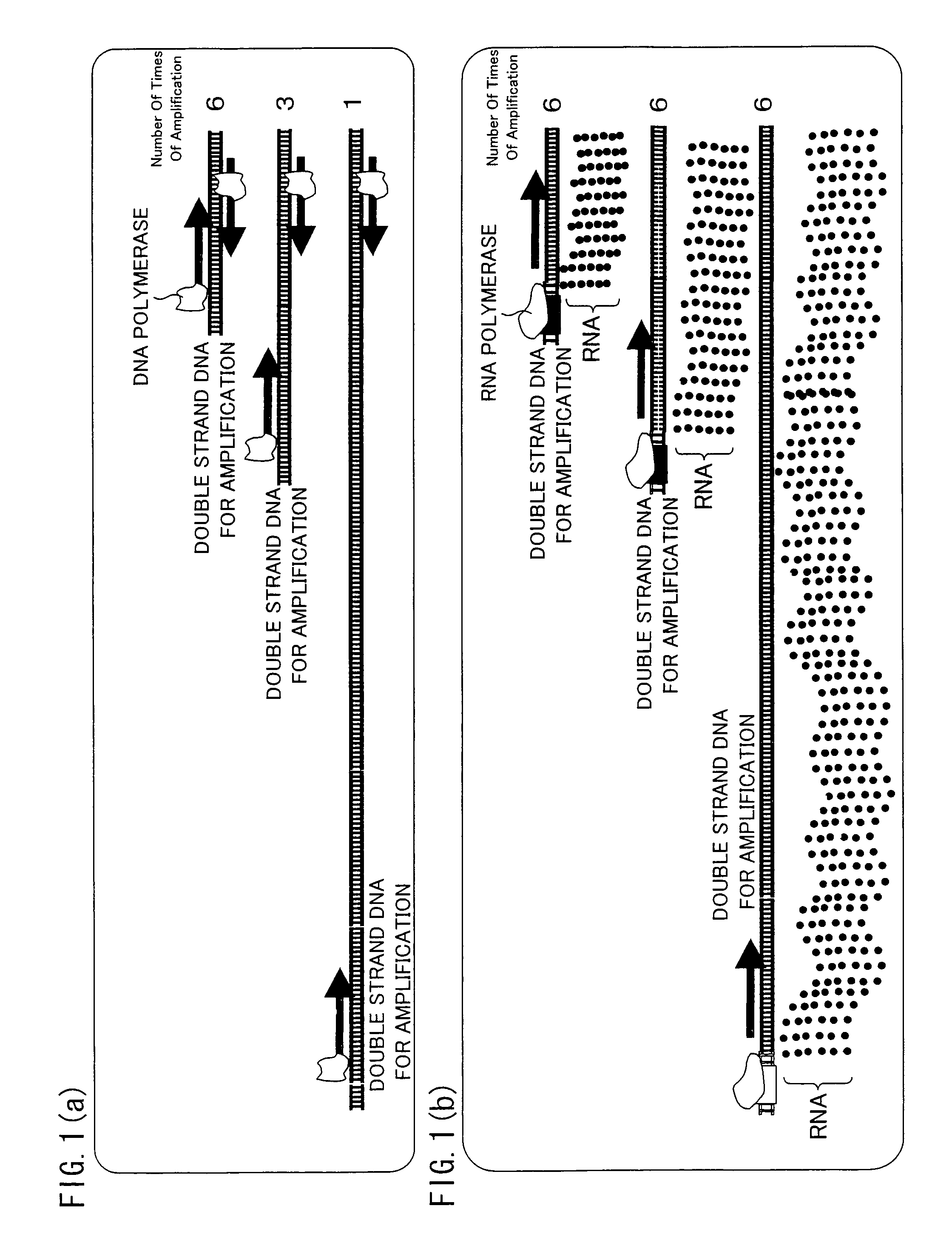
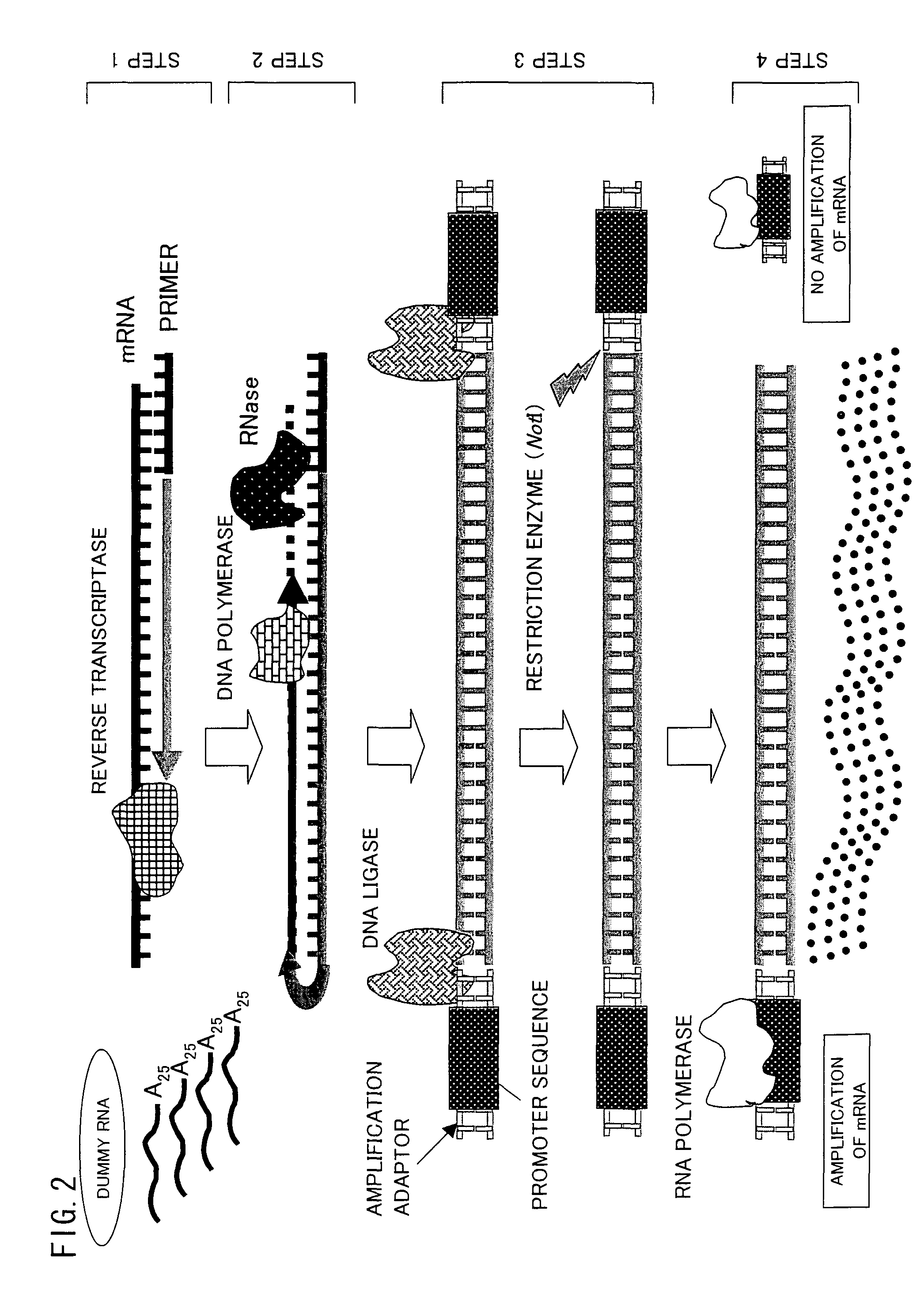
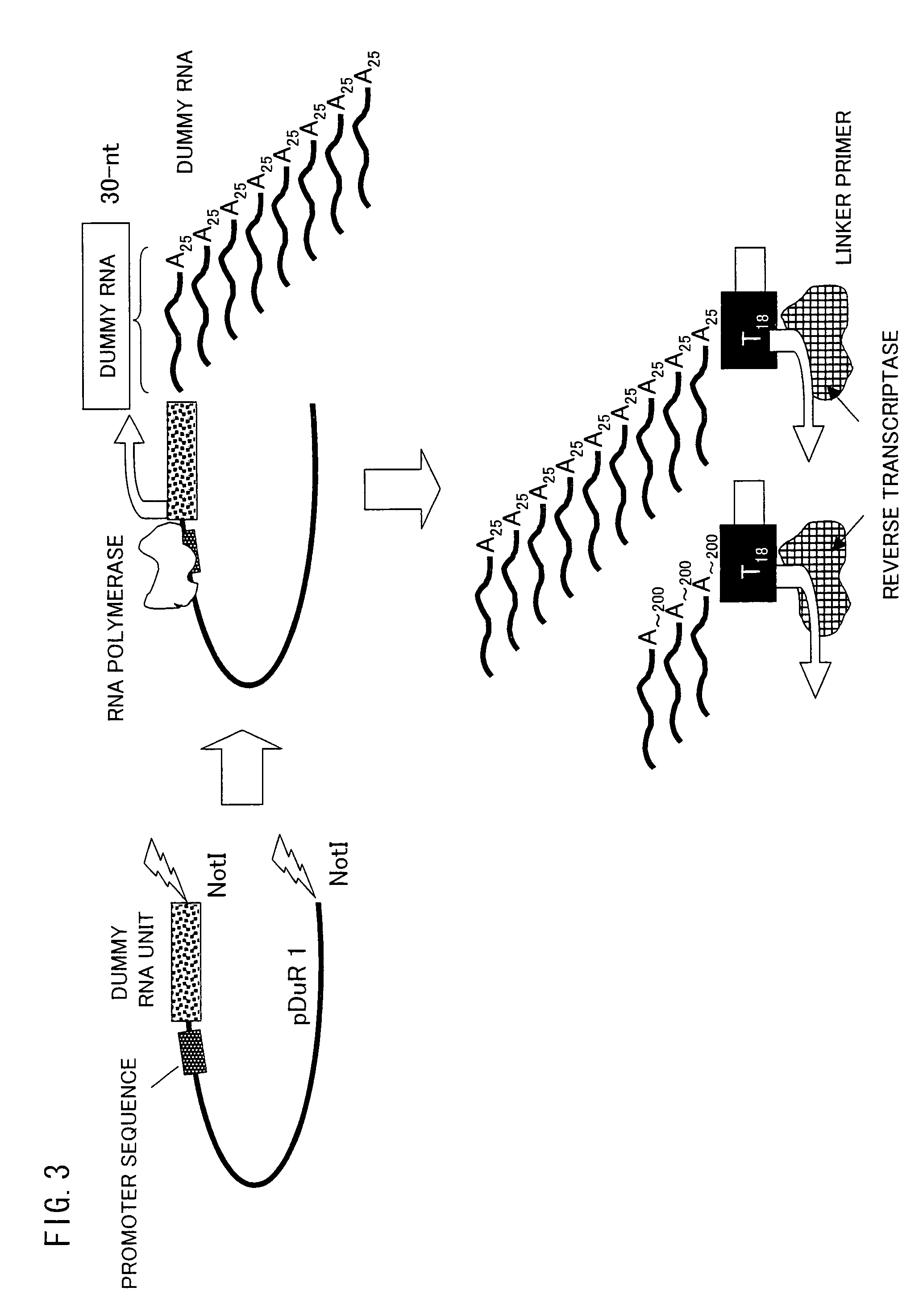
Trace mRNA amplification method and use thereof
InactiveUS8206924B2Efficiently amplify a long mRNASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAntisense DNATrace Amounts
A method for amplifying a trace amount of mRNA includes adding a dummy RNA to a solution containing the trace amount of mRNA, so as to prepare a mixed solution; synthesizing an anti-sense DNA by reverse transcription, which uses the mixed solution as a template; synthesizing a sense DNA which is complementary to the anti-sense DNA thus synthesized, so as to generate a double-strand DNA made of the sense DNA and the anti-sense DNA; ligating an RNA polymerase promoter sequence to the double-strand DNA thus generated, on a sense DNA 5′ end side of the double-strand DNA, so as to prepare a double-strand DNA for amplification; and amplifying, by using RNA polymerase, an RNA from the double-strand DNA for amplification.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
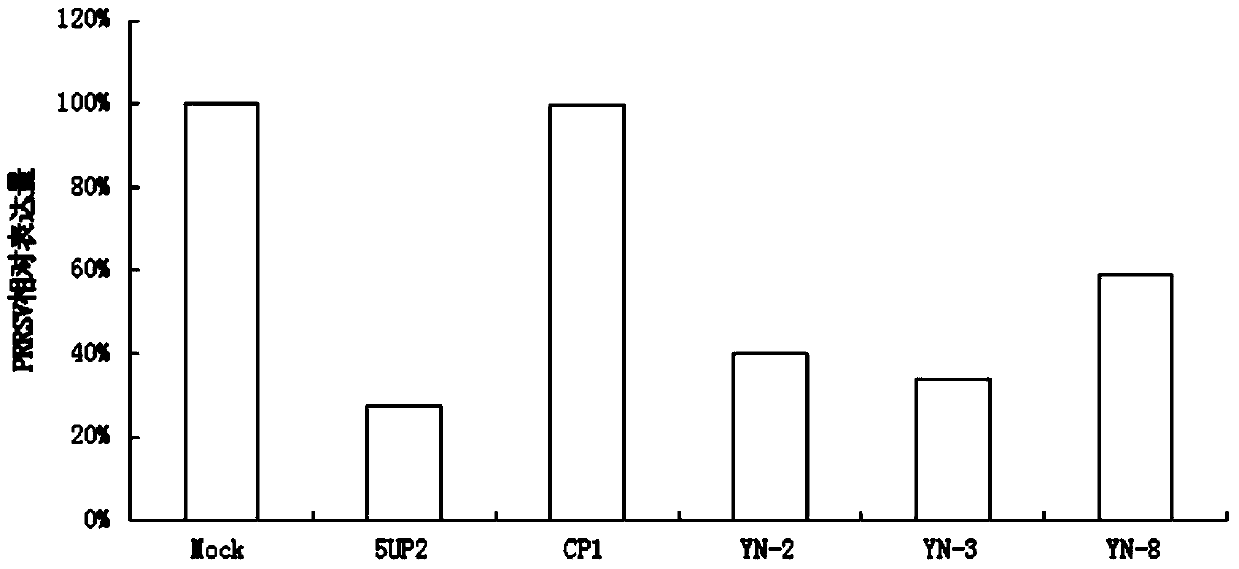
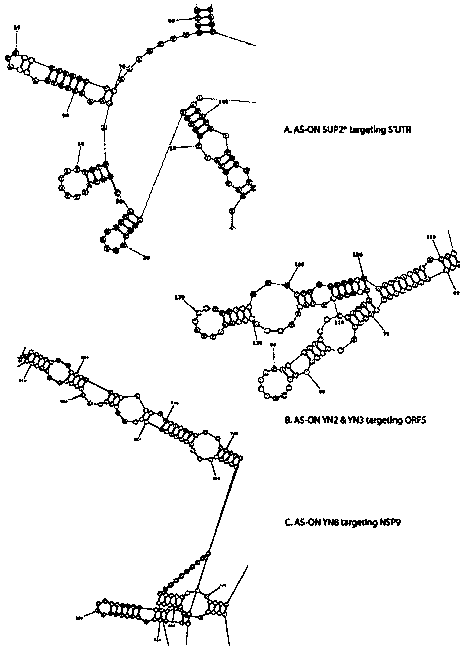
Antisense DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sequence for treating and preventing porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome and application thereof
ActiveCN104195139ADownregulation of gene expressionDefinite antiviral effectGenetic material ingredientsAntiviralsFluorescenceFhit gene
The invention provides an antisense DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sequence for treating and preventing PRRS (Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome) and an application thereof. The single-chain antisense DNA sequence is 20nt antisense DNA which is designed and synthesized by taking the partial sequence of a PRRSV (Porcine Reproductive And Respiratory Syndrome Virus) gene as a target spot without other chemical modifications. Monkey kidney epithelial Marc-145 cells are transfected by adopting a lipidosome mediated method, so that the proliferation of the PRRSV on the Marc-145 cells can be outstandingly inhibited; and the antisense DNA sequence is detected through a fluorescent quantitative RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) method and an indirect immunofluorescence experiment method to have the effects of outstandingly reducing the nucleoprotein gene expression of the PRRSV and inhibiting virus multiplication. Thus, the antisense DNA sequence provided by the invention has a wide application prospect on the treatment and control of infection of the PRRSV and important value on the gene therapy of the PRRS and has the advantages of easiness for source, low cost and great market value.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for identifying drug-sensitizing antisense DNA fragments and use thereof
The invention provides a method for generating and selecting drug-sensitizing antisense DNA fragments. In one embodiment, the method includes identifying a gene of interest using knowledge of bacterial physiology, biochemistry, genetics, genomics, and other means. The method includes PCR amplification of a gene of interest using genomic DNA as a template; fragmentation of the DNA by sonication or other means; selecting DNA fragments no longer than 400 base pairs; ligating the DNA fragments into a suitable expression plasmid with a selectable marker; transforming the plasmids containing the DNA fragments into the organism from which the gene of interest originated; and selecting clones from transformed cells that show a phenotypic difference of the clone grown in the presence of the inducer relative to the phenotype in the absence of inducer.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Plasmid for constructing interference vector and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN101880683BImprove qualityHigh interference efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsInverted Repeat SequencesPlanting seed
The invention discloses a plasmid for constructing an interference vector, a construction method thereof and application thereof. The invention provides a plasmid pFGC-NAP obtained by inserting a DNA presented by sequence 1 in a sequence list between an Stu I enzyme cutting site and an Asc I enzyme cutting site of a plasmid pFGC1008. The interference vector can be obtained by respectively inserting a plus-sense DNA fragment and an anti-sense DNA fragment into a multiple cloning site of the plasmid pFGC-NAP, wherein the plus-sense DNA fragment and the anti-sense DNA fragment are inverted repeat sequences designed for a target gene to be interfered and expressed. The plasmid constructs the interference vector capable of specially expressing a promoter during a seed development period, has high interference efficiency, can control a spatial temporal specificity expression, can be used for a specific gene expressed in silent plant seeds, and improves quality of oil crop seeds or other plant seeds.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
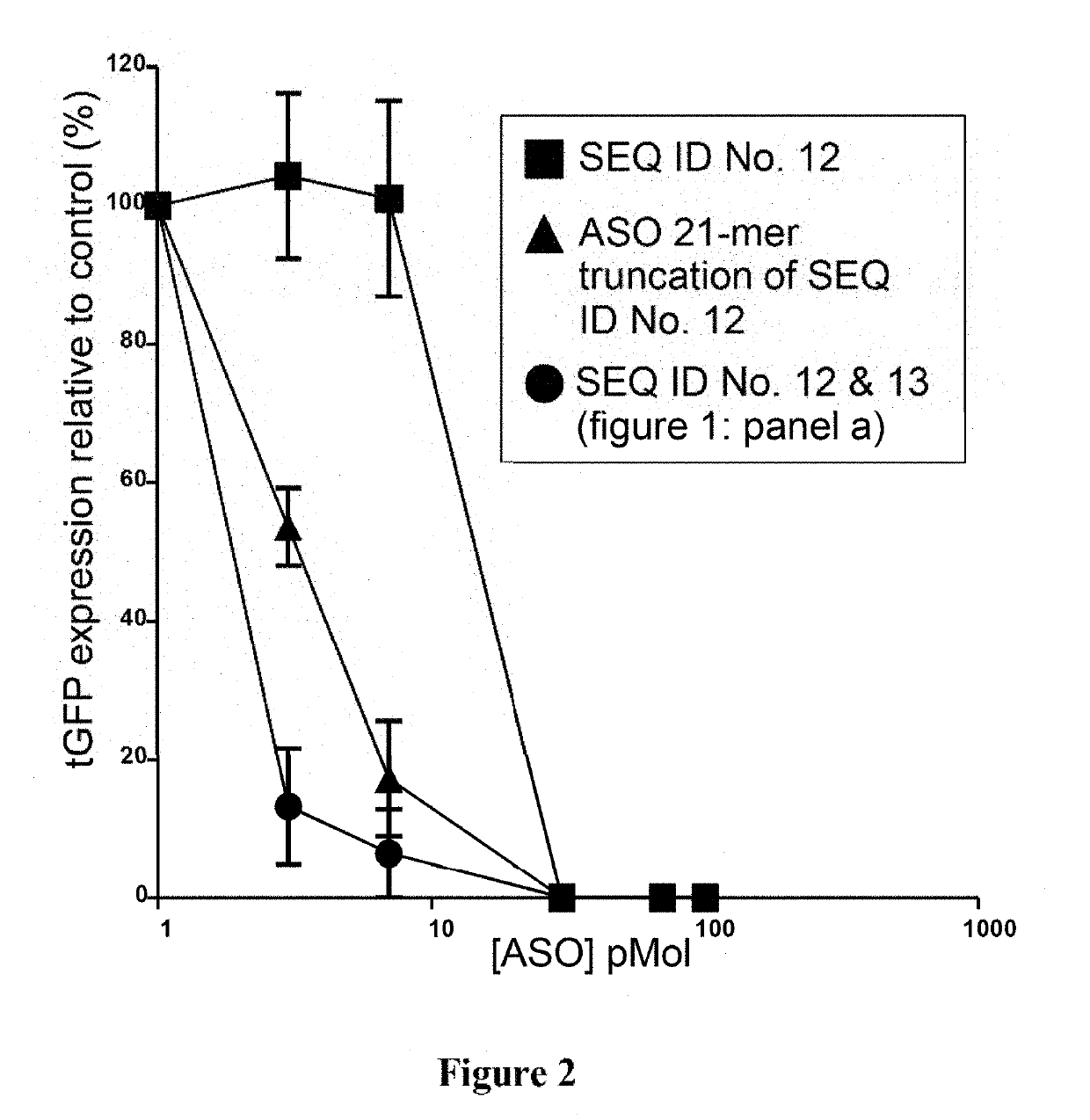
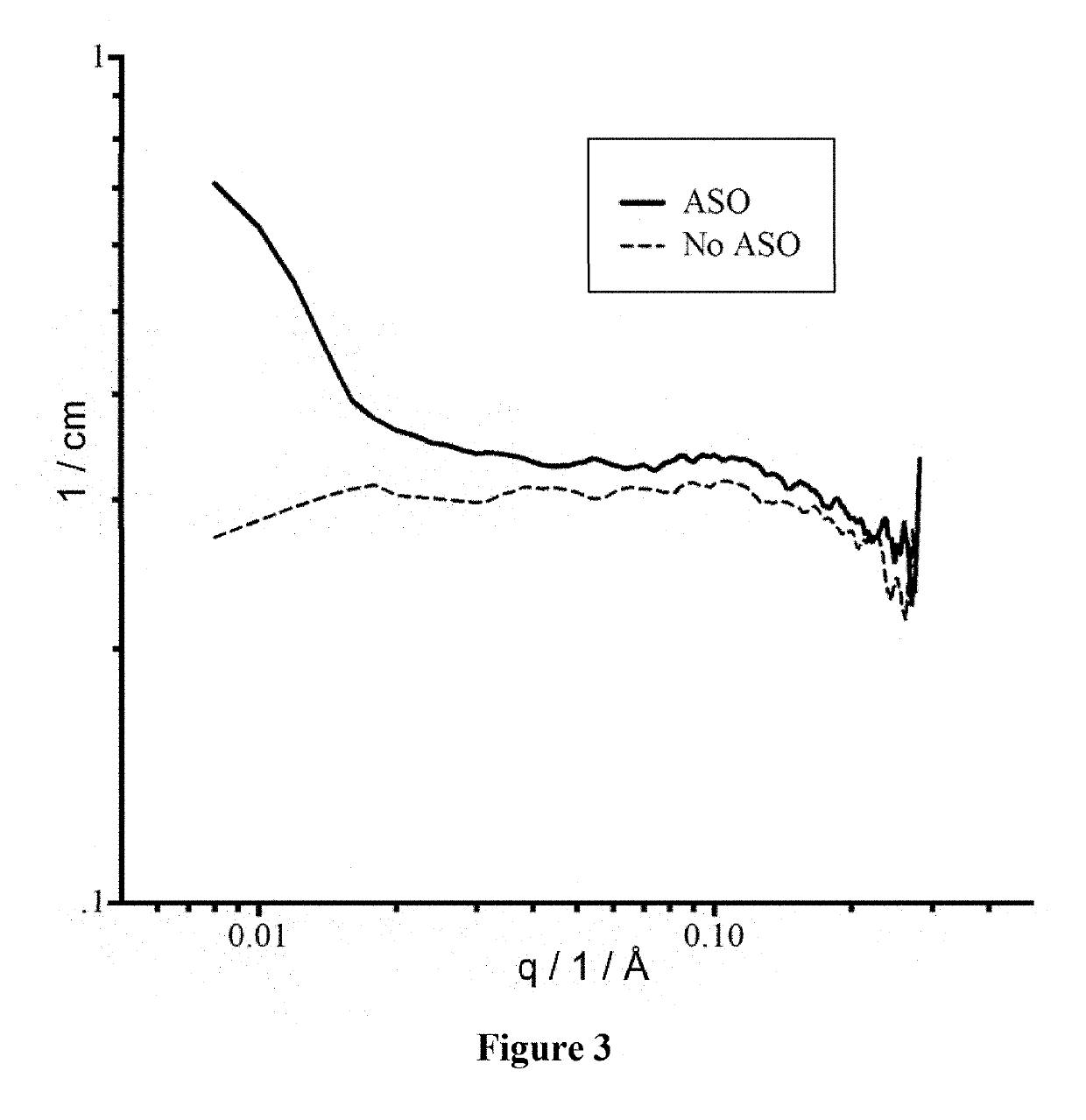
Antisense oligonucleotide compositions
ActiveUS10400241B2Improve stabilityReduce deliverySpecial deliveryAntiviralsAntisense DNASingle strand
The present invention relates to antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) compositions and particularly to compositions and methods for the cytosolic delivery of antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs). Hybrid ASOs, part single-stranded and part double-stranded, are provided, hybridizing to form a double-stranded region that can non-covalently bond to nucleic-acid-binding protein regions. In this way, ASO::protein complexes may be produced that facilitate delivery of antisense DNA into target cells. Such complexes may be used to down-regulate gene expression in cells.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GREENWICH
Inhibitor of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha coactivator 1
InactiveCN101166751AControl effectivenessOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDiseaseTolerability
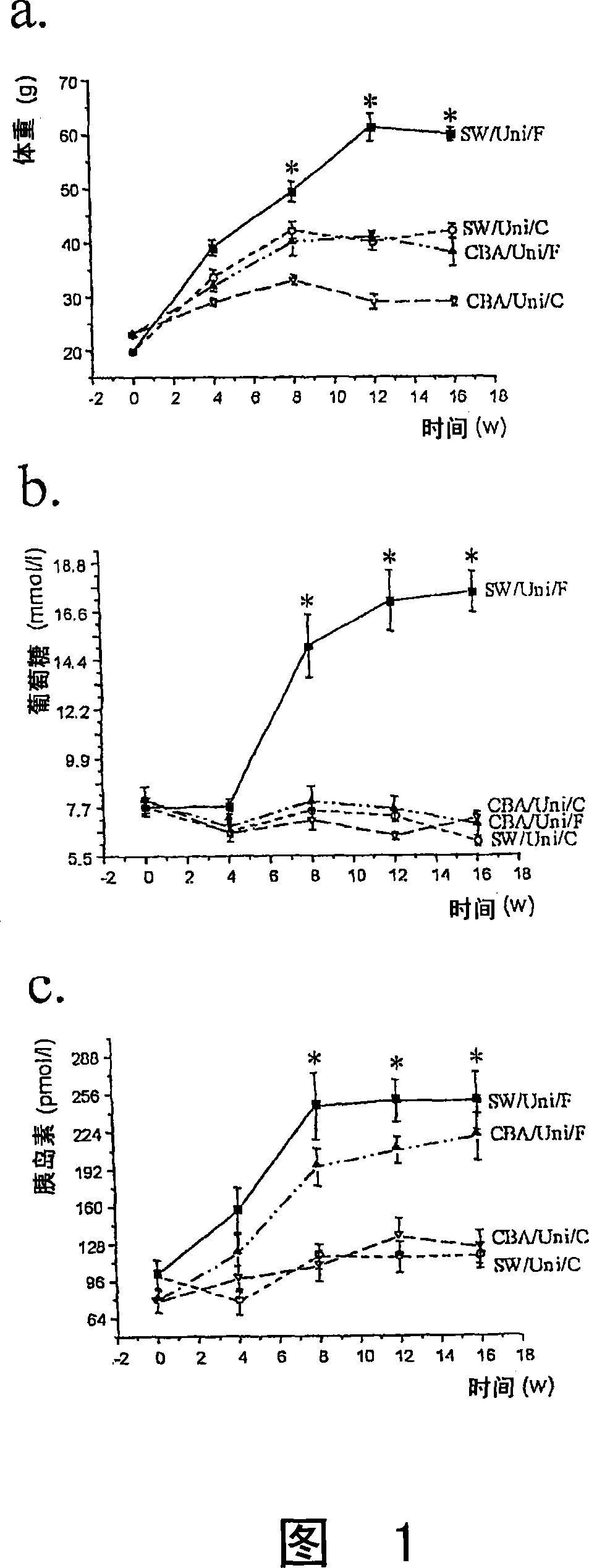
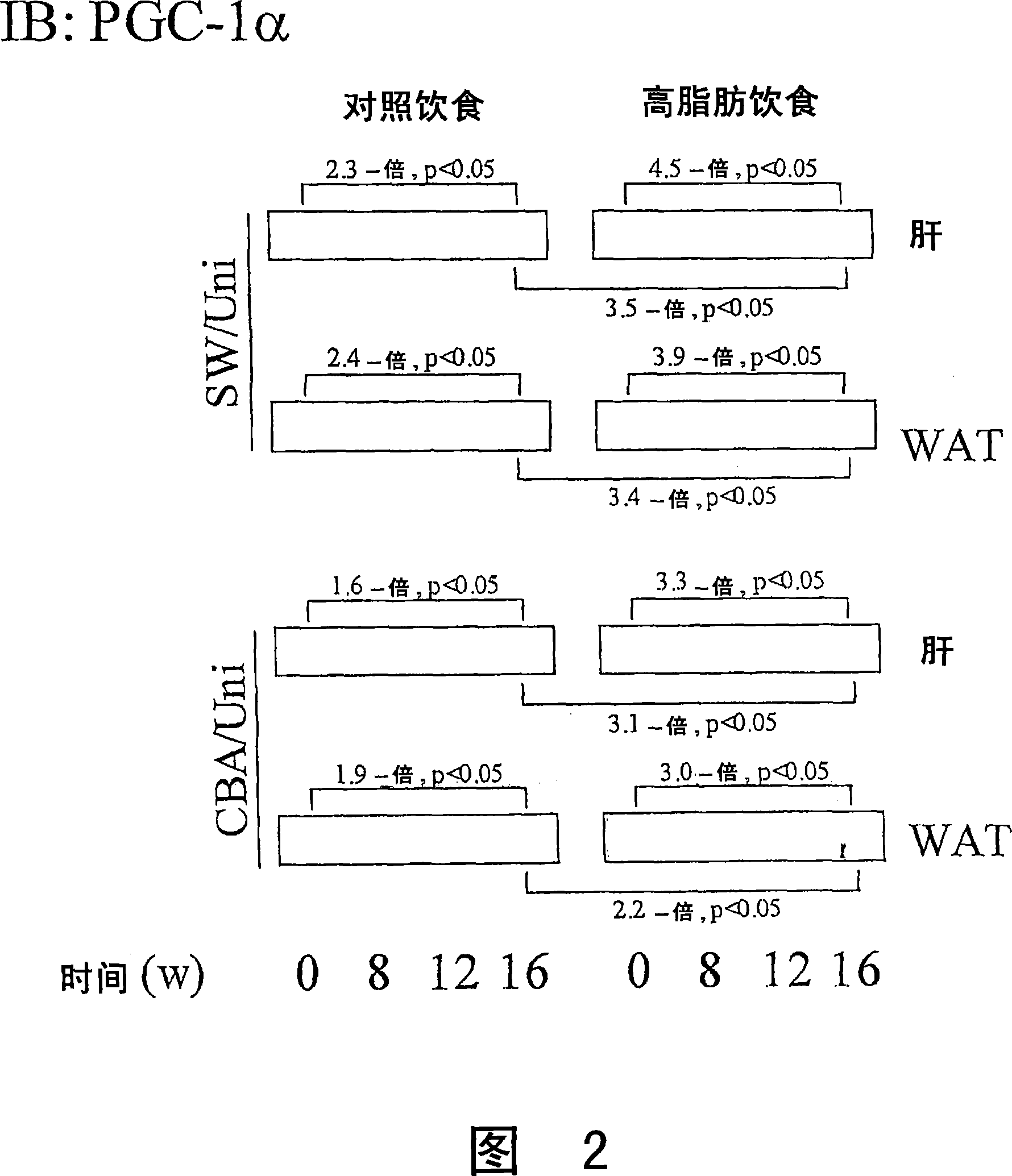
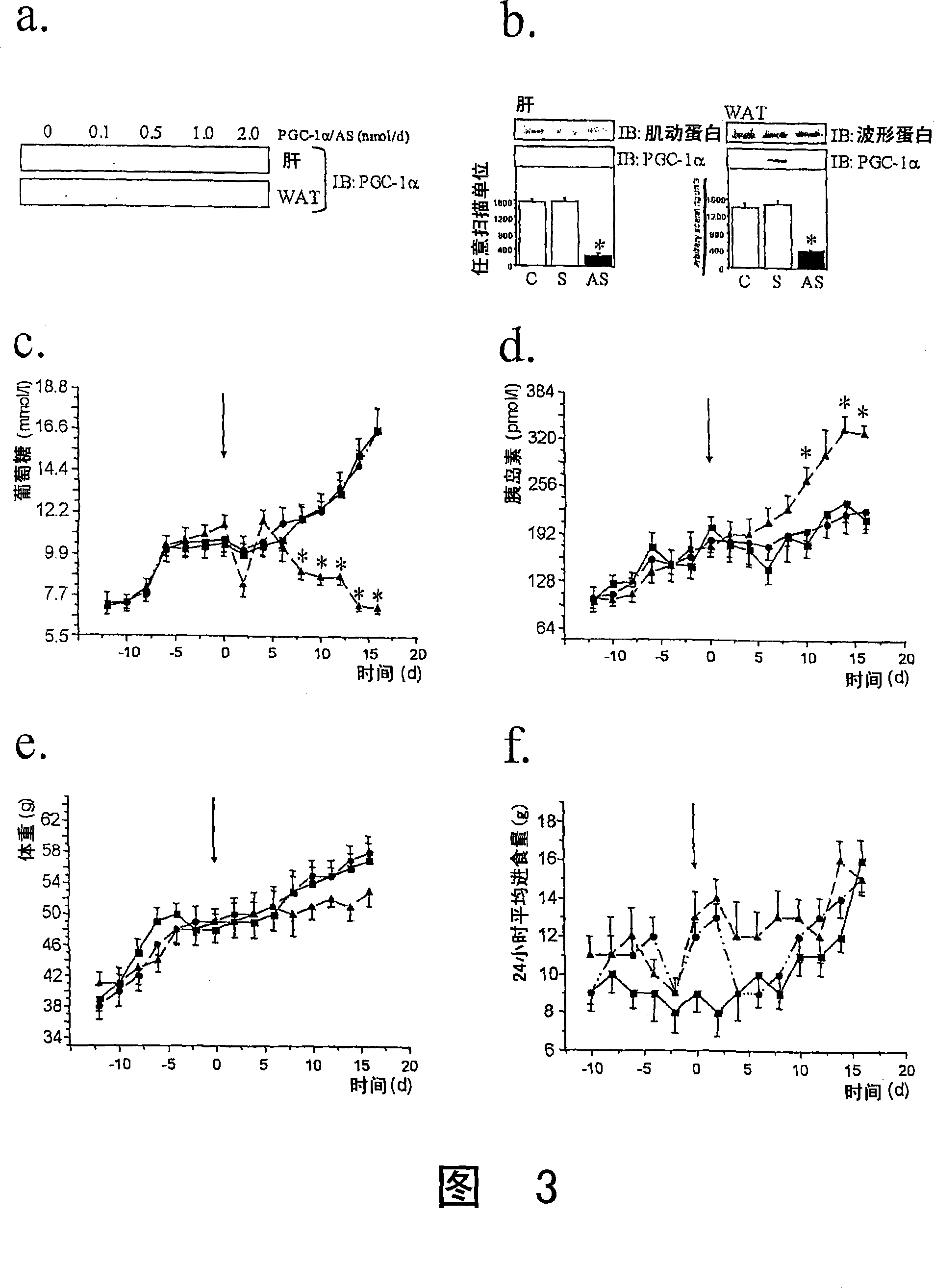
The present invention refers to the use of an antisense DNA oligonucleotide for the messenger RNA of the PGC-la protein, useful as drug for the treatment of diabetes mellitus, insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. More specifically, the present invention deals with a compound used as drug, through enteral or parenteral route, preferably, with the property of inhibiting the protein expression peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha Coactivator 1 (PGC-la) leading to the reduction of the blood glucose levels. It deals, therefore, with a pharmacological compound that promotes, in diabetic and insulin-resistant individuals, improvement of the glucose serum levels, increase of the plasmatic insulin concentration and reduction of insulin resistance. The present invention presents a more effective control of the glucose levels and acts beneficially on other complications associated to the Diabetes and obesity conditions, according to tests performed in animal models. In this manner, the principal advantage of the present invention over others alike already existing in the market is the effectiveness that controls blood glucose levels and the fact of acting beneficially on other complications that accompany the disease.
Owner:坎皮纳斯州立大学 UNICAMP
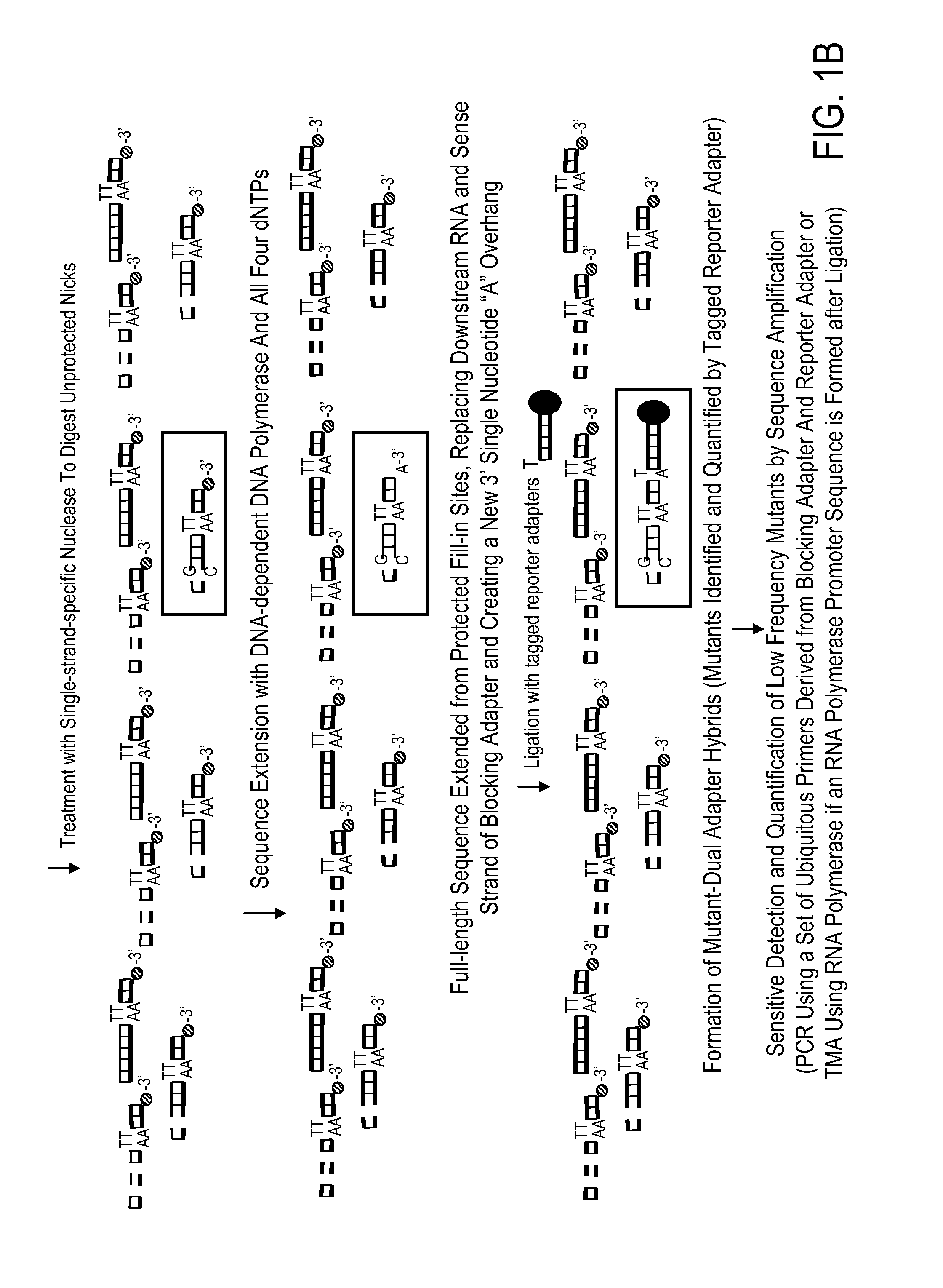
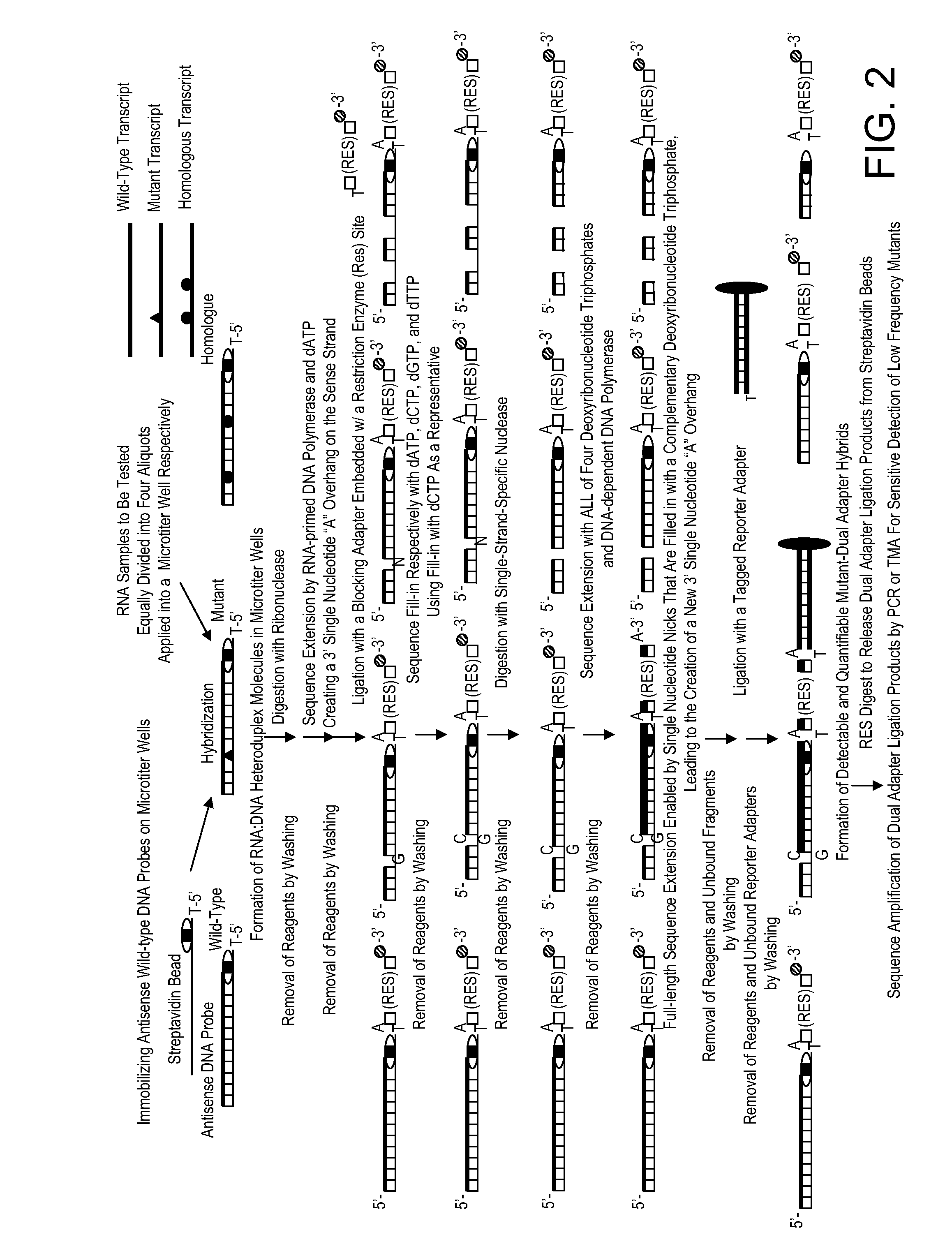
Kit for high throughput mutation screening methods
Owner:LEE MING SHENG +2
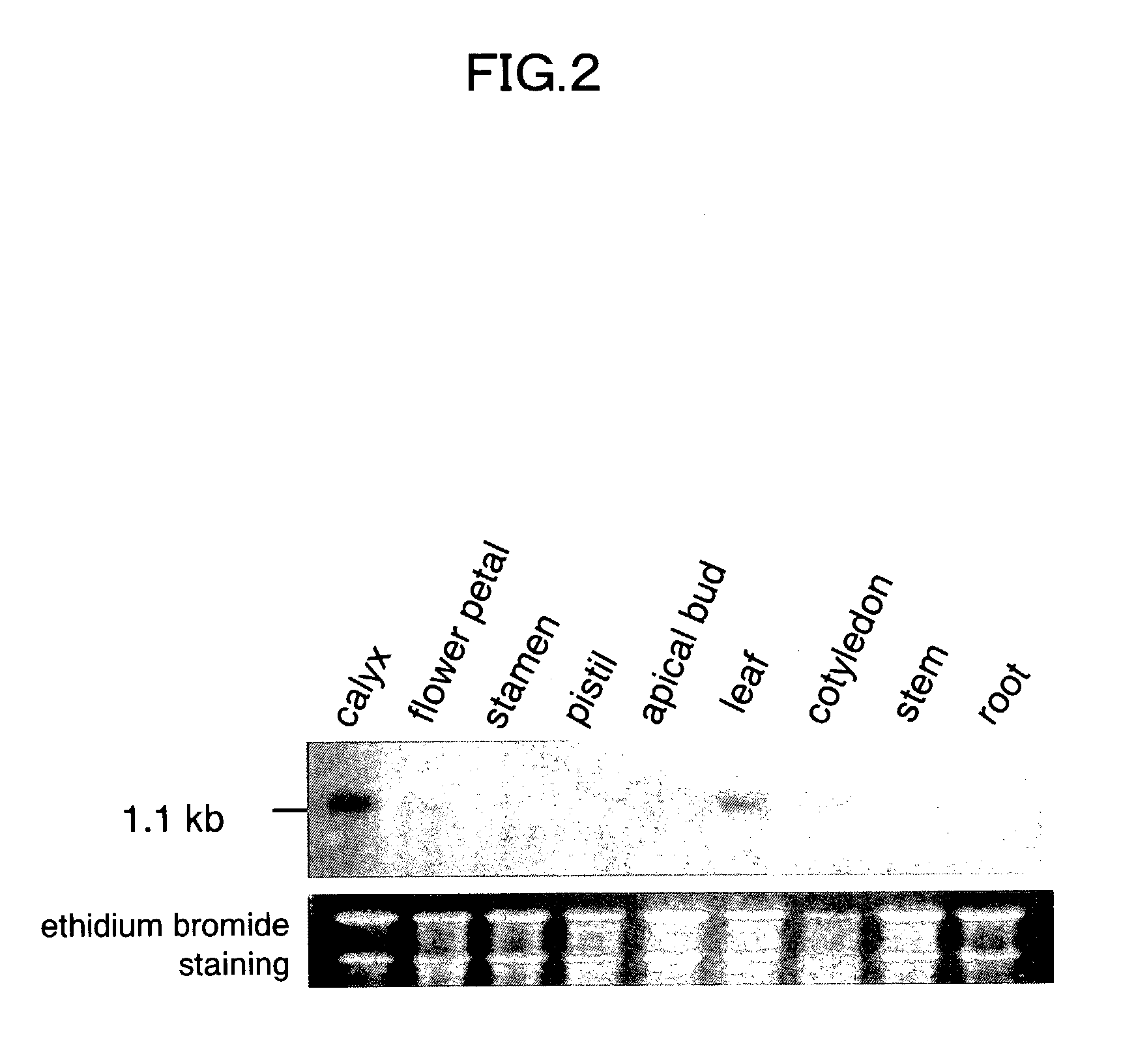
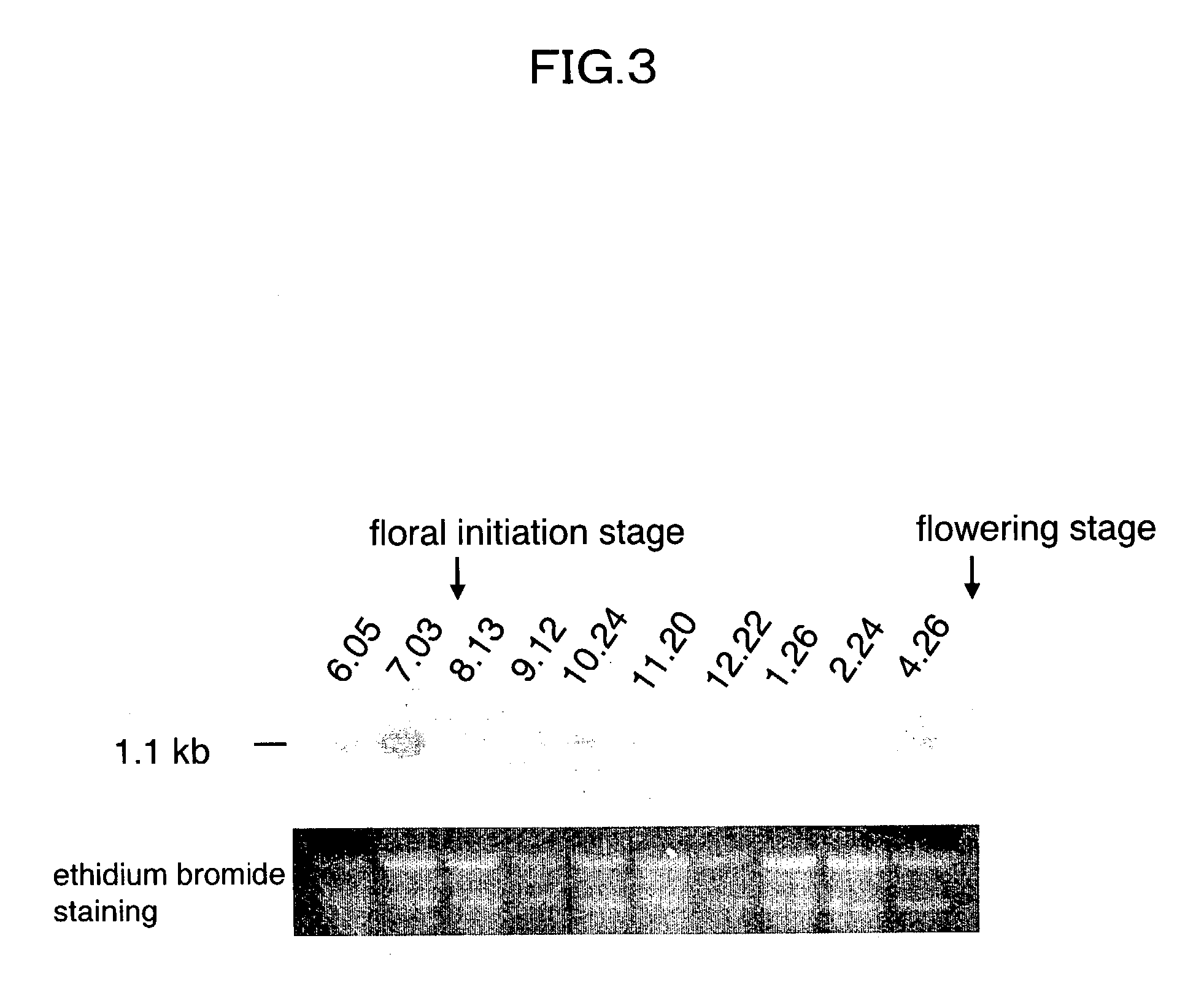
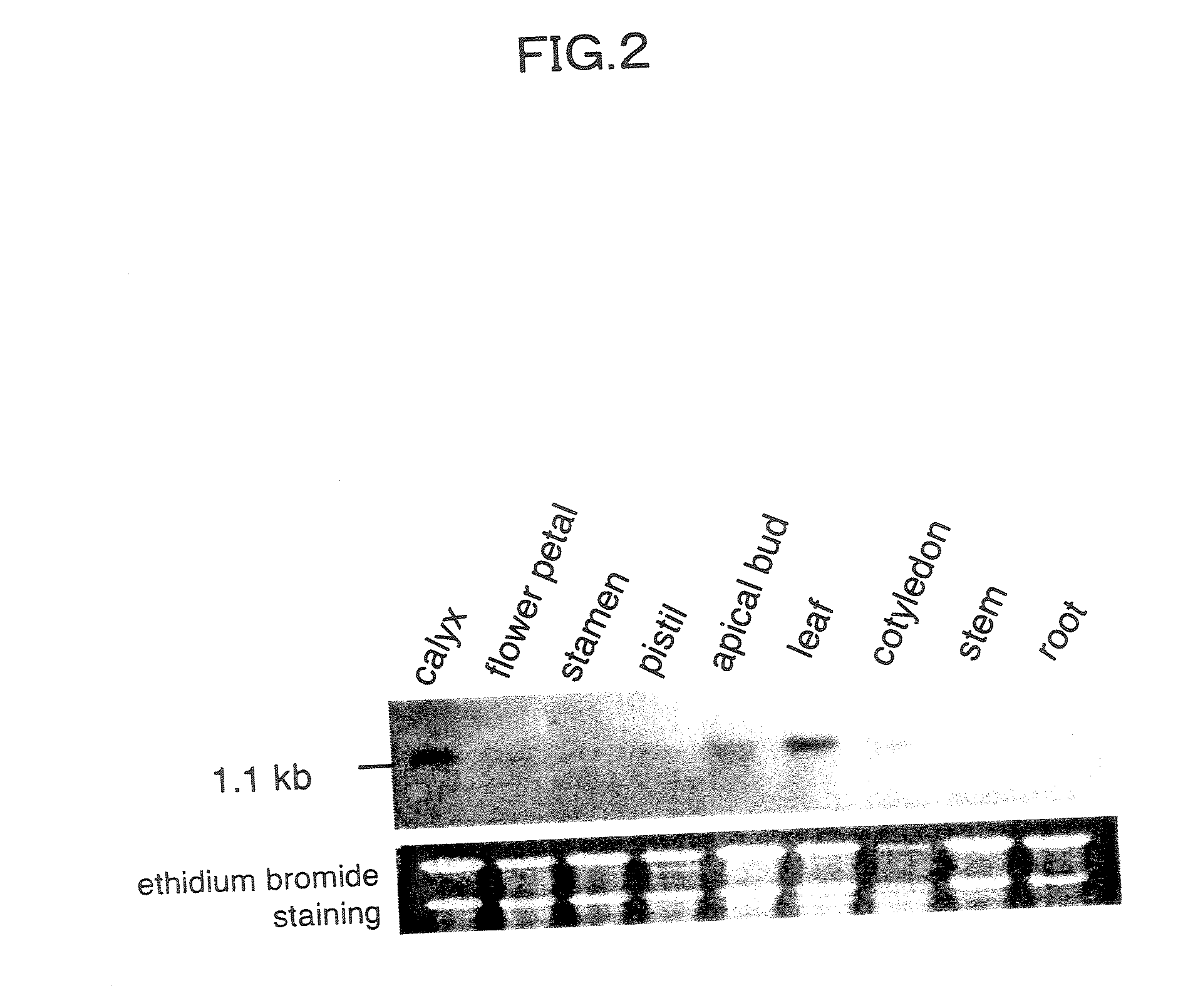
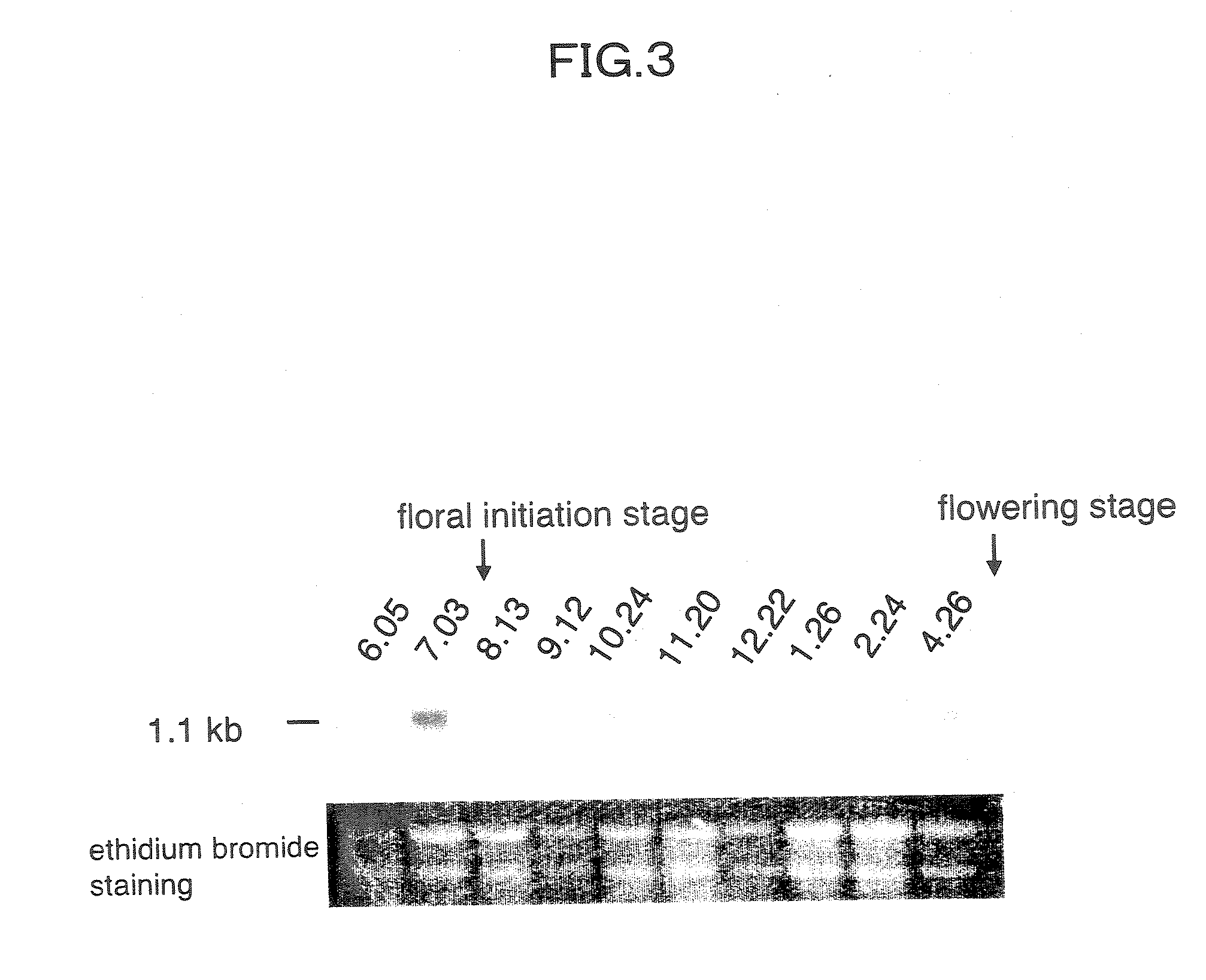
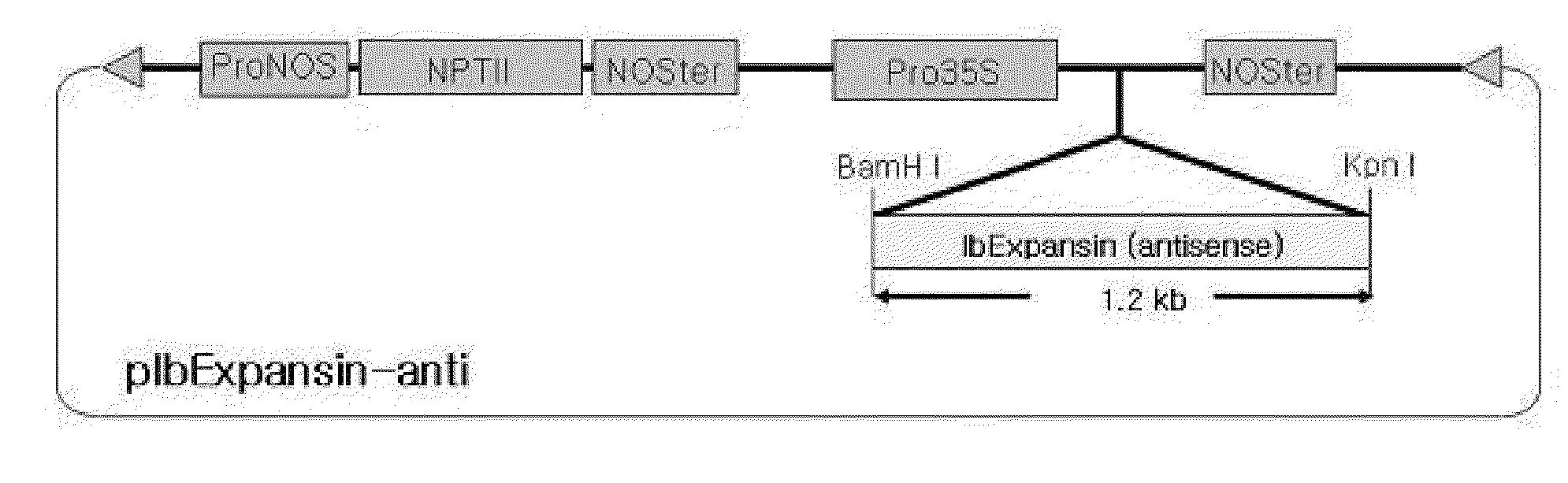
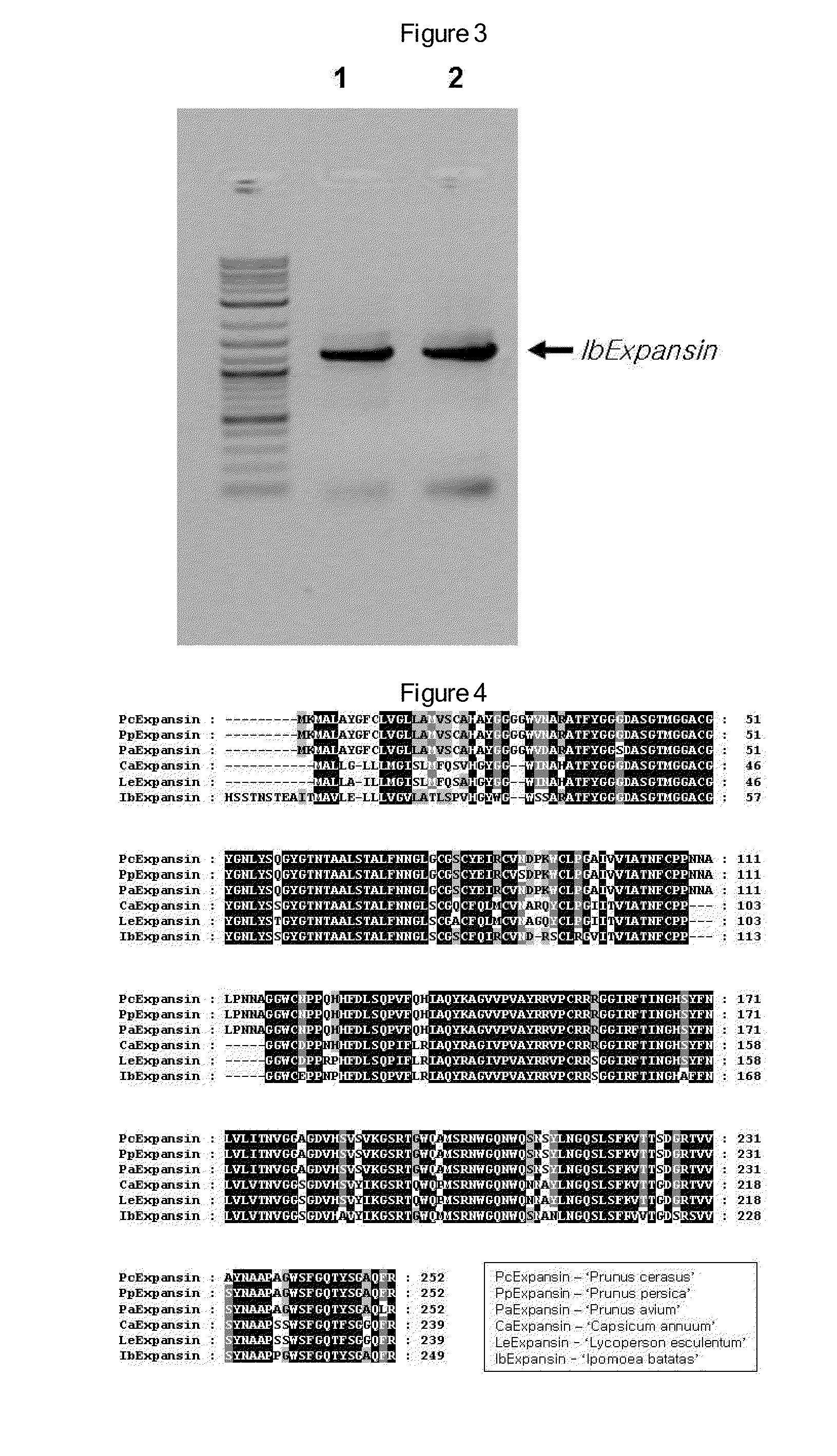
Antisense DNA of Sweetpotato Expansin cDNA and Method For Increasing Storage Root Yield Using The Same
InactiveUS20090249515A1Improve scalabilitySuppressing elongation growthSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationAntisense DNABiotechnology
Disclosed herein are antisense DNA of a sweetpotato expansin (IbExpansin) cDNA, a plant transformation vector carrying the same, and a method for increasing storage root production using the same. The transgenic sweetpotatoes prepared using the antisense DNA of IbExpansin cDNA have storage root production increased by up to one and half times. Thus, the gene is useful in the generation of highly productive transgenic storage roots for the increase of bioethanol production.
Owner:KOREA UNIV IND & ACADEMIC CALLABORATION FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com