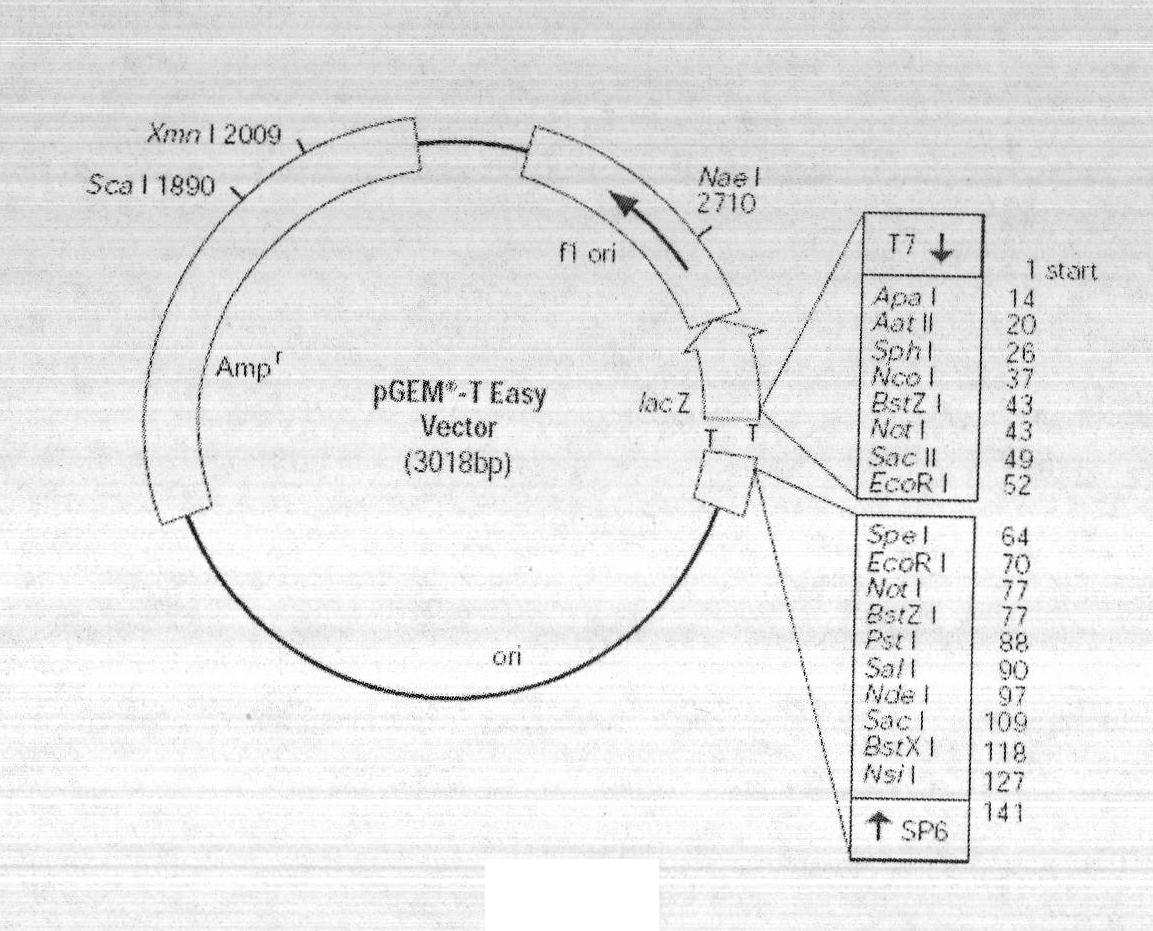
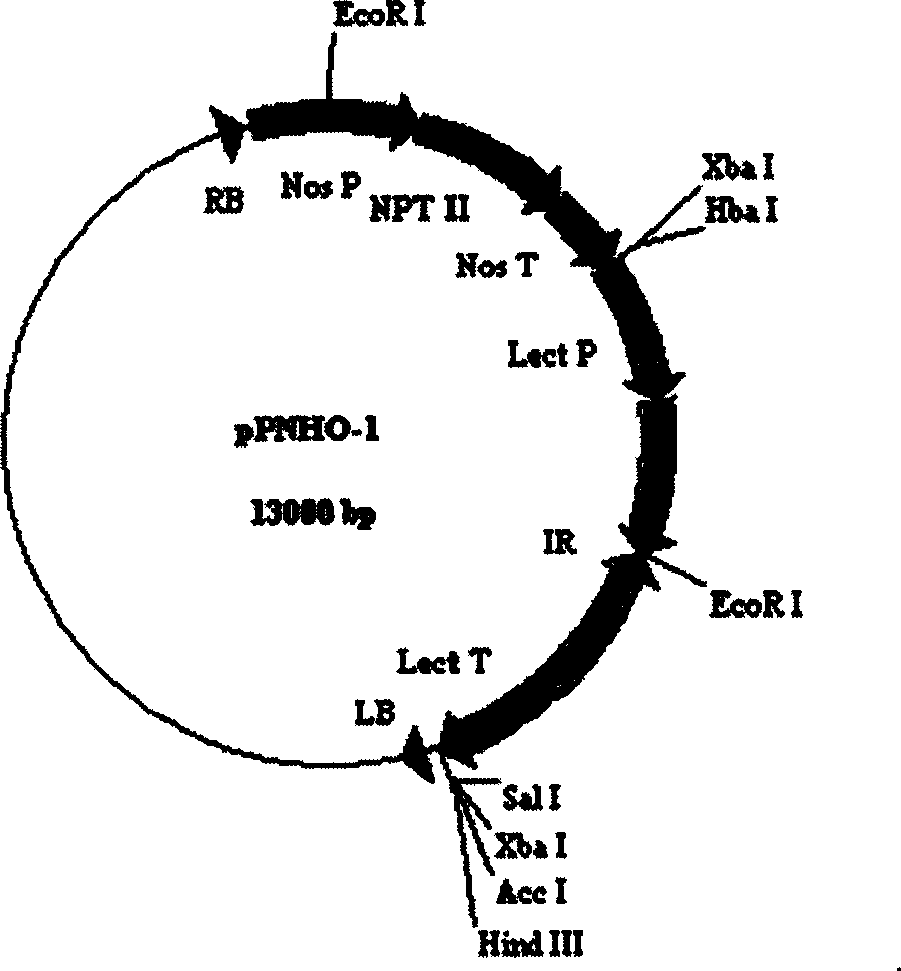
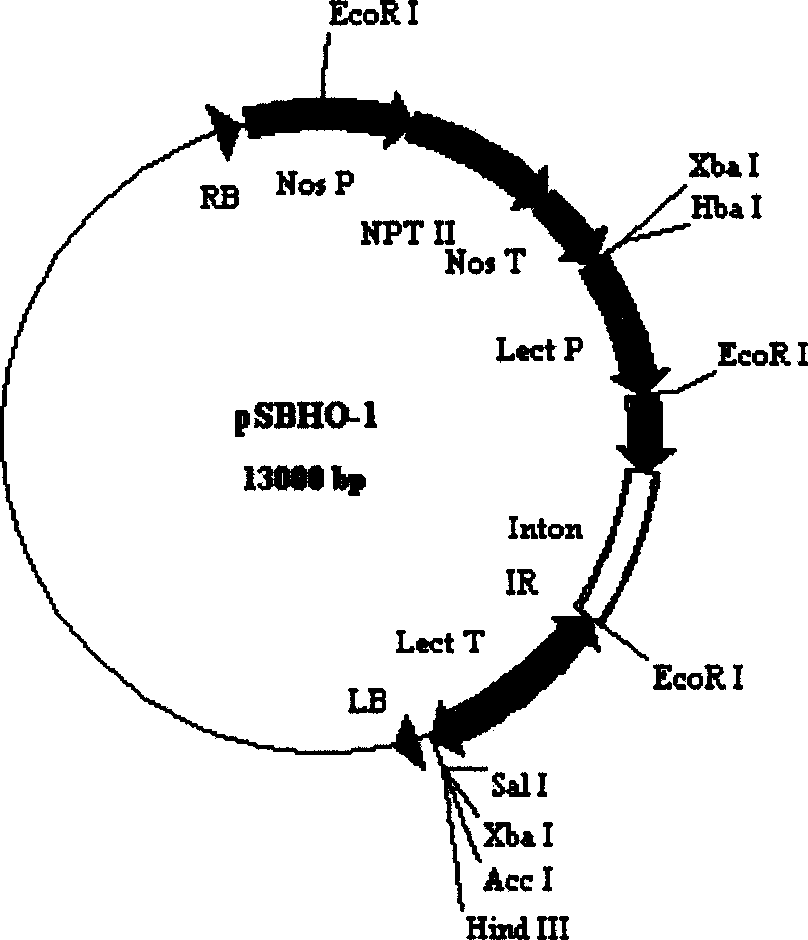
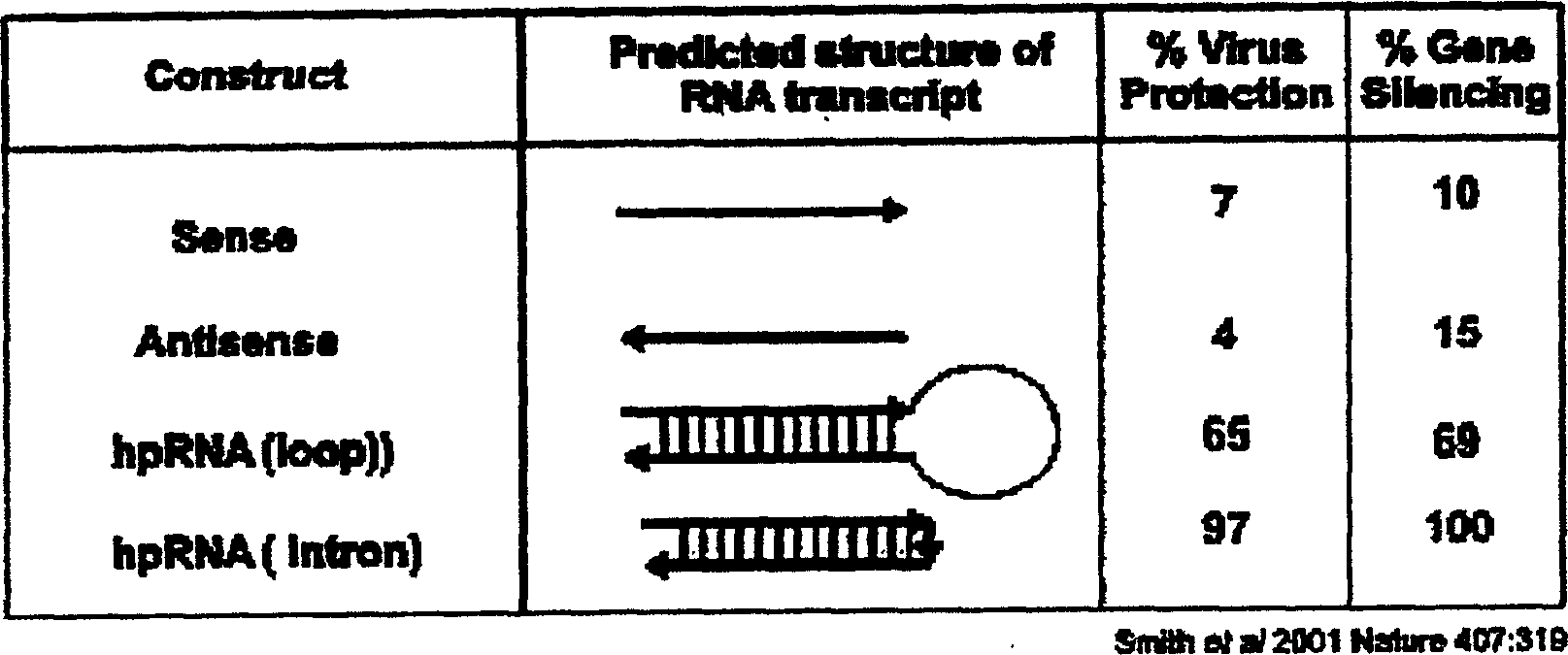
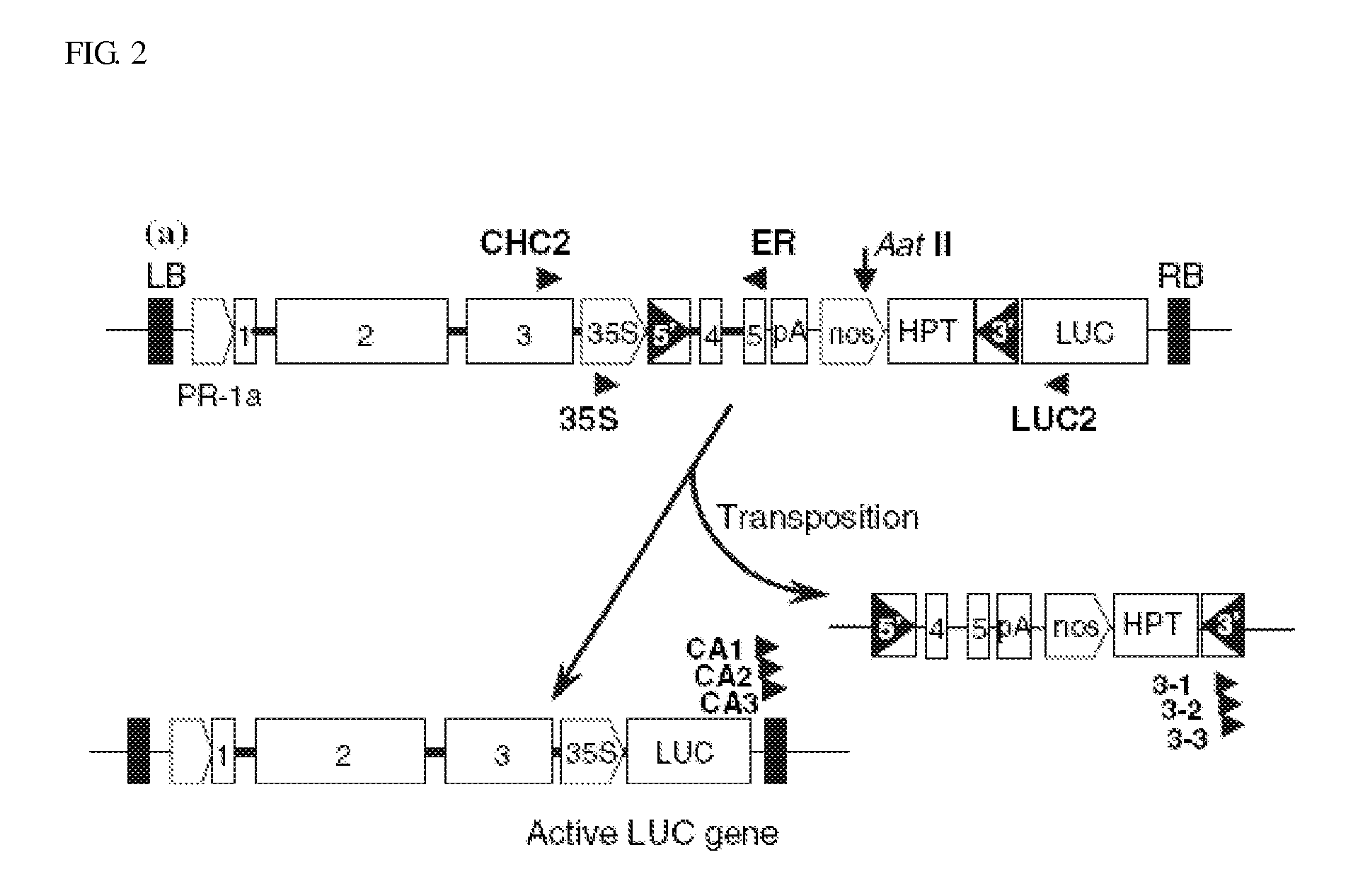
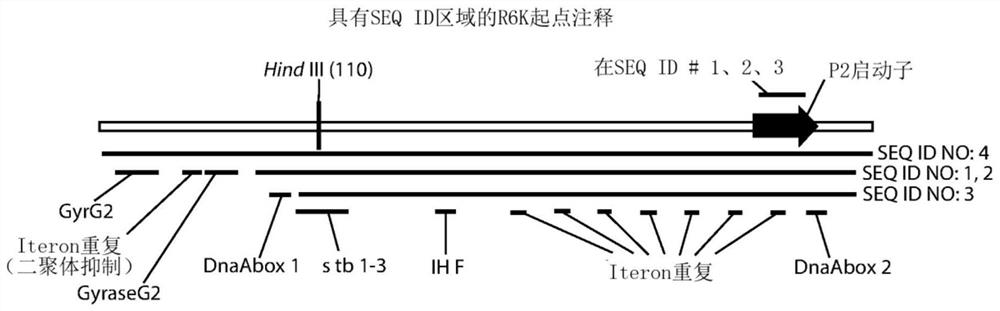
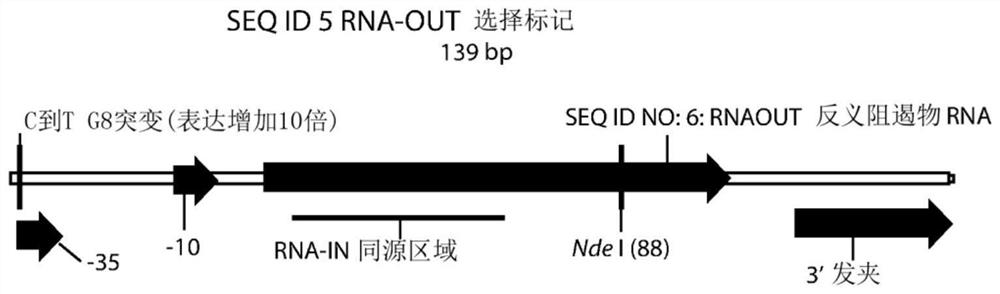
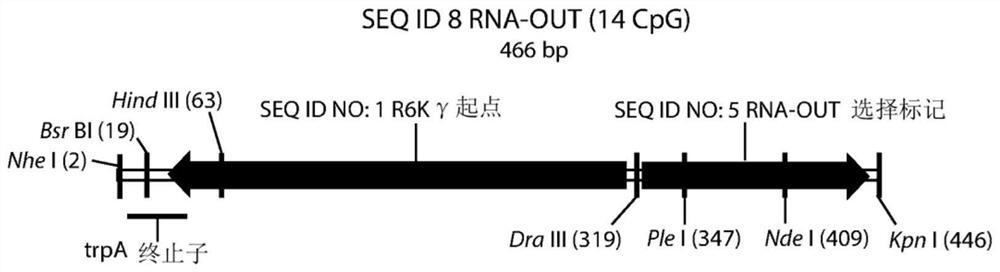
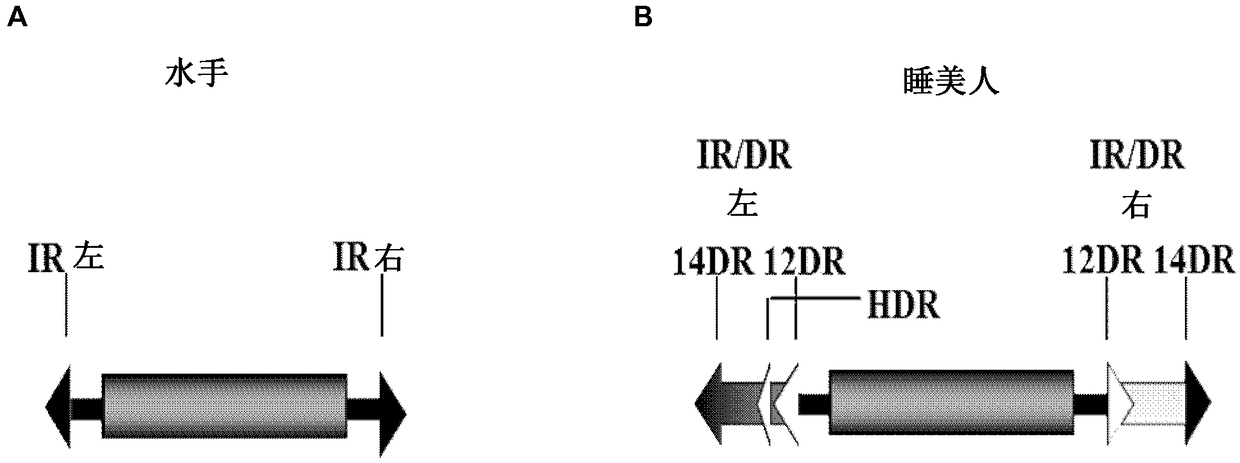
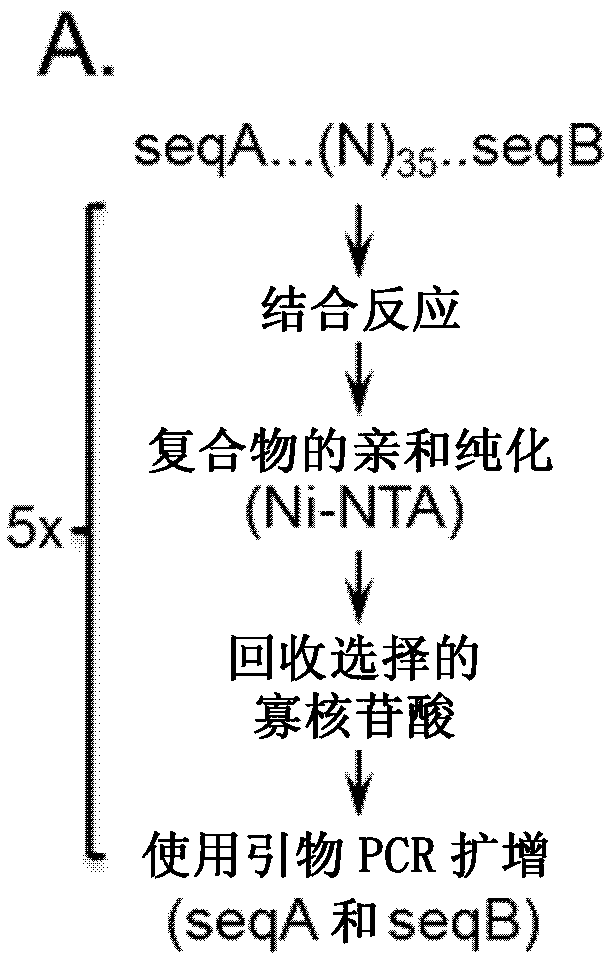
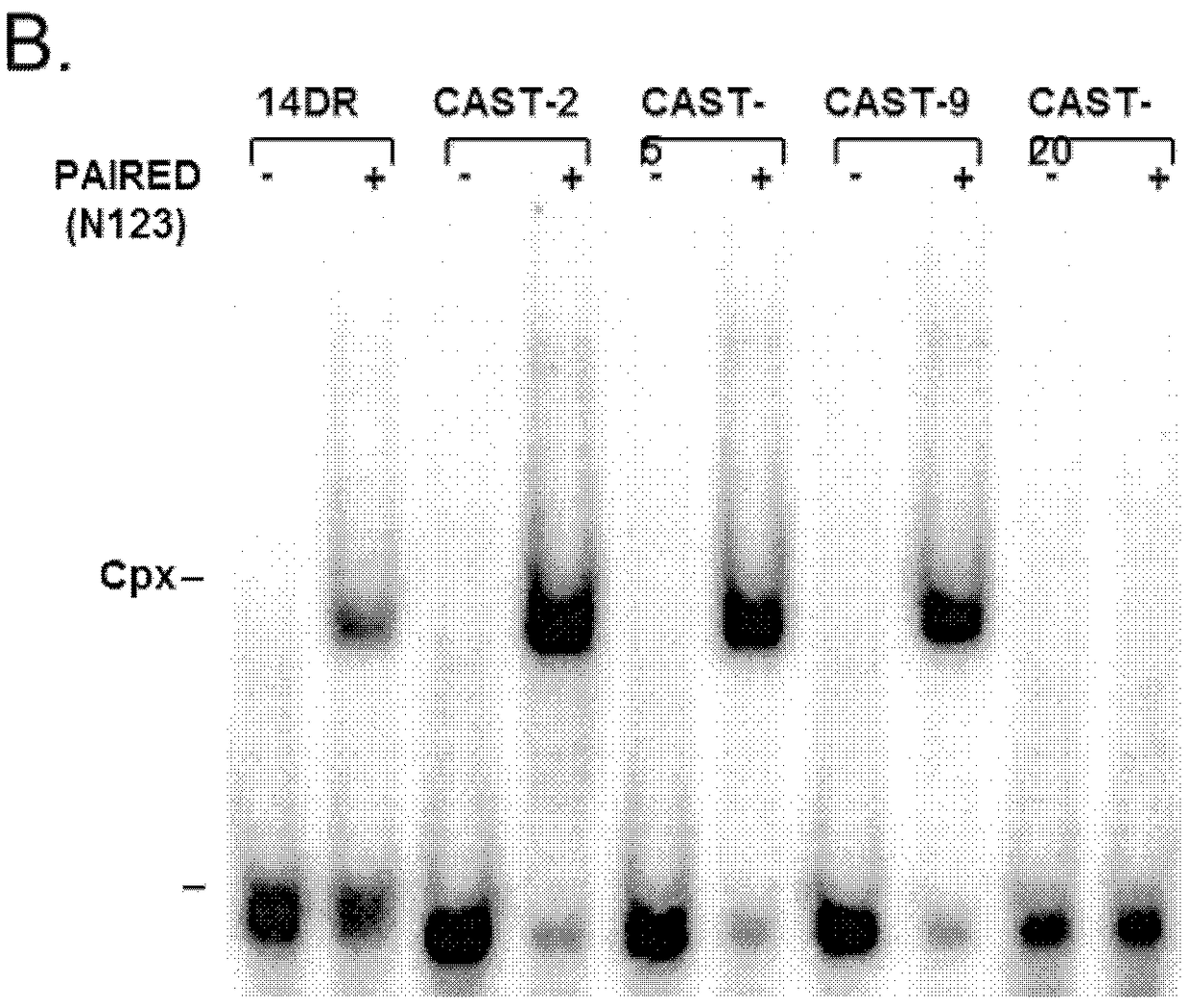
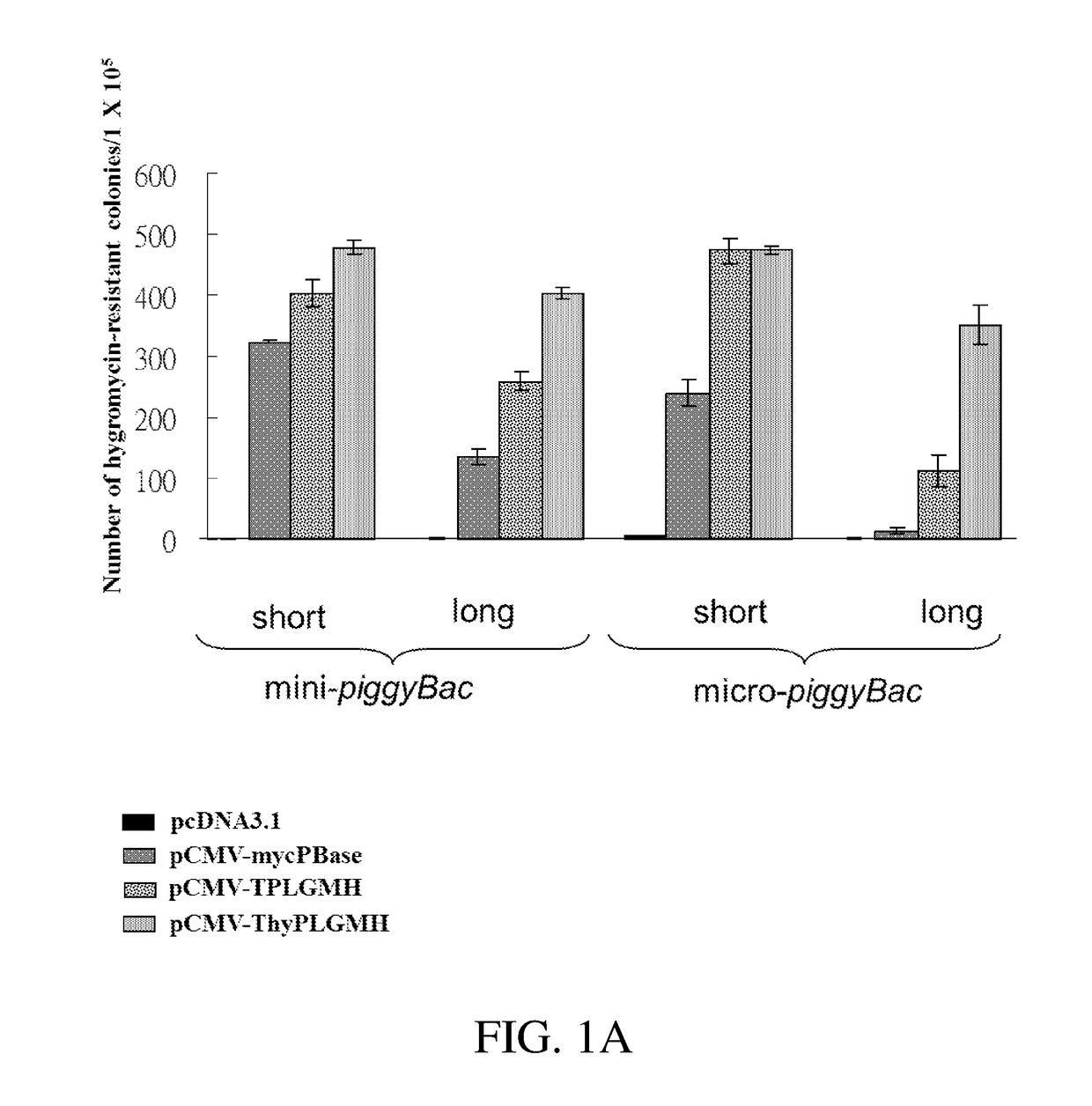
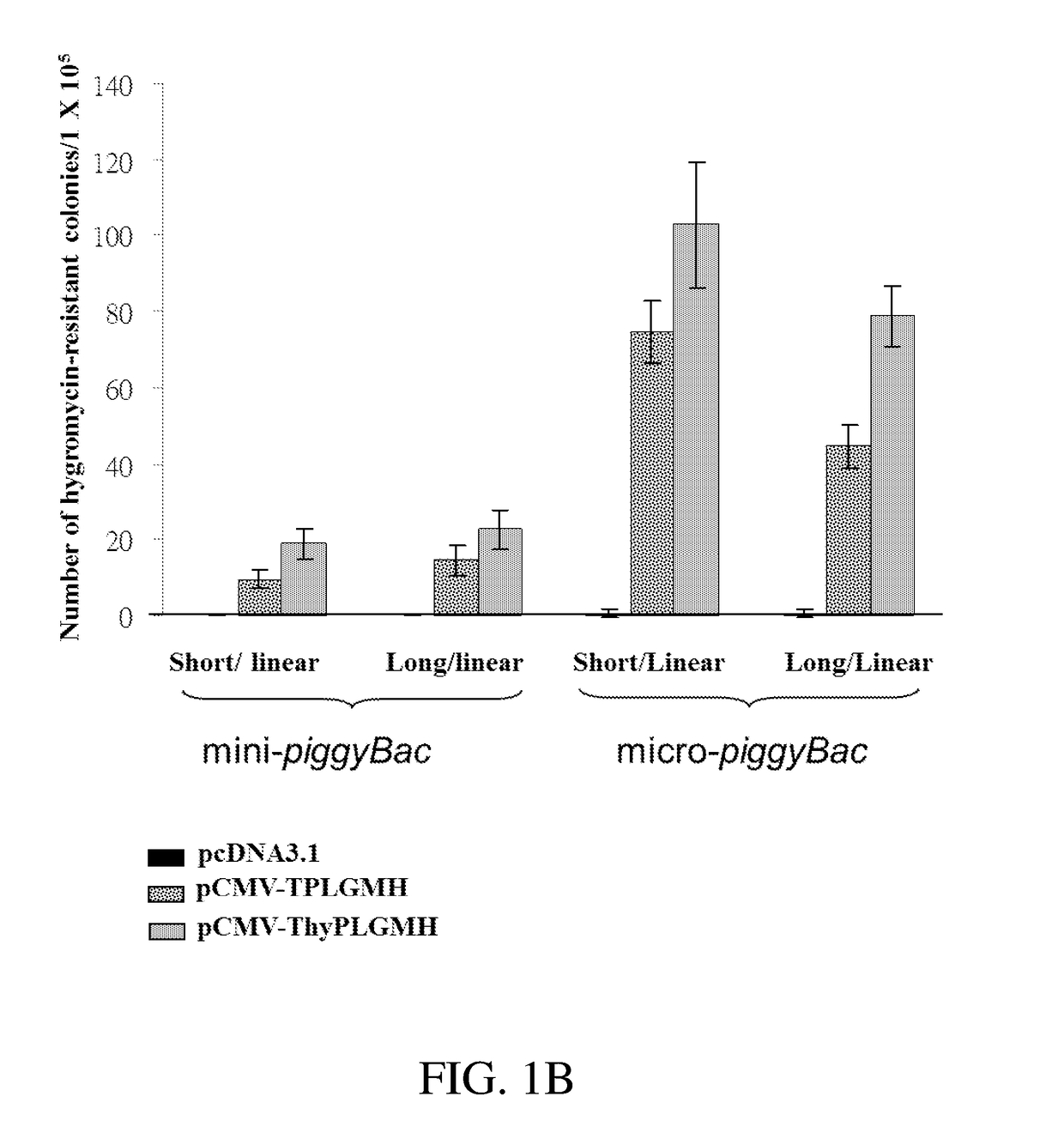
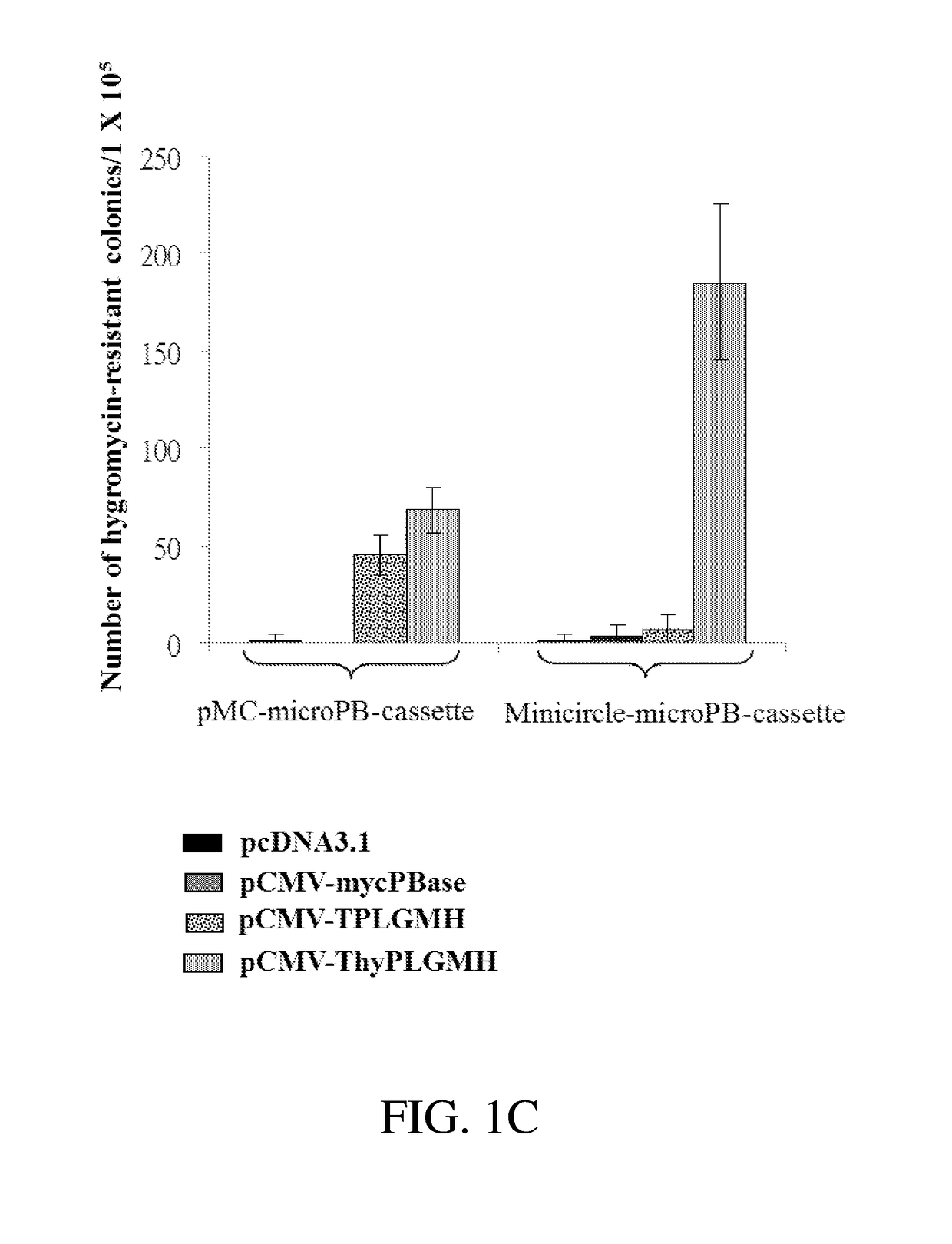
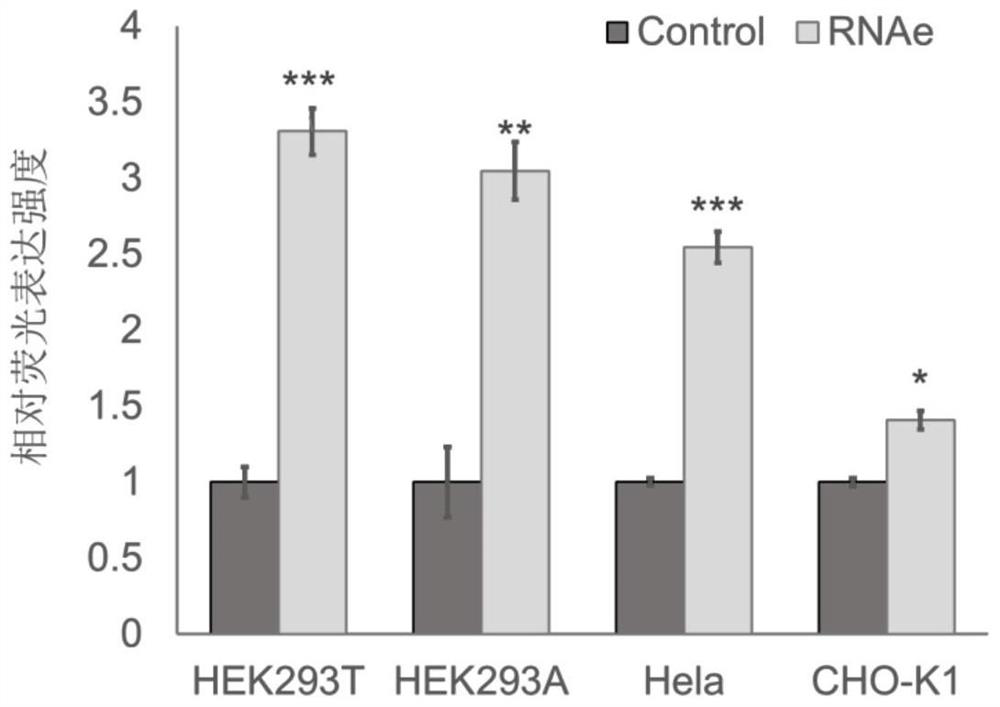
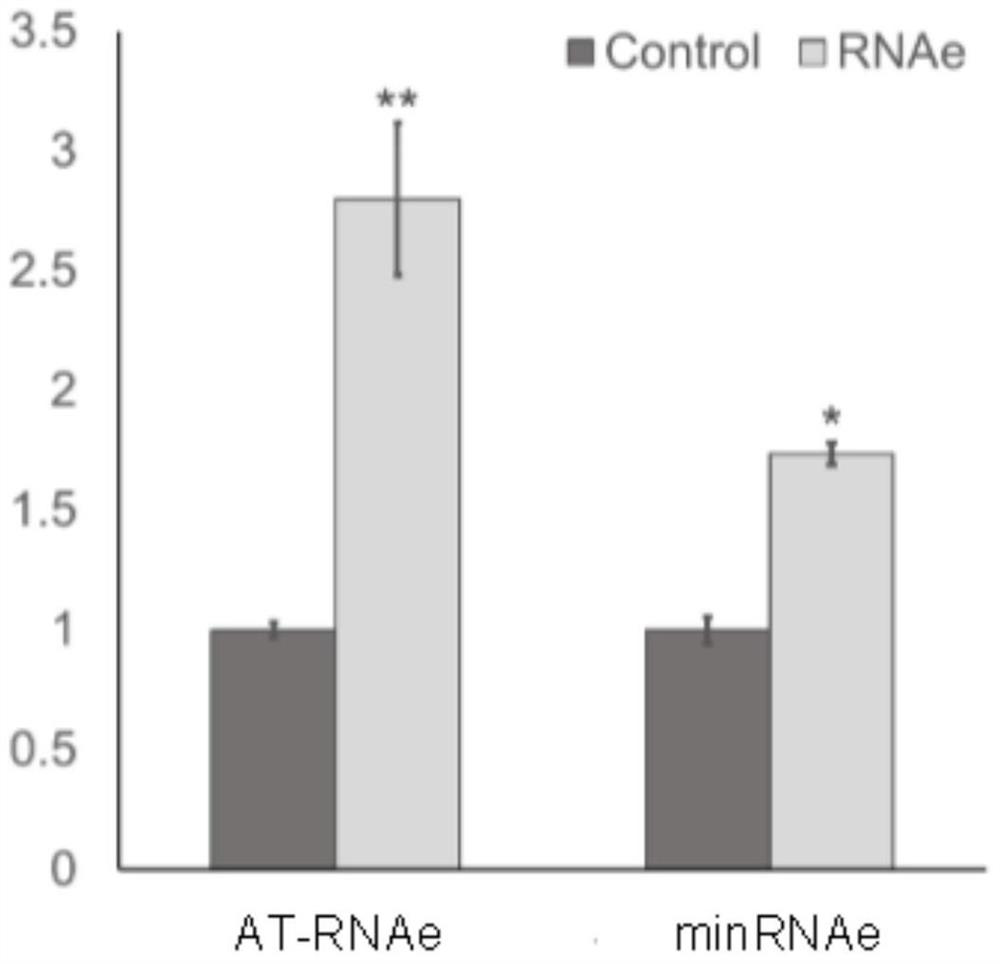
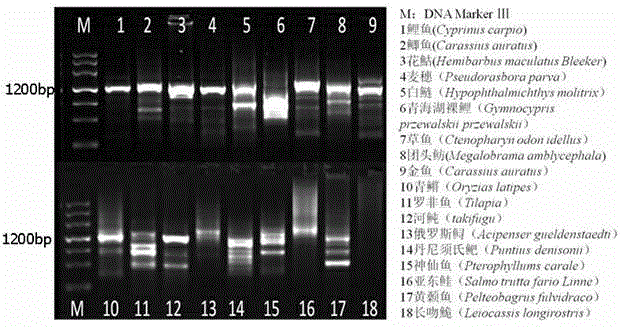
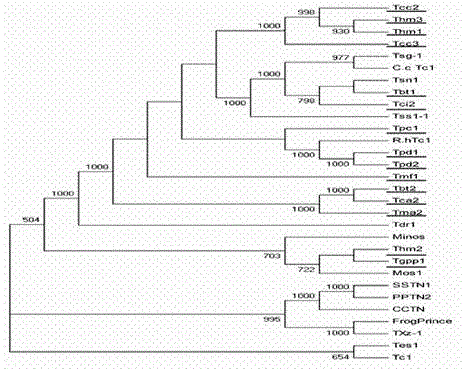
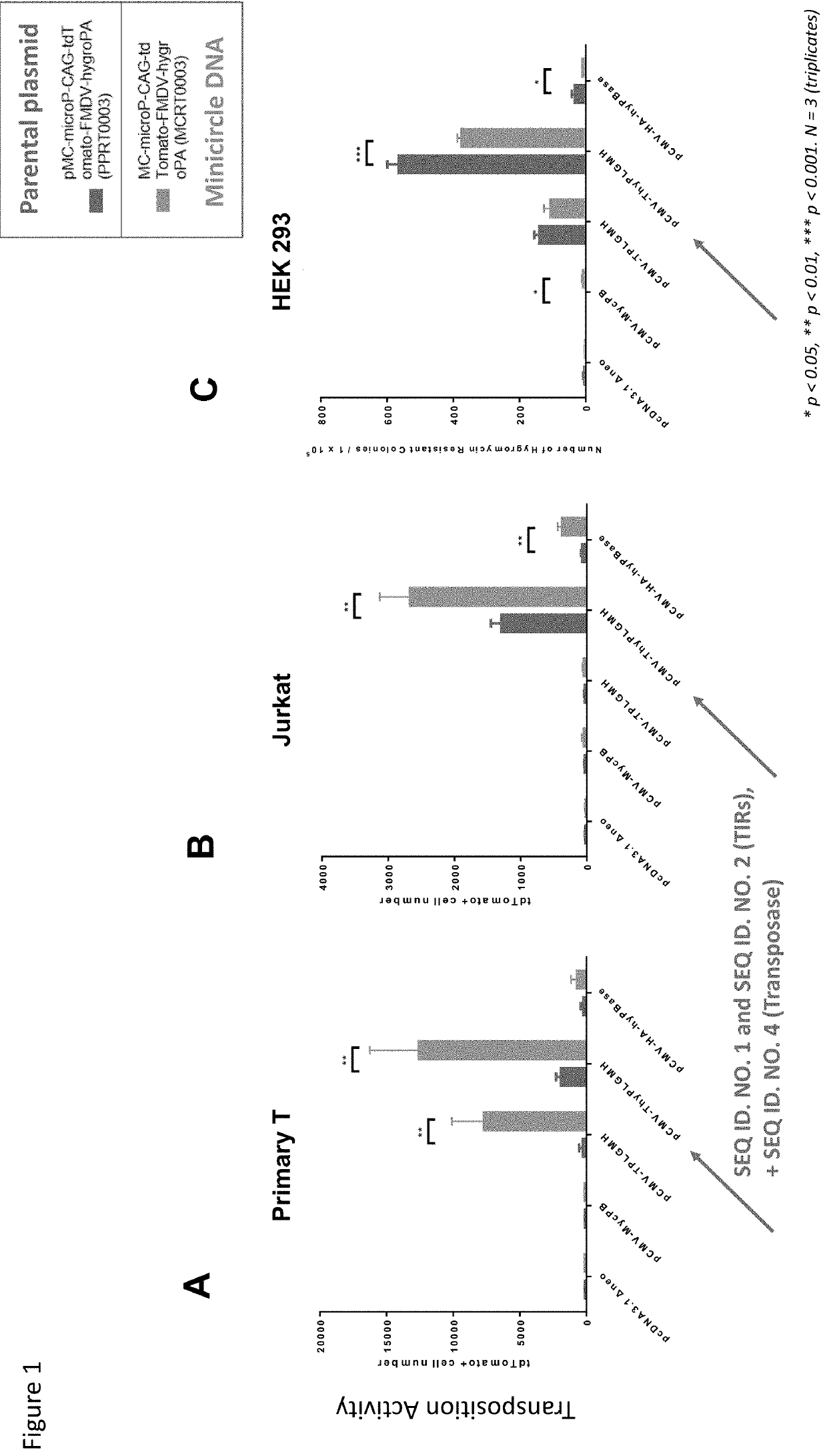
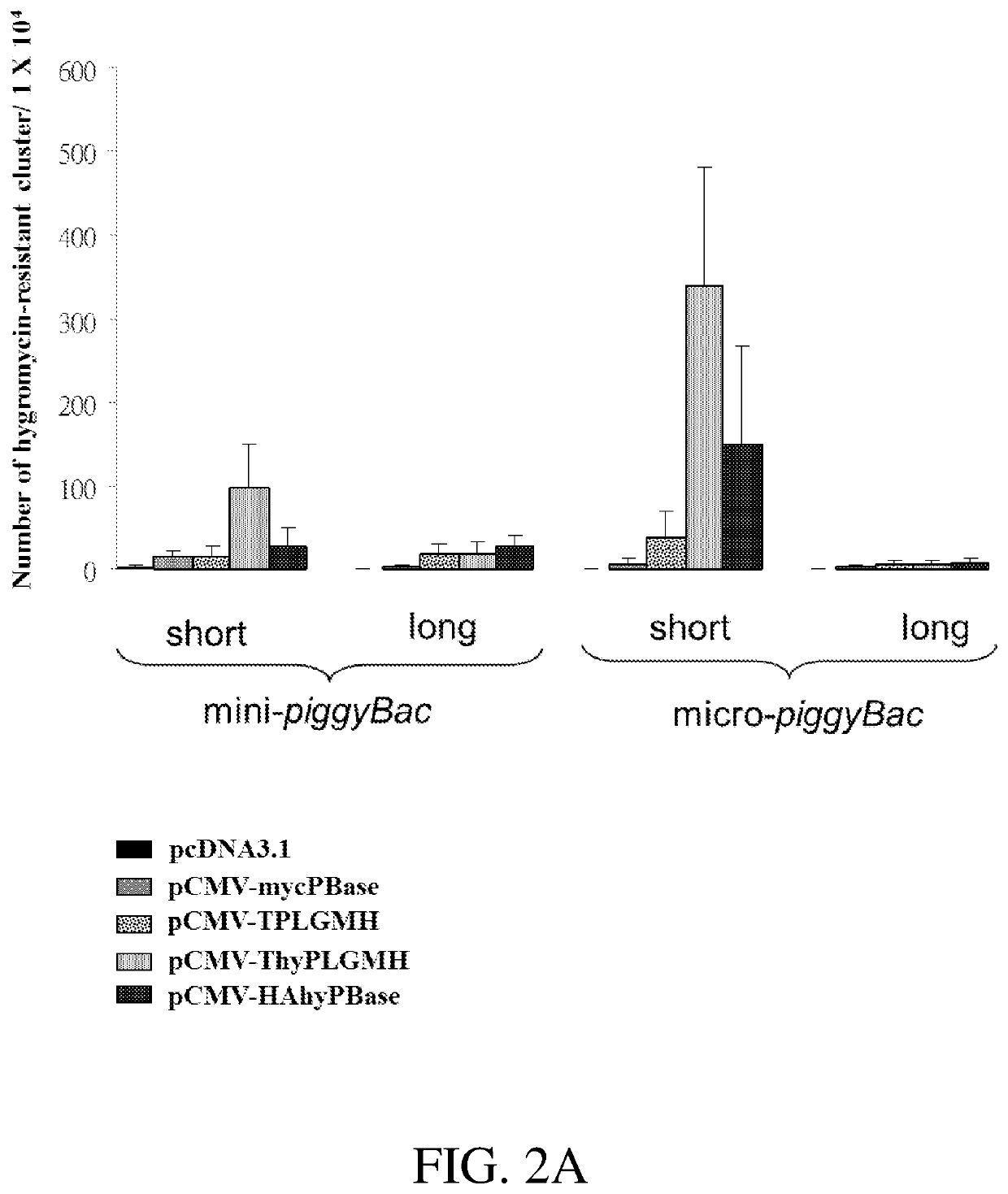
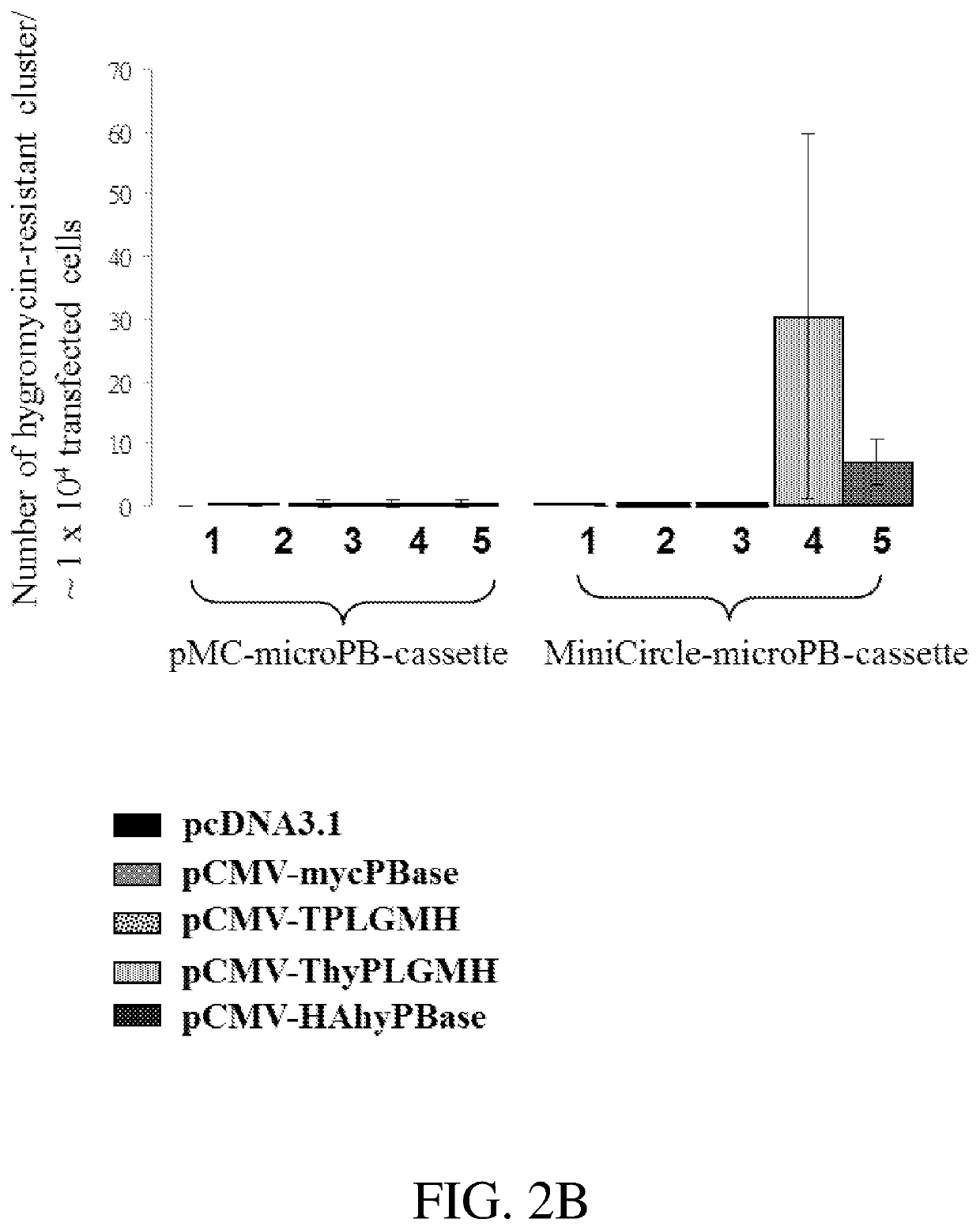
Patents
Literature
43 results about "Inverted Repeat Sequences" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Copies of nucleic acid sequence that are arranged in opposing orientation. They may lie adjacent to each other (tandem) or be separated by some sequence that is not part of the repeat (hyphenated). They may be true palindromic repeats, i.e. read the same backwards as forward, or complementary which reads as the base complement in the opposite orientation. Complementary inverted repeats have the potential to form hairpin loop or stem-loop structures which results in cruciform structures (such as CRUCIFORM DNA) when the complementary inverted repeats occur in double stranded regions.
Artificially synthesized Bt insect-resistant gene Cry1Ab-t and application thereof
ActiveCN102010873AHigh expressionEfficient and stable expressionBiocideBacteriaResistant genesInverted Repeat Sequences
The invention provides an insect-resistant gene Cry1Ab-t and an encoding protein thereof. In the gene, by using a plant bias codon and reducing a sequence rich in AT, an inverted repeat sequence and a subsequence-containing undefined eucaryotic deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) sequence in the original DNA sequence on the premise of keeping part of amino acid sequences of a Bacillus thuringHansis (Bt) protein Cry1Ab unchanged, a new Cry1Ab-t gene sequence is synthesized by artificial modification, then a prokaryotic expression carrier and a plant expression carrier are constructed for the gene, and a corresponding host cell is converted. In vitro experiments prove that a synthesized Bt toxoprotein has an obvious insecticidal effect on corn borers. The insect-resistant gene Cry1Ab-t and a target protein expressed by the gene can be steadily and efficiently expressed in corns, so that the gene can be used for culturing Cry1Ab-t transgene insect-resistant corns. The artificially synthesized Bt insect-resistant gene Cry1Ab-t can be also used for improving the insect resistance of other crops, fruit trees, vegetables and the like.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Tobacco virus-resisting RNAi carrier
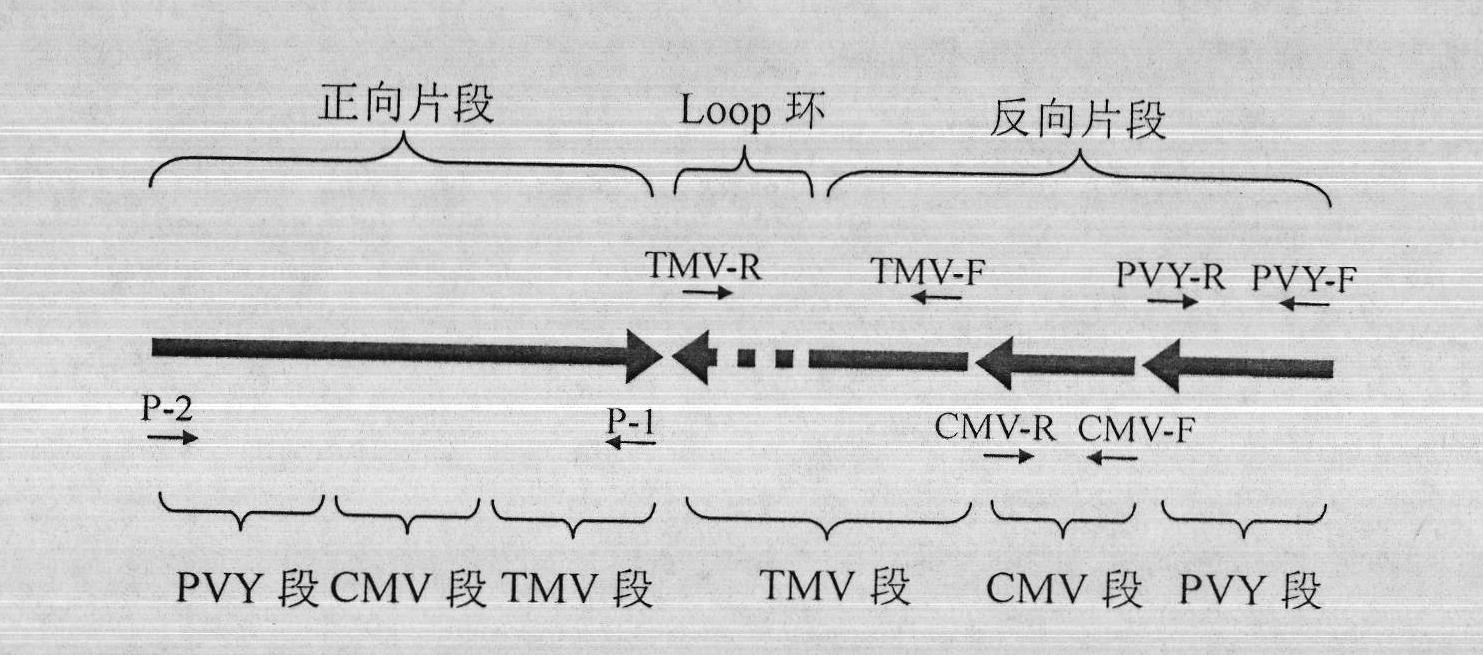
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and provides an RNAi vector pGEM-PCTRi capable of mediating the resistance to tobacco viral diseases in China. Analyzing the genome characteristics of main virus groups in China, which comprise Potato Virus Y (PVY), Cucumber Mosaic Virus (CMV) and Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV) and then selecting three segments of conserved effective sequences capable of inducing RNAi in PVY CP, CMV RNA1 and TMV CP; and integrating the three segments in a tabling manner and constructing an inverted repeat sequence so as to obtain an RNAi vector pGEM-PCTRi. Massproduction of dsRNA can be realized in escherichia coli by utilizing the vector, and the resistance of tobacco to PVY, CMV and TMV can be induced to generate after the tobacco treatment. The invention has the potential of being applicable to the prevention of viral diseases for tobacco farmland production, and endowed with the advantages of broad spectrum, high efficiency, no reference to transgenosis, and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
Method in increasing oleic acid content of soybean and peanut seed by applying gene silent technology
The invention belongs to plant breeding field, especially the biology engineering breeding to improve the quality of soybean and earthnut. It uses PCR method to clone the specific gene section from the gene of soybean and earthnut. According to gene silence principle, the gene section would be rebuilt into reverse repeating sequence structure, which would be built into the carrier that of promoter and terminator of the specific expression. The gene would be transferred, cultivated, and filtered by farm bacilli induce transformation. The invention could improve the quality of the soybean and the earthnut.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for efficiently modifying filamentous fungi and strain of modified filamentous fungi
InactiveCN103497968AReduce expressionLess quantityFungiMicroorganism based processesInverted Repeat SequencesPromoter
The invention discloses a method for efficiently modifying filamentous fungi and a strain of the modified filamentous fungi. The method is characterized by introducing a multi-gene interference constructing body and a target protein expression constructing body into filamentous fungus cells simultaneously, and then screening to obtain efficiently modified filamentous fungi, wherein the multi-gene interference constructing body comprises promoters, inverted repeat sequences and a terminator, wherein the promoters can initiate transcription in the filamentous fungus cells, the inverted repeat sequences are separated by introns and are connected together by coding sequences of 2-30 target genes in a mosaic manner, and the terminator can terminate transcription in the filamentous fungus cells; the target protein expression constructing body comprises promoters, coding sequences of target proteins and a terminator, wherein the promoters can initiate transcription in the filamentous fungus cells, and the terminator can terminate transcription in the filamentous fungus cells. The method and the strain have the advantages that the modification efficiency of the filamentous fungi is improved; the downstream separation and purification costs of the target proteins are reduced; the filamentous fungus cells modified through one-time transformation can be used for producing food safety level enzyme preparations.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
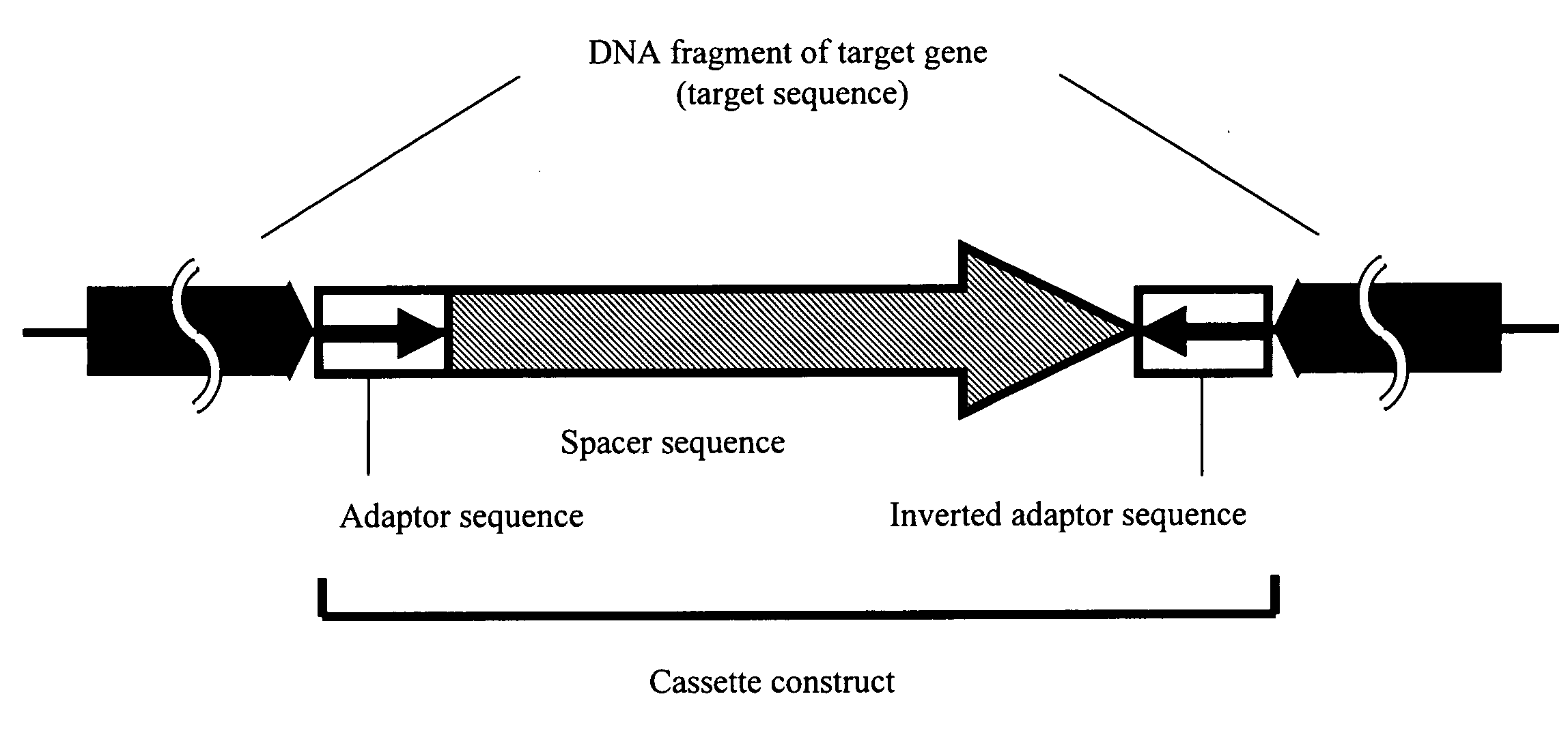
Efficient Method of Preparing Dna Inverted Repeat
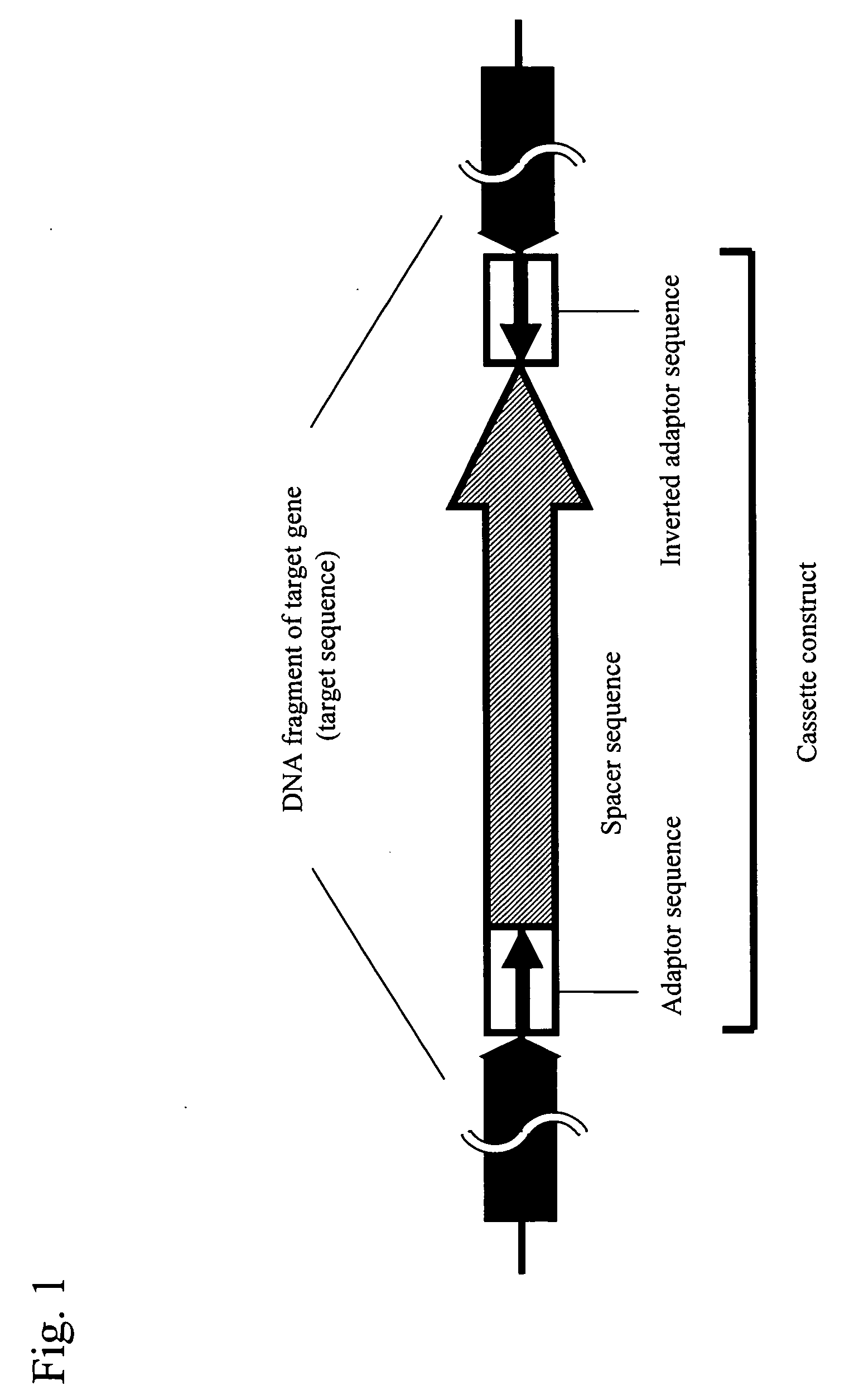
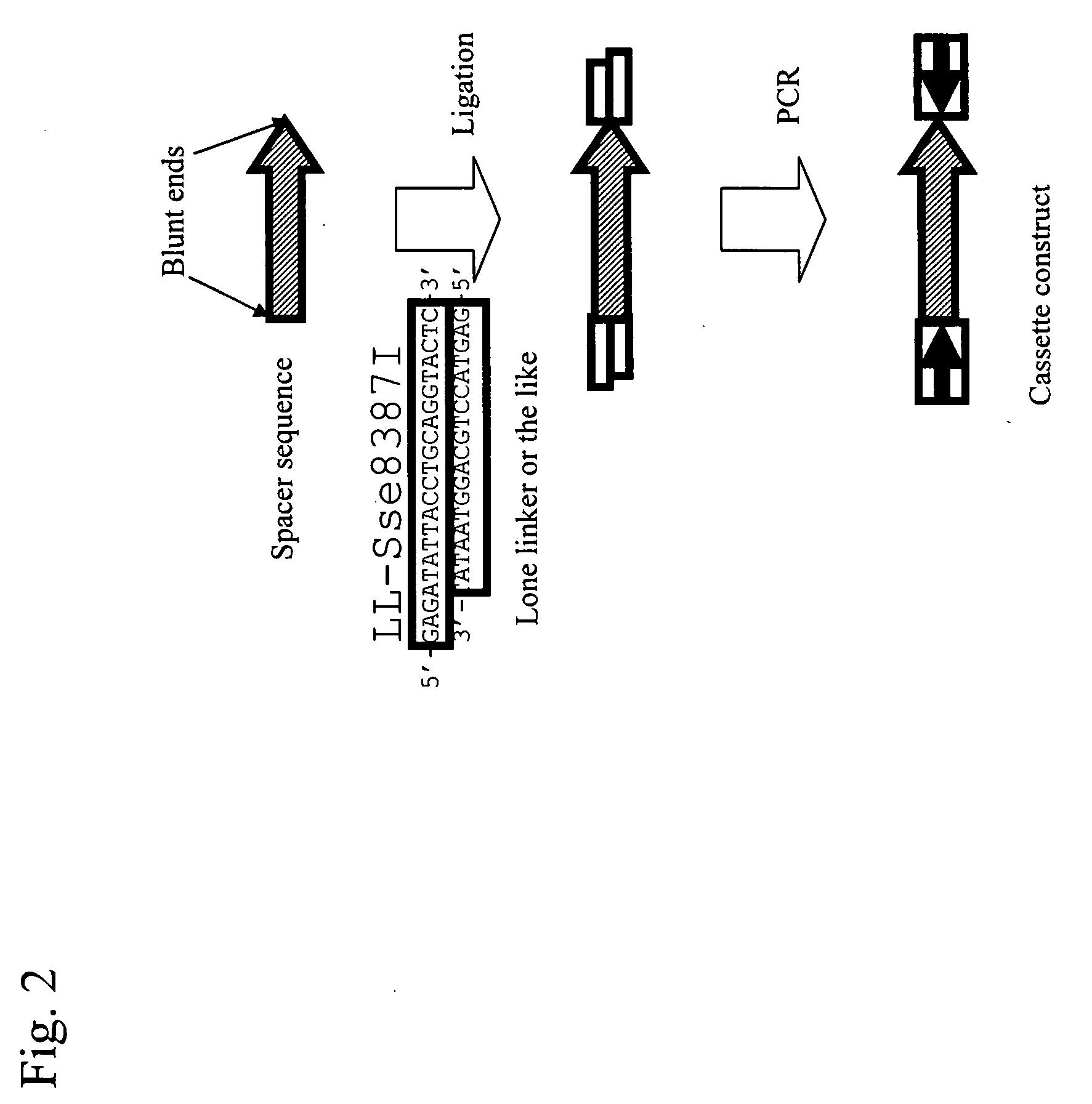
Conventional techniques for preparing a chimera gene having an inverted repeat sequence of a target sequence suffer from complications since a target sequence is inserted into 2 sites on a vector in sense and antisense orientations, and restriction enzyme recognition sequences must be independently provided at an insertion site of a vector and both ends of the target sequence.In this invention, a cassette construct comprising an arbitrary adaptor sequence and an inverted adaptor sequence separated by an arbitrary spacer sequence or a plasmid vector comprising such cassette construct incorporated therein is prepared, a target sequence is ligated to either or both ends of the cassette construct, or a target sequence is inserted into one end of the cassette construct on the plasmid vector, followed by PCR. Thus, a chimera gene having an inverted repeat sequence is prepared.
Owner:RIKEN
Method for cultivating anti-TYLCV (Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus) tomato plant by using RNAi technology
The invention relates to a method for cultivating an anti-TYLCV (Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus) tomato plant by using an RNAi (RNA interference) technology, belonging to the field of biotechnology. According to the method, the conserved sequences in genes of V2 and C1 of TYLCV are inosculated, an RNAi carrier with inverted repeat sequences is constructed, the aseptic seedling cotyledons or hypocotyl explants of the tomato are transformed through an agrobacterium-mediated transformation method, the transgenic tomato expresses resistance to the TYLCV after the inoculation of the agrobacterium infectious clone injection of the TYLCV and the TYLCV-carrying Bemisia tabaci virus, and no obvious disease symptoms are observed. According to the method, the anti-TYLCV transgenic tomato plant can be cultivated by using the RNAi technology, so that the technical support for the control of the TYLCV is provided.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
DNA fragment for inhibiting expression of omega secaline gene in wheat 1B/1R translocation line and application thereof
The invention discloses a DNA fragment for inhibiting the expression of an omega secaline gene in a wheat 1B / 1R translocation line and application thereof. The DNA fragment consists of an omega secaline gene coding region partial sequence, a plant intron sequence and the inverted repeat sequence of the omega secaline gene coding region partial sequence which are connected in turn. An RNAi genetic expression vector containing the DNA fragment is transferred to the wheat 1B / 1R translocation line in a transgenic way, so that the expression of the endogenous omega secaline gene can be inhibited, the adverse effects of omega secaline on the food processing quality of the wheat 1B / 1R translocation line are relieved or eliminated and the food processing quality of the wheat 1B / 1R translocation line is improved.
Owner:HEBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI INST OF GENETICS & PHYSIOLOGY
Method for positioning and integrating transgenosis and application thereof
ActiveCN103361342AVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryInverted Repeat SequencesWild type
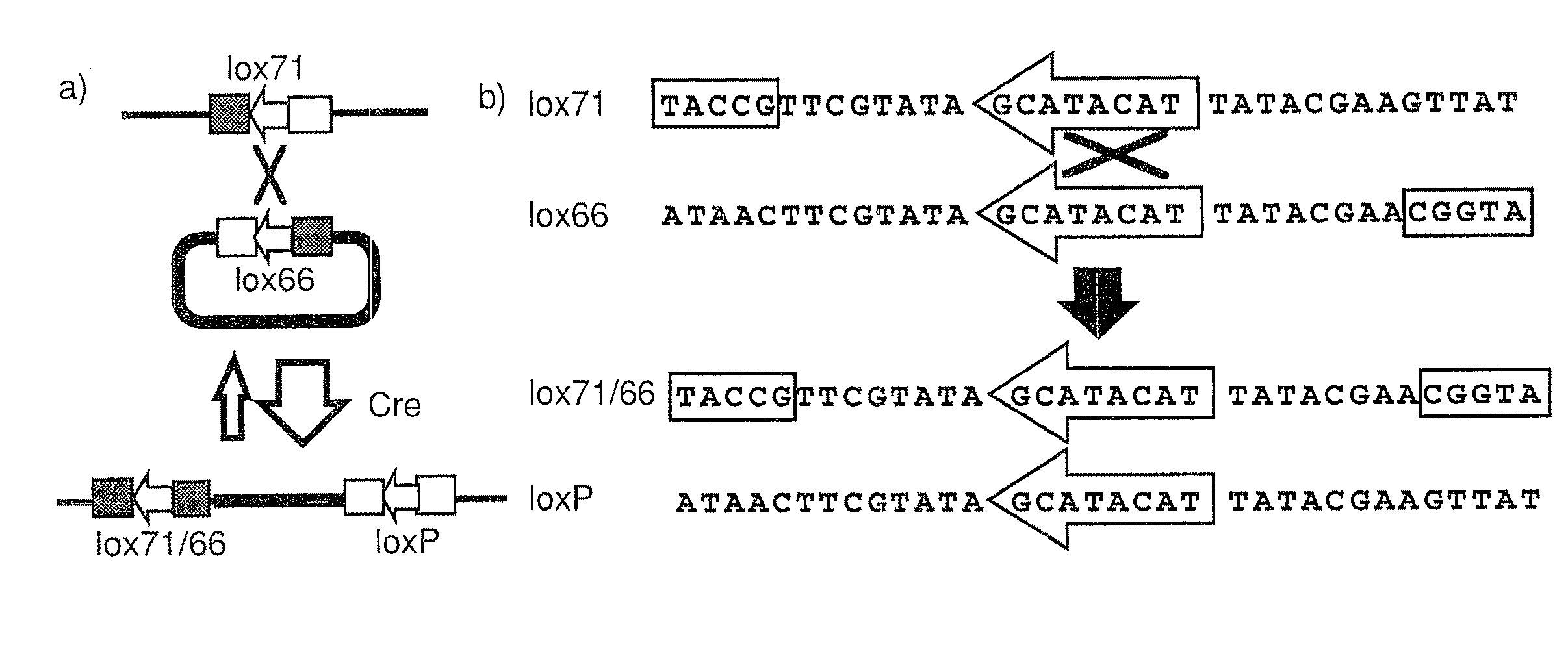
The invention relates to a method for positioning and integrating transgenosis and an application of the method, and particularly provides a variant loxP element. The method is characterized in that a sequence 'ATAAC' of an inverted repeat sequence in a wild type loxP locus mutates into 'CACCT', and thus the variant loxP element can be obtained. The variant loxP element can greatly improve the integration specificity and integration efficiency of a cre-loxP system, and therefore, efficient local integration of genes can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI TRANSGENIC RES CENT
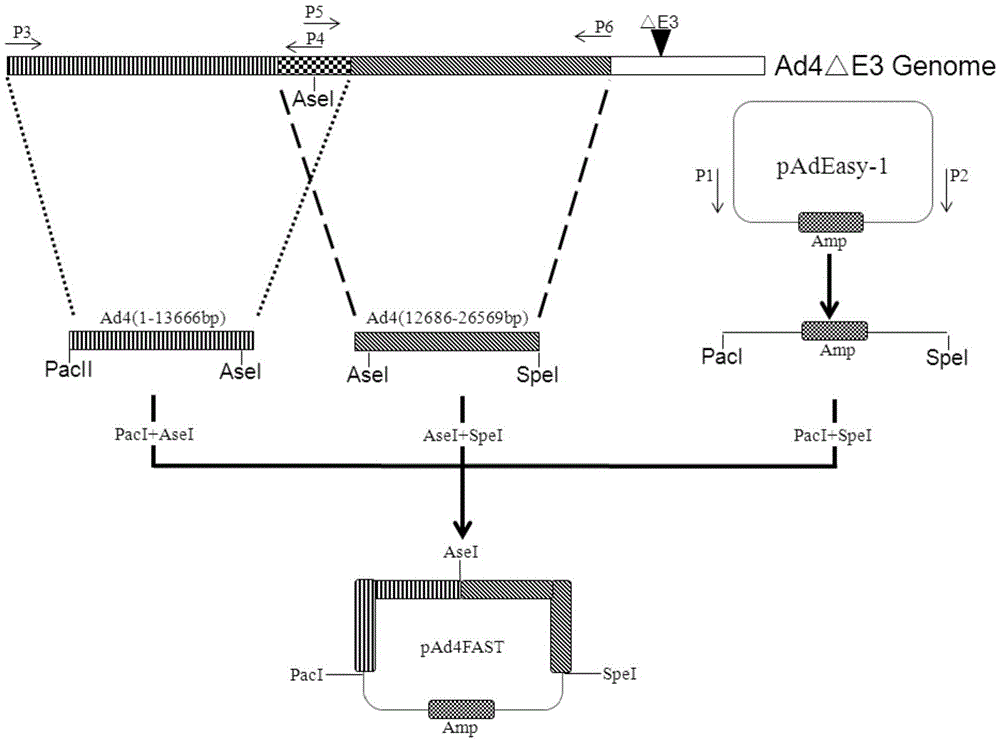
Construction and application of E3 region-deleted complete-copy-type recombinant adenovirus 4 carrier system
The invention relates to construction and application of an E3 region-deleted complete-copy-type recombinant adenovirus 4 carrier system. The system comprises a framework plasmid, a shuttle plasmid and a packaging cell line; the framework plasmid contains 1-26569bp segments on the left side of an adenovirus (AdV) 4 genome, and the adenovirus (AdV) 4 genome has E3 region genes serving as deletion genes; the shuttle plasmid contains cloning sites used for being inserted into a target gene and an inverted repeat sequence on the right side of the adenovirus (AdV) 4 genome; an HEK-293 cell line is adopted as the packaging cell line. Due to the fact that the anthropogenic adenovirus (AdV) 4 genome is safe and reliable, the recombinant adenovirus (AdV) 4 is expected to be applied to gene therapy and a recombinant vaccine in a host which can be infected by the recombinant adenovirus (AdV) 4, that is, the produced recombinant adenovirus (AdV) 4 has safe and wide application.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
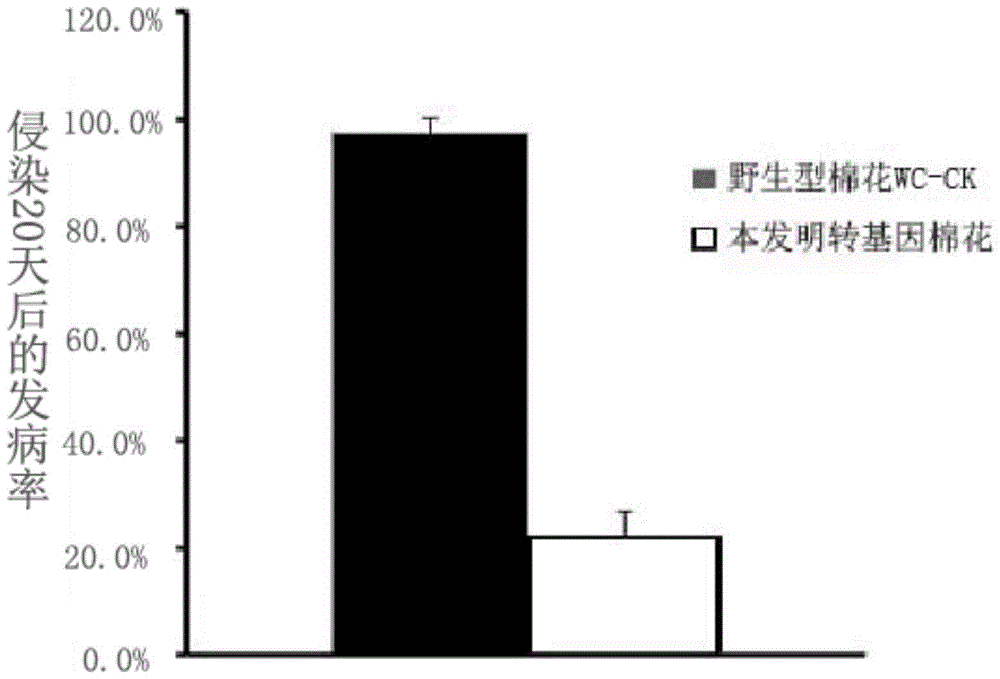
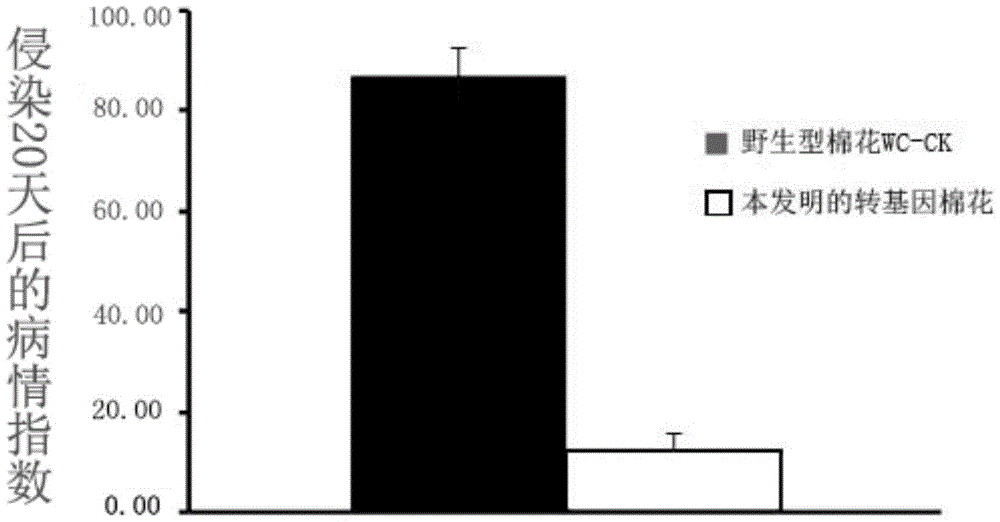
Method for cultivating cotton resisting verticillium dahliae
ActiveCN104988139AReduce pathogenicityFermentationPlant genotype modificationDicerVerticillium species
The invention relates to a method for cultivating cotton resisting verticillium dahliae. The method comprises the step that genes of a sequence shown in the SEQ ID NO.1 and genes of the inverted repeat sequence are guided into a cotton genome. According to the method, verticillium dahliae virulence genes are guided into a cotton plant, so that the genes are transcribed in the cotton plant to generate a double-stranded RNA structure corresponding to the verticillium dahliae virulence genes, Dicer-like protein in the cotton plant cuts the double-stranded RNA structure into siRNA with the size being 20-25nt, and the siRNA can recognize the virulence genes mRNA complementary with the sequence in verticillium dahlia infecting the cotton, degrades the virulence genes and lowers the pathogenicity of verticillium dahlia.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
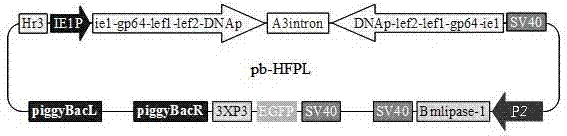
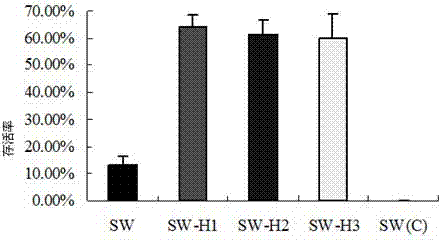
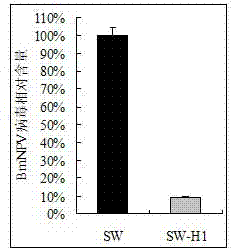
Application and recombinant vector of bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus polygene inverted repeat sequence and bombyx mori lipase-1 gene
ActiveCN102925484AControlled reproductionReduce contentVector-based foreign material introductionInverted Repeat SequencesEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses an application of a bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus (BmNPV) polygene inverted repeat sequence and a bombyx mori lipase-1 gene and specifically an application of the BmNPV polygene inverted repeat sequence and the bombyx mori lipase-1 gene to the construction of a recombinant vector; the vector can express a hairpin RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) for interfering with BmNPV multiple genes and bombyx mori lipase-1; BmNPV is inactivated by the incremental expression of bmlipase-1 (bombyx mori lipase-1) in the intestinal juice of a bombyx mori, and the number of BmNPV which invades intestinal cells of the bombyx mori is reduced; the expressed hairpin RNA can degrade the mRNA (Messenger Ribonucleic Acid) of a BmNPV gene and inhibit the replication and the proliferation of the virus in the Bombyx mori; and after the vector is used for producing a transgenic bombyx mori, the proliferation of BmNPV in the transgenicbombyx mor can be effectively inhibited, and the virus content is reduced, so that the survival rate of the bombyx mori infected with BmNPV is greatly increased.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Termination of transgene expression via transposon-mediated break
ActiveUS8524979B2Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesInverted Repeat SequencesIntein
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Termination of transgene expression via transposon-mediated break
ActiveUS20090260103A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesInverted Repeat SequencesA-DNA
This invention provides a genetic construct comprising: (a) a DNA cut-and-paste transposon genetic unit which comprises a transposase gene flanked on either side by inverted repeat sequences and operably under the control of a first promoter; and (b) a transgene unit which comprises an expressable transgene, placed operably under the control of a second promoter; wherein the transposon genetic unit and the transgene unit are linked with one of the inverted repeat sequence located in an intron of the transgene.This invention also provides methods of transiently expressing a transgene in a stably transformed eukaryote.This invention further provides methods for obtaining marker-free transgenic plants.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
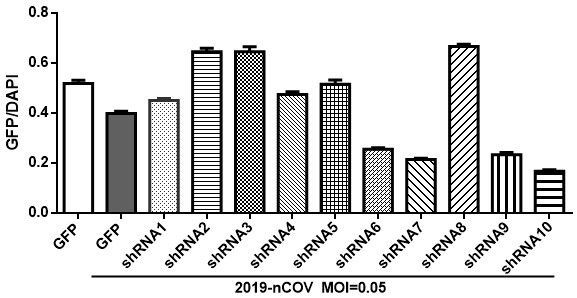
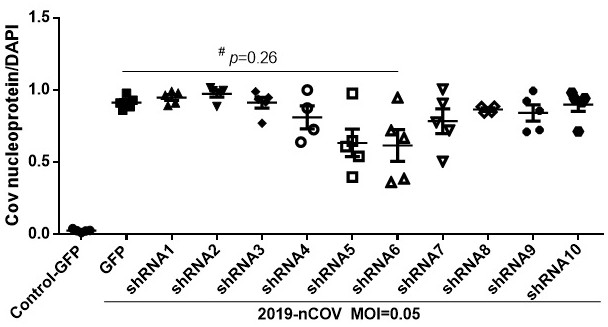
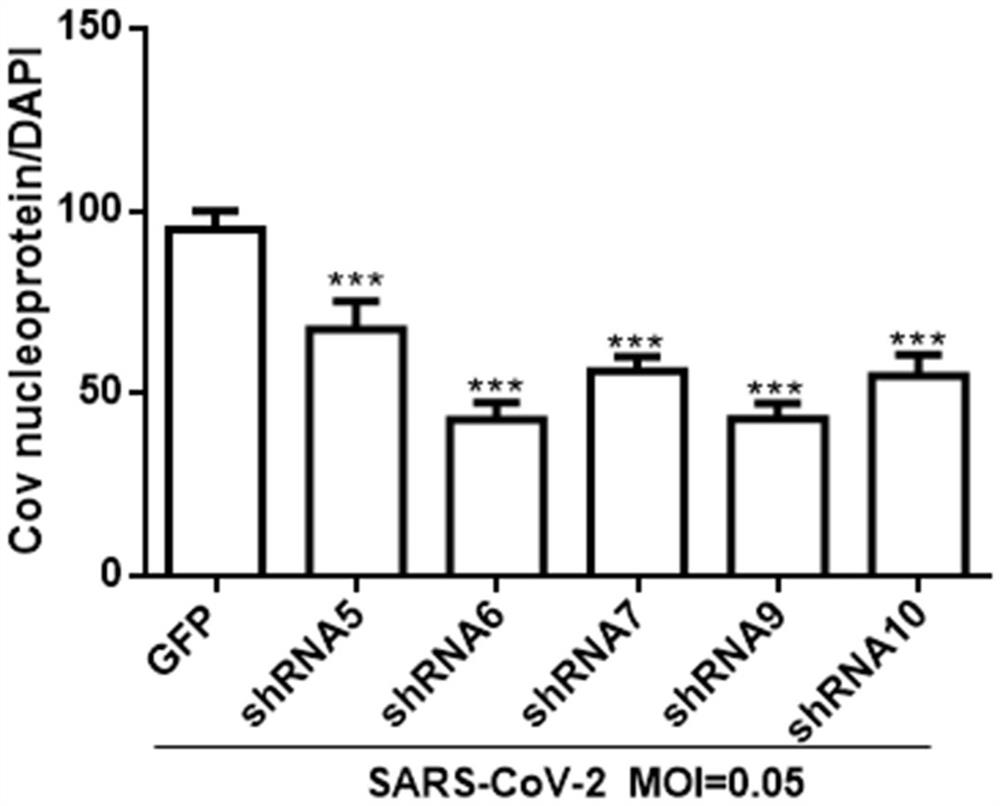
ShRNA for inhibiting replication of SARS-COV-2 virus and application of shRNA
InactiveCN112111489AOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsRepetitive SequencesInverted Repeat Sequences
The invention discloses shRNA for inhibiting replication of an SARS-COV-2 virus and an application of the shRNA. The shRNA targets one of E, M and N genes of the SARS-COV-2 virus and comprises any onepair of sequences selected from the following combinations: (a) a reverse repetitive sequence pair consisting of complementary SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO: 2; (b) a reverse repetitive sequence pair consisting of complementary SEQ ID NO: 3 and SEQ ID NO: 4; (c) a reverse repetitive sequence pair consisting of complementary SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 6; (d) a reverse repetitive sequence pair consisting of complementary SEQ ID NO: 7 and SEQ ID NO: 8; and (e) a reverse repetitive sequence pair consisting of complementary SEQ ID NO: 9 and SEQ ID NO: 10. The invention also discloses a drug for inhibiting the replication of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in a subject. The drug comprises a vector and a nucleic acid sequence encoding one or more of the shRNAs.
Owner:SHENZHEN INT INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
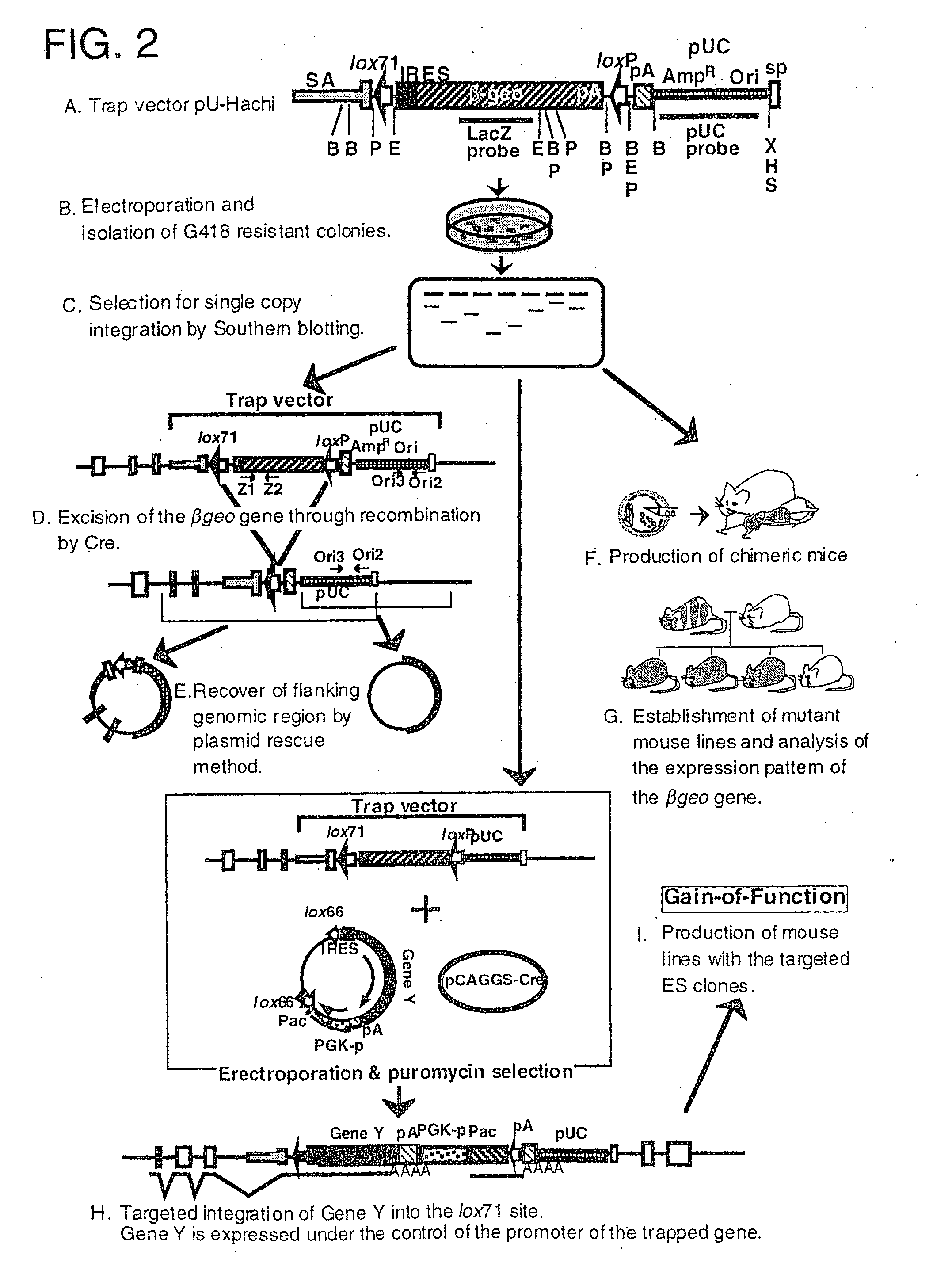
Trap vectors and gene trapping using the same
InactiveUS20090202988A1Specificity specificity can be easilyTime can be easilyMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue cultureInverted Repeat SequencesGenetics
Owner:TRANSGENIC
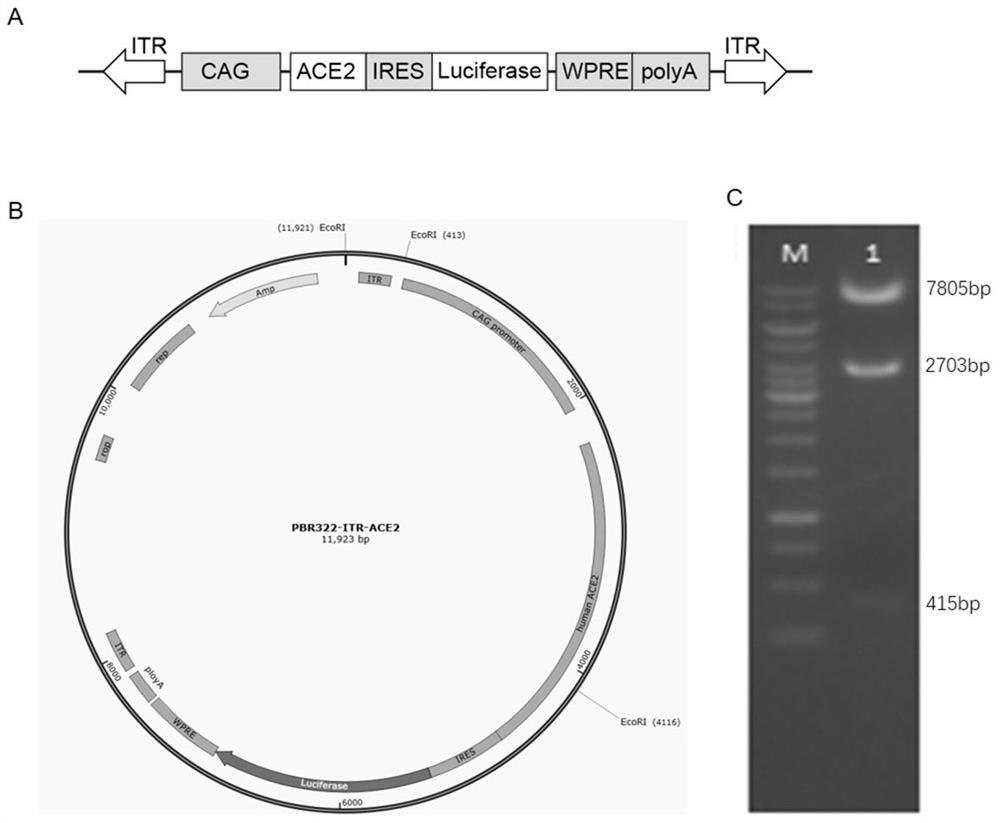
Rapid construction method and application of ACE2 humanized mouse model
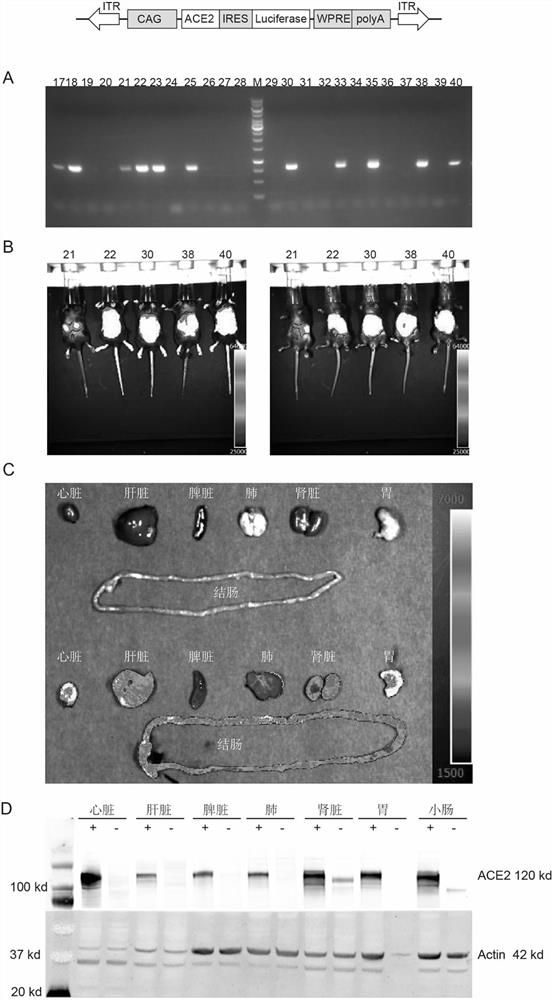
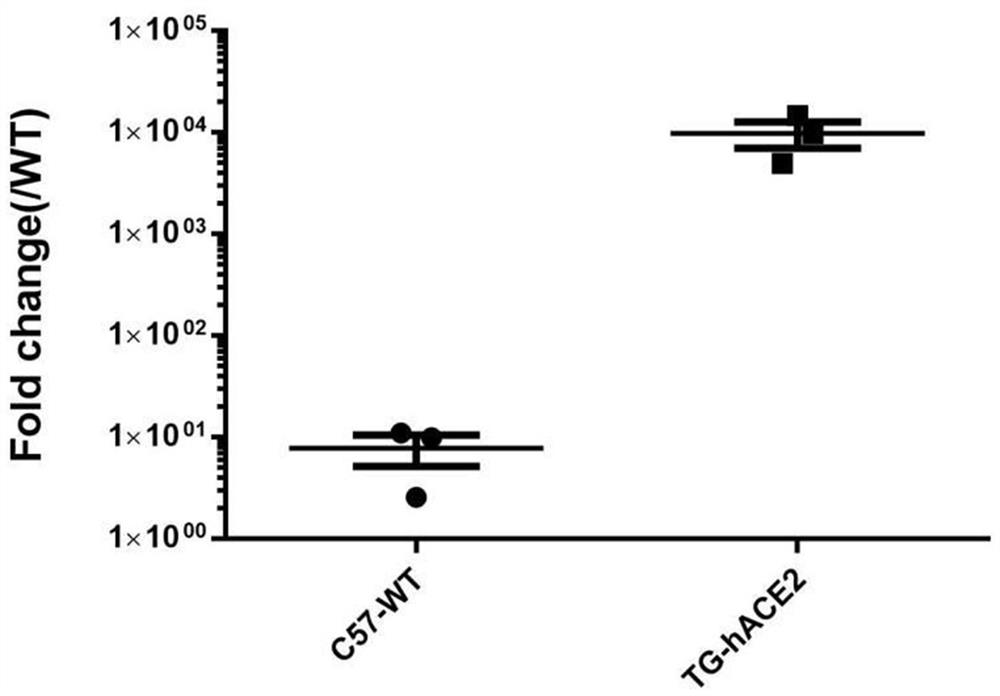
ActiveCN113684227ANucleic acid vectorOxidoreductasesInverted Repeat SequencesTranscriptional Regulatory Elements
The invention provides a transgenic vector, a method for rapidly constructing an ACE2 humanized animal model by using the transgenic vector, and application of the ACE2 humanized animal model by aiming at research and development of SARS-CoV-2 drugs. The transgenic vector comprises a PiggyBac transposon 5'end inverted repeat sequence (ITR), a CAG promoter, a human ACE2 coding region, a ribosome access site (IRES), firefly luciferase, a dial rat hepatitis post-transcriptional regulatory element (WPR), a polyA site and a 3 'end inverted repeat sequence (ITR), the transgenic vector can efficiently insert human ACE2 and luciferase gene expression cassettes into a mouse genome, and the luciferase and human ACE2 expressed transgenic mice can be rapidly screened through a luciferase living body imaging system.
Owner:SHANGHAI BIOMODEL ORGANISM SCI & TECH DEV +2
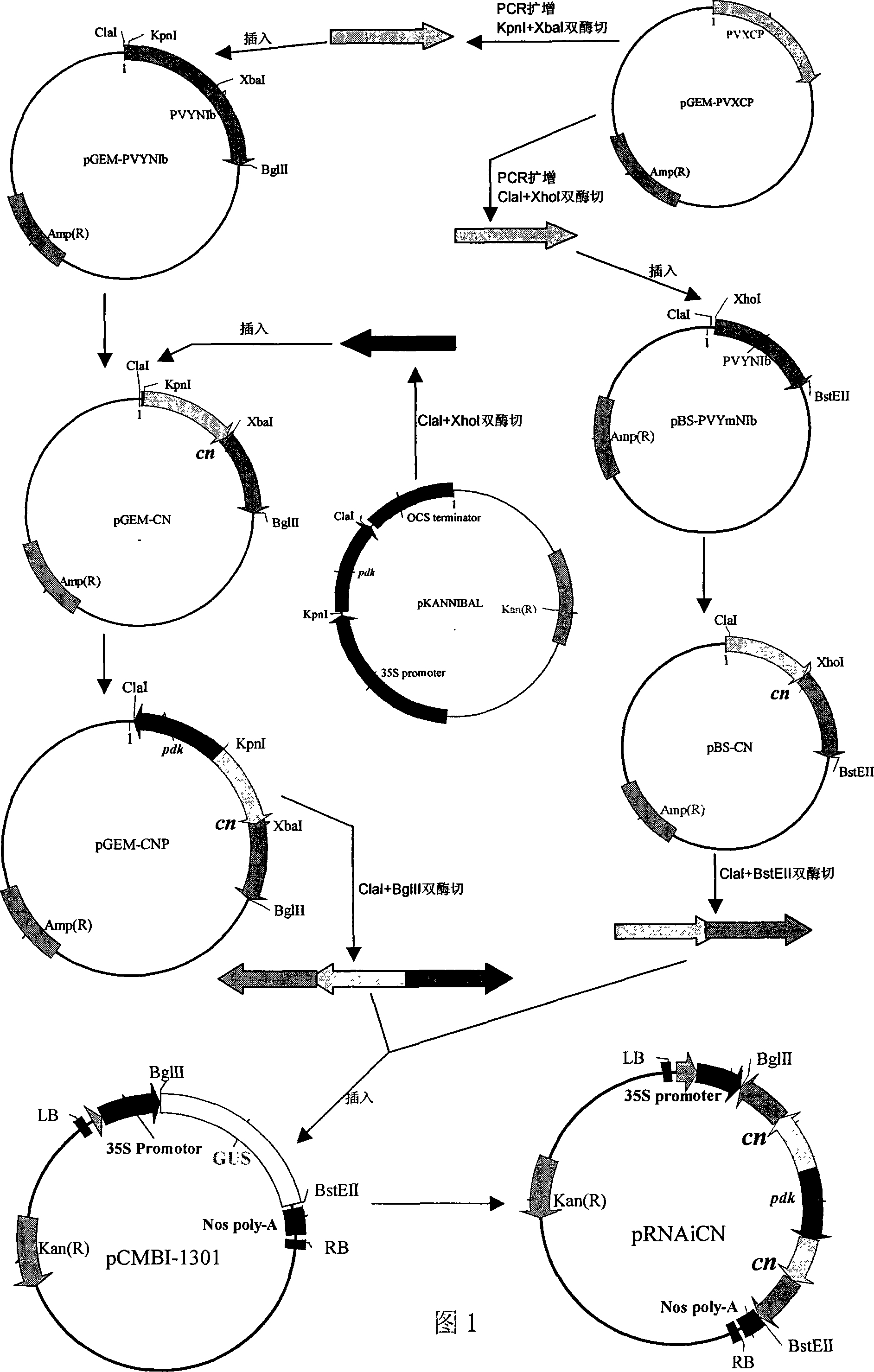
Method for constructing gene of raining dual resistances of potato on PVX virus and PVY virus
InactiveCN101092624AInhibition of replicationSolve the degradation of shrunken flower and leaf typeFermentationPlant genotype modificationEnzymeInverted Repeat Sequences
This invention relates to a method for constructing fusion gene for improving both PVX resistance and PVY resistance of potato. The method comprises: (1) extracting total RNA from PVX-infected and PVY-infected plants, and performing RT-PCR to obtain coat protein (cp) gene of PVX, and replicase gene Nib of PVY; (2) performing PCR to amplify conserved sequences of cp gene and Nib gene; (3) digesting the conserved sequences, and ligating to obtain fusion gene cn; (4) constructing inverted repeat sequence with an intron, a forward cn gene sequence and a backward cn gene sequence to obtain double-resistance gene RNAiCN; (5) connecting the flanking sequences of RNAiCN with promoter and terminator. When the fusion gene is transferred into potato, both PVX resistance and PVY resistance of the potato are improved.
Owner:山西省农业科学院作物遗传研究所
Producing improved viral and non-viral nanoplasmid vectors
PendingCN112154208AImprove product qualityImprove throughputNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionOrigin of replicationInverted Repeat Sequences
A method for improving the replication of a covalently closed circular plasmid is provided. The method includes providing a covalently closed circular plasmid having a Pol I-dependent origin of replication, and an insert including a structured DNA sequence selected from the group consisting of inverted repeat sequence, direct repeat sequence, homopolymeric repeat sequence, eukaryotic origin of replication or eukaryotic promoter enhancer sequence, wherein the structured DNA sequence is located at a distance of less than 1000 bp from the Pol I-dependent origin of replication in the direction ofreplication. The method also includes modifying the covalently closed circular recombinant molecule such that the Pol I-dependent origin of replication is replaced with a Pol III-dependent origin of replication, whereby the resultant Pol III-dependent origin of replication covalently closed circular plasmid has improved replication. An antibiotic marker free covalently closed circular recombinantDNA molecule is also provided.
Owner:阿尔德夫隆有限责任公司
Enhanced sleeping beauty transposons, kits and methods of transposition
The present invention relates to enhanced Sleeping Beauty-type transposons and methods of transposition. In particular, the invention relates to a polynucleotide comprising a cargo nucleic acid flanked by a left and a right inverted repeat / direct repeat (IR / DR), wherein IR / DRs, having specific sequences, are recognized by a Sleeping Beauty transposase protein and the polynucleotide is capable of integrating into the DNA of a cell. The invention also relates to a kit for transposing a nucleic acid comprising said polynucleotide as well as to further components such as co-factors of transposition capable of depleting a component of the FACT (facilitates chromatin transcription) complex, namely, SSRP1 and / or SUPT16H / SPT16,or an inhibitor of cathepsin selected from the group comprising H,S,V,and L; or a cofactor capable of depleting or inhibiting HSP90; or a factor temporally arresting cells cell cycle in cell cycle phase G0 / G1, G1 / S, or G2 / M; or a factor inhibiting the ubiquitination ofPCNA,or cells wherein these components have been knocked down or inhibited,or the cell cyle arrested in any of said stages. Alternatively or additionally, the kit may comprise as a co-factor of transposition an agent capable of increasing concentration and / or signaling of ATR or a cell wherein concentrationand / or signaling of ATR are increased. The invention further provides methods using said transposon polynucleotide as well as host cells and pharmaceutical compositions. It also relates to use of said co-factors of transposition or specific cells for enhancing transposition efficiencies, e.g., for preparing genetically modified nucleic acids or cells.
Owner:MAX DELBRUECK CENT FUER MOLEKULARE MEDIZIN
Plasmid for constructing interference vector and construction method and application thereof
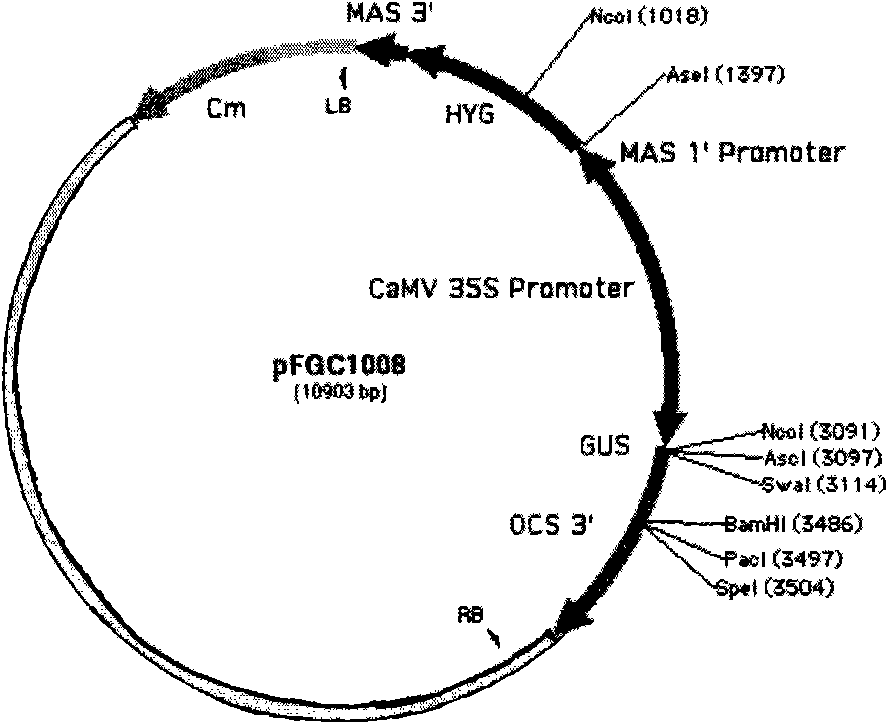
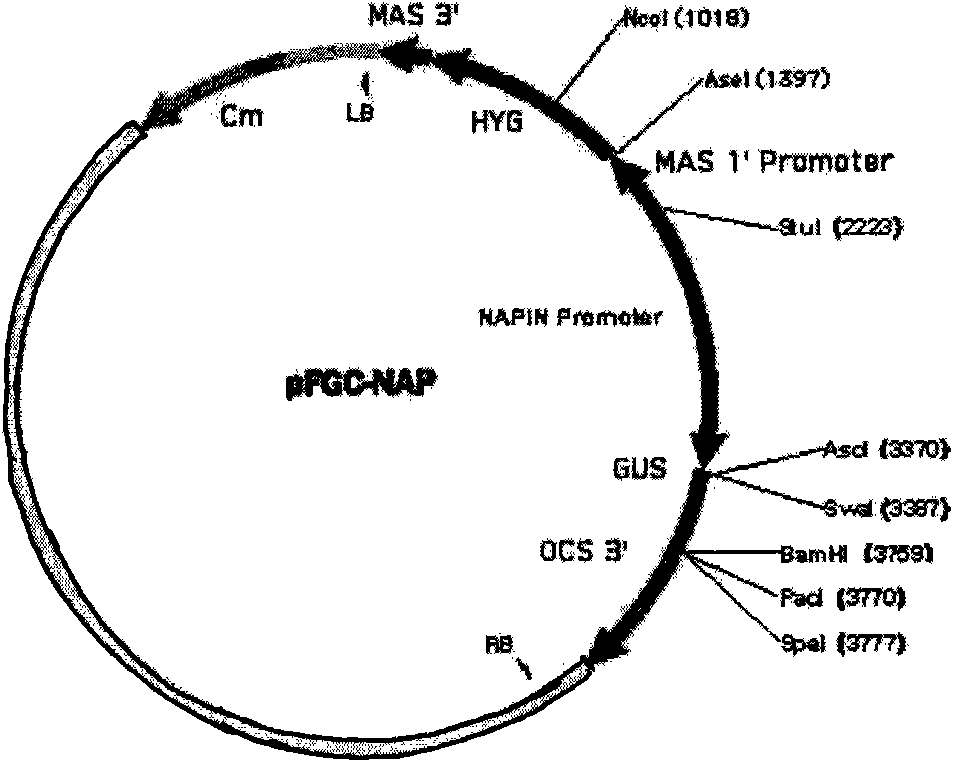
InactiveCN101880683AImprove qualityHigh interference efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsInverted Repeat SequencesA-DNA
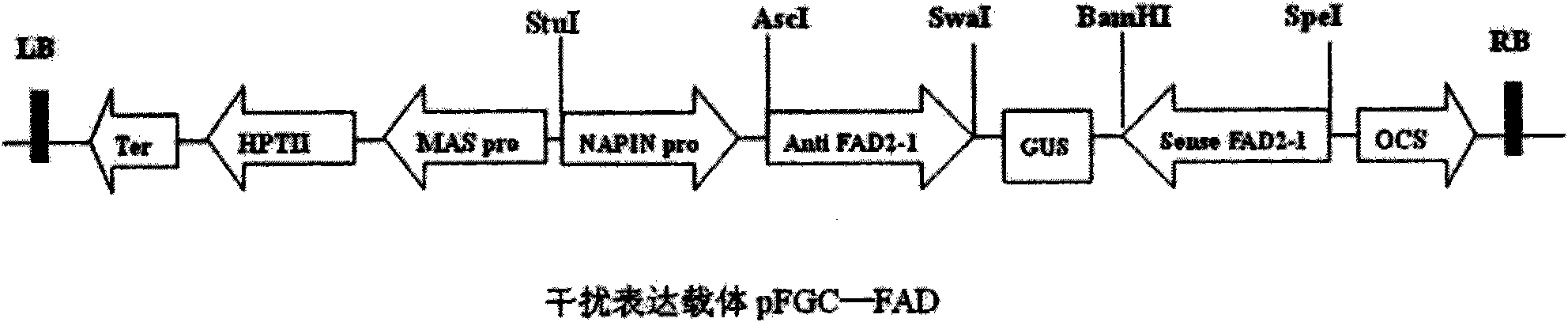
The invention discloses a plasmid for constructing an interference vector, a construction method thereof and application thereof. The invention provides a plasmid pFGC-NAP obtained by inserting a DNA presented by sequence 1 in a sequence list between an Stu I enzyme cutting site and an Asc I enzyme cutting site of a plasmid pFGC1008. The interference vector can be obtained by respectively inserting a plus-sense DNA fragment and an anti-sense DNA fragment into a multiple cloning site of the plasmid pFGC-NAP, wherein the plus-sense DNA fragment and the anti-sense DNA fragment are inverted repeat sequences designed for a target gene to be interfered and expressed. The plasmid constructs the interference vector capable of specially expressing a promoter during a seed development period, has high interference efficiency, can control a spatial temporal specificity expression, can be used for a specific gene expressed in silent plant seeds, and improves quality of oil crop seeds or other plant seeds.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Artificially synthesized Bt insect-resistant gene Cry1Ab-t and application thereof
ActiveCN102010873BHigh expressionEfficient and stable expressionBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyInverted Repeat Sequences
The invention provides an insect-resistant gene Cry1Ab-t and an encoding protein thereof. In the gene, by using a plant bias codon and reducing a sequence rich in AT, an inverted repeat sequence and a subsequence-containing undefined eucaryotic deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) sequence in the original DNA sequence on the premise of keeping part of amino acid sequences of a Bacillus thuringHansis (Bt) protein Cry1Ab unchanged, a new Cry1Ab-t gene sequence is synthesized by artificial modification, then a prokaryotic expression carrier and a plant expression carrier are constructed for the gene, and a corresponding host cell is converted. In vitro experiments prove that a synthesized Bt toxoprotein has an obvious insecticidal effect on corn borers. The insect-resistant gene Cry1Ab-t and a target protein expressed by the gene can be steadily and efficiently expressed in corns, so that the gene can be used for culturing Cry1Ab-t transgene insect-resistant corns. The artificially synthesizedBt insect-resistant gene Cry1Ab-t can be also used for improving the insect resistance of other crops, fruit trees, vegetables and the like.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for controlling soot lice by silencing two resistance genes
InactiveCN102690837BVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsInverted Repeat SequencesResistant genes
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, and in particular relates to a method for controlling soot lice by silencing two resistance genes.. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting bemisia tabaci drug-resistant CYP6CM1 gene and coe1 gene as RNAi target gene; embedding partial sequences of the CYP6CM1 gene and the coe1 gene by overlap polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and using the embedded sequence to build an RNAi carrier with inverted repeat sequence; and transforming the RNAi carrier into a target plant, and obtaining transgenic plant capable of controlling the bemisia tabaci. The method is an important supplement of a method for controlling the bemisia tabaci mainly by an insecticide. The method can be used for interfering with the expression of related drug-resistant genes in the bemisia tabaci by the RNAi technology, thus providing technical support for controlling the bemisia tabaci.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
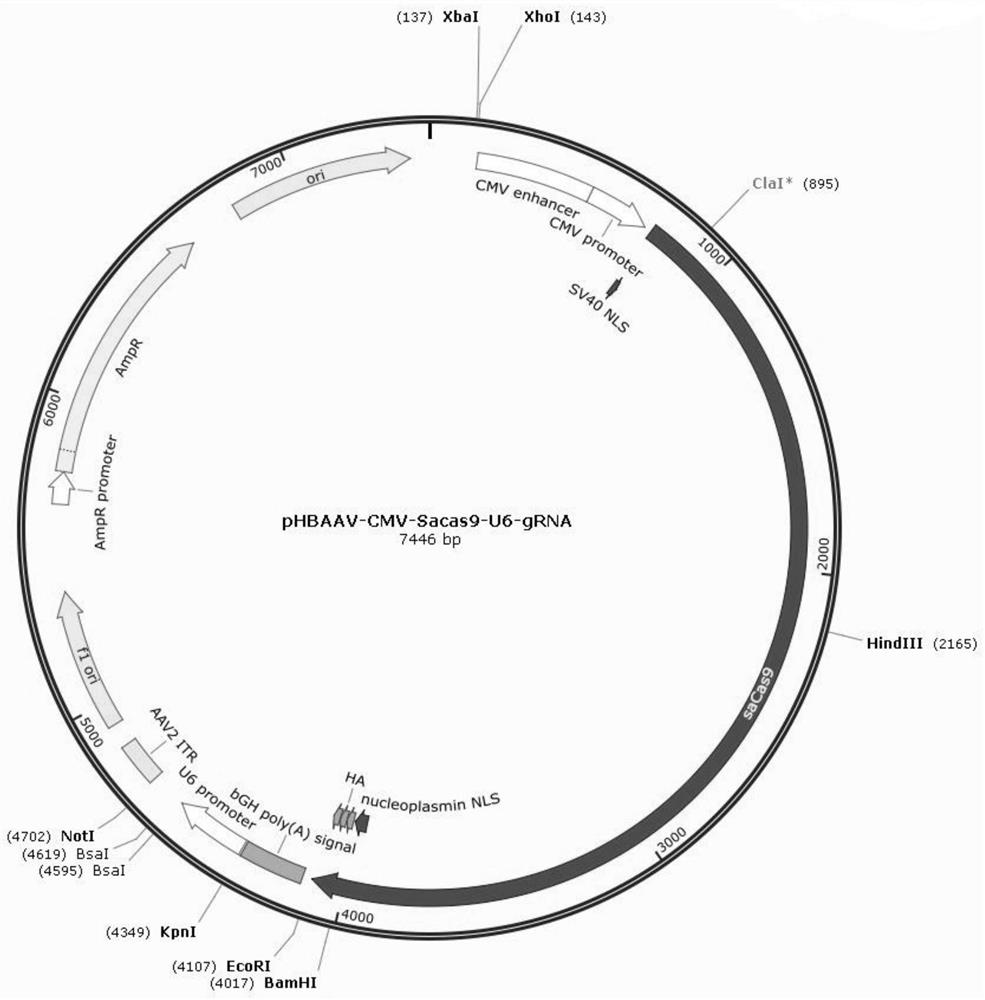
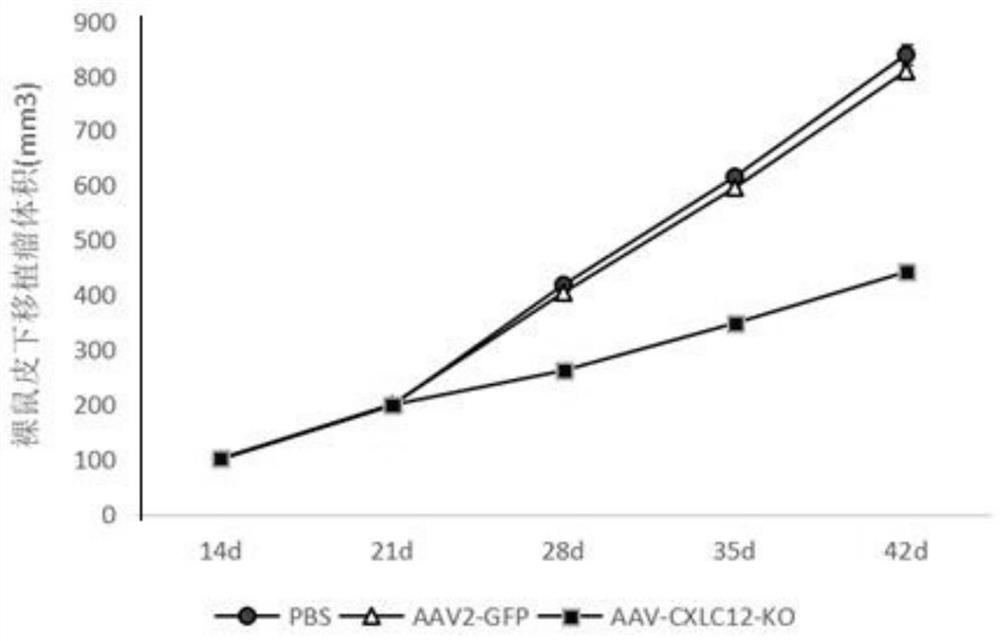
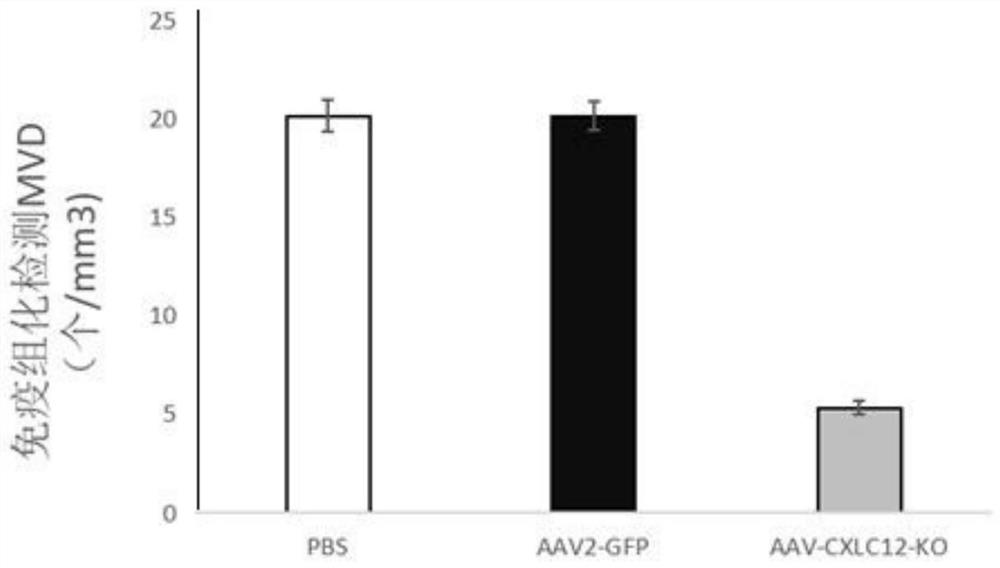
Adeno-associated virus recombinant vector for knocking out CXCL12 gene and its construction method and application
The present invention provides an adeno-associated virus recombinant vector for knocking out the CXCL12 gene, the recombinant vector at least includes the following sequence elements operably linked: 5' terminal inverted repeat sequence, CMV promoter, sacas9 sequence, polyA signal sequence, U6 promoter sequence, gRNA sequence, 3'-end inverted repeat sequence. The inventors found that the CXCL12 gene knockout vector can effectively inhibit the growth of transplanted tumors and tumor angiogenesis in the U87 cell glioma model, and can effectively inhibit the tumor growth and tumor angiogenesis in the U87 cell subcutaneous glioma model in nude mice. It shows that the technical scheme of the present invention can be applied to the treatment of glioma diseases.
Owner:汉恒生物科技(上海)有限公司
ShRNA of CXCR4 gene and application of shRNA
InactiveCN111235151AReduce expressionOrganic active ingredientsPeptidesInverted Repeat SequencesCXCR4
The invention provides shRNA of a CXCR4 gene and an application of the shRNA. The shRNA comprises siRNA of the CXCR4 gene and an inverted repeat sequence of the siRNA. According to the invention, a constructed slow virus vector realizes hereditary silencing to the CXCR4 gene in a T cell; the expression level of the CXCR4 gene in an edited T cell is significantly reduced; and a novel method and thought are provided for treatment of tumors and immune diseases.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BIO GENE TECH CO LTD
Transposon system, kit comprising the same, and uses thereof
An in vitro method for integrating an exogenous DNA sequence into the genome of a cell using a transposon system. The transposon system includes a first vector carrying inverted repeat sequences and an exogenous DNA, and a second vector that expresses a transposases. Also provided is a kit including the transposon system for integrating an exogenous DNA into the genome of a cell. A method for treating a subject is described that includes engineering an immune cell to carry an exogenous DNA sequence using the method and / or the kit described above and administering an effective amount of the engineered immune cell to the subject.
Owner:GENOMEFRONTIER THERAPEUTICS INC
DNA fragment for inhibiting expression of omega secaline gene in wheat 1B/1R translocation line and application thereof
The invention discloses a DNA fragment for inhibiting the expression of an omega secaline gene in a wheat 1B / 1R translocation line and application thereof. The DNA fragment consists of an omega secaline gene coding region partial sequence, a plant intron sequence and the inverted repeat sequence of the omega secaline gene coding region partial sequence which are connected in turn. An RNAi geneticexpression vector containing the DNA fragment is transferred to the wheat 1B / 1R translocation line in a transgenic way, so that the expression of the endogenous omega secaline gene can be inhibited, the adverse effects of omega secaline on the food processing quality of the wheat 1B / 1R translocation line are relieved or eliminated and the food processing quality of the wheat 1B / 1R translocation line is improved.
Owner:HEBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI INST OF GENETICS & PHYSIOLOGY
Method for detecting mutation and method of inducing the same
InactiveUS20070009896A1Efficient inductionEasy to detectBacteriaSugar derivativesInverted Repeat SequencesNucleotide
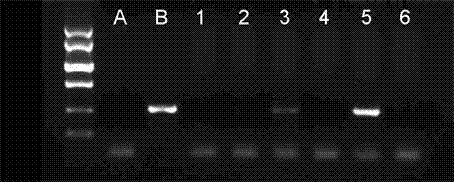
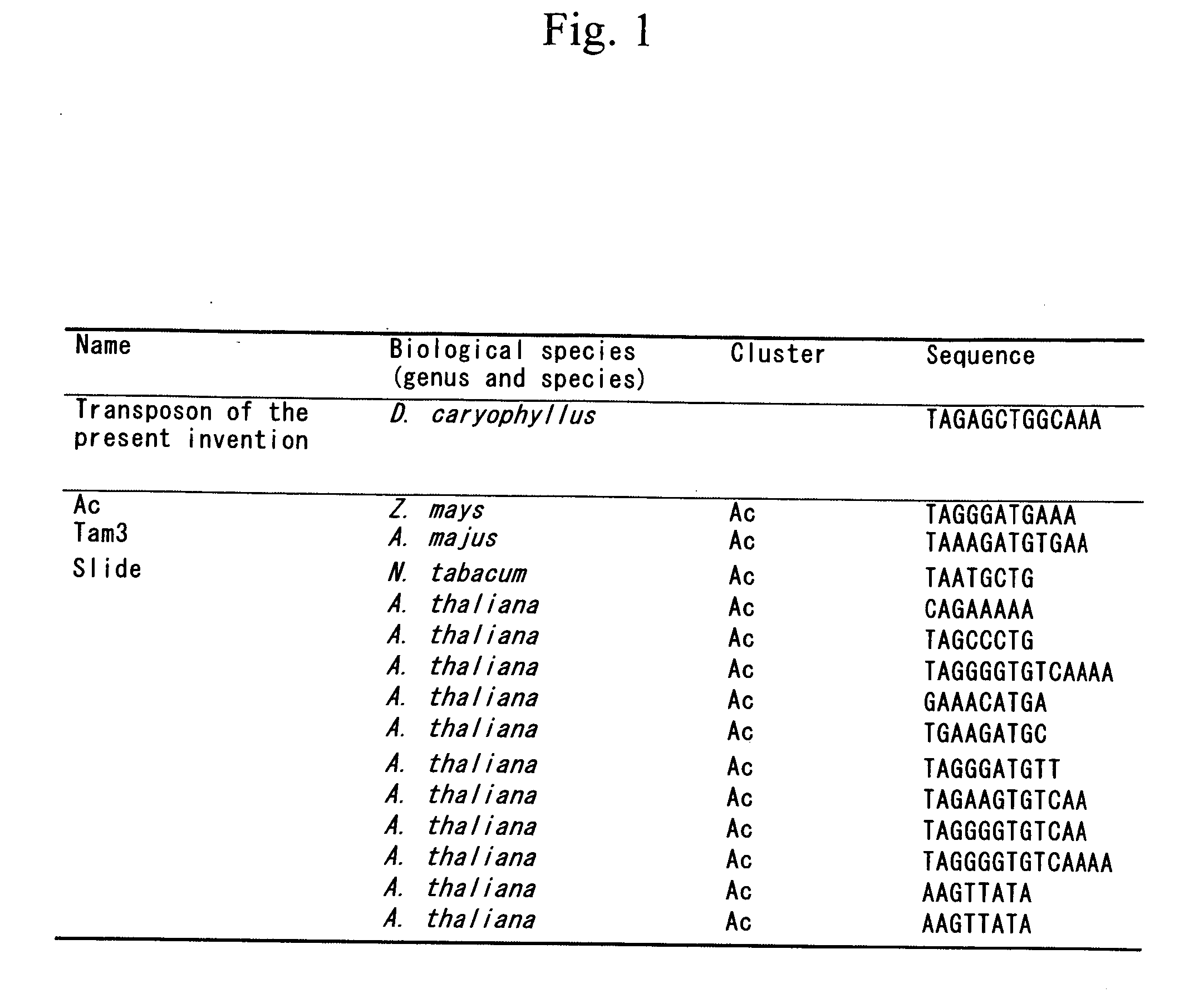
A novel plant transposon that induces bud mutation, transposase thereof, and a method for efficiently inducing bud mutation by improvement in the transposition efficiency are provided. A novel transposon having terminal inverted repeat sequences (SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO: 2) shown below has been isolated for the first time from carnation (Dianthus caryophyllus) and the nucleotide sequence thereof has been determined. The transposon has contained a gene encoding the transposase in its sequence. The transposon induces bud mutation when it is inserted into a gene. The transposition frequency is elevated due to environmental stress. TAGAGCTGGCAAA—TTTGCCAGCTCTA (SEQ ID NOS 1 & 2, respectively in order of appearance).
Owner:KIRIN BREWERY CO LTD
Artificial noncoding RNAs containing inverted sineb2 repeats and their use in enhancing translation of target proteins
ActiveCN105624156BPrevent proliferationMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionInverted Repeat SequencesProtein target
The present invention relates to an artificial non-coding RNA containing an inverted SINEB2 repeat sequence and its use in enhancing the translation of a target protein. Specifically, the present invention provides a nucleic acid molecule, which is: (1) an RNA molecule consisting of the following elements: a pairing region complementary to the target mRNA, an inverted SINEB2 sequence, and an optional poly(A) signal region , and optionally regulatory elements; or (2) a DNA molecule capable of transcribing the RNA molecule.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Active transposon of fish Tc1-like and application of active transposon
InactiveCN103589717BEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyInverted Repeat Sequences
The invention relates to a fish Tc1-like active transposon and its application. Specifically provided are transposons with complete left and right terminal inverted repeat sequences, transposons capable of encoding transposases and transposases encoded therein, gene vectors and gene transfer systems containing the above transposons and transposases. Through the verification of transposition activity in zebrafish, it is confirmed that the above-mentioned transposon has transposition activity, and the gene transfer system can perform high-efficiency transposition in zebrafish, so the present invention is to further verify the transposition efficiency of transposon And the use of the transposon in vertebrate related research and application has laid a foundation.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Transposon system, kit comprising the same, and uses thereof
An in vitro method for integrating an exogenous DNA sequence into the genome of a cell using a transposon system. The transposon system includes a first vector carrying inverted repeat sequences and an exogenous DNA, and a second vector that expresses a transposases. Also provided is a kit including the transposon system for integrating an exogenous DNA into the genome of a cell. A method for treating a subject is described that includes engineering an immune cell to carry an exogenous DNA sequence using the method and / or the kit described above and administering an effective amount of the engineered immune cell to the subject.
Owner:GENOMEFRONTIER THERAPEUTICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com