Producing improved viral and non-viral nanoplasmid vectors
A plasmid, origin of replication technology, applied in the direction of viruses/phages, viruses, vectors, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0287] Example 1: pUC and R6K origin of replication plasmid replication and production
[0288] pUC origin vector replication and production background: The vast majority of therapeutic plasmids use the pUC origin, which is a high-copy derivative of the pMB1 origin (closely related to the ColE1 origin). For pMB1 replication, plasmid DNA synthesis is unidirectional and does not require a plasmid-borne initiator protein. The pUC origin is a high-copy derivative of the pMB1 origin that deletes the helper ROP(rom) protein and has an additional temperature-sensitive mutation that destabilizes the RNAI / RNAII interaction. Moving cultures containing these origins from 30°C to 42°C resulted in an increase in plasmid copy number. The pUC plasmid can be produced in many E. coli cell lines.
[0289] RNA-OUT No Antibiotic Selectable Marker Background: Antibiotic-free selection was performed in an E. coli strain containing pCAH63-CAT RNA-IN-SacB (P5 / 66 / 6) chromosomally integrated at t...
Embodiment 2
[0305] Example 2: Production of pUC and R6K origin vectors
[0306] Shake flask production: Shake flask production using proprietary plasmid + shake flask medium. Seed cultures were started from glycerol stocks or colonies and streaked onto LB medium agar plates containing 50 μg / mL antibiotic (for ampR or kanR selection plasmids) or 6% sucrose (for RNA-OUT selection plasmids). Plates were grown at 30-32°C; cells were resuspended in medium and used to provide approximately 2.5 OD for 500 mL plasmid + shake flasks 600 The shake flask contained 50 μg / mL of antibiotics for ampR or kanR selection plasmids or 0.5% sucrose for selection of RNA-OUT plasmids. The flasks were grown to saturation at the growth temperatures shown in Tables 5, 6, 7 and 9 with shaking.
[0307] Fermentation production: Fermentations were performed in New Brunswick BioFlo 110 bioreactors using a proprietary fed-batch medium (NTC3019, HyperGRO medium) as described (Carnes and Williams, Supra, 2011). Se...
Embodiment 3
[0324] Embodiment 3: Construction and preparation of pUC and R6K starting point structure carrier
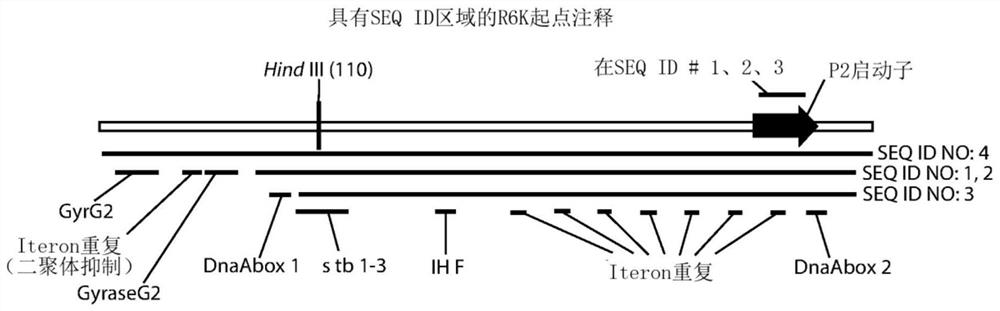
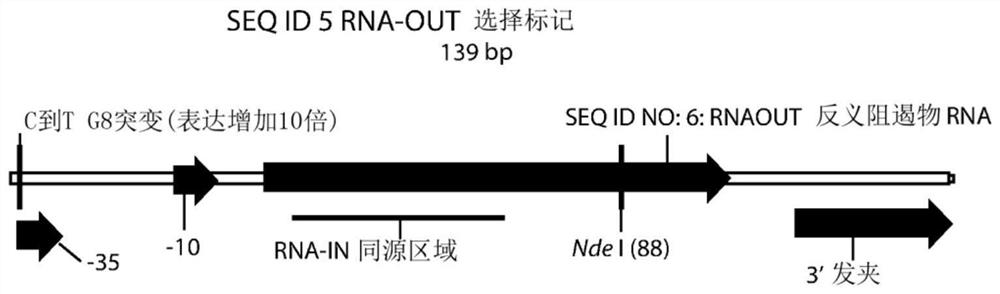
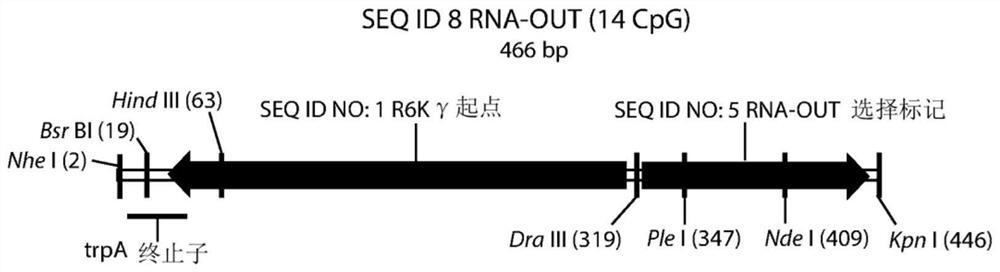
[0325] The R6Kγ origin (SEQ ID NO: 1; Figure 1E )-RNA-OUT (SEQ ID NO: 5; Figure 1B ) bacterial replication selection region (SEQ ID NO: 8; Figure 1C ) were cloned into the polylinker region of various pUC57-based vectors to generate pNTC-NP1, pNTC-NP2, pNTC-NP3, pNTC-NP4, pNTC-NP5, pNTC-NP6, pNTC-NP7 vectors. Each vector has different flanking restriction sites that can be used to engineer the destination vector for R6K replication-RNA-OUT selection. Table 4 shows the 5' and 3' polylinker sequences flanking the R6K-RNA-OUT insert in the pNTC-NP1-7 vector. A 1 CpG R6Kγ origin-2 CpG RNA-OUT bacterial replication selection region based on pUC57 was also created (SEQ ID NO: 9; Figure 1D ) version (pNTC-3xCpGNP1), as shown in Table 4.
[0326] The R6Kγ origin (SEQ ID NO: 1) is the modified R6K origin of the 6-repeat ( Figure 1E ). A 7-repeat based R6K gamma origin (SEQ ID...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com