Patents
Literature
40 results about "Direct repeat" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
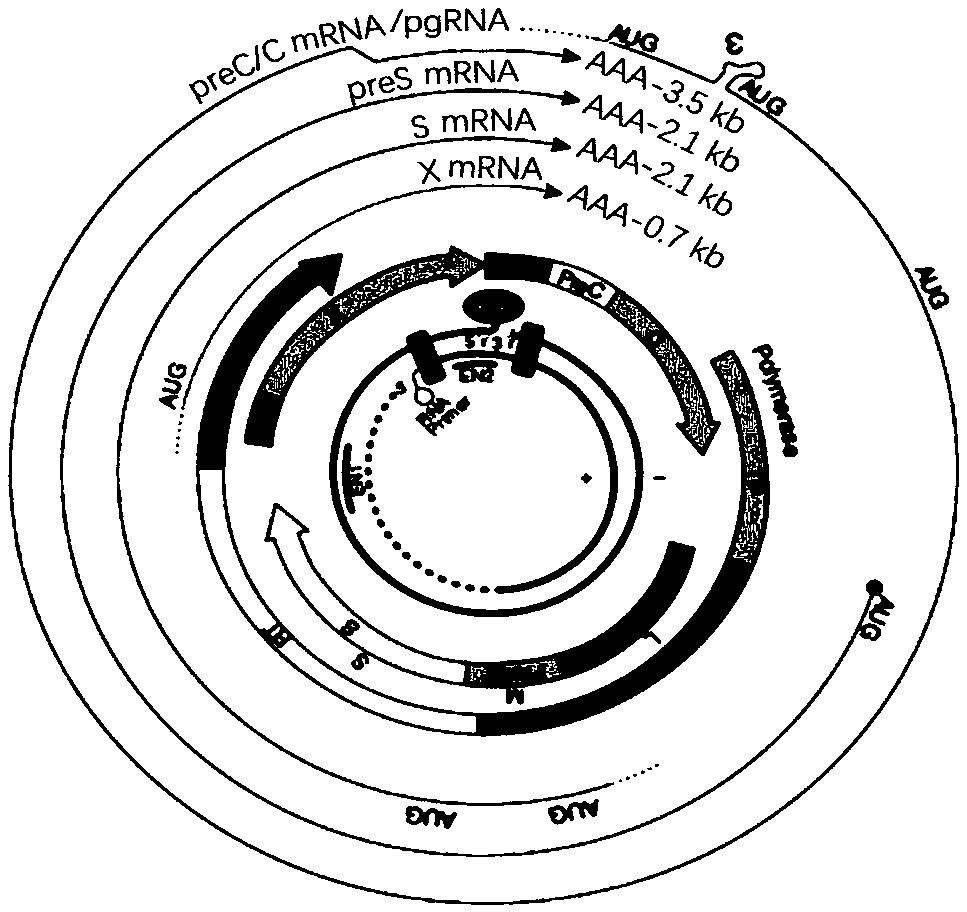
Direct repeats are a type of genetic sequence that consists of two or more repeats of a specific sequence. In other words, the direct repeats are nucleotide sequences present in multiple copies in the genome. Generally, a direct repeat occurs when a sequence is repeated with the same pattern downstream. There is no inversion and no reverse complement associated with a direct repeat. It may or may not have intervening nucleotides. The nucleotide sequence written in bold characters signifies the repeated sequence.
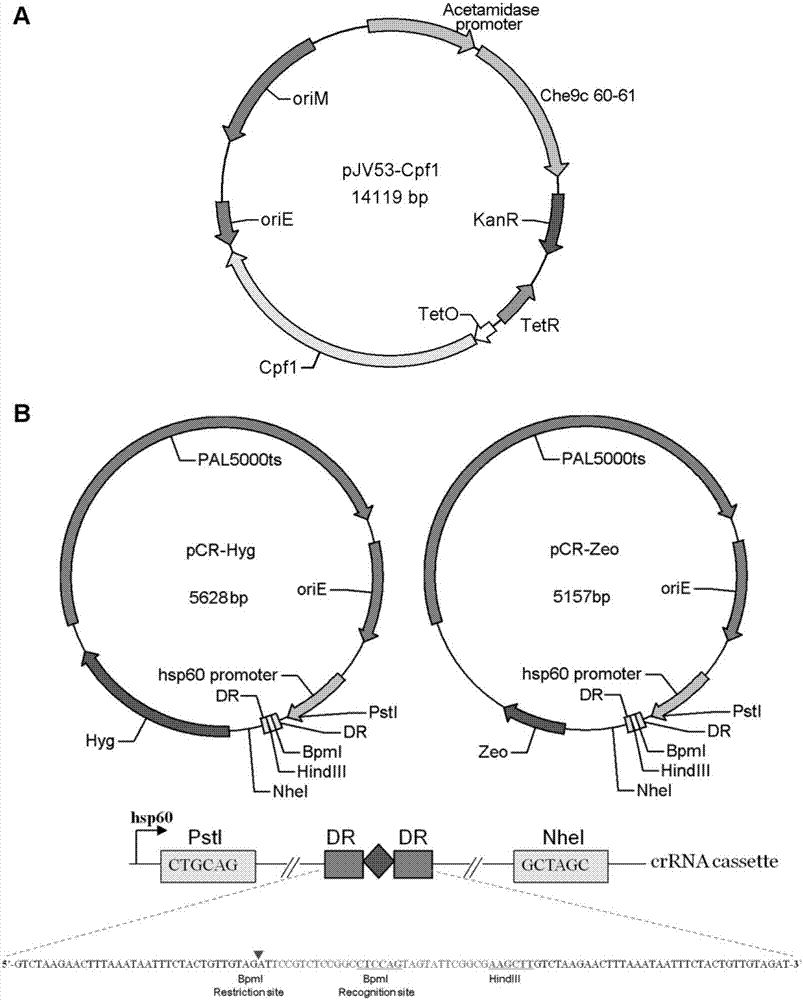
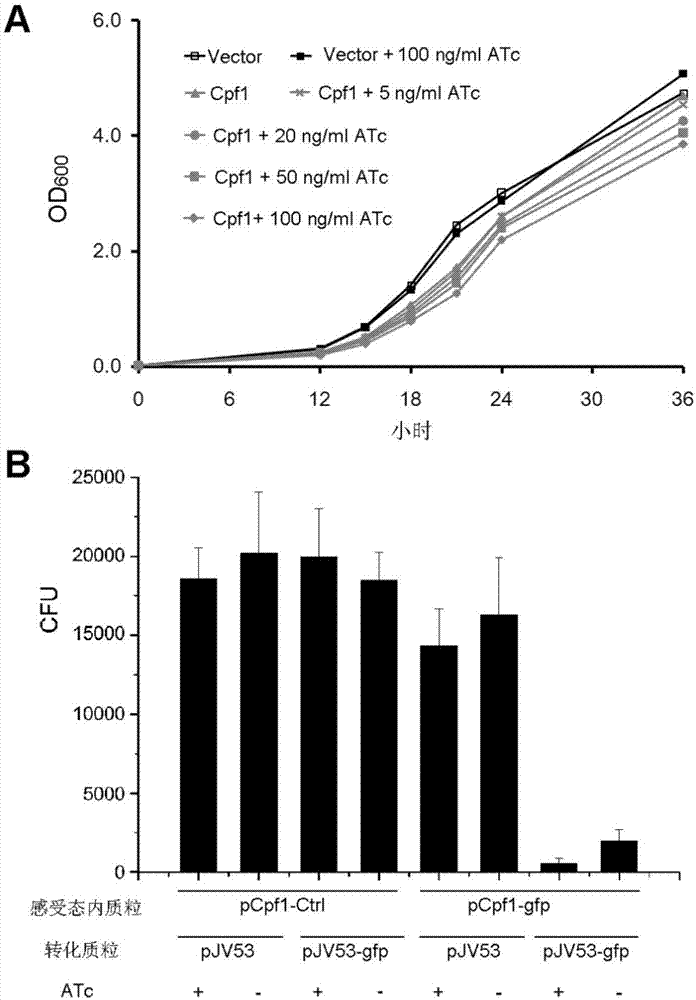
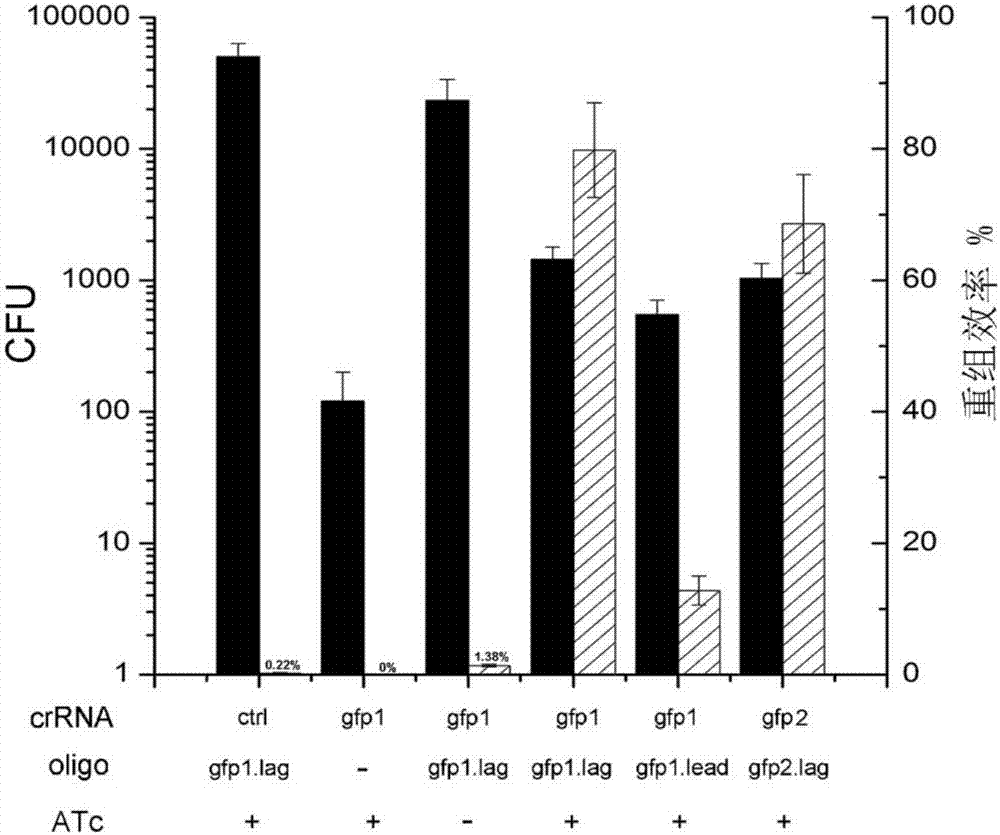
CRISPR/Cpf1 gene editing system and application of system in mycobacteria
ActiveCN107083392AAchieve mutationWork lessHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAEscherichia coliShuttle vector
The invention discloses a CRISPR / Cpf1 gene editing system and application of the system in mycobacteria. The CRISPR / Cpf1 gene editing system comprises a recombinant vector carrying optimized FnCpf1 genes and pCR plasmids, wherein the sequence of the optimized FnCpf1 genes is shown in SEQ ID No:1, and the recombinant vector is a colibacillus-mycobacterium shuttle vector containing recombinant enzyme gp60 and gp61 genes; the pCR plasmids contain promoter-driven direct repeat sequence-spacer sequence-direct repeat sequence units, wherein the spacer sequence contains target sequence connection sites. When the CRISPR / Cpf1system is used in the mycobacteria for CRISPR / Cpf1 assisted homologous recombination, high recombination efficiency can be obtained, and gene editing of the mycobacteria can be achieved.
Owner:INST OF PATHOGEN BIOLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
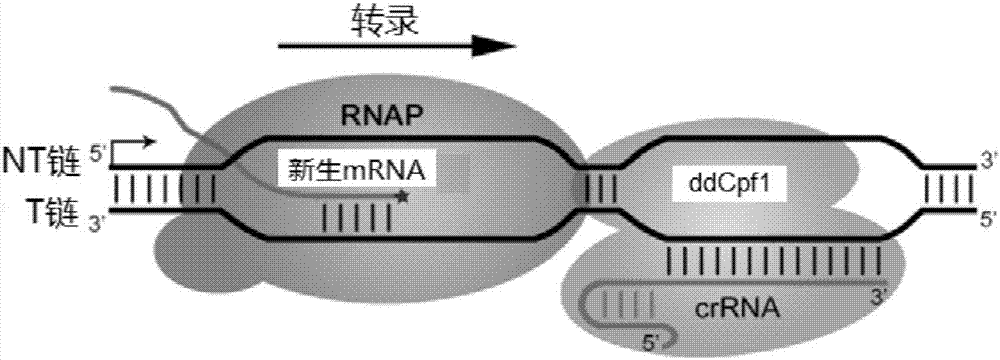
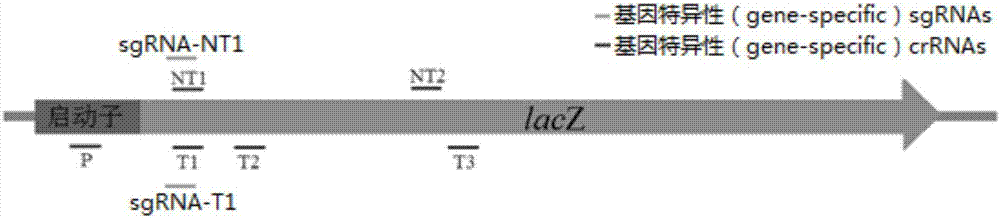
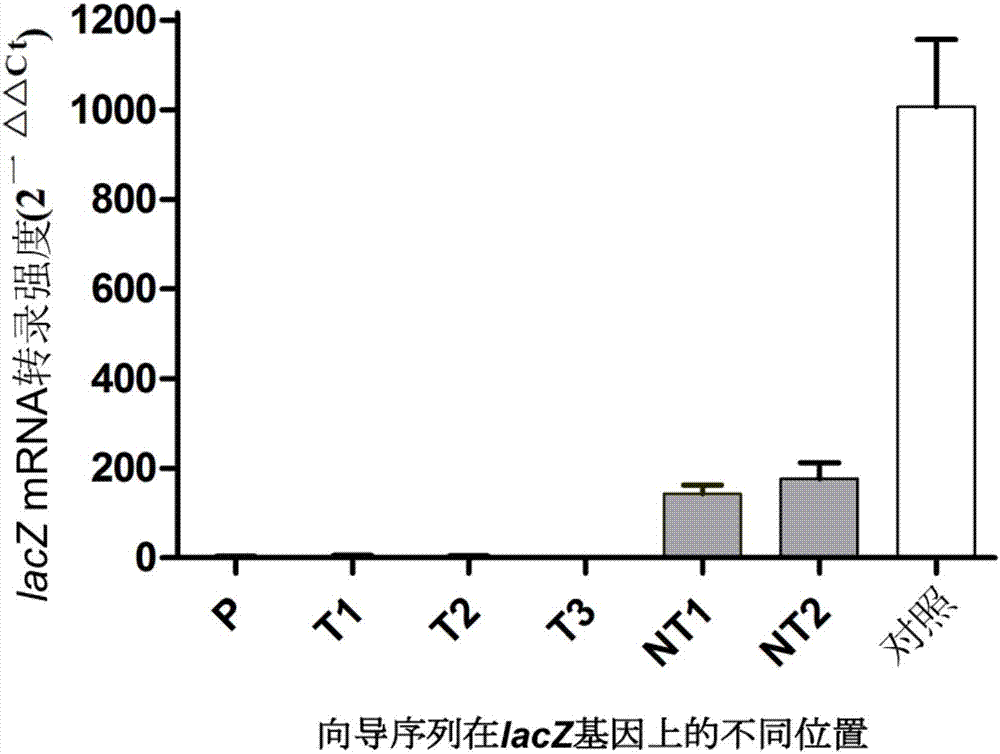
Cas protein specific binding target DNA, method for regulating and controlling target gene transcription and kit
The invention relates to a method for binding Cas protein to DNA, and in particular to a method which is capable of conveniently, rapidly and efficiently regulating and controlling gene transcription for one or more targets as well as a kit applicable to the method. The method comprises the following steps: determining a target on genome, finding out a PAM site required by binding of the Cas protein (the Cas protein is a Cas protein mutant having an RNA enzymatic activity and in lack of a DNA enzymatic activity) within left and right regions of the target, designing a go-ahead sequence in accordance with the PAM site, determining direct repeat of the Cas protein and constructing crRNA plasmid for transcribing a crRNA sequence, connected to the go-ahead sequence, of the direct repeat; and promoting co-expression of an encoding gene of the Cas protein and the transcription crRNA plasmid in cells, so that the specific binding of the Cas protein to the target is achieved. With the application of the method provided by the invention, transcription of one or more target genes can be inhibited; and the method, in comparison with CRISPR / dCas9, is quite simple in entire operating process and is equivalent to dCas9 in editing efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI TOLO BIOTECH CO LTD +1
Method and device for identifying clustered regularly interspaces short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)
ActiveCN104504304AImprove accuracyIncrease diversitySpecial data processing applicationsDirect repeatFirst generation
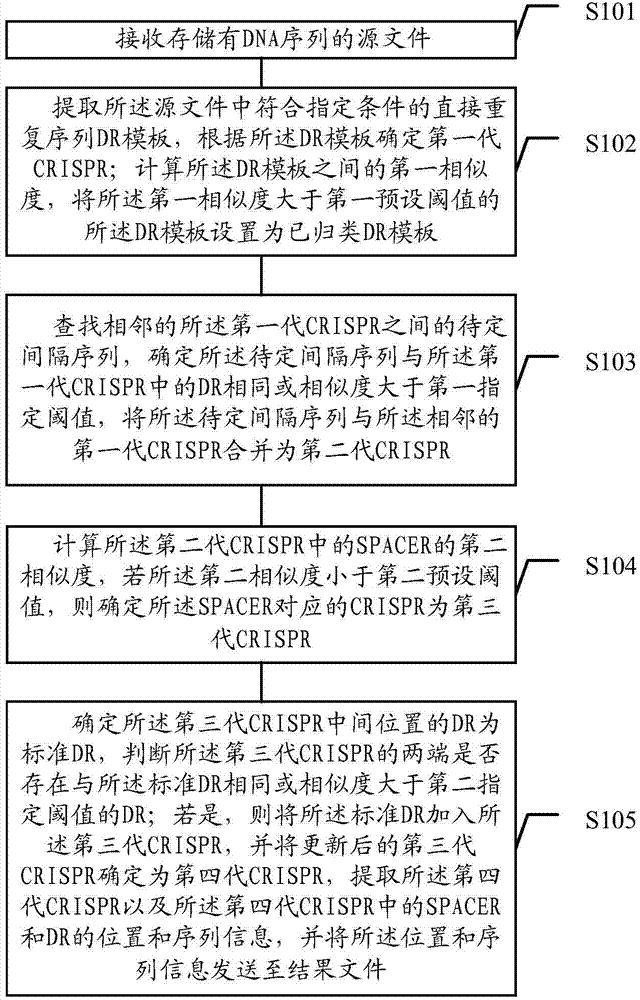
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method for identifying clustered regularly interspaces short palindromic repeats (CRISPR). The method comprises the following steps: according to a DR (Direct Repeats) template in a source file, determining a first-generation CRISPR; after the missed DR in an undetermined spacer sequence between two pieces of adjacent first-generation CRISPR is added, determining a second-generation CRISPR; determining the CRISPR of which the SPACER similarity is lower than a preset threshold value in the second-generation CRISPR as a third-generation CRISPR; and determining the third-generation CRISPR of which two ends are provided with the DR as a four-generation CRISPR. The embodiment of the method can reduce misinformation or ignore the cut-off DR so as to improve the identification accuracy and comprehensiveness of the CRISPR.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
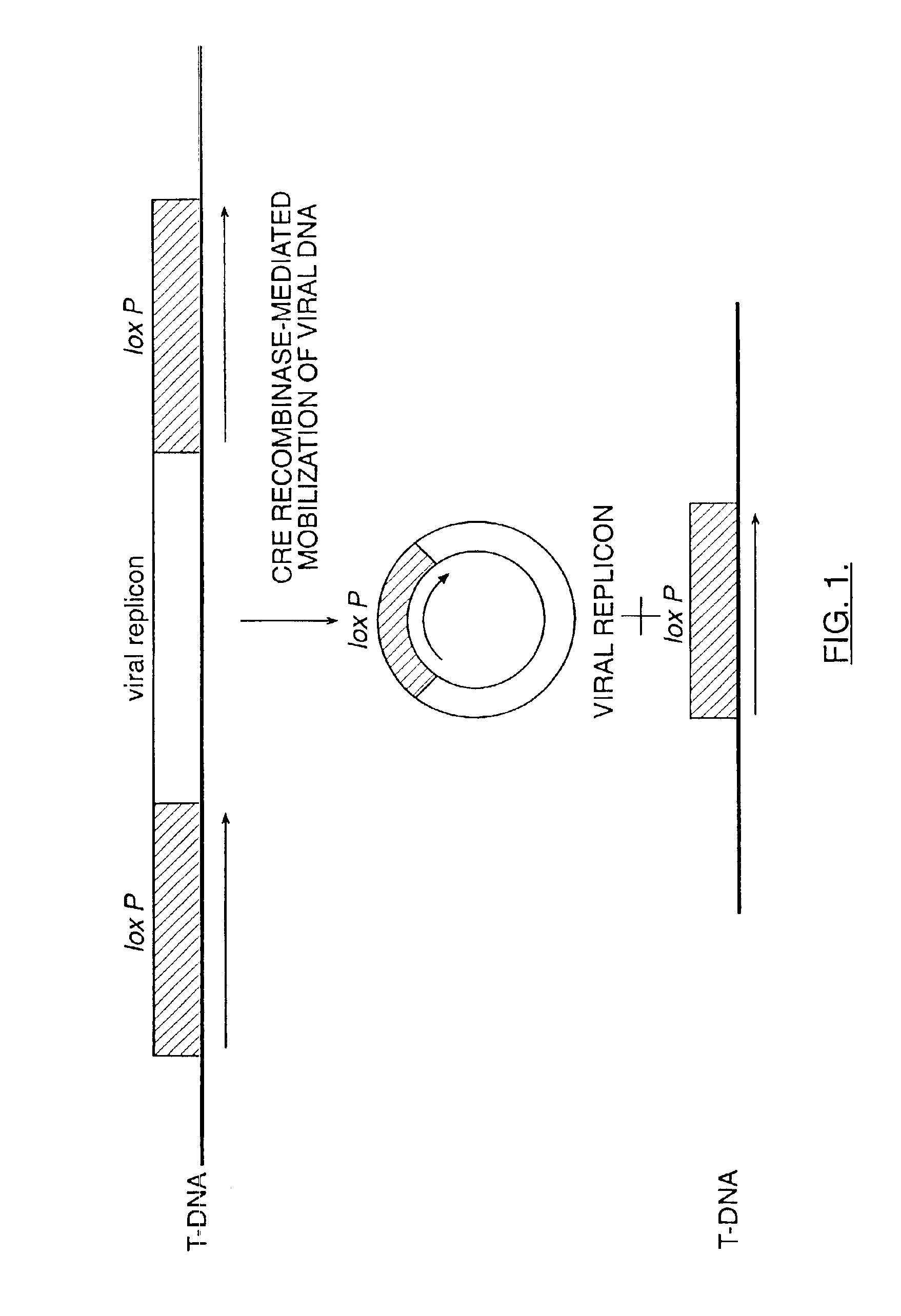
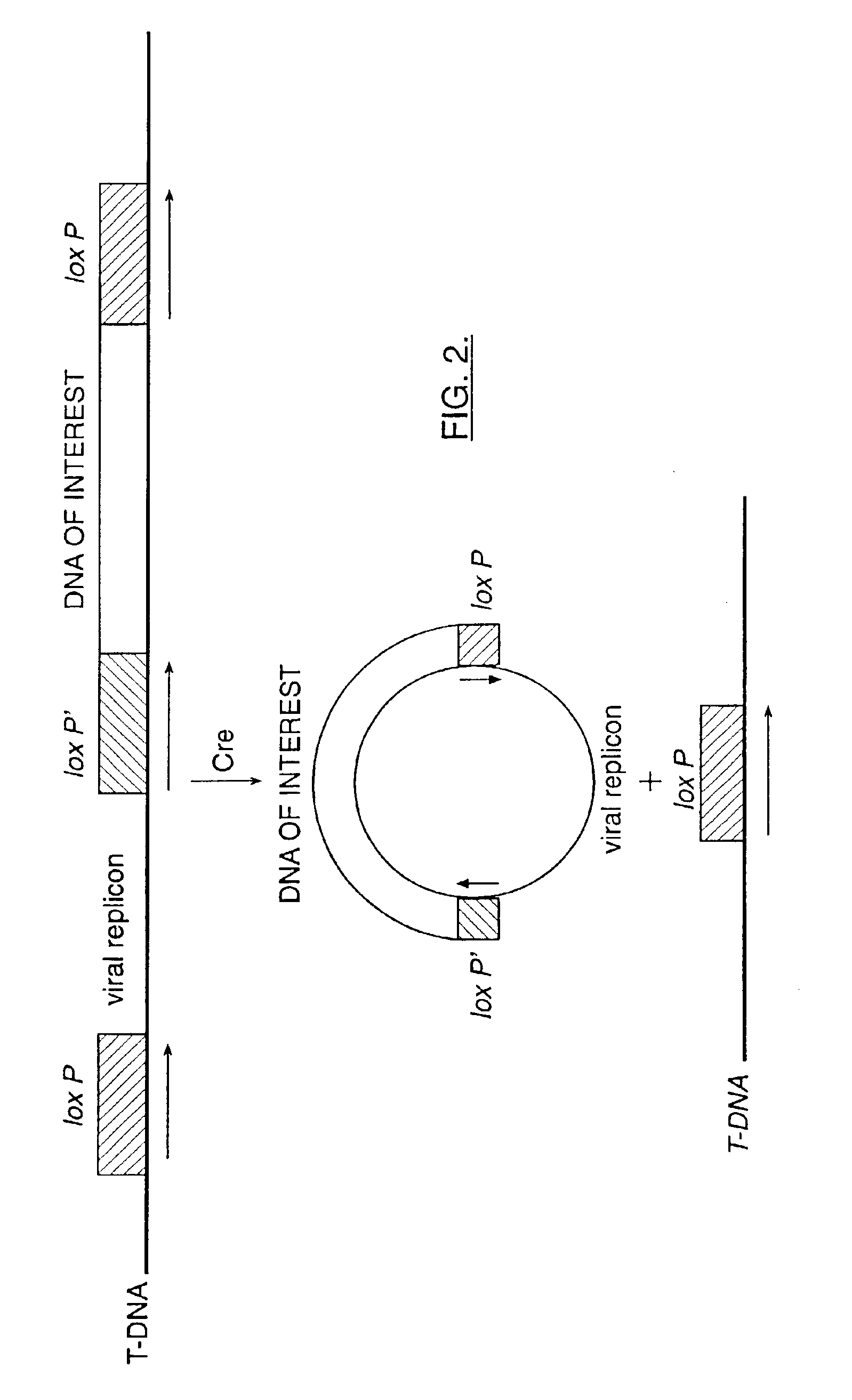
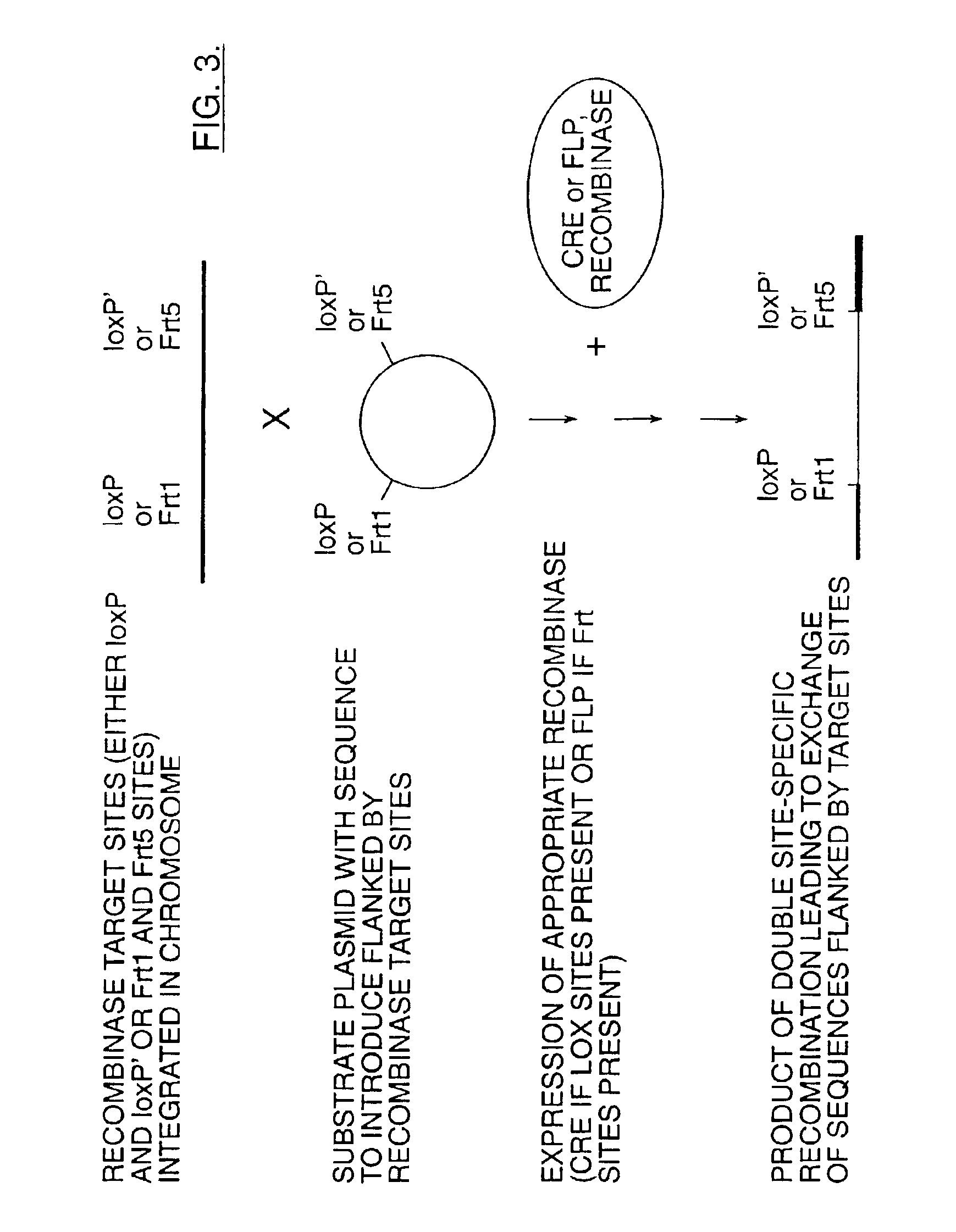
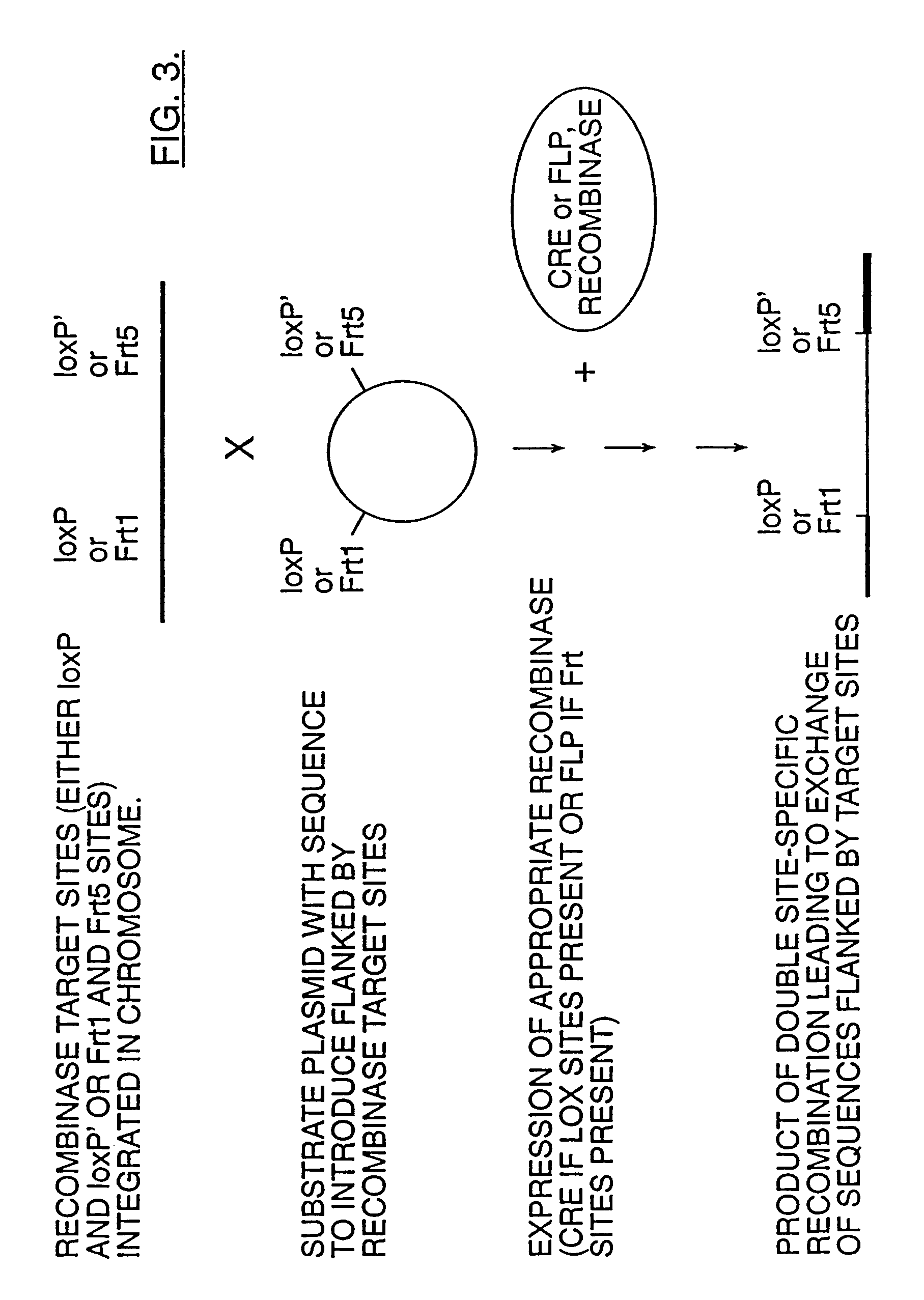
Mobilization of viral genomes from T-DNA using site-specific recombination systems
InactiveUS7179599B2Simplifying construction and stable maintenanceImprove efficiencyBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSite-specific recombinationPlant cell
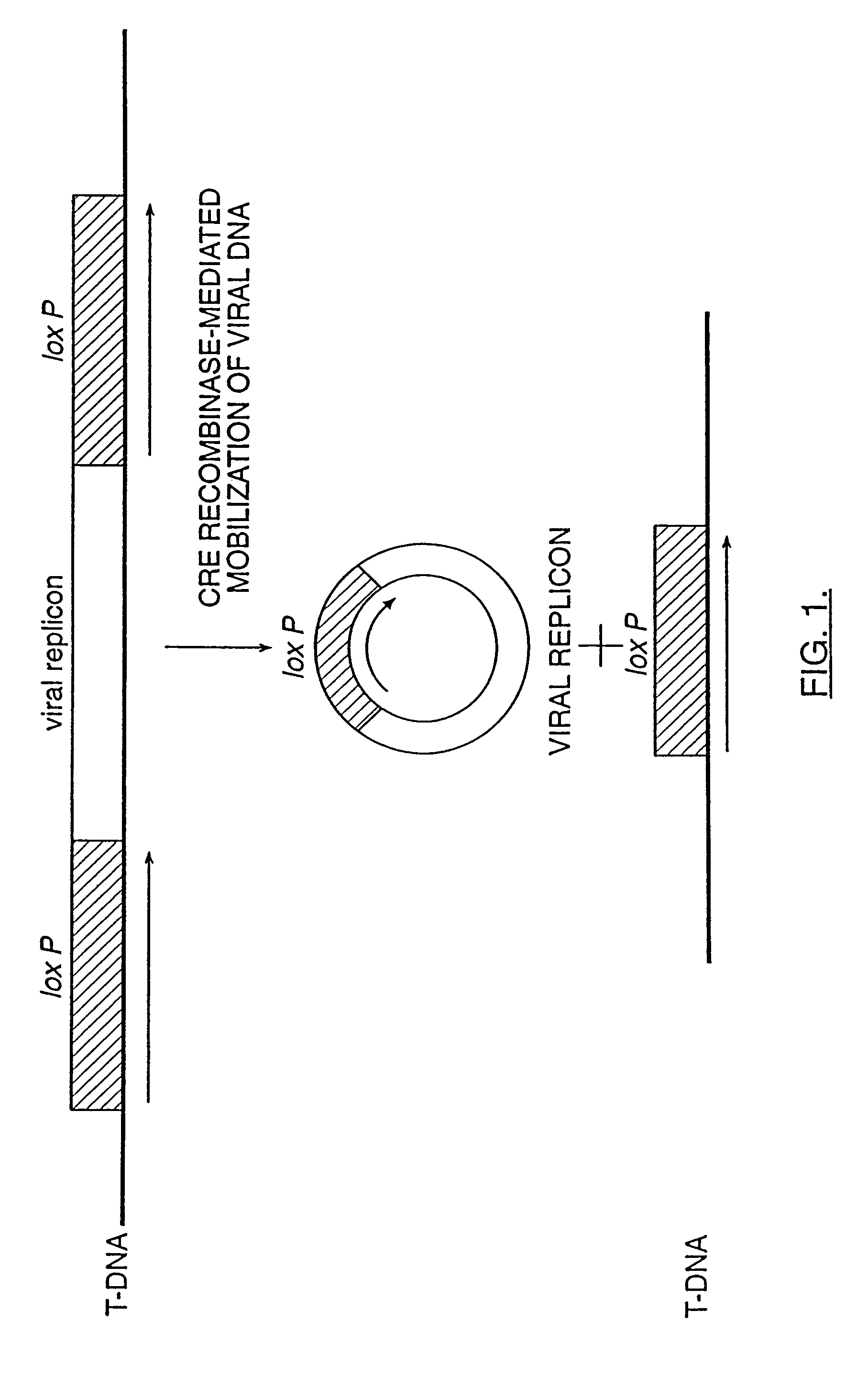
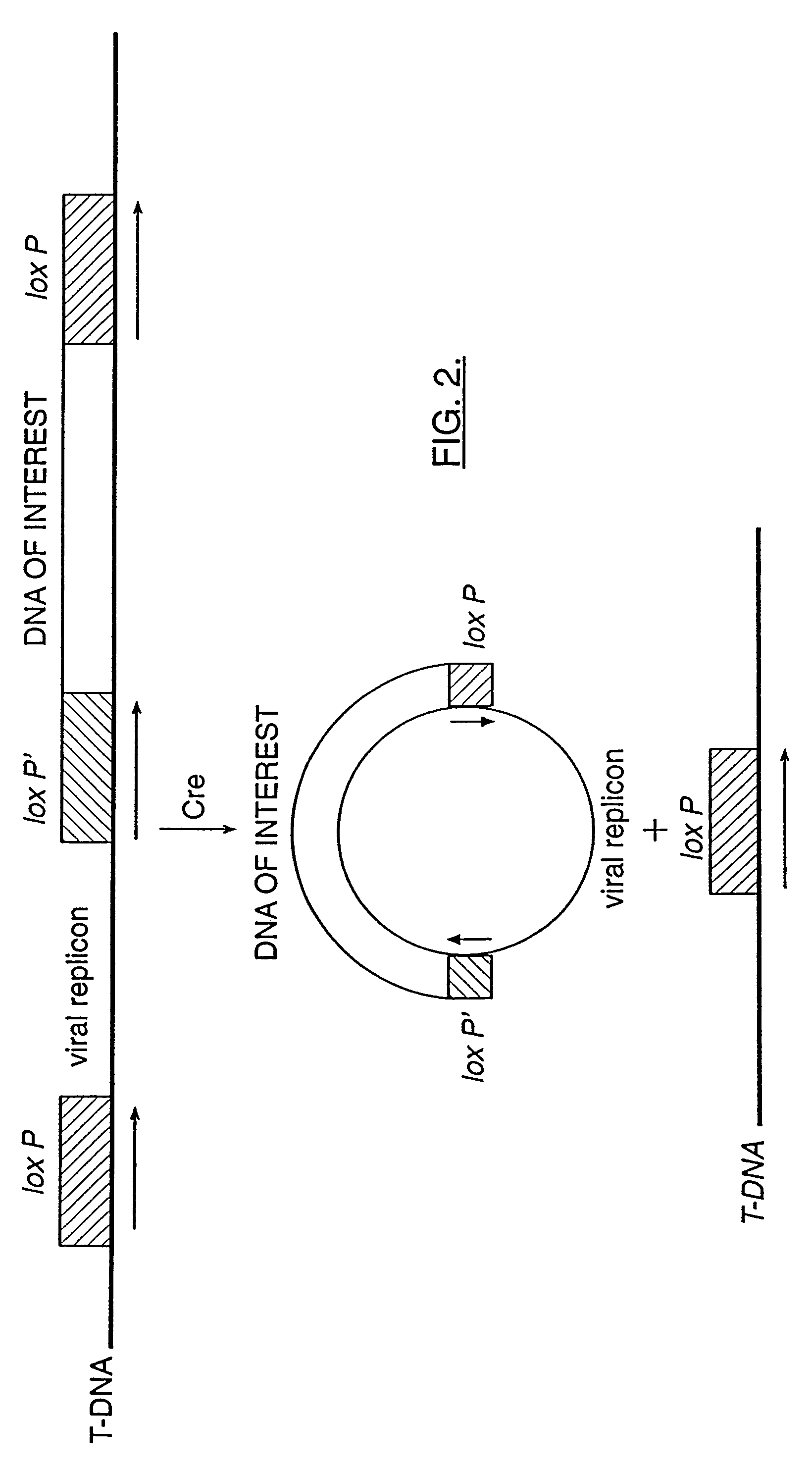
The invention relates to methods and compositions for site-specific recombinase-mediated mobilization of viral replicons and associated DNAs of interest from T-DNA. The methods of the invention comprise Agrobacterium-mediated transfer of T-DNA to a plant cell, wherein the T-DNA contains a viral replicon flanked by directly repeated target sites for a site-specific recombinase and optionally a DNA of interest linked to the viral replicon. The DNA of interest may also contain a non-identical target site for the recombinase. An expression cassette for the site-specific recombinase is present on the T-DNA or the plant genome, or is transiently introduced into the plant cell. Expression of the site-specific recombinase in the plant cell results in excision of the viral replicon and the associated DNA of interest. The viral replicon and DNA of interest are then replicated to high copy number in the host plant cell. The compositions of the invention comprise nucleic acids, such as T-DNAs containing a viral DNA flanked by directly repeated target sites for a site-specific recombinase. The nucleic acids of the invention may additionally contain expression cassettes encoding the cognate site-specific recombinase for the target sites flanking the viral genome. The compositions of the invention further comprise Agrobacterium containing the nucleic acids of the invention. The compositions and methods of the invention have use in increasing the efficiency of agroinfection, providing high copy numbers of a DNA of interest for transient expression or for integration into a plant chromosome, and in simplifying the construction and stable maintenance of vectors for agroinfection and transformation.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
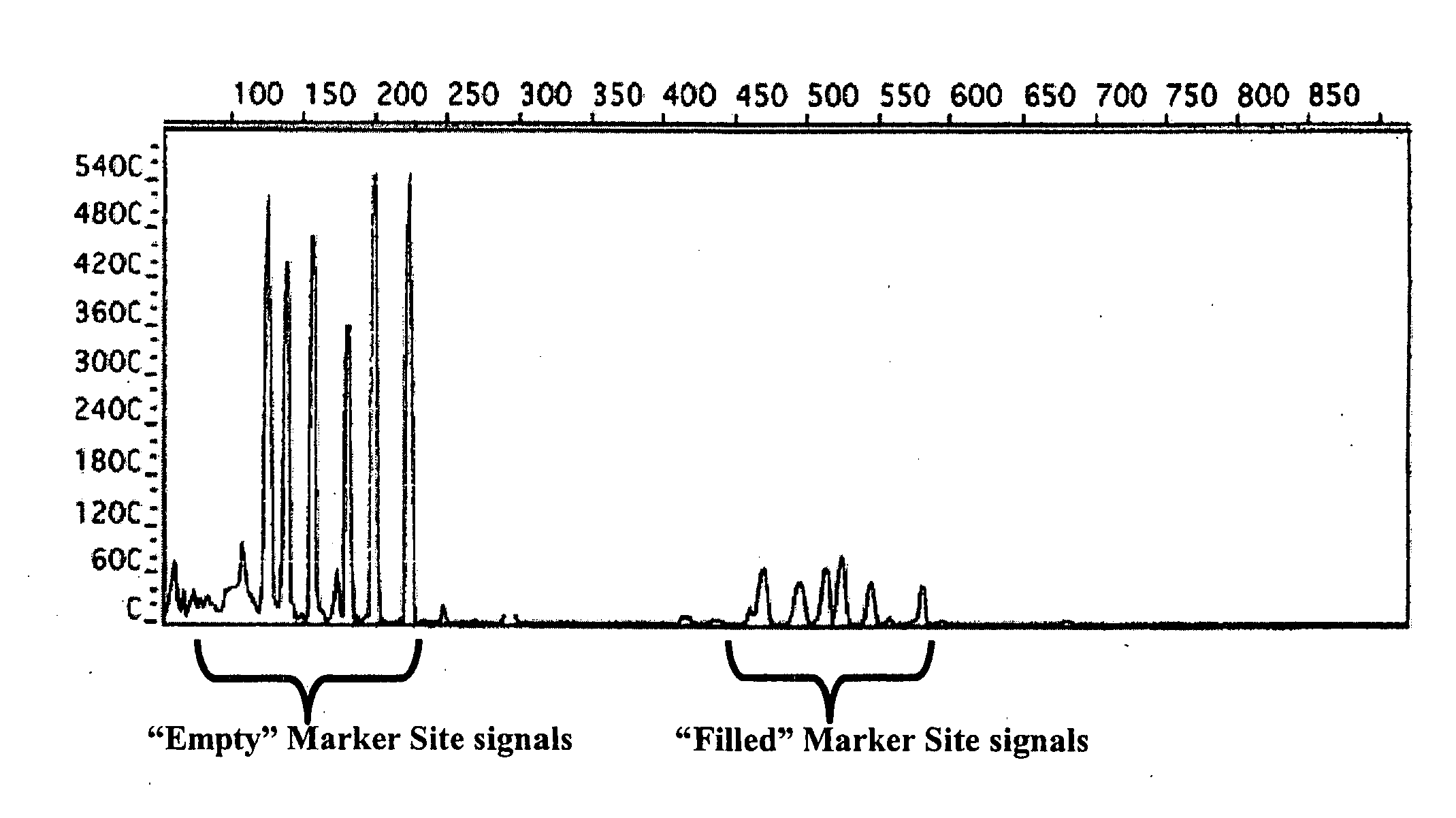
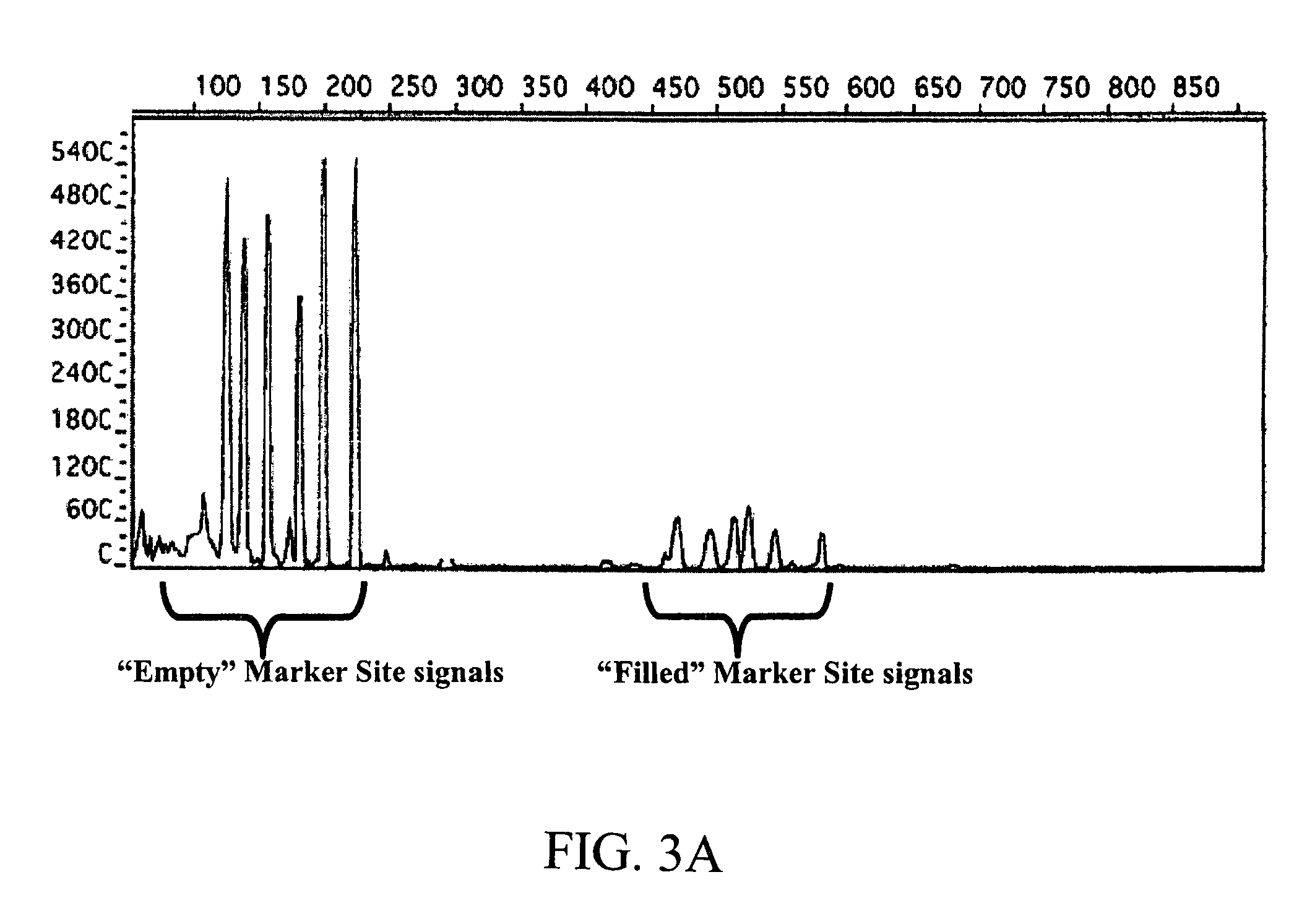
Method for genetic detection using interspersed genetic elements
ActiveUS20080206755A1Easy to testSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsGenetic element
The way to design a “filled” site (which contains an interspersed element) primer set to target a particular locus is to design one of the two primers such that it encompasses that unique information (e.g., interspersed element+flanking genomic sequence+direct repeat). The way to design an “empty” site primer is to design one of the two primers such that the entire direct repeat sequence in addition to flanking genomic sequence is included on both sides. To improve efficiency, the “empty” site primer designed around the direct repeat should not be too long. This primer design of the present invention allows for the ability to test any type of interspersed genetic element containing characteristic direct repeat sequences (direct repeats). This gives the option of many new polymorphic marker sites because Alu elements are not the only interspersed genetic elements having direct repeats flanking their core sequence.
Owner:RELIAGENE TECH INC A CORP CHARTERED IN & EXISTING UNDER THE LAWS OF THE STATE OF LOUISIANA +1
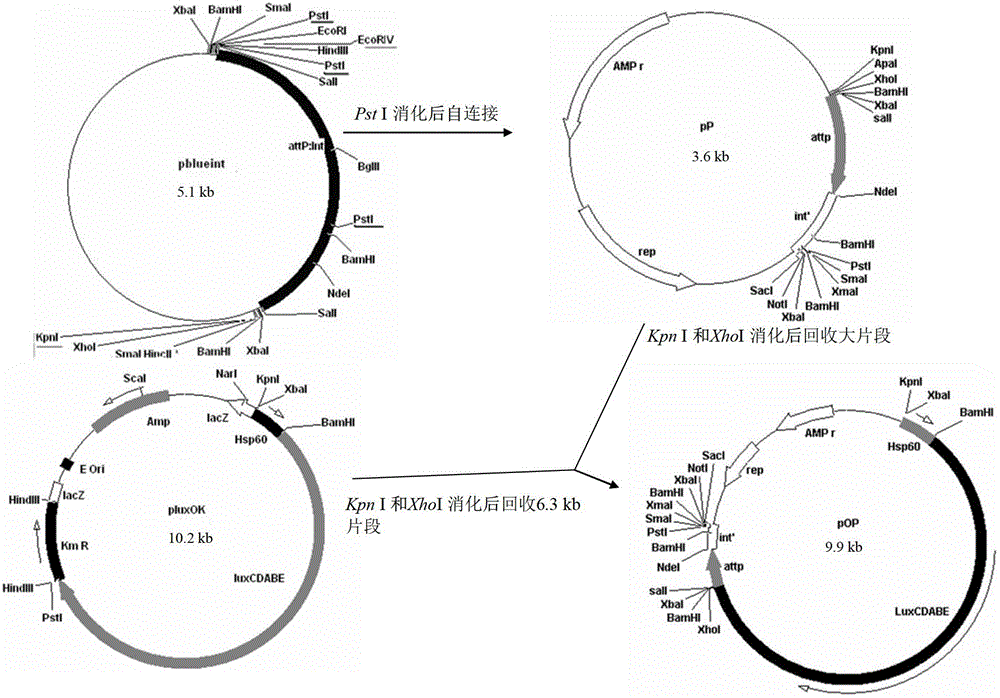
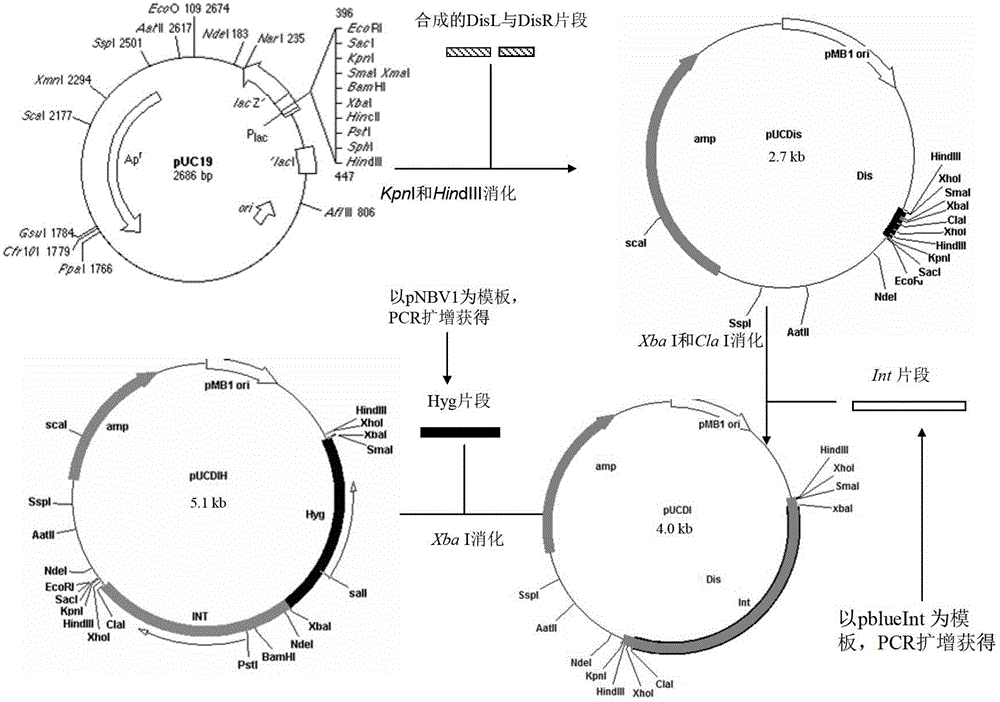
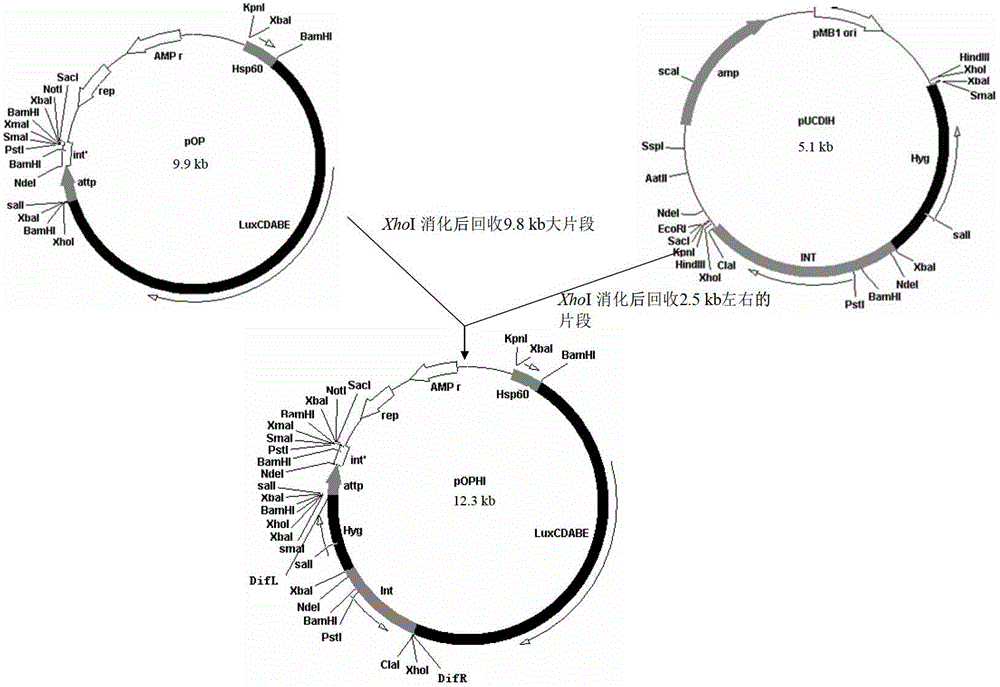
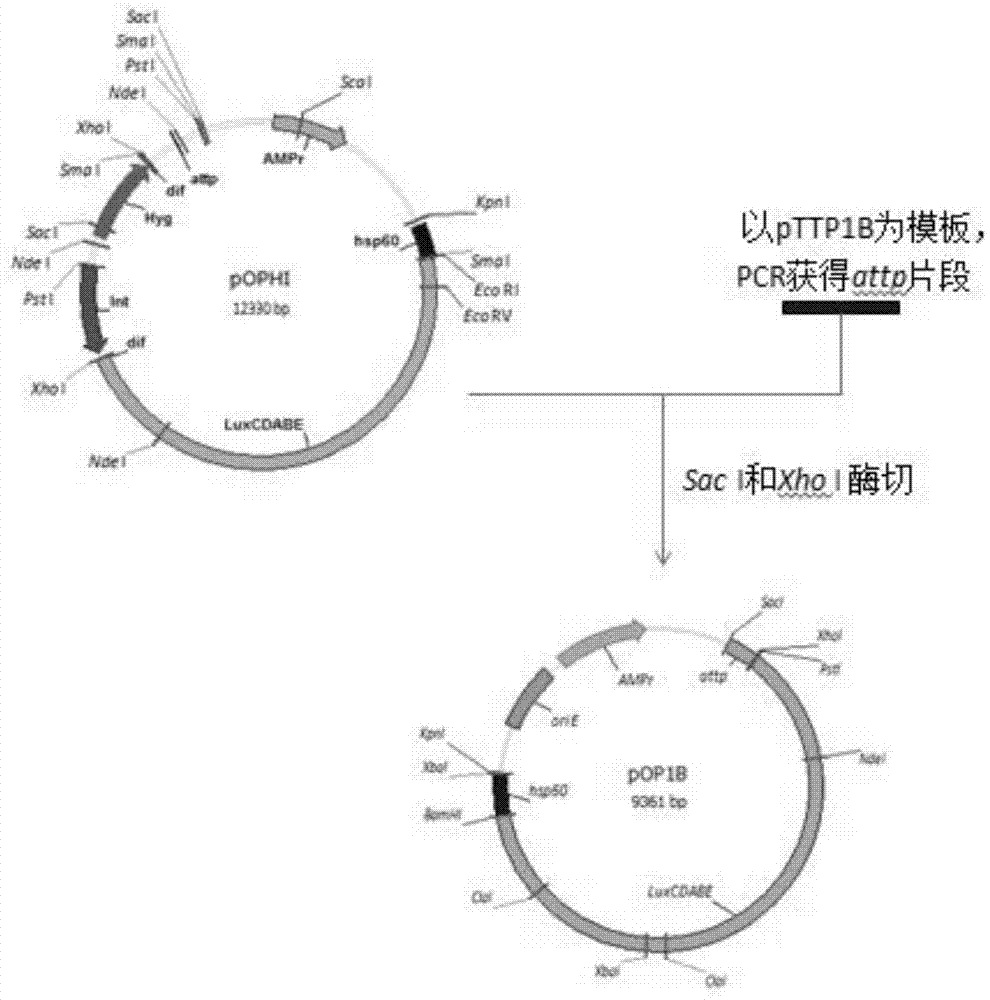
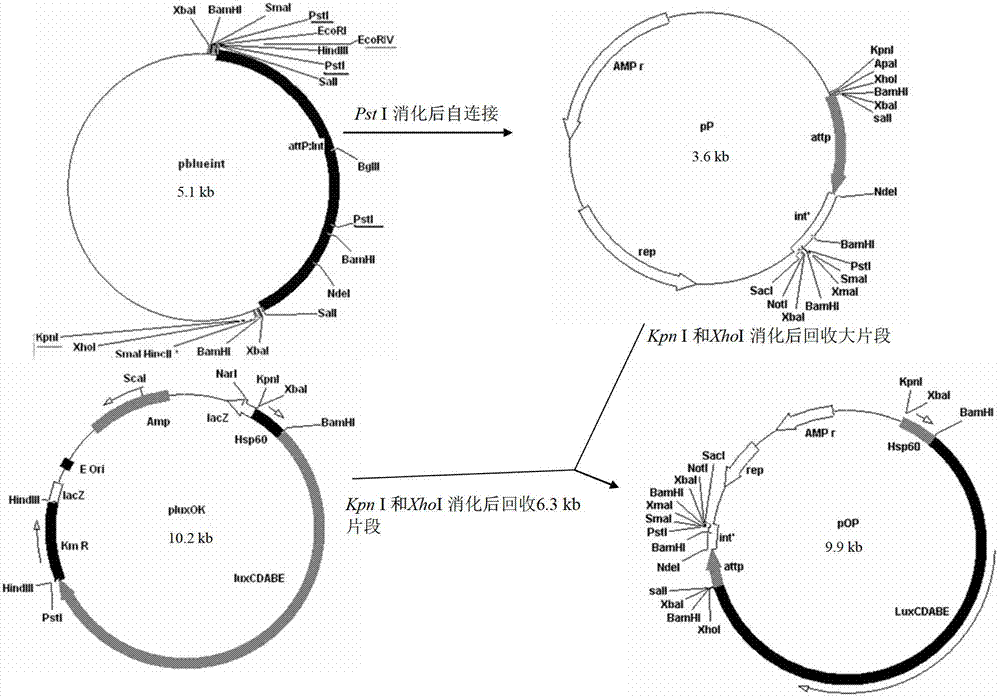
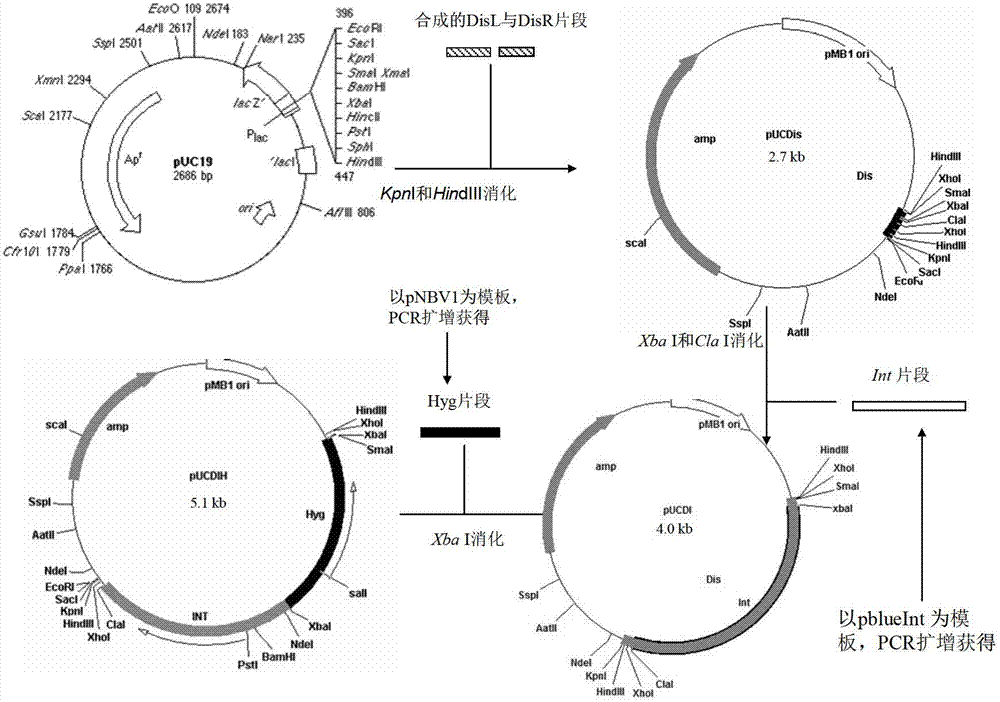
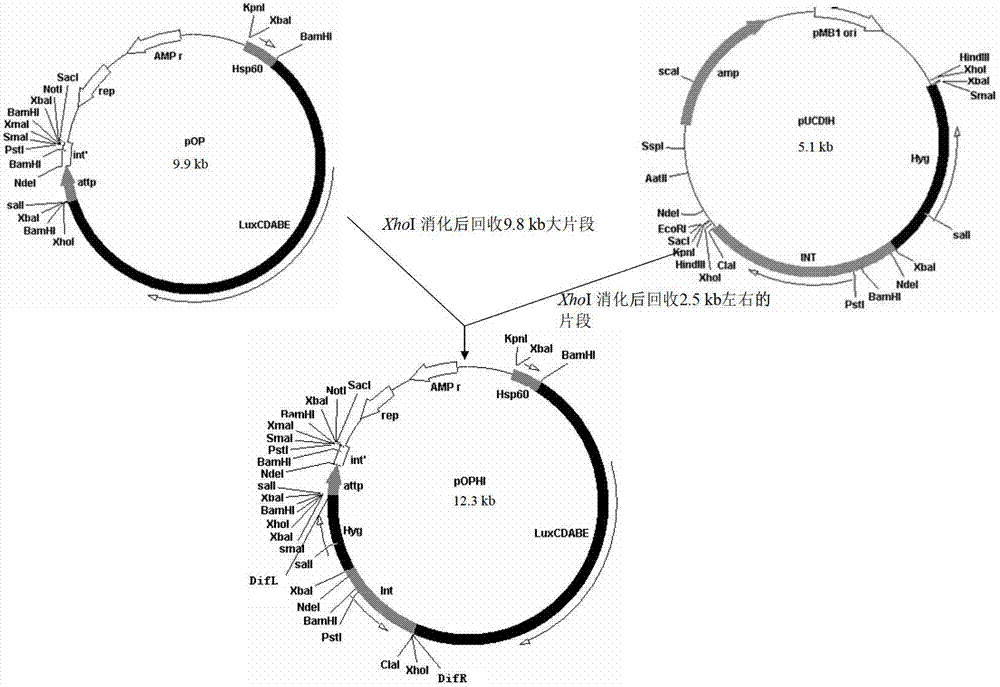
Integrative plasmid pOPHI and resistance screening marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium
ActiveCN102719471AExperimental data is credibleHigh sensitivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneDirect repeat
The invention discloses an integrative plasmid pOPHI and a resistance screening marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium. The integrative plasmid pOPHI comprises a promoter, an enzyme gene (LuxCDABE) needed for luminescence, a fusion gene of an integrase gene (Int) and a resistance screening gene, direct repeat sequences DifR and DifL positioned on two ends of the fusion gene, a phage integration site (attP) and a replicon. After the integrative plasmid pOPHI is transferred into the mycobacteria, a photobacterium of which the resistance gene and the integrase gene are lost is screened out by subculturing, and the photobacterium is the resistance screening marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium. Whether the resistance screening marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium obtained by construction is dead or not is judged according to whether the bacterium is luminescent or not, the mycobacterium can be used for a plurality of detections of experiments, and credible experimental data can be quickly obtained.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
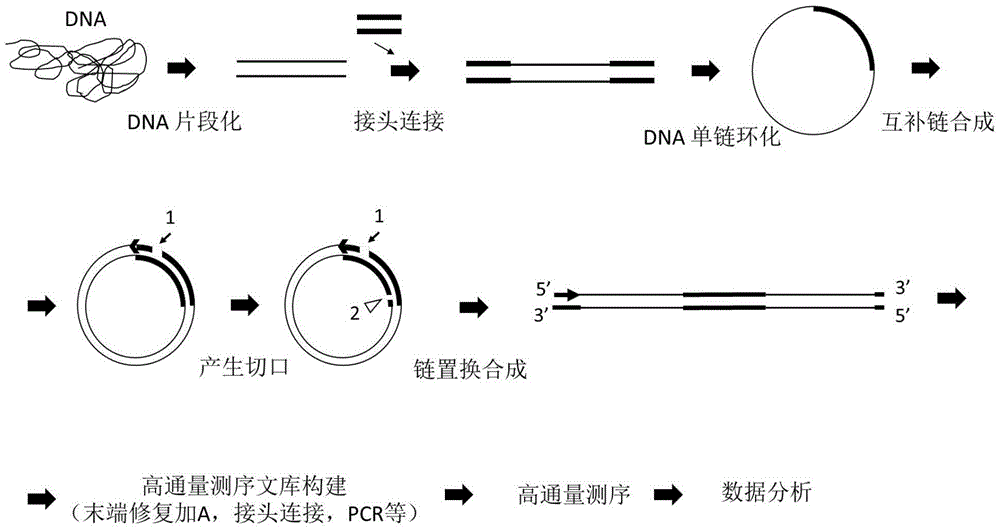
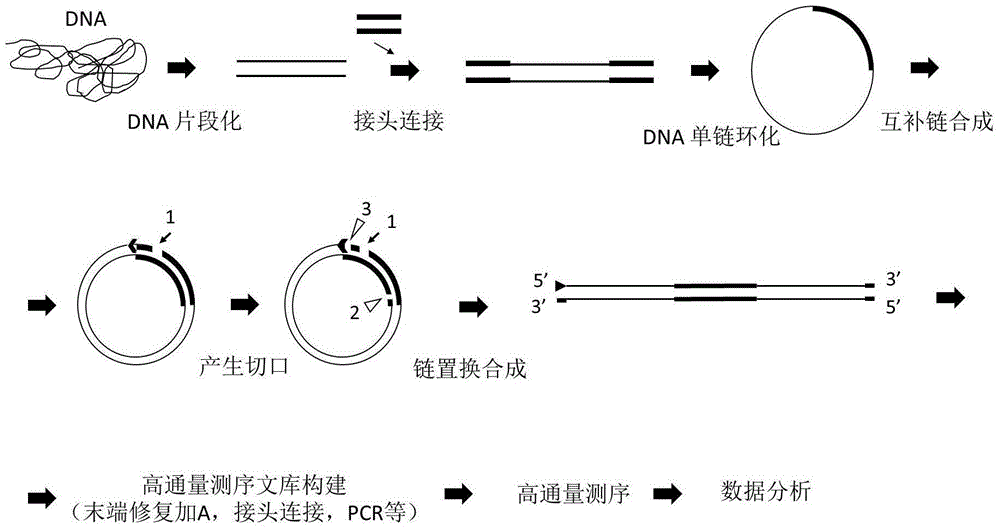
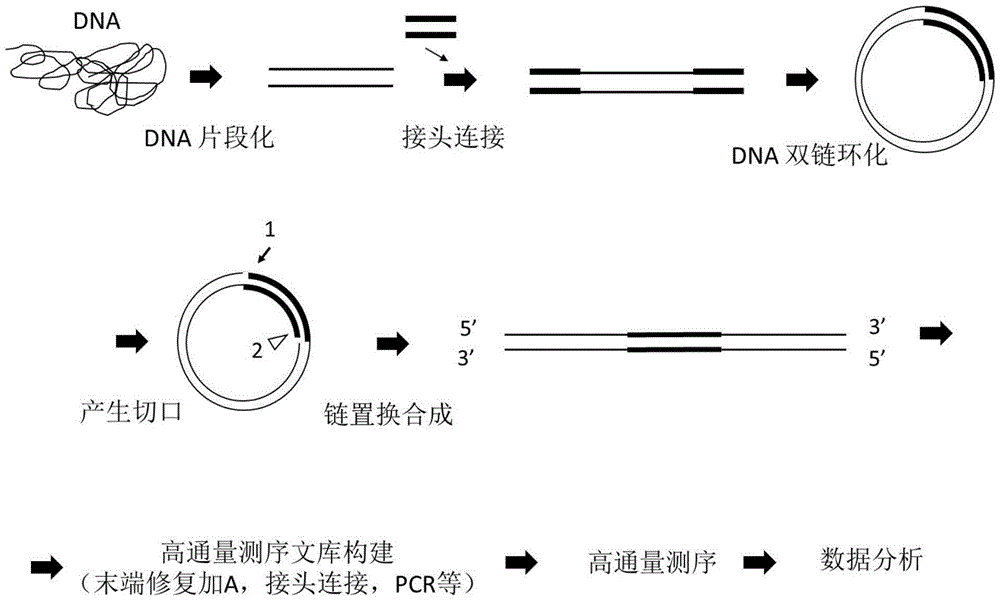
Sequencing library and preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN106554957AReduce errorsReduce error rateNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideDirect repeat
The invention discloses a sequencing library. The library comprises a nucleotide sequence. The nucleotide sequence comprises a connecting sequence and two target sequences. Two ends of the connecting sequence are separately connected to the target sequences and the target sequences are direct repeat sequences. The invention further discloses preparation and an application of the sequencing library. The sequencing library solves the problem that the DNA sequencing accuracy in the prior art cannot satisfy the actual demand.
Owner:AGRI GENOME INST OF SHENZHEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
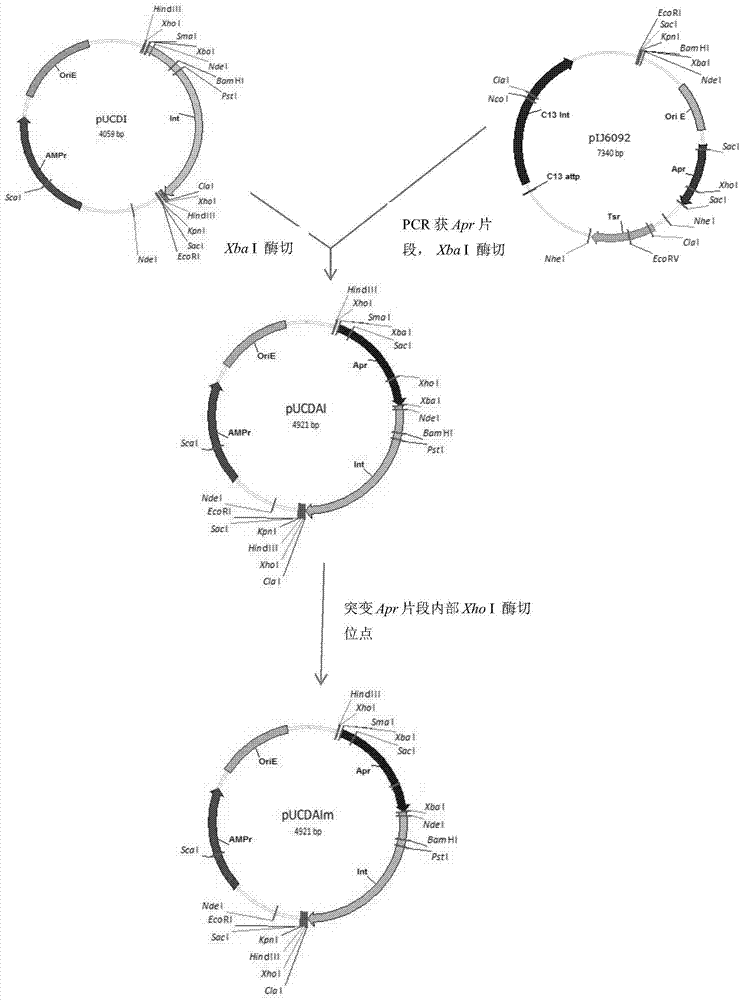
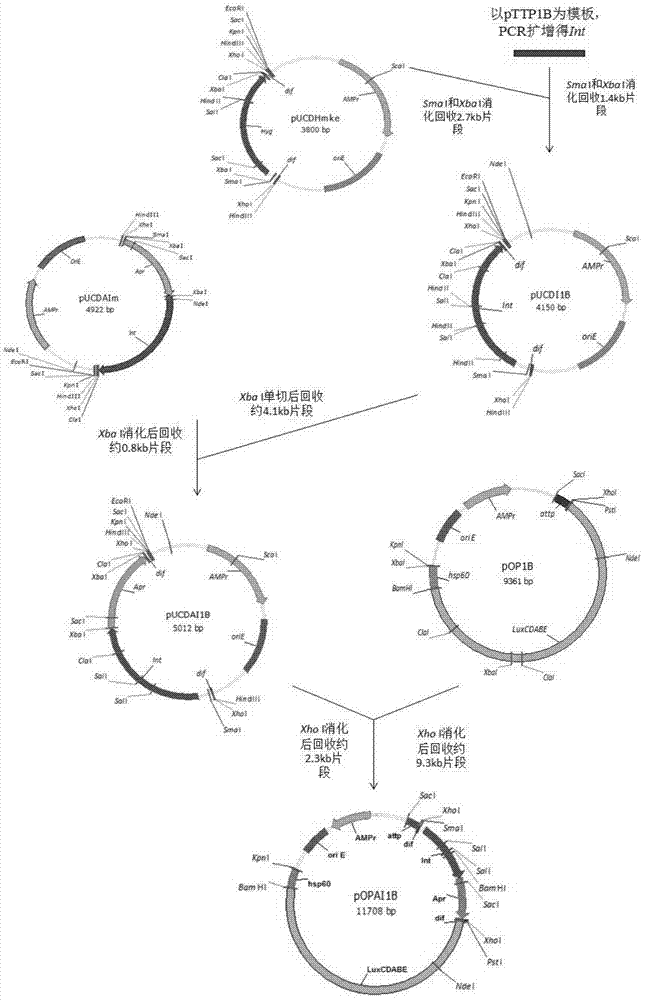
Method of constructing selection-marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium abscessus and establishment of corresponding in-vitro high-flux medicine-screening model
InactiveCN104762312ANo effect on growthNo effect on drug sensitivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneDirect repeat
The invention discloses a method of constructing selection-marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium abscessus and establishment of a corresponding in-vitro high-flux medicine-screening model. During the construction process, a key factor is the construction of a recombinant plasmid pOPAI1B, which contains a fused gene including a luminescent required enzyme gene LuxCDABE, a resistance screening gene Apr and an integrase gene Int; direct repeat sequences DifR and DifL at the two ends of the fused gene respectively; and a phage integration site attP and a replicon. The recombinant plasmid pOPAI1B is transformed into the mycobacterium abscessus and then is screened to obtain the selection-marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium abscessus of which a resistance gene and the integrase gene are both lost. The self-luminescent mycobacterium abscessus can screen drugs in a high flux, can determine sterilizing or bacteria-resistant effects of the drug by means of detection of luminescent situation of bacteria, can be used for in-vitro drug activity detection, is free of any substrates, can continuously detect the same sample, is high in sensitivity and is strong in repeatability.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
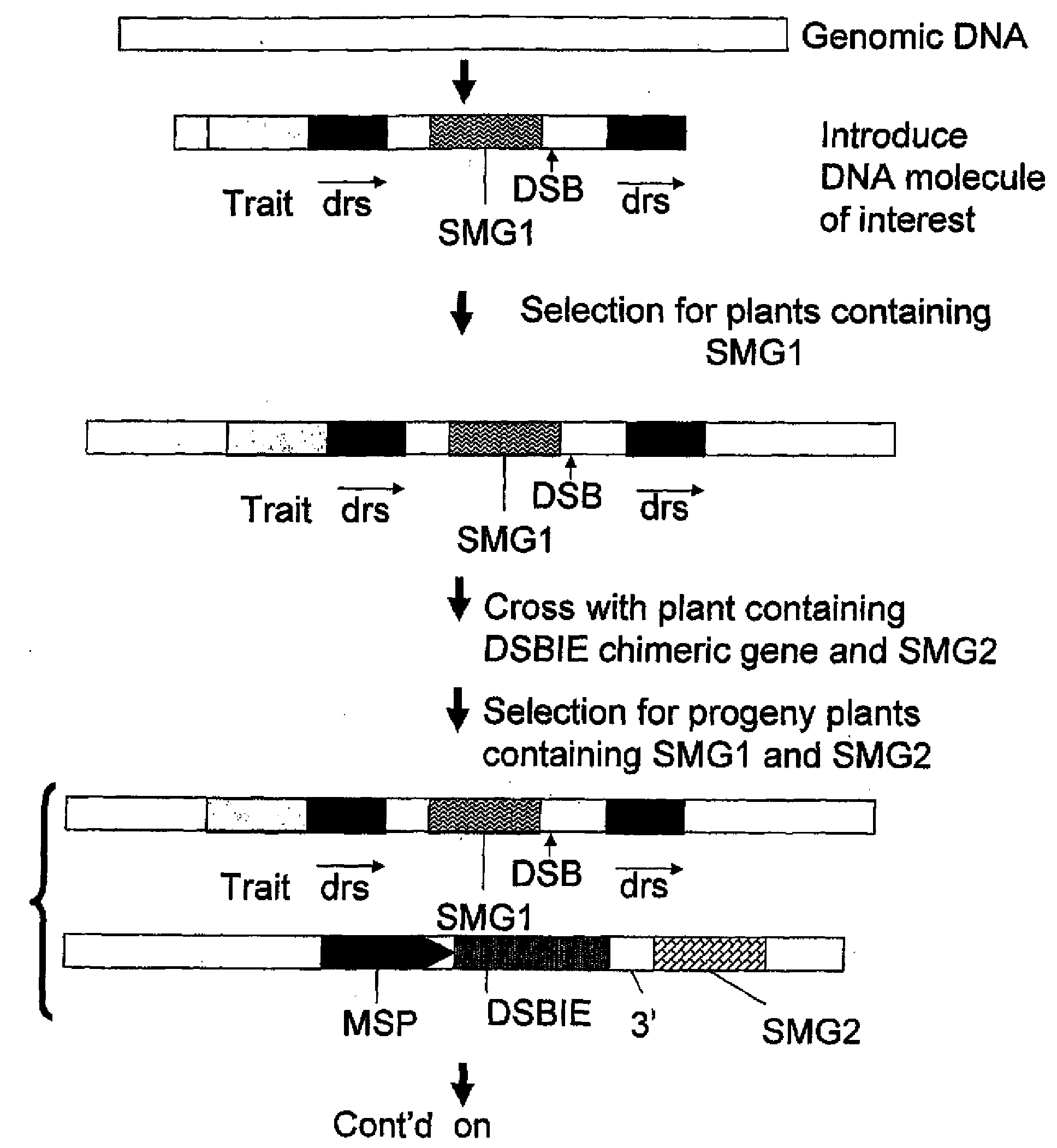
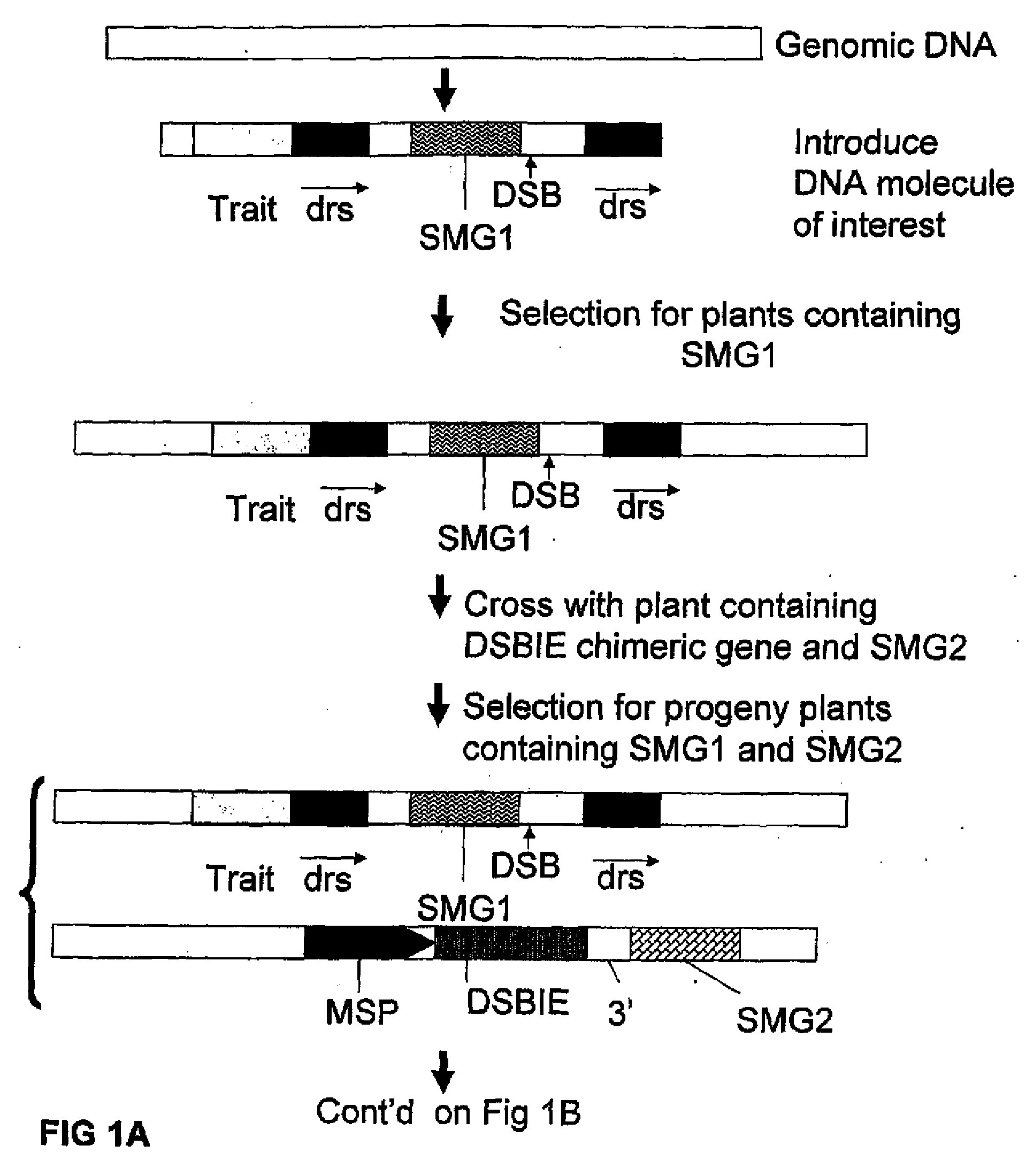
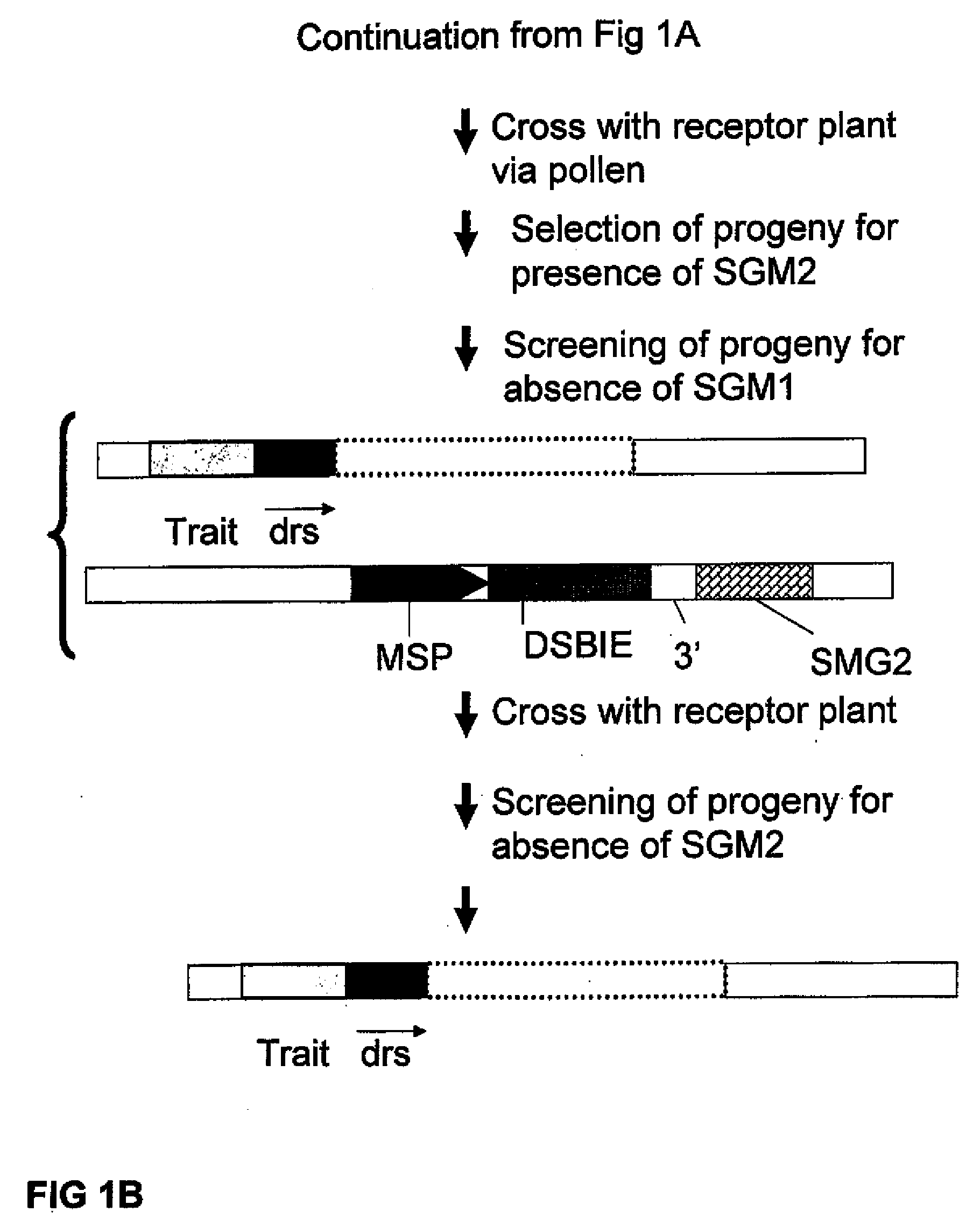
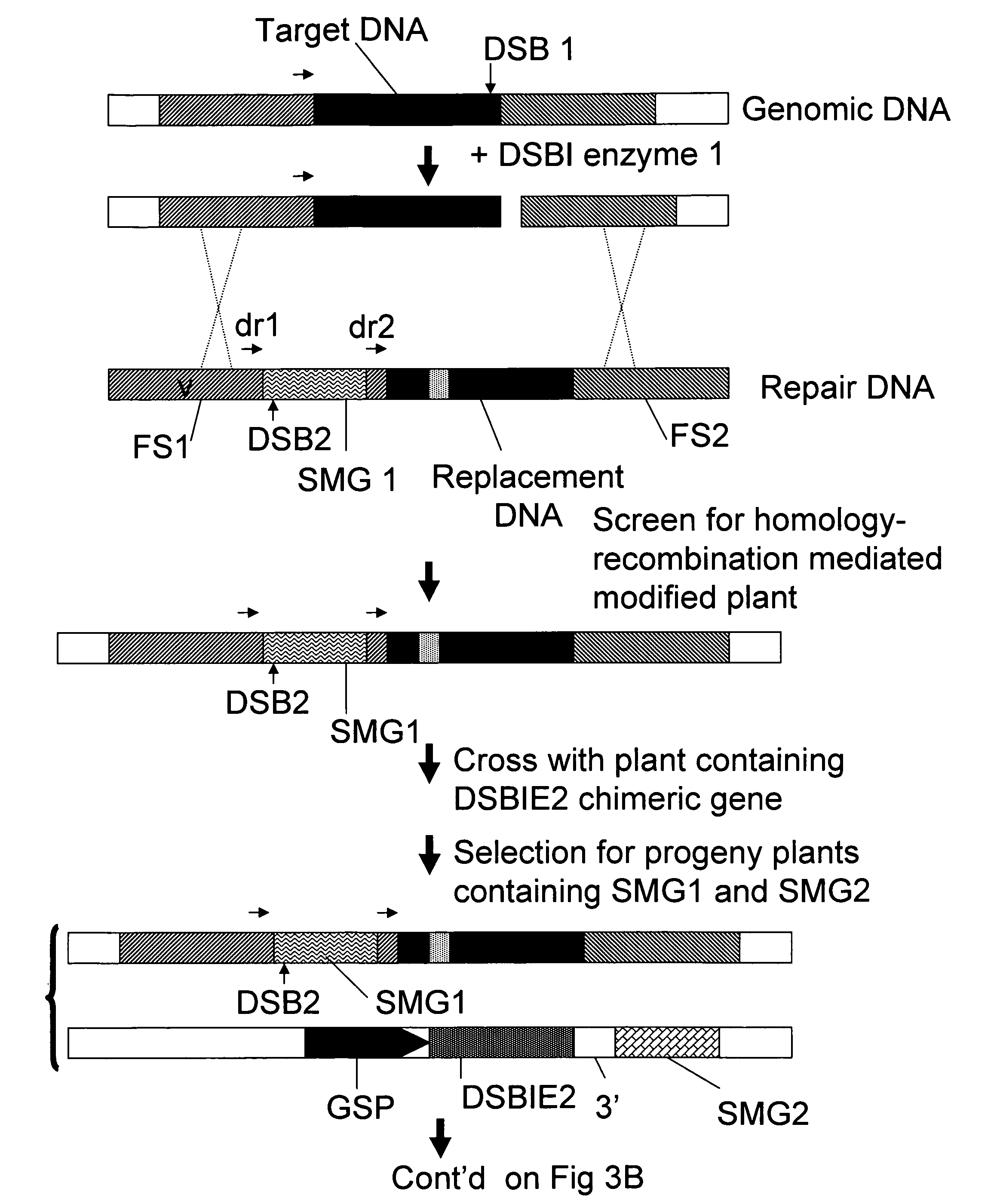
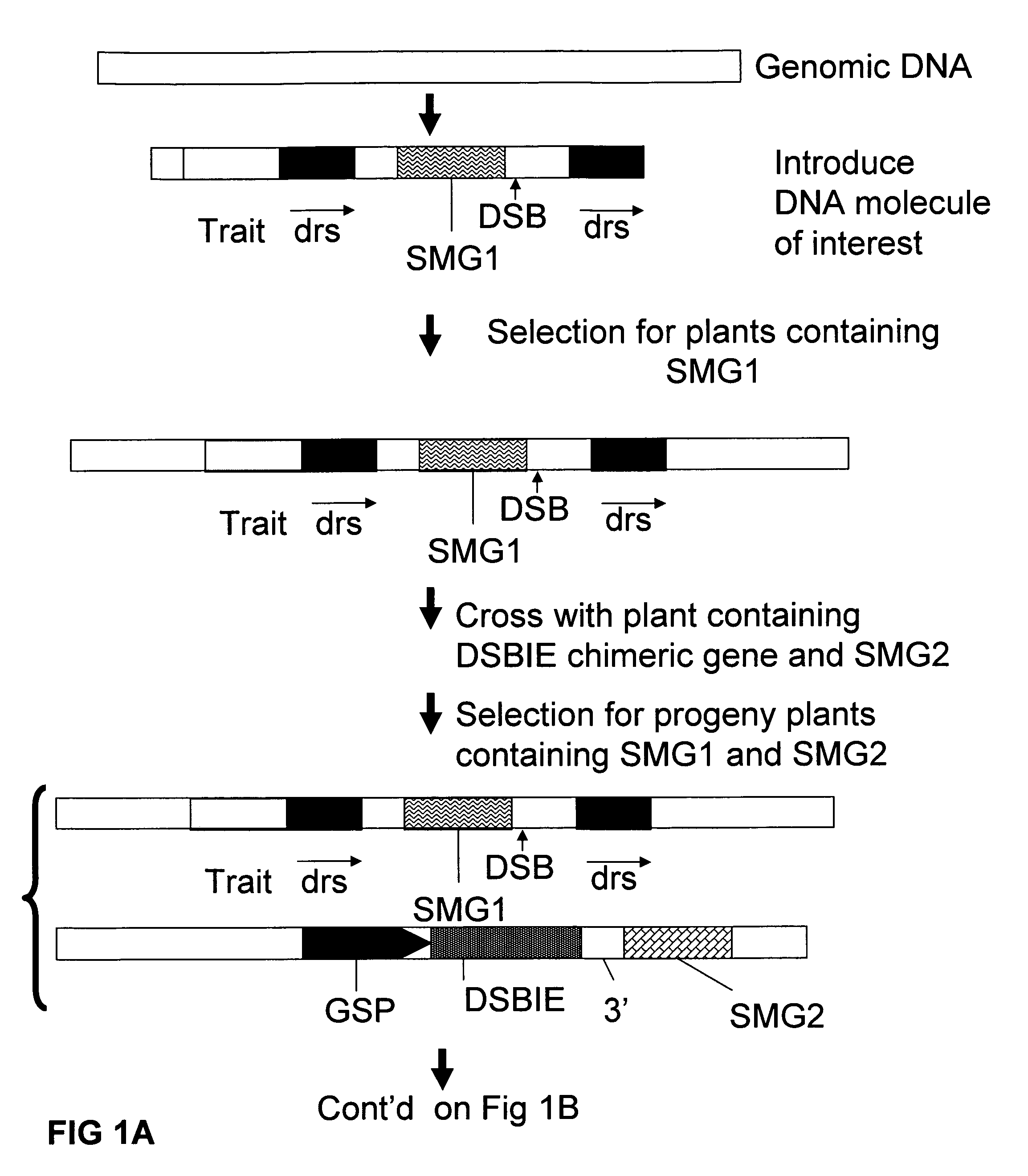
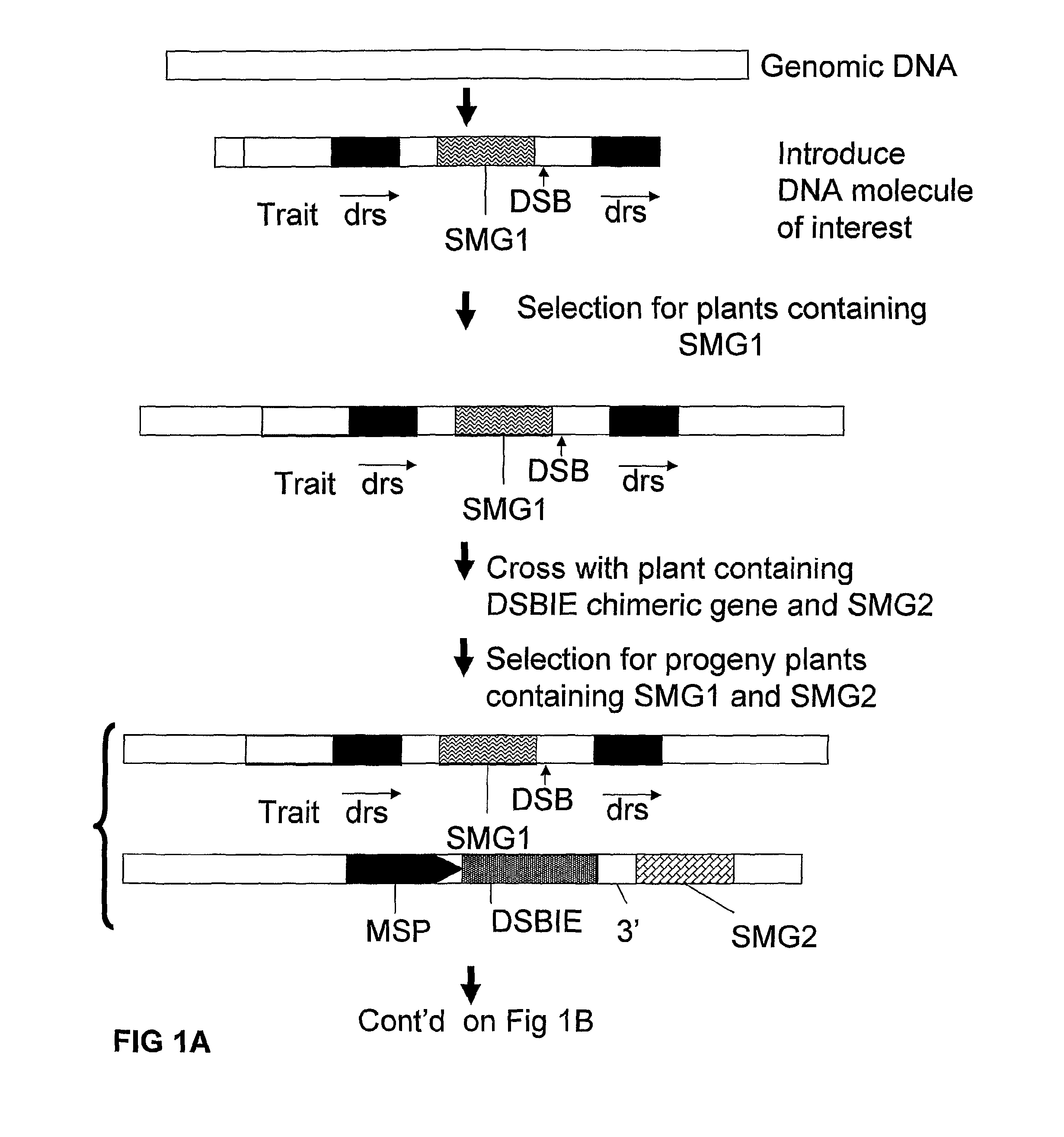
Methods and means for removal of a selected DNA sequence
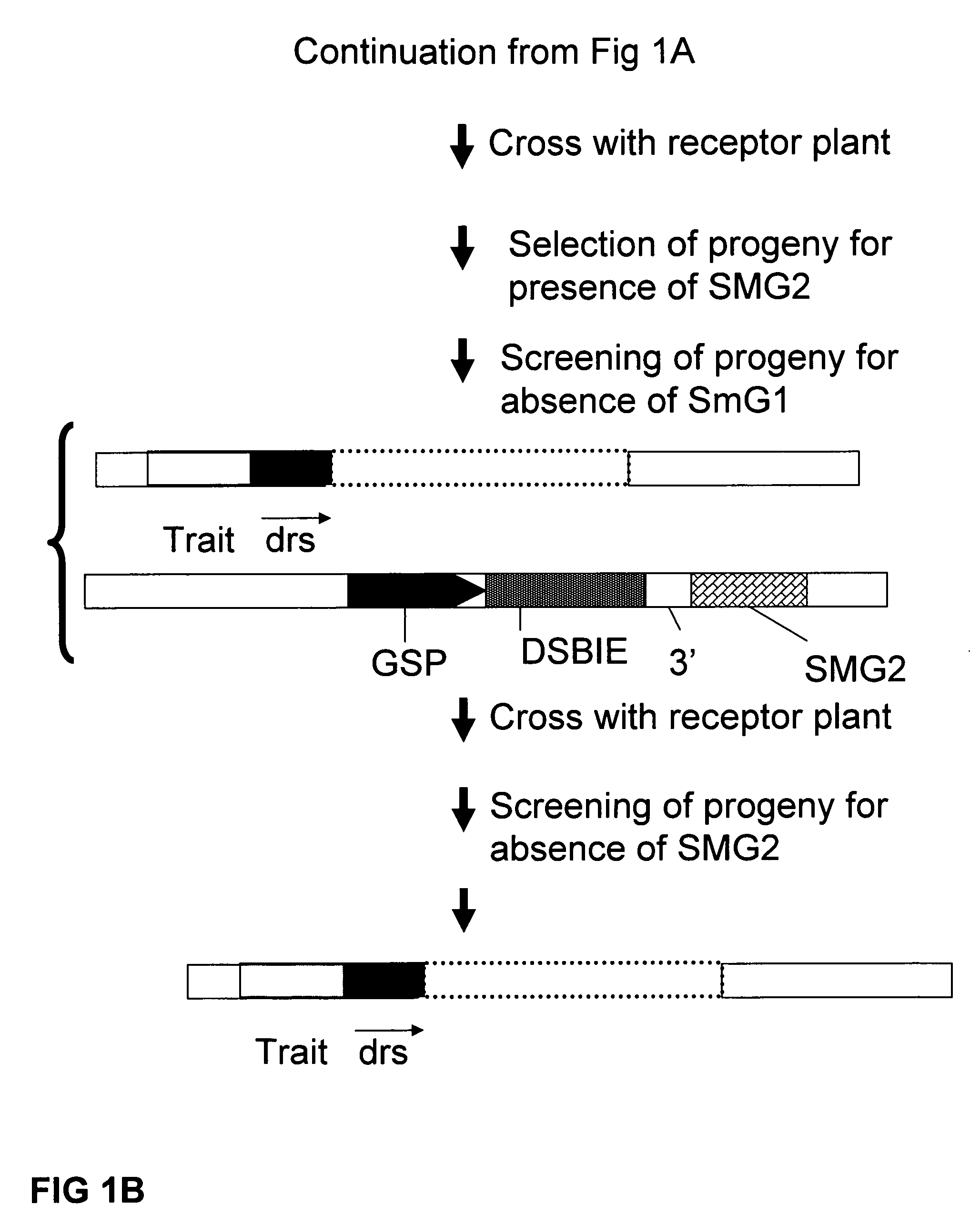
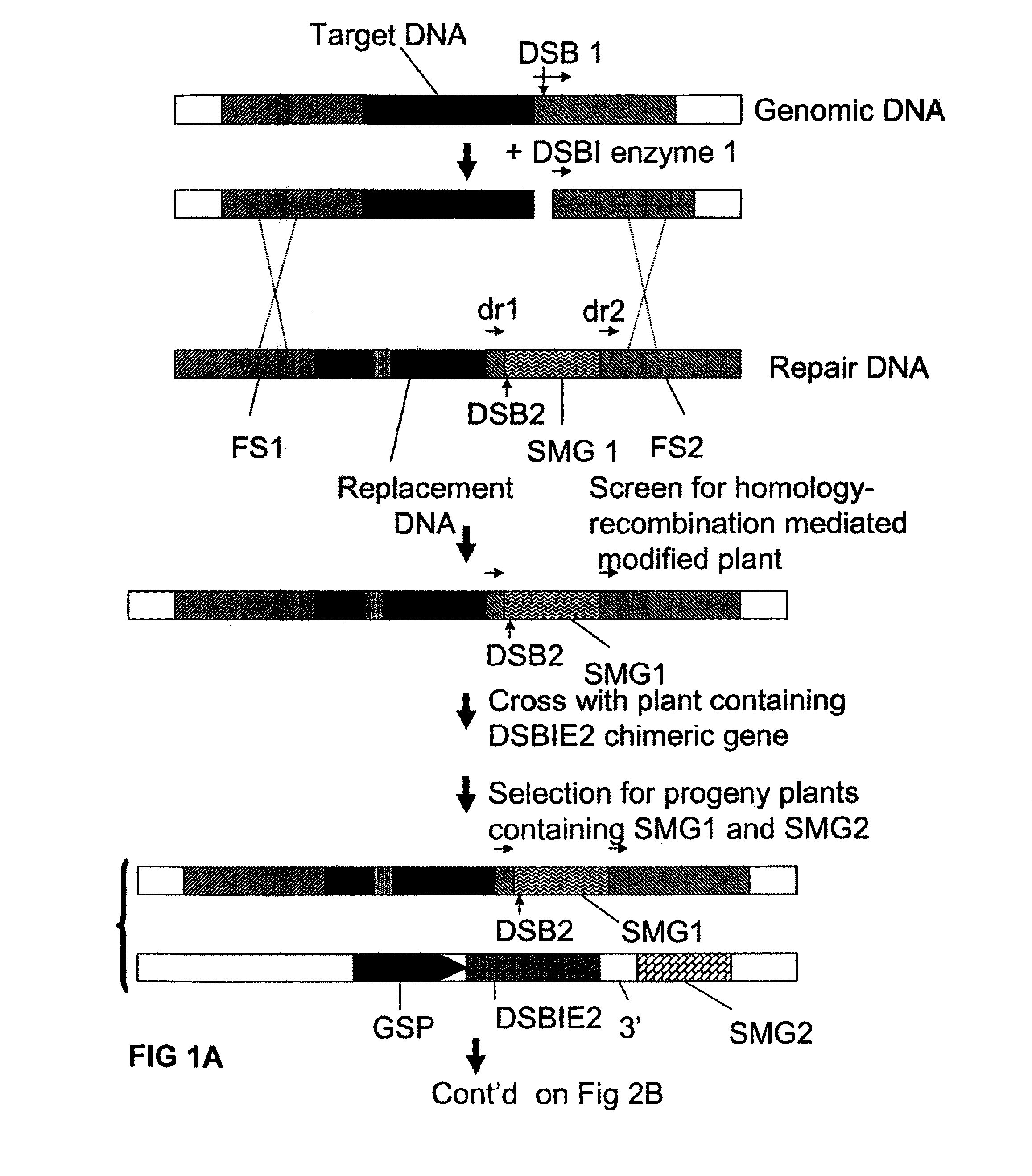
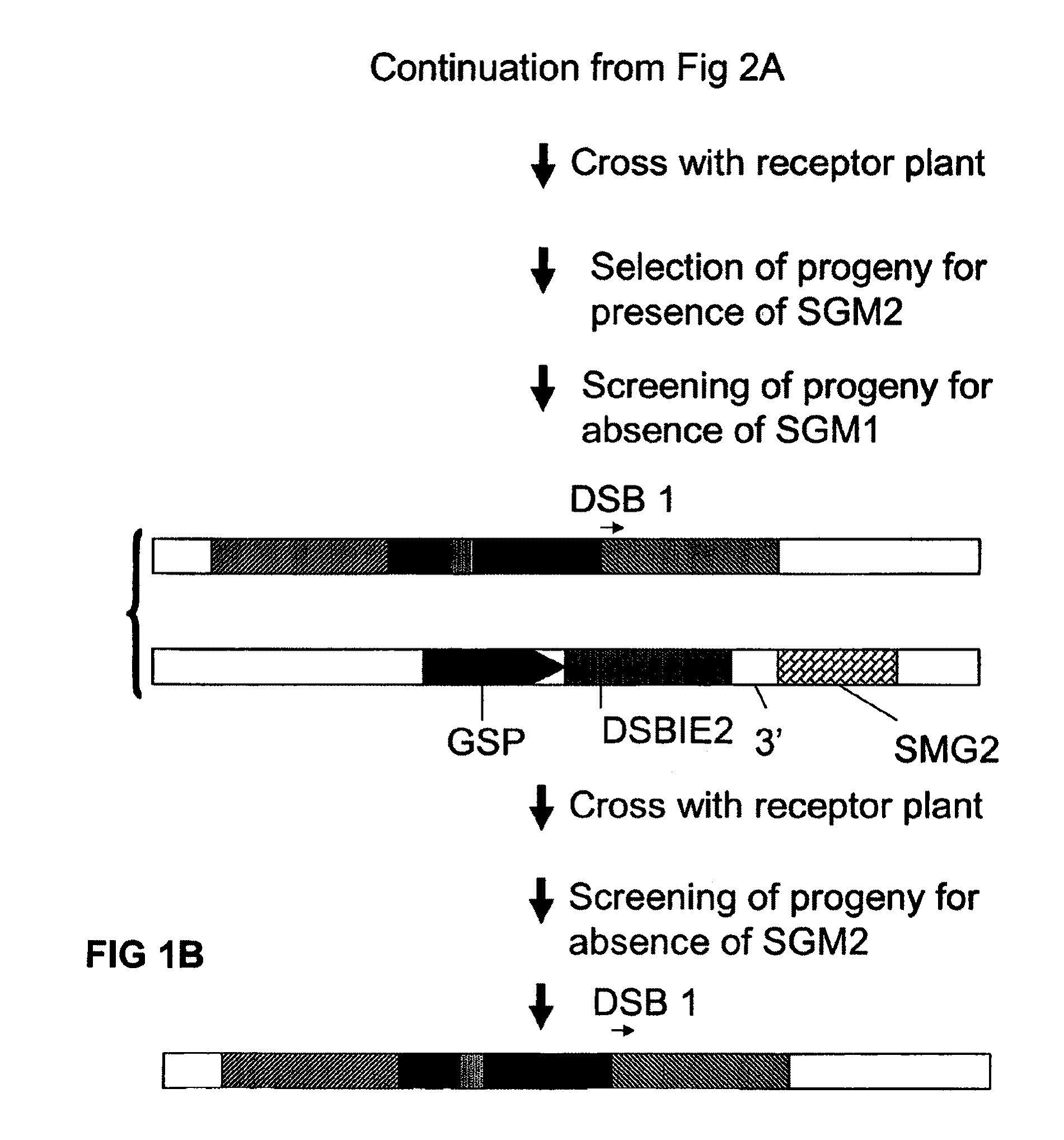
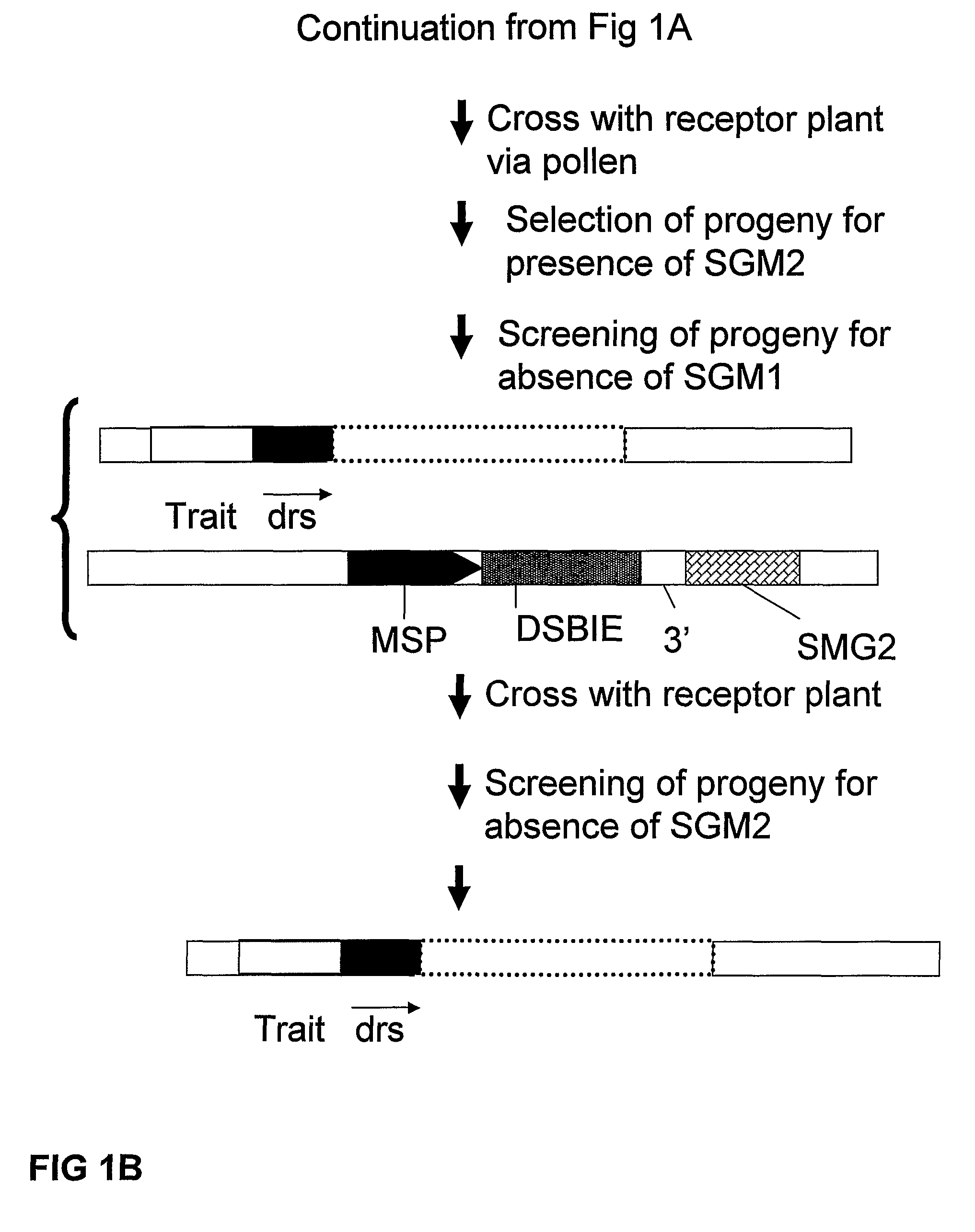
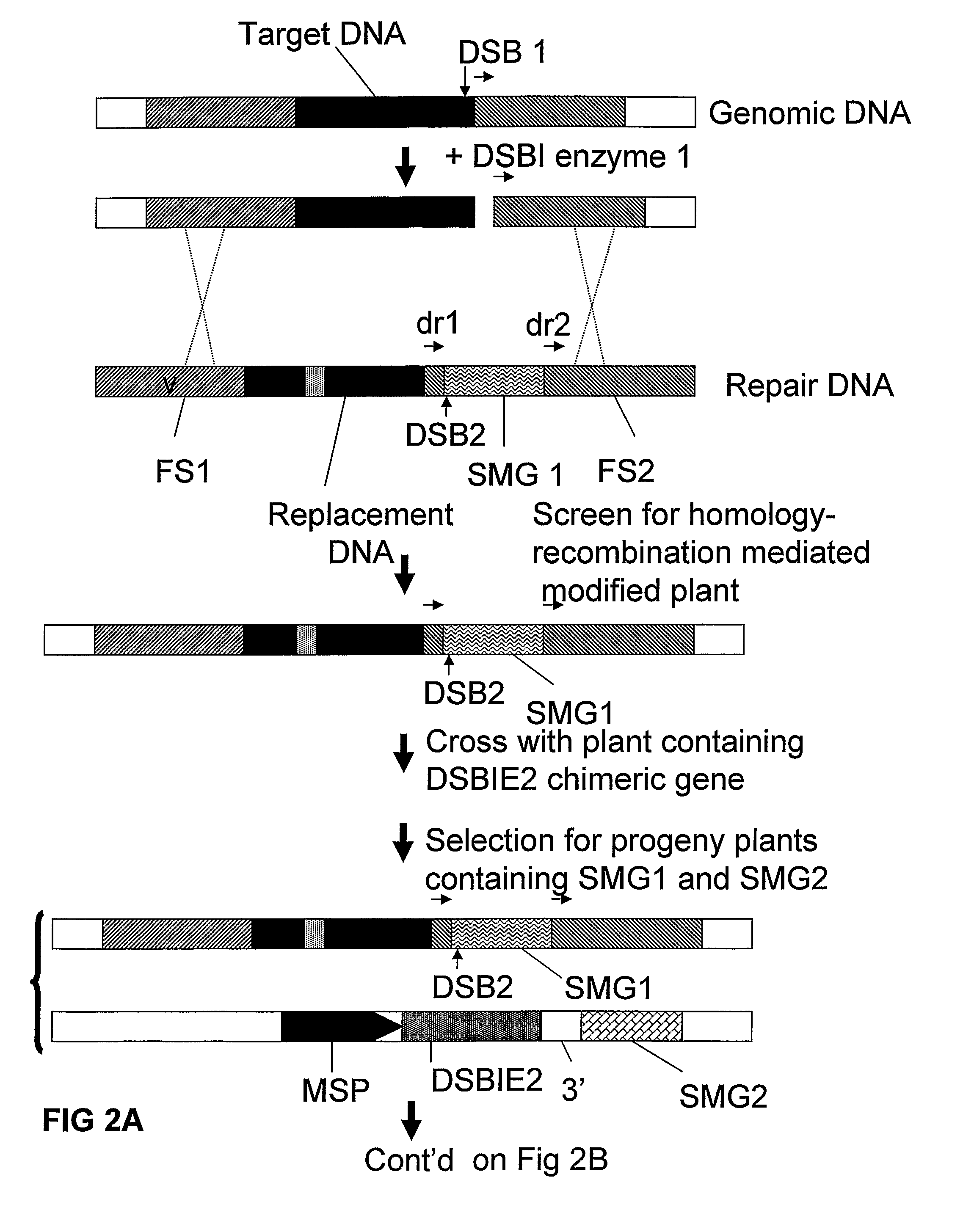
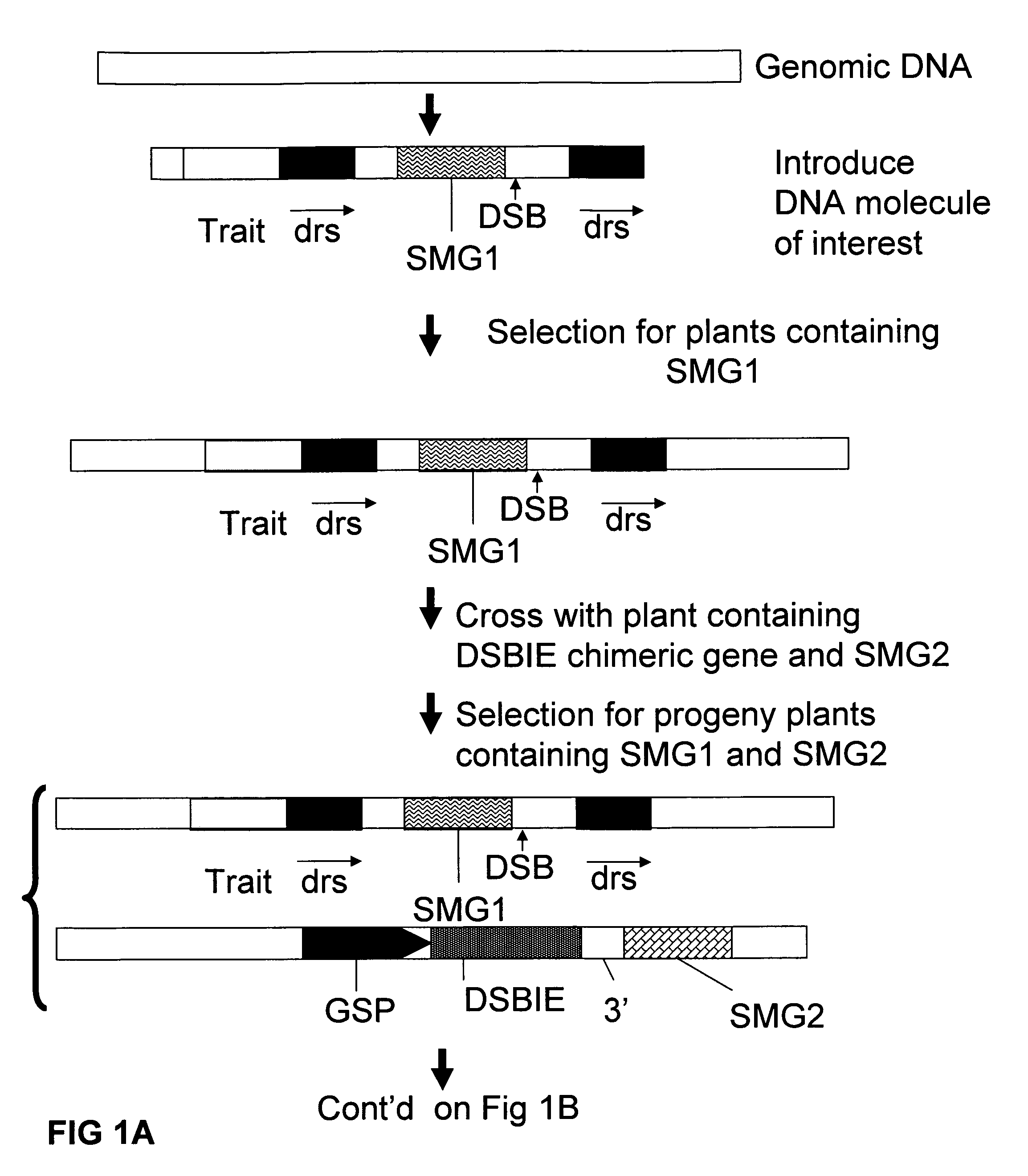
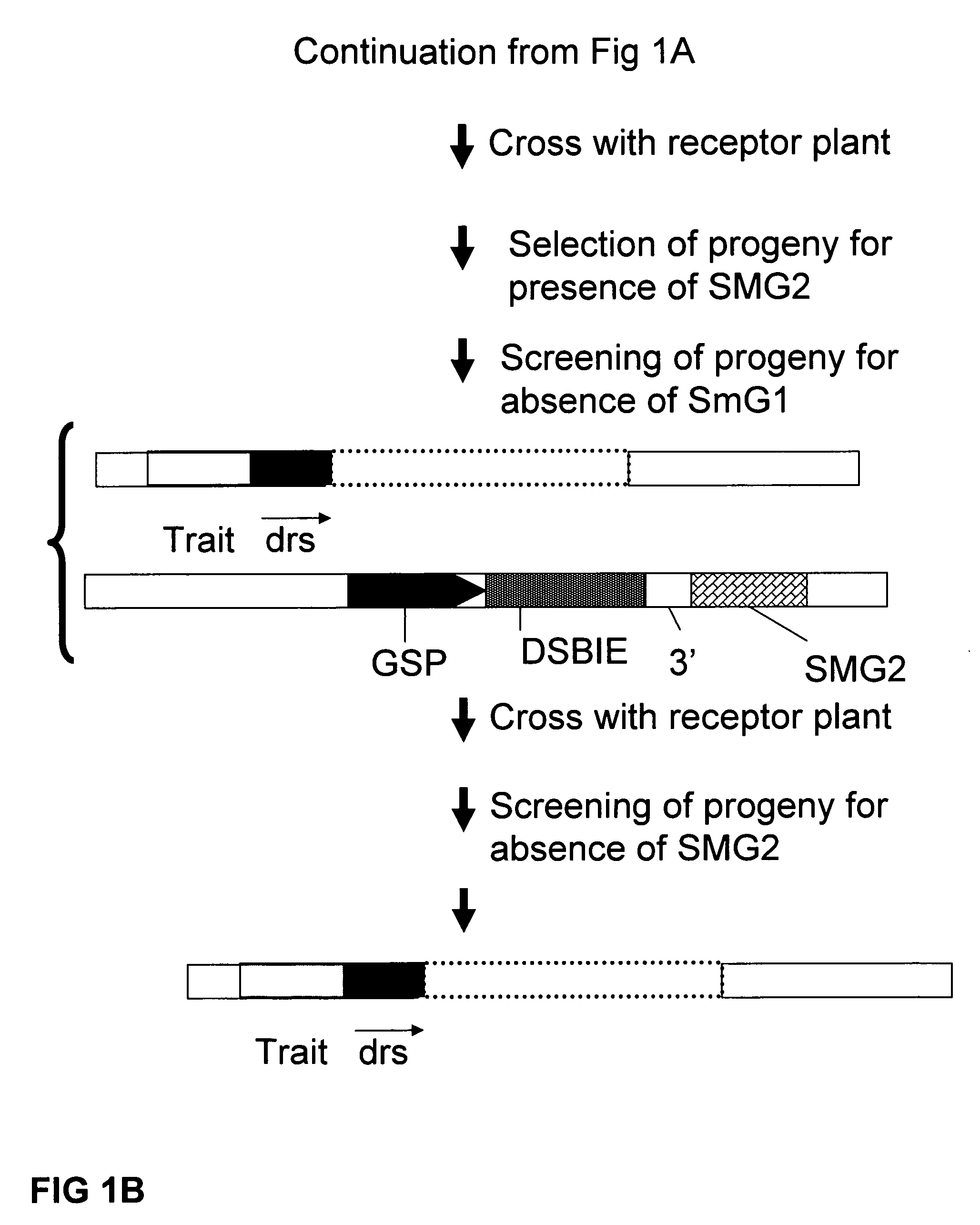
A method is described for the exact removal of a selected subfragment from a DNA molecule by intrachromosomal recombination between two directly repeated DNA sequences using a rare-cleaving double stranded break inducing DNA endonuclease expressed under control of a micro-spore specific promoter. This method can be applied in a method for the exact exchange of a target DNA fragment for a DNA fragment of interest in plant cells and plants.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
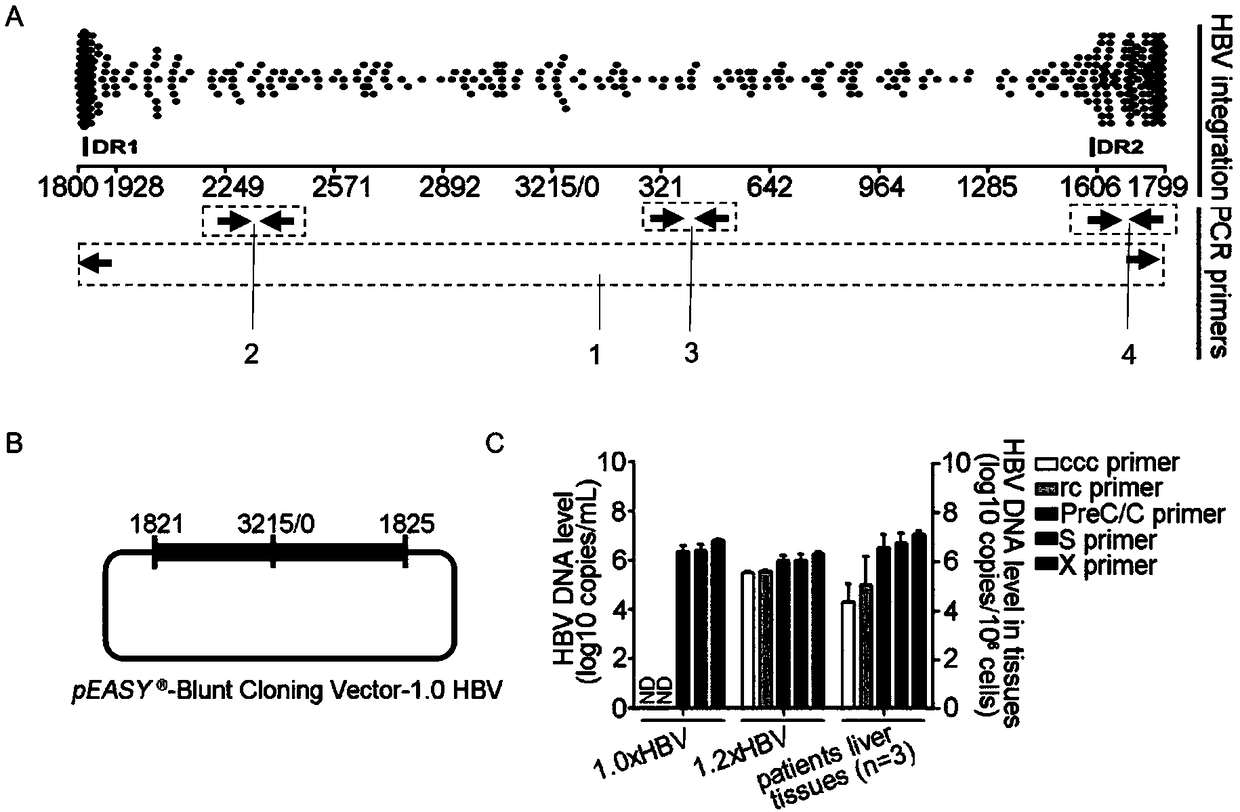
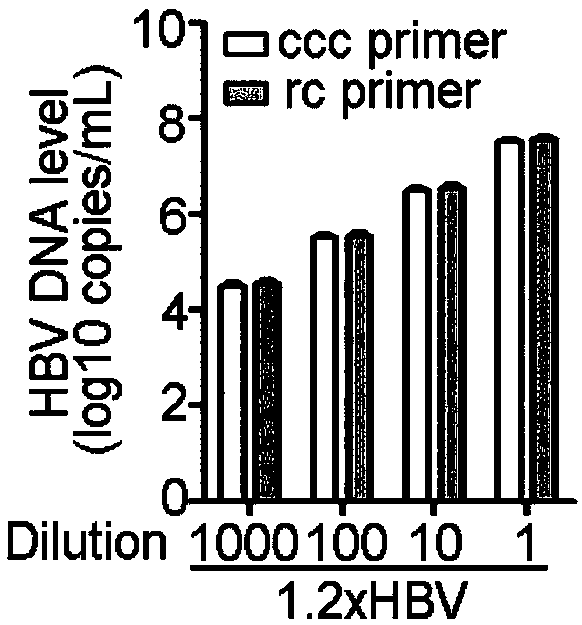
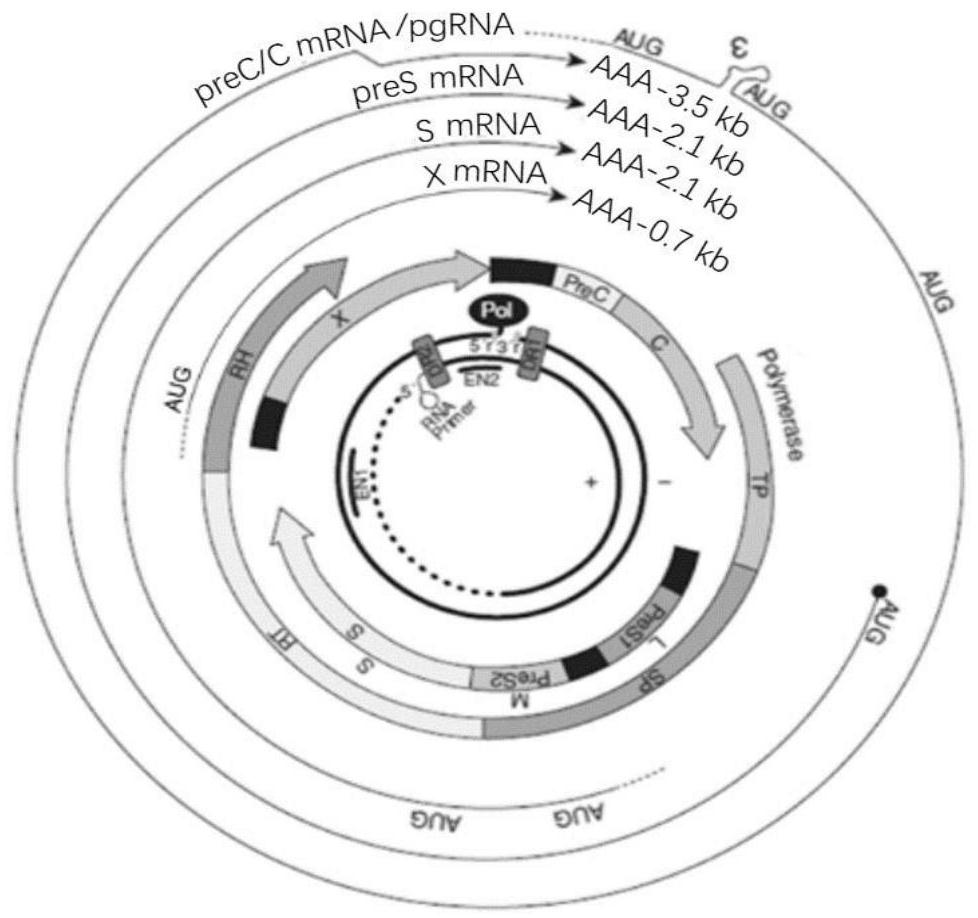
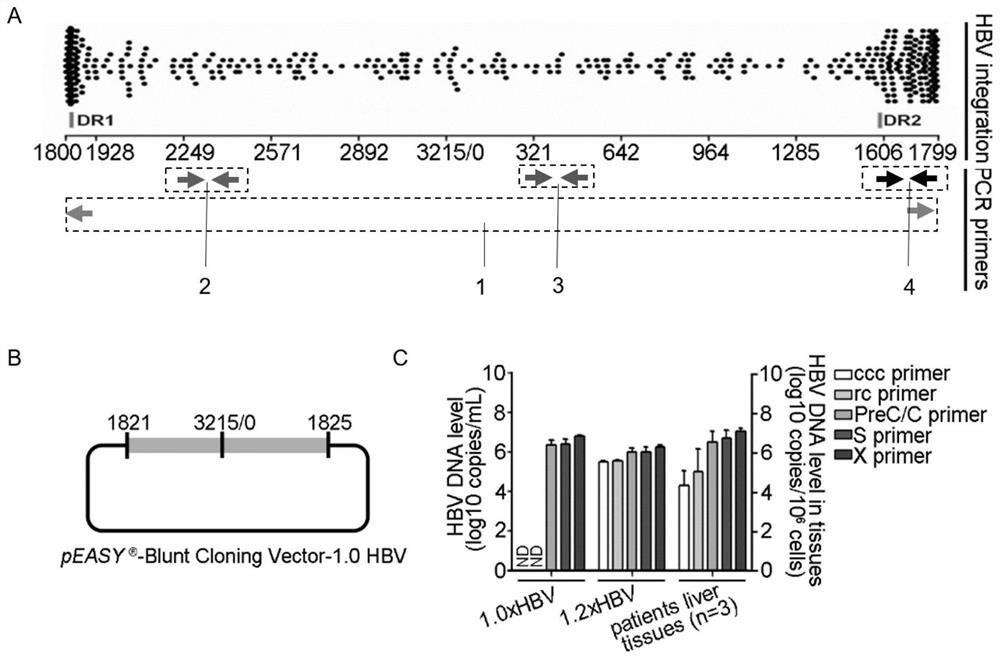
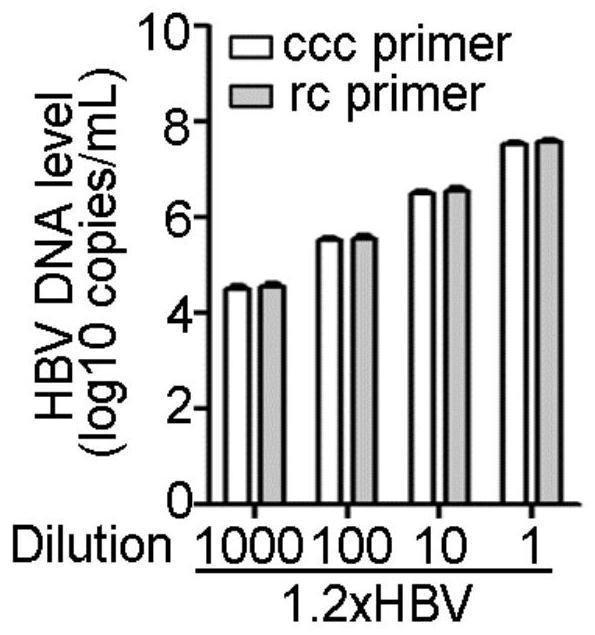
Oligonucleotide composition and method for detecting hepatitis B virus (HBV) rcDNA (Relaxed Circular deoxyribonucleic acid) and/ or cccDNA (Covalently Closed Circular DNA), kit and application of oligonucleotide composition
ActiveCN109321679AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDirect repeatHepatitis B virus
The invention discloses an oligonucleotide composition and a method for detecting hepatitis B virus (HBV) rcDNA (Relaxed Circular deoxyribonucleic acid) and / or cccDNA (Covalently Closed Circular DNA), a kit and application of the oligonucleotide composition. The oligonucleotide composition comprises first oligonucleotide, second oligonucleotide, or oligonucleotide complementary with the sequenceof the first oligonucleotide and oligonucleotide complementary with the sequence of the second oligonucleotide; the first oligonucleotide is specifically combined with at least one part of continuoussequence of the first sequence, and the second oligonucleotide is specifically combined with at least one part of continuous sequence of the second sequence; in addition, a distance between two continuous sequences is 30-350 nt; the first sequence is a sequence between DR (Direct Repeat) 2-DR1 of the HBV DR sequence of a cross-notch area which contains cccDNA or rcDNA, and the second sequence is asequence after the fifth basic group of the DR1. According to the oligonucleotide composition, the level of HBV rcDNA and / or cccDNA can be effectively detected without being affected by integrated HBV DNA.
Owner:北京旌准医疗科技有限公司
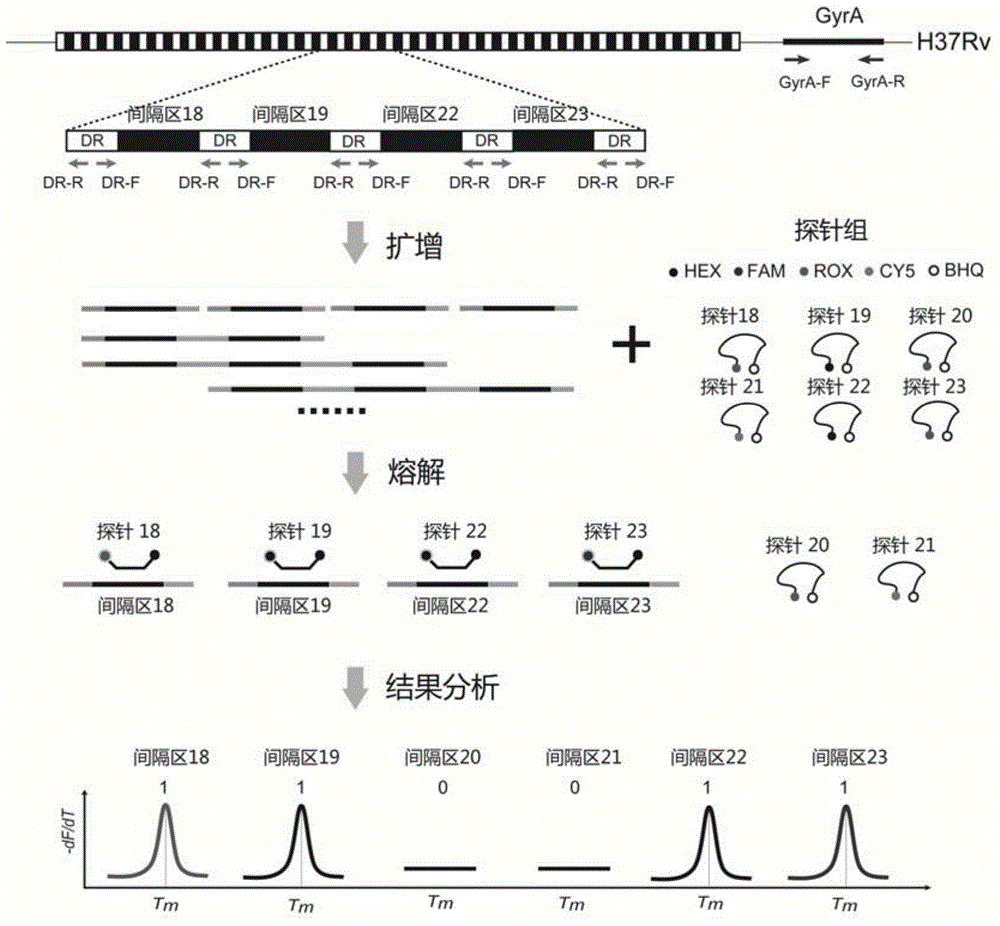
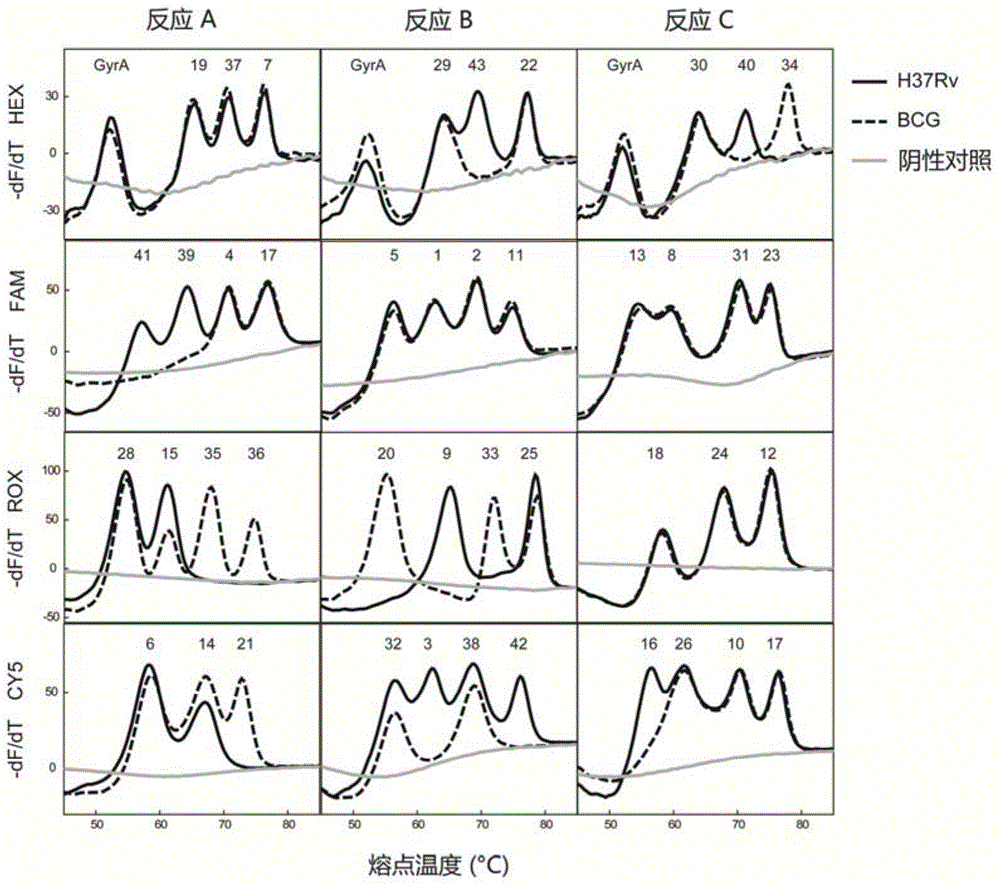
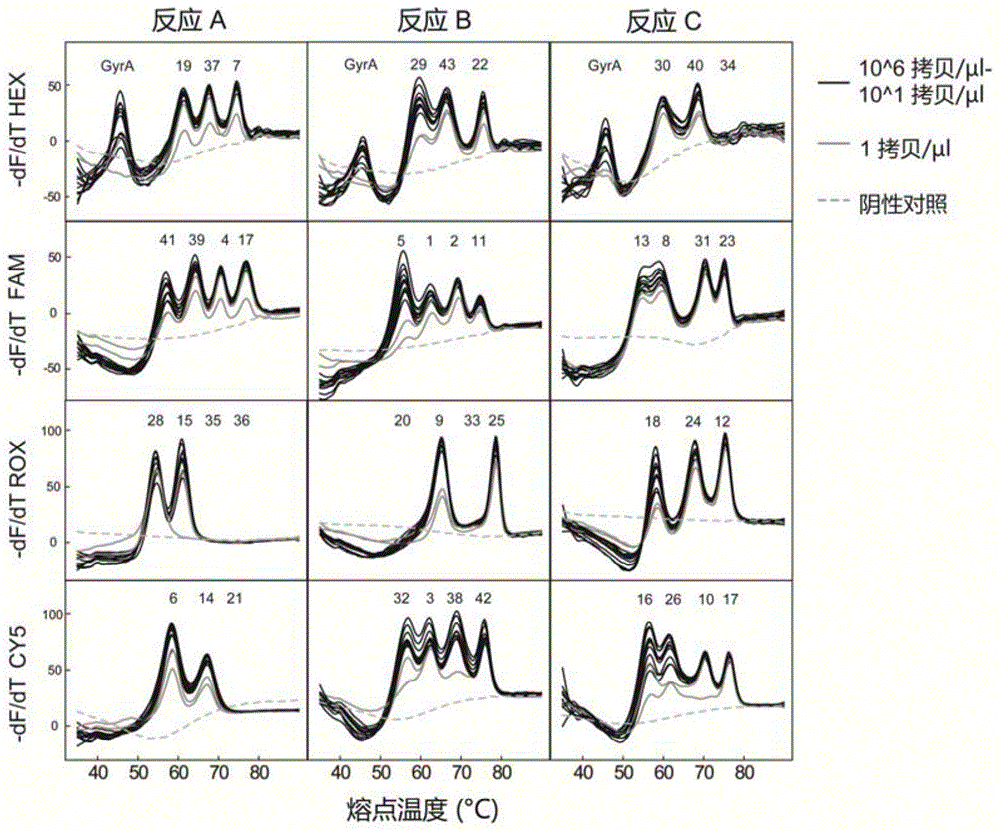
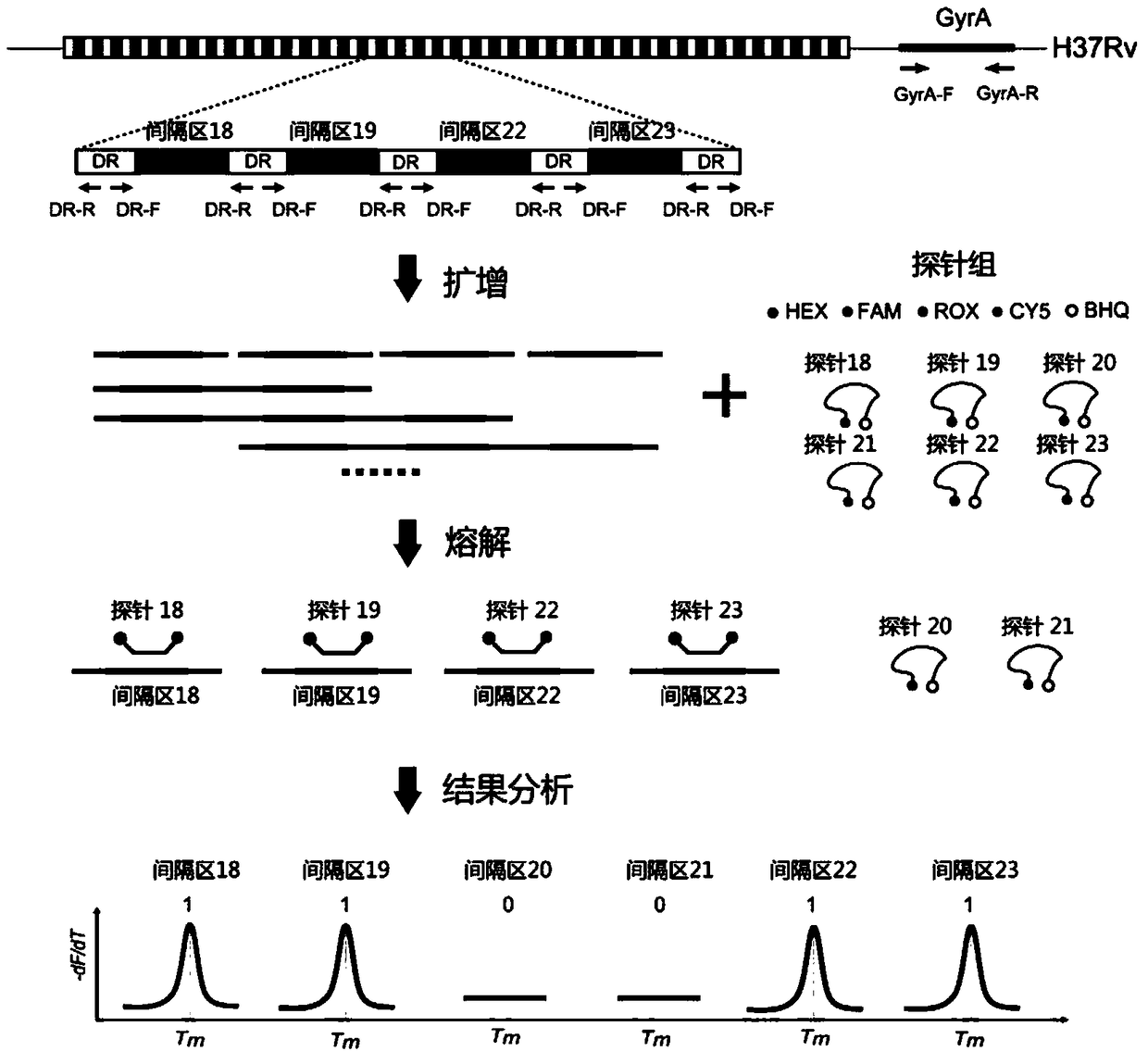
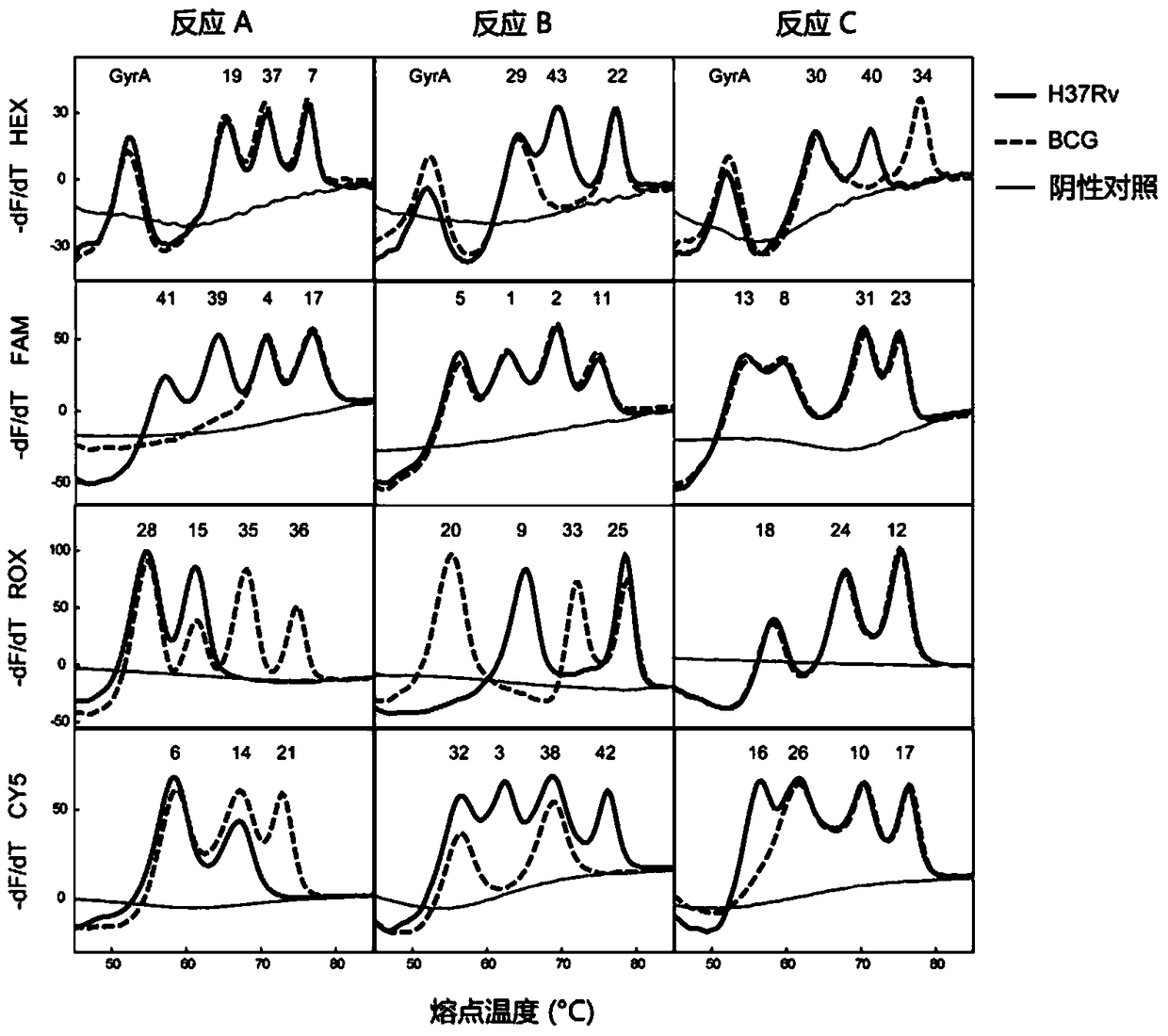
Mycobacterium tuberculosis spacer oligonucleotide typing method based on melting point coding
ActiveCN104862403AShort timeReduce manual operation timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSpacer Oligonucleotide TypingFluorescence
The invention discloses a mycobacterium tuberculosis spacer oligonucleotide typing method based on melting point coding and relates to mycobacterium tuberculosis. The method comprises the following steps: (1) designing a pair of universal primers on a direct repeat sequence to amplify all spacers, and designing a pair of primers in a GyrA conserved region; (2) designing four groups of double-tagging fluorescent probes specifically hybridized therewith according to 43 spacer sequences and GyrA sequences, and manually controlling the welding point value of each probe by adjusting the probe length and / or a base composition, wherein each probe is provided with the same fluorescent group; (3) distributing the fluorescent probes in three reaction tubes, wherein by the combination of the reaction tubes, the fluorescent groups and the welding point values, each spacer forms a three-dimensional code, and software automatically reads a result. The method has the advantages of simple and convenient one-step operation, high specificity, high repeatability, low time consumption and relatively low price, and a powerful tool is provided for exploration and research of the prevalence and propagation rule of tuberculosis in China.
Owner:XIAMEN ZEESAN BIOTECH
Methods and means for removal of a selected DNA sequence
Alternative and / or improved methods are described for the exact removal of a selected subfragment from a DNA molecule by intrachromosomal recombination between two directly repeated DNA sequences using a rare-cleaving double stranded break inducing DNA endonuclease expressed under control of a micro-spore specific promoter. These methods can be applied for the exact exchange of a target DNA fragment for a DNA fragment of interest in plant cells and plants.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Probe combination for detection of cancer
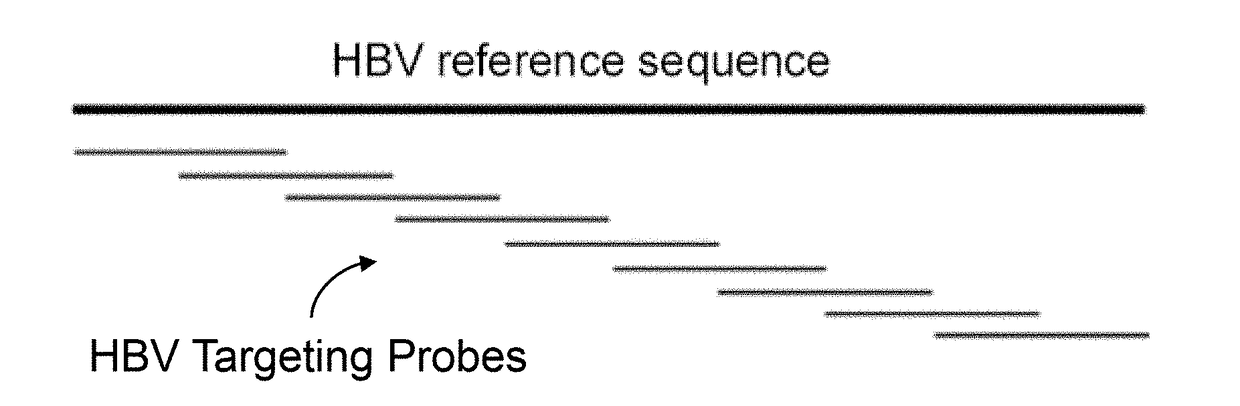
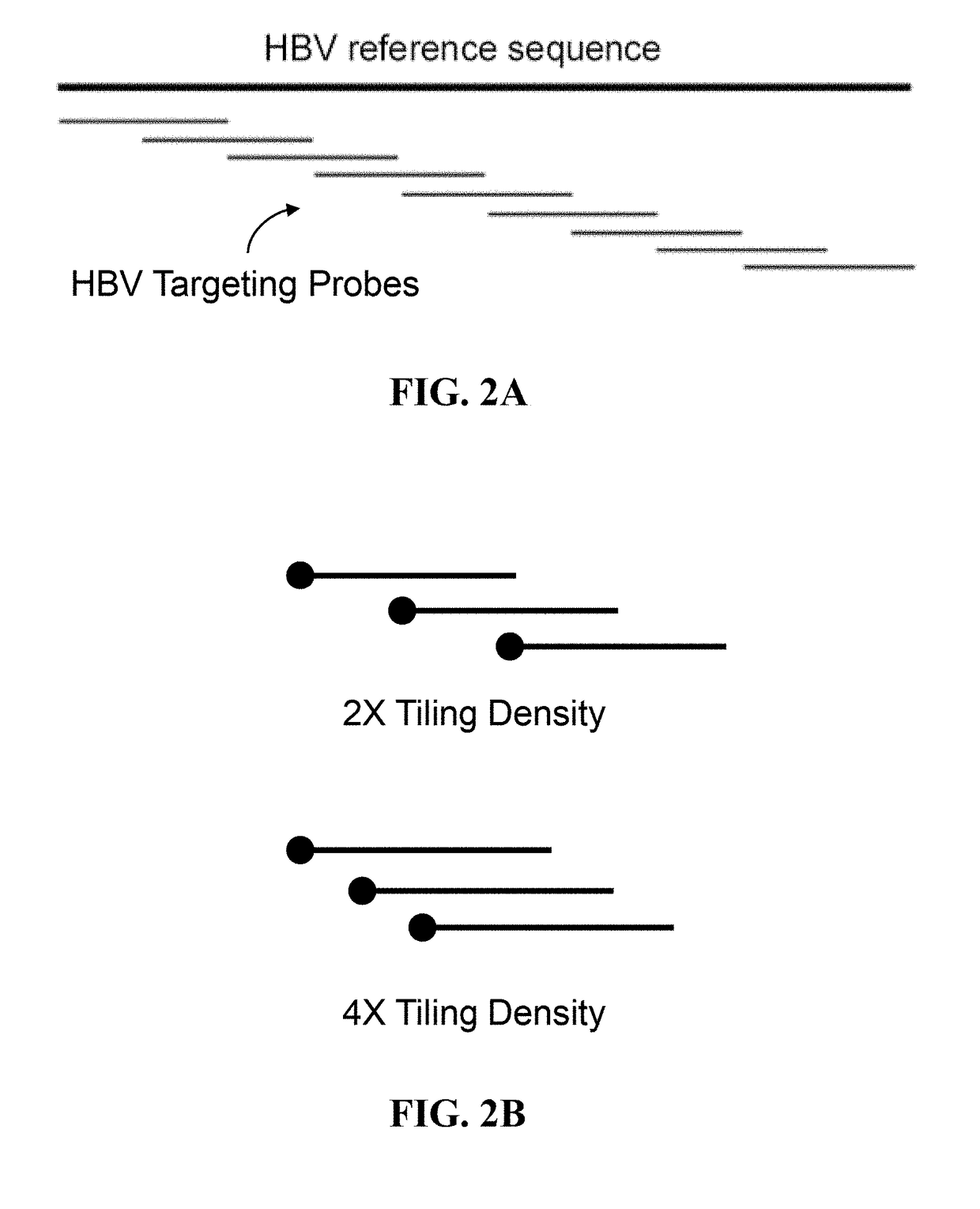
ActiveUS20180223380A1Detect presenceHighly sensitive, efficient, and reliableMicrobiological testing/measurementGene targetsHbv genotype
A probe combination for detecting cancer includes one or more sets of partial hepatitis B virus (HBV) targeting probes. When sequences of each of the sets of partial HBV targeting probes are aligned, an overall sequence of the aligned set of probes matches a reference sequence of a genome of a HBV genotype or a direct repeat (DR) region on the genome. In the aligned set of probes, each of the probes overlap with one or two adjacent probes by a portion of a length of the probe. The probe combination may further includes one or more sets of hotspot gene targeting probes targeting cancer hotspot genes such as CTNNB1, TERT, and TP53 genes, one or more sets of exogenous gene targeting probes targeting portions of a lambda phage genome, and endogenous gene targeting probes targeting endogenous genes such as GAPDH and GdX genes.
Owner:TCM BIOTECH INT CORP
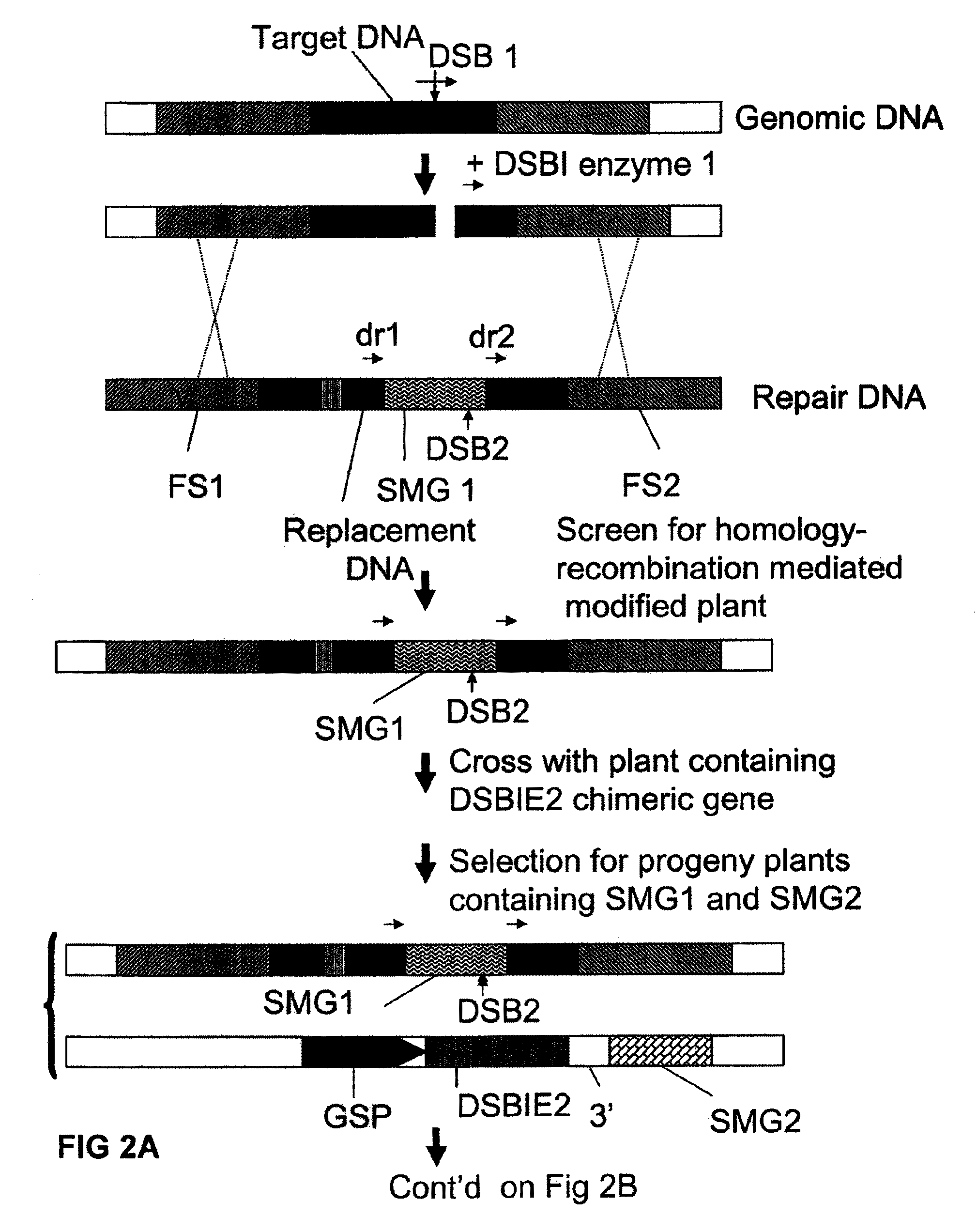
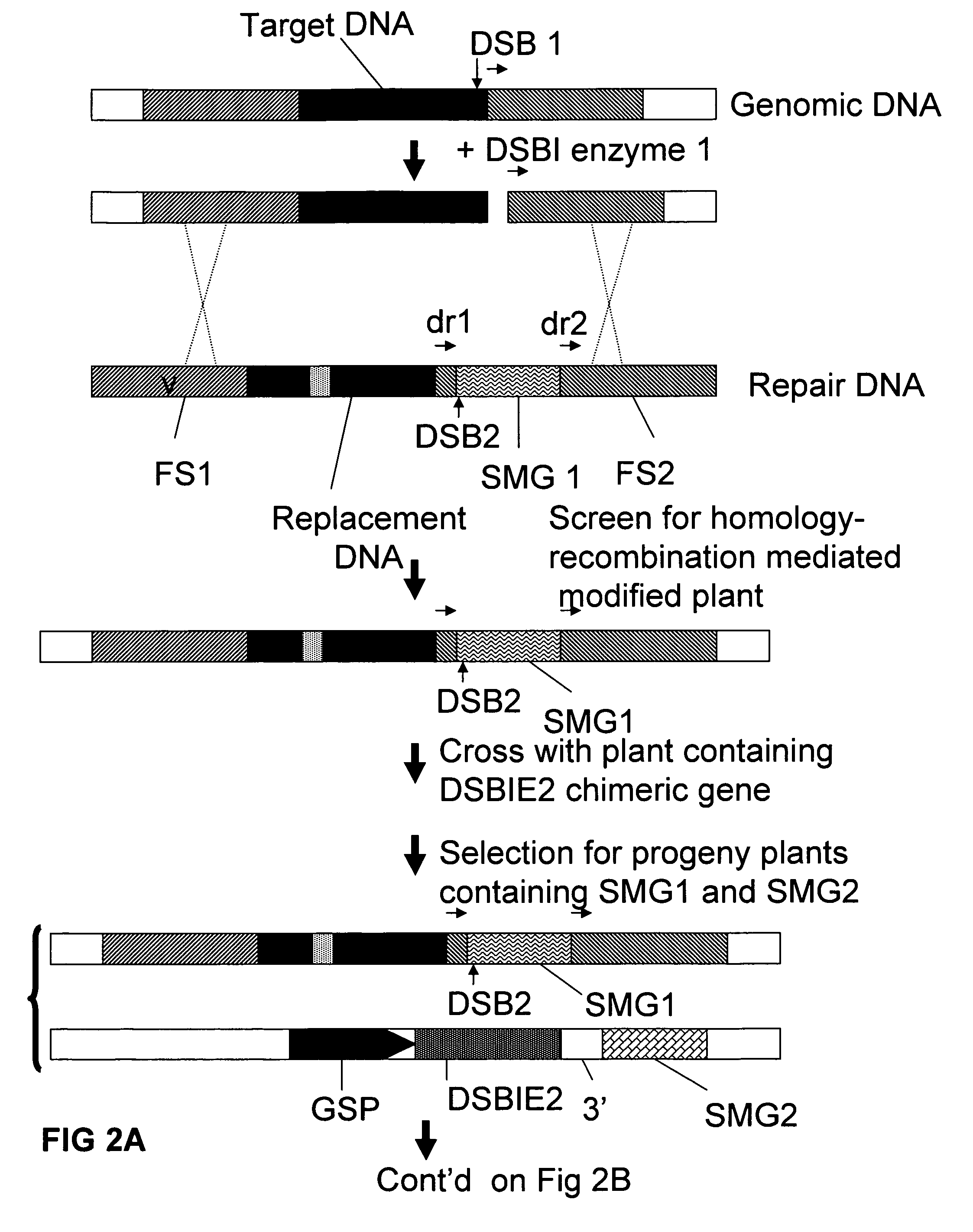
Methods and means for exact replacement of target DNA in eukaryotic organisms
Methods and means are provided for the exact exchange in eukaryotic cells, such as plant cells, of a target DNA sequence for a DNA sequence of interest through homologous recombination, whereby the selectable or screenable marker used during the homologous recombination phase for temporal selection of the gene replacement events can subsequently be removed without leaving a foot-print employing a method for the removal of a selected DNA flanked by two nucleotide sequences in direct repeats.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Method for batch inspection of plant genome LTR-retrotransposon
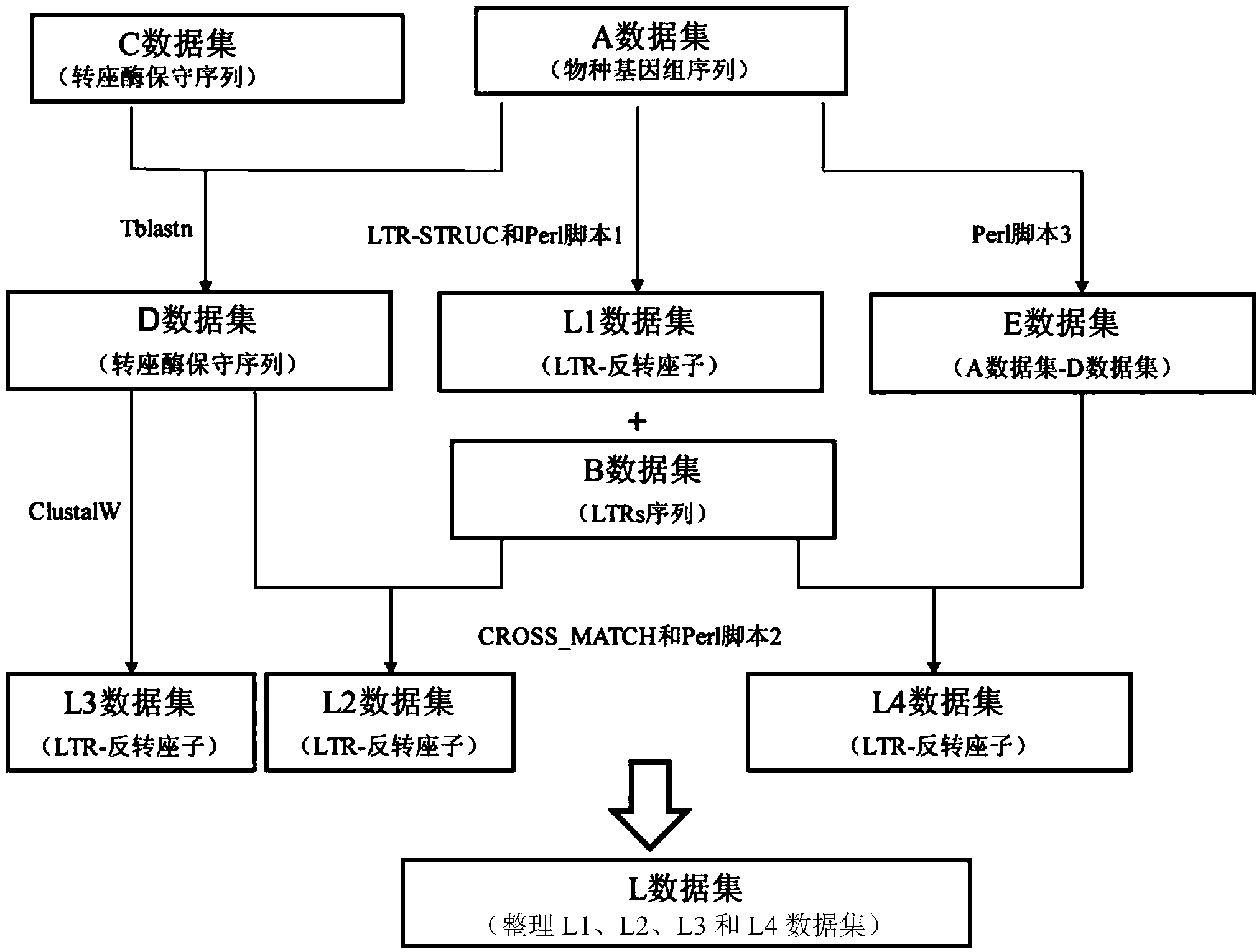
The invention discloses a method for batch inspection of plant genome LTR-retrotransposon. An LTR_STRUC program based on structural characteristics and searching from the beginning, a CROSS_MATCH program based on homology searching and a CLUSTALW comparison program based on sequence similarity are comprehensively applied in the method for the batch inspection of the plant genome LTR-retrotransposon, and Perl scripting language programming and other methods are combined. Experimental results show that the method for the batch inspection of the plant genome LTR-retrotransposon is relatively systematic, the effect for detecting the direct repeat of the inserting sites of the plant genome LTR-retrotransposon is good, speed is high, and process operation is easy to achieve. According to the method, the frequently-used software for detecting the plant genome LTR-retrotransposon and the Perl scripting language programming are combined, and certain defects of the frequently-used software are made up. The method can play an important role in genome annotation and the batch inspection of the plant genome LTR-retrotransposon.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for genetic detection using interspersed genetic elements
ActiveUS7794983B2Easy to testSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsGenetic element
Owner:RELIAGENE TECH INC A CORP CHARTERED IN & EXISTING UNDER THE LAWS OF THE STATE OF LOUISIANA +1
Methods and means for removal of a selected DNA sequence
A method is described for the exact removal of a selected subfragment from a DNA molecule by intrachromosomal recombination between two directly repeated DNA sequences using a rare-cleaving double stranded break inducing DNA endonuclease expressed under control of a micro-spore specific promoter. This method can be applied in a method for the exact exchange of a target DNA fragment for a DNA fragment of interest in plant cells and plants.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
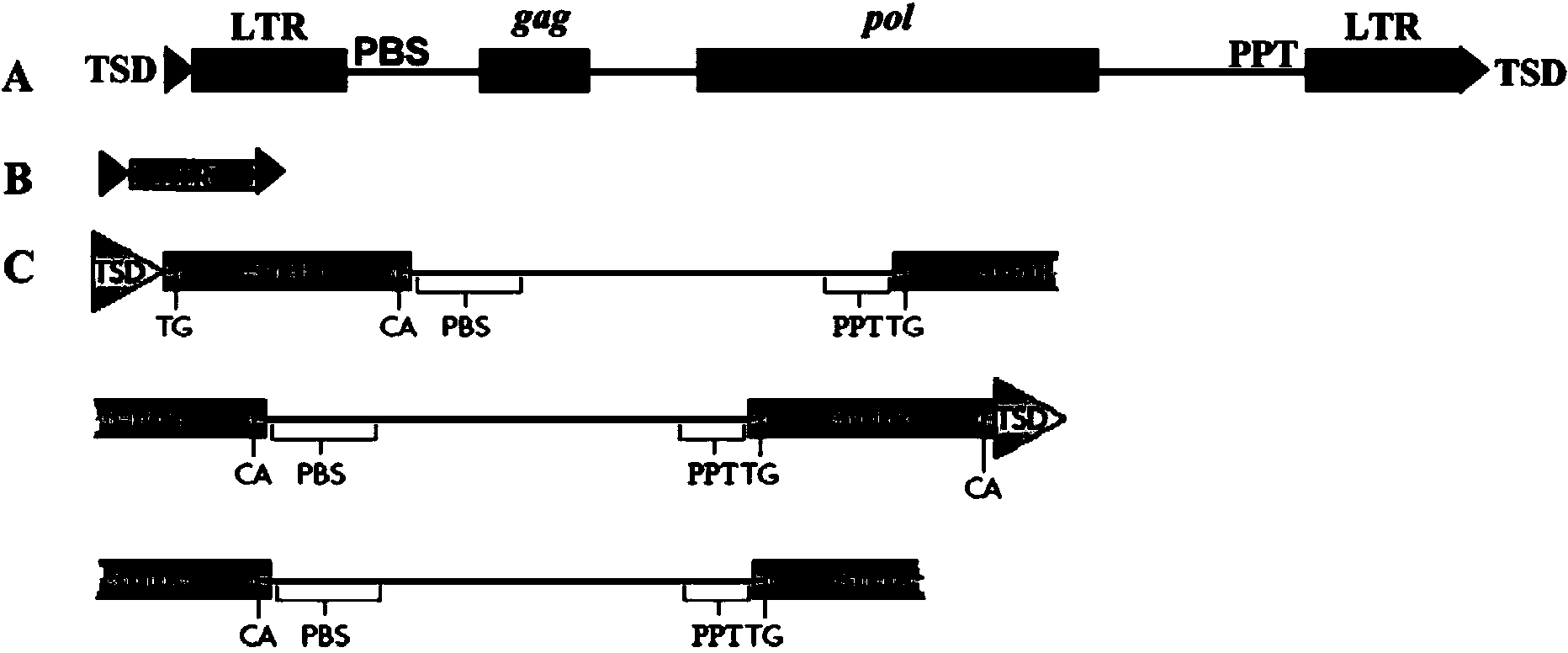
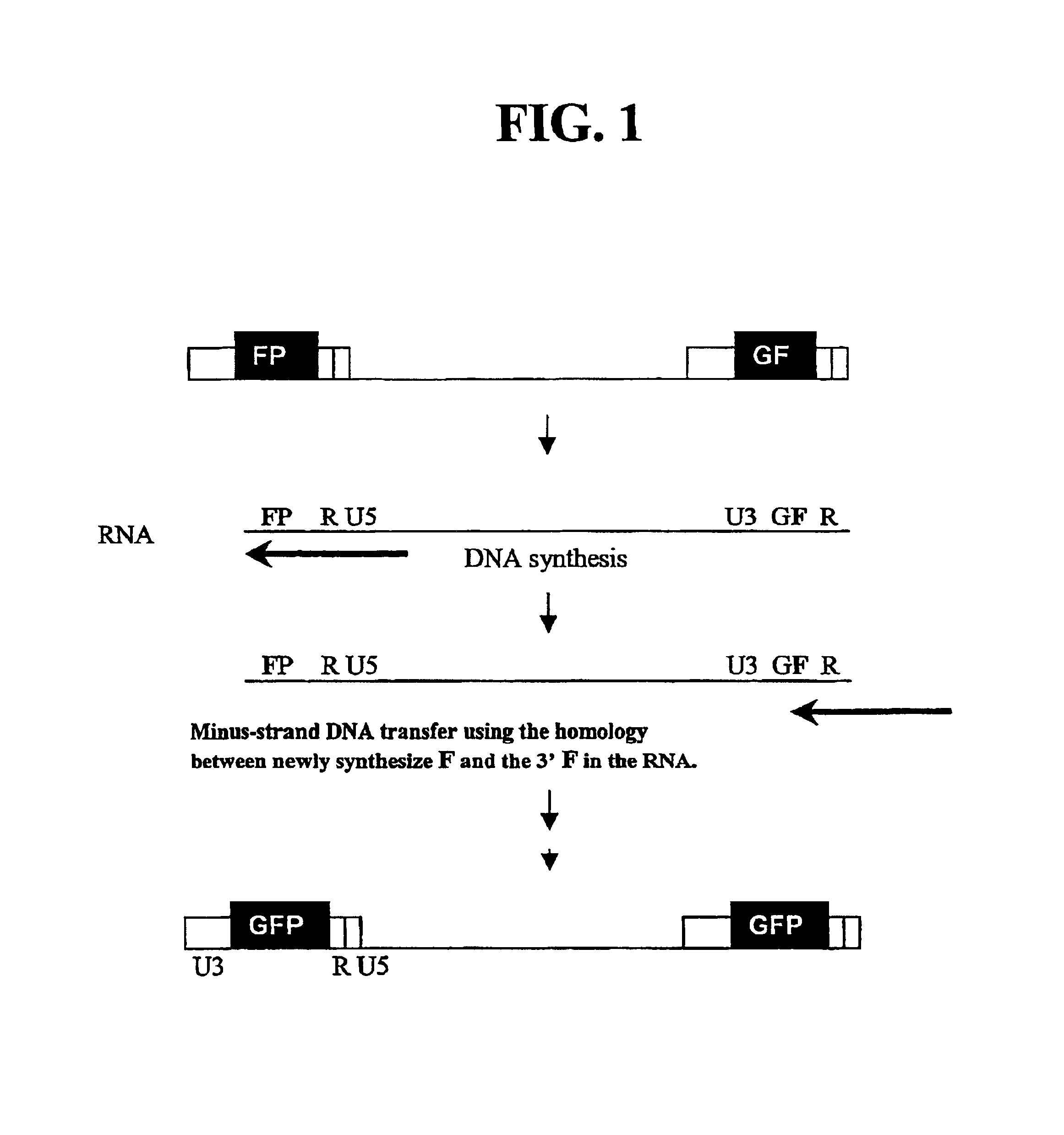
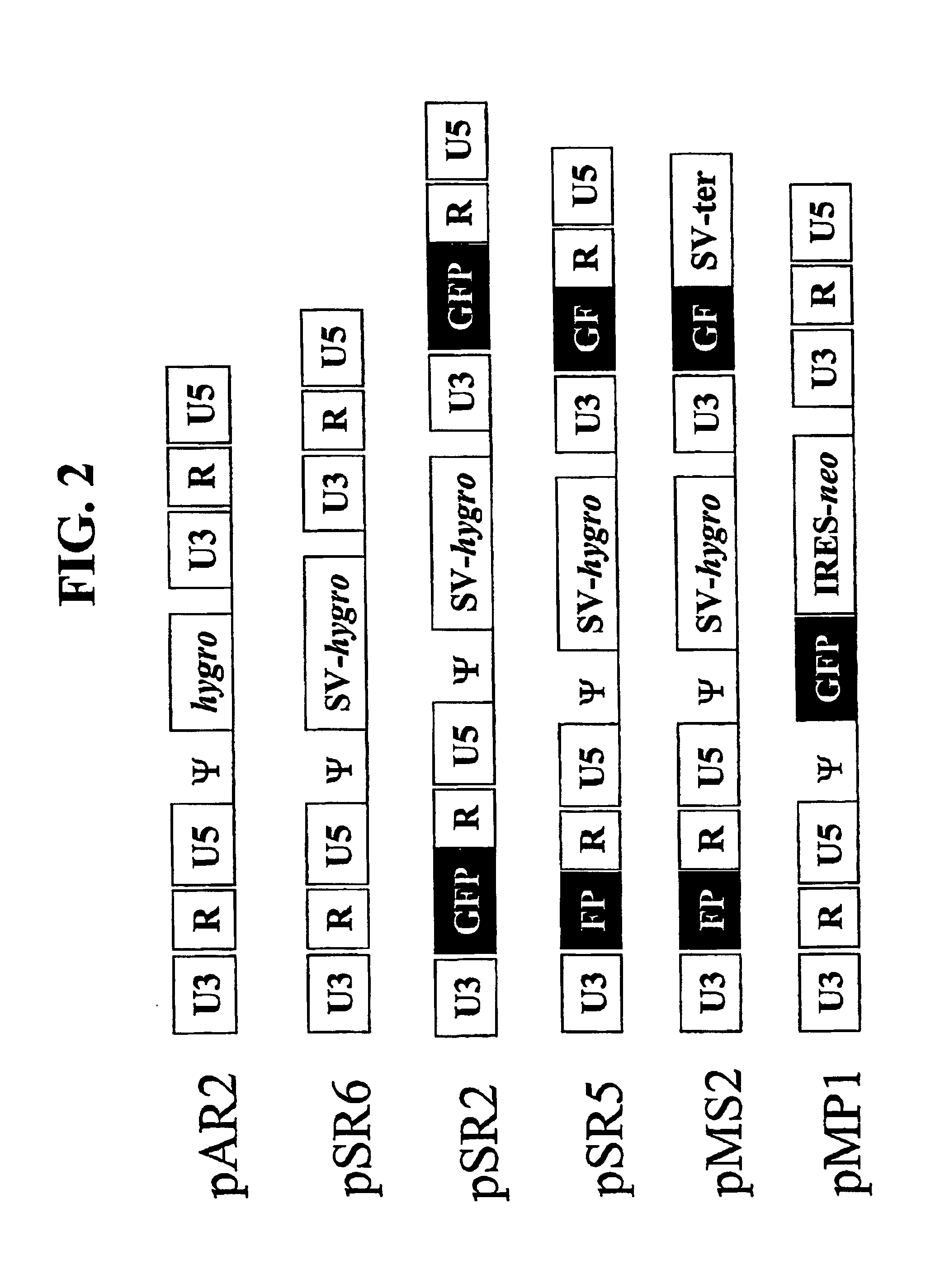
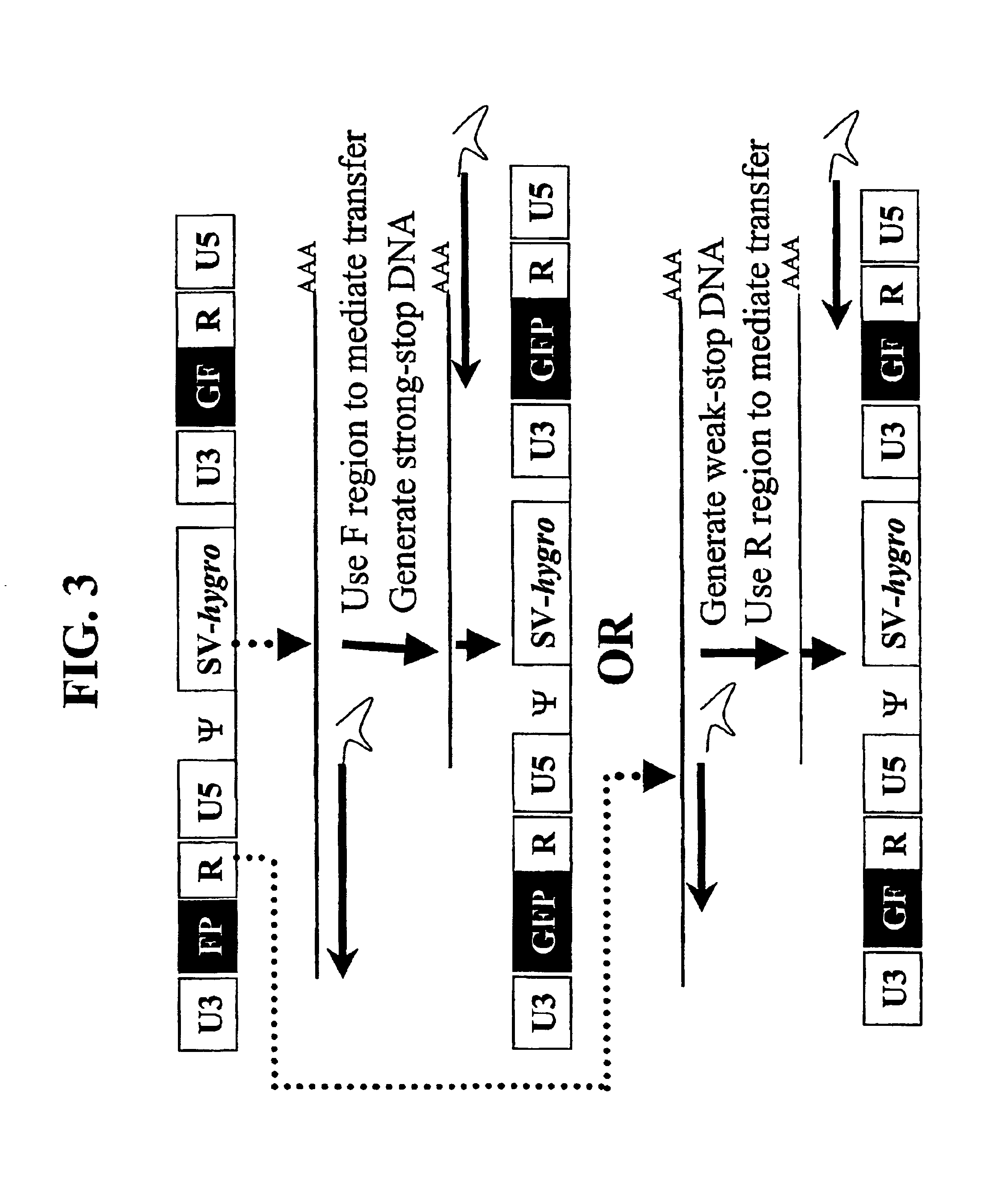
Utilization of non-viral sequences for minus-strand DNA transfer and gene reconstitution
A retroviral vector for gene reconstitution is provided that includes a 3′ portion of a heterologous nucleic acid sequence 5′ of a first att site and a 5′ portion of the heterologous nucleic acid sequence 3′ of a second att site. A sub-portion of the 3′ portion of the heterologous nucleic acid sequence and a sub-portion the 5′ portion of the heterologous nucleic acid sequence are direct repeats. A retroviral vector for gene reconstitution is also provided that includes a 3′ portion of a heterologous nucleic acid sequence inserted into or adjacent to a 5′ retroviral terminal repeat of the retroviral vector, and a 5′ portion of the heterologous nucleic acid sequence inserted into or adjacent to a 3′ retroviral terminal repeat of the retroviral vector, wherein the 3′ and the 5′ retroviral terminal repeats each comprise an att site. Methods and kits are also provided.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES THE
Producing improved viral and non-viral nanoplasmid vectors
PendingCN112154208AImprove product qualityImprove throughputNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionOrigin of replicationInverted Repeat Sequences
A method for improving the replication of a covalently closed circular plasmid is provided. The method includes providing a covalently closed circular plasmid having a Pol I-dependent origin of replication, and an insert including a structured DNA sequence selected from the group consisting of inverted repeat sequence, direct repeat sequence, homopolymeric repeat sequence, eukaryotic origin of replication or eukaryotic promoter enhancer sequence, wherein the structured DNA sequence is located at a distance of less than 1000 bp from the Pol I-dependent origin of replication in the direction ofreplication. The method also includes modifying the covalently closed circular recombinant molecule such that the Pol I-dependent origin of replication is replaced with a Pol III-dependent origin of replication, whereby the resultant Pol III-dependent origin of replication covalently closed circular plasmid has improved replication. An antibiotic marker free covalently closed circular recombinantDNA molecule is also provided.
Owner:阿尔德夫隆有限责任公司
Tobacco chloroplast genome recombination hotspot short-sequence NtcpRH23
InactiveCN102220317ABreak through the technical barriers of low integration efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationNicotiana tabacumChloroplast
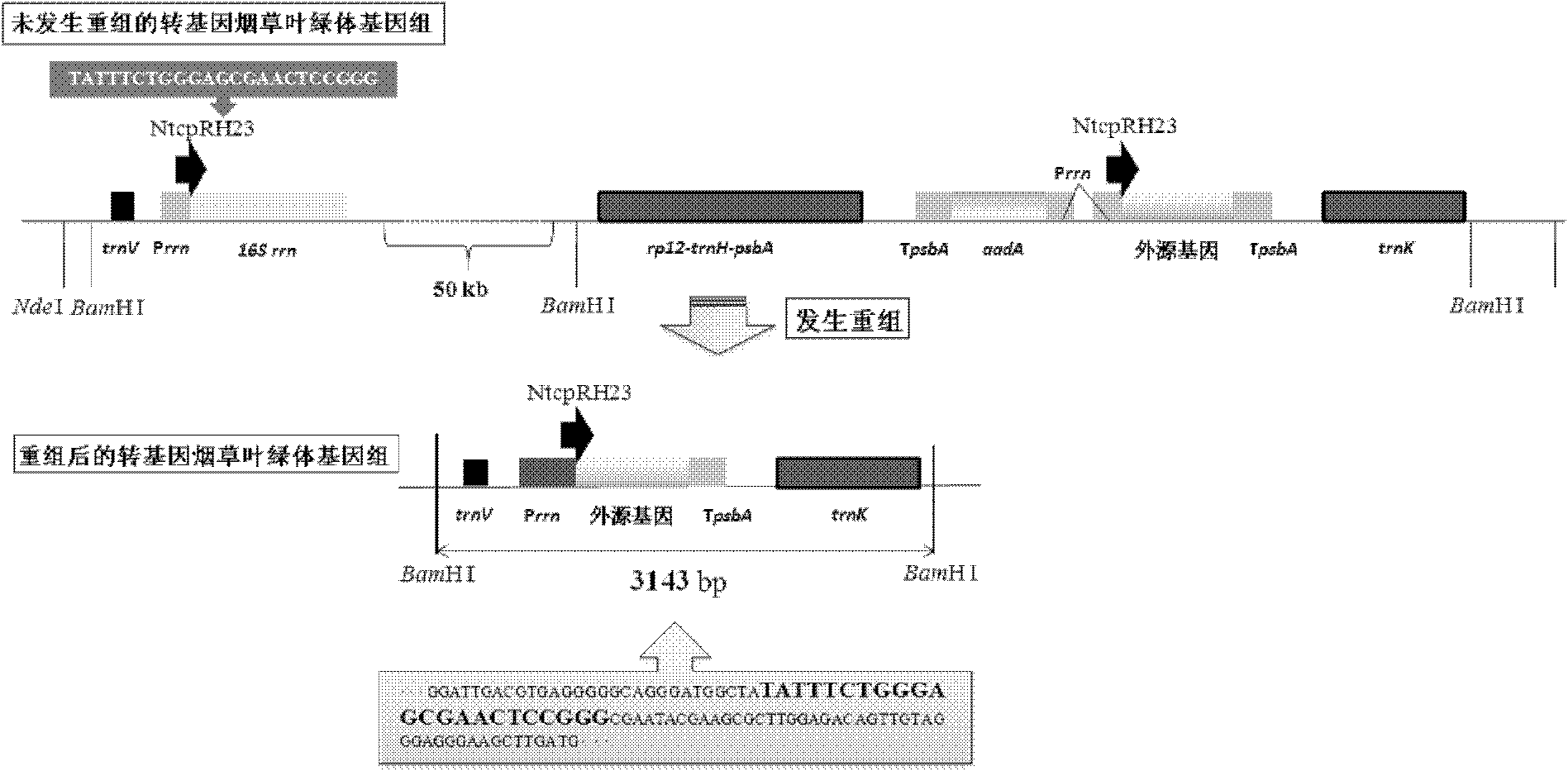
The invention relates to a tobacco chloroplast genome recombination hotspot short-sequence NtcpRH23. According to the invention, the obtaining of chloroplast-converted tobacco material is employed as a basis, and a discovery is that: a segment of 23bp short-sequence NtcpRH23 on the constructed carrier can be subject to high-frequency recombinations with upstream direct repeats. According to PCR verifications, recombination events occur in four obtained conversion materials, and tobacco chloroplast genome recombinants are produced. The discovery of the segment of sequence assists in providing a novel molecular biological tool for the construction of chloroplast conversion novel carrier, and for the researches of relevant biological hot problems of chloroplast genome copying, chloroplast genome recombination, and chloroplast genome restoring mechanism.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
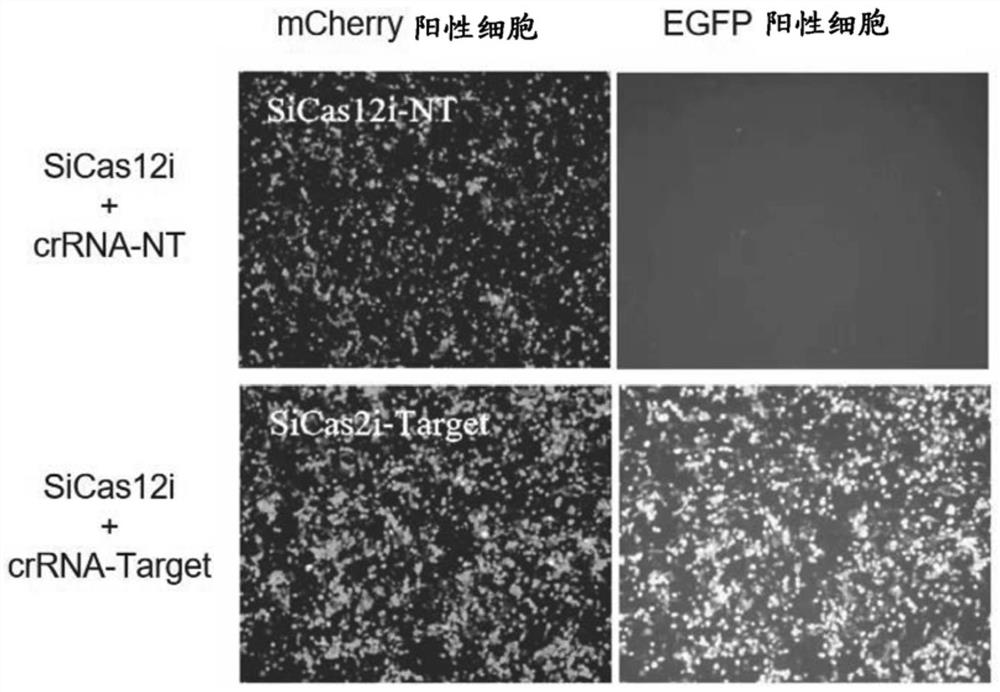
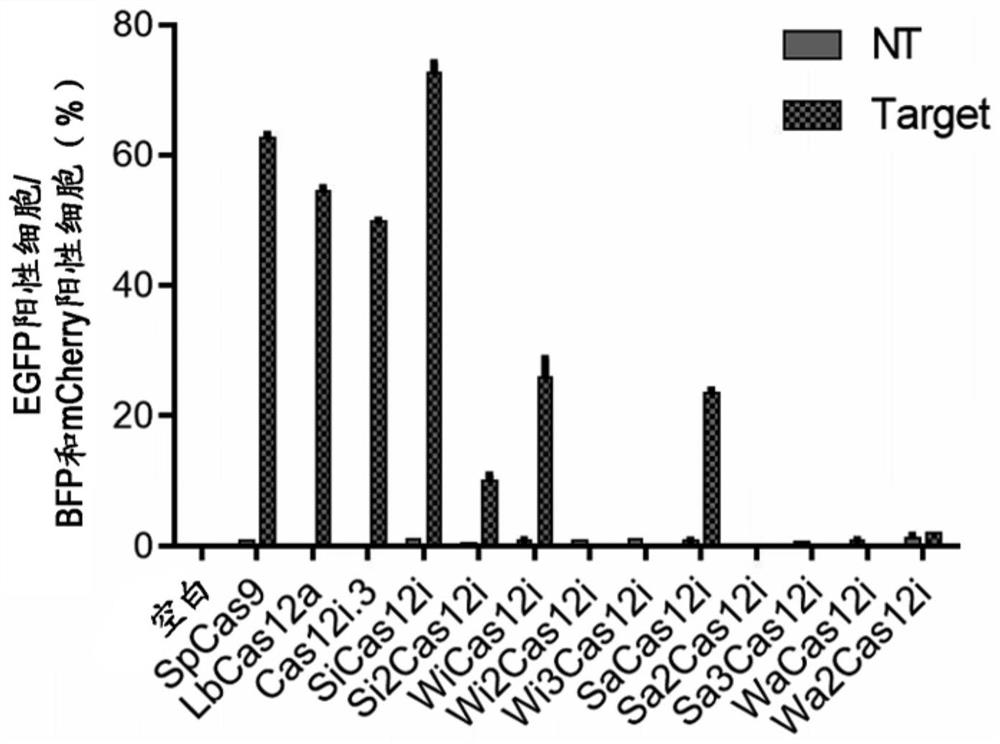
Novel CRISPR-Cas12i system
The present disclosure provides a Cas12i protein comprising an amino acid sequence having at least 80%, 81%, 82%, 83%, 84%, 85%, 86%, 87%, 88%, 89%, 90%, 91%, 92%, 93%, 94%, 95%, 96%, 97%, 98%, 99%, 99.5% or 100% identity with the amino acid sequence represented by any one of SEQ ID NO: 1-10 (preferably, SEQ ID NO: 1-3 and 6, more preferably, SEQ ID NO: 1). The present disclosure also provides an engineered, non-naturally occurring CRISPR-Cas system comprising: (1) the Cas12i protein or a polynucleotide encoding the Cas12i protein; and (2) a CRISPR RNA (crRNA) or a polynucleotide encoding the crRNA, the crRNA comprising: (i) a spacer sequence capable of hybridizing to a target sequence of a target DNA, and (ii) a direct repeat (DR) sequence linked to the spacer sequence capable of directing the binding of the Cas12i protein to the crRNA to form a CRISPR-Cas complex that targets the target sequence.
Owner:HUIGENE THERAPEUTICS CO LTD
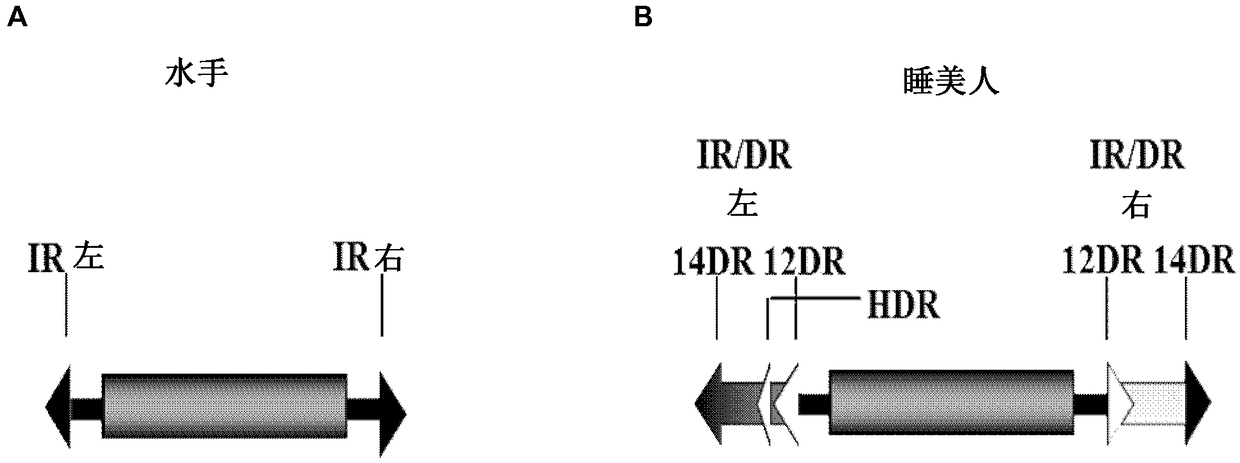
Enhanced sleeping beauty transposons, kits and methods of transposition
The present invention relates to enhanced Sleeping Beauty-type transposons and methods of transposition. In particular, the invention relates to a polynucleotide comprising a cargo nucleic acid flanked by a left and a right inverted repeat / direct repeat (IR / DR), wherein IR / DRs, having specific sequences, are recognized by a Sleeping Beauty transposase protein and the polynucleotide is capable of integrating into the DNA of a cell. The invention also relates to a kit for transposing a nucleic acid comprising said polynucleotide as well as to further components such as co-factors of transposition capable of depleting a component of the FACT (facilitates chromatin transcription) complex, namely, SSRP1 and / or SUPT16H / SPT16,or an inhibitor of cathepsin selected from the group comprising H,S,V,and L; or a cofactor capable of depleting or inhibiting HSP90; or a factor temporally arresting cells cell cycle in cell cycle phase G0 / G1, G1 / S, or G2 / M; or a factor inhibiting the ubiquitination ofPCNA,or cells wherein these components have been knocked down or inhibited,or the cell cyle arrested in any of said stages. Alternatively or additionally, the kit may comprise as a co-factor of transposition an agent capable of increasing concentration and / or signaling of ATR or a cell wherein concentrationand / or signaling of ATR are increased. The invention further provides methods using said transposon polynucleotide as well as host cells and pharmaceutical compositions. It also relates to use of said co-factors of transposition or specific cells for enhancing transposition efficiencies, e.g., for preparing genetically modified nucleic acids or cells.
Owner:MAX DELBRUECK CENT FUER MOLEKULARE MEDIZIN
Integrative plasmid pOPHI and resistance screening marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium
ActiveCN102719471BExperimental data is credibleHigh sensitivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneDirect repeat
The invention discloses an integrative plasmid pOPHI and a resistance screening marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium. The integrative plasmid pOPHI comprises a promoter, an enzyme gene (LuxCDABE) needed for luminescence, a fusion gene of an integrase gene (Int) and a resistance screening gene, direct repeat sequences DifR and DifL positioned on two ends of the fusion gene, a phage integration site (attP) and a replicon. After the integrative plasmid pOPHI is transferred into the mycobacteria, a photobacterium of which the resistance gene and the integrase gene are lost is screened out by subculturing, and the photobacterium is the resistance screening marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium. Whether the resistance screening marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium obtained by construction is dead or not is judged according to whether the bacterium is luminescent or not, the mycobacterium can be used for a plurality of detections of experiments, and credible experimental data can be quickly obtained.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for introducing site-specific mutagenesis rapidly and efficiently
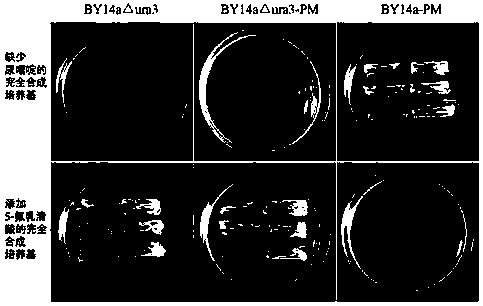
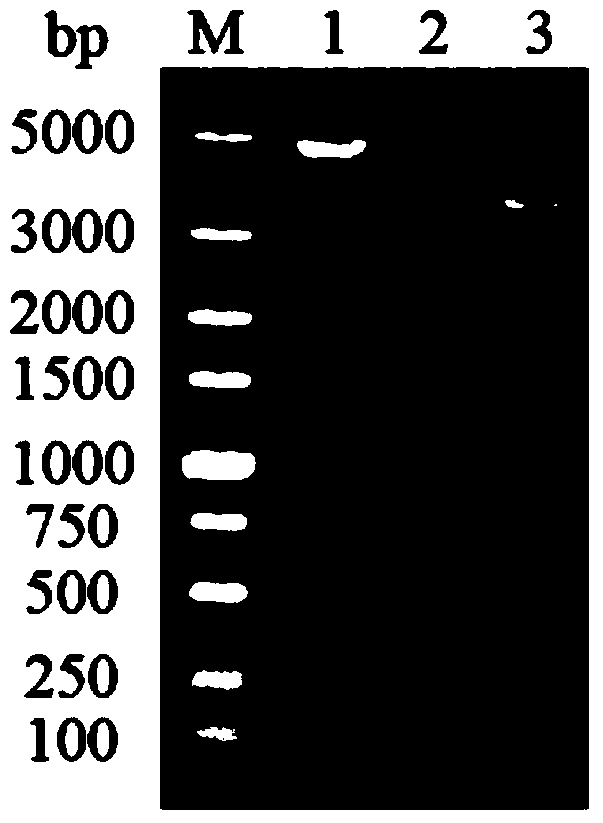
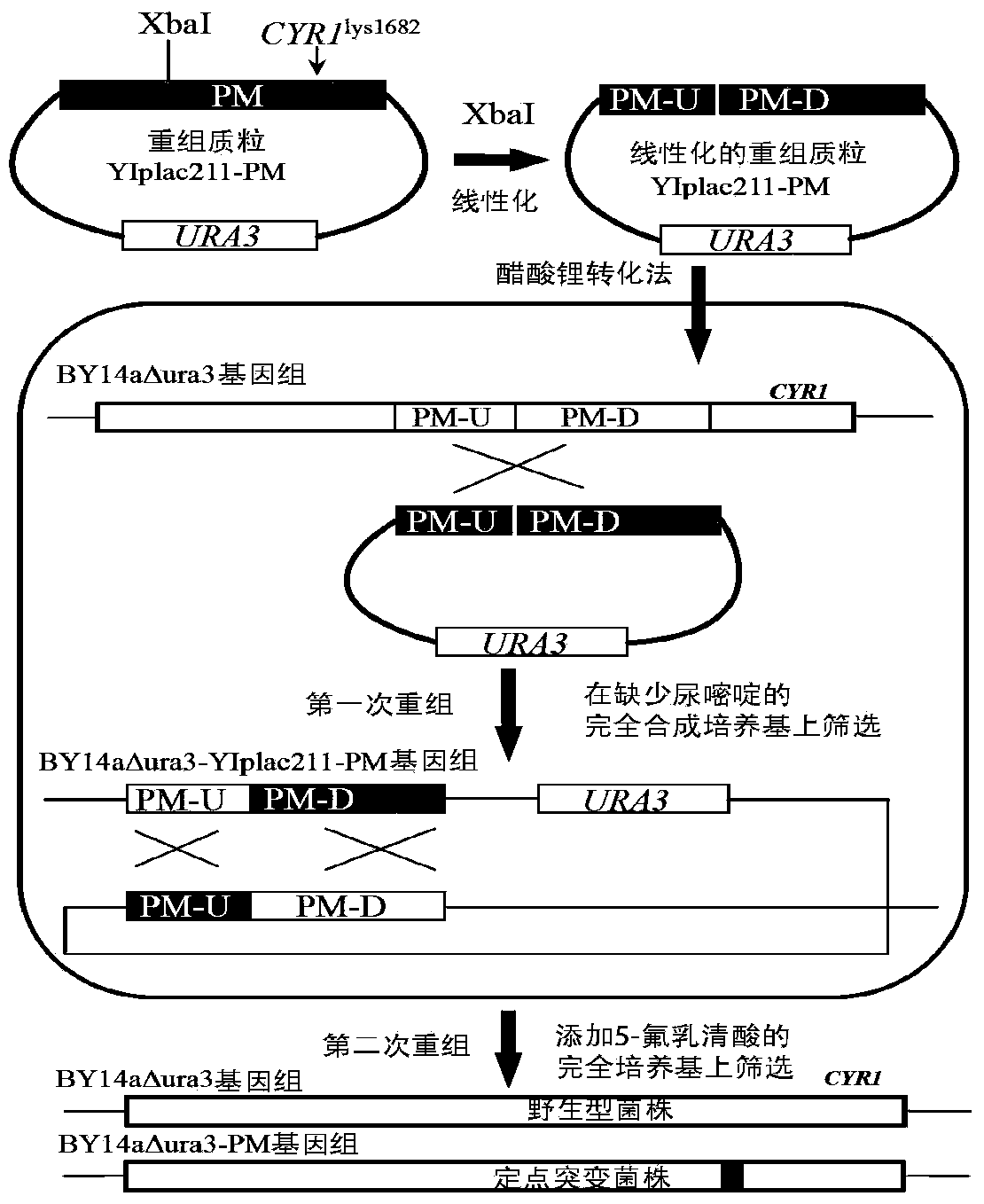
InactiveCN103589748AAvoid spreadingEasy to operateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyYeast
The invention discloses a method for introducing site-specific mutagenesis rapidly and efficiently. The method provided by the invention can realize the introduction of site-specific mutagenesis by using an integrated plasmid YIplac211 as the carrier, selecting URA3 gene carried by the integrated plasmid as selection marker, and carrying out homologous recombination of direct repeats twice. According to the invention, no exogenous gene remains during the introduction of site-specific mutagenesis so as to ensure the safety of strains. Additionally, the method provided by the invention can also use other industrial strains besides yeast.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
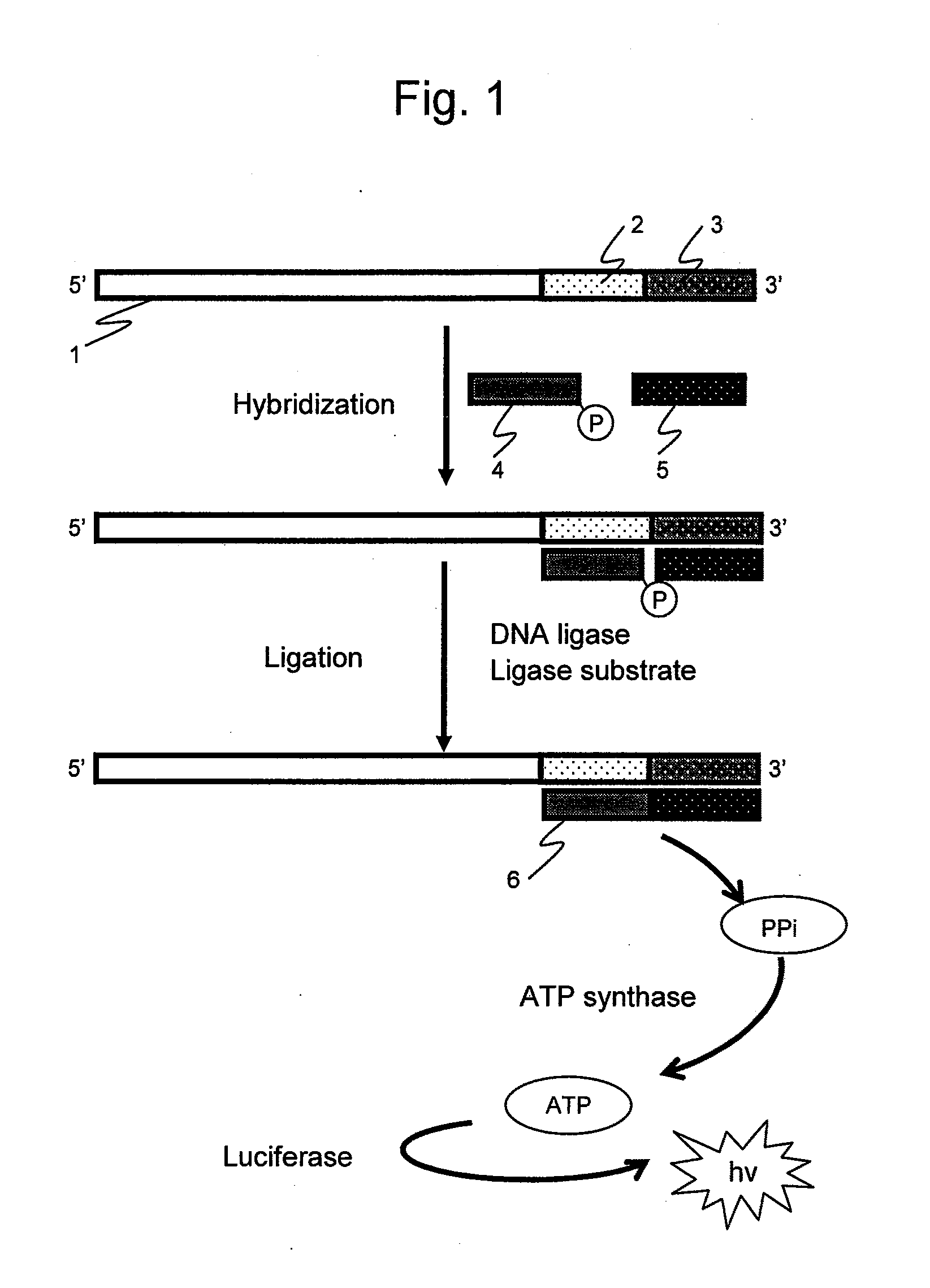
Sequence analysis method
InactiveUS20100167281A1Easy to detectFacilitate conductionMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisNucleotide
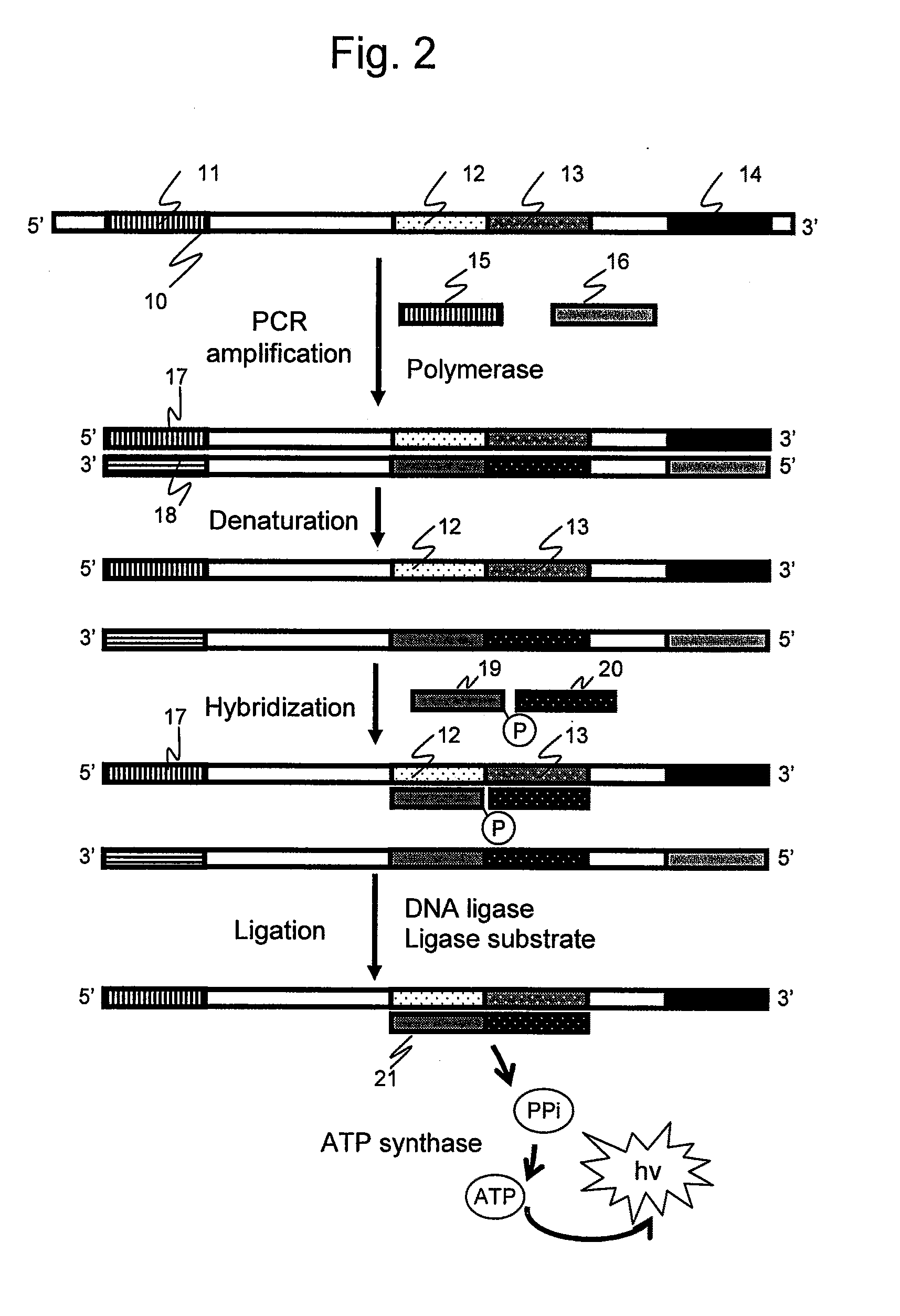
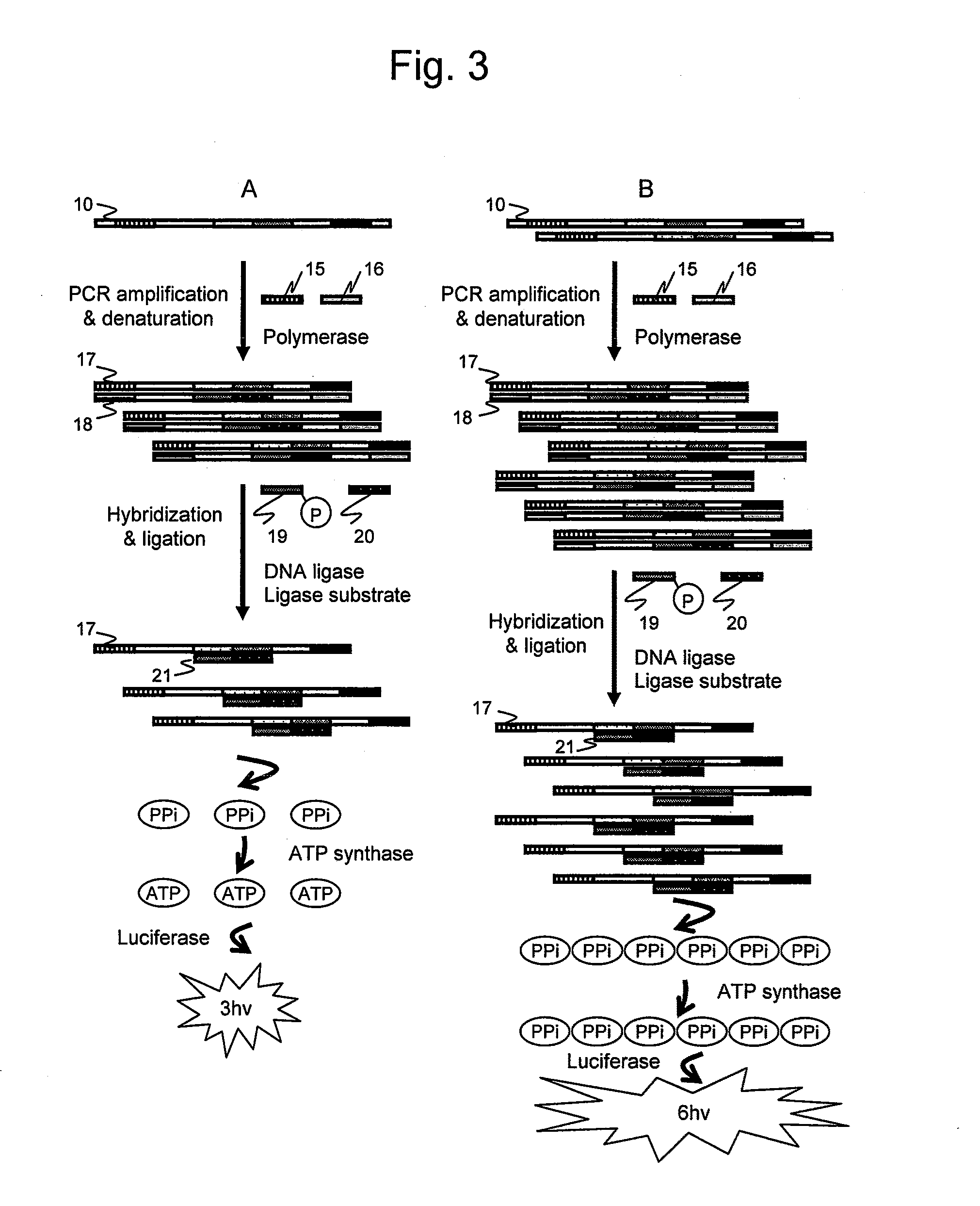
It is intended to provide an assay for the presence, absence or amount of a nucleic-acid fragment having a certain nucleotide sequence, for example, a polyA length, a difference in the number of repetition of a direct repeat sequence (e.g., microsatellite), single nucleotide substitution (or single nucleotide polymorphism), and nucleotide sequence insertion or deletion, and to provide a genetic testing using the same. The present invention relates to a nucleotide analysis method, comprising: hybridizing at least two probes to a nucleic-acid fragment; ligating the at least two probes using ligase; exchanging, to ATP, pyrophosphoric acid produced through the ligation reaction; and detecting chemiluminescence reaction dependent on the ATP.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Mobilization of viral genomes from T-DNA using site-specific recombination systems
InactiveUS7364902B2Simplifying construction and stable maintenanceImprove efficiencySugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSite-specific recombinationPlant cell
The invention relates to methods and compositions for site-specific recombinase-mediated mobilization of viral replicons and associated DNAs of interest from T-DNA. The methods of the invention comprise Agrobacterium-mediated transfer of T-DNA to a plant cell, wherein the T-DNA contains a viral replicon flanked by directly repeated target sites for a site-specific recombinase and optionally a DNA of interest linked to the viral replicon. The DNA of interest may also contain a non-identical target site for the recombinase. An expression cassette for the site-specific recombinase is present on the T-DNA or the plant genome, or is transiently introduced into the plant cell. Expression of the site-specific recombinase in the plant cell results in excision of the viral replicon and the associated DNA of interest. The viral replicon and DNA of interest are then replicated to high copy number in the host plant cell. The compositions of the invention comprise nucleic acids, such as T-DNAs containing a viral DNA flanked by directly repeated target sites for a site-specific recombinase. The nucleic acids of the invention may additionally contain expression cassettes encoding the cognate site-specific recombinase for the target sites flanking the viral genome. The compositions of the invention further comprise Agrobacterium containing the nucleic acids of the invention.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Oligonucleotide composition, kit, method and application for detecting hepatitis B virus rcDNA and/or cccDNA
ActiveCN109321679BMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHepatitis B immunizationNucleotide
The invention discloses an oligonucleotide composition and a method for detecting hepatitis B virus (HBV) rcDNA (Relaxed Circular deoxyribonucleic acid) and / or cccDNA (Covalently Closed Circular DNA), a kit and application of the oligonucleotide composition. The oligonucleotide composition comprises first oligonucleotide, second oligonucleotide, or oligonucleotide complementary with the sequenceof the first oligonucleotide and oligonucleotide complementary with the sequence of the second oligonucleotide; the first oligonucleotide is specifically combined with at least one part of continuoussequence of the first sequence, and the second oligonucleotide is specifically combined with at least one part of continuous sequence of the second sequence; in addition, a distance between two continuous sequences is 30-350 nt; the first sequence is a sequence between DR (Direct Repeat) 2-DR1 of the HBV DR sequence of a cross-notch area which contains cccDNA or rcDNA, and the second sequence is asequence after the fifth basic group of the DR1. According to the oligonucleotide composition, the level of HBV rcDNA and / or cccDNA can be effectively detected without being affected by integrated HBV DNA.
Owner:北京旌准医疗科技有限公司
Methods and means for removal of a selected DNA sequence
Alternative and / or improved methods are described for the exact removal of a selected subfragment from a DNA molecule by intrachromosomal recombination between two directly repeated DNA sequences using a rare-cleaving double stranded break inducing DNA endonuclease expressed under control of a micro-spore specific promoter. These methods can be applied for the exact exchange of a target DNA fragment for a DNA fragment of interest in plant cells and plants.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
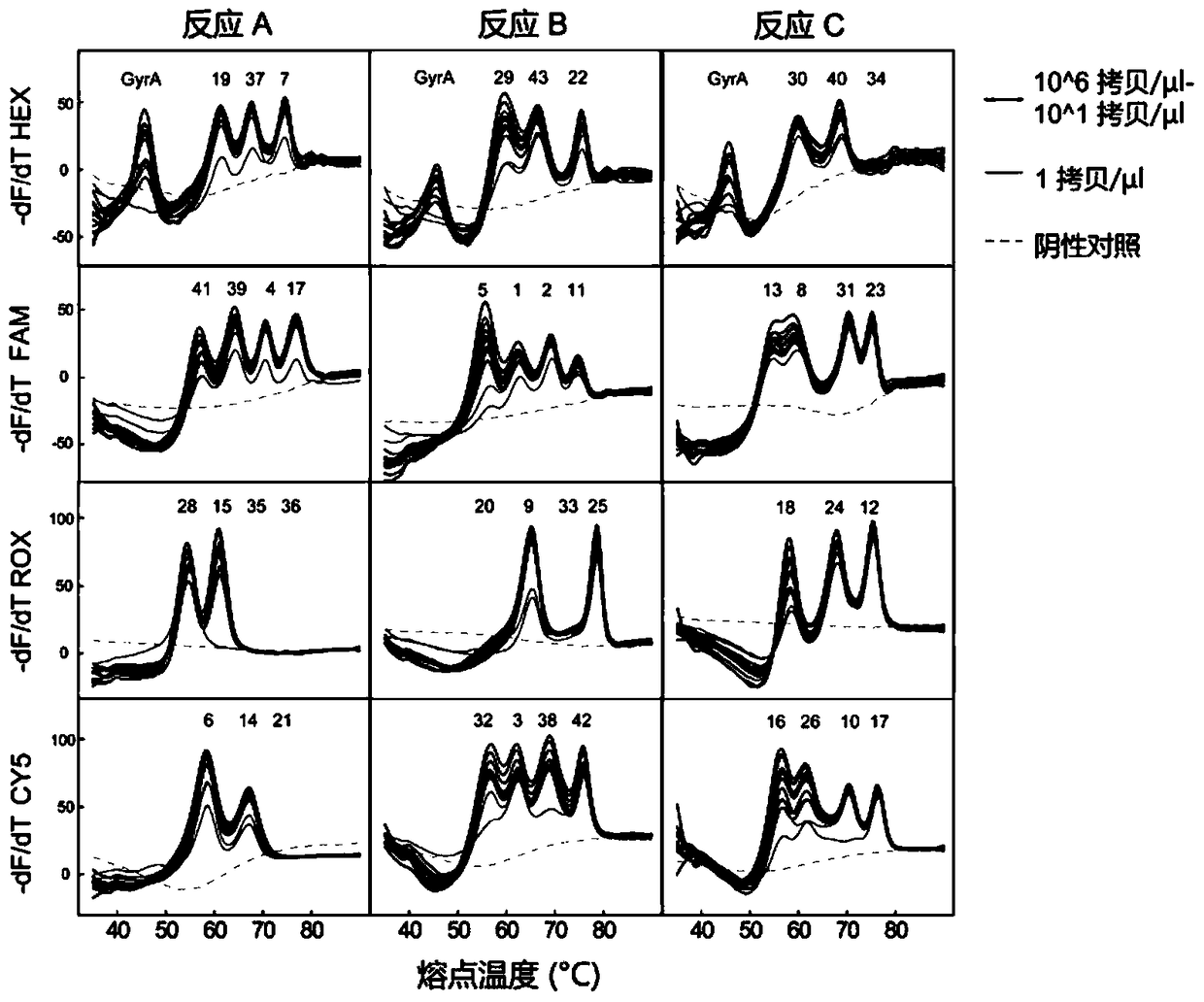
A method for genotyping Mycobacterium tuberculosis spacer oligonucleotides encoded by melting point
ActiveCN104862403BShort timeReduce manual operation timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFluorescenceDirect repeat
The invention discloses a mycobacterium tuberculosis spacer oligonucleotide typing method based on melting point coding and relates to mycobacterium tuberculosis. The method comprises the following steps: (1) designing a pair of universal primers on a direct repeat sequence to amplify all spacers, and designing a pair of primers in a GyrA conserved region; (2) designing four groups of double-tagging fluorescent probes specifically hybridized therewith according to 43 spacer sequences and GyrA sequences, and manually controlling the welding point value of each probe by adjusting the probe length and / or a base composition, wherein each probe is provided with the same fluorescent group; (3) distributing the fluorescent probes in three reaction tubes, wherein by the combination of the reaction tubes, the fluorescent groups and the welding point values, each spacer forms a three-dimensional code, and software automatically reads a result. The method has the advantages of simple and convenient one-step operation, high specificity, high repeatability, low time consumption and relatively low price, and a powerful tool is provided for exploration and research of the prevalence and propagation rule of tuberculosis in China.
Owner:XIAMEN ZEESAN BIOTECH
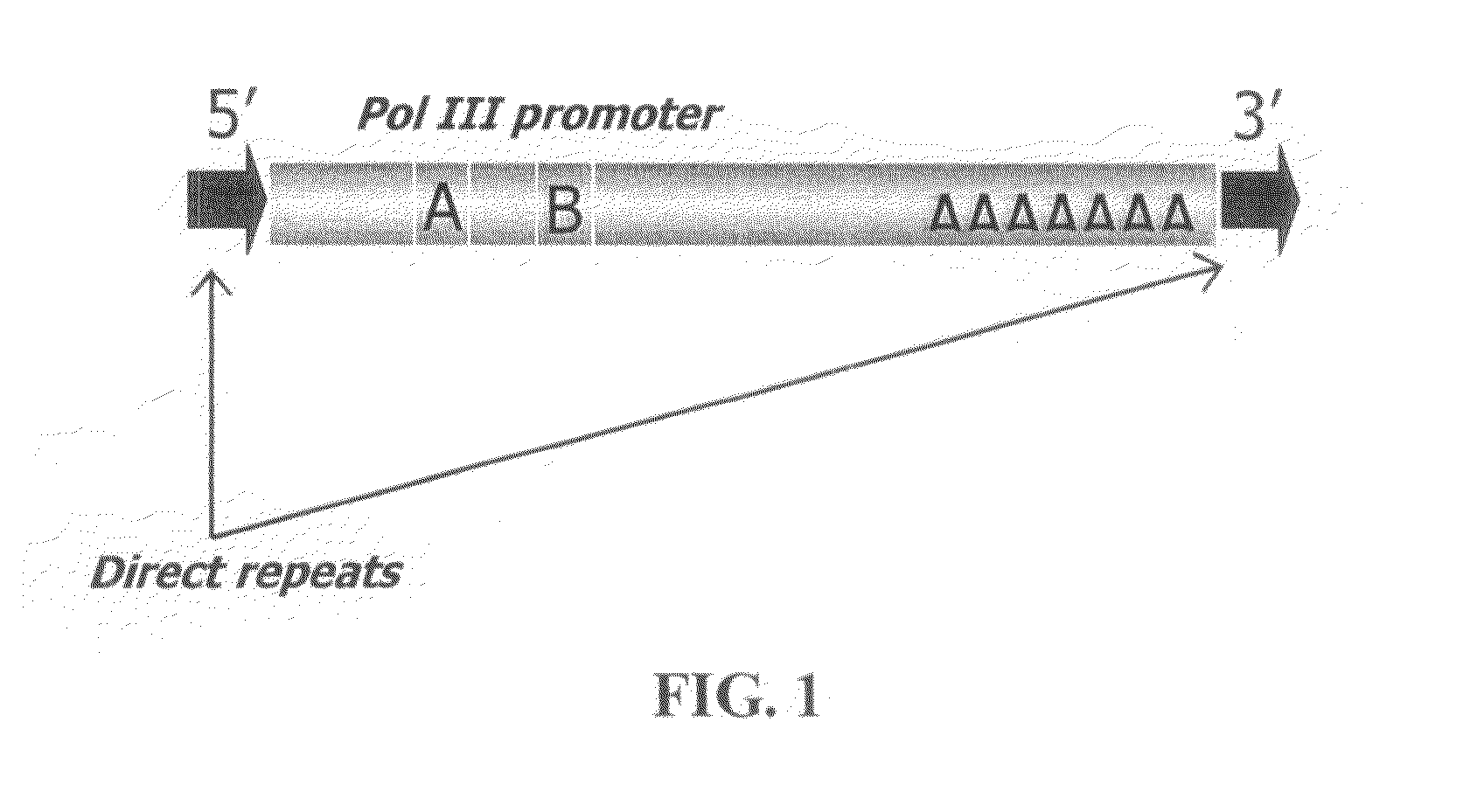
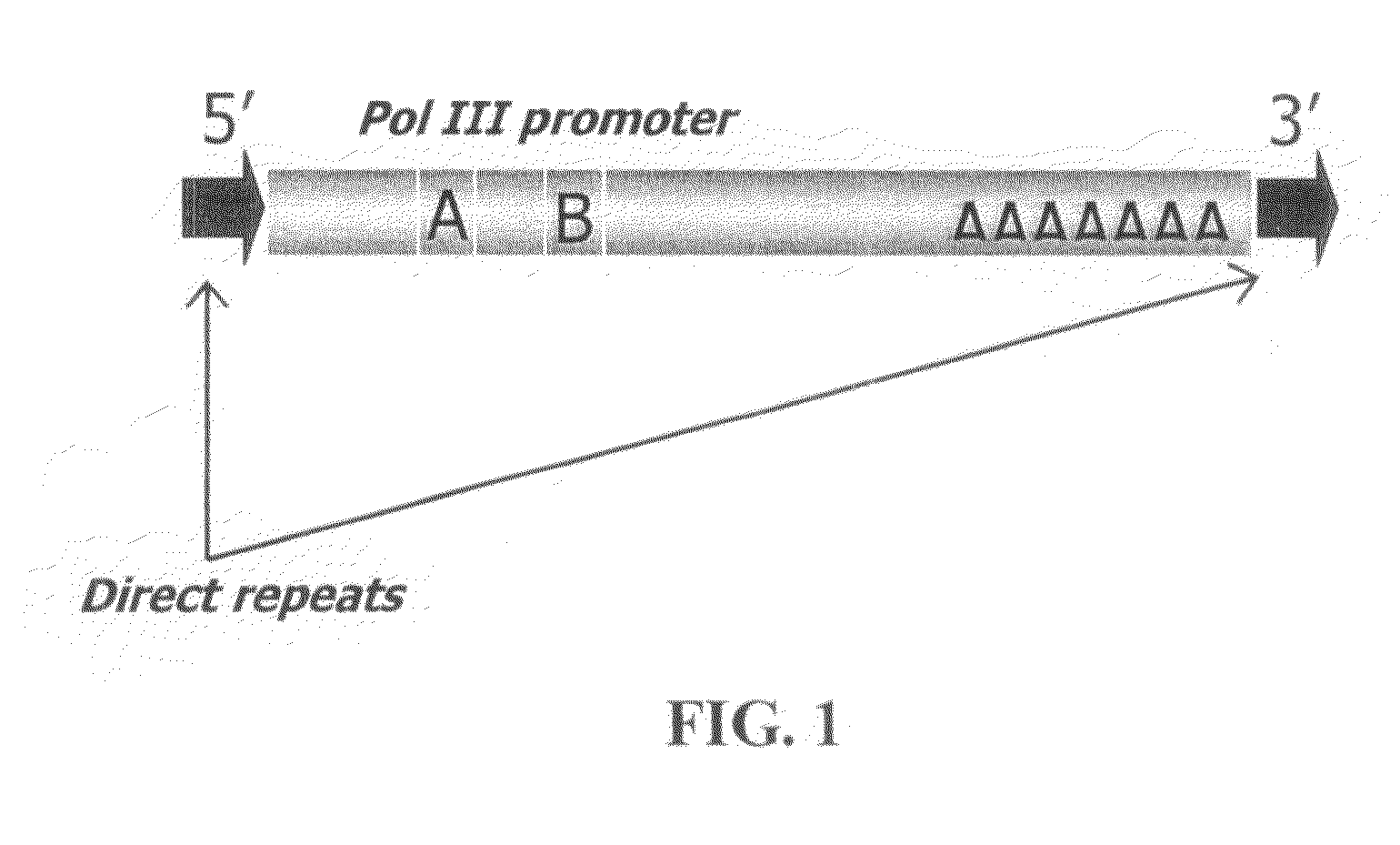
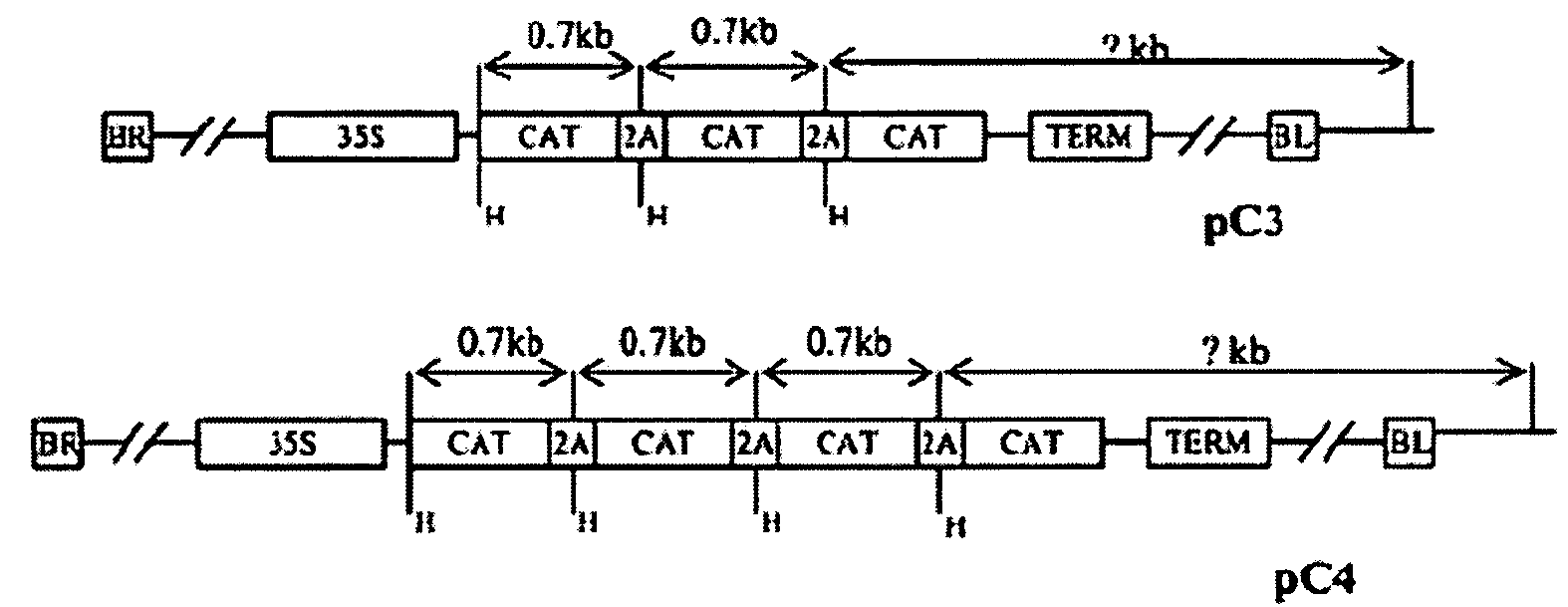
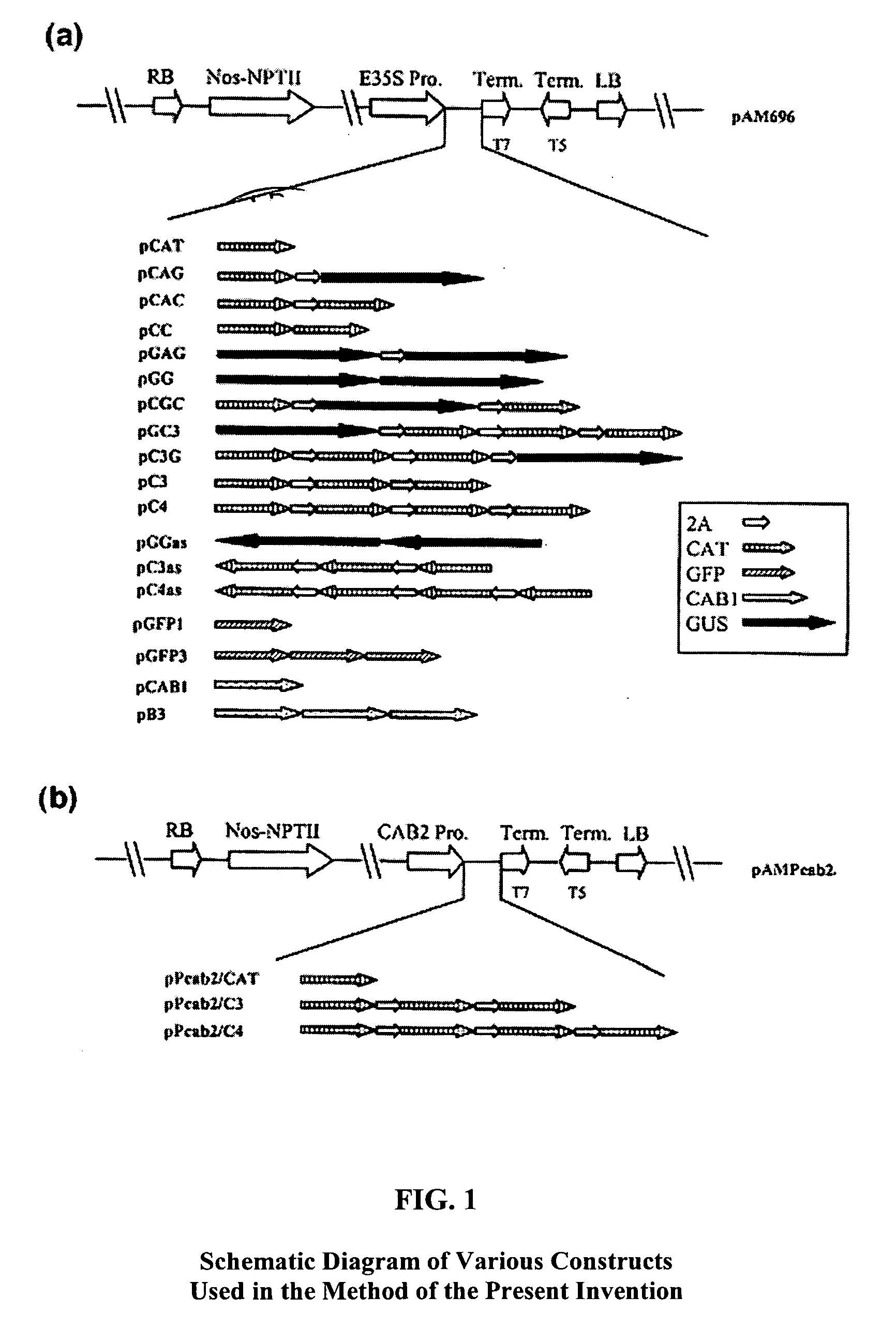
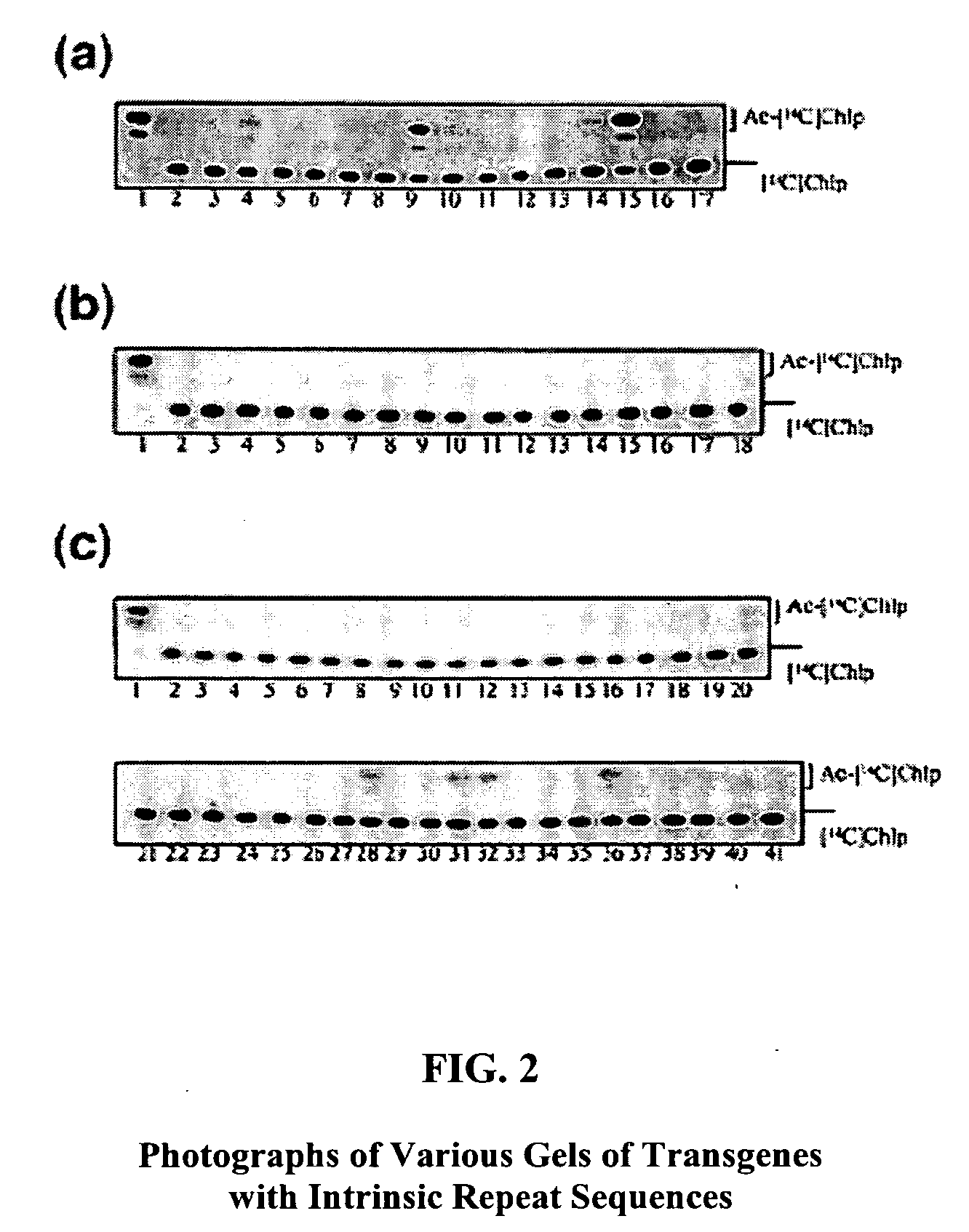
Method for efficient post-transcriptional gene silencing using intrinsic direct repeat sequences and utilization thereof in functional genomics
InactiveUS20080131874A1Efficient gene silencingMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenomicsNicotiana tabacum
It is well documented that transgenes with inverted repeats can efficiently trigger post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), presumably via a double stranded RNA induced by complementary sequences in their transcripts. We show here that transgenes with intrinsic direct repeats can also induce PTGS at a very high frequency (80-100%). A transgene with three or four repeats induced PTGS in almost 100% of the primary transformants, regardless of whether a strong (enhanced 35S promoter) or a relatively weak (chlorophyll a / b binding protein promoter) promoter was used. The PTGS induced by three or four repeats is consistently inherited in subsequent generations, and can inactivate homologous genes in trans. Based on the high frequency and consistent heritability, we propose that the intrinsic direct repeat within a transgene may act as a primary determinant of PTGS referred to as direct repeat-induced PTGS (driPTGS). Silencing occurred in all five genes, in this and two previous reports, suggesting that driPTGS might be a universal gene silencing mechanism both in dicotyledonous tobacco plants and monocotyledonous rice cells. In addition, driPTGS may help dissect the gene silencing mechanism and generate silenced phenotypes useful for research and plant biotechnology products.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com