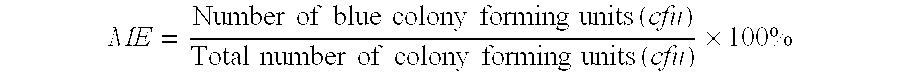Patents
Literature
168 results about "Circular DNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
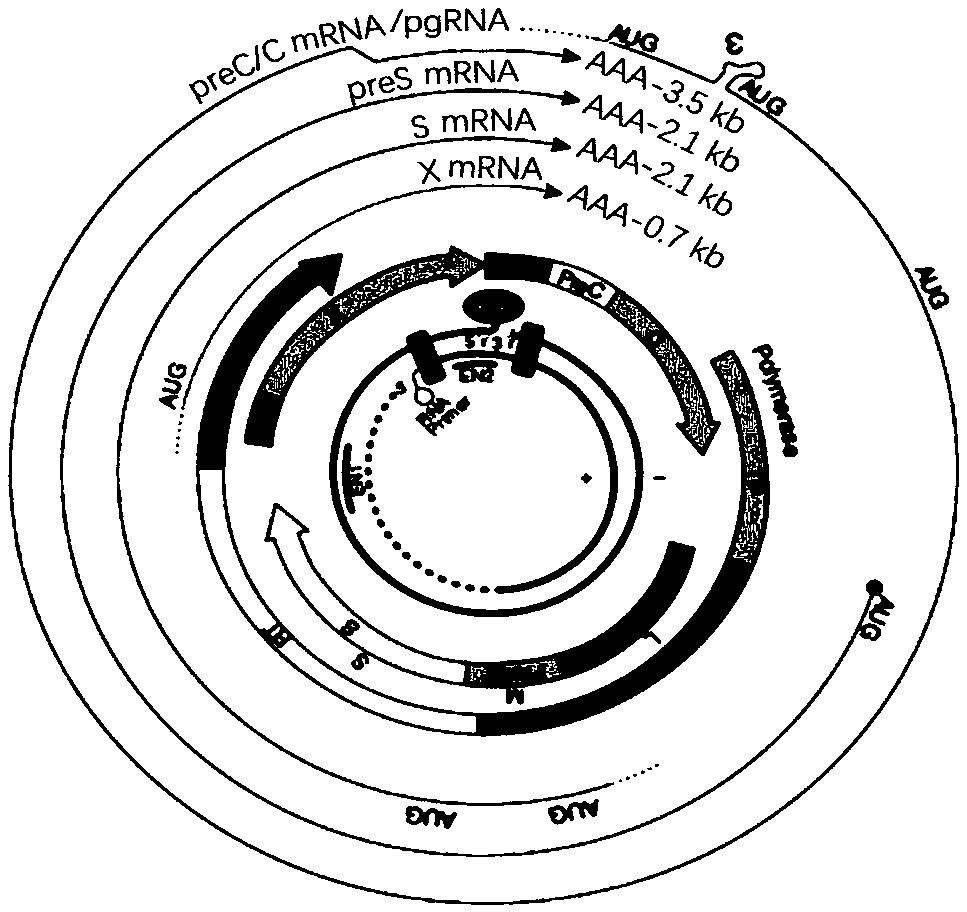
Circular DNA is a form of DNA that is found in viruses, bacteria and archaea as well as in eukaryotic cells in the form of either mitochondrial DNA or plastid DNA. This form of DNA does not contain histones. While the individual strands of a linear double helix represent two distinct and separable molecules, this need not be true for circular DNA.
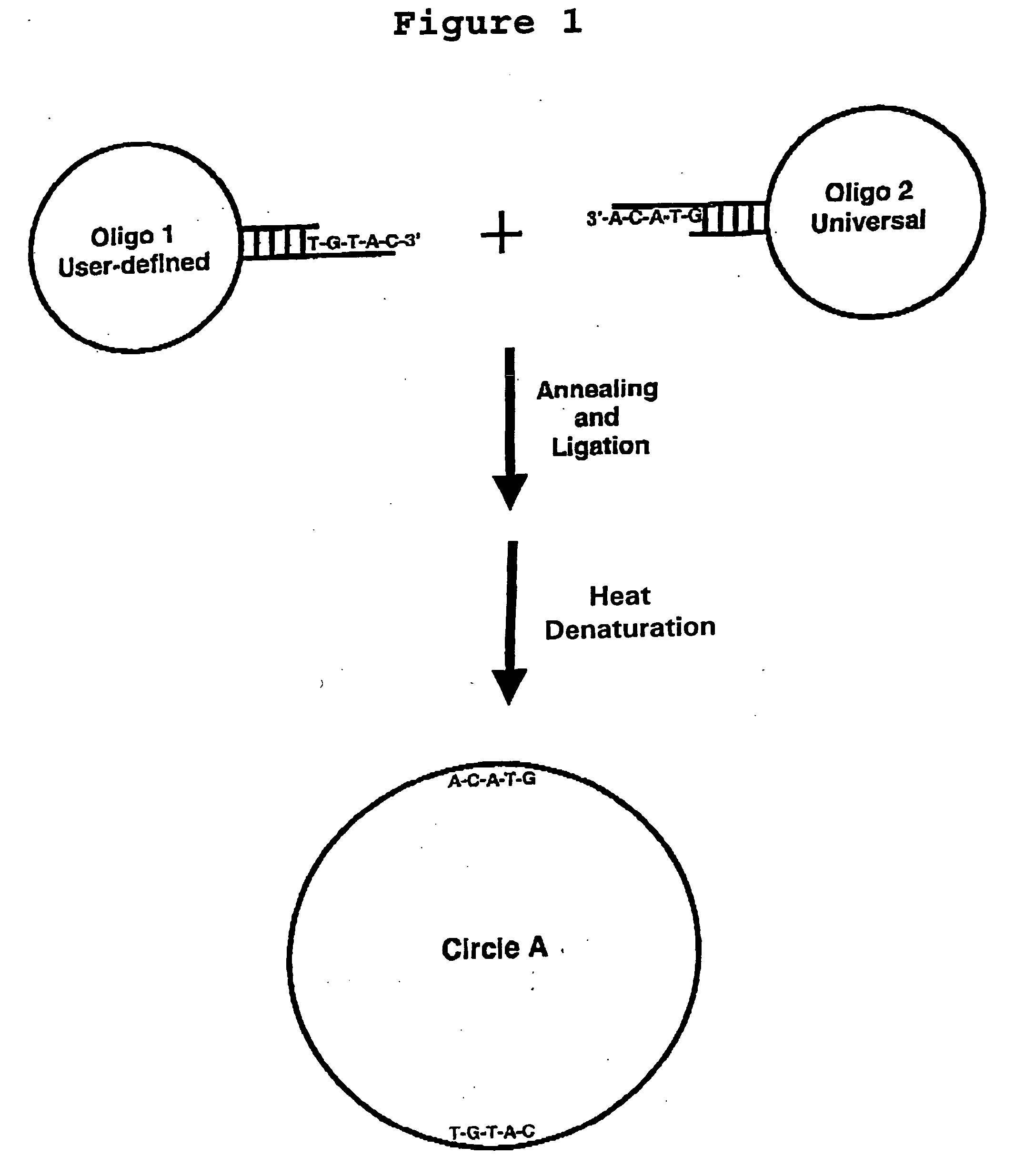
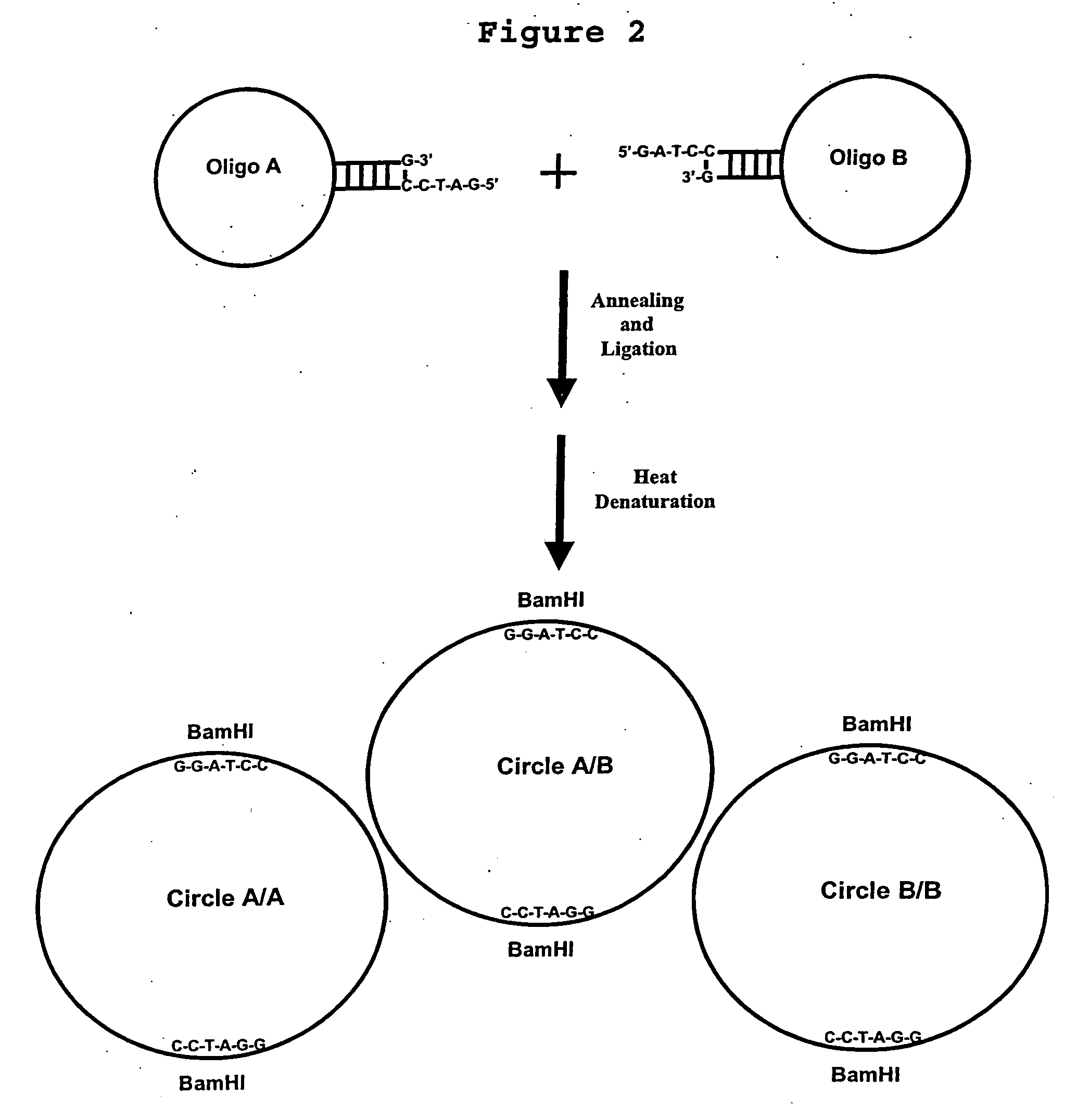
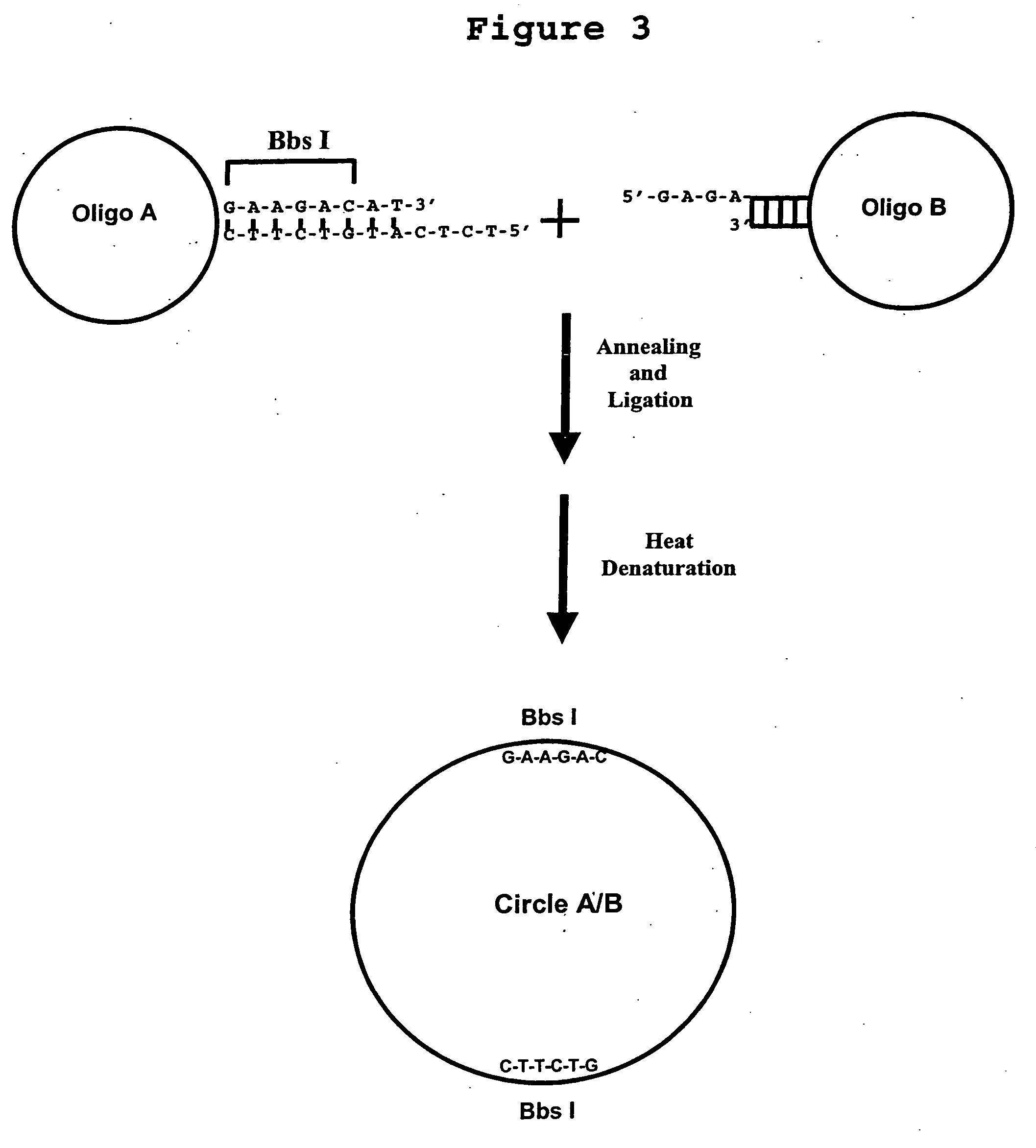
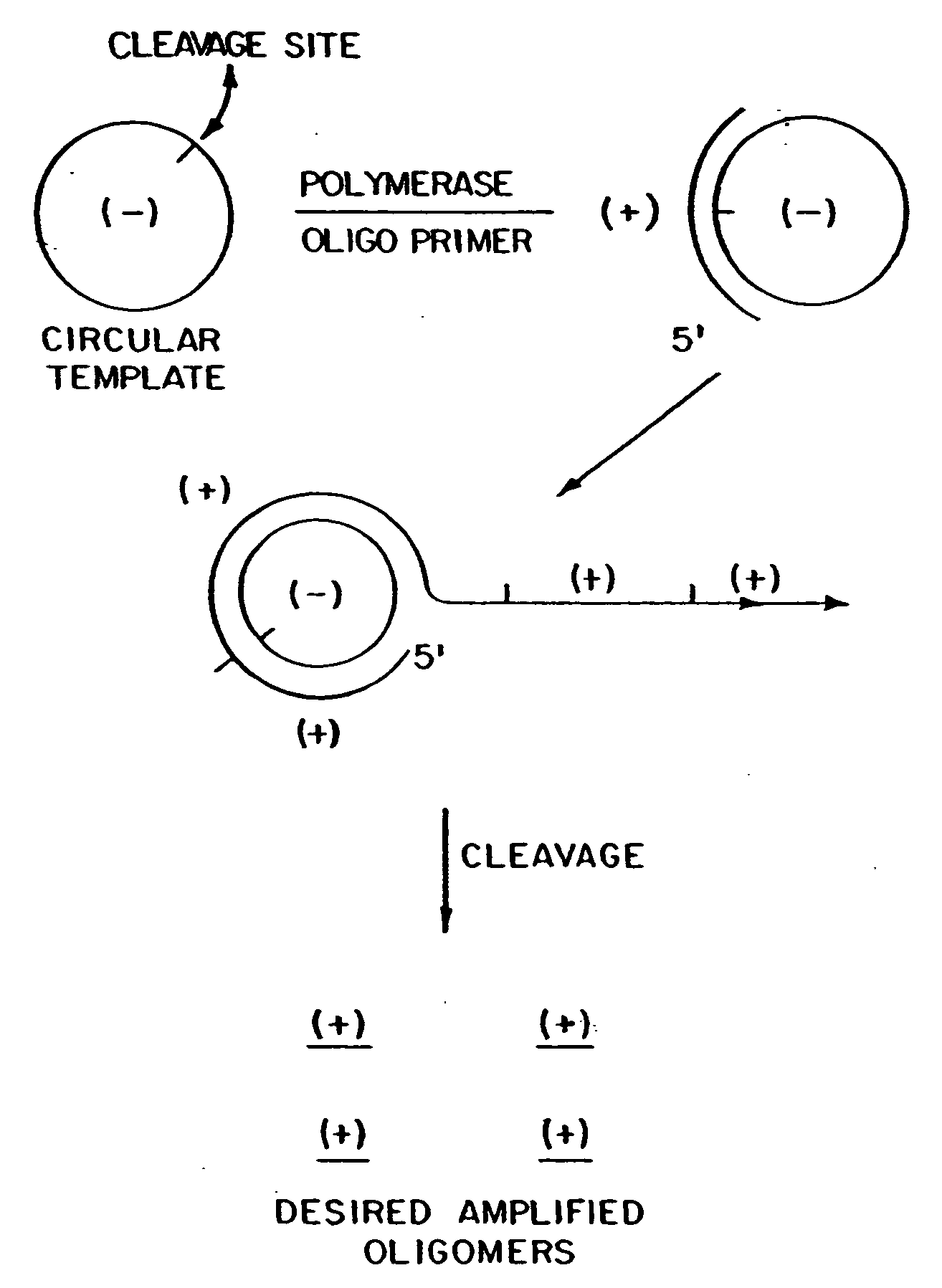
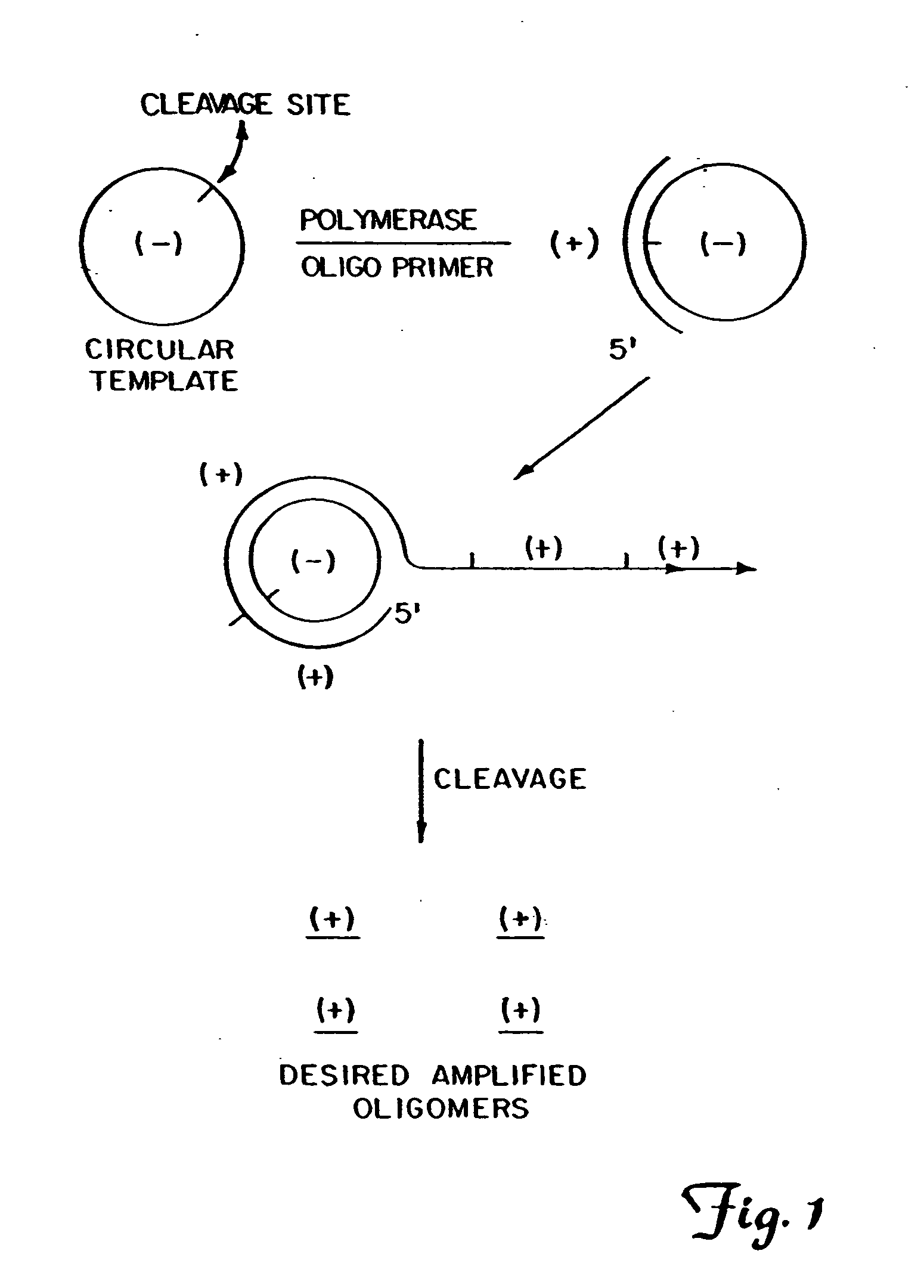
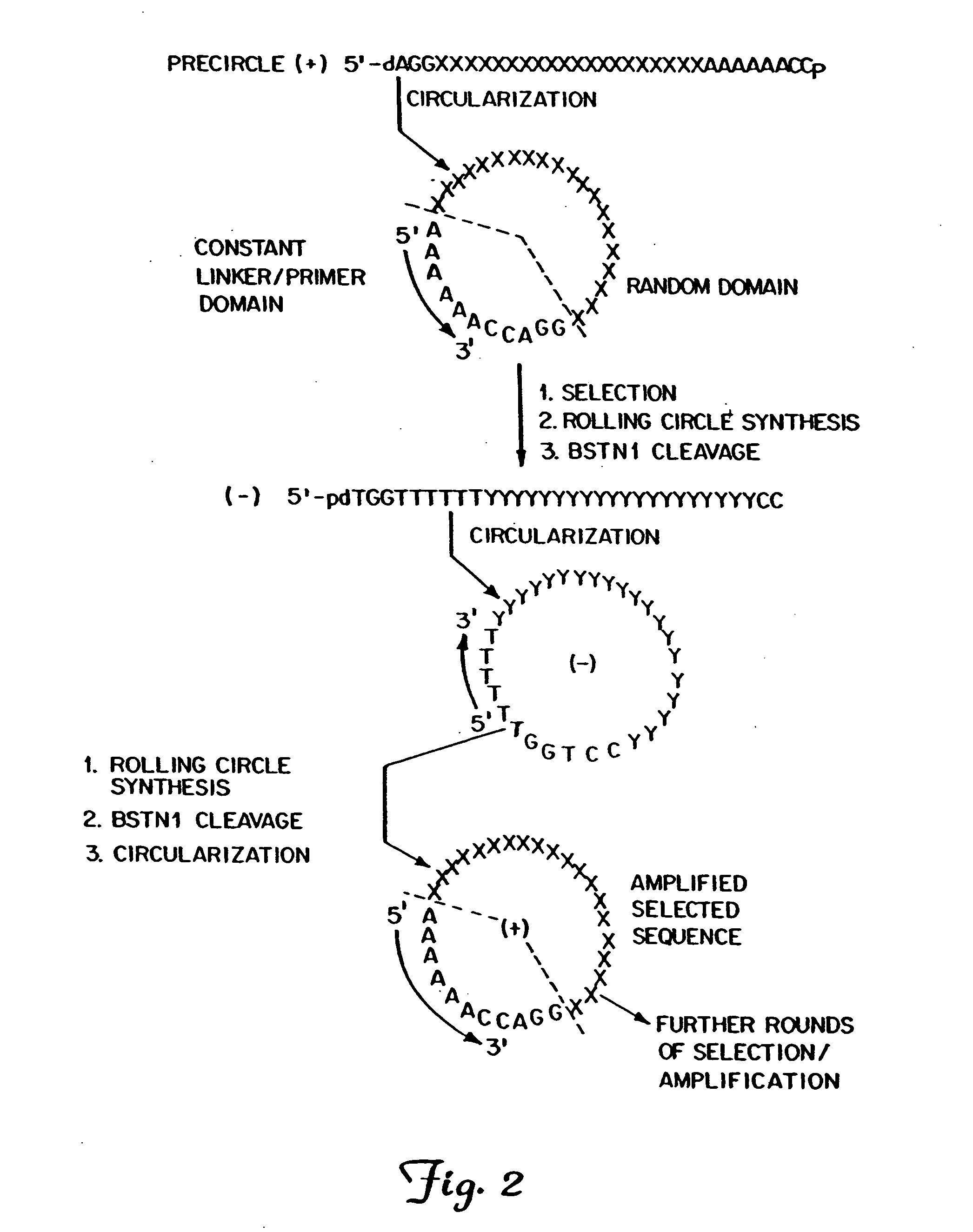
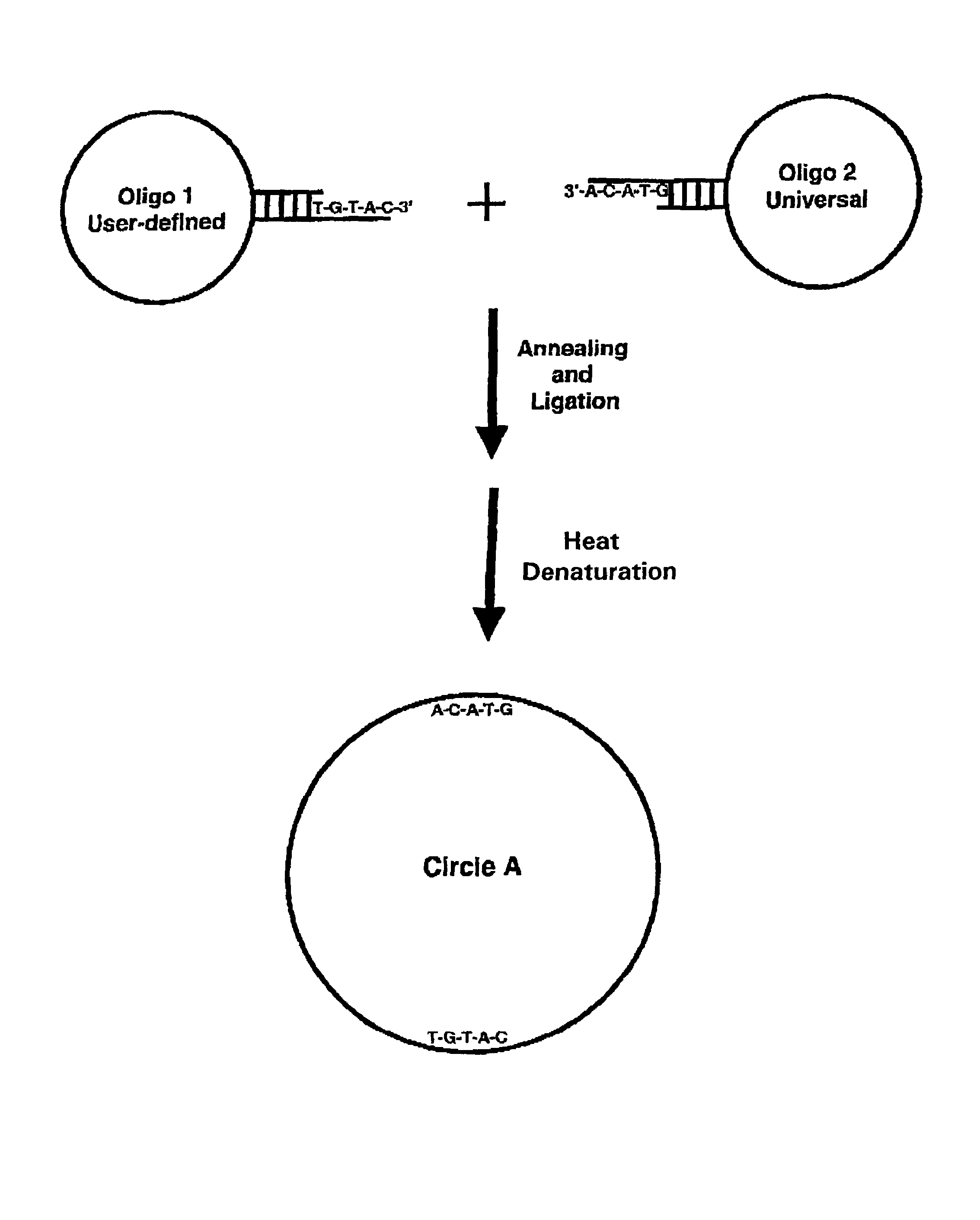
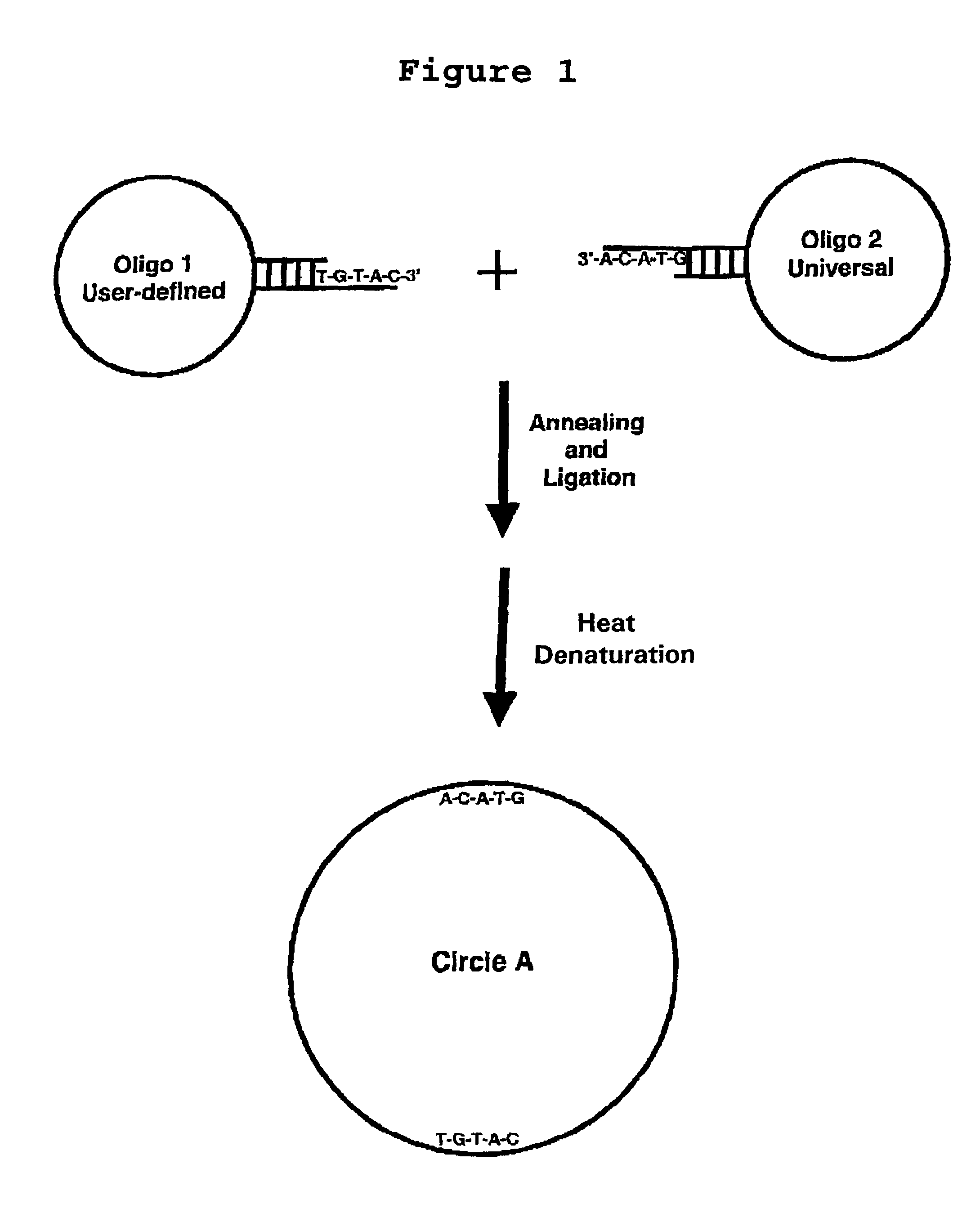
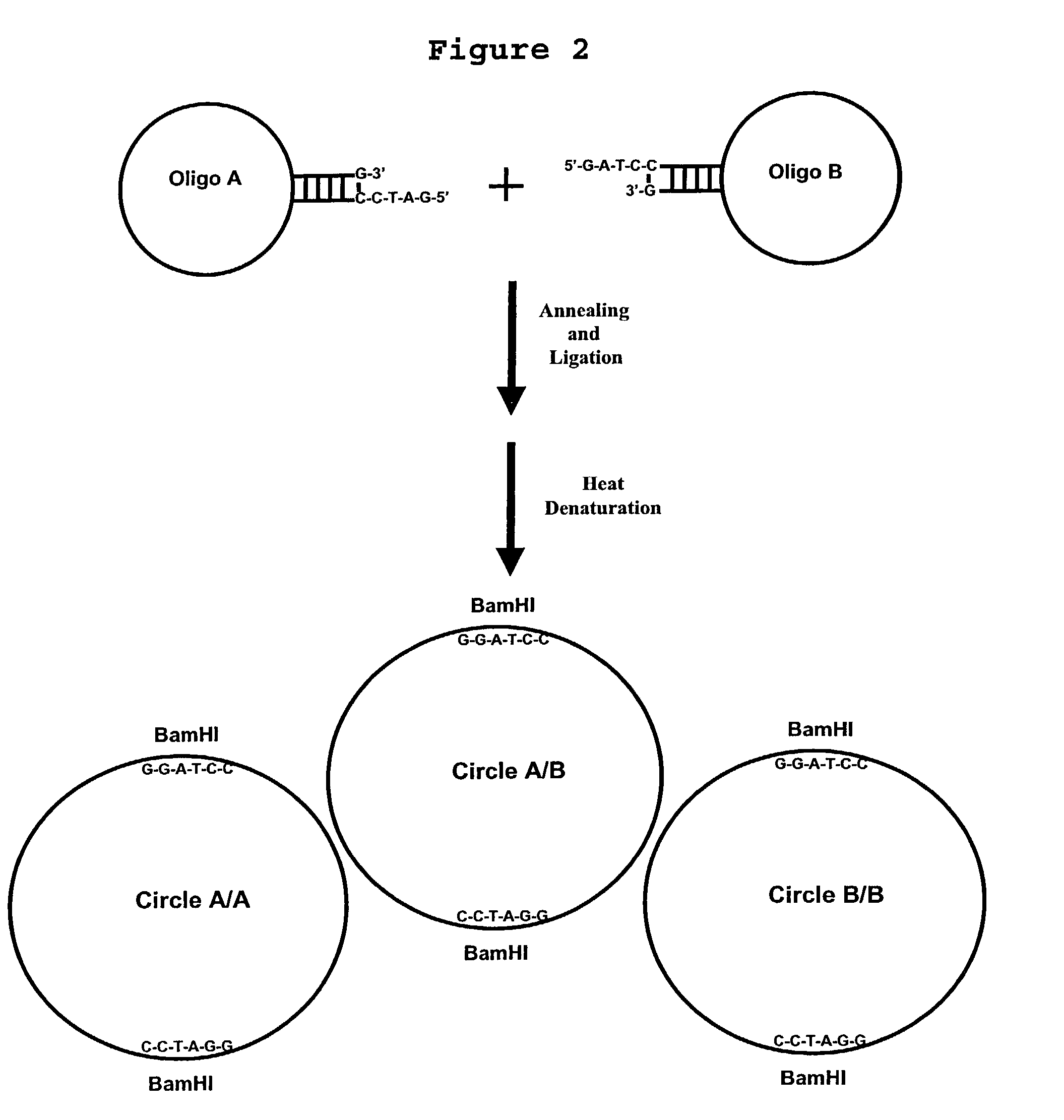
Generation of single-strand circular DNA from linear self-annealing segments
InactiveUS20070015182A1Convenient ligationEasy to copyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideSingle strand
The present invention provides a method for the rapid simultaneous production of a plurality of single-stranded DNA circles having a predetermined size and nucleotide sequence using pre-designed hairpin oligonucleotides containing complementary sequences for directing ligation to form dumbbell-shaped monomers followed by heat denaturation to yield single-stranded DNA circles.
Owner:ABARZUA PATRICIO
Protein expression profiling
InactiveUS6921642B2Easy to detectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteProtein expression profile
Disclosed are compositions and methods for detecting small quantities of analytes such as proteins and peptides. The method involves associating a primer with an analyte and subsequently using the primer to mediate rolling circle replication of a circular DNA molecule. Amplification of the DNA circle is dependent on the presence of the primer. Thus, the disclosed method produces an amplified signal, via rolling circle amplification, from any analyte of interest. The amplified DNA remains associated with the analyte, via the primer, and so allows spatial detection of the analyte. The disclosed method can be used to detect and analyze proteins and peptides. Multiple proteins can be analyzed using microarrays to which the various proteins are immobilized. A rolling circle replication primer is then associated with the various proteins using a conjugate of the primer and a molecule that specifically binds the proteins to be detectable. Rolling circle replication from the primers results in production of a large amount of DNA at the sites in the array where the proteins are immobilized. The amplified DNA serves as a readily detectable signal for the proteins. The disclosed method can also be used to compare the proteins expressed in two or more different samples. The information generated is analogous to the type of information gathered in nucleic acid expression profiles. The disclosed method allows sensitive and accurate detection and quantitation of proteins expressed in any cell or tissue.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Circular DNA vectors for synthesis of RNA and DNA
InactiveUS20080227160A1Low-cost and efficientEasy to identifySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsRibonucleotide synthesisRibonucleotide
The present invention provides methods for synthesis and therapeutic use of DNA and RNA oligonucleotides and analogs. RNA oligonucleotides are synthesized using a small, circular DNA template which lacks an RNA polymerase promoter sequence. The RNA synthesis is performed by combining a circular single-stranded oligonucleotide template with an effective RNA polymerase and at least two types of ribonucleotide triphosphate to form an RNA oligonucleotide multimer comprising multiple copies of the desired RNA oligonucleotide sequence. Preferably, the RNA oligonucleotide multimer is cleaved to produce RNA oligonucleotides having well-defined ends. Preferred RNA oligonucleotide multimers contain ribozymes capable of both cis (autolytic) and trans cleavage.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
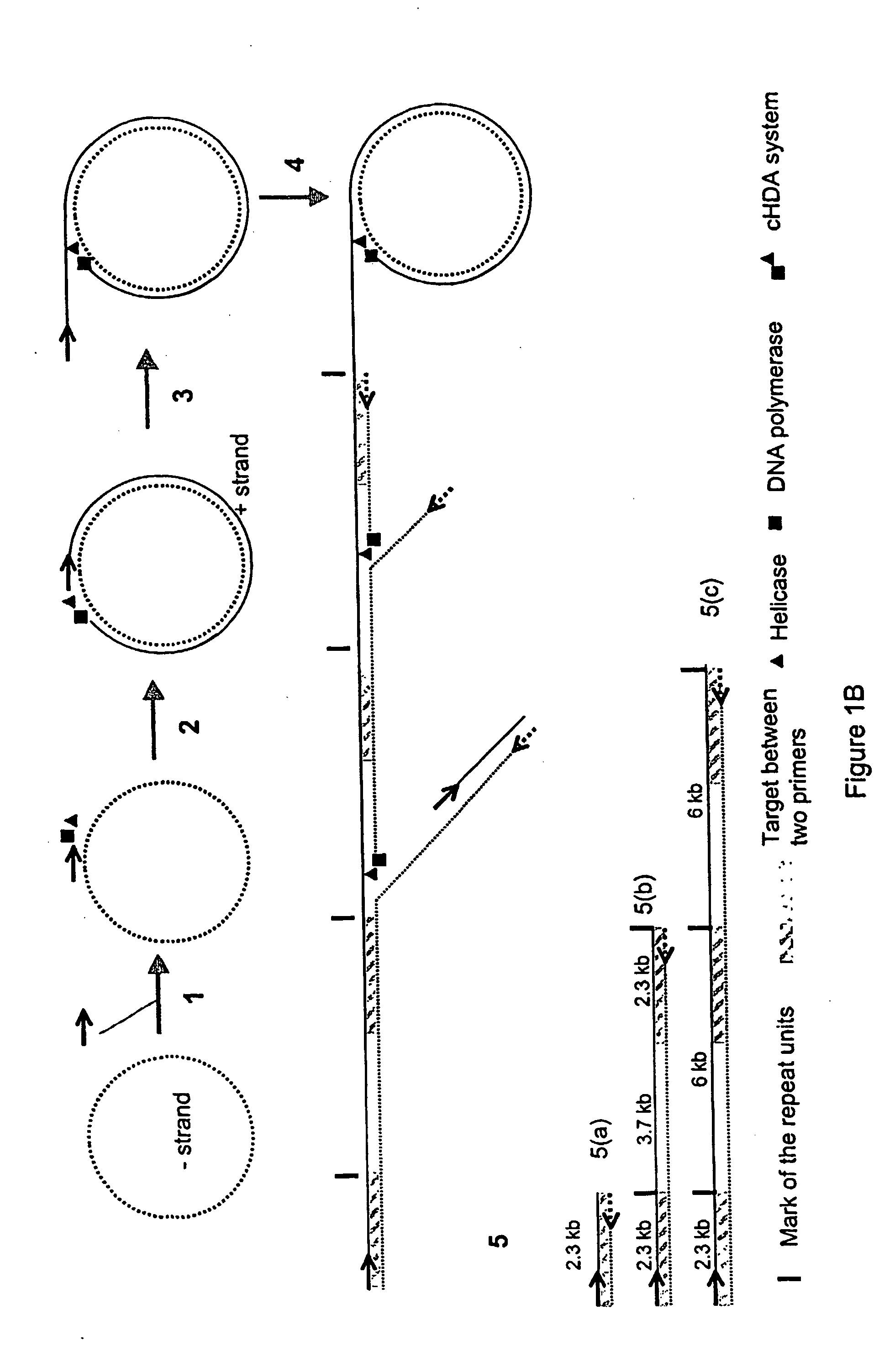
Helicase-dependent amplification of circular nucleic acids
InactiveUS20100075384A1Microbiological testing/measurementTransferasesDNA unwinding enzymePolymerase L
A helicase-mediated amplification method for circular DNA templates and target DNA sequences within the templates is provided. The method combines a DNA polymerase and a helicase preparation to amplify a target sequence as well as the entire circular DNA template.
Owner:BIOHELIX CORP
Amplification and cloning of single DNA molecules using rolling circle amplification
ActiveUS8497069B2Easy to startMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCell freeAmplification dna
Owner:TELESIS BIO INC
Methods for nucleic acid mapping and identification of fine-structural-variations in nucleic acids
ActiveUS20090325239A1Quick buildEfficient sortingSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid mappingA-DNA
A method of juxtaposing sequence tags (GVTs) that are unique positional markers along the length of a population of target nucleic acid molecules is provided, the method comprising: fragmenting the target nucleic acid molecule to form target DNA insert; ligating the target DNA insert to a DNA vector or backbone to create a circular molecule; digesting the target DNA insert endonuclease to cleave the target DNA insert at a distance from each end of the target DNA insert yielding two GVTs comprising terminal sequences of the target DNA insert attached to an undigested linear backbone; recircularizing the linear backbone with the attached GVTs to obtain a circular DNA containing a GVT-pair having two juxtaposed GVTs; and recovering the GVT-pair DNA by nucleic acid amplification or digestion with endonuclease having sites flanking the GVT-pair. Cosmid vectors are provided for creating GVT-pairs of ˜45- to 50-kb separation sequencable by next-generation DNA sequencers.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
Method of amplifying a target nucleic acid by rolling circle amplification
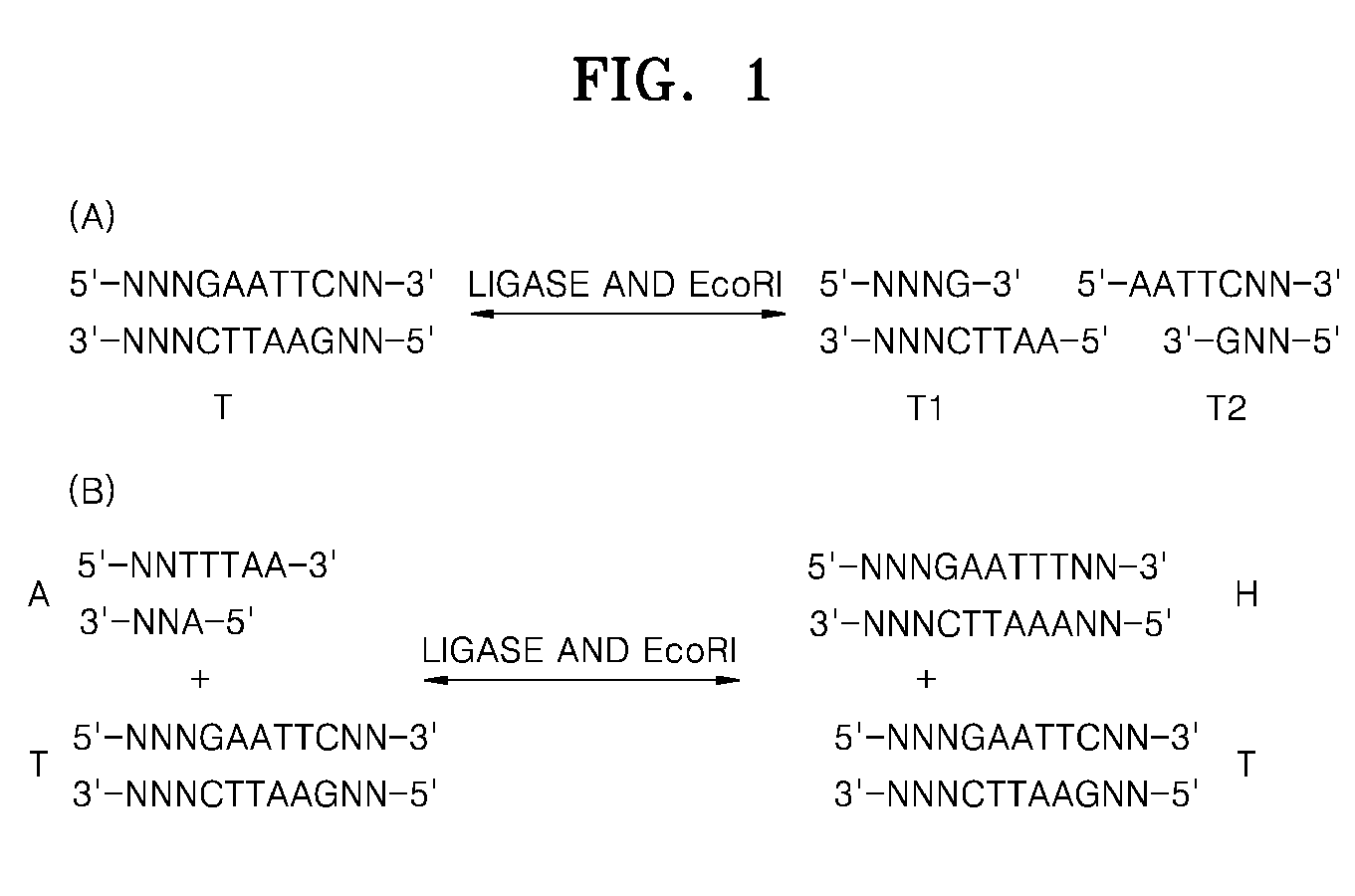
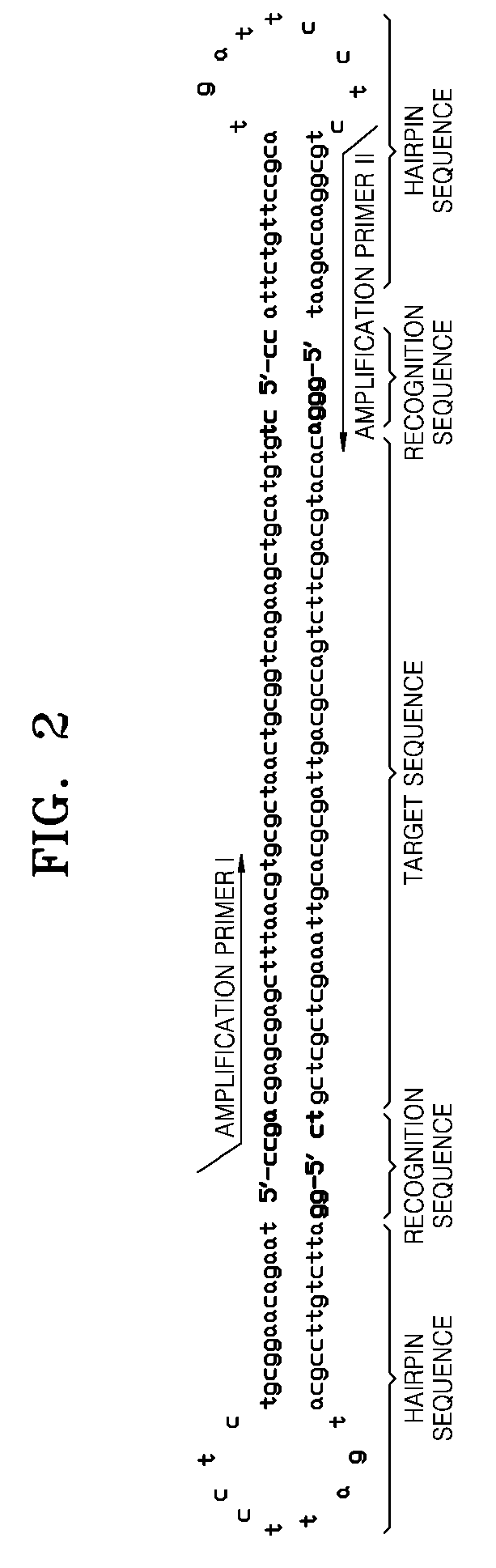
Provided is kit for and a method of amplifying a nucleic acid using rolling cyclic amplification (RCA), including amplifying a nucleic acid together with formation of a single-strand circular DNA template using RCA by reacting a reaction solution including: (a) two hairpin oligos, (b) a target nucleic acid, (c) a DNA ligase,(d) an endonuclease, (e) a DNA polymerase, and (f) a primer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Paired-end library construction method and method for sequencing genome by using library
InactiveCN102181943AReduce workloadLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionGenomic sequencingDNA fragmentation
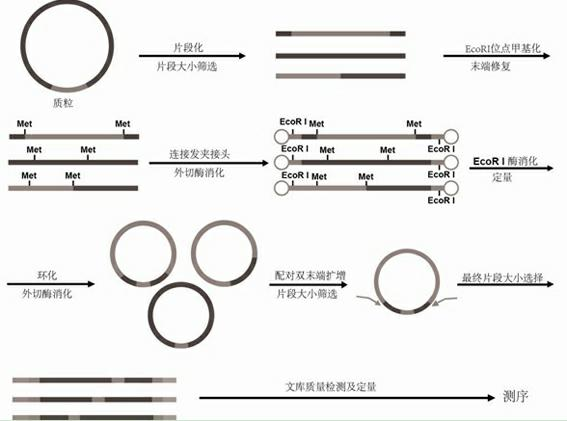
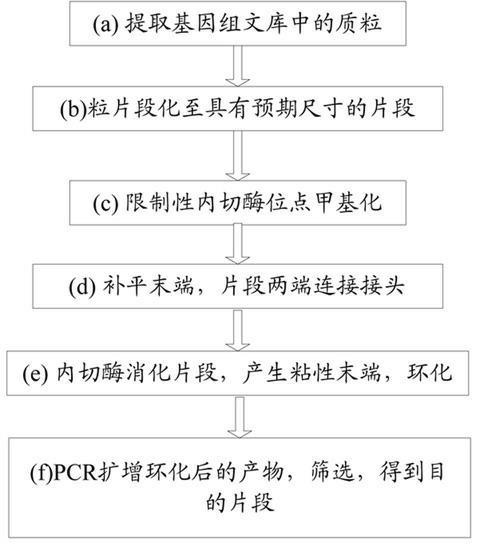
The invention relates to a paired-end library construction method and a method for sequencing a genome by using the library. The paired-end library construction method comprises the following steps of: performing plasmid extraction on clone in a constructed genome DNA library, fragmenting the extracted plasmid DNA, performing methyl protection on the restriction endonuclease site on the fragmented DNA, adding a hairclip type joint, performing enzyme cutting and cyclization to obtain circular DNA, then amplifying the genome library paired-end fragment in the circular DNA through a pair of composite primers to obtain a paired-end sequence of ultra-long span, and finally performing high flux sequencing. The paired-end sequence obtained by using the method can be applied to splicing of a new species genome sequence so as to further improve the splicing quality.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for using DNA tetrahedron as scaffold on nano-particle surface and initiating rolling circle amplification reaction
InactiveCN104388563AEffective control of distribution densityImprove hybridization efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle strandA-DNA
The invention relates to a method for using a DNA tetrahedron as a scaffold on a nano-particle surface and initiating rolling circle amplification reaction; after the prepared DNA tetrahedron is assembled on the nano-particle surface, a section of single-stranded DNA extending on the DNA tetrahedron can be used as primer DNA; circular DNA complementary with a special aptamer sequence is used as an amplification template; the circular DNA is hybridized with the primer DNA while the rolling circle amplification reaction is initiated; and the prepared product is multiple long single-stranded DNA composed of multiple apatmer structures on the nano-particle surface. The method disclosed by the invention is capable of effectively regulating and controlling the DNA distribution density on the nano-particle surface, so that the hybridization efficiency of the primer DNA and the circular DNA is increased; by means of long single-stranded DNA composed of the multiple aptamer structures prepared through the rolling circle amplification technology, the CTC (Carbon Tetra Choride) capture efficiency is greatly increased; and thus, the method disclosed by the invention has potential application value in the research fields, such as cell detection, cell capture, cell imaging and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
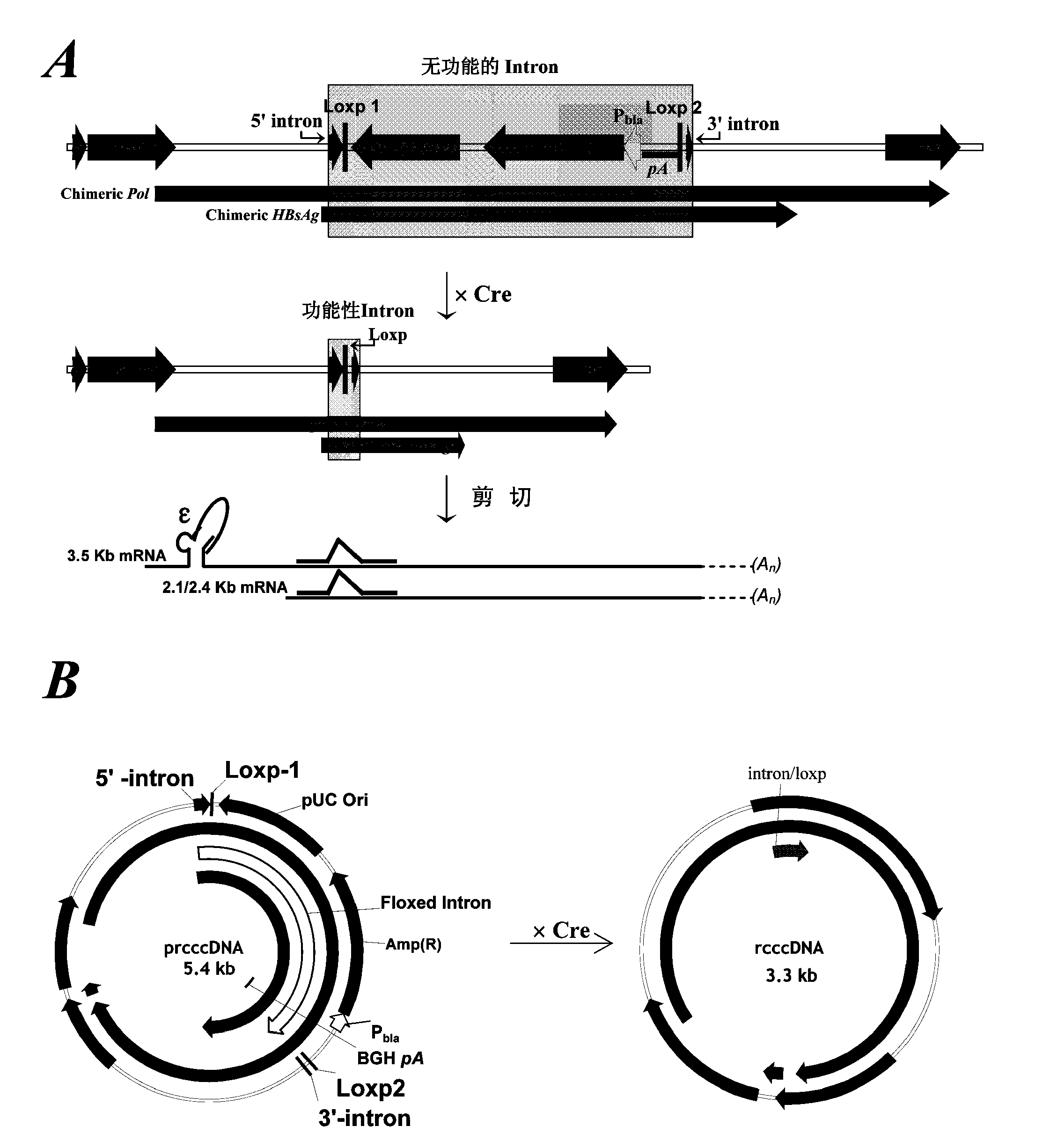
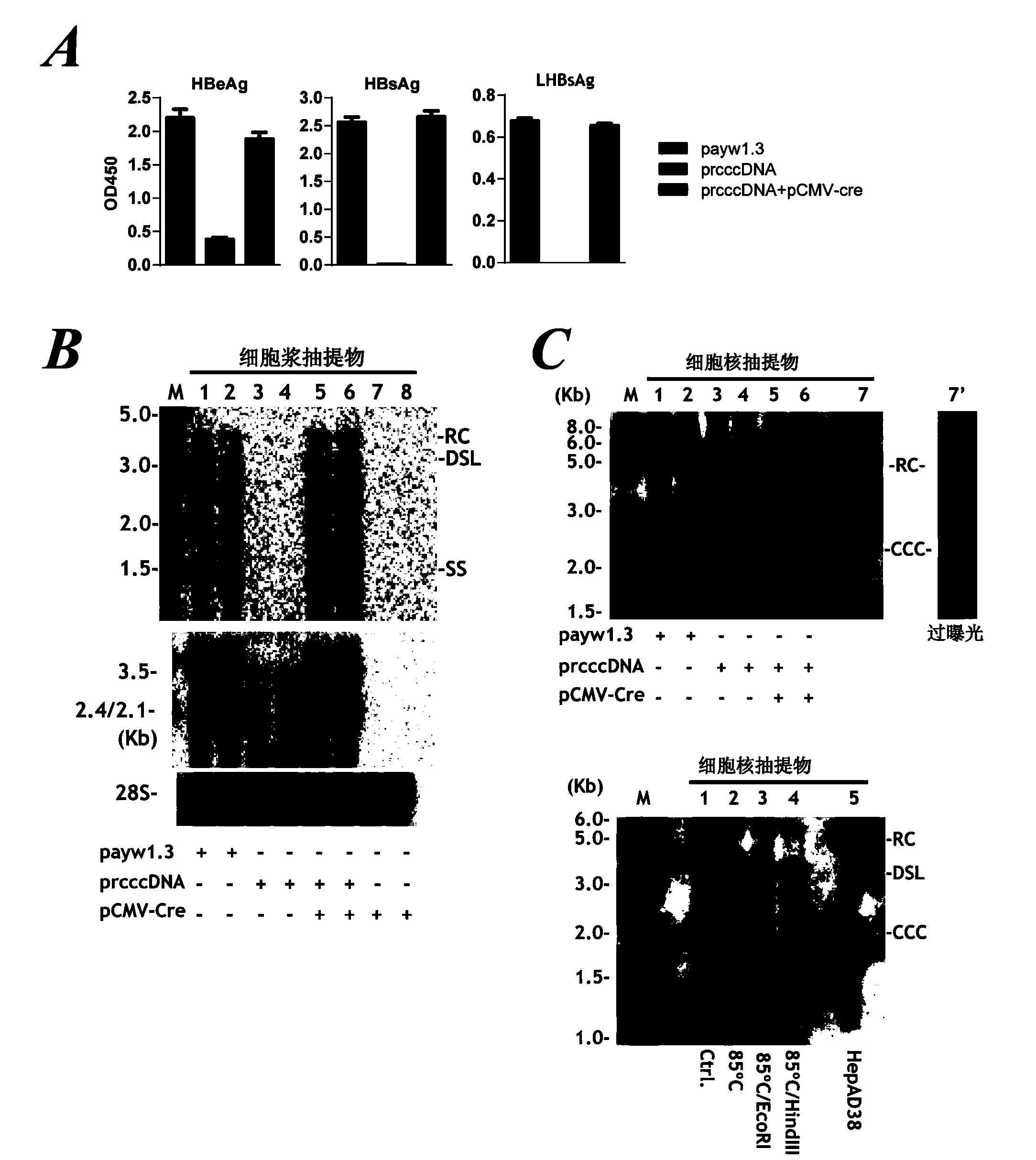
Inhibitors of hepatitis b virus convalently closed circular DNA formation and their method of use
Pharmaceutical compositions of the invention comprise covalently closed circular DNA formation inhibitors having a disease-modifying action in the treatment of diseases associated with the formation of covalently closed circular DNA that include hepatitis B infection, and any disease involving formation of covalently closed circular DNA.
Owner:PHILADELPHIA HEALTH & EDUCATION CORP +2
Protein expression profiling
InactiveUS20060166227A1Easy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationAnalyteProtein Expression Profiling
Disclosed are compositions and methods for detecting small quantities of analytes such as proteins and peptides. The method involves associating a primer with an analyte and subsequently using the primer to mediate rolling circle replication of a circular DNA molecule. Amplification of the DNA circle is dependent on the presence of the primer. Thus, the disclosed method produces an amplified signal, via rolling circle amplification, from any analyte of interest. The amplified DNA remains associated with the analyte, via the primer, and so allows spatial detection of the analyte. The disclosed method can be used to detect and analyze proteins and peptides. Multiple proteins can be analyzed using microarrays to which the various proteins are immobilized. A rolling circle replication primer is then associated with the various proteins using a conjugate of the primer and a molecule that specifically binds the proteins to be detectable. Rolling circle replication from the primers results in production of a large amount of DNA at the sites in the array where the proteins are immobilized. The DNA produced by rolling circle replication can be further amplified in secondary and higher order amplification processes using second-stage or higher order primers in conjunction with second-stage or higher order amplification target circles. The amplified DNA serves as a readily detectable signal for the proteins. The disclosed method can also be used to compare the proteins expressed in two or more different samples. The information generated is analogous to the type of information gathered in nucleic acid expression profiles. The disclosed method allows sensitive and accurate detection and quantitation of proteins expressed in any cell or tissue.
Owner:KINGSMORE STEPHEN +2
Generation of single-strand circular DNA from linear self-annealing segments
InactiveUS7041480B2Convenient ligationEasy to copySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideHeat denaturation
The present invention provides a method for the rapid simultaneous production of a plurality of single-stranded DNA circles having a predetermined size and nucleotide sequence using pre-designed hairpin oligonucleotides containing complementary sequences for directing ligation to form dumbbell-shaped monomers followed by heat denaturation to yield single-stranded DNA circles.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
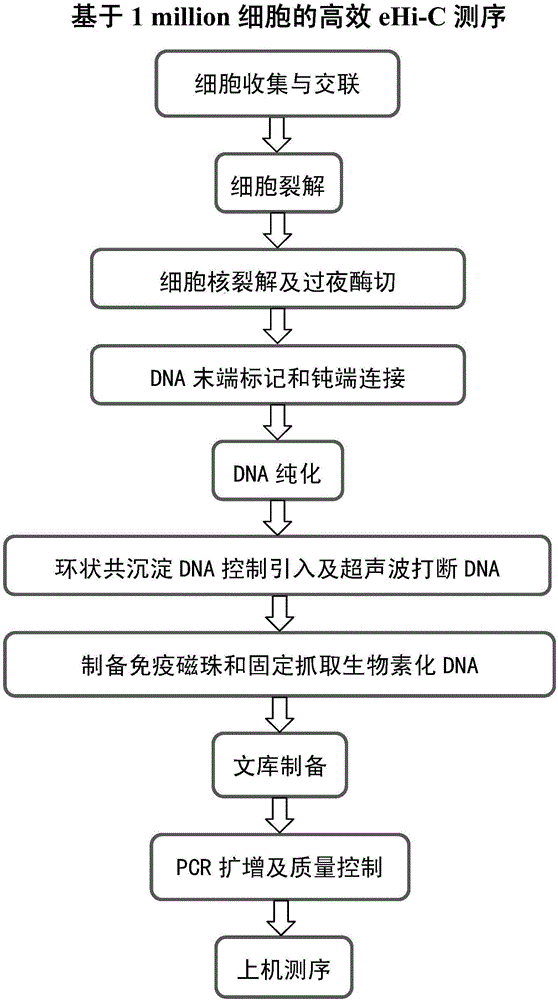
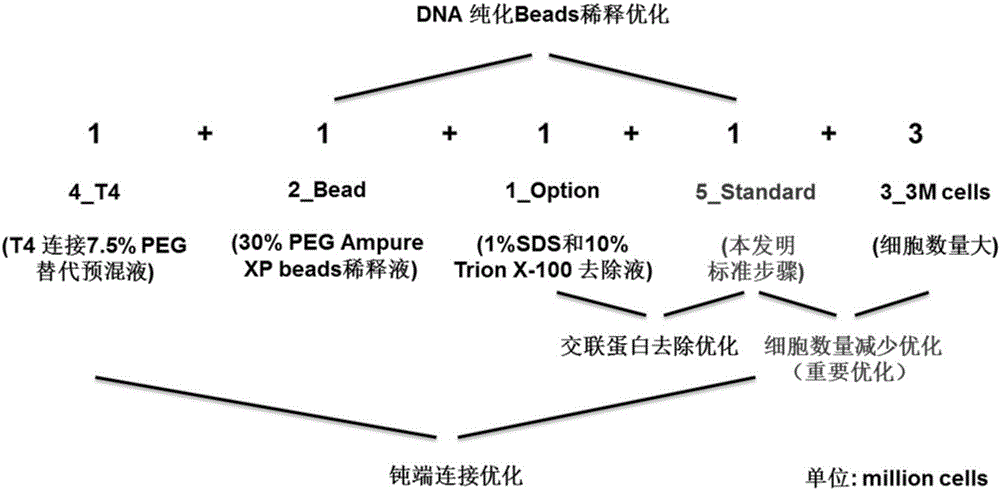
Efficient whole-genome chromosome conformation capture technology (eHi-C)
ActiveCN106566828AReduce demandReduce the cost of trainingMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationEnzyme digestionMagnetic bead
The invention discloses an efficient whole-genome chromosome conformation capture technology (eHi-C). The invention provides an eHi-C sequencing technology for cells. The eHi-C sequencing technology comprises the following steps: 1) subjecting the cells to disintegration so as to obtain chromatin; 2) subjecting the chromatin to enzyme digestion, DNA end labeling, cyclization connection of a blunt end and DNA purification so as to obtain purified circular DNA; 3) introducing a circular co-precipitation DNA molecule used as internal reference; 4) carrying out ultrasonic breaking; 5) capturing all the labeled DNA fragments with immunomagnetic beads; and 6) preparing eHi-C sequencing library from the labeled DNA fragments. The technology provided by invention is low in the amount of needed cells, can easily acquire an experiment material, reduces time in acquisition of the material, greatly lowers cell culture cost and cost for reagent consumables and decreases test errors.
Owner:AGRI GENOMICS INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Detection method using dissociated rolling circle amplification
Disclosed are compositions and methods for detecting small quantities of analytes such as proteins and peptides. The method involves associating a DNA circle with the analyte and subsequent release and rolling circle replication of the circular DNA molecule. In the method, an amplification target circle is associated with analytes using a conjugate of the circle and a specific binding molecule that is specific for the analyte to be detected. Amplification target circles not associated with the proteins are removed, the amplification target circles that are associated with the proteins are decoupled from the specific binding molecule and amplified by rolling circle amplification. The amplification is isothermic and can result in the production of a large amount of nucleic acid from each primer. The amplified DNA serves as a readily detectable signal for the analytes.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Methods for nucleic acid mapping and identification of fine-structural-variations in nucleic acids
ActiveUS8329400B2Quick buildEfficient sortingSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementA-DNADigestion
A method of juxtaposing sequence tags (GVTs) that are unique positional markers along the length of a population of target nucleic acid molecules is provided, the method comprising: fragmenting the target nucleic acid molecule to form target DNA insert; ligating the target DNA insert to a DNA vector or backbone to create a circular molecule; digesting the target DNA insert endonuclease to cleave the target DNA insert at a distance from each end of the target DNA insert yielding two GVTs comprising terminal sequences of the target DNA insert attached to an undigested linear backbone; recircularizing the linear backbone with the attached GVTs to obtain a circular DNA containing a GVT-pair having two juxtaposed GVTs; and recovering the GVT-pair DNA by nucleic acid amplification or digestion with endonuclease having sites flanking the GVT-pair. Cosmid vectors are provided for creating GVT-pairs of ˜45- to 50-kb separation sequencable by next-generation DNA sequencers.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
Protein expression profiling
InactiveCN1446050ABiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein insertionGene expression profiling
Compositions and methods for detecting small quantities of analytes such as proteins and polypeptides are disclosed. The method involves linking a primer to an analyte, which is then used to mediate rolling circle replication of circular DNA molecules. The replication of DNA circles is dependent on the presence of primers. Thus, the methods disclosed herein can generate an amplified signal from any analyte of interest by rolling circle replication. The amplified DNA remains attached to the analyte via the primer, allowing stereoscopic detection of the analyte. The methods of the invention can be used to detect and analyze proteins or polypeptides. Various proteins can be analyzed by microarrays to which various proteins are immobilized. Thus, rolling circle replication primers are linked to various proteins using a conjugate of the primer and a molecule capable of specifically binding the protein to be tested. Rolling circle replication of the primers produces a large amount of DNA product at the site in the matrix where the protein is anchored. The amplified DNA serves as a signal for easy detection of the protein. The methods of the invention can also be used to compare proteins expressed in two or more samples. The resulting information is similar to the type of information gathered in nucleic acid expression systems. The method of the present invention can detect and quantify the protein expressed in any cell or tissue sensitively and accurately.
Owner:MOLECULAR STAGING
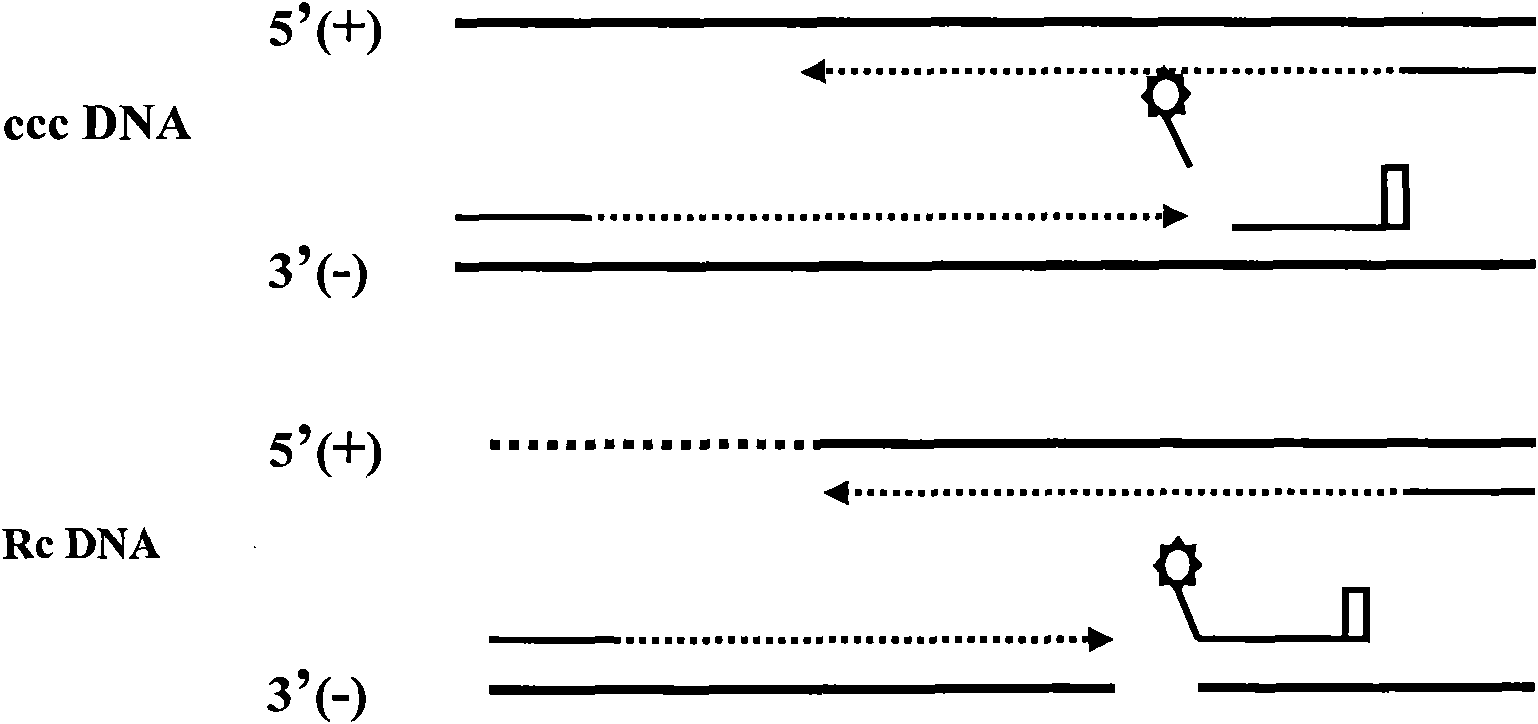
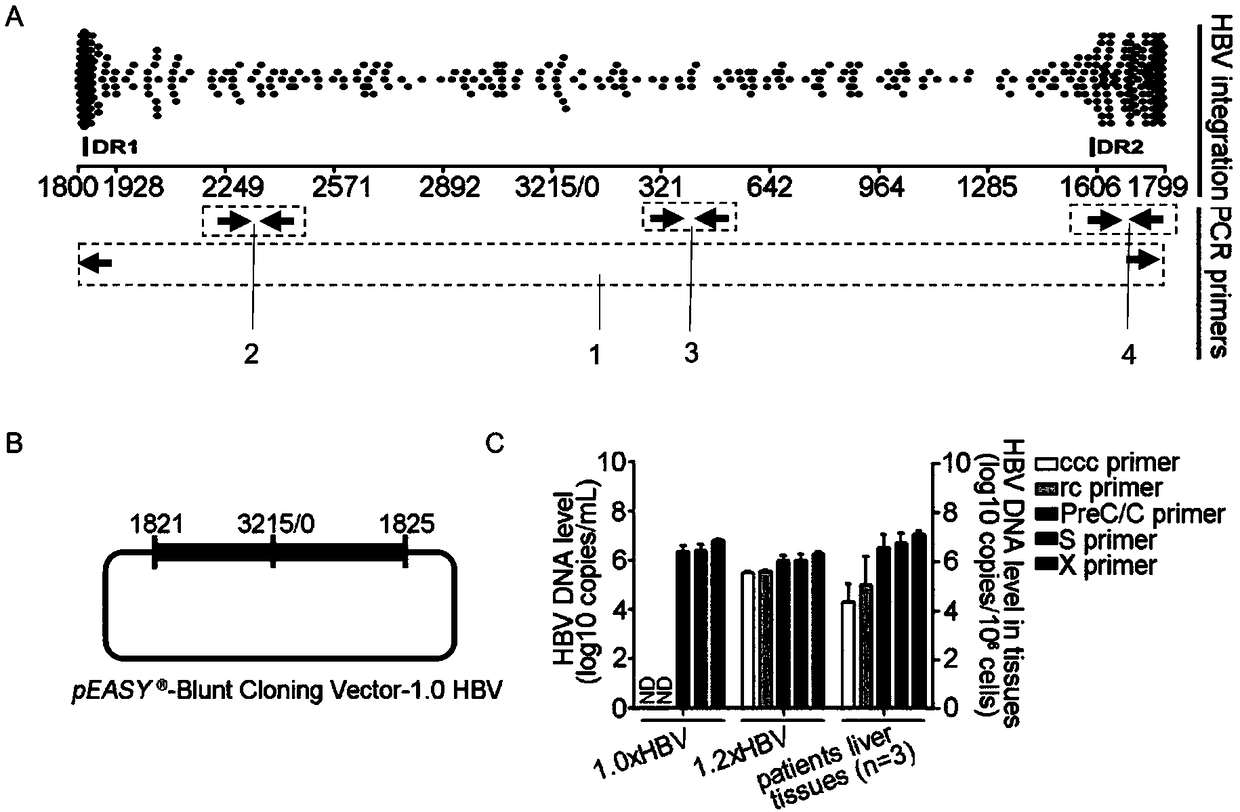
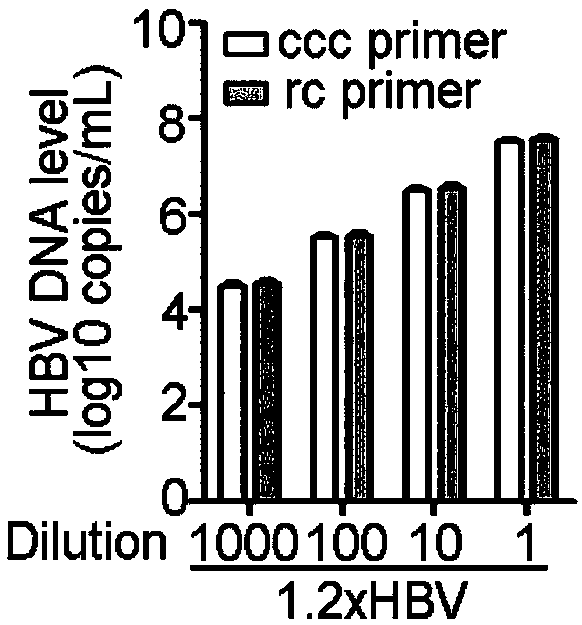
Nest type-real time quantitative PCR method for detecting hepatitis B virus cccDNA
InactiveCN101104867AImprove featuresHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementNegative strandFluorescence
The invention relates to a nested quantitative PCR detection method for virus covalently closed circular DNA (ccc DNA) of hepatitis b virus. The particular detection steps are: 1) extraction DNA of hepatitis b virus; 2) design and synthesis primers and probe: design an internal and an external primer at conservative region of both sides of negative chain gap of HVB DNA, with Taqman fluorescence probe arranged at the lower part of the negative chain gap; 3) Plasmid-SafeTM ATP-Dependent DNase restriction enzyme purification; 4) nested real time quantitative PCR amplification, comprising: common PCR-template with external primer amplification purification and real time quantitative PCR-fluorescence quantitative amplification to common PCR production with internal primer and fluorescence probe. The invention can improve the specificity and sensitivity of detection reactive to make the operation process and result analysis much more accurate, simple and time saving.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Reagent and method for preparation of HBV persistently infected animal model
ActiveCN104278055AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPersistently infectedHepatitis B virus
The invention relates to a reagent and method for preparation of an HBV (hepatitis B virus) persistently infected animal model. According to the invention, a construct able to conditionally induce HBV covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) molecules in the liver of mice is constructed, and the HBV persistently infected animal model is successfully established.
Owner:INST PASTEUR OF SHANGHAI CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Nucleic acid detection method based on DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) hairpin and RCA (Rolling Circle Amplification)
InactiveCN103014168AHigh sensitivitySimple processMicrobiological testing/measurementA-DNADna hairpin
The invention provides a nucleic acid detection method based on a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) hairpin and RCA (Rolling Circle Amplification). The detection method comprises the steps of: modifying the DNA hairpin to a solid carrier, wherein the circular part of the DNA hairpin is complementary with a target DNA and the stem part of the DNA hairpin is complementary with an an annular DNA; adding the annular DNA, an enzyme, an amplification raw material and the like; complementing and pairing a target nucleic acid molecule and the loop of the DNA hairpin when the target nucleic acid molecule is added into a detection system; opening a hairpin-loop structure; hybridizing a base of the hairpin and the circular DNA; performing RCA; opening different hairpin-loop structures when the target nucleic acid molecular weights are different; and quantifying the target nucleic acid molecule by using an optical or electric method. According to the nucleic acid detection method, as the DNA hairpin is used as a detection probe of RCA, the step of detecting the molecule by RCA is simplified, the detection cost is reduced, the advantage of high sensitivity of RCA for nucleic acid detection is simultaneously kept, and the nucleic acid detection method is suitable for popularization and use.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
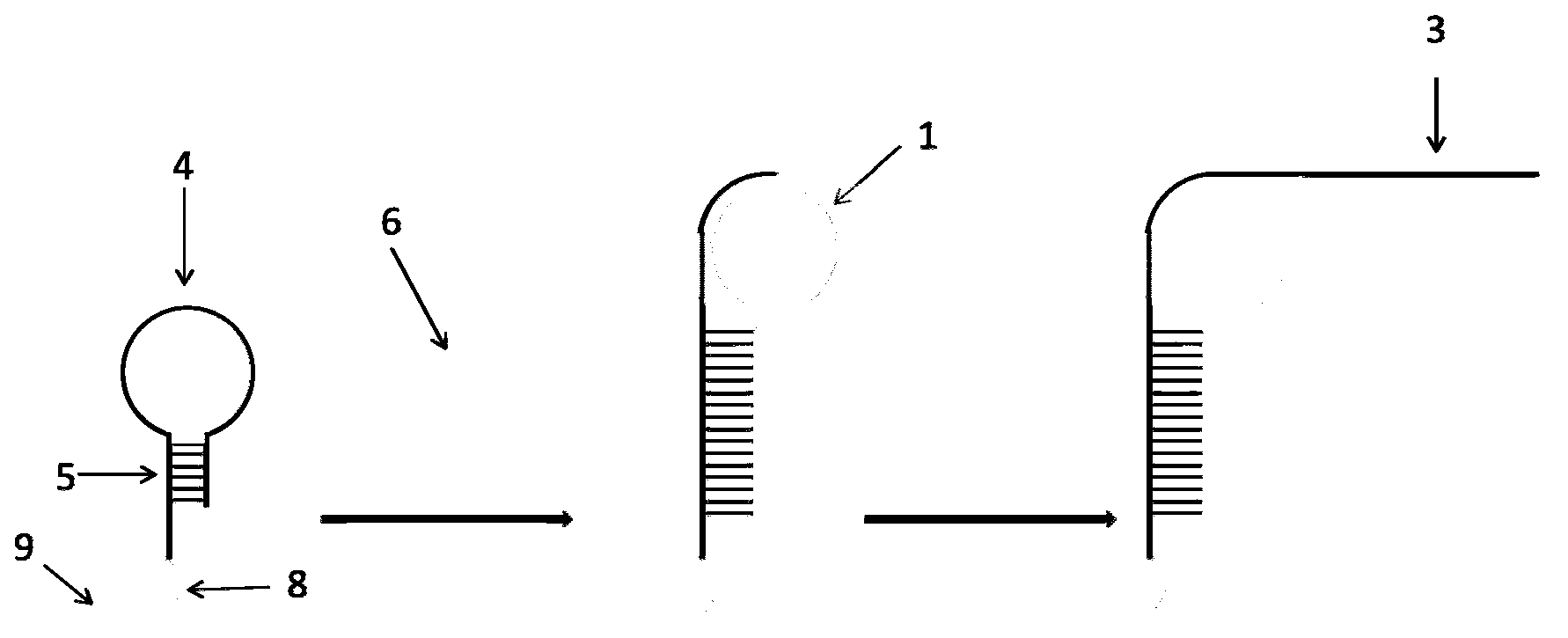
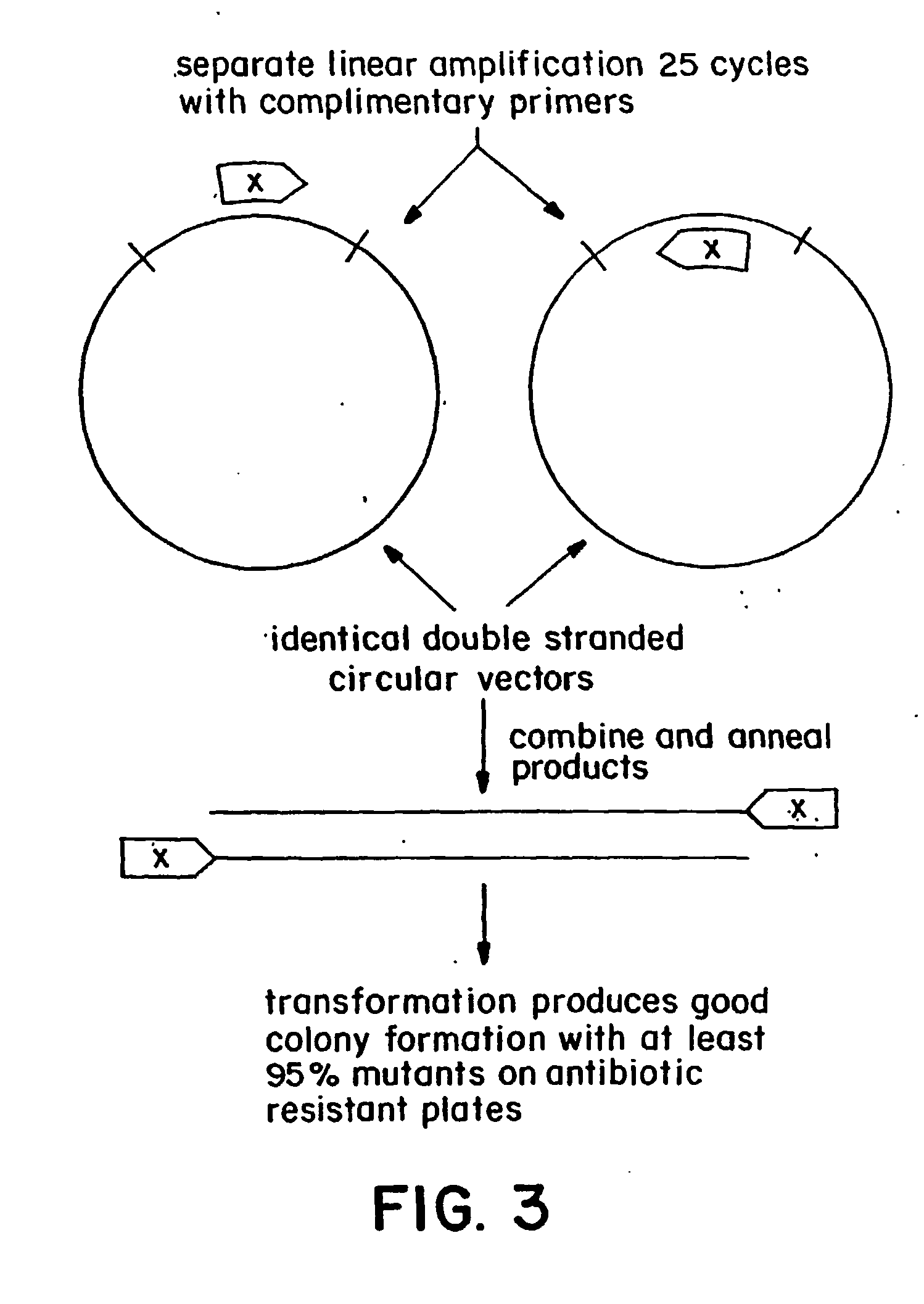
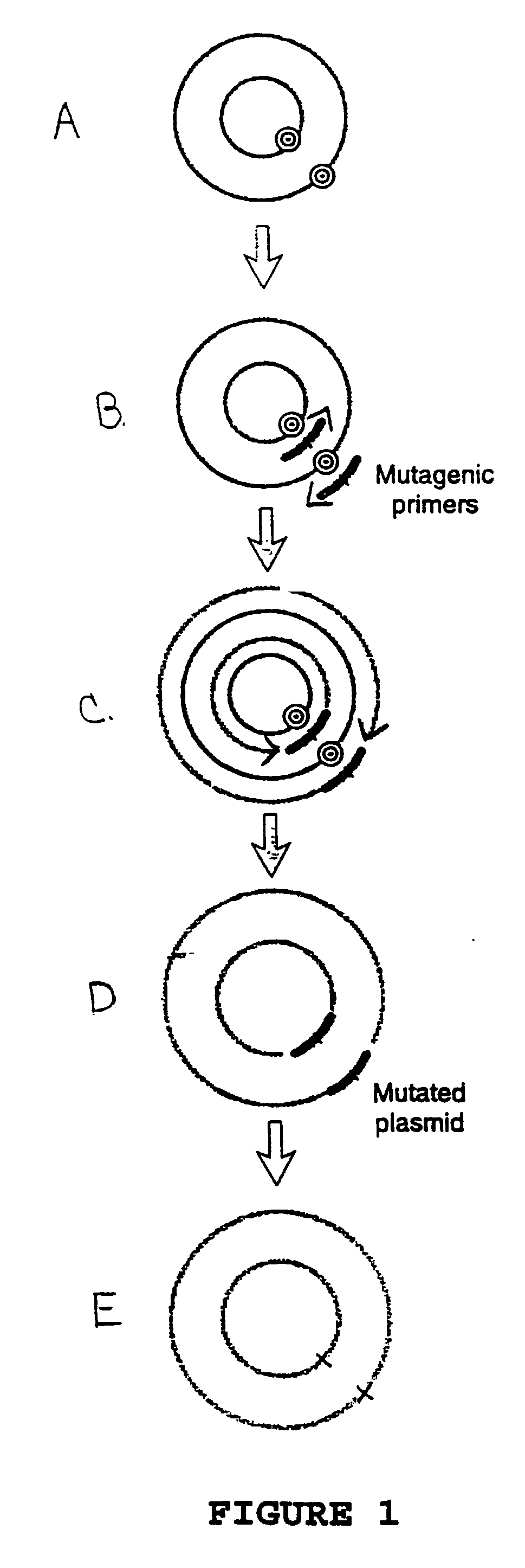
Polymerase-based protocols for the introduction of deletions and insertions
InactiveUS20060228786A1Simple procedureReduce the amount requiredFermentationDNA preparationSingle stagePolymerase L
The present invention relates to improved methods of introducing site-directed mutations into circular DNA without the need for subcloning. The invention comprises single-stage, polymerase-based, mutagenesis procedures which eliminate the need for the second-stage linear cyclic amplification reaction of the prior art. In accordance with the invention, production of complimentary mutagenized DNA strands is accomplished in separate, single-primer, linear amplification reactions carried out for each primer of a mutagenic primer pair. The mutagenized DNA strands produced in the separate primer reactions are combined and annealed and the resulting double-stranded mutagenized DNA intermediate may then be used directly to transform a host cell for further production of the desired mutant DNA. Major applications of this method include directed evolution and other areas that benefit from the development of diversity.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Method for preparing antitumor drug carrier by using rolling circle amplification technology
The invention relates to a method for preparing an antitumor drug carrier by using a rolling circle amplification technology. An amplification primer DNA is assembled on the surface of a nano-mateiral, a circular DNA amplification template and other amplification mixtures are added and then rolling circle amplification is performed, and the prepared product is a long single-stranded DNA antitumor drug carrier obtained by extension from the surface of nano-gold. The primer DNA is extended to a microsize scale by means of room temperature amplification and can be in comparison with a non-amplified gold-DNA control group by means of agarose electrophoresis; after amplification, the DNA becomes longer, resulting in delay in the electrophoresis experiment. Besides, in an atomic force microscopy image, the amplified long-chain DNA extending from the surface of the nano-material can be intuitively observed. The nano-scale biological composite structure constructed by the rolling circle amplification technology can be used for the researches on novel antitumor drug carriers.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
Application of circular DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) in detecting and imaging sense RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) and gene therapy
PendingCN107988351AImprove stabilityImprove recognition efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsFluorescenceRNA Sequence
The invention provides application of circular DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) in detecting and imaging sense RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) and gene therapy. The circular DNA at least comprises one or more DNA probe fragments complementary to a detection target sense RNA sequence, and is formed by connecting and cyclizing 3' and 5' terminals of ssDNA (single-stranded Deoxyribonucleic Acid). The circular DNAand the detection target sense RNA form heterozygous double strands, and the heterozygous double strands are separated from a carrier, so that (1) the application in detecting and imaging through a corresponding fluorescence signal change is realized; (2) the sense RNA in the heterozygous double strands is enzymically decomposed, so that the aim of gene therapy is achieved.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
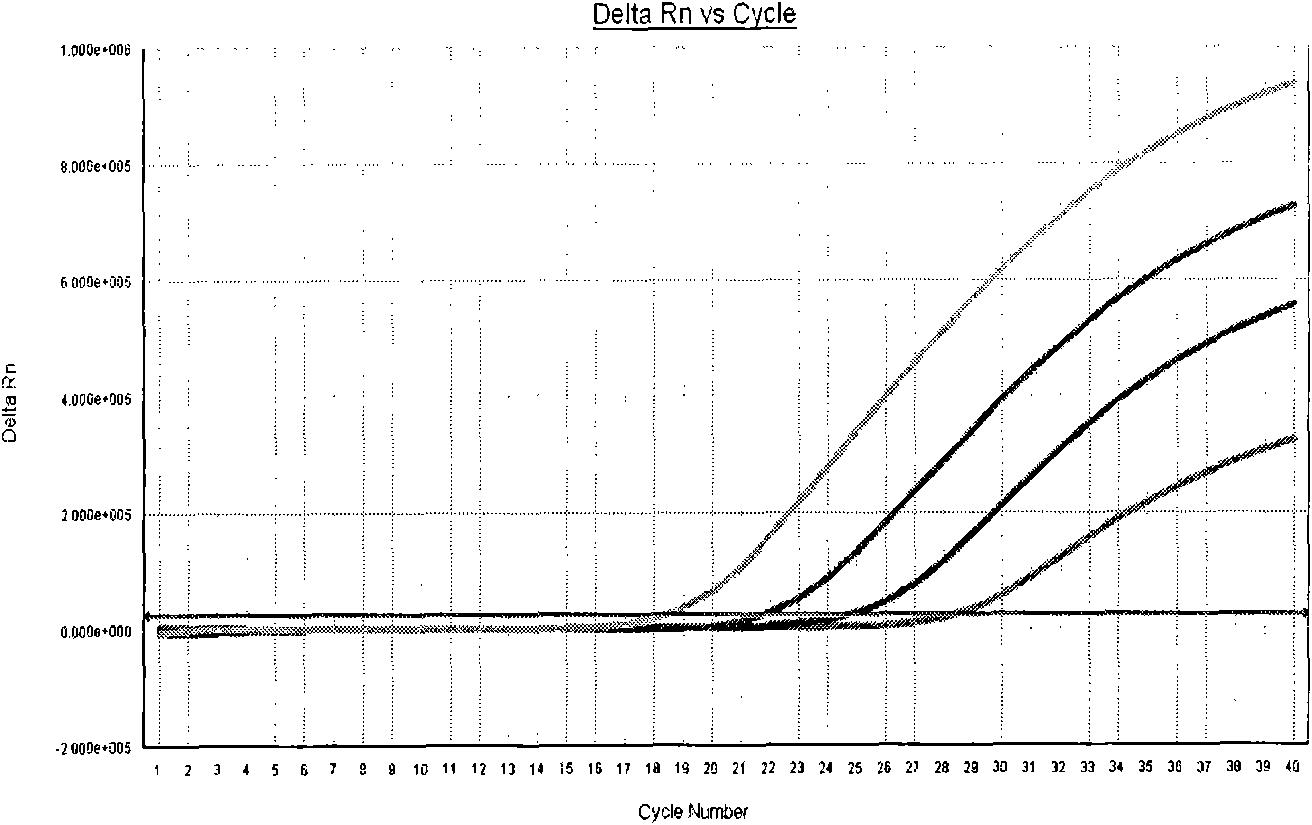
Method for performing two-color fluorescence polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection on hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular (ccc) DNA, and application of kit
InactiveCN101967522AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesQuality controlHepatitis B virus
The invention provides a method for detecting hepatitis B virus covalently-closed circular DNA (HBV ccc DNA) from the samples of peripheral blood, hepatic tissues and the like by utilizing two-color fluorescence polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology, namely a PCR-two-color fluorescence probe method, and a kit therefor. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) collecting the samples; (2) extracting the DNA; (3) detecting the samples by a two-color fluorescence quantitative PCR in-vitro amplification method; and (4) analyzing the samples according to the fluorescence intensity of the amplification reaction of the corresponding samples after the amplification reaction is finished, thereby judging the existence of the HBV ccc DNA in the collected samples and accurately quantifying the HBV ccc DNA by using the standard curve of a positive quality control material to realize the real-time, fast and quantitative detection of the HBV ccc DNA.
Owner:BEIJING SUOAO BIOMEDTECH
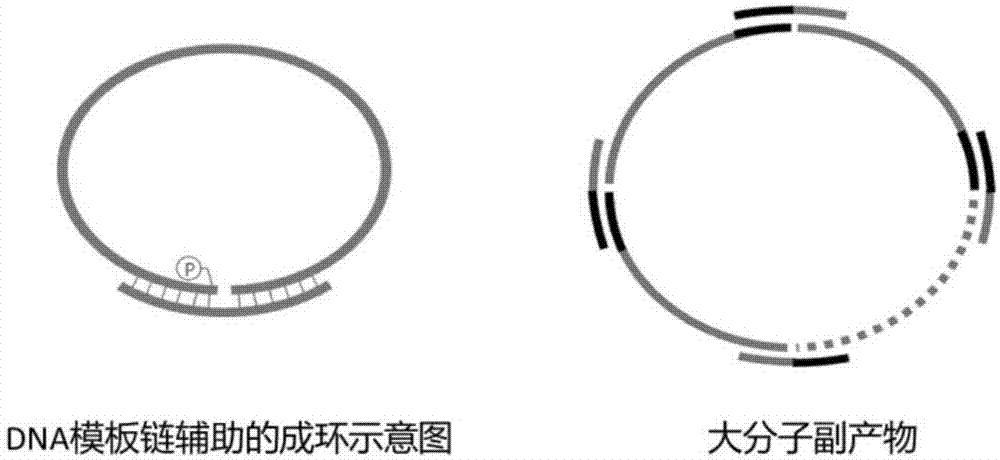
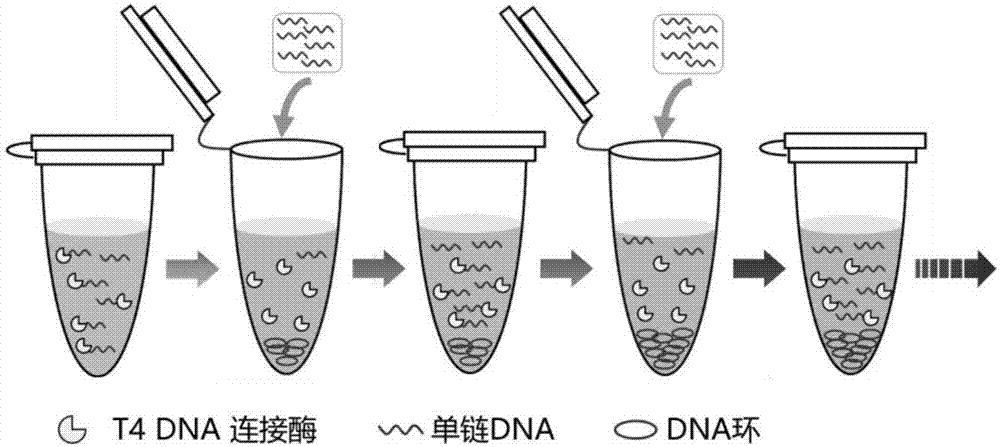
Method of preparing circular DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) or RNA (ribonucleic acid)
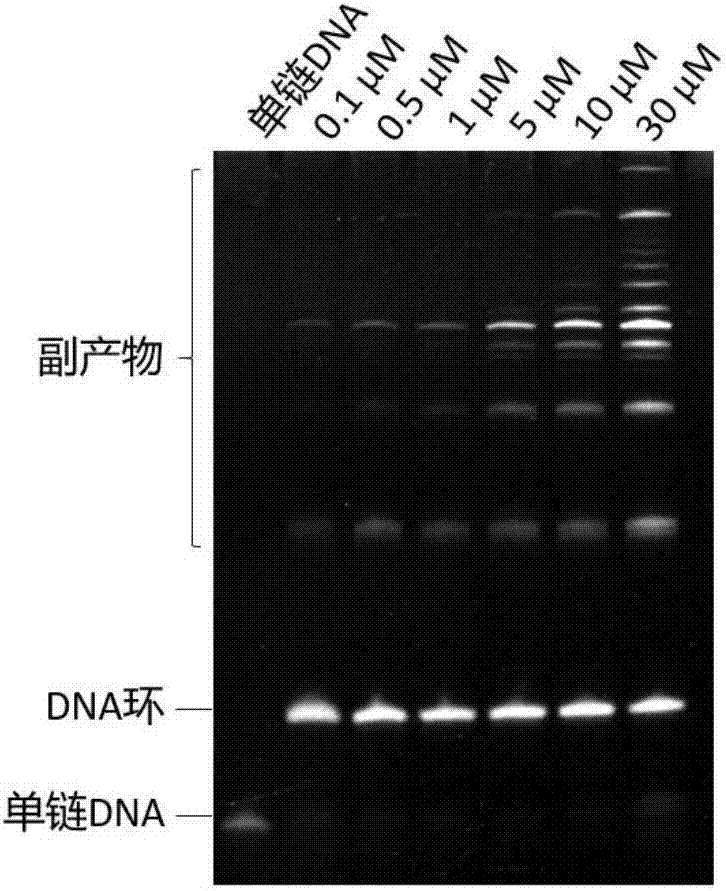
The invention belongs to the technical field of nucleic acid and particularly relates to a preparation method of high-concentration circular DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) or RNA (ribonucleic acid). The method comprises the following steps of: mixing assistant template DNA (hereinafter referred to as a splint), ligase and a buffer solution of the ligase required by a cyclic reaction to prepare an initial system, preparing an addition solution from single-stranded DNA or RNA (hereinafter referred to as a cyclic strand) and the buffer solution of the ligase, adding a certain amount of the addition solution containing the cyclic strand into the initial system every other certain time, allowing a concentration of the cyclic strand in the system to increase 0.1-5 micrometers after adding the new cyclic strand each time, repeating the procedure for several times, after adding the addition solution containing the cyclic strand for the last time, allowing for reaction for 2-15h, and allowing a concentration mole ratio of the splint to the cyclic strand in the system to be (1-10):1. The method is simple and easy to operate, does not require extreme conditions, and can achieve high yield preparation of circular DNA or RNA at the ultrahigh concentration of the cyclic strand (greater than or equal to 10 micrometers).
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Oligonucleotide composition and method for detecting hepatitis B virus (HBV) rcDNA (Relaxed Circular deoxyribonucleic acid) and/ or cccDNA (Covalently Closed Circular DNA), kit and application of oligonucleotide composition
ActiveCN109321679AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDirect repeatHepatitis B virus
The invention discloses an oligonucleotide composition and a method for detecting hepatitis B virus (HBV) rcDNA (Relaxed Circular deoxyribonucleic acid) and / or cccDNA (Covalently Closed Circular DNA), a kit and application of the oligonucleotide composition. The oligonucleotide composition comprises first oligonucleotide, second oligonucleotide, or oligonucleotide complementary with the sequenceof the first oligonucleotide and oligonucleotide complementary with the sequence of the second oligonucleotide; the first oligonucleotide is specifically combined with at least one part of continuoussequence of the first sequence, and the second oligonucleotide is specifically combined with at least one part of continuous sequence of the second sequence; in addition, a distance between two continuous sequences is 30-350 nt; the first sequence is a sequence between DR (Direct Repeat) 2-DR1 of the HBV DR sequence of a cross-notch area which contains cccDNA or rcDNA, and the second sequence is asequence after the fifth basic group of the DR1. According to the oligonucleotide composition, the level of HBV rcDNA and / or cccDNA can be effectively detected without being affected by integrated HBV DNA.
Owner:北京旌准医疗科技有限公司
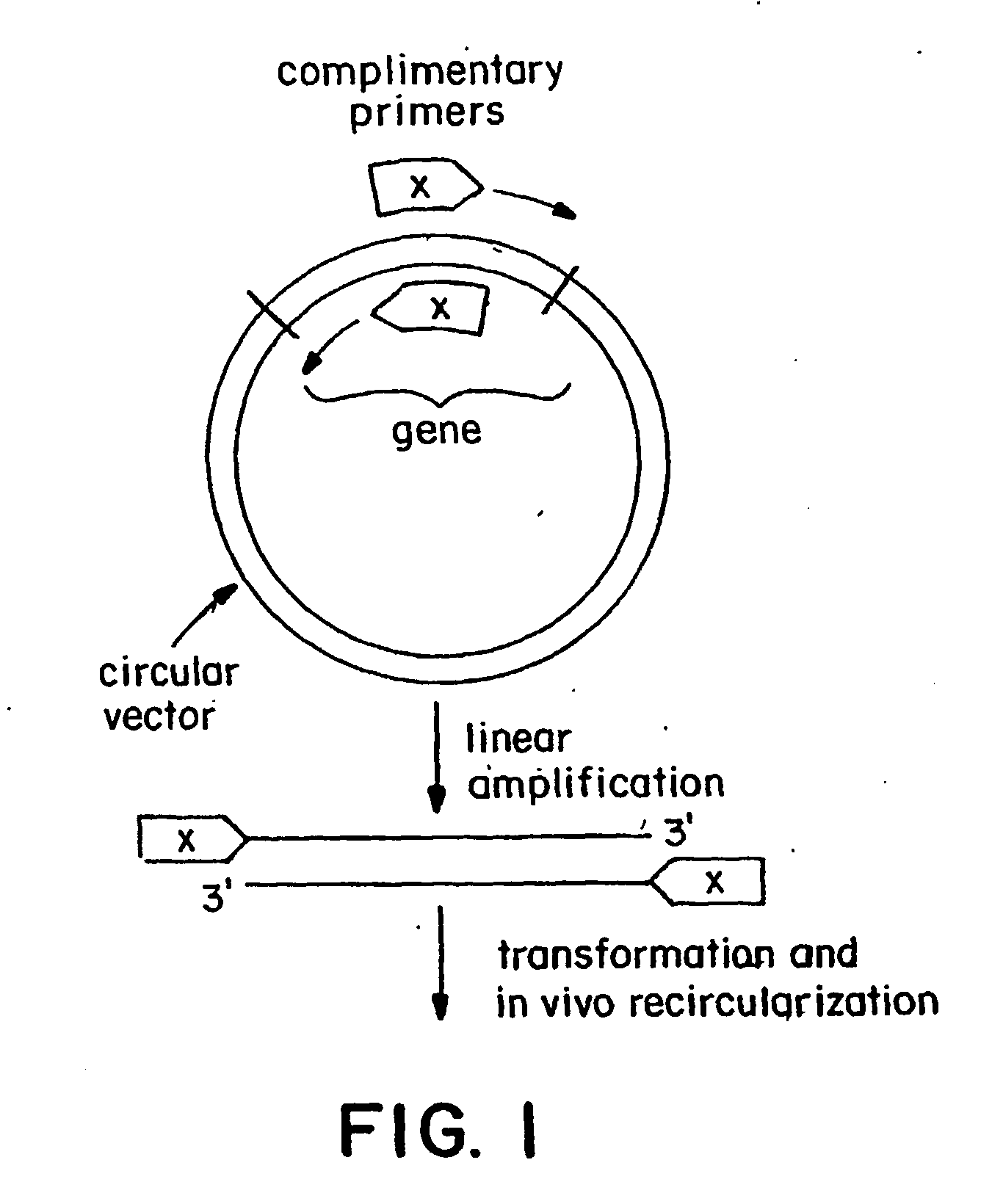
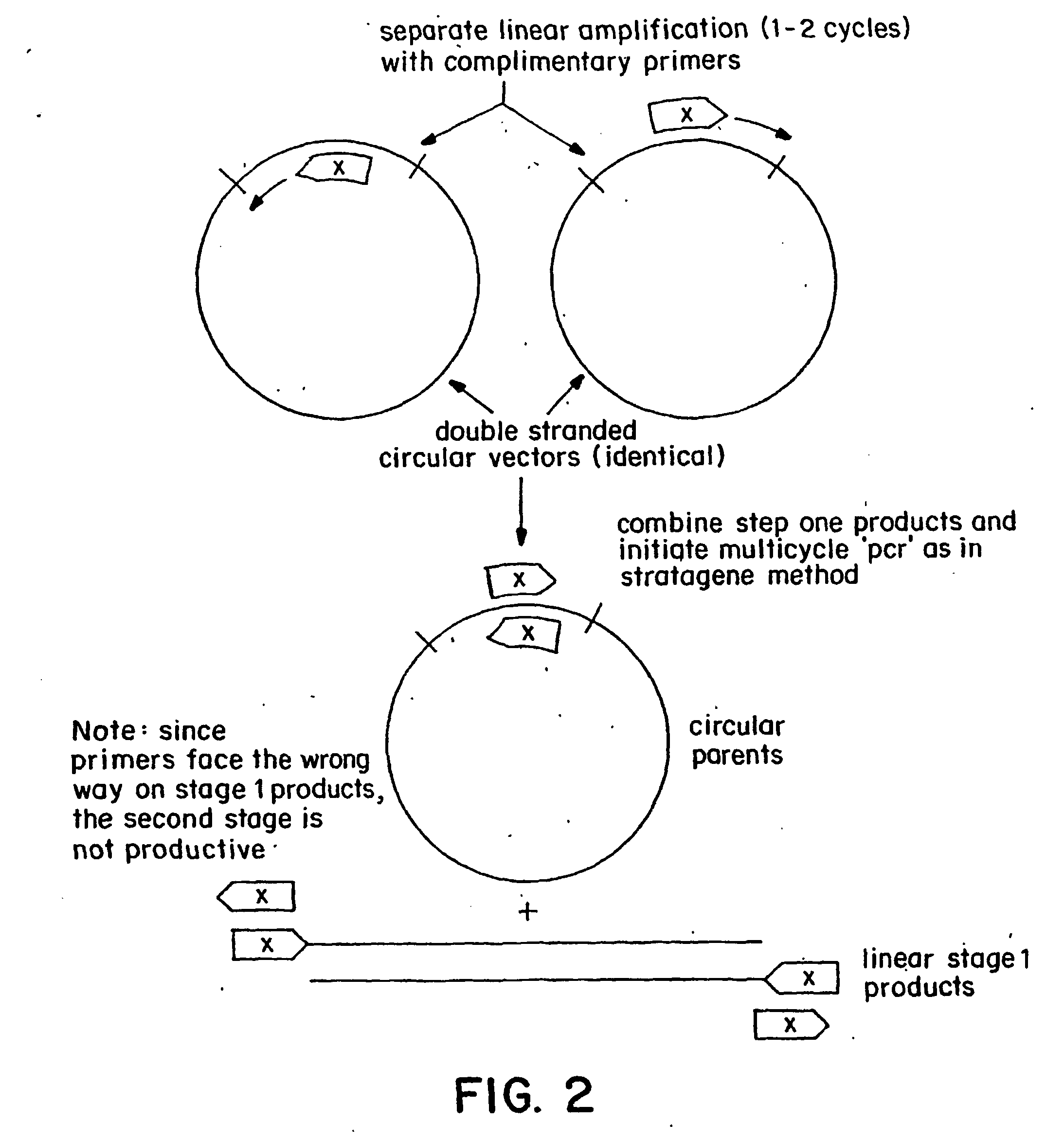
Circular site-directed mutagenesis
InactiveUS20030032037A1Simple methodEfficiently introducing specific mutationsMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymologyOligonucleotide primersSite-directed mutagenesis
The invention provides improved methods of introducing site-directed mutations into circular DNA molecules of interest by means of mutagenic primer pairs. The mutagenic primer pairs are also selected so as to be either completely complementary or partially complementary to each other, wherein the mutation site (or sites) is located within the region of complementarity. A mutagenic primer pair is annealed to opposite strands of a circular DNA molecule containing the DNA sequence to be mutagenized. After annealing, first and second mutagenized DNA strands, each incorporating a member of the mutagenic oligonucleotide primer pair is synthesized by a linear cyclic amplification reaction. After the linear cyclic amplification mediated synthesis step is completed, the reaction mixture is treated with a selection enzyme that digests the parental template strands. After the digesting step, a double-stranded circular DNA intermediate is formed. The double-stranded circular DNA intermediates is transformed in suitable competent host cells and closed circular double- stranded DNA corresponding to the parental template molecules, but containing the desired mutation or mutations of interest, may be conveniently recovered from the transformed cells. The invention also provide kits for site-directed mutagenesis in accordance with methods of the present invention.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
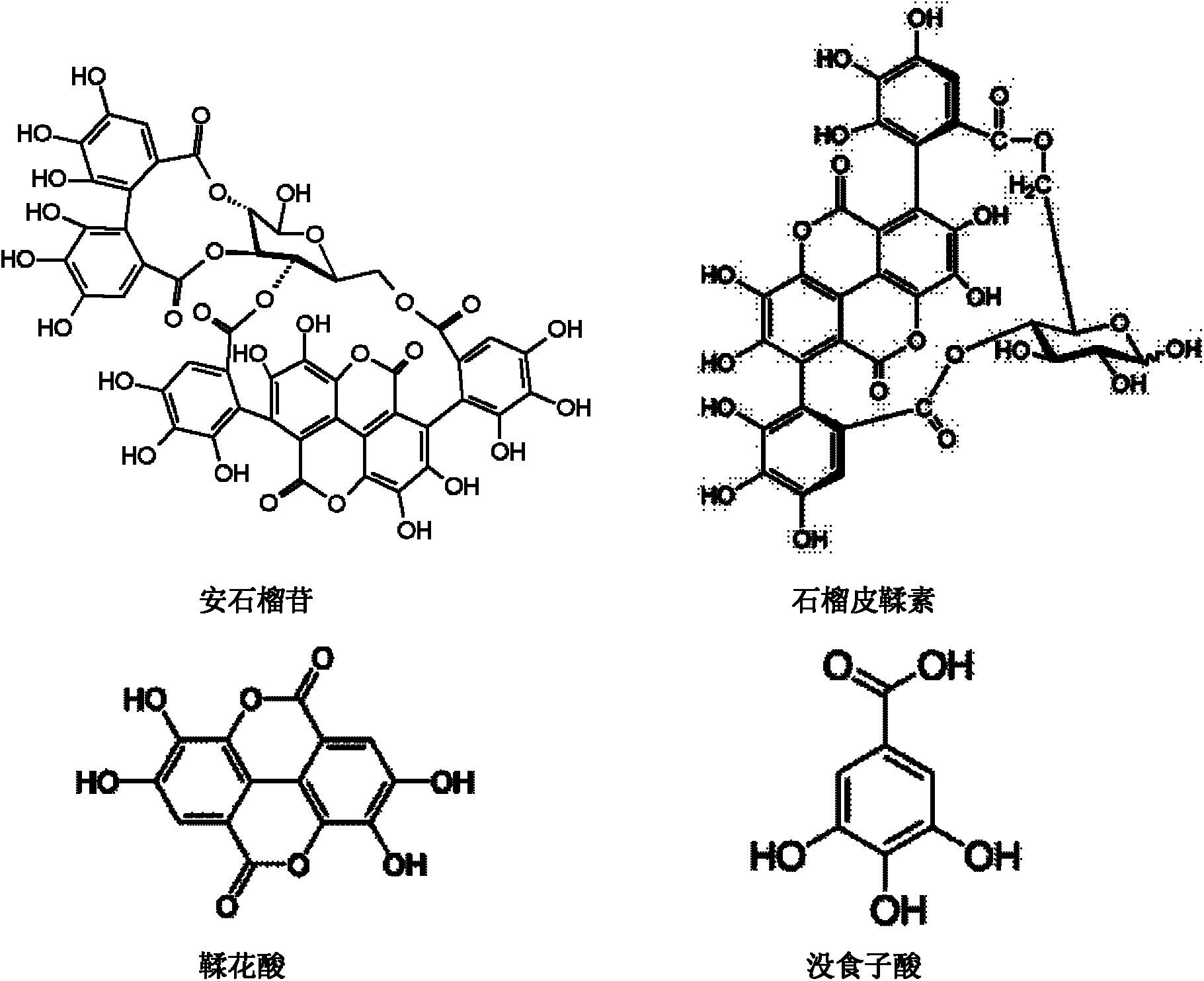
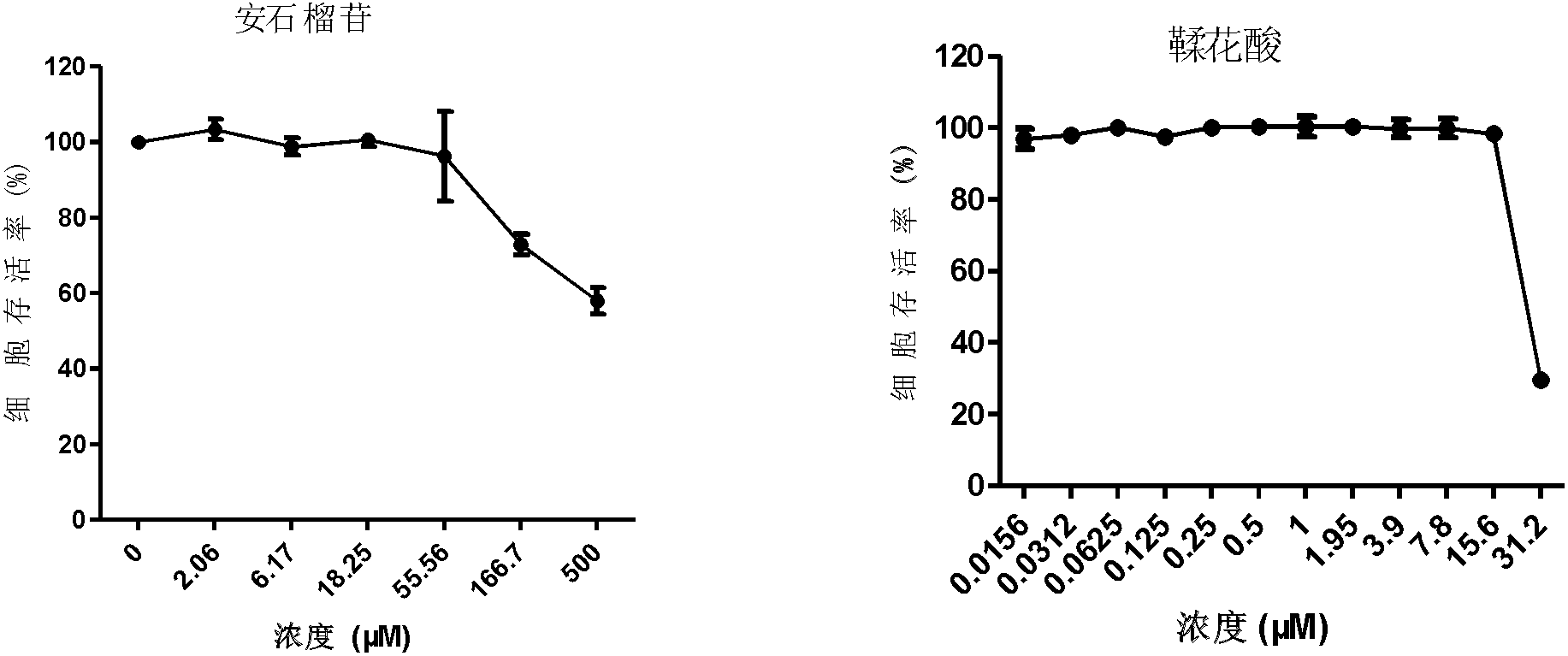
Application of pomegranate in preparing medicament for treating or preventing hepatitis B virus infection
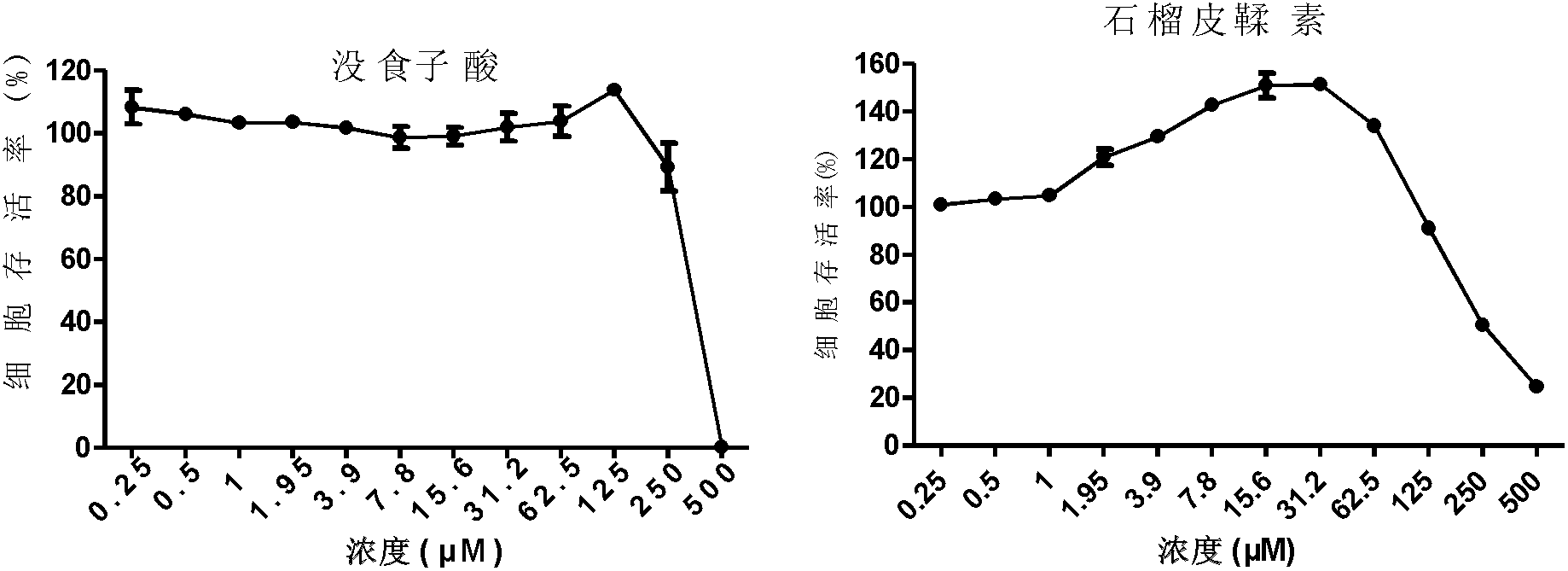
InactiveCN102631384ASmall side effectsLow toxicityOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemGallic acid esterCytotoxicity
The invention discloses application of pomegranate in preparing a medicament for treating or preventing hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. The application is implemented through the following steps: detecting the cytotoxicity of each pomegranate sourced medicament to HepG2.117, wherein the CC50 of punicalagin, gallic acid and punicalin is sequentially more than 500mu M, 334mu M and 218.86mu M; and then detecting the effects of the punicalagin, ellagic acid, gallic acid and punicalin to HBeAg and HBsAg, and the effect of punicalagin to DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) of virus. Results indicate that the four compounds can be used for inhibiting HBeAg and HBsAg, wherein the punicalagin can be used for remarkably reducing the cccDNA (covalently closed circular DNA). The punicalagin can be used for remarkably reducing the contents of HBeAg and cccDNA in an HepG2.2.15 cell, and does not have effect to the total HBV DNA in the cell, which indicates that the punicalagin takes the cccDNA as a target to directly clear the cccDNA in a liver cell. Currently, the anti-HBV infection medicament in clinical treatment cannot directly act on the cccDNA, and cannot completely remove the virus. Experiment results disclose that the medicament has the prospect of being developed into anti-HBV infection medicaments.
Owner:陈绪林
Precise quantification method of HBV (hepatitis B virus) cccDNA (covalent closed circular DNA)
InactiveCN106636466ASolve the problem of false positive interferenceRealize closed tube operationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPositive controlMicroparticle
The invention relates to a precise quantification method of HBV (hepatitis B virus) cccDNA (covalent closed circular DNA). The precise quantification method of the HBV cccDNA comprises steps as follows: the copy number of a sample is quantitatively controlled within 10,000 copes through nucleic acid; primers and probes of cccDNA and rcDNA are designed and detected with a double-gap method; digital PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification is performed; analysis parameters are adjusted in digital PCR instrument analysis software, 1 / 2-1 / 3 of the average fluorescence intensity of positive particles in positive control holes is set as a positive threshold, the to-be-detected sample is analyzed and the copy number of cccDNA in the sample is calculated using software of the digital PCR instrument, and false positive caused by non-specific amplification is eliminated. The method solves the false positive interference problem of double-gap method and the PCR method for rcDNA; compared with other digital PCR detection methods for cccDNA, the method has the advantages that specific DNA enzyme is not required to treat the sample, closed pipe operation is realized, the cross-pollution risk is reduced, and the operation process is simplified.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
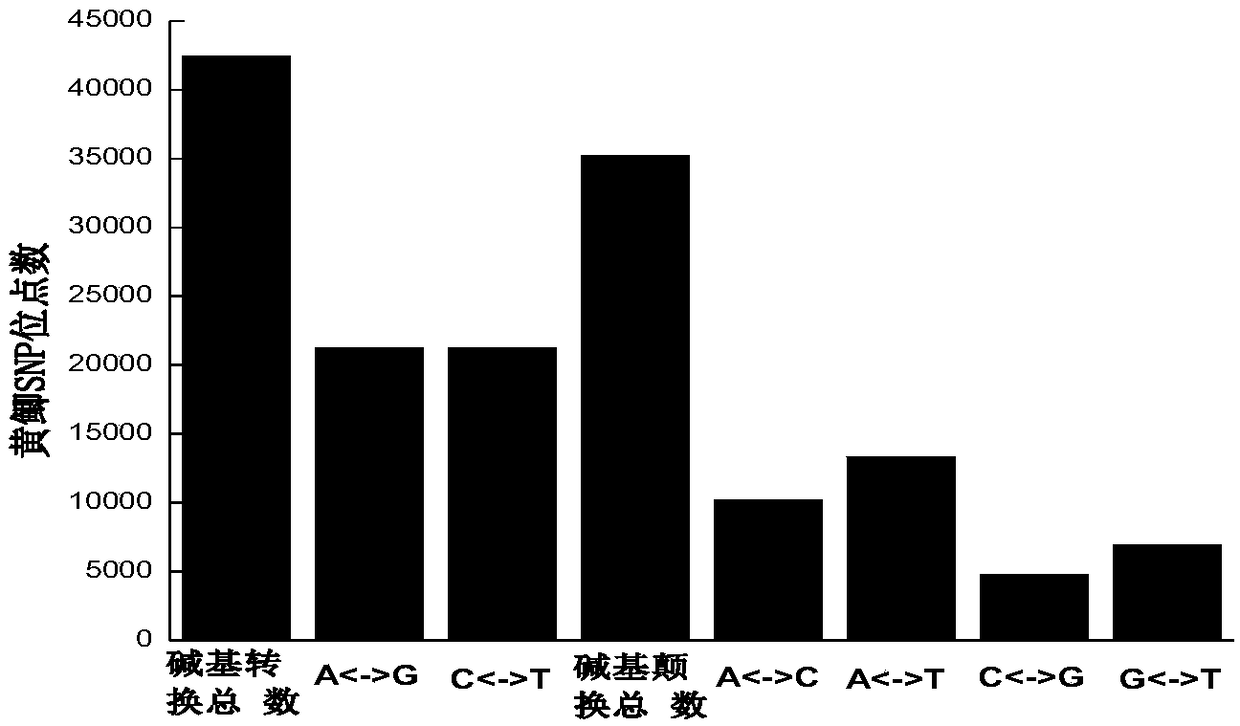
Yellow crucian carp high-density SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) marker screening method and application
InactiveCN109439739AConsistent amplification efficiencyLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic diversityScreening method
The invention discloses a yellow crucian carp high-density SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) marker screening method, which includes extracting genomic DNA, constructing a RAD library and high-throughput sequencing, filtering original sequence data, and detecting and screening SNP information sites; adding circular DNA and chitin in the process of extracting the genomic DNA to effectively improve the screening accuracy of SNP markers; and adding chitin fluid into a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification system to improve the reaction sensitivity of PCR amplification and help to obtain the complete high-density SNP sites. The high-density SNP sites obtained by the method can be applied to analyze the genetic diversity level, population genetic structure and the like of the yellowcrucian carp population. The method for obtaining the high-density SNP marker sites of the yellow crucian carp has the advantages of simplicity, high efficiency, high SNP marker screening accuracy, good repeatability, low cost and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
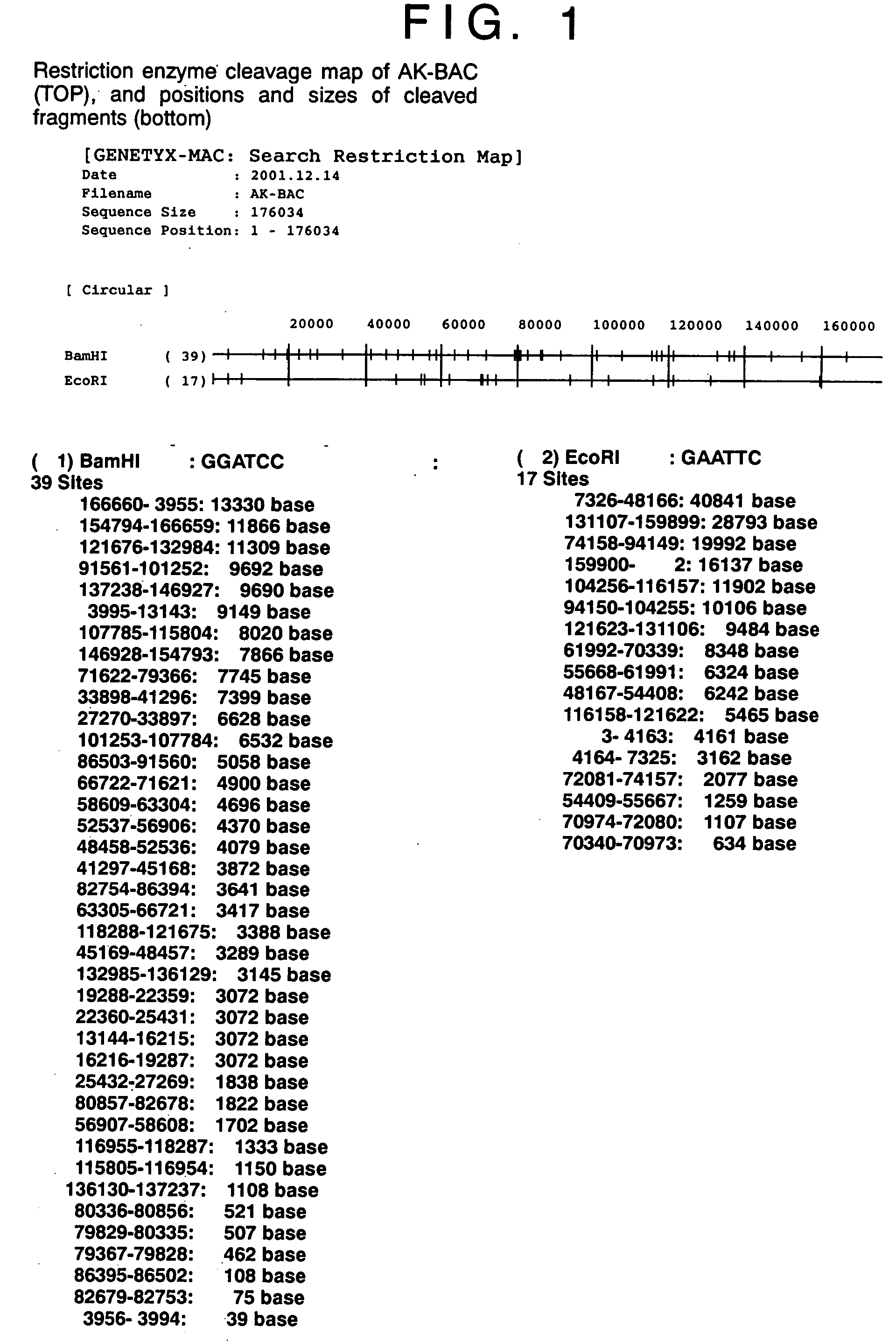
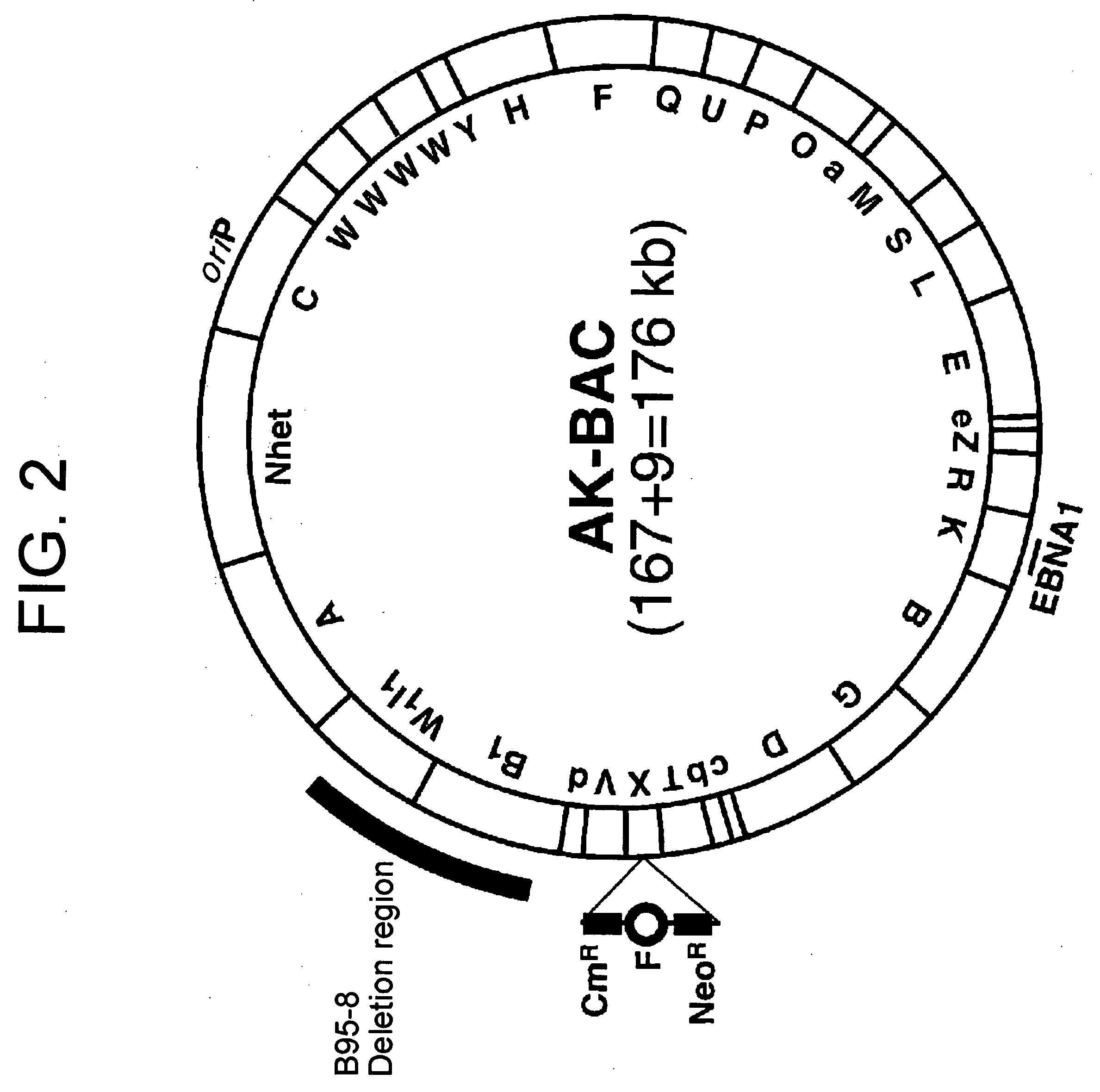
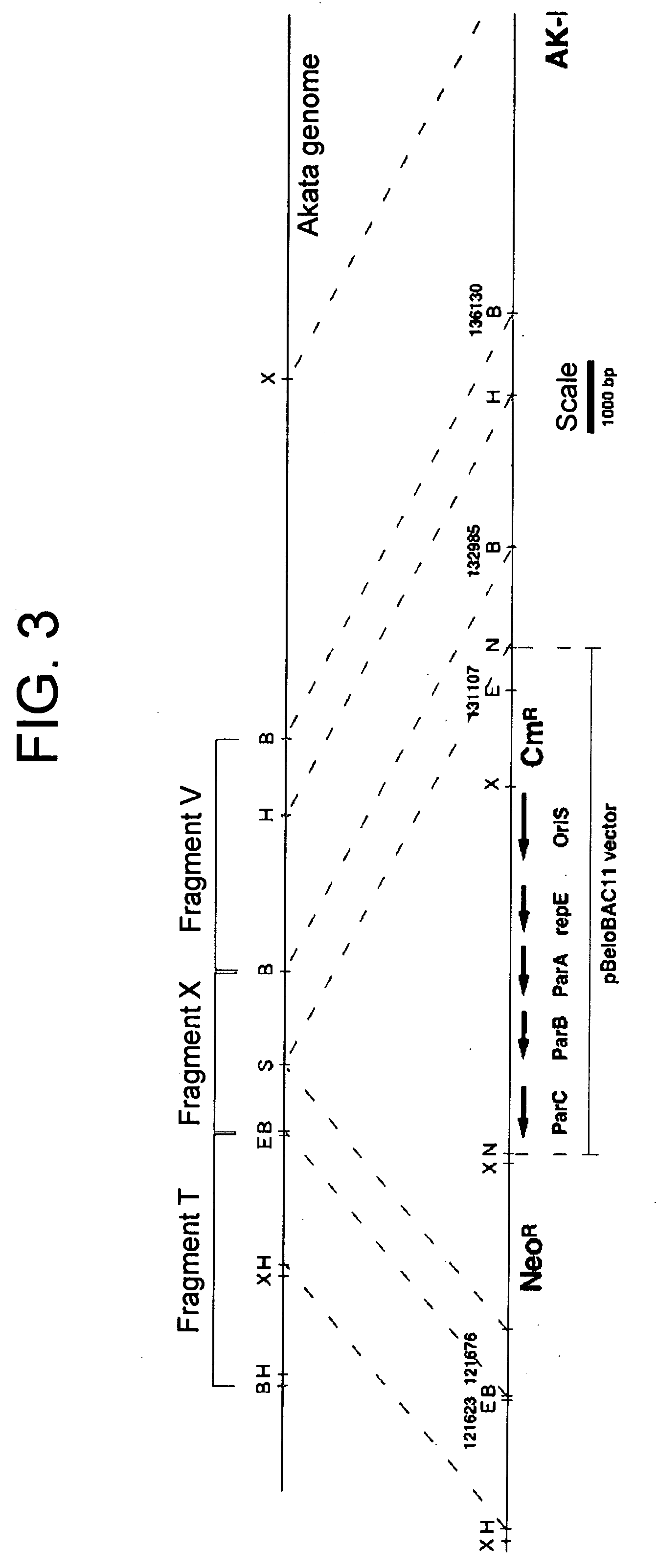
Double-stranded cyclic dna capable of proliferating as a bacterial e coli chromosome
InactiveUS20050106733A1Easy to modifyEasy to produceBacteriaInactivation/attenuationEscherichia coliGenomic DNA
(PROBLEM) To establish a system enabling modification and proliferation of EB virus circular DNA in Escherichia coli and large-scale production of recombinant EB virus virions in the cells. (Means for Resolution) The present invention enables modification and proliferation of a circular EB virus genome derived from Akata cells in Escherichia coli by inserting a DNA sequence of a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) into a circular EB virus DNA in Akata cells via homologous recombination. The recombinant EB virus can be produced in a large quantity by introducing the resulting genomic DNA into Akata cells.
Owner:EVEC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com