Patents
Literature
104 results about "Microarray profiling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
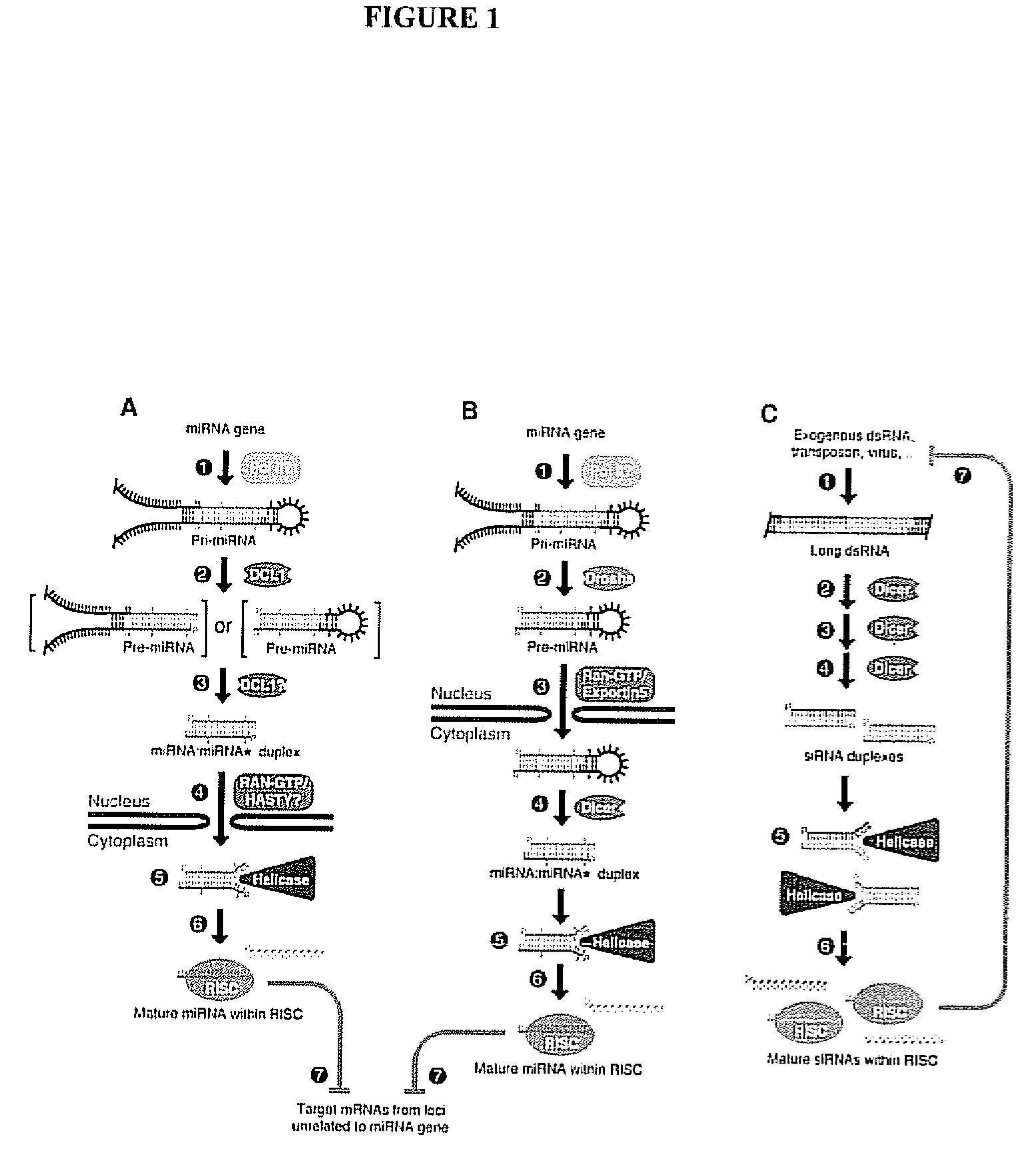
Microarrays are important tools for profiling gene expression, and are based on complementary binding between probes that are attached to glass chips and nucleic acids derived from samples.
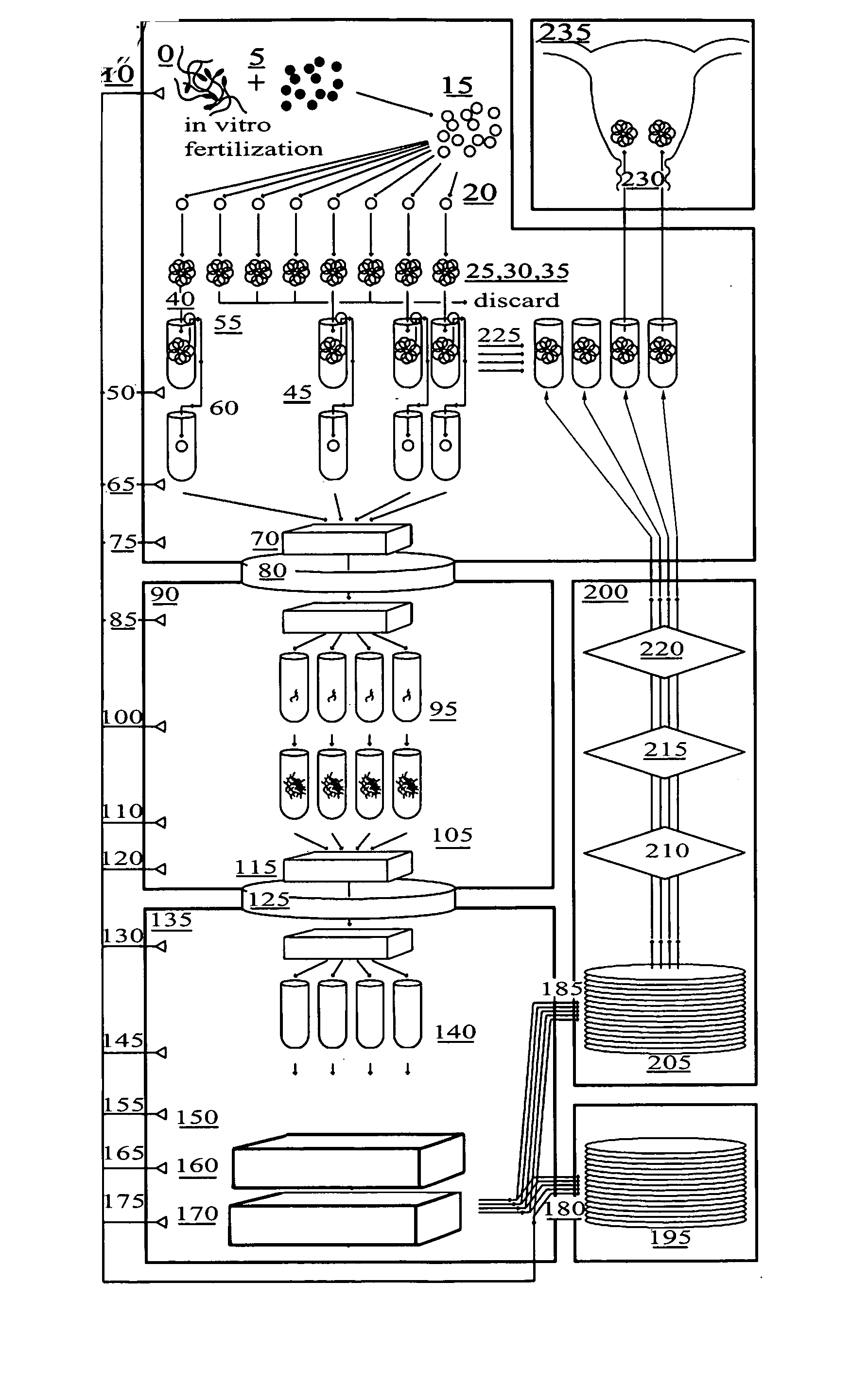
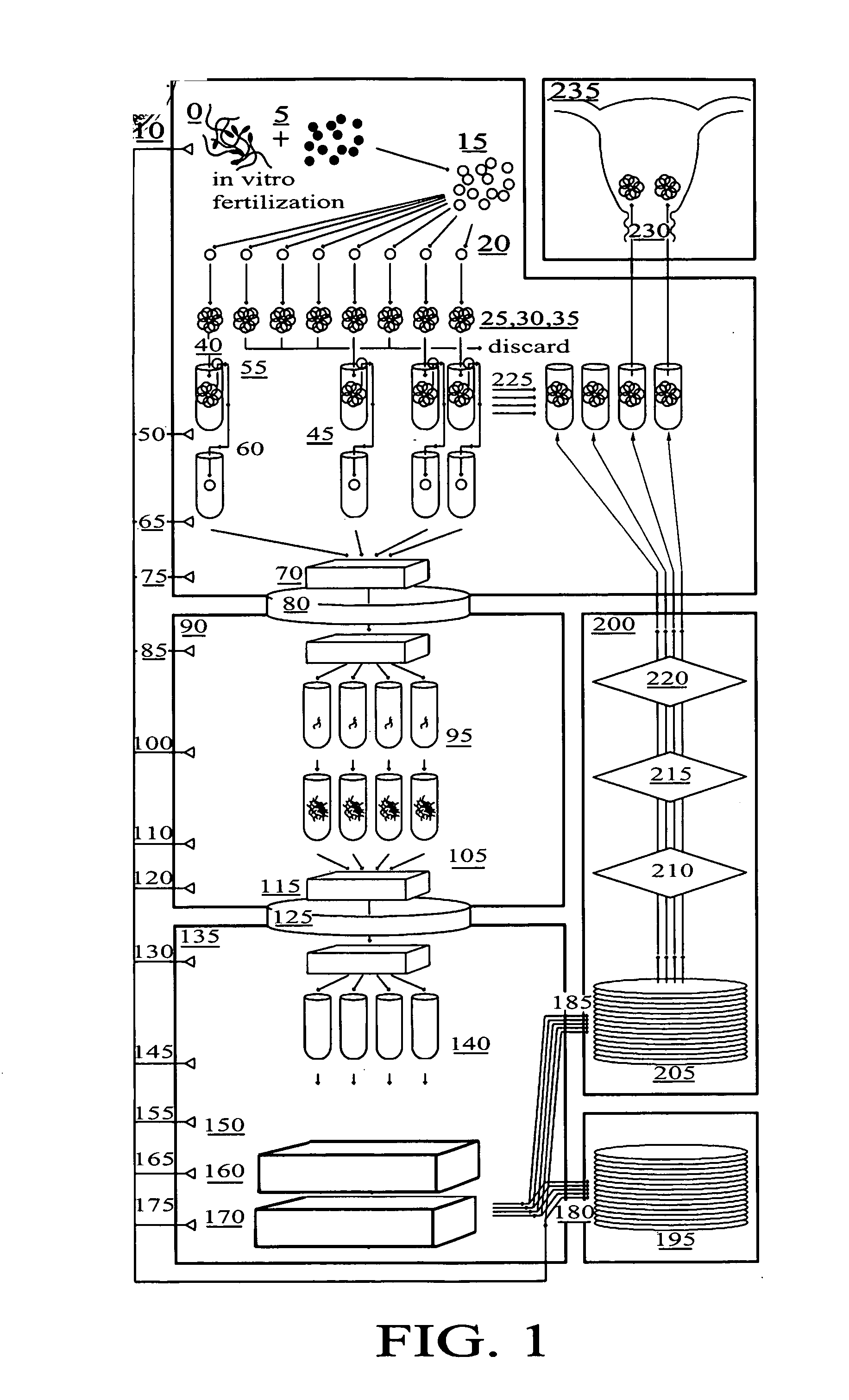
Method for genetic testing of human embryos for chromosome abnormalities, segregating genetic disorders with or without a known mutation and mitochondrial disorders following in vitro fertilization (IVF), embryo culture and embryo biopsy
InactiveUS20080085836A1Reduce significant riskImprove the level ofLibrary screeningLibrary member identificationLess invasiveContamination
We describe a method for interrogating the content and primary structure of DNA by microarray analyses and to provide comprehensive genetic screening and diagnostics prior to embryo transfer within an IVF setting. We will accomplish this by the following claims: 1) an optimized embryo grading system, 2) a less invasive embryo biopsy with reduced cellular contamination, 3) an optimized DNA amplification protocol for single cells, 4) identify aneuploidy and structural chromosome abnormalities using microarrays, 5) identifying sub-telomeric chromosome rearrangements, 6) a modified DNA fingerprinting protocol, 7) determine imprinting and epigenetic changes in developing embryos, 8) performing genome-wide scans to clarify / diagnose multi-factorial genetic disease and to determine genotype / haplotype patterns that may predict future disease, 9) determining single gene disorders with or without a known DNA mutation, 10) determining mtDNA mutations and / or the combination of mtDNA and genomic (nuclear) DNA aberrations that cause genetic disease.
Owner:KEARNS WILLIAM G +1
Prostate cancer-related nucleic acids
ActiveUS7642348B2Late detectionSpecific hybridizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsTumor rejection antigen precursorsDiseaseNucleotide
Described herein are novel polynucleotides associated with prostate cancer. The polynucleotides are miRNAs, miRNA precursors, and associated nucleic acids. Methods and compositions are described that can be used for diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of prostate cancer. Also described herein are methods that can be used to identify modulators of the disease-associated polynucleotides. Also described herein are methods and compositions for linear amplification and labeling of a targeted nucleic acid. The amplified targeted molecules may be used in hybridization techniques like Luminex and Microarray analysis.
Owner:ROSETTA GENOMICS
Protein expression profiling
InactiveUS6921642B2Easy to detectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteProtein expression profile
Disclosed are compositions and methods for detecting small quantities of analytes such as proteins and peptides. The method involves associating a primer with an analyte and subsequently using the primer to mediate rolling circle replication of a circular DNA molecule. Amplification of the DNA circle is dependent on the presence of the primer. Thus, the disclosed method produces an amplified signal, via rolling circle amplification, from any analyte of interest. The amplified DNA remains associated with the analyte, via the primer, and so allows spatial detection of the analyte. The disclosed method can be used to detect and analyze proteins and peptides. Multiple proteins can be analyzed using microarrays to which the various proteins are immobilized. A rolling circle replication primer is then associated with the various proteins using a conjugate of the primer and a molecule that specifically binds the proteins to be detectable. Rolling circle replication from the primers results in production of a large amount of DNA at the sites in the array where the proteins are immobilized. The amplified DNA serves as a readily detectable signal for the proteins. The disclosed method can also be used to compare the proteins expressed in two or more different samples. The information generated is analogous to the type of information gathered in nucleic acid expression profiles. The disclosed method allows sensitive and accurate detection and quantitation of proteins expressed in any cell or tissue.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
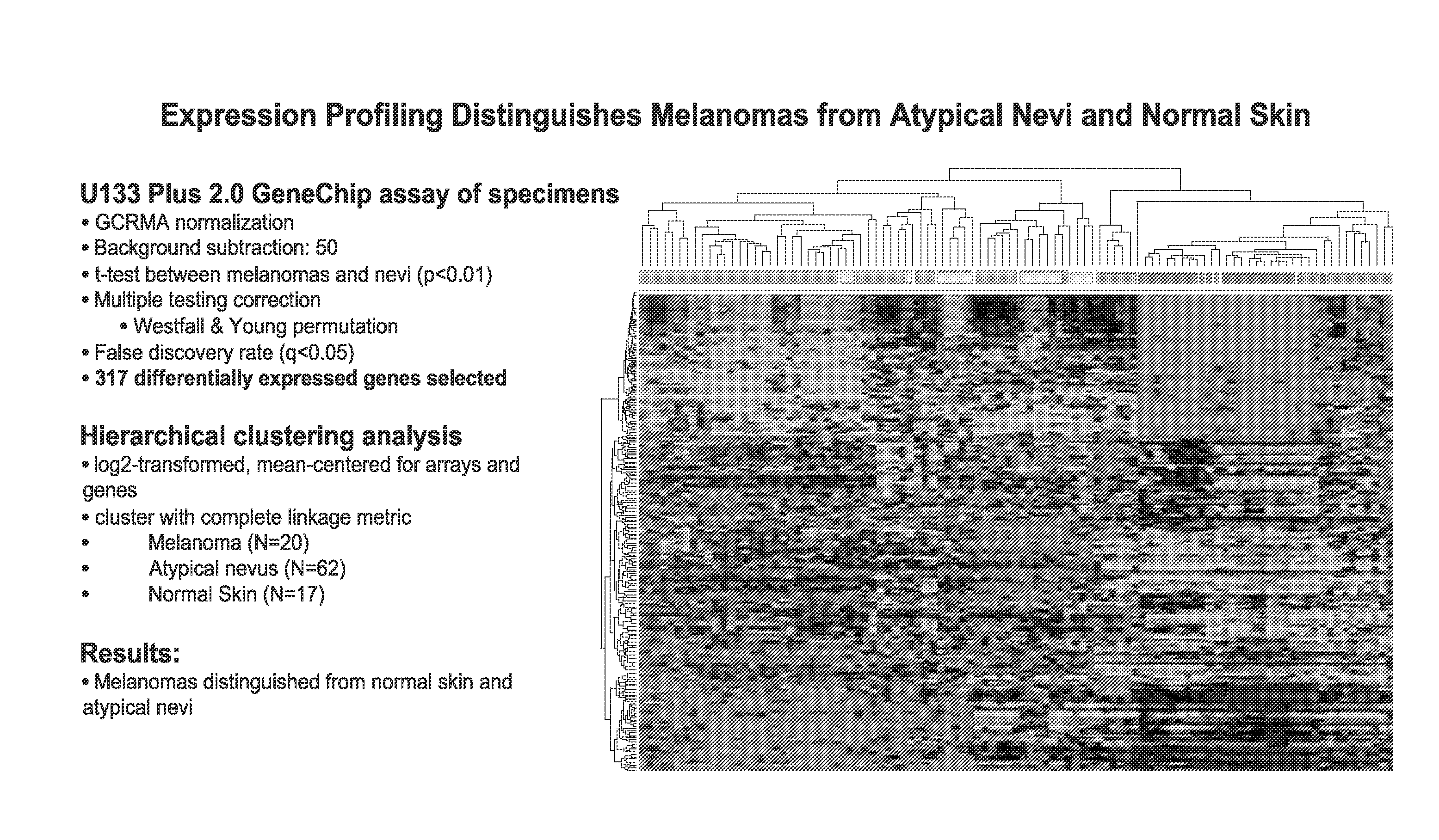
Diagnosis of melanoma by nucleic acid analysis
InactiveUS20080274908A1Less traumaticMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningProtein profilingCuticle
The present invention provides methods for diagnosing melanoma in a subject by analyzing nucleic acid molecules obtained from the subject. The present invention also provides methods for distinguishing melanoma from dysplastic nevi and / or normal pigmented skin. The methods include analyzing expression or mutations in epidermal samples, of one or more skin markers. The methods can include the use of a microarray to analyze gene or protein profiles from a sample.
Owner:DERMTECH INT
Prostate cancer-related nucleic acids
ActiveUS20070259352A1Increase signal strengthSpecific hybridizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsTumor rejection antigen precursorsNucleotideProstate cancer
Described herein are novel polynucleotides associated with prostate cancer. The polynucleotides are miRNAs, miRNA precursors, and associated nucleic acids. Methods and compositions are described that can be used for diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of prostate cancer. Also described herein are methods that can be used to identify modulators of the disease-associated polynucleotides. Also described herein are methods and compositions for linear amplification and labeling of a targeted nucleic acid. The amplified targeted molecules may be used in hybridization techniques like Luminex and Microarray analysis.
Owner:ROSETTA GENOMICS
Gene discovery using microarrays
InactiveUS20020045169A1Improved and robustQuick fixBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenomeMicroarray profiling
The invention relates to methods and systems (e.g., computer systems and computer program products) for identifying and characterizing genes using microarrays. In particular, the invention provides for improved, robust methods for detecting genes through the use of microarrays to analyze the expression state of the genome. Genes which are expressed can be mapped to their respective positions in the genome, and the structure of such genes can be determined.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
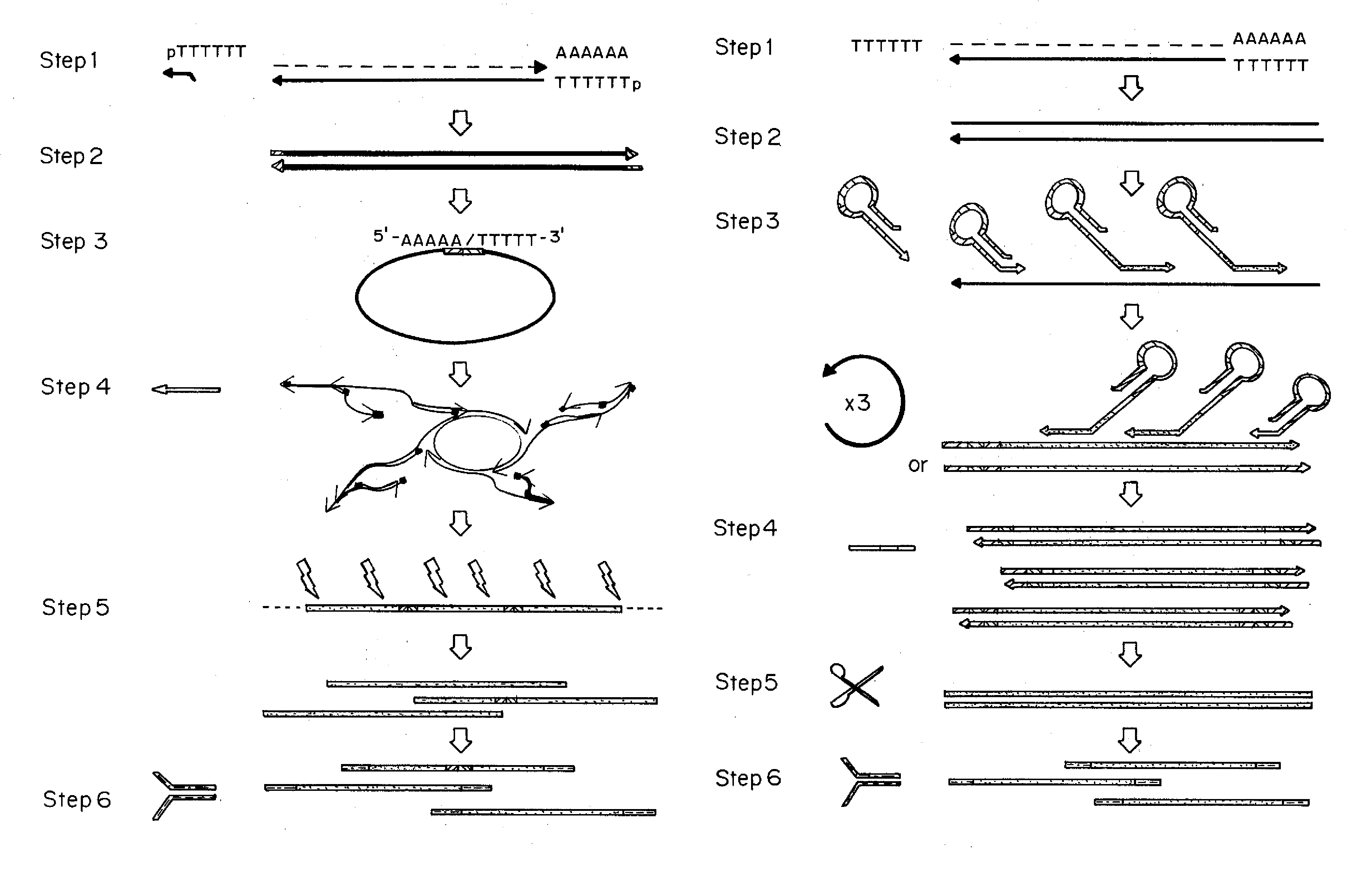
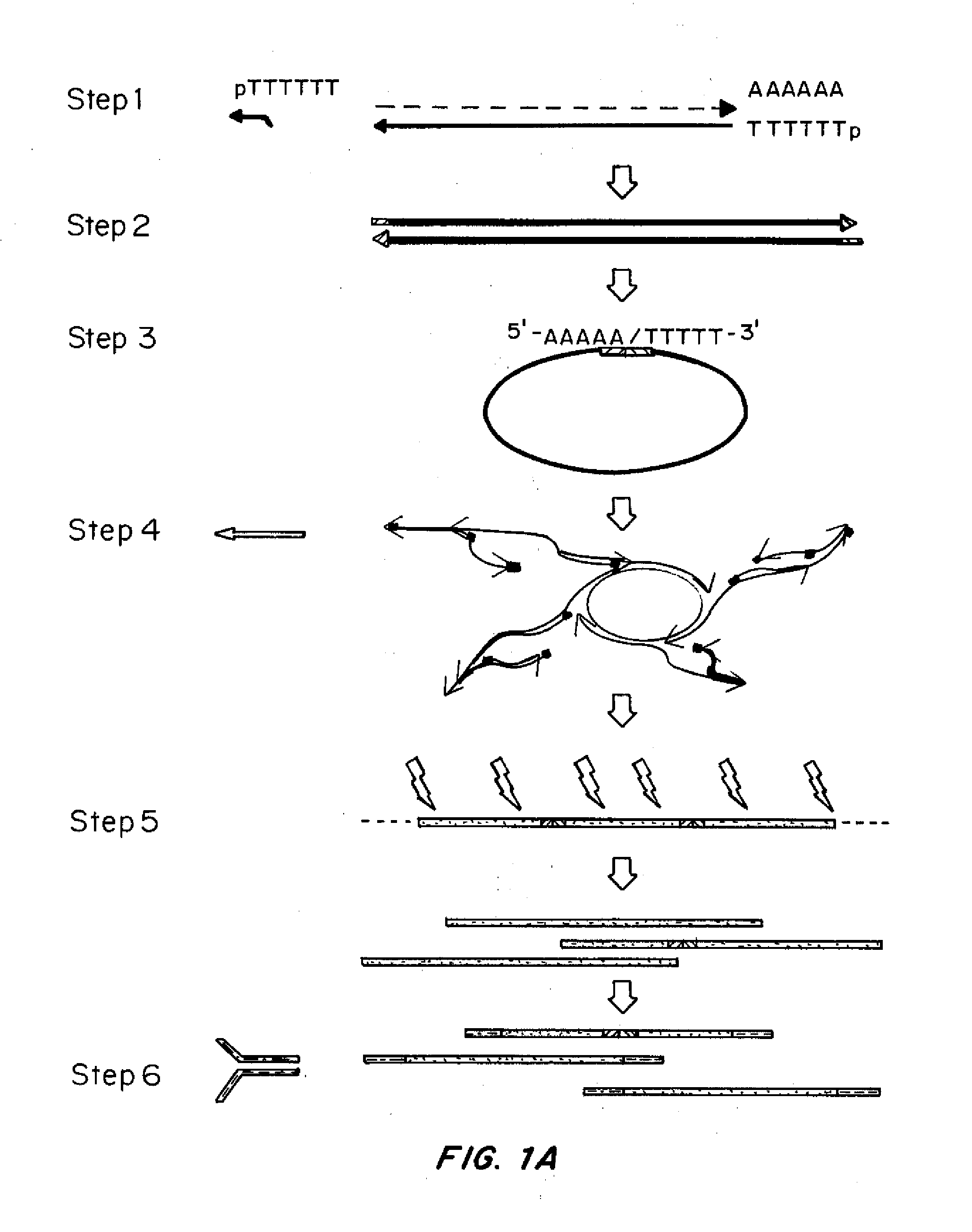
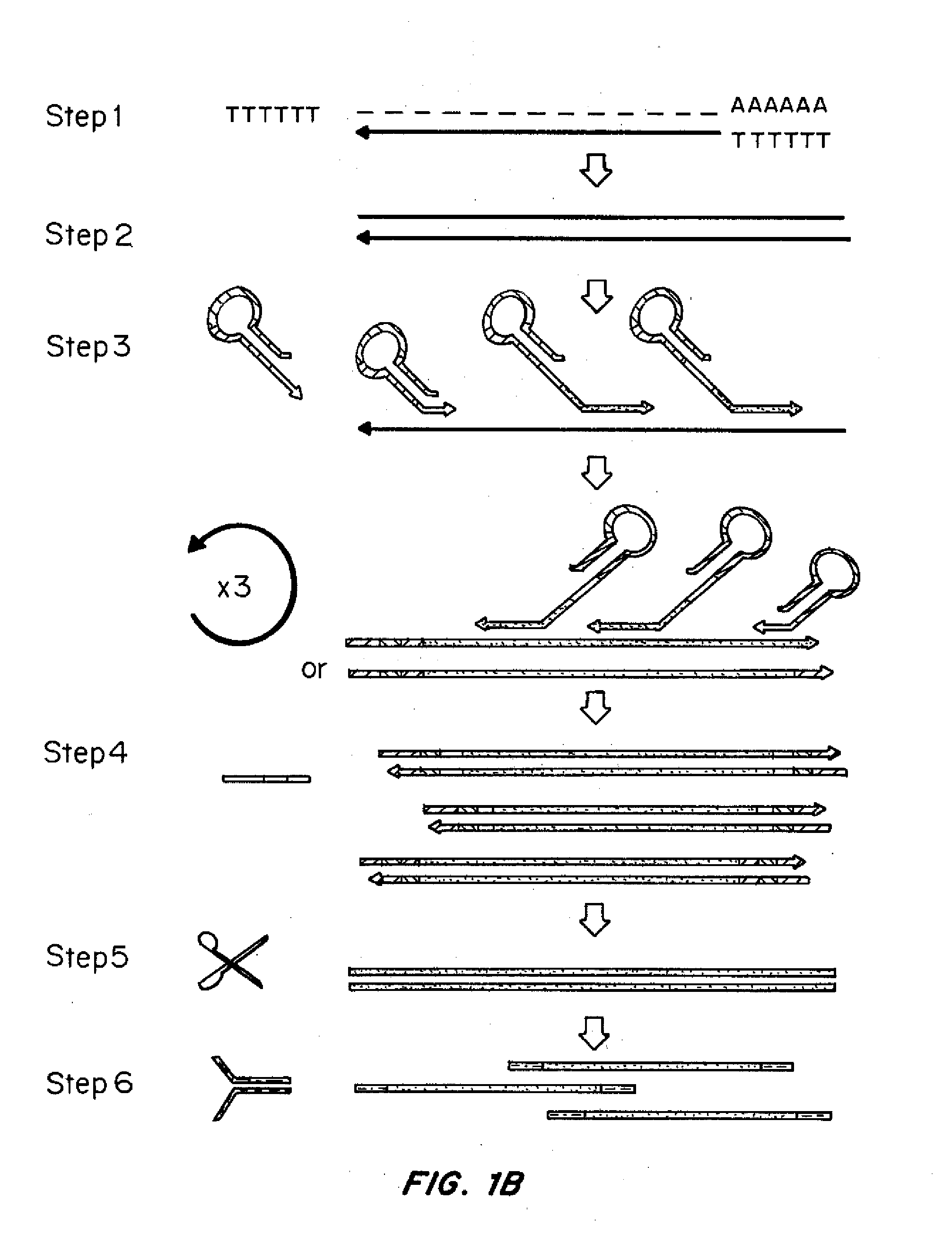
Methods and kits for 3'-end-tagging of RNA
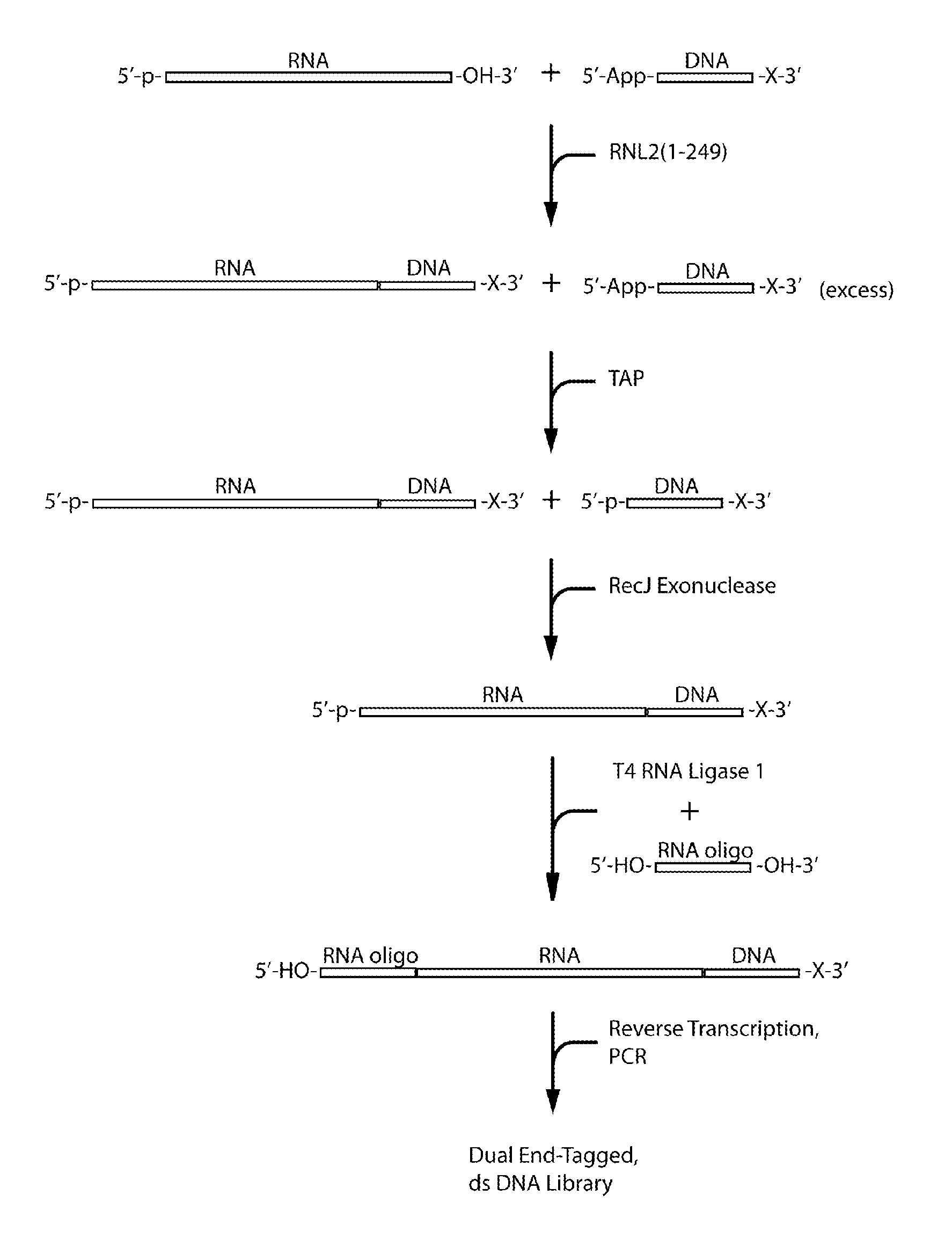
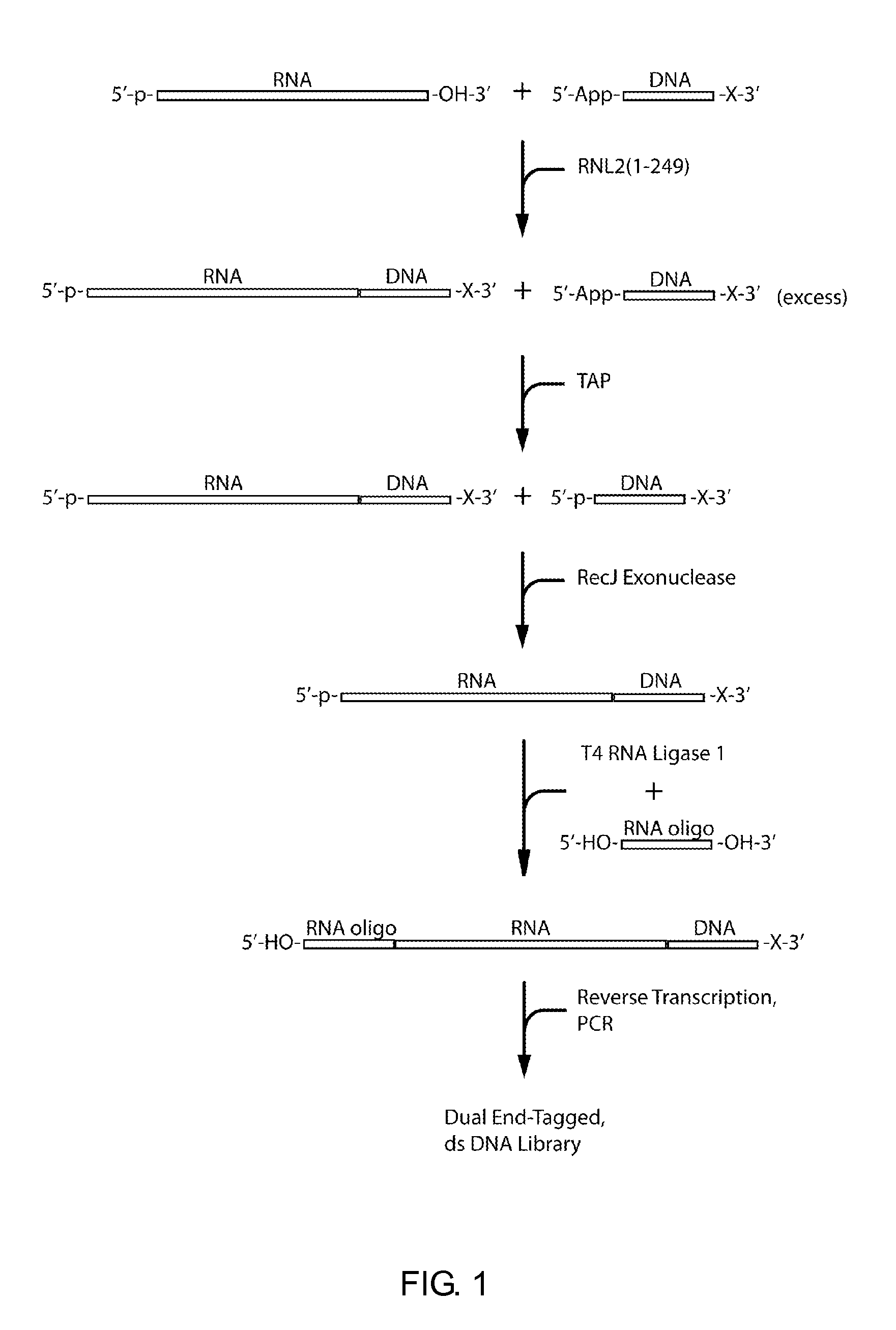
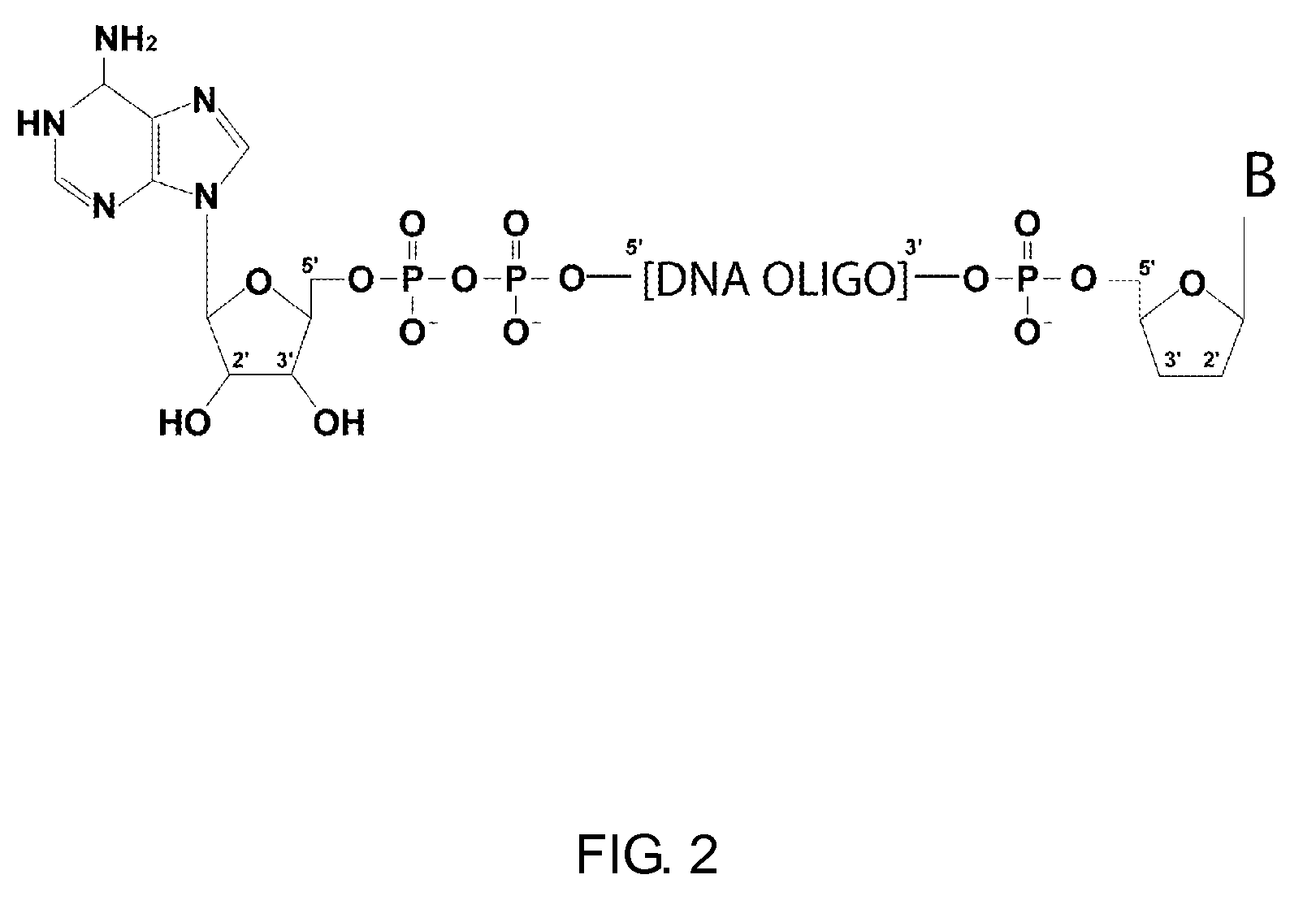
ActiveUS20110104785A1High detection sensitivityRapid and efficient enzymaticHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementRNA SequenceSingle strand dna
The present innovation provides methods and kits that enable rapid and efficient dual end-tagging of RNA to prepare libraries for analysis by applications such as next-generation RNA sequencing, qPCR, microarray analysis, or cloning. The methods do not require time-consuming and inefficient gel-purification steps that are common to methods known in the art. In addition, the present invention provides methods and kits for rapid, high-throughput enzymatic preparation of 5′-activated, 3′-blocked DNA oligonucleotides from standard, single-stranded DNA oligonucleotides.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Adam12 as a biomarker for bladder cancer
InactiveUS20090029372A1Improve the level ofLower Level RequirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisTissue ArraysAffymetrix genechip
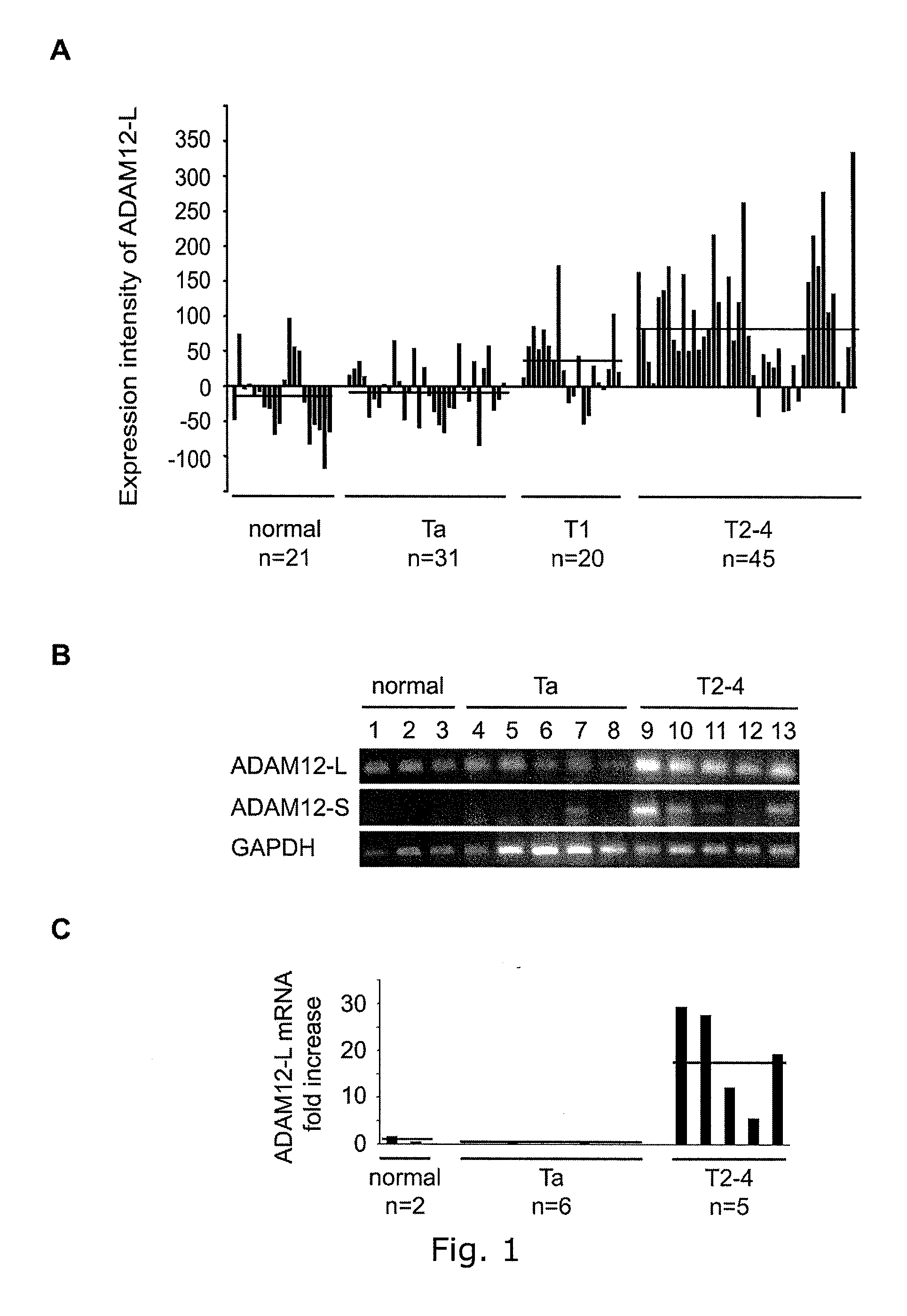
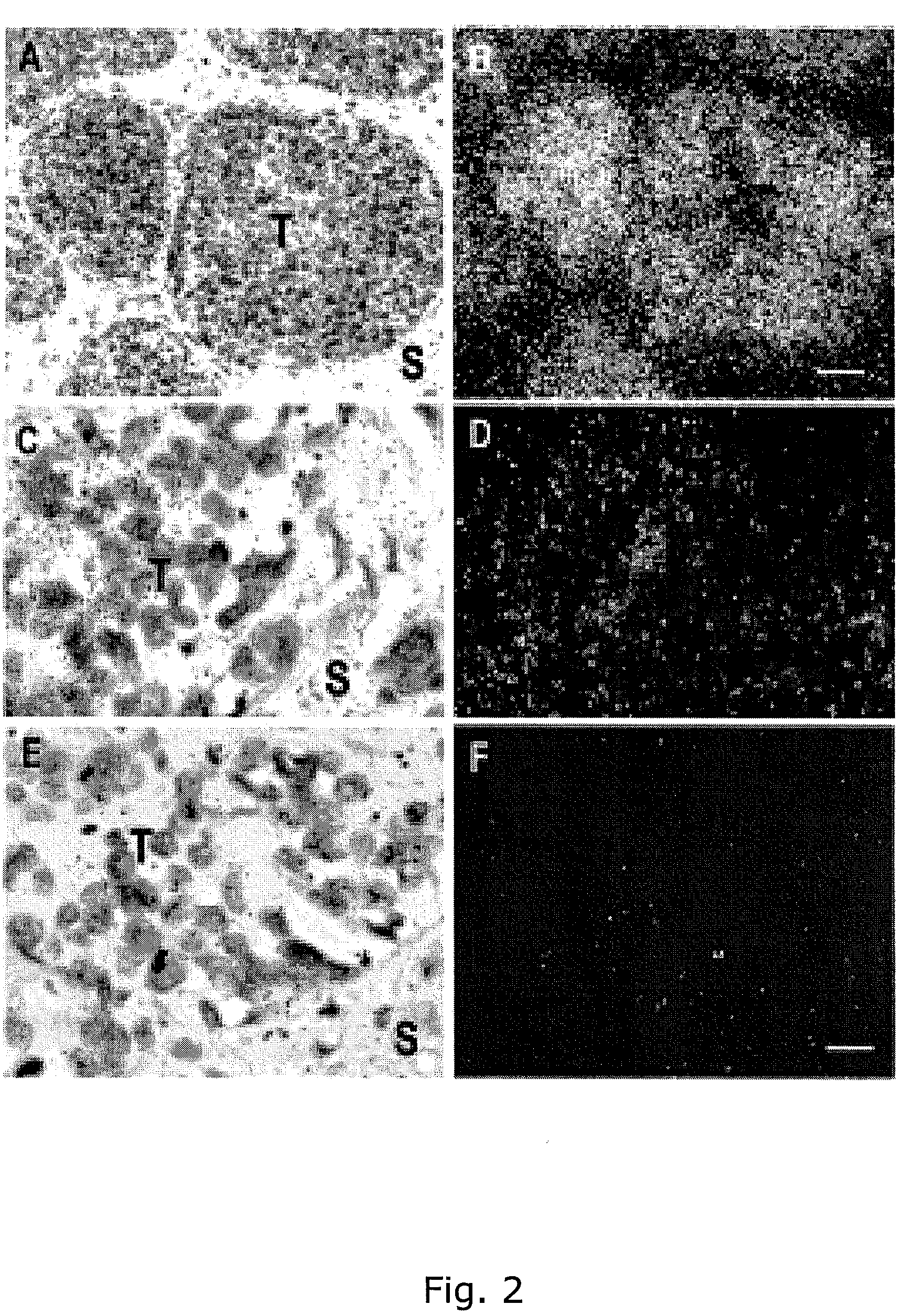
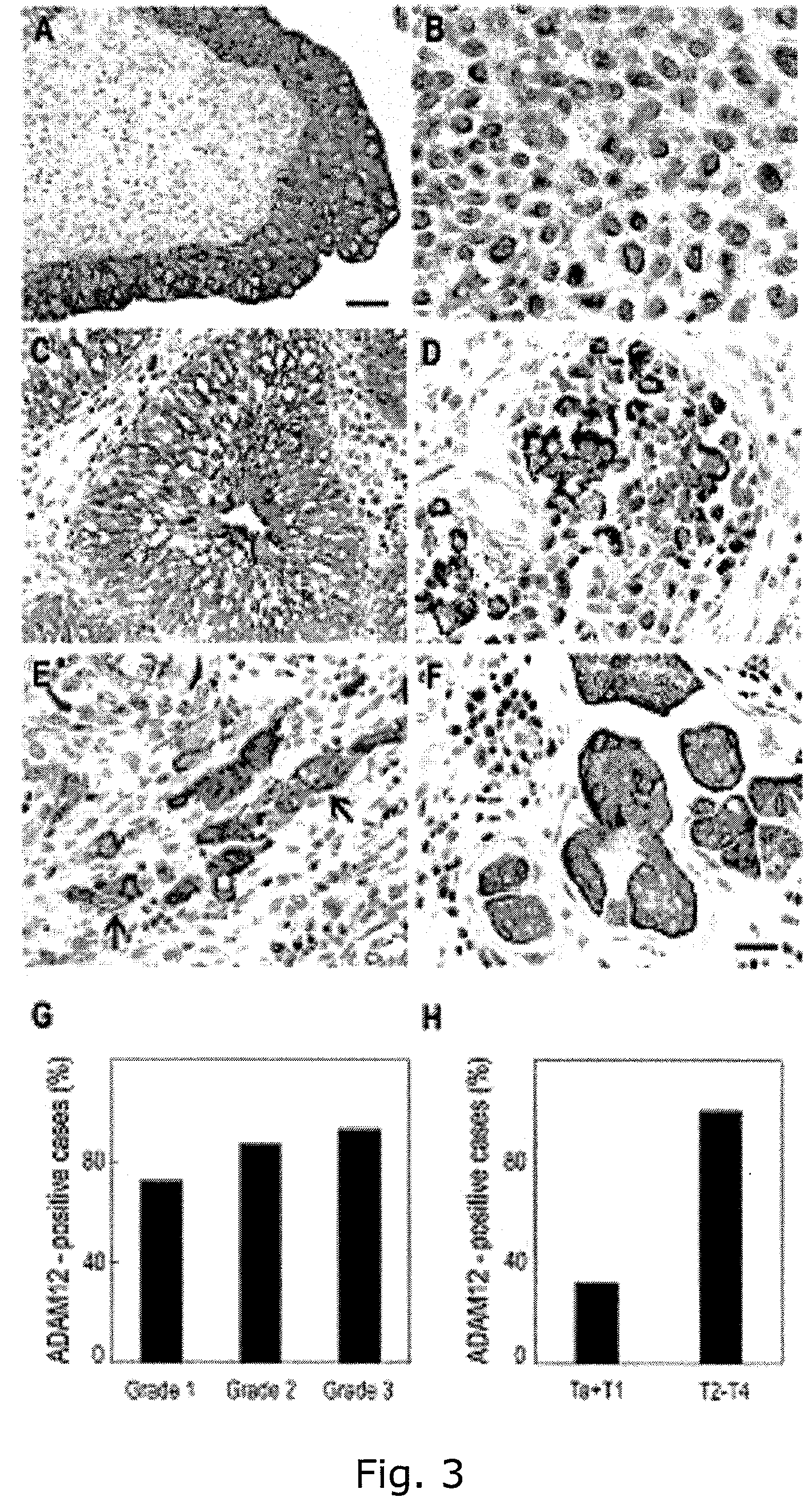
The present inventors have shown that the gene and protein expression profiles of ADAM8, ADAM10 and ADAM12 in different grades and stages of bladder cancer.ADAM12 gene expression was evaluated in tumors from 96 patients with bladder cancer using a customized Affymetrix GeneChip. Gene expression in bladder cancer was validated using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), quantitative PCR, and in situ hybridization. Protein expression was evaluated by immunohistochemical staining on tissue arrays of bladder cancers.The presence and relative amount of ADAM12 in the urine of cancer patients were determined by Western blotting and densitometric measurements, respectively.Particularly ADAM12 mRNA expression was significantly upregulated in bladder cancer, as determined by microarray analysis, and the level of ADAM12 mRNA correlated with disease stage. ADAM12 protein expression correlated with tumor stage and grade. ADAM12 was present in higher levels in the urine from bladder cancer patients than in urine from healthy individuals. Significantly, following removal of tumor by surgery, in most bladder cancer cases examined the level of ADAM12 in the urine decreased and, upon recurrence of tumor, increased.
Owner:PHYSICIANS CHOICE LAB SERVICES +1
Liver cancer-related nucleic acids
ActiveUS7592441B2Late detectionSpecific hybridizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsTumor rejection antigen precursorsNucleotideLinear amplification
Described herein are novel polynucleotides associated with liver cancer. The polynucleotides are miRNAs, miRNA precursors, and associated nucleic acids. Methods and compositions are described that can be used for diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of liver cancer. Also described herein are methods that can be used to identify modulators of the disease-associated polynucleotides. Also described herein are methods and compositions for linear amplification and labeling of a targeted nucleic acid. The amplified targeted molecules may be used in hybridization techniques like Luminex and Microarray analysis.
Owner:ROSETTA GENOMICS
Integrated microarray analysis
ActiveUS7364848B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPorous substrateAnalyte
The present invention relates to methods for identifying analyte nucleic acids present in a sample comprising nucleic acid molecules, said method comprising the steps of: (a) providing a porous substrate, said substrate comprising a plurality of micro-channels, wherein said micro-channels have immobilized thereon a target molecule capable of binding to an analyte present in said sample; wherein said channels are further provided with analyte amplification components, a reporter system; and said sample; (b) amplifying analyte nucleic acid molecules present within said sample; and (c) allowing binding to take place between an amplified analyte nucleic acid obtained in step (b), said target molecule immobilized onto the channels of said substrate and said reporter system, wherein said reporter system allows detecting whether binding has occurred between said target molecule and said analyte nucleic acid. The present invention further relates to the use of said methods as well as kits for carrying out said methods.
Owner:PAMGENE
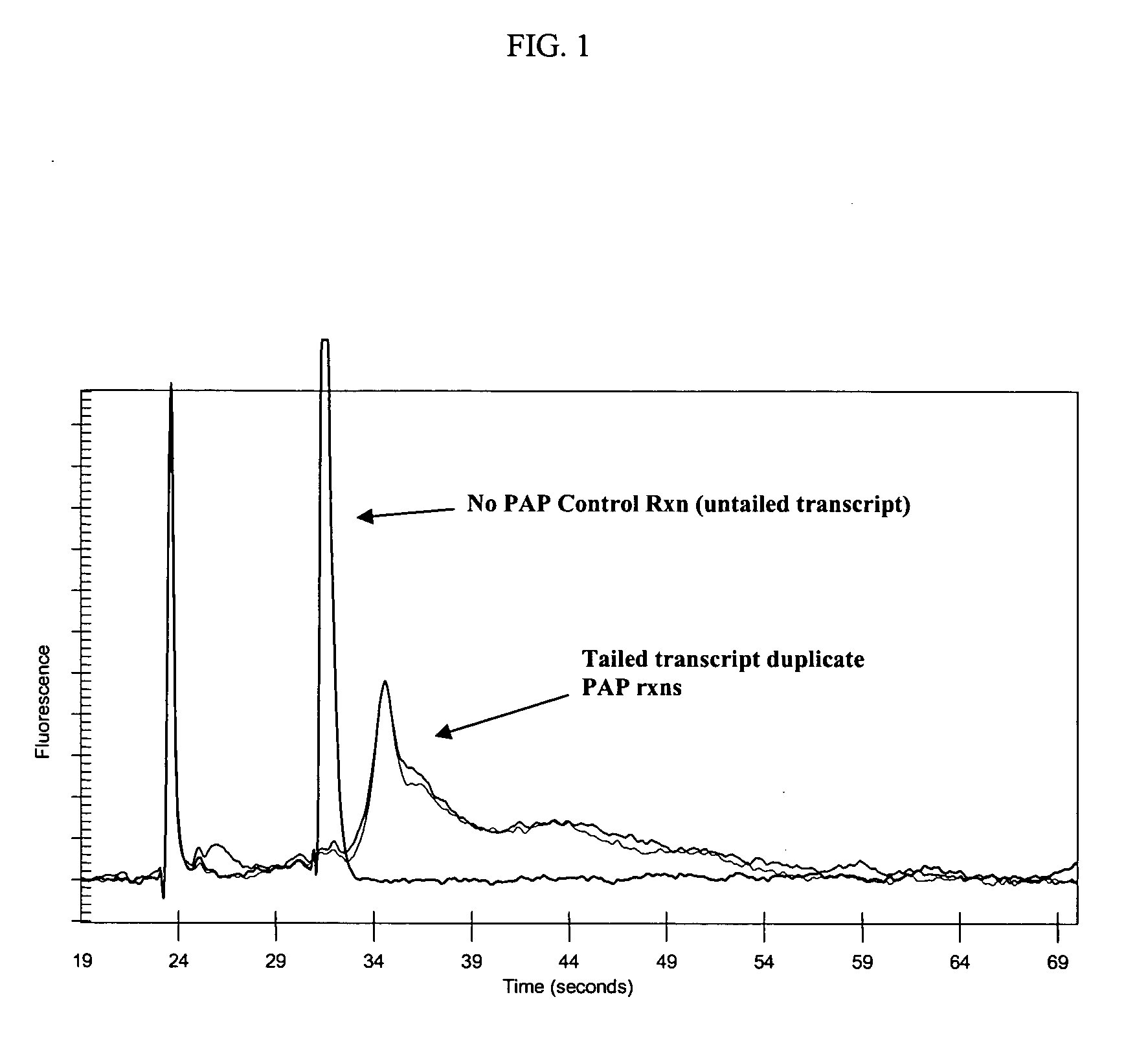
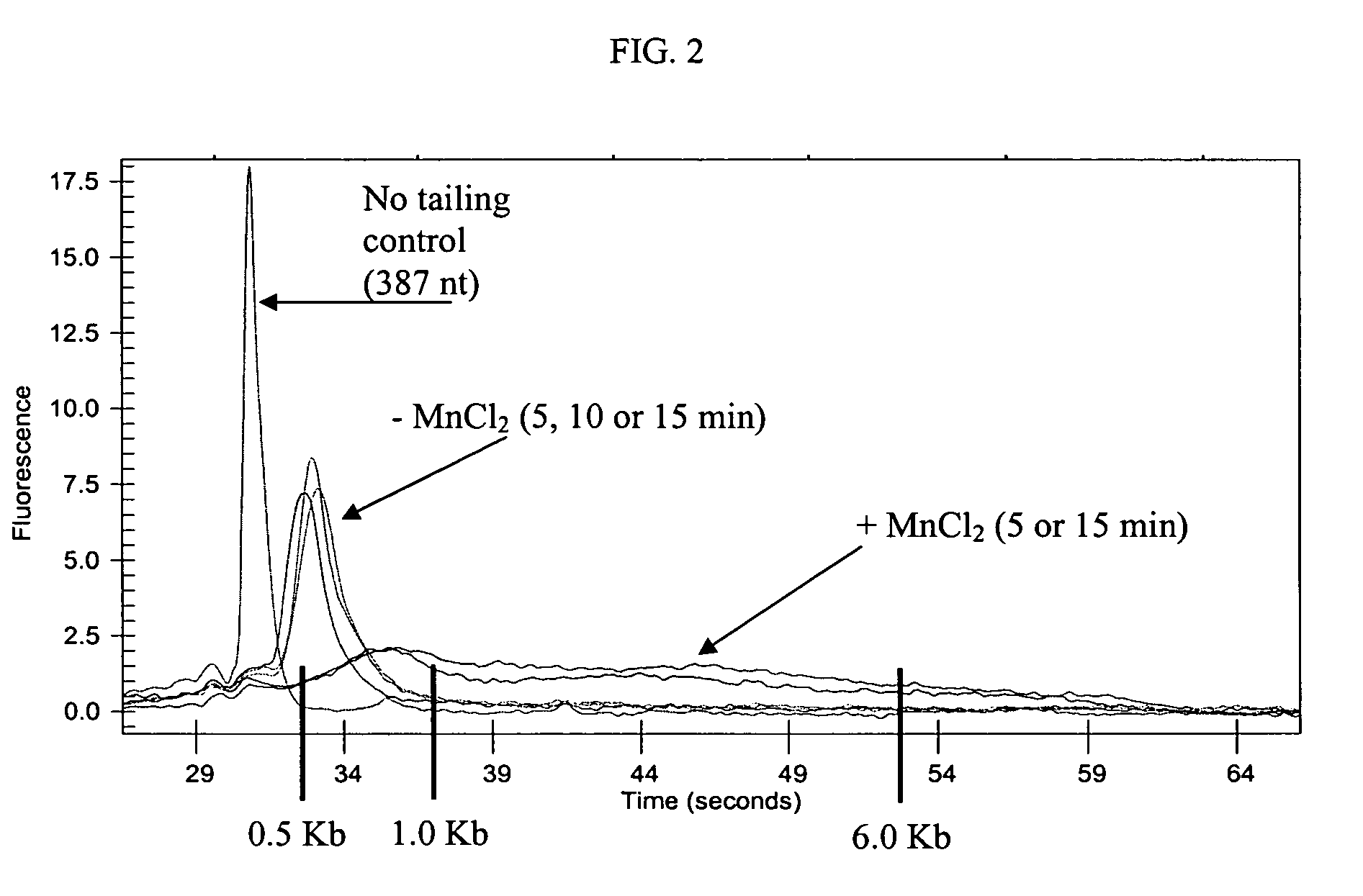
Methods and compositions for tailing and amplifying RNA
ActiveUS20060051771A1Efficiently and uniformlyEfficiently and uniformly tailMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenome wide expressionGenome
The present invention provides methods and compositions that enable tagging and amplification of targeted RNA molecules. A targeted RNA molecule is any non-polyadenylated RNA molecule including, for example, miRNA, siRNA, rRNA, tRNA, synthetic RNA, or non-polyadenylated mRNA such as mRNA from bacteria. In certain aspects, the invention provides methods and compositions for the genome-wide expression analysis of bacterial genes. Significantly, the methods enable genome-wide expression analysis in circumstances where bacterial numbers were previously too low to purify adequate amounts of RNA for DNA microarray analysis or other applications. Such methods are particularly useful for the study of bacterial gene expression during host-cell infection. The invention also provides kits for tagging and amplifying targeted RNA molecules.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
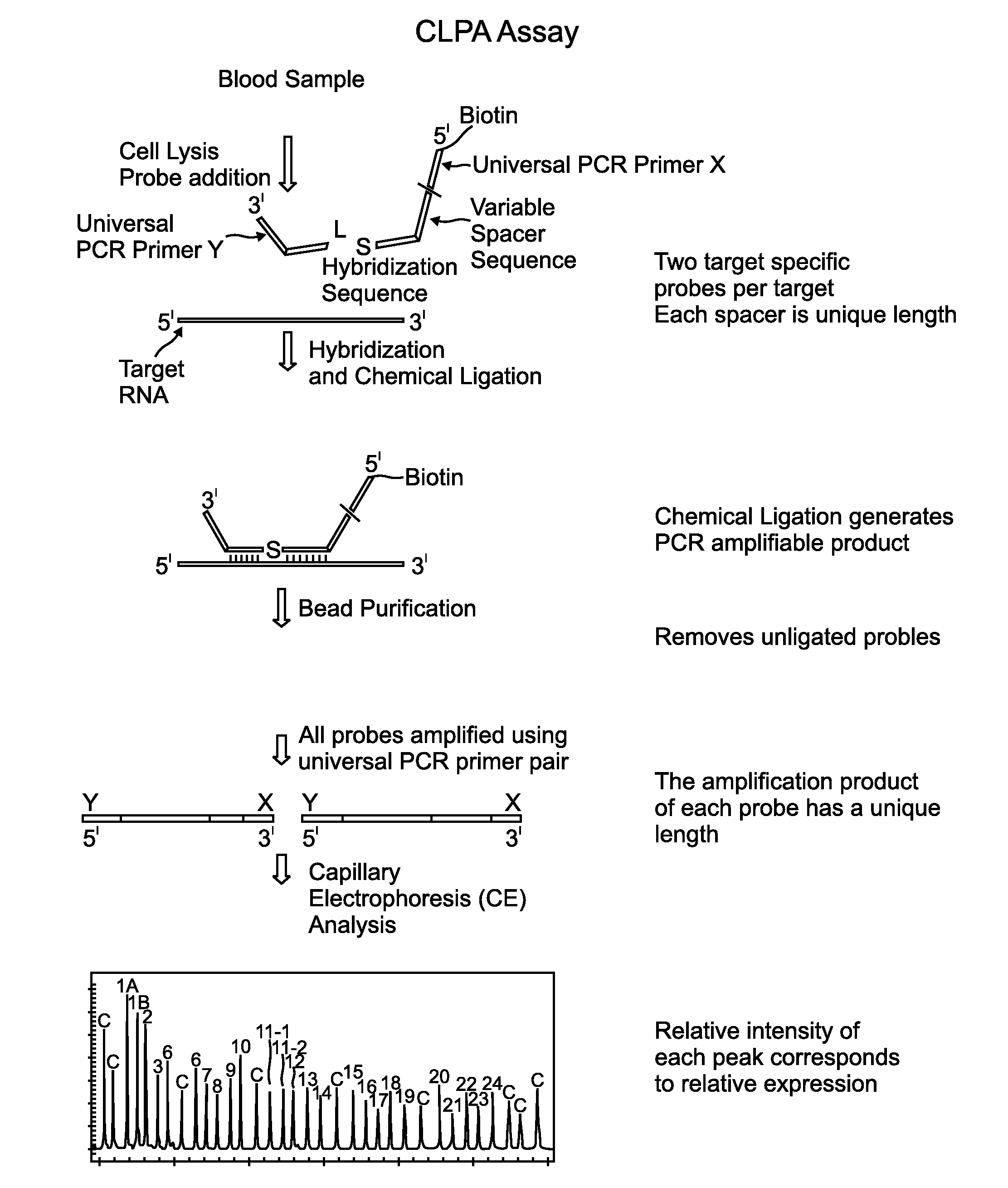
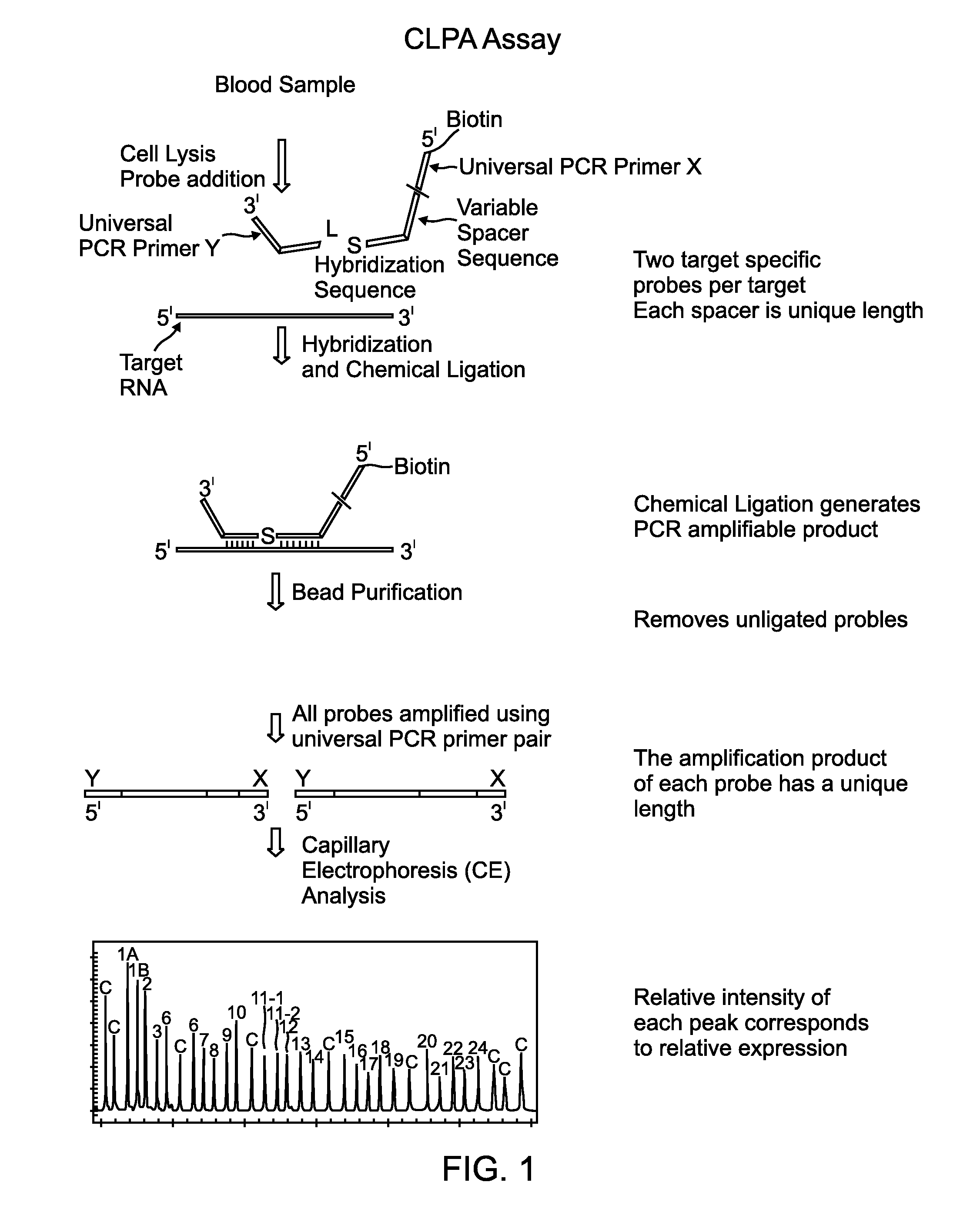
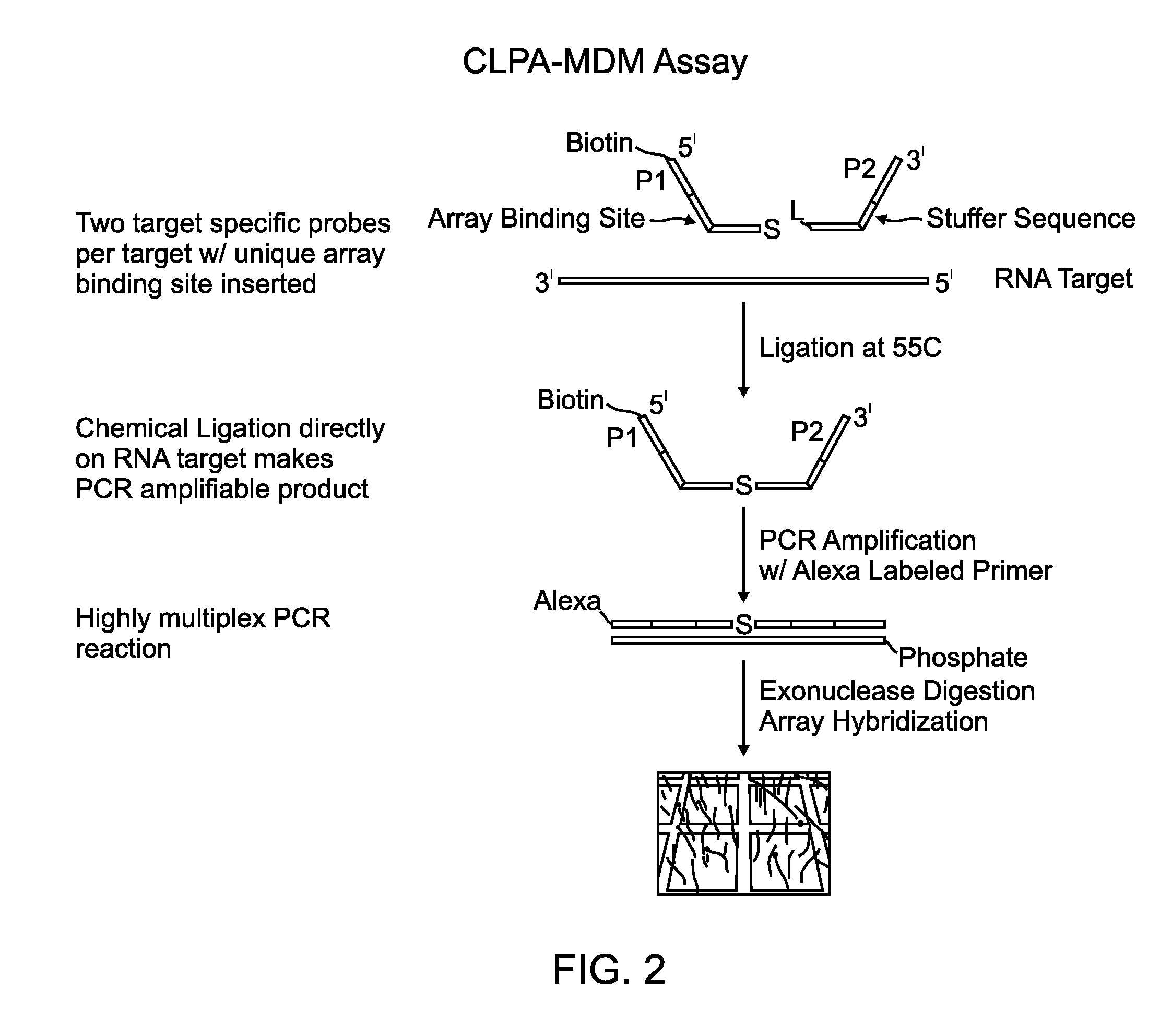
Chemical ligation dependent probe amplification (CLPA)
ActiveUS20100267585A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical ligationCapillary electrophoresis
The present invention provides compositions, apparatuses and methods for detecting one or more nucleic acid targets present in a sample. Methods of the invention include utilizing two or more oligonucleotide probes that reversibly bind a target nucleic acid in close proximity to each other and possess complementary reactive ligation moieties. When such probes have bound to the target in the proper orientation, they are able to undergo a spontaneous chemical ligation reaction that yields a ligated oligonucleotide product. In one aspect, the ligation product is of variable length that correlates with a particular target. Following chemical ligation, the probes may be amplified and detected by capillary electrophoresis or microarray analysis.
Owner:DXTERITY DIAGNOSTICS
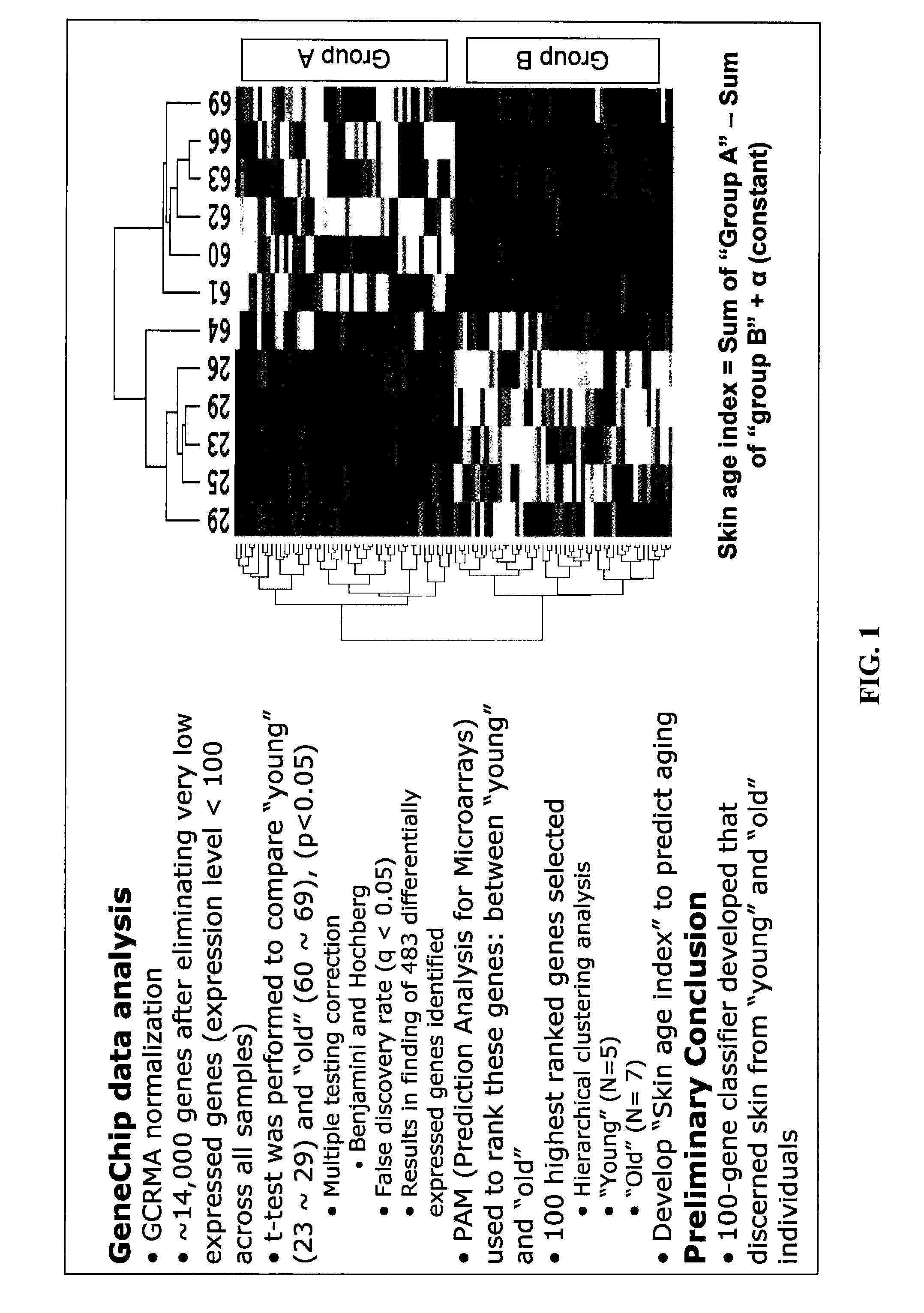
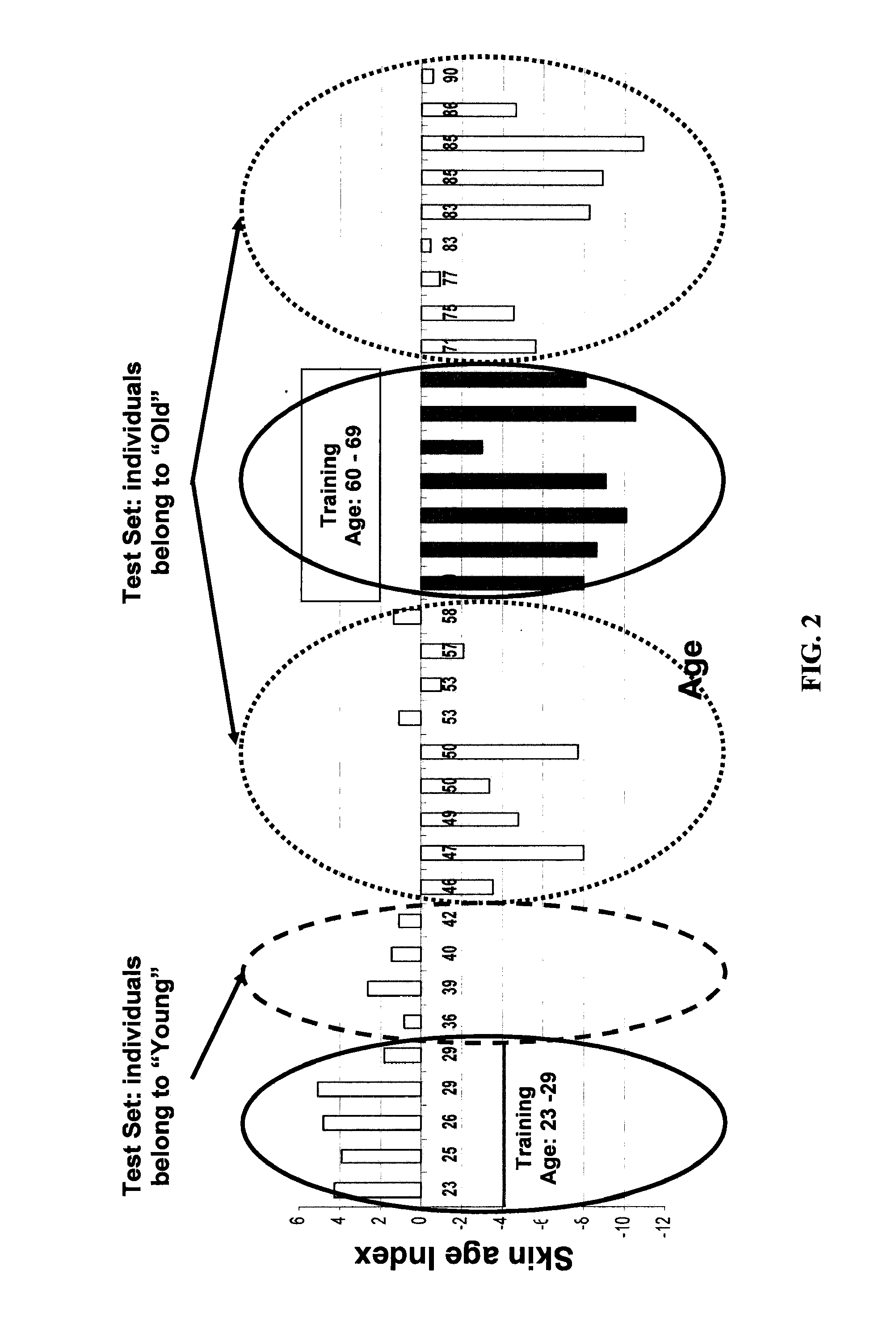
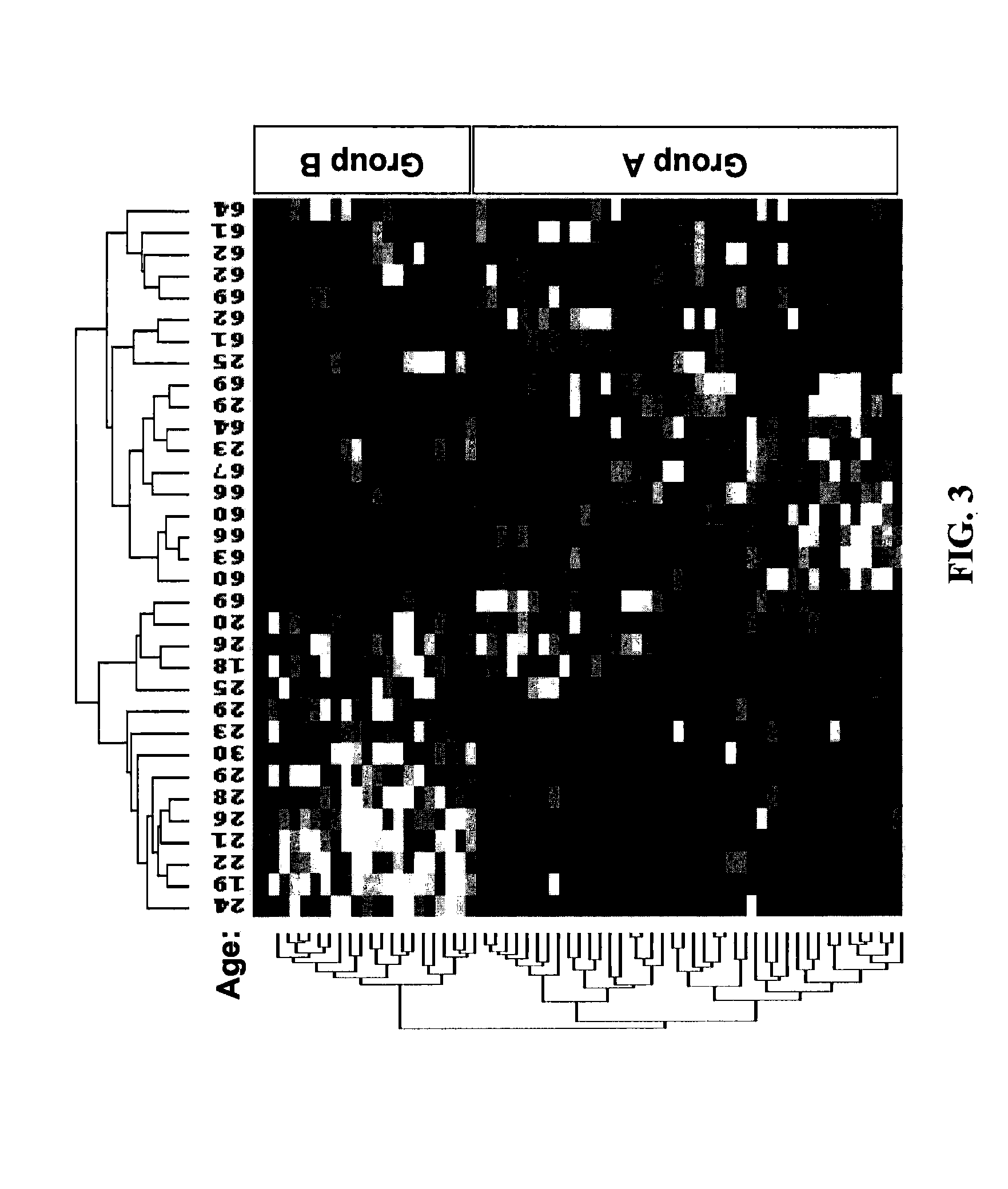
Determining Age Ranges of Skin Samples
InactiveUS20100086501A1Ensure adequate isolationReducing and increasing expression of geneCosmetic preparationsCompound screeningProtein profilingProtein molecules
The present invention provides methods for characterizing a skin sample of a subject as belonging to an age range by analyzing nucleic acid or protein molecules obtained from the subject. The methods include analyzing expression or mutations in epidermal samples, of one or more skin markers. The methods can include the use of a microarray to analyze gene or protein profiles from a sample and compare them with a known skin age index. Therapeutic and cosmetic formulations are also provided herein.
Owner:DERMTECH INT
Lung cancer-related nucleic acids
ActiveUS20080182237A1Increase signal strengthSpecific hybridizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDiseaseNucleotide
Described are polynucleotides associated with lung cancer. The polynucleotides are miRNAs, miRNA precursors, and associated nucleic acids. Methods and compositions are described that can be used for diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of lung cancer. Also described are methods that can be used to identify modulators of the disease-associated polynucleotides. Also described are methods and compositions for linear amplification and labeling of a targeted nucleic acid. The amplified targeted molecules may be used in hybridization techniques like Luminex and Microarray analysis.
Owner:ROSETTA GENOMICS
Translucent solid matrix assay device dor microarray analysis
InactiveUS20060211044A1Low production costImprove the level ofBioreactor/fermenter combinationsImage enhancementNitrocelluloseCellophane
The present invention concerns methods and compositions relating to translucent matrix arrays. In certain embodiments, the arrays are reconfigurable. Reconfigurable arrays may be produced using small linker molecules, such as aptamers or affibodies, which preferably bind to an IgG specific portion of antibodies. Such arrays may be used to detect any target that binds selectively or specifically to an IgG. Translucent matrix arrays may utilize cellophane, rayon or a translucent, colloidal form of nitrocellulose to coat the substrate. Other embodiments concern methods of data analysis and apparatus for analyte detection. Certain embodiments concern a total optical assay device (TOAD™), which may be used with GRABBER™ slides and / or FOOTPAD™ microtiter well assay devices.
Owner:PRITEST
Use Of Genes As Molecular Markers In Diagnosis Of Schizophrenia And Diagnostic Kit For The Same
InactiveUS20080274455A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementQuantitative Real Time PCRScreening method
Drug-naive and drug-free schizophrenic PBL were screened to identify additional markers that are differentially expressed compared to healthy individuals using microarray and quantitative real-time PCR (QRT-PCR) techniques. Genes for dopamine D2 receptor (DRD2) and inwardly rectifying potassium channel (Kir2.3) were found to be overexpressed in microarray analysis. Increased mRNA levels were confirmed by QRT-PCR using SybrGreen method and dual labeled TaqMan probes.The invention relates to a method for diagnosing schizophrenia in a subject comprising assessing the level or the expression level of at least one of the following genes or proteins: Kir2.3 or DRD2 or a gene encoding Kir2.3 or DRD2. The invention further relates to agents and uses thereof, said agents specifically binding to said proteins or nucleic acids encoding them, diagnostic kits and screening methods.Use of both molecular markers allow prediction of schizophrenia and help to follow efficiency of drugs in therapy in order to provide a more tailored medication for schizophrenic patients.
Owner:THE BIOLOGICAL RES CENT OF THE HUNGARIAN ACAD OF SCI
Methods of determining acute myeloid leukemia response to treatment with farnesyltransferase
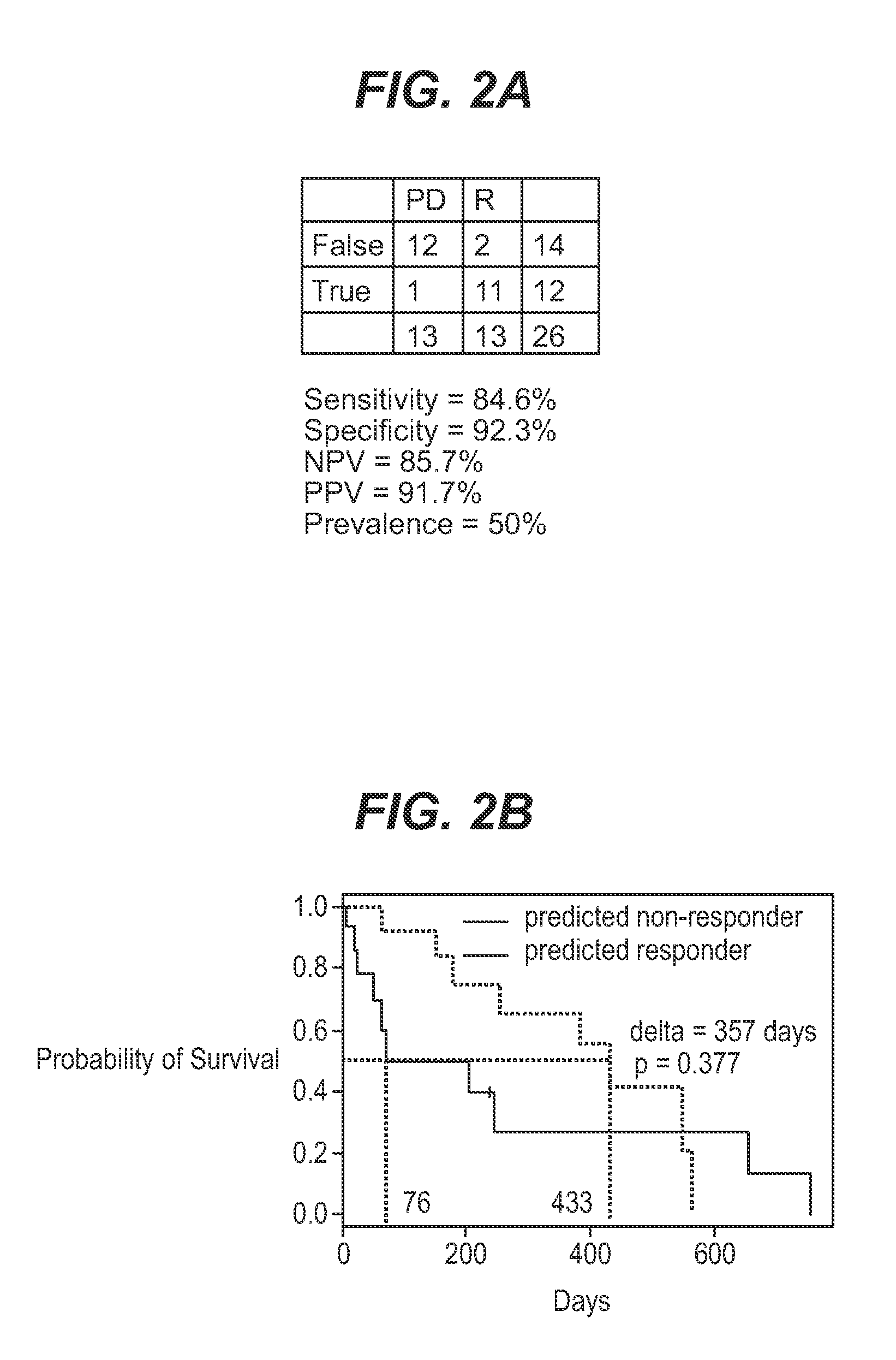
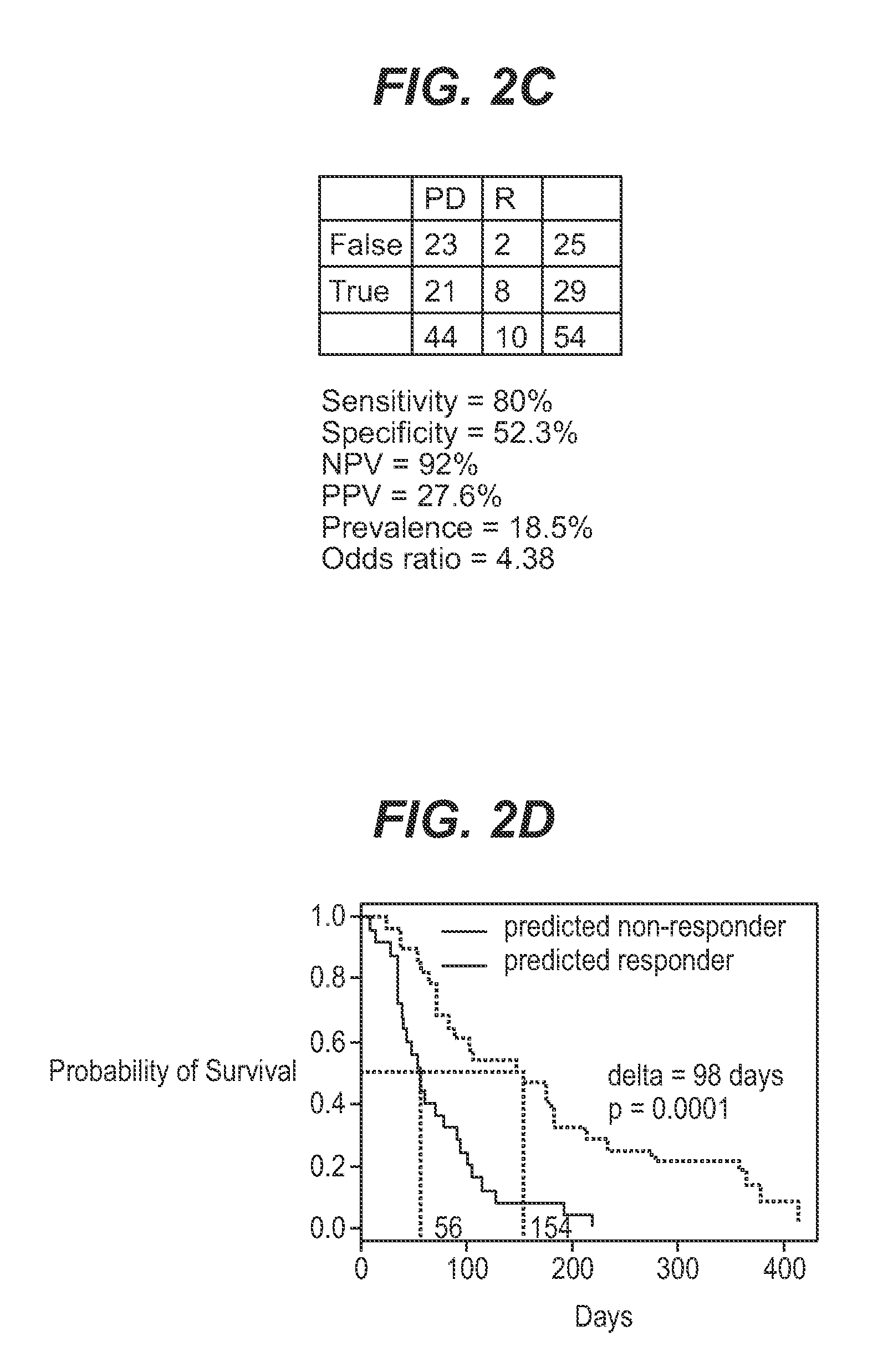
InactiveUS7932036B1Improve accuracyHigh response rateSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNewly diagnosedClinical study
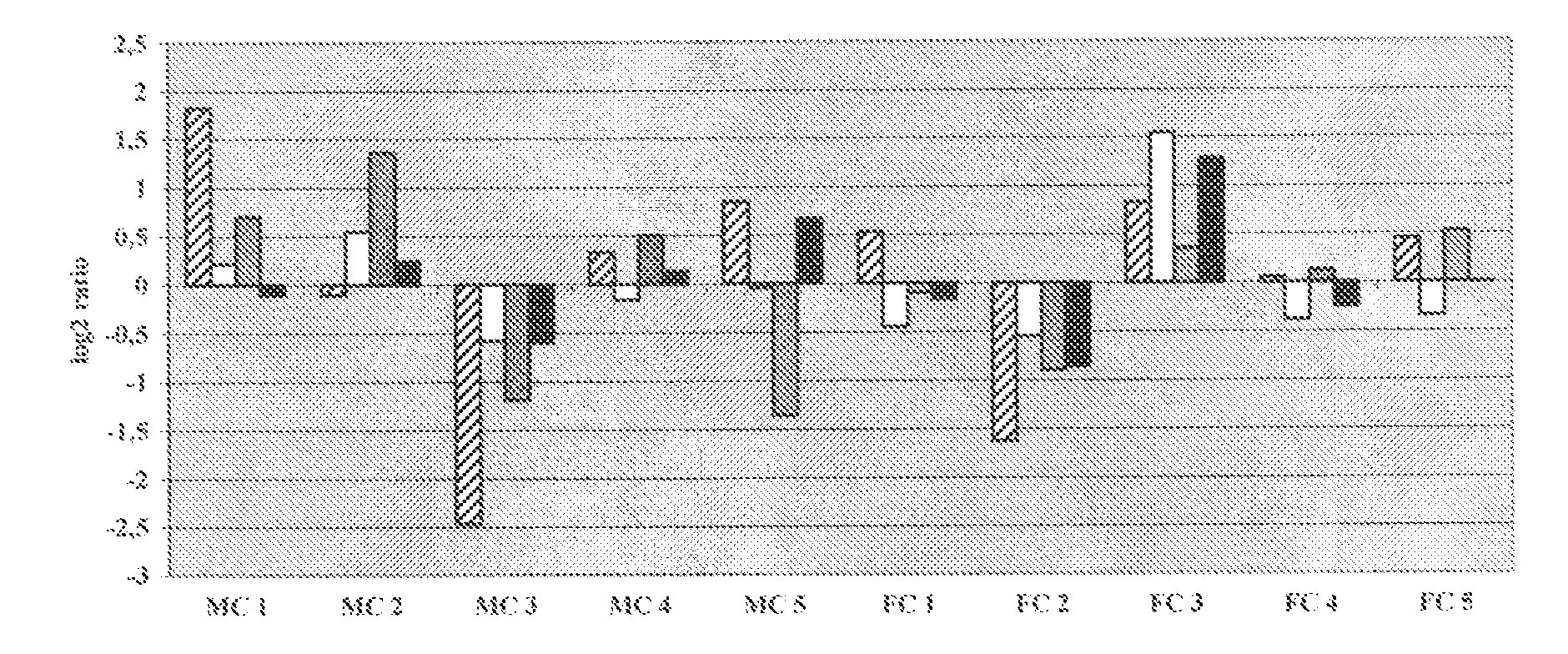
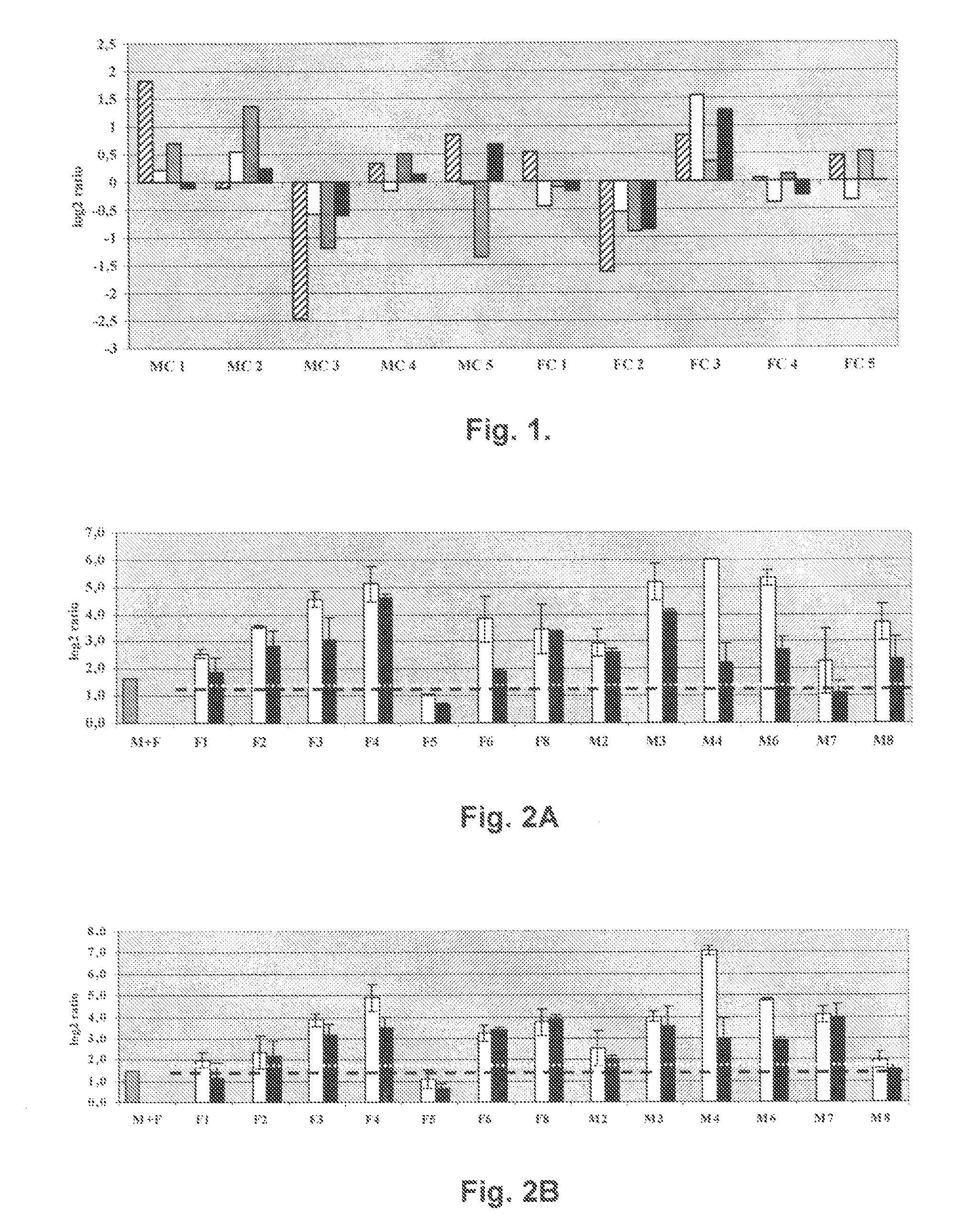
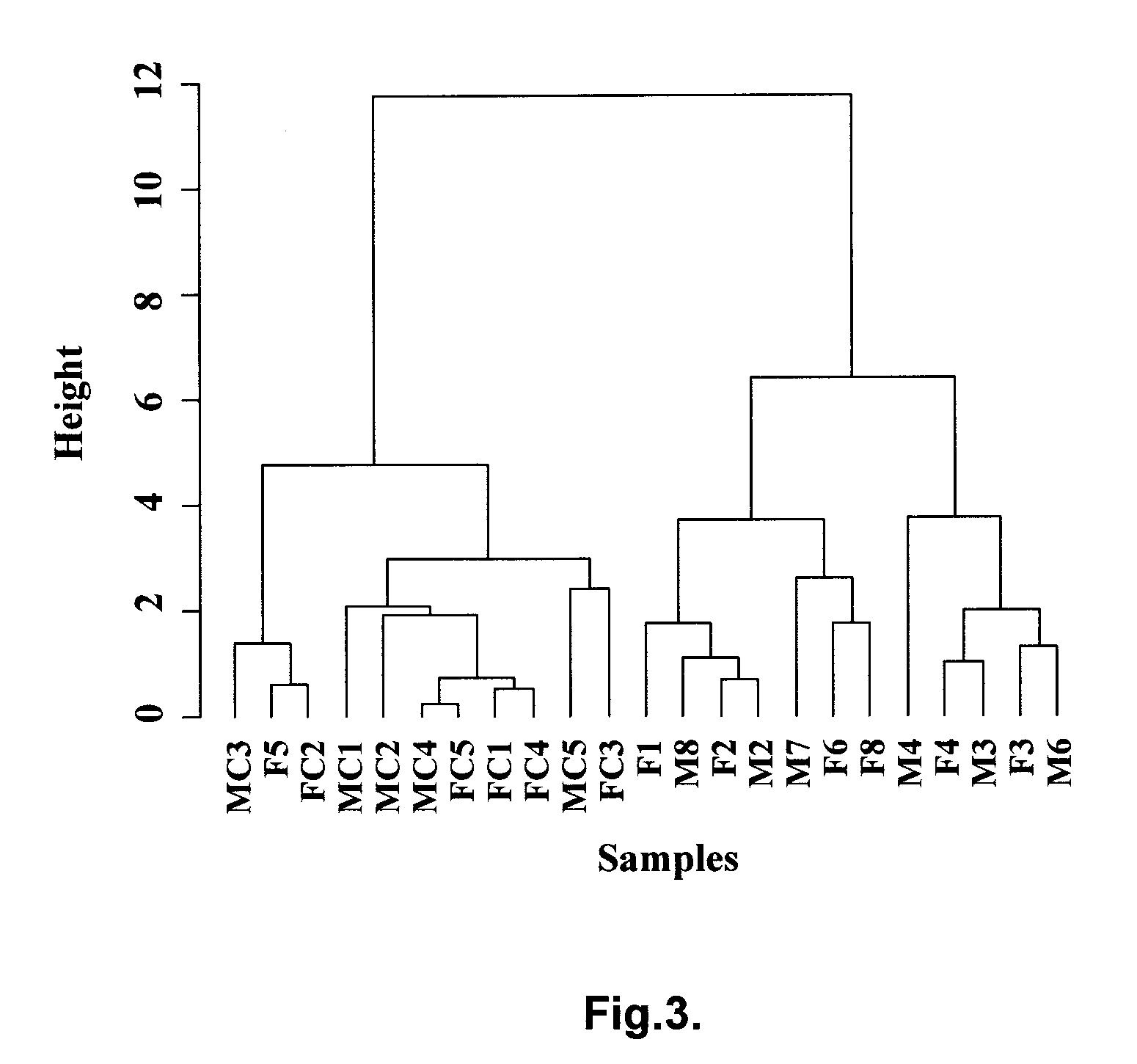
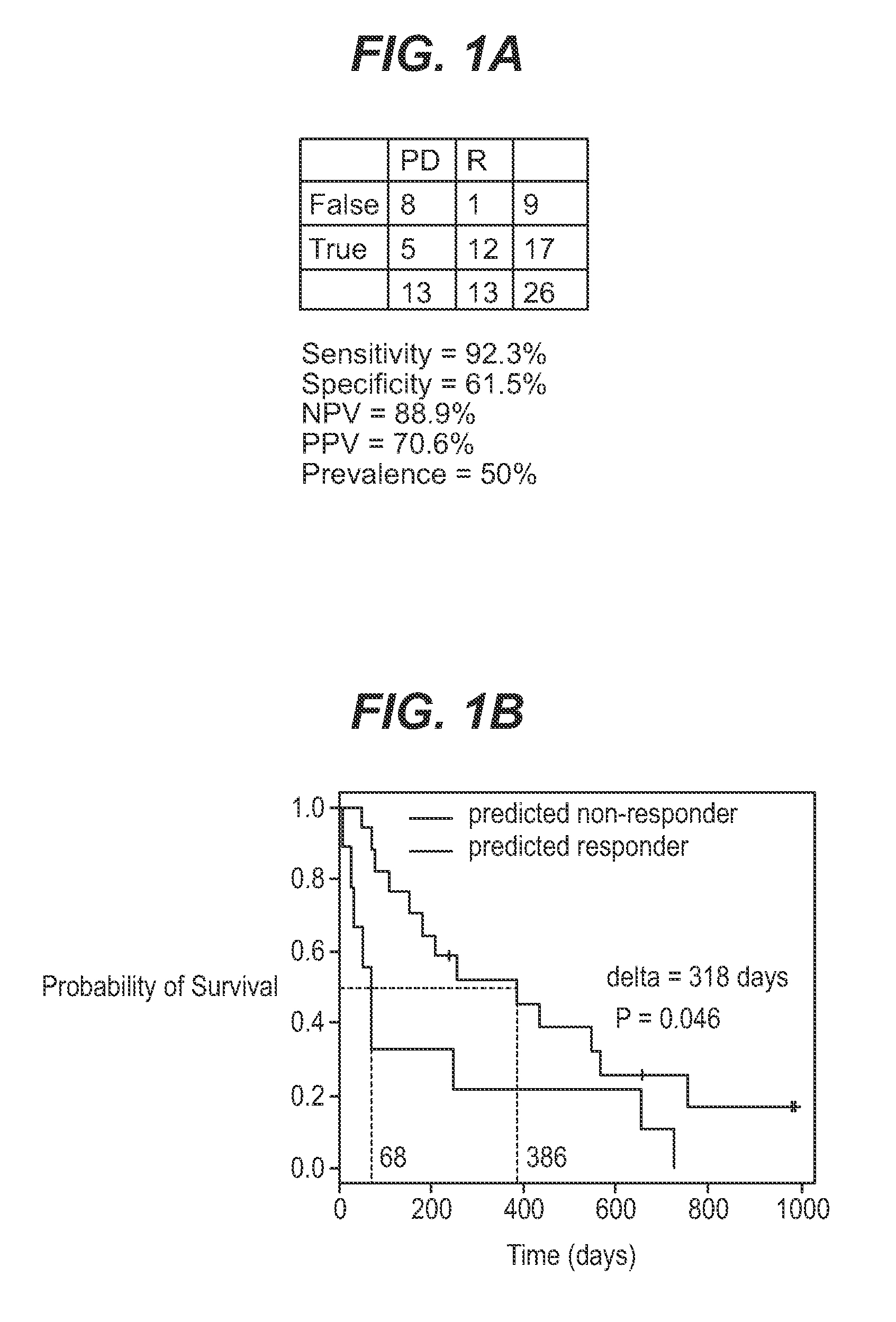
We analyzed bone marrow from 67 patients from a phase 2 study of farnesyltransferase inhibition with tipifarnib (R115777, ZARNESTRA®), in older adults with previously untreated, poor-risk acute myeloid leukemia (AML) for N-Ras mutations, global gene expression, and / or quantitative PCR (qPCR) of specific genes. Microarray profiling identified a two-gene expression ratio (RASGRP1:APTX) which provided the greatest accuracy for predicting response to tipifarnib. We demonstrated that this classifier could predict response to tipifarnib in an independent set of 54 samples from relapsed or refractory AML, with a NPV and PPV of 92% and 28%, respectively (odds ratio of 4.4). Therefore, in both newly diagnosed and relapsed or refractory AML, this classifier improves the overall response rate by approximately 50% while maintaining a high NPV, and significantly improves patient overall survival. The two-gene classifier was also validated by qPCR in thirty AML samples from the same clinical study demonstrating a negative predictive value (NPV) and positive predictive value (PPV) of 81% and 50%, respectively (odds ratio of 4.3). These data indicate that a simple two-gene expression assay may have utility in diagnosing a population of AML patients who are more likely to respond to tipifarnib.
Owner:JANSSEN DIAGNOSTICS LLC
Microarray for detecting viable organisms
InactiveUS20140155283A1Rapid and selective detection and enumerationLower levelNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismPropidium monoazide
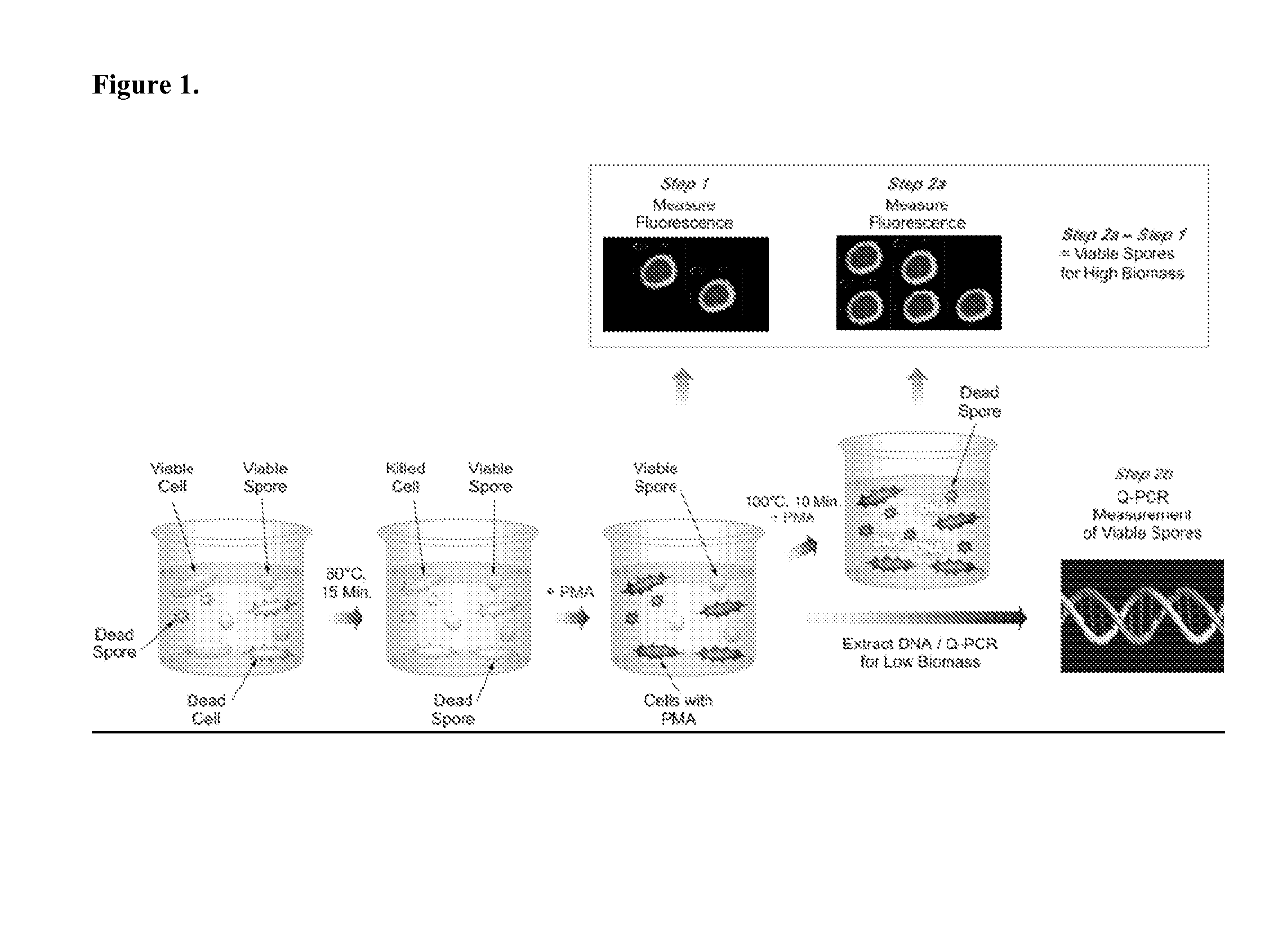
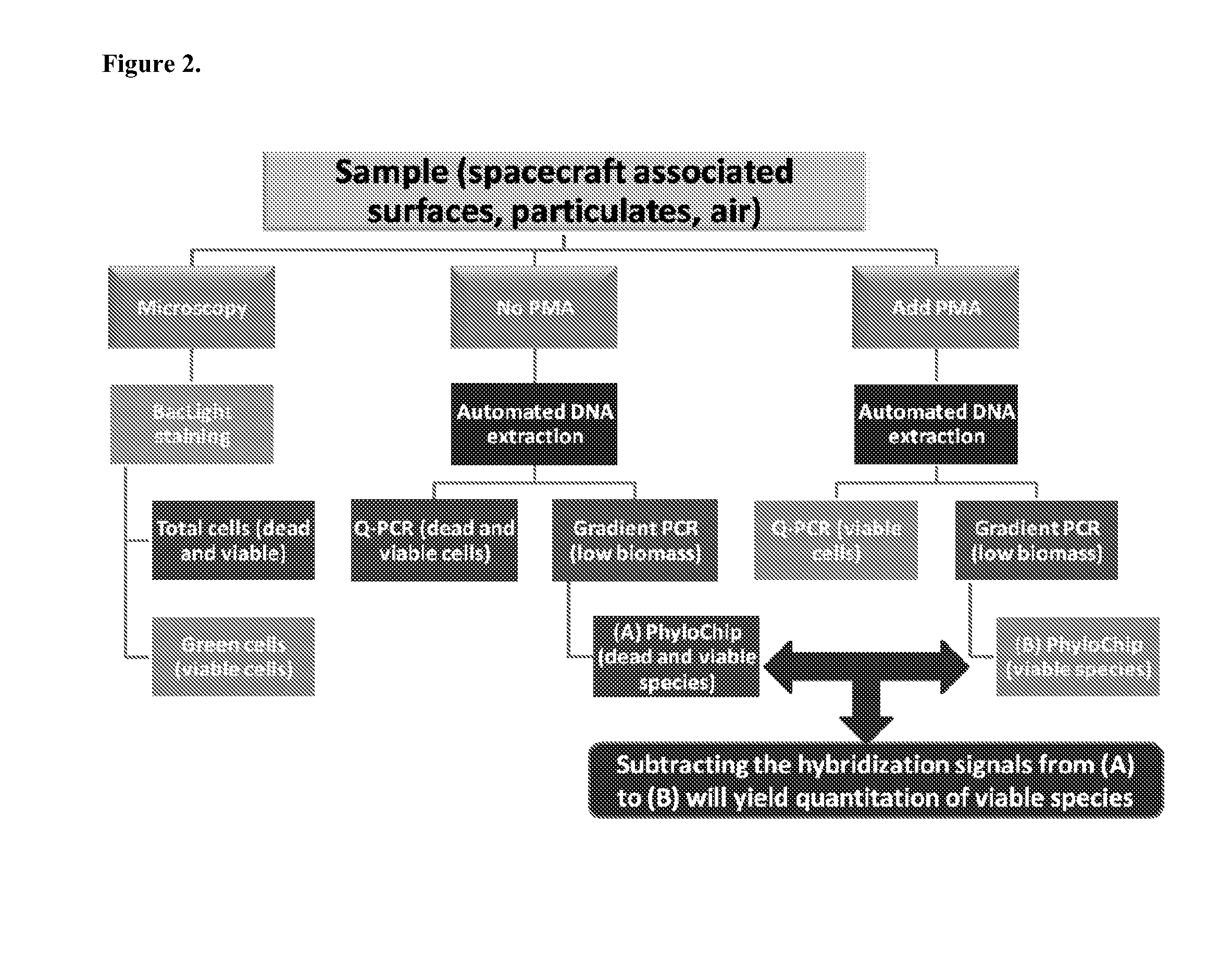
A methodology of microarray using the fluorescent DNA intercalating agent propidium monoazide (PMA) to selectively block DNA of dead cells from amplification and its application in detecting and enumerating viable microbes in complex microbial communities is described. A phylogenetic array is used in the preferred embodiment to enhance the sensitivity of the method. The PMA-Microarray assay is particularly applicable for monitoring samples from environments with extremely low microbial burden such as spacecraft surfaces.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
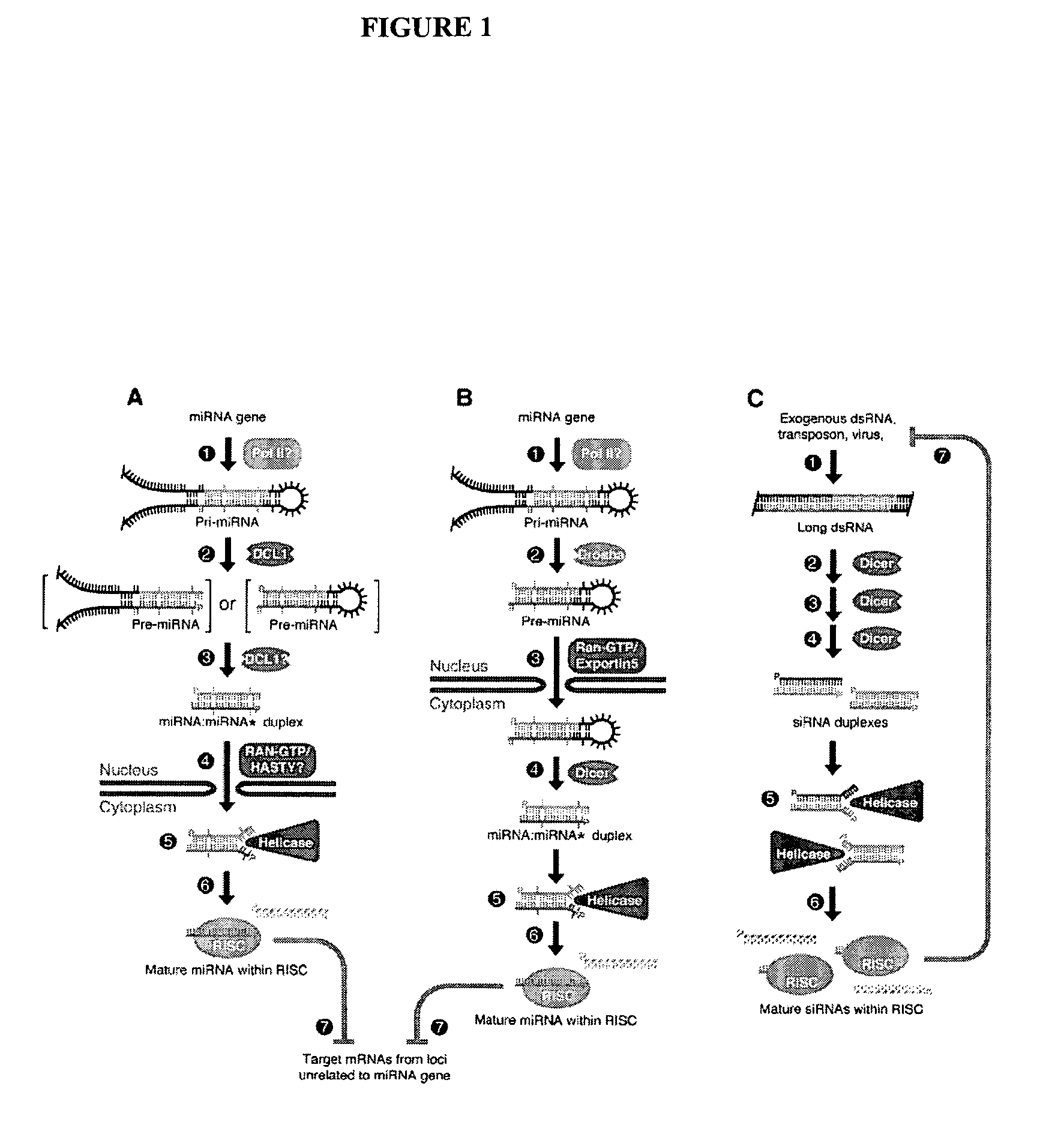
Methods for detection of microrna molecules
InactiveUS20060094025A1Quenching can be reducedIncrease intensitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroRNAMicroarray profiling
Methods and kits are provided for the production and use in microarray assays of labeled miRNA molecules and labeled cDNA molecules complementary to miRNA molecules.
Owner:GENISPHERE LLC
Method for fabrication of biochips with a macroporous polymer substrate
InactiveUS20050042363A1Large capacityImprove accessibilityNucleotide librariesPharmaceutical containersAnalytePolymer substrate
Macroporous polymer substrates have greater immobilization capacity for large biomolecules and better access for analytes than substrates used previously for microarrays. Microarrays are fabricated with macroporous polymer substrates, and nucleic acids, proteins and peptides are immobilized in the substrate. Microarrays with macroporous polymer substrates are useful in immunoassays, drug discovery studies and other biotechnological applications that involve large scale macromolecular interactions. Nucleic acid hybridizations, protein binding, and antigen-antibody interactions are analyzed using microarrays with macroporous polymer substrates.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY +2
Translucent solid matrix assay device for microarray analysis
InactiveUS6861251B2Low production costImprove the level ofMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsColloidBiology
The present invention concerns methods and compositions relating to matrix arrays. In certain embodiments, the arrays are translucent. In other embodiments, the arrays are reconfigurable. In preferred embodiments, the arrays are translucent and reconfigurable. Reconfigurable arrays may be produced using small linker molecules, such as aptamers or affibodies, attached to the array substrate. Preferably, the small linker molecules bind to an IgG specific portion of antibodies. Such arrays may be used to detect any target that binds selectively or specifically to an IgG, allowing great flexibility of use. Translucent matrix arrays may utilize a translucent, colloidal form of nitrocellulose to coat the array substrate.
Owner:PRITEST
Lung cancer-related nucleic acids
Described are polynucleotides associated with lung cancer. The polynucleotides are miRNAs, miRNA precursors, and associated nucleic acids. Methods and compositions are described that can be used for diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of lung cancer. Also described are methods that can be used to identify modulators of the disease-associated polynucleotides. Also described are methods and compositions for linear amplification and labeling of a targeted nucleic acid. The amplified targeted molecules may be used in hybridization techniques like Luminex and Microarray analysis.
Owner:ROSETTA GENOMICS
Diagnostic microarray for inflammatory bowel disease, crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis
InactiveUS20040077020A1Compound screeningApoptosis detectionIntestinal tract diseasesUlcerative colitis
Using RNA samples from mononuclear blood cells, gene sequences were identified that can be used to identify patients with IBD, and then distinguish patients with Crohn's disease from those with ulcerative colitis. Sequences were identified whose overexpression was distinct to patients with IBD, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis when compared to patients with non-IBD intestinal disorders. Additionally, cluster analysis was used to identify twenty-five sequences that are IBD-related, and whose transcription pattern can be used in a microarray analysis to identify patients with IBD with a sensitivity of 84% and a specificity of 100%. Cluster analysis also identified thirty-six genes that could be used to distinguish patients with Crohn's disease from those with ulcerative colitis with a sensitivity of 89% and a specificity of 80%.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Methods for preparing cDNA from low quantities of cells
ActiveUS10017761B2Easy to collectMinimize contaminationDNA preparationCDNA libraryMicroarray profiling
Methods for preparing cDNA libraries from single and low quantities of cells are disclosed. The methods are based on the principles of multi-strand displacement amplification or semi-random primed polymerase chain reaction. The methods typically include a step of reverse transcription and subsequent amplification of cDNA. The methods can be adapted for preparation of cDNA libraries that are representative of mRNA or whole RNA expressed by the cell or cells. The cDNA is suitable for sequencing or microarray analysis.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Methods For Preparing cDNA From Low Quantities of Cells
ActiveUS20140213485A1Minimize contaminationEasy to collectNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementCDNA libraryMicroarray profiling
Methods for preparing cDNA libraries from single and low quantities of cells are disclosed. The methods are based on the principles of multi-strand displacement amplification or semi-random primed polymerase chain reaction. The methods typically include a step of reverse transcription and subsequent amplification of cDNA. The methods can be adapted for preparation of cDNA libraries that are representative of mRNA or whole RNA expressed by the cell or cells. The cDNA is suitable for sequencing or microarray analysis.
Owner:YALE UNIV
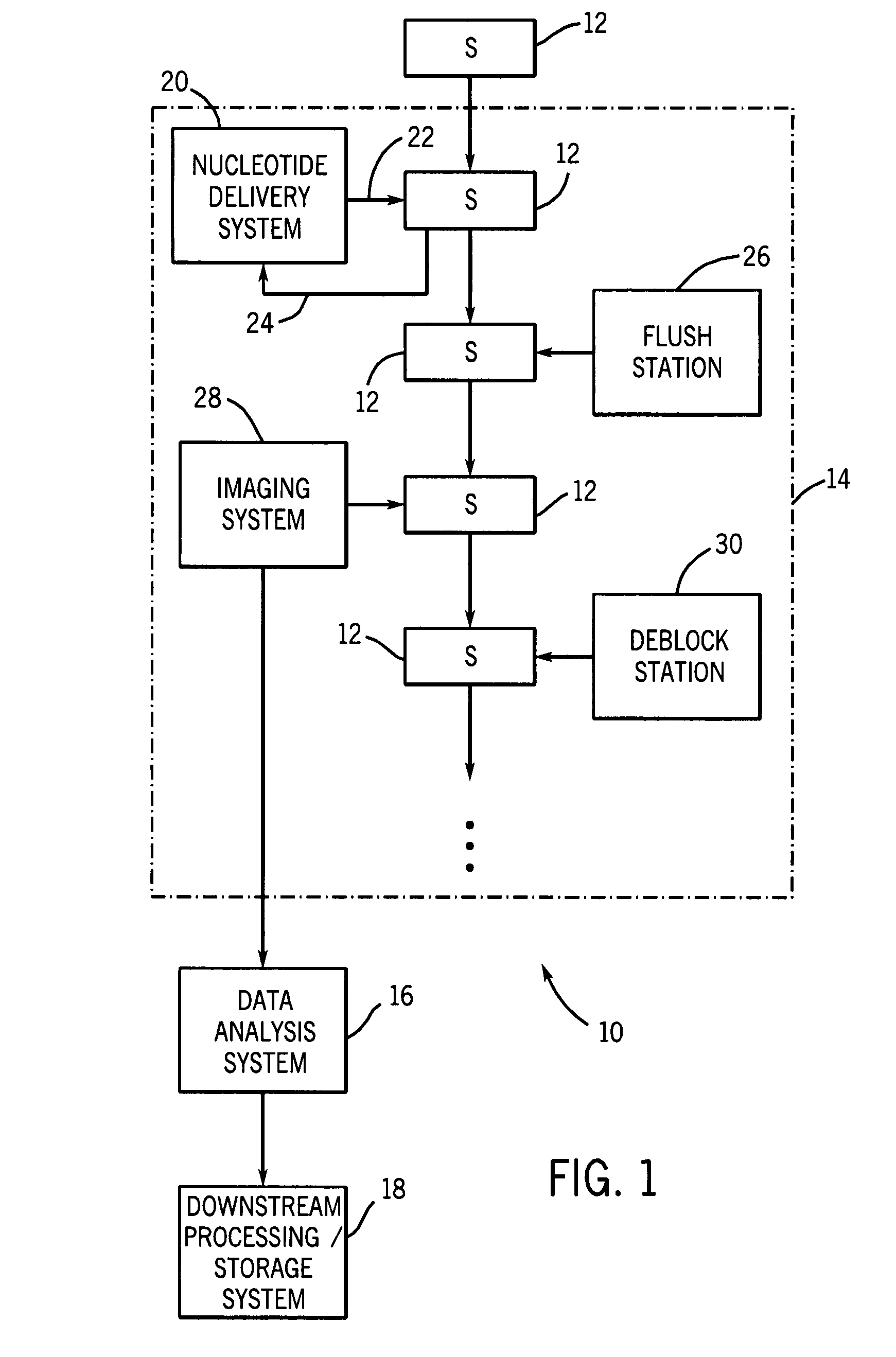
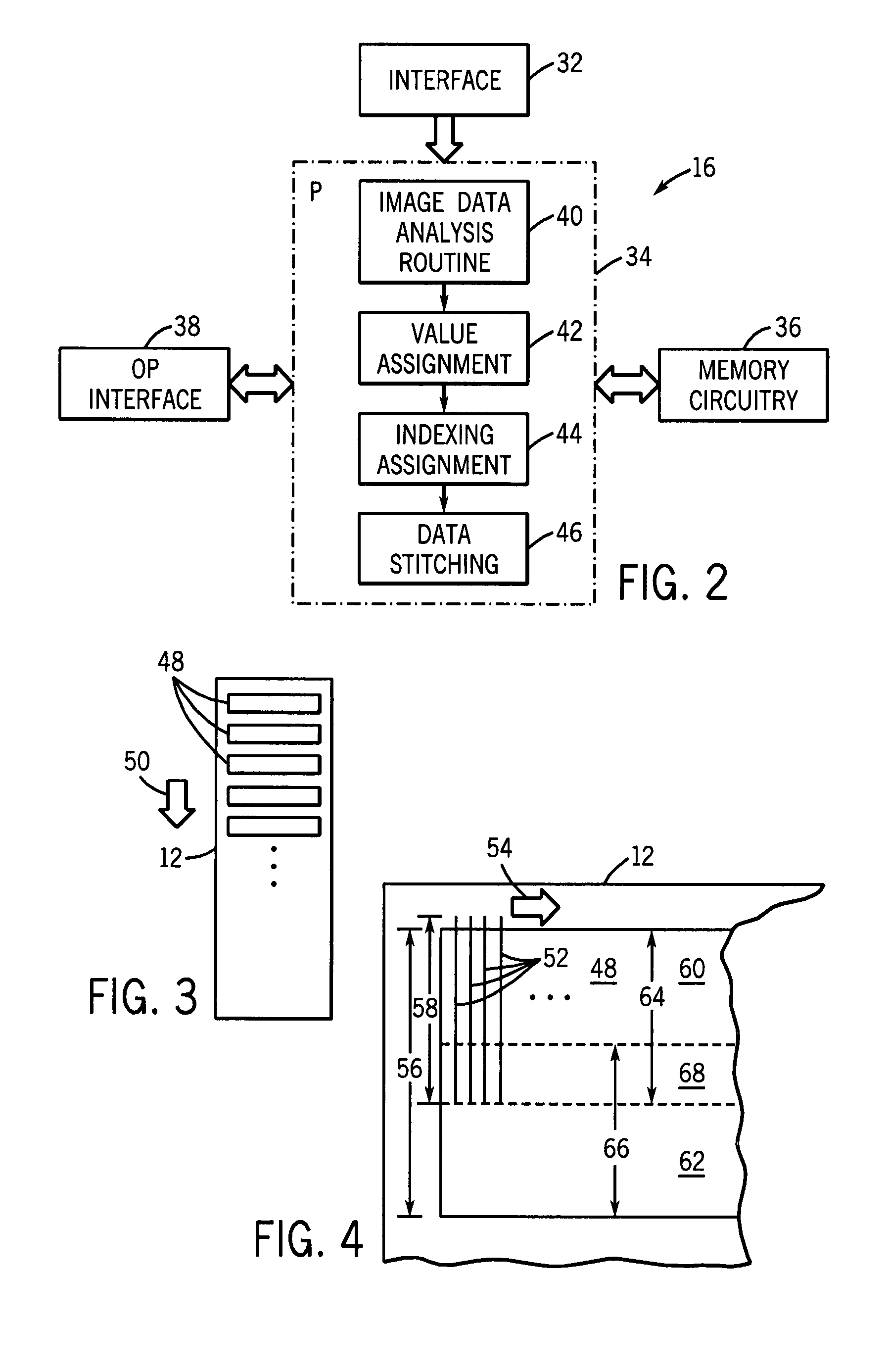
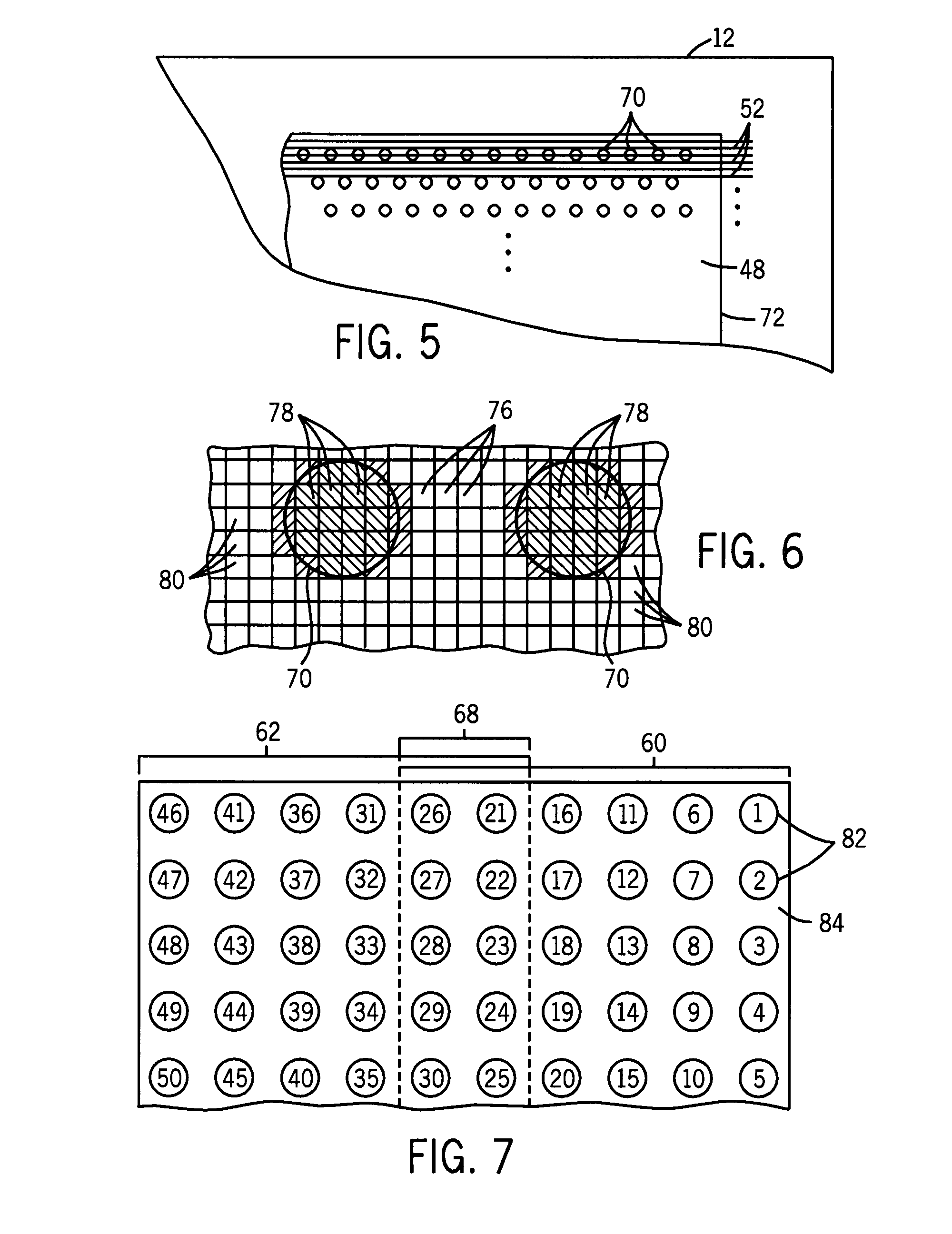
Microarray analytical data stitching system and method
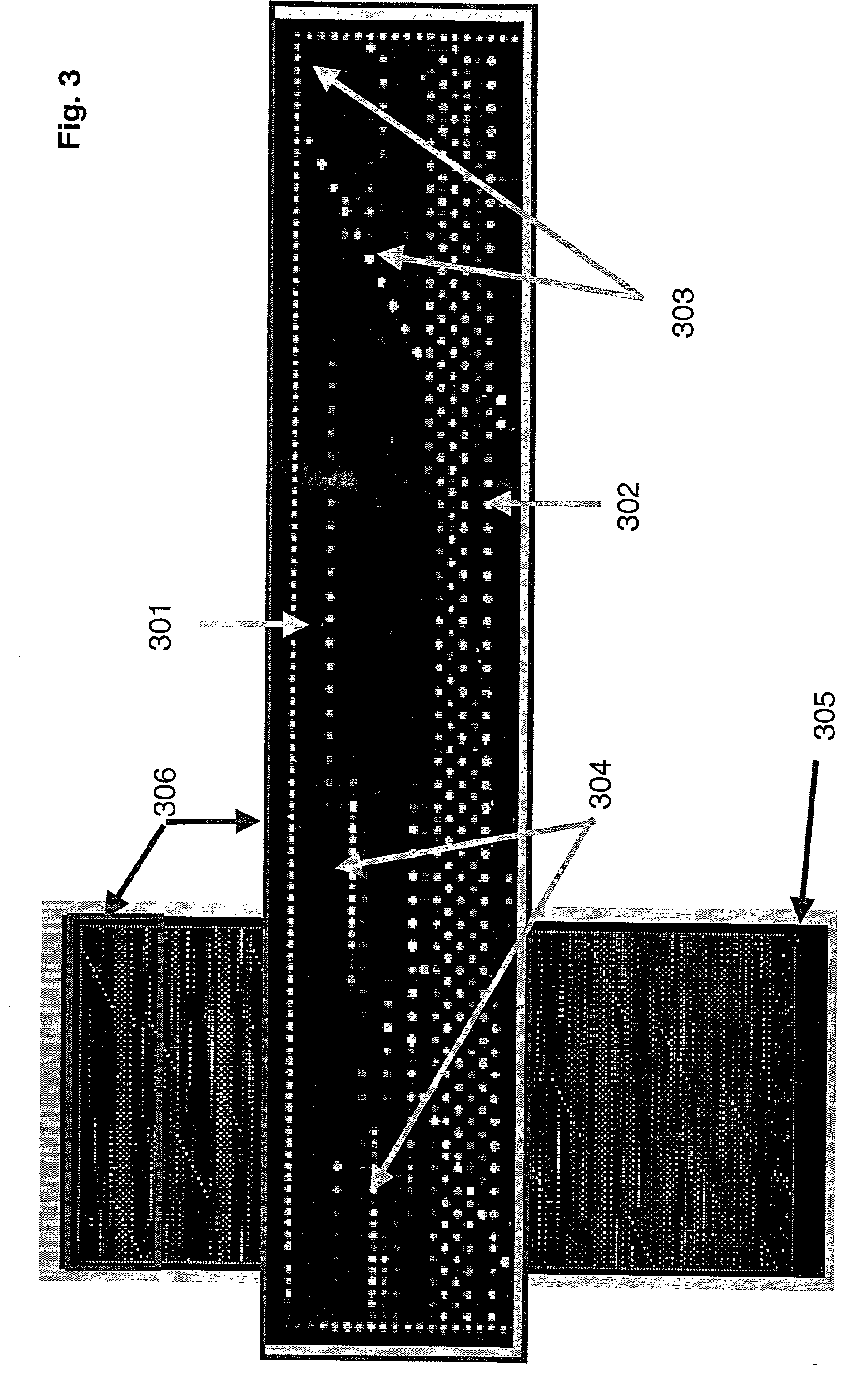
ActiveUS7769548B2Improve efficiencyReduced computer memory requiredCharacter and pattern recognitionBiological testingSite locationMultiple pass
A technique is provided for analyzing image data for biological microarrays. Images are made of multiple swaths in multiple passes of an imaging system. Sites encoded by the image data are assigned a value and these values are indexed by site location. An overlapping region of the swaths may be identified by analysis of the indexed site values. The site values for all image sites are then stitched and the data is integrated and stored for later analysis.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
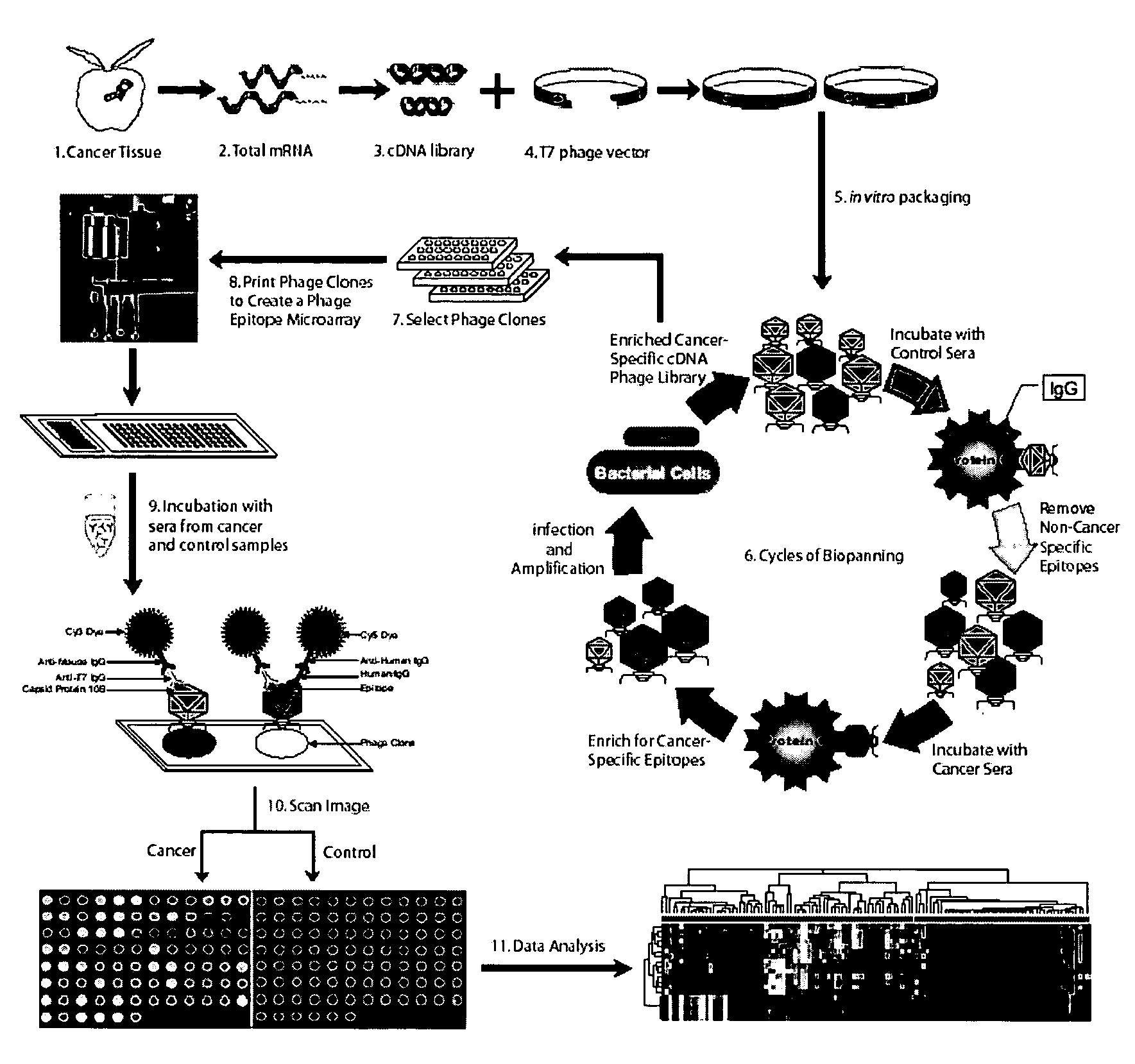
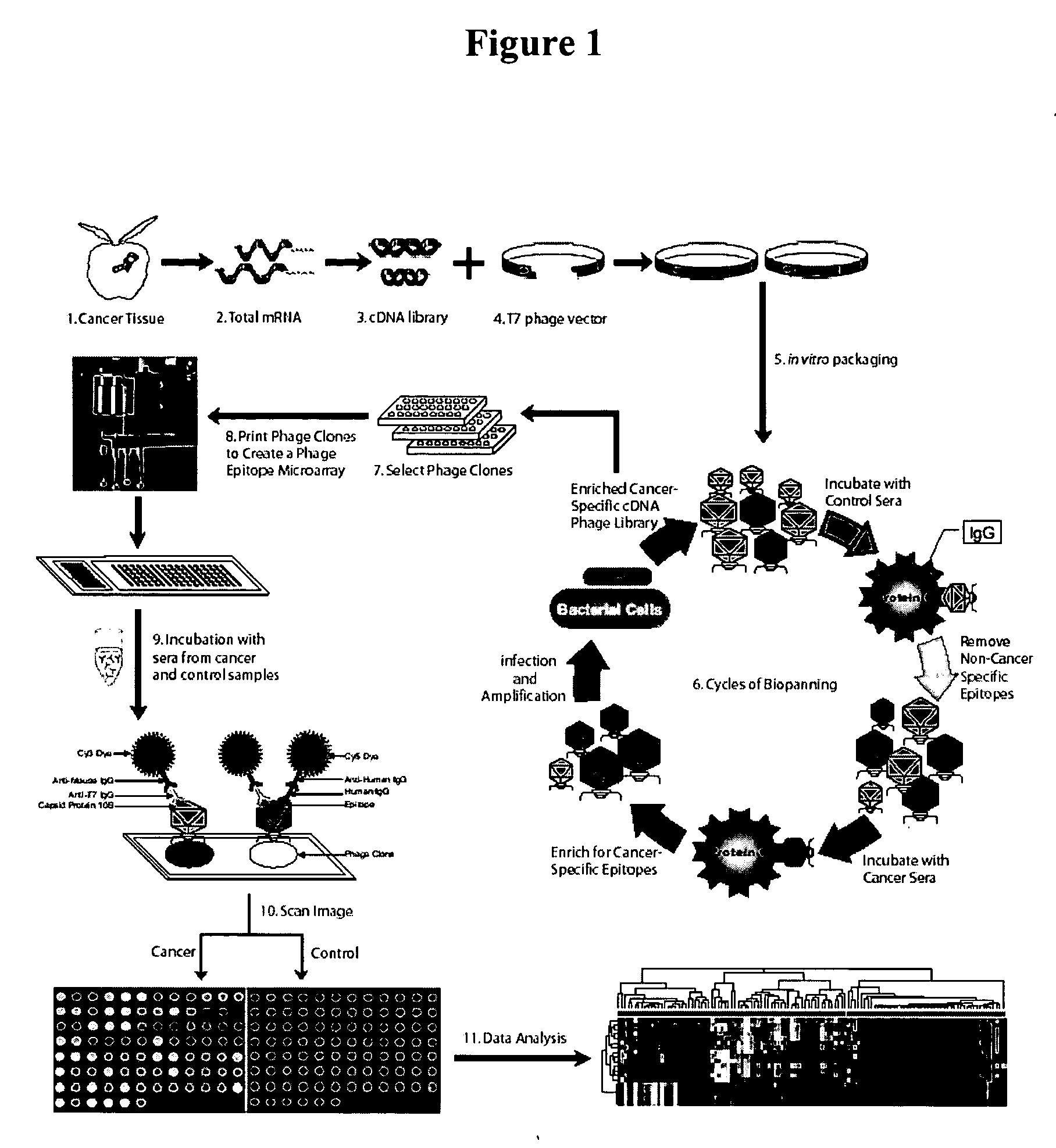
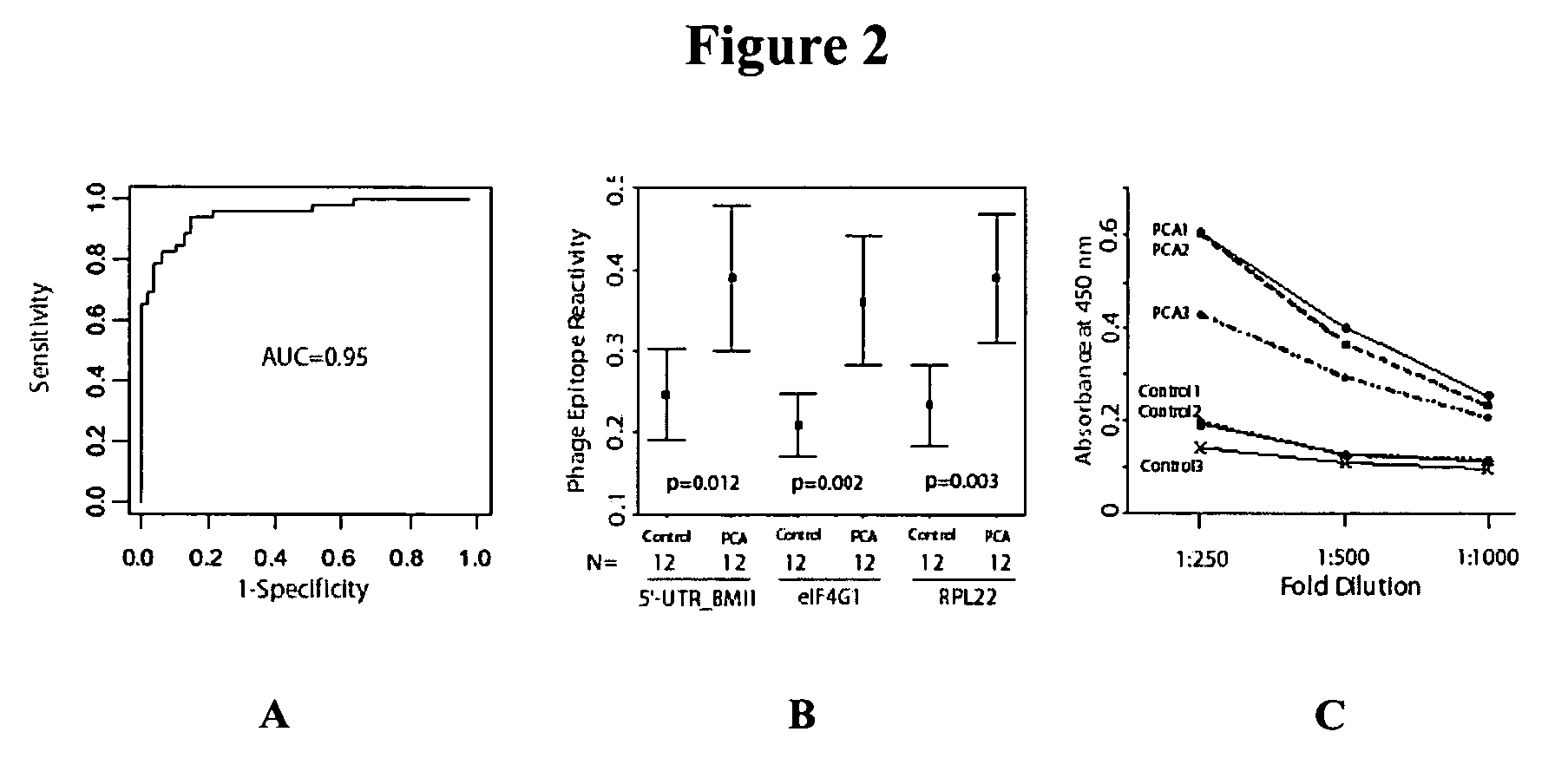
Phage microarray profiling of the humoral response to disease
InactiveUS20060014138A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsTumor rejection antigen precursorsProstate cancerBacteriophage
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for cancer diagnostics, including but not limited to, cancer markers. In particular, the present invention provides methods and compositions for phage microarray profiling of cancer (e.g., prostate, lung, or breast cancer). The present invention further provides novel markers useful for the diagnosis, characterization, and treatment of cancers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
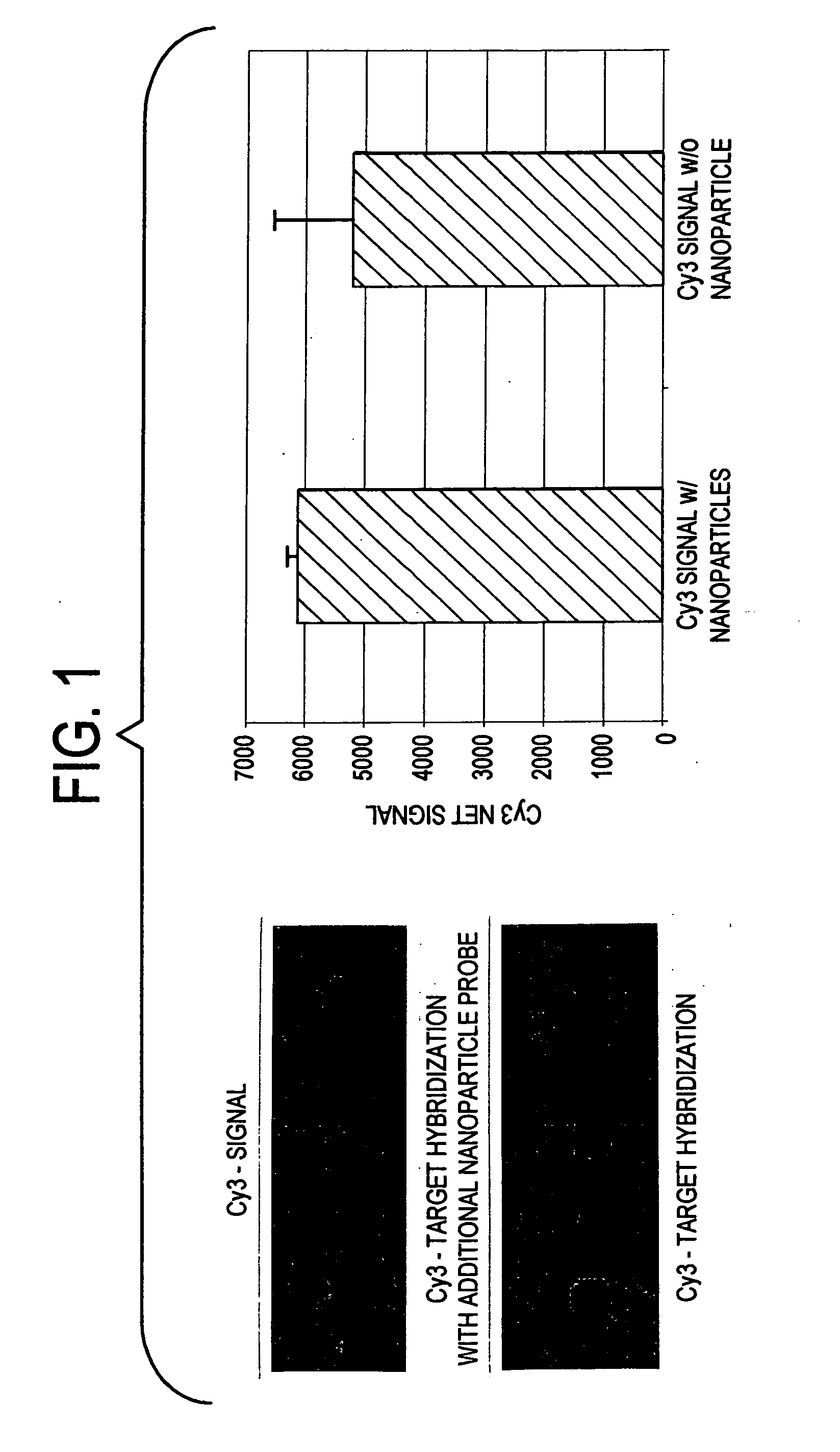
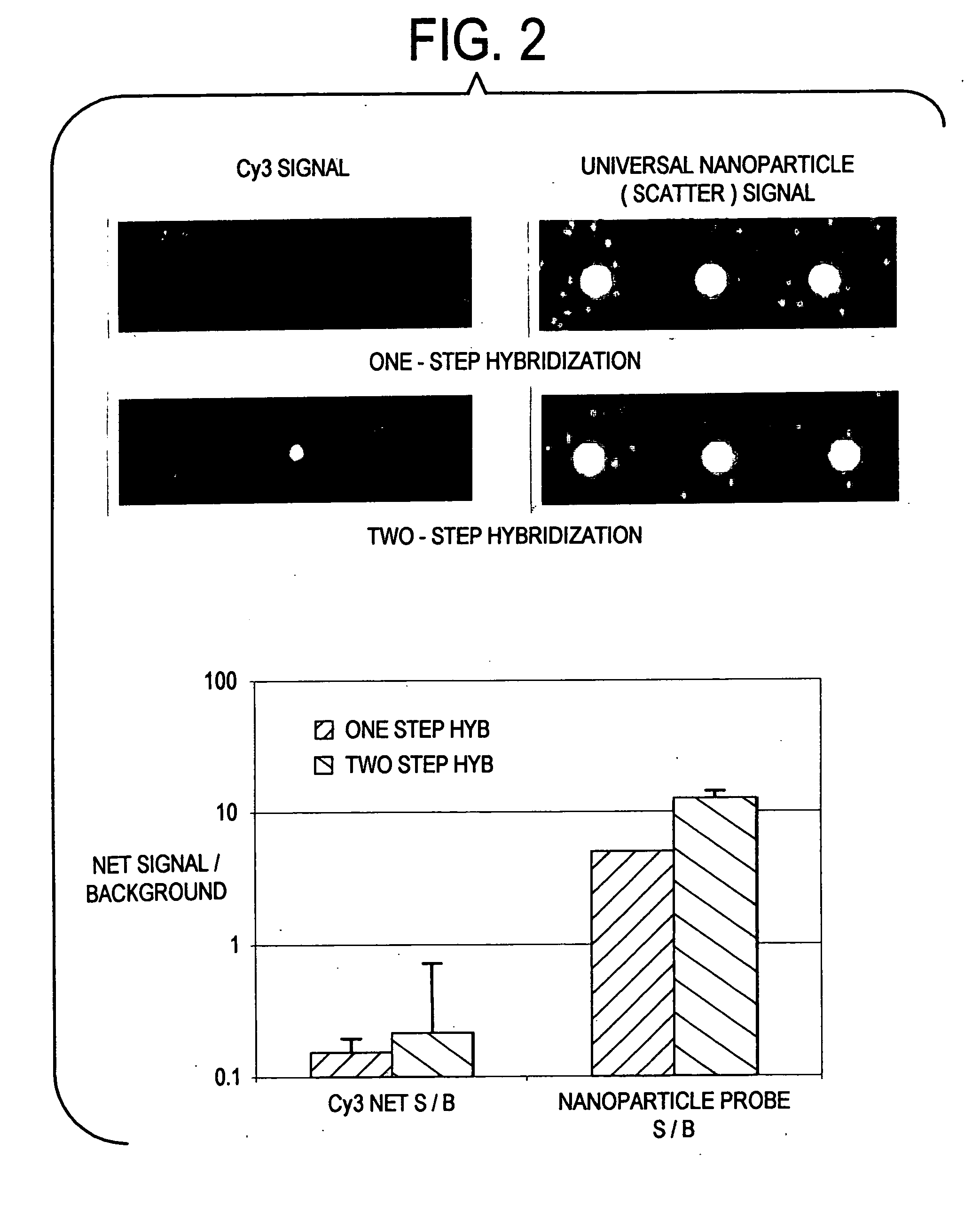
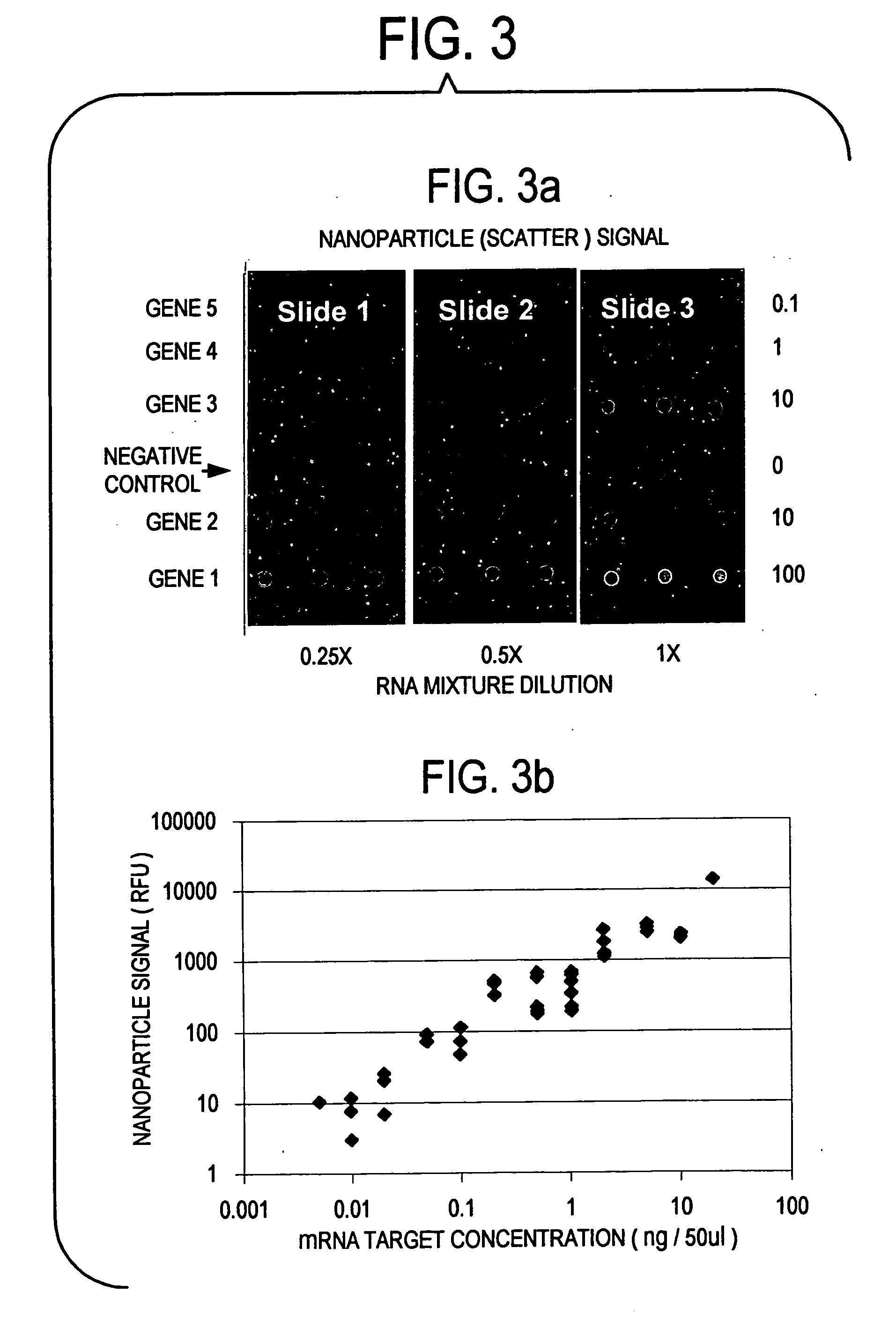
Label-free gene expression profiling with universal nanoparticle probes in microarray assay format
InactiveUS20050130174A1Strong specificityHigh sensitivity detectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAssayExpression gene
A method and kit for the label-free detection of global gene expression using nanoparticle probes in an array assay format is described. The method avoids the problems associated with fluorescent labeling and target amplification.
Owner:NANOSPHERE INC
Diagnosis of Melanoma and Solar Lentigo by Nucleic Acid Analysis
InactiveUS20110160080A1Less traumaticMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningProtein profilingPigments skin
The present invention provides methods for diagnosing melanoma and / or solar lentigo in a subject by analyzing nucleic acid molecules obtained from the subject. The present invention also provides methods for distinguishing melanoma from solar lentigo and / or dysplastic nevi and / or normal pigmented skin. The methods include analyzing expression or mutations in epidermal samples, of one or more skin markers. The methods can include the use of a microarray to analyze gene or protein profiles from a sample.
Owner:DERMTECH INT
Protein expression profiling
InactiveUS20060166227A1Easy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationAnalyteProtein Expression Profiling
Disclosed are compositions and methods for detecting small quantities of analytes such as proteins and peptides. The method involves associating a primer with an analyte and subsequently using the primer to mediate rolling circle replication of a circular DNA molecule. Amplification of the DNA circle is dependent on the presence of the primer. Thus, the disclosed method produces an amplified signal, via rolling circle amplification, from any analyte of interest. The amplified DNA remains associated with the analyte, via the primer, and so allows spatial detection of the analyte. The disclosed method can be used to detect and analyze proteins and peptides. Multiple proteins can be analyzed using microarrays to which the various proteins are immobilized. A rolling circle replication primer is then associated with the various proteins using a conjugate of the primer and a molecule that specifically binds the proteins to be detectable. Rolling circle replication from the primers results in production of a large amount of DNA at the sites in the array where the proteins are immobilized. The DNA produced by rolling circle replication can be further amplified in secondary and higher order amplification processes using second-stage or higher order primers in conjunction with second-stage or higher order amplification target circles. The amplified DNA serves as a readily detectable signal for the proteins. The disclosed method can also be used to compare the proteins expressed in two or more different samples. The information generated is analogous to the type of information gathered in nucleic acid expression profiles. The disclosed method allows sensitive and accurate detection and quantitation of proteins expressed in any cell or tissue.
Owner:KINGSMORE STEPHEN +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com