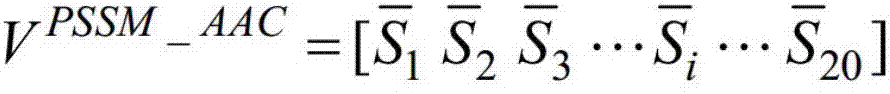Patents
Literature
227 results about "Bacterial genes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A bacterial genome is the collection of a bacterium's entire genetic information. Essentially, it determines how a bacterium looks and functions, both externally and internally. This genetic information is organized into genes, which are encoded in the organism’s deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Those genes are further organized into chromosomes.
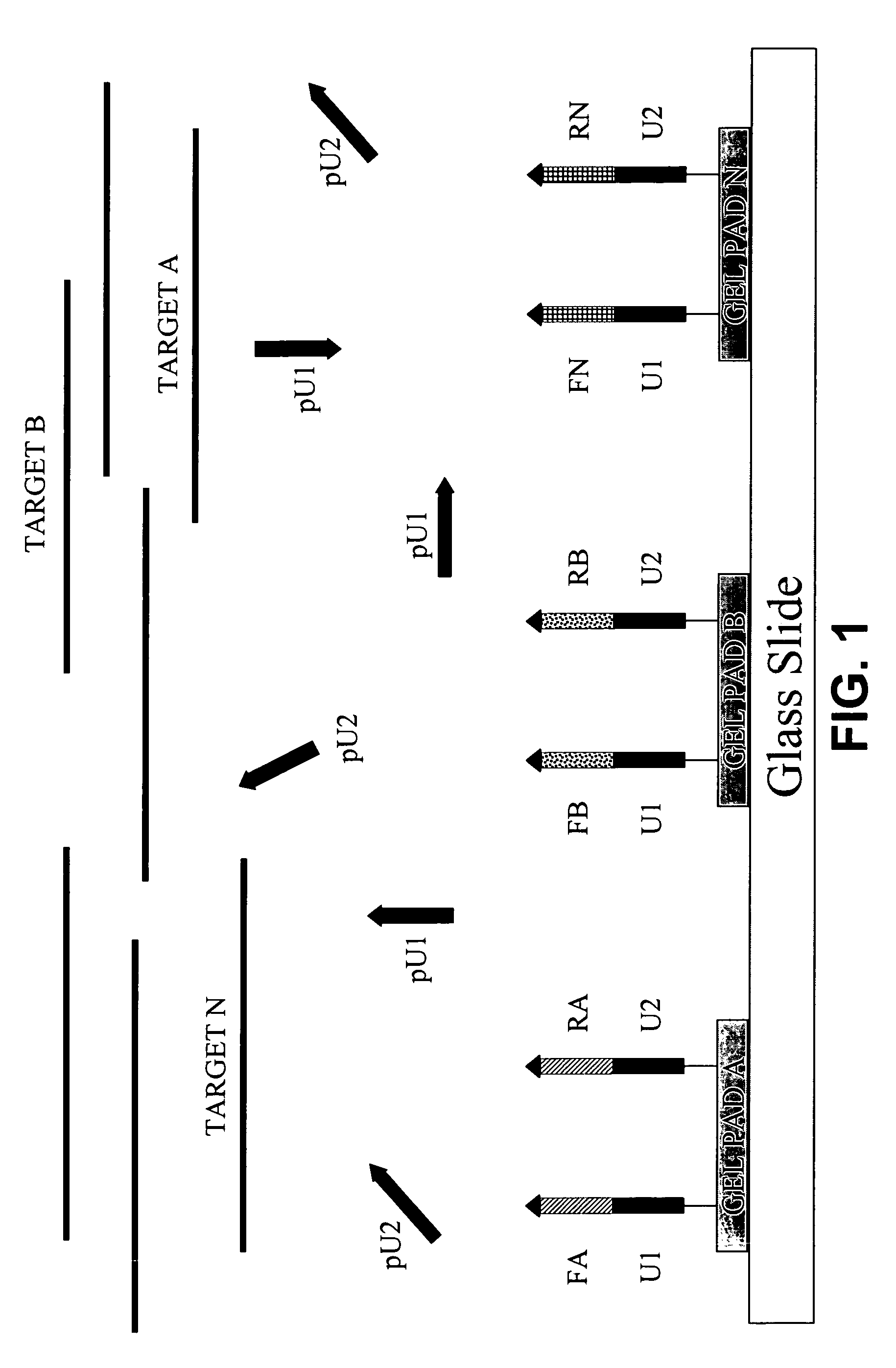
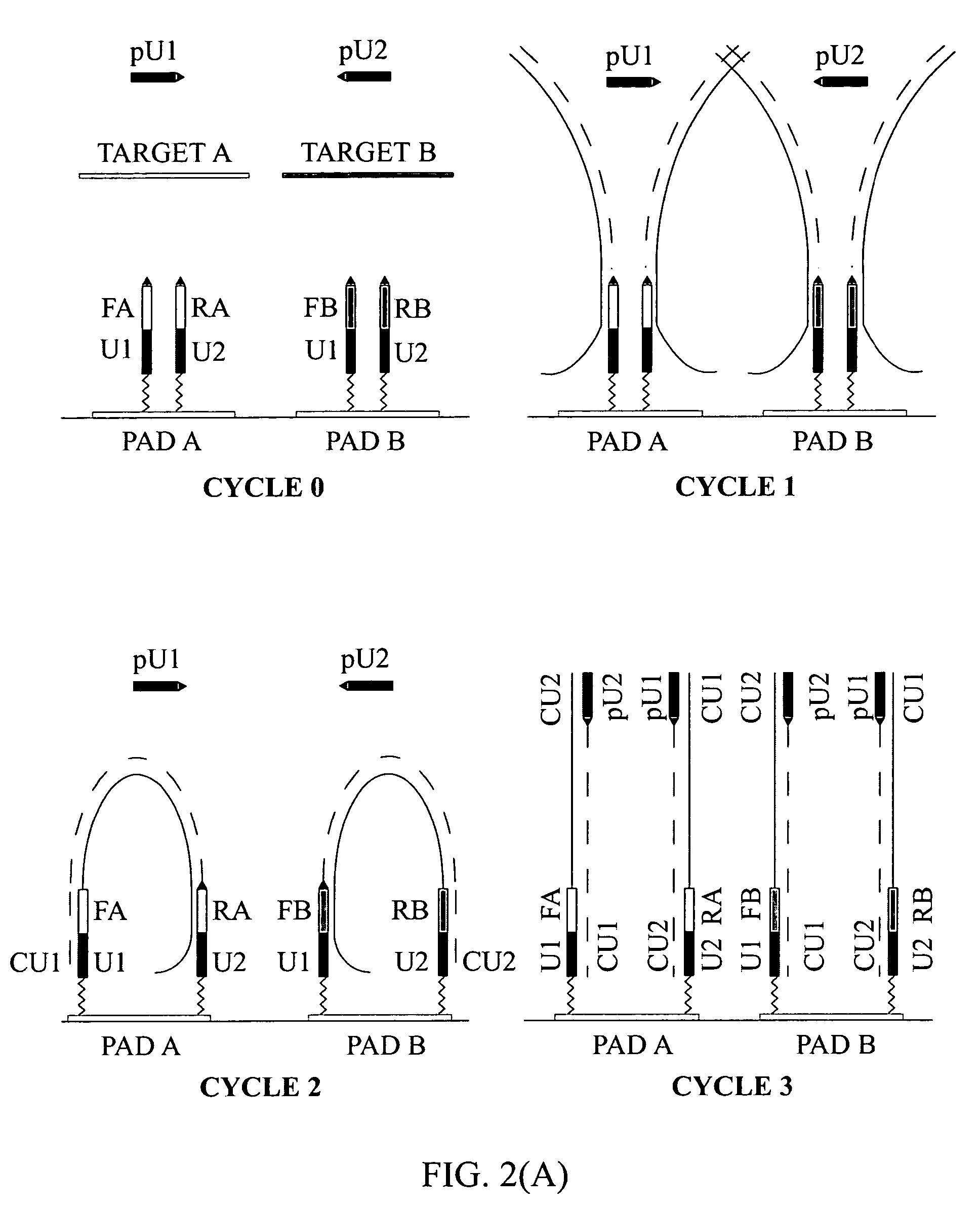
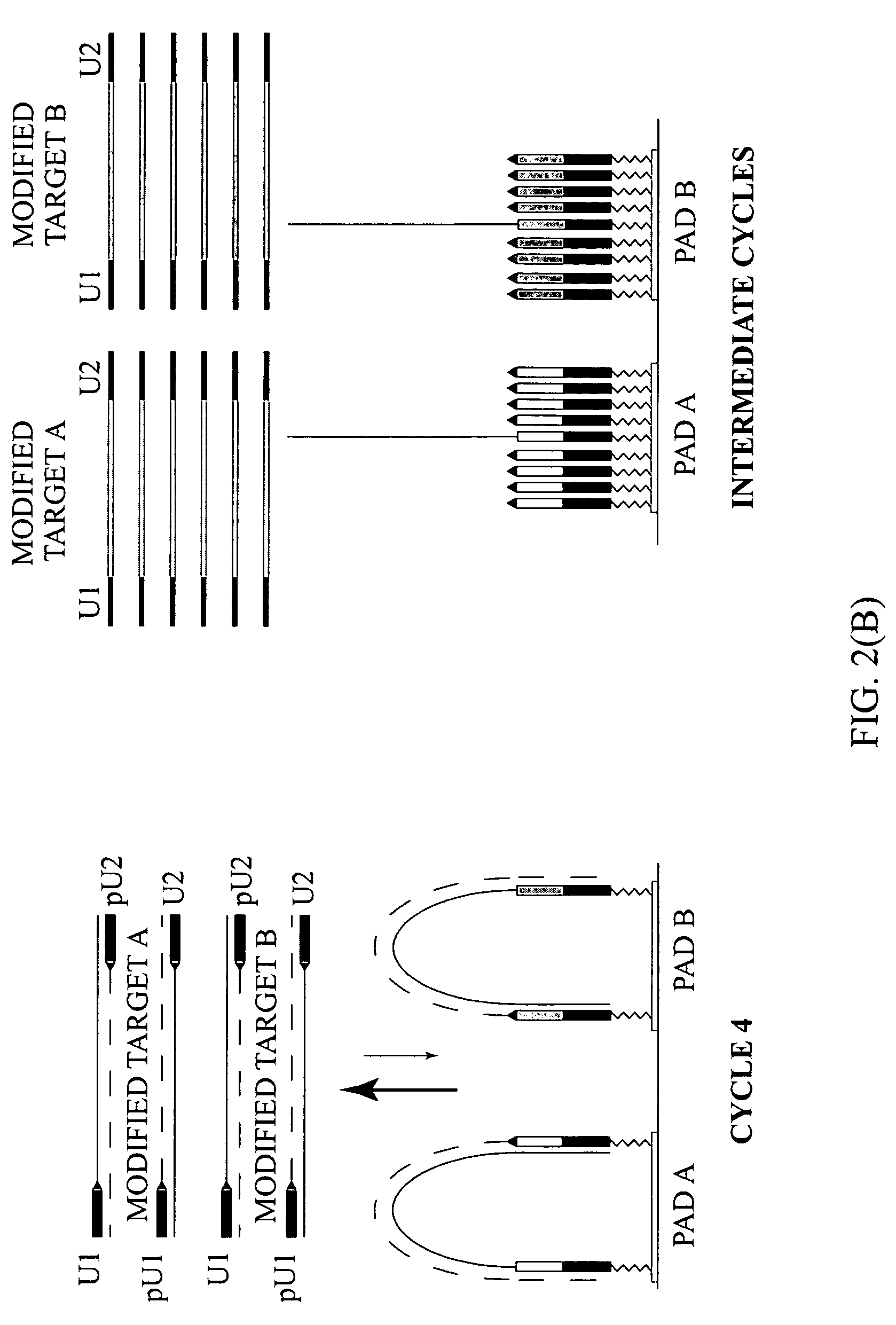
Dual phase multiplex polymerase chain reaction
ActiveUS7432055B2Further amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationGenomic DNASingle pair
Highly specific and sensitive methods were developed for multiplex amplification of nucleic acids on supports such as microarrays. Based on a specific primer design, methods include five types of amplification that proceed in a reaction chamber simultaneously. These relate to four types of multiplex amplification of a target DNA on a solid support, directed by forward and reverse complex primers immobilized to the support and a fifth type—pseudo-monoplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of multiple targets in solution, directed by a single pair of unbound universal primers. The addition of the universal primers in the reaction mixture increases the yield over the traditional “bridge” amplification on a solid support by approximately ten times. Methods that provide multitarget amplification and detection of as little as 0.45-4.5×10−12 g (equivalent to 102-103 genomes) of a bacterial genomic DNA are disclosed.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC +1
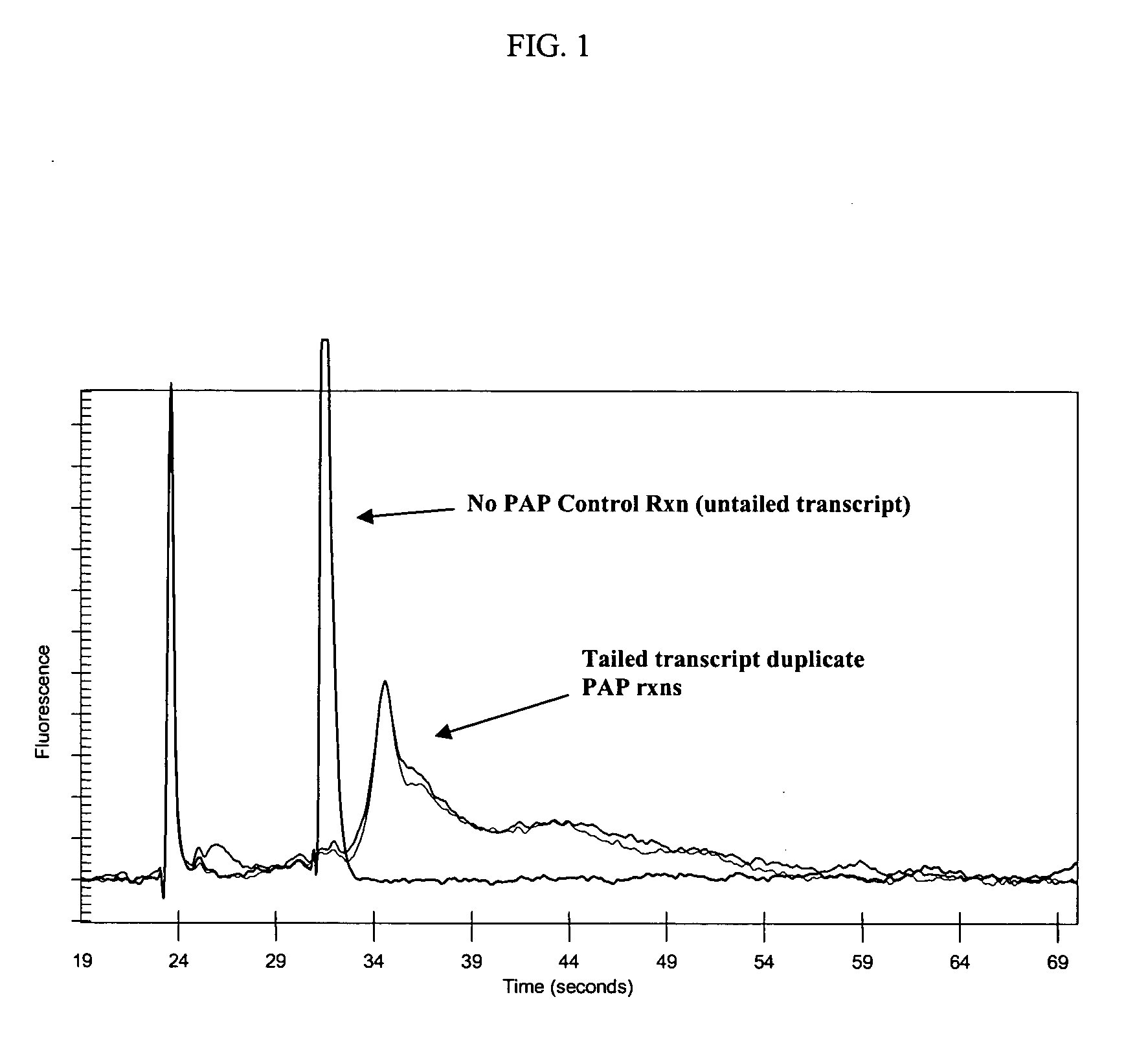
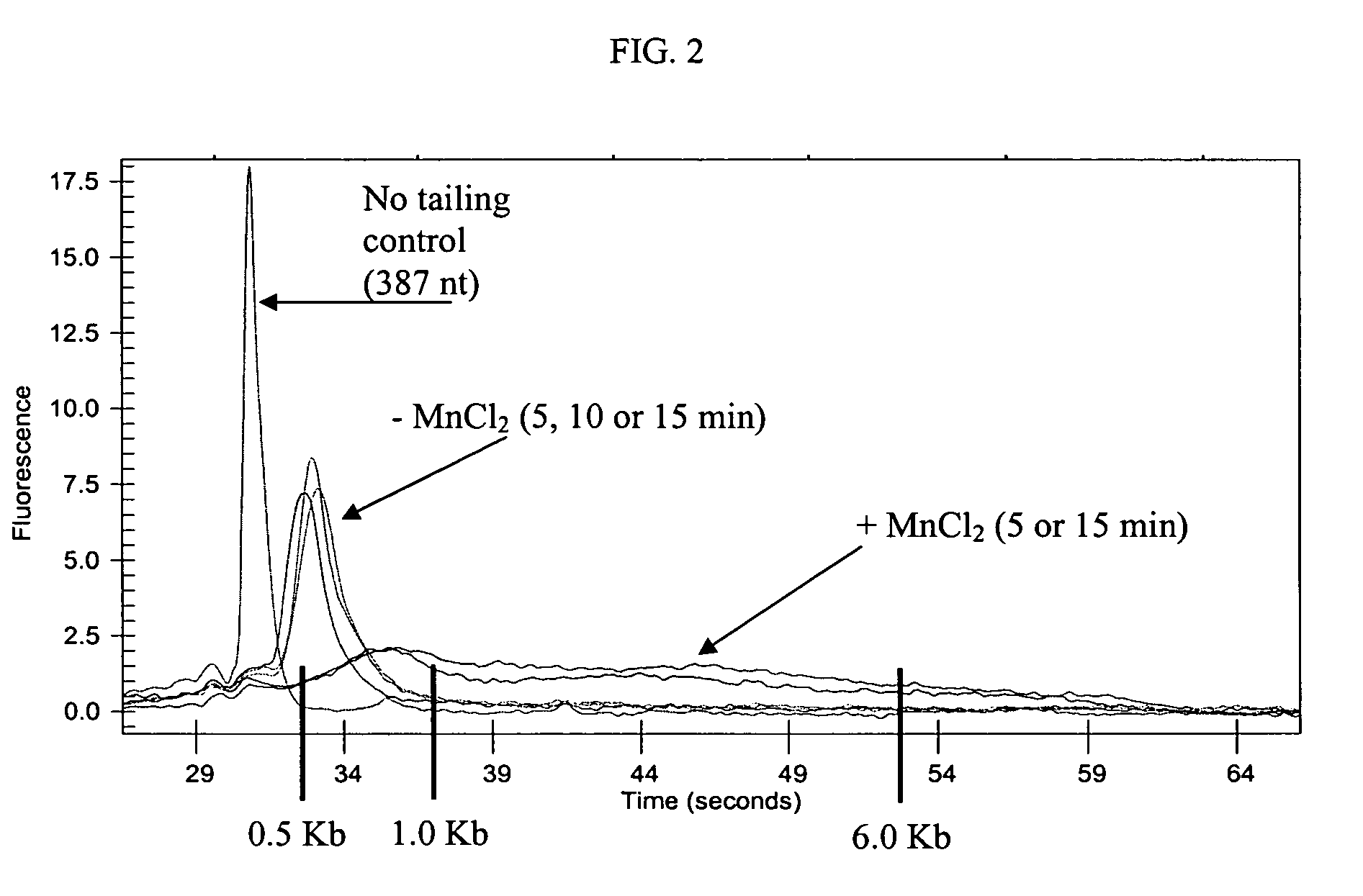
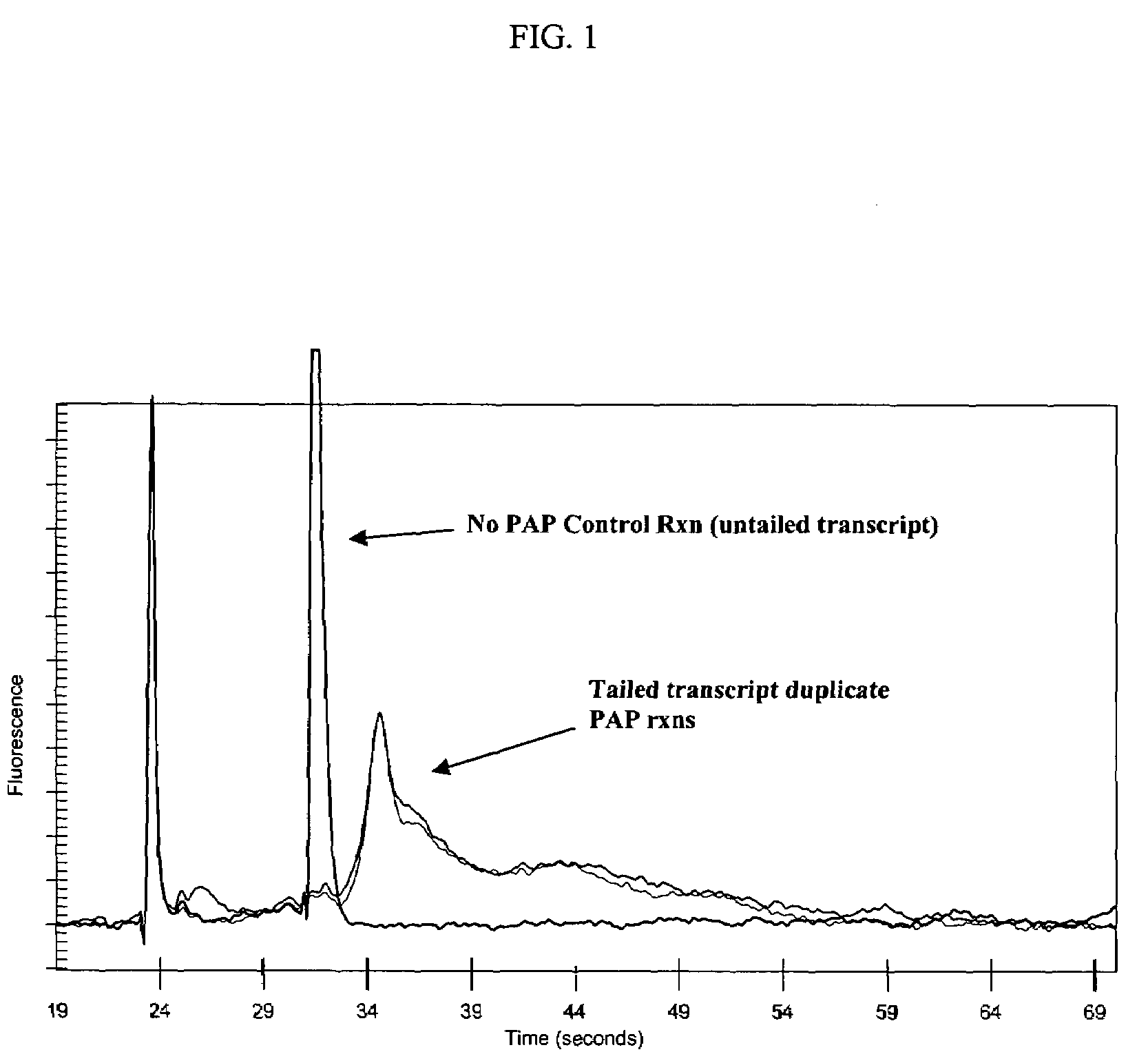
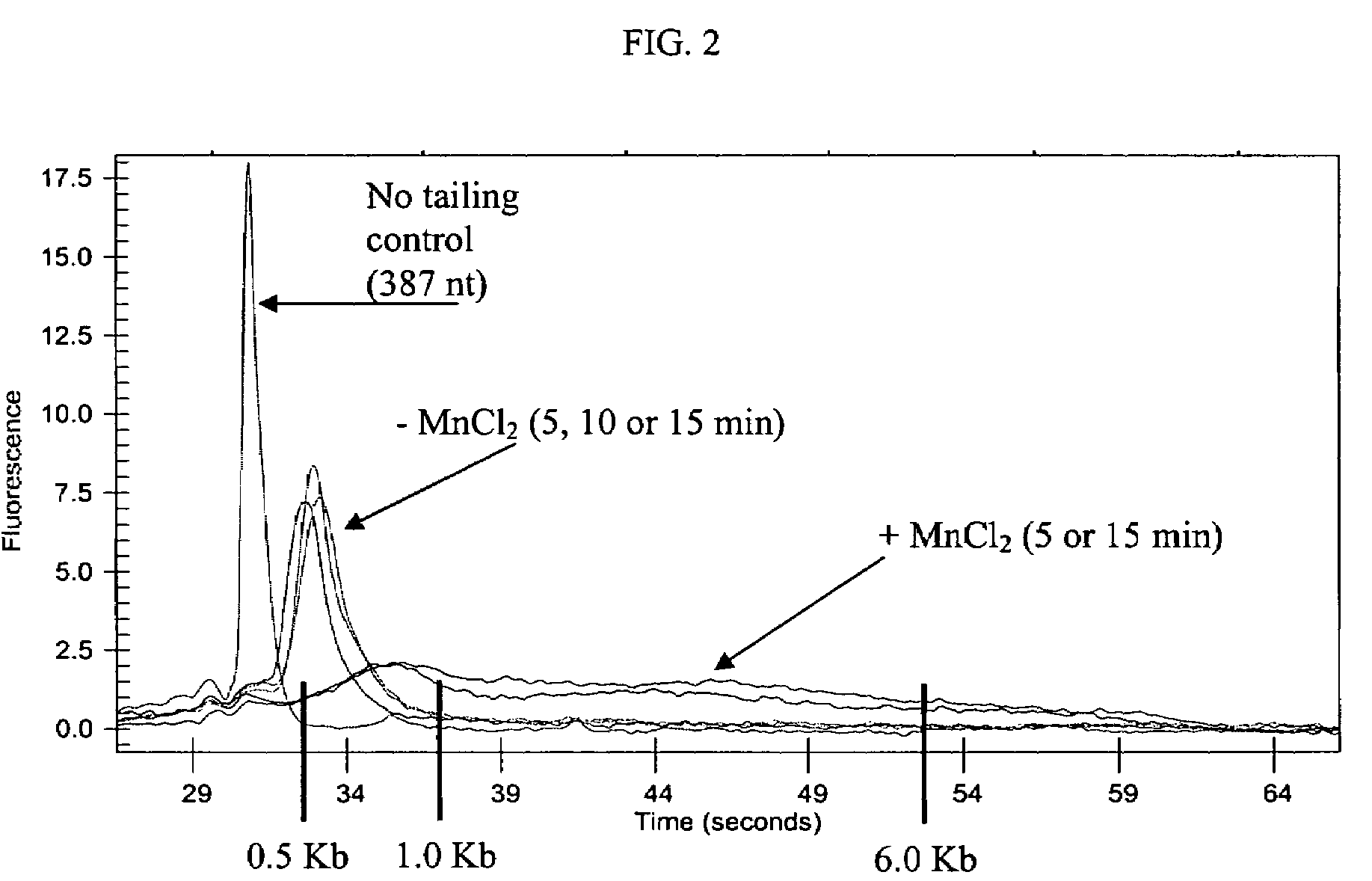
Methods and compositions for tailing and amplifying RNA
ActiveUS20060051771A1Efficiently and uniformlyEfficiently and uniformly tailMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenome wide expressionGenome
The present invention provides methods and compositions that enable tagging and amplification of targeted RNA molecules. A targeted RNA molecule is any non-polyadenylated RNA molecule including, for example, miRNA, siRNA, rRNA, tRNA, synthetic RNA, or non-polyadenylated mRNA such as mRNA from bacteria. In certain aspects, the invention provides methods and compositions for the genome-wide expression analysis of bacterial genes. Significantly, the methods enable genome-wide expression analysis in circumstances where bacterial numbers were previously too low to purify adequate amounts of RNA for DNA microarray analysis or other applications. Such methods are particularly useful for the study of bacterial gene expression during host-cell infection. The invention also provides kits for tagging and amplifying targeted RNA molecules.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
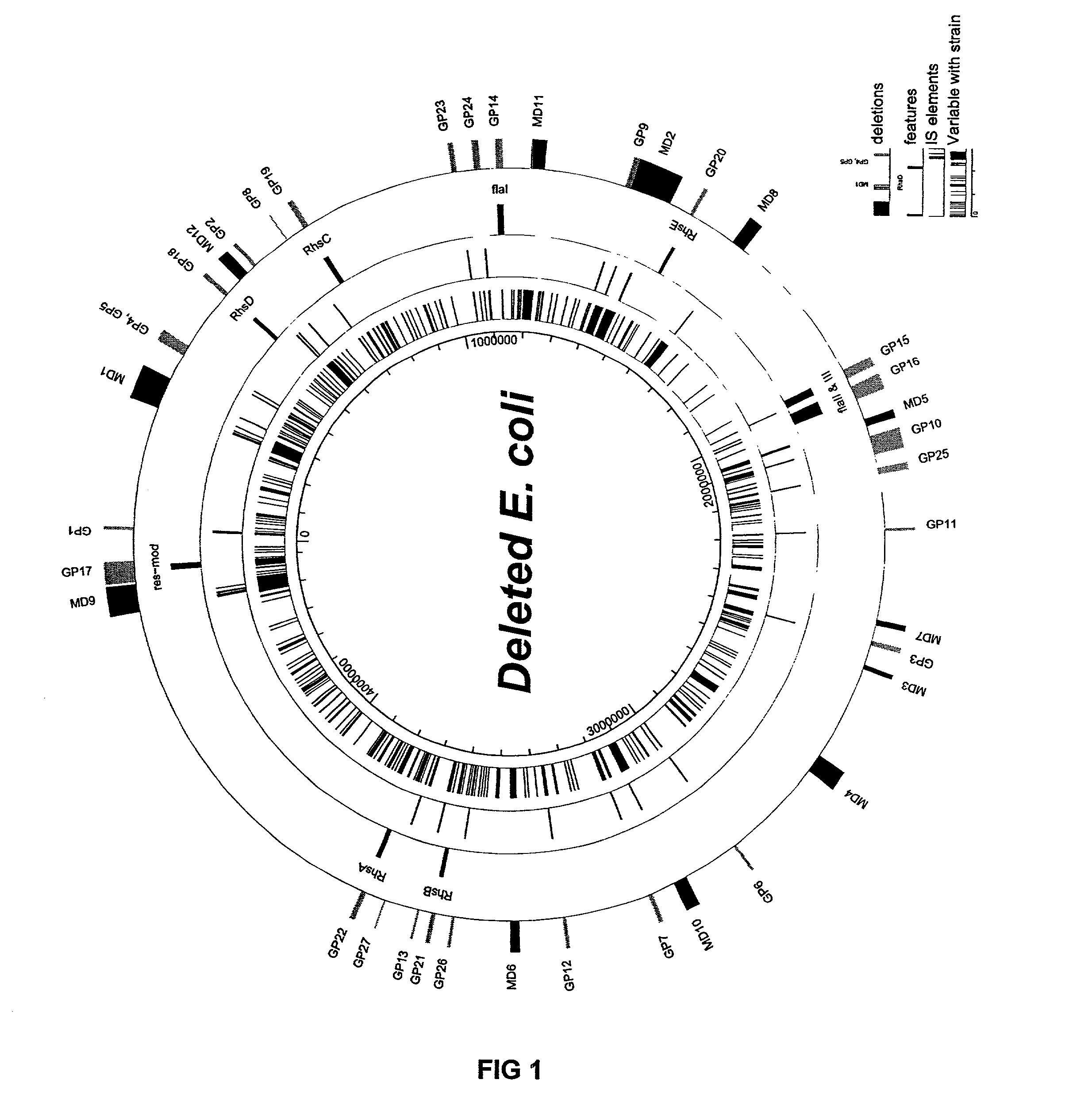
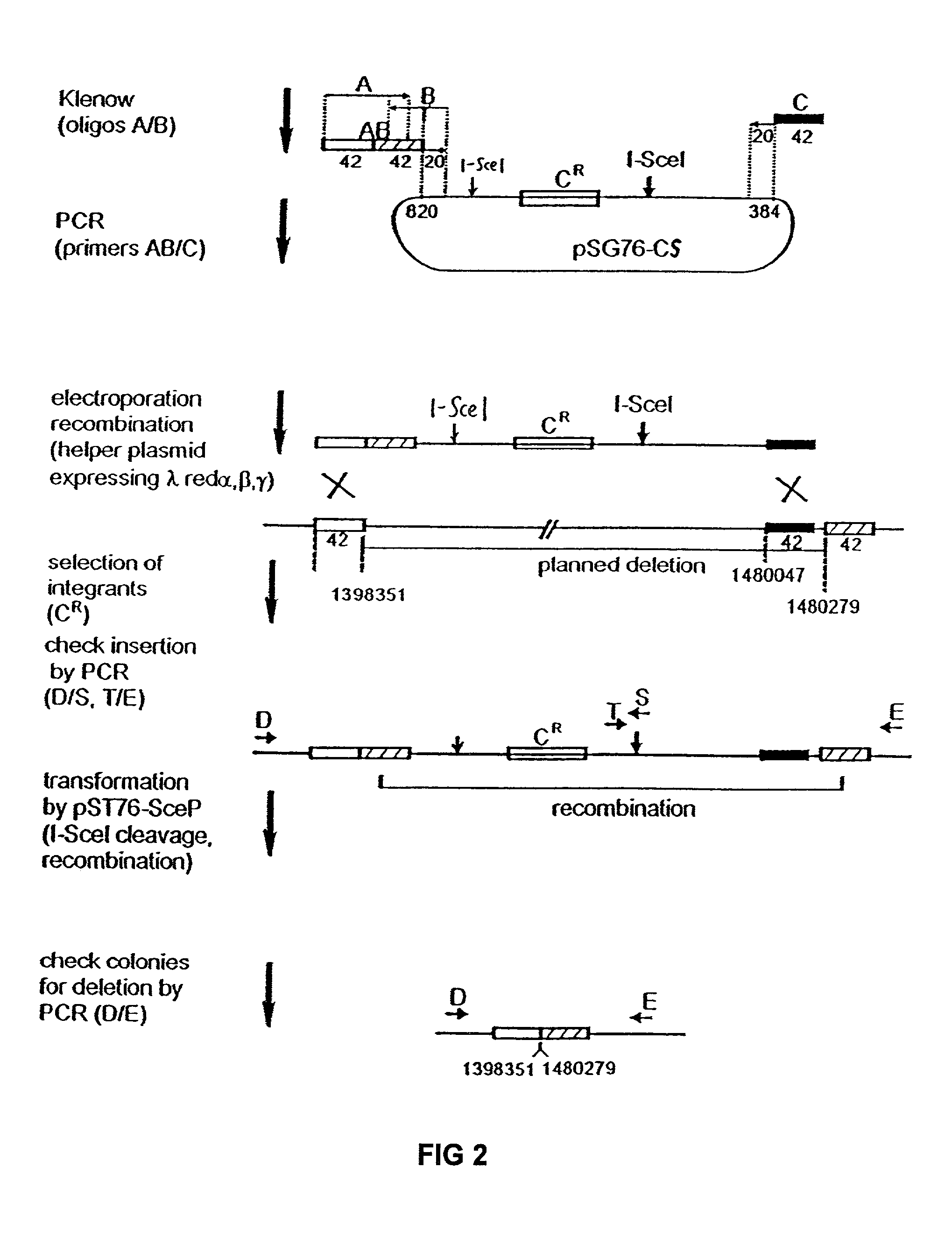
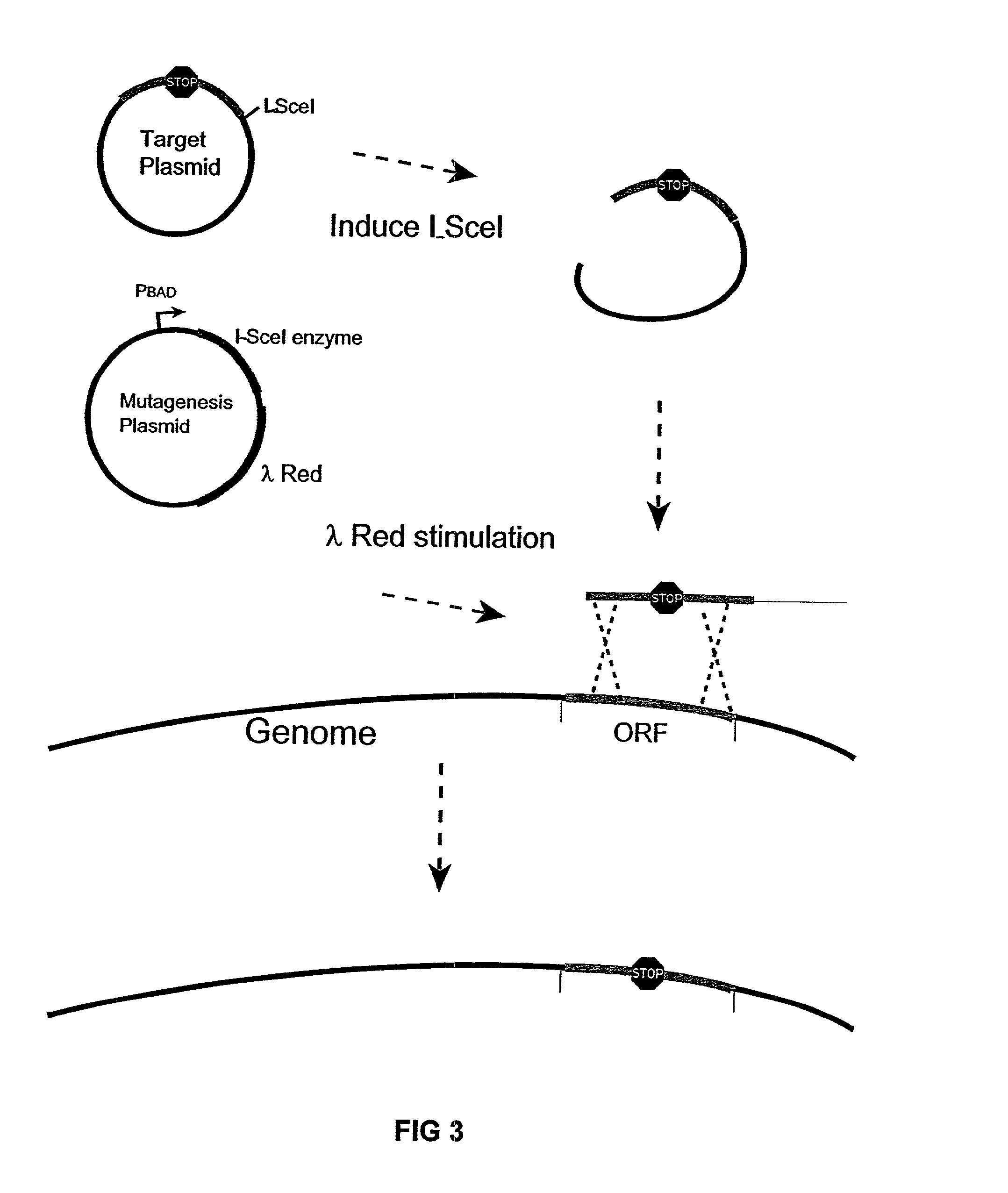
Bacteria with reduced genome
InactiveUS6989265B2Efficient processingEasy to purifyBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAGenetically engineered
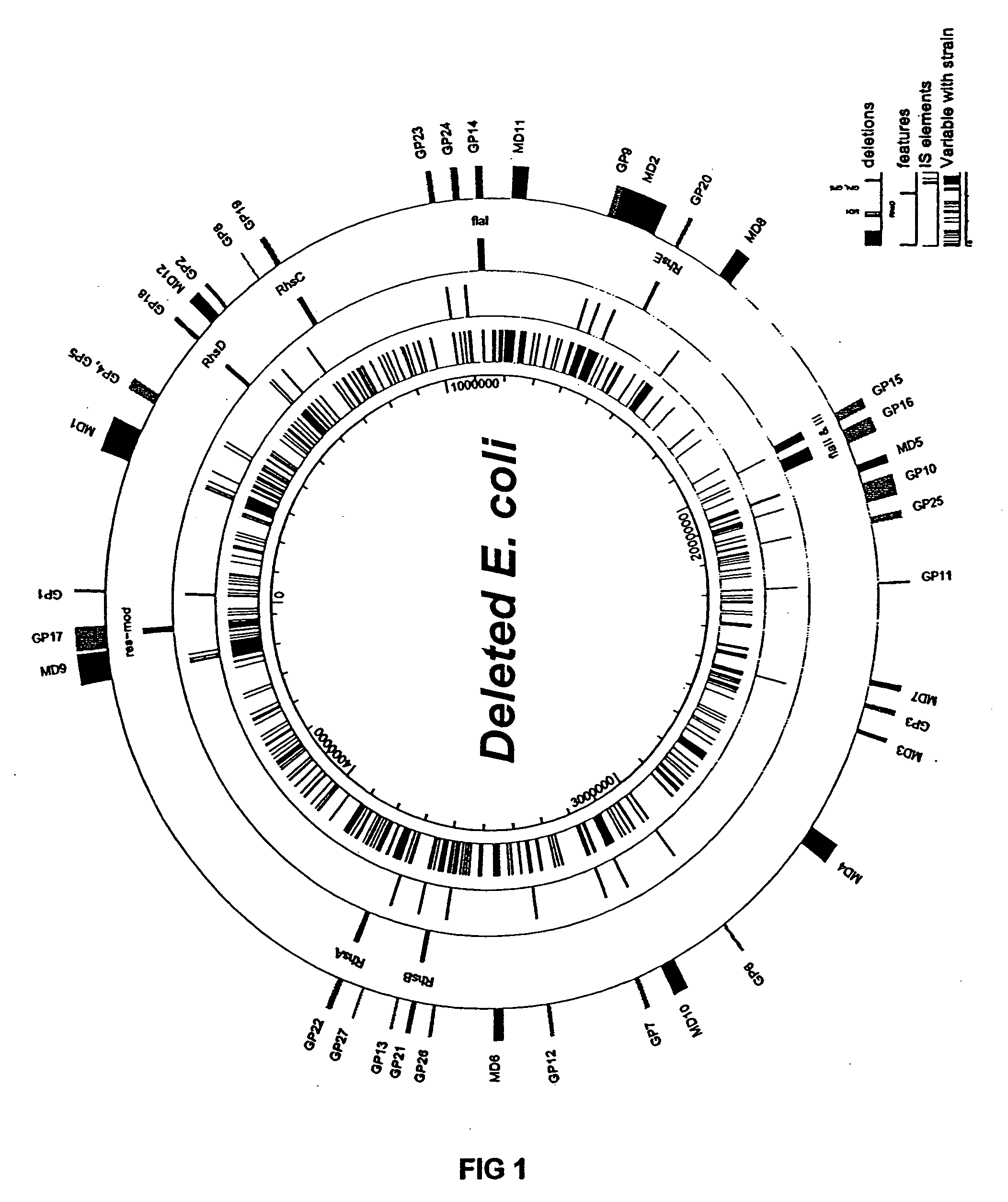
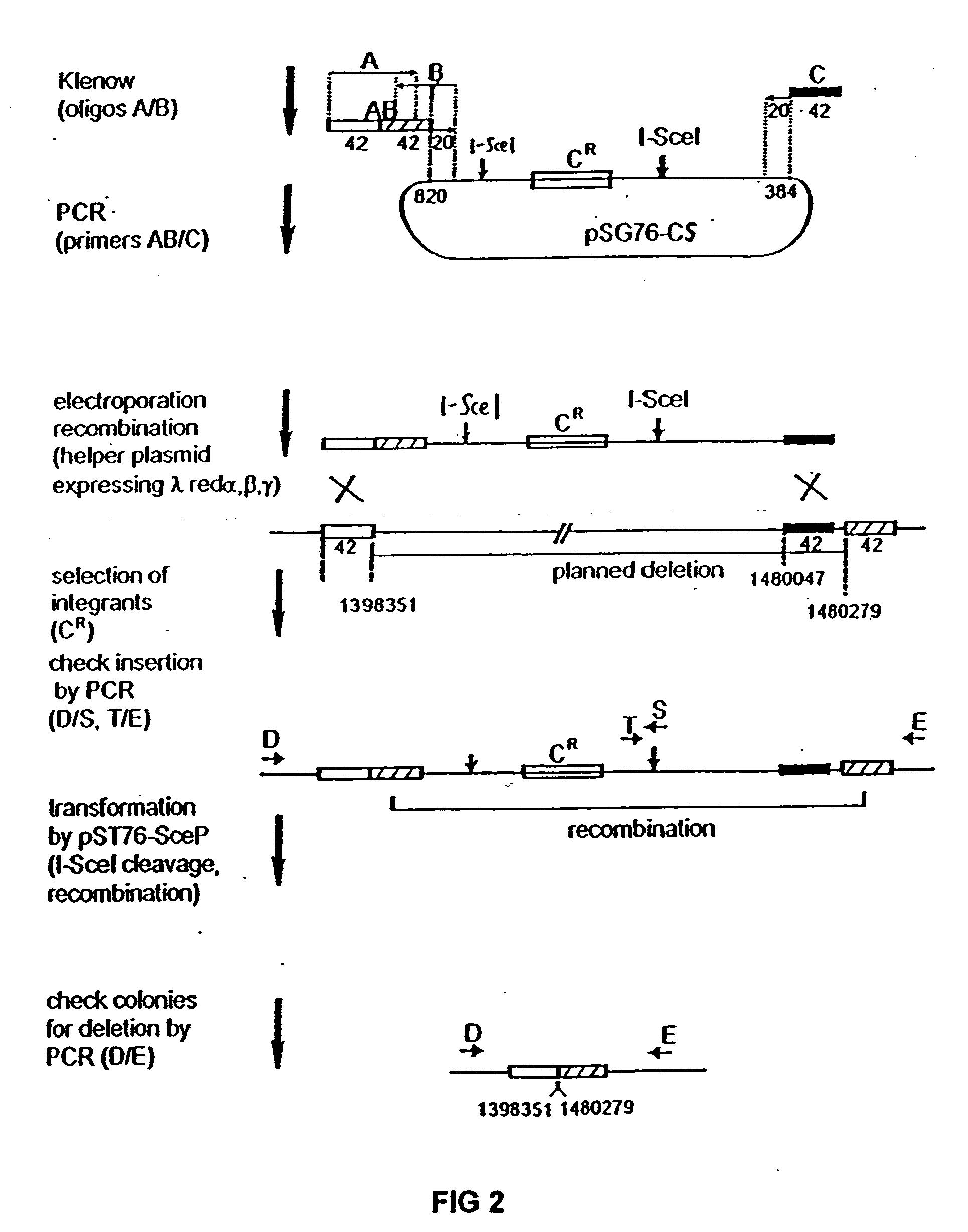
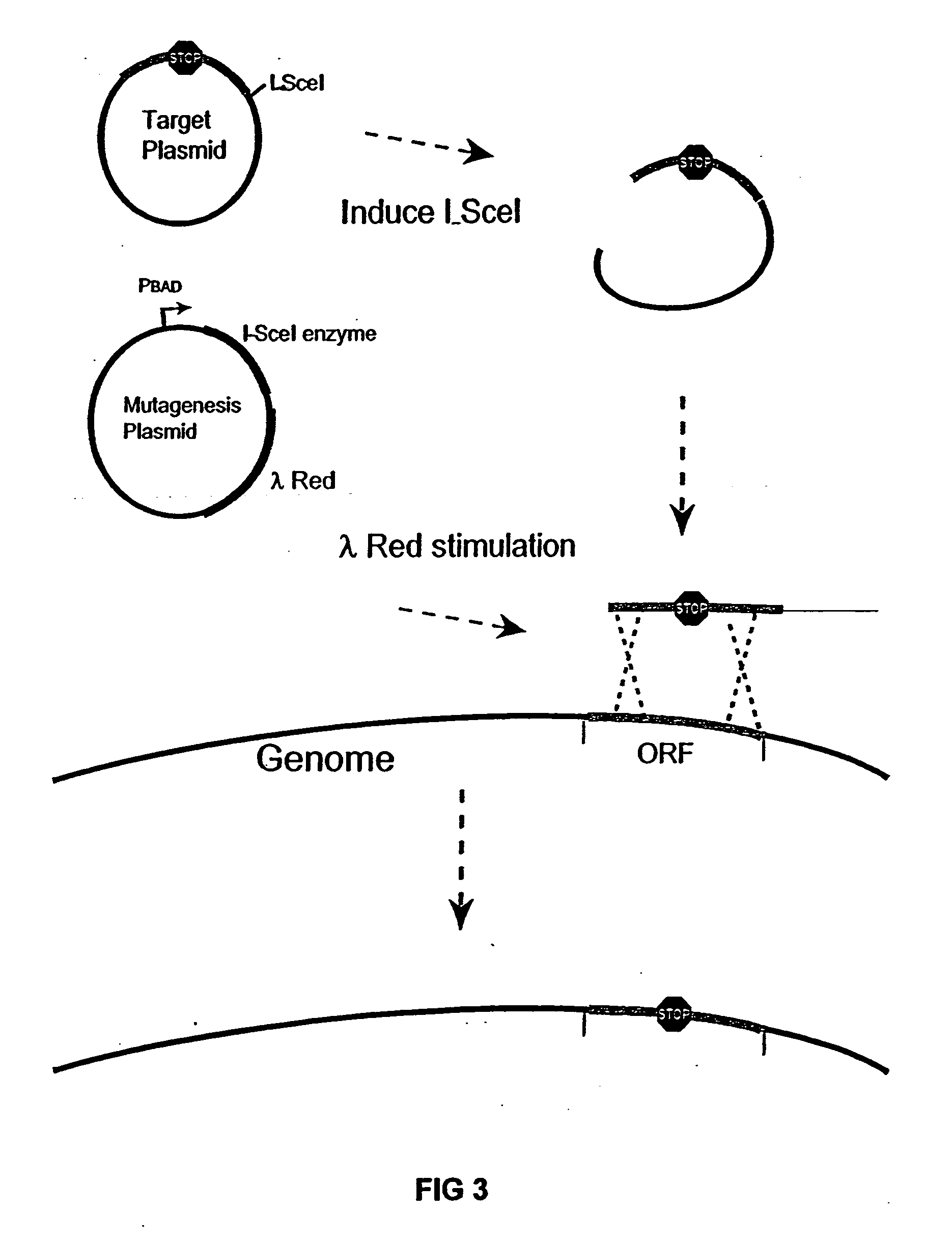
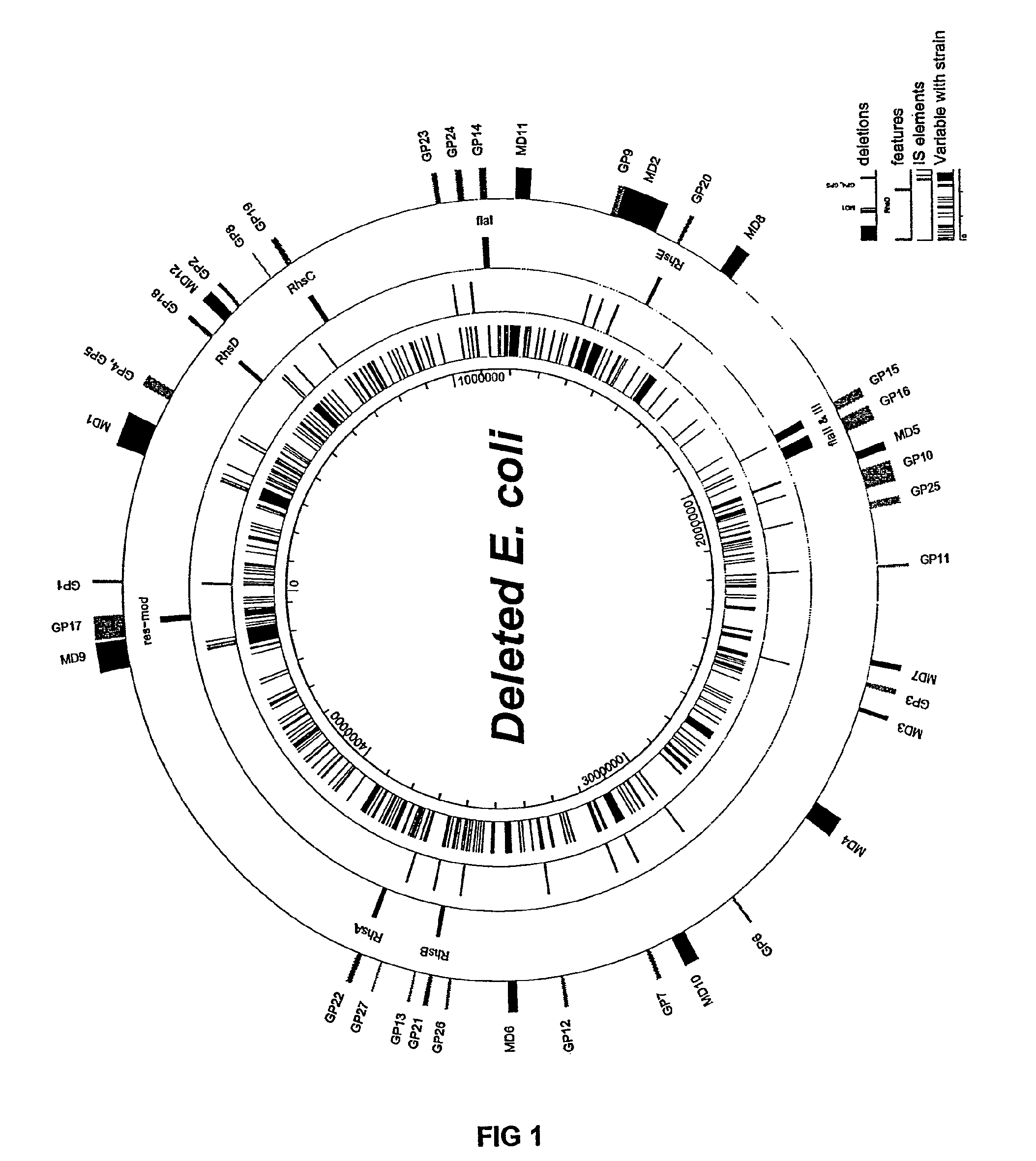
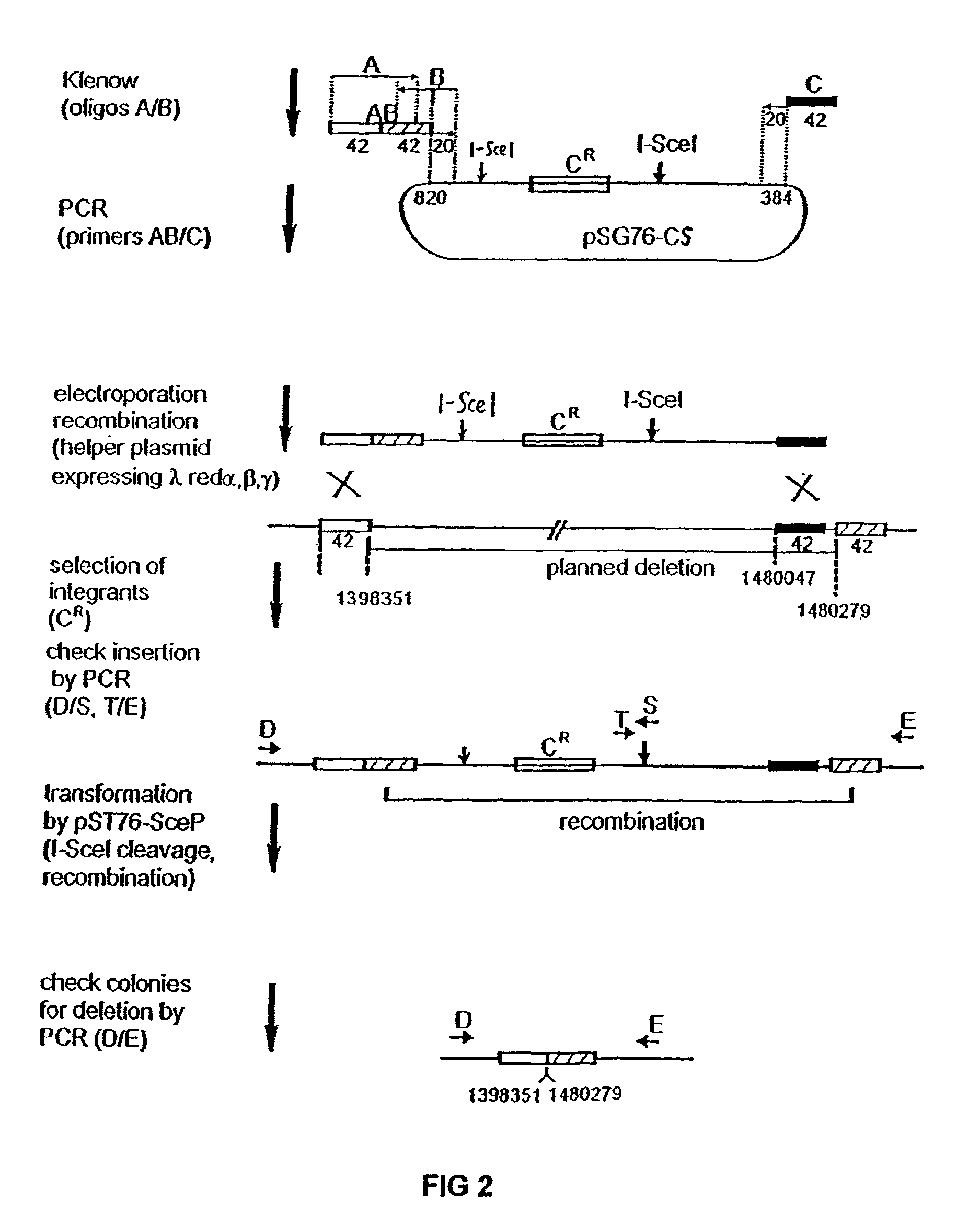
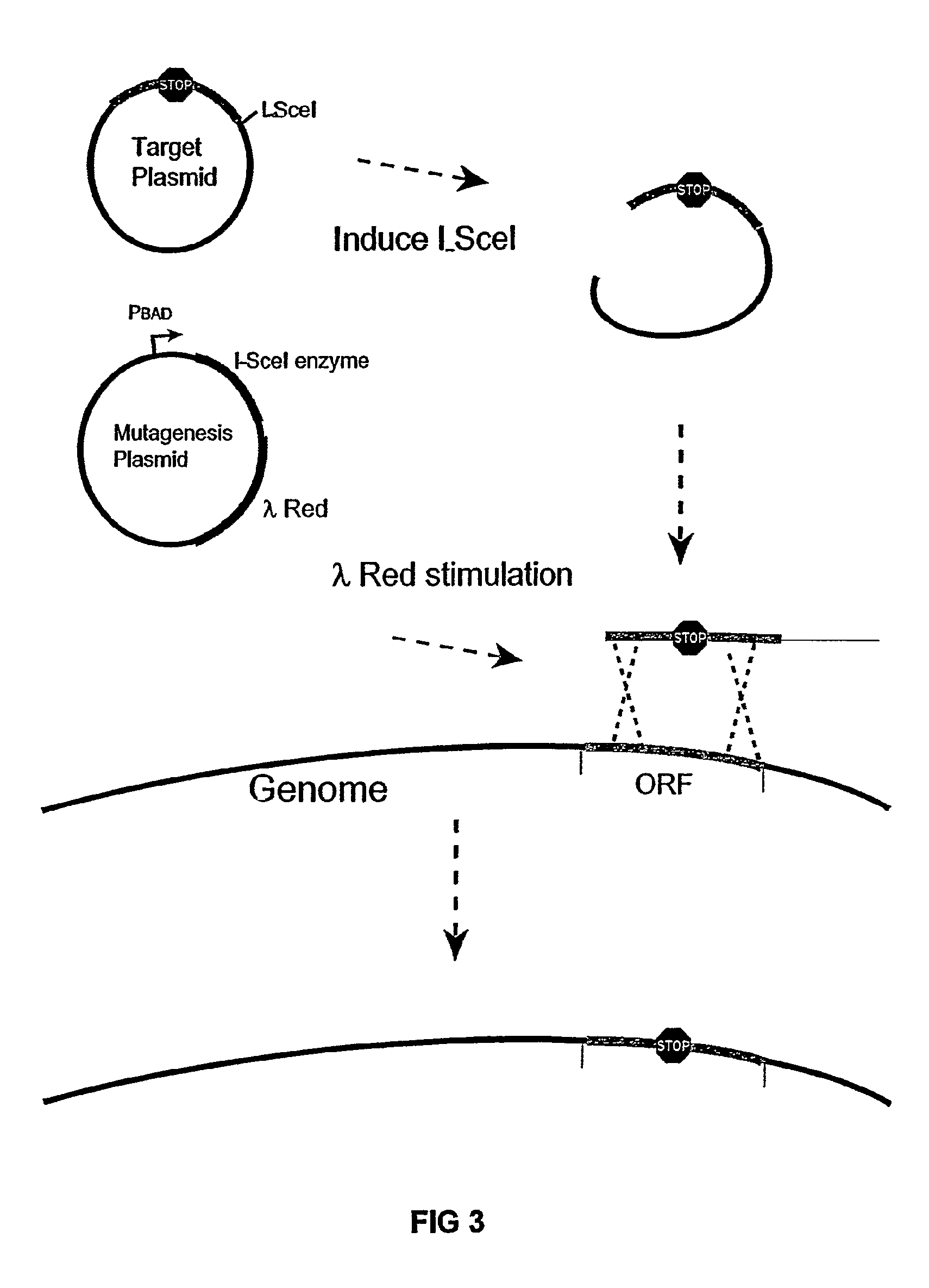
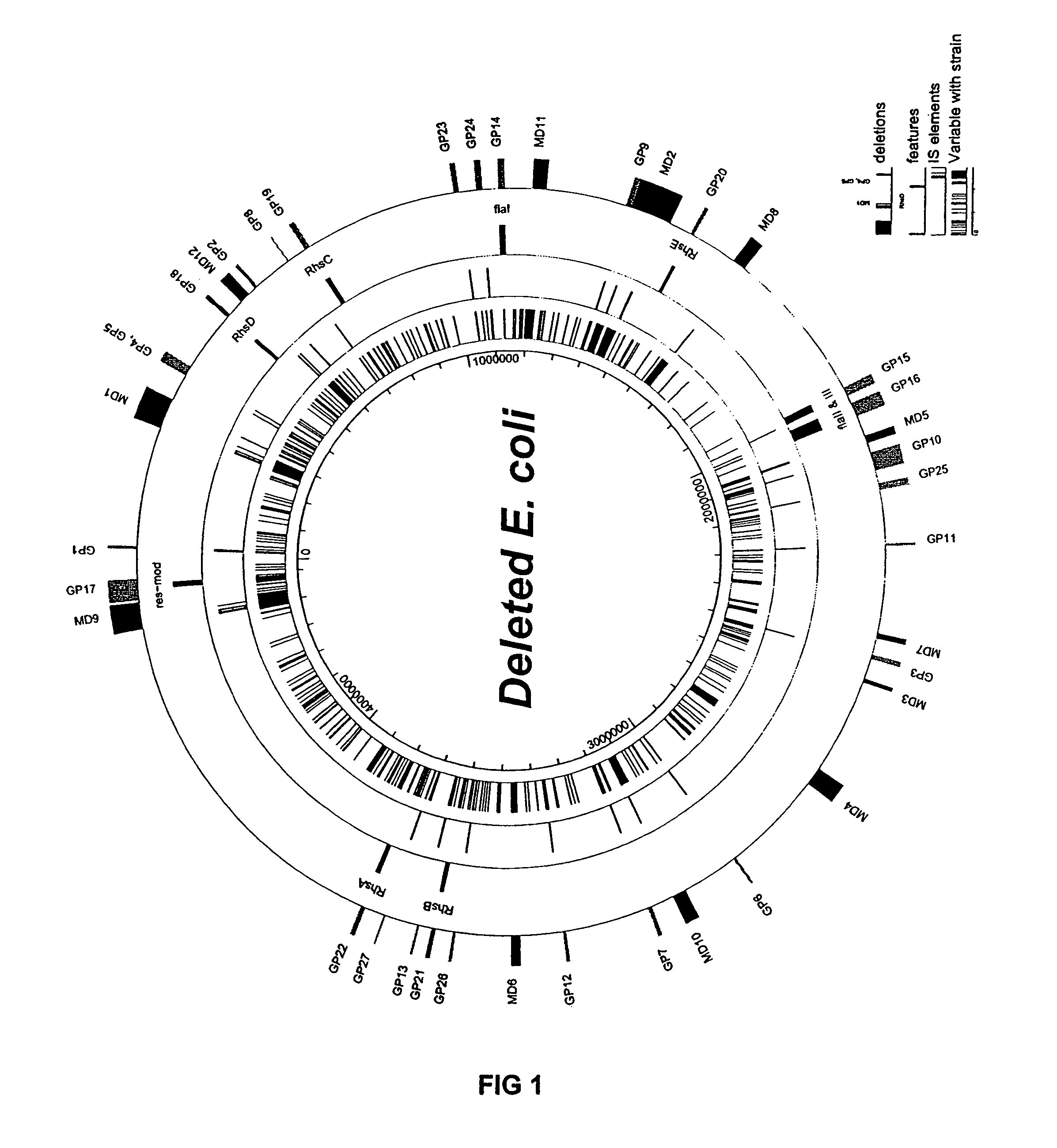
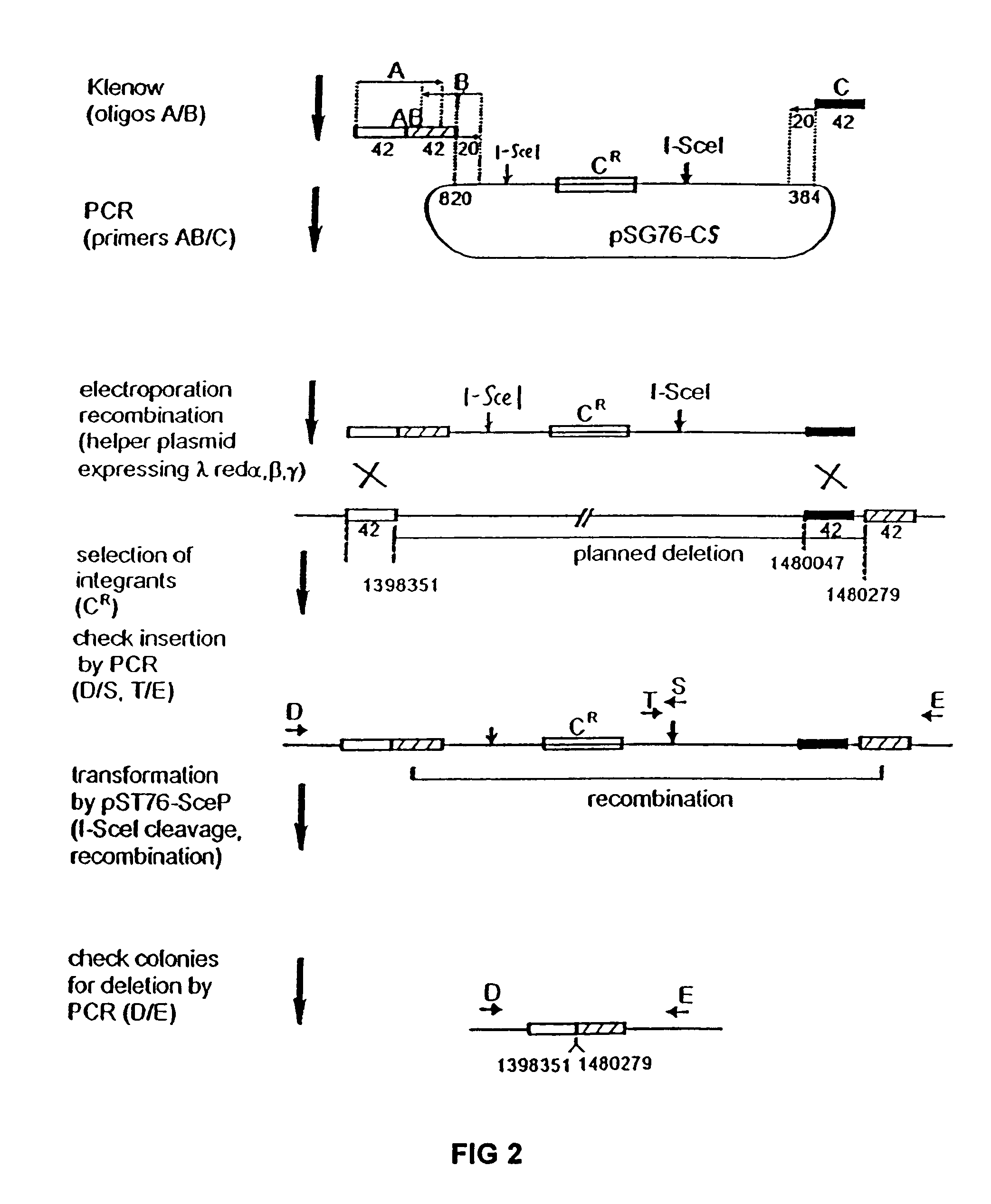
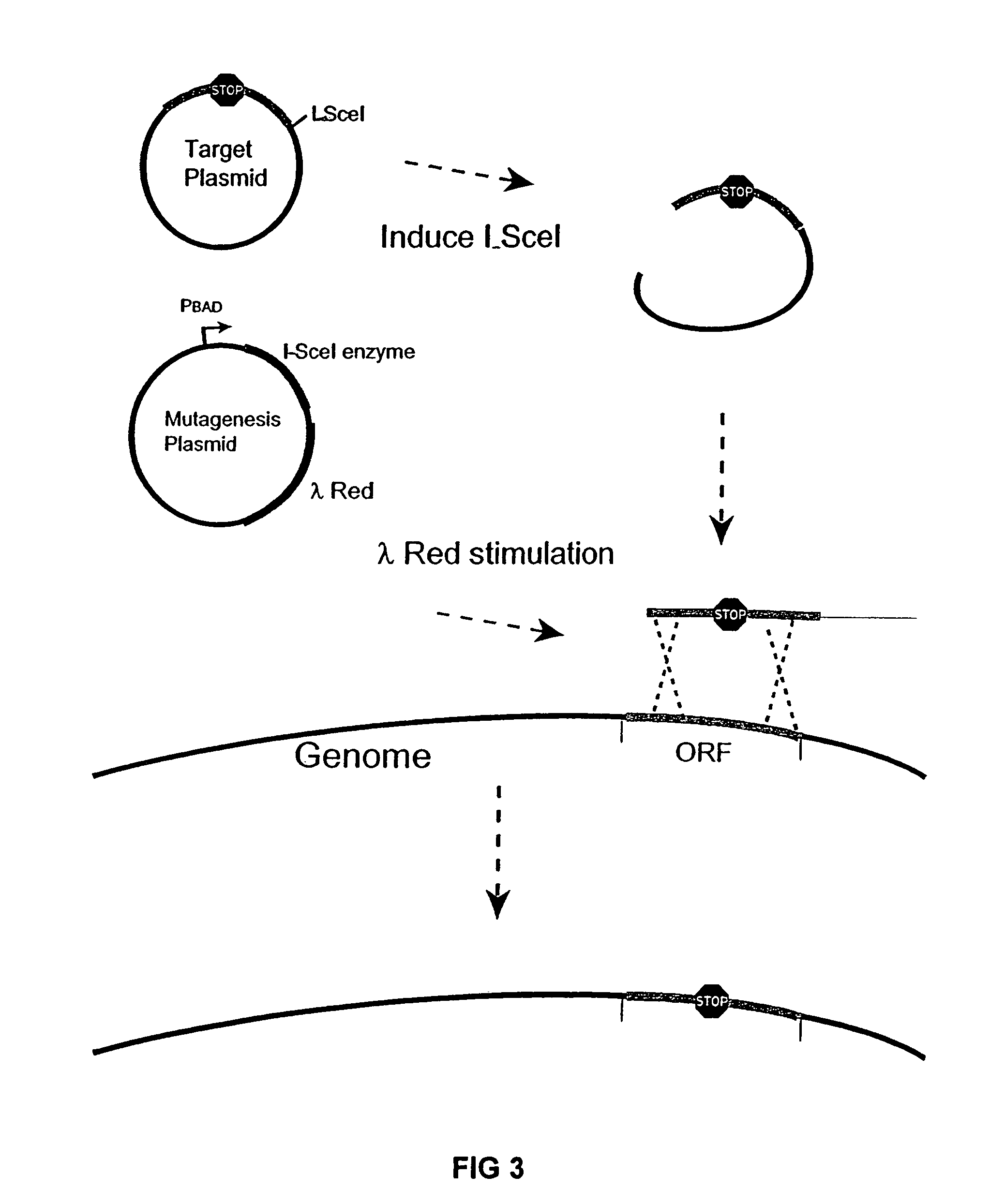
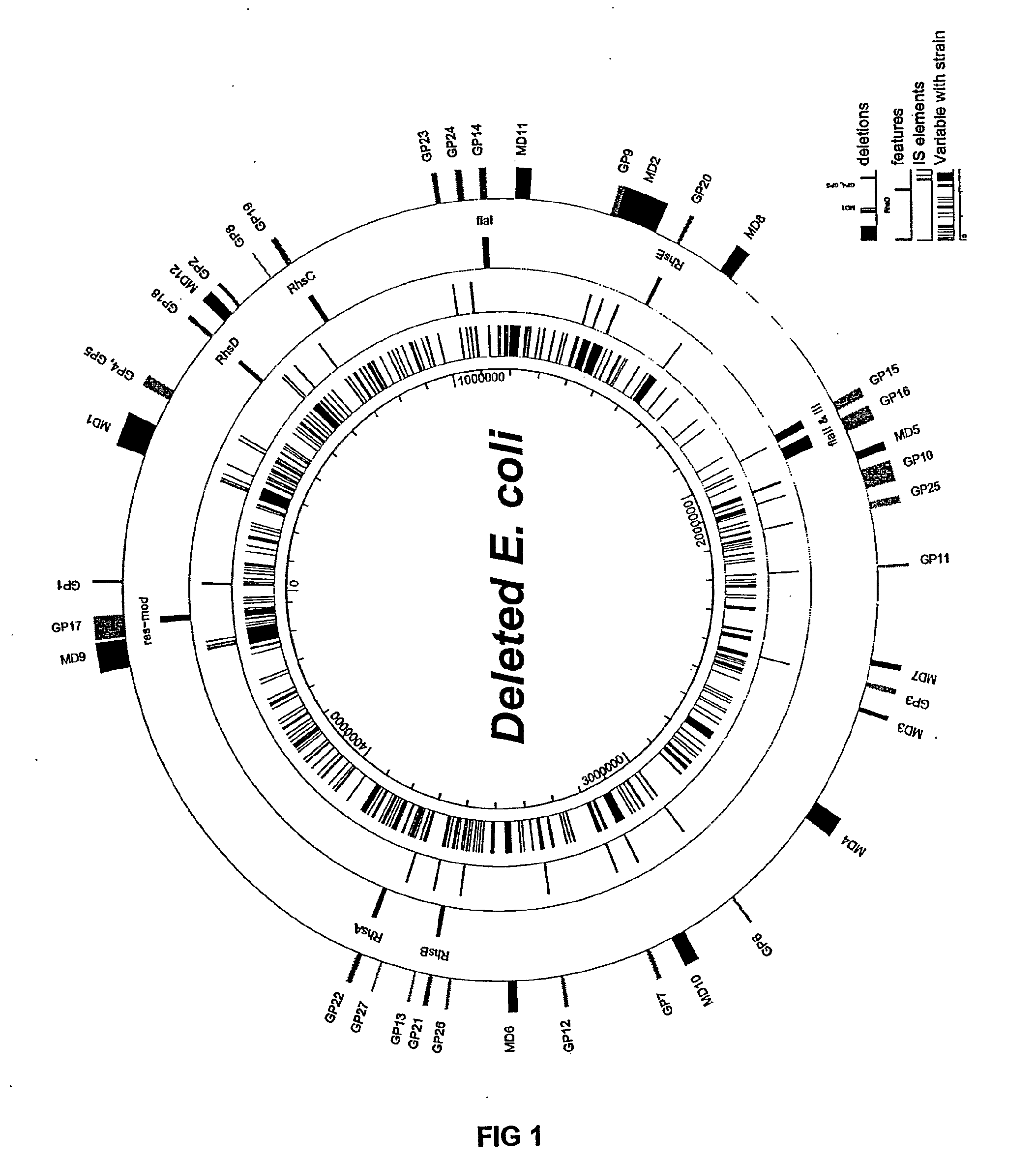
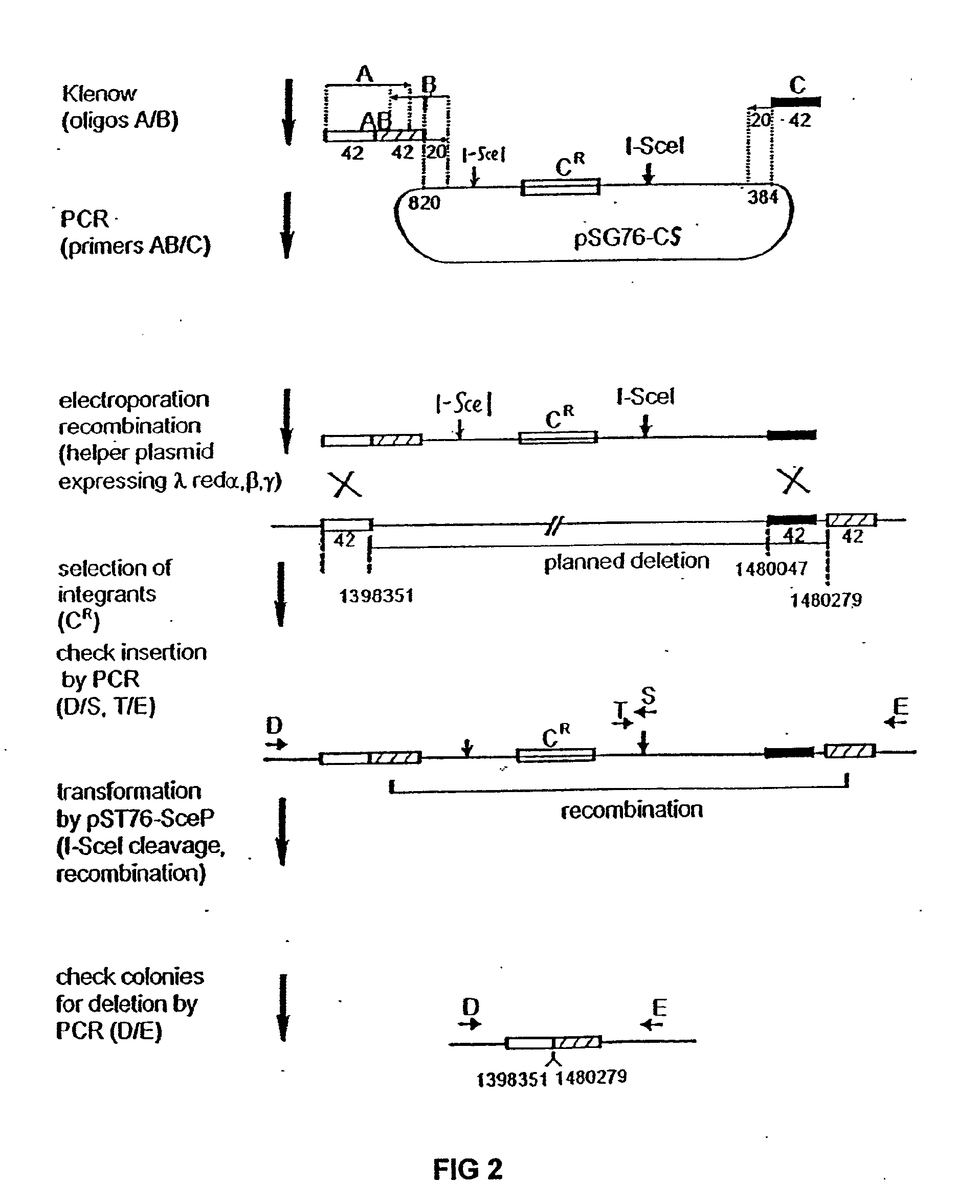
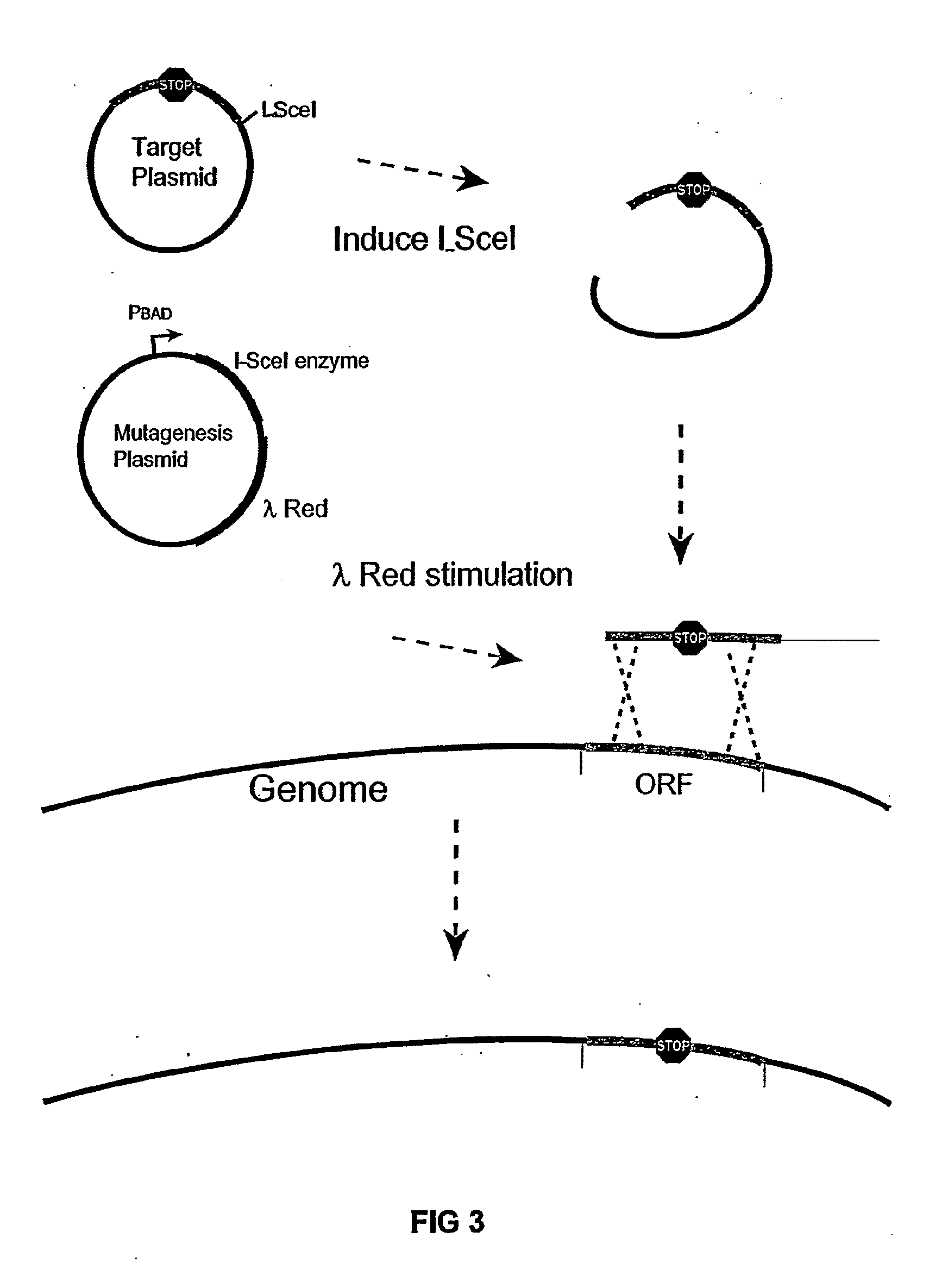
The present invention provides a bacterium having a genome that is genetically engineered to be at least 2 to 14% smaller than the genome of its native parent strain. A bacterium with a smaller genome can produce a commercial product more efficiently. The present invention also provides methods for deleting genes and other DNA sequences from a bacterial genome. The methods provide precise deletions and seldom introduces mutations to the genomic DNA sequences around the deletion sites. Thus, the methods can be used to generate a series of deletions in a bacterium without increasing the possibility of undesired homologous recombination within the genome. In addition, some of the methods provided by the present invention can also be used for replacing a region of a bacterial genome with a desired DNA sequence.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Bacteria with reduced genome
InactiveUS20060270043A1Reducing genomeEfficient processingBacteriaFermentationGenomic DNAGenetically engineered
The present invention provides a bacterium having a genome that is genetically engineered to be at least 2 to about 20% smaller than the genome of its native parent strain. A bacterium with a smaller genome can produce a commercial product more efficiently. The present invention also provides methods for deleting genes and other DNA sequences from a bacterial genome. The methods provide precise deletions and seldom introduces mutations to the genomic DNA sequences around the deletion sites. Thus, the methods can be used to generate a series of deletions in a bacterium without increasing the possibility of undesired homologous recombination within the genome. In addition, some of the methods provided by the present invention can also be used for replacing a region of a bacterial genome with a desired DNA sequence.
Owner:BLATTNER FREDERICK R +4
Targeted elimination of bacterial genes
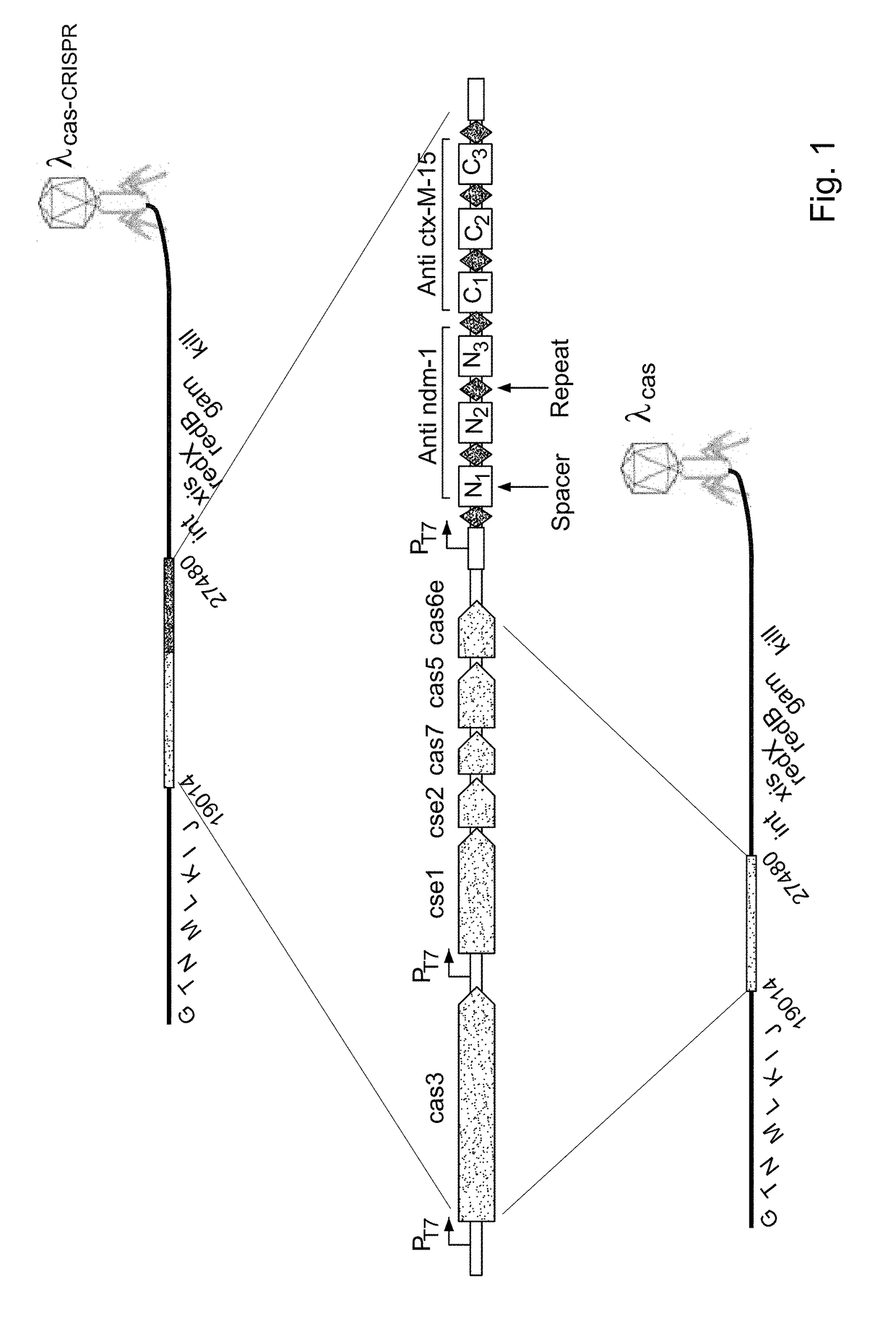
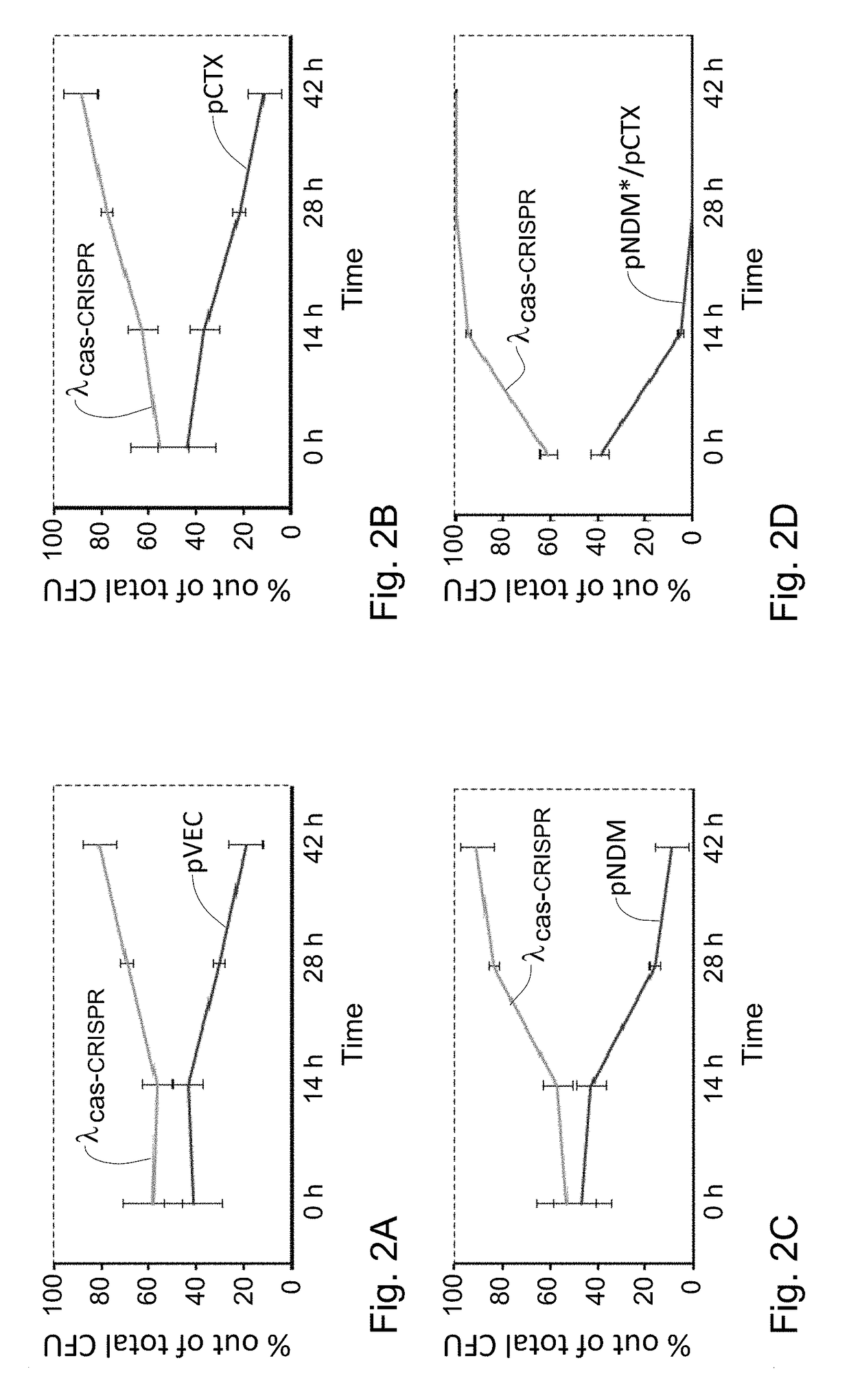
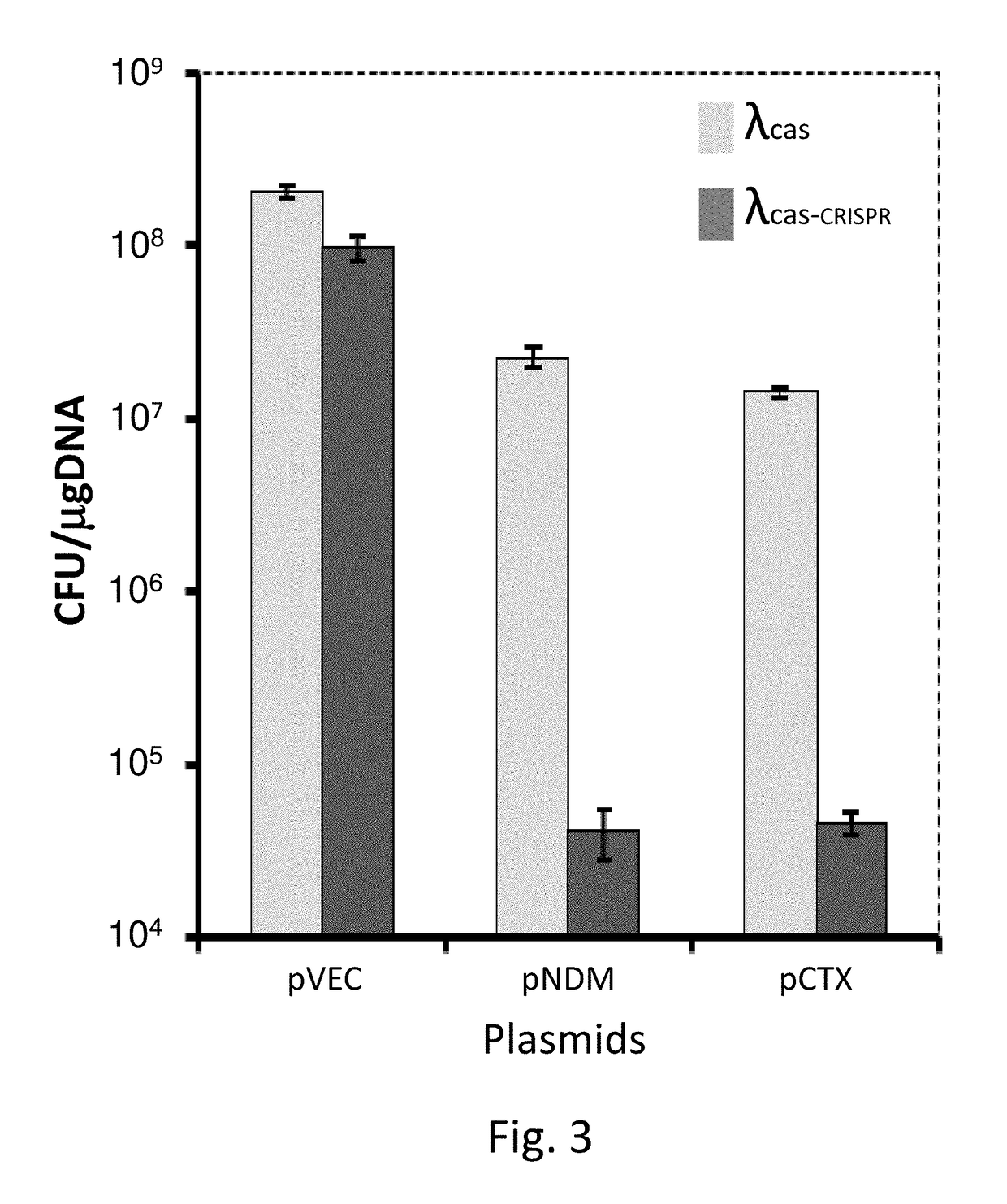
Provided is a kit or a system including two elements or components. The first component (i) is a selective component including a nucleic acid sequence and at least one proto-spacer. The second component (ii) includes at least one sensitizing component including at least one cas gene and at least one CRISPR array. At least one spacer of the CRISPR targets a proto-spacer included within a pathogenic gene of a bacterium so as to specifically inactivate said pathogenic gene in said bacterium and wherein at least one spacer of said CRISPR targets a proto-spacer included within said selective component of (i) so as to specifically inactivate said selective component. Further provided is a method using the components or kits of the invention for interference with a horizontal transfer of a pathogenic gene between bacteria and for preventing a pathologic condition in a mammalian subject caused by a bacterial infection.
Owner:TECH INNOVATION MOMENTUM FUND ISRAEL
Insertion sequence-free bacteria
InactiveUS8039243B2Reducing genomeEfficient processingBacteriaSugar derivativesBacteroidesBacterial genome size
The present invention provides a bacterium having a genome that is genetically engineered to be smaller than the genome of its native parent strain. A bacterium with a smaller genome can produce a commercial product more efficiently. The present invention also provides methods for deleting genes and other DNA sequences from a bacterial genome. The methods provide precise deletions and seldom introduces mutations to the genomic DNA sequences around the deletion sites. Thus, the methods can be used to generate a series of deletions in a bacterium without increasing the possibility of undesired homologous recombination within the genome. In addition, some of the methods provided by the present invention can also be used for replacing a region of a bacterial genome with a desired DNA sequence.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Bacteria with reduced genome
InactiveUS8043842B2Efficient processingEasy to purifyBacteriaStable introduction of DNAGenomic DNAGenetically engineered
The present invention provides a bacterium having a genome that is genetically engineered to be at least 2 to 14% smaller than the genome of its native parent strain. A bacterium with a smaller genome can produce a commercial product more efficiently. The present invention also provides methods for deleting genes and other DNA sequences from a bacterial genome. The methods provide precise deletions and seldom introduces mutations to the genomic DNA sequences around the deletion sites. Thus, the methods can be used to generate a series of deletions in a bacterium without increasing the possibility of undesired homologous recombination within the genome. In addition, some of the methods provided by the present invention can also be used for replacing a region of a bacterial genome with a desired DNA sequence.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Methods and compositions for tailing and amplifying RNA
ActiveUS7361465B2Efficiently and uniformly tailImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenome wide expressionGenome
The present invention provides methods and compositions that enable tagging and amplification of targeted RNA molecules. A targeted RNA molecule is any non-polyadenylated RNA molecule including, for example, miRNA, siRNA, rRNA, tRNA, synthetic RNA, or non-polyadenylated mRNA such as mRNA from bacteria. In certain aspects, the invention provides methods and compositions for the genome-wide expression analysis of bacterial genes. Significantly, the methods enable genome-wide expression analysis in circumstances where bacterial numbers were previously too low to purify adequate amounts of RNA for DNA microarray analysis or other applications. Such methods are particularly useful for the study of bacterial gene expression during host-cell infection. The invention also provides kits for tagging and amplifying targeted RNA molecules.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Multiplex LAMP detection primer, kit and method for six food-borne pathogenic bacteria in fruits and vegetables
InactiveCN107022644AStrong specificityHigh amplification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBacteroides
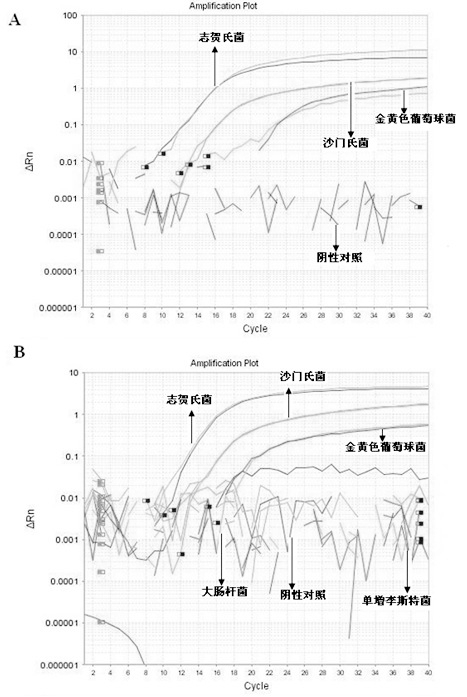
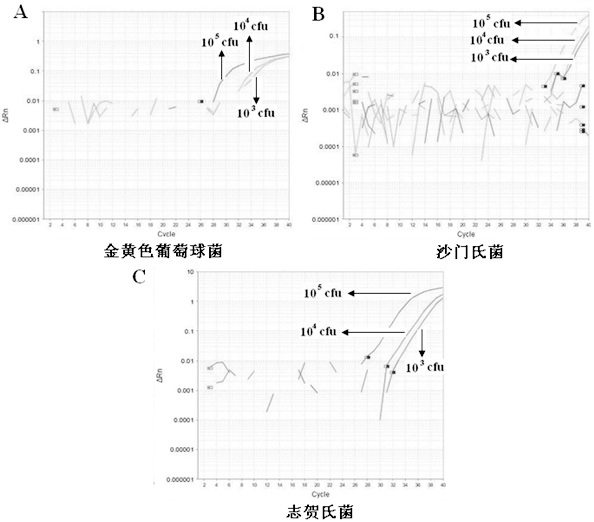
The invention discloses a multiplex LAMP detection primer, kit and method for six food-borne pathogenic bacteria in fruits and vegetables and belongs to the technical field of bacterial gene detection. A rapid detection primer set for the six pathogenic bacteria including listeria monocytogenes, enterobacter sakazakii, shigella spp, staphylococcus aureus, salmonella spp and escherichia coli O157:H7 is designed, and multiplex LAMP reaction is performed on the genome DNA of the bacteria extracted from a sample to be detected in the same reaction system by use of the detection kit including the primer set to determine whether the sample contains the six food-borne pathogenic bacteria or not. The multiplex LAMP detection primer is high in specificity and sensitivity and can accurately detect the genome DNA of the six food-borne pathogenic bacteria in the same reaction system, can realize simple and convenient, quick and accurate detection, is suitable for on-site rapid detection and has significance on improving the pathogenic bacterium analysis and detection technology and the fruit and vegetable edible quality security.
Owner:INST OF QUALITY STANDARDS & TESTING TECH FOR AGRO PROD OF SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Nucleic acid molecules for detecting bacteria and phylogenetic units of bacteria
InactiveUS7202027B1Sure easyEasy to compareSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesPhylogenetic tree
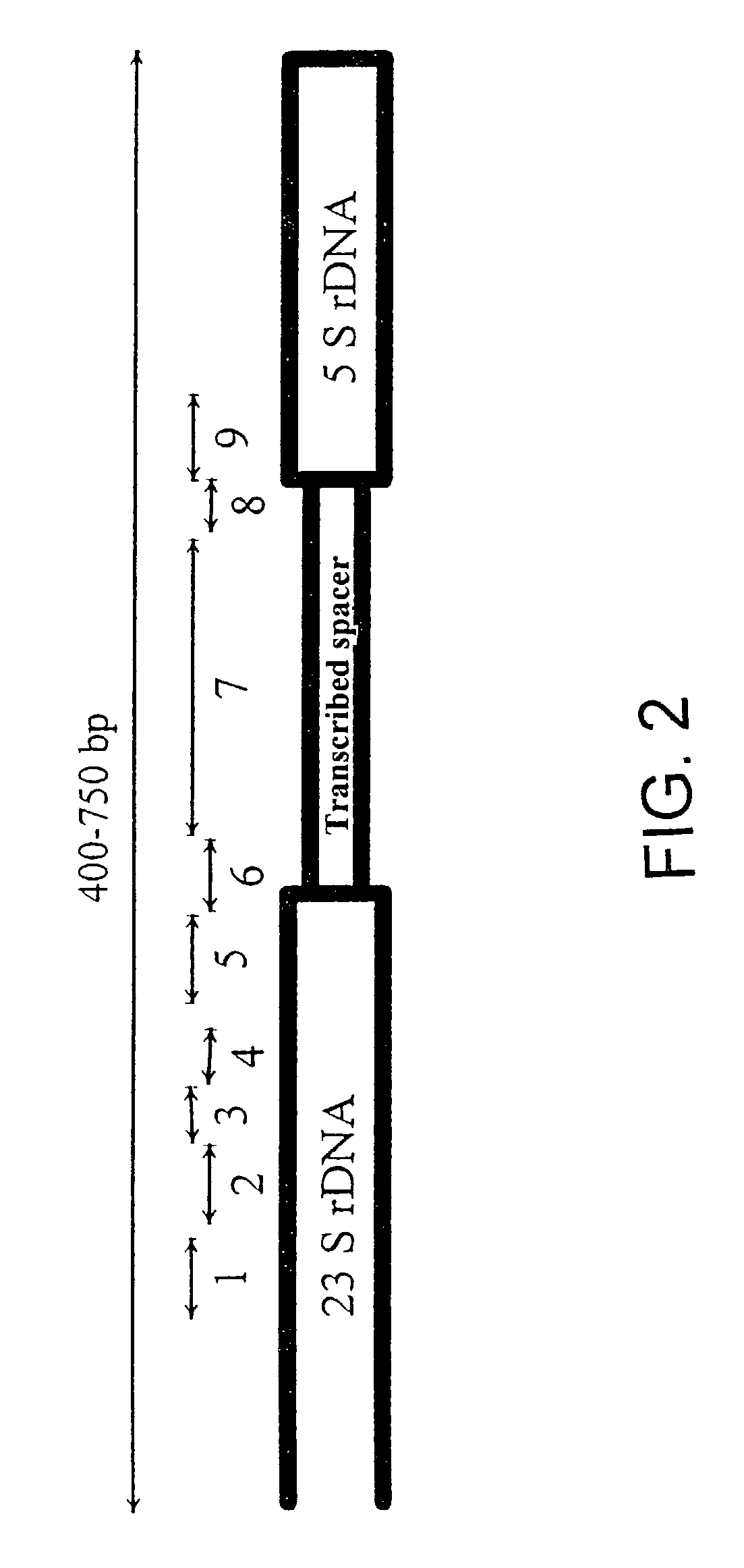
The present invention relates to nucleic acid molecules which allow the identification of bacteria or groups of bacteria. For detection, the region of the bacterial genome containing the 23 S / 5 S rRNA is used as the target sequence for the bacterial detection.
Owner:BIOTECON DIAGNOSTICS
Method for predicting outer membrane protein of germs on basis of machine learning technique
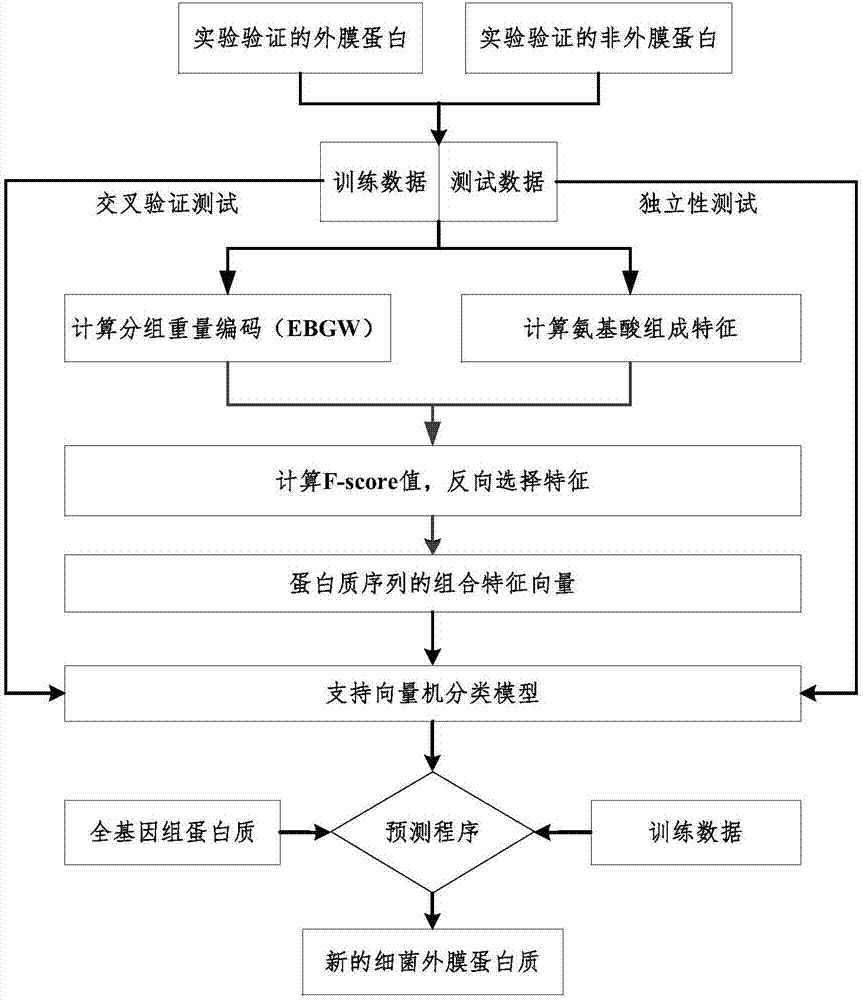
InactiveCN108009405AQuick forecastEasy to identifyBiostatisticsCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorSupport vector machine
The invention discloses a method for using a machine learning technique for predicting outer membrane protein coded on genomes of germs. The method includes the steps of utilizing a PSI-BLAST algorithm to calculate a location specificity feature vector of the protein, adopting an autocorrelation function for conducting feature conversion, building a classification device based on a supporting vector machine, conducting classification on the outer membrane protein and non-outer membrane protein, receiving a protein sequence input by a user through a local computer program, and predicting whether or not the protein sequence belongs to the outer membrane protein. By means of the method, calculation prediction can be conducted on the protein sequence coded by the whole genome of the germs, thesensitivity is high, the calculation speed is high, and an effective tool is provided for fast identification and screening of inner and outer membrane protein of the genomes of the germs. The methodis an accurate and effective screening method for the outer membrane protein and can be widely applied to identification of the outer membrane protein of new sequencing genomes of germs.
Owner:上海韦翰斯生物医药科技有限公司
Micro-reactor for gene inspection
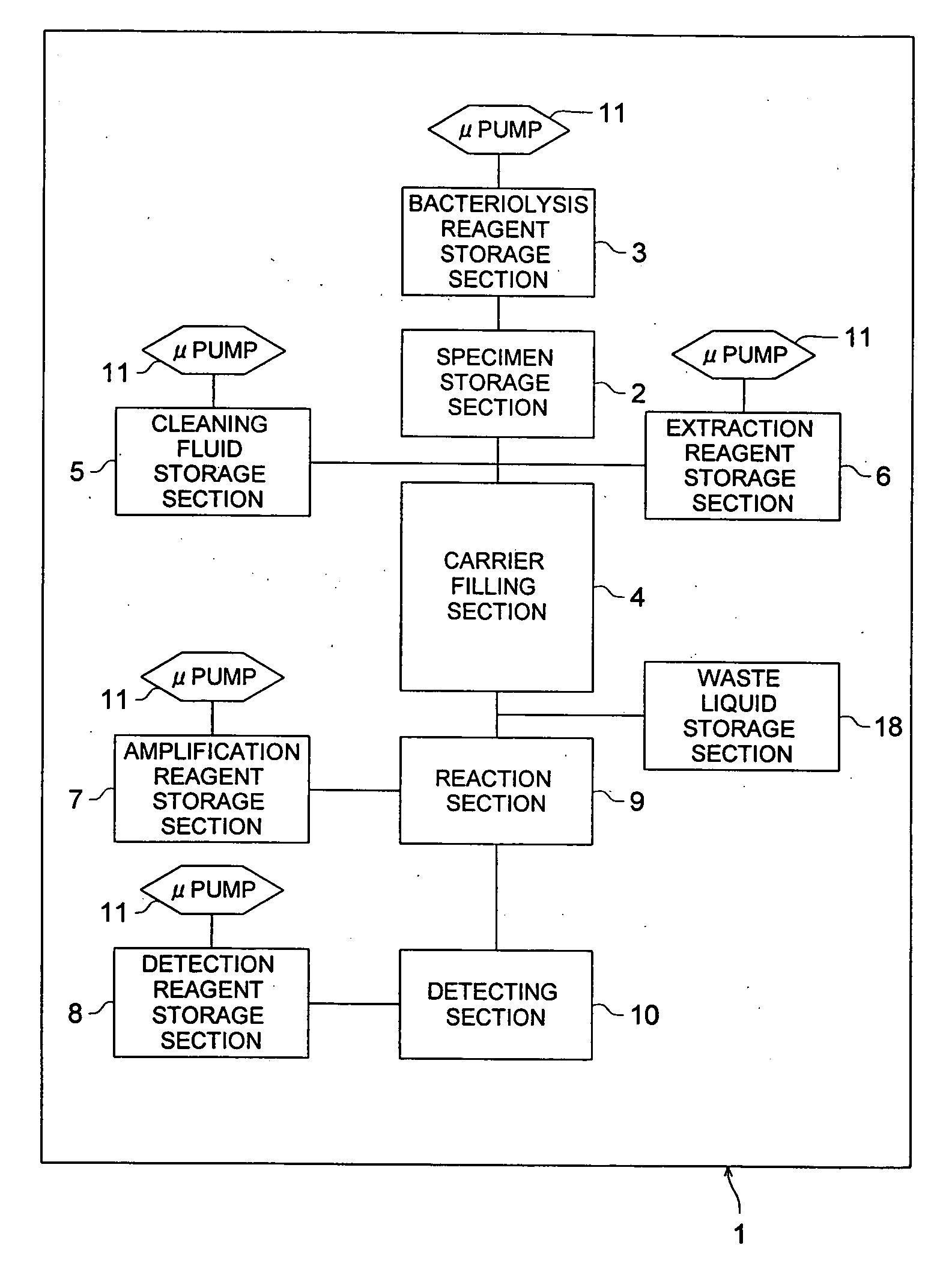
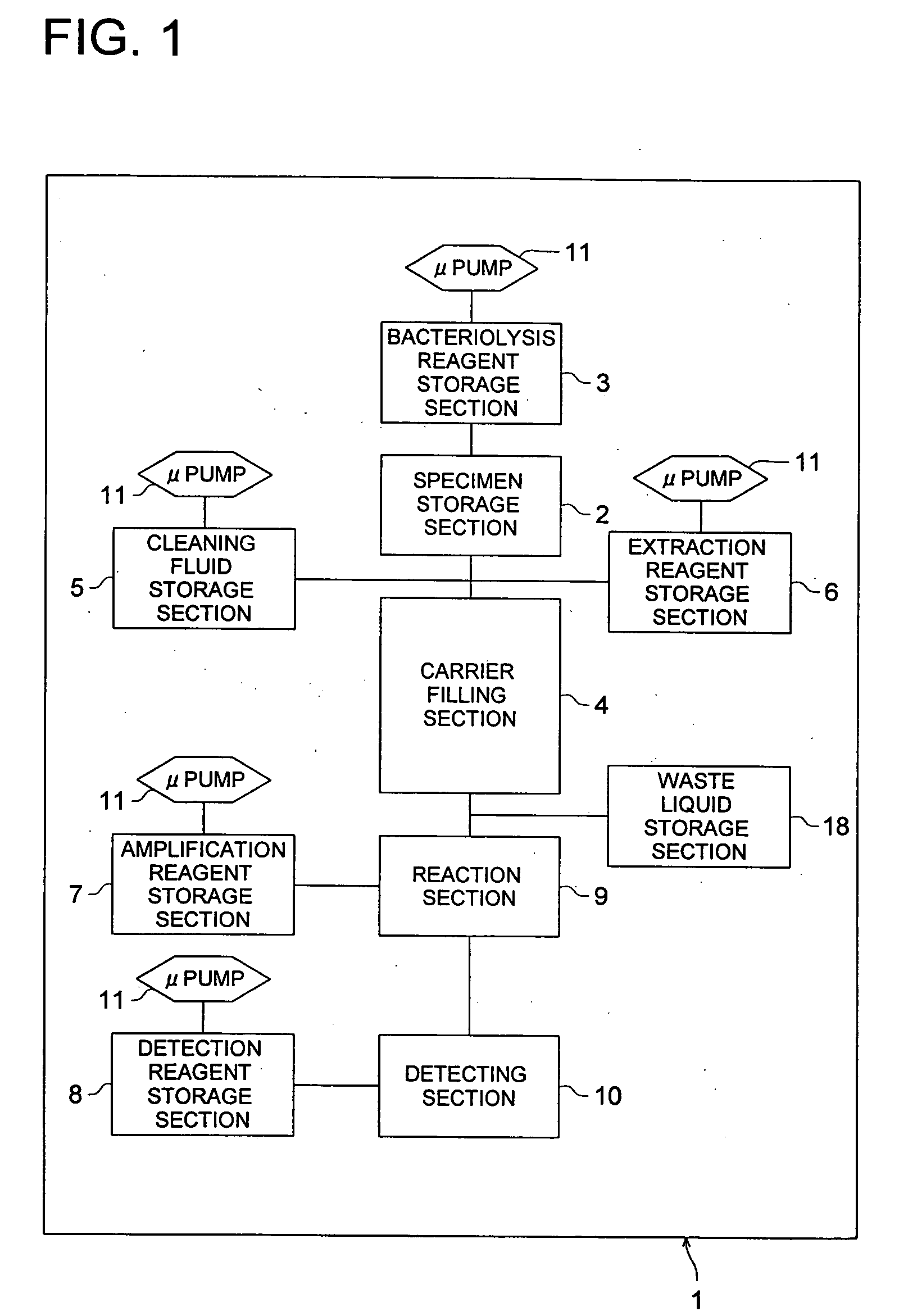
InactiveUS20060088929A1Reliable inspectionSimple structureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroreactorCheck valve
The invention provides gene-inspecting micro-reactor for detecting a bacterial cell wherein flexibility and high sensitivity are secured, low cost by a disposable type is realized, highly accurate detection is possible in a simple structure, and preliminary processing suitable for amplification reaction can be done for specimen efficiently and rapidly. After lysing a bacterial cell in the specimen by bacteriolysis reagent stored in bacteriolysis reagent storage section 3, and after adsorbing bacterial genes on carriers filled in carrier filling section 4, there is conducted preliminary processing for washing and detecting bacterial genes. Further, there are provided a control means that switches the direction of liquid-feeding for a liquid containing bacterial genes fed to carrier filling section 4, a check valve, amplified reagent storage section 7 and a cooling means such as Pertier element that cools reagent mixing section.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA MEDICAL & GRAPHICS INC
Kit for magnetic bead method for bacterial genome DNA extraction and extraction method thereof
ActiveCN104212793AHarm reductionReduce special requirementsDNA preparationMagnetic beadNaCl - Sodium chloride
The invention discloses a kit for a magnetic bead method for bacterial genome DNA extraction and an extraction method thereof. The kit includes the following seven components: a buffer solution A, a buffer solution B, a buffer solution C, a magnetic bead suspension solution D, a buffer solution E, a buffer solution F and a buffer solution G. composition of the magnetic bead suspension solution D is 50mg of monodisperse Fe3O4 @ SiO2 AEAPS nanometer magnetic beads in each 200 mmol / L sodium chloride aqueous solution. The extraction method for the kit comprises six steps: thallus re-suspension, cracking, nucleic acid deposition, magnetic bead adsorption, washing and elution. The kit provided by the invention adopts efficient monodisperse nano magnetic beads combined with a unique buffer system, so that the extracted bacterial genome DNA has large fragment, high purity and stable and reliable quality, and can meet the requirements of the follow-up experiments.
Owner:INST OF PLA FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Primer of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for detecting multidrug-resistant cfr gene as well as kit and method for detecting multidrug-resistant cfr gene
ActiveCN102230019AQuick checkStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenomic DNABacterial strain
The invention belongs to the technical field of bacterial gene detection and provides primers of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for detecting a multidrug-resistant cfr gene, which include a pair of outer primers, a pair of inner primers and a loop primer, wherein the molar ratio of the outer primers to the inner primers is 1:8, and the molar ratio of the outer primers to the loop primer is 1:4. The invention also provides a kit for detecting the multidrug-resistant cfr gene; and the kit comprises a plurality of LAMP tubes each of which has a reaction liquid composed of an isothermal reaction buffer solution, BstDNA polymerase, an inner primer FIP, an inner primer BIP, an outer primer F3, an outer primer B3, a loop primer L and sterile double-distilled water. The invention further provides a method for detecting the multidrug-resistant cfr gene, which comprises the following steps of: extracting the genomic DNA of a bacterial strain to be detected and detecting by using the kit under such a condition that the amplification reaction is carried out for 35 minutes in a water bath of 63 DEG C. Based on the LAMP technique, the specificity is enhanced and higher than that of the PCR detection method, the detection time is greatly reduced and the detection is simple and rapid.
Owner:RECOM QINGDAO BIOTECH CO LTD
Method and system for reducing the likelihood of colorectal cancer in a human being
ActiveUS10086018B2Preventing cell entryReduce the amount requiredBacteria material medical ingredientsTetracycline active ingredientsHuman DNA sequencingIntestinal microorganisms
A system and method for reducing the likelihood of colorectal cancer in a human being includes the modification of an individual's gut microbes by employing a Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats-CRISPR-associated system (CRISPR-Cas) or Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats from Prevotella and Francisella 1 (CRISPR / Cpf1) system to modify only bacterial genes of bacteria that reside in the human gut that are non-homologous to those encompassed in the human genome, and in particular, to administer a therapeutically effective amount of a bacterial formulation comprising F. prausnitzii that has been modified to produce one of alliin or butyrate.
Owner:SEED HEALTH INC
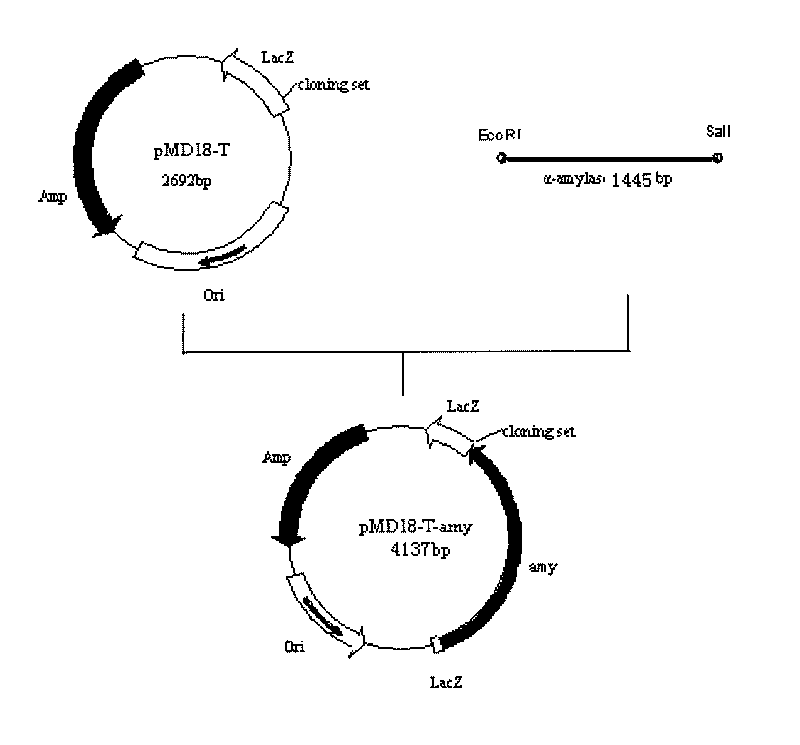
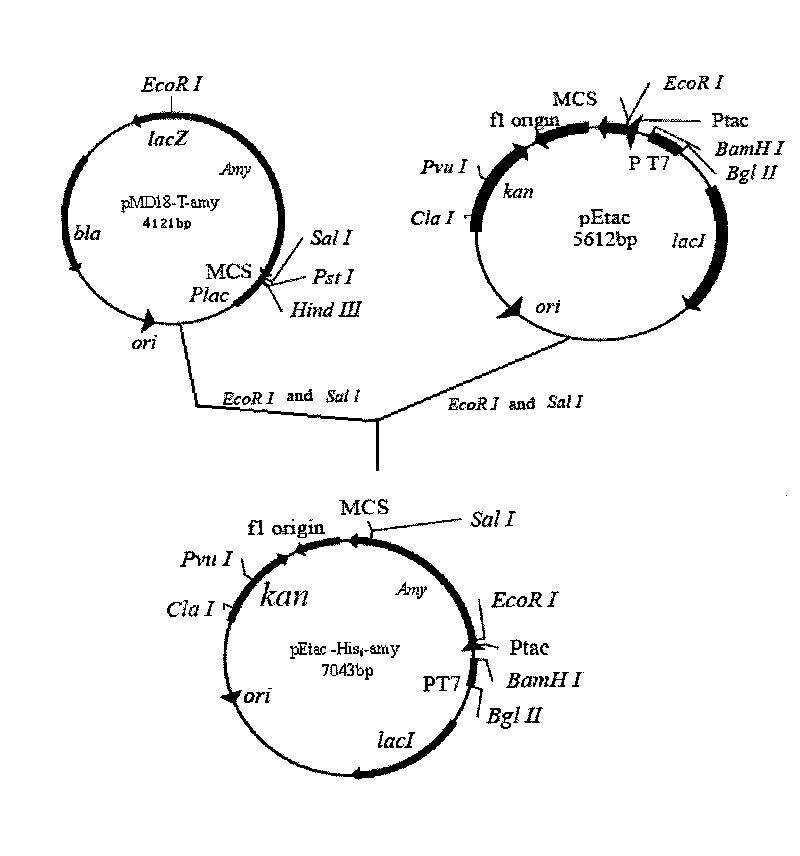
Marine low temperature alpha-amylase gene engineering bacteria, recombinant enzyme and application
InactiveCN101691579ASimple preparation processLow action temperatureBacteriaMicroorganism based processesIon exchangeAlpha-amylase
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH +1
Method and system for reducing the likelihood of colorectal cancer in a human being
ActiveUS10548761B2Reduce the possibilityEliminate symptomsOrganic active ingredientsBacteria material medical ingredientsHuman DNA sequencingGenome human
A system and method for reducing the likelihood of colorectal cancer in a human being includes the modification of an individual's gut microbes by employing a Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats-CRISPR-associated system (CRISPR-Cas) or Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats from Prevotella and Francisella 1 (CRISPR / Cpf1) system to modify only bacterial genes of bacteria that reside in the human gut that are non-homologous to those encompassed in the human genome, and in particular, to administer a therapeutically effective amount of a bacterial formulation comprising F. prausnitzii that has been modified to produce one of alliin or butyrate.
Owner:SEED HEALTH INC
Porcine mycoplasmal pneumonia and porcine infectious actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serum 1 type gene engineering strain vaccine and application thereof
InactiveCN101603024AEasy to buildStimulate systemic immunityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteroidesNucleotide
The invention belongs to the technical field of domestic animal infectious disease, relating to the technical field of bacterial gene engineering, in particular to a construction, vaccine preparation and application of a reconstruction porcine actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serum 1 type and porcine mycoplasmal pneumonia double-gene engineering strain. The invention is characterized in that a strain of reconstruction porcine actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serum 1 type low virulent strain SLW05, the reconstruction strain is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection, the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M209068, porcine mycoplasmal pneumonia antigenicity P36 gene segment is inserted into the chromosome of porcine actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serum 1 type low virulent strain SLW03, and the nucleotide sequence of the P36 gene segment is shown in sequence table SEQ ID NO: 1. the invention also discloses a bivalent gene engineering vaccine prepared by using the reconstruction strain and an application thereof.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
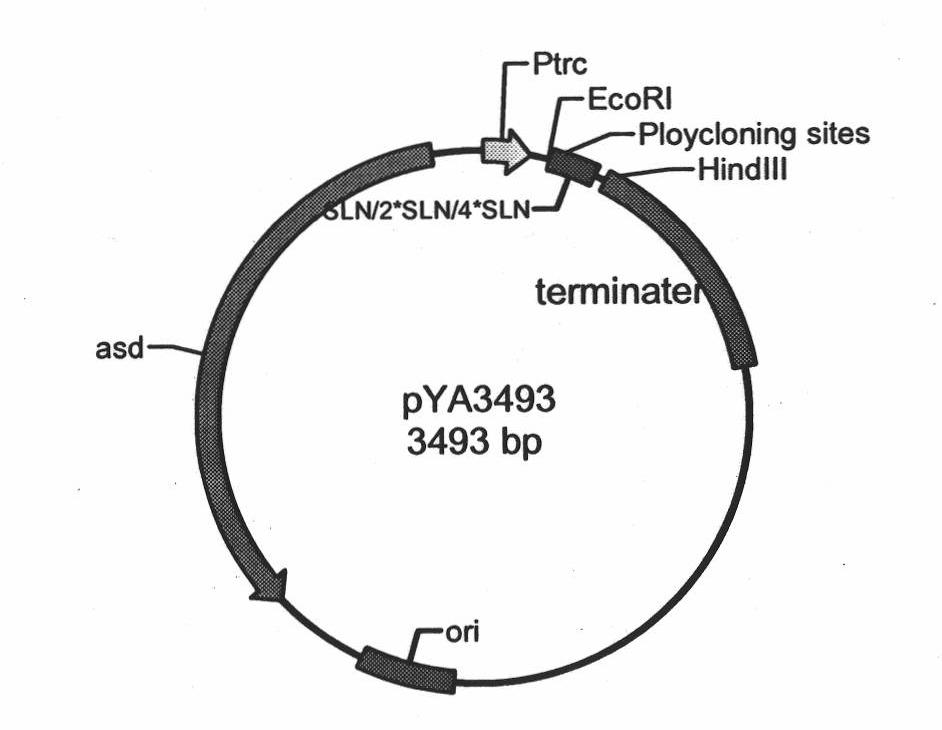
Recombinant salmonella choleraesuis, bivalent genetic engineering vaccine and application
InactiveCN101880647AGood immune protectionPreserve immune efficiencyAntibacterial agentsBacteriaBacteroidesRecombinant vaccines
The invention belongs to the technical field of bacterial gene engineering of animals, and in particular relates to the construction of a recombinant salmonella choleraesuis strain which does not contain resistance markers and expresses major antigenic loci of porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus, vaccine preparation and application. In the recombinant salmonella choleraesuis strain C500 (pYA-2SLN) which does not contain the resistance markers and expresses the major antigenic loci of the porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus, the preservation No. is CCTCC NO: M 209189, and the strain misses asd genes which are necessary for the growth of salmonella choleraesuis and contains plasmid capable of expressing the asd genes, genes of an antigenic locus A, an antigenic locus D and an antigenic locus N321 of the porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus in the strain. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the salmonella choleraesuis and porcine transmissible gastroenteritis vaccine by utilizing the recombinant strain and application thereof. The prepared recombinant vaccine can stimulate pigs to generate protective immune response for resisting the salmonella choleraesuis and the porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus, and prevent the infection of the salmonella choleraesuis and the porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus effectively.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Multiple fluorescence quantitative PCR method for simultaneous and fast detecting three types of pathogenic bacteria in food
InactiveCN101974641APracticalGuaranteed reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceSalmonella danDisease
The invention belongs to the technical field of food quality safety detection, and particularly relates to a method in which the processes of fast extraction of co-enrichment and bacterium gene groups and multiple Taqman fluorescence quantitative PCR are used to carry out simultaneous and fast detection on salmonella, staphylococcus aureus and shigella in food and a recombined positive internal reference DNA is designed to monitor PCR reaction so as to guarantee the accuracy of a detected result. The result proves that the method has good specificity for target pathogenic bacteria, the detection limit can reach 101cfu / PCR, and all components of a reaction system do not generate cross interference. Blind sample detection on artificially contaminated foods verifies the practicability of the method. Positive internal reference DNA effectively guarantees the reliability of detection, and avoids the occurrence of false negative results. In conclusion, the invention establishes a multiple fluorescence quantitative PCR method for simultaneous and fast detecting staphylococcus aureus, salmonella and shigella in the food, and provides a new method for high-throughput detection of food origin diseases.
Owner:NANJING INST OF PROD QUALITY INSPECTION
Low-endotoxin escherichia coli prokaryotic expression engineering bacterial mutant strain and construction method
ActiveCN104388368AReduce pollutionReduce inflammationBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliBio engineering
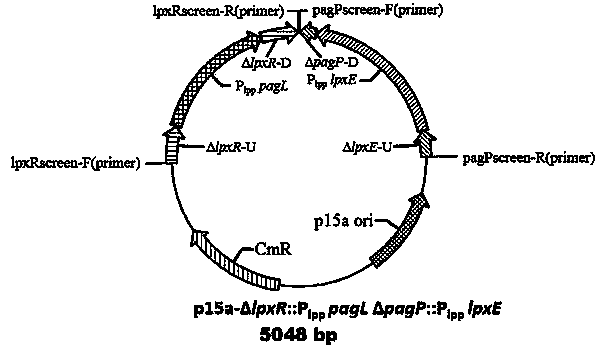
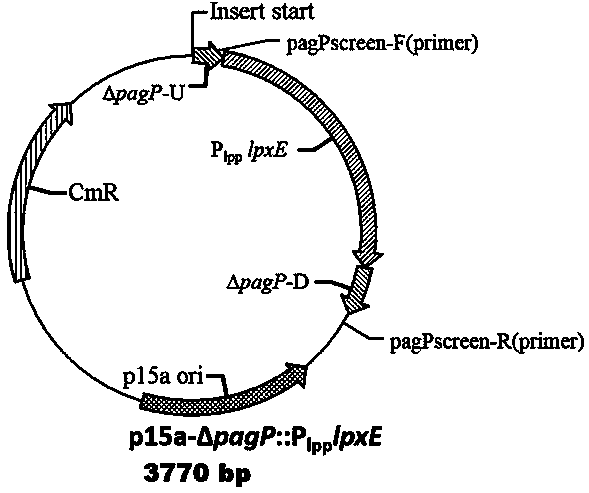
The invention discloses a low-endotoxin escherichia coli prokaryotic expression engineering bacterial mutant strain and a construction method and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The low-endotoxin escherichia coli prokaryotic expression engineering bacterial mutant strain can achieve the purpose of reducing the toxicity of lipopolysaccharides by knocking out an msbB gene and a pagP gene for regulating and controlling synthesis of lipoid A fatty acid chains on a bacterial genome with suicide plasmids and a homologous recombination method to reduce the quantity of the lipoid A fatty acid chains and further achieve the purpose of reducing the activity of endotoxin of the strain by expressing pagL and lpxE proteins with exogenous low-copy expression plasmids to simultaneously remove the fatty acid chains and phosphate groups of lipoid A. The lipopolysaccharides produced by the low-endotoxin escherichia coli prokaryotic expression engineering bacterial mutant strain Escherichia coli BL21(DE3)S004 constructed by using the technology, with collection number of CCTCCNO. M2014473 and collection time of October 14, 2014, can stimulate cells to show an obvious effect of reducing the activity of the endotoxin, thereby laying a foundation for subsequent exogenous proteins and targeting medicines using the expression of the engineering bacteria for treatment.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Insertion Sequence-Free Bacteria
InactiveUS20060199257A1Reducing genomeEfficient processingSugar derivativesBacteriaGenomic DNAInsertion sequence
The present invention provides a bacterium having a genome that is genetically engineered to be smaller than the genome of its native parent strain. A bacterium with a smaller genome can produce a commercial product more efficiently. The present invention also provides methods for deleting genes and other DNA sequences from a bacterial genome. The methods provide precise deletions and seldom introduces mutations to the genomic DNA sequences around the deletion sites. Thus, the methods can be used to generate a series of deletions in a bacterium without increasing the possibility of undesired homologous recombination within the genome. In addition, some of the methods provided by the present invention can also be used for replacing a region of a bacterial genome with a desired DNA sequence.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
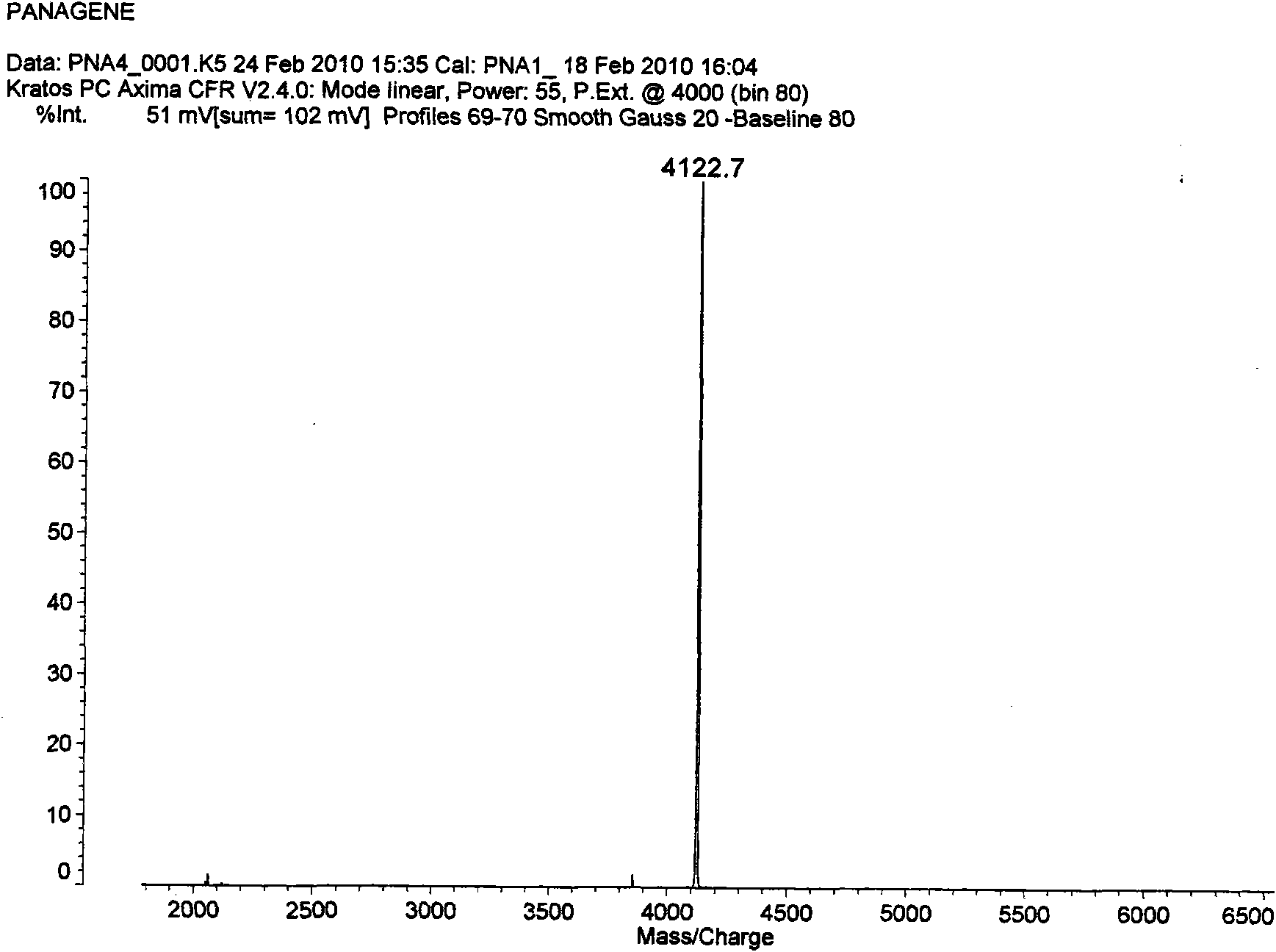
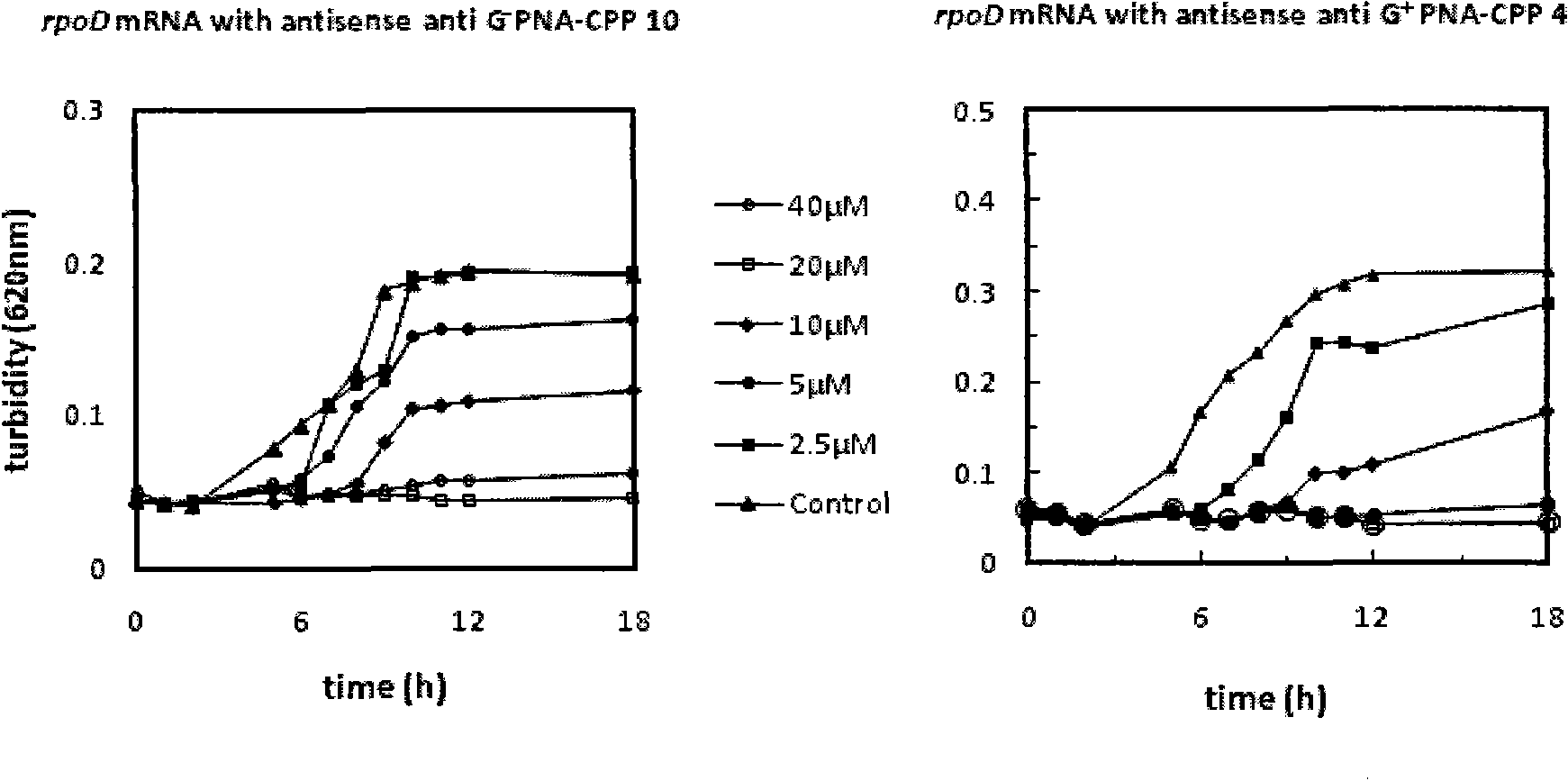
Antisense peptide nucleic acid of cell penetrating peptide-mediated antibacterial RNA polymerase sigma 70 factor gene rpoD
InactiveCN101891804AGrowth inhibitionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBacteroidesDisease
The invention provides a group of peptide nucleic acid-cell penetrating peptide antisense antibacterial sequences taking bacterial gene rpoD as a target. The cell penetrating peptide-mediated antibacterial RNA polymerase sigma 70 factor gene rpoD which is antisense nucleic acid of a specificity target can selectively inhibit the expression of in-vivo ropD genes of Gram-negative bacterium (containing sensitive and multidrug resisting clinical pathogenicity Escherichia coli, salmonellatyphimurium, Klebsiella pneumoniae and pseudomonas aeruginosa) or gram-positive bacterium (containing sensitiveand multidrug resisting staphylococcus aureus) and further inhibit bacteria growth and reproduction, thus having the advantages of good antibacterial effect, low toxicity, good stability and better tolerance. The invention also discloses a chemical preparation method of a peptide nucleic acid-cell penetrating peptide solid phase. The antibacterial peptide synthesized in the invention can be used for preparing multidrug-resistant bacteria infection proofing antisense drugs and has the potency of being developed into a broad-spectrum antisense antibacterial agent which is expressed by efficiently transferred and peculiarly blocked bacterium disease-causing genes.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
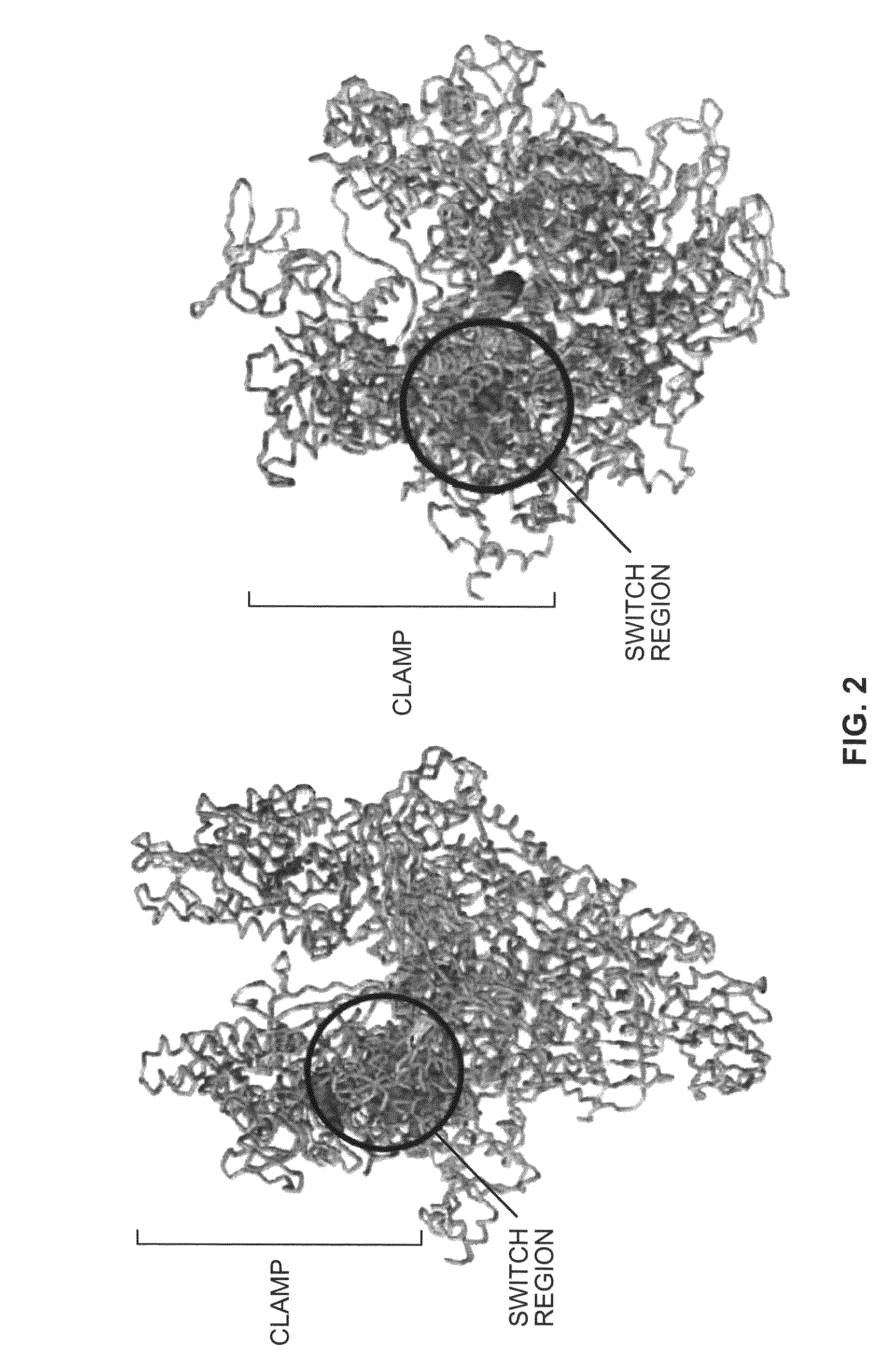
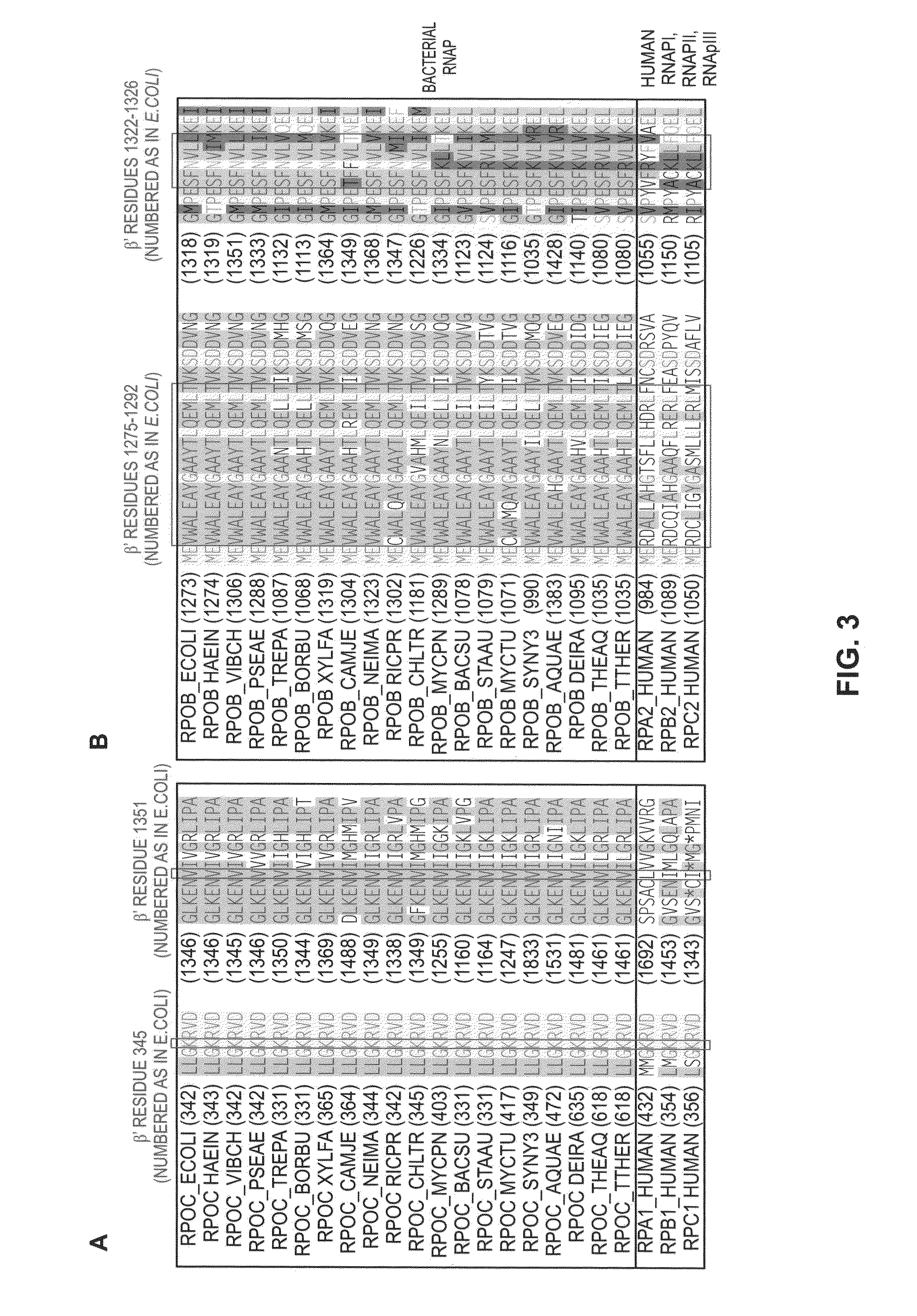
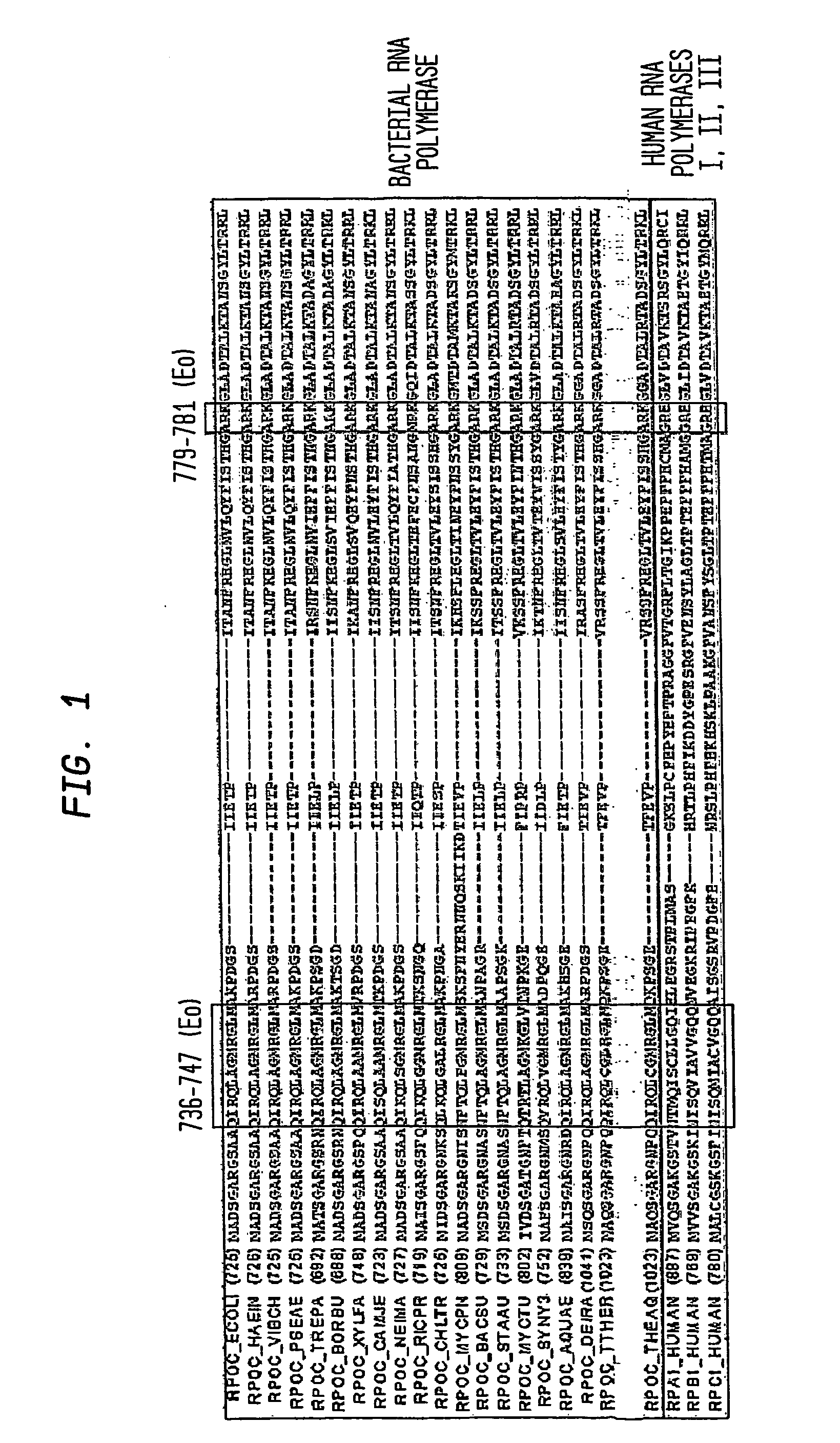
Switch-region: target and method for inhibition of bacterial RNA polymerase
ActiveUS8114583B2Inhibition is effectivePronounced antibacterial activityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionBacterial RNAMicrobiology
A target and methods for specific binding and inhibition of RNA polymerase from bacterial species are provided, including methods for identifying agents that bind to a bacterial RNA polymerase, and that inhibit an activity of a bacterial RNA polymerase, through interactions with a bacterial RNA polymerase homologous switch-region amino-acid sequence. The methods can include preparation of a reaction solution comprising the compound to be tested and an entity containing a bacterial RNAP homologous switch-region amino-acid sequence, and detection of binding or inhibition. Applications in control of bacterial gene expression, control of bacterial viability, control of bacterial growth, antibacterial chemistry, and antibacterial therapy are also provided.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Method for screening important characteristic genes related to drug resistance phenotype of bacteria based on machine learning
ActiveCN114067912AFacilitate translational applied researchExpand Screening MiningMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsAntibiotic resistanceCorrelation analysis
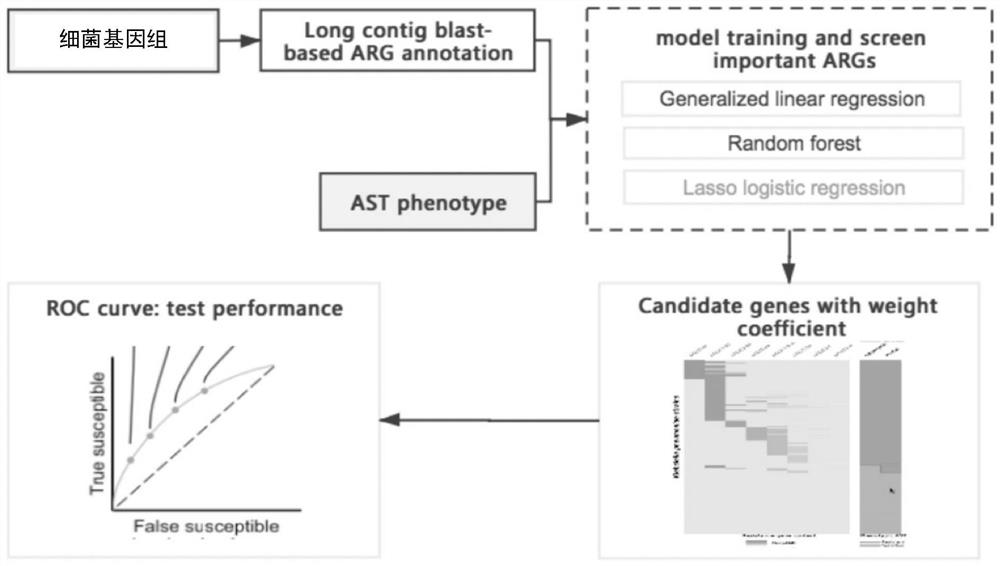
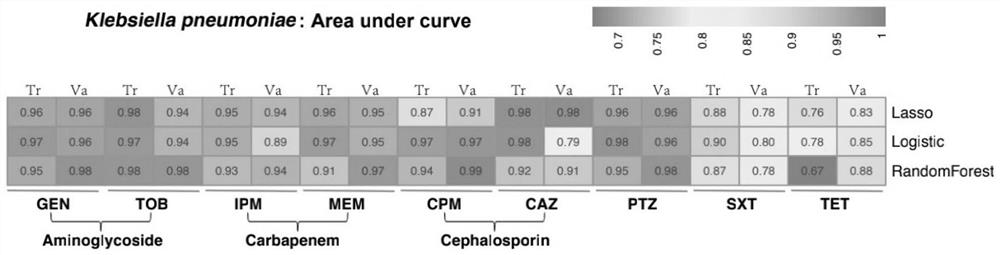
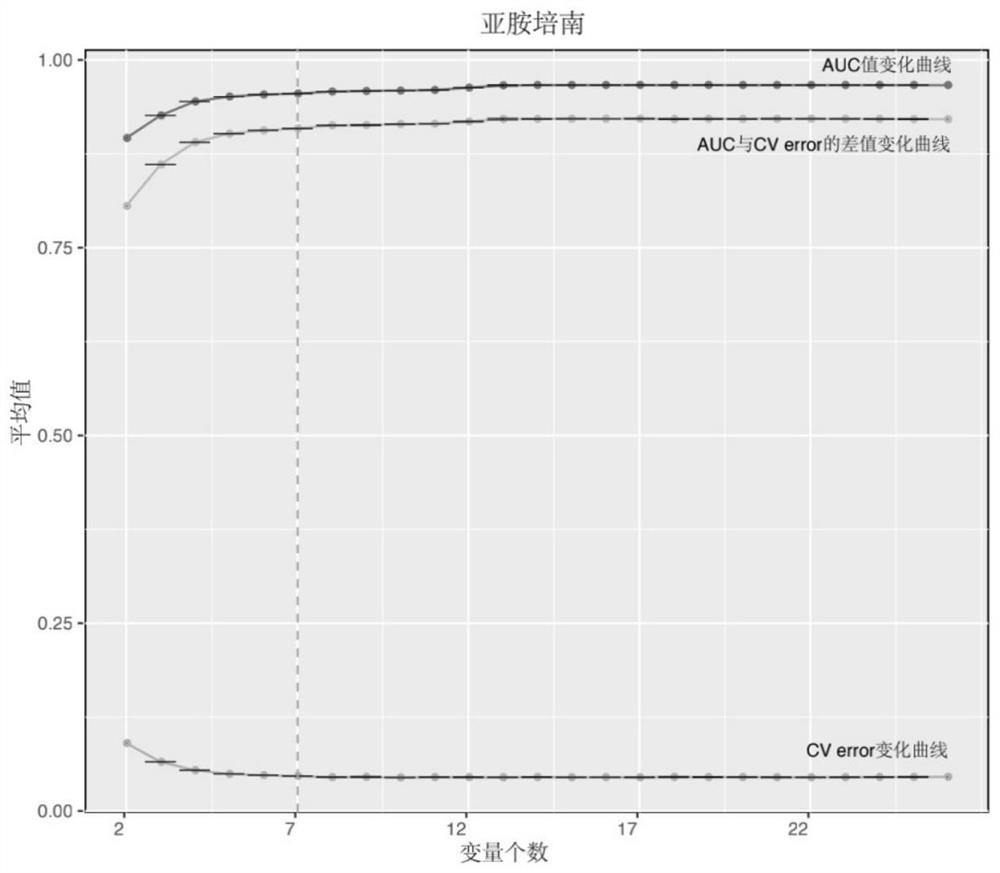
The invention relates to a method for screening important characteristic genes related to the drug resistance phenotype of bacterial based on a machine learning technology. According to the method, for the antibiotic resistance of the bacterial, on the basis of the BGWAS thought, target bacterial genomes on a public platform or large-sample-size bacterial strain genome data obtained after current collection, sequencing and assembly, and corresponding antibiotic drug susceptibility test results are collected, and correlation analysis between genotypes and drug resistance phenotypes is carried out by using the machine learning method, so that important characteristic genes (non-core drug-resistant genes) related to the drug resistance phenotypes are screened out, weight coefficients of the important characteristic genes are obtained;and finally the reliability of the drug-resistant genes related to drugs is determined by using ROC analysis.
Owner:天津金匙医学科技有限公司 +2
Gene chip for detecting important drug resistant gene of pseudomonas aeruginosa and kit thereof
InactiveCN101967508ASimplified quantityLow costNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesA-DNA
The invention provides a gene chip for detecting an important drug resistant gene of pseudomonas aeruginosa and a kit thereof. The gene chip comprises a solid-phase carrier and an oligonucleotide probe fixed on the solid-phase carrier, wherein the probe comprises a DNA fragment or a complementary DNA fragment thereof selected from carb, tem, imp, oxa group I, oxa group II, aac (6')-Ib, aac (6')-II, aac (3')-I, aac (3')-II, aadB and a bacterium 16S rRNA gene. The gene chip and the detecting kit can achieve the aim of simultaneously detecting the 10 drug resistant genes of the pseudomonas aeruginosa, have the characteristics of high pertinence, high specificity, high sensitivity, high detecting speed, high repeatability, and the like and are suitable for a hospital, a disease preventing control mechanism and other clinical laboratories to carry out drug resistant gene detection and drug resistance monitoring on the pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOCHIP TECH CO LTD
Quick detection method for scallop pathogenic vibrio splendidus
ActiveCN103468806AQuick checkWide detection rangeMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesVolumetric Mass Density
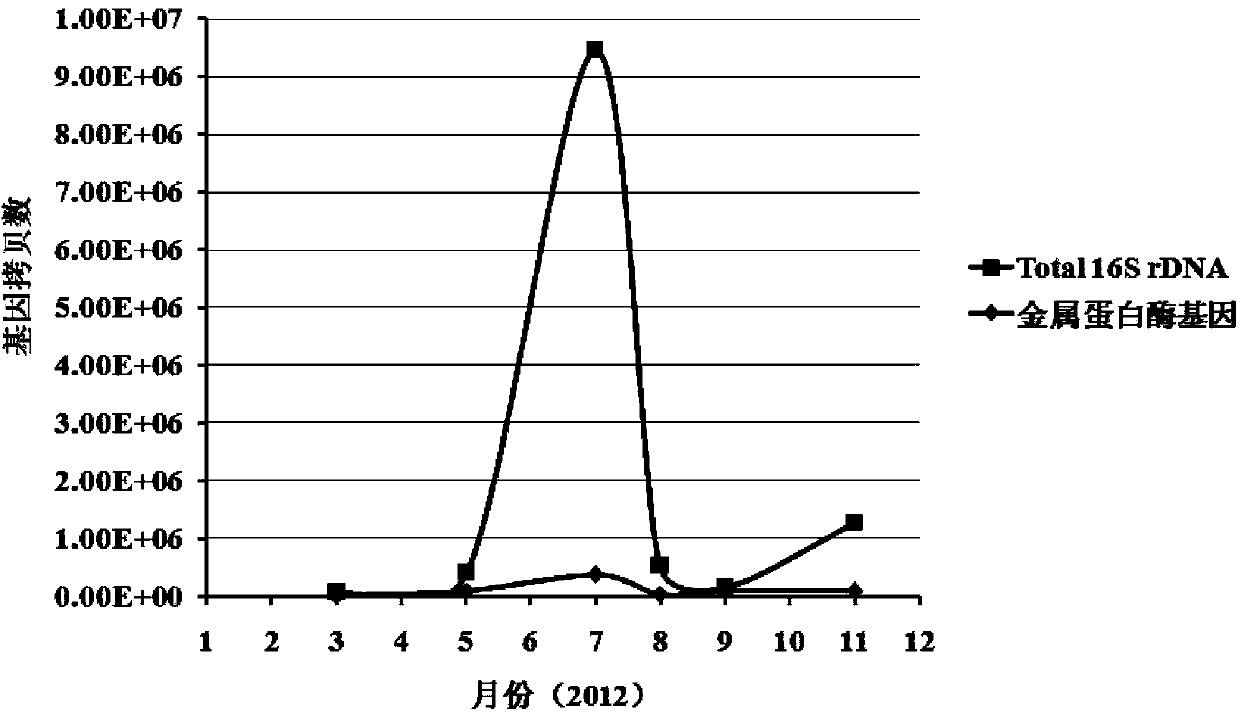
The invention belongs to the technical field of aquatic organisms and in particular relates to a quick detection method for scallop pathogenic vibrio splendidus. Total DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of bacterial genomes in a filtered seawater sample to be detected is taken as a template, fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification is carried out by a bacterial 16SrDNA conserved region and a specific primer of a pathogenic vibrio splendidus metalloproteinases gene, and the scallop pathogenic vibrio splendidus in the culture environment is quantitatively analyzed and detected; the detection method comprises the steps of extracting the DNA of the bacterial genomes and carrying out fluorescent quantitative PCR detection. The method has the advantages that the quickness is achieved, the specificity is good, the bacterial density detection range is wide, and a quantitative result can be close to a real situation.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
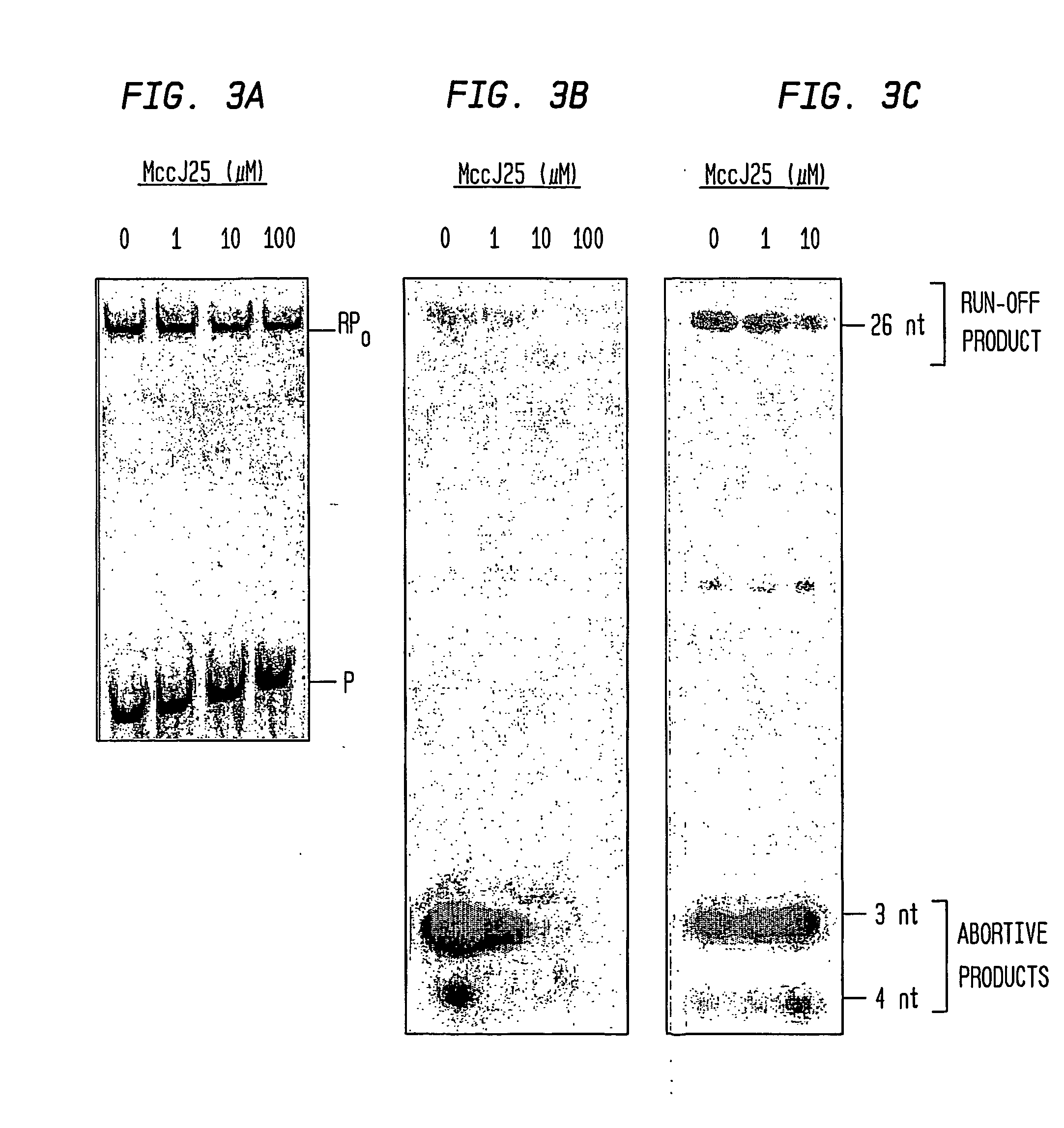
Target And Method For Inhibition Of Bacterial Rna Polymerase Minimized Derivatives Of Peptide Antibiotic Mccj25
InactiveUS20070196886A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBacterial RNAPolymerase L
Disclosed are targets, methods, and reagents for specific binding and inhibition of RNAP from bacterial species. The invention has applications in analysis of RNAP structure and function, control of bacterial gene expression, control of bacterial growth, antibacterial chemistry, antibacterial therapy, and drug discovery.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
LAMP (Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification) superbacteria NDM-1 (New Delhi Metallo-beta-lactamase-1) gene as well as kit and method for detecting superbacteria NDM-1 gene
ActiveCN102242210AQuick checkStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The invention belongs to the technical field of bacteria gene detection, relating to a primer of an LAMP (Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification) superbacteria NDM-1 (New Delhi Metallo-beta-lactamase-1) gene, wherein the primer consists of a pair of external primers, a pair of interior primers and a pair of loop primers, the molar ratio of the external primers to the interior primers is 1:8, and the molar ratio of the external primers to the loop primers is 1:4. A kit for detecting the superbacteria NDM-1 gene comprises a plurality of LAMP reaction tubes containing reaction solutions, each reaction solution comprises a 2* isothermal reaction buffer solution, BstDNA polymerase, an interior primer FIP, an interior primer BIP, an external primer F3, an external primer B3, a loop primer LF, aloop primer LB and sterilized double-distilled water. The invention further discloses a method for detecting the superbacteria NDM-1 gene by using the kit. Defects of long time, large work load, cross-contamination, complex operation and the like in the prior art are overcome; and the invention has the advantages of strong specificity, high sensitivity, fastness, low cost, more simpler operation method and applicability in field fast detection.
Owner:RECOM QINGDAO BIOTECH CO LTD
Diagnostic method for quickly detecting drug resistance gene CMY-2 of germ AmpC enzyme
InactiveCN104946764AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationA-DNADrug resistance
The invention discloses an LAMP kit and method for quickly detecting drug resistance gene CMY-2 of a bacterial AmpC enzyme. The kit comprises a pair of outer primers, a pair of inner primers and a pair of loop primers. DNAs of to-be-detected bacterial genomes are extracted respectively like SEQ ID NO. 1-6, six specific primers and DNA polymerase with strand displacement activity are adopted to amplify a DNA sample at 60-65 DEG C, and a color-developing agent is added to observe color changes in a reaction tube to judge whether the amplification occurs. The LAMP kit and method for quickly detecting drug resistance gene CMY-2 of the bacterial AmpC enzyme have the advantages of quickness, efficiency, simpleness and convenience in operation, high specificity, high sensitivity, simple and convenience in detection and suitability for field testing, and is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com