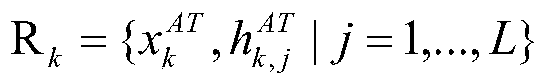Patents
Literature
118 results about "Genome human" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Human genome. The human genome is the genome of Homo sapiens. It is made up of 23 chromosome pairs with a total of about 3 billion DNA base pairs. There are 24 distinct human chromosomes: 22 autosomal chromosomes, plus the sex-determining X and Y chromosomes.
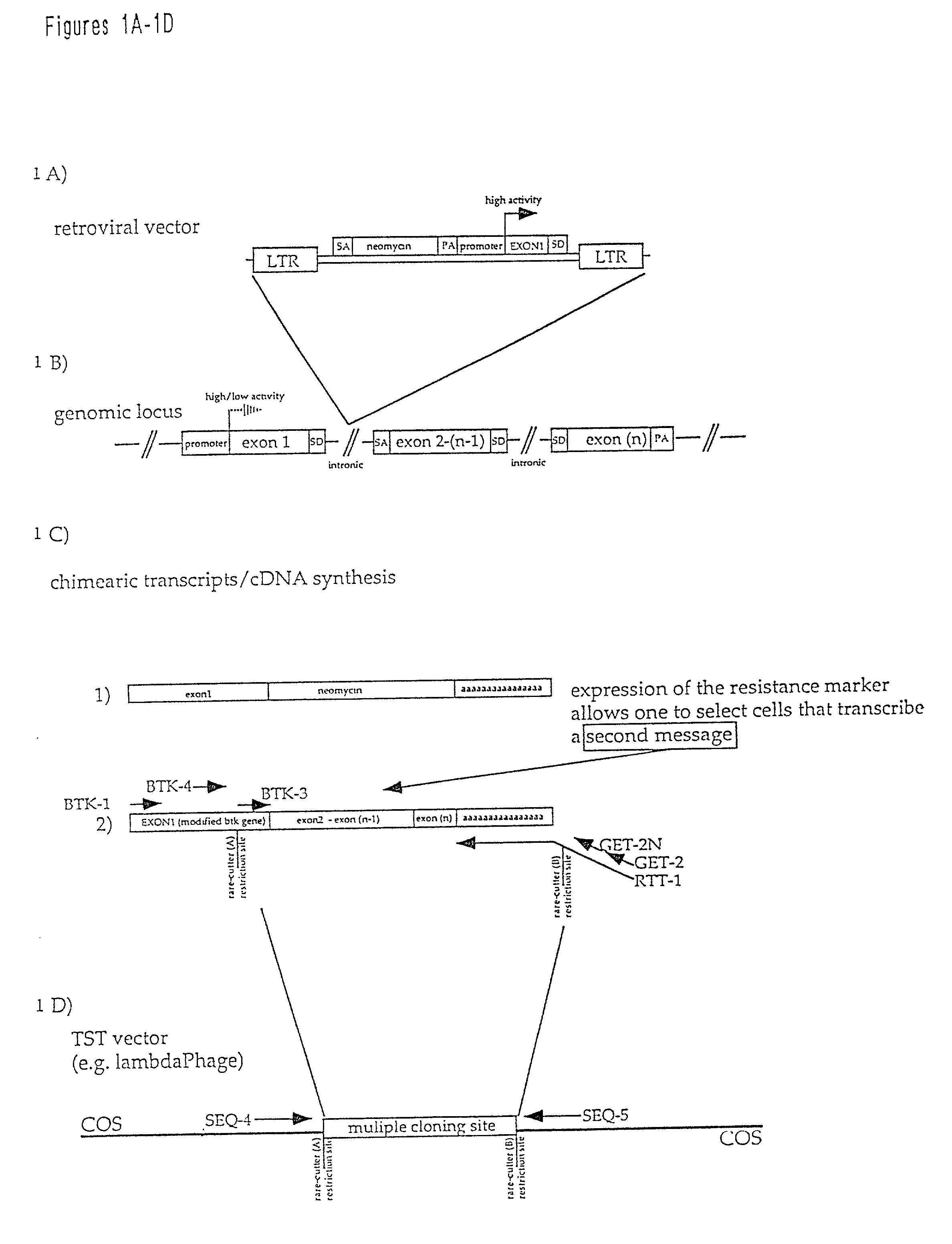
Massively parallel contiguity mapping
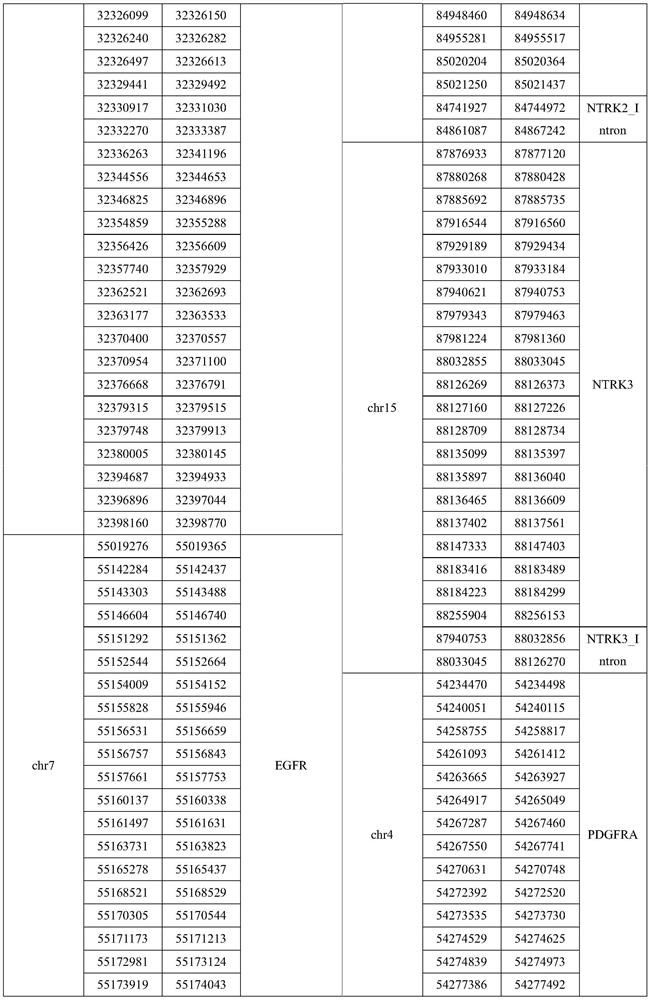
ActiveUS20130203605A1Reducing sequenceLimited to sequenceLibrary member identificationChemical recyclingHuman DNA sequencingMammalian genome
Contiguity information is important to achieving high-quality de novo assembly of mammalian genomes and the haplotype-resolved resequencing of human genomes. The methods described herein pursue cost-effective, massively parallel capture of contiguity information at different scales.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
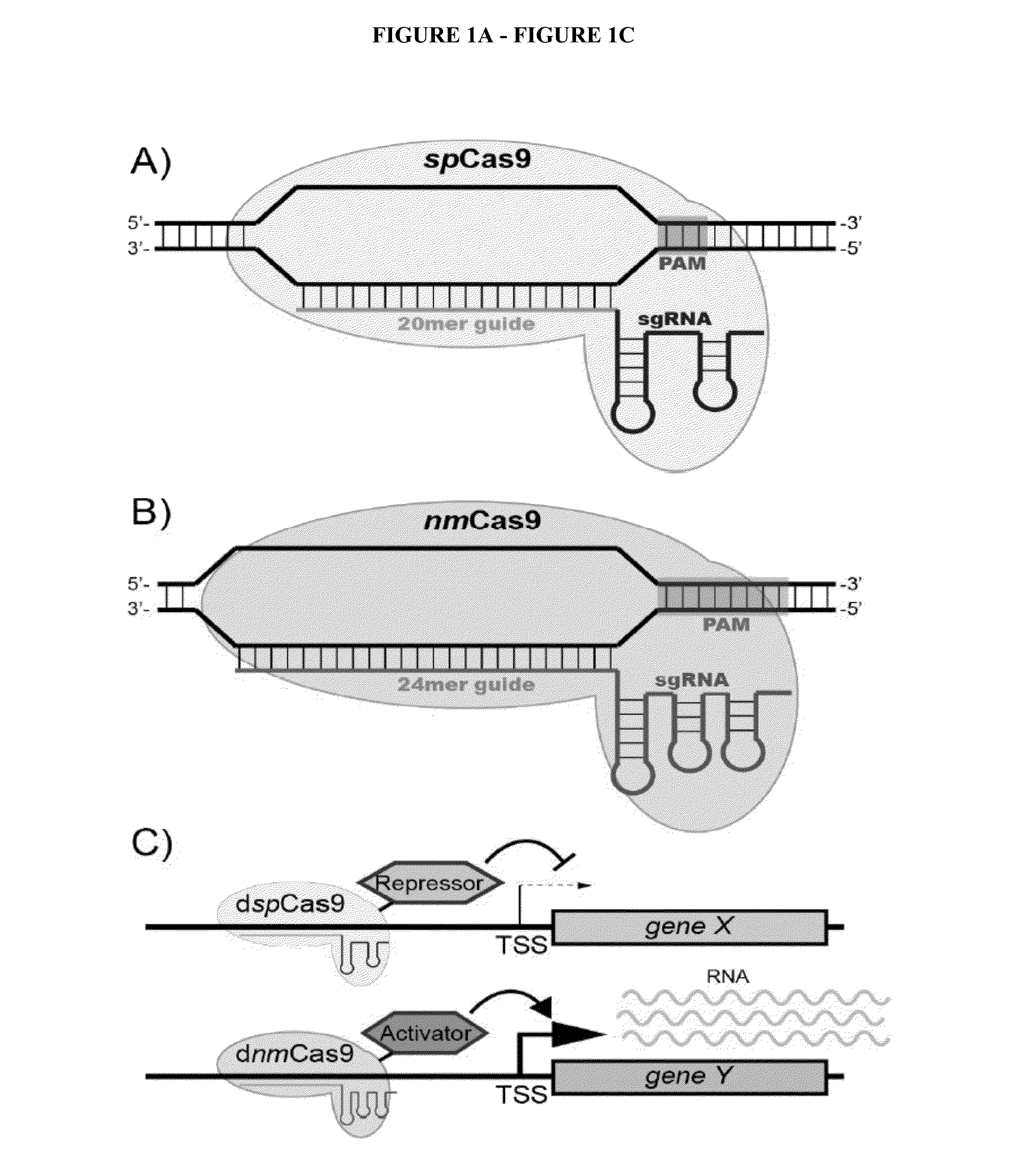
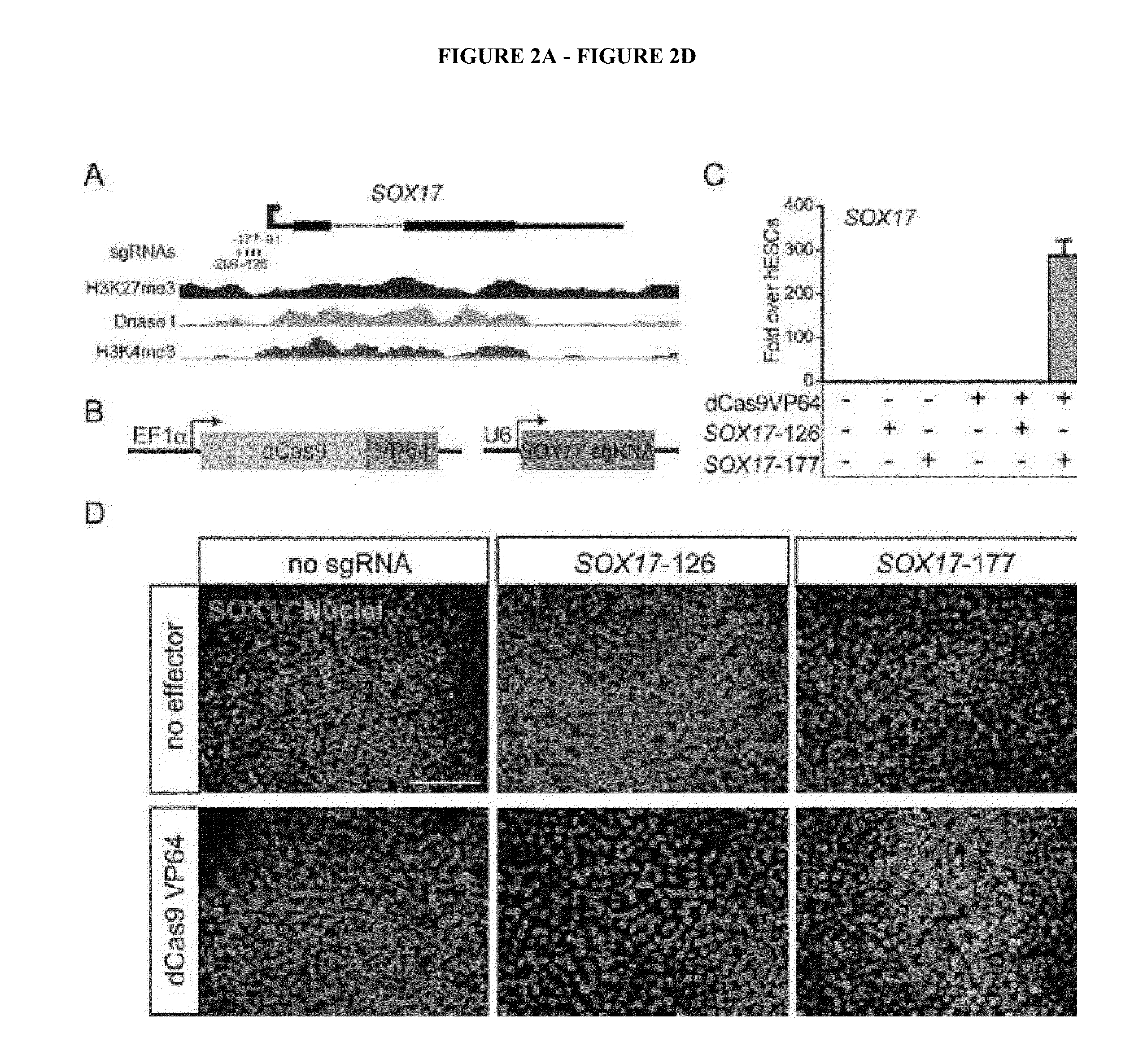
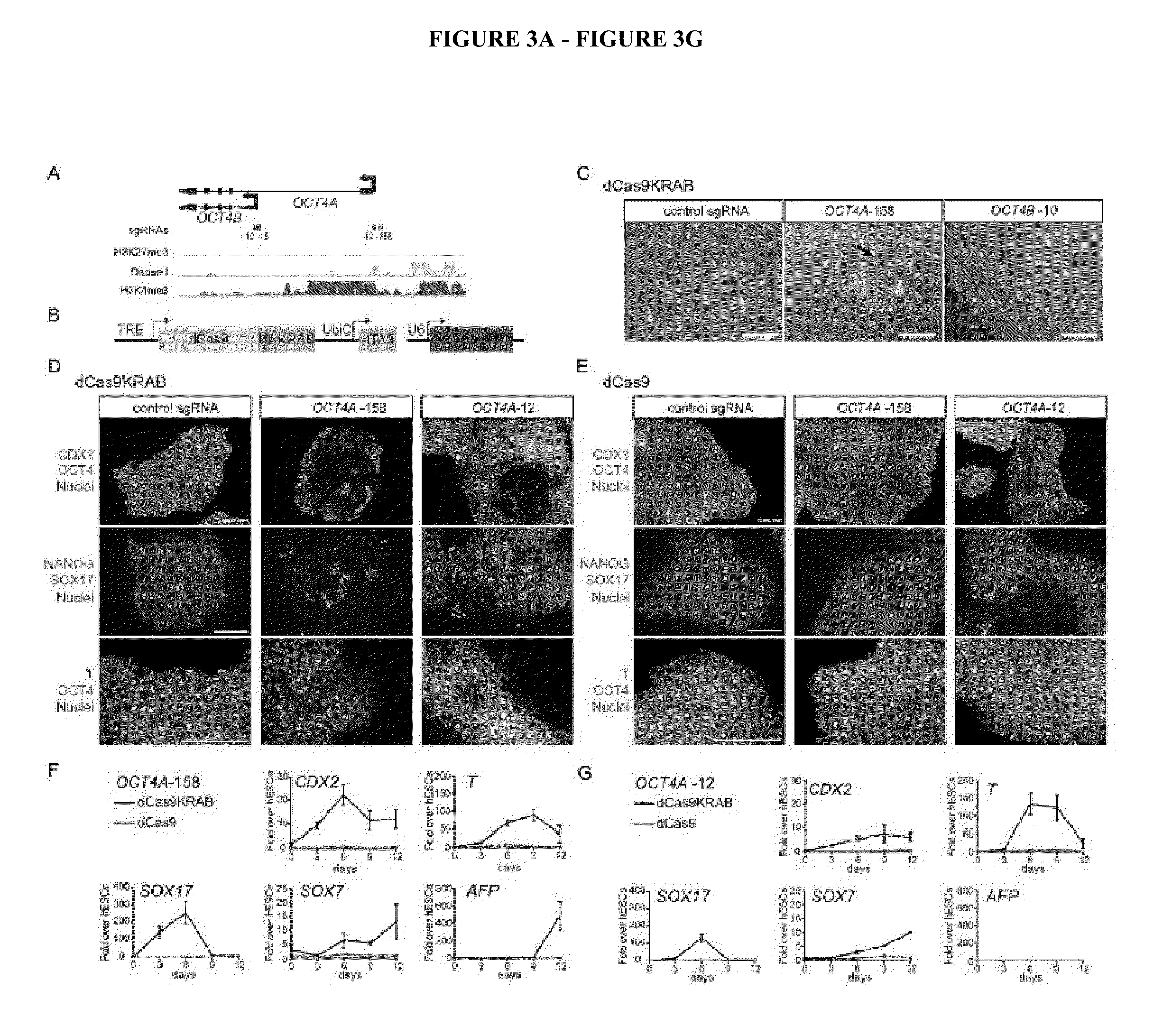
Cas9 effector-mediated regulation of transcription, differentiation and gene editing/labeling
InactiveUS20150191744A1Prevent degradationHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementProgenitorReprogramming
The present disclosure relates to methods of and systems for modifying the transcriptional regulation of stem or progenitor cells to promote their differentiation or reprogramming of somatic cells. Further, the labeling and editing of human genomic loci in live cells with three orthogonal CRISPR / Cas9 components allow multicolor detection of genomic loci with high spatial resolution, which provides an avenue for barcoding elements of the human genome in the living state.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
Methods for correcting alpha-antitrypsin point mutations
InactiveUS20150166984A1Nervous disorderFusion with DNA-binding domainHuman DNA sequencingObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
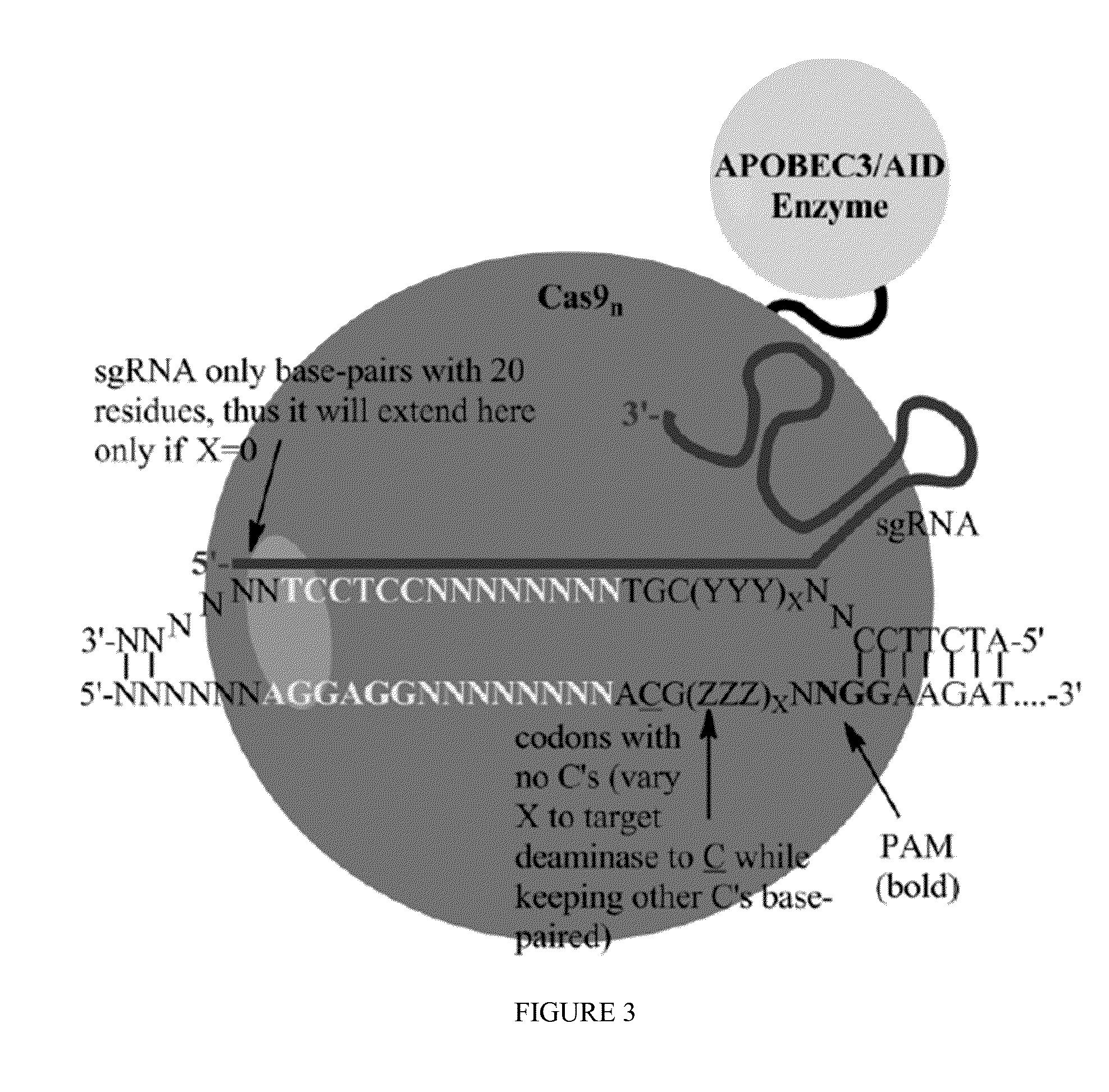
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a nucleic acid encoding a mutant α-antitrypsin protein to correct a point mutation associated with a disease or disorder, e.g., with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) disease. The methods provided are useful for correcting an α-antitrypsin point mutation within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
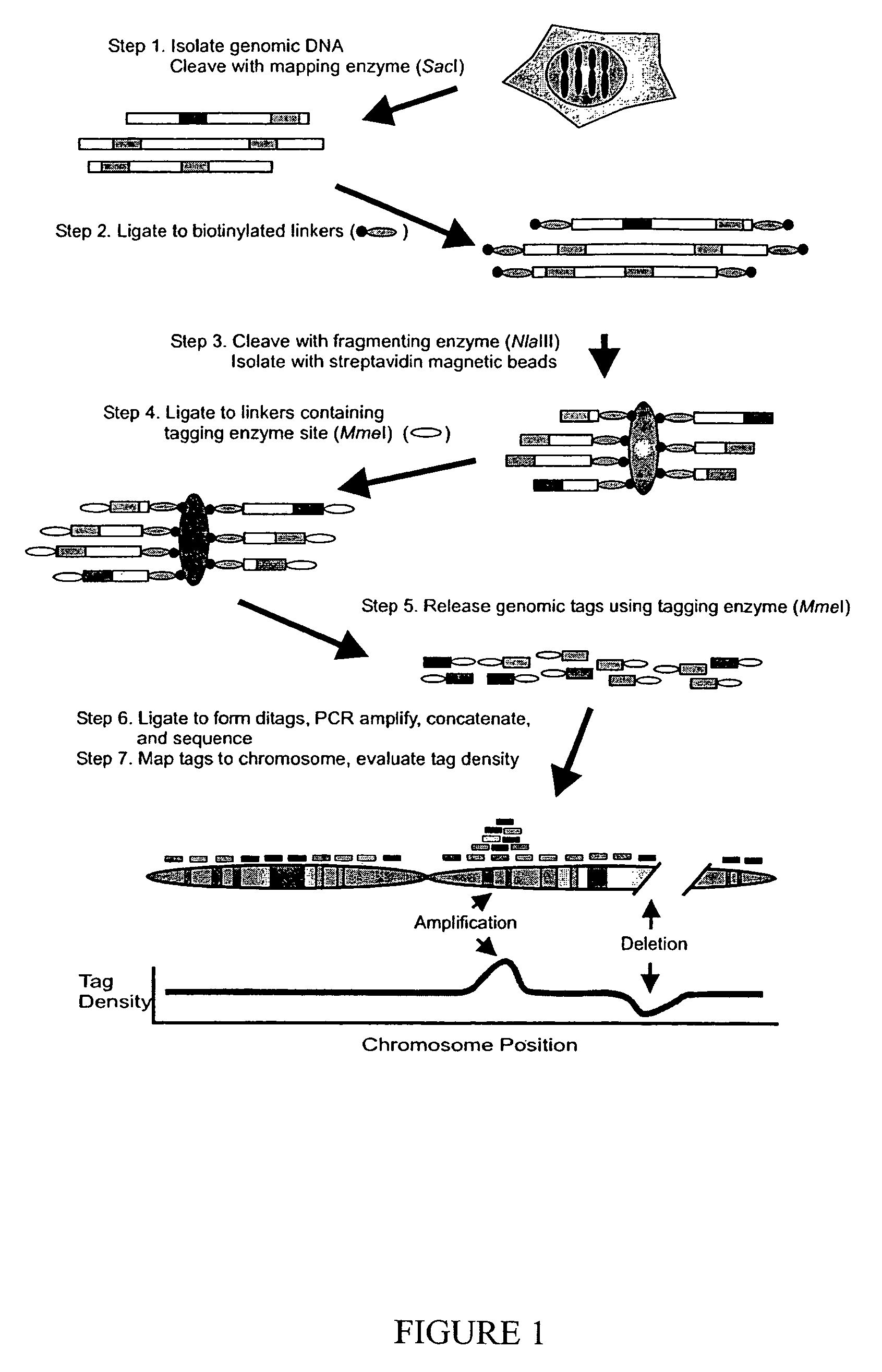
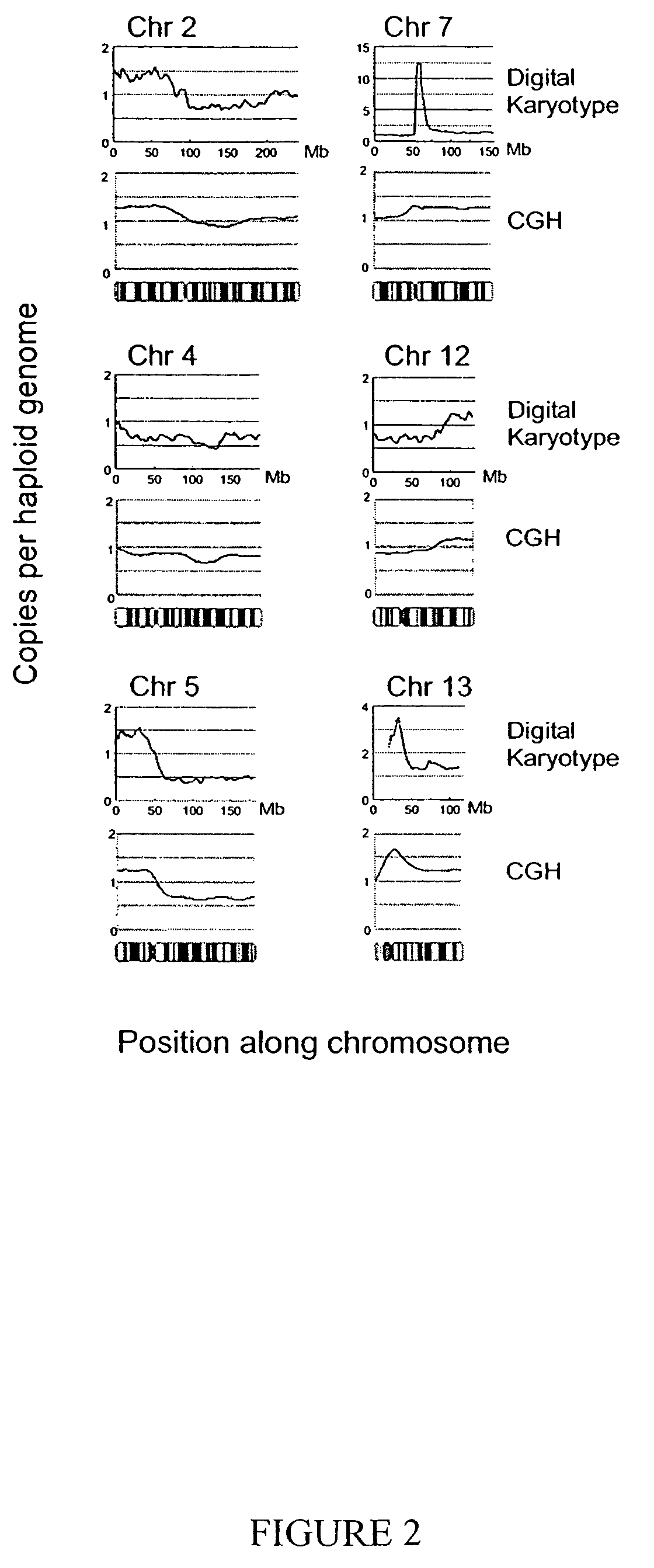
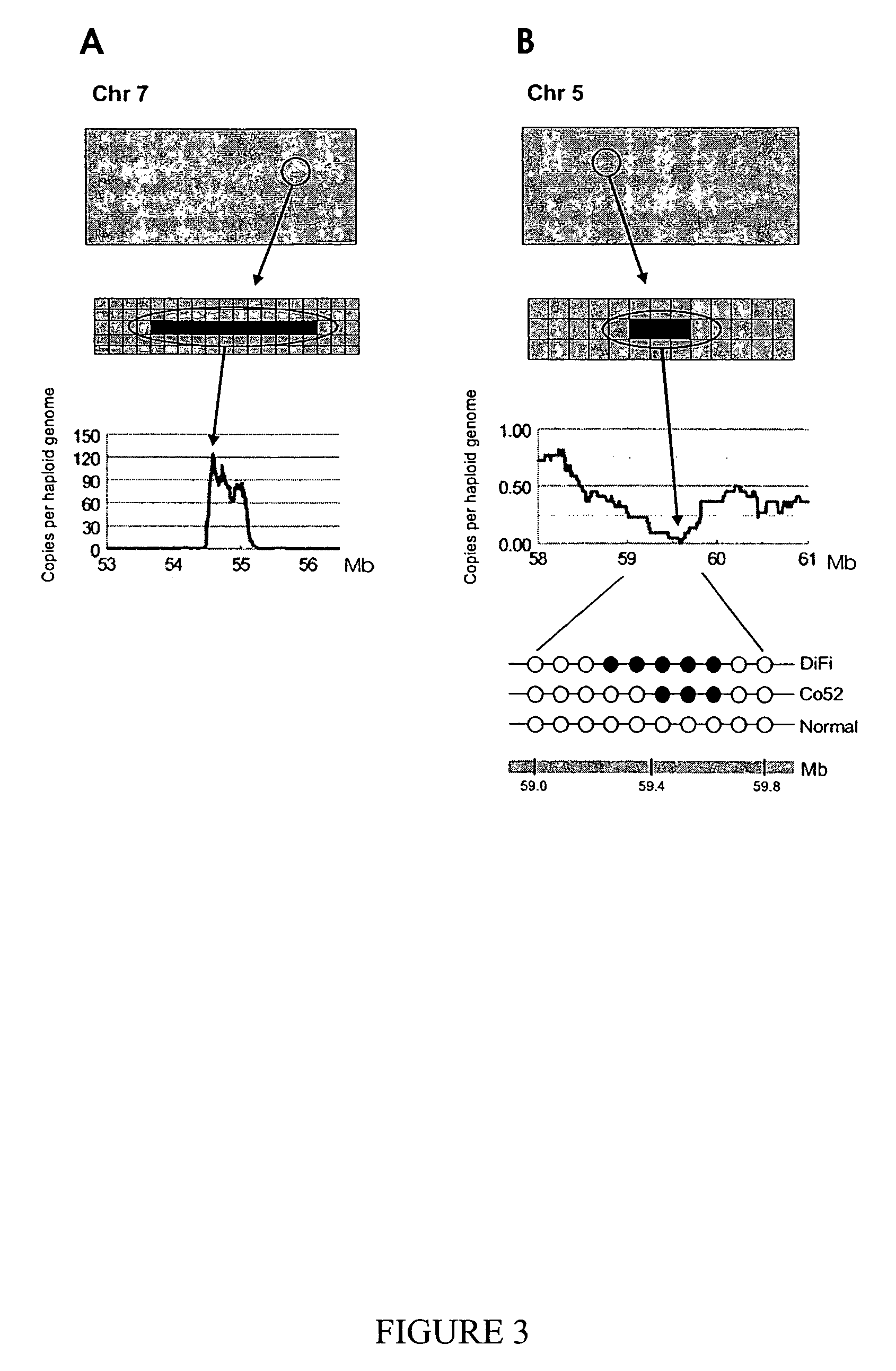
Digital karyotyping
ActiveUS7704687B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingHuman DNA sequencingHuman cancer
Alterations in the genetic content of a cell underlie many human diseases, including cancers. A method called Digital Karyotyping provides quantitative analysis of DNA copy number at high resolution. This approach involves the isolation and enumeration of short sequence tags from specific genomic loci. Analysis of human cancer cells using this method identified gross chromosomal changes as well as amplifications and deletions, including regions not previously known to be altered. Foreign DNA sequences not present in the normal human genome could also be readily identified. Digital Karyotyping provides a broadly applicable means for systematic detection of DNA copy number changes on a genomic scale.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
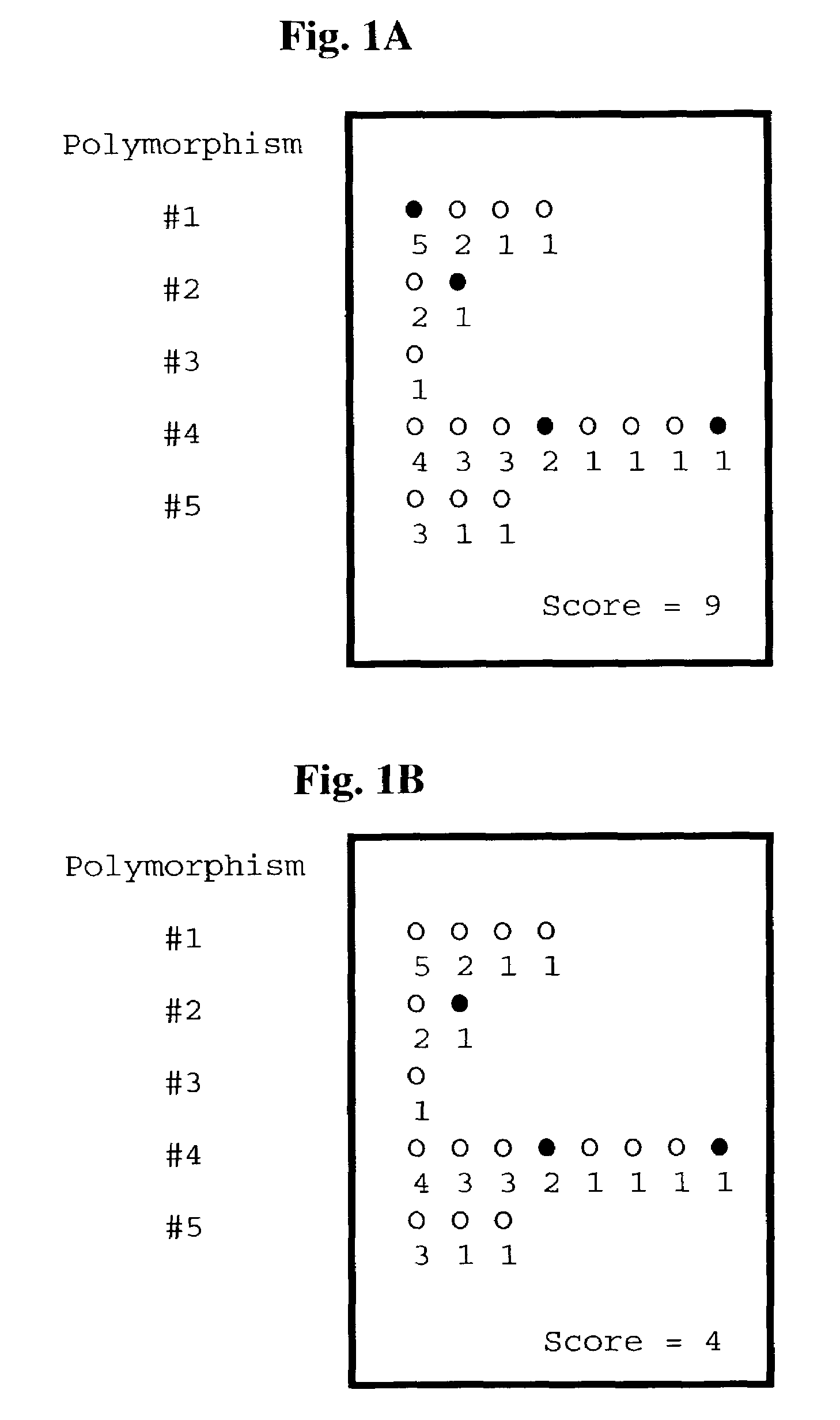
Identification and mapping of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the human genome
InactiveUS20060057564A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingGenome human
The invention relates to the role of genes in human diseases. More particularly, the invention relates to compositions and methods for identifying genes that are involved in human disease conditions. The invention provides identification and mapping of a very large number of SNPs throughout the entire human genome. This contribution allows scientists to isolate and identify genes that are relevant to the prevention, causation, or treatment of human disease conditions.
Owner:SNP CONSORTIUM
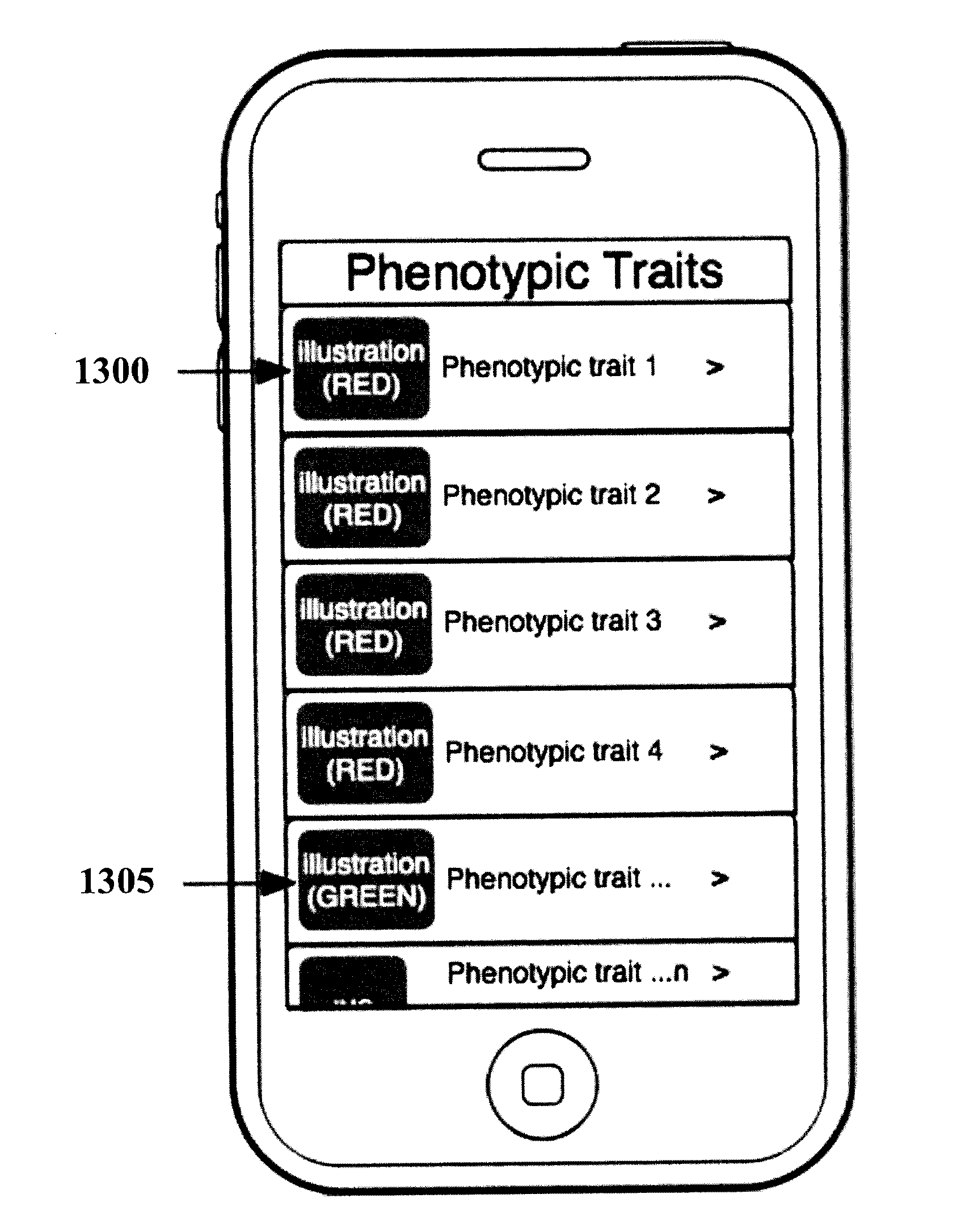
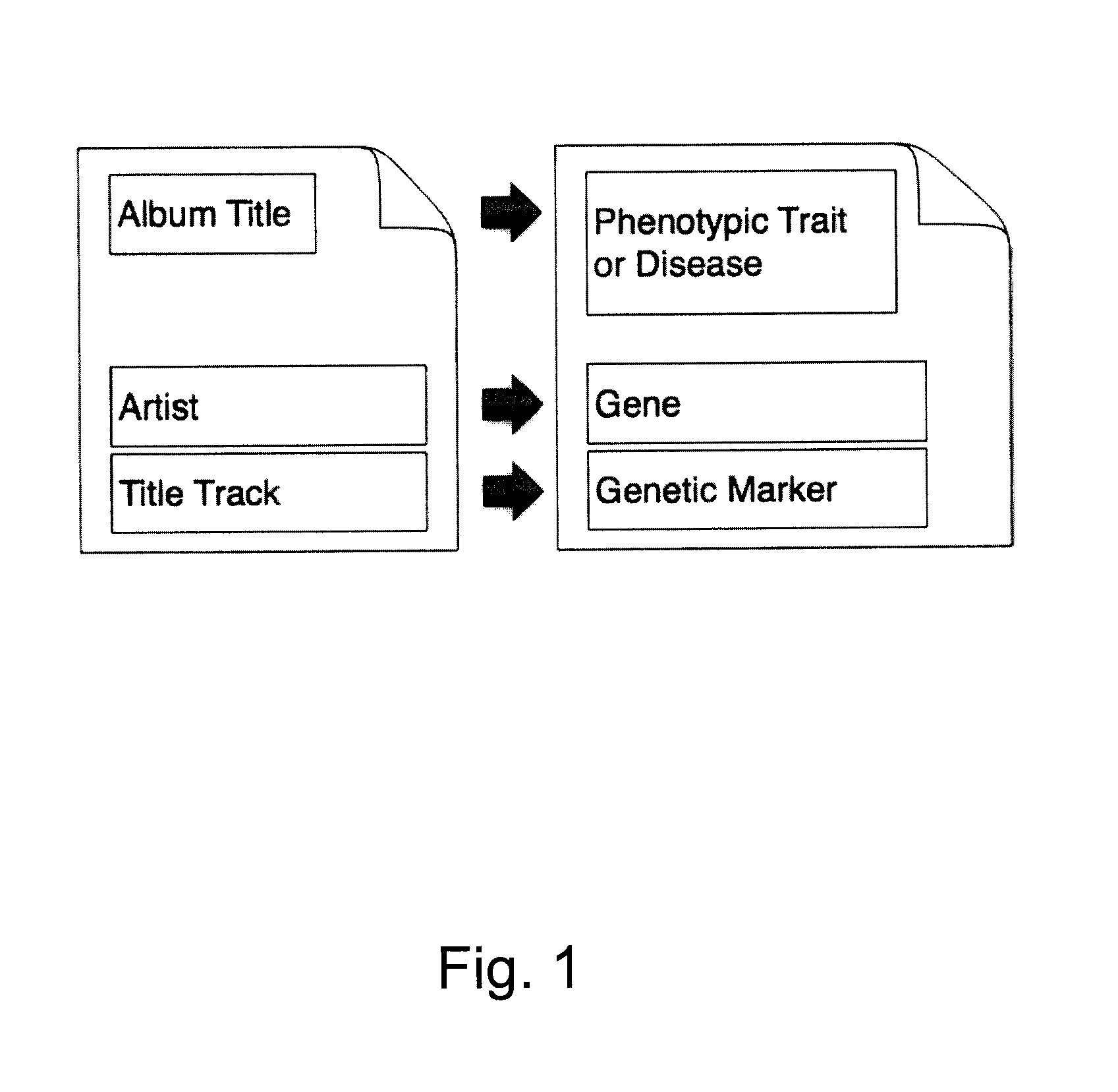
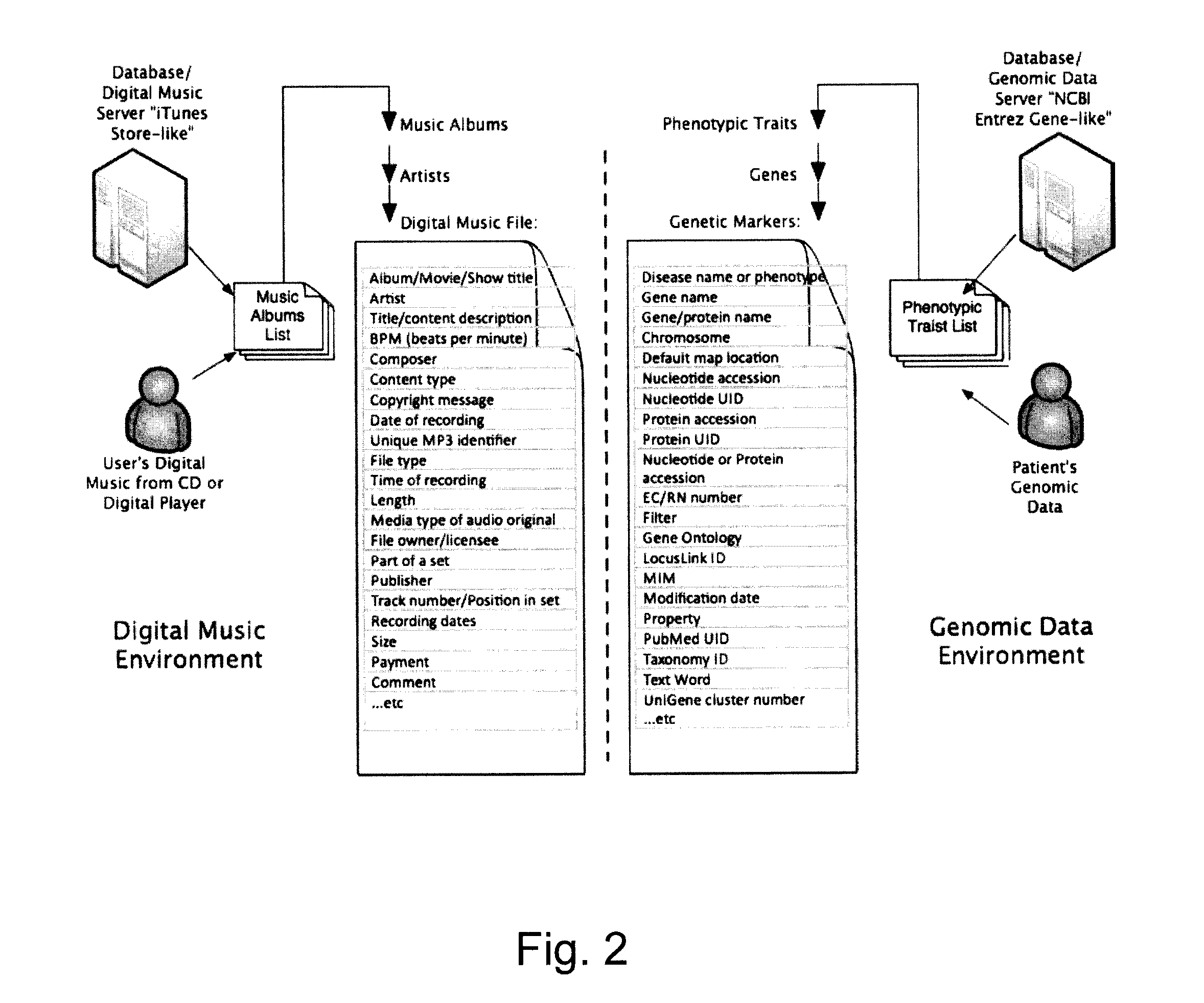
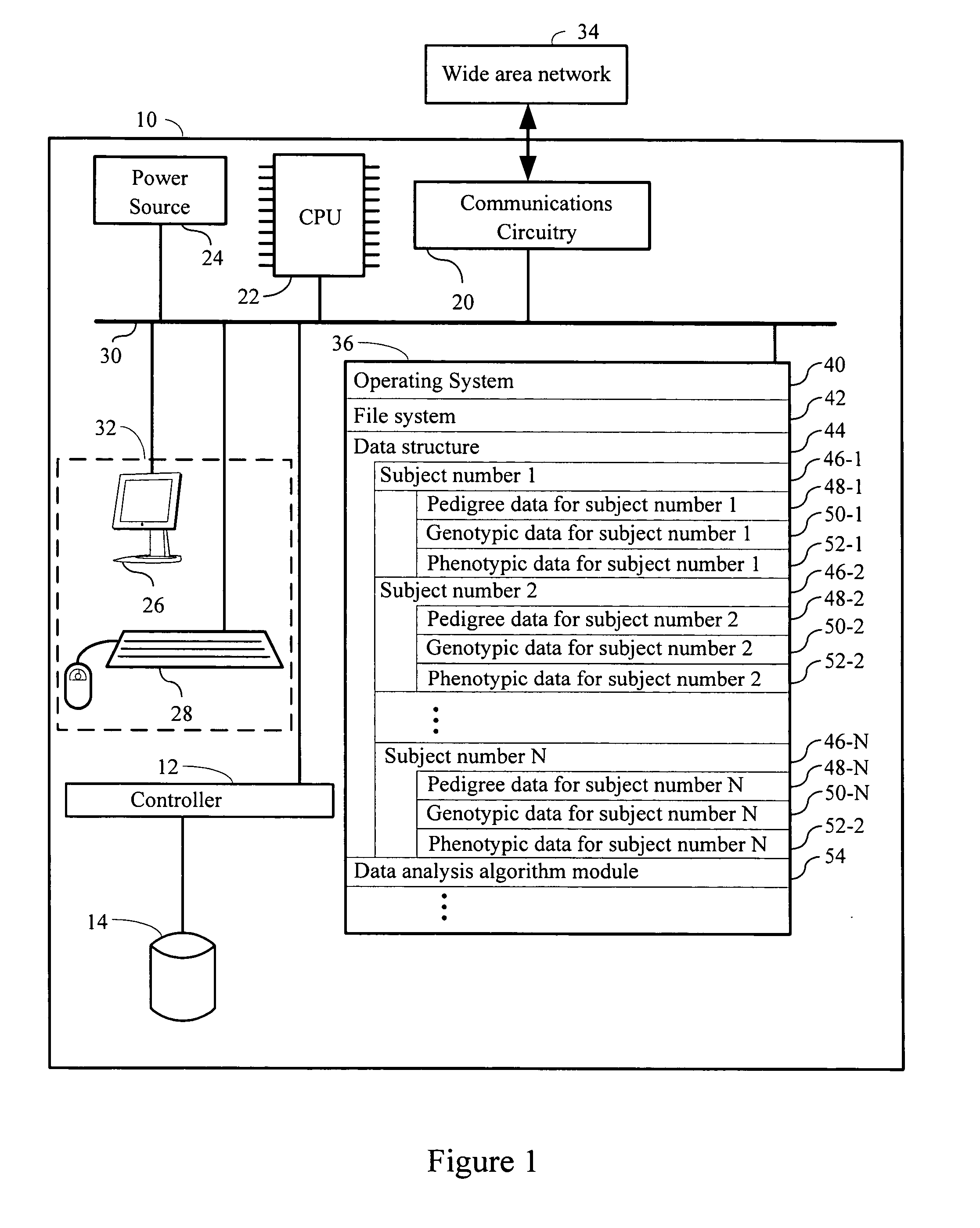
Organization, visualization and utilization of genomic data on electronic devices
InactiveUS20140033125A1Simple organization and visualization and useData visualisationSpecial data processing applicationsHuman DNA sequencingPersonalization
Described herein are methods, devices and systems for simple organization, visualization and use of genome data (e.g. human genome data) on electronic devices (e.g. portable devices). In some embodiments, the data are organized and / or visualized according to phenotype traits, genes, and / or markers in a similar manner to the organization and / or visualization of digital music contents. This concept allows a new procedure for genomic data organization and facilitates the development of genomic data visualization tools. The methods described herein can be implemented with consumer-oriented software on electronic devices, computers, and portable devices, for the use of genomic related data in the field of personalized medicine for predictive, preventive and participative wireless healthcare.
Owner:PORTABLE GENOMICS
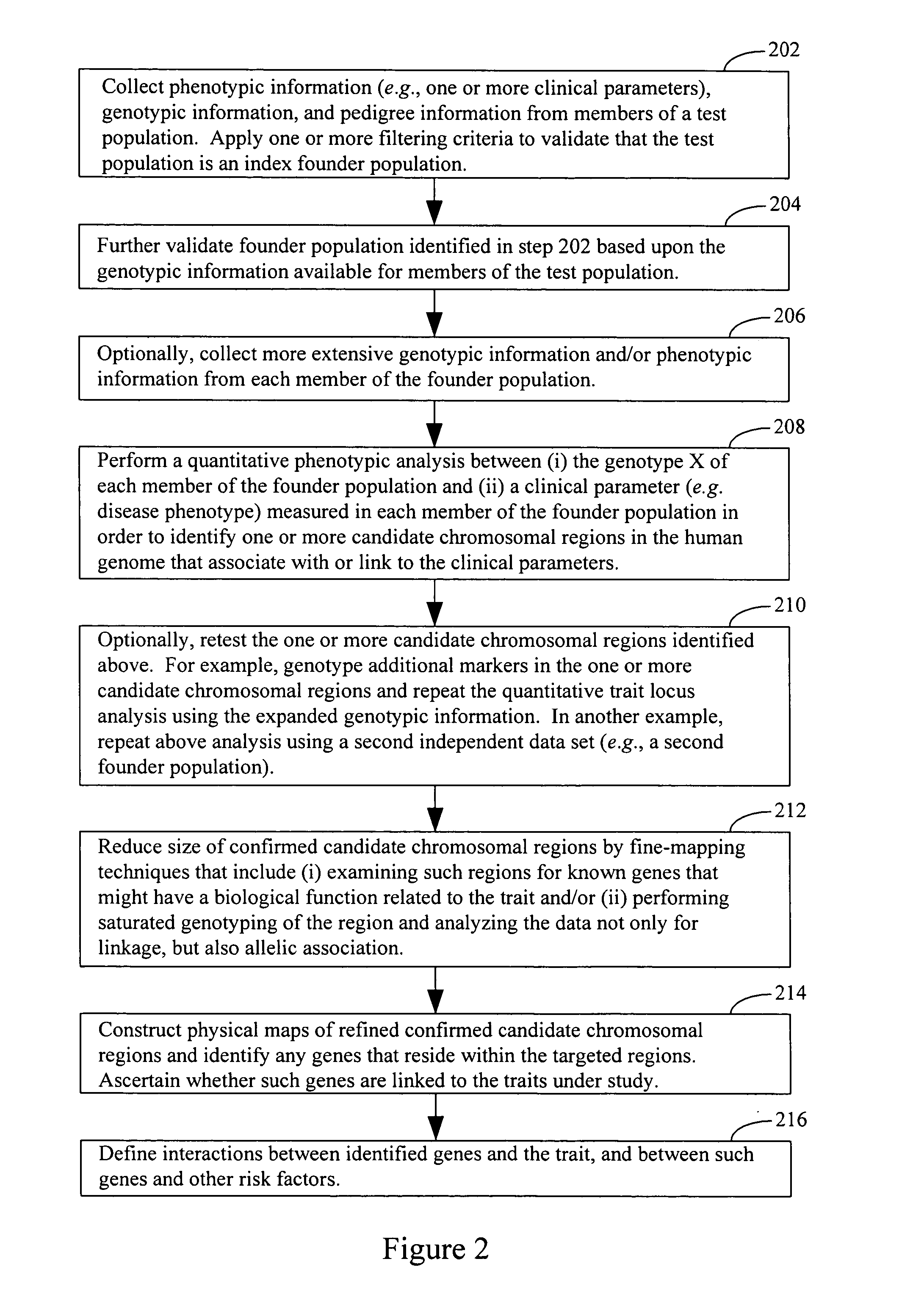
Systems and methods for the biometric analysis of index founder populations
InactiveUS20070111247A1Medical data miningMicrobiological testing/measurementPopulation basedHuman DNA sequencing
Systems, methods and apparatus for associating a clinical parameter with one or more candidate chromosomal regions in the human genome are provided. An index founder population is identified in a test population based upon the genotype X of each member of the test population such that the posterior probability Pr(K|X) for the index founder population is greater for K=1 than any other integer K, where K is the number of subpopulations in the index founder population. The clinical parameter is measured for each respective member of the index founder population. Then a quantitative phenotypic analysis is performed between (i) the genotype X of each respective member of the index founder population and (ii) the clinical parameter thereby identifying one or more candidate chromosomal regions in the human genome that associate with the clinical parameter.
Owner:MOTIF BIOSCI
Kits and methods for assessing skin health
InactiveUS7211383B2Increase stringencyPromotes skin healthOrganic active ingredientsBiocideGenome humanNucleotide
The invention relates to kits and methods for assessing skin health for a human and the human's susceptibility to skin disorders. The methods involve assessing occurrence in the human's genome of one or more polymorphisms (e.g., single nucleotide polymorphisms) that occur in one or more genes associated disclosed herein and that are associated with a disorder in humans. Preferred assessment and scoring methods are disclosed, as are kits for performing the methods.
Owner:LACORE ENTERPRISES LLC
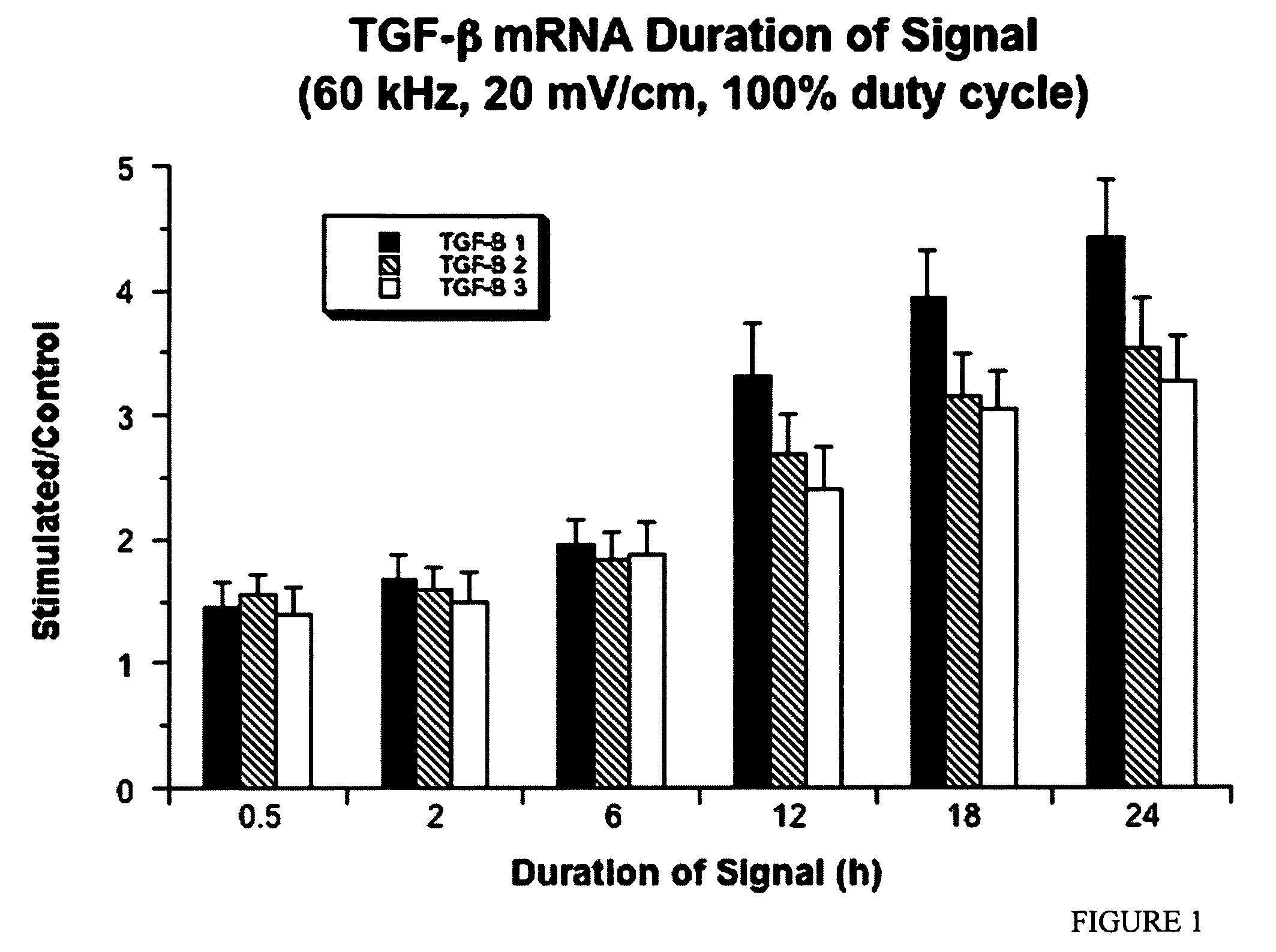
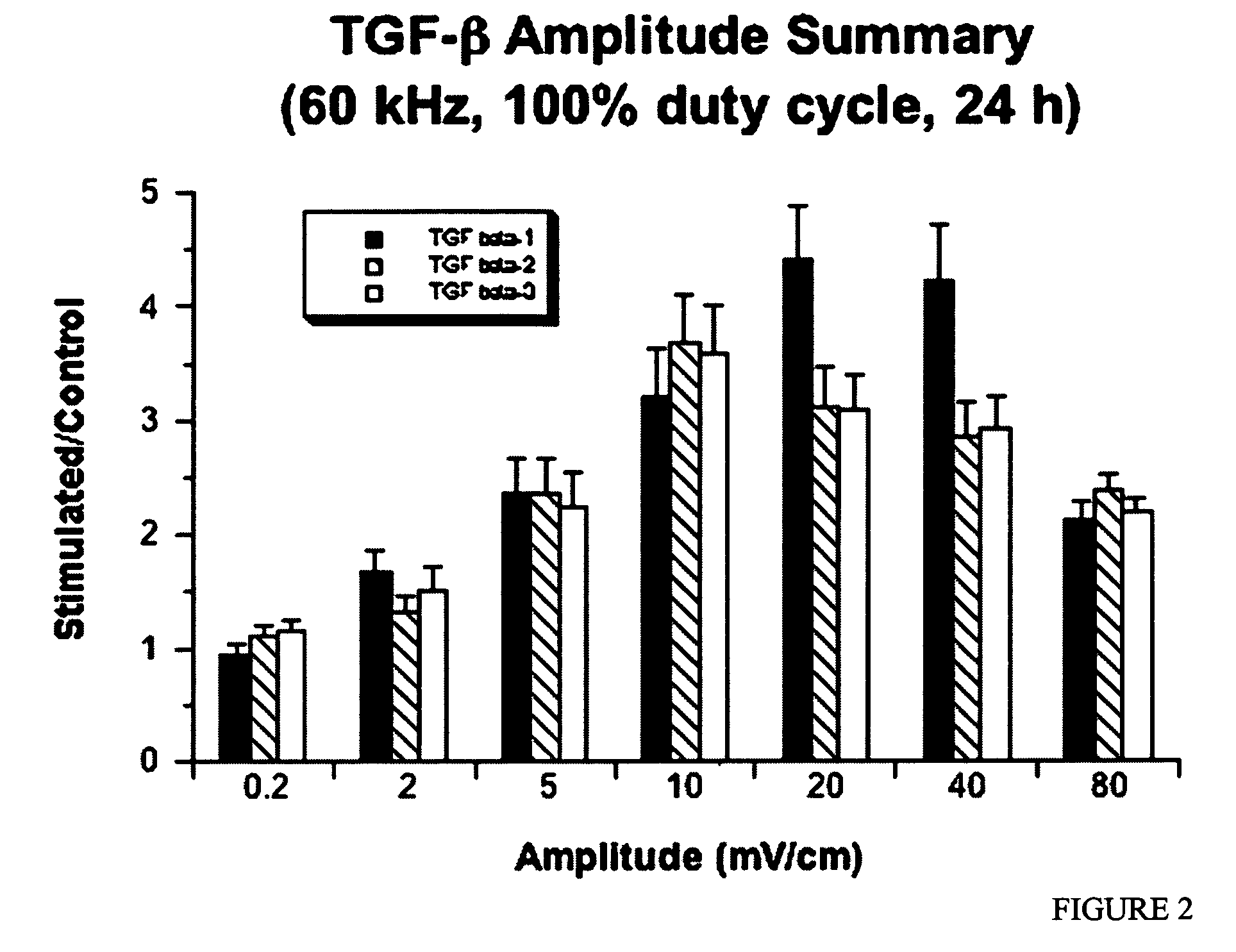
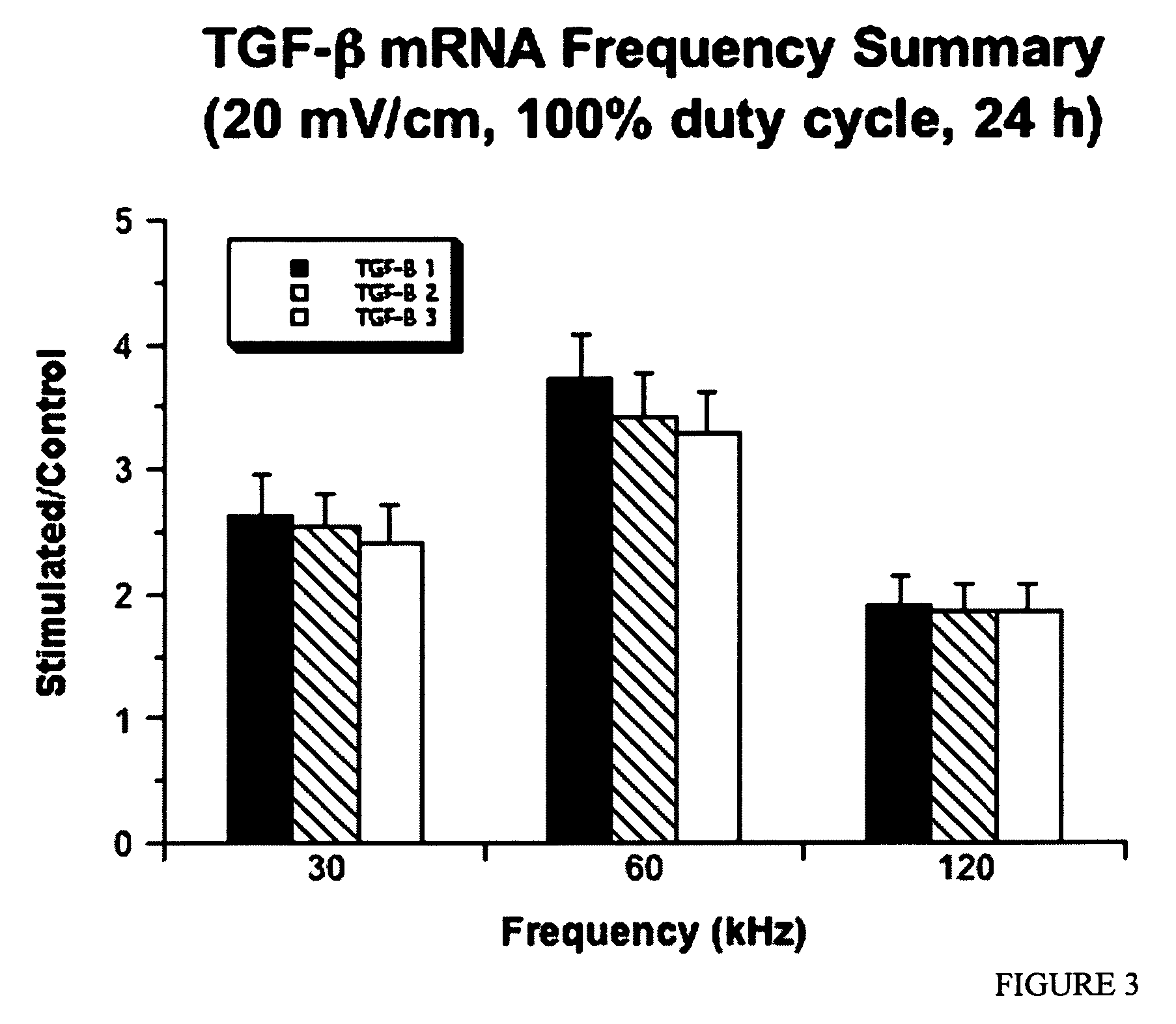
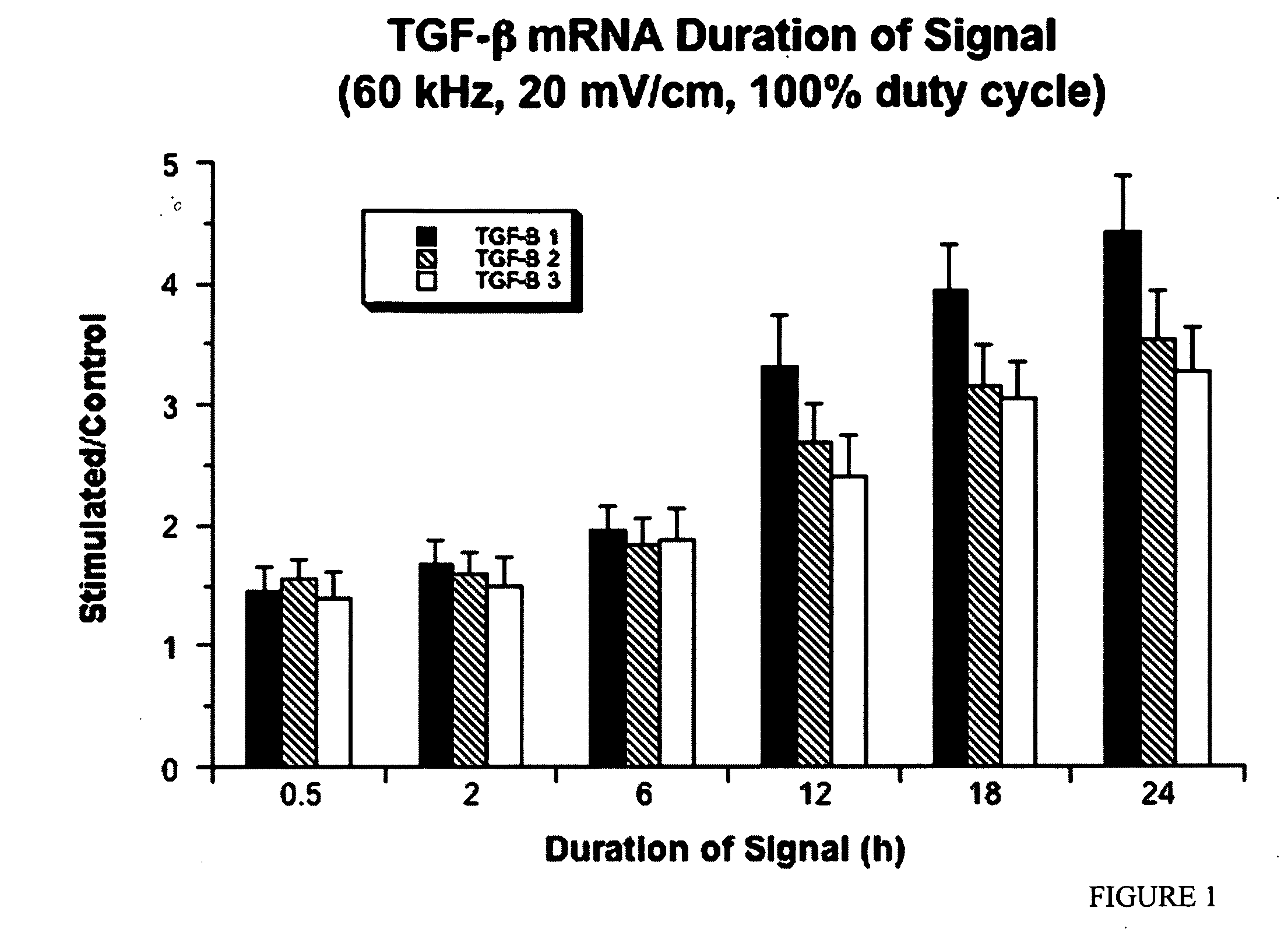
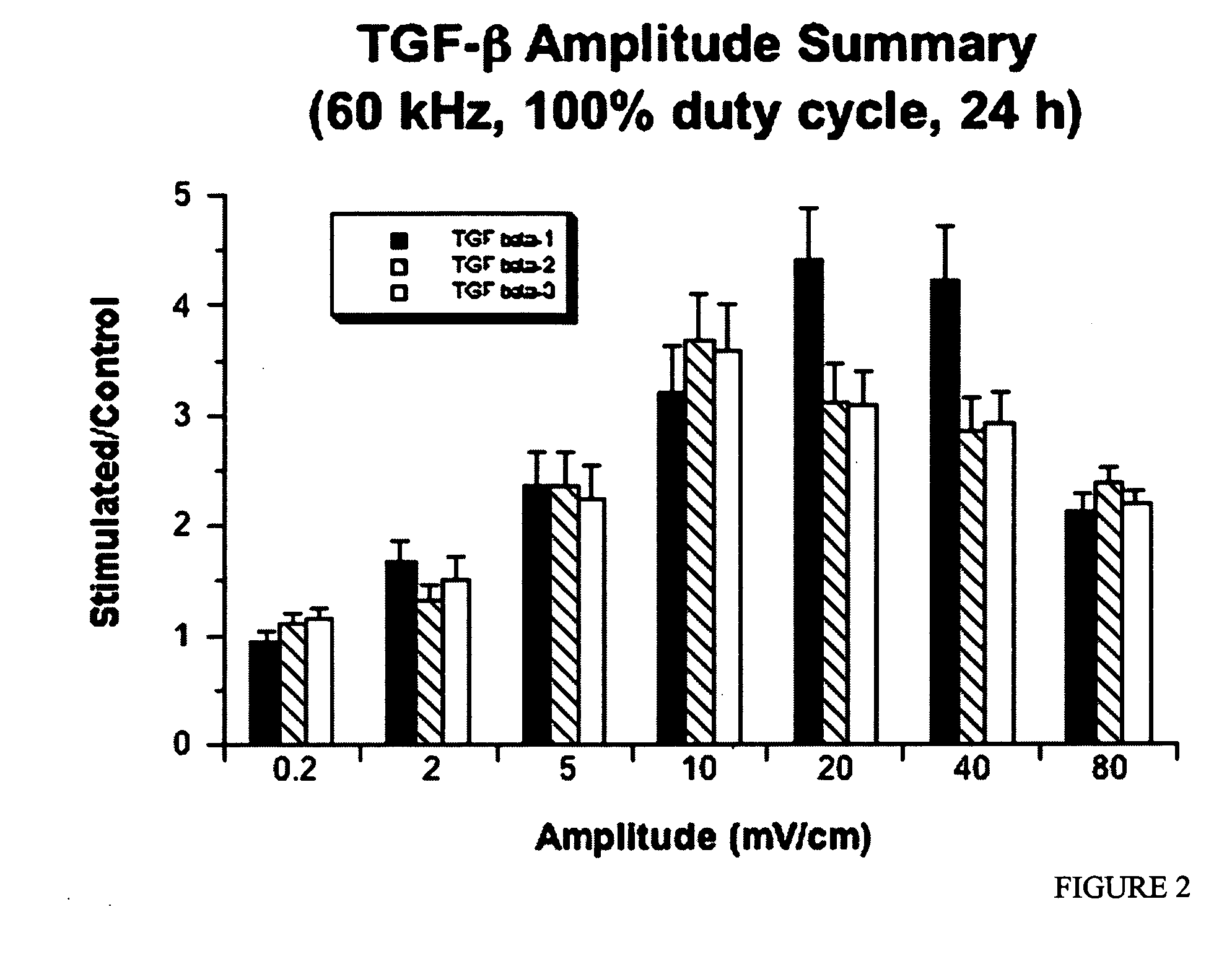
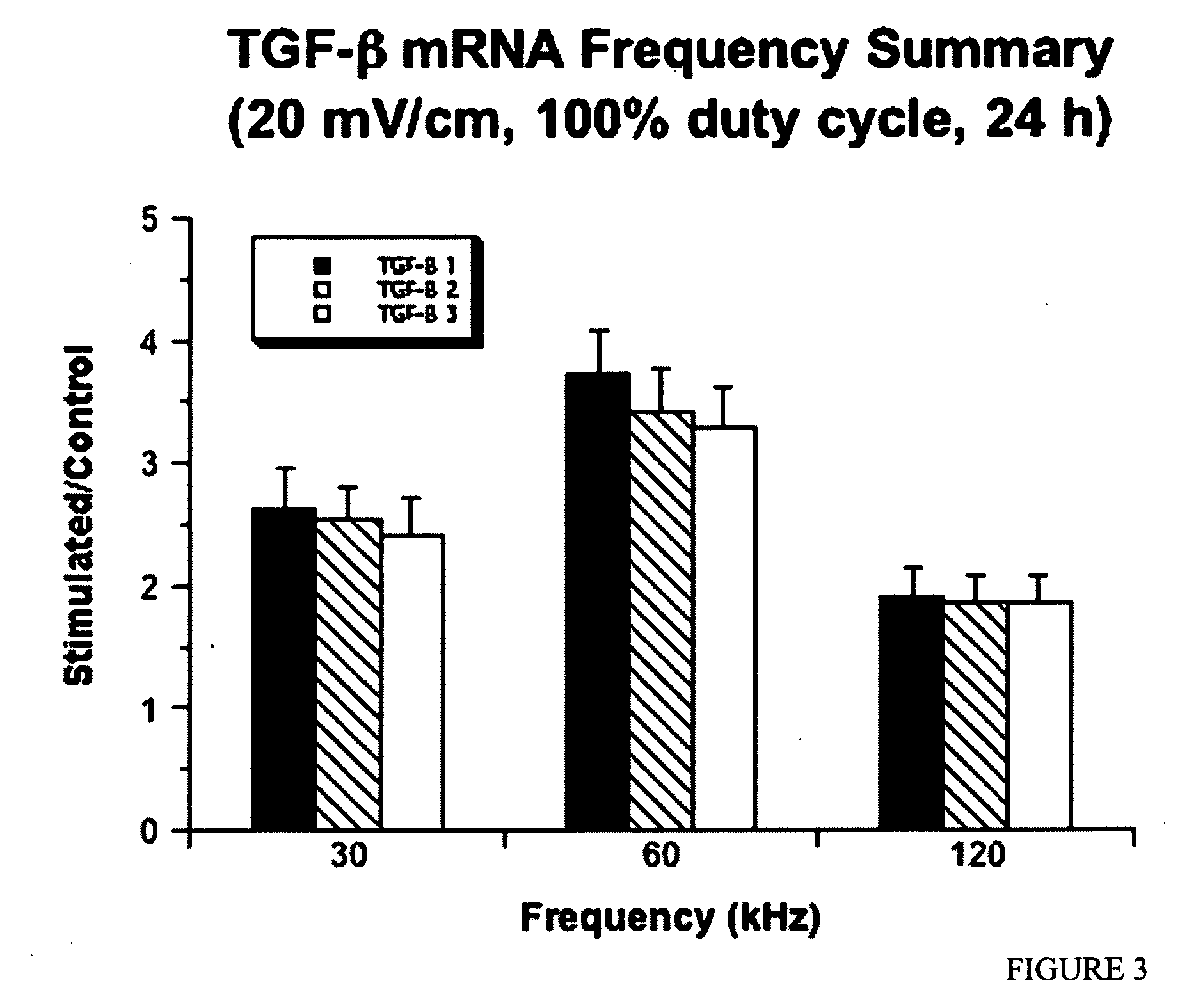
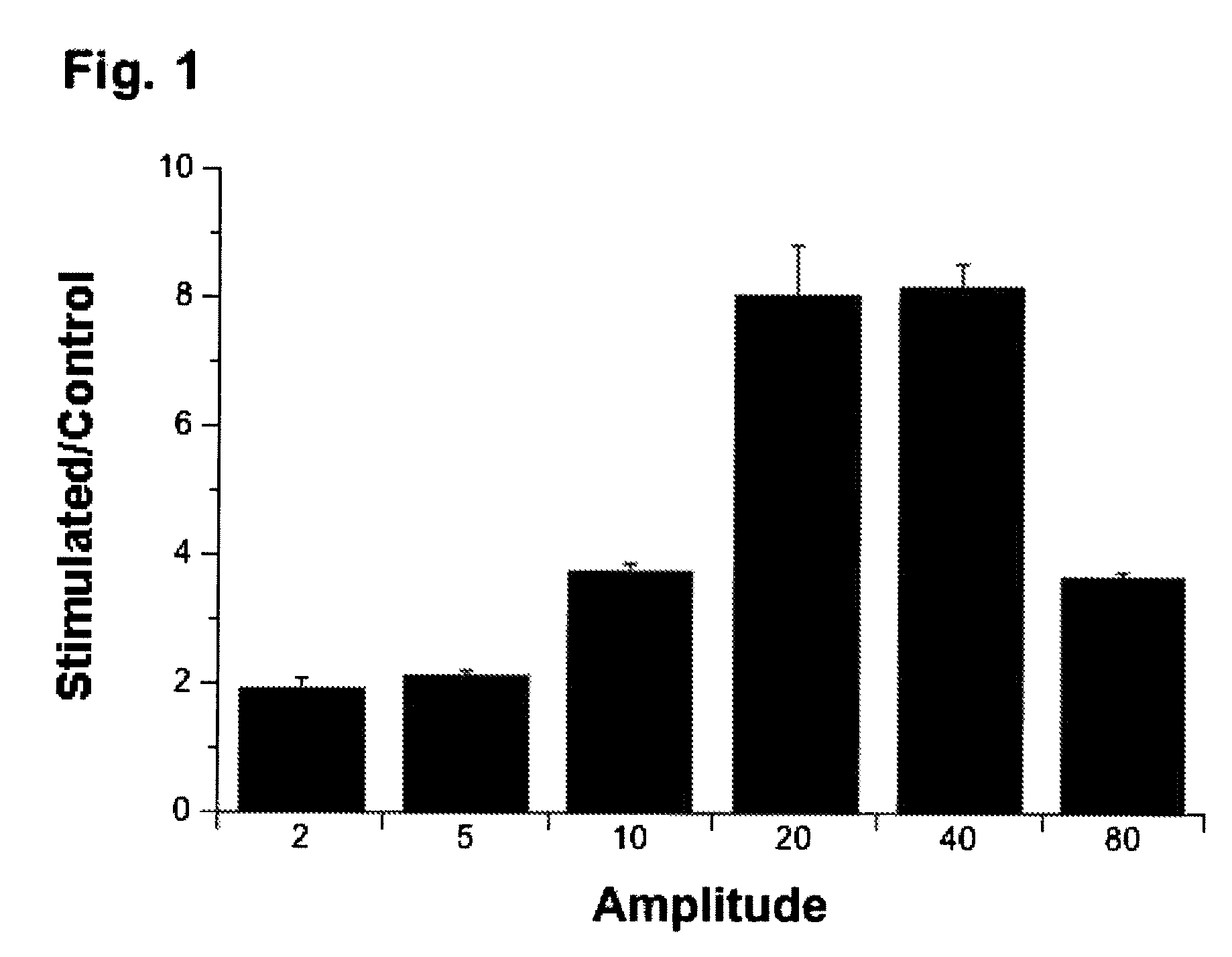
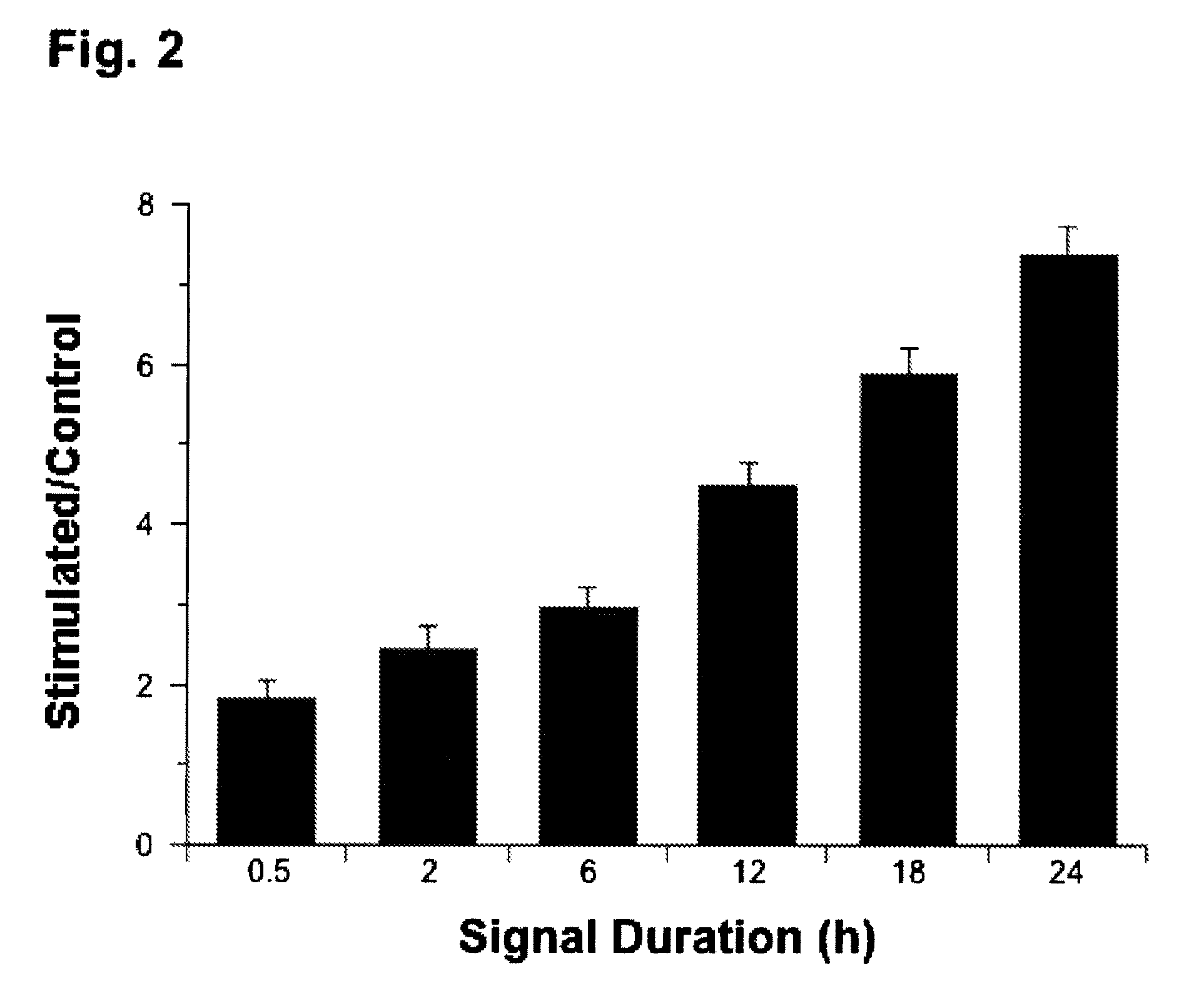
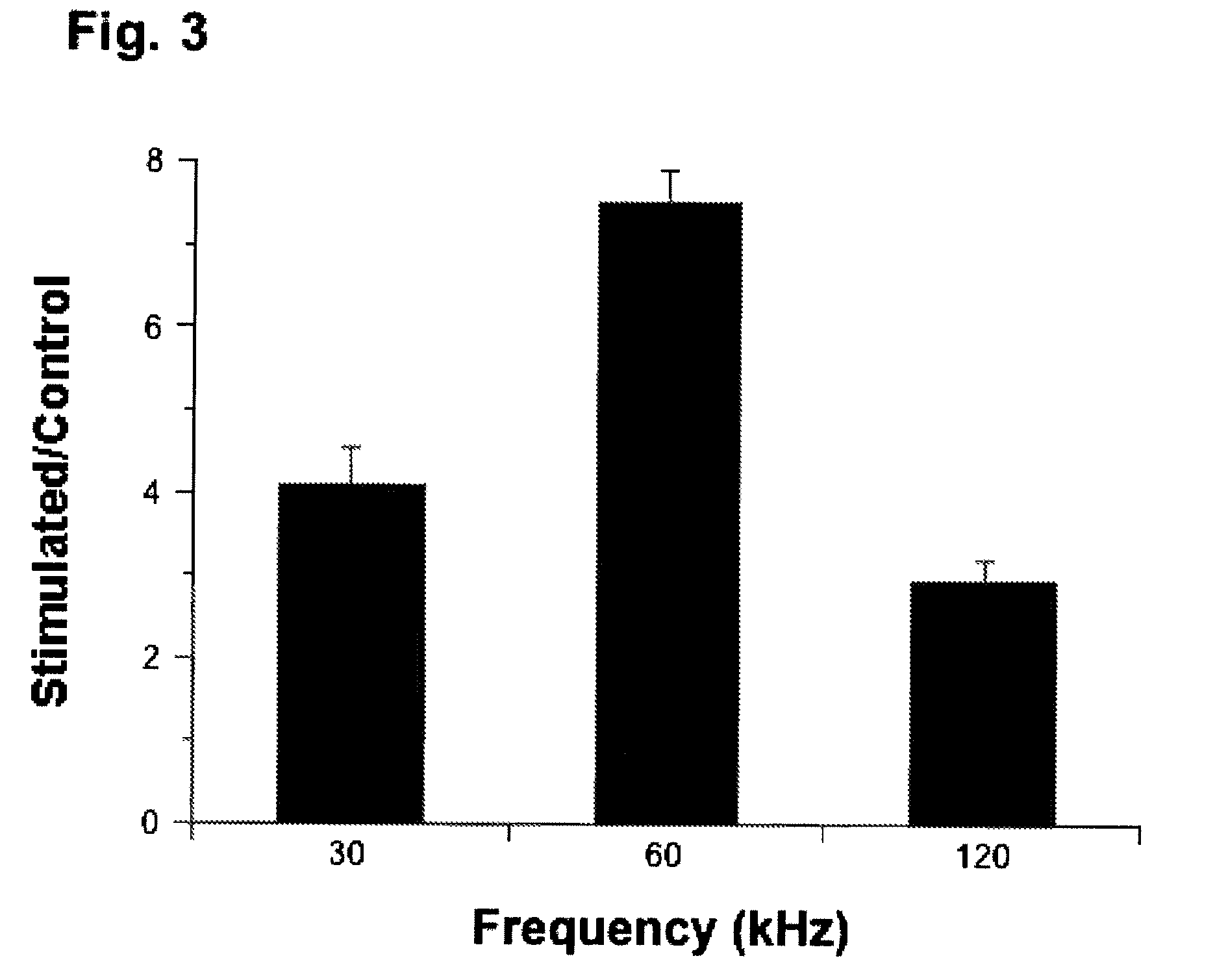
Regulation of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) gene expression in living cells via the application of specific and selective electric and electromagnetic fields
InactiveUS7465546B2ElectrotherapyMicrobiological testing/measurementElectromagnetic fieldTarget tissue
Methods and devices are described for the regulation of Transforming Growth actor (TGF)-β1, β2, and / or β3 protein gene expression in bone cells and other tissues via the capacitive coupling or inductive coupling of specific and selective electric fields to the bone cells or other tissues, where the specific and selective electric fields are generated by application of specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals to electrodes or one or more coils or other field generating device disposed with respect to the bone cells or other tissues so as to facilitate the treatment of diseased or injured bone and other tissues. By gene expression is meant the up-regulation or down-regulation of the process whereby specific portions (genes) of the human genome (DNA) are transcribed into mRNA and subsequently translated into protein. Methods and devices are provided for the targeted treatment of injured or diseased bone and other tissue that include generating specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals that generate fields in the target tissue optimized for increase of TGF-β1, β2, and / or β3 protein gene expression and exposing bone and other tissue to the fields generated by specific and selective signals so as to regulate TGF-β1, β2, and / or β3 protein gene expression in such tissue. The resulting methods and devices are useful for the targeted treatment of bone fractures, fractures at risk, delayed unions, nonunion of fractures, bone defects, spine fusions, osteonecrosis or avascular necrosis, as an adjunct to other therapies in the treatment of one or all of the above, in the treatment of osteoporosis, and in other conditions in which TGF-β1, β2, and / or β3 protein may be implicated.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
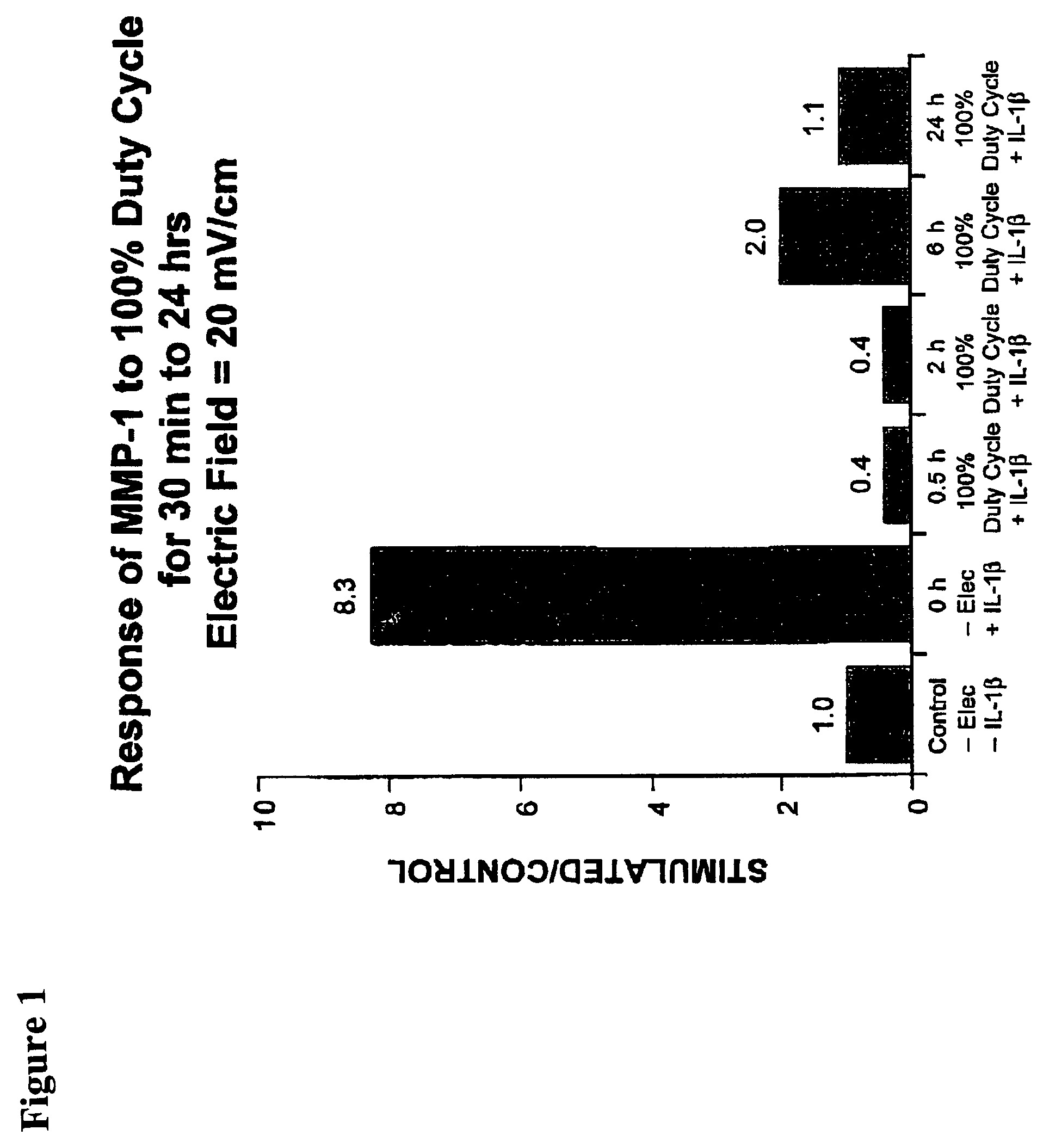
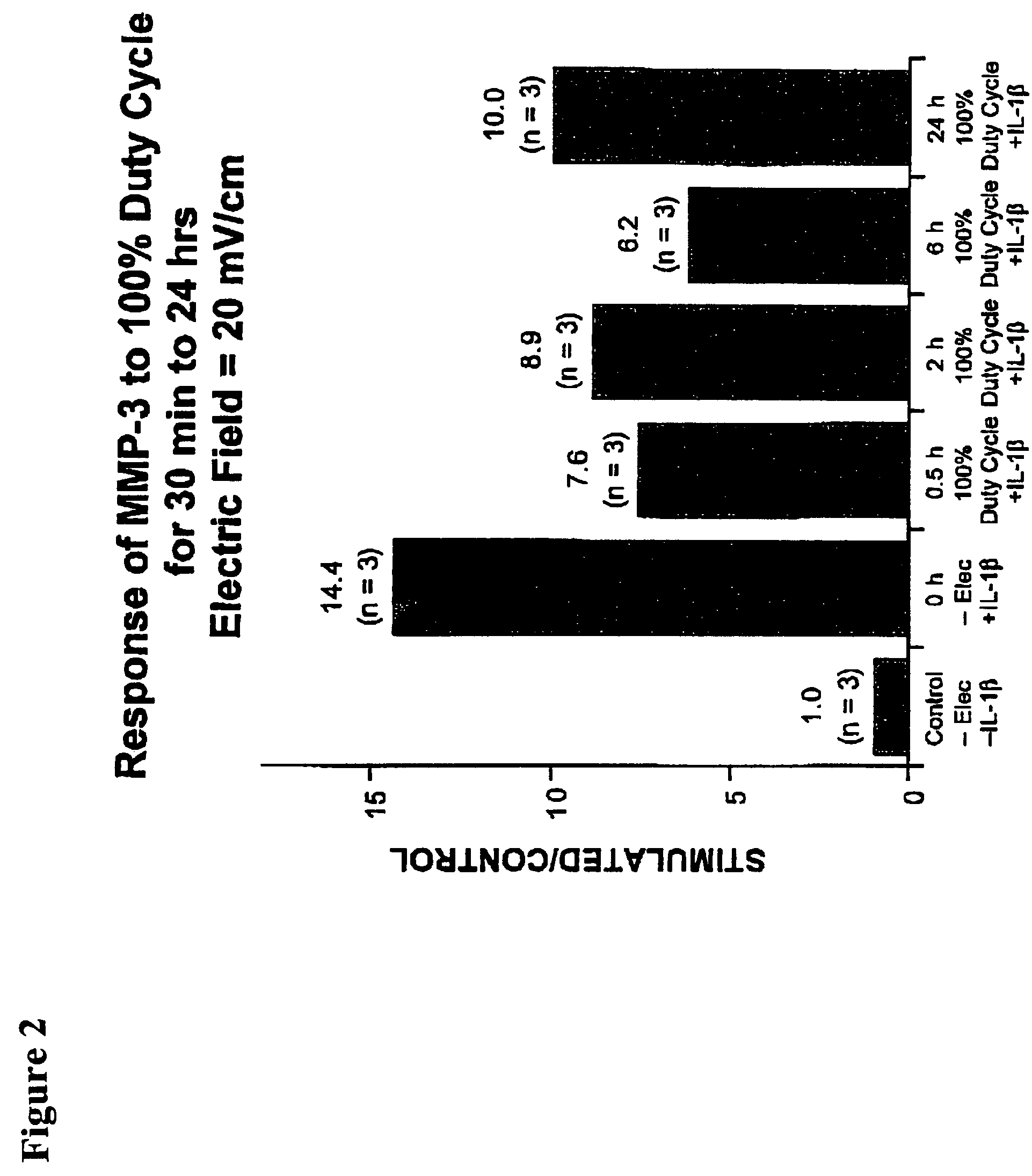
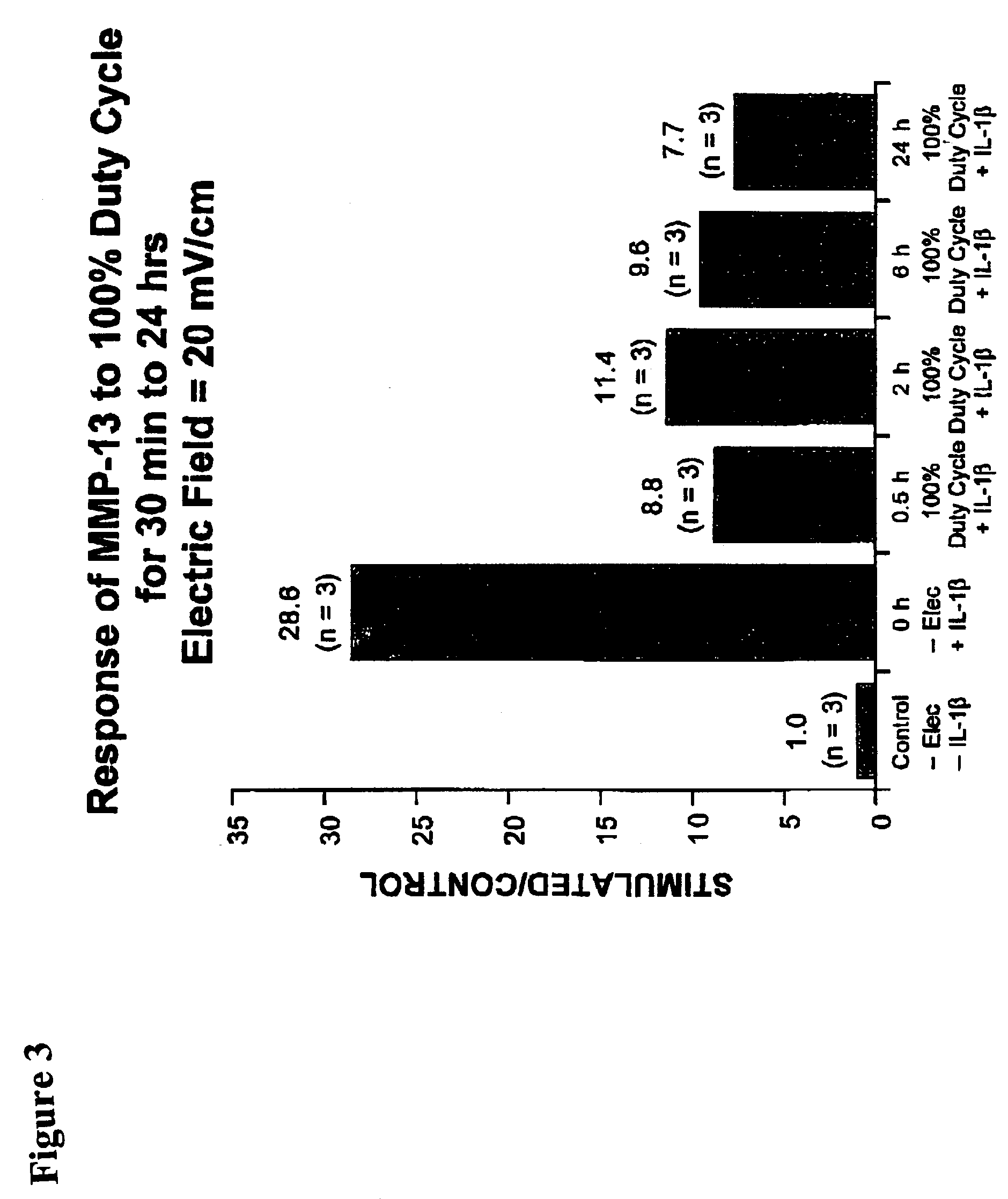
Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase gene expression using specific and selective electrical and electromagnetic signals
Methods and devices for the regulation of matrix metalloproteinase gene expression in cartilage cells via the application of fields generated by specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals in the treatment of diseased or injured articular cartilage. By gene expression is meant the up-regulation or down-regulation of the process whereby specific portions (genes) of the human genome (DNA) are transcribed into mRNA and subsequently translated into protein. Methods and devices are provided for the targeted treatment of injured or diseased cartilage tissue that include generating specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals that generate fields optimized for reduction of matrix metalloproteinase gene expression and exposing cartilage tissue to the fields generated by specific and selective signals so as to regulate matrix metalloproteinase gene expression in such cartilage tissue. The resulting methods and devices are useful for the targeted treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, cartilage injury, cartilage defects, and tumor metastasis.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Rationally-designed meganucleases with recognition sequences found in dnase hypersensitive regions of the human genome
Rationally-designed LAGLIDADG meganucleases and methods of making such meganucleases are provided. In addition, methods are provided for using the meganucleases to generate recombinant cells and organisms having a desired DNA sequence inserted into a limited number of loci within the genome, as well as methods of gene therapy, for treatment of pathogenic infections, and for in vitro applications in diagnostics and research.
Owner:PRECISION BIOSCI
Regulation of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) gene expression in living cells via the application of specific and selective electric and electromagnetic fields
InactiveUS20060235473A1ElectrotherapyMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingElectromagnetic field
Methods and devices are described for the regulation of Transforming Growth actor (TGF)-β1, β2, and / or β3 protein gene expression in bone cells and other tissues via the capacitive coupling or inductive coupling of specific and selective electric fields to the bone cells or other tissues, where the specific and selective electric fields are generated by application of specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals to electrodes or one or more coils or other field generating device disposed with respect to the bone cells or other tissues so as to facilitate the treatment of diseased or injured bone and other tissues. By gene expression is meant the up-regulation or down-regulation of the process whereby specific portions (genes) of the human genome (DNA) are transcribed into mRNA and subsequently translated into protein. Methods and devices are provided for the targeted treatment of injured or diseased bone and other tissue that include generating specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals that generate fields in the target tissue optimized for increase of TGF-β1, β2, and / or β3 protein gene expression and exposing bone and other tissue to the fields generated by specific and selective signals so as to regulate TGF-β1, β2, and / or β3 protein gene expression in such tissue. The resulting methods and devices are useful for the targeted treatment of bone fractures, fractures at risk, delayed unions, nonunion of fractures, bone defects, spine fusions, osteonecrosis or avascular necrosis, as an adjunct to other therapies in the treatment of one or all of the above, in the treatment of osteoporosis, and in other conditions in which TGF-β1, β2, and / or β3 protein may be implicated
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
High-throughput sequencing detection method used for HPV typing and integration
PendingCN107739761AImprove accuracyGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementSanger sequencingBiology
The invention discloses a high-throughput sequencing detection method used for HPV typing and integration. According to the method, the genes of current HPV subtypes are selected, in combination witha second-generation high-throughput sequencing technology, the type of HPV infected by a patient is detected more comprehensively, and the method overcomes the difficulties that a traditional detection method is low in accuracy rate, high in false positive result, low in repeatability and high in rate of missed diagnosis. In the field of molecular diagnosis, the mostly direct and specific technology is gene sequencing, and the second-generation high-throughput sequencing technology has the advantages of higher detection flux, higher sequencing speed, higher accuracy, lower cost and more abundant information contents compared with a classical Sanger sequencing method mostly adopted at present. According to the method, with the help of the second-generation high-throughput sequencing technology, accurate typing can be carried out on high-risk HPV and low-risk HPV, whether the integration of a human genome occurs is detected, accurate individual assessment is carried out on a detector, and the risk of a disease is prevented, so that the occurrence of a tumor is prevented.
Owner:JIAXING YUNYING MEDICAL INSPECTION CO LTD
Rationally-designed meganucleases with recognition sequences found in dnase hypersensitive regions of the human genome
InactiveUS20130224863A1Affect specificityAffect activitySugar derivativesHydrolasesHuman DNA sequencingBiological body
Rationally-designed LAGLIDADG meganucleases and methods of making such meganucleases are provided. In addition, methods are provided for using the meganucleases to generate recombinant cells and organisms having a desired DNA sequence inserted into a limited number of loci within the genome, as well as methods of gene therapy, for treatment of pathogenic infections, and for in vitro applications in diagnostics and research.
Owner:PRECISION BIOSCI
Gene panel used for detecting breast cancer gene mutation, detection method used for detecting breast cancer gene mutation and application of gene panel
InactiveCN111647648AComprehensive immunotherapyComprehensive treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisHuman DNA sequencingGenome human
The invention relates to a gene panel used for detecting breast cancer gene mutation, and a detection method and application of the gene panel. The panel disclosed by the invention comprises 54419 pieces of targeted DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) probes. The targeted DNA comprises the exon regions of 445 pieces of genes on the human genomes, 2573 pieces of MSI (microsatellite instability) sites and 566 position intervals used for detecting gene fusion. The detection method in the invention can be used for detecting SNV (single nucleotide variation), Indel (Insertion and Deletion), CNV (Copy Number Variation), Fusion, MSI, TMB (Tumor Mutational Burden), HLA (human leucocyte antigen) parting and the like of a tumor somatic cell multi-site DNA mutation. An optimal individual treatment medicine and scheme can be conveniently selected according to the genome features of patients in a breast cancer immunotherapy process.
Owner:北斗生命科学(广州)有限公司 +1
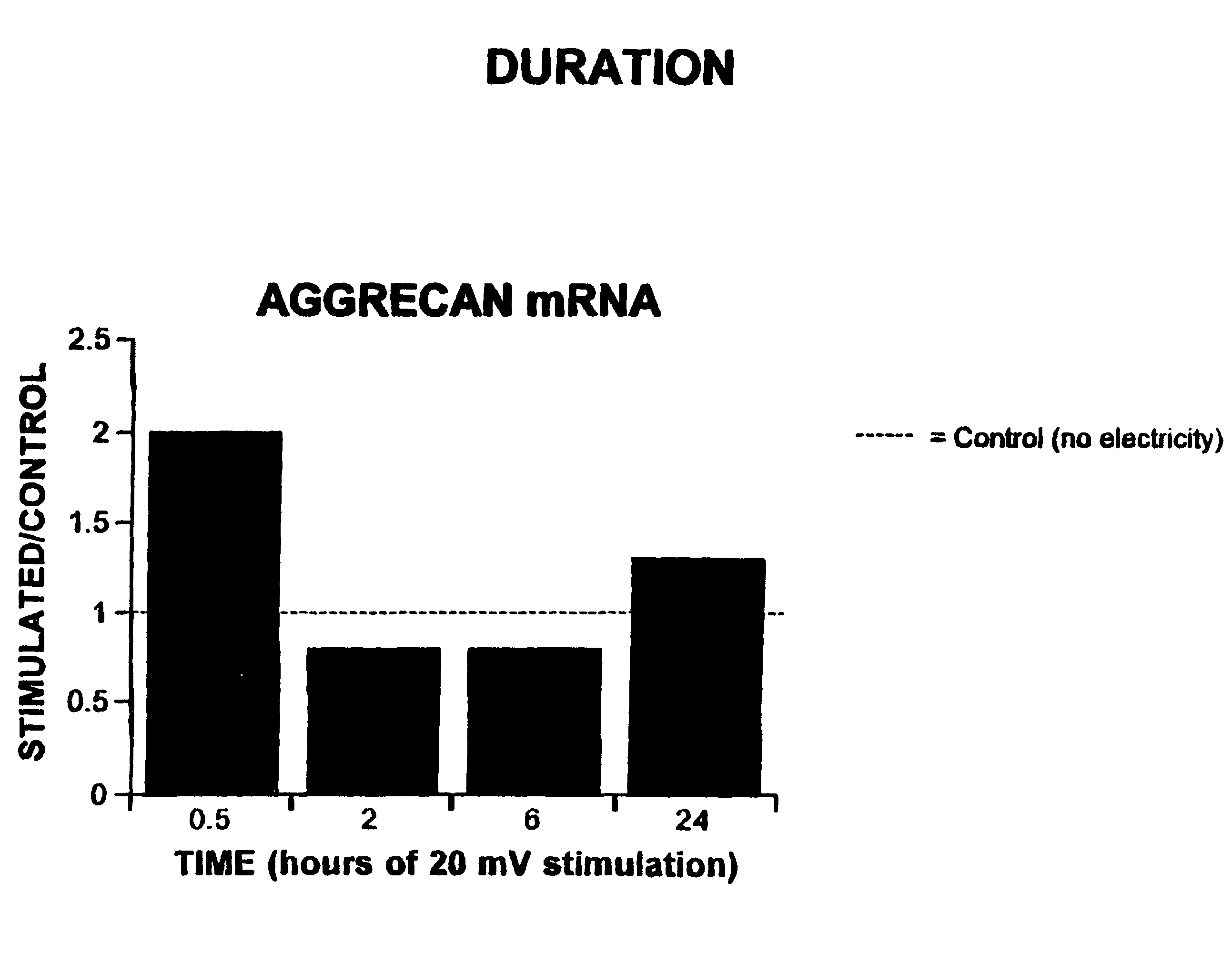
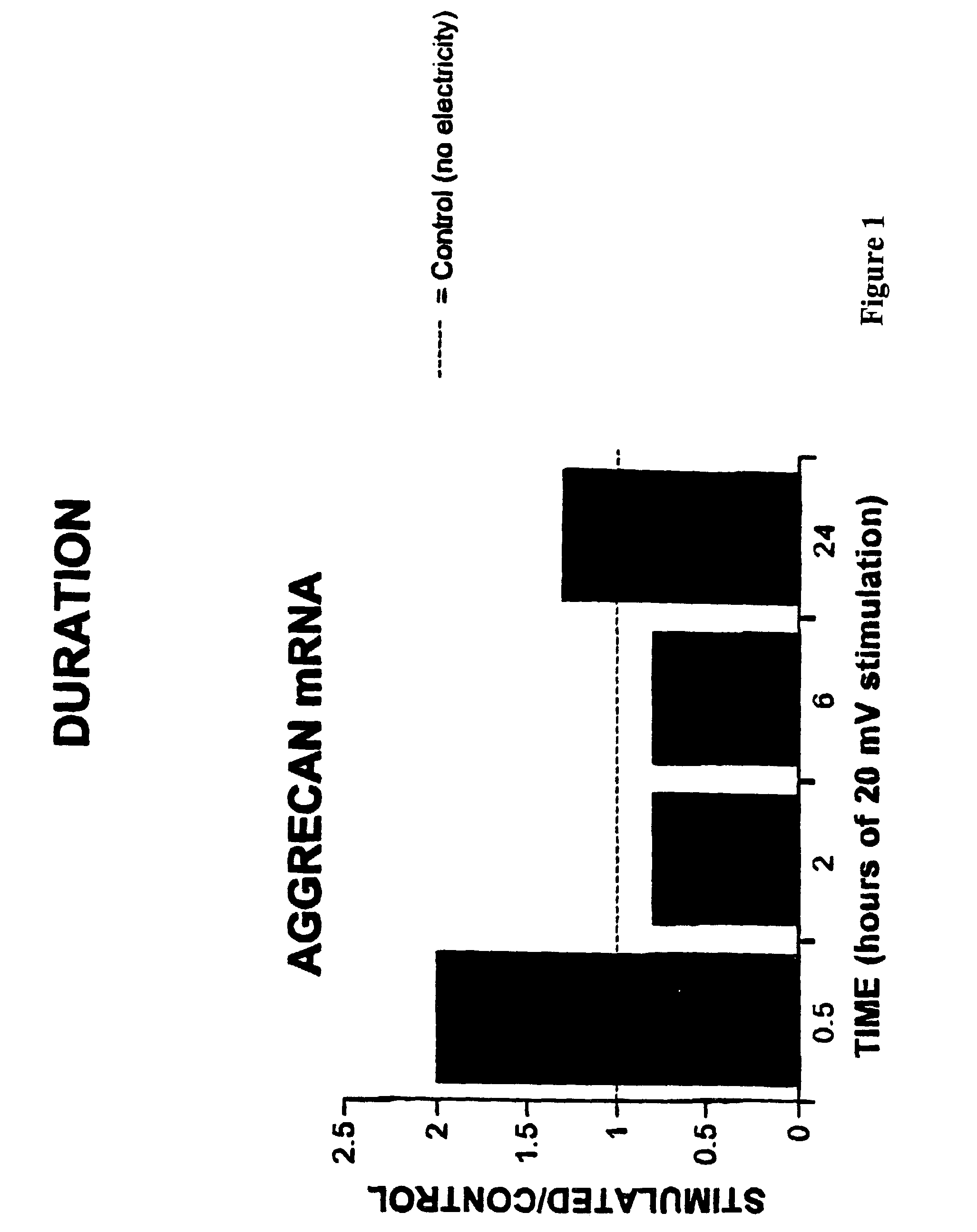
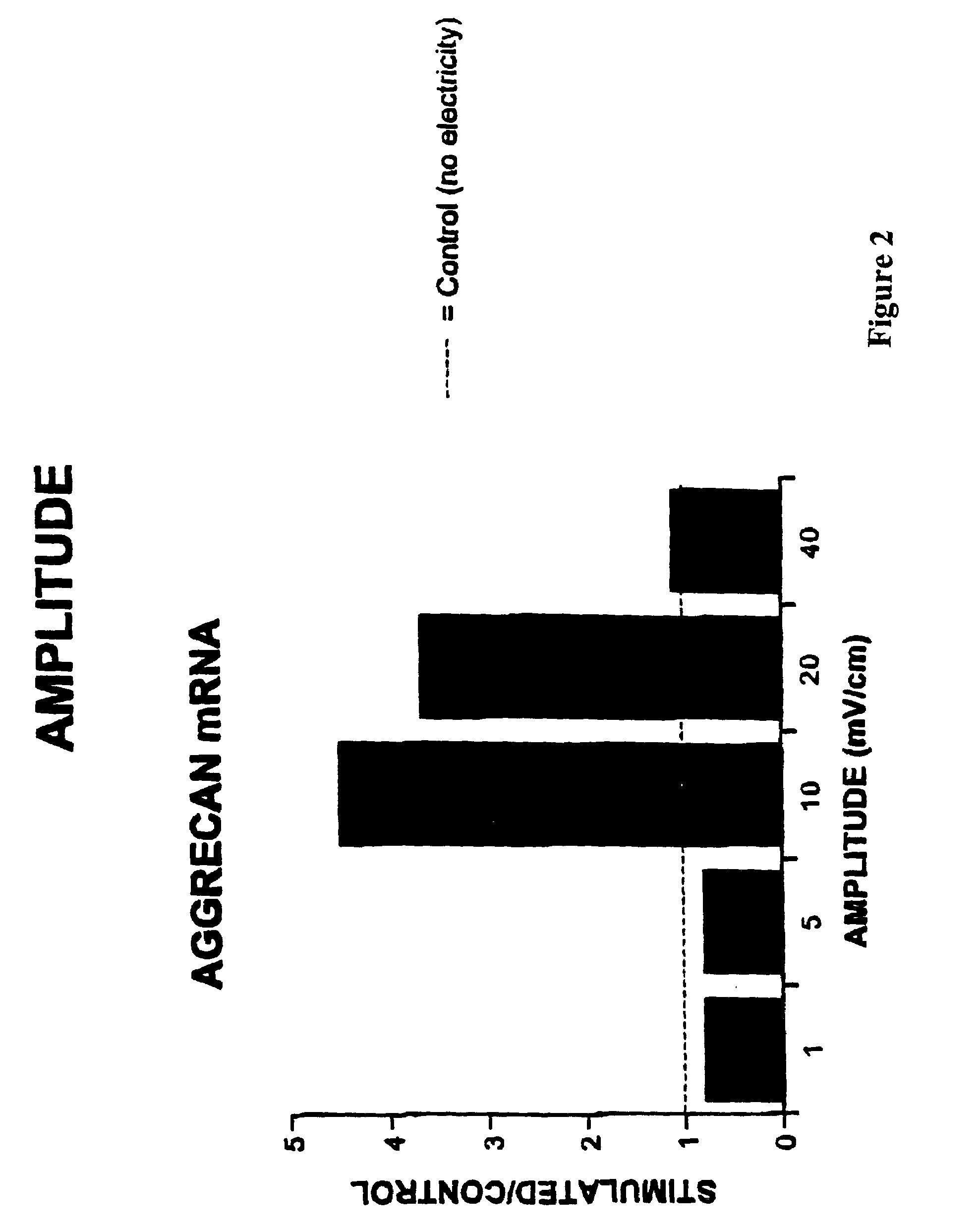
Regulation of aggrecan gene expression using specific and selective electrical and electromagnetic signals
Methods and devices for the regulation of aggrecan gene expression in cartilage cells via the application of fields generated by specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals in the treatment of diseased or injured articular cartilage. By gene expression is meant the up regulation or down regulation of the process whereby specific portions (genes) of the human genome (DNA) are transcribed into mRNA and subsequently translated into protein. Methods and devices are provided for the targeted treatment of injured or diseased cartilage tissue that include generating specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals that generate fields optimized for aggrecan gene expression and exposing cartilage tissue to the fields generated by specific and selective signals so as to regulate aggrecan gene expression in such cartilage tissue. The resulting methods and devices are useful for the targeted treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, cartilage injury, and cartilage defects.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
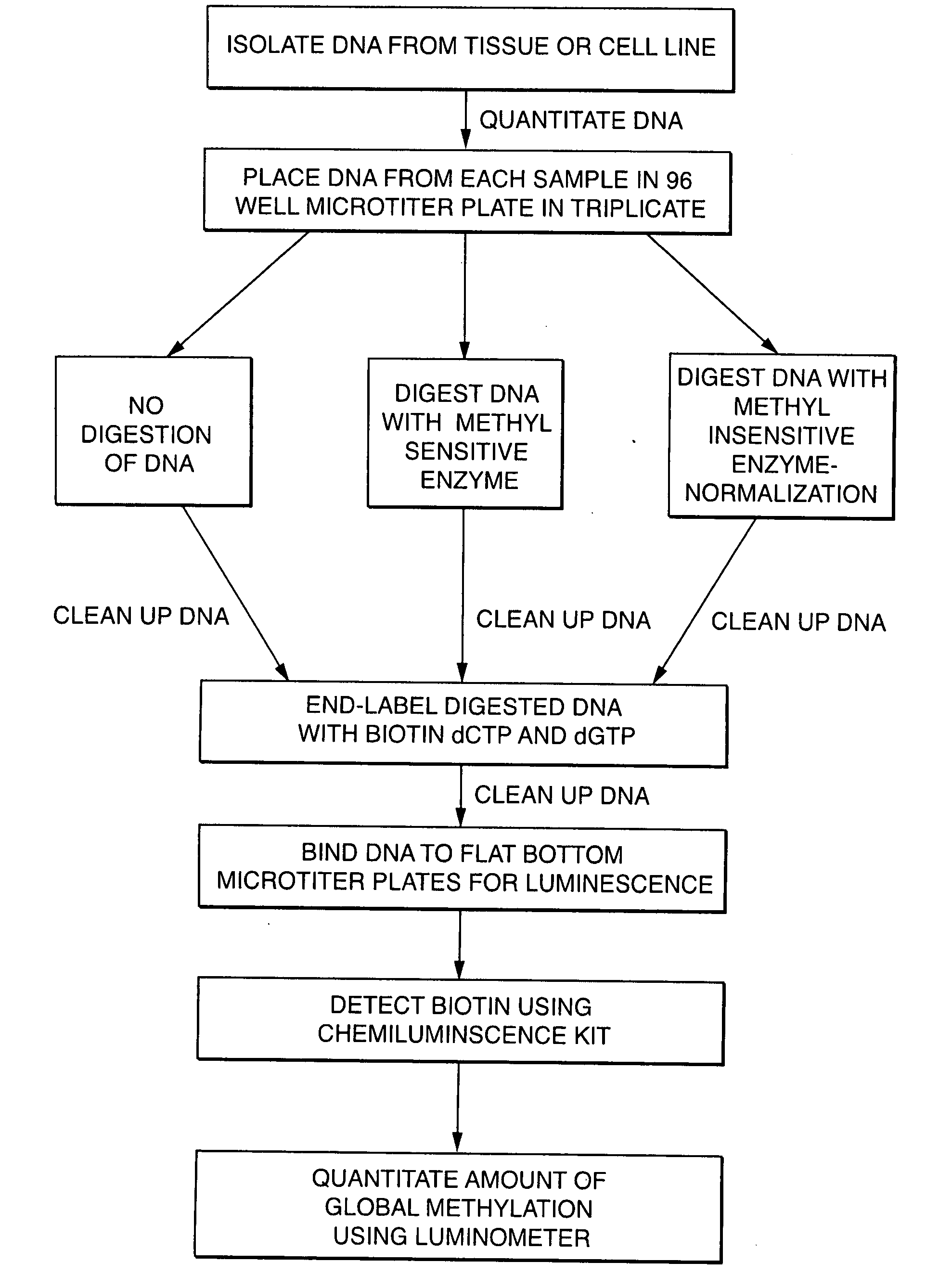
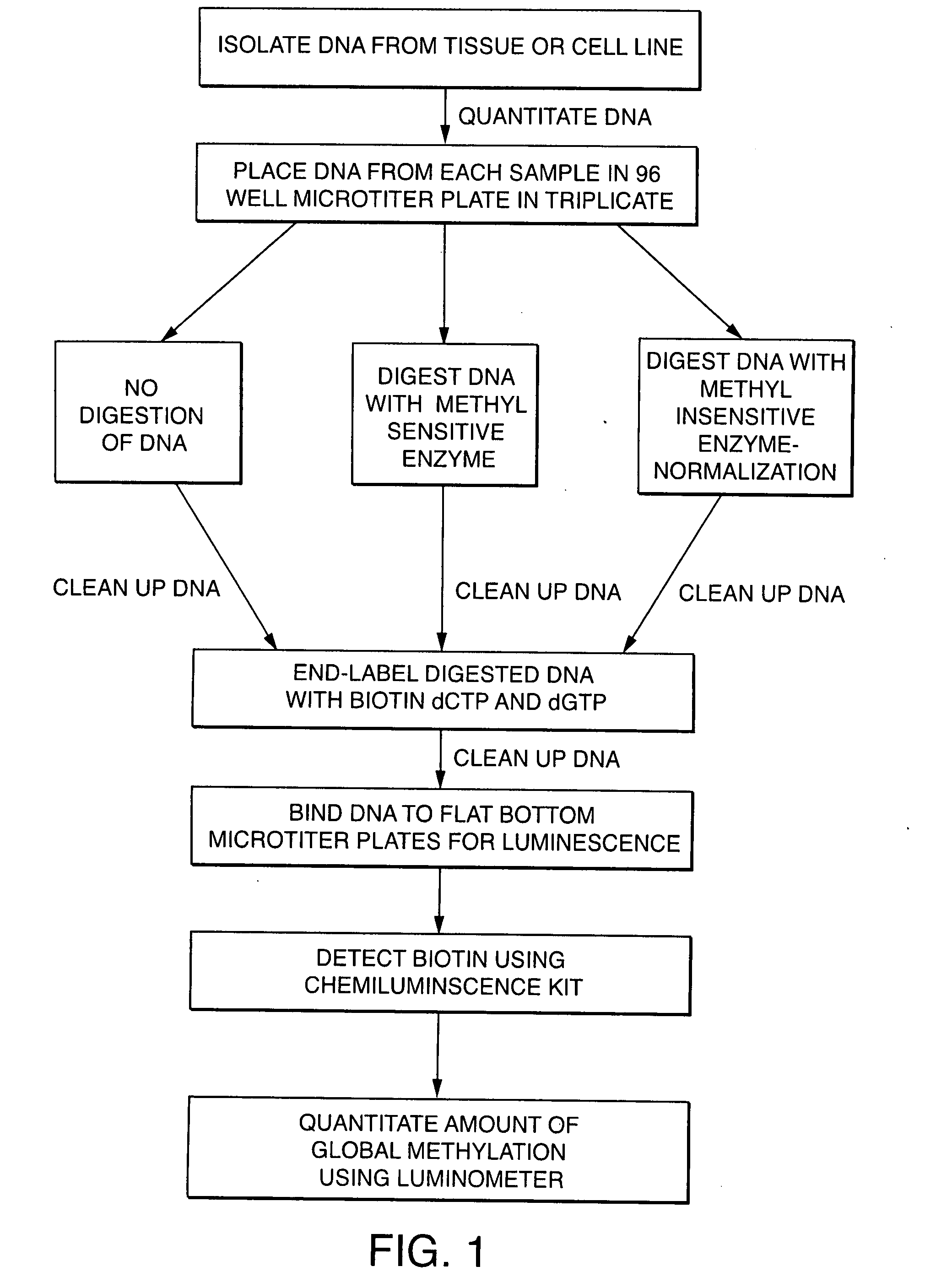
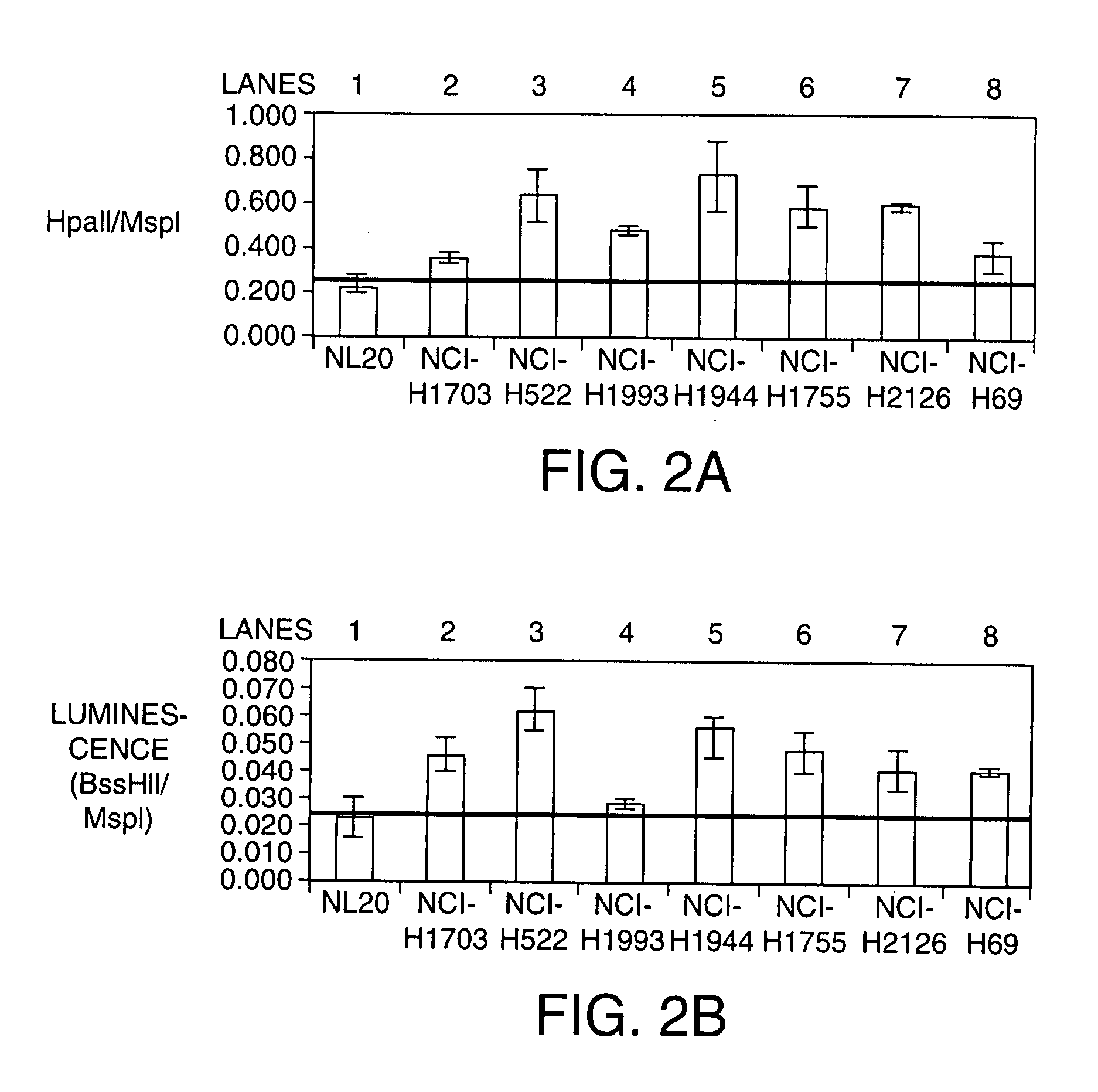
Diagnosing human diseases by detecting DNA methylation changes
This invention relates to methodologies that detect global changes in the methylation of human genomic DNA as well as changes in methylation in specific regions of the human genome. The methodologies have utility in the diagnosis, prognosis and monitoring of therapeutic treatment for any human disease. Further, the invention relates to methodologies that can detect global changes in the methylation of human genomic DNA that is a consequence of diet and / or dietary supplements. The invention also relates to identifying novel DNA methylation biomarkers that are associated with human disease.
Owner:AMBERGEN INC
Thalassemia gene detection method based on high-throughput sequencing technology
InactiveCN105886617ALess DNARealize detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingBeta thalassemia
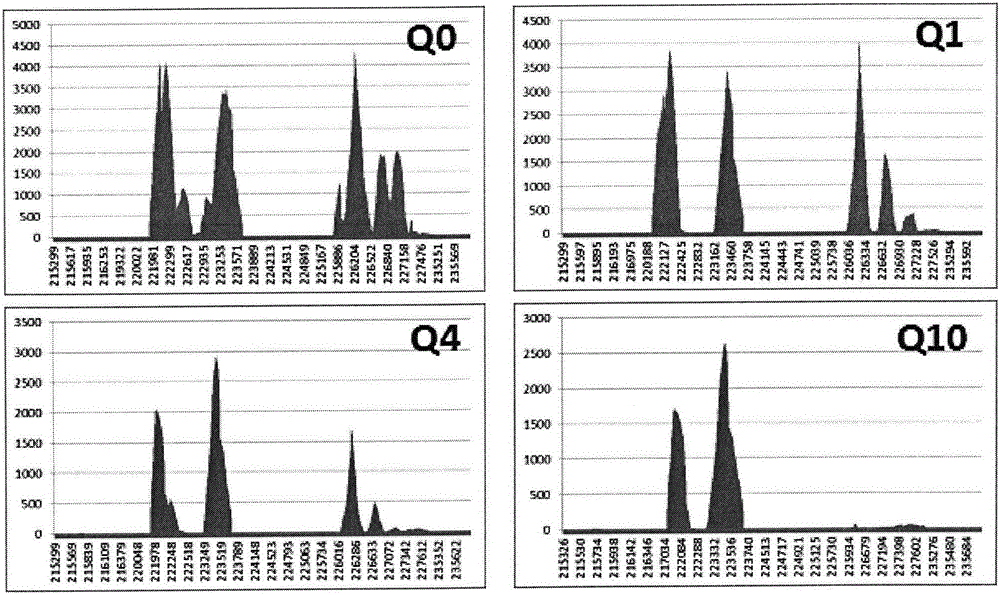
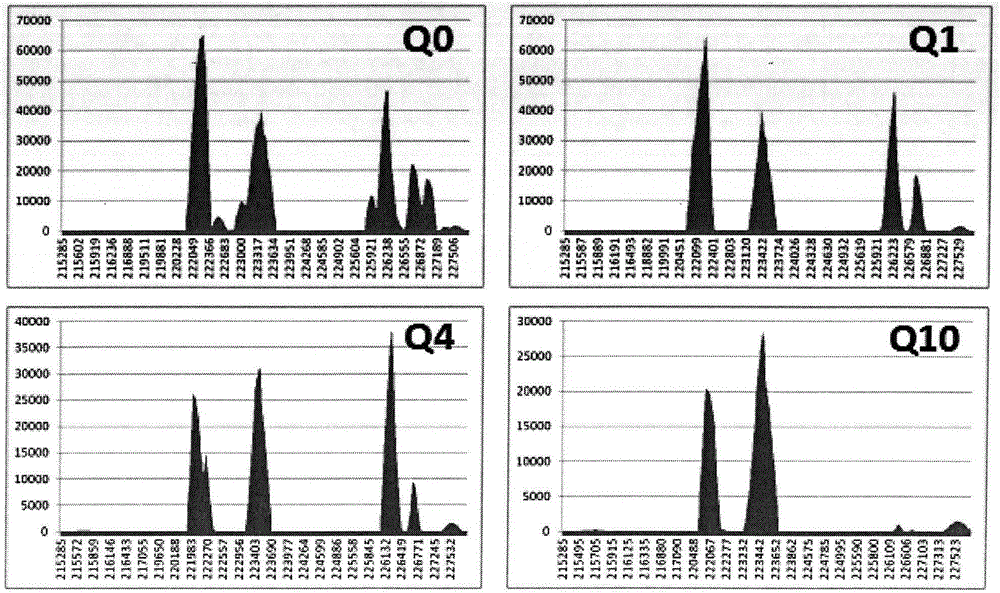
The invention discloses a thalassemia gene detection method based on a high-throughput sequencing technology. The thalassemia gene detection method mainly comprises the following steps that alpha & beta-thalassemia related gene fragments are specifically amplified based on PCR amplification primers of a span breakpoint and a mutation site designed by adopting a Gap-PCR method, library establishment is conducted on PCR products, library products are subjected to high-throughput sequencing, sequencing data uses a human genome hg19 as a reference sequence, sequencing depth values of gene loci in a target area chr16: 215000-236000 are analyzed according to a sequence alignment score Q10, and alpha-thalassemia deletion types are determined according to the distribution of the sequencing depth values of different loci; meanwhile sequence alignment is performed through the target area chr16: 215000-236000 and a target area chr16: 5246400-5248600, and alpha & beta-thalassemia mutation types are determined according to the basic types of specific sites. By the adoption of the thalassemia gene detection method, simultaneous detection of 6 mutation genetypes of alpha-thalassemia and 26 mutation genetypes of beta-thalassemia can be achieved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DARUI BIOTECH
Genome copy number variation detection method and device
PendingCN111916150AAccurate identificationAccurate detectionProteomicsGenomicsHuman DNA sequencingGenomic sequencing
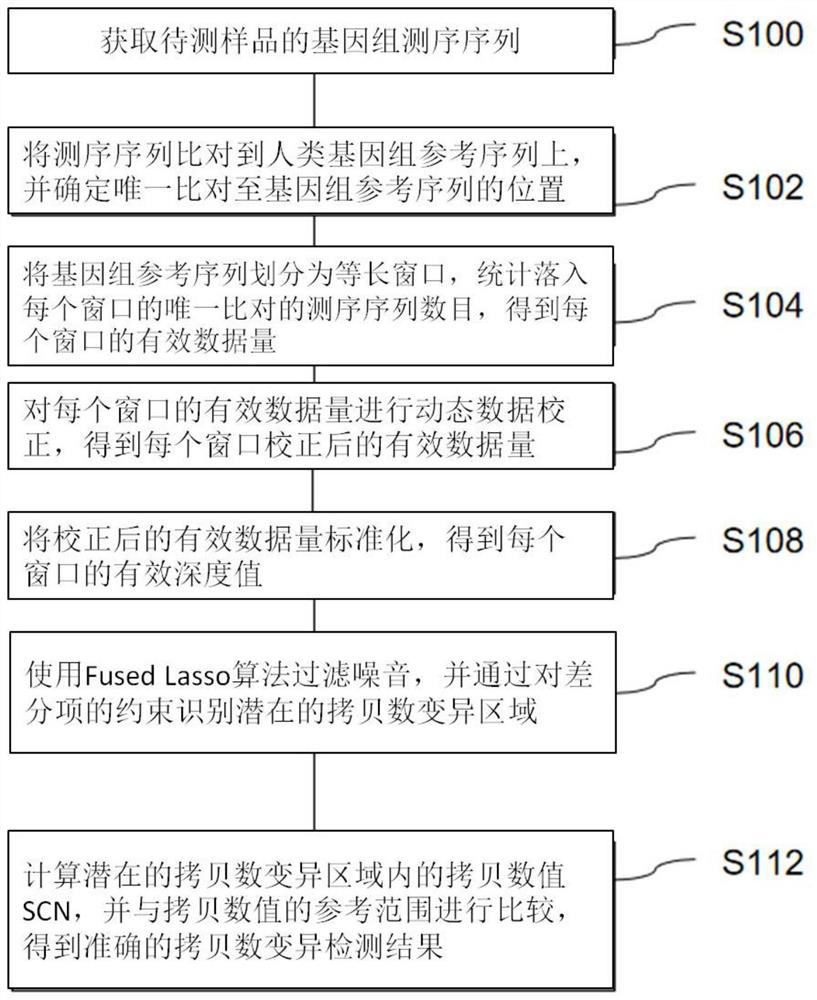
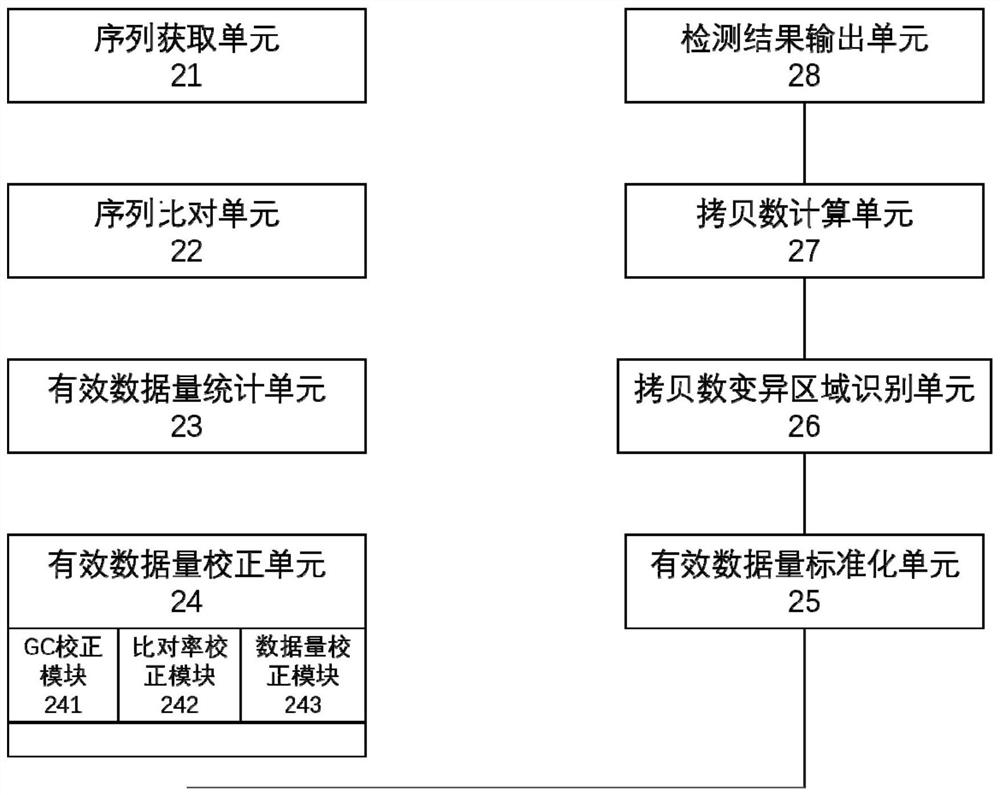
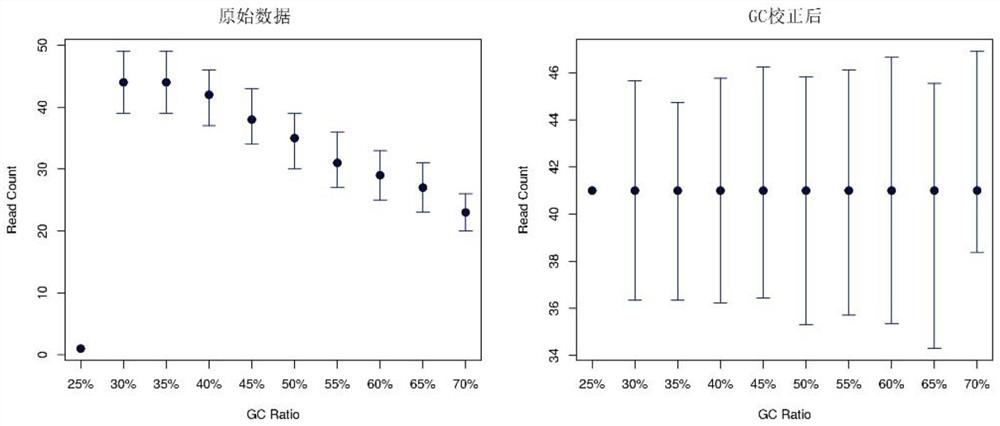
The invention provides a genome copy number variation detection method. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a genome sequencing sequence of a to-be-detected sample; aligning the sequencing sequence to a human genome reference sequence, and determining the position of the unique alignment to the genome reference sequence; dividing the genome reference sequence into equal-length windows, and counting the number of sequencing sequences which fall into each window and are uniquely compared to obtain the effective data volume of each window; performing dynamic data correction on theeffective data volume of each window to obtain the corrected effective data volume of each window; standardizing the corrected effective data volume to obtain an effective depth value of each window;filtering noise by using a Fuded Lasso algorithm, and identifying a potential copy number variation region by constraining a differential item; and calculating a copy number value (SCN) in the potential copy number variation region, and comparing the copy number value (SCN) with the reference range of the copy number to obtain an accurate copy number variation detection result. The invention further provides a device and equipment for implementing the method. According to the method, a mathematical model for calculating the copy number SCN is established for the first time, and the referenceinterval of the copy number state of the genome region is determined. In addition, the noise in the sequencing data can be effectively processed, and the copy number variation region can be accuratelyidentified.
Owner:BERRYGENOMICS CO LTD
Method and system for reducing the likelihood of colorectal cancer in a human being
ActiveUS10548761B2Reduce the possibilityEliminate symptomsOrganic active ingredientsBacteria material medical ingredientsHuman DNA sequencingGenome human
A system and method for reducing the likelihood of colorectal cancer in a human being includes the modification of an individual's gut microbes by employing a Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats-CRISPR-associated system (CRISPR-Cas) or Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats from Prevotella and Francisella 1 (CRISPR / Cpf1) system to modify only bacterial genes of bacteria that reside in the human gut that are non-homologous to those encompassed in the human genome, and in particular, to administer a therapeutically effective amount of a bacterial formulation comprising F. prausnitzii that has been modified to produce one of alliin or butyrate.
Owner:SEED HEALTH INC
Quantitative multiplex amplification on a genomic scale, and applications for detecting genomic rearrangements
InactiveUS20050244830A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingMultiplex
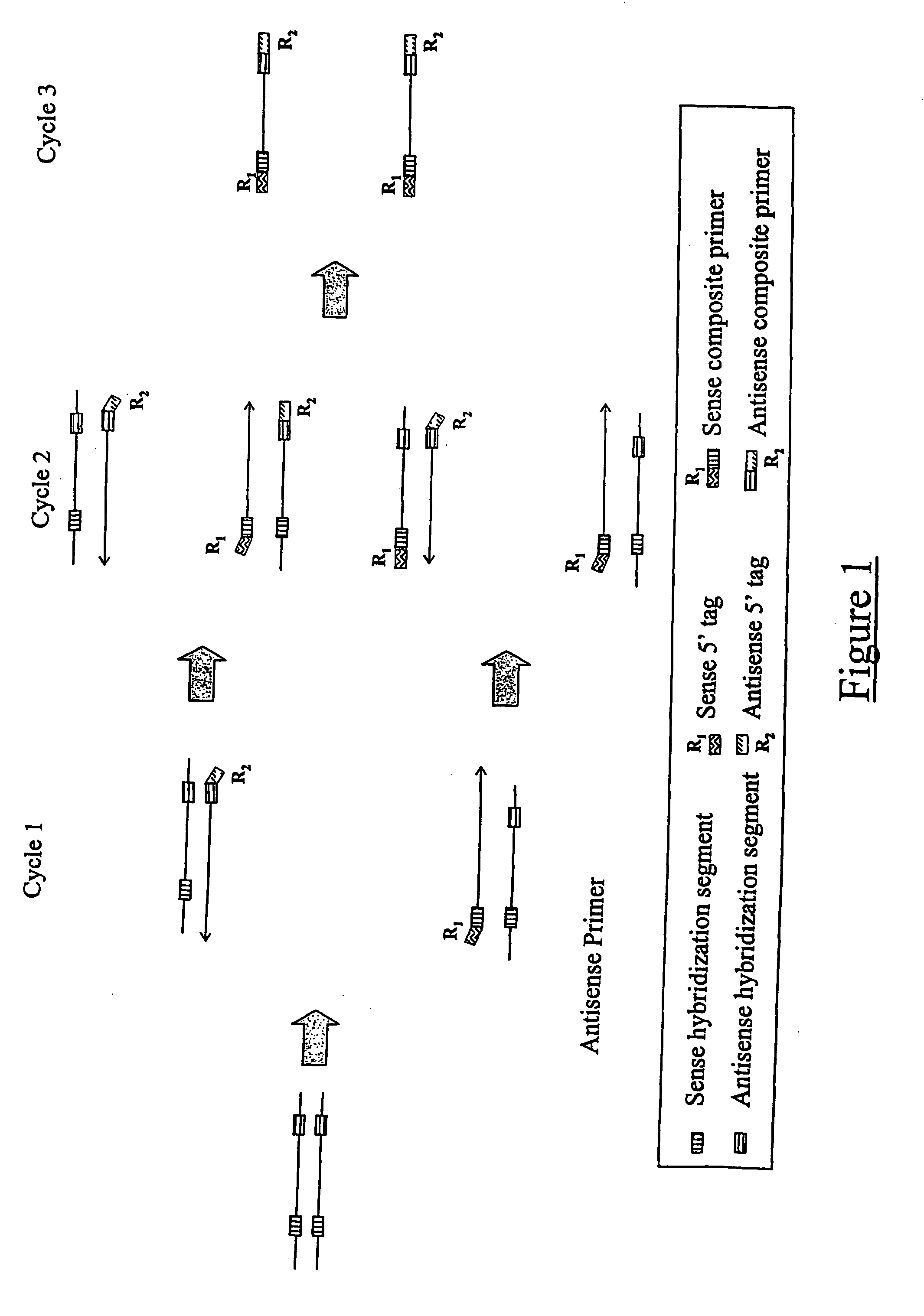
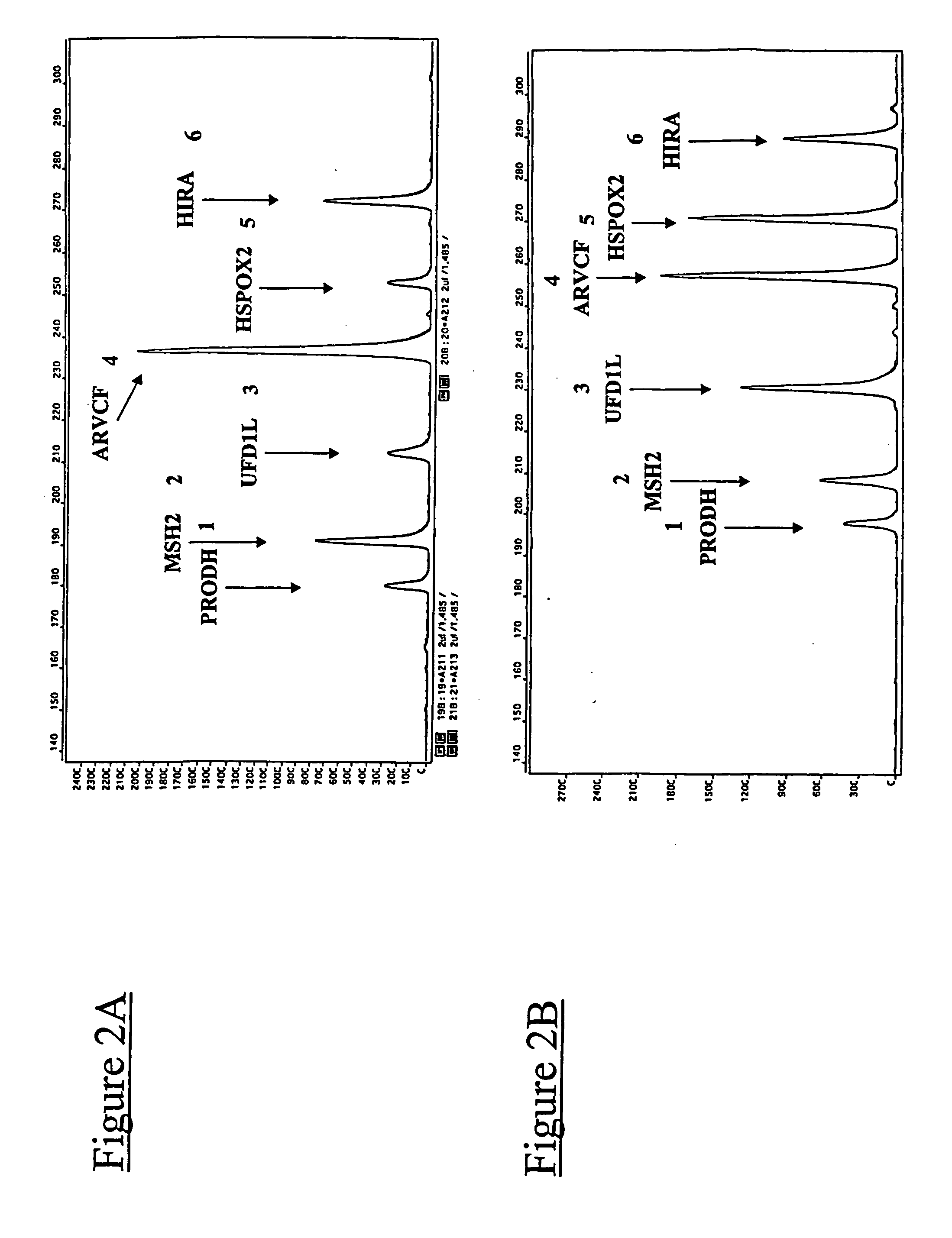
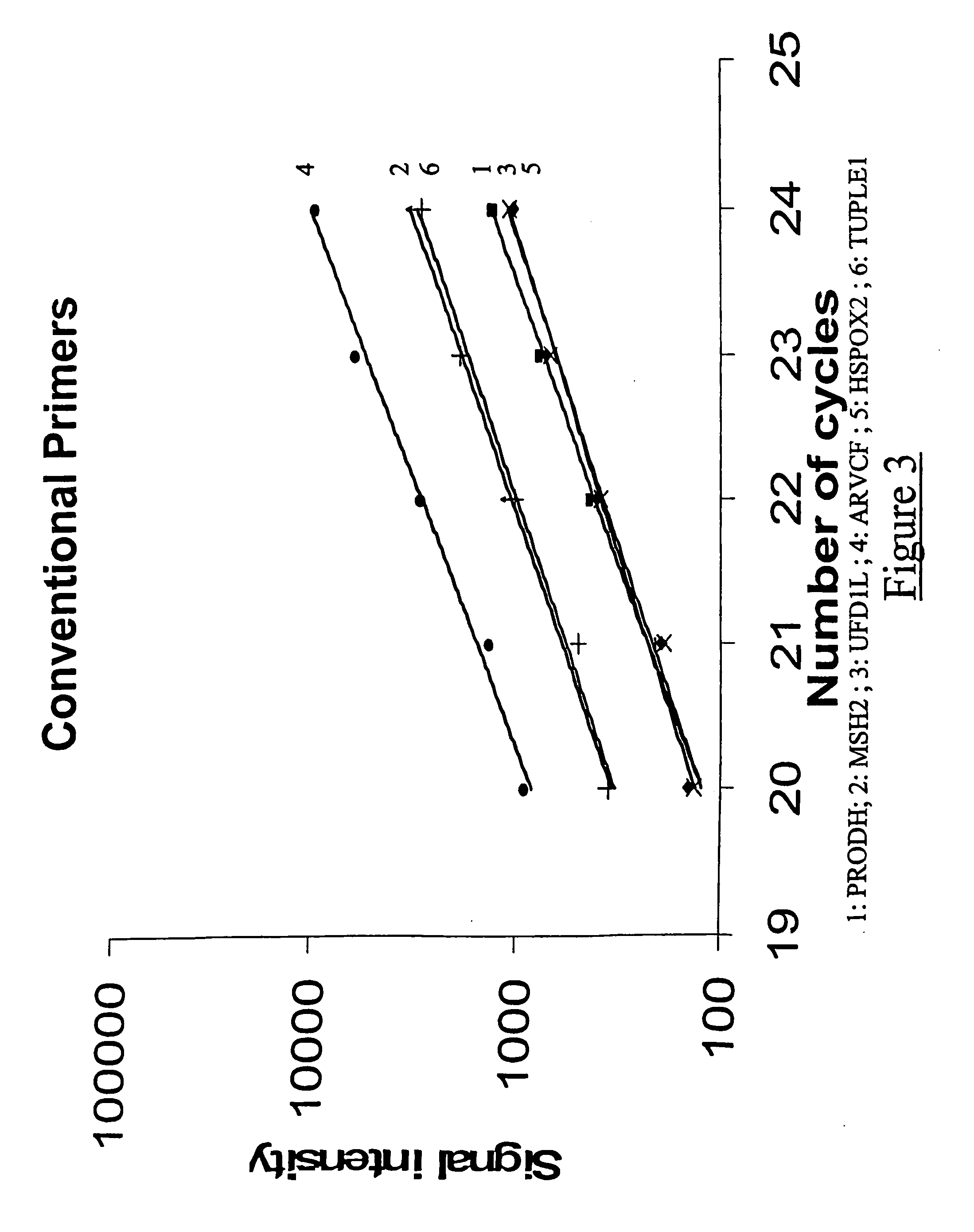
The present application relates to novel composite primers which make it possible to amplify in multiplex at a quantitative level of precision, and to the application of these composite primers for detecting gnomic rearrangements in general and cryptic chromosomal rearrangements in particular. These composite primers contain a tag the sequence of which is absent from or poorly represented in the genome analyzed, and which exhibits a very low propensity to form stable pairings. The composite primers, which contain them, make it possible to carry out multiplex amplifications with quantitative precision on the scale of a genome such as the human genome.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
Capturing probe for detecting human genome mutation load based on high-throughput sequencing and application thereof
PendingCN107488717AEfficient captureShort analysis timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHuman DNA sequencingSingle sample
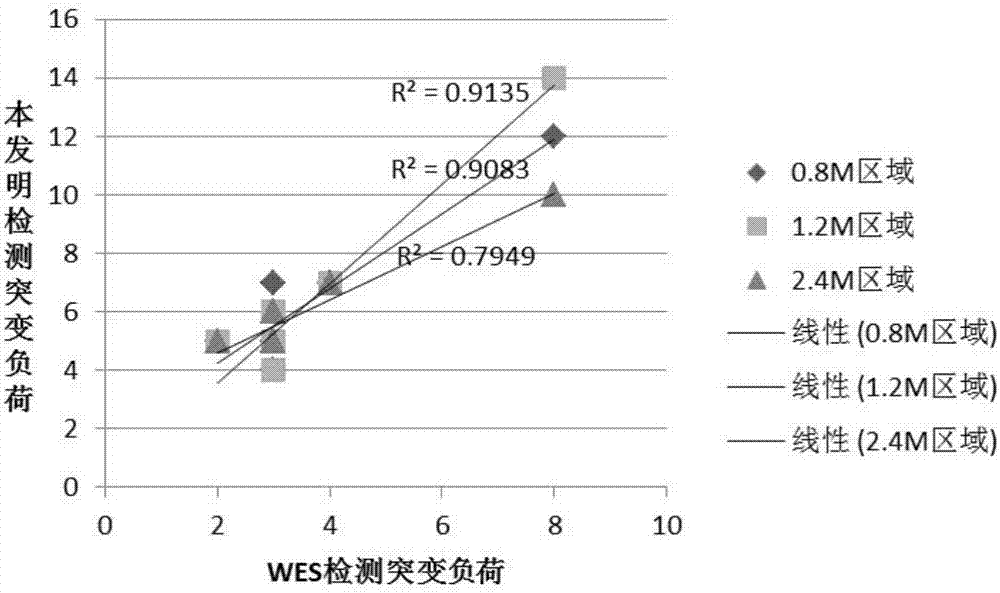
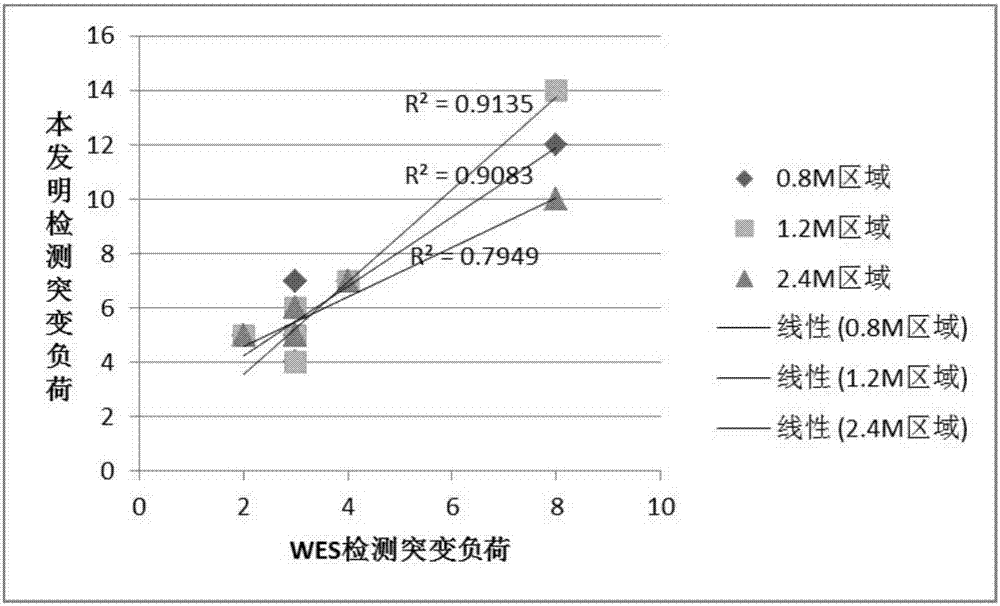
The invention relates to the field of gene detection, in particular to a capturing probe for detecting human genome mutation load based on high-throughput sequencing and application thereof. The capturing probe for detecting the human genome mutation load based on high-throughput sequencing, provided by the invention, comprises a capturing probe 1, a capturing probe 2 and a capturing probe 3; the sequences of the capturing probe 1 are shown as SEQ ID NO. 1-275; the sequences of the capturing probe 2 are shown as SEQ ID NO. 276-550; the sequences of the capturing probe 3 are shown as SEQ ID NO. 551-825; the probe designed and synthesized by the invention can capture an encoding exon area in a human genome target area and an exon and intron junction area, the nonspecific capture is reduced, and meanwhile, the hybrid temperature is uniform. As the capturing probe provided by the invention is adopted for capturing the human genome target area, the sequencing depth is significantly improved, so that mutation load test results are highly correlated with WES, the detection cost and the sequencing data volume are greatly reduced, and the single sample analysis time is shortened.
Owner:3D BIOMEDICINE SCI & TECH CO LTD
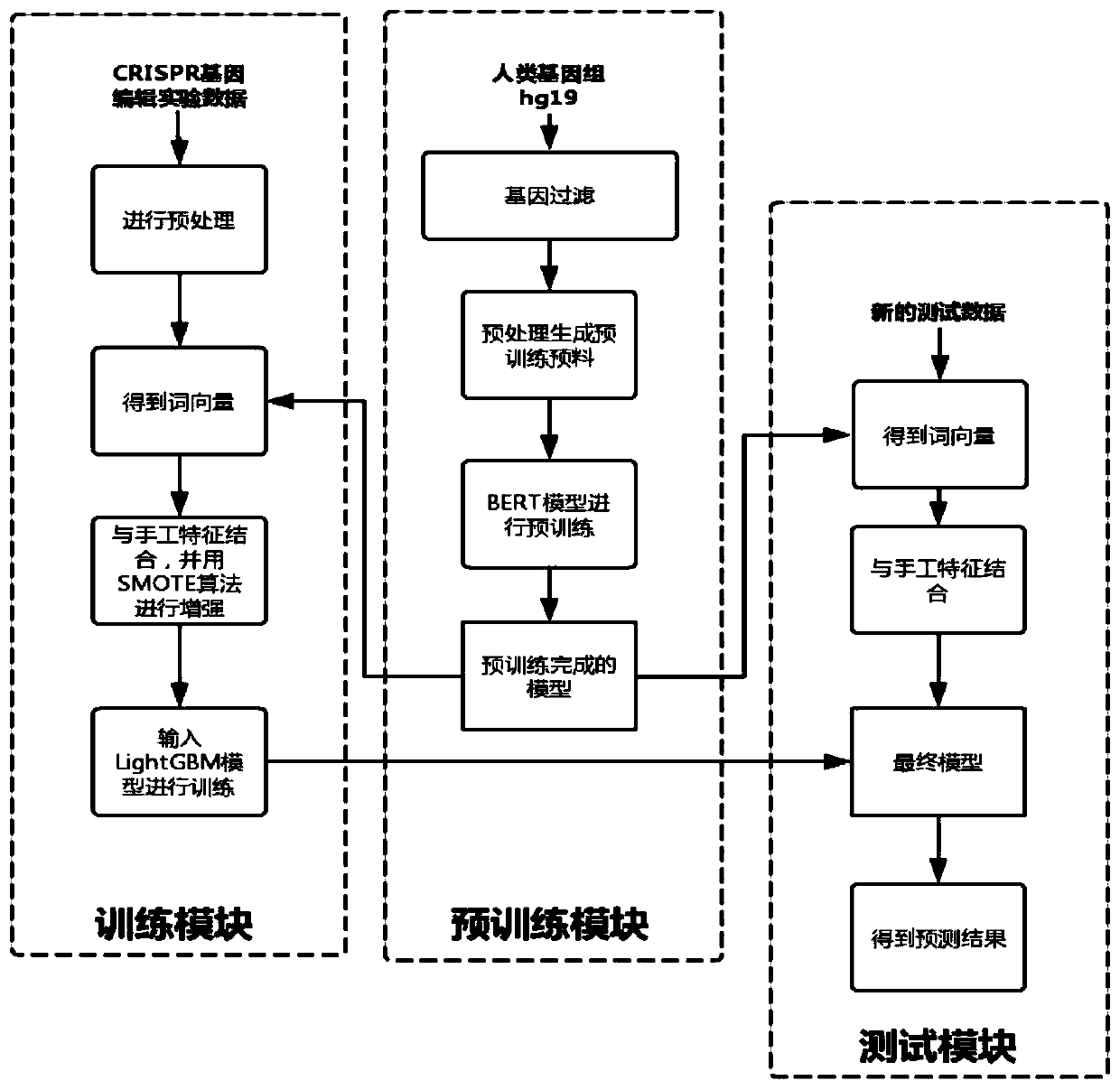
CRISPR off-target effect prediction method based on deep learning
ActiveCN111261223ASolve the imbalanceImprove accuracyBiostatisticsSequence analysisHuman DNA sequencingData imbalance
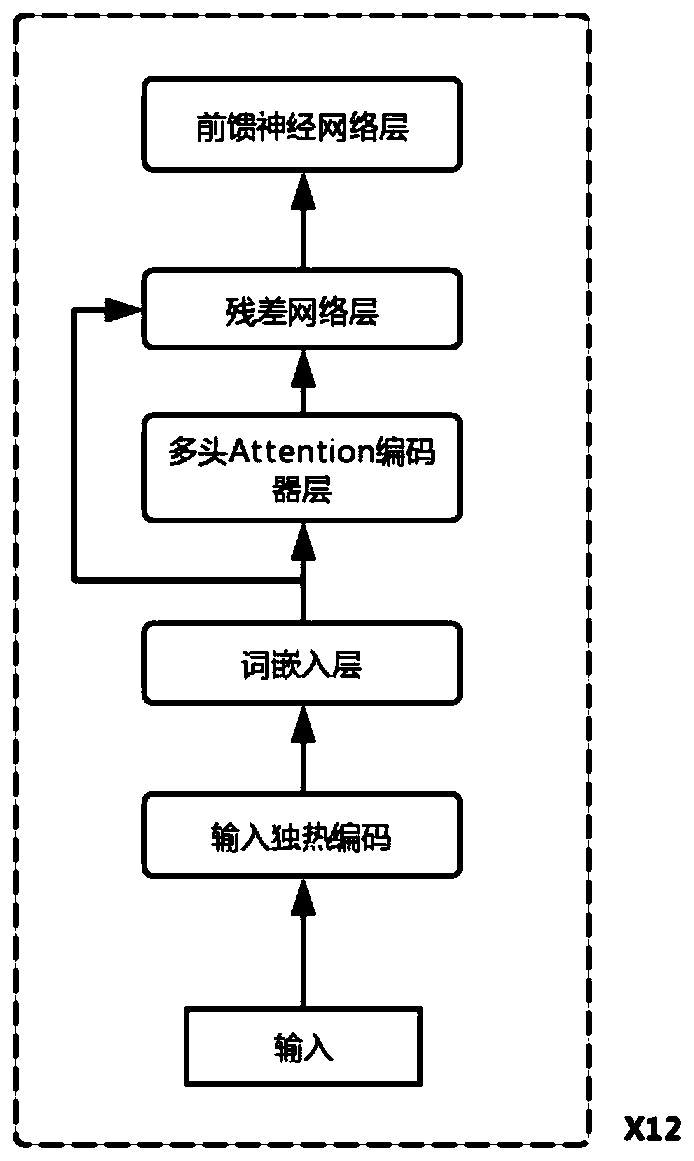
The invention belongs to the field of bioinformatics, and discloses a CRISPR off-target effect prediction method based on deep learning. According to the method, information of a human genome is utilized by using a BERT model, priori information of the genome is effectively utilized, the data is effectively reinforced, and obtained characteristics are input to a LightGBM method for training and predication. The problems of small data volume and data imbalance are solved, effective prediction of the CRISPR off-target effect is realized, and the CRISPR off-target effect prediction method has high popularization and application values.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method and kit for detecting mutational load of human genome based on high-throughput sequencing
PendingCN107338292AImprove consistencyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingGenome human
Owner:3D BIOMEDICINE SCI & TECH CO LTD
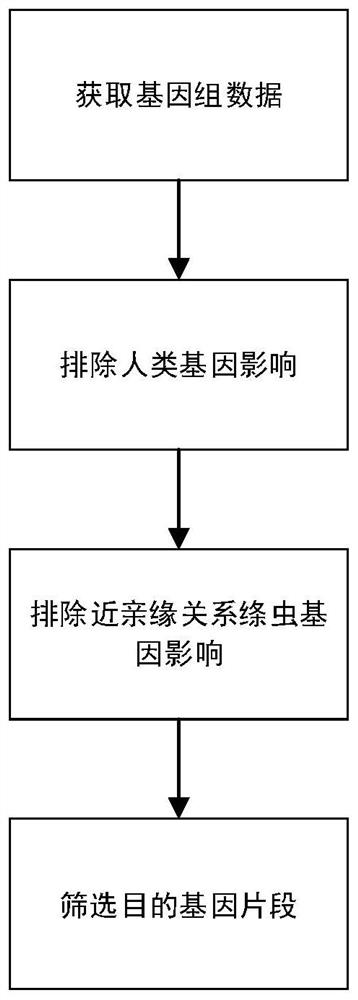
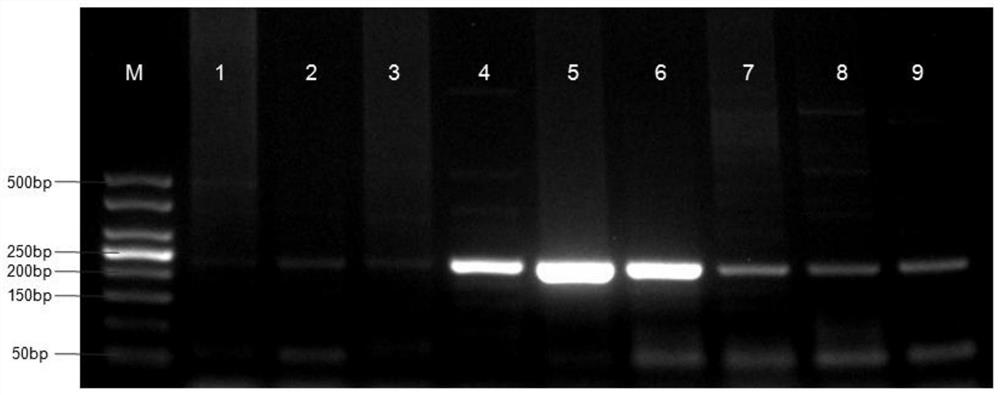
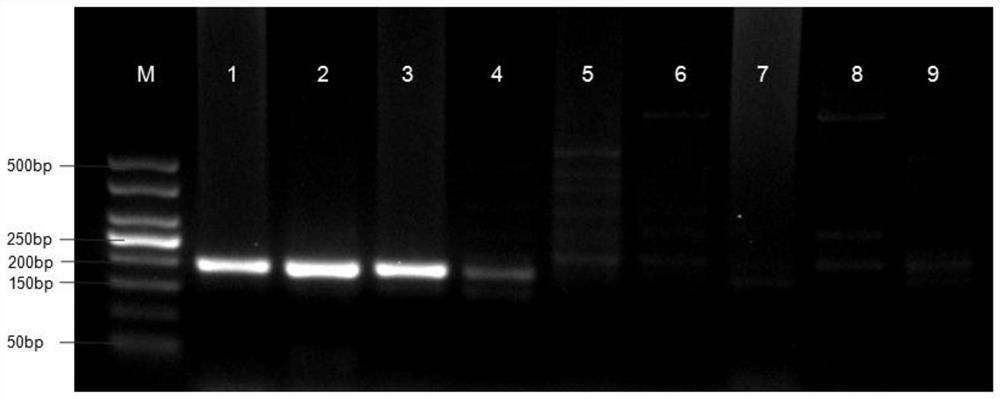
Liver echinococcus gene segment screening method, amplification primer and kit
PendingCN113355431AImprove accuracyImprove clinical outcomesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisHuman DNA sequencingEchinococcus multilocularis
The invention discloses a liver echinococcus gene segment screening method, an amplification primer and a kit.The screening method comprises the following steps: eliminating an influence of a human genome and a close genetic relationship tapeworm group genome from whole genomes of echinococcus granulosus and echinococcus multilocularis; and screening to obtain a third echinococcus granulosus gene segment, a third echinococcus multilocularis gene segment and a common gene segment, and designing three types of amplification primers by using three types of the gene segments respectively. A primer pair group for detecting echinococcosis of human tissues is obtained by further screening and a kit and a use method of the kit are provided based on the primer pair group. False positive results caused by human genes or close genetic relationship tapeworm genes existing in to-be-detected tissue DNA is avoided from the source, the to-be-detected DNA aiming at the primer during design is a human tissue sample, the false negative results in clinical detection are remarkably reduced, specific primers have higher accuracy and higher specificity, and clinical use effects of the primer pair and the kit are obviously enhanced.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
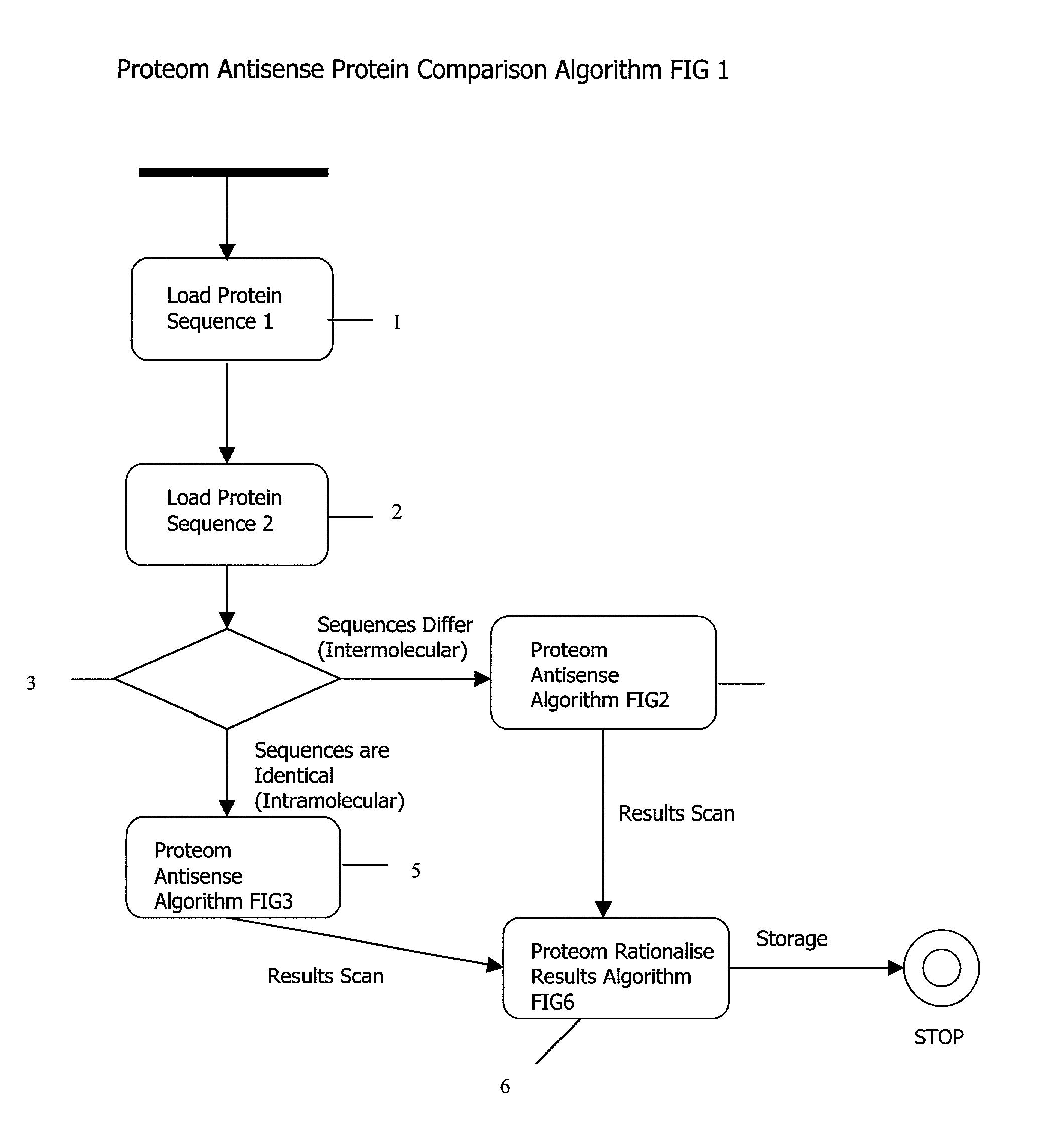
Complementary peptide ligands generated from the human genome
InactiveUS20030078374A1Reduce complexityEnhance drug designPeptide-nucleic acidsSugar derivativesHuman DNA sequencingGenome human
In the current invention the application of our novel informatics approach to the databases containing nucleotide and peptide sequences from the human genome generates the sequence of many peptides which form the basis of an innovative and novel approach to developing new therapeutic agents. This invention claims the use of specific complementary peptides to the proteins encoded in the human genome as reagents and drugs for drug discovery programmes.
Owner:PROTEOM
Method and System for Identifying Clinical Phenotypes in Whole Genome DNA Sequence Data
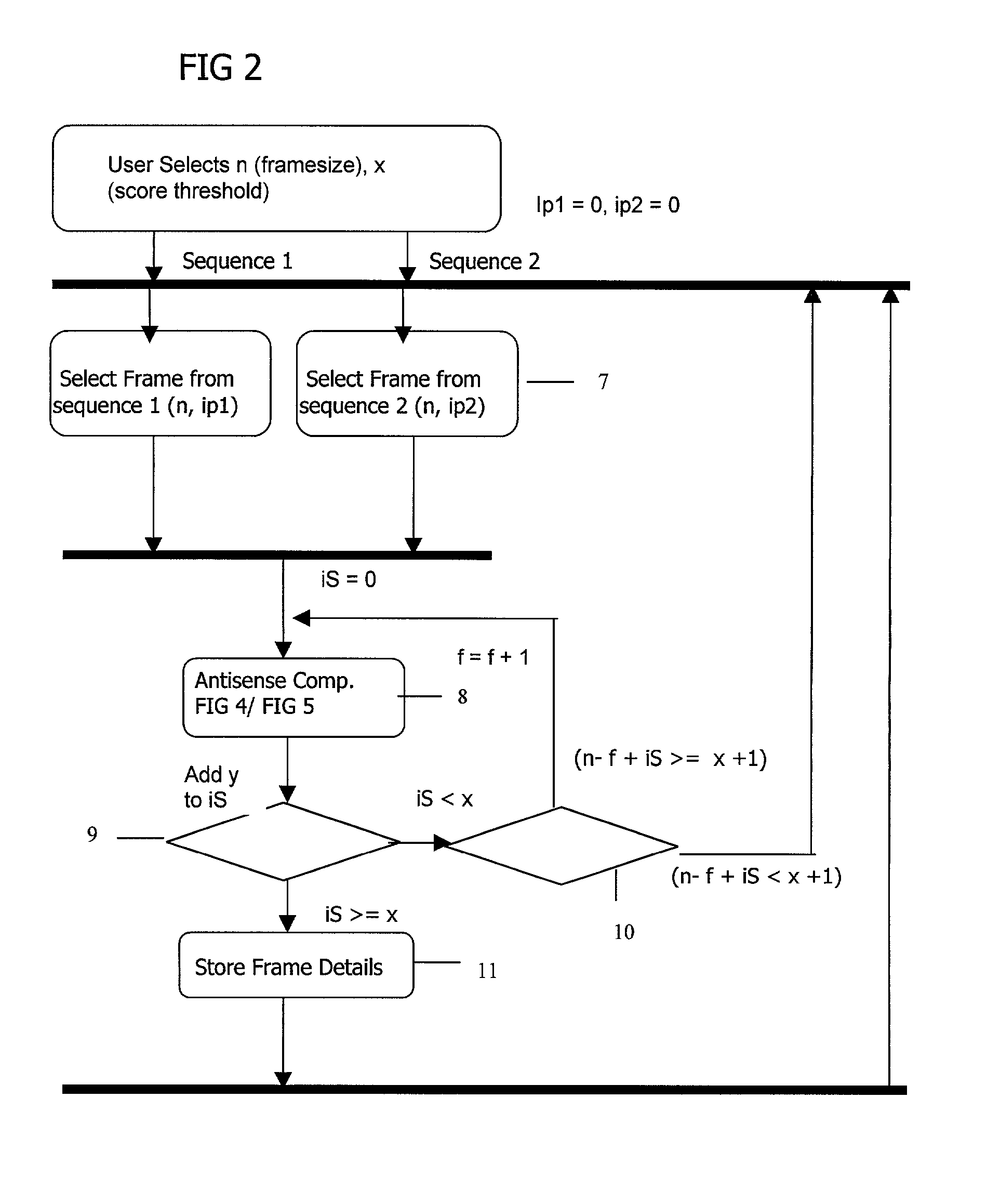
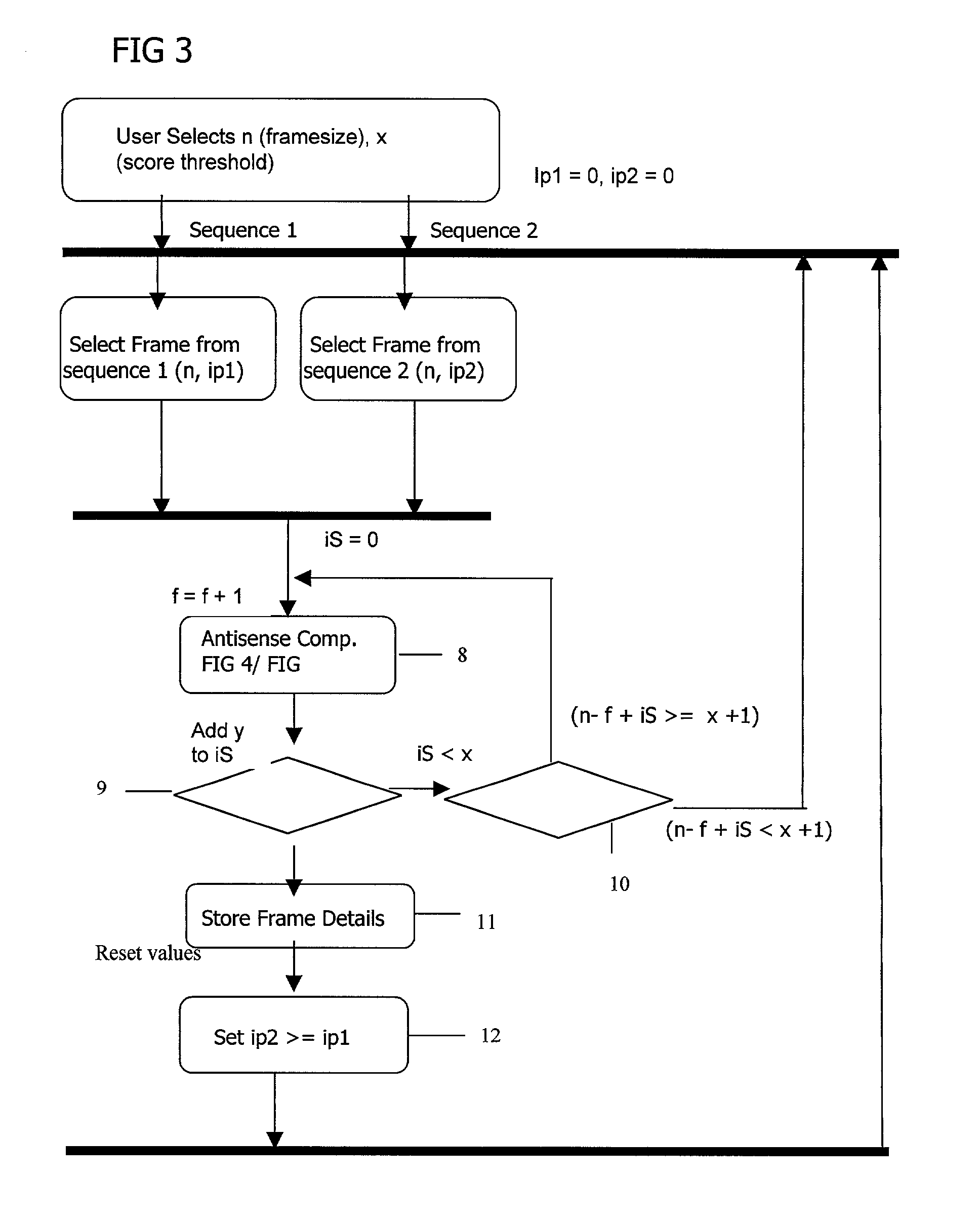
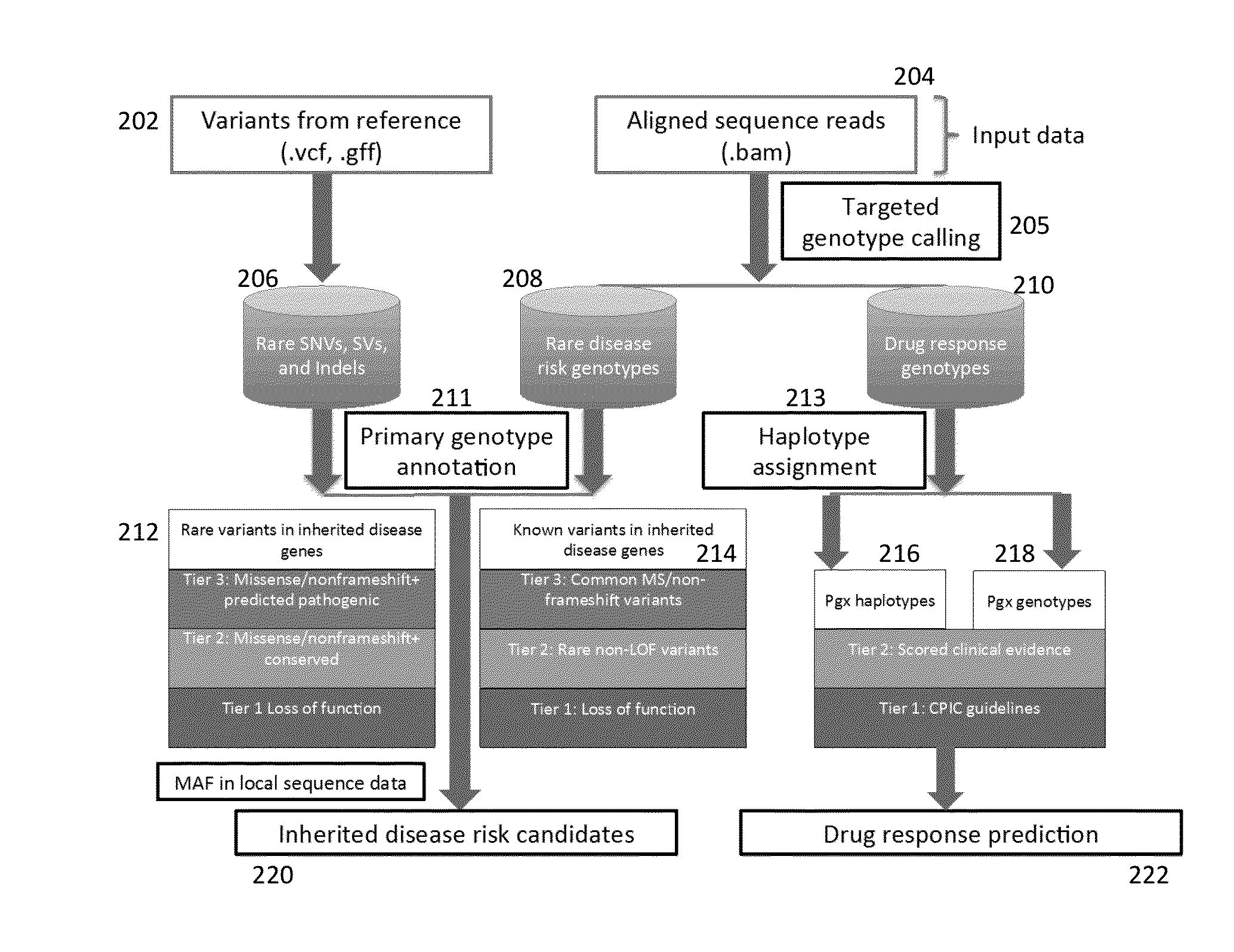
High throughput sequencing has facilitated a precipitous drop in the cost of whole genome human DNA sequencing, prompting predictions of a revolution in medicine via personalization of diagnostic and therapeutic strategies to individual genetics. Disclosed is a comprehensive series of methods for identification of genetic variants and medical genotypes, phasing genetic data and using Mendelian inheritance for quality control, and providing predictive genetic information about risk for rare disease phenotypes and response to pharmacological therapy in single individuals and father-mother-child trios.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Regulation of fibroblastic growth factor-2 (FGF-2) gene expression in living cells with the application of specific and selective electric and electromagnetic fields
InactiveUS7981611B2ElectrotherapyMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingElectromagnetic field
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Novel human polynucleotides and polypeptides encoded thereby
InactiveUS20020110809A1Microbiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsNucleotideTRAP Sequence
Novel human polynucleotides are disclosed that correspond to human gene trapped sequences, or GTSs. The disclosed GTSs are useful for gene discovery and as markers for, inter alia, gene expression analysis, identifying and mapping the coding regions of the mammalian, and particularly human, genome, forensic analysis, and determining the genetic basis of human disease.
Owner:LEXICON GENETICS INC (US)
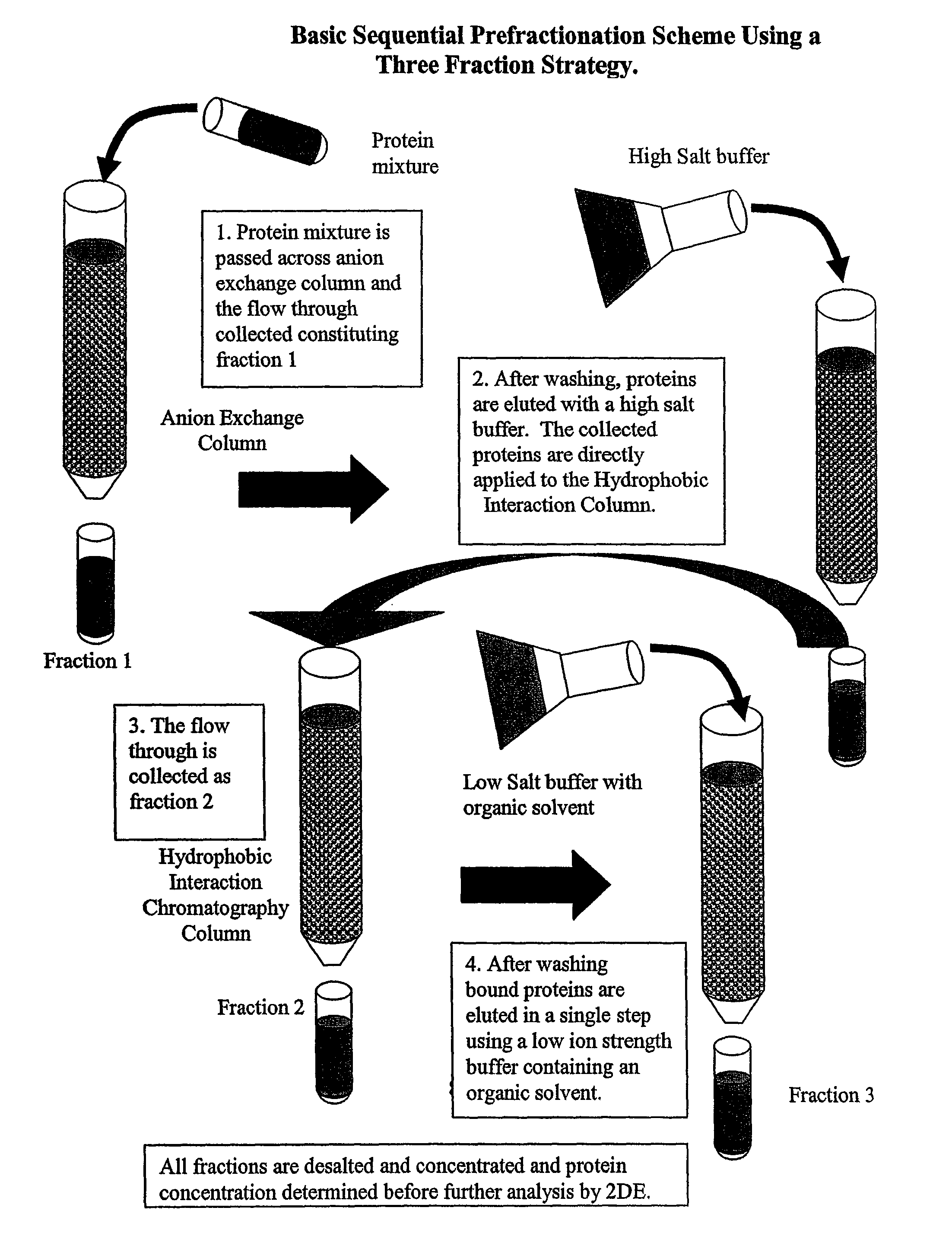
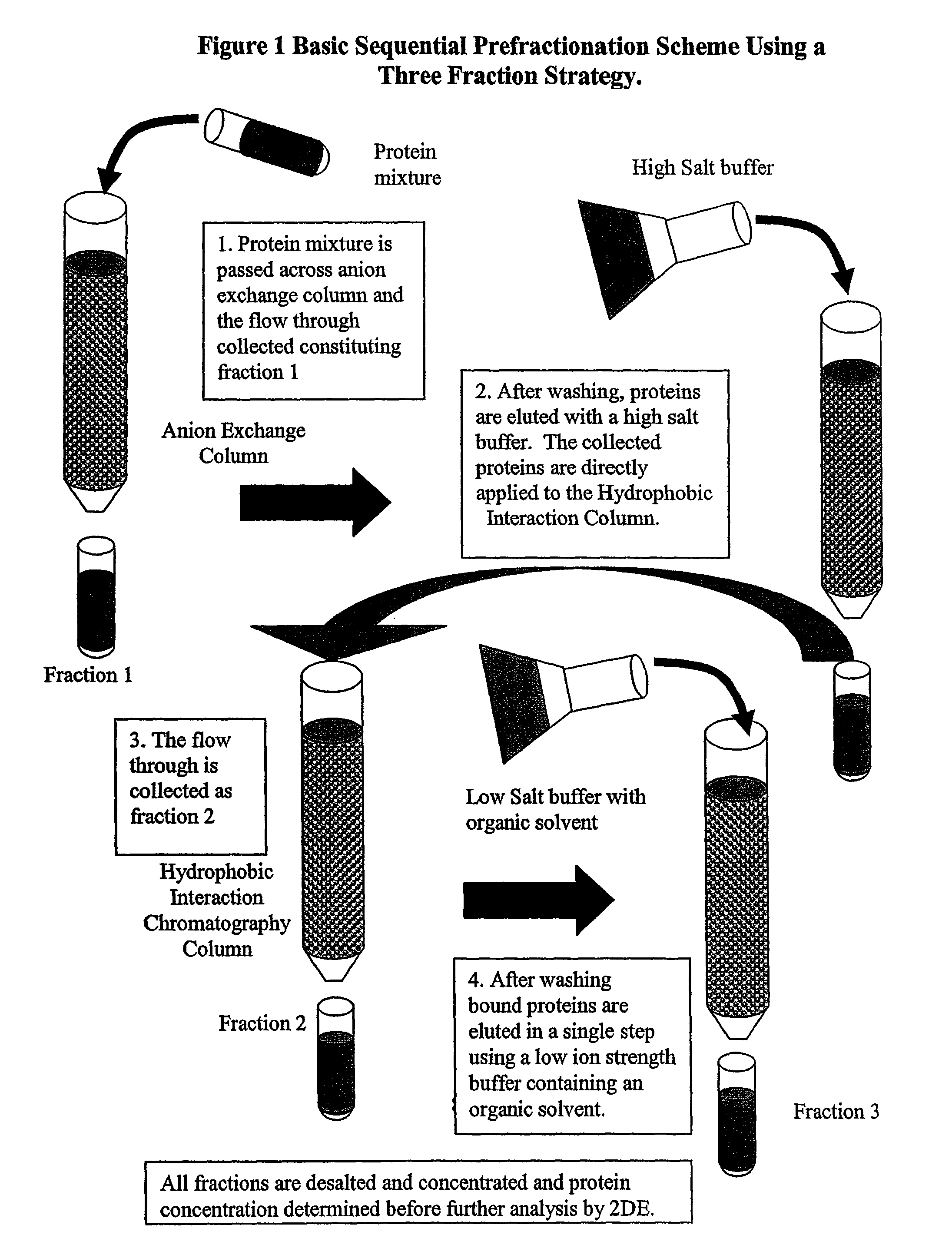
Procedure for the fractionation of proteins by using sequential ion exchange and hydrophobic interaction chromatography as prefractionation steps before analysis by two dimensional electrophoresis
InactiveUS7795405B2Reduce incidenceSimplifying chromatographyElectrolysis componentsPeptide/protein ingredientsHuman DNA sequencingGenome human
After the sequencing of the human genome, great interest has developed in trying to discern the complementary proteome of humans and other species. The present disclosure provides devices, systems, and methods for proteomic fractionation that may increase the number of protein spots visualized by 2DE analysis, and may allow enrichment of proteins normally not detectable by standard 2DE analysis. According to some embodiments of the disclosure, devices, systems, and methods of the disclosure relate to fractionating a proteome on the basis of surface charge, hydrophobicity, isoelectric point and / or size.
Owner:GUILD ASSOCS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com