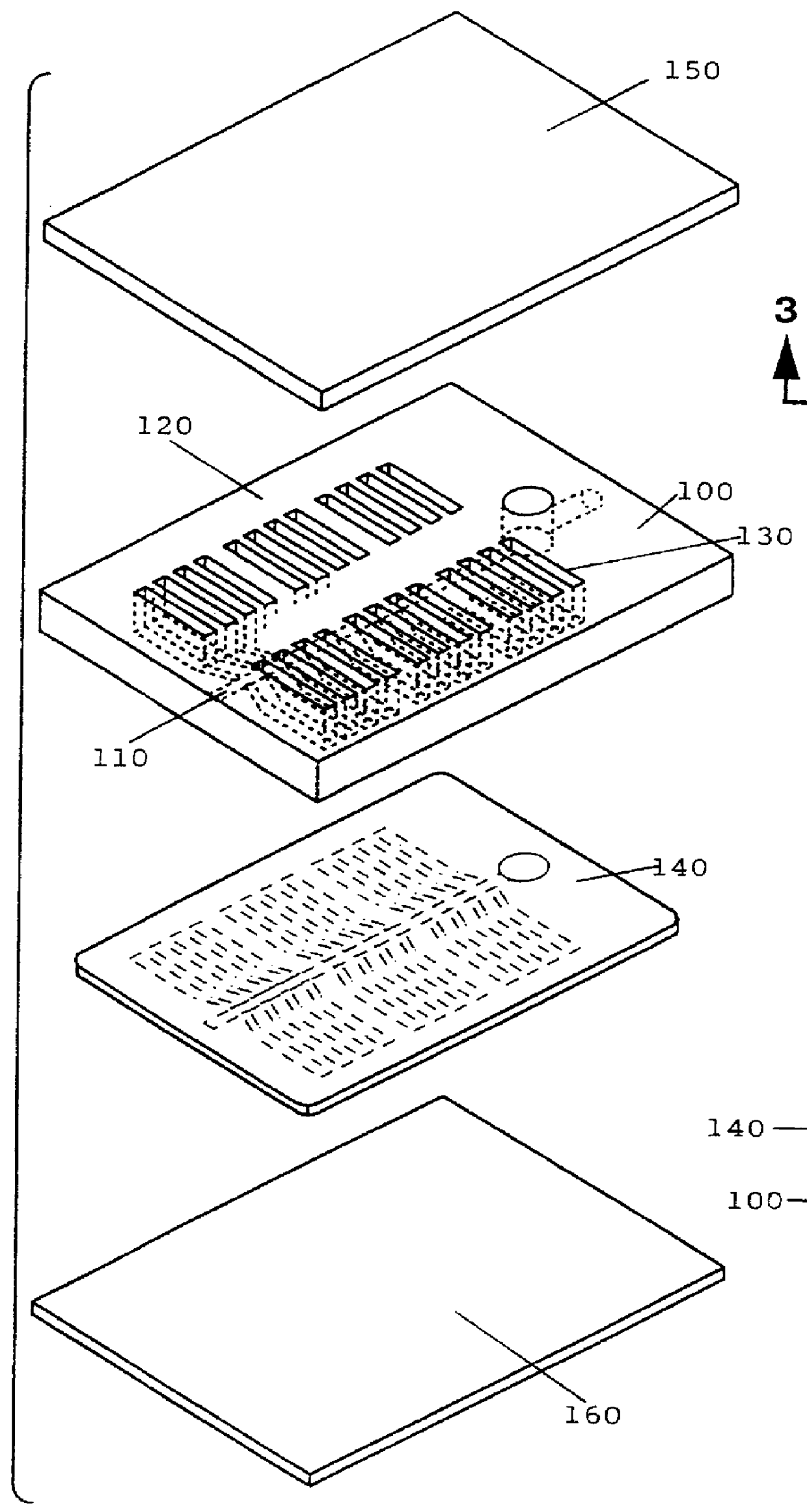
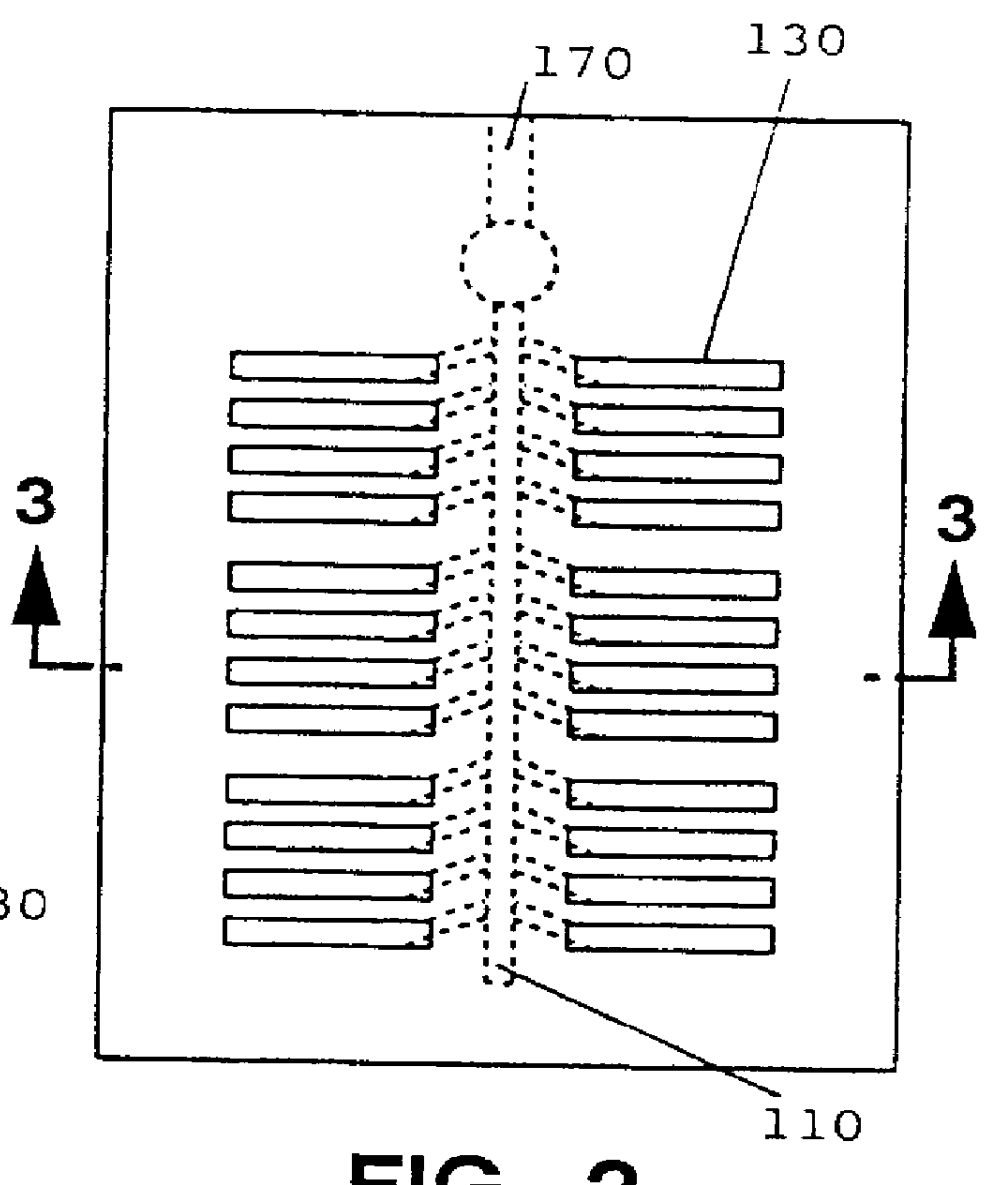
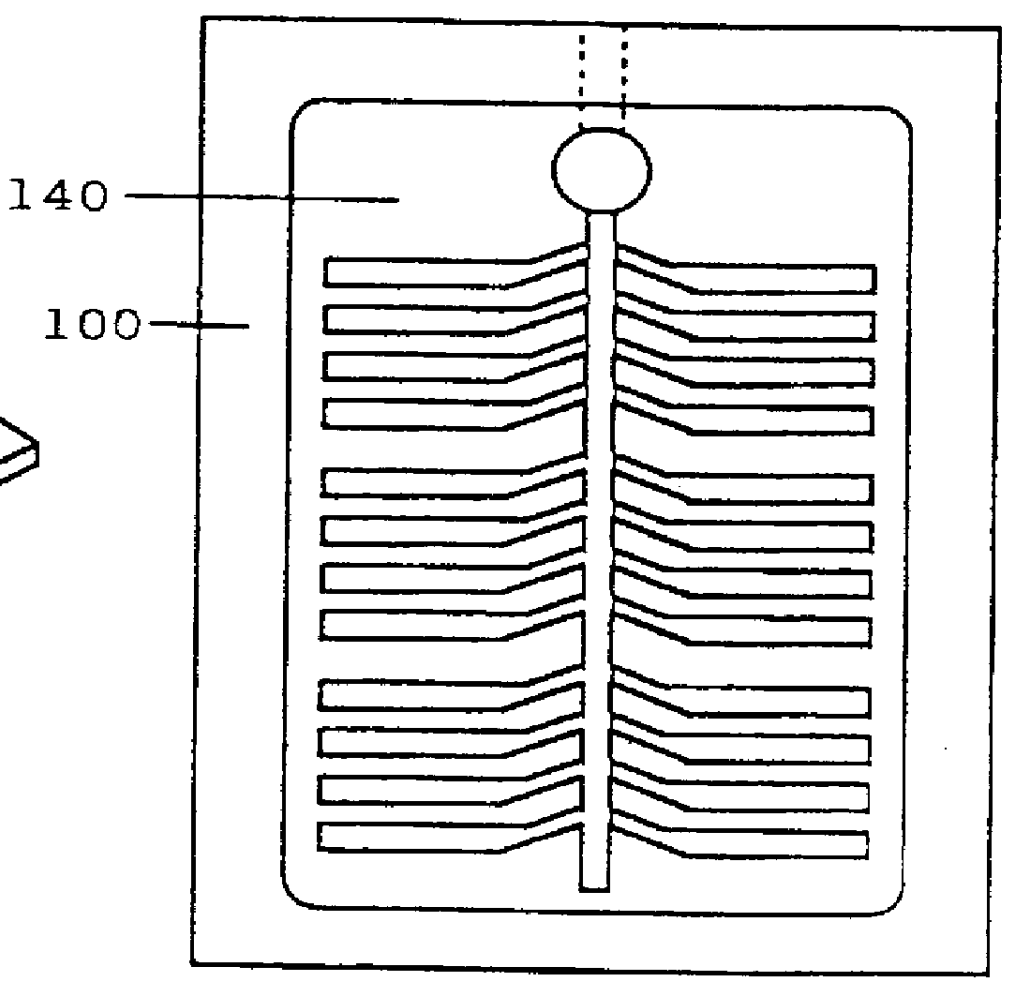
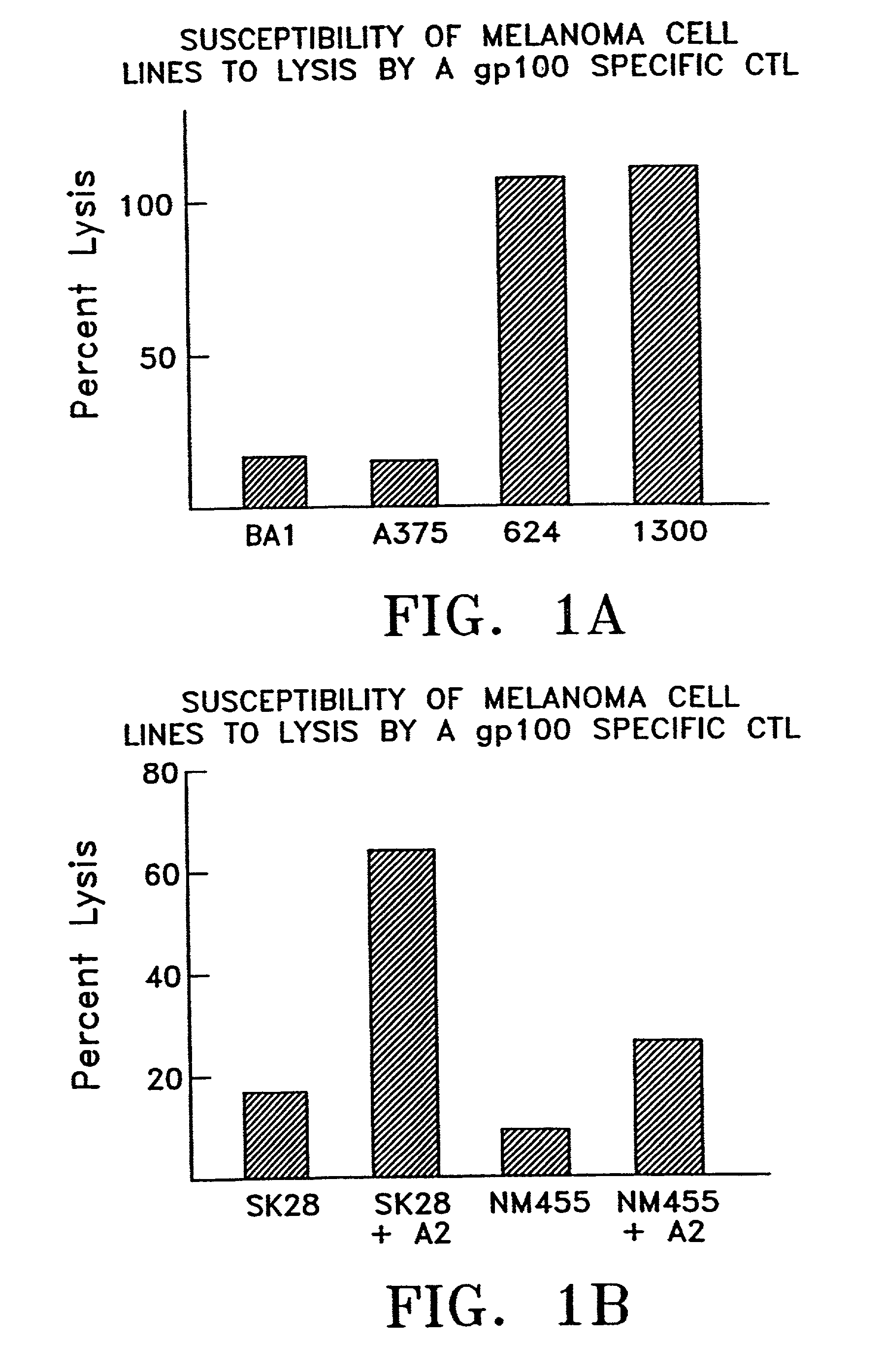
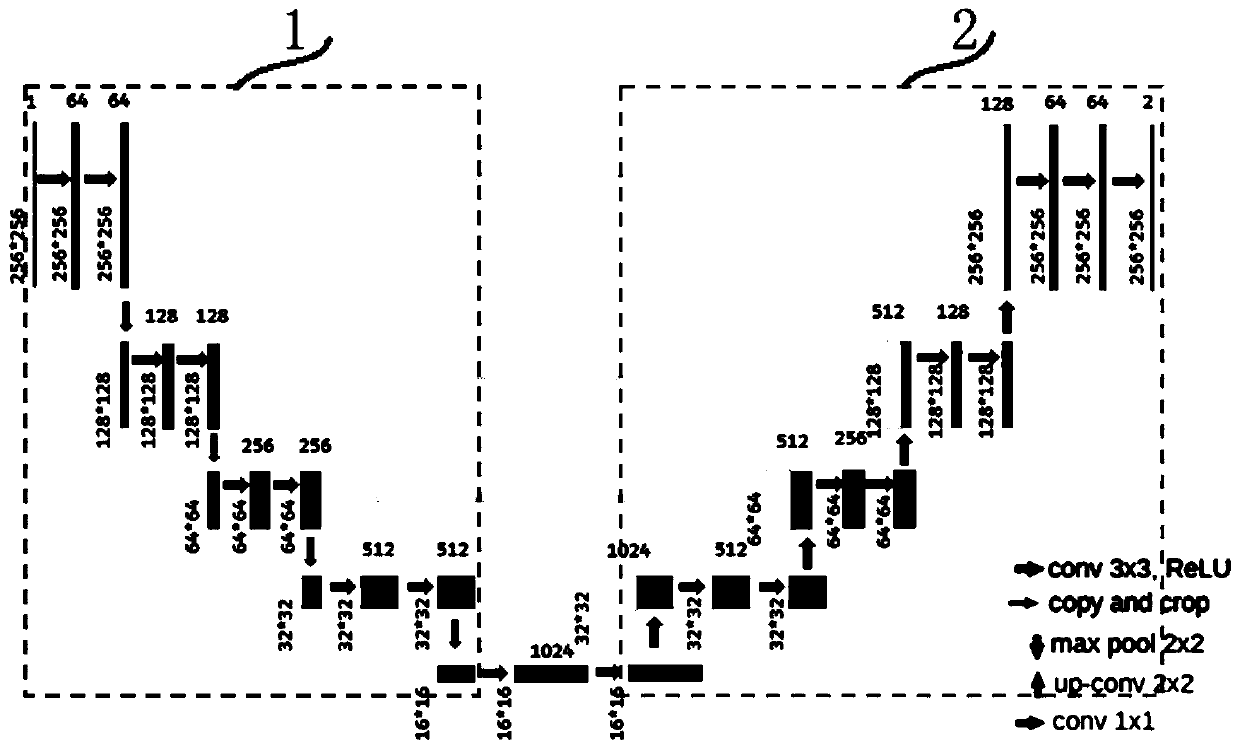
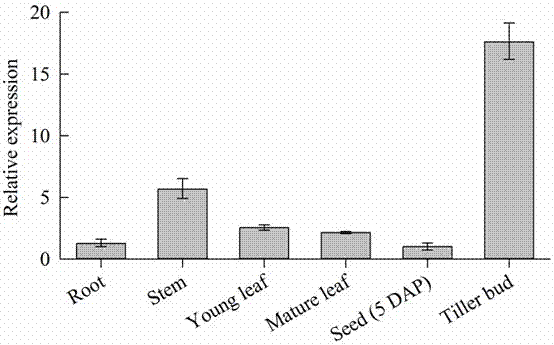
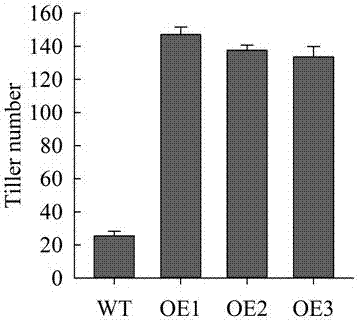
Patents
Literature
95 results about "Phenotypic analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
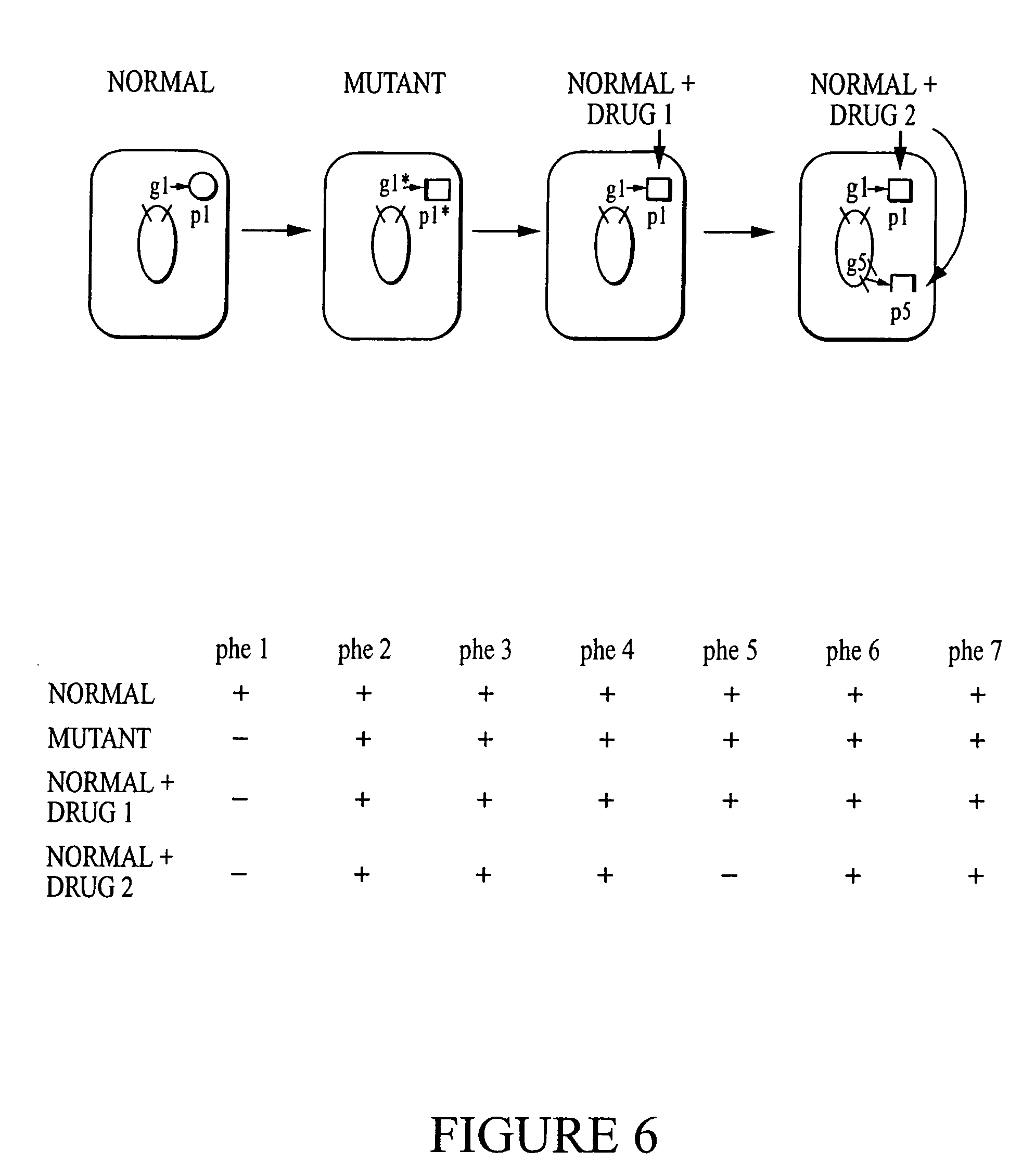
View phenotypic analysis data. Growth curves. A primary phenotype we assay is simply the ability of a mutant strain to grow in either minimal media or Luria Broth. Mutant strains are diluted into appropriate media contained in a 96-well microtiter plate, grown at 37 with shaking using a plate reader (SpectroMax).
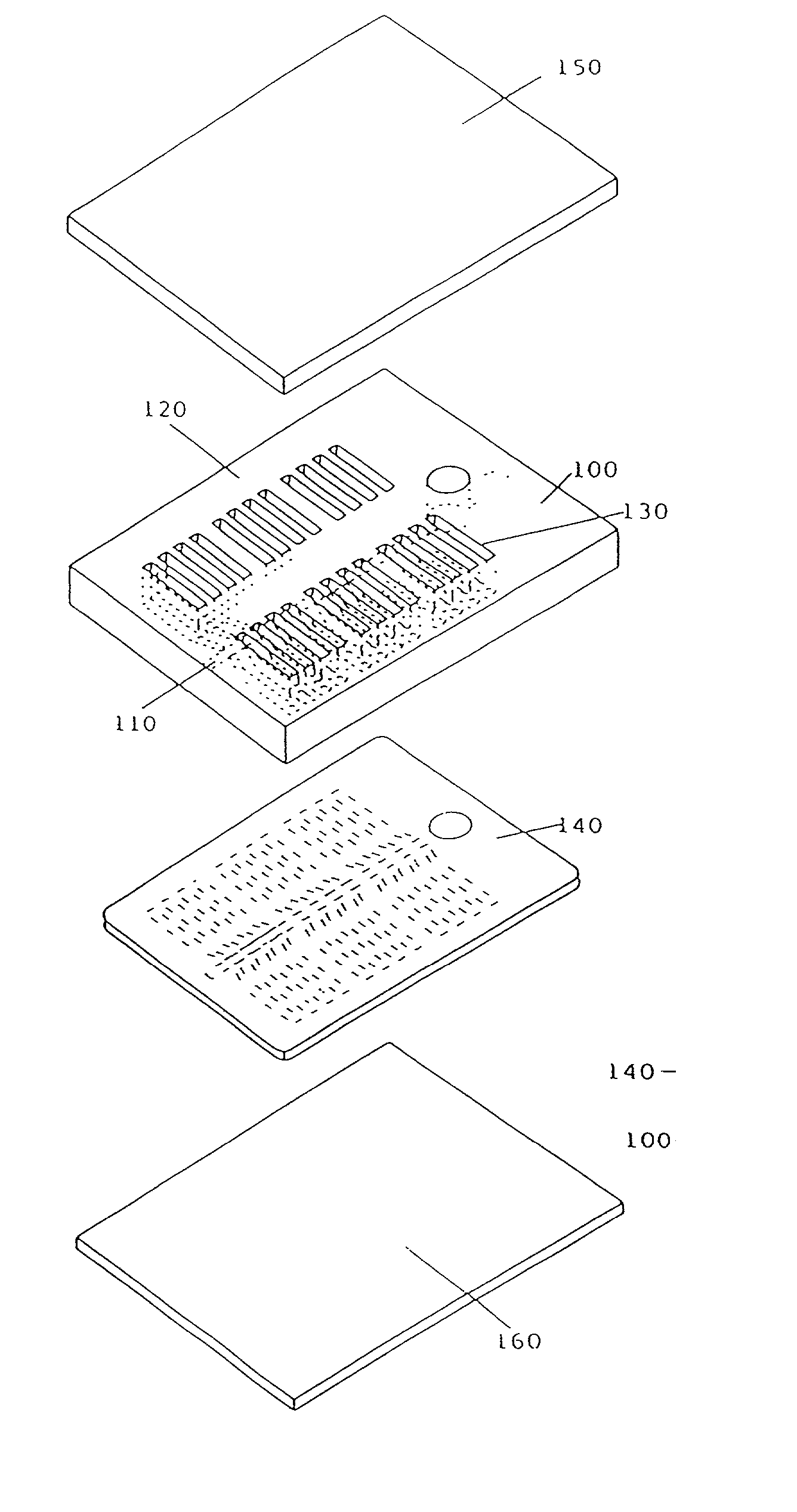
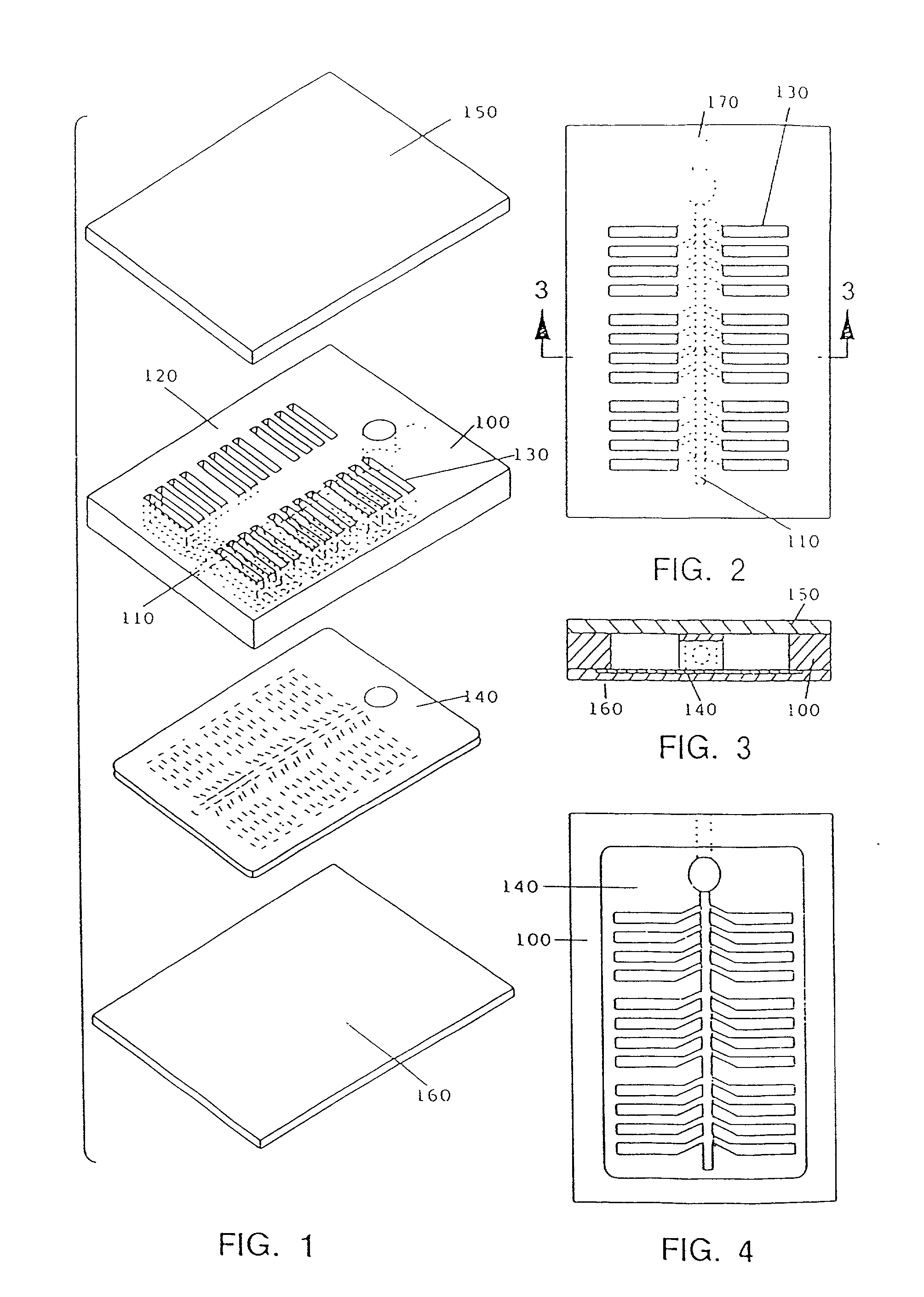
Comparative phenotype analysis of two or more microorganisms using a plurality of substrates within a multiwell testing device
InactiveUS6046021ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEscherichia coliPlant cell
The present invention relates to growing and testing microorganisms in a multitest format which utilizes a gel forming matrix for the rapid screening of clinical and environmental cultures. The present invention is suited for the characterization of commonly encountered microorganisms (e.g., E. coli, S. aureus, etc.), as well as commercially and industrially important organisms from various and diverse environments (e.g., the present invention is particularly suited for the growth and characterization of the actinomycetes and fungi). The present invention is also particularly suited for comparative analysis of phenotypic differences between cell types, including strains of microorganisms that have been designated as the same genus and species, as well as other cell types (e.g., mammalian, insect, and plant cells).
Owner:BIOLOG
Genes differentially expressed in cancer cells to design cancer vaccines
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Comparative phenotype analysis of two or more microorganisms using a plurality of substrates within a multiwell device
InactiveUS6387651B1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEscherichia coliPlant cell
The present invention relates to growing and testing microorganisms in a multitest format which utilizes a gel forming matrix for the rapid screening of clinical and environmental cultures. The present invention is suited for the characterization of commonly encountered microorganisms (e.g., E. coli, S. aureus, etc.), as well as commercially and industrially important organisms from various and diverse environments (e.g., the present invention is particularly suited for the growth and characterization of the actinomycetes and fungi). The present invention is also particularly suited for comparative analysis of phenotypic differences between cell types, including strains of microorganisms that have been designated as the same genus and species, as well as other cell types (e.g., mammalian, insect, and plant cells).
Owner:BIOLOG
Comparative phenotype analysis of cells, including testing of biologically active compounds
InactiveUS20030162164A1Easy to atomizeReduce chanceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTest organismPlant cell
The present invention relates to growing and testing any cell type in a multitest format. The present invention is suited for the characterization of microorganisms, as well as animal and plant cells. The present invention is also particularly suited for analysis of phenotypic differences between strains of organisms, including cultures that have been designated as the same genus and species. The present invention is also suited for the analysis of phenotypic differences between cell lines. In some embodiments, a gel forming matrix is used. The present invention provides methods and compositions for the phenotypic analysis and comparison of eukaryotic, as well as prokaryotic cells. The present invention further provides novel methods and compositions for testing the effect(s) of biologically active chemicals on various cells.
Owner:BIOLOG
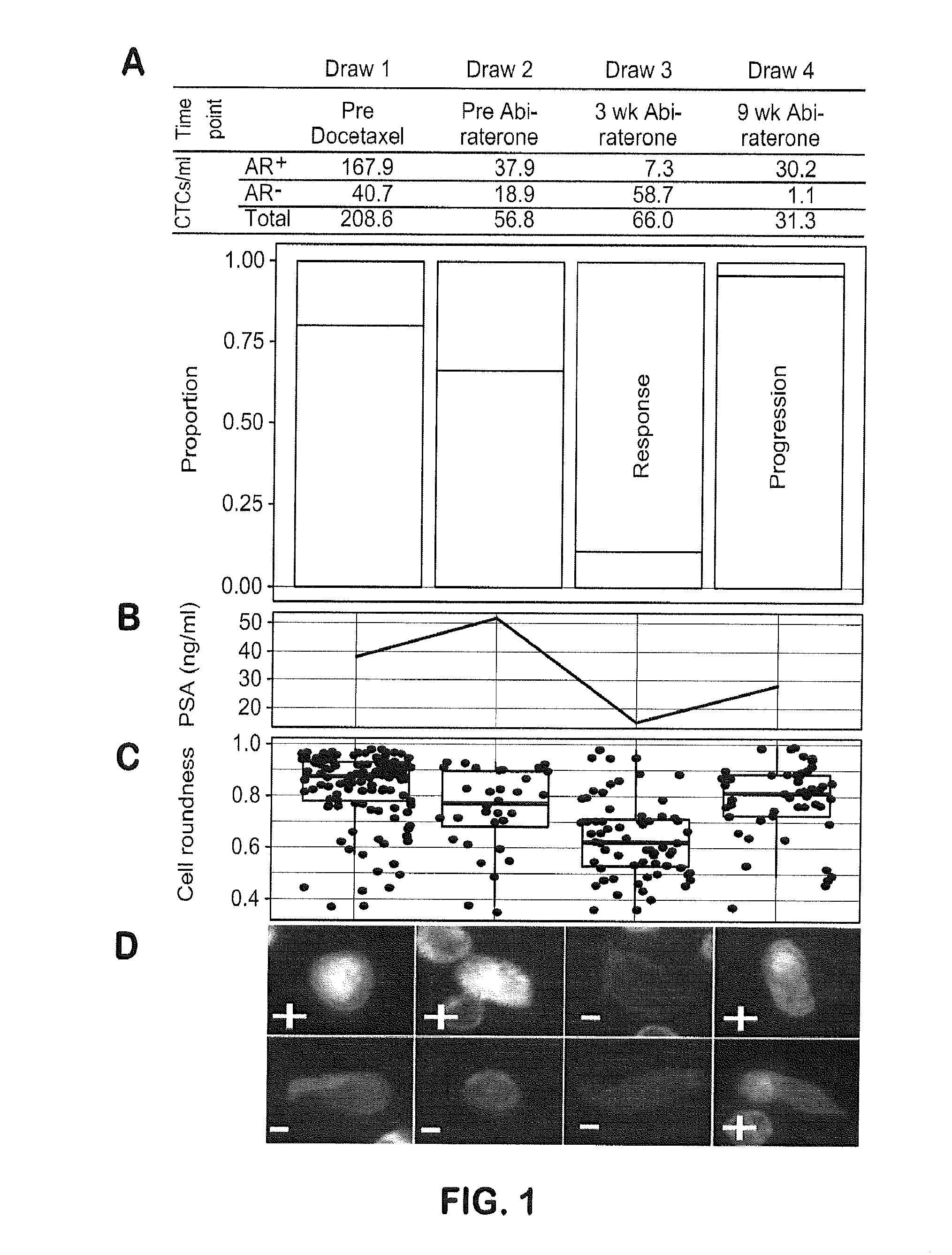
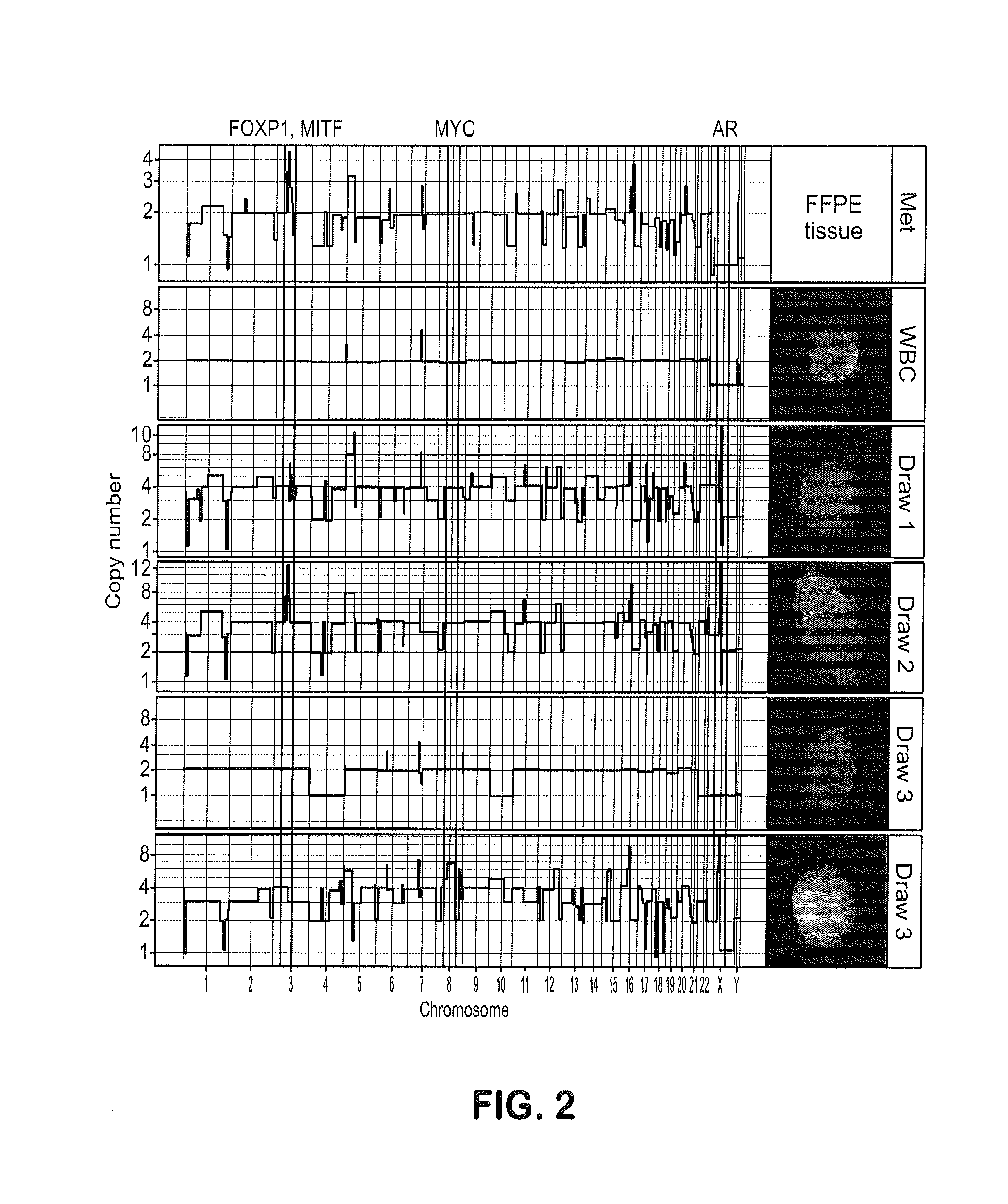
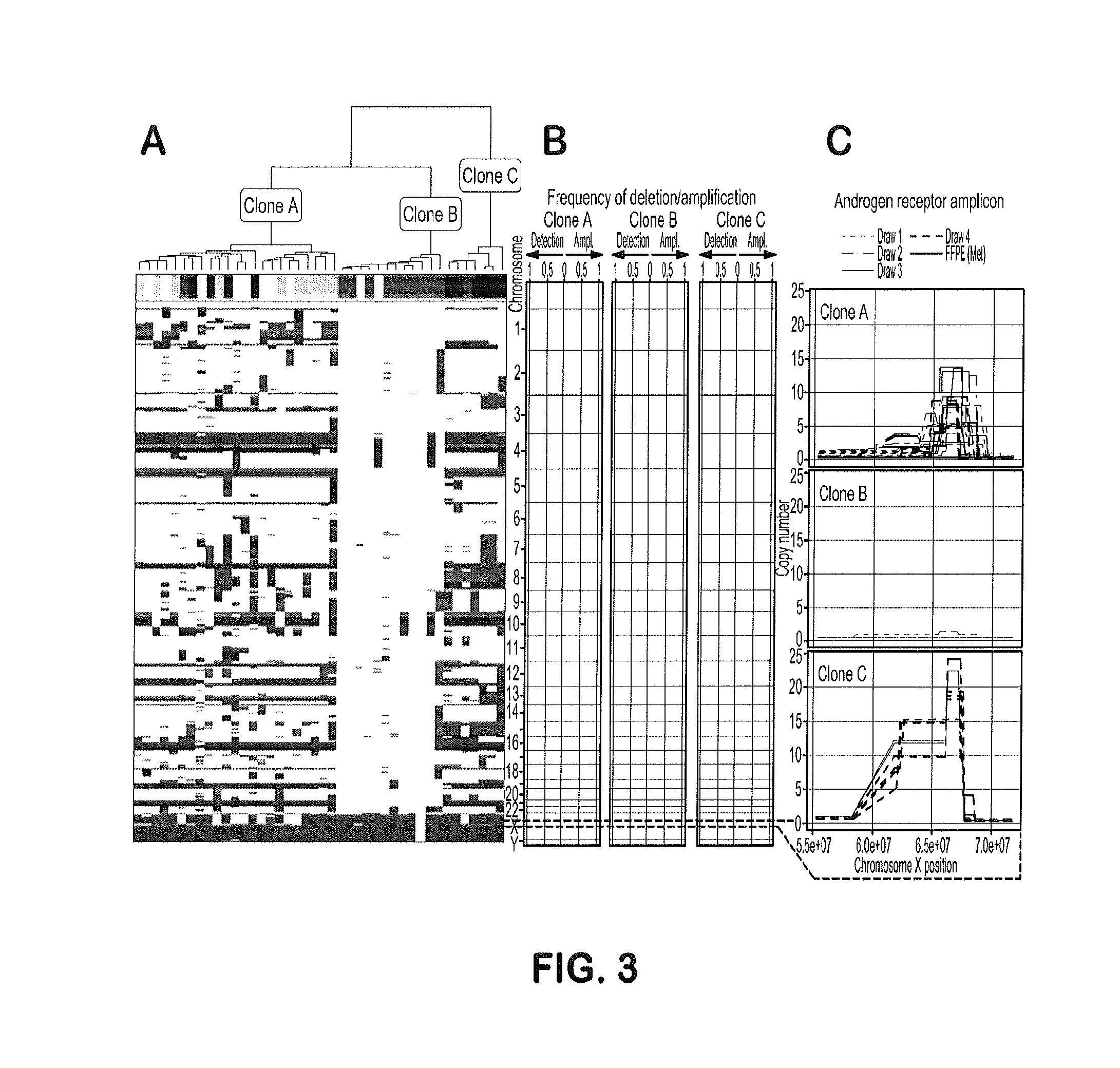
Genotypic and Phenotypic Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells to Monitor Tumor Evolution in Prostate Cancer Patients
The present invention provides methods for predicting response to a hormone-directed therapy or chemotherapy in a prostate cancer (PCa) patient comprising (a) performing a direct analysis comprising immunofluorescent staining and morphological characterization of nucleated cells in a blood sample obtained from the patient to identify and enumerate circulating tumor cells (CTC); (b) individually characterizing genotypic, morphometric and protein expression parameters to generate a profile for each of the CTCs, and (c) predicting response to hormone-directed therapy in the prostate cancer PCa patient based on said profile. In some embodiments, the methods comprise repeating steps (a) through (c) at one or more timepoints after initial diagnosis of prostate cancer to sequentially monitor said genotypic, morphometric and protein expression parameters.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC +1
Analysis of single cell mechanical phenotyping for metastatic detection
The present invention relates to a method and system for analyzing mechanical signatures of a plurality of cells for metastatic detection. Specifically, a data set characterized by at least one metric (such as Brillouin frequency shift and / or Brillouin linewidth) representing a cell mechanical signature is acquired for the plurality of cells by using a label-free Brillouin spectroscopy. A merit function is calculated based on one or more statistical characteristics of the data set, such as sensitivity and specificity. Then, the plurality of cells can be classified to detect metastatic cells based on mechanical signatures provided by the data set and an optimal metric value delivering maximum to the merit function.
Owner:CANON USA
Microfluid system used for detecting circulating tumor cells (CTCs) of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and application thereof
The invention discloses a microfluid system used for detecting CTCs of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. The microfluid system is prepared through the following steps: 1, preparation of a microfluid pipeline system which is divided into two or more parallel microfluid channels from an inlet, wherein the microfluid channels are provided with a plurality of fishbone structures; 2, etching of a silicon nanowire substrate; 3, surface modification and biotin bio-functionalization of silicon nanowires; and 4, modification of the silicon nanowire substrate and assembling of a PDMS microfluid chip. In use of the system, cells of a to-be-detected sample and 200 [mu]L of a PBS solution of biotin-modified p-EpCAM and p-cKit are subjected to co-incubation for 1 h, and then a co-incubation product is injected into the microfluid system for detection. The microfluid system provided by the invention can recognize and bind to CTCs with extremely low content, and is applicable to traditional immunofluorescence dyeing; obtained detection results and phenotypic analysis results can be subjected to further specific release; so purification of CTCs is realized, and the purity of CTCs is improved so as to meet requirements of gene detection limits.
Owner:无锡准因生物科技有限公司
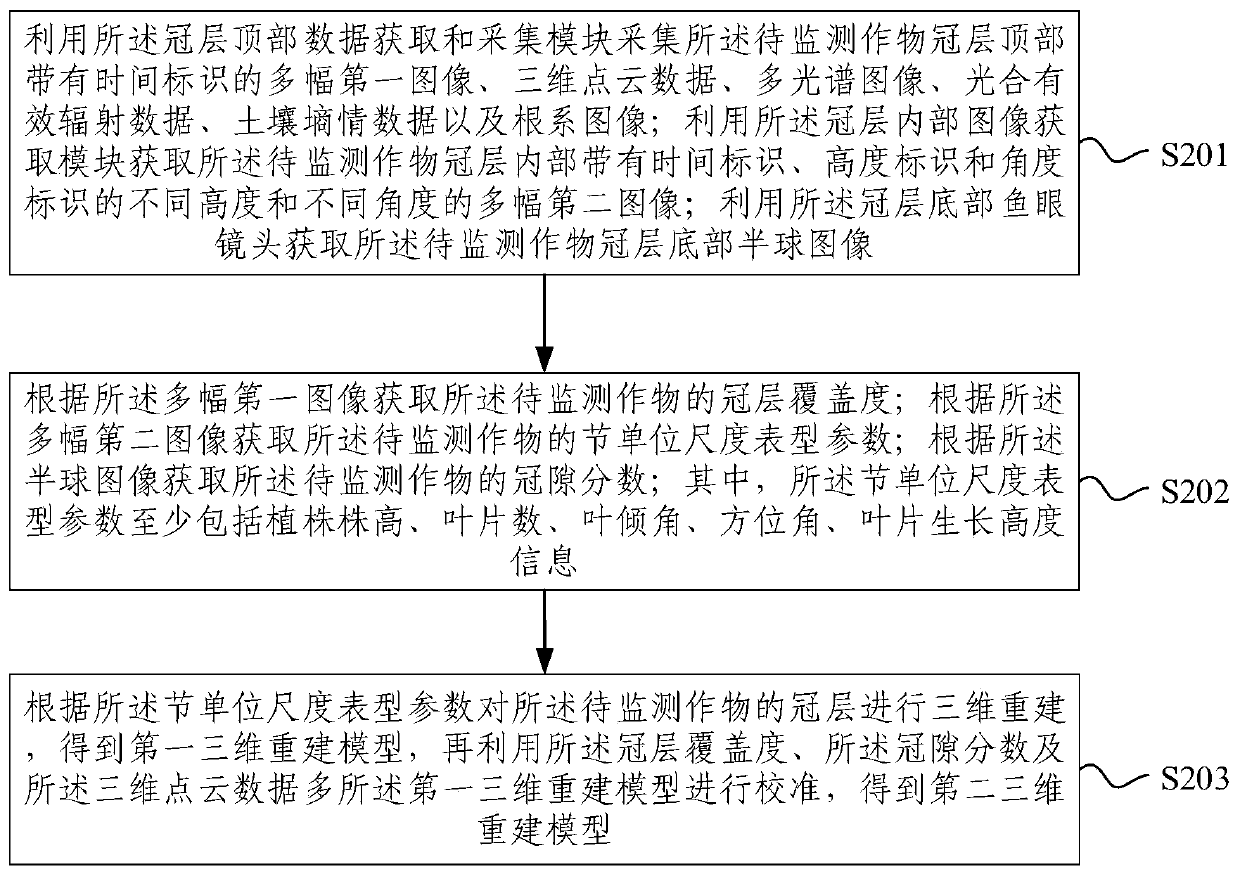
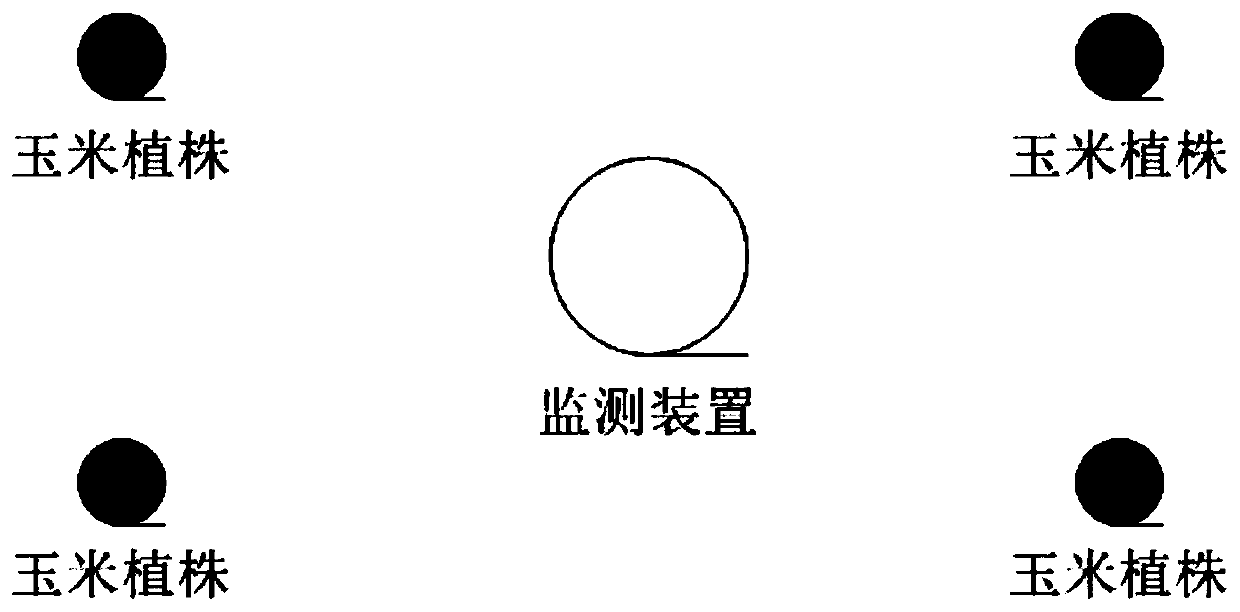
Crop canopy in-situ growth phenotype monitoring device and three-dimensional reconstruction method
PendingCN110046613AAccurate growth phenotype monitoringHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognition3D modellingFisheye lensData acquisition
The embodiment of the invention provides a crop canopy in-situ growth phenotype monitoring device and a three-dimensional reconstruction method. Through a data acquisition and collection module arranged on a canopy top, an image acquisition module arranged in a canopy, and a fisheye lens arranged on a canopy bottom, the morphological structure data of the top, the interior and the bottom of the canopy of the crop to be detected can be obtained, and the height and the angle of the image obtaining module in the canopy can be adjusted, so that the morphological structure data in the canopy are richer, and finally, the growth monitoring of the canopy of the crop to be monitored is more accurate and overall, and the universality is very good. The canopy growth monitoring device is used for obtaining the morphological structure data of the top, the interior and the bottom of the canopy, the morphological structure data are used for phenotypic analysis and three-dimensional reconstruction after certain pretreatment, the workload is small, the efficiency is high, and the obtained three-dimensional reconstruction model is high in precision.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT FOR INFORMATION TECH & AGRI
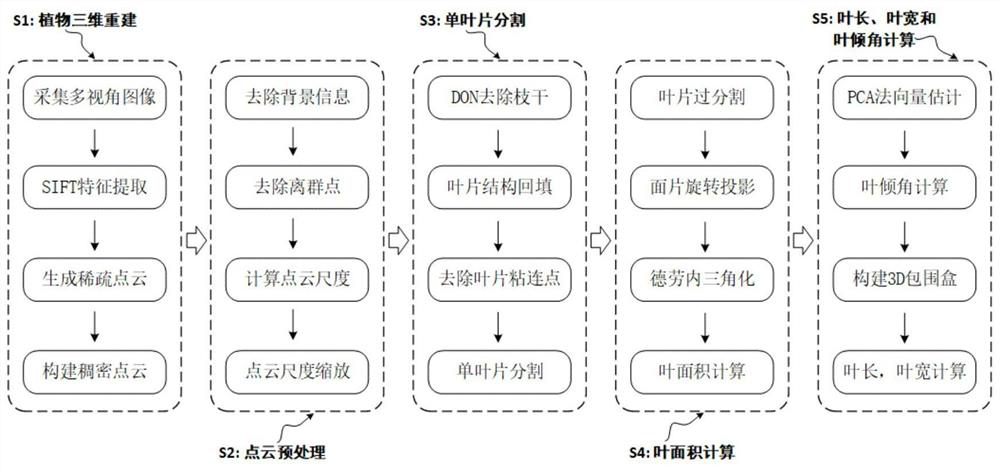
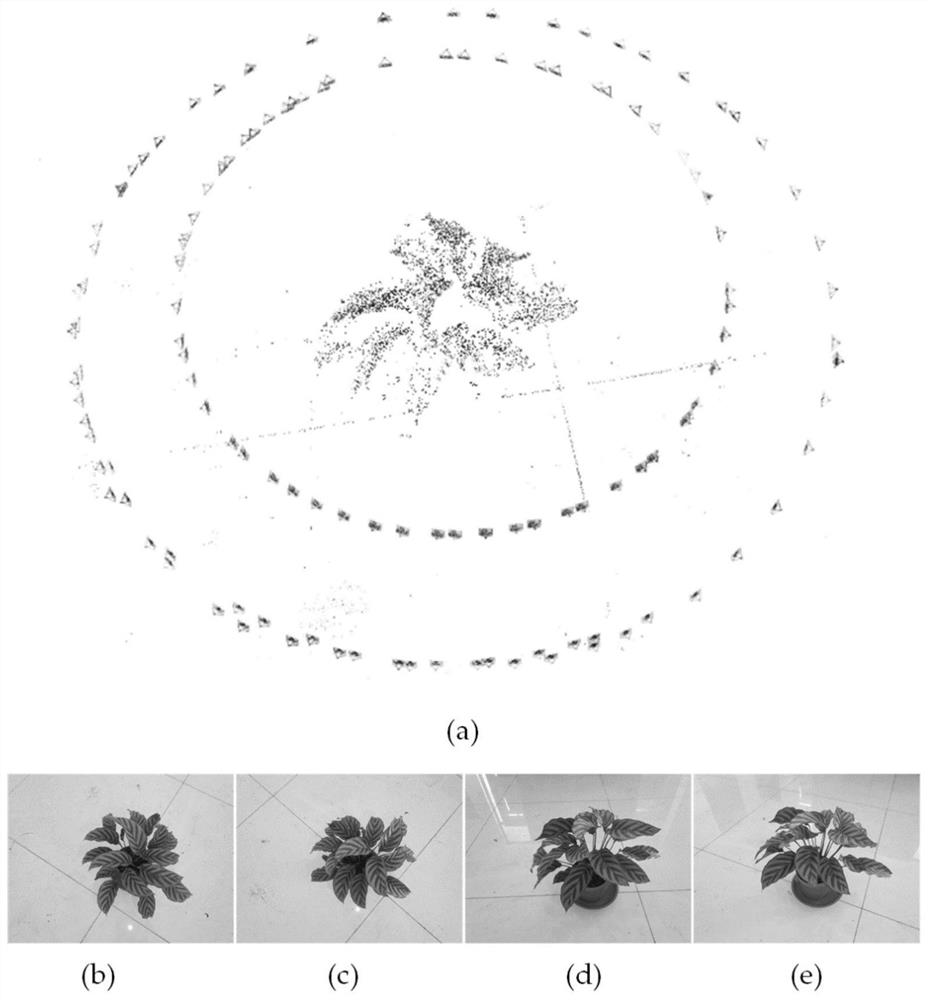
Plant point cloud blade segmentation and phenotypic characteristic measurement method
InactiveCN111667529AEliminate structural defectsHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisVision algorithmsEngineering
The invention provides a plant point cloud blade segmentation and phenotypic characteristic measurement method, comprising the steps: firstly, performing accurate point cloud three-dimensional reconstruction on potted plants by using a multi-view stereoscopic vision algorithm; secondly, removing non-blade parts in the plant point cloud by using a region and color-based filter and a normal vector difference algorithm; and then realizing single-blade segmentation on the canopy with the blade overlapping phenomenon by means of curvature information and a multi-feature region growth algorithm. Foreach single blade, a 3D bounding box of the blade is estimated by utilizing PCA, and the blade inclination angle can be calculated as an included angle between the height direction of the bounding box and the Z axis of a crop coordinate system, and the blade length and the blade width are the length and the width of the bounding box. The plant point cloud blade segmentation and phenotypic characteristic measurement method can realize automatic blade segmentation of potted plants with overlapped and clustered blades, has high precision and real-time performance for extracting phenotypic information such as blade area, blade length, blade width, blade inclination angle and the like, and is suitable for high-throughput blade phenotypic analysis.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
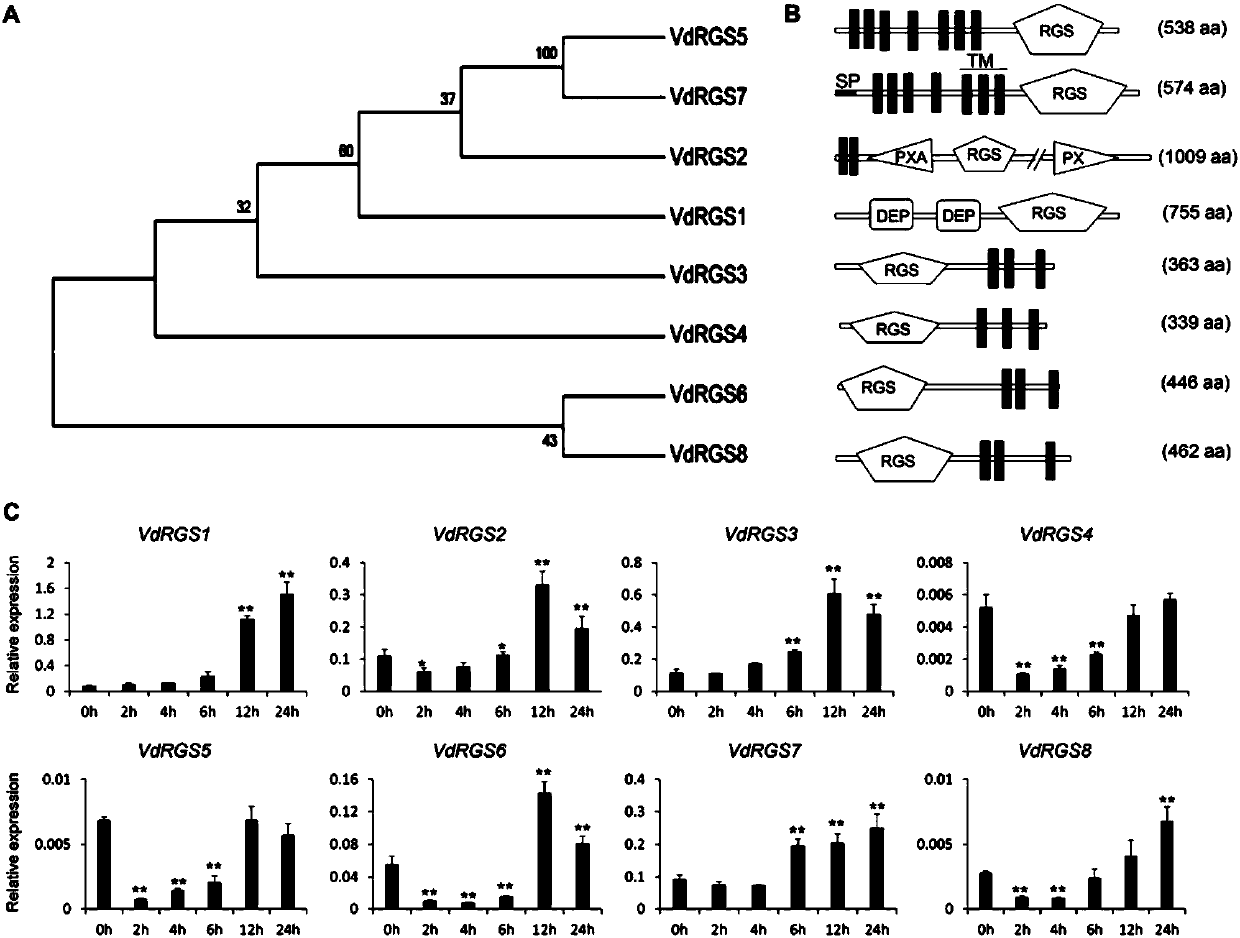
Method for remarkably improving resistance of cotton to greensickness through verticillium dahlia interference VdRGS1 gene expression
The invention discloses a method for remarkably improving resistance of cotton to greensickness through verticillium dahlia interference VdRGS1 gene expression and belongs to the field of biological technique application. The invention provides a nucleotide sequence of a VdRGS1 gene and an ORF sequence and an amino acid sequence of cDNA. Function and phenotypic analysis shows that VdRGS1 is capable of regulating and controlling pathogenicity of verticillium dahlia, formation of microsclerotia, growth of spores and hyphae, and the like, and plays a significant role when verticillium dahlia invades and infect a host. By using a transgenic technique, a greensickness bacterium which can express green fluorescent protein (GFP) is created, by using a virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) technique, a GFP gene of the transgenosis verticillium dahlia can be efficiently silenced in cotton, the result shows that host induced gene silencing (HIGS) is achieved on the basis of the VIGS technique, andinvading verticillium dahlia genes can be successfully silenced in cotton by using the technique. By using an HIGS technique based on VIGS, the verticillium dahlia VdRGS1 is silenced in cotton, and the resistance of cotton to verticillium dahlia is remarkably improved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
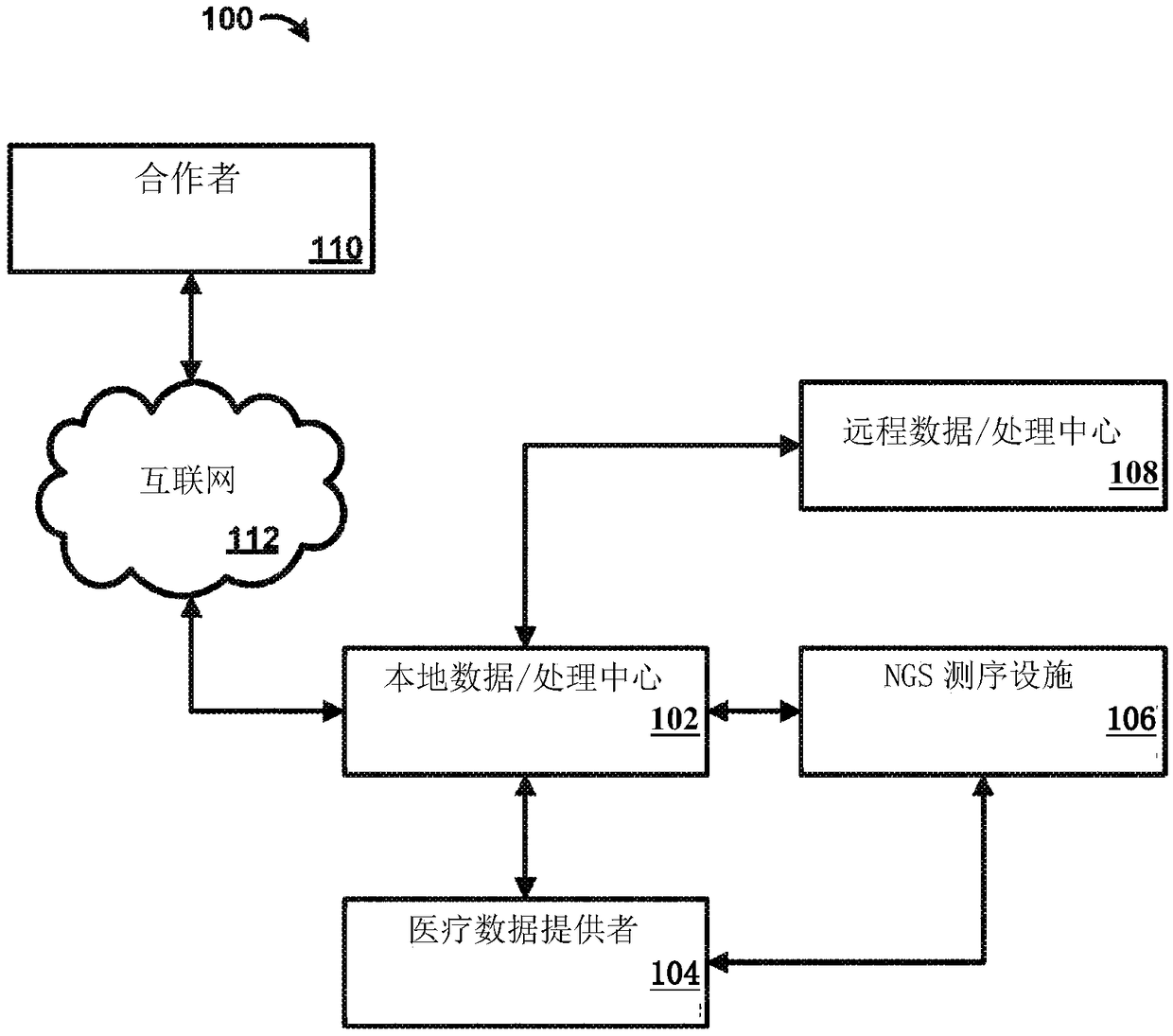
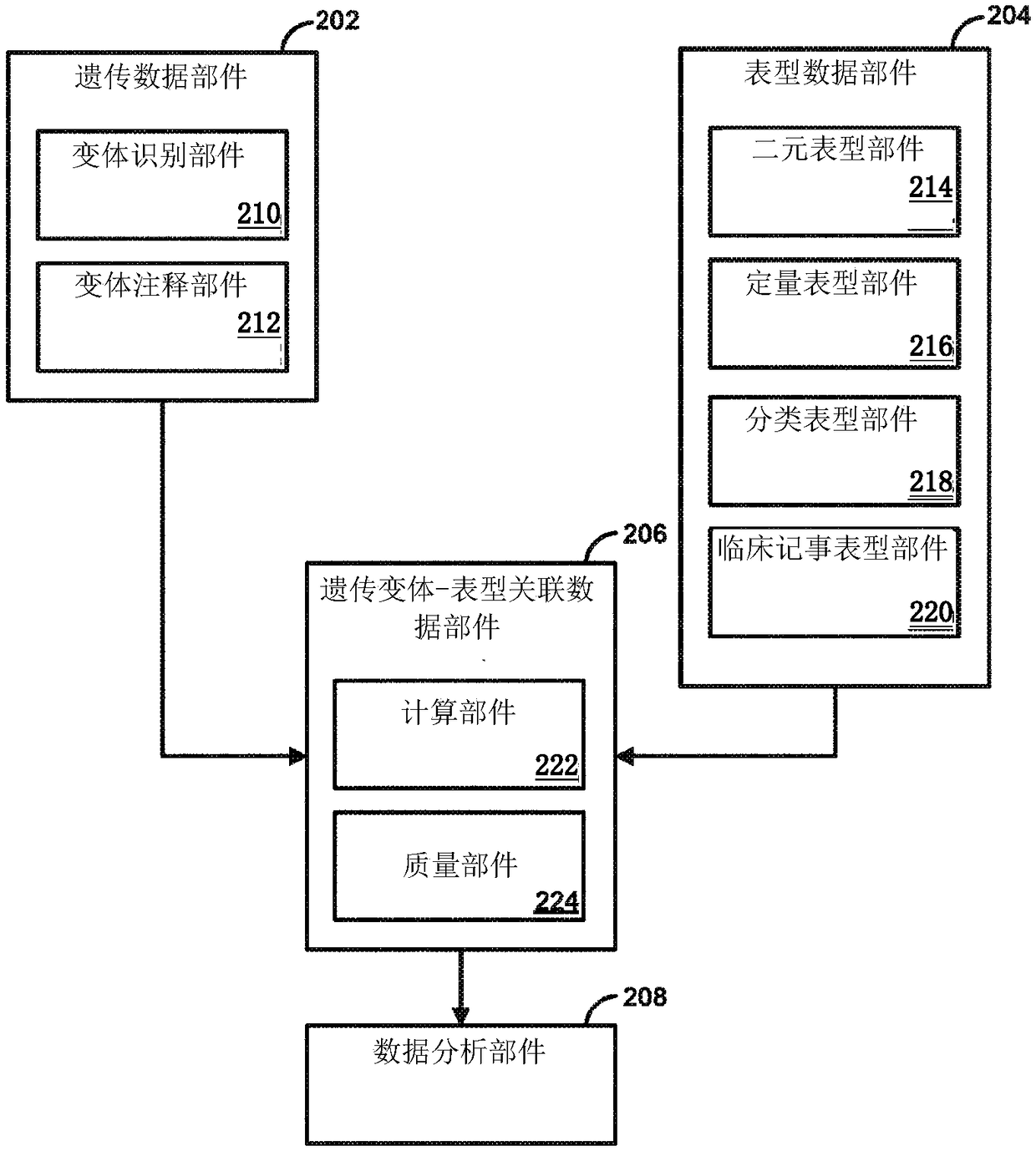
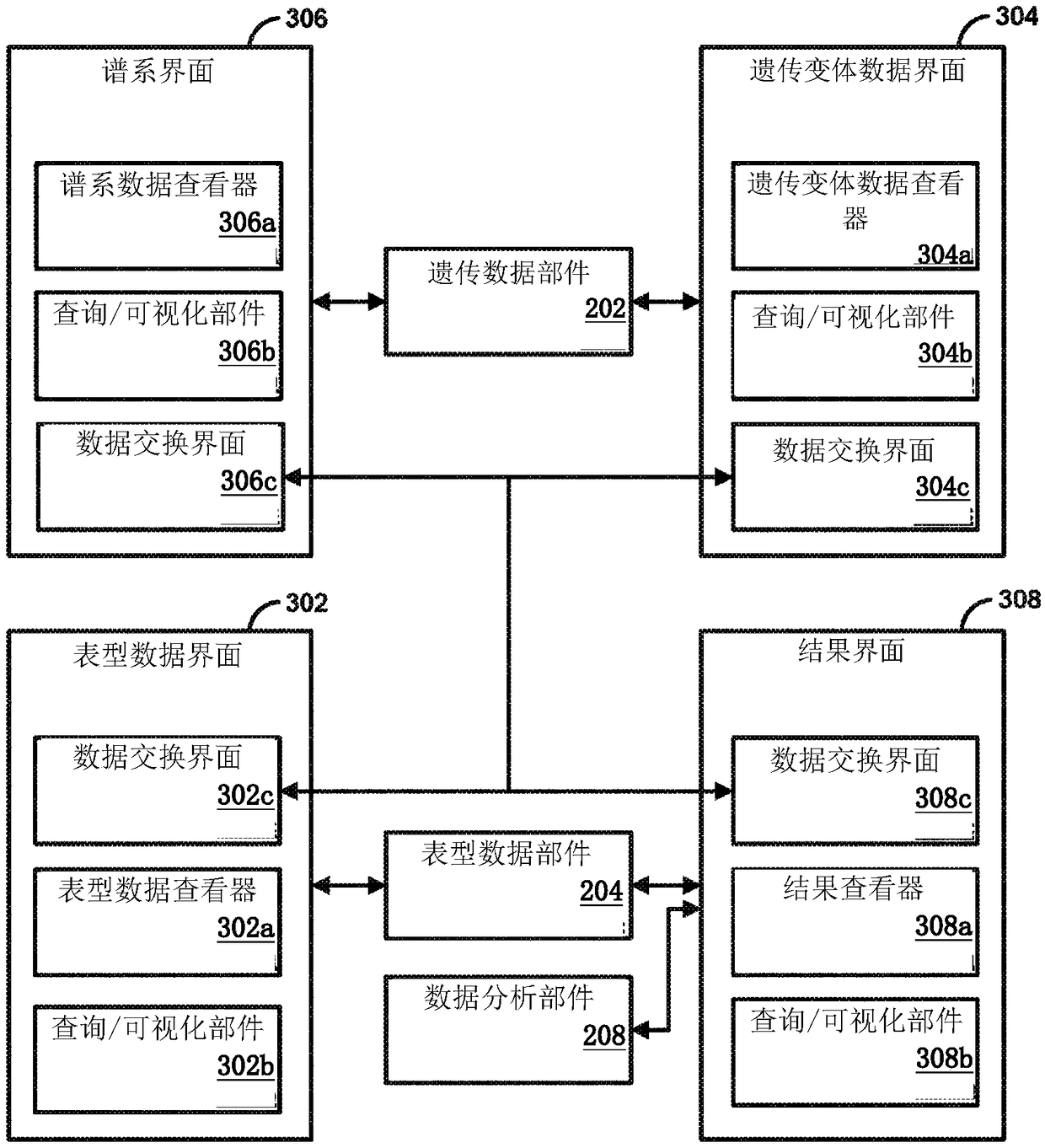
Genetic variant-phenotype analysis system and methods of use
Methods and systems for generating and analyzing genetic variant-phenotype association results are disclosed.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
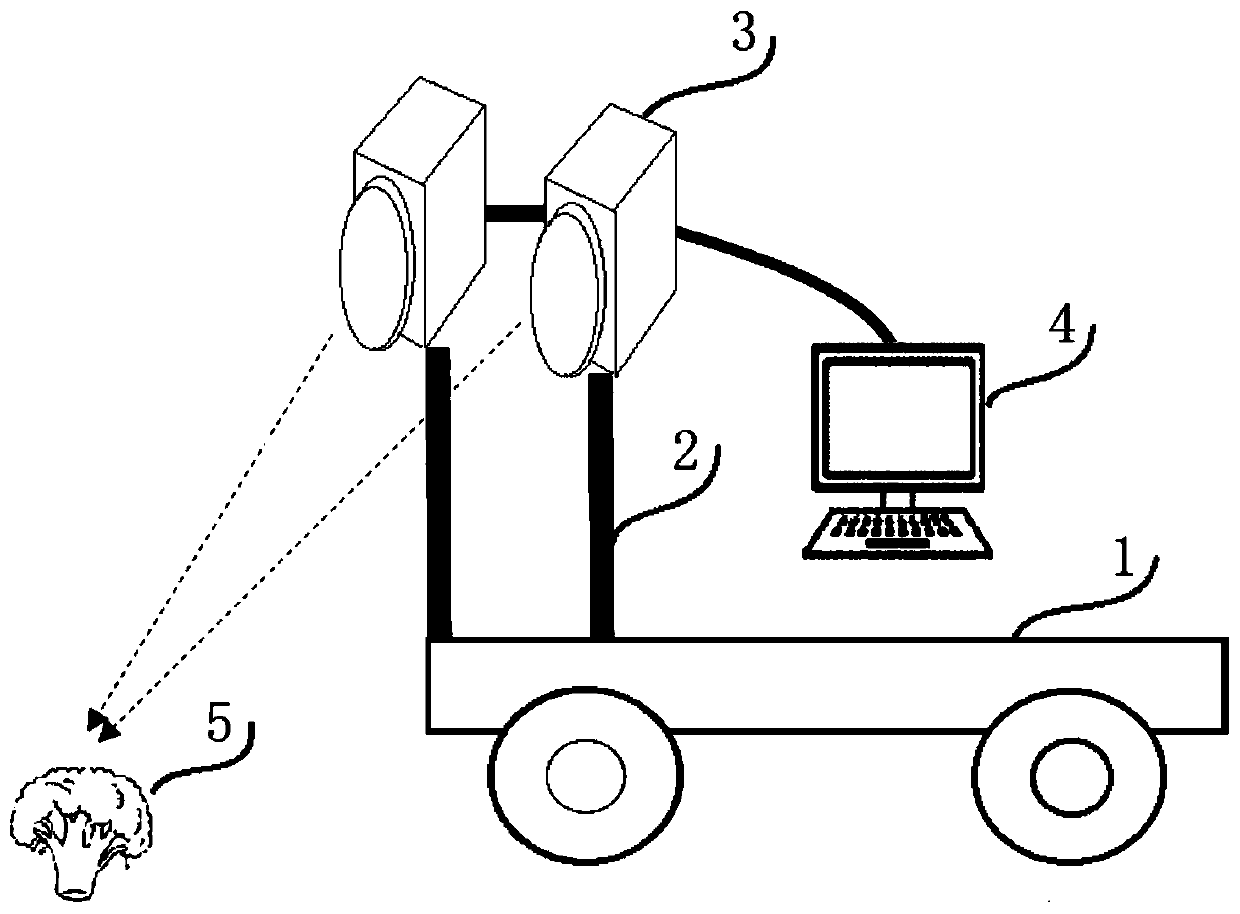
Field broccoli growth vigor monitoring system and method based on deep learning
ActiveCN111460903AHigh precisionImprove anti-interference abilityData processing applicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionAutomatic controlAgricultural engineering
The invention discloses a field broccoli growth vigor monitoring system and method based on deep learning. The system comprises a field mobile platform and an image acquisition system. The field moving platform comprises a wheel type base, a three-degree-of-freedom support and an automatic control device. The image acquisition system comprises two industrial cameras and a workstation, the three-degree-of-freedom support is arranged on the wheel type base, the two industrial cameras are fixedly installed on the three-degree-of-freedom support, the industrial cameras are in communication connection with the workstation, and the automatic control device is used for achieving automatic and synchronous shooting of the industrial cameras and controlling the three-degree-of-freedom support to conduct lifting operation. According to the invention, machine vision and deep learning technologies are combined; a self-developed ground platform is used for training and learning annotation data basedon an improved U-Net full convolutional neural network, an Otsu algorithm is used for further achieving flower ball freshness analysis, precision performance is good, high robustness is achieved, anda certain reference value is achieved for phenotypic analysis of field broccoli in the future.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
A gene OsHT1 controlling rice tillering and applications thereof
InactiveCN106868019AGenetic stabilityIncrease the number of tillersPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyOpen reading frame
A gene OsHT1 controlling rice tillering is disclosed. The gene is derived from oryza sativa L. cv. Zhonghua 11. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is SEQ ID NO.1, the nucleotide sequence of the open reading frame of the gene is SEQ ID NO.2, and an amino acid sequence encoded by cDNA of the gene is SEQ ID NO.3. Phenotypic analysis shows that after overexpression of the gene OsHT1, the tiller number of rice is increased from about 20-27 to 135-145, plant height is reduced and the setting rate is not changed. The gene OsHT1 is a critical regulating gene for rice tillering, and therefore rice tillering characters can be regulated by utilizing a genetic engineering technology, and the gene has important application value in the field of regulating and controlling plant shape characters on purpose by utilizing a bioengineering technology, and adjusting a plant population structure to achieve a high yield and good quality. The gene can be used for cultivating high-yield varieties of rice, wheat, and other cereal crops.
Owner:ZHOUKOU NORMAL UNIV
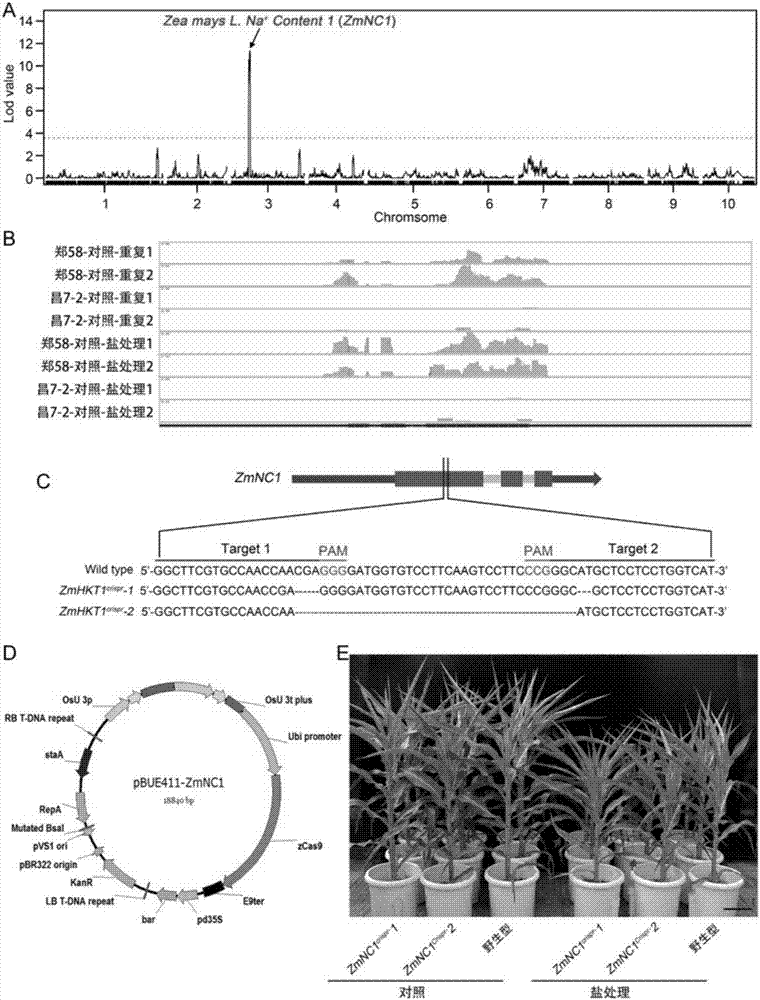
Corn salt-resistant main-effect QTL (Quantitative Trait Loci) as well as related genes, molecular markers and application thereof
ActiveCN107574171ASpeed up the breeding processMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesSalt resistanceAgricultural science
The invention discloses a corn salt-resistant main-effect QTL (Quantitative Trait Loci) as well as related genes, molecular markers and an application thereof. The coded nucleotide sequences of the corn salt-resistant QTL genes are selected from: (a) a sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1; and (b) a nucleotide sequence which is formed by substituting, deleting and / or adding one or more nucleotides on thebasis of the sequence shown in SEQ ID No.1 and expresses proteins with the same function. In the salt-resistant QTL genes, an insertion / deletion marker which is positioned in exon of the genes and has differences between resistant and sensitive materials is identified. The marker is interlinked with the corn salt resistance and can serve as a corn salt-resistant molecular marker. The invention provides a primer and a method for detecting the salt-resistant molecular marker. Due to corn salt-resistant quantity inheritance of characters, the phenotypic analysis is time-consuming and labor-consuming, and the QTL genes, the molecular marker and the primer can be applied to salt-resistant breeding of corn.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
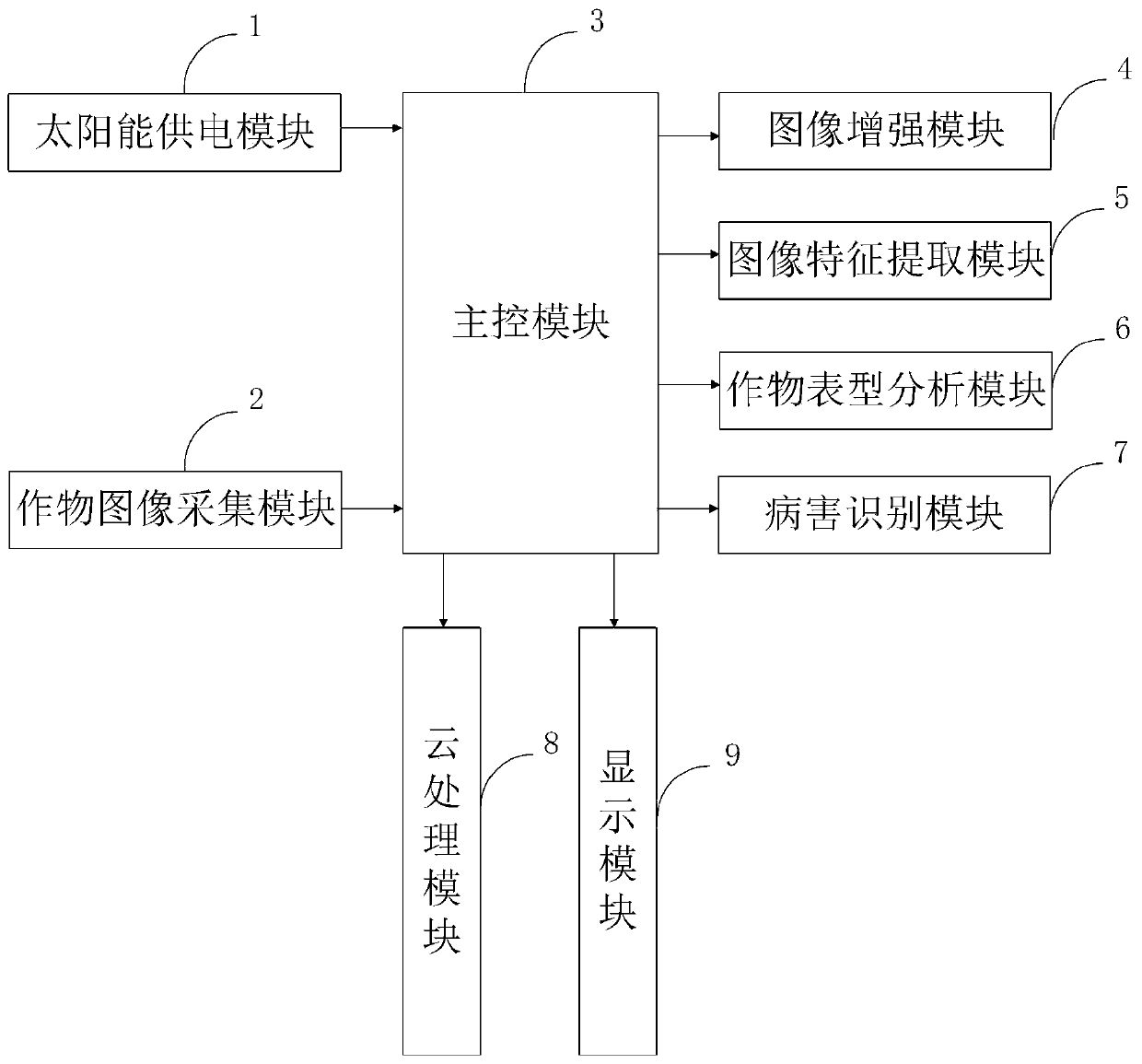
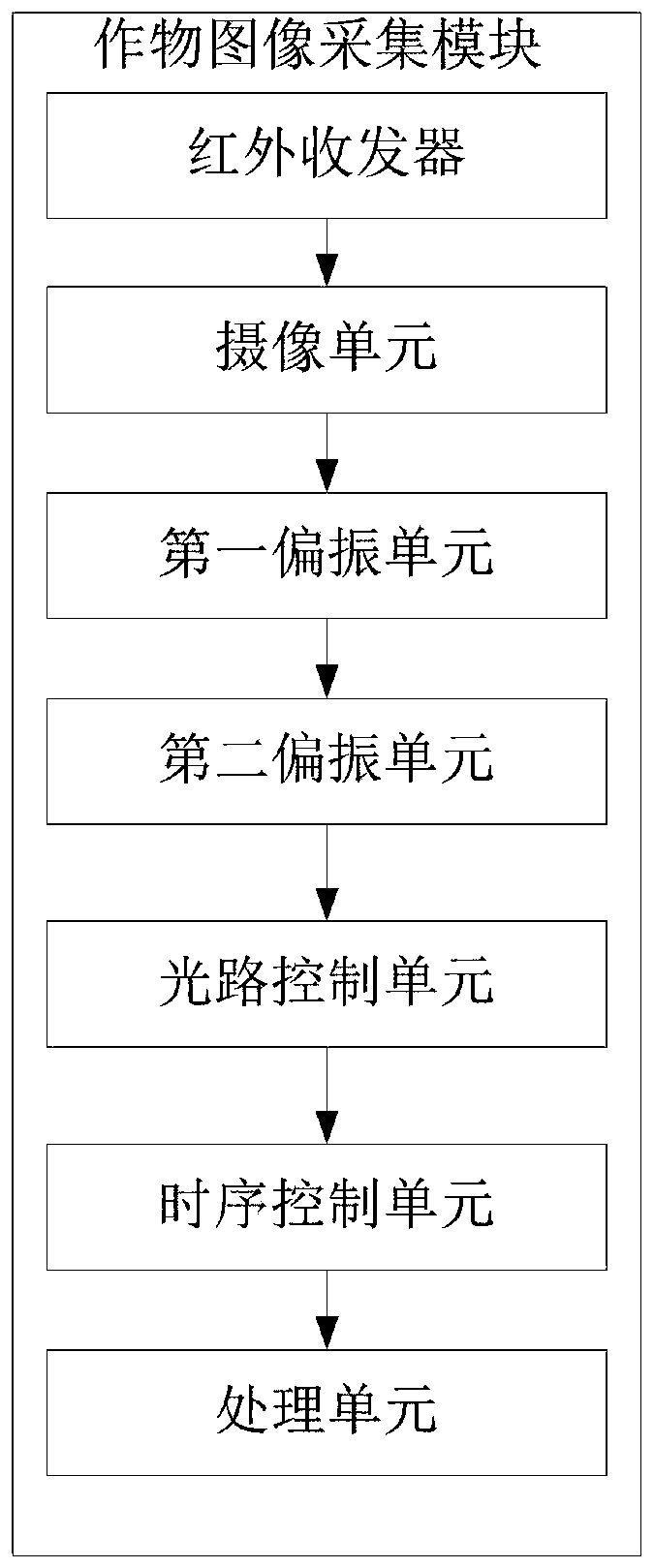
Field crop phenotypic information high-throughput peer-to-peer monitoring system and monitoring method
PendingCN110532935AImprove image qualityHighlight useful informationProgramme controlComputer controlDiseaseCloud processing
The invention belongs to the technical field of information monitoring, and discloses a field crop phenotypic information high-throughput peer-to-peer monitoring system and method, and the system comprises a solar power supply module, a crop image collection module, a main control module, an image enhancement module, an image feature extraction module, a crop phenotypic analysis module, a diseaserecognition module, a cloud processing module, and a display module. The robustness of the disease recognition model is improved, and a good recognition effect can be obtained. The recognition speed of the disease type of the to-be-recognized crop is increased, the crop disease prevention and treatment time is shortened, and economic benefits are improved. The field crop image quality is improvedthrough the image enhancement module; the problems of color distortion, unobvious enhancement effect and the like in the prior art are solved. Meanwhile, the robustness of the disease recognition model is improved through the disease recognition module, and a good recognition effect can be obtained. The identification speed of the disease type of the to-be-identified crop can be improved, the prevention and control time of crop diseases is shortened, and economic benefits are improved.
Owner:李清华
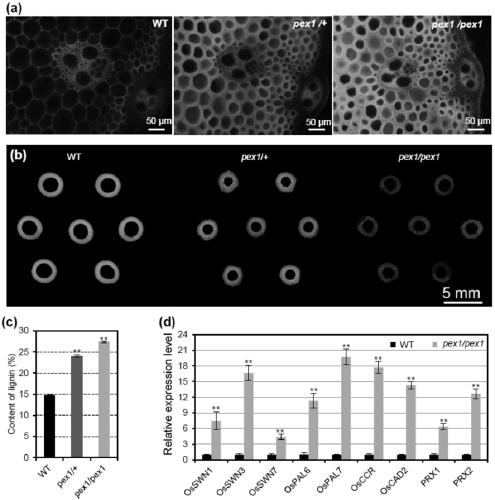
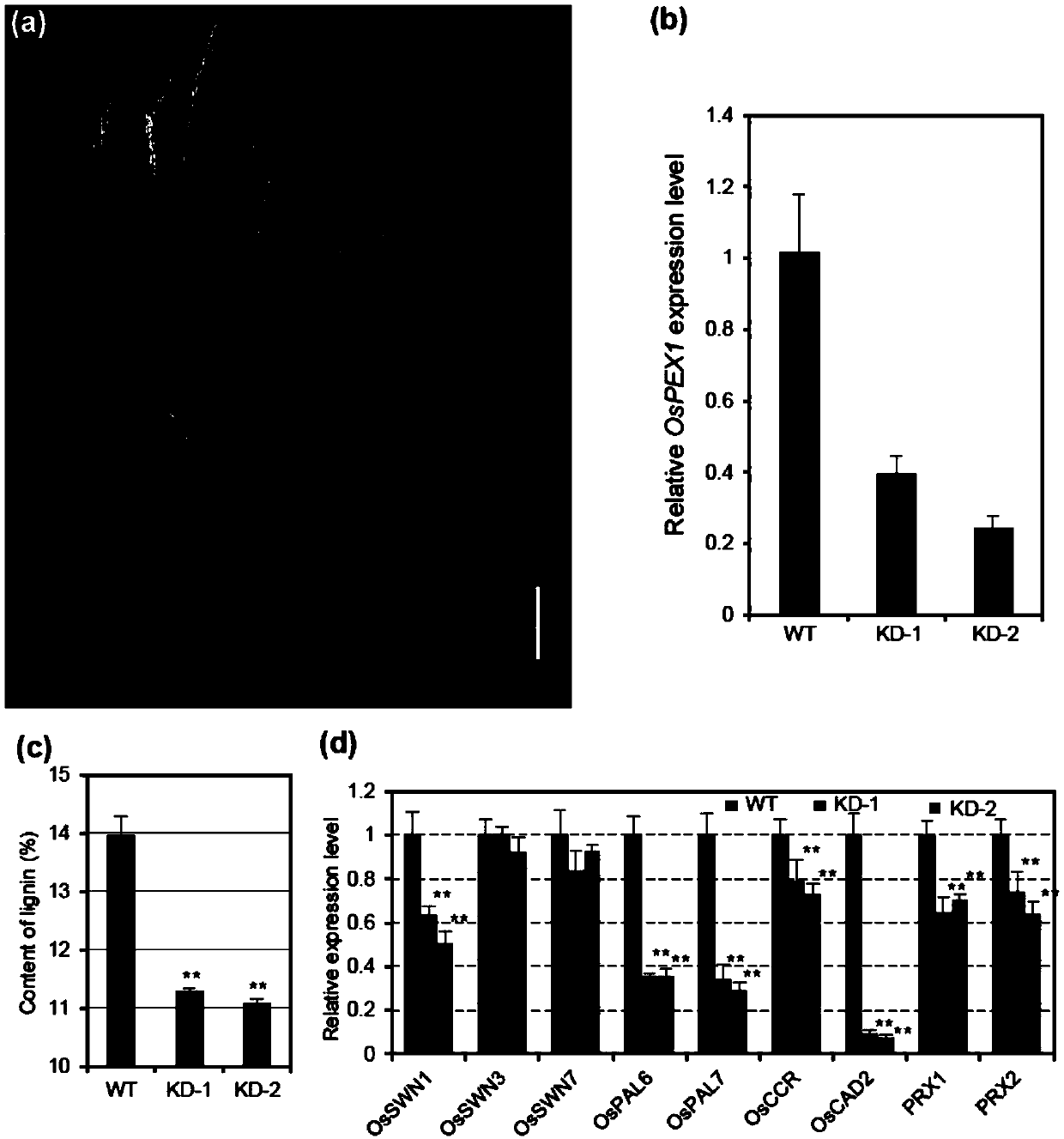
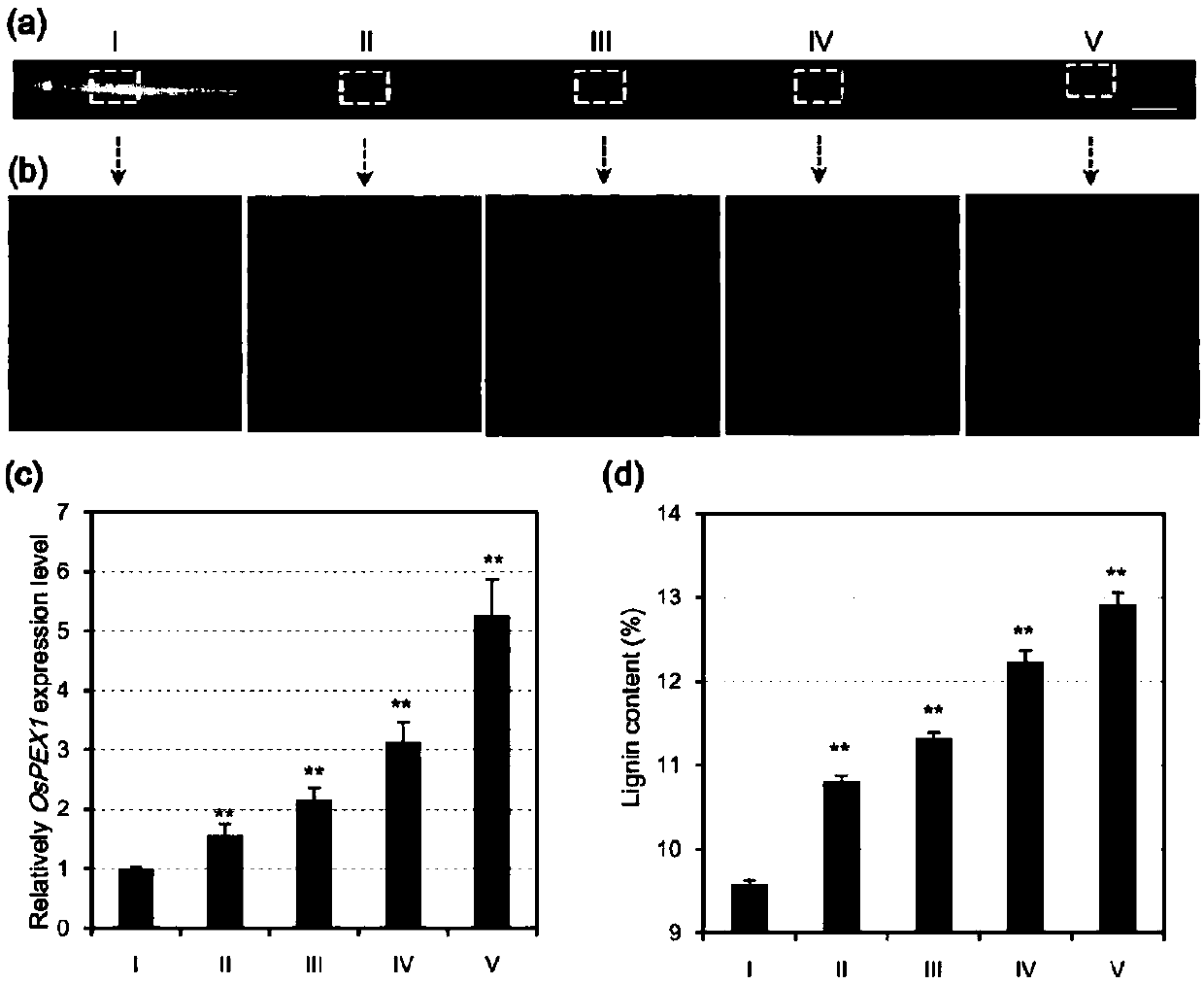
Application of paddy OsPEX1 gene in regulating lignin metabolism
ActiveCN109575113AEnriched Molecular MechanismsImprove lodging resistancePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyA-DNA
The invention discloses application of a paddy OsPEX1 gene in regulating lignin metabolism and belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering. The OsPEX1 gene disclosed by the invention has a DNA sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:1; phenotypic analysis for mutants and analysis for antisense suppression of transgenic progeny strains prove that the OsPEX1 gene plays an important role in regulating lignin metabolism; the cloning of OsPEX1 gene is capable of enriching a molecular mechanism for regulating the lignin metabolism of paddy, supplying a new gene resource to lodging-resistant genetic improvement of paddy, and supplying a new material choice for molecular design and breeding of paddy; the paddy variety with increased lignin content and improved lodging resistance can be bred in the manner of increasing the OsPEX1 expression in paddy; operability is ultrahigh; a new path is established for broadening the genetic basis of present lodging-resistant variety.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Comparative phenotype analysis of cells including testing of biologically active chemicals
InactiveUS20050260558A1Improve effectivenessImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingPlant cellTest organism
The present invention relates to growing and testing any cell type in a multitest format. The present invention is suited for the characterization of microorganisms, as well as animal and plant cells. The present invention is also particularly suited for analysis of phenotypic differences between strains of organisms, including cultures that have been designated as the same genus and species. The present invention is also suited for the analysis of phenotypic differences between cell lines. In some embodiments, a gel forming matrix is used. The present invention provides methods and compositions for the phenotypic analysis and comparison of eukaryotic, as well as prokaryotic cells. The present invention further provides novel methods and compositions for testing the effect(s) of biologically active chemicals on various cells.
Owner:BIOLOG
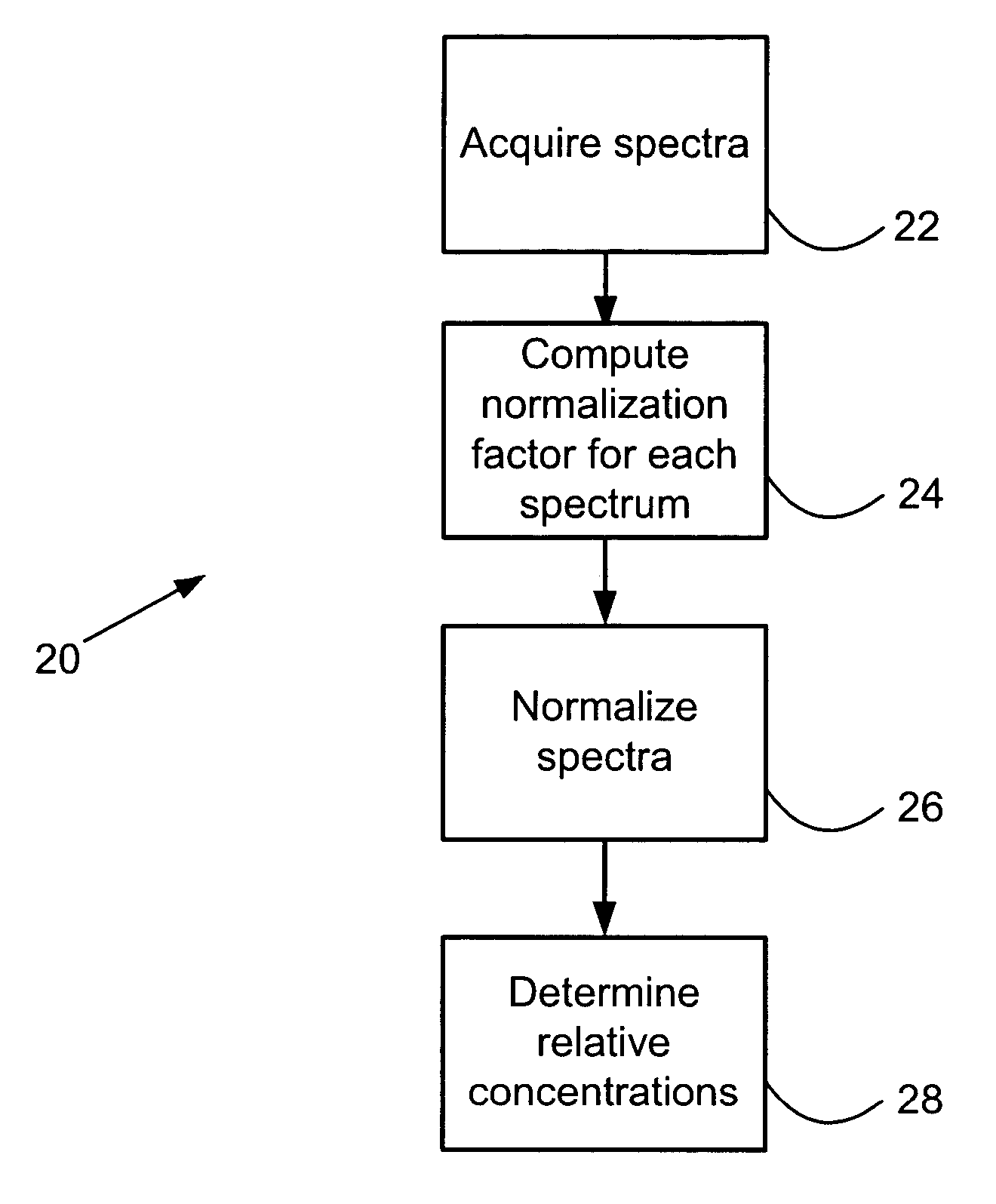
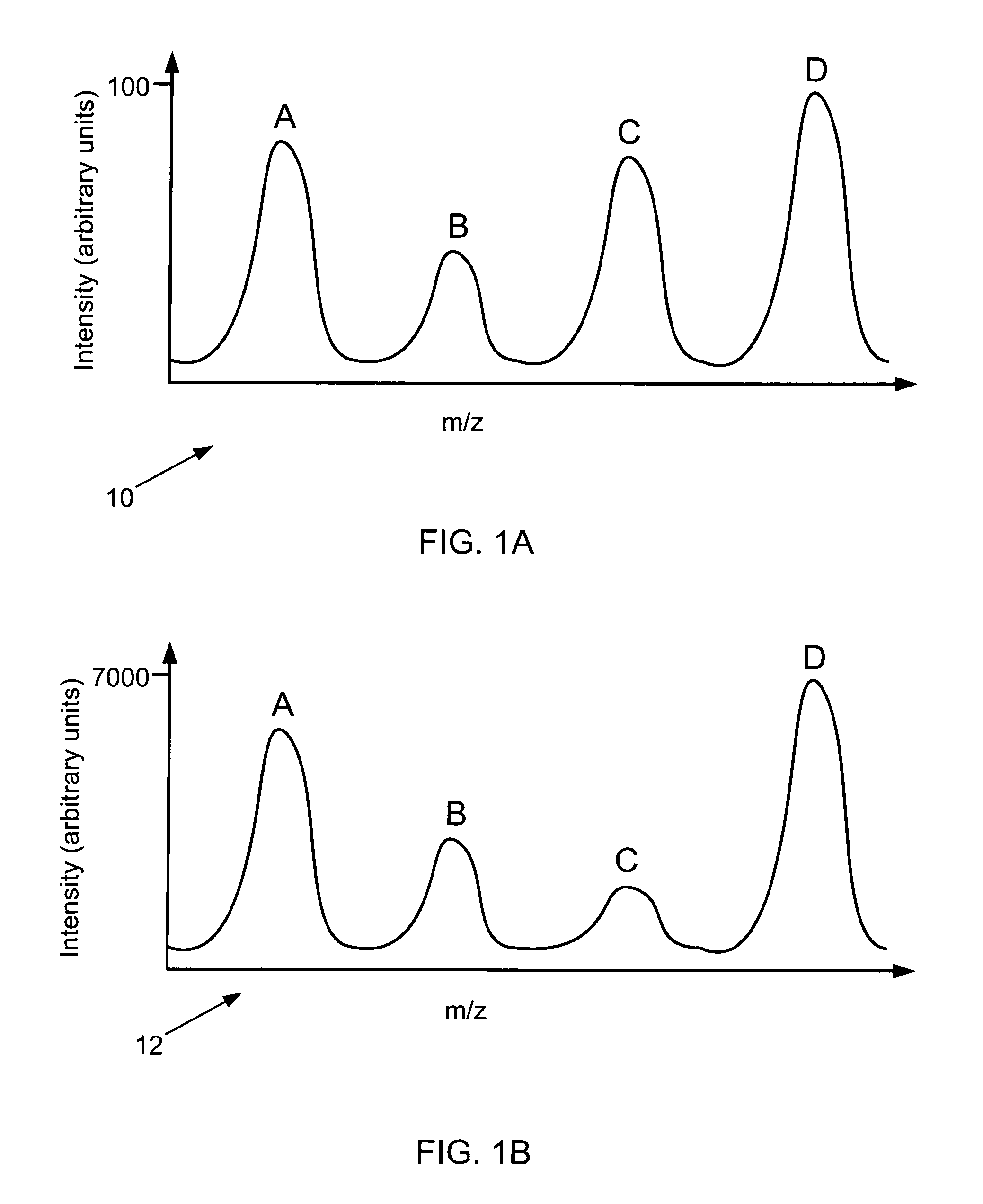
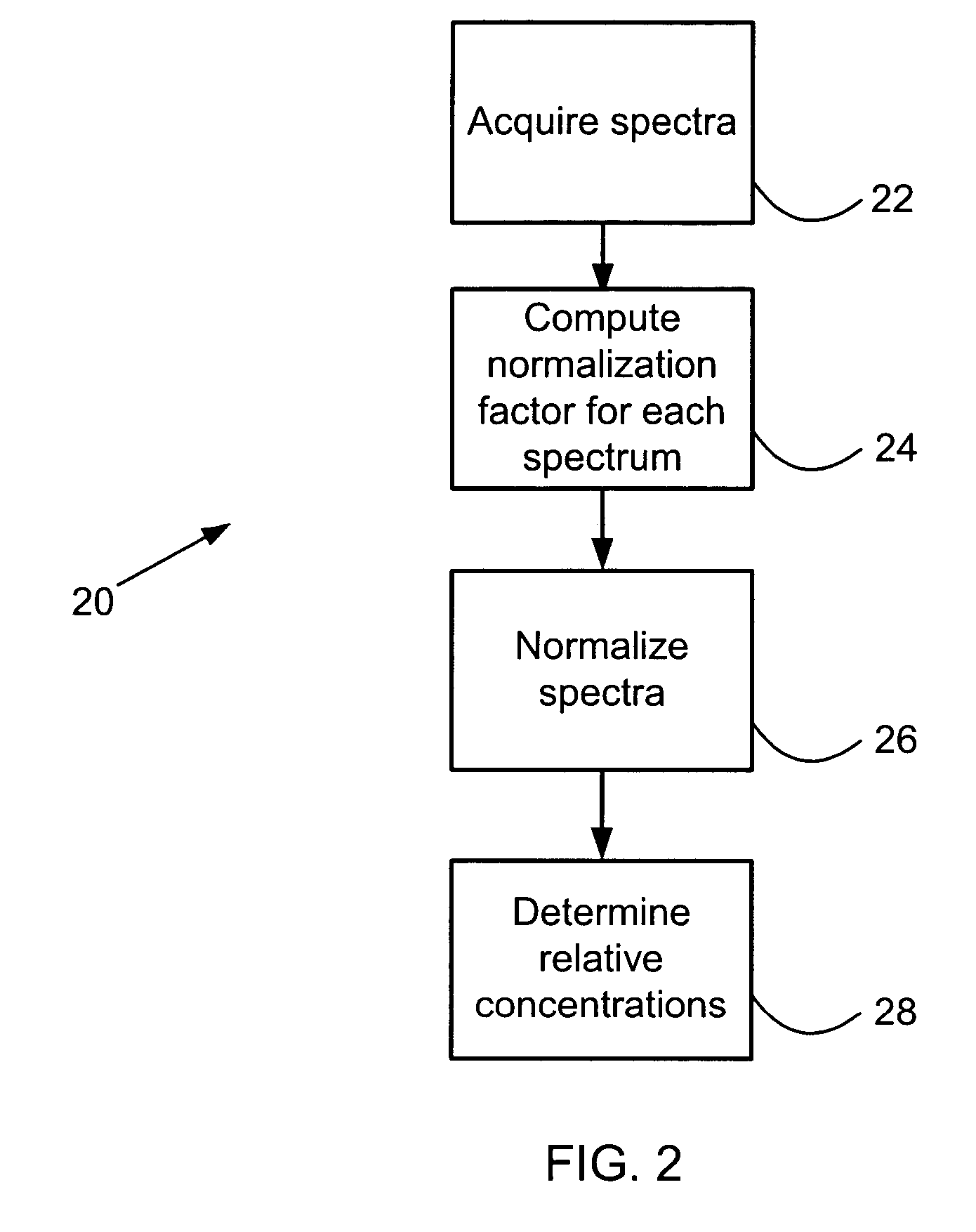
Mass spectrometric quantification of chemical mixture components
Relative quantitative information about components of chemical or biological samples can be obtained from mass spectra by normalizing the spectra to yield peak intensity values that accurately reflect concentrations of the responsible species. A normalization factor is computed from peak intensities of those inherent components whose concentration remains constant across a series of samples. Relative concentrations of a component occurring in different samples can be estimated from the normalized peak intensities. Unlike conventional methods, internal standards or additional reagents are not required. The methods are particularly useful for differential phenotyping in proteomics and metabolomics research, in which molecules varying in concentration across samples are identified. These identified species may serve as biological markers for disease or response to therapy.
Owner:CAPRION PROTEOMICS INC
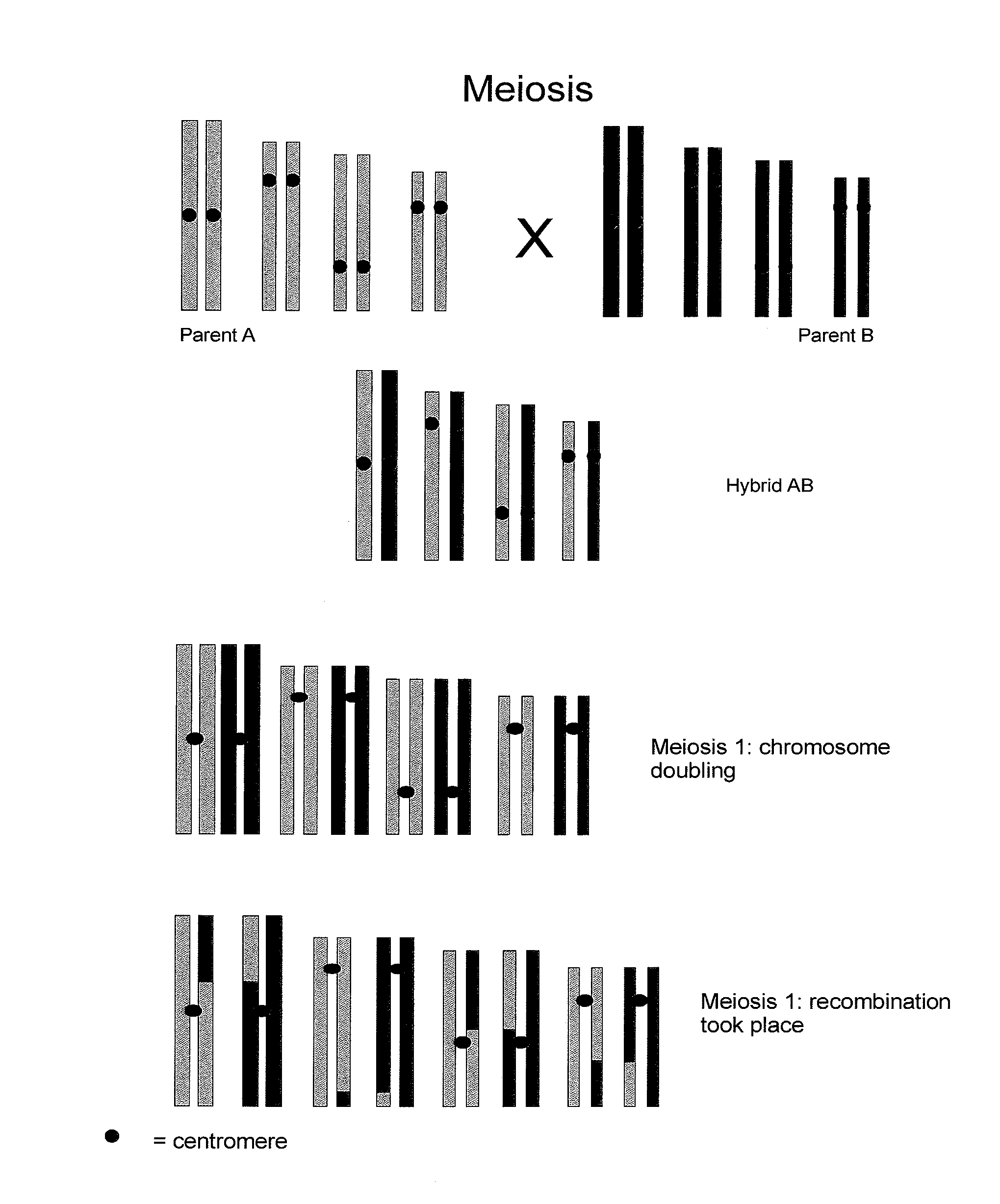
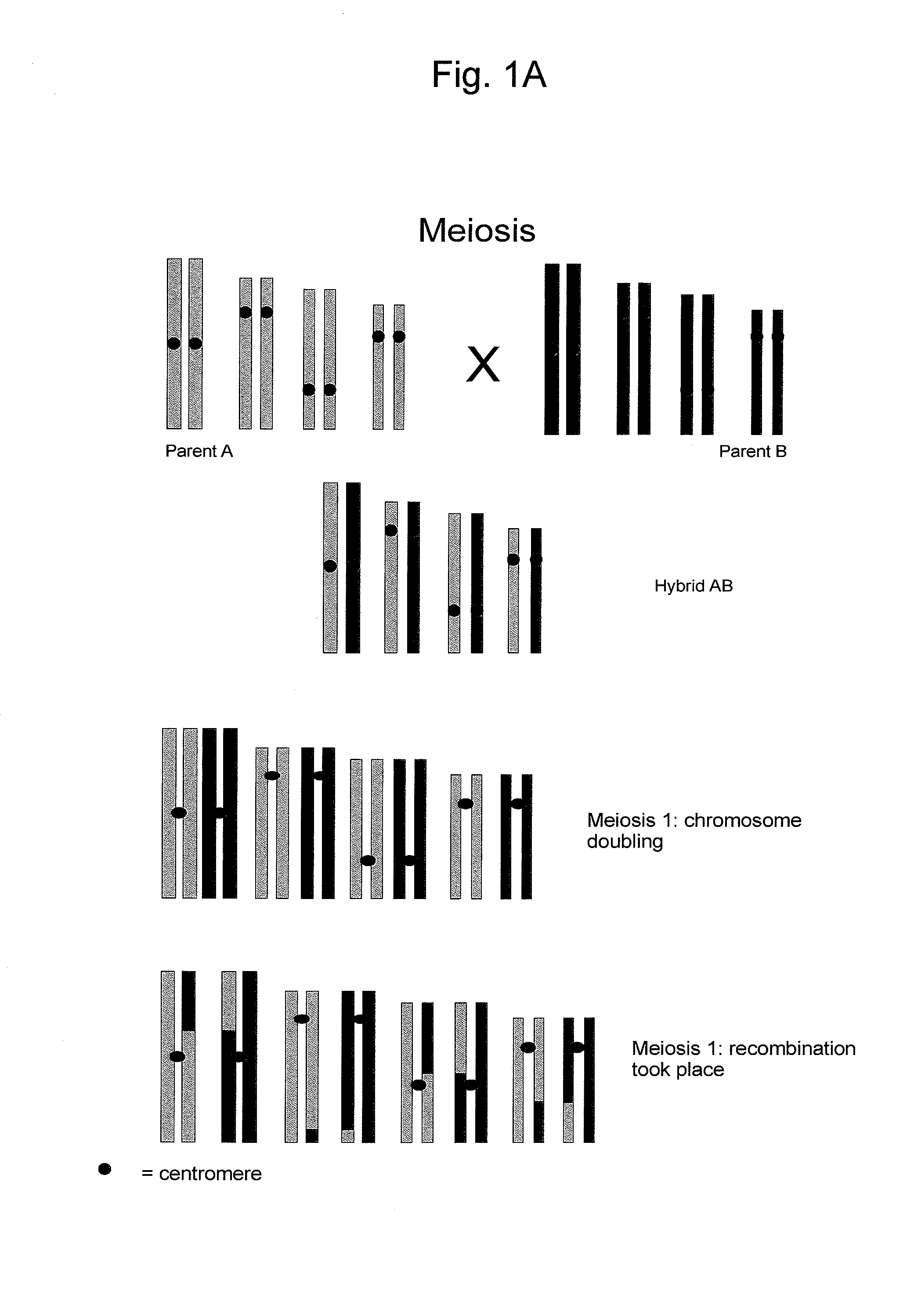
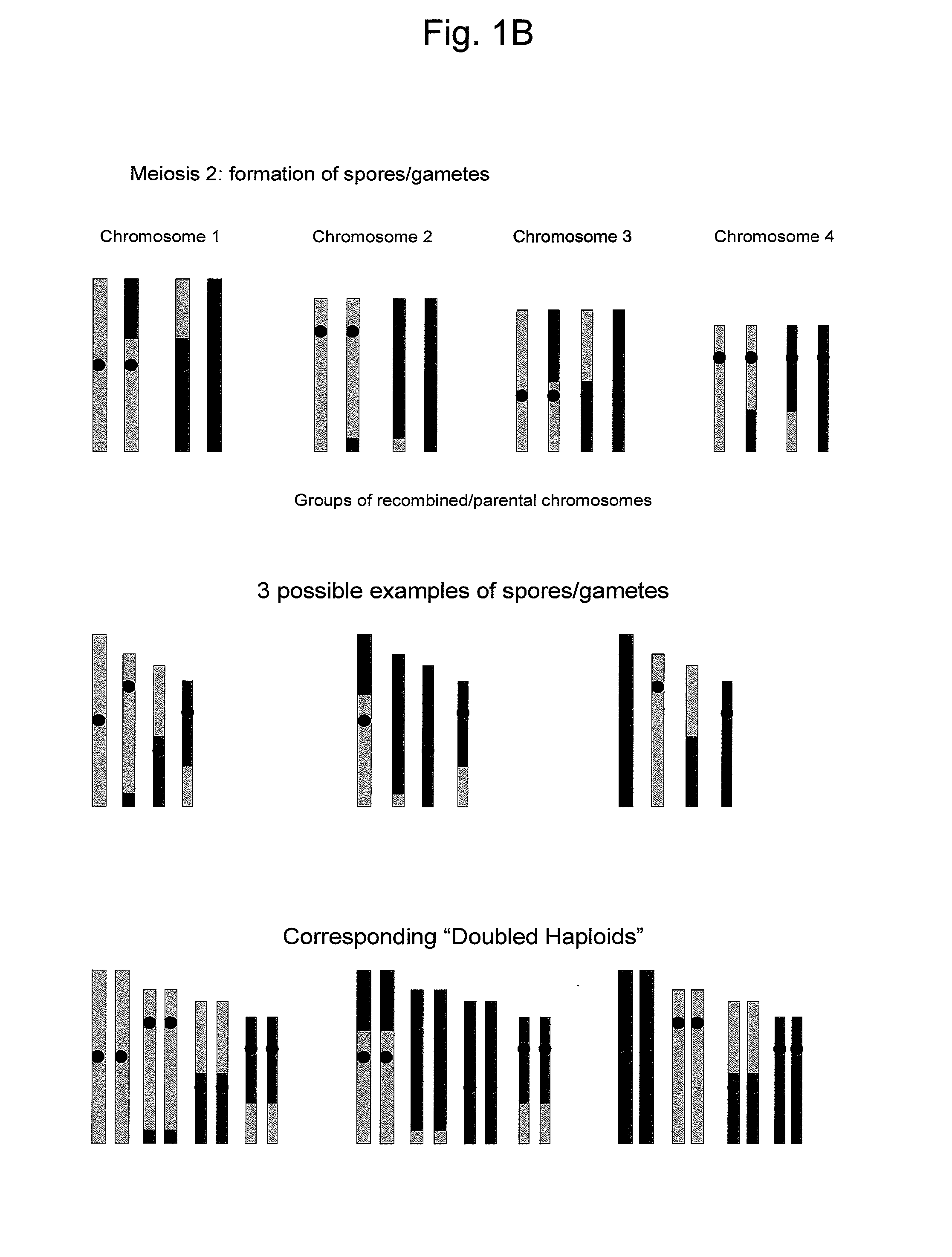
Reverse Progeny Mapping
ActiveUS20080057583A1Easy mappingEasily mappedMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationSporeBiological body
Provided is a method for mapping traits in organisms, in particular in plants. The method comprises a) providing a population of SDR-0 organisms, in particular plants, that each arise from one member of a population of unreduced cells resulting from second division restitution, in particular a population of unreduced spores; b) producing SDR-1 progeny populations of each of these SDR-0 organisms; c) phenotyping the SDR-1 progeny populations to identify segregating traits within each SDR-1 progeny population; d) if segregating progeny are present in a SDR-1 progeny population, genotyping the corresponding SDR-0 organism and comparing the genotype thereof with the genotype of the other SDR-0 organisms to identify heterozygous chromosomal regions associated with the occurrence of the segregating trait identified in the SDR-1 progeny population.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
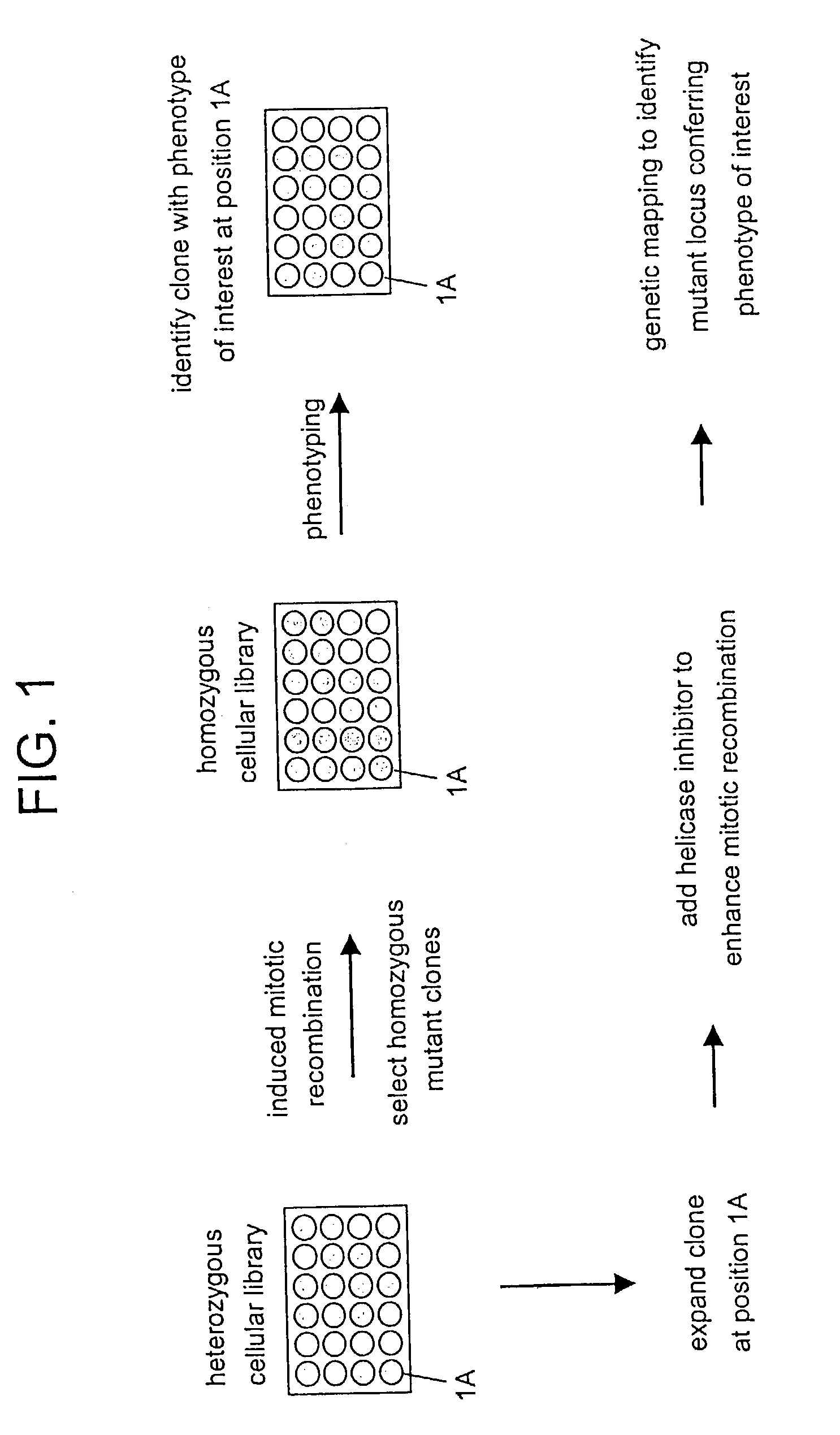
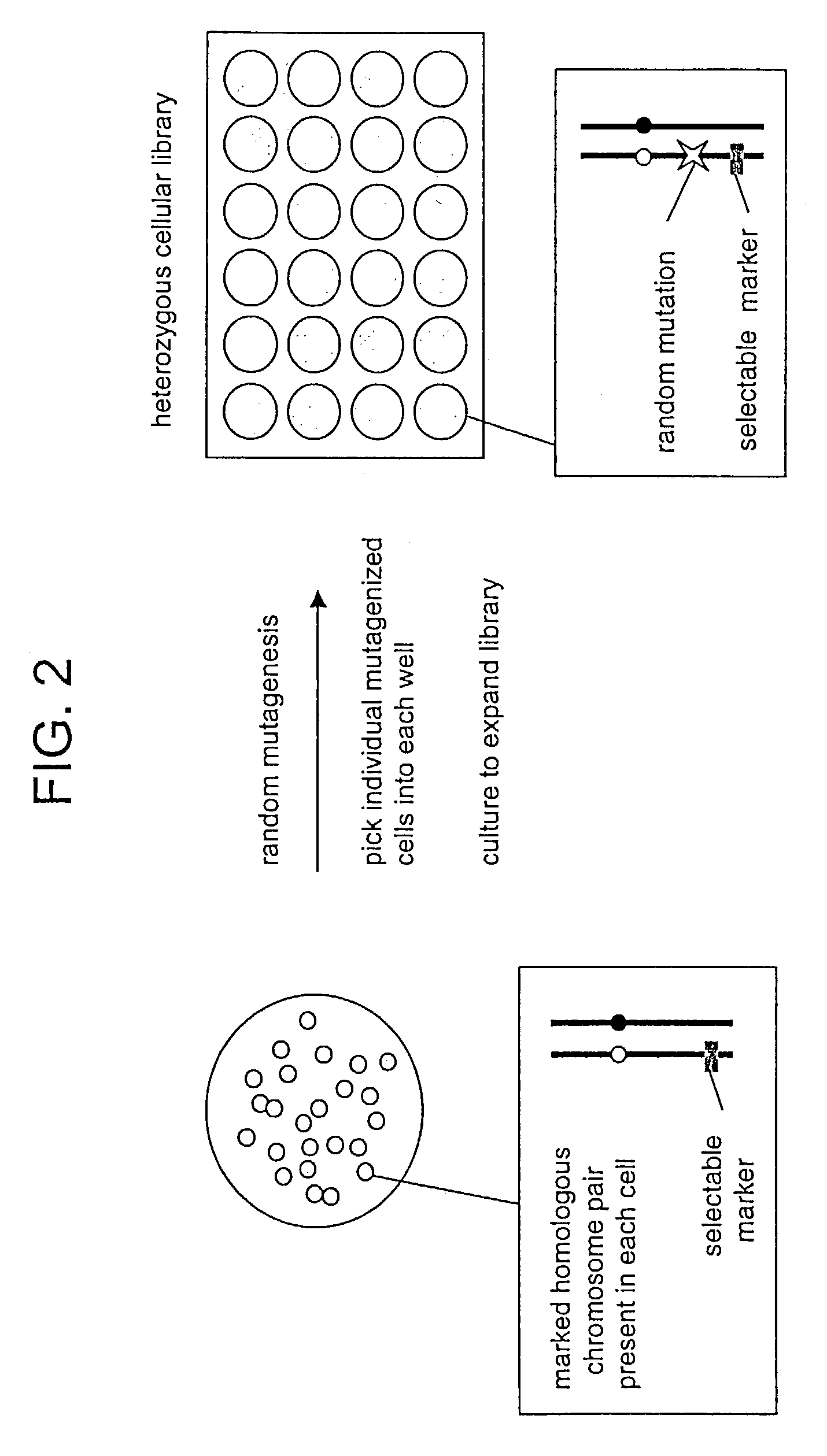
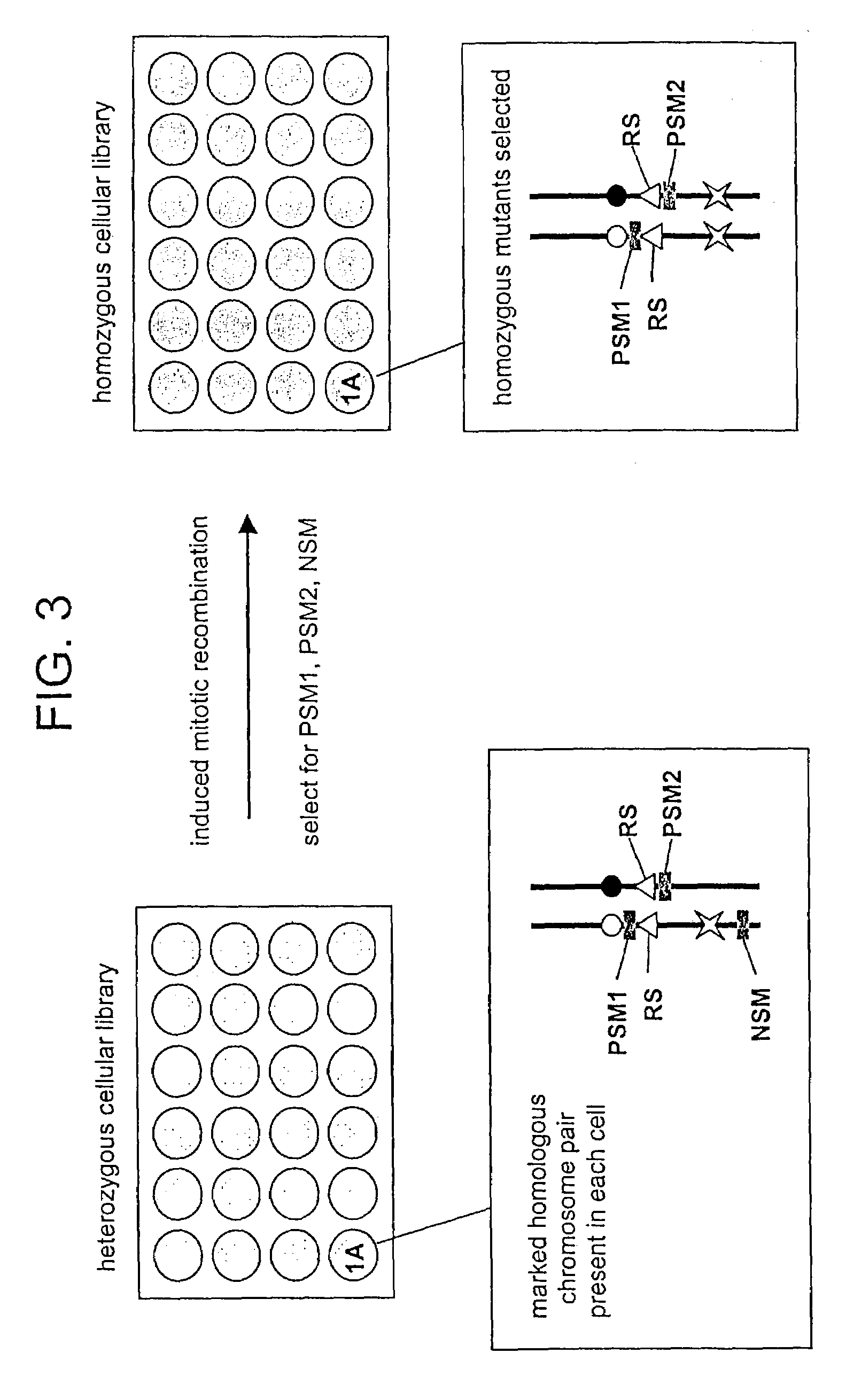
In Vitro mutagenesis, phenotyping, and gene mapping
Cellular libraries useful for in vitro phenotyping and gene mapping. In a representative approach, a method for preparing a homozygous cellular library includes the steps of providing a heterozygous cellular library comprising a plurality of isolated parent cells; inducing site-specific mitotic recombination in the plurality of isolated parent cells; culturing the plurality of isolated parent cells, whereby a population of daughter cells is produced; and selecting daughter cells comprising a homozygous genetic modification, whereby a homozygous cellular library is prepared.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
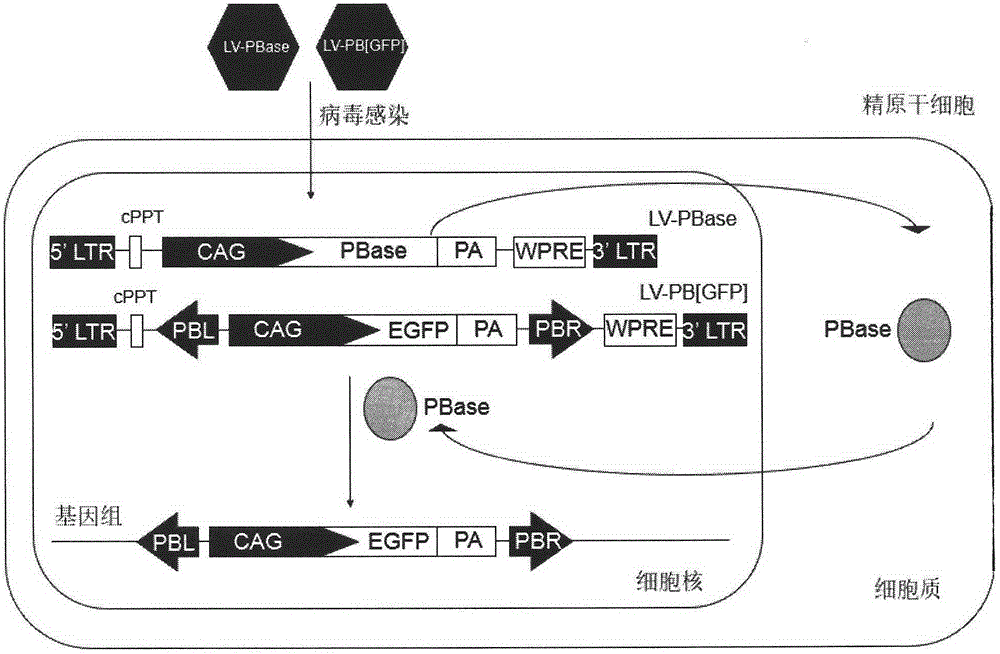
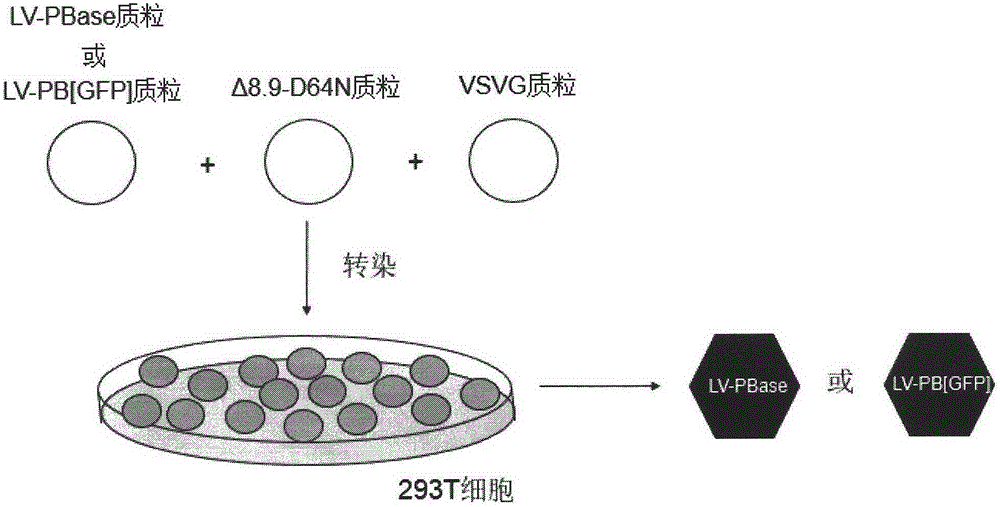
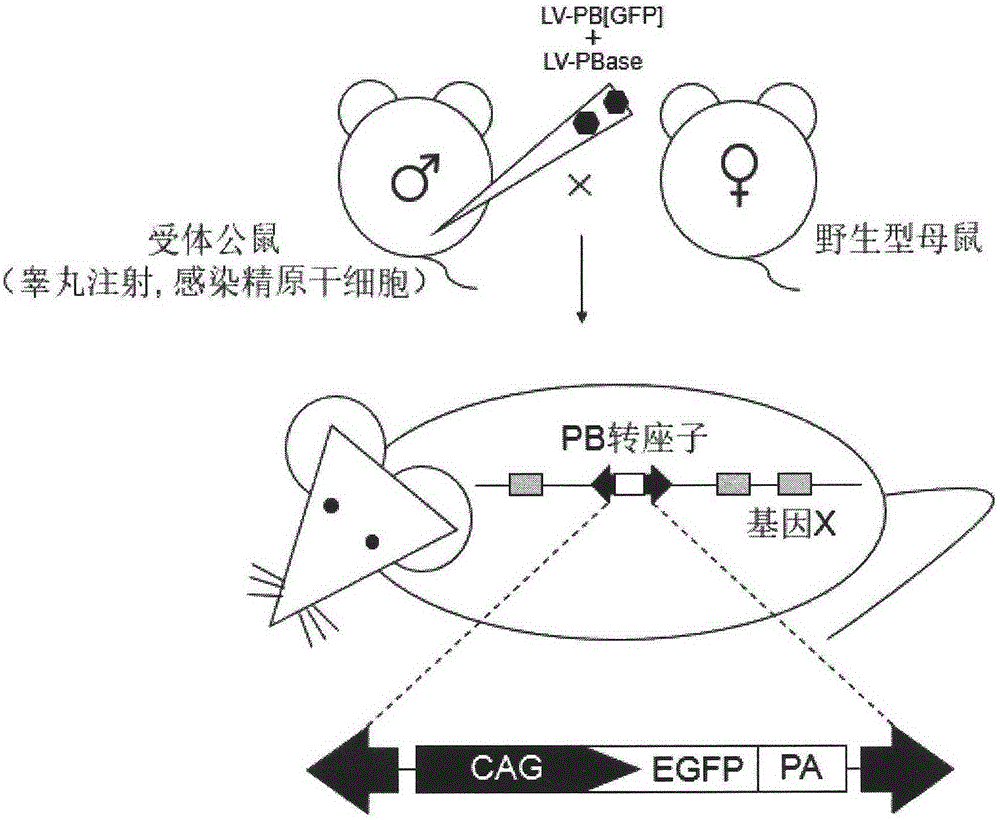
Method of introducing random insertion mutation to genome of in-vivo spermatogonial stem cells
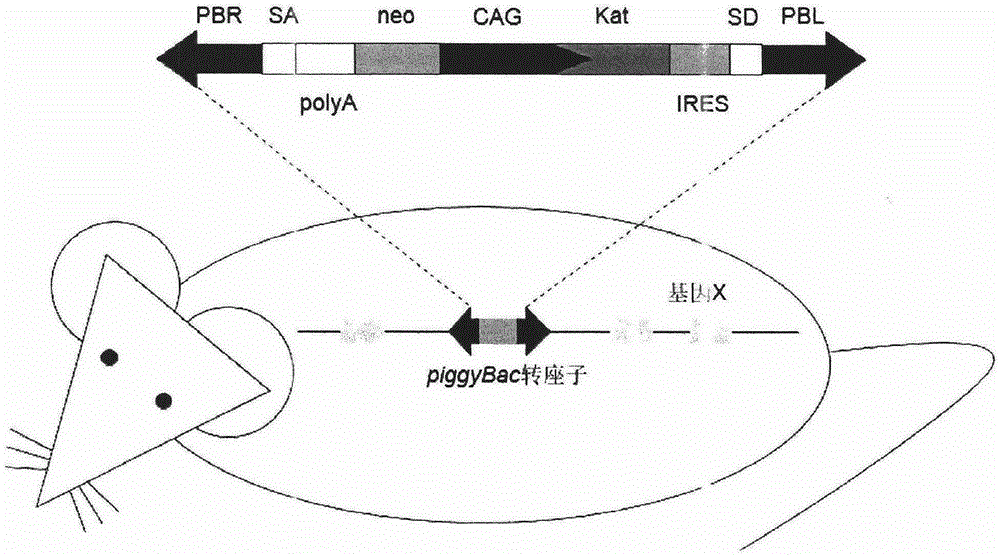
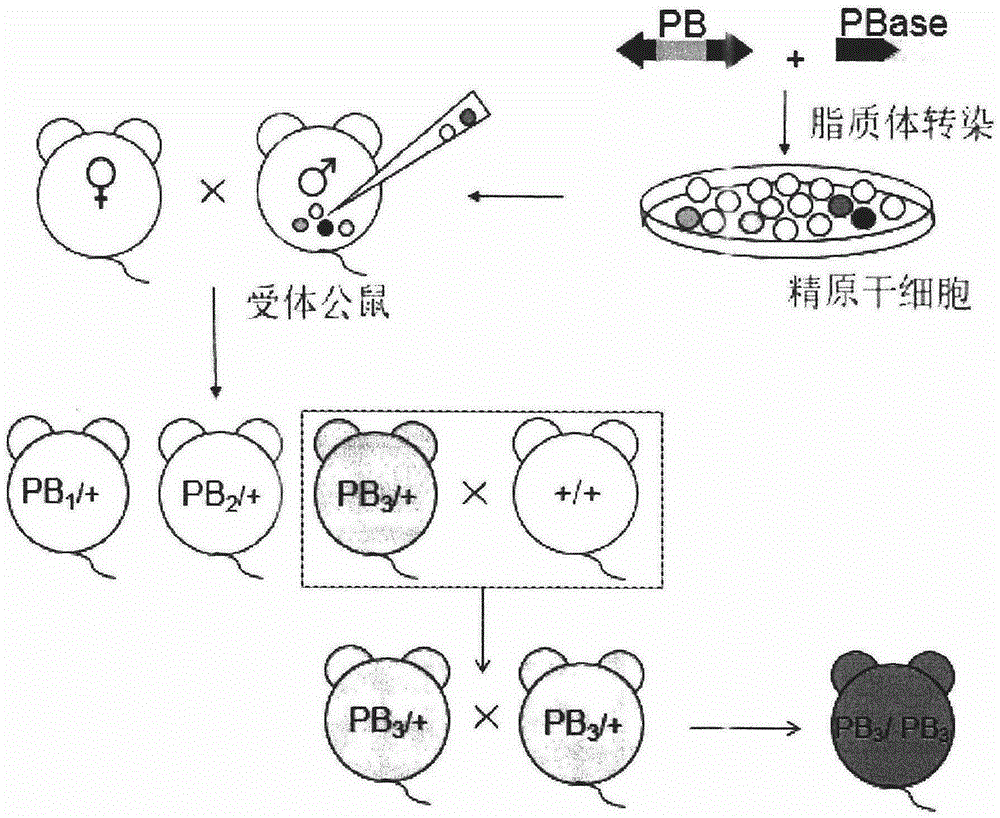
InactiveCN105238818AEfficient preparationFermentationGenetic engineeringDiseasePiggyBac Transposon System
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and relates to a method of introducing random insertion mutation to genome of in-vivo spermatogonial stem cells. In the introduction of insertion mutation, provided is a non-integrated lentivirus composite carrier carrying a piggyBac transposon system and its preparation method. The carrier and the method are applicable to efficiently preparing non-human gene mutation animals. A gene mutation animal prepared by the method is applicable to animal phenotypic analysis, gene function research, Human genetic disease simulation, novel drug screening and novel drug target finding.
Owner:浙江耶大生物医药有限公司
Method for detecting content of soluble CD28 in blood of patients suffering Graves disease
InactiveCN102735841APromote secretionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDendritic cellAutoimmune disease
The invention discloses a method for detecting the content of soluble CD28 in blood of patients suffering Graves disease. The method comprises: preparing materials, reagents and blood specimens, then sequentially conducting biotin labeling of a monoclonal antibody, identification of the biotin-labeled monoclonal antibody, drawing of an sCD28 standard work curve, separation and purification of T cells in Graves-suffering patient blood, phenotypic analysis of the T cells of the Graves-suffering patients, determination of the content of soluble CD28 in the Graves-suffering patient blood, immunoblotting analysis of the soluble CD28 in the patient blood, determination of the influence of the soluble CD28 on cytokines secreted by dendritic cells, determination of the influence of the soluble CD28 on dendritic cell NF-kB nuclear translocation and other determination steps, as well as statistical analysis. The method for detecting the content of soluble CD28 in blood of patients suffering Graves disease in the invention provides an experimental basis and theoretical base for further investigating the establishment of an optimized in vitro detection scheme by combining other soluble costimulatory molecules and the promotion significance in clinical diagnosis, treatment and prognosis assessment of autoimmune diseases, and for searching new immunologic intervention means.
Owner:SUZHOU HEALTH COLLEGE
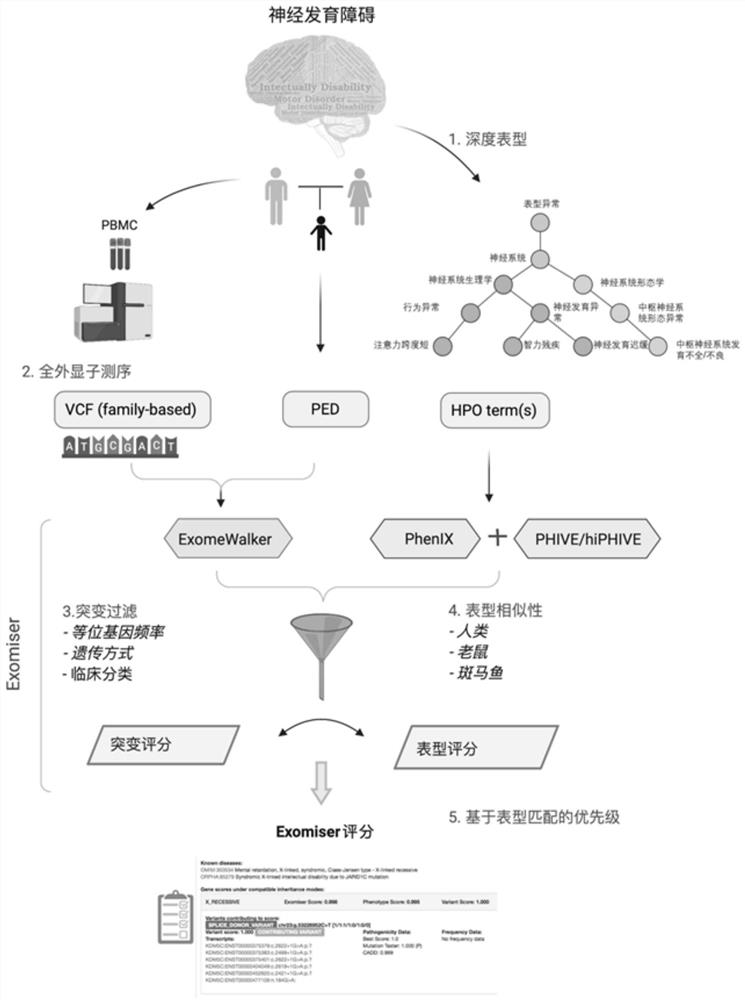
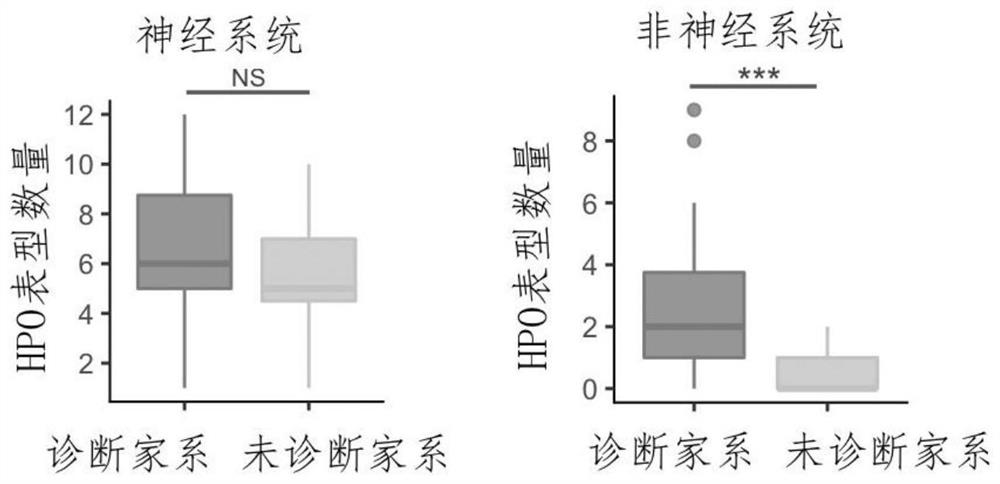
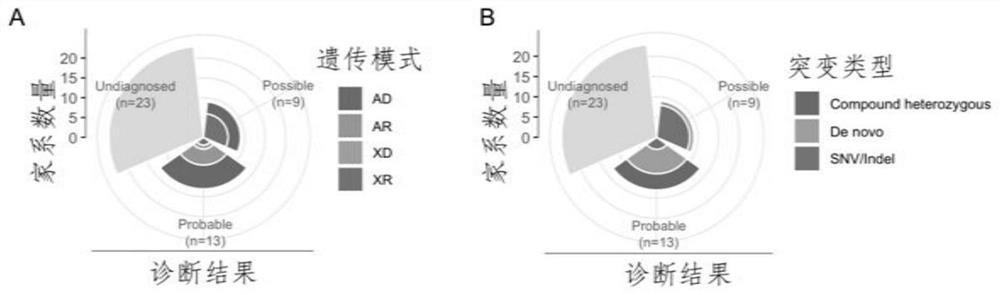
Evaluation method for judging rare hereditary diseases
PendingCN112735599AImprove evaluabilityReduce birthMedical data miningProteomicsDisease phenotypeGenes mutation
The invention discloses an evaluation method for judging rare hereditary diseases, which comprises the steps of deep phenotype analysis, whole exon group sequencing, gene mutation identification and filtration, mutation optimization combined with a genetic pattern and a disease phenotype, whole exon group sequencing and human phenotype ontology. Clinical doctors can be assisted to judge and evaluate pathogenic factors of rare hereditary diseases in time, the evaluable rate of the rare hereditary diseases is increased, a basis is provided for determining appropriate treatment measures and clinical management strategies, genetic counseling and prenatal evaluation are provided for families, birth of similar child patients is reduced, and economic burdens of the families and the society are relieved. Therefore, the method has important significance for judging the hereditary diseases with high phenotypic heterogeneity and low morbidity.
Owner:PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF HENAN PROV
Comparative phenotype analysis
InactiveUS20020110848A1Easy to atomizeReduce chanceMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEscherichia coliMammal
Owner:BIOLOG
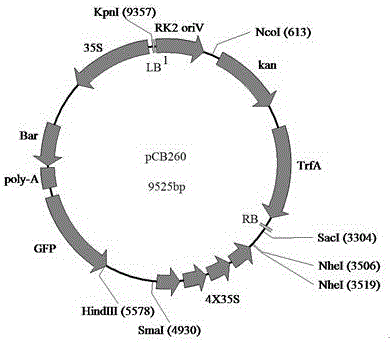
Method for obtaining brassica napus material suitable for high-density planting and mechanized harvesting
InactiveCN106834340AHigh speedLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionPlanting seedPlant genetic engineering
The invention relates to a method for obtaining a brassica napus material suitable for high-density planting and mechanized harvesting, belonging to the technical field of plant genetic engineering and biology. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: transforming an activation tagging vector pCB260 into brassica napus by adopting an agrobacterium flower soaking method; screening transformed plant seeds by utilizing a green fluorescent protein (GFP); screening brassica napus transformation plants by using herbicide phosphinothricin; and finally, identifying the transformed plants by using a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method. Phenotypic analysis of the transformed plants discovers that subramose brassica napus mutants are obtained and recorded as sfz. The plant accords with Mendel's law in F2-generation growth, the leaf surface at the seedling stage is bright, a few branches can grow at the maturation stage, the effective branch height is increased, and the siliques are centralized on the top of the plant. The brassica napus mutant obtained by transforming the brassica napus by utilizing the activation tagging vector pCB260 provides a novel material for large-scale mechanized production study and has important application prospect.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
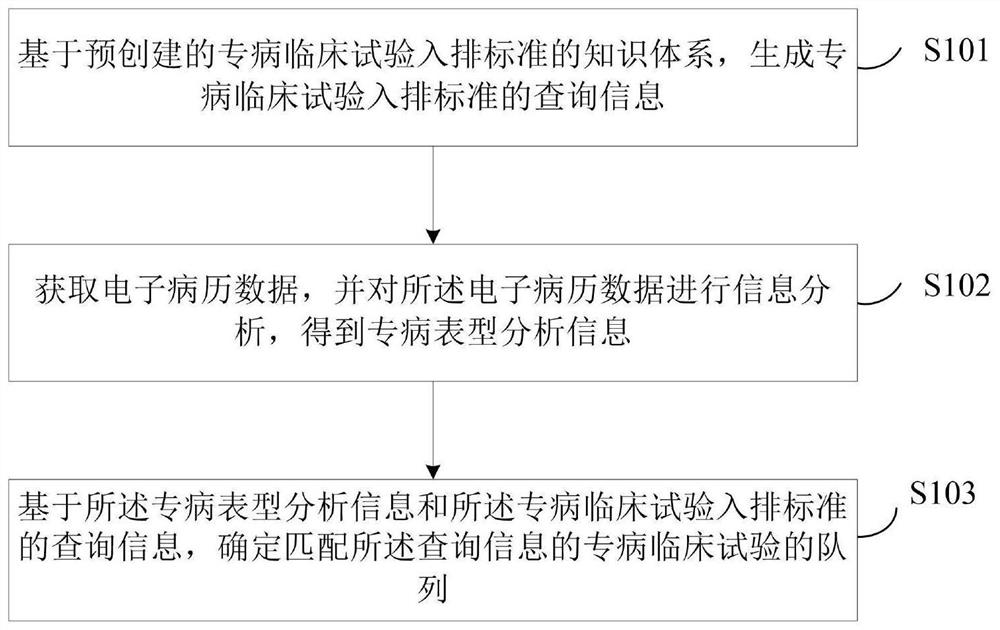
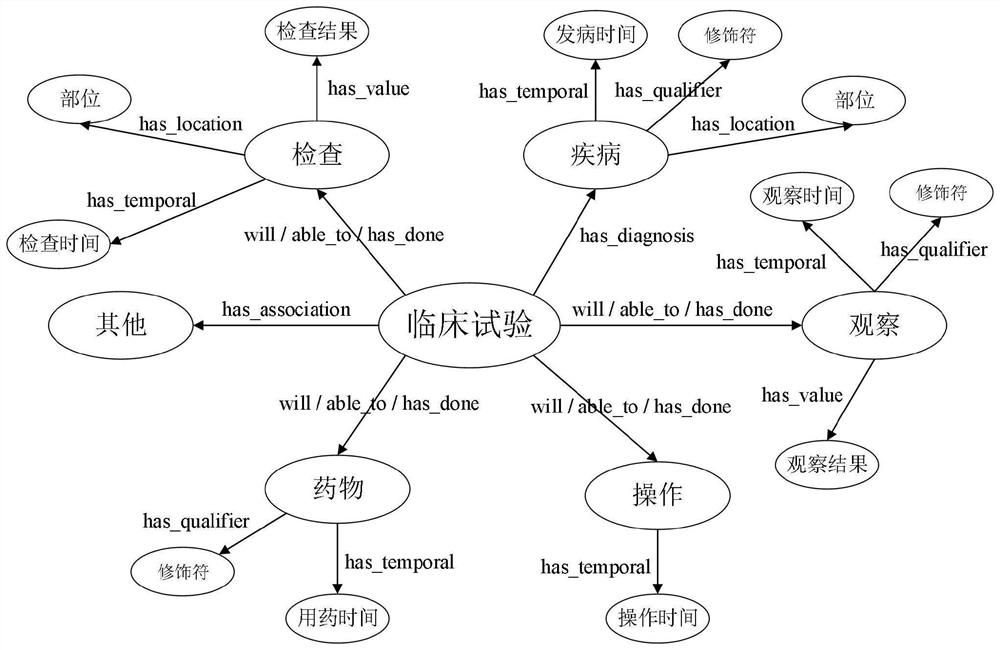
Queue identification method and device applied to special disease clinical test
PendingCN111667891AImprove processing efficiencyImprove accuracyMedical data miningLaboratory analysis dataMedical recordDisease phenotype
The invention discloses a queue identification method and device applied to a special disease clinical test. The method comprises the following steps: based on a pre-established knowledge system of aspecial disease clinical test in-and-out standard, generating query information of the special disease clinical test in-and-out standard; acquiring electronic medical record data, and performing information analysis on the electronic medical record data to obtain special disease phenotype analysis information; and based on the special disease phenotypic analysis information and the query information of the special disease clinical test in-and-out standard, determining a special disease clinical test queue matched with the query information. According to the invention, the knowledge system of the special disease clinical test in-and-out standard is a system for expressing the special disease clinical test in-and-out standard by knowledge of computer recognizable information; the in-and-outstandard is automatically converted into the structured query language, the electronic medical record data can be directly processed, a subject meeting the special disease clinical test is obtained, the information conversion processing efficiency is improved, and the accuracy of the queue identification work of the clinical test is improved.
Owner:中国医学科学院医学信息研究所
Resource library of rat with gene mutation and preparation method thereof
PendingCN106521638ANucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant Germ CellsDrug target
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and relates to a resource library of rat strains with gene mutation and a preparation method thereof. The rats with gene mutation in the resource library can be obtained from rat spermatogonial stem cells, embryonic stem cells or fertilized ovum with piggyBac transposon insertion mutation. The rats with gene mutation in the resource library also can be obtained from shifting the transposon in germ cells of male rats with mutation. The library can be applied to animal phenotype analysis, gene function research, human disease simulation, medicament screening and drug target development.
Owner:浙江耶大生物医药有限公司
Cloning and application of flowering period BnFLC.A2 and Bnflc.a2 genes of brassica napus
The invention provides cloning and application of flowering period BnFLC.A2 and Bnflc.a2 genes of brassica napus, and particularly provides isolation cloning, functional verification and application of two DNA fragments of an early flowering Bnflc.a2 gene and a later flowering BnFLC.A2 allele of rape. The early flowering Bnflc.a2 allogene is a loss-of-function mutant of the BnFLC.A2 gene. A functional marker of the early flowering gene is developed; the Bnflc.a2 gene has remarkable influence on the flowering period in a natural population under seven environments through the natural population genotype and flowering period phenotypic analysis of 495 portions of brassica napus, which shows that the copy function loss caused by the insertion of long fragments in the Bnflc.a2 is an important factor influencing the natural variation of the flowering time of the brassica napus. A serial design functional marker of the Bnflc.a2 itself is used for carrying out assisted selection of molecular markers and breeding early-flowering materials, thereby breeding early-flowering and early-maturing rape. The invention has the characteristics of accuracy, high efficiency and economy.
Owner:武汉联农种业科技有限责任公司
Method for identifying camellia japonica color bud mutation varieties
ActiveCN110133141AClear relationshipGood repeatabilityComponent separationHorticulture methodsTime-of-flight mass spectrometryPetal
The invention discloses a method for identifying camellia japonica color bud mutation varieties. A high performance liquid chromatography-photodiode array detection and ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole rod-gas chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry is used for researching the composition and content of anthocyanins in red petals of the camellia japonica variety andpetals of pink and white bud mutation varieties, combined with the phenotypic analysis of flower colors, the camellia japonica color bud mutation is effectively identified, the relationship between the camellia japonica color bud mutation and the anthocyanins is determined, and the material base of forming the camellia japonica color bud mutation is revealed, so that a scientific basis is providedfor the breeding of the camellia japonica color bud mutation.
Owner:RES INST OF SUBTROPICAL FORESTRY CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Cold sensitivity related OfHSF11 gene of cinnamomum rixiangxiense as well as encoding protein and application of cold sensitivity related OfHSF11 gene
PendingCN114317558AHigh cold sensitivityPlant peptidesGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a osmanthus fragrans cold sensitivity related OfHSF11 gene as well as an encoding protein and application thereof, and belongs to the field of plant molecular biology. A transcription factor which is separated and cloned from osmanthus fragrans based on a plant gene cloning technology is named OfHSF11, and the nucleotide sequence of the transcription factor is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. On the basis, an over-expression vector is constructed, instantaneous transformation of nicotiana benthamiana is carried out, and phenotypic analysis before and after low-temperature treatment shows that the transcription factor is a transcription factor which is named as OfHSF11 and is named as OfHSF11. The cold sensitivity of the OfHSF11 transfected plant is obviously higher than that of the non-OfHSF11 transfected plant, which indicates that the OfHSF11 gene is a potential cold resistance indicator gene, and a useful gene resource is provided for cold resistance genetic improvement breeding of sweet osmanthus.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com