Patents
Literature
59 results about "Natural variation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Natural variation is another term for reproductive variation, or descent with modification. This basically means that the offspring is never entirely like its parents. In all life forms, genetic mutation is one source of reproductive variation.
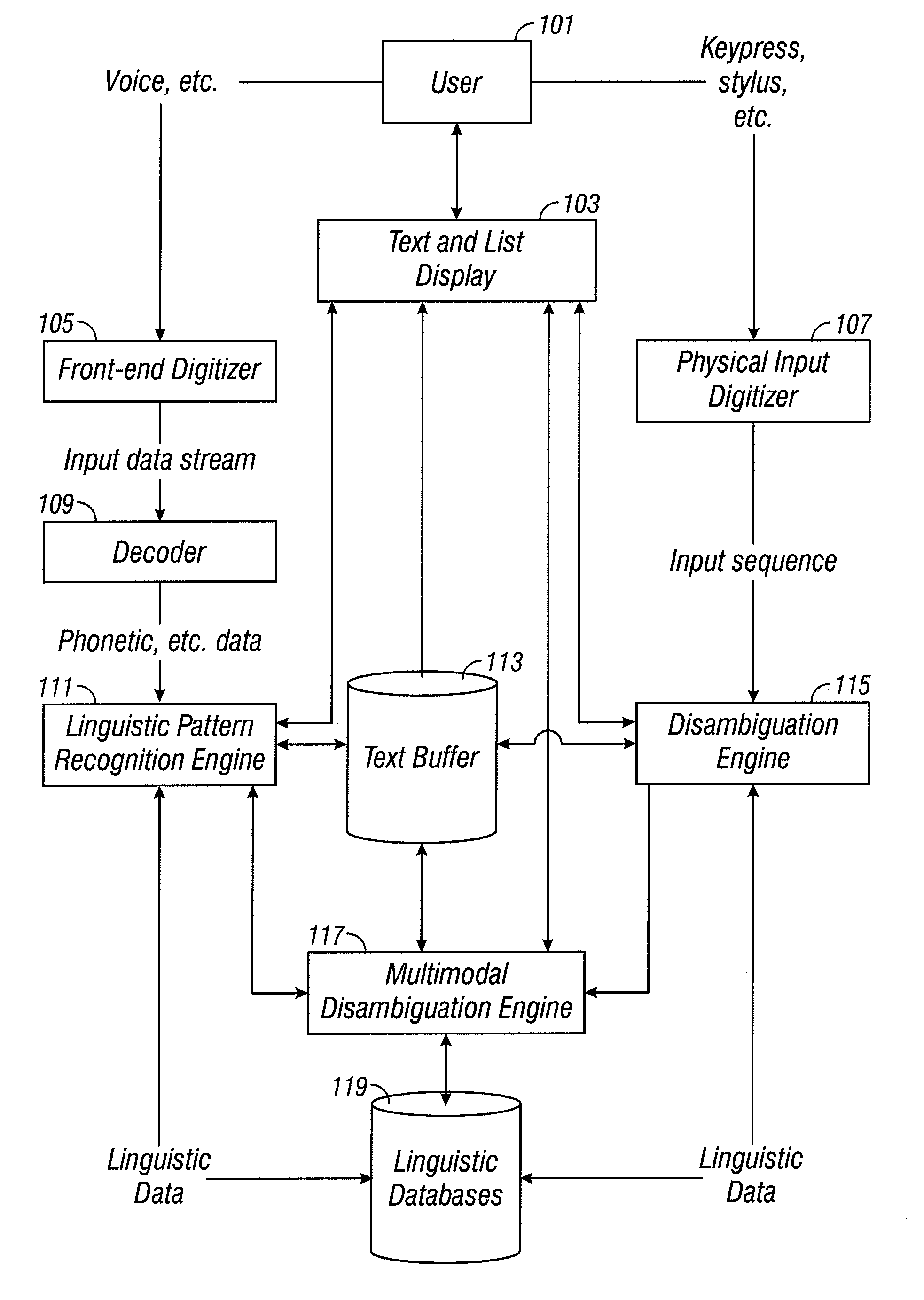
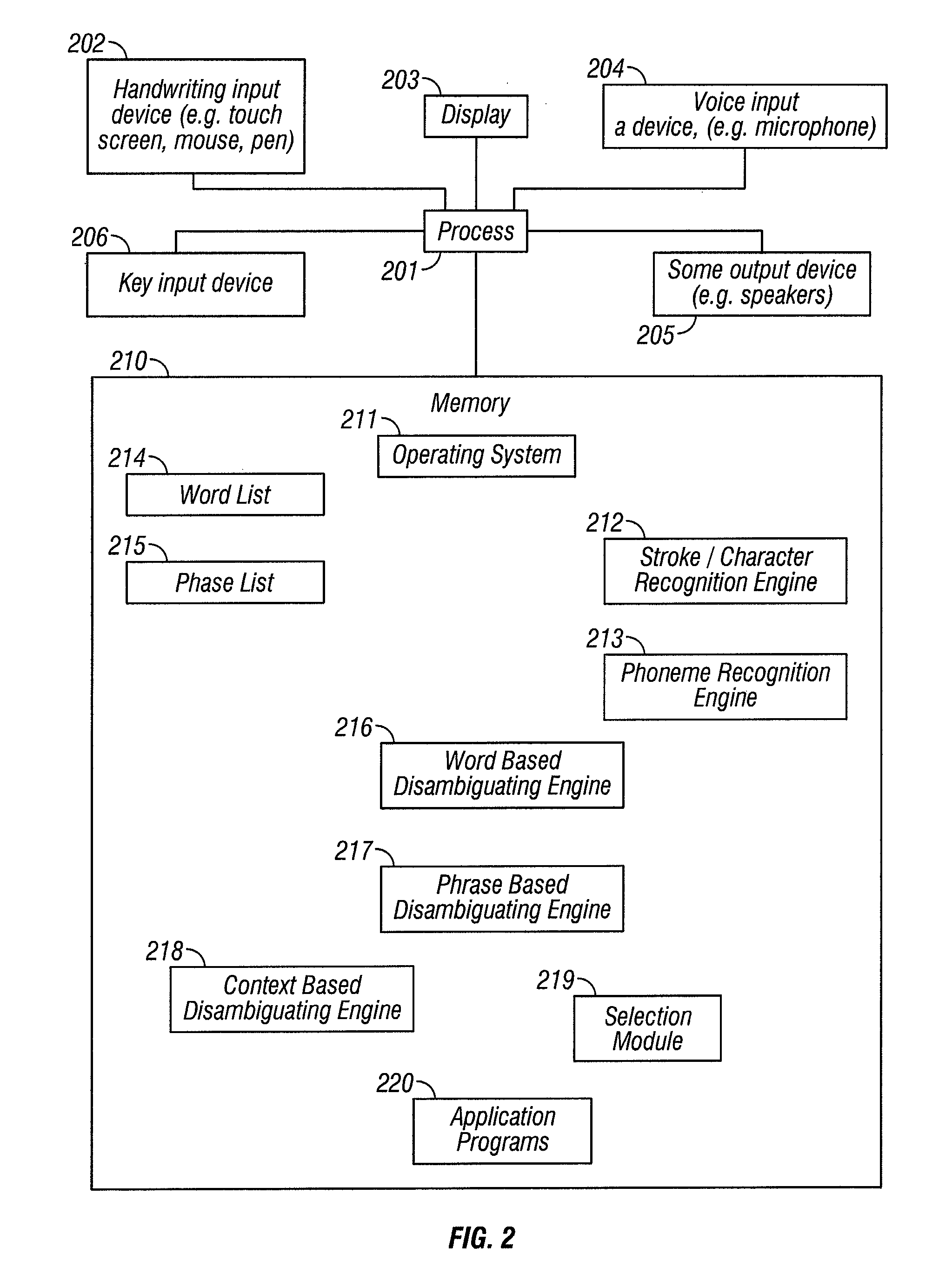
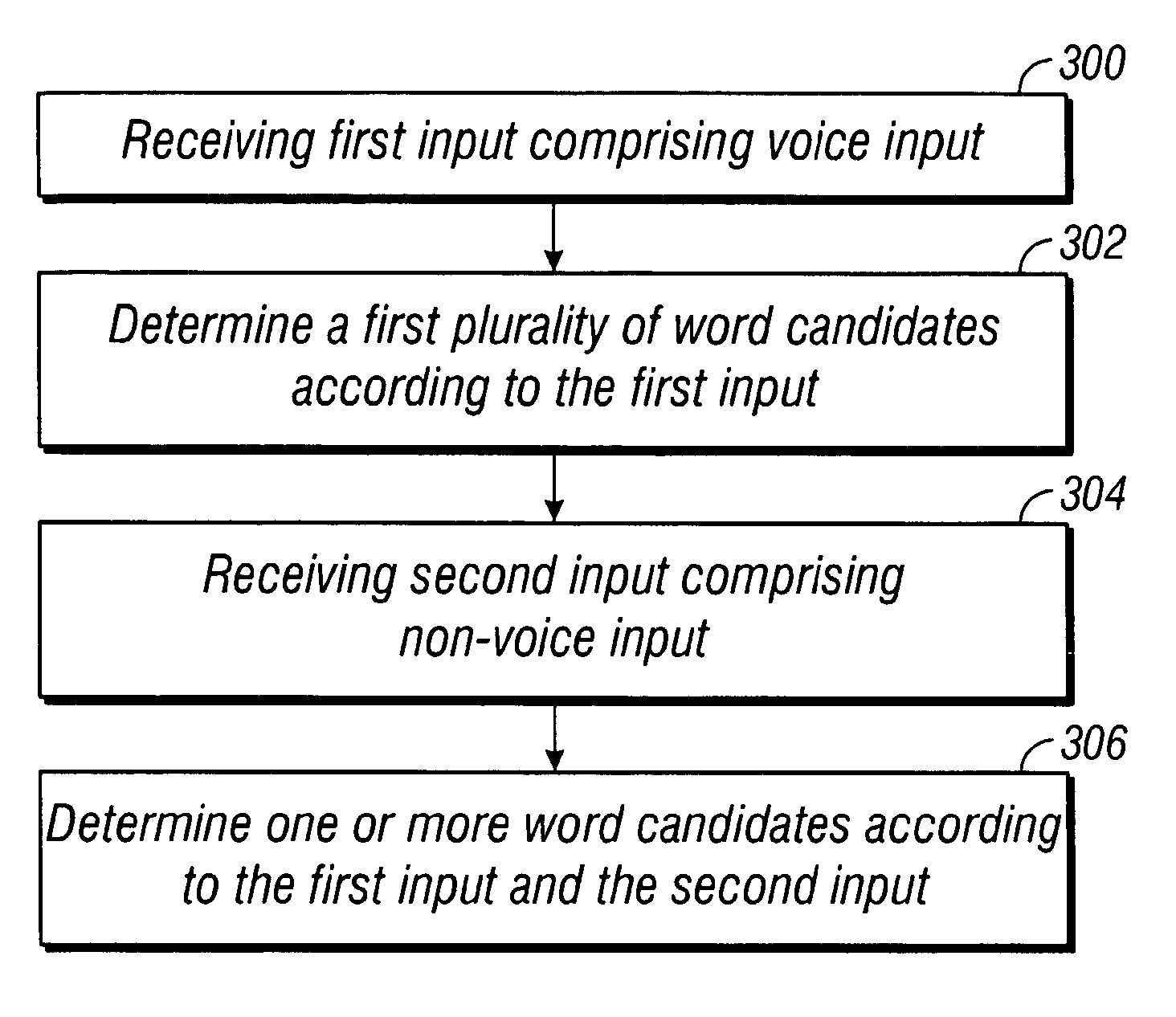
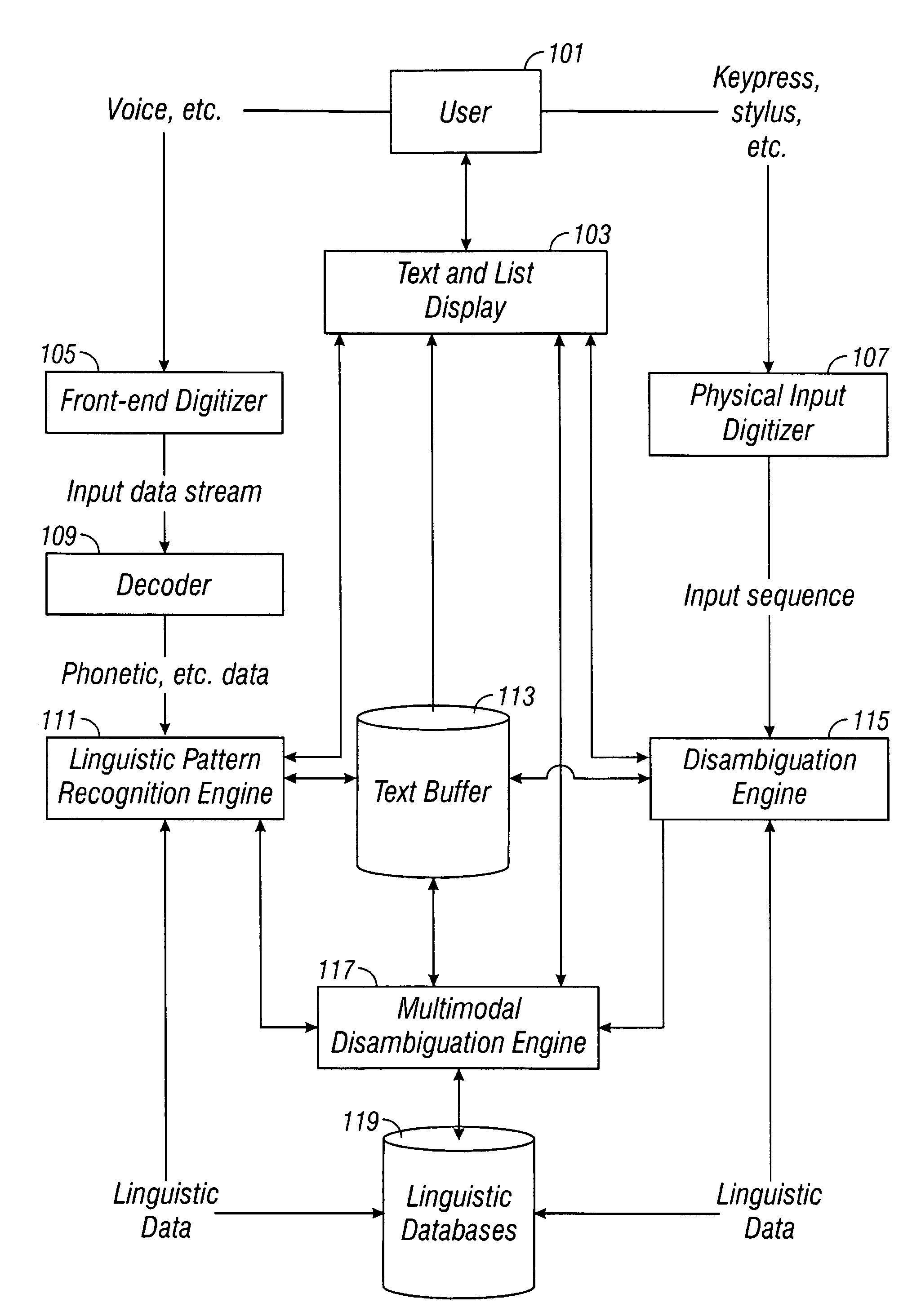
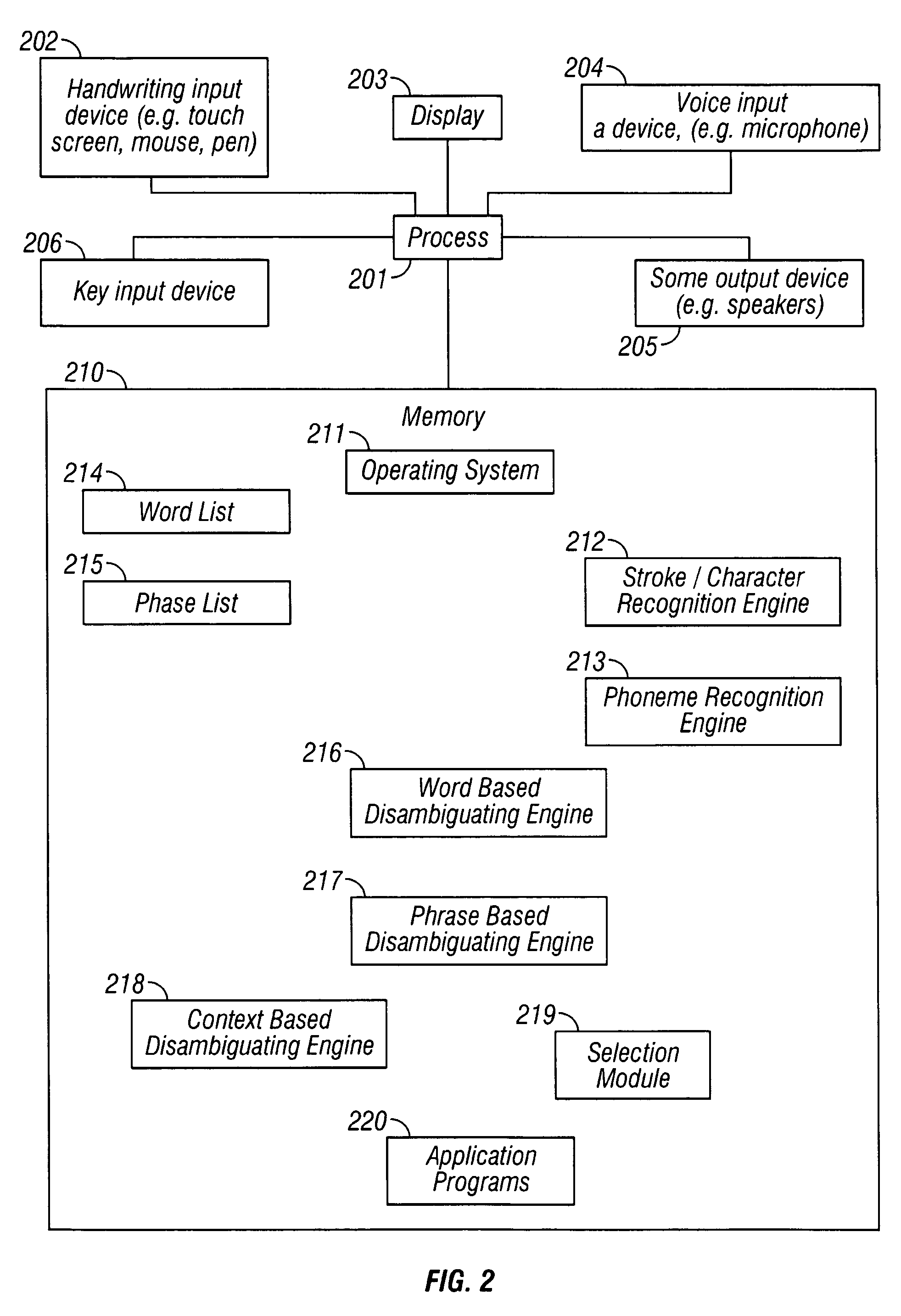
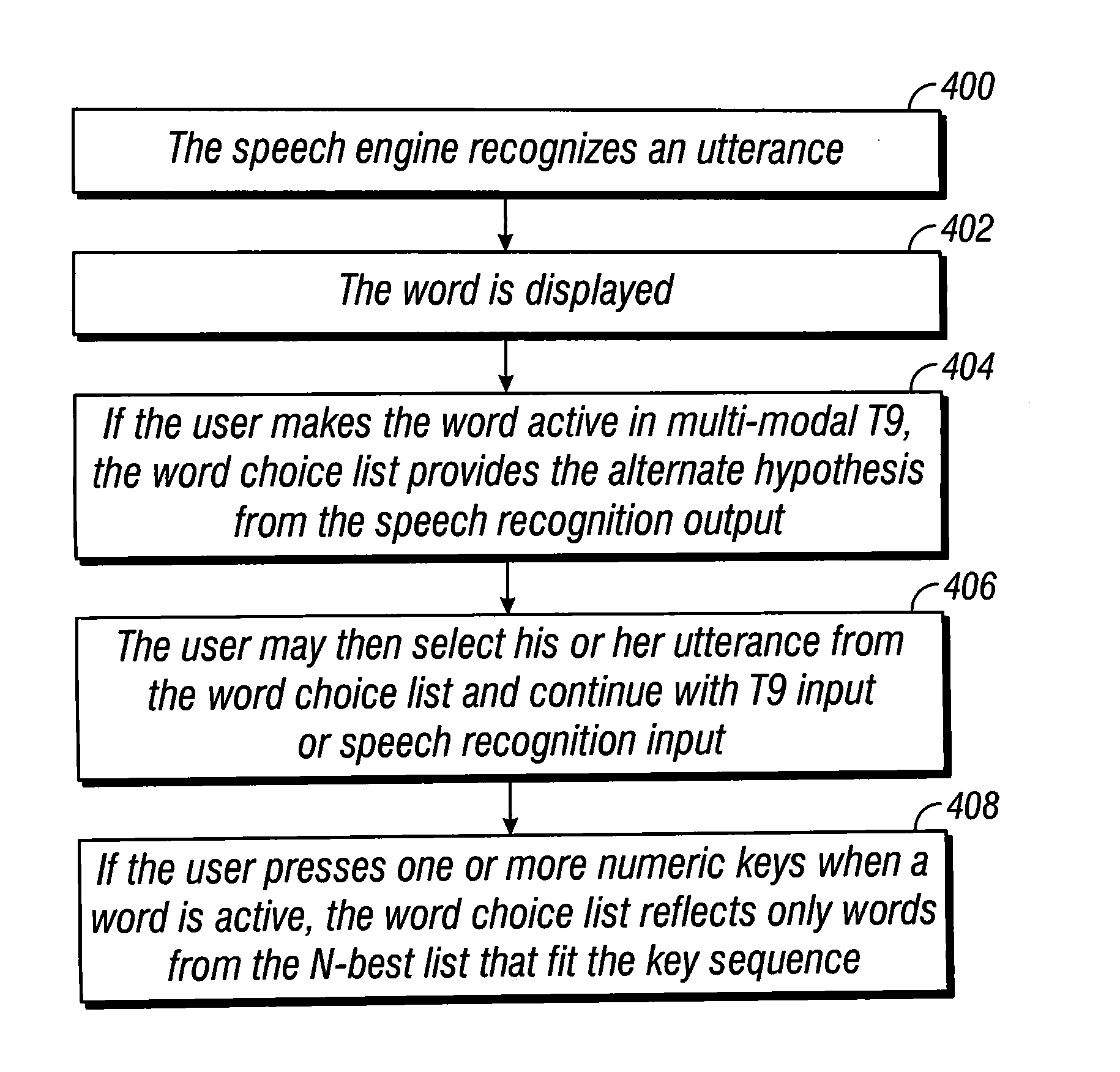
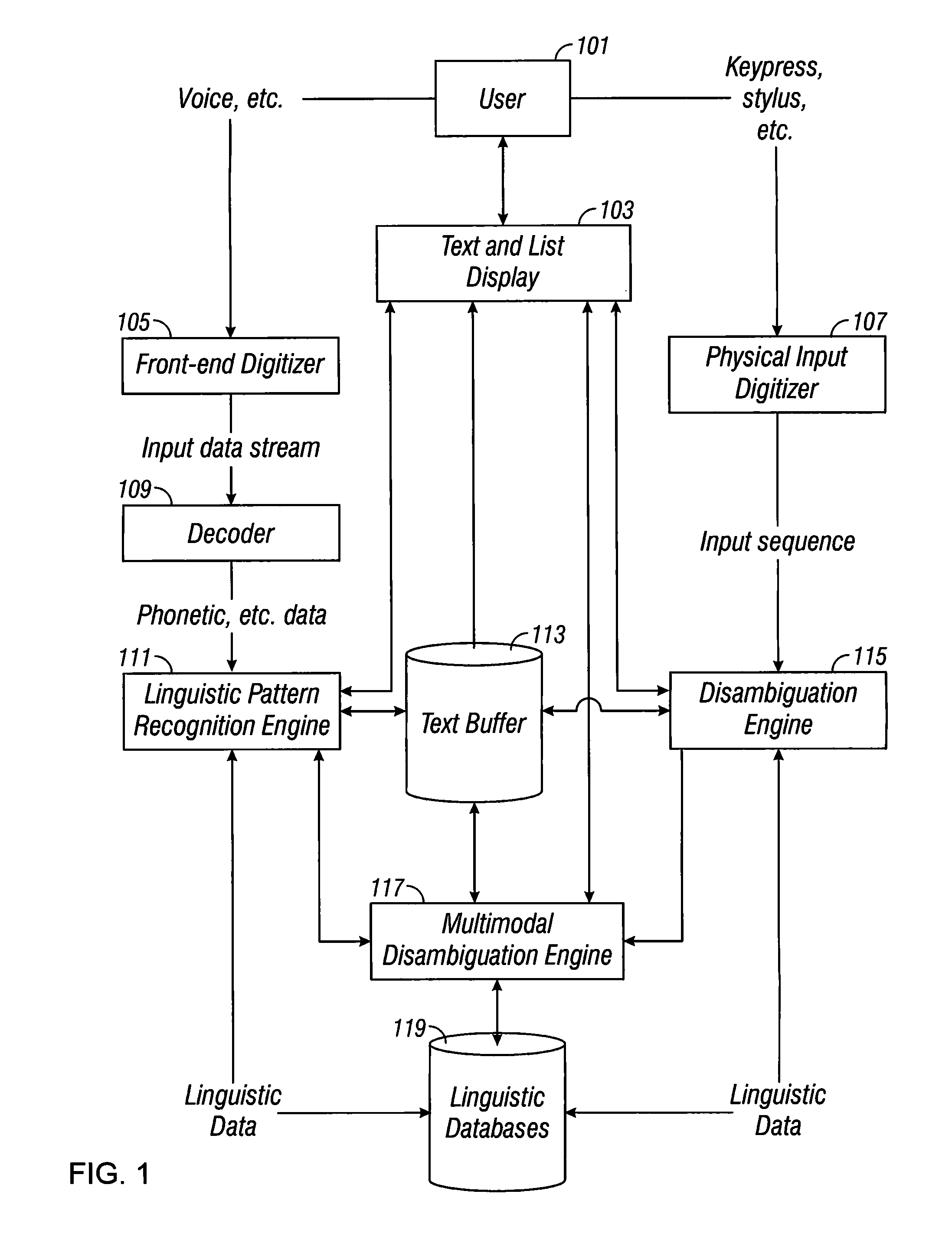
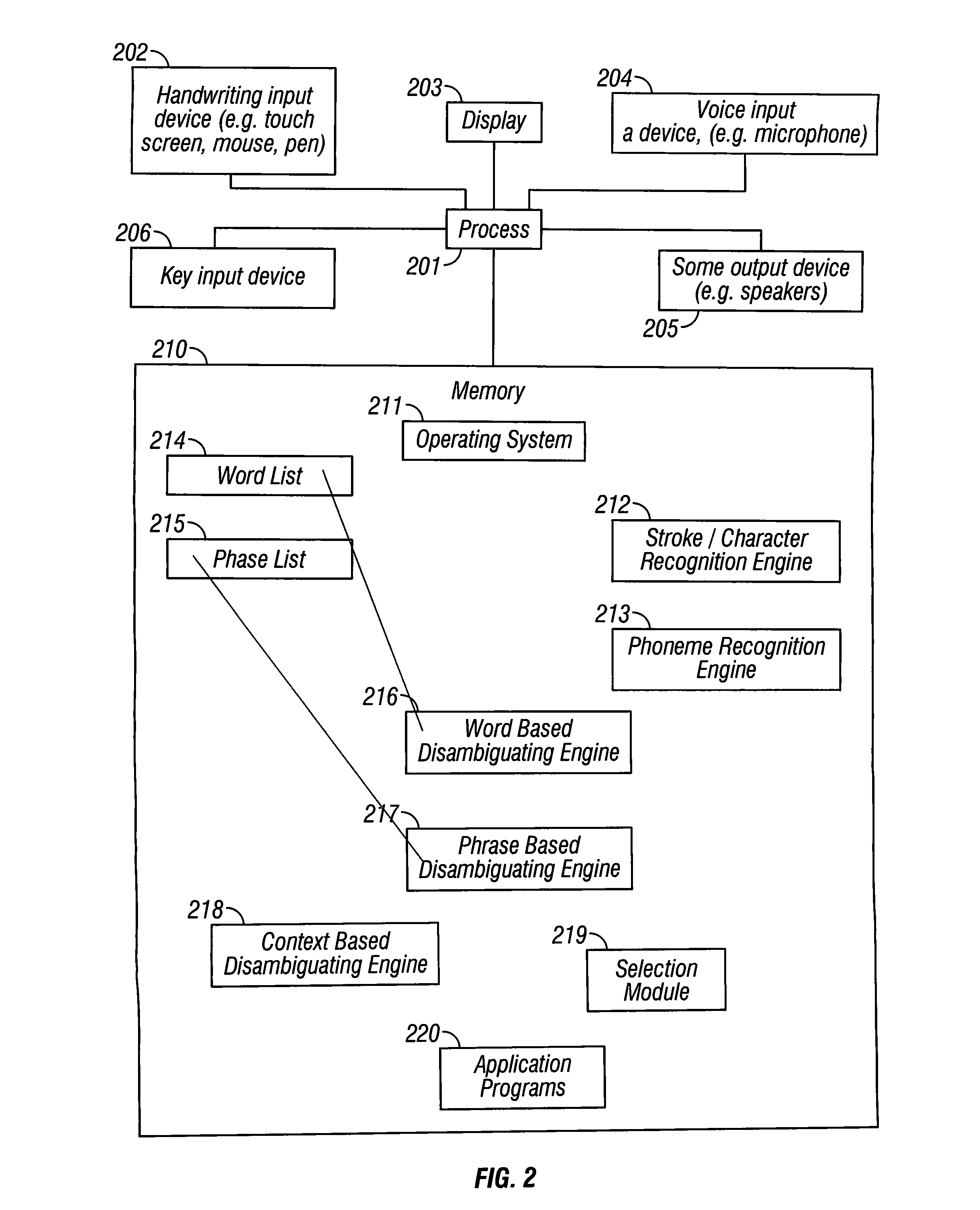
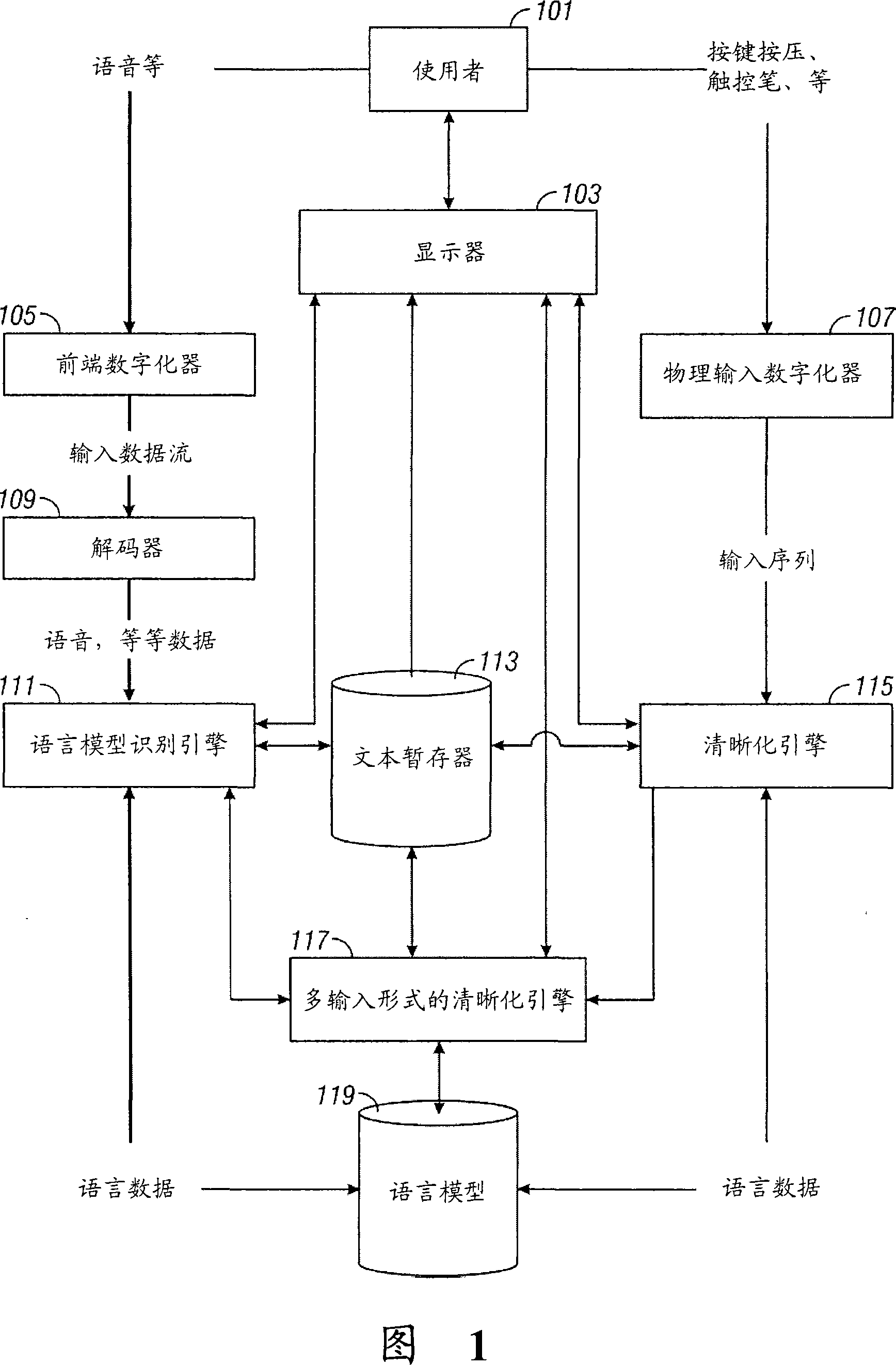
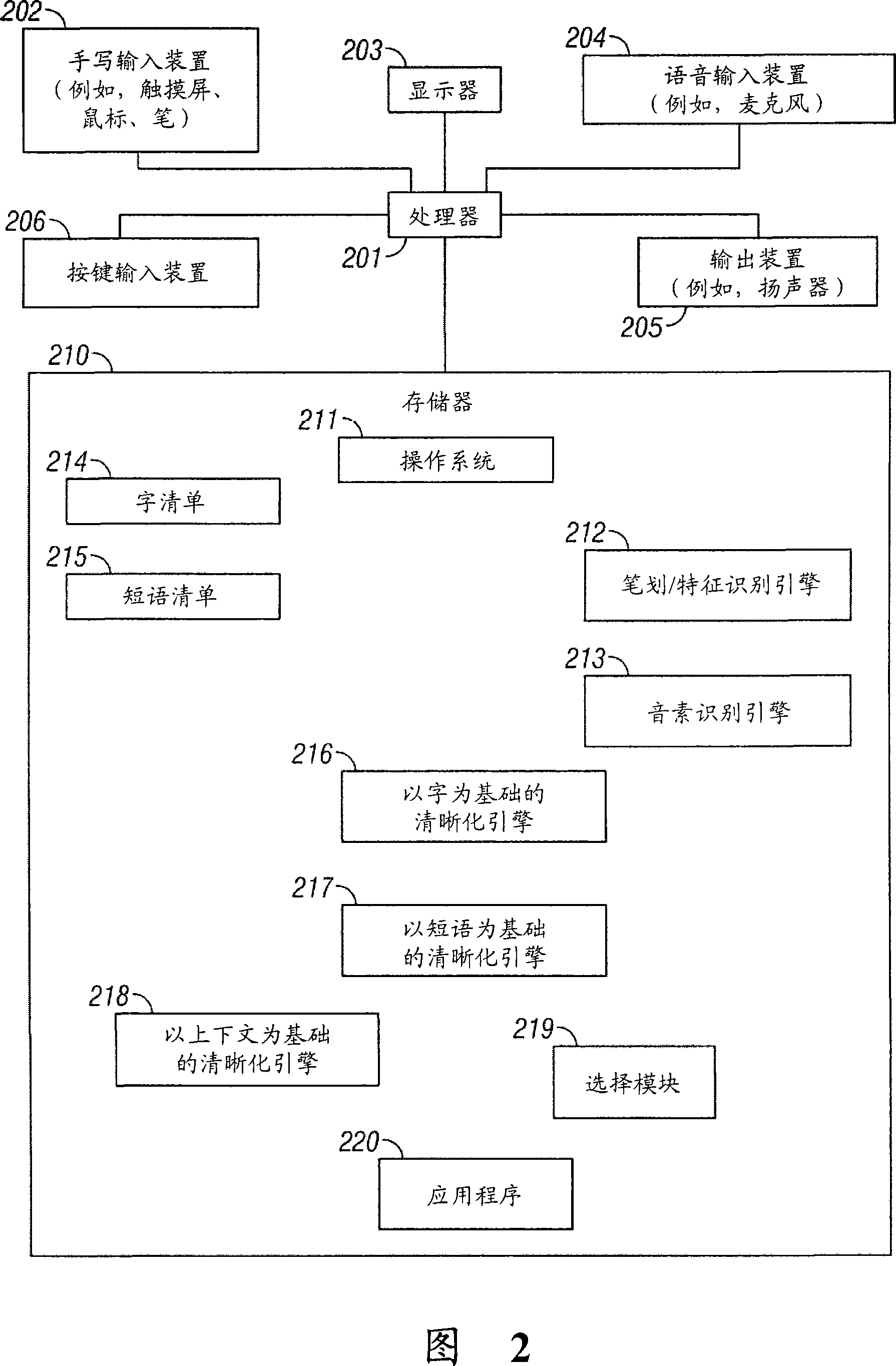
Multimodal disambiguation of speech recognition
InactiveUS8095364B2Resolves the recognition errors efficiently and accuratelySpeech recognitionEnvironmental noiseAmbiguity
The present invention provides a speech recognition system combined with one or more alternate input modalities to ensure efficient and accurate text input. The speech recognition system achieves less than perfect accuracy due to limited processing power, environmental noise, and / or natural variations in speaking style. The alternate input modalities use disambiguation or recognition engines to compensate for reduced keyboards, sloppy input, and / or natural variations in writing style. The ambiguity remaining in the speech recognition process is mostly orthogonal to the ambiguity inherent in the alternate input modality, such that the combination of the two modalities resolves the recognition errors efficiently and accurately. The invention is especially well suited for mobile devices with limited space for keyboards or touch-screen input.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
Multimodal disambiguation of speech recognition
InactiveUS20050283364A1Efficient and accurate text inputLow accuracyCathode-ray tube indicatorsSpeech recognitionEnvironmental noiseDiagnostic Radiology Modality
The present invention provides a speech recognition system combined with one or more alternate input modalities to ensure efficient and accurate text input. The speech recognition system achieves less than perfect accuracy due to limited processing power, environmental noise, and / or natural variations in speaking style. The alternate input modalities use disambiguation or recognition engines to compensate for reduced keyboards, sloppy input, and / or natural variations in writing style. The ambiguity remaining in the speech recognition process is mostly orthogonal to the ambiguity inherent in the alternate input modality, such that the combination of the two modalities resolves the recognition errors efficiently and accurately. The invention is especially well suited for mobile devices with limited space for keyboards or touch-screen input.
Owner:TEGIC COMM
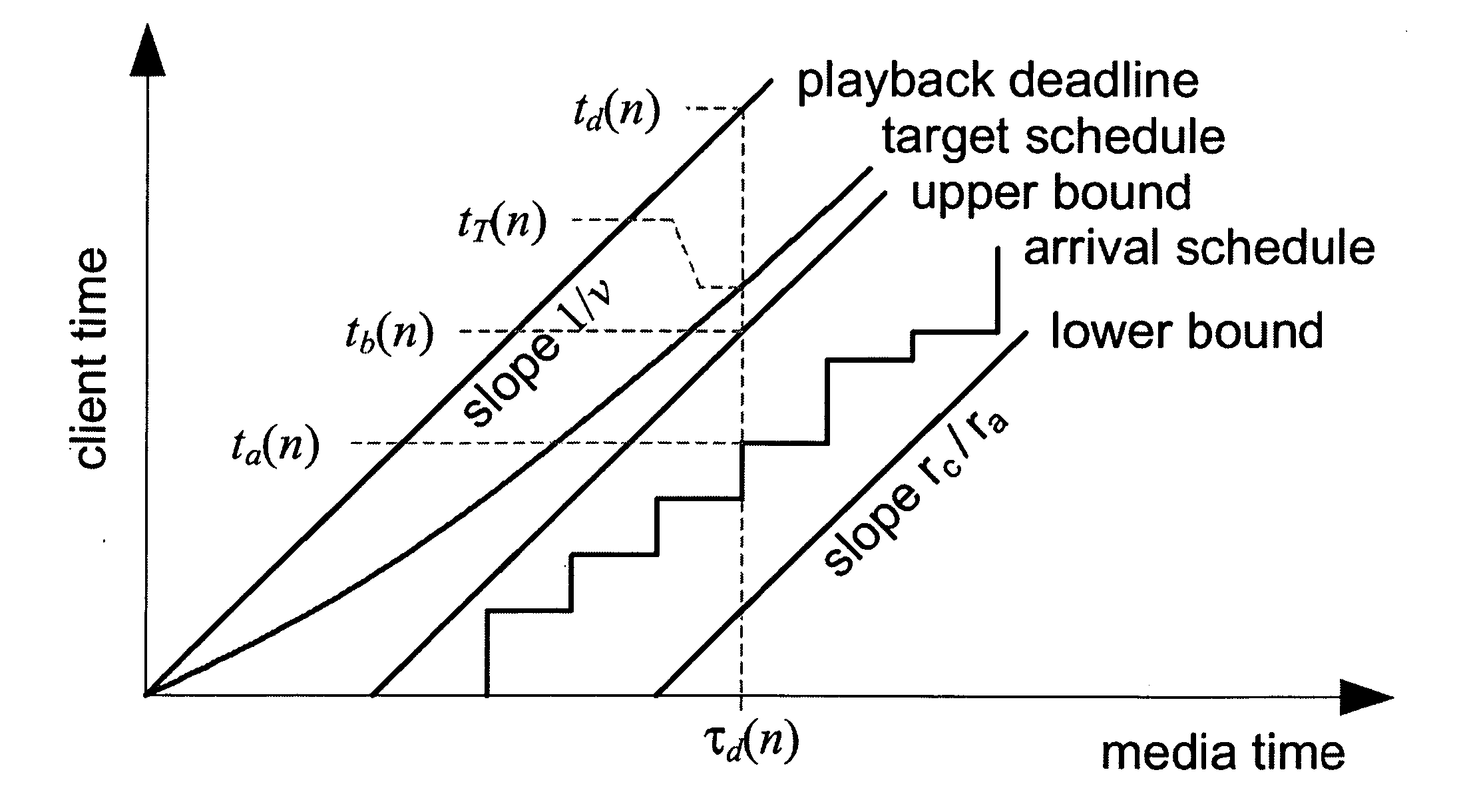
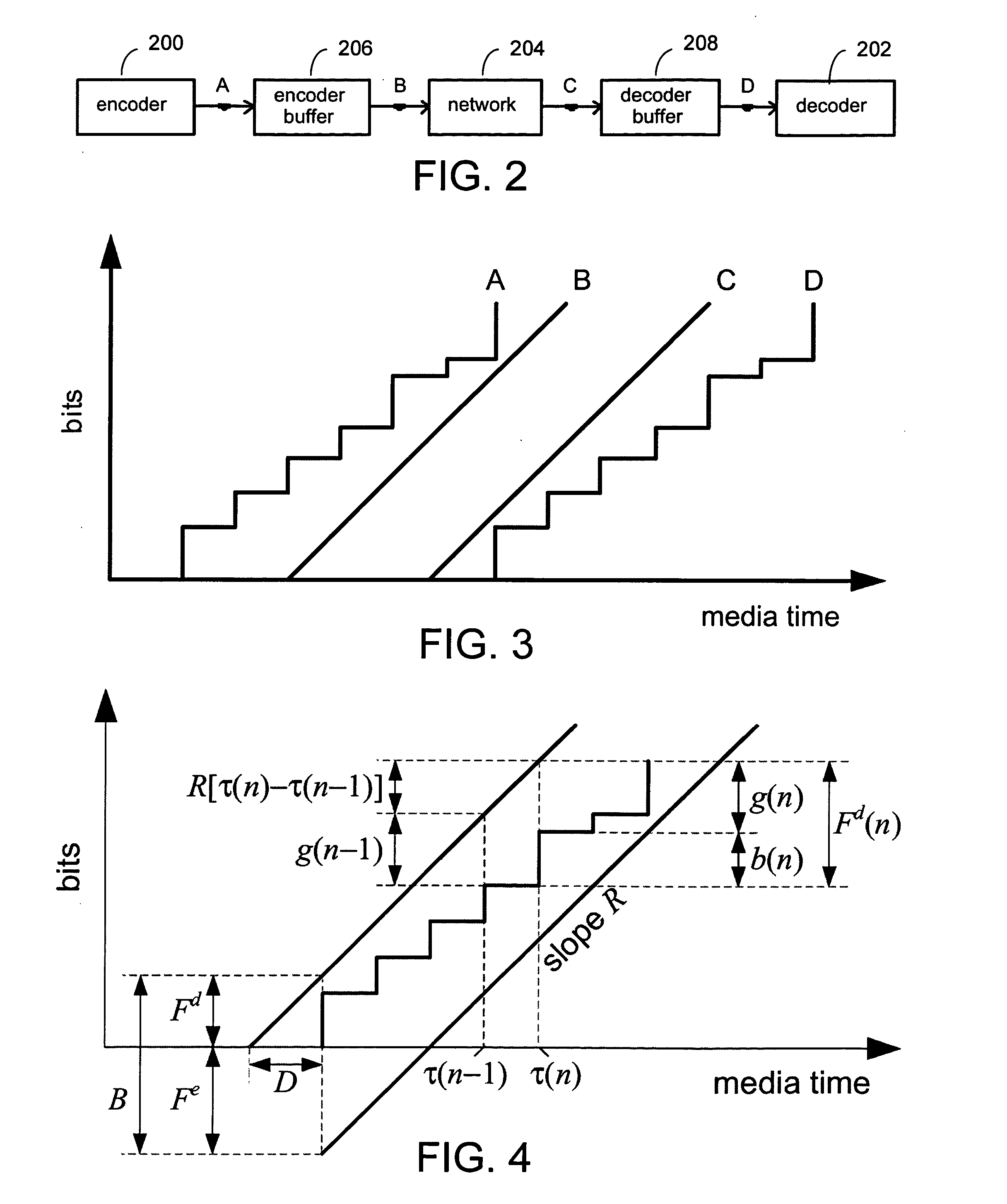
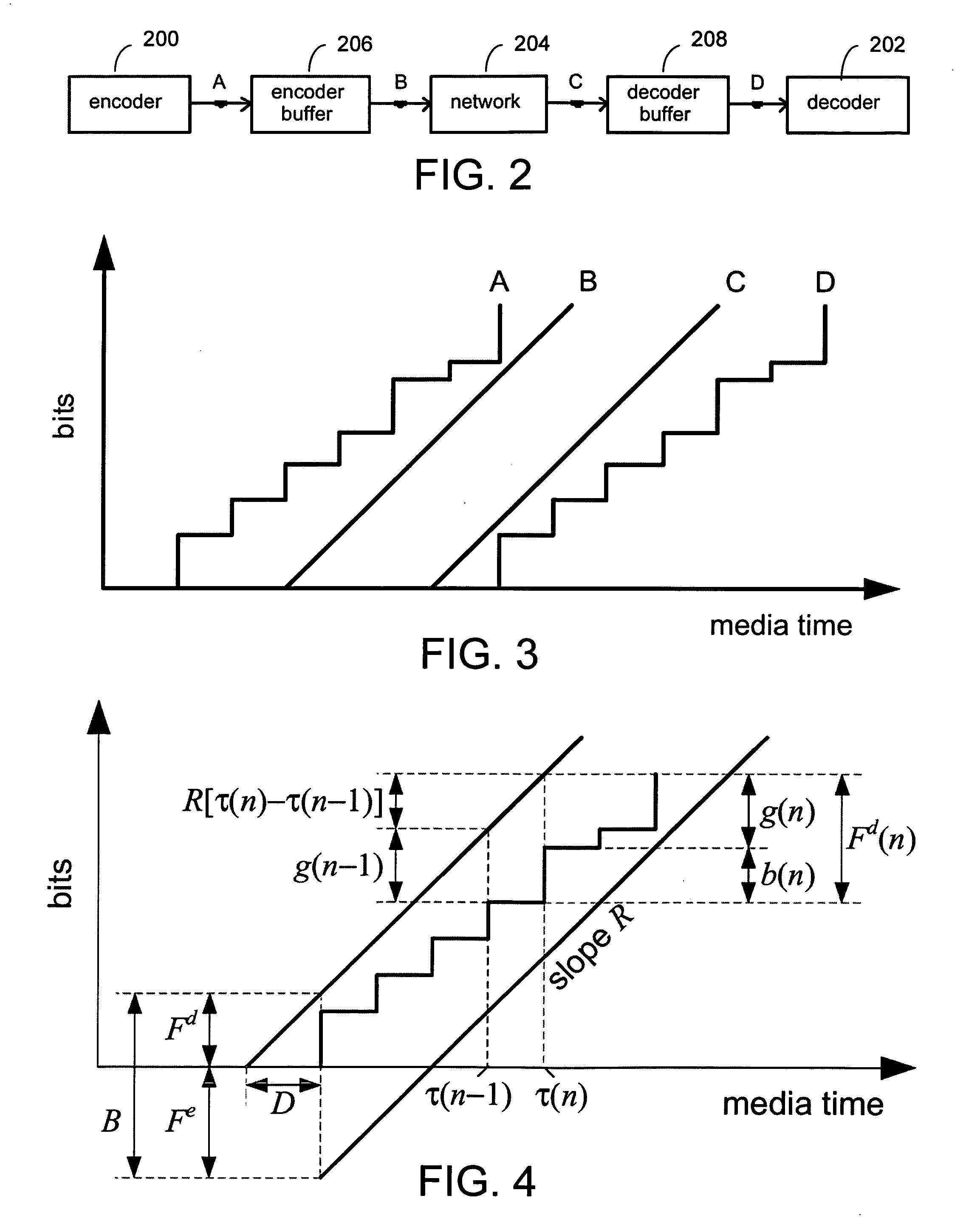
System and process for controlling the coding bit rate of streaming media data employing a limited number of supported coding bit rates
InactiveUS20060165166A1Maximize qualityStable and high qualityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningStreaming dataNatural variation
A system and process for controlling the coding bit rate of streaming media data is presented where a server streams data that exhibits one of a number of coding bit rates supported by the server. Initially, the server chooses the coding bit rate. However, after this startup period, the client provides coding bit rate requests. The server transmits the streaming media data at the most appropriate supported coding bit rate closest to the rate requested. The coding bit rates requested are those estimated to provide a high quality playback of the streaming data while still keeping a decoder buffer of the client filled to a desired level. A leaky bucket model is incorporated so that the changes in buffer duration due to natural variation in the instantaneous coding bit rate are not mistaken for changes in buffer duration due to network congestion.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and process for controlling the coding bit rate of streaming media data employing a linear quadratic control technique and leaky bucket model
InactiveUS20060143678A1Maximize qualitySmoothness of the average coding bit rate over consecutiveTwo-way working systemsDigital video signal modificationModel controlClient buffer
A system and process for controlling the coding bit rate of streaming media data is presented. This coding bit rate control involves dynamically adjusting the coding bit rate to control client buffer duration to prevent the buffer from underflowing, while keeping the average coding bit rate close to the average transmission bit rate of the network (an thus maximizing the quality of the data playback). Using the theory of optimal linear quadratic control, the client buffer duration is kept as close as possible to a target level while still keeping the coding bit rate (and hence the quality) as constant as possible. In addition, a leaky bucket model is incorporated into the control loop so that the changes in buffer duration due to natural variation in the instantaneous coding bit rate are not mistaken for changes in buffer duration due to network congestion.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
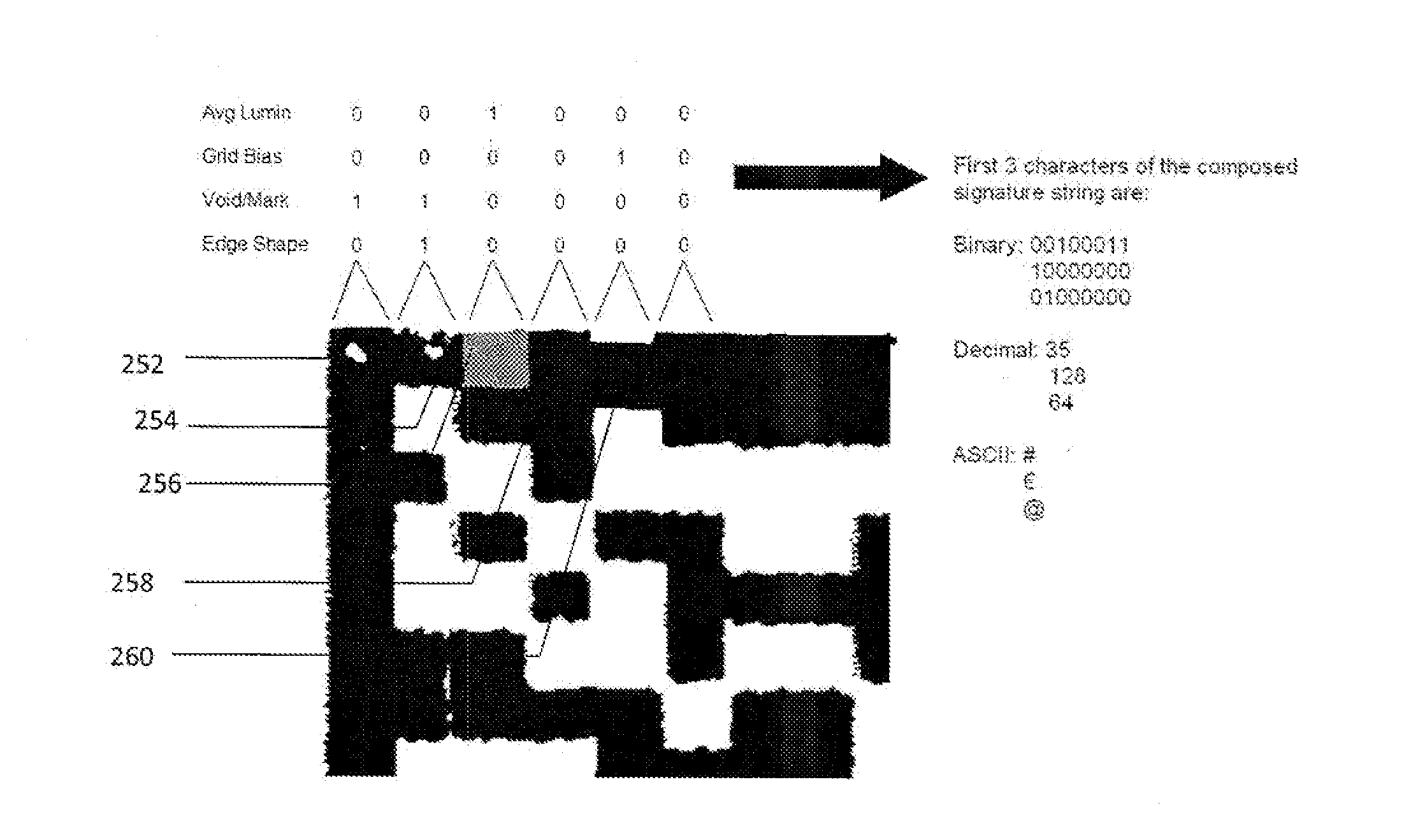
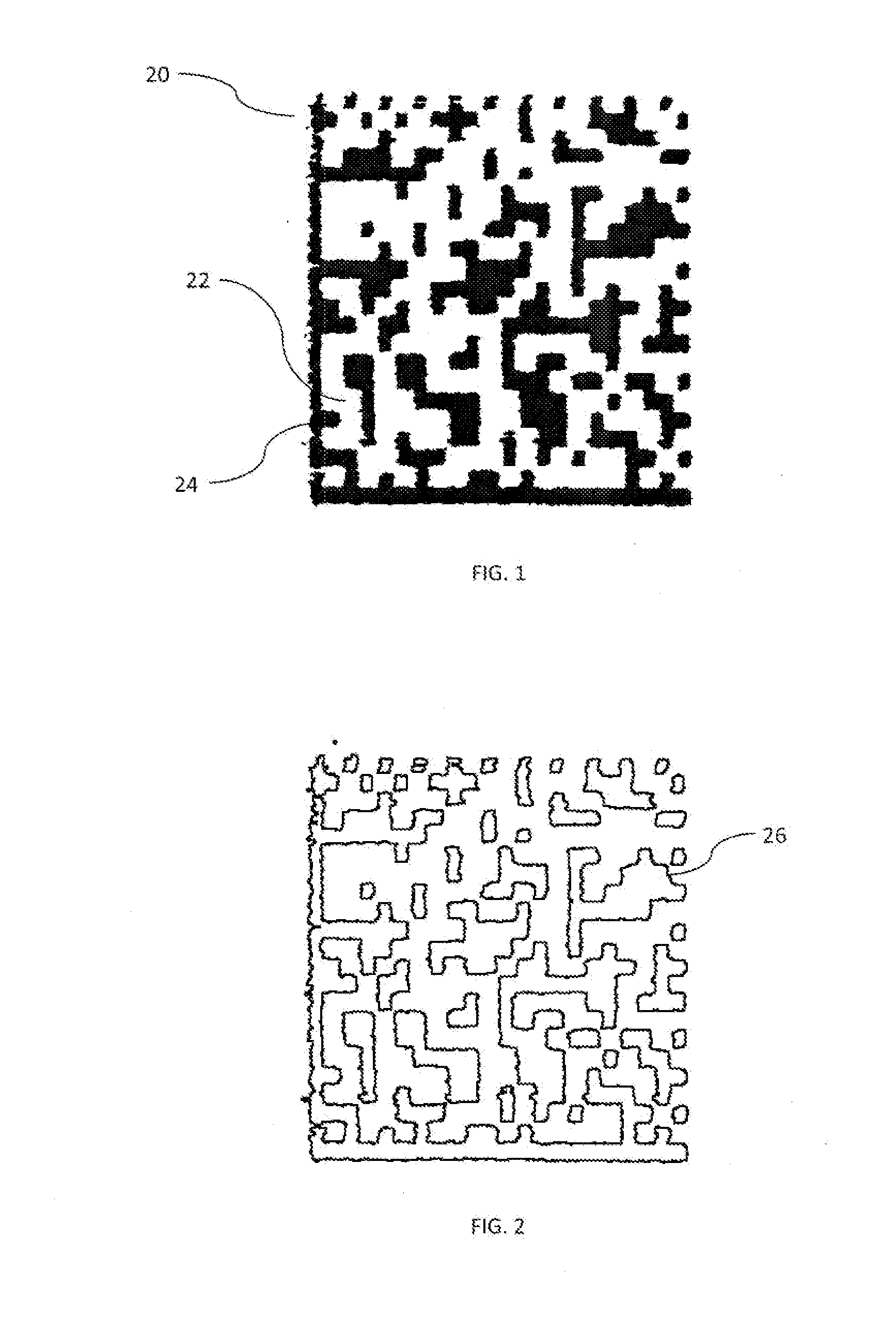
Unique Identification Information From Marked Features
Owner:SYS TECH SOLUTIONS
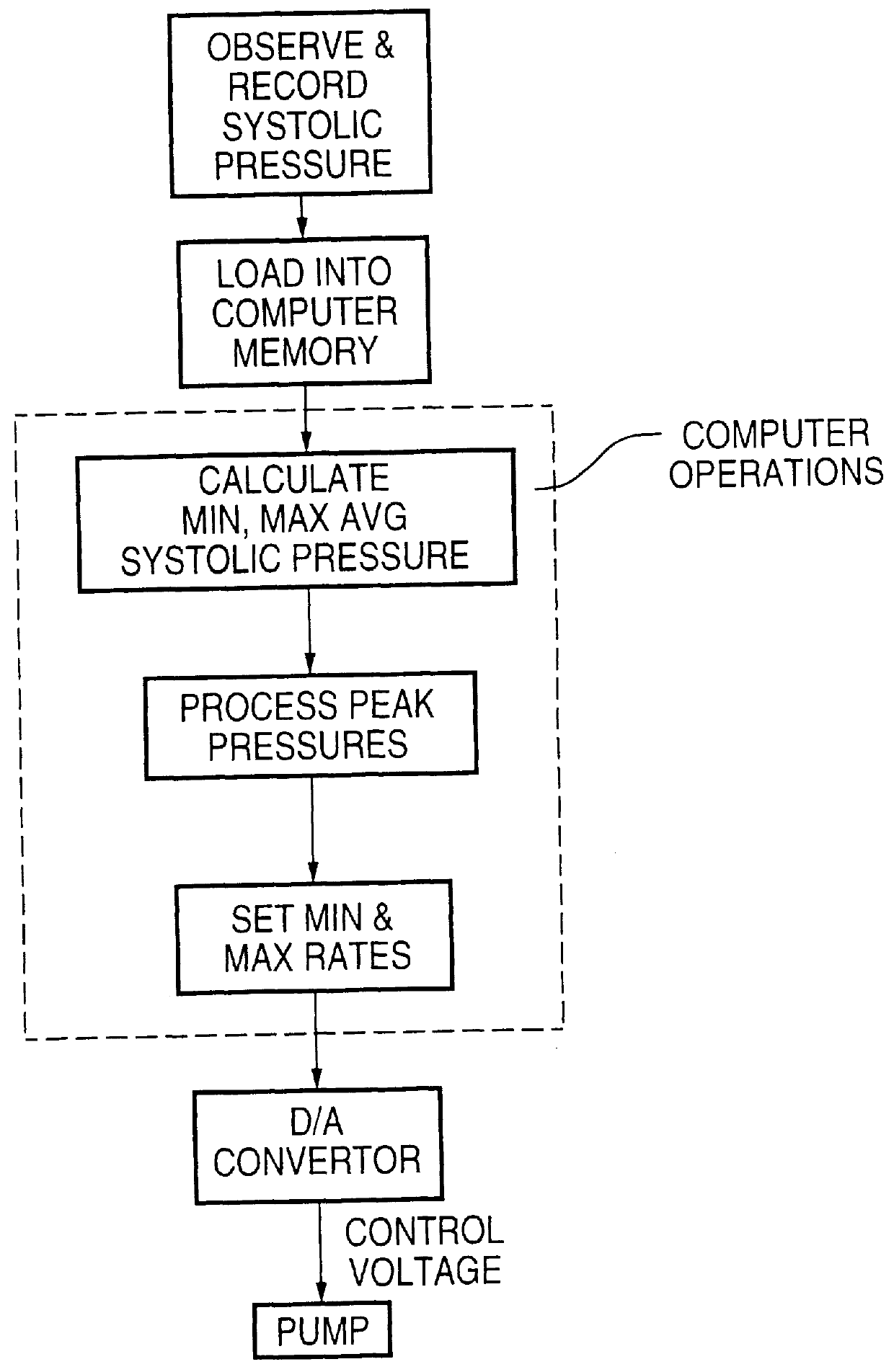
Control of life support systems
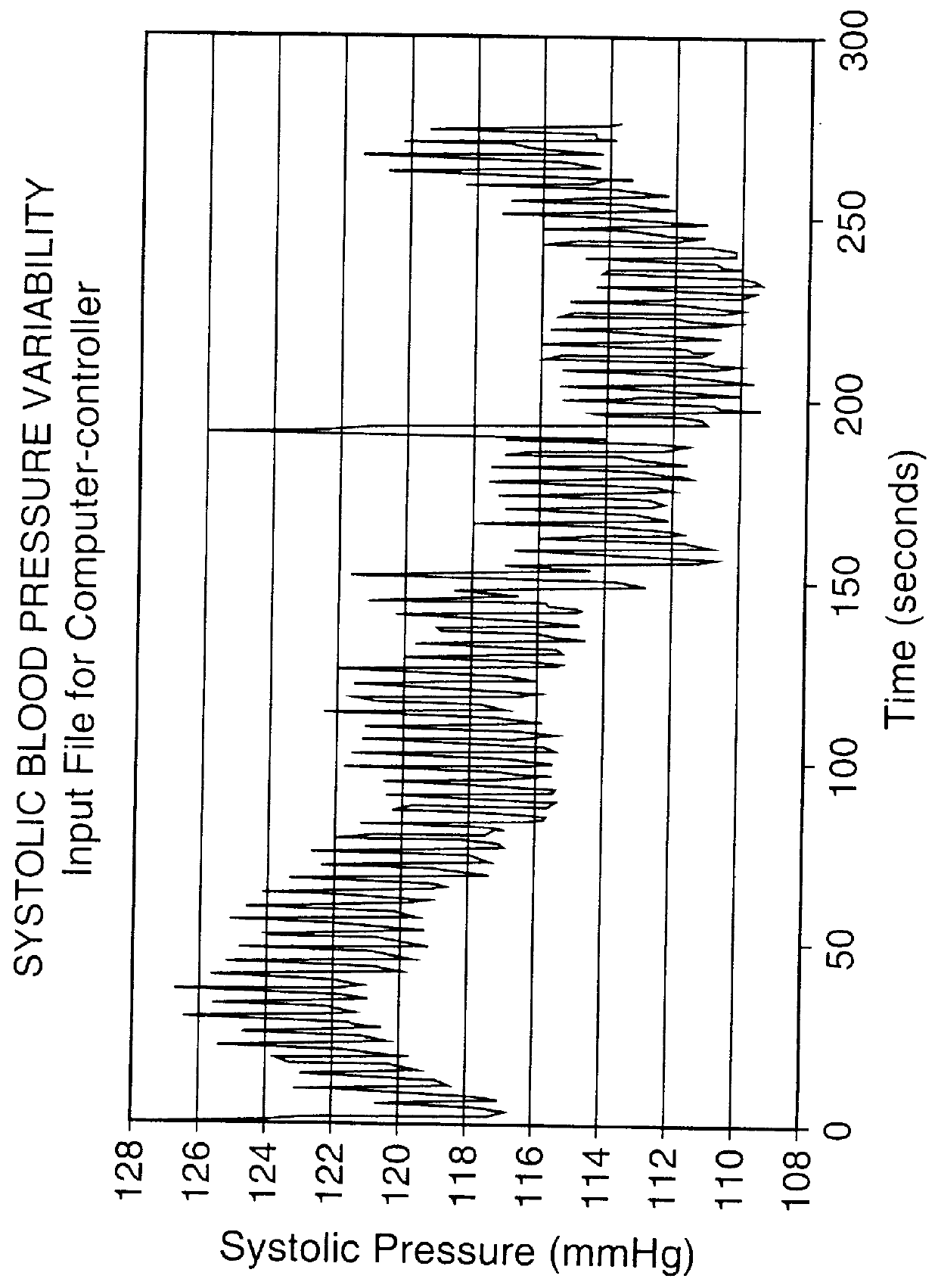
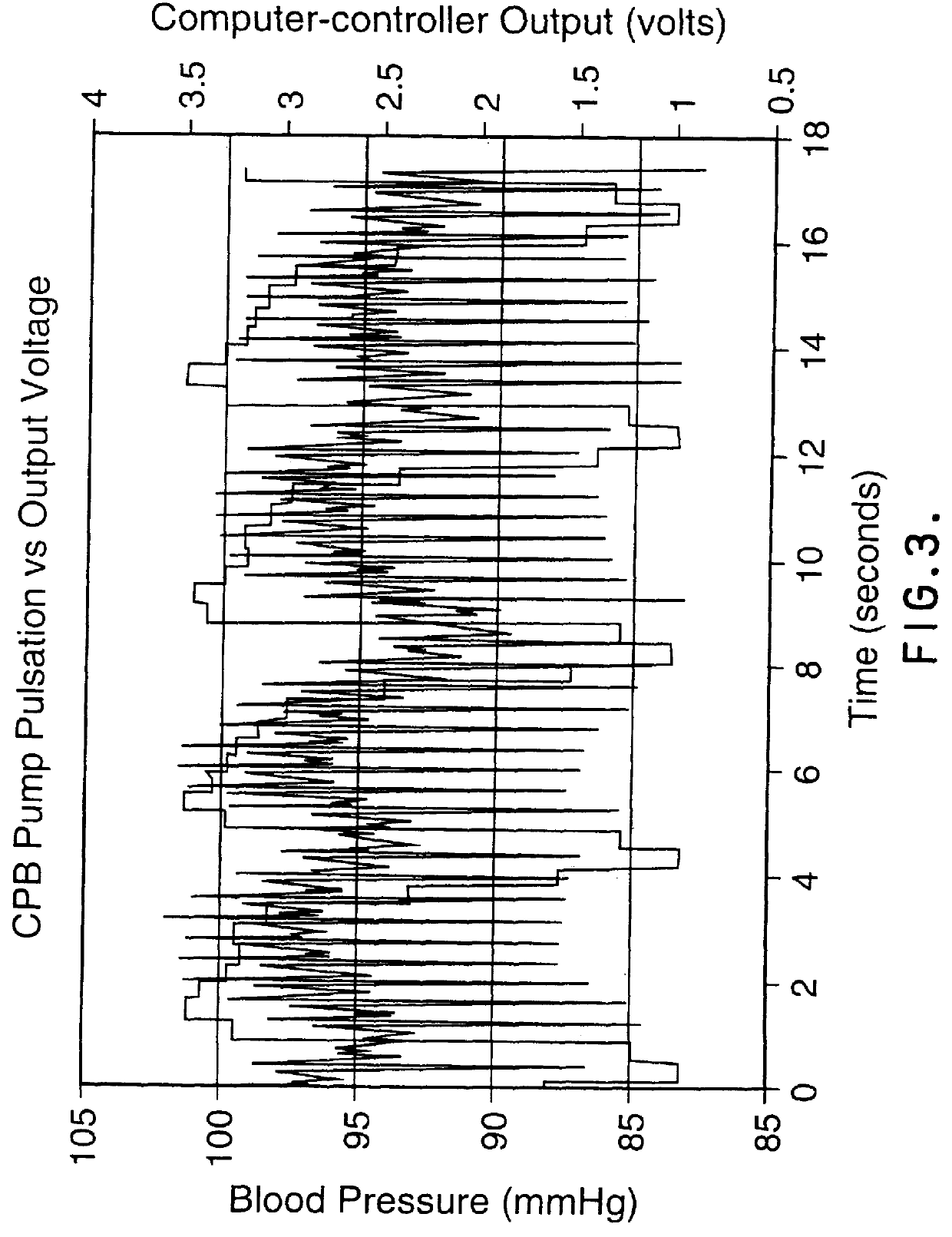
PCT No. PCT / CA95 / 00144 Sec. 371 Date Jan. 6, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Jan. 6, 1997 PCT Filed Mar. 15, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO95 / 24936 PCT Pub. Date Sep. 21, 1995The flow of a biological fluid to an organ is computer controlled so that natural variation of such flow is simulated. Specifically described are control of a blood pump flow output during CPB to mimic normal pulsatile blood flow from the heart and control of a ventilator output To mimic normal breathing of healthy lungs. A pattern of variation over Time of instantaneous flow of a biological fluid to an organ of a mammalian species is established, a variable control parameter for regulation of flow of the biological fluid to the organ is generated in accordance with the pattern, and the flow of biological fluid is to the organ is controlled in accordance with the variable control parameter.
Owner:BIOVAR LIFE SUPPORT
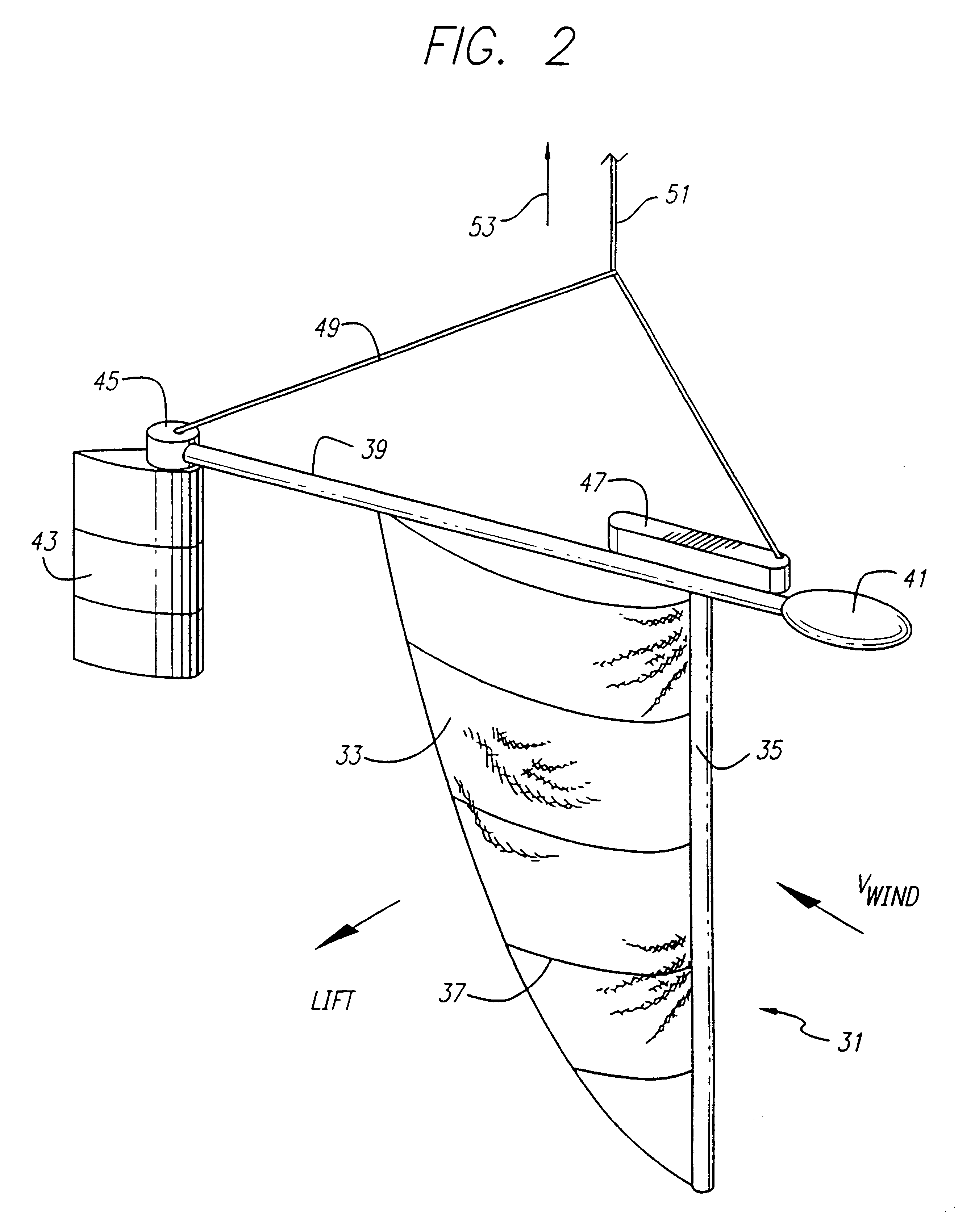
Balloon trajectory control system
InactiveUS6402090B1Little powerEasy to operateMovable targetsBalloon aircraftsControl systemLanding zone
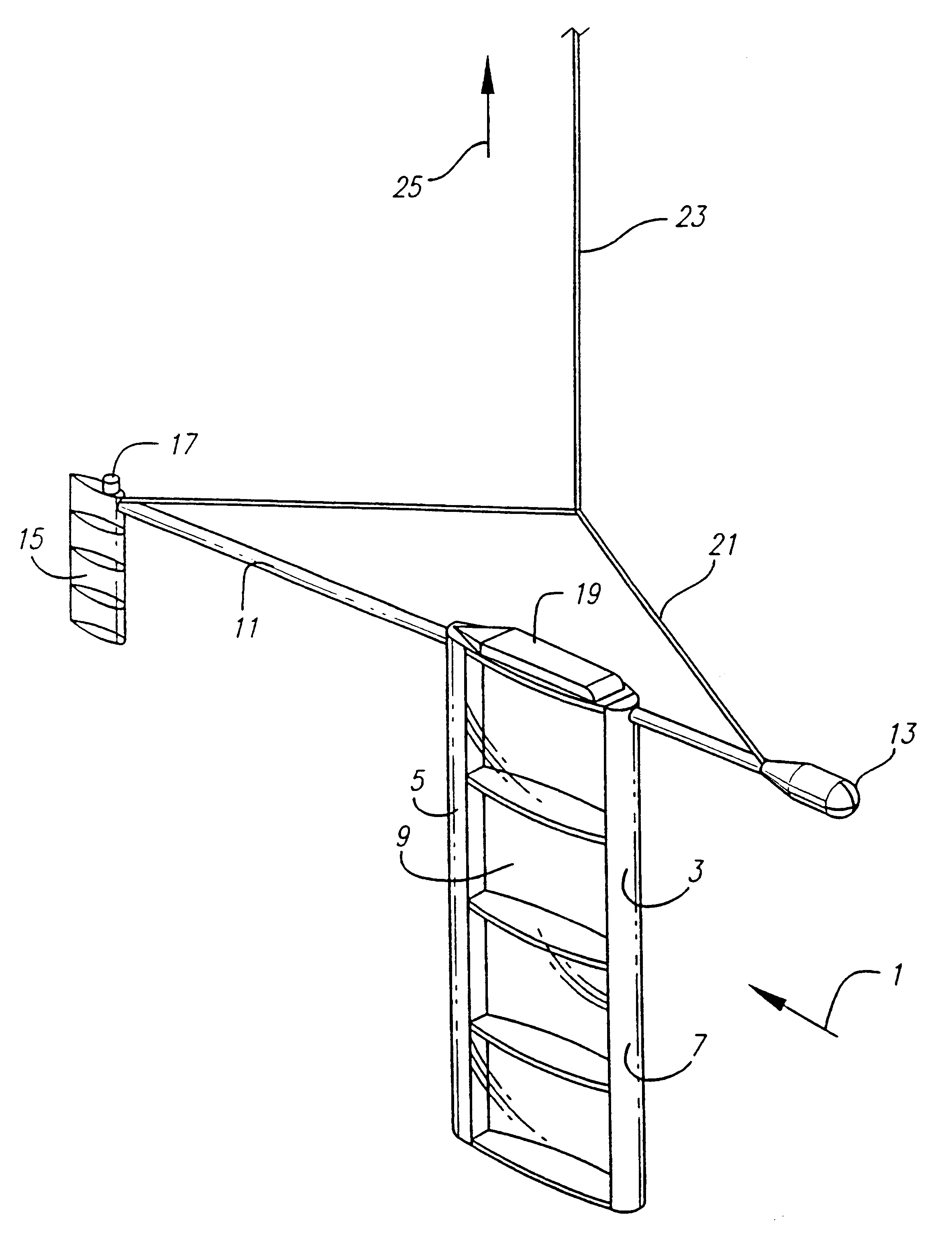
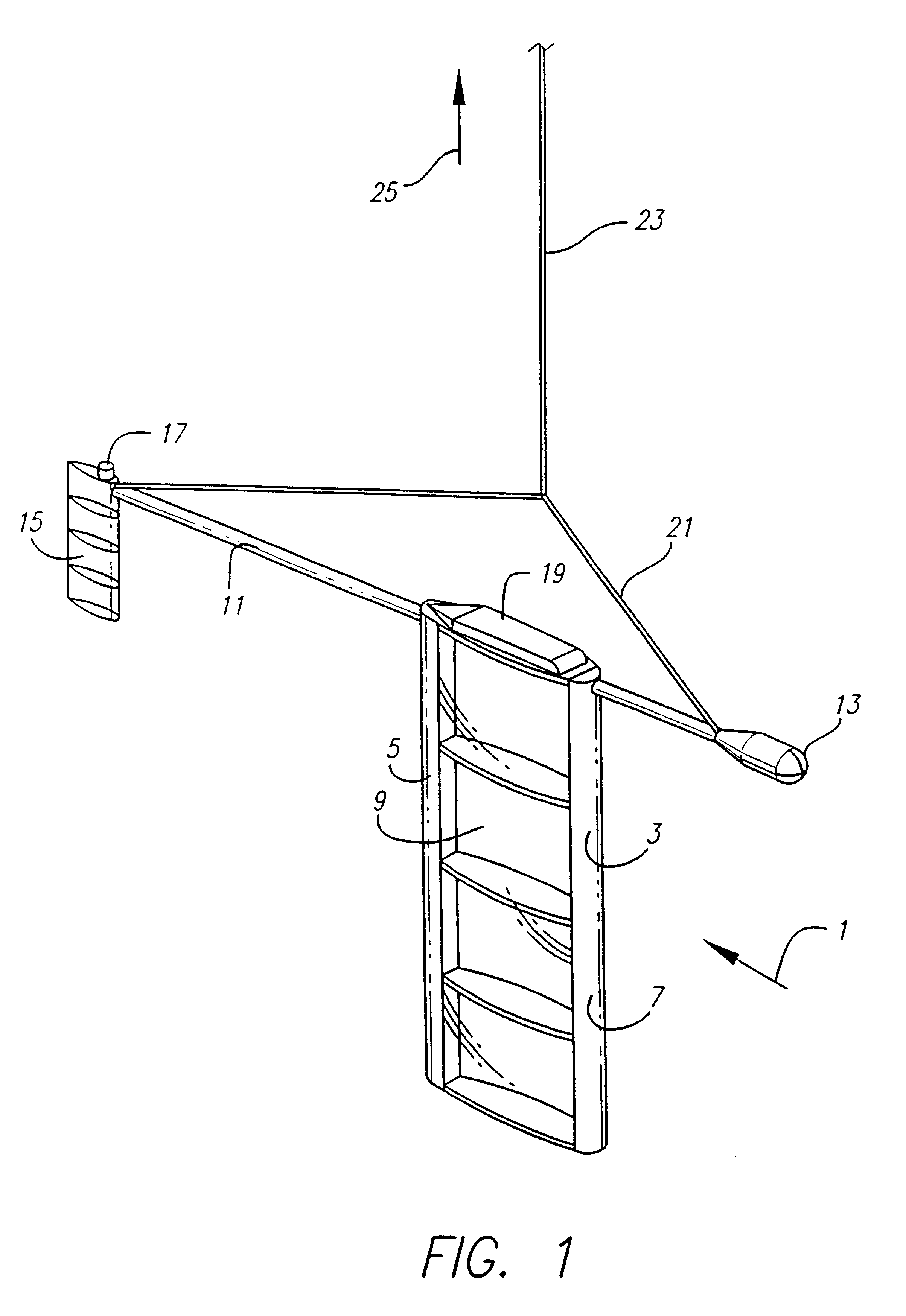
A device to provide control of the trajectory of a lighter than air vehicle, such as a balloon, is provided. A lifting device, such as a wing on end, is suspended on a tether well below the balloon to take advantage of the natural variation in winds at different altitudes. The wing can generate a horizontal lift force that can be directed over a wide range of angles. This force is transmitted to the balloon by the tether. Due to this force, the balloon's path is altered depending on the relative sizes of the balloon and the wing. A relatively small amount of power is needed to control the system, possibly with a rudder. As the energy of the wind provides most of the force, the wind's energy does most of the work. The balloon is able to avoid hazards, to reach desired targets, to select convenient landing zones, and to provide other operational advantages. As a result, fewer flights must be terminated early due to an inability to control the trajectory, and it is easier to obtain permission to launch since a planned flight path can be achieved within a greater range of conditions.
Owner:GLOBAL AEROSPACE
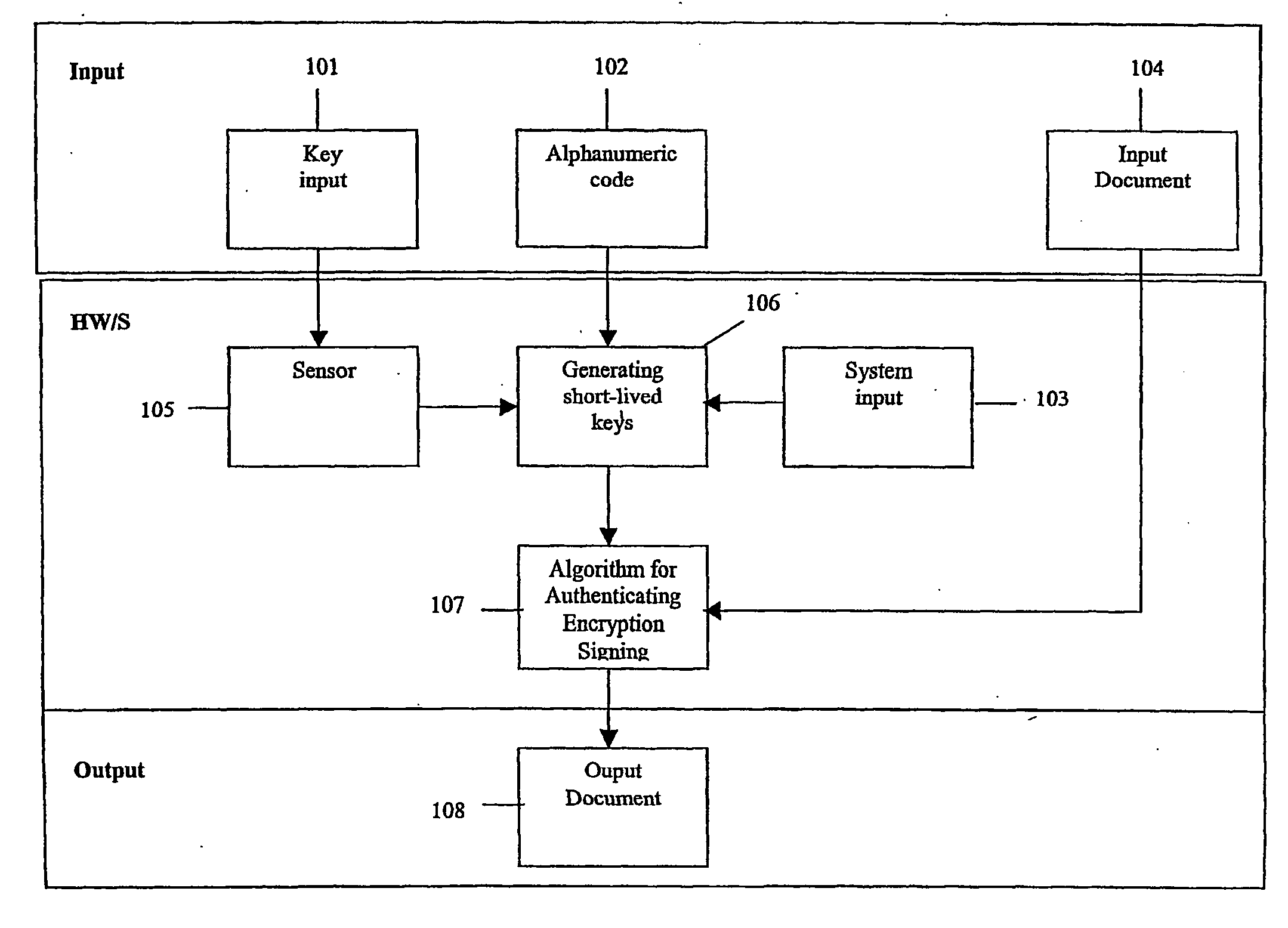
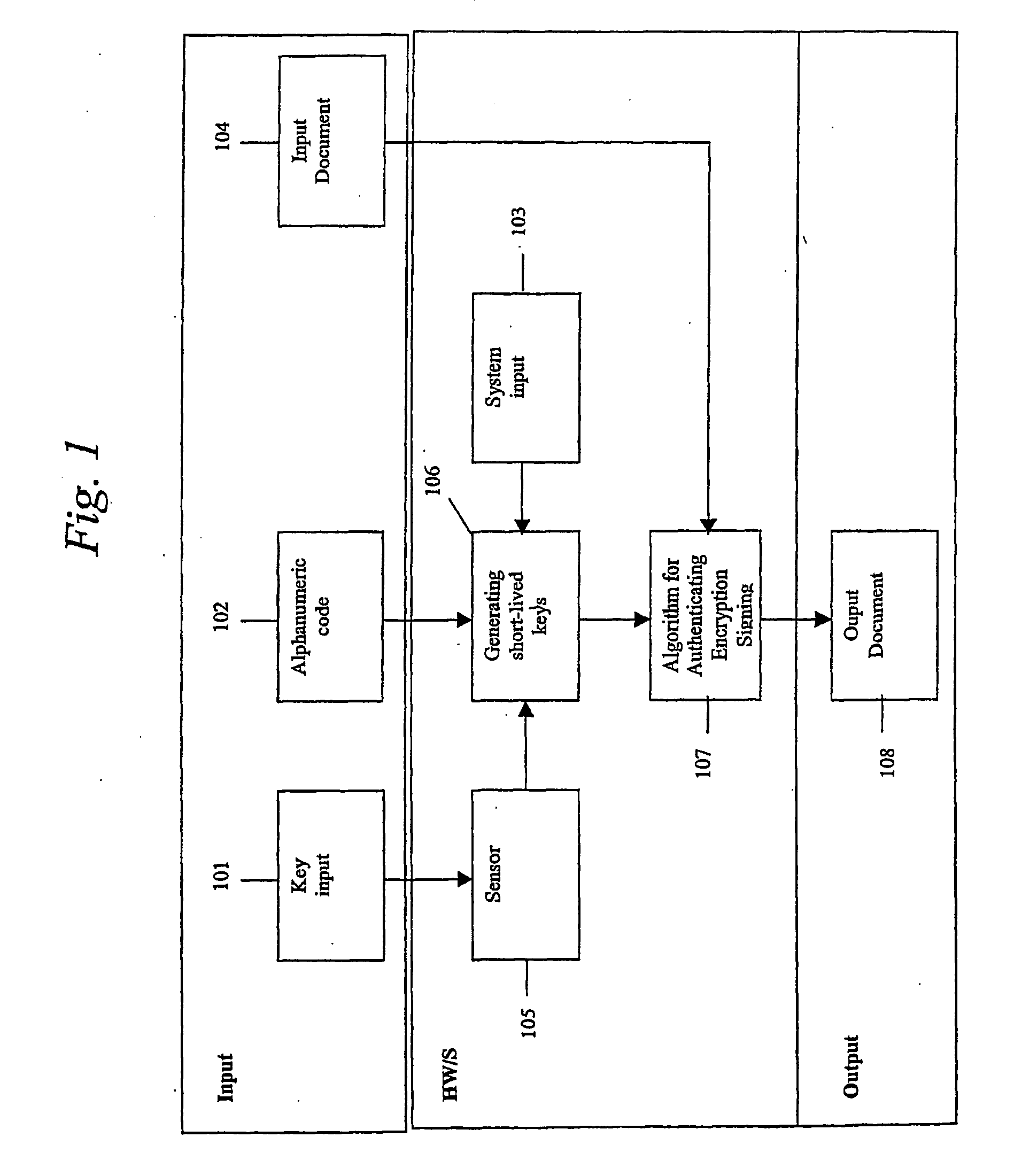
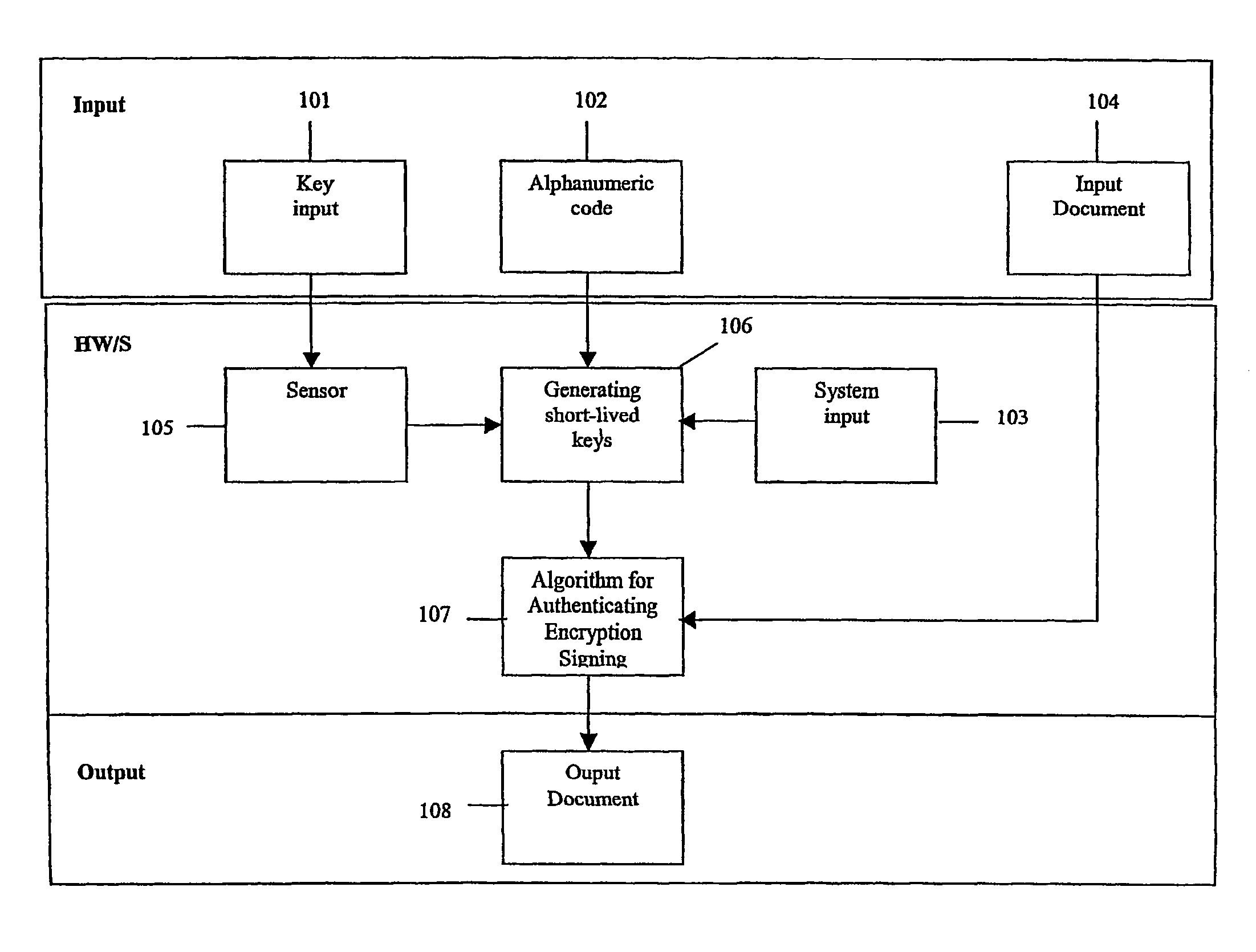
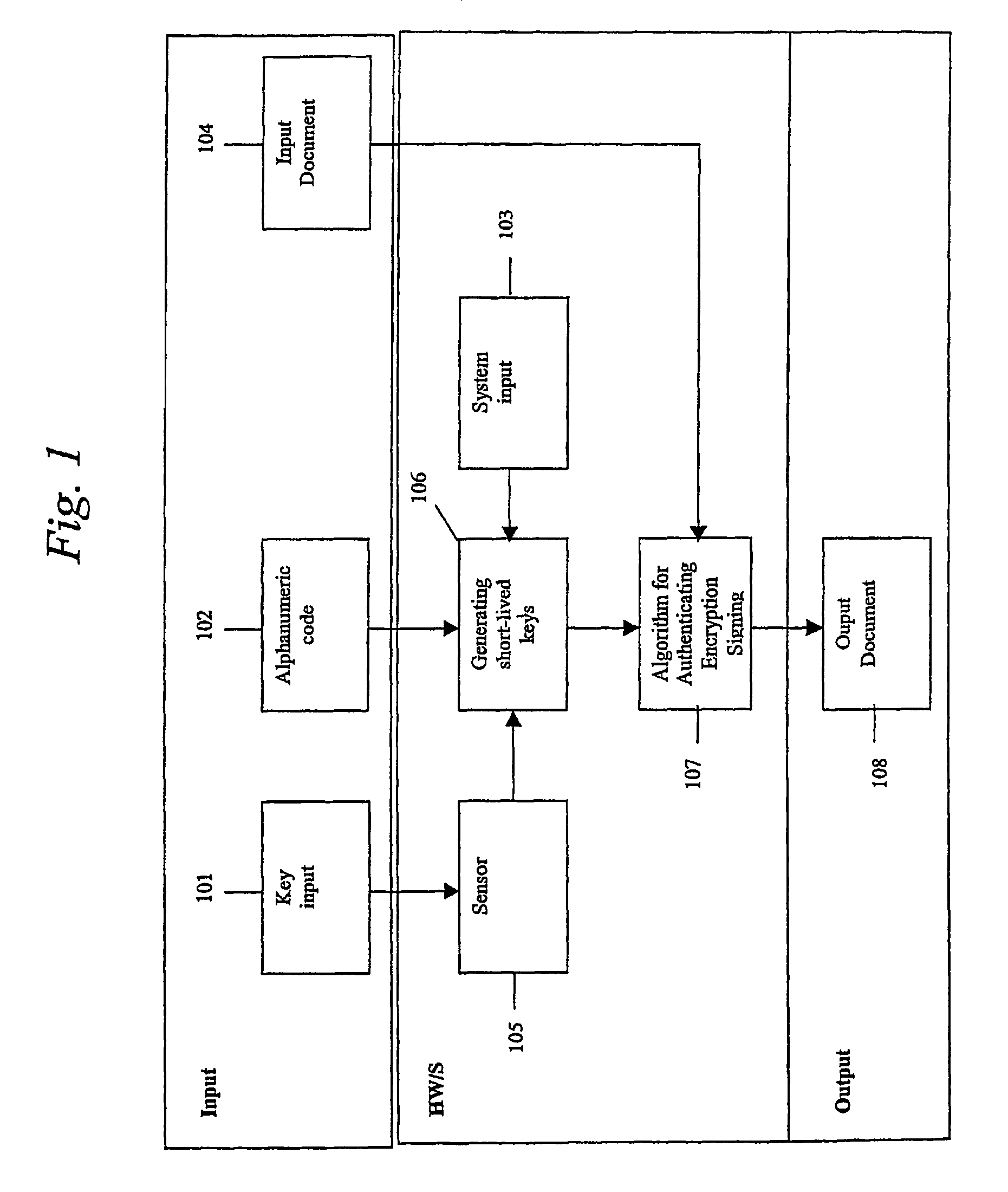
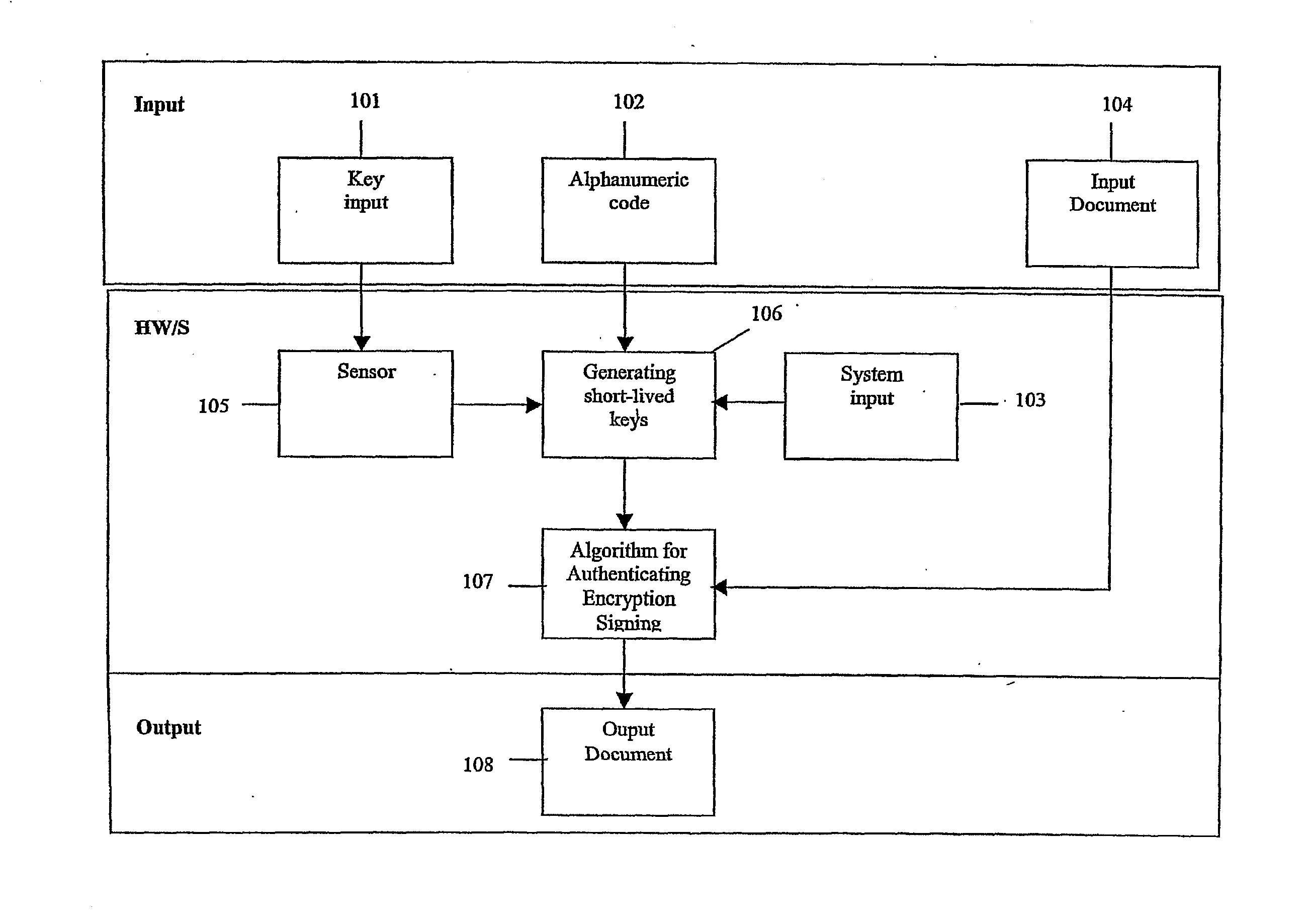
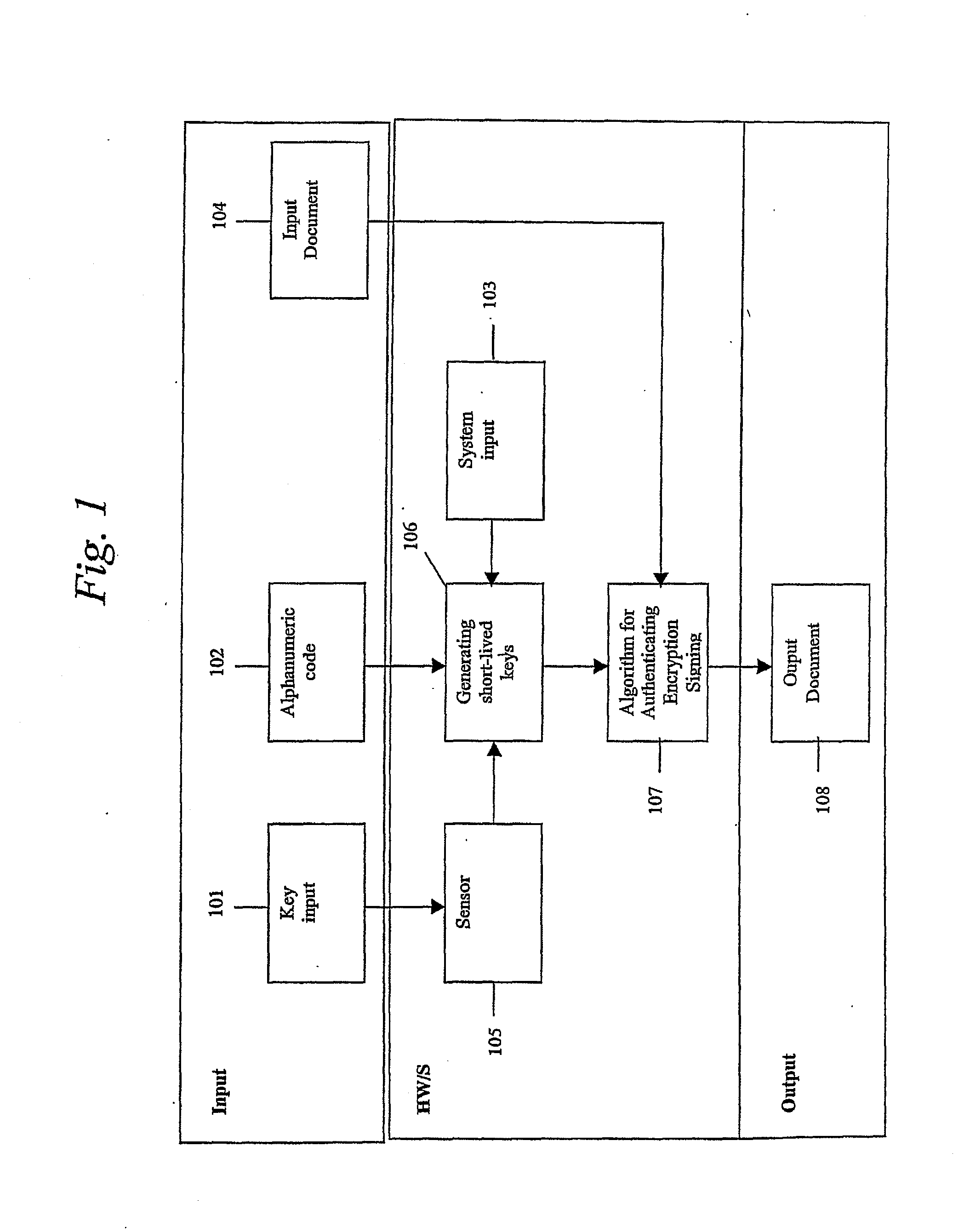
System, portable device and method for digital authenticating, crypting and signing by generating short-lived cryptokeys
ActiveUS20060198514A1Improve securityLower requirementKey distribution for secure communicationElectric signal transmission systemsUser inputNatural variation
A system for authentication, encryption and / or signing, as well as corresponding devices and methods, that use temporary but repeatable encryption keys uniquely connected to the user and generated from a unique set of input parameters. The system comprises an input device (105) designed to extract predetermined characteristic values from value input by the user, which value is specific to the user, by means of a given algorithm, which algorithm is designed to remove the natural variation in the characteristic values in order to yield an identical set of characteristic values upon input of the same value, and a device (106) designed to generate at least one user specific encryption key comprising said characteristic values.
Owner:GENKEY NETHERLANDS
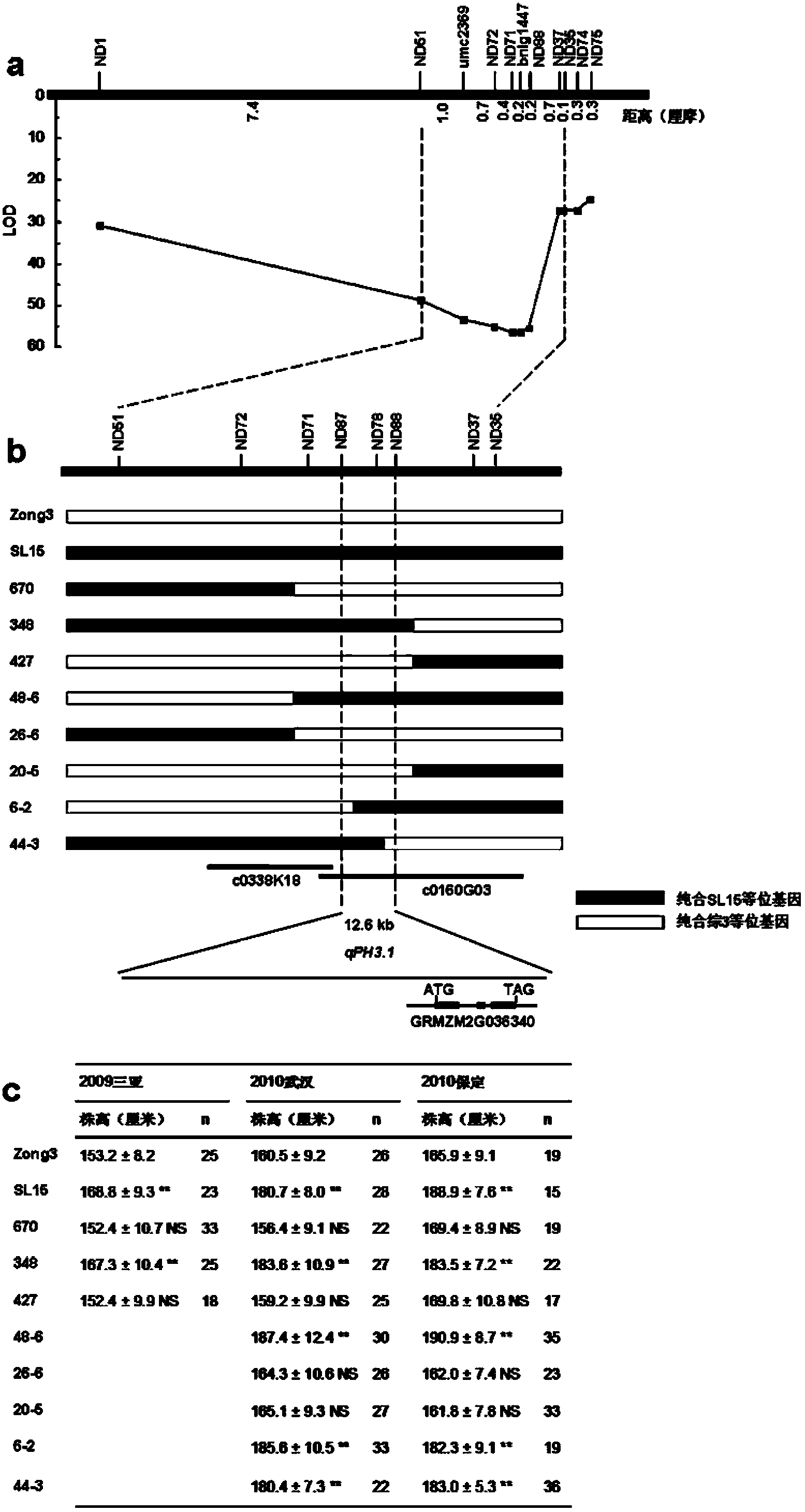
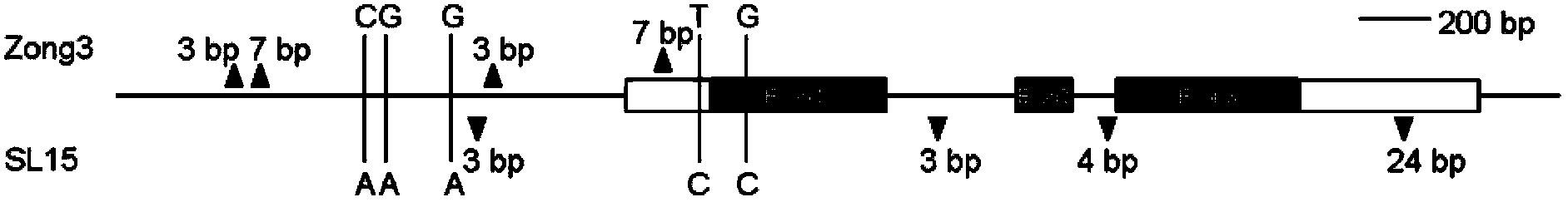
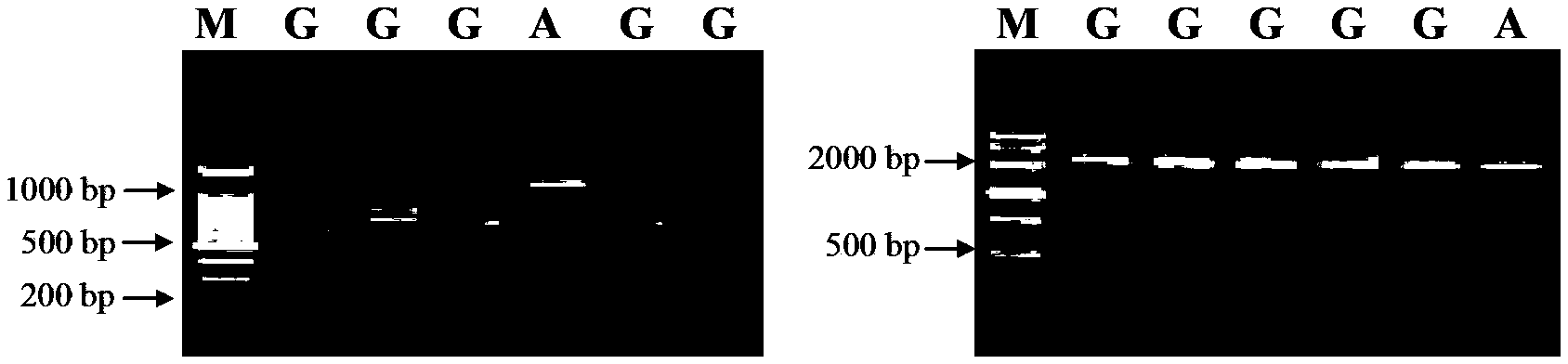
Molecular marker for controlling corn plant height and applications thereof
InactiveCN103451200AConfirm the synthetic relationshipYield is not affectedMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationAgricultural scienceNucleotide
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Molecular marker related with wheat thousand grain weight and applications thereof
InactiveCN104342484AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceGrain weight
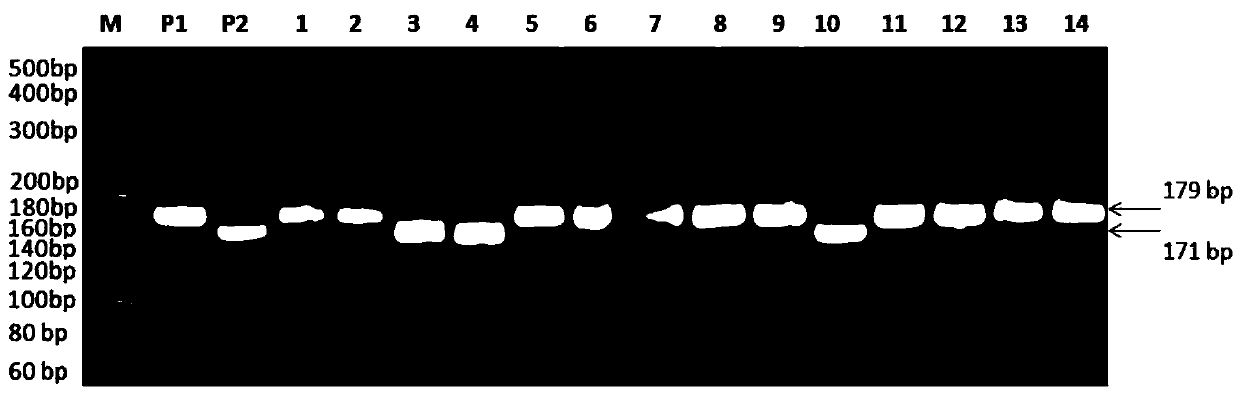
The invention discloses a molecular marker related with wheat thousand grain weight and applications thereof. Through the heritable variation analysis on 6-SFT gene of a wheat natural variation group, people find that the 6-SFT gene has two SNPs corresponding to the 1371st and 2450th positions in the tail ends from 1 to 5' in the sequence one. Three haplotypes exist in the two SNP, namely haplotype A (G,G) haplotype B (G,A), and haplotype C (A,G). Through correlation analysis, the wheat thousand grain weights of the three homozygous haplotypes are accord with a relationship as follows: the wheat thousand grain weight of homozygous haplotype C > the wheat thousand grain weight of homozygous haplotype B > the wheat thousand grain weight of homozygous haplotype C. The invention also provided a CAPS label for detecting the two SNPs. Experiments have proved that the wheat with a higher thousand grain weight can be found through detecting the two SNPs. A novel method is provided for the wheat breeding assisted by a molecular labeling technology, and the provided molecular maker has an important meaning for the breeding and researches of wheat species with a high yield.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
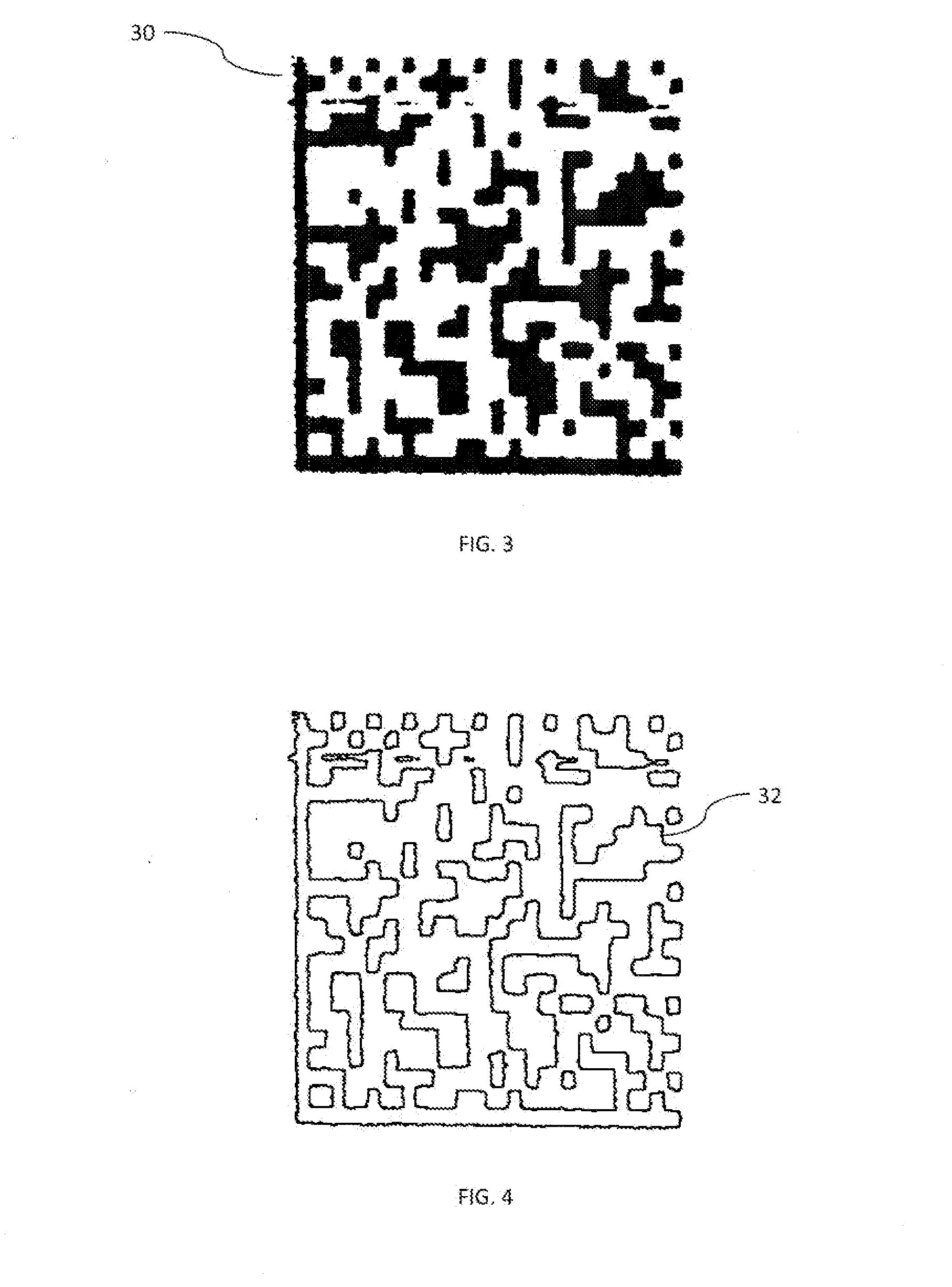
Unique identification information from marked features
Owner:SYS TECH SOLUTIONS
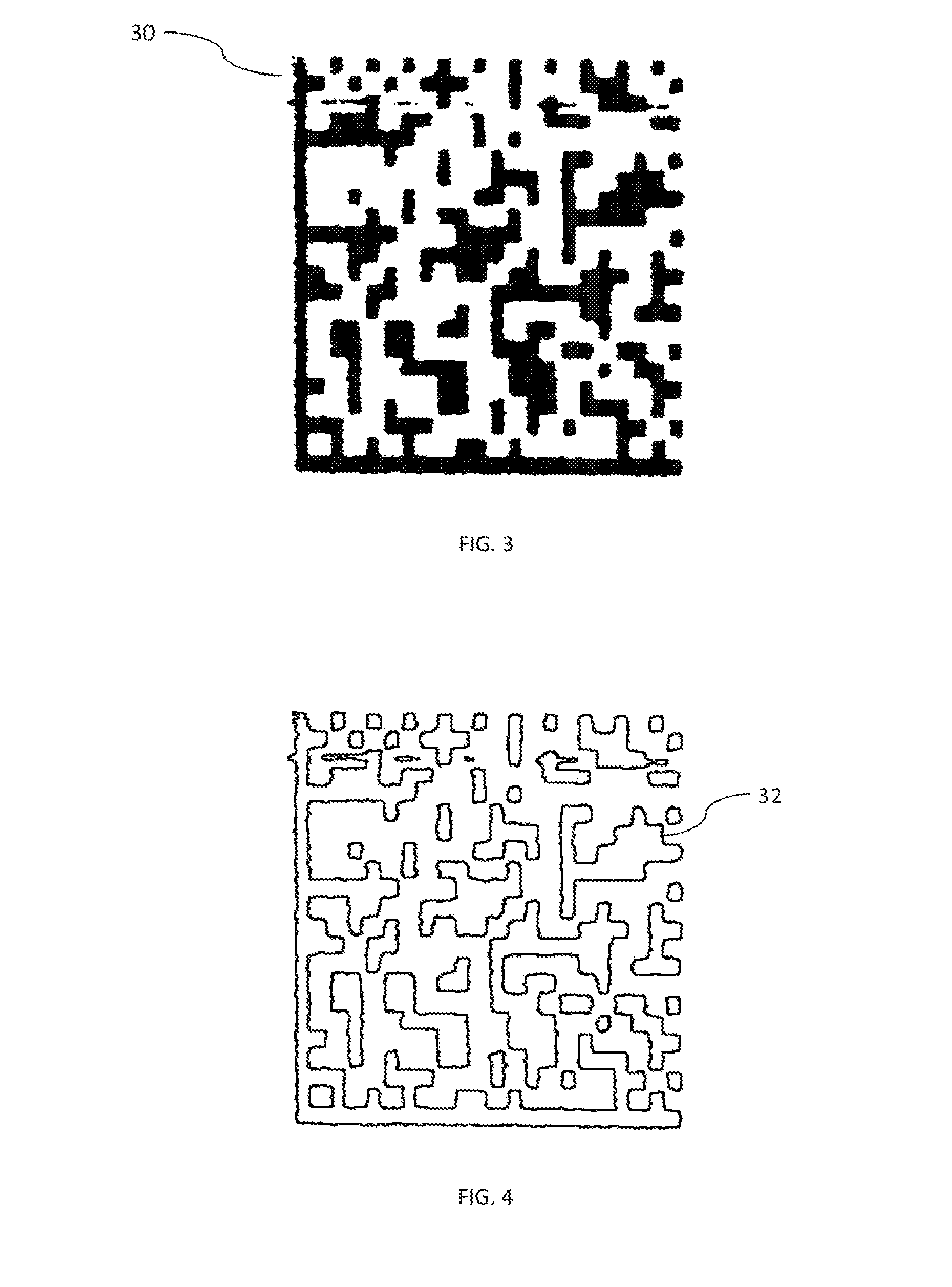
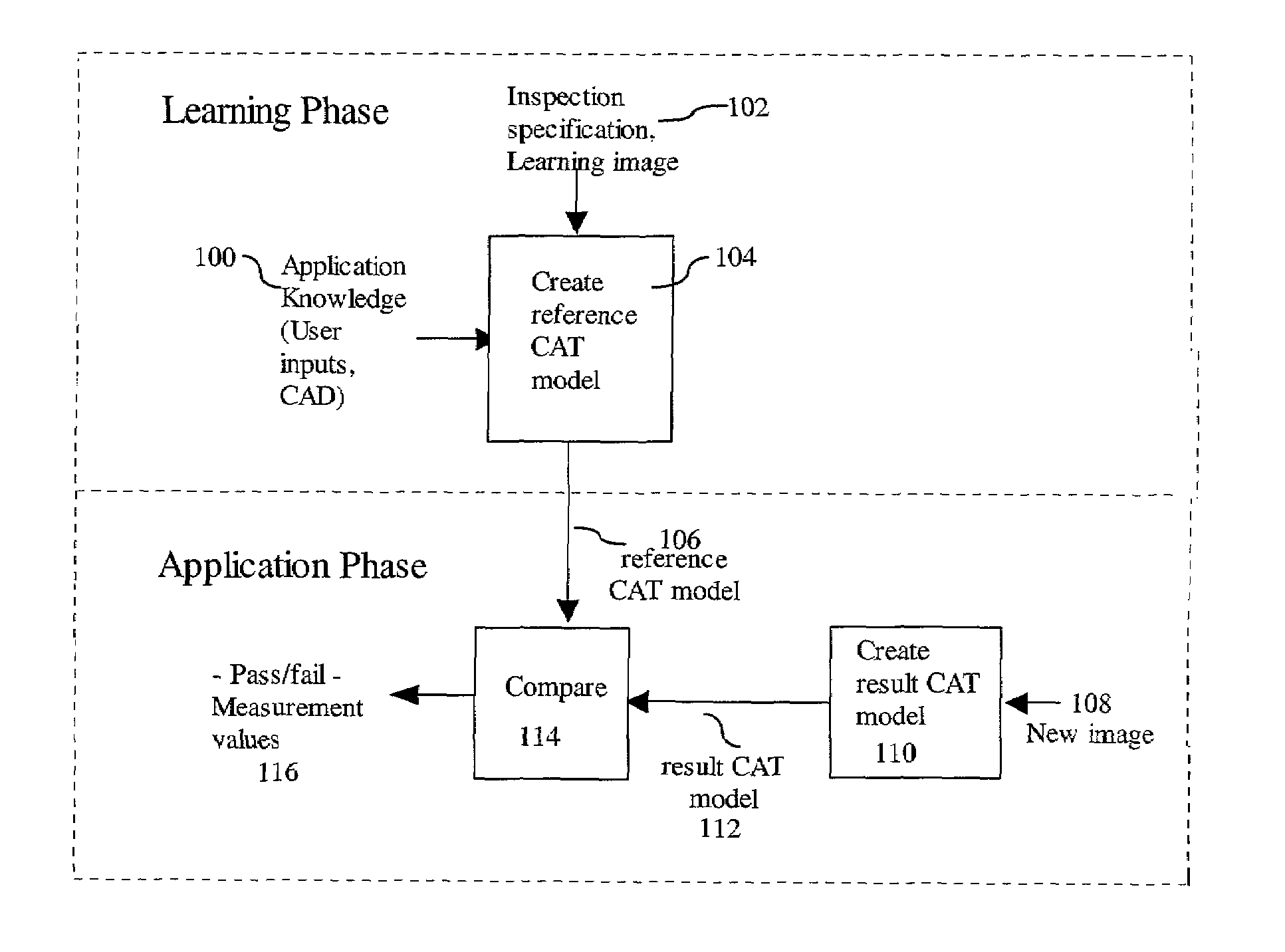
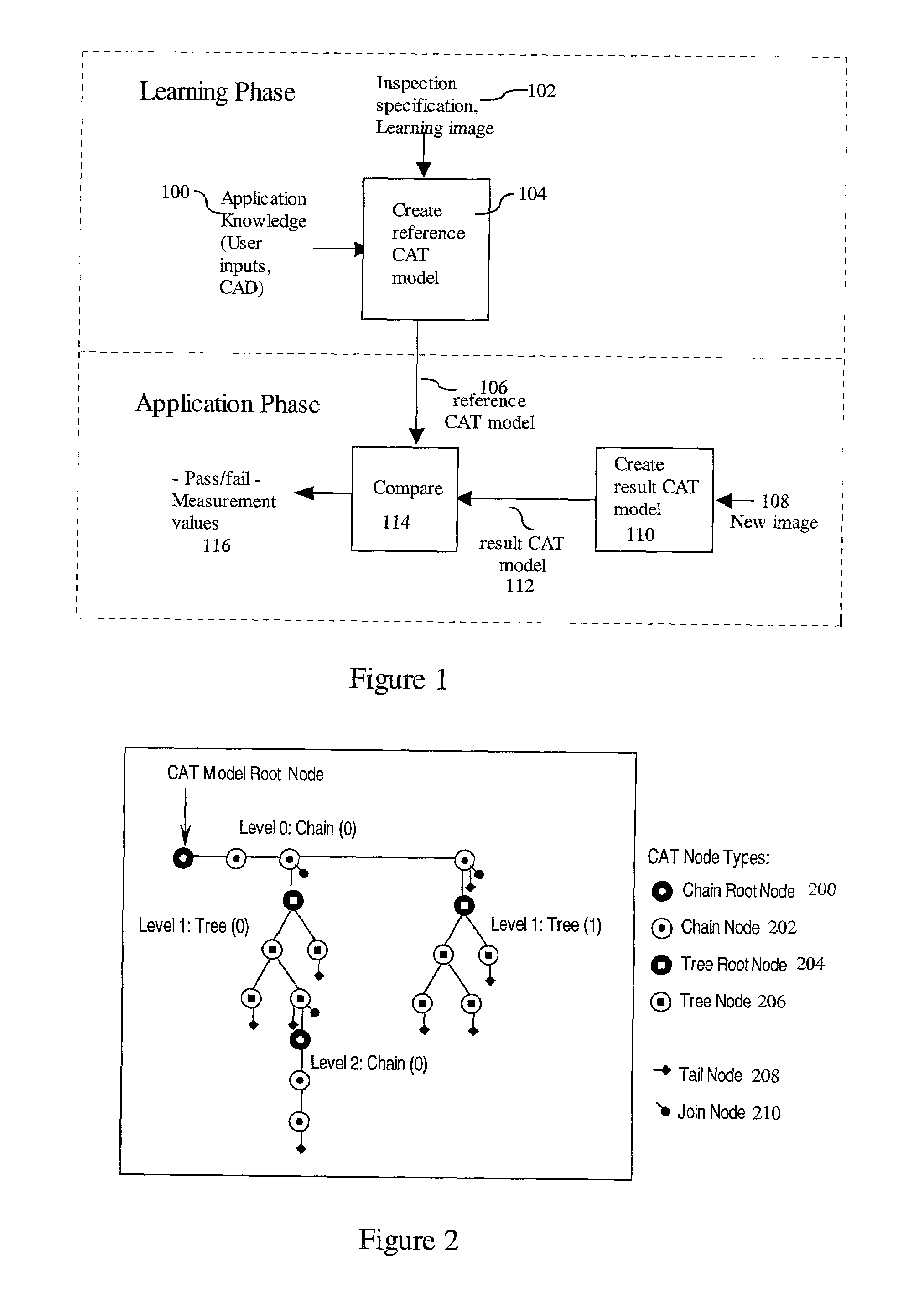
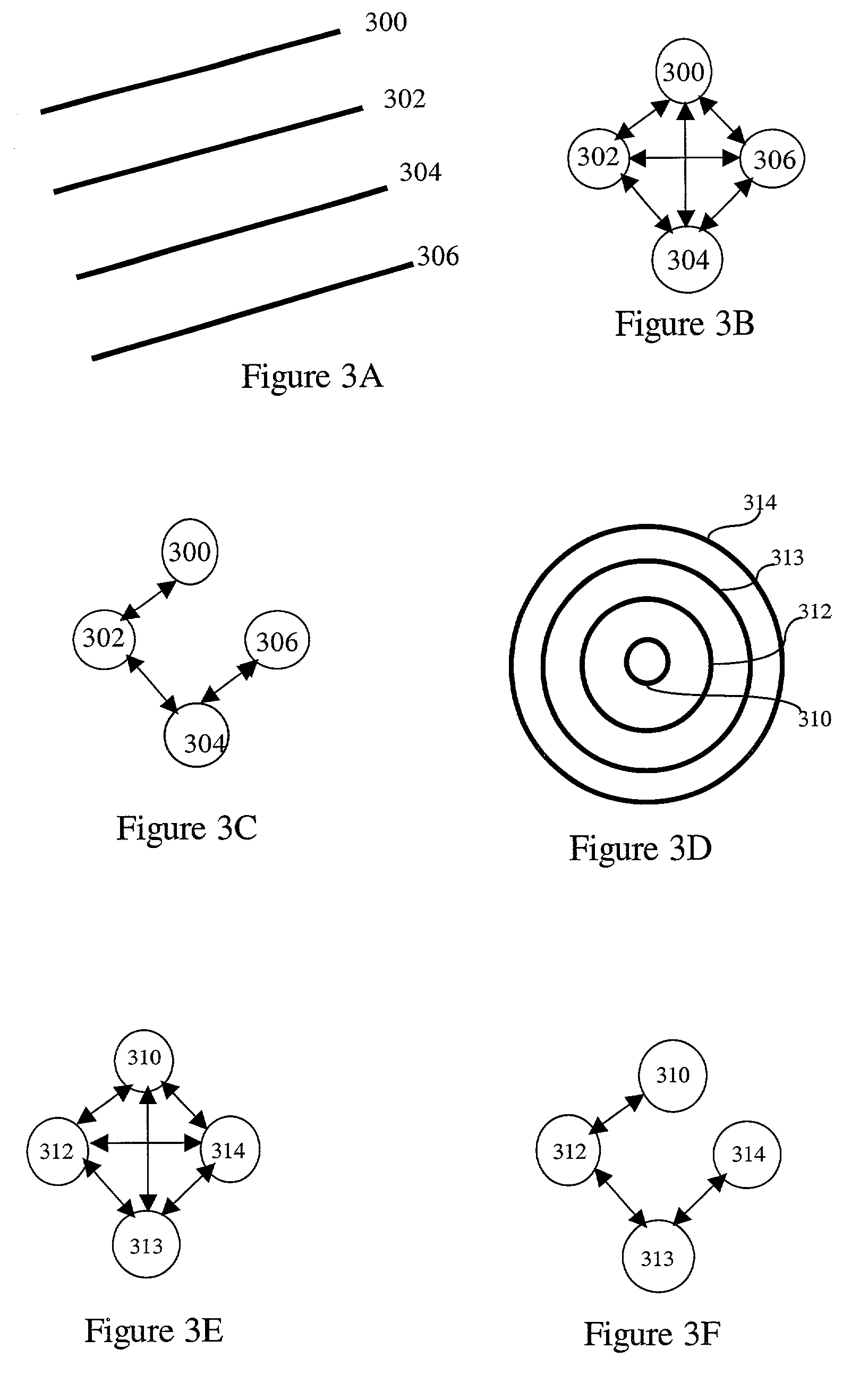
Multilevel chain-and-tree model for image-based decisions
A multilevel Chain-And-Tree model provides a framework for an image based decision system. The decision system enables separation of effects of defects within one component from other components within a common subject. The framework provides for linking of structure constraints of components of a common subject and for checking and resolving their consistency. The framework allows discrimination between subtle image changes and natural variations of the subject. The framework for standard data representation facilitates production process control.
Owner:NIKON CORP
System, portable device and method for digital authenticating, crypting and signing by generating short-lived cryptokeys
ActiveUS7996683B2Improve securityKey distribution for secure communicationElectric signal transmission systemsNatural variationEncryption
A system for authentication, encryption and / or signing, as well as corresponding devices and methods, that use temporary but repeatable encryption keys uniquely connected to the user and generated from a unique set of input parameters. The system comprises an input device (105) designed to extract predetermined characteristic values from value input by the user, which value is specific to the user, by means of a given algorithm, which algorithm is designed to remove the natural variation in the characteristic values in order to yield an identical set of characteristic values upon input of the same value, and a device (106) designed to generate at least one user specific encryption key comprising said characteristic values.
Owner:GENKEY NETHERLANDS
Modified gum arabic
ActiveUS20050124805A1Low protein nitrogen contentDifferent molecular weightCosmetic preparationsTransportation and packagingNatural variationGum arabic
The present invention provides a water-soluble modified gum arabic with a weight average molecular weight not less than 0.9 million and arabinogalactan protein not less than 17% by weight obtained by heating Acacia Senegal gum arabic and modified water-soluble gum arabic with a weight average molecular weight not less than 2.5 million and with protein containing high molecular weight components of not less than 25% by weight. Moreover, the present invention provides modified gum arabic with standardized and predictable molecular properties and methods for providing the modified gum arabic endowed with high emulsification efficiency and stability and for uniforming natural variations in unmodified gum arabic. The present invention changes the natural protein distribution of gum arabic, and increases AGP content.
Owner:SAN EI GEN F F I
Method and apparatus to simulate rotational sound
InactiveUS6873708B1Improve noiseElectrophonic musical instrumentsTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsAngular velocityPeak value
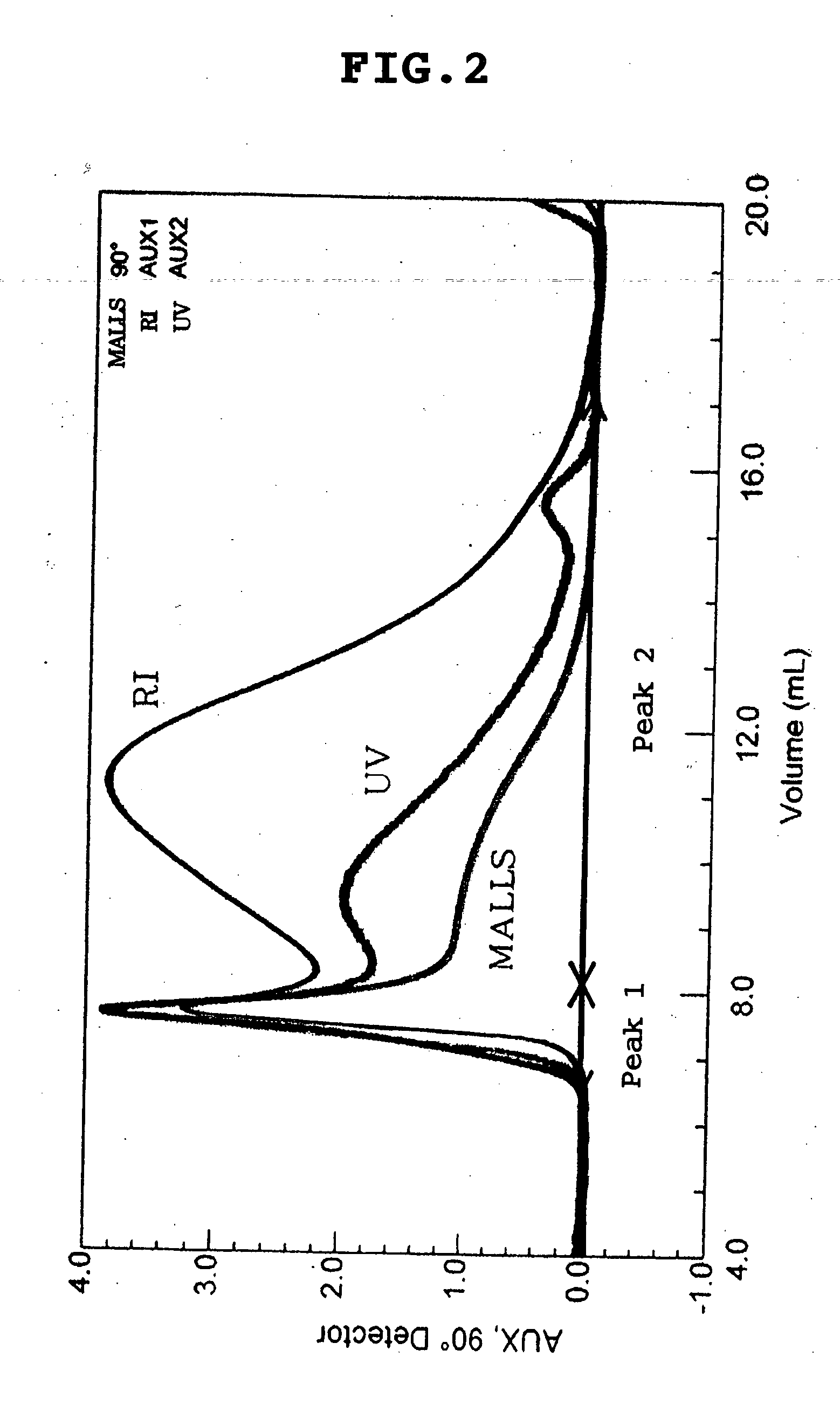
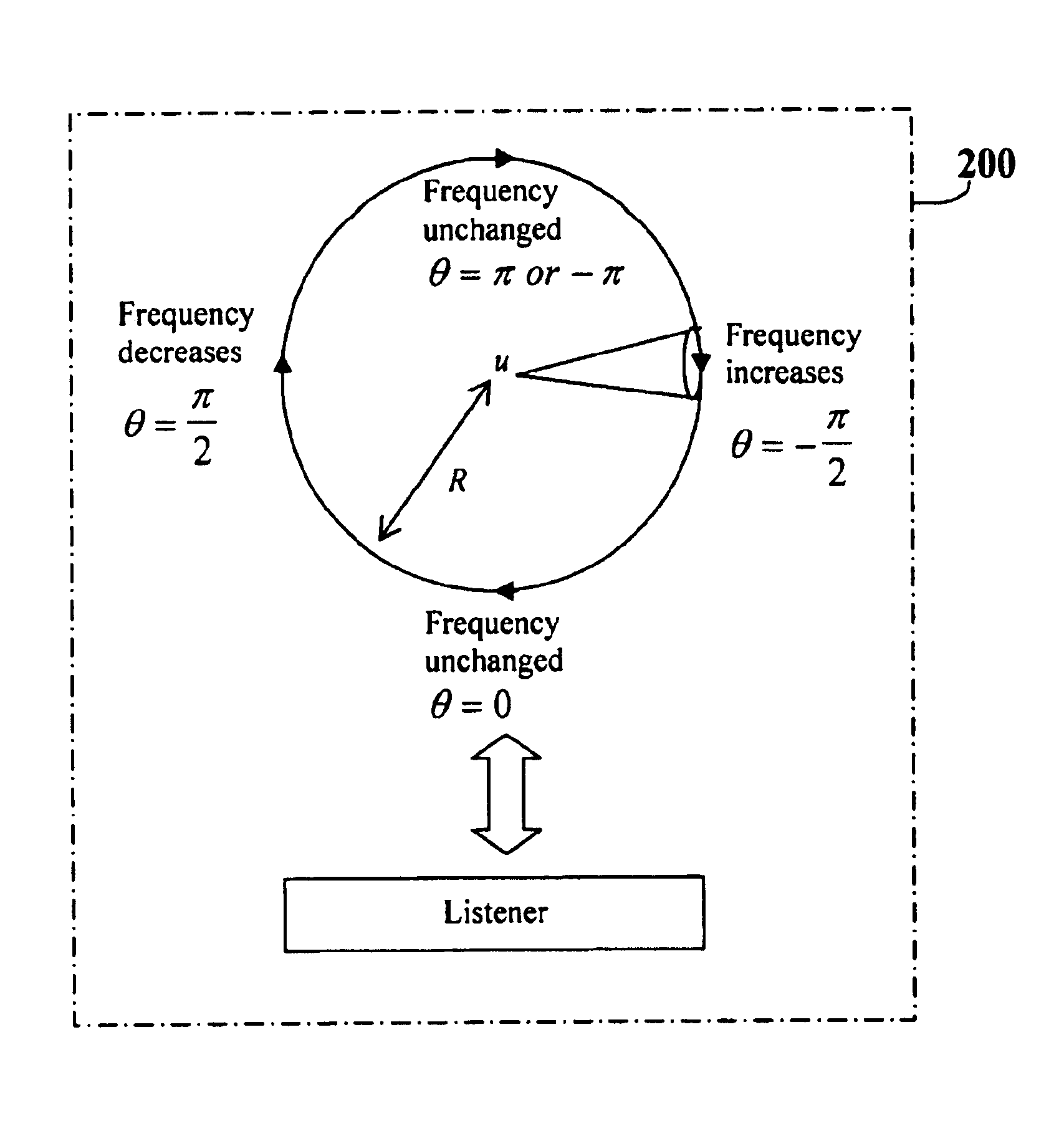
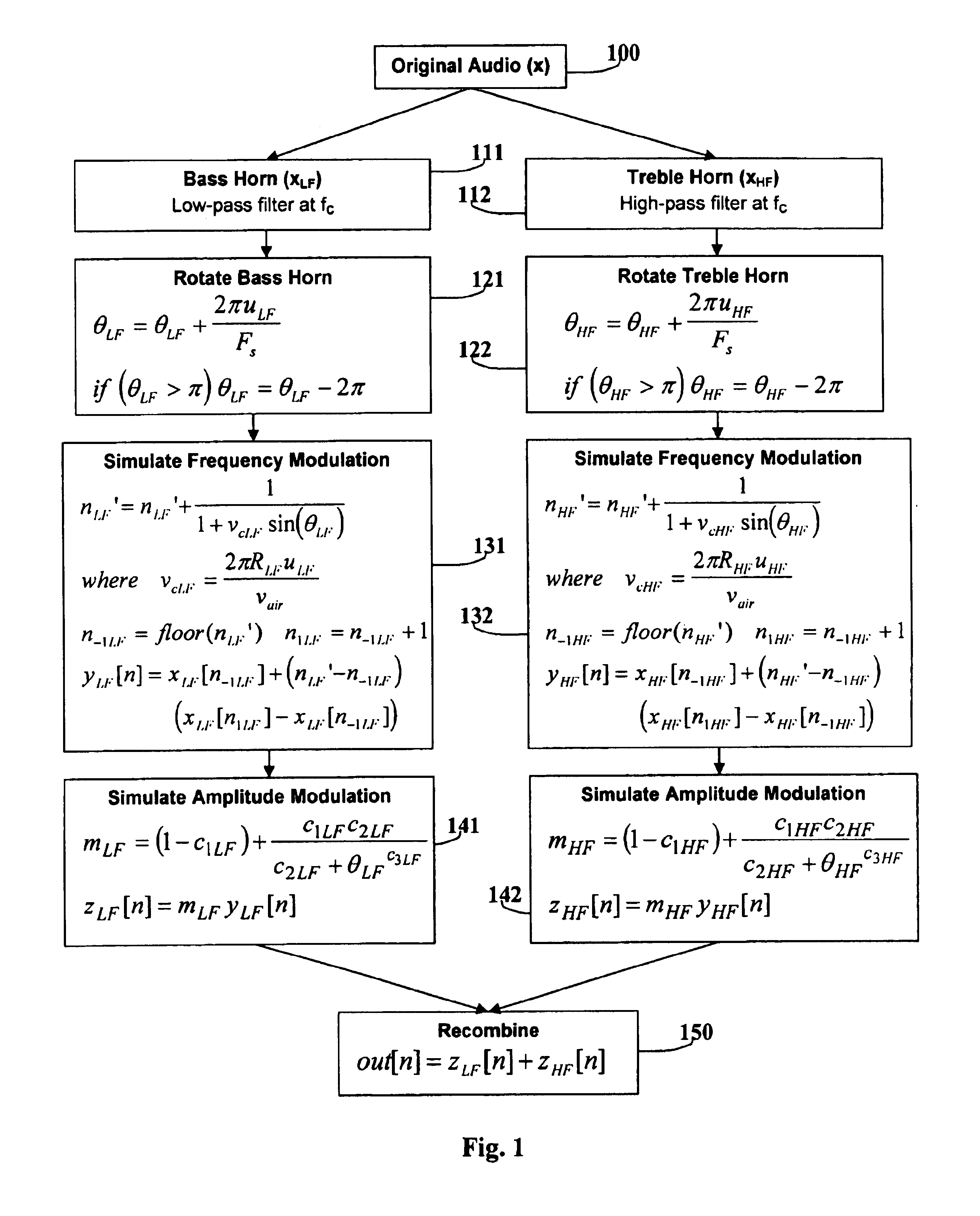
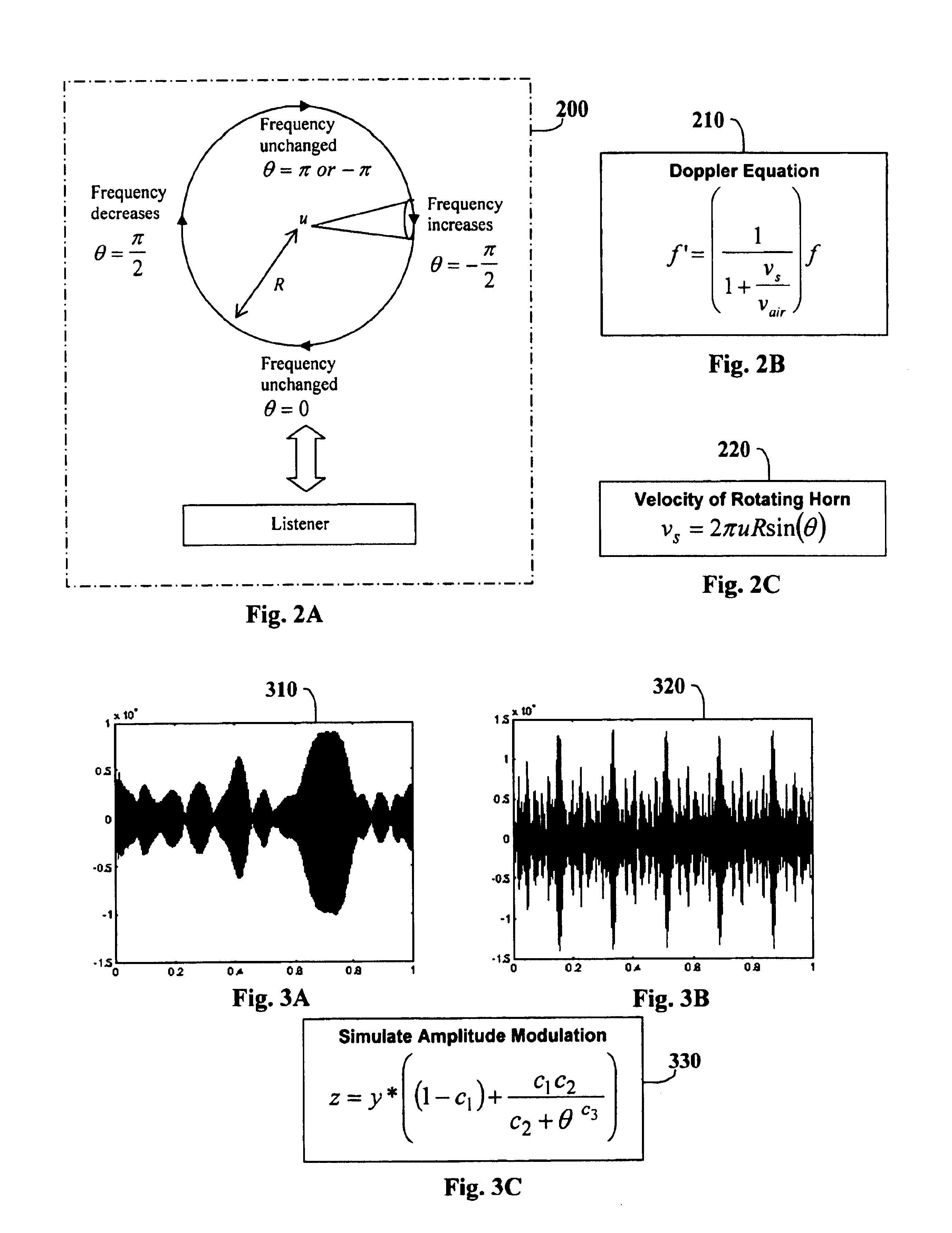
Since the prior-art is based upon analog circuitry, it uses sinusoidal frequency and / or amplitude modulation to simulate a rotating speaker at a reasonable cost. This invention uses a process based upon theoretically derived frequency modulation (FM) and experimentally measured amplitude modulation (AM) to simulate the rotating speaker. The main FM equation is based upon the Doppler effect and is equal to one over one plus a sinusoidal velocity coefficient. The main AM equation has a much narrower peak than sinusoidal modulation. This invention also contains several novel methods to control the angular velocity of the speakers, including changing the horn's speed dependent upon the original audio, modeling the speaker's acceleration to allow the physically realistic transitions between angular velocities, and adding noise to simulate natural variations in rotation. The digital apparatus that implements this invented process includes a digital processor and memory. In summary, the invented process is much more realistic sounding than prior-art.
Owner:ACOUSTIC INFORMATION PROCESSING LAB
Method of speech conversion in a cochlear implant
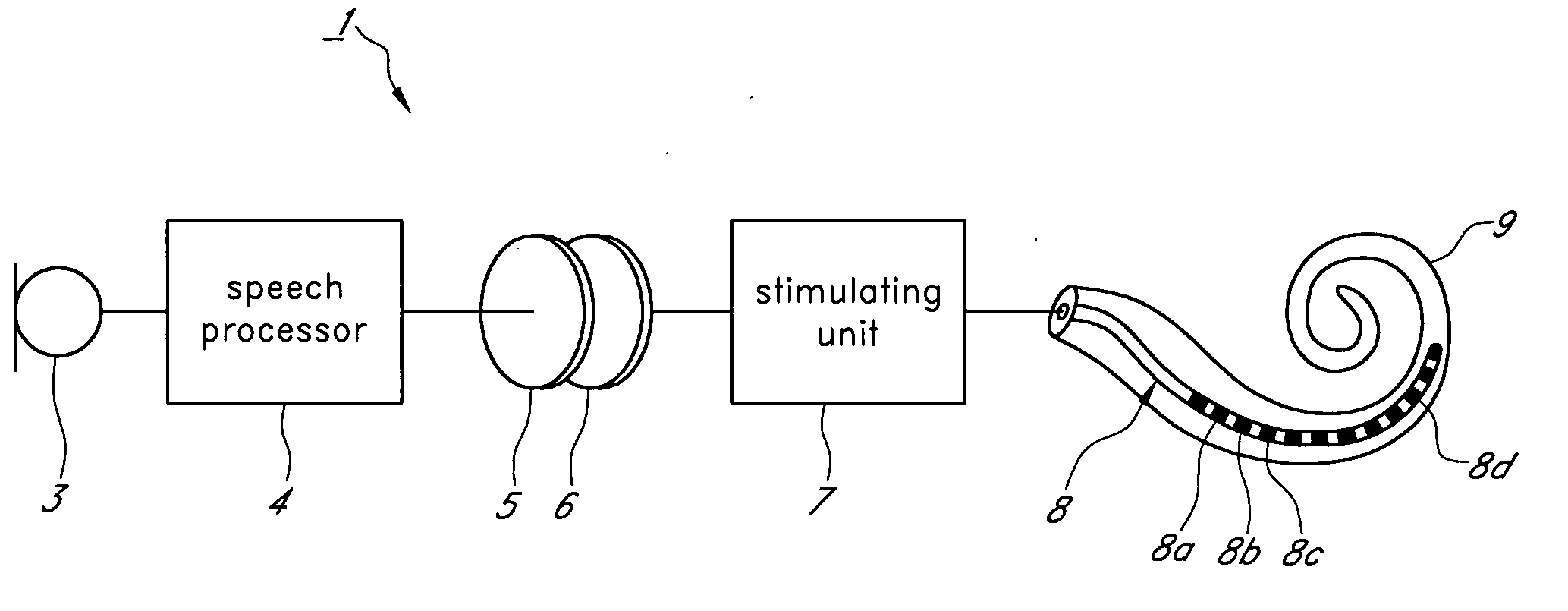
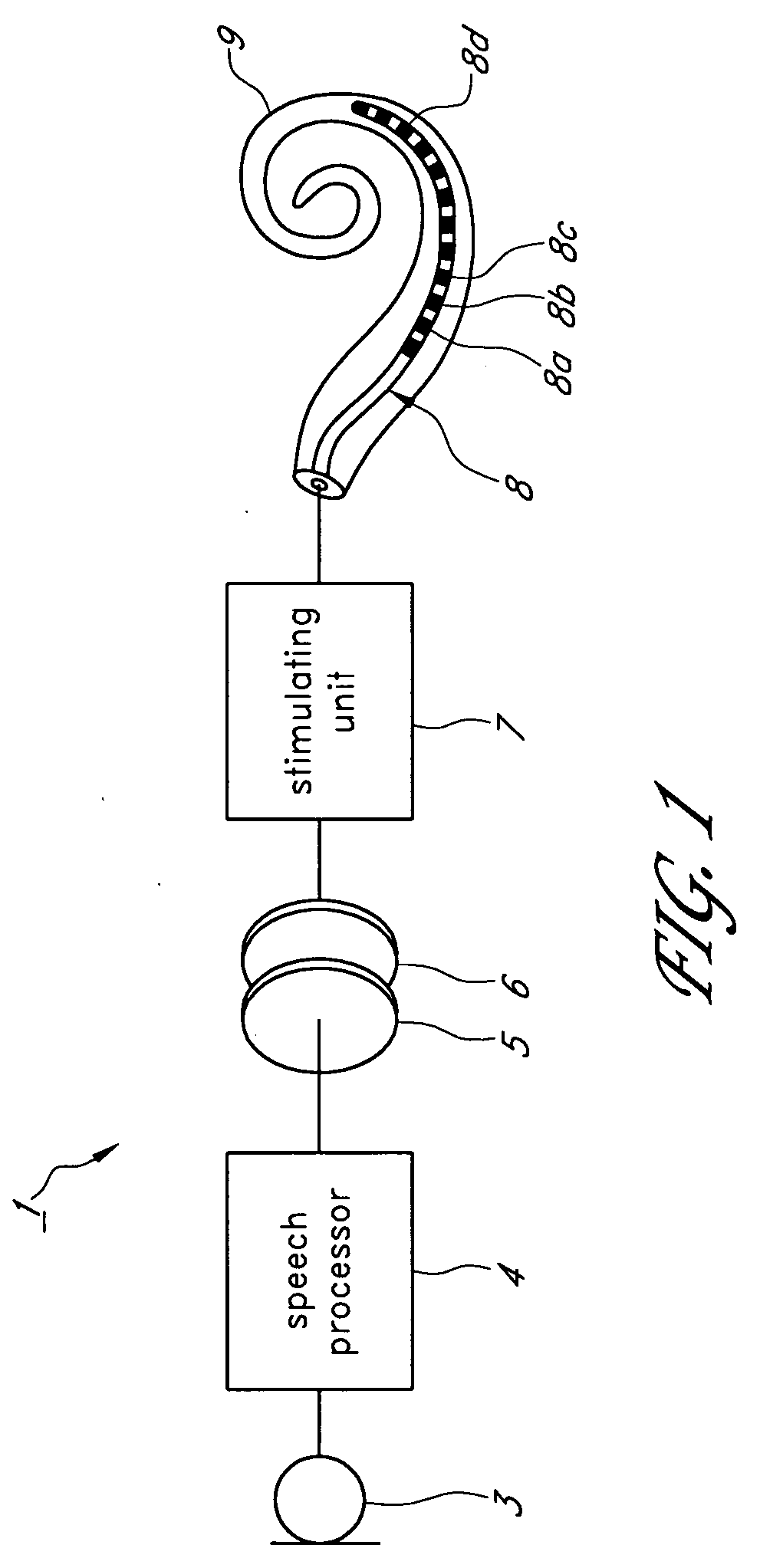
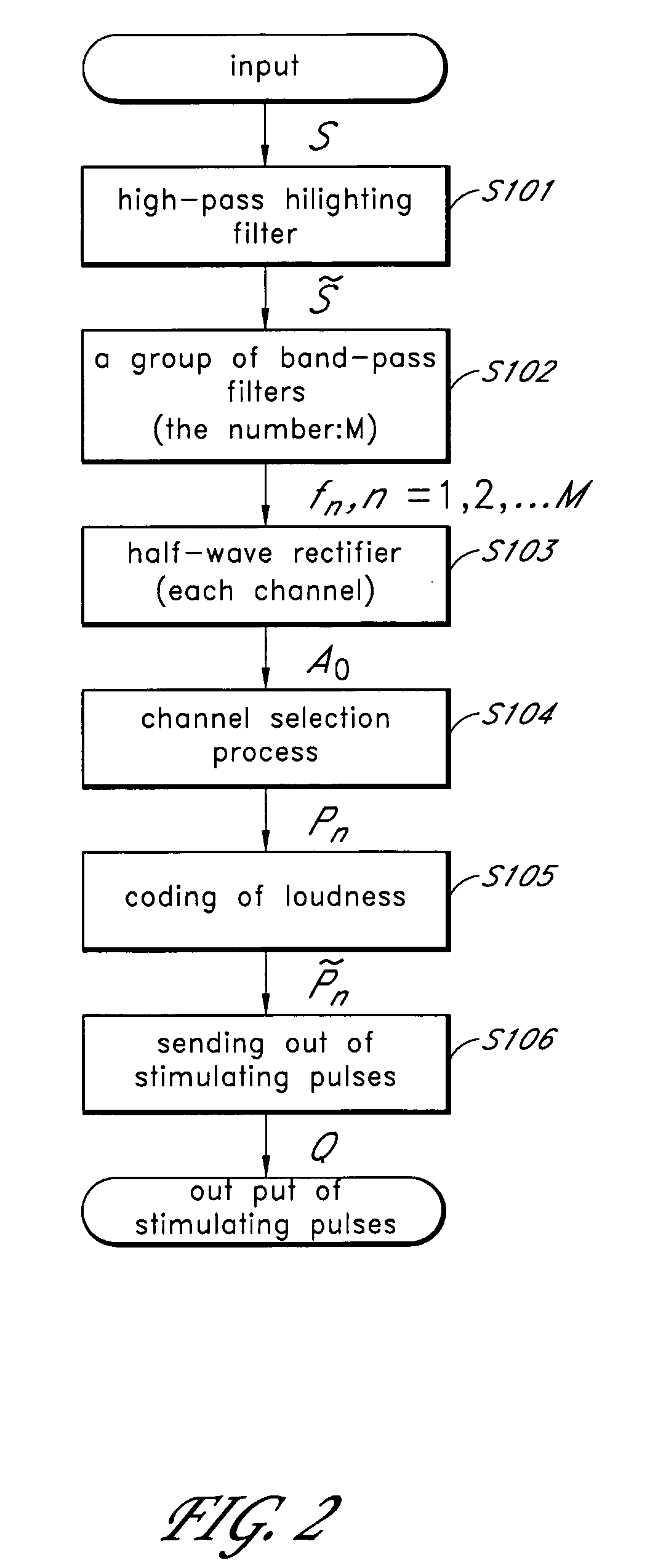
A cochlear implant and a method of speech conversion in the cochlear implant which can provide a user with more natural-sounding reproduced speech and can regenerate a natural variation at a value near the natural period of respective channels. A method of speech conversion in a cochlear implant in which an electrode array of a plurality of electrodes is arranged within a cochlea, electrically stimulation pulses are generated by transmitting speech information sampled via a microphone to the electrodes, and the acoustic sense is reinforced by transmitting the speech information to the cochlea as electrically stimulation pulses. The method can include discriminating the speech information into respective frequency bands using a plurality of band pass filters within a signal frame being a predetermined sampling period, adding an information of a channel corresponding to the frequency band to the speech information, adjusting the number of the stimulation pulses to a frequency allowed in one channel by leaving in respective channels a speech information having a higher signal level in one channel, adjusting the number of the stimulation pulses to a frequency allowed in all channels by leaving a speech information having a higher signal level in all speech information left in respective channels, and generating the stimulation pulses by providing the left speech information to the electrode corresponding to the channel.
Owner:KITAZAWA SHIGEYOSHI
Tissue-culture breeding method for high-borneol-content cinnamomum camphora
InactiveCN104365476AEasy accessHigh in essential oilsHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureCinnamomum camphoraCinnamomum
The invention discloses a tissue-culture breeding method for high-borneol-content cinnamomum camphora. The tissue-culture breeding method comprises: selecting and culturing a cinnamomum camphora individual with the borneol content of 90% or more from cinnamomum camphora natural variation plant, acquiring a semi-lignification stem segment with annual sprouting as an explant, performing disinfection processing, establishing an aseptic line, and then forming a regenerated plant through bud primary induction, propagation culture, rooting culture and the like. Proper formulas and culture conditions of all links for tissue-culture breeding of high-borneol-content cinnamomum camphor are screened out, and the high-borneol-content cinnamomum camphor regenerated plant is successively obtained. Therefore, the method effectively solves the technical problems that browning and dead seedlings are generated during tissue-culture breeding of cinnamomum camphor with the borneol content of 90% or more, and provides seedling guarantee for construction of an excellent cinnamomum camphor raw material forest base.
Owner:JIANGXI ACAD OF FORESTRY
Multimodal disambiguation of speech recognition
InactiveUS20120143607A1Efficient and accurate text inputLow accuracySpeech recognitionEnvironmental noiseAmbiguity
The present invention provides a speech recognition system combined with one or more alternate input modalities to ensure efficient and accurate text input. The speech recognition system achieves less than perfect accuracy due to limited processing power, environmental noise, and / or natural variations in speaking style. The alternate input modalities use disambiguation or recognition engines to compensate for reduced keyboards, sloppy input, and / or natural variations in writing style. The ambiguity remaining in the speech recognition process is mostly orthogonal to the ambiguity inherent in the alternate input modality, such that the combination of the two modalities resolves the recognition errors efficiently and accurately. The invention is especially well suited for mobile devices with limited space for keyboards or touch-screen input.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
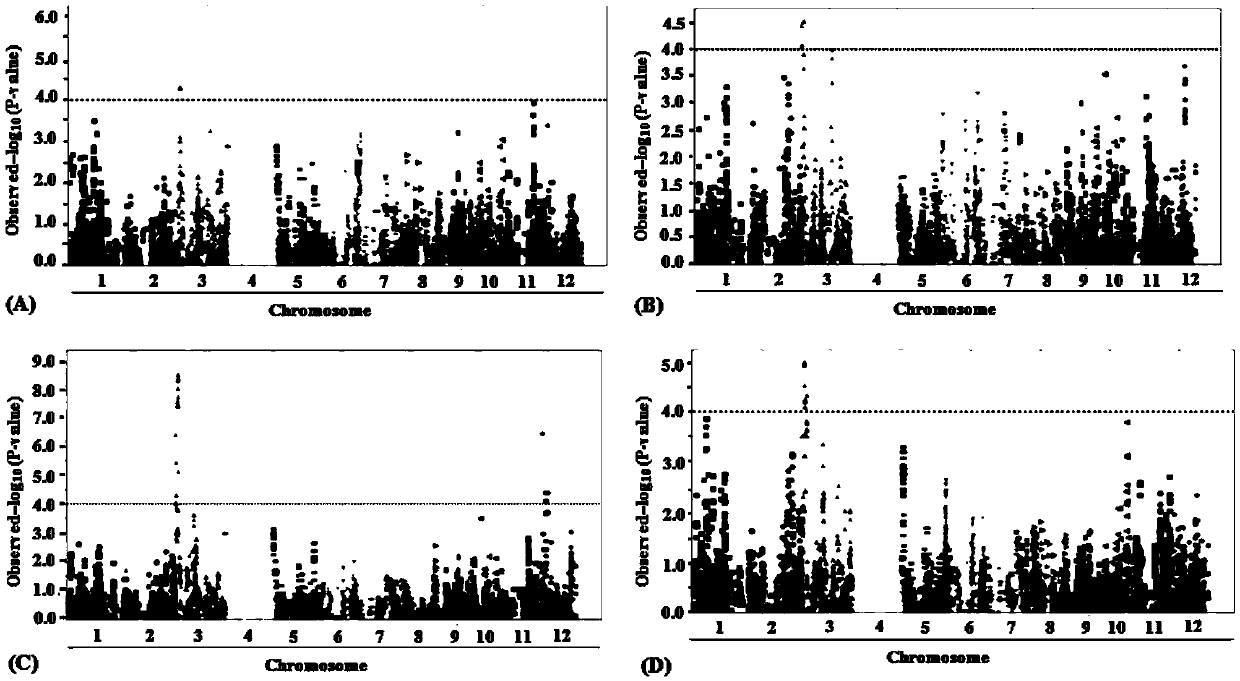
SNP locus related to wheat spikelet number per spike and application thereof
ActiveCN110184381AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMarker-assisted selectionTriticeae
The invention discloses an SNP locus related to wheat spikelet number per spike and application thereof. Through genetic variation analysis of a WFZP-A gene promoter region in a wheat natural variation population, the invention finds an SNP corresponding to 1501st site at the 5'end of a sequence table 1. The SNP has two genotypes: genotype A (A) and genotype B (G). The correlation analysis shows that in the homozygous types of the two genotypes, the spikelet number per spike is as follows: the number of genotype A-homozygous wheat is larger than that of genotype B-homozygous wheat. The invention also provides a dCAPS marker for detecting the SNP. Experiments prove that the wheat with higher spikelet number per spike can be found by detecting the SNP. The invention provides a new method formolecular marker-assisted selection breeding of wheat, and has important significance in the breeding or research high-yield wheat varieties.
Owner:中国科学院遗传与发育生物学研究所农业资源研究中心
Application of maize gene ZmGFT1 in increasing folic acid content in plants
ActiveCN105647942AAlleviate hidden hungerMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesBiotechnologyNutrition
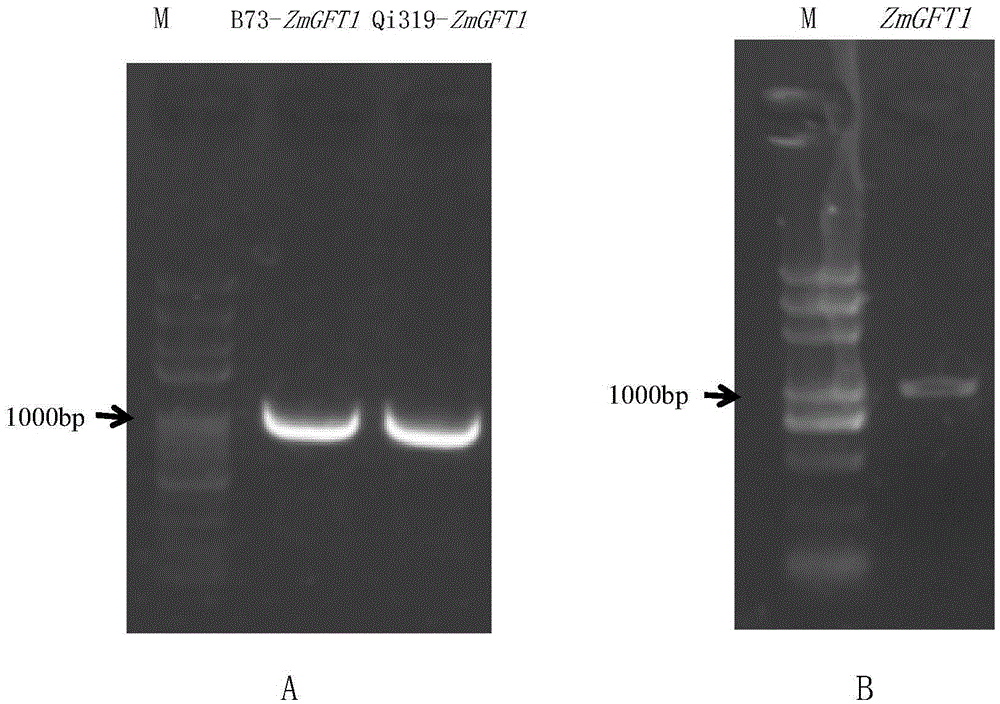
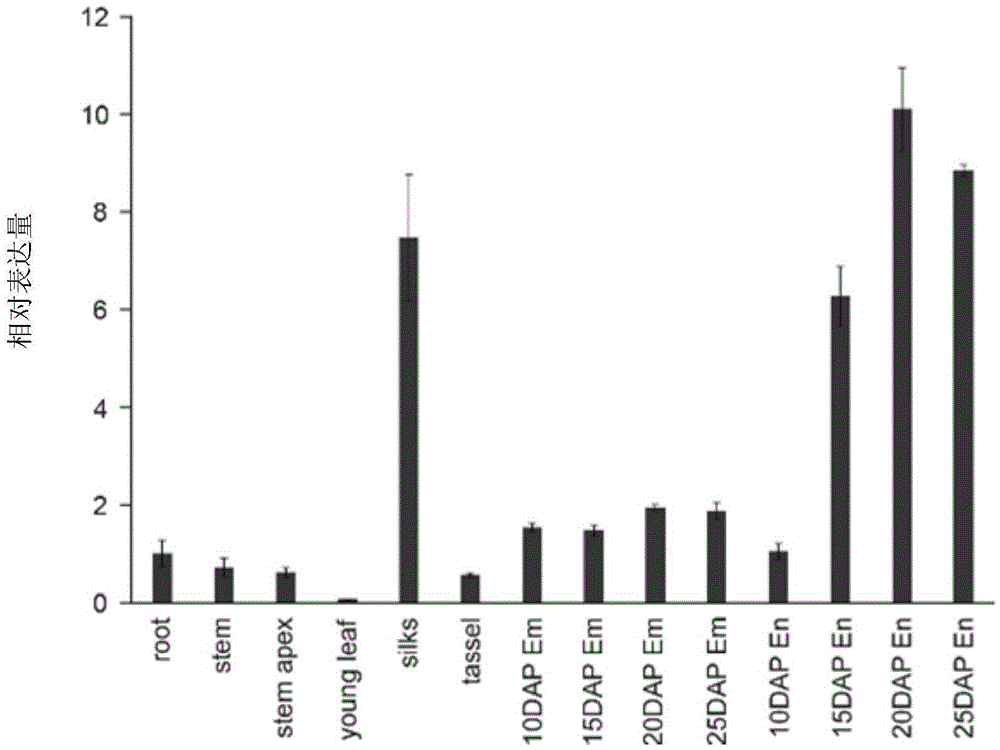
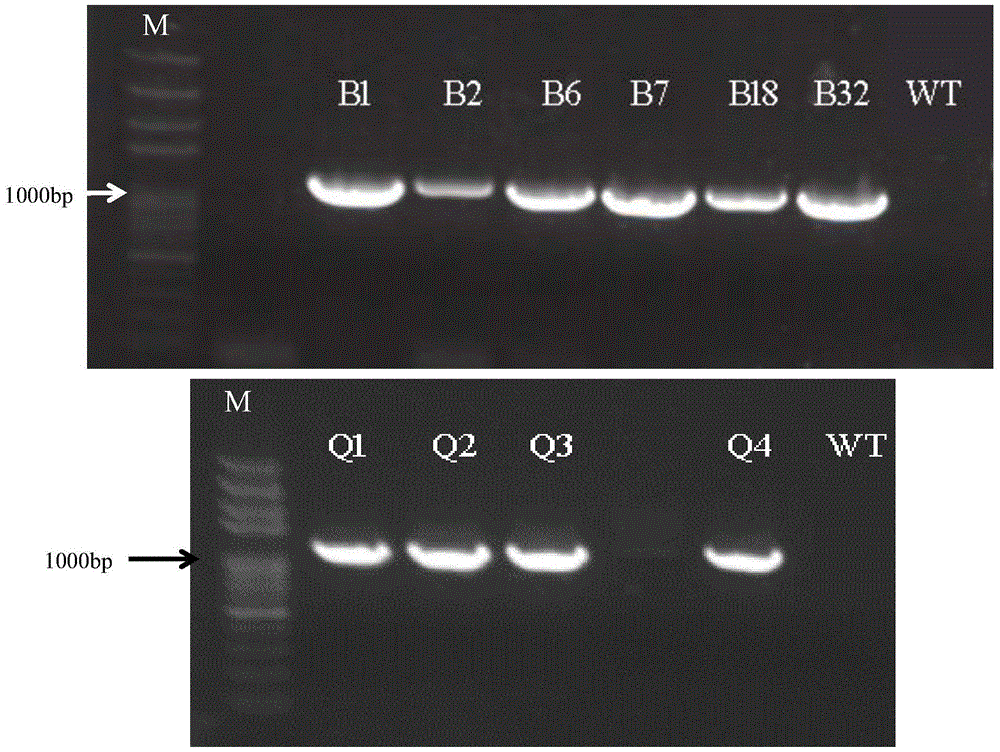
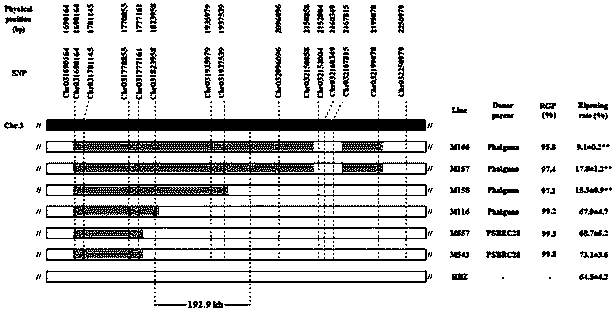
The invention provides application of maize gene ZmGFT1 in increasing folic acid content in plants. 5-Formyltetrahydrofolate content in 513 selfing line materials of a maize natural variant group is measured, the influence of group structure and genetic relationship of the natural variant group is estimated in connection with genotype data mined from RNA-Seq data, gene GFT1 having significant influence on the 5-formyltetrahydrofolate content and located on maize 5th chromosome is located by means of genome-wide association study, and the gene GFT1 encodes glutamate formiminotransferase 1. The invention also provides an SNP marker associated with maize folic acid content and its application. The maize gene ZmGFT1 and discovery of the key SNP site therein having significant influence on the 5-formyltetrahydrofolate content not only provide theoretical basis for studying folic acid metabolism in maize and other crops, but also enable the hidden hunger problem of human in terms of folic acid nutrition to be solved through the increase in the folic acid content of transgenic plants.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for breeding new species by fusion between various plants and distant induced mutagenesis
InactiveCN101480163AEasy to operateWide range of breeding materialPlant genotype modificationHorticultureRootstockFructification
The invention relates to a method for culturing new species by merging distant mutagenesis among various plants, which comprises the following steps: 1, the root or the tuberous stalk of a plant is selected as a parental stock; 2, the root of the selected plant is fully removed and used as a graft, and the fully root-removing part is a merging surface; 3, before the parental stock is merged, the merging surface is selected; 4, the graft and the parental stock are merged, the cross sections of the graft and the parental stock are tightly merged and aligned to form a layer; 5, a merging opening is fixed, the pierced part of the root or the tuberous stalk by an iron nail or a bamboo pegwood is fixed and covered by soil and compacted; 20 to 25 days later after mergence, the merging opening is healed, and tissue starts to merge; the graft starts to grow, a new root grows up at the merging opening 20 to 30 days later for facilitating the smooth growth, the blossom and the fructification of the graft, and a new species is mutagenized. In the distant adverse mutagenesis method, plants of different species are crossed and mutagenized by the distant mutagenesis, mutagenized offspring mutagenesis is far higher than natural mutagenesis, and the characteristics of the mutagenesis can be stably inherited. The method is simple to operate, has wide breeding material, rapidly stabilizes the offspring characteristics, accelerates the breeding process and is easy to generate new species and breeds.
Owner:曹长义
Cold-tolerance gene qCT-3-2HHZ for rice booting stage stable expression and molecular marking method thereof
ActiveCN105505922ARich diversityImprove cold resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyChilling injury
The invention provides a cold-tolerance gene qCT-3-2HHZ for rice booting stage stable expression and a molecular marking method thereof, and belongs to the field of rice high-yield stress-tolerance breeding and molecular genetics. According to the linkage and linkage disequilibrium phenomenon, the Huang zhanhua variety and eight associated breeding populations derived from donor parents rich in diversity are used, a whole-genome relational analysis and physical mapping method is adopted, the cold-tolerance gene qCT-3-2HHZ for the rice booting stage stability expression is precisely positioned and verified, and a practical economical marker ZCT-7 based on common PCR is further developed. The cold-tolerance gene qCT-3-2HHZ and the molecular marking method are applied to rice chilling-injury-tolerance assisted selection and pyramid breeding, defects of natural variation genes in the prior art can be effectively made up for, negative effects caused by assistant breeding conducted through primary positioning results can be remarkably reduced, genotype selection can be carried out on low-generation breeding populations in the seedling stage, cold-tolerance individuals are obtained, hybridization and transfer are facilitated in time, the process of identifying low-temperature resistance in the adult-plant stage is omitted, breeding efficiency is improved, and the breeding process is accelerated.
Owner:AGRI GENOME INST OF SHENZHEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
System, portable device and method for digital authenticating, crypting and signing by generating short-lived cryptokeys
InactiveUS20120110340A1Improve securityKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationUser inputNatural variation
A system for authentication, encryption and / or signing, as well as corresponding devices and methods, that use temporary but repeatable encryption keys uniquely connected to the user and generated from a unique set of input parameters. The system comprises an input device designed to extract predetermined characteristic values from value input by the user, which value is specific to the user, by means of a given algorithm, which algorithm is designed to remove the natural variation in the characteristic values in order to yield an identical set of characteristic values upon input of the same value, and a device designed to generate at least one user specific encryption key comprising said characteristic values.
Owner:LYSEGGEN JORN +2
Induction type broadband 3-component borehole magnetic measuring sensor and borehole electromagnetic tomography method using the same
ActiveCN104656044AEasy to set upAccurate explorationElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleThree dimensional measurementBroadband
Borehole electromagnetic exploration or tomography (EM tomography). An induction type broadband 3-component borehole magnetic measuring sensor can accurately and precisely measure a broadband magnetic field about x, y and z axes using a three-dimensional (3D) model within a borehole by monitoring natural variations in the earth's magnetic field or based on EM tomography using the borehole. The measuring sensor is applicable to energy resource fields such as petroleum and coal, mineral resources fields and civil engineering and environmental fields.
Owner:KOREA INST OF GEOSCI & MINERAL RESOURCES
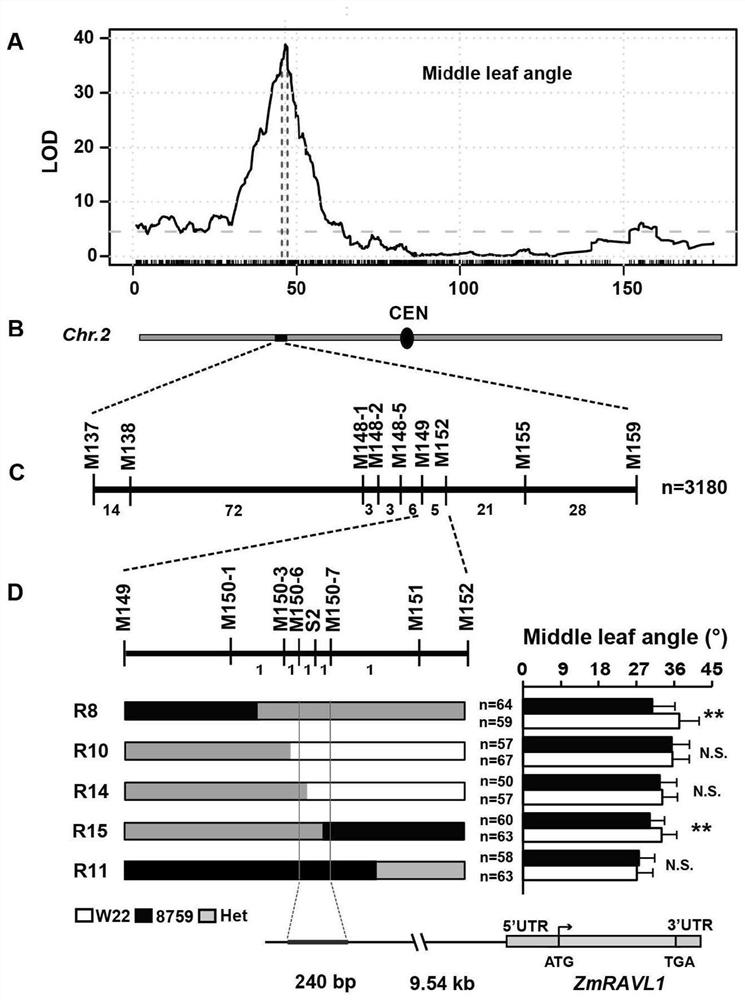
Corn gene ZmRAVL1 and functional site and application thereof
ActiveCN112063626AExpand sourceBroaden the genetic baseMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyGenome editing
The invention relates to a corn gene ZmRAVL1 and a functional site and application thereof. According to the method, the functional site controlling angle between leaf and stem phenotype is positionedto 240 bp through fine mapping, and different angle between leaf and stem phenotypes are generated through insertion or deletion of the region. The invention proves that the corn yield can be increased under high planting density by utilizing the excellent natural variation improved inbred line from Teosinte, and the sources of available excellent alleles in plant breeding are broadened. The invention proves that the reduction of the expression of ZmRAVL1 can influence plant type, for example, the reduction of angle between leaf and stem by a genetic engineering technology (RNAi), and provides an excellent gene resource for genetic engineering breeding. More excellent alleles are generated by the invention through a gene editing technology, so that the selection process of the excellent alleles is greatly shortened, and a new thought for obtaining available excellent alleles in breeding practice is provided. By combining a molecular assisted selection technology, an excellent inbred line can be rapidly and accurately improved or generated, and the invention provide the possibility for wide application of excellent alleles.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Application of Ghd7 gene in regulating rice flag leaf chlorophyll content
InactiveCN106148354AReduce chlorophyll contentFermentationGenetic engineeringAgricultural scienceChloroplast
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. It is found that a significant hot spot region exists in the range of 9.13 Mb to 9.17 Mb of a chromosome 7 through genome-wide association study (GWAS), nine signal peak values which have an extremely significant effect on the rice flag leaf chlorophyll content from different GWAS can be detected repeatedly, and the peak values correspond to Ghd7 gene positions. It is verified through near-isogenic lines and genetically modified materials that Ghd 7 serves as a main natural variation site to regulate the rice flag leaf chlorophyll content by down-regulating related gene expressions such as chlorophyll metabolism and chloroplast synthesis. The Ghd 7 has important breeding value in optimizing the rice flag leaf chlorophyll content.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
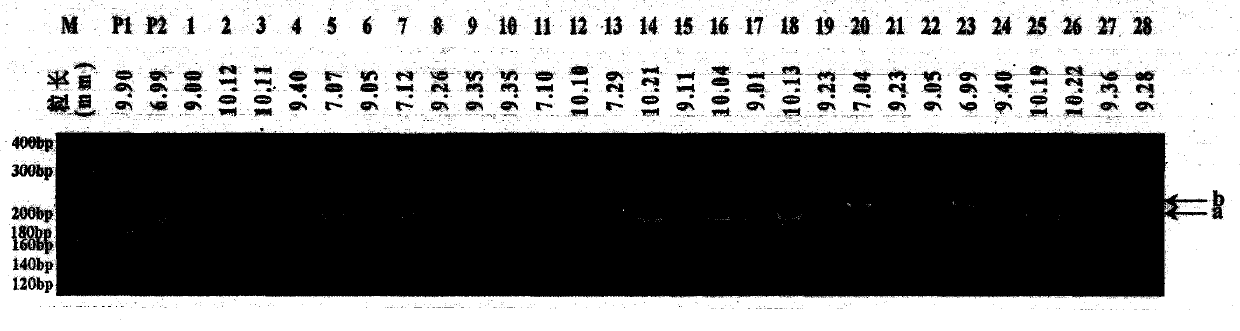
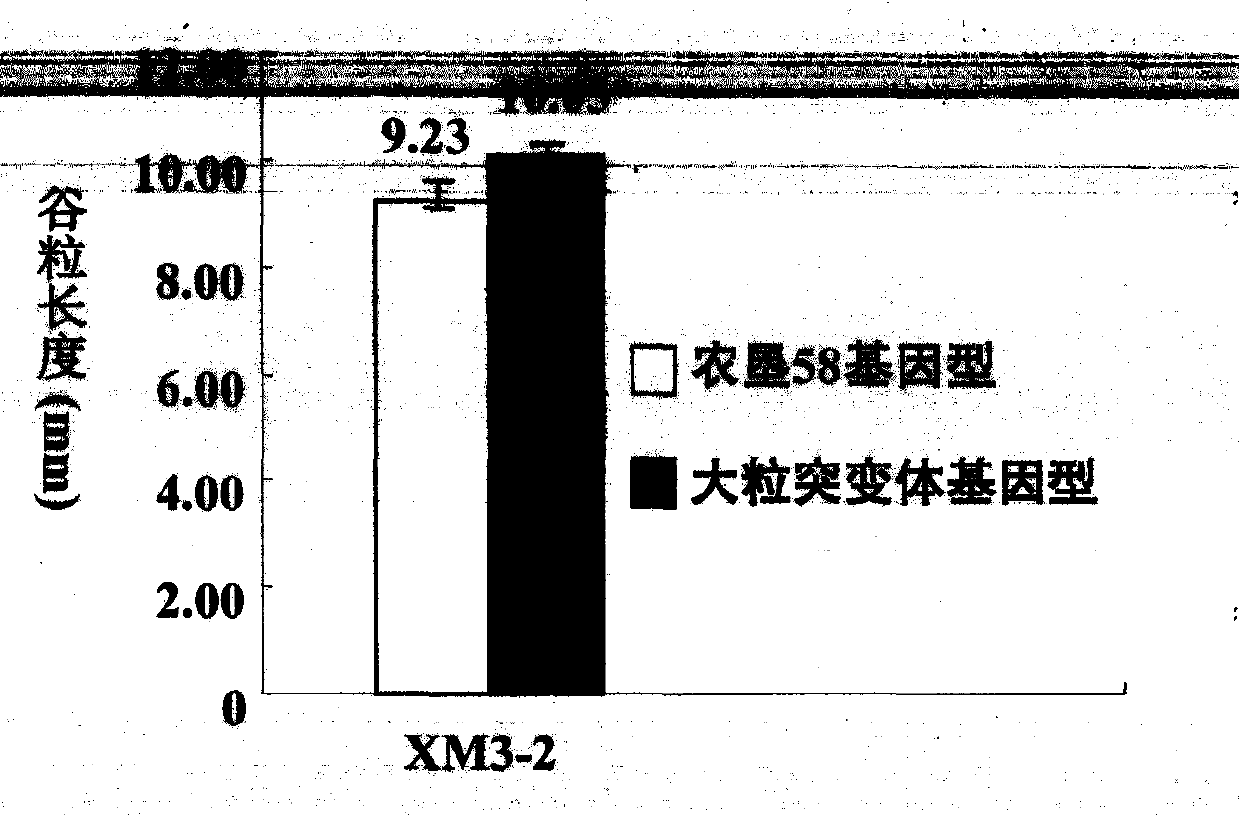
New space-mutated rice grain length gene qGS3a and molecular marker method thereof
InactiveCN103468715AGood appearanceGood yieldMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringAgricultural scienceMarker analysis
The invention relates to a new gene qGS3a for simultaneously increasing rice grain length and grain weight and a molecular marker method thereof, belonging to the fields of rice high-yield good-quality breeding and molecular genetics. The invention is characterized in that single marker analysis is performed according to the linkage segregation law by using F2 population of large-grain mutant and original parent Nongken 58 and derivative F3 family to locate the new grain length gene qGS3a on the 3rd chromosome, thereby obtaining PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification-based practical and economical marker XM3-2 which is closely linked with the new qGS3a. The new gene qGS3a is used for auxiliary selective breeding and polymerization breeding of appearance quality and yield of rice, can effectively overcome the defects in spontaneous mutant genes, can perform genotype selection on the low-generation breeding population in the seedling stage to obtain the breeding material with better appearance quality and yield components, omits the grain identification process in the adult-plant stage, enhances the breeding efficiency and accelerates the breeding process.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
High-nitrogen yeast and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102337224AIrradiation mutagenesisEnriched mutagenesis methodFungiMutant preparationMicroorganismHeavy ion radiation
The invention relates to to a high-nitrogen yeast (particularly referring to Saccharomyces cerevisiae) and a preparation method thereof. Saccharomyces cerevisiae is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) with the preservation number of CGMCC No.5004; and Saccharomyces cerevisiae is obtained by heavy ion radiation mutation, the content of nitrogen in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is 40-60%. A heavy ion mutation technology has the following main advantages that (1) variation rate is high, generally 1000 times higher than natural variation rate; (2) variation spectrum is wide, namely type of variation is diverse, and a new type of microbe strain can be obtained; (3) variation stability is strong, relatively stable strains (coexistence of positive and negative mutations) can be obtained, and screening period can be shortened; and (4) mutation operability is strong, and the radiation mutation of the microbe can be easily completed.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Multimodal disambiguation of speech recognition
The present invention provides a speech recognition system combined with one or more alternate input modalities to ensure efficient and accurate text input. The speech recognition system achieves less than perfect accuracy due to limited processing power, environmental noise, and / or natural variations in speaking style. The alternate input modalities use disambiguation or recognition engines to compensate for reduced keyboards, sloppy input, and / or natural variations in writing style. The ambiguity remaining in the speech recognition process is mostly orthogonal to the ambiguity inherent in the alternate input modality, such that the combination of the two modalities resolves the recognition errors efficiently and accurately. The invention is especially well suited for mobile devices with limited space for keyboards or touch-screen input.
Owner:AOL LLC A DELAWARE LLC
SSR molecular marker primer capable of rapidly identifying robinia pseudoacacia polyploids
InactiveCN107760796ARapid identificationGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationYellow LocustGenetic diversity
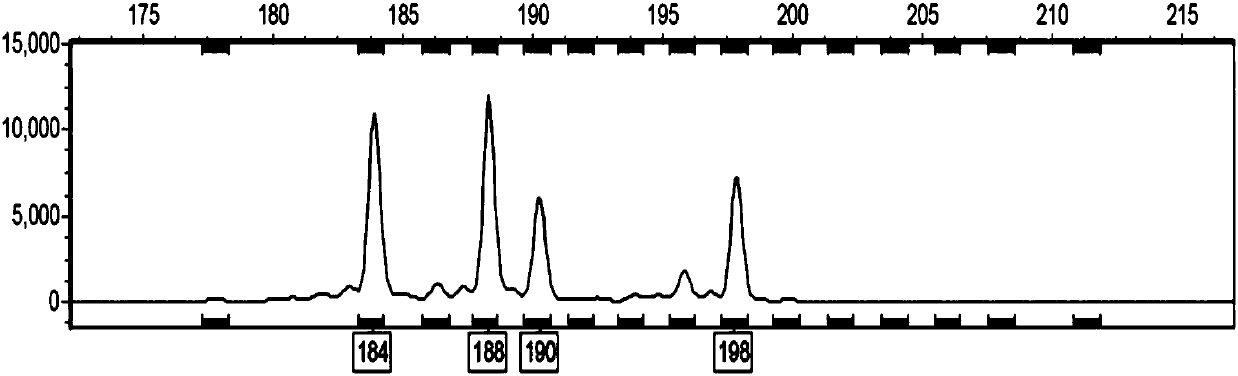
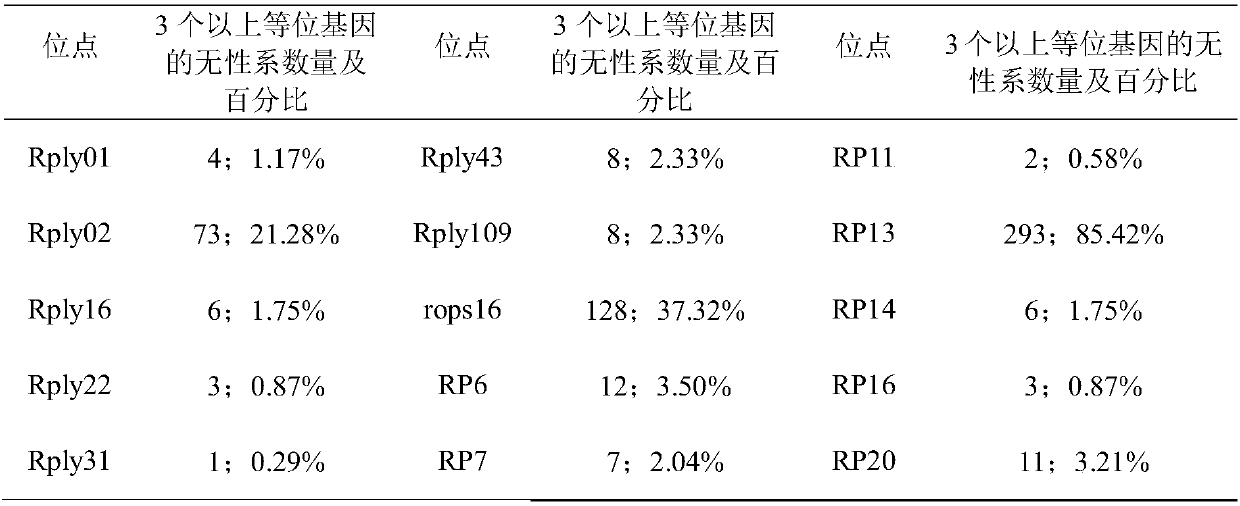
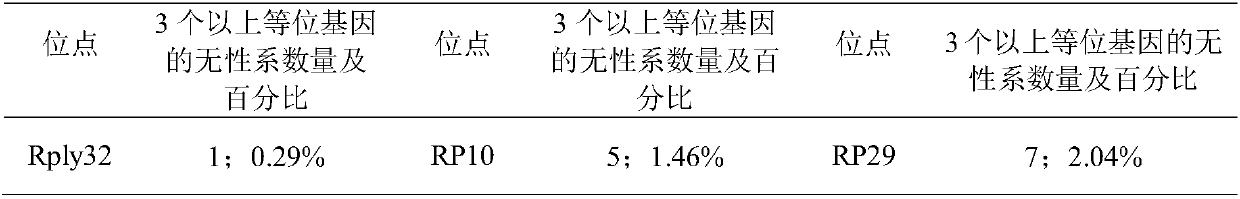
The invention discloses an SSR molecular marker primer capable of rapidly identifying robinia pseudoacacia polyploids, wherein the primer base sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2. According to the invention, robinia pseudoacacia polyploids can be rapidly identified from the molecular level without being affected by season, plant development stage and growing environment, so that reference and basis are provided for researches of rapid identification of robinia pseudoacacia polyploids, new variety protection, genetic diversity analysis evaluation and genetic breeding. By adopting the primer taken as an example in the invention, the detection rate of polyploids in 343 robinia pseudoacacia clones is up to 85.42%, thus sufficiently indicating high efficiency and applicability of the SSR primer, and verifying that multiple robinia pseudoacacia polyploids generating natural variation really exist in the natural world.
Owner:SHANDONG FOREST SCI RES INST +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com