Patents
Literature
97 results about "Leaky bucket" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
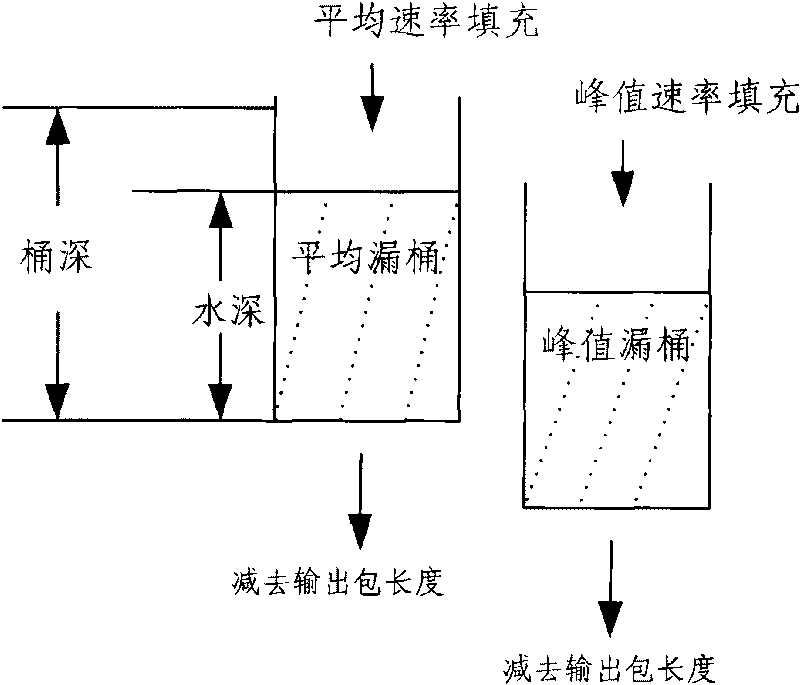
The leaky bucket is an algorithm based on an analogy of how a bucket with a leak will overflow if either the average rate at which water is poured in exceeds the rate at which the bucket leaks or if more water than the capacity of the bucket is poured in all at once, and how the water leaks from the bucket at an (almost) constant rate. It can be used to determine whether some sequence of discrete events conforms to defined limits on their average and peak rates or frequencies, or to directly limit the actions associated to these events to these rates, and may be used to limit these actions to an average rate alone, i.e. remove any variation from the average.
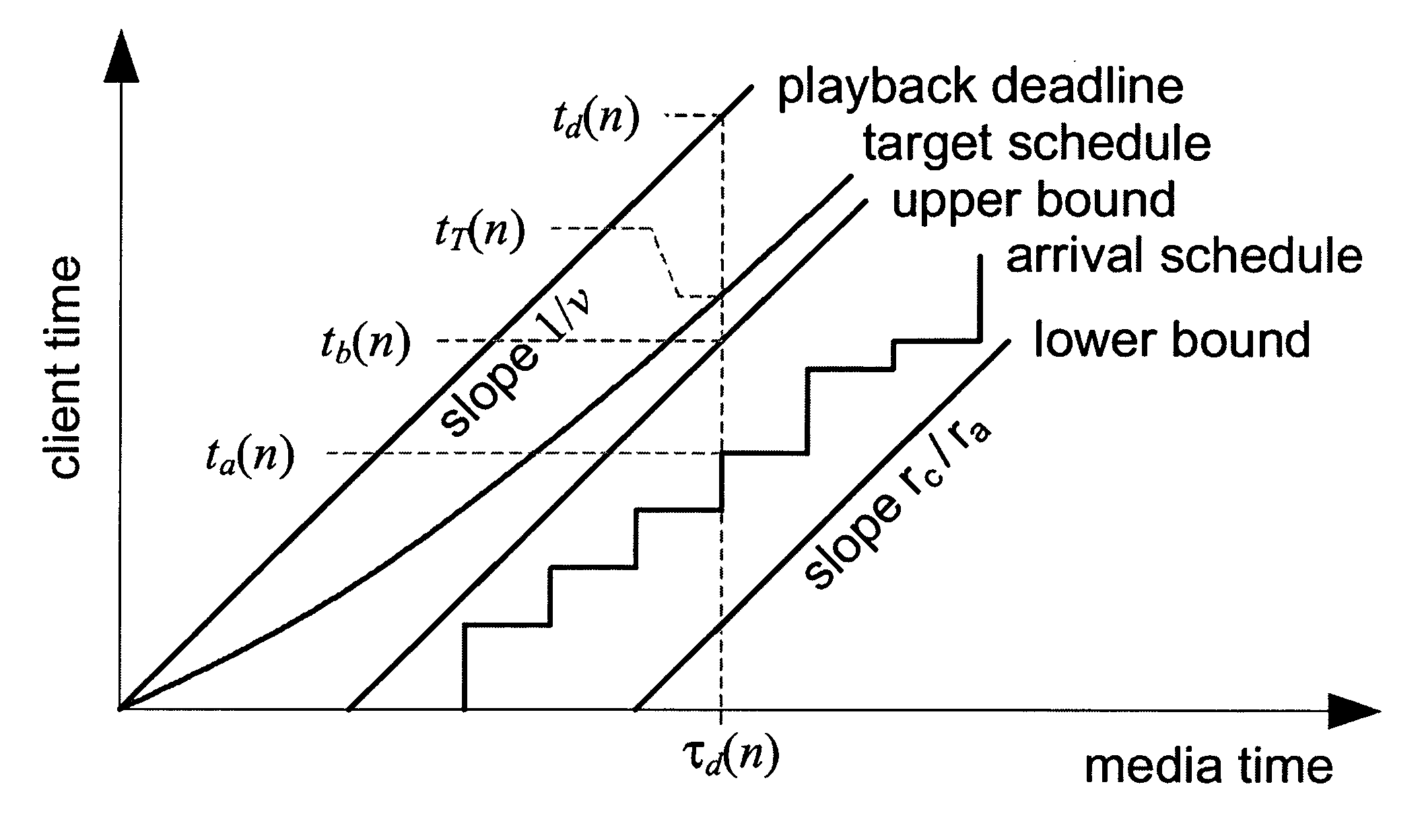
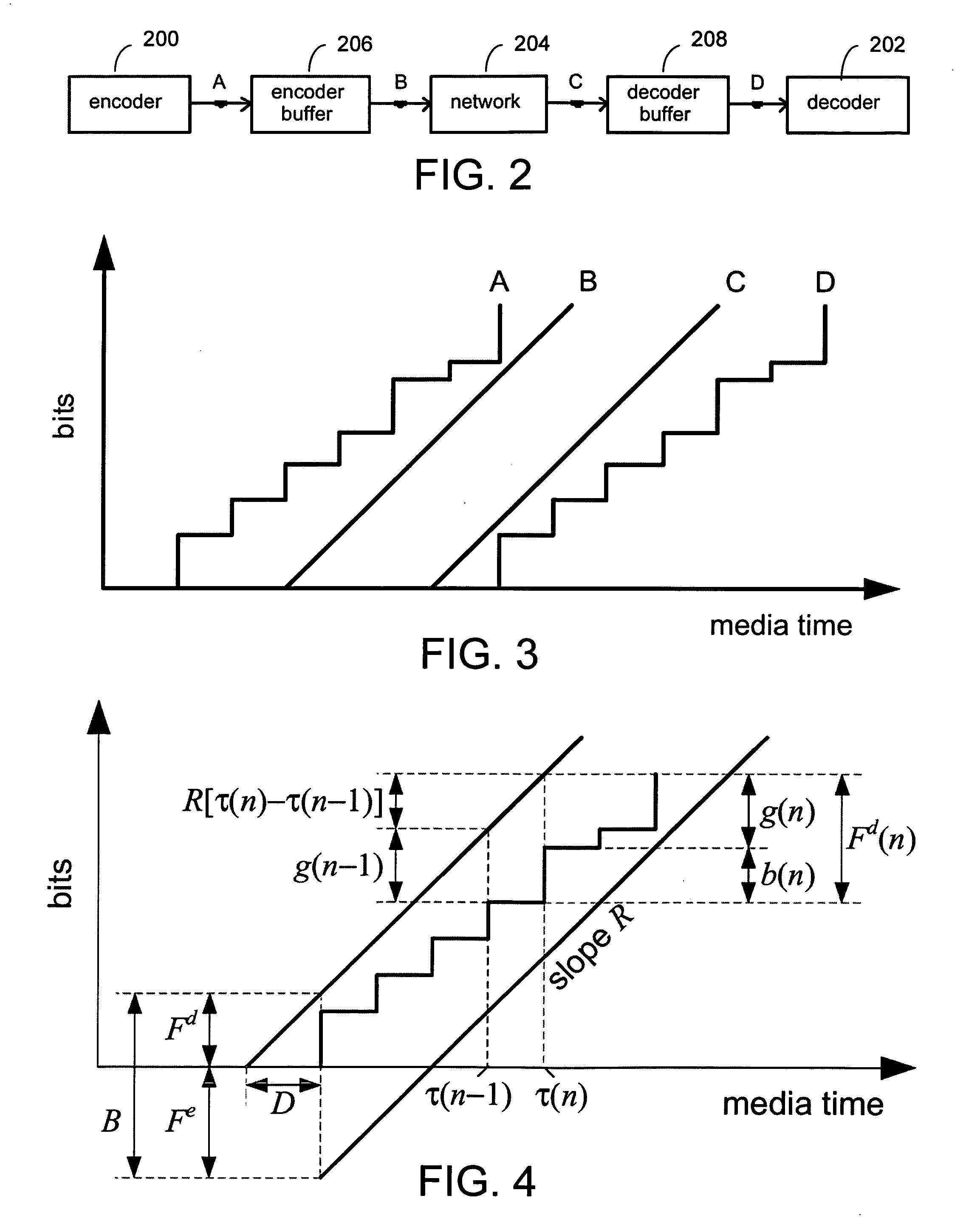
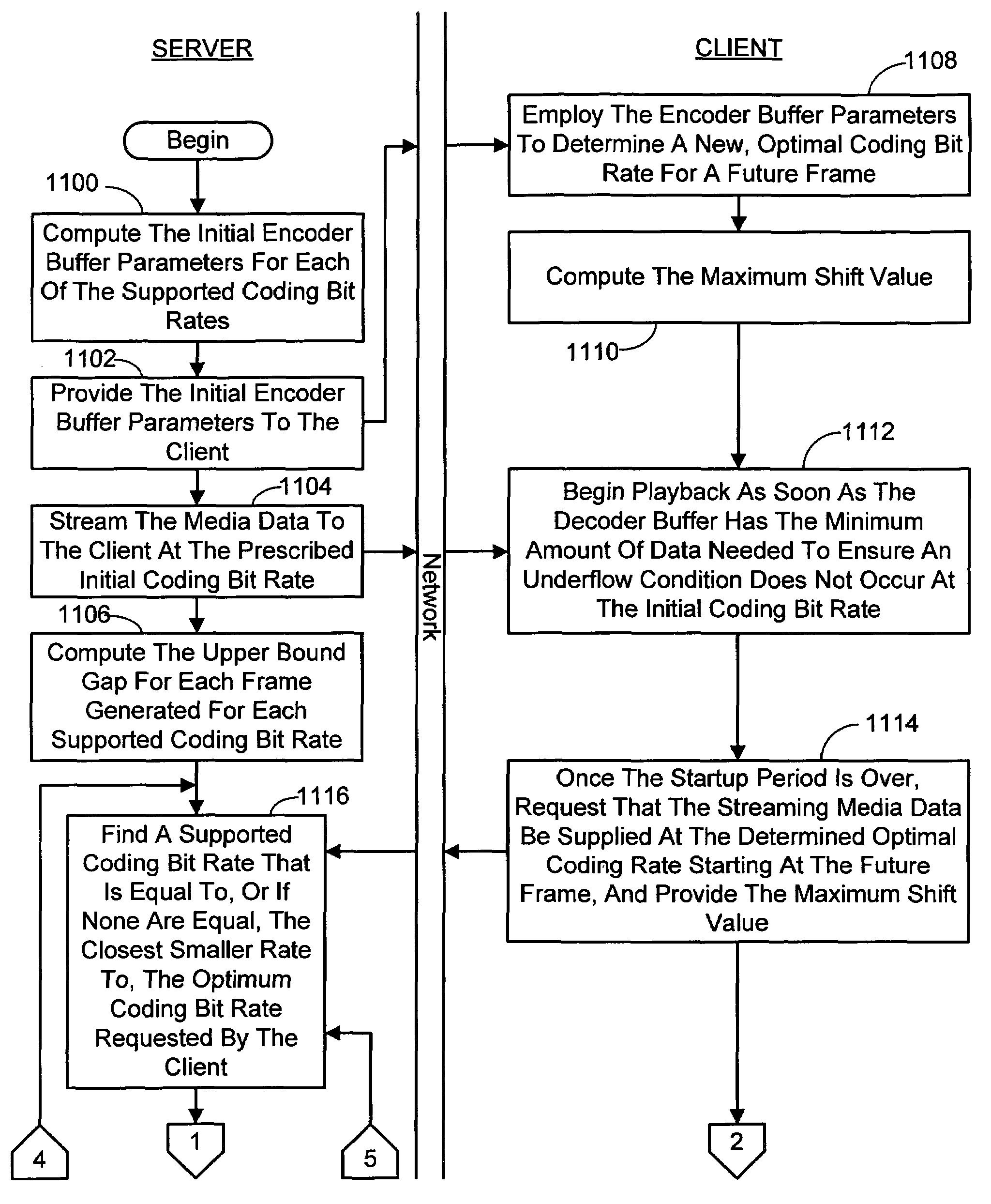
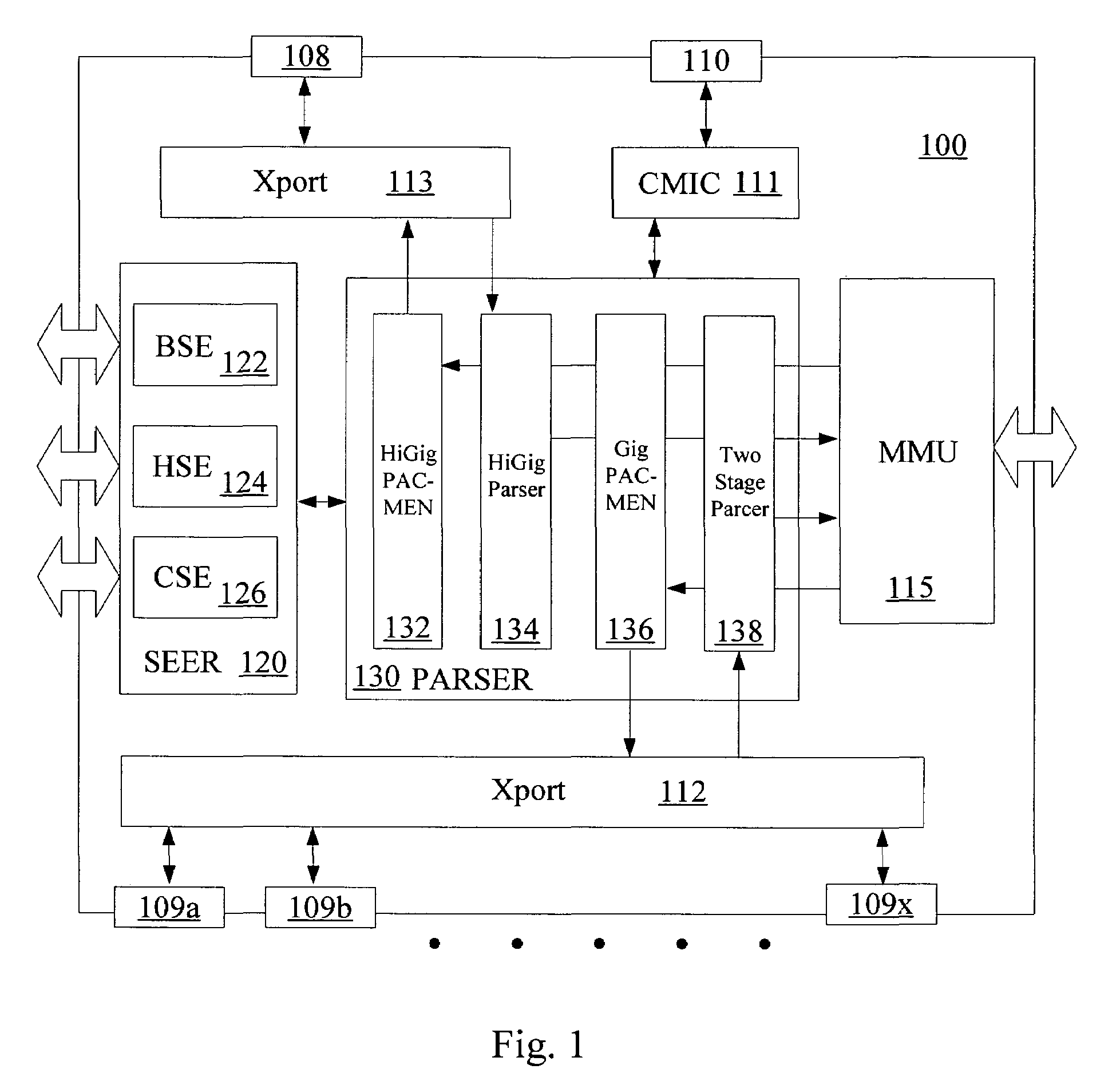
System and process for controlling the coding bit rate of streaming media data employing a limited number of supported coding bit rates
InactiveUS20060165166A1Maximize qualityStable and high qualityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningStreaming dataNatural variation
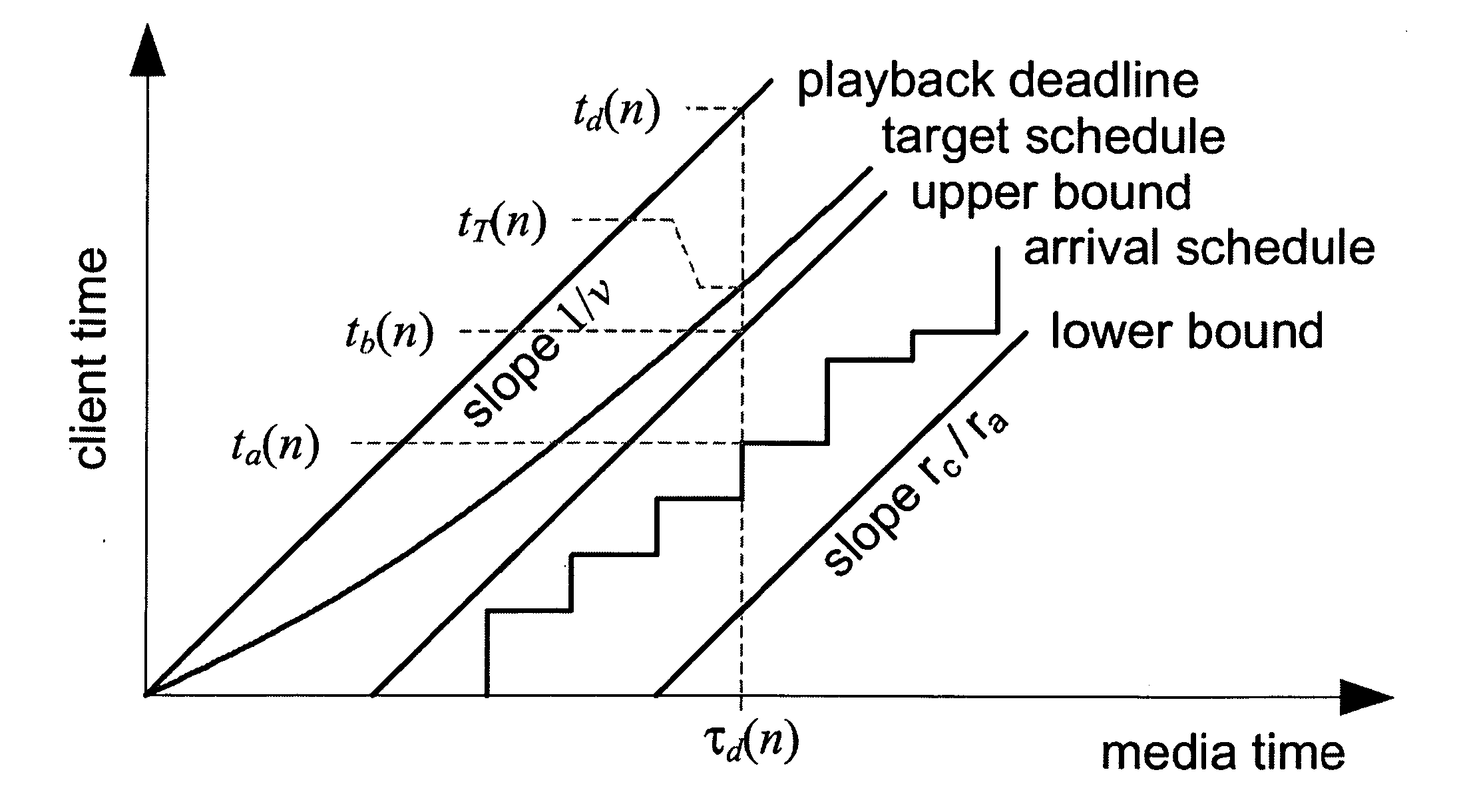
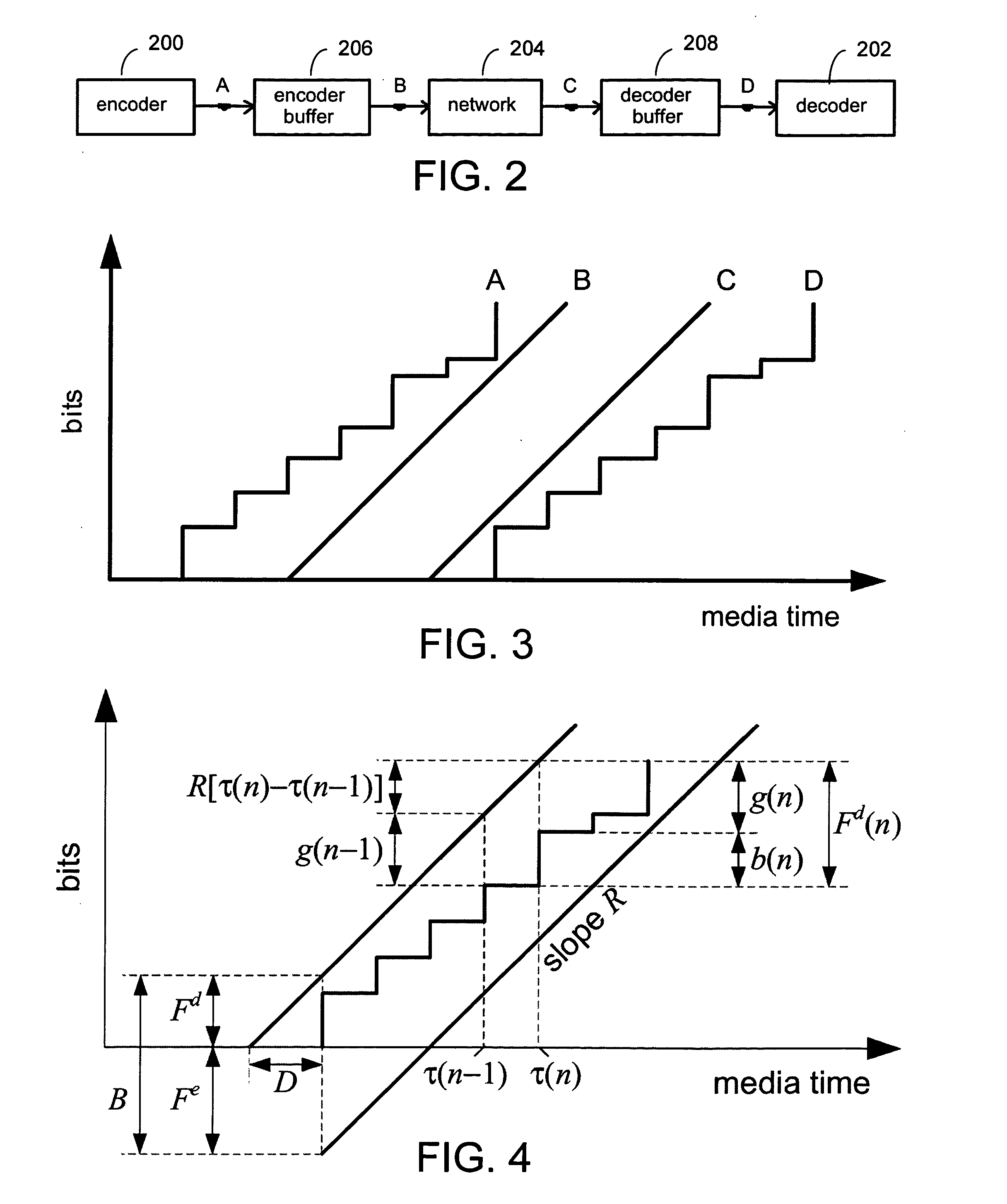
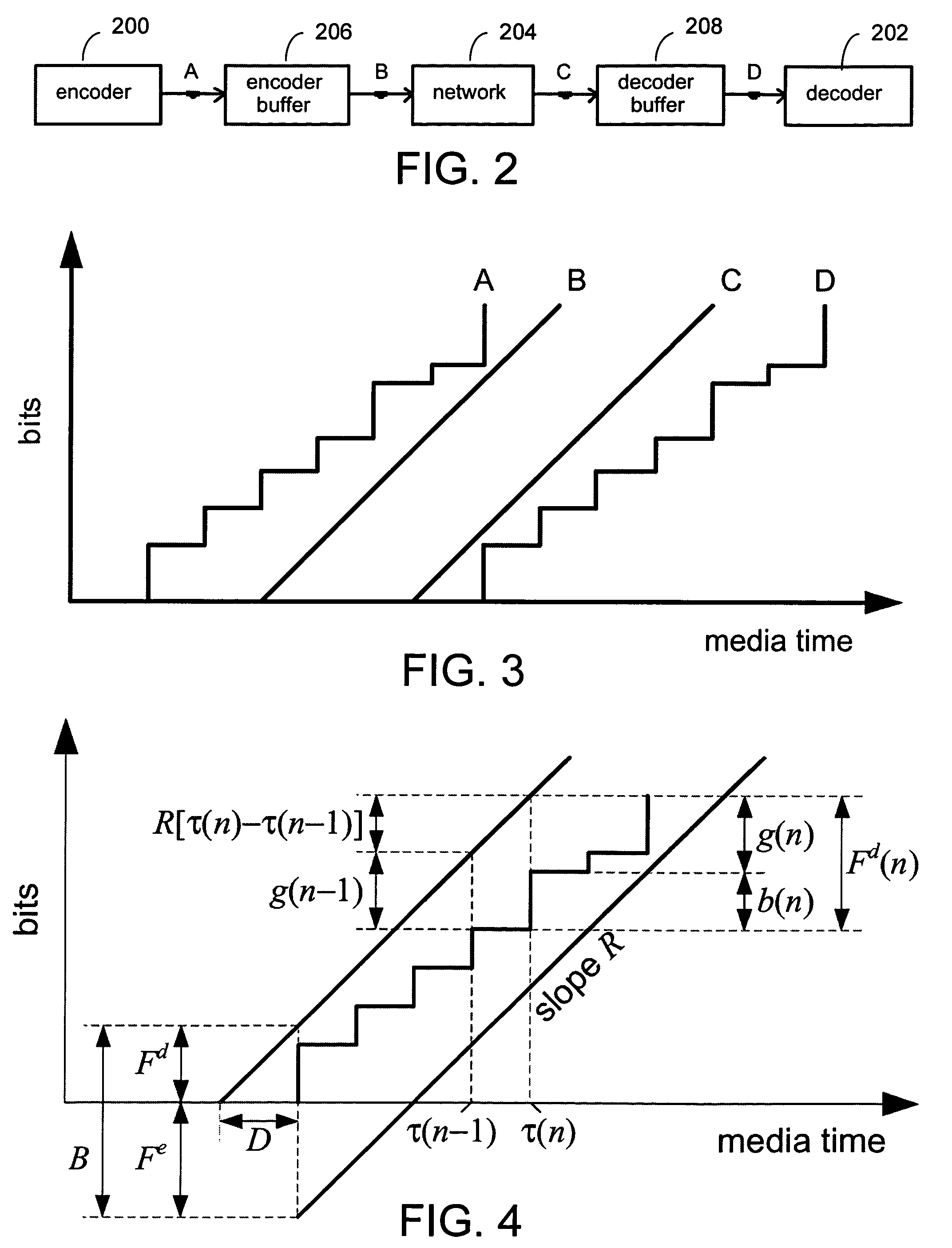
A system and process for controlling the coding bit rate of streaming media data is presented where a server streams data that exhibits one of a number of coding bit rates supported by the server. Initially, the server chooses the coding bit rate. However, after this startup period, the client provides coding bit rate requests. The server transmits the streaming media data at the most appropriate supported coding bit rate closest to the rate requested. The coding bit rates requested are those estimated to provide a high quality playback of the streaming data while still keeping a decoder buffer of the client filled to a desired level. A leaky bucket model is incorporated so that the changes in buffer duration due to natural variation in the instantaneous coding bit rate are not mistaken for changes in buffer duration due to network congestion.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System for real time transmission of variable bit rate MPEG video traffic with consistent quality
InactiveUS20020090029A1Quality improvementPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningReal time transmissionTransmission system
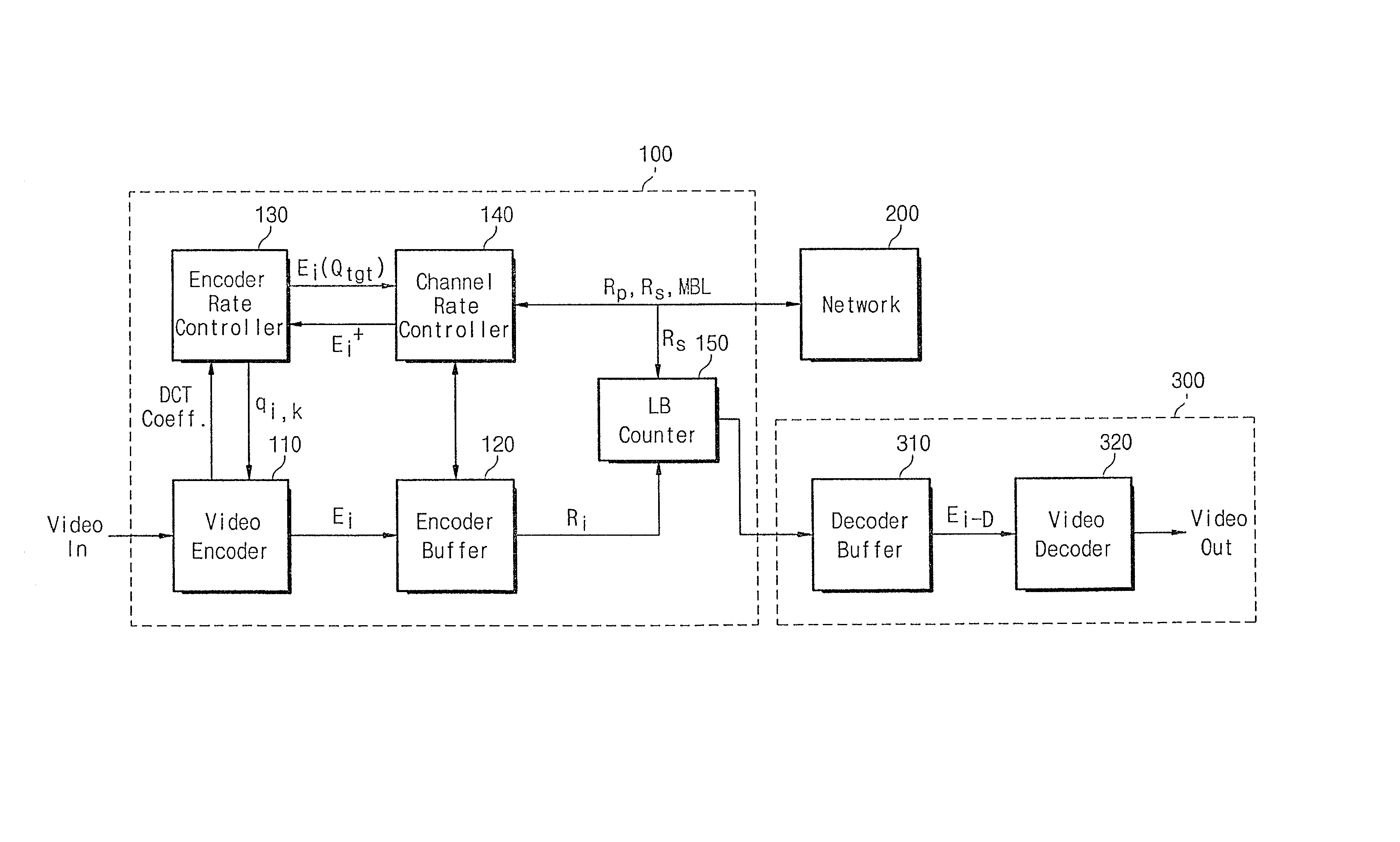
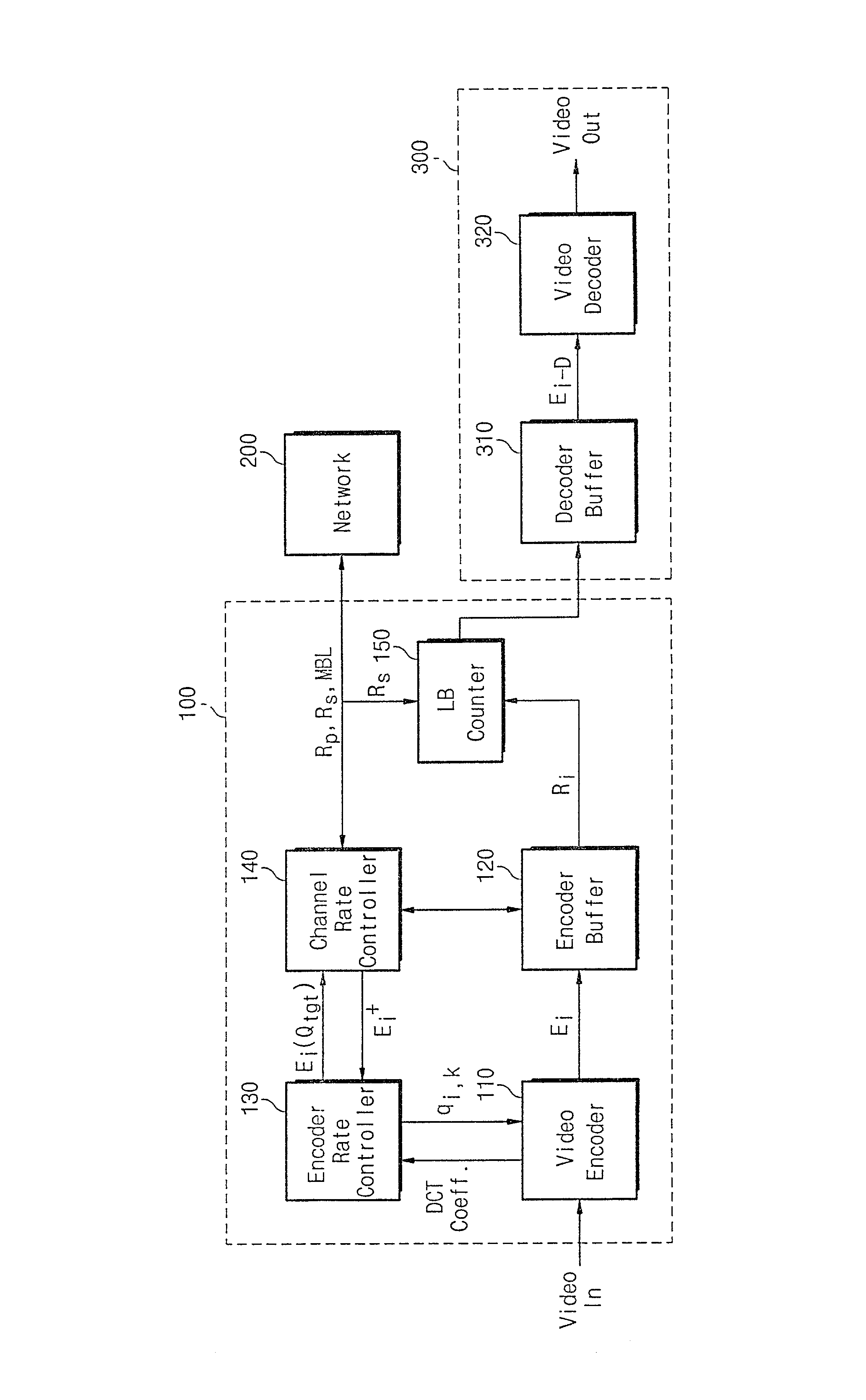
A system and method for real time transmission of variable bit rate MPEG video traffic with consistent quality, wherein each frame is encoded with quantization parameter generated from an encoder rate controller, and encoded data is transmitted to an encoder buffer. Transmission rate about each frame interval is determined by a channel rate controller at the beginning of the frame interval. Data transmission buffered at the encoder buffer is first regulated by Leaky Bucket counter, and the regulated data is transferred to a decoder buffer in a video receiving system through network. The encoder rate controller and channel rate controller included in the VBR video transmission system control the transmission rate generated from the video encoder and that from the network with satisfying imposed constrained conditions, respectively.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
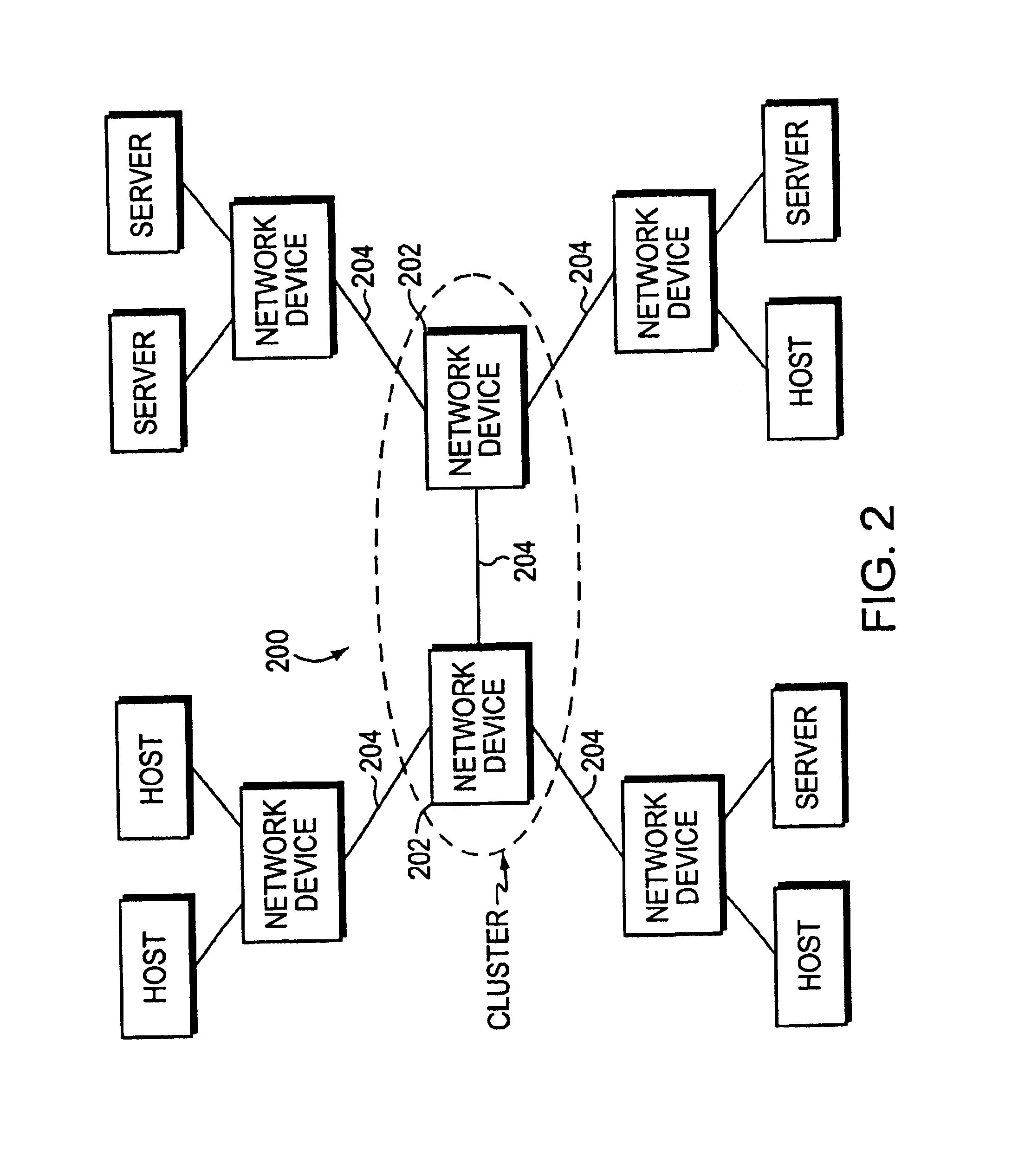
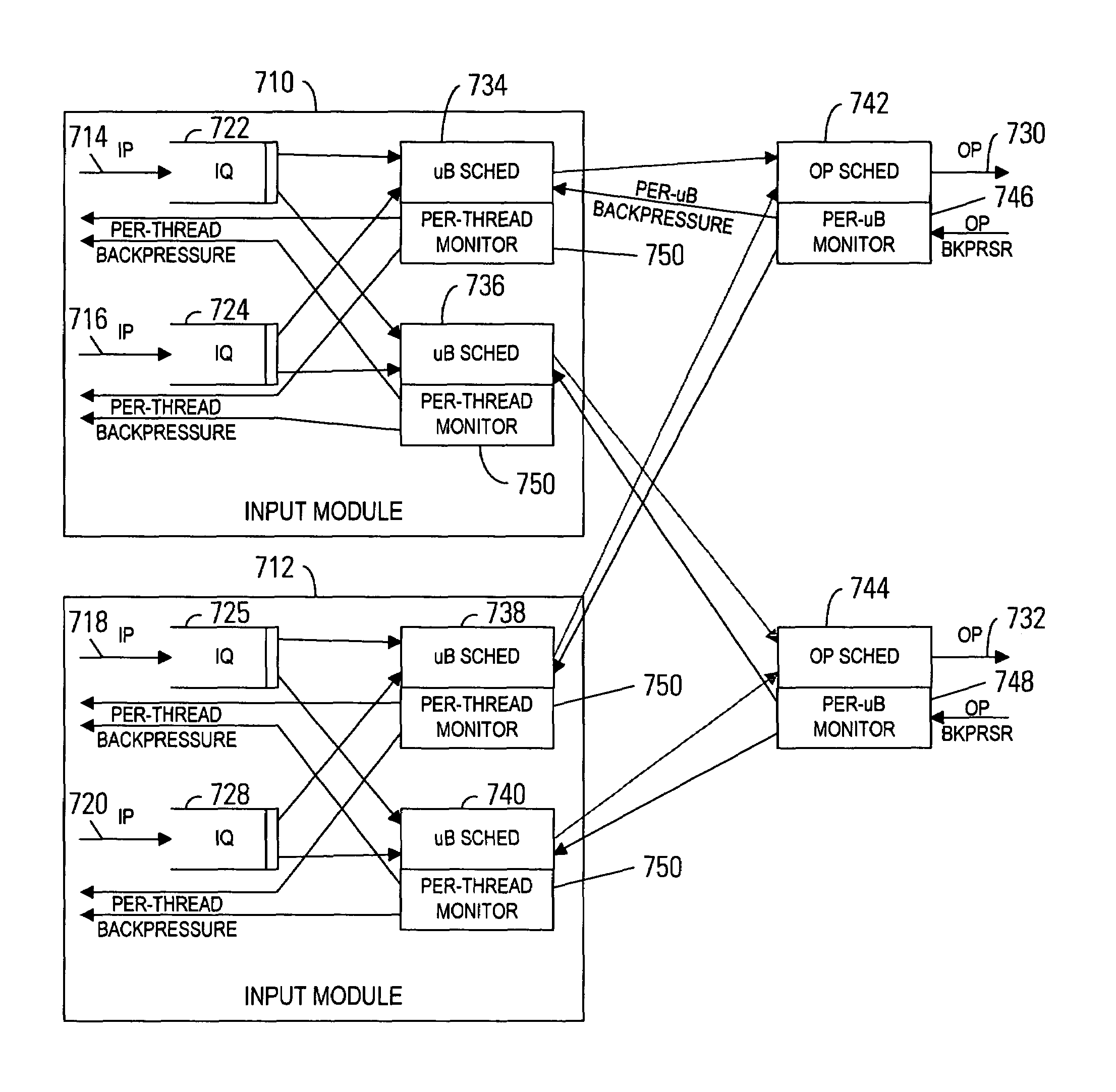
Backpressure mechanism for switching fabric
InactiveUS20080212472A1Reduce transmissionSimple processError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDistributed computingPacket switching
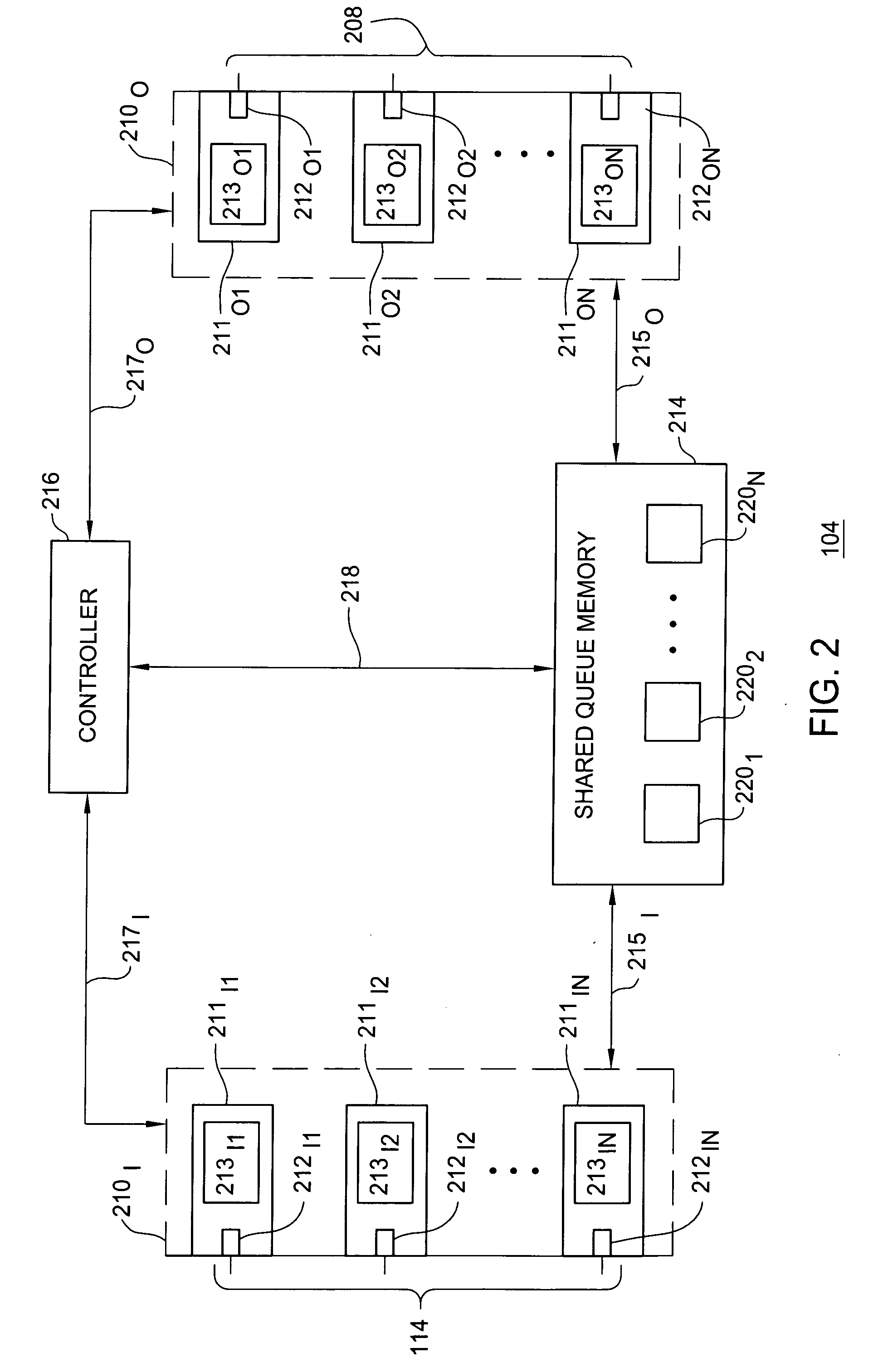
Roughly described, a packet switching fabric contains a separate queue scheduler for each combination of an input module and a fabric output port. The schedulers may also be specific to a single class of service. Each queue scheduler schedules its packets without regard to state of other input queues and without regard to packets destined for other output ports. In an aspect, the fabric manages per-flow bandwidth utilization of output port bandwidth capacity by monitoring the same and asserting backpressure toward the queue scheduler for any thread that is exceeding its bandwidth allocation. In another aspect, a switching fabric uses leaky buckets to apply backpressure in response to overutilization of downstream port capacity by particular subflows. In another aspect, a switching fabric includes a cascaded backpressure scheme.
Owner:INTEL CORP
System and process for controlling the coding bit rate of streaming media data employing a linear quadratic control technique and leaky bucket model
InactiveUS20060143678A1Maximize qualitySmoothness of the average coding bit rate over consecutiveTwo-way working systemsDigital video signal modificationModel controlClient buffer
A system and process for controlling the coding bit rate of streaming media data is presented. This coding bit rate control involves dynamically adjusting the coding bit rate to control client buffer duration to prevent the buffer from underflowing, while keeping the average coding bit rate close to the average transmission bit rate of the network (an thus maximizing the quality of the data playback). Using the theory of optimal linear quadratic control, the client buffer duration is kept as close as possible to a target level while still keeping the coding bit rate (and hence the quality) as constant as possible. In addition, a leaky bucket model is incorporated into the control loop so that the changes in buffer duration due to natural variation in the instantaneous coding bit rate are not mistaken for changes in buffer duration due to network congestion.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and process for controlling the coding bit rate of streaming media data employing a limited number of supported coding bit rates
InactiveUS7536469B2Maximize qualitySmoothness of the average coding bit rate over consecutivePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningStreaming dataDatasheet
A system and process for controlling the coding bit rate of streaming media data is presented where a server streams data that exhibits one of a number of coding bit rates supported by the server. Initially, the server chooses the coding bit rate. However, after this startup period, the client provides coding bit rate requests. The server transmits the streaming media data at the most appropriate supported coding bit rate closest to the rate requested. The coding bit rates requested are those estimated to provide a high quality playback of the streaming data while still keeping a decoder buffer of the client filled to a desired level. A leaky bucket model is incorporated so that the changes in buffer duration due to natural variation in the instantaneous coding bit rate are not mistaken for changes in buffer duration due to network congestion.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Distriburted QoS policing system and method
InactiveUS6826150B1Optimizing cost-accuracy tradeoffReduce information exchangeError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityTraffic congestion
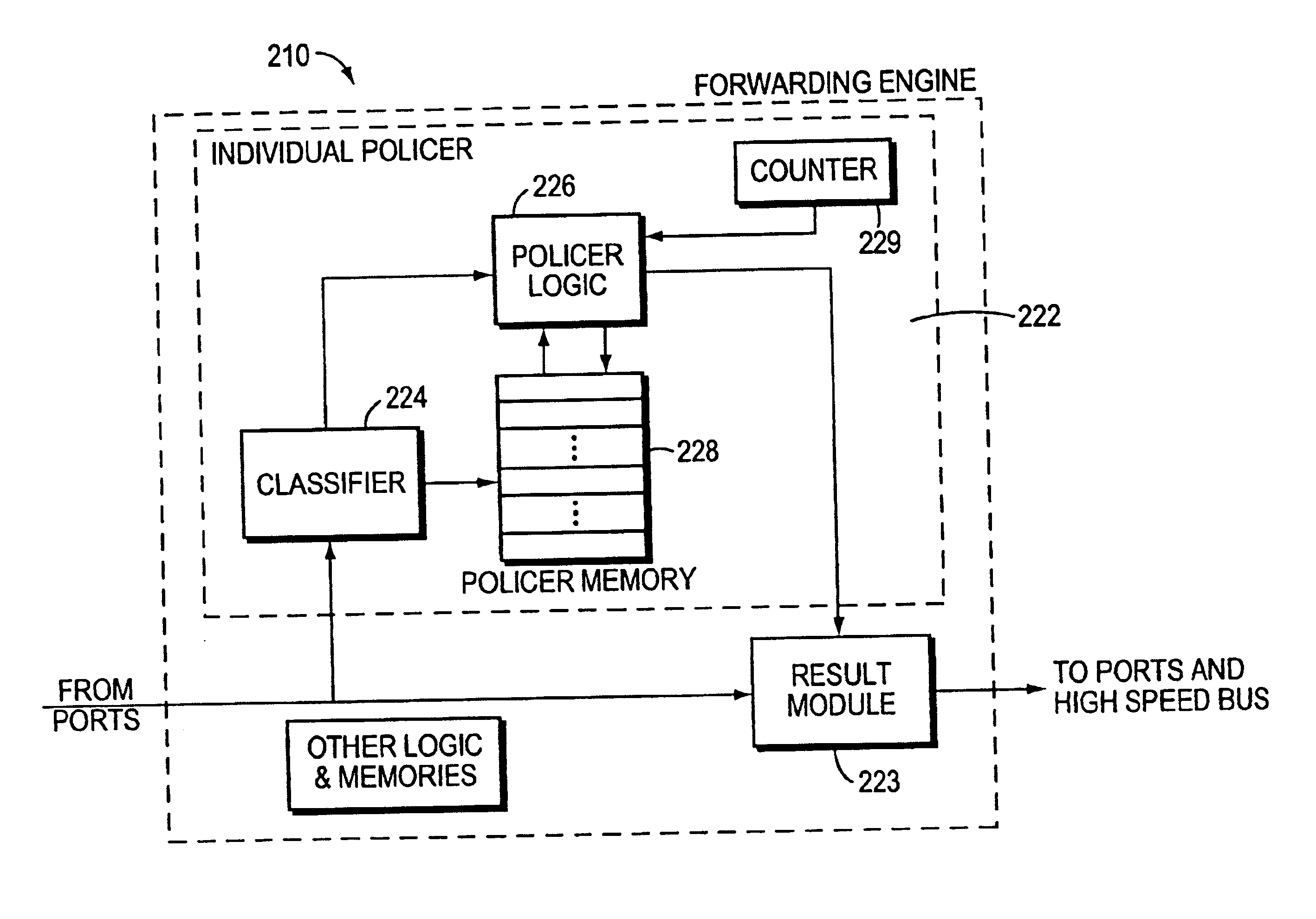
A method for policing traffic on a computer communications network having a multitude of nodes interconnected by various communications media. An individual policer is established at each node for monitoring and / or policing the traffic incoming to that node. Traffic policy parameters are established for traffic-classes and the policy is implemented at each individual policer. Thresholds may be established and when the thresholds are met or exceeded the individual policer will export the traffic conditions at the respective node. The other individual policers or a master policer will receive the exported information. -The individual policers police the traffic incoming to its associated node depending on the traffic condition information received from all the nodes. Several classes may be handled by each individual policer. Leaky bucket algorithms may be used in some instances.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Backpressure mechanism for switching fabric
InactiveUS7426185B1Reduce transmissionSimple processError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDistributed computingPacket switching
Owner:INTEL CORP
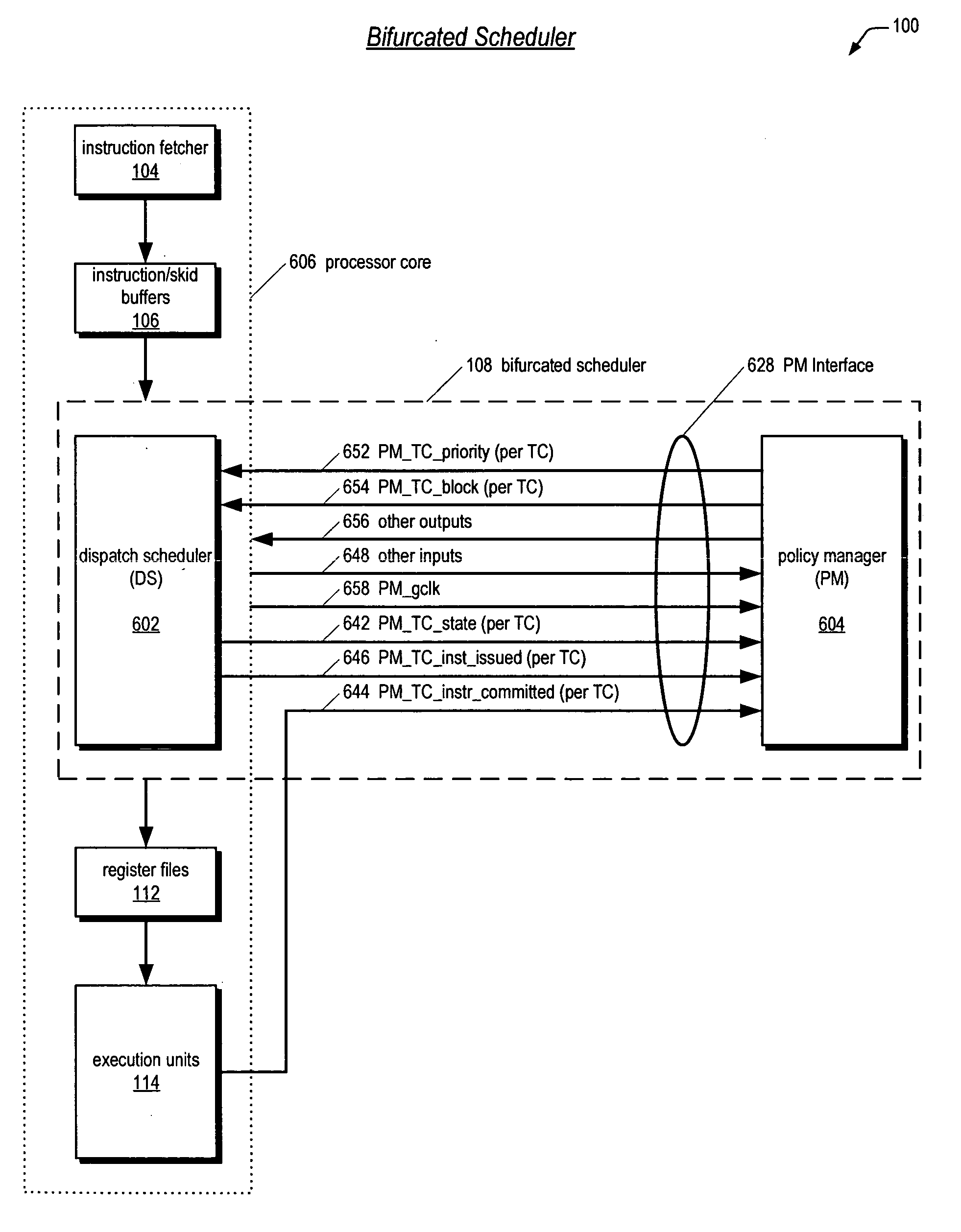
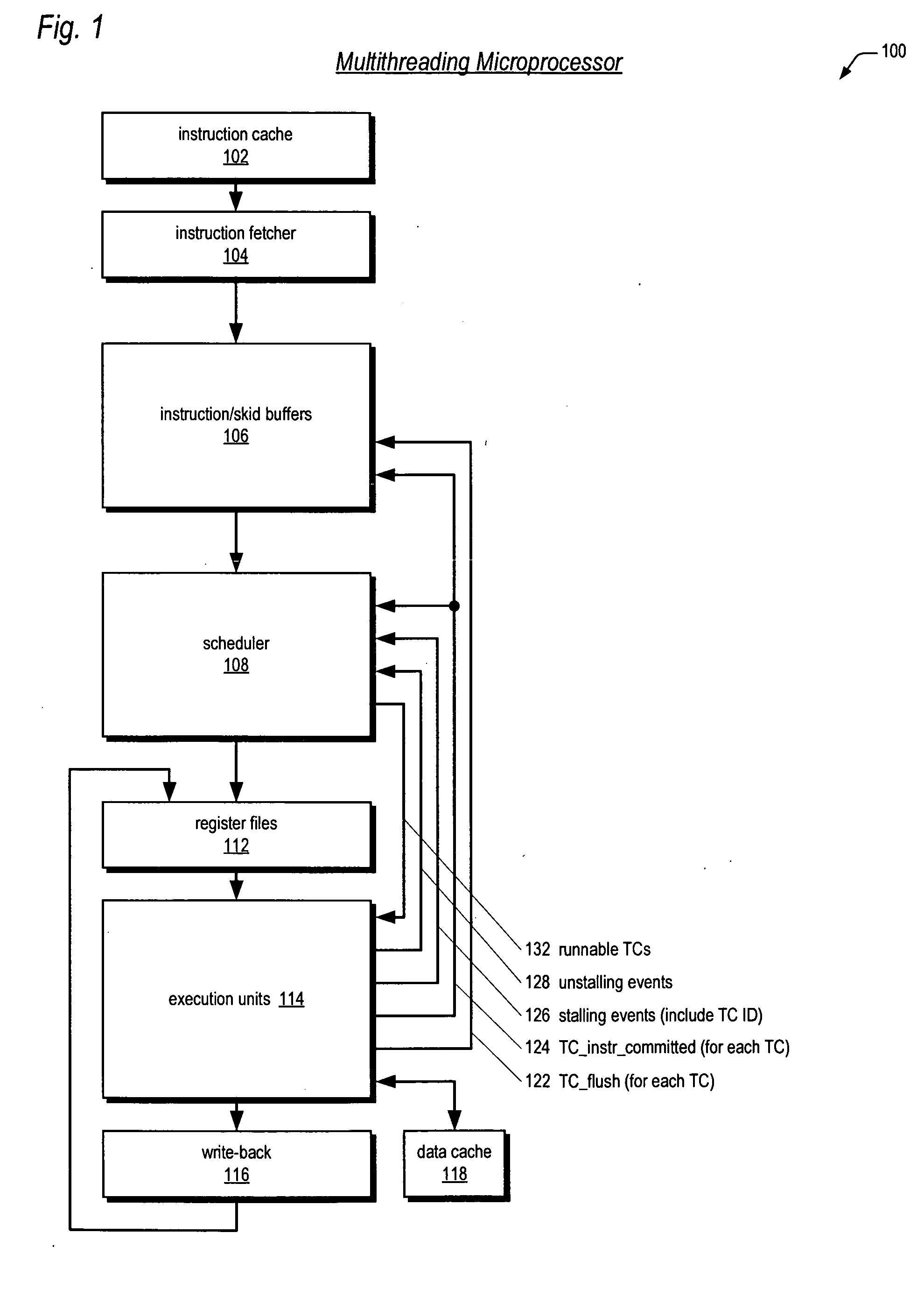
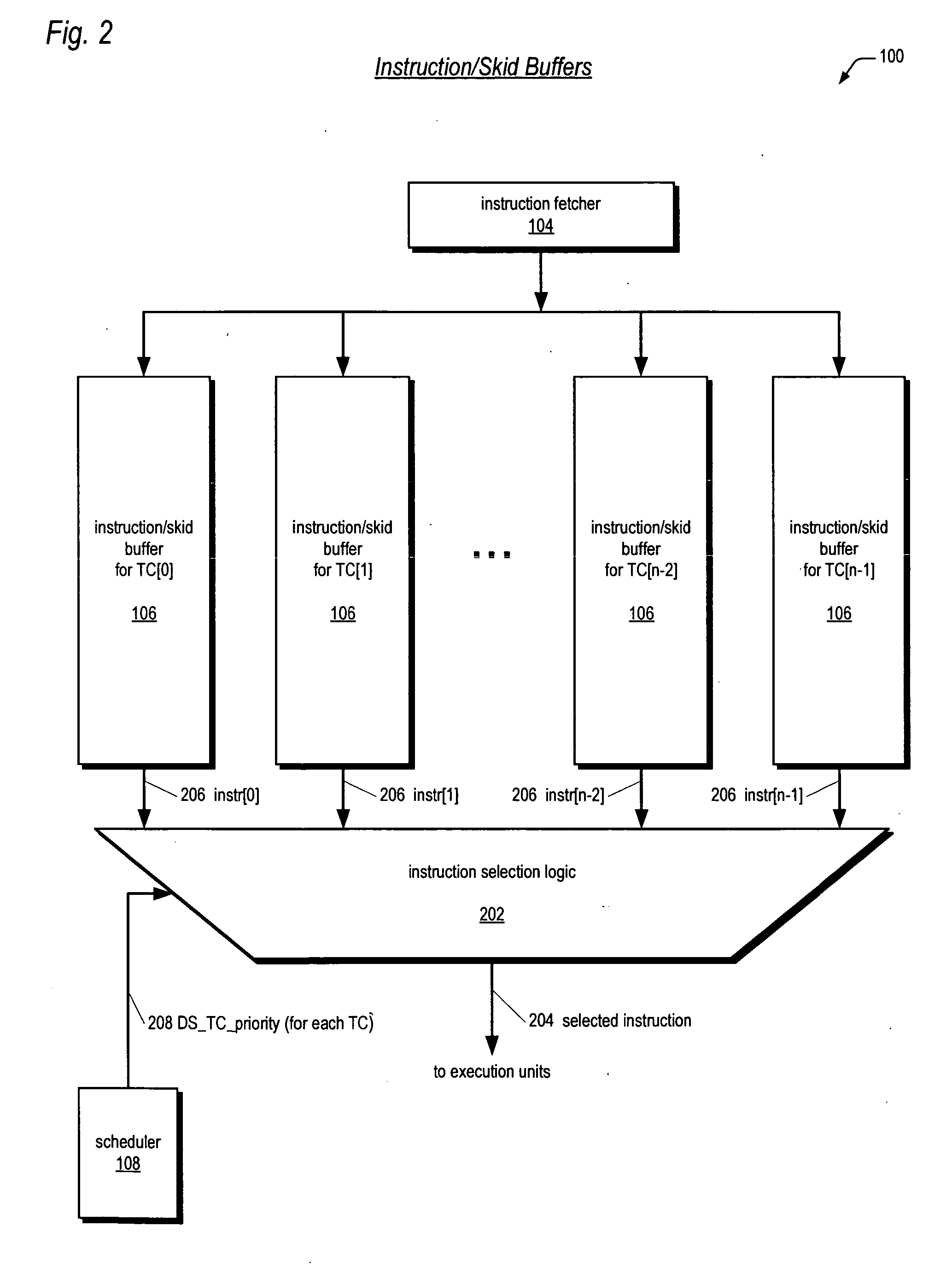
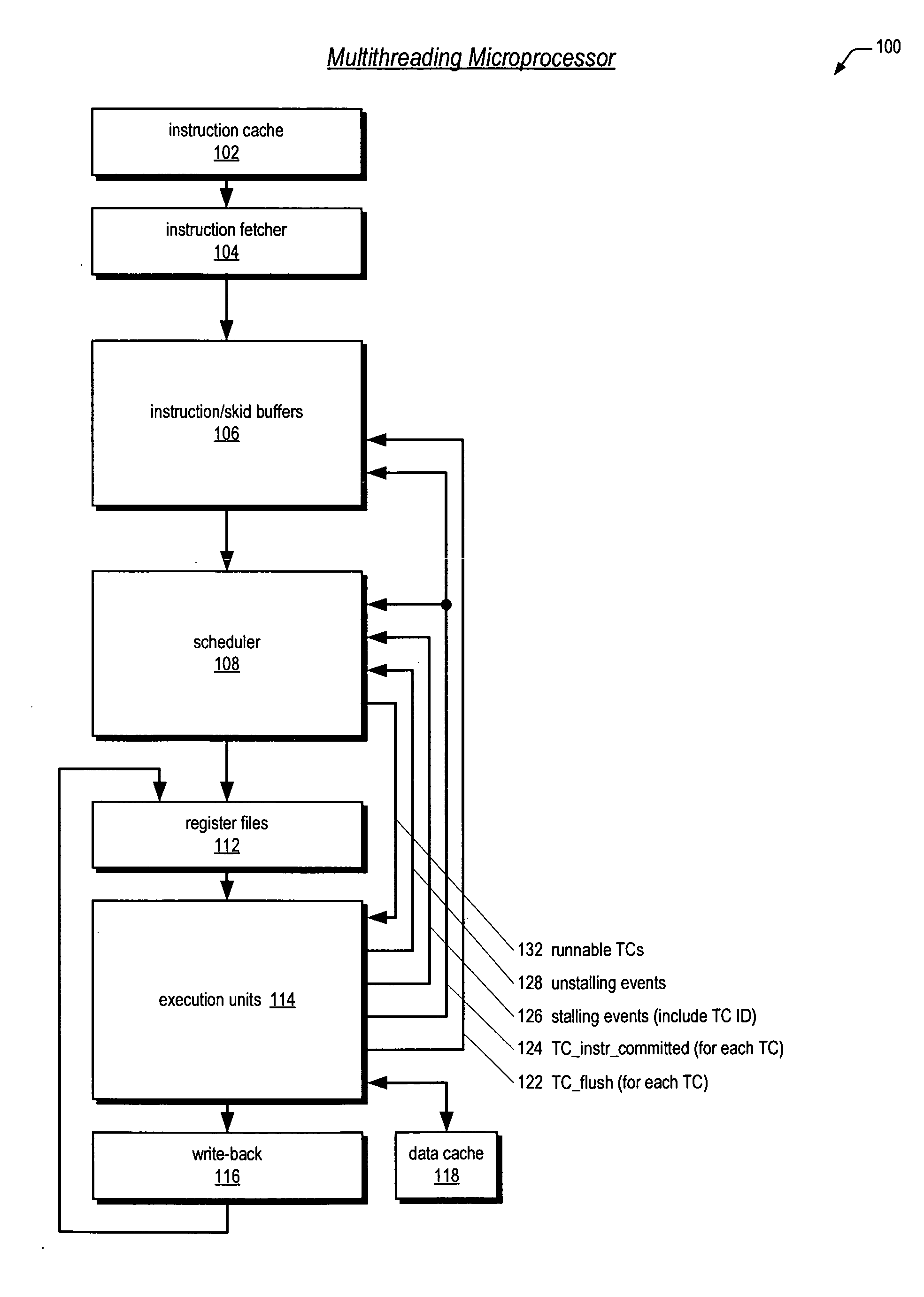
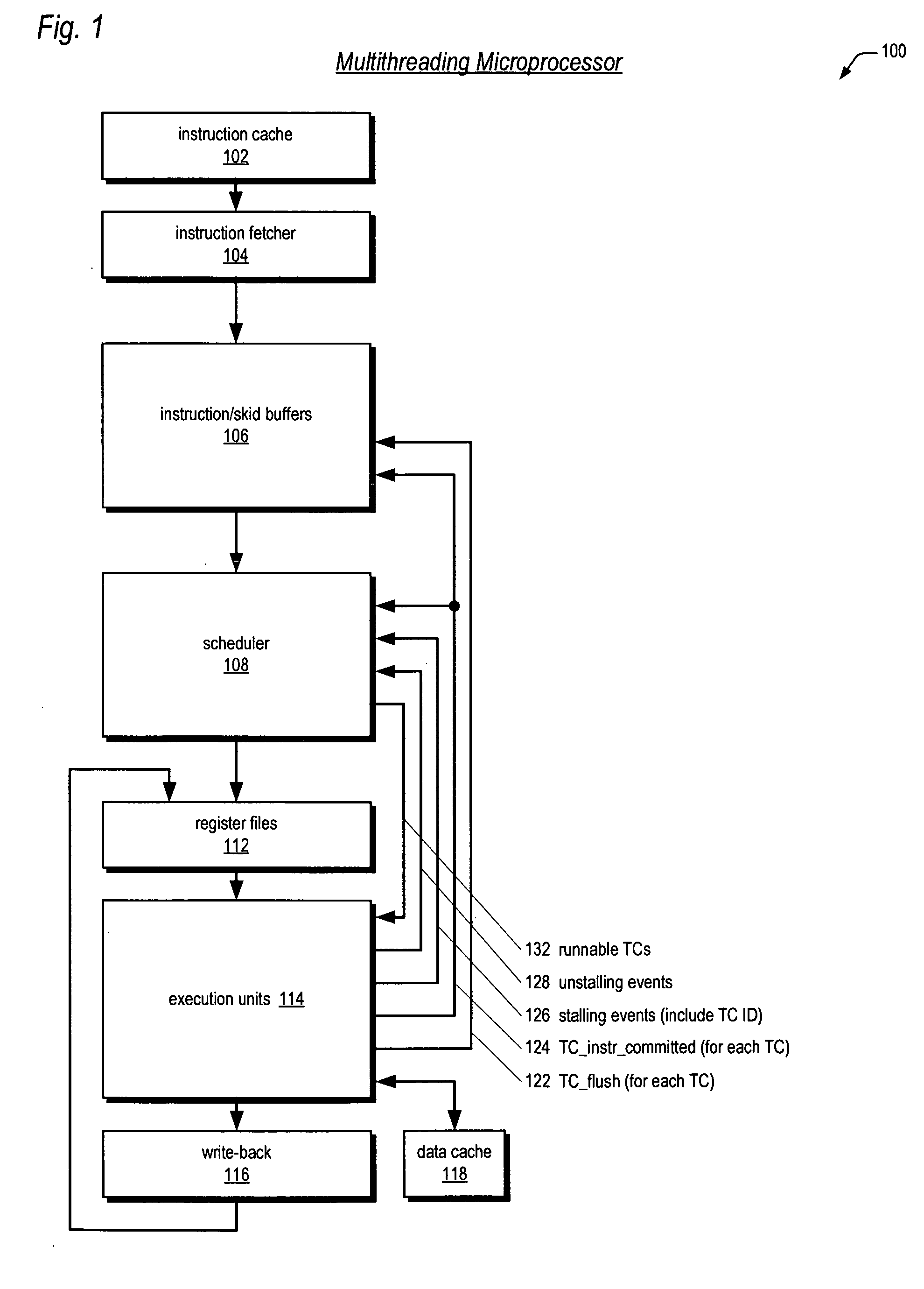
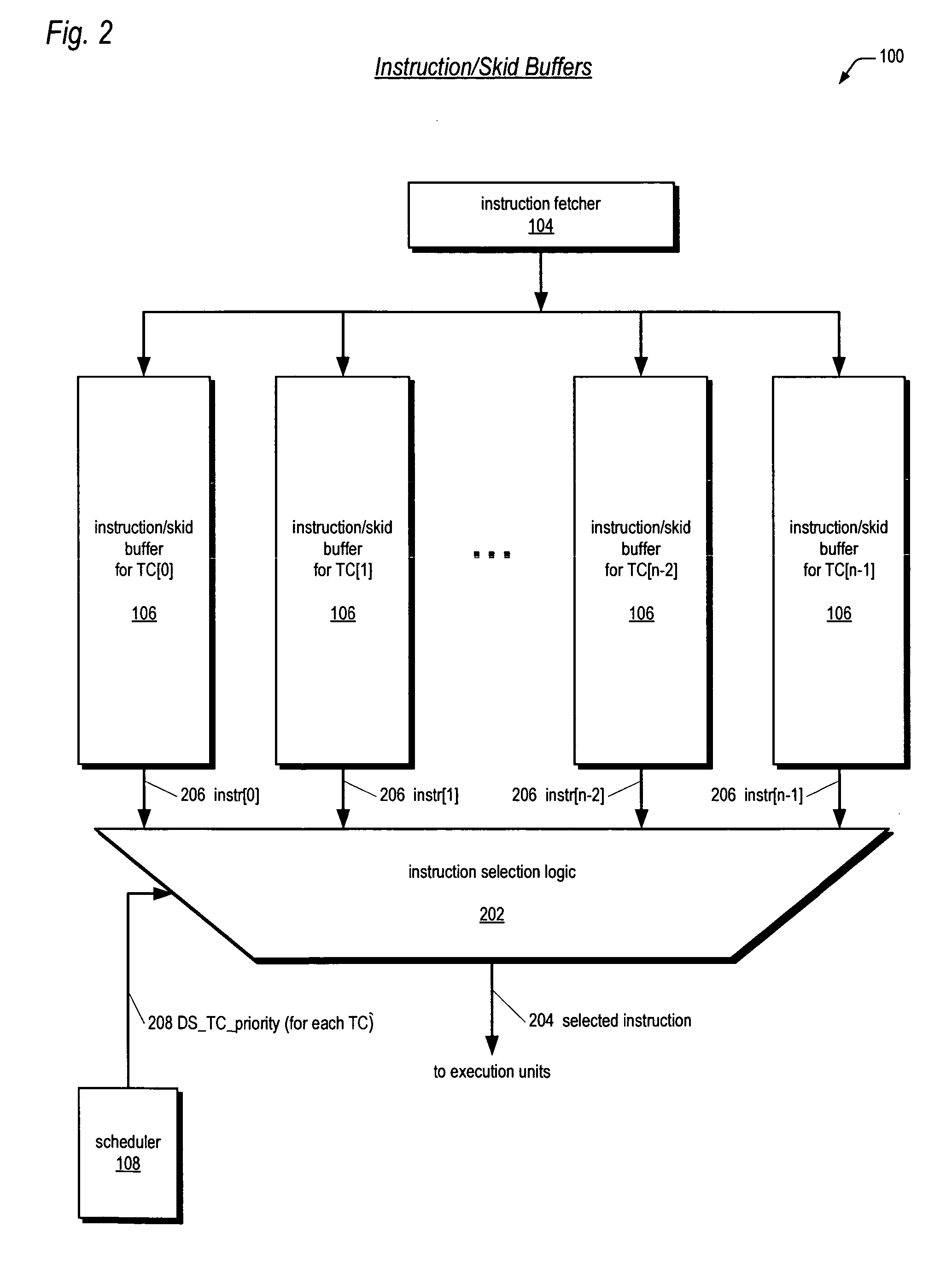
Leaky-bucket thread scheduler in a multithreading microprocessor
ActiveUS20060179439A1Energy efficient ICTDigital computer detailsThread schedulingParallel computing
A leaky-bucket style thread scheduler for scheduling concurrent execution of multiple threads in a microprocessor is provided. The execution pipeline notifies the scheduler when it has completed instructions. The scheduler maintains a virtual water level for each thread and decreases it each time the execution pipeline executes an instruction of the thread. The scheduler includes an instruction execution rate for each thread. The scheduler increases the virtual water level based on the requested rate per a predetermined number of clock cycles. The scheduler includes virtual water pressure parameters that define a set of virtual water pressure ranges over the height of the virtual water bucket. When a thread's virtual water level moves from one virtual water pressure range to the next higher range, the scheduler increases the instruction issue priority for the thread; conversely, when the level moves down, the scheduler decreases the instruction issue priority for the thread.
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
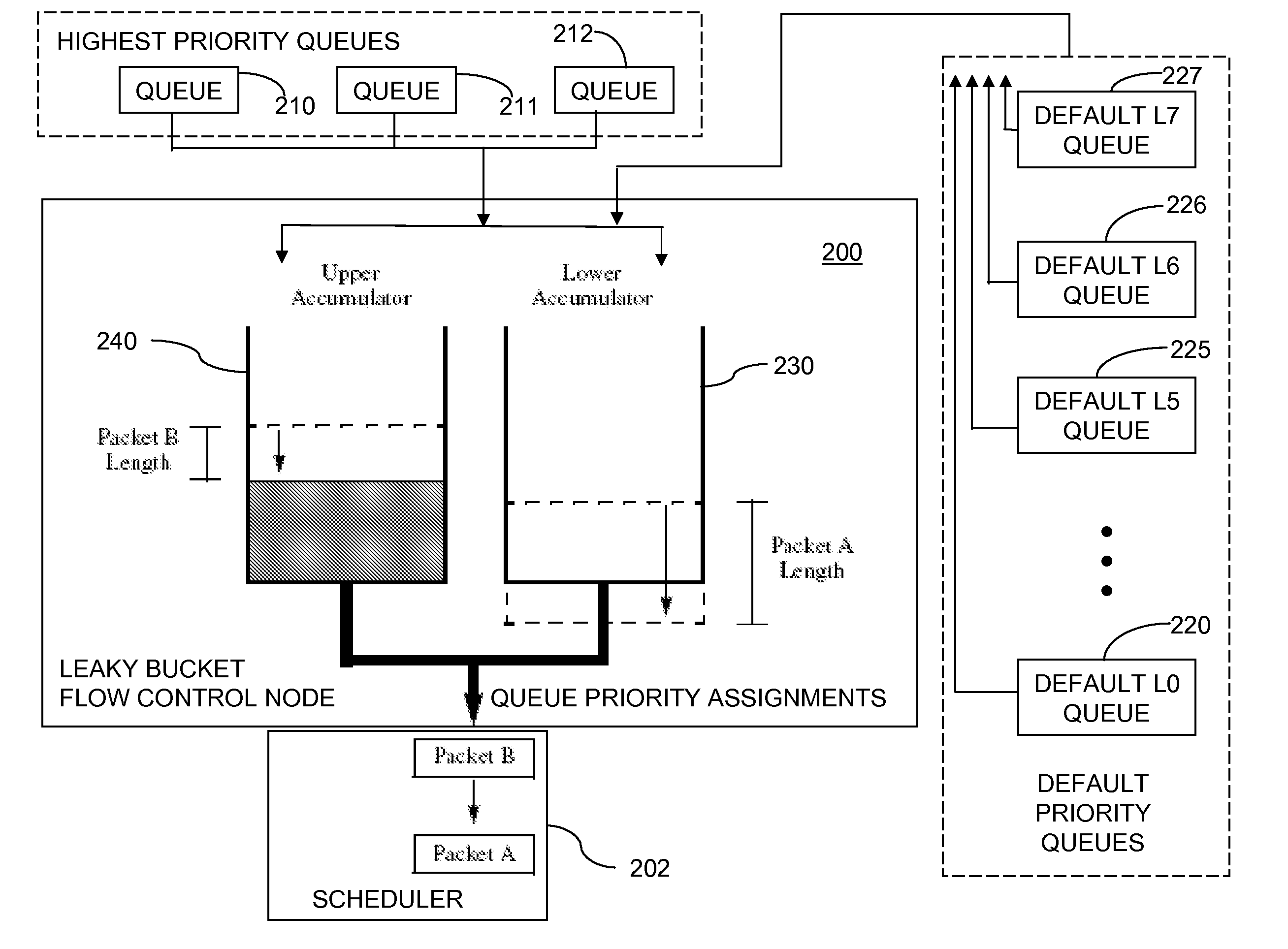
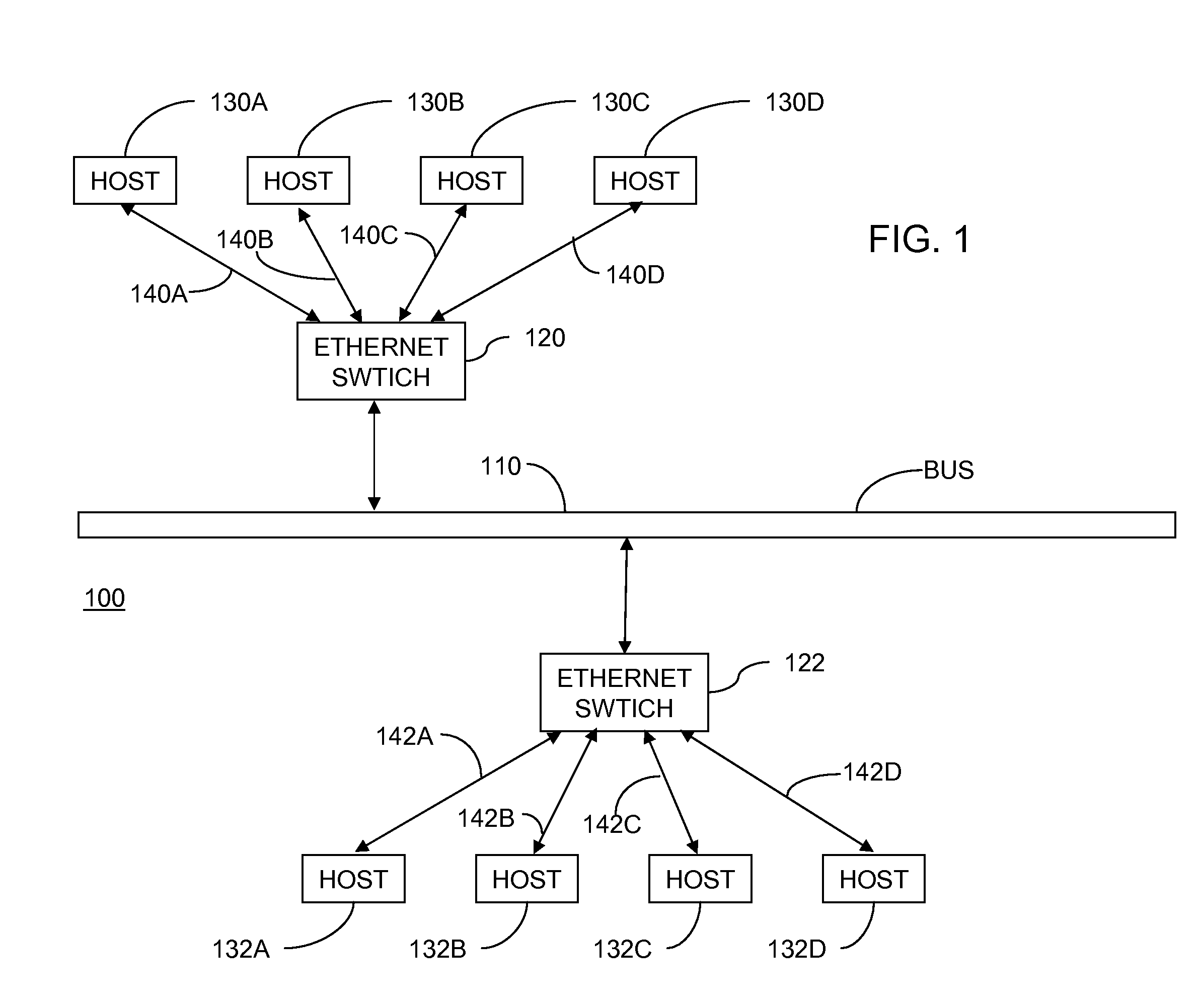
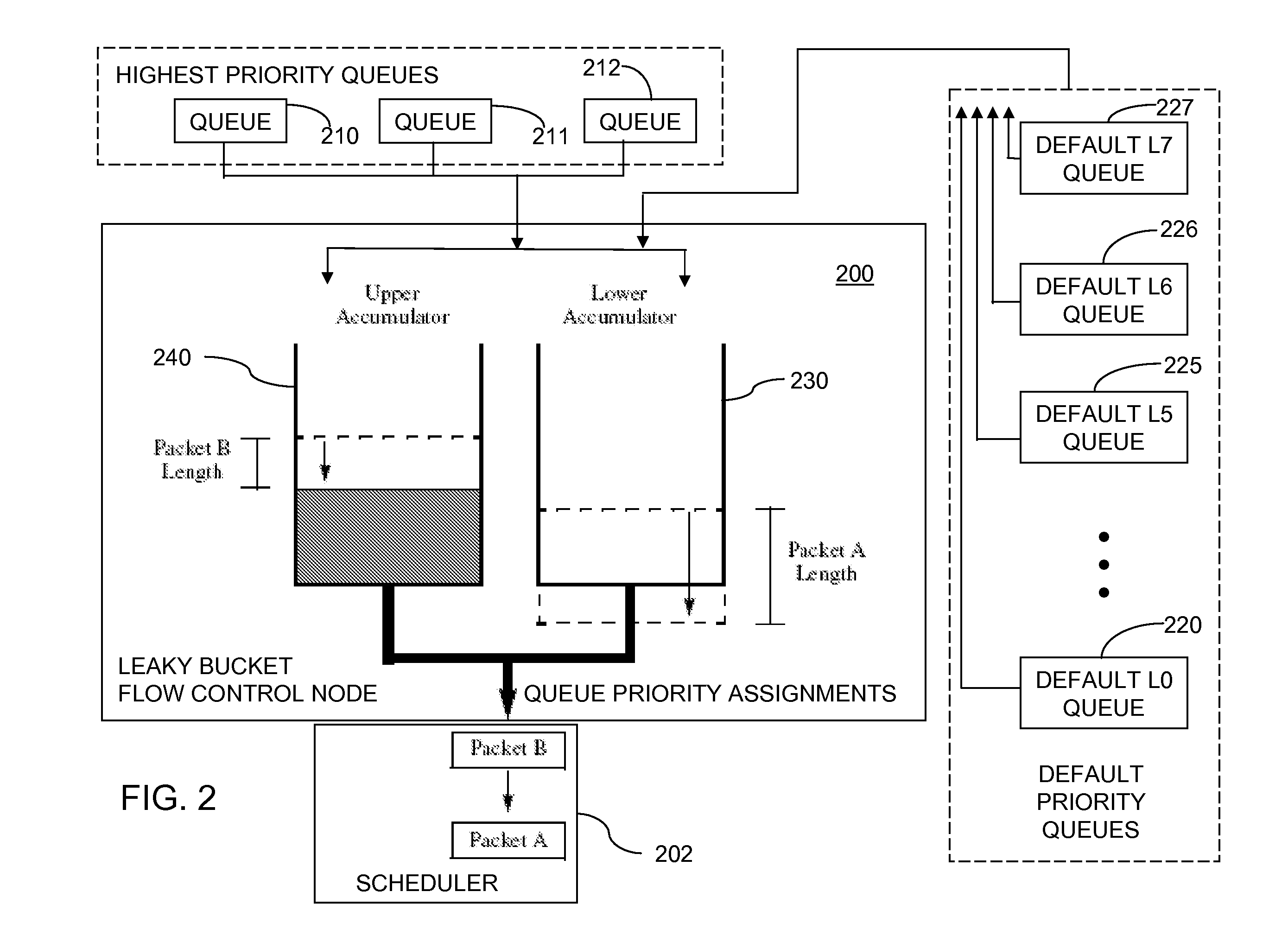
Dual Leaky Bucket Flow Control Method and System
A method for scheduling a network resource comprises adding tokens to first and second accumulators at first and second fill rates, respectively. A number of tokens corresponding to a size of a packet is subtracted from the first accumulator and a highest priority is assigned to a queue with which the packet is associated, if a number of tokens in the first accumulator is greater than zero. The number of tokens is subtracted from the second accumulator, and a default priority assigned to the queue, if the number of tokens in the first accumulator is less than zero and a number of tokens in the second accumulator is greater than zero. The network resource is assigned for transmission of the packet from the queue using a schedule that is based on the priority assigned to the queue. The packet is transmitted using the assigned network resource.
Owner:INTEL CORP
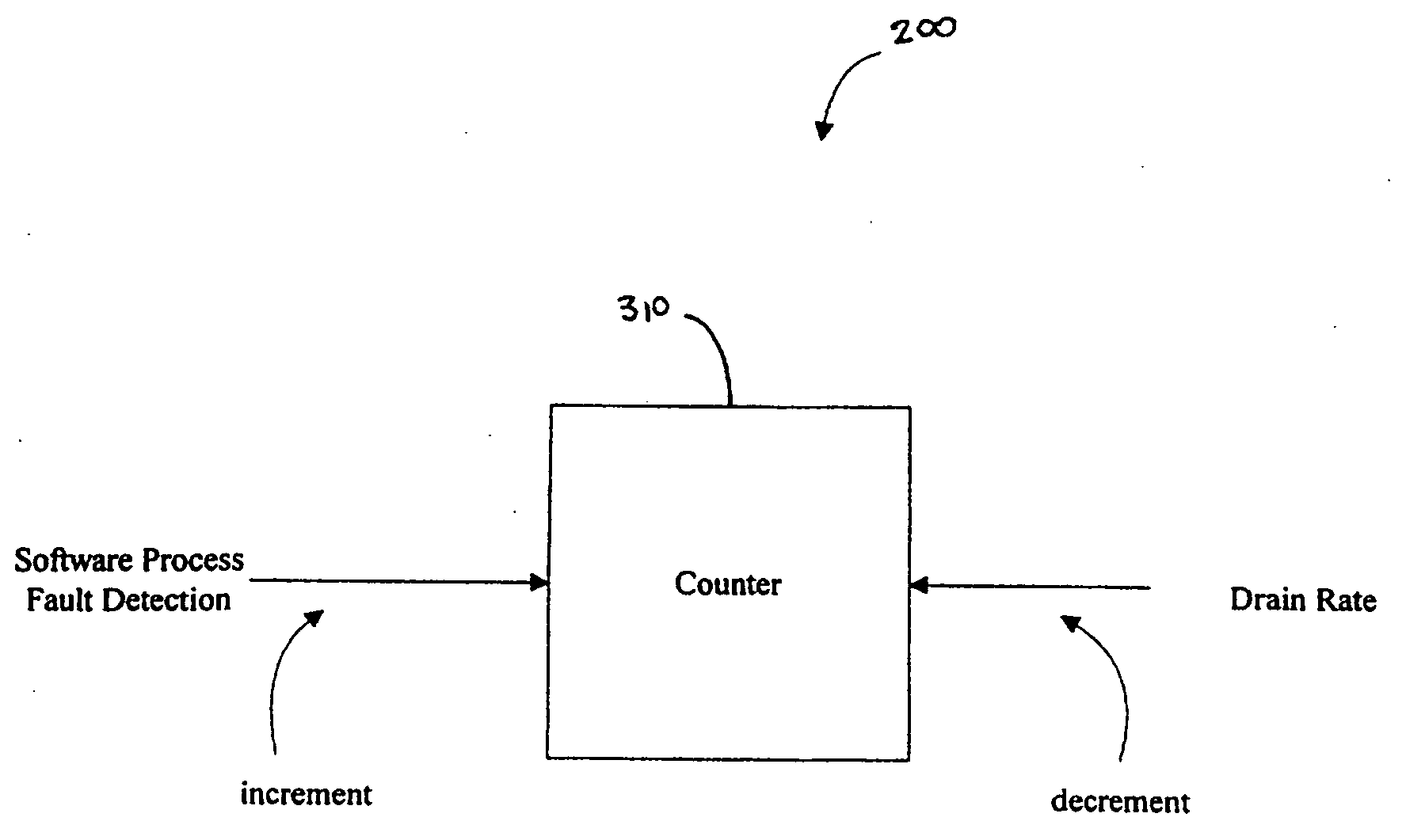
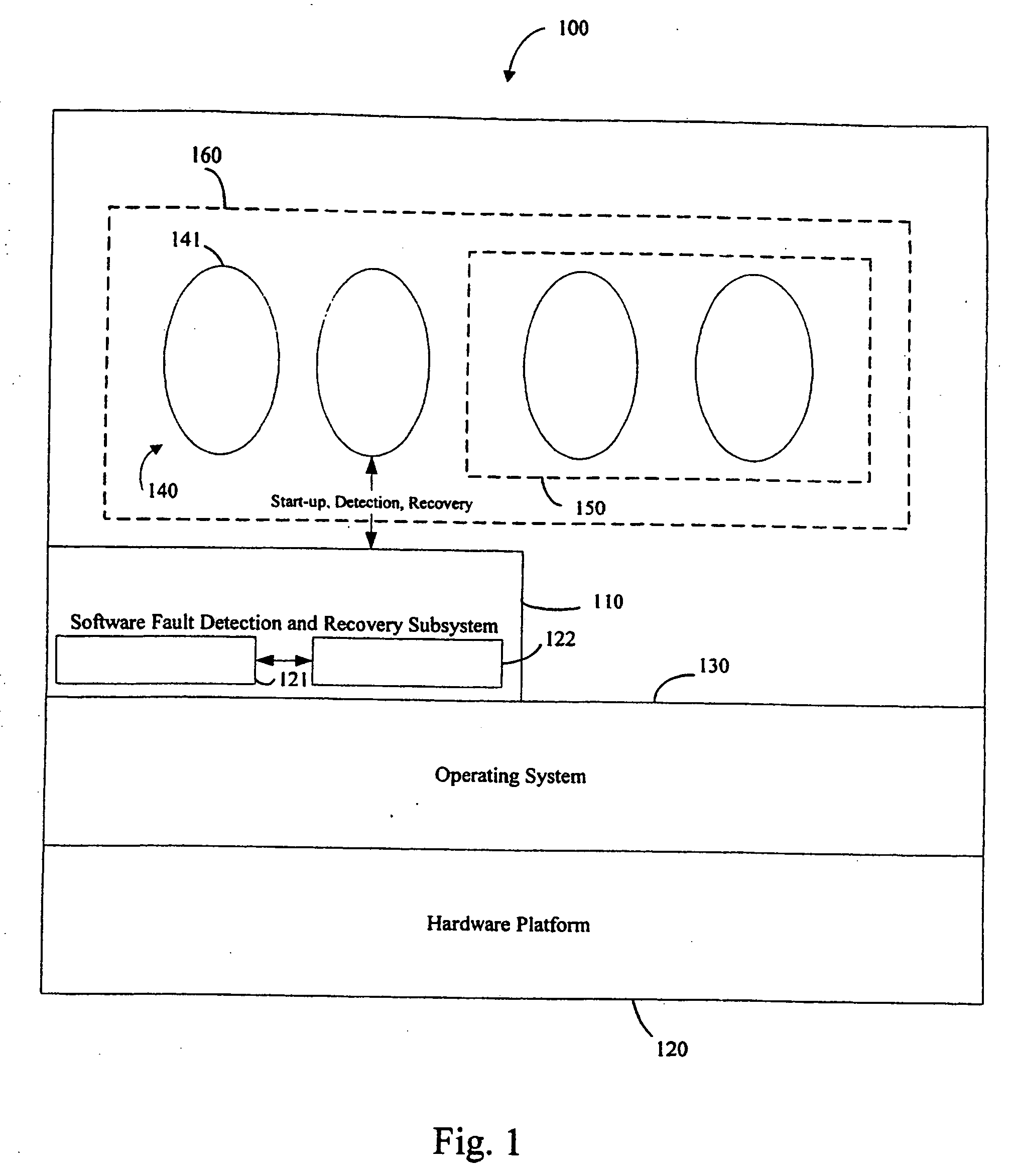
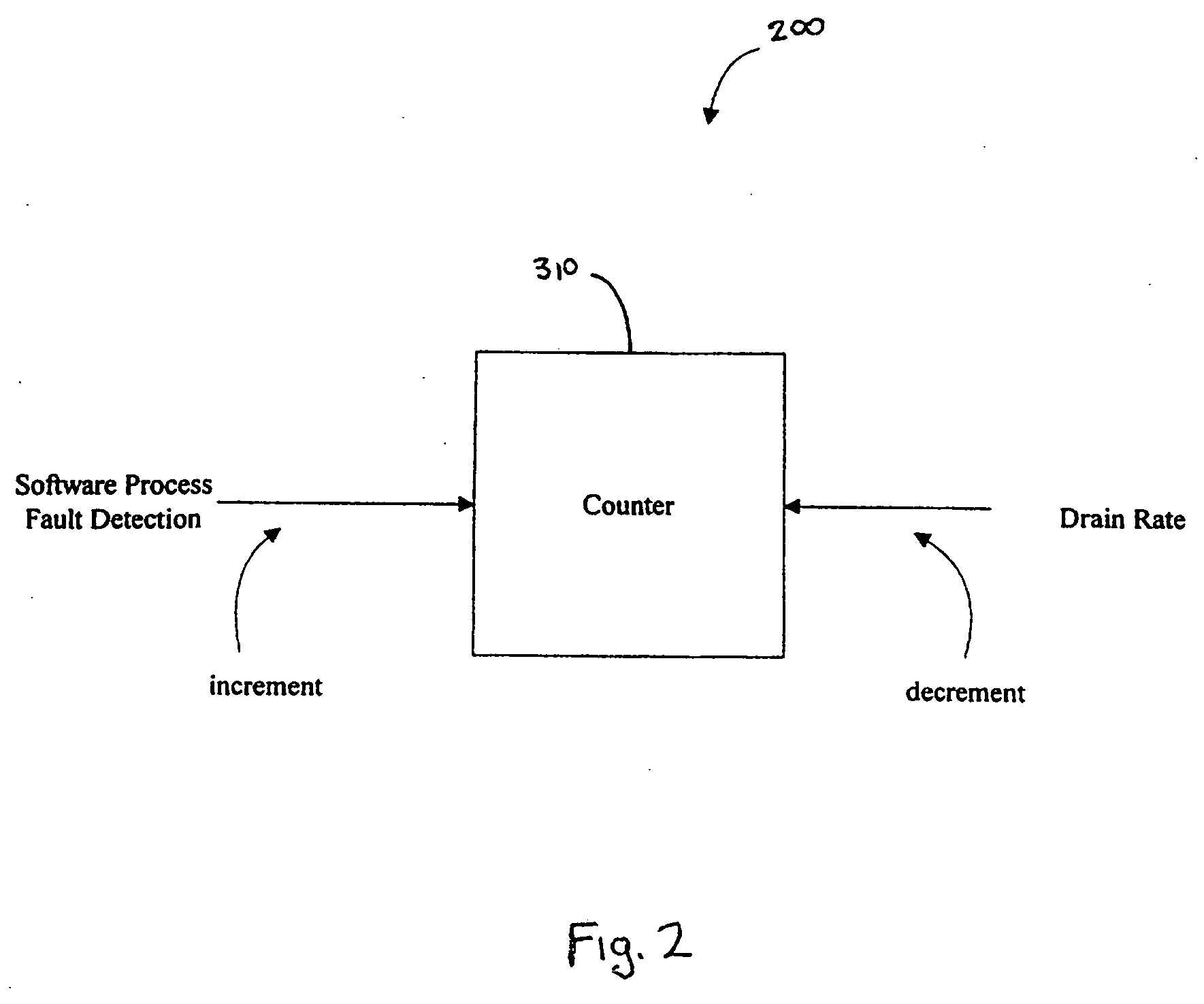
System and method for fault detection and recovery
An apparatus and method for automatically detecting and recovering from a fault in a microprocessor-based system. The apparatus and method utilizes a leaky bucket routine and an event handler procedure. The method may further use Object Oriented techniques that abstracts differences between hardware and software faults to allow for the development of a common framework.
Owner:INTEL CORP
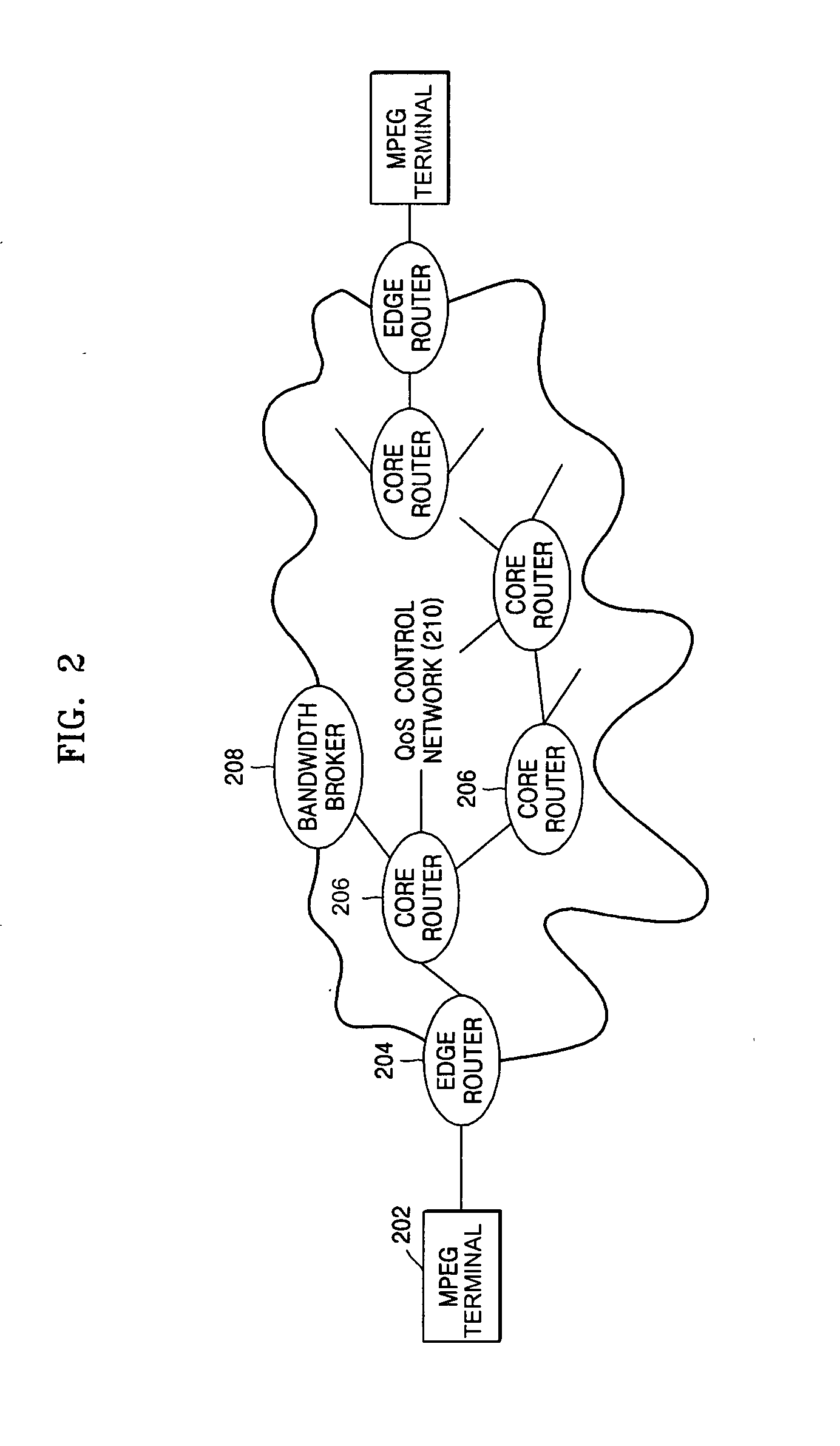
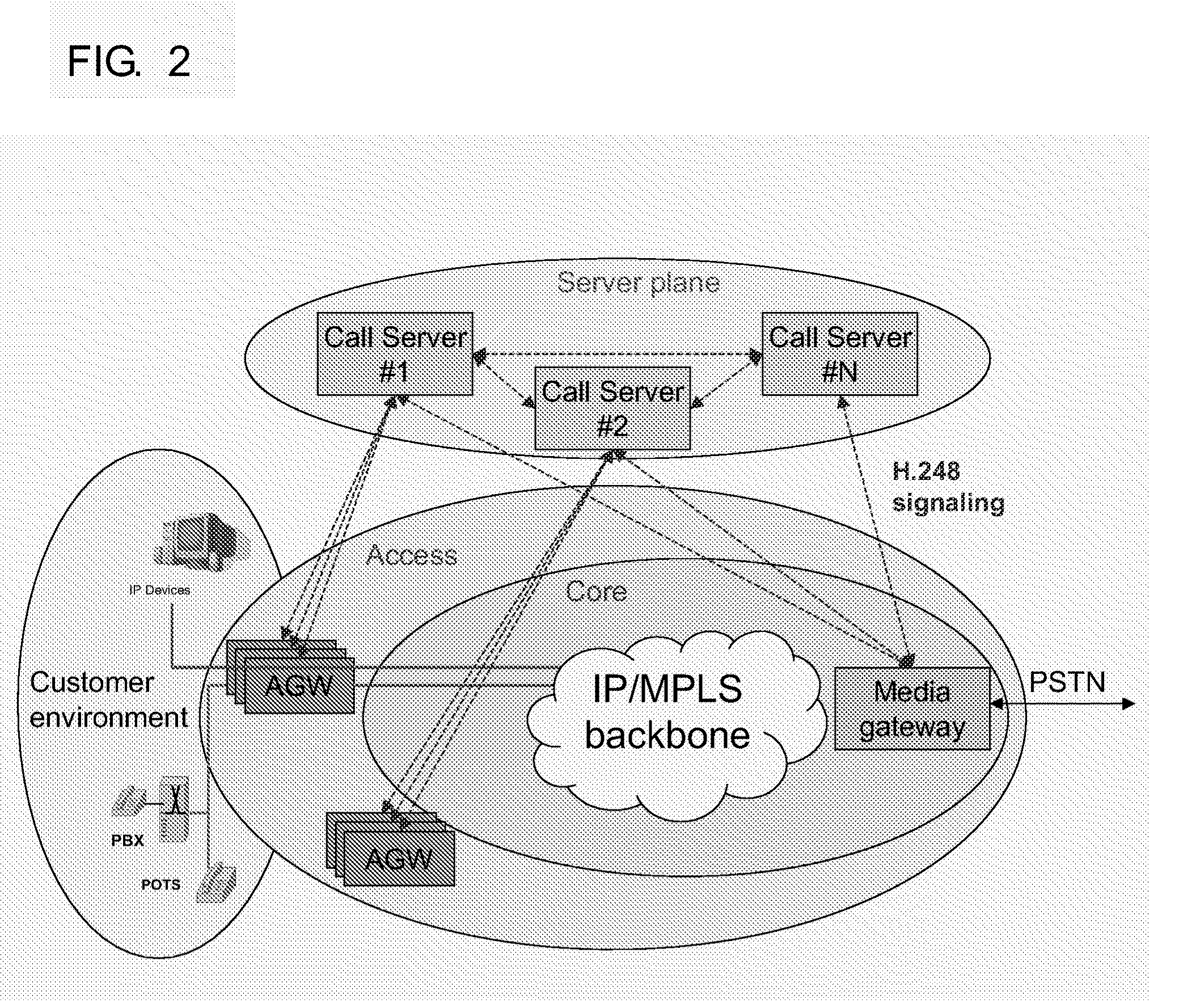
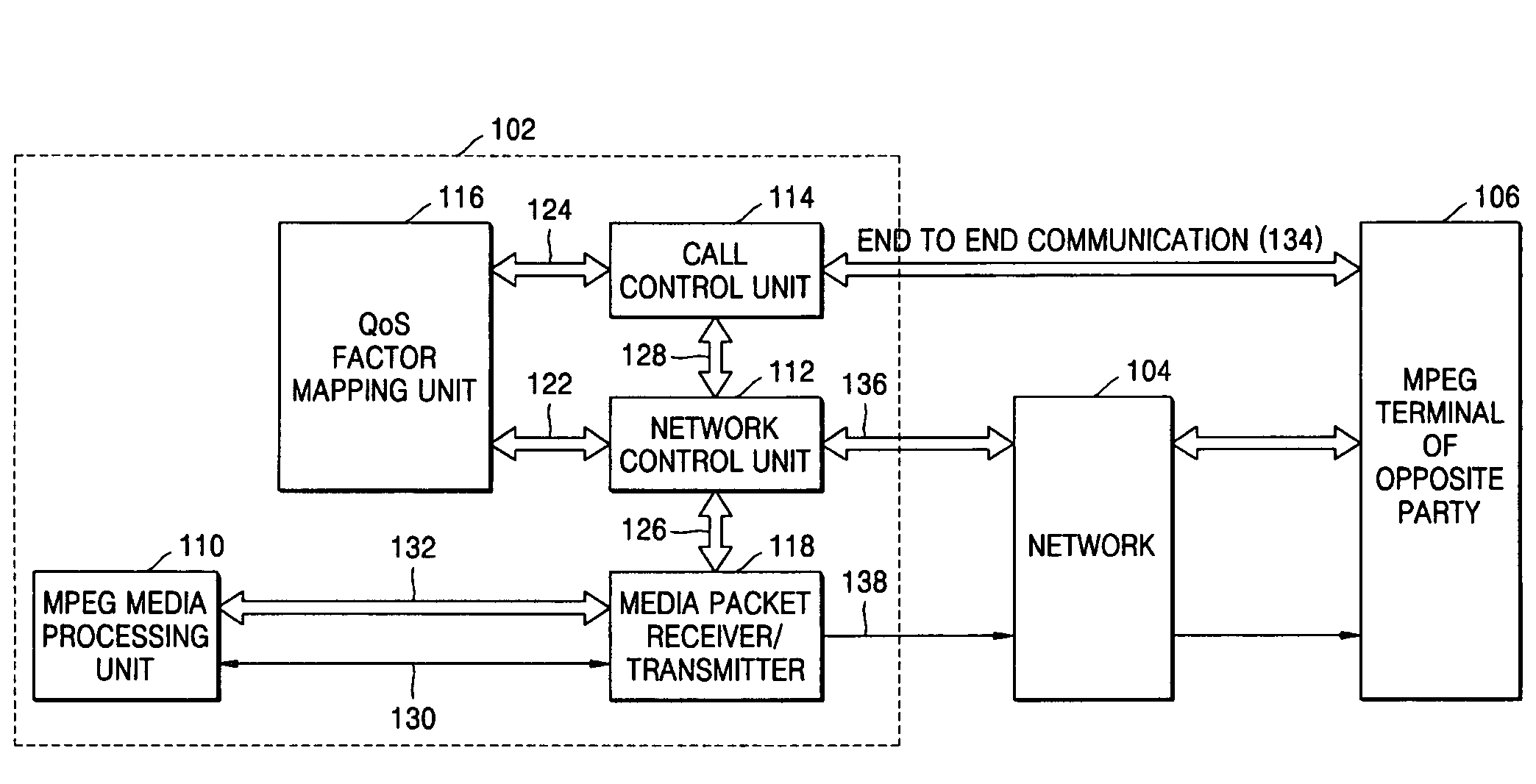
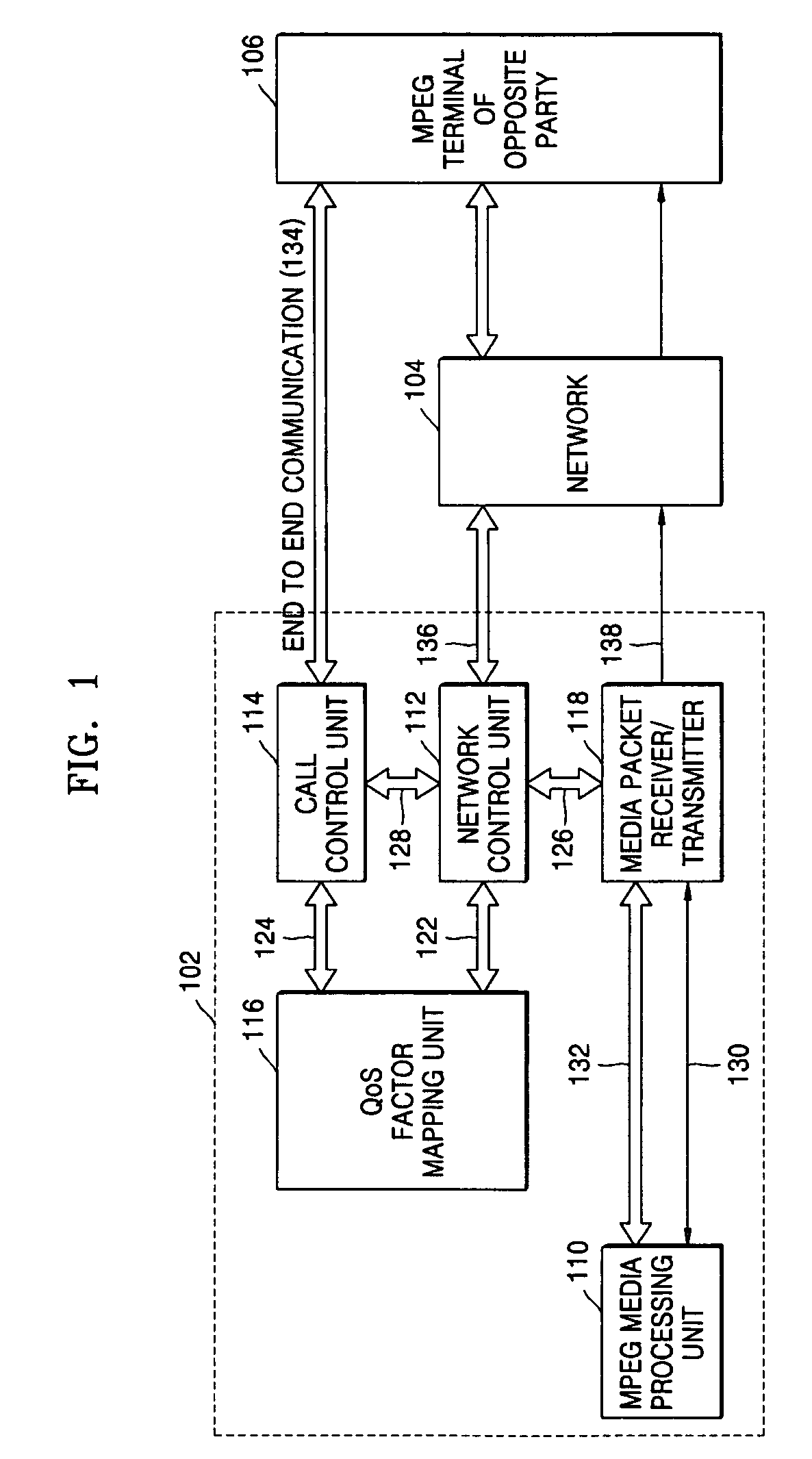
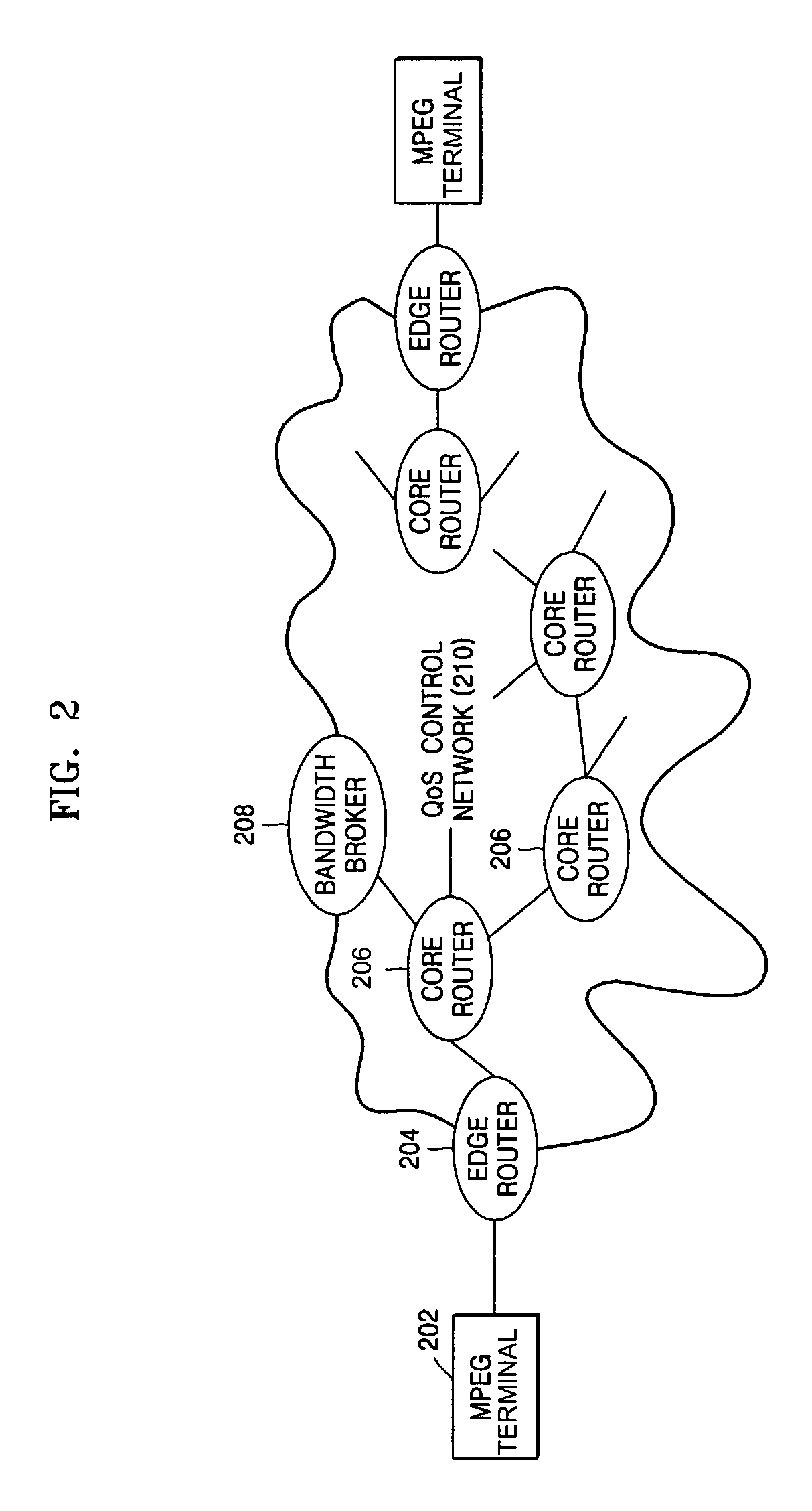
Method and device for delivering multimedia data using IETF QoS protocols
InactiveUS20050047345A1Guaranteed normal transmissionPulse modulation television signal transmissionError preventionComputer scienceReal-time computing
Owner:UNIV IND COOP GRP OF KYUNG HEE UNIV +1
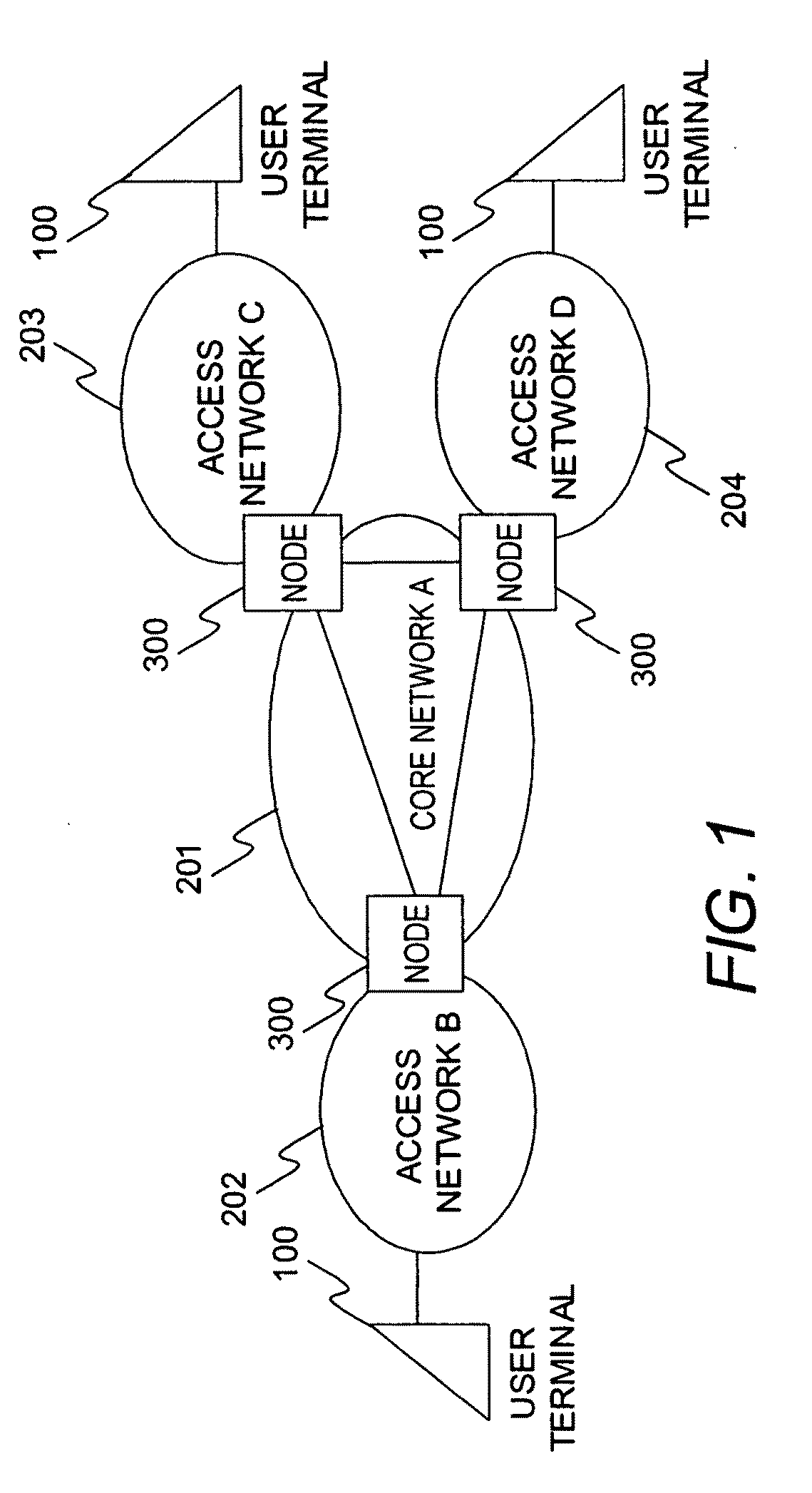
Distributed flow control system and method for GPRS networks based on leaky buckets
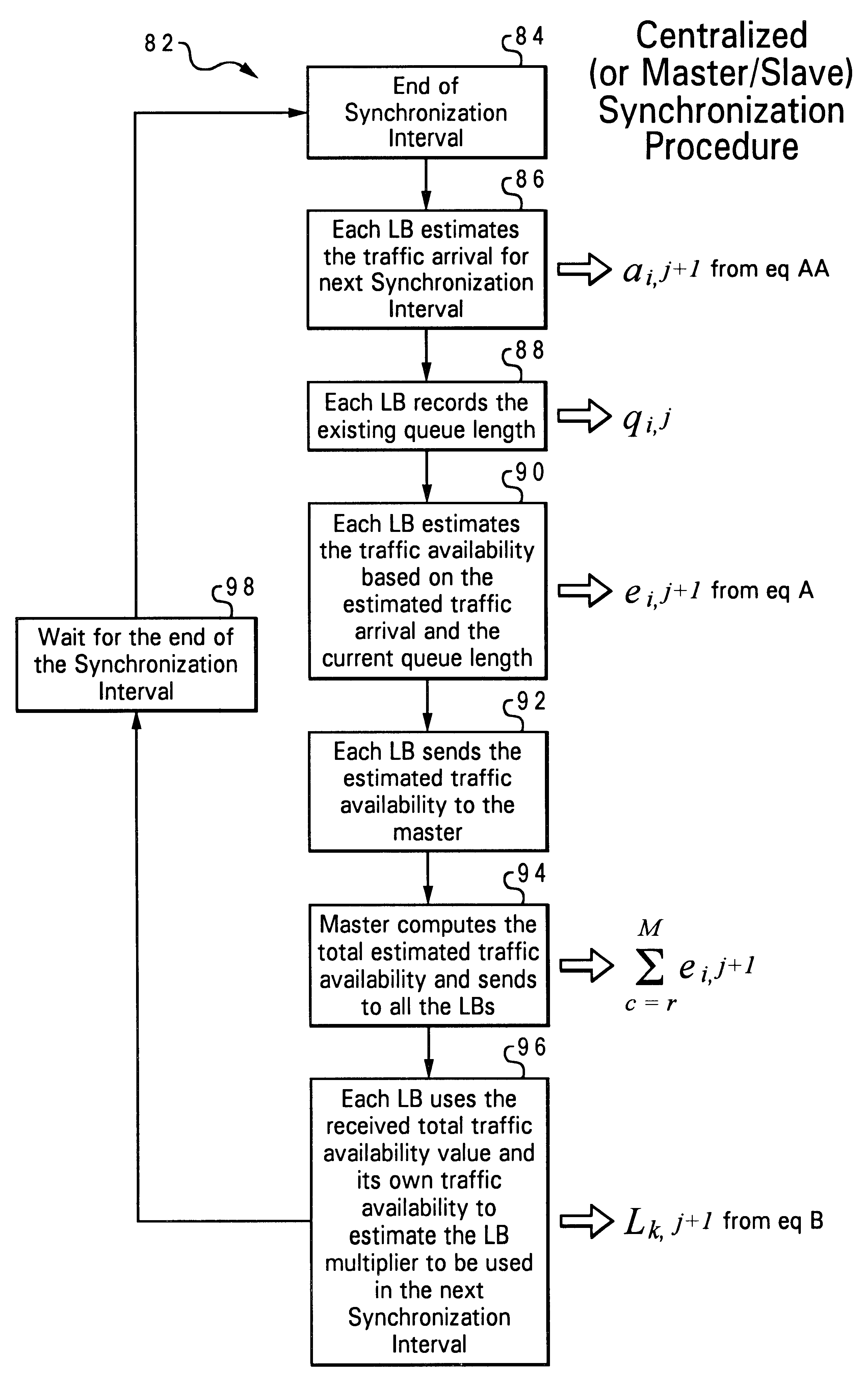
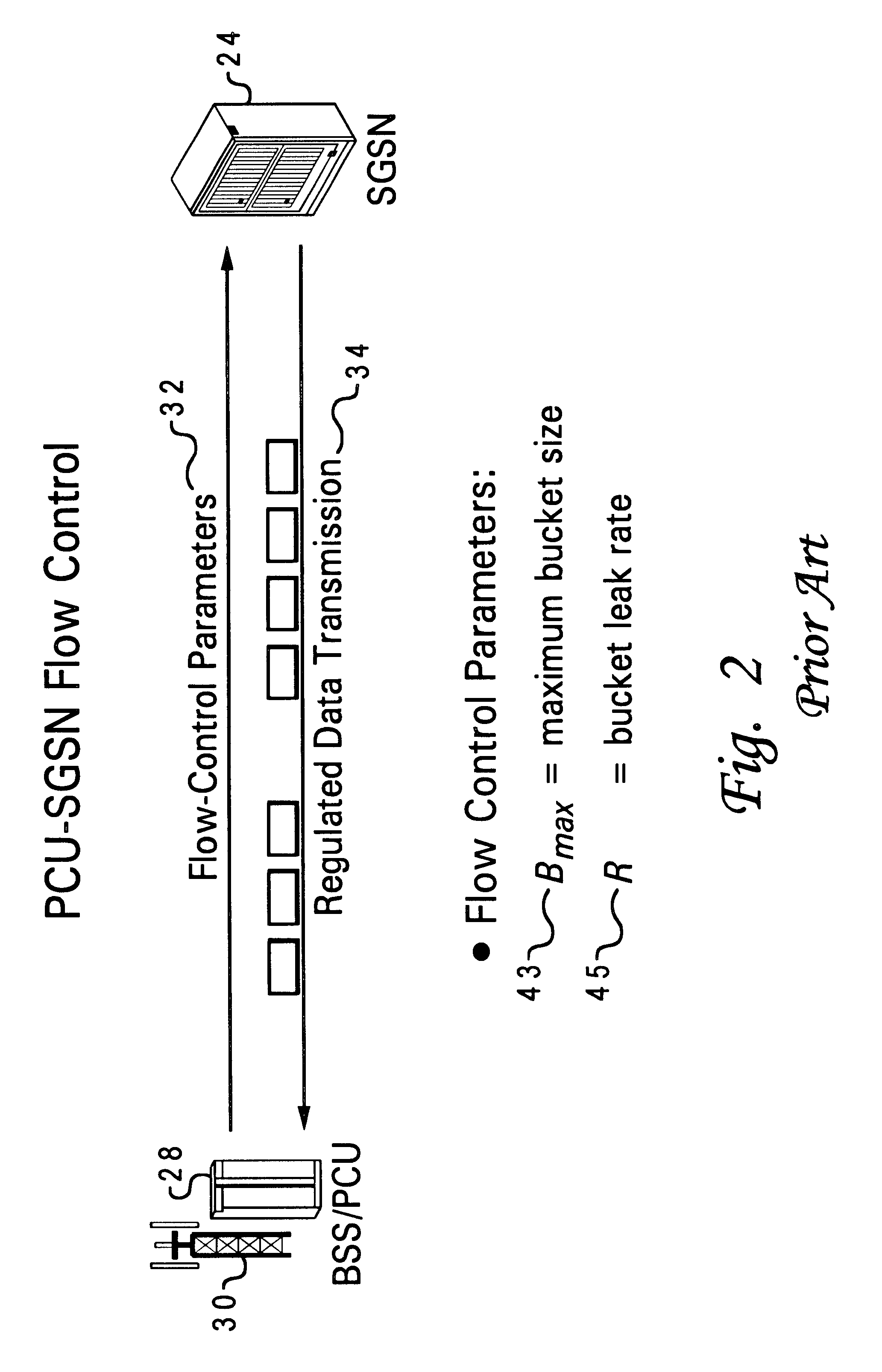
A distributed flow control system and method for GPRS networks to control and regulate data flow between multiple sources and a single destination within a GPRS network. The present system and method ensures the departing traffic from all of the sources conforms to the peak and average rate requirements that have been set forth by the BSS / PCU. A leaky bucket flow control mechanism is used at each respective one of the multiple sources for controlling flow of data from each respective source to the single destination. A maximum bucket size of a leaky bucket and a bucket leak rate are defined for each leaky bucket flow control mechanism. A multiplier (L) is estimated and determined for each respective source based on recent data arrival behaviors of the multiple sources. When a frame of the data is sent from the respective source to the single destination, a number of bytes equal to the size of the transmitted frame times the multiplier L is added to the leaky bucket.
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
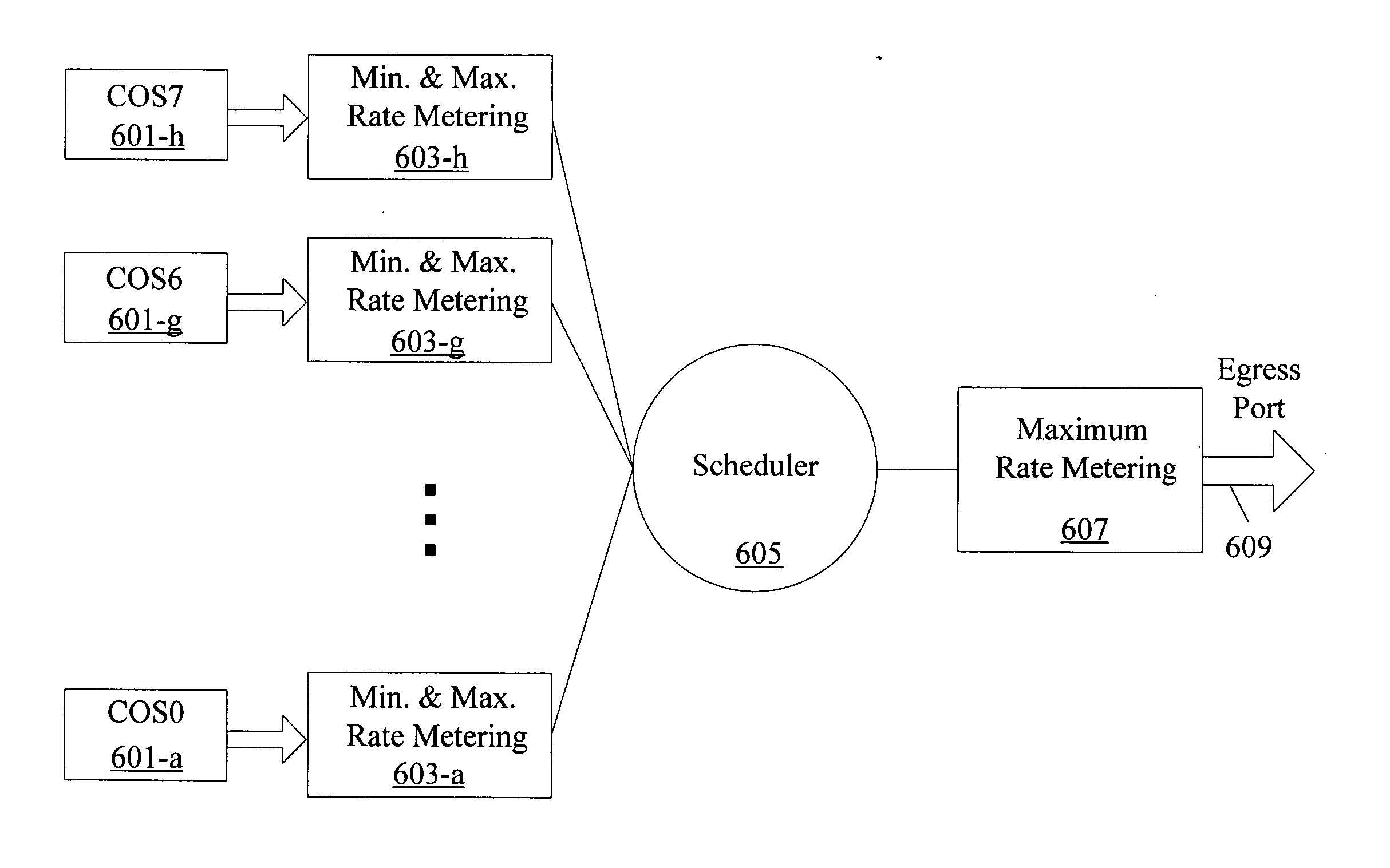
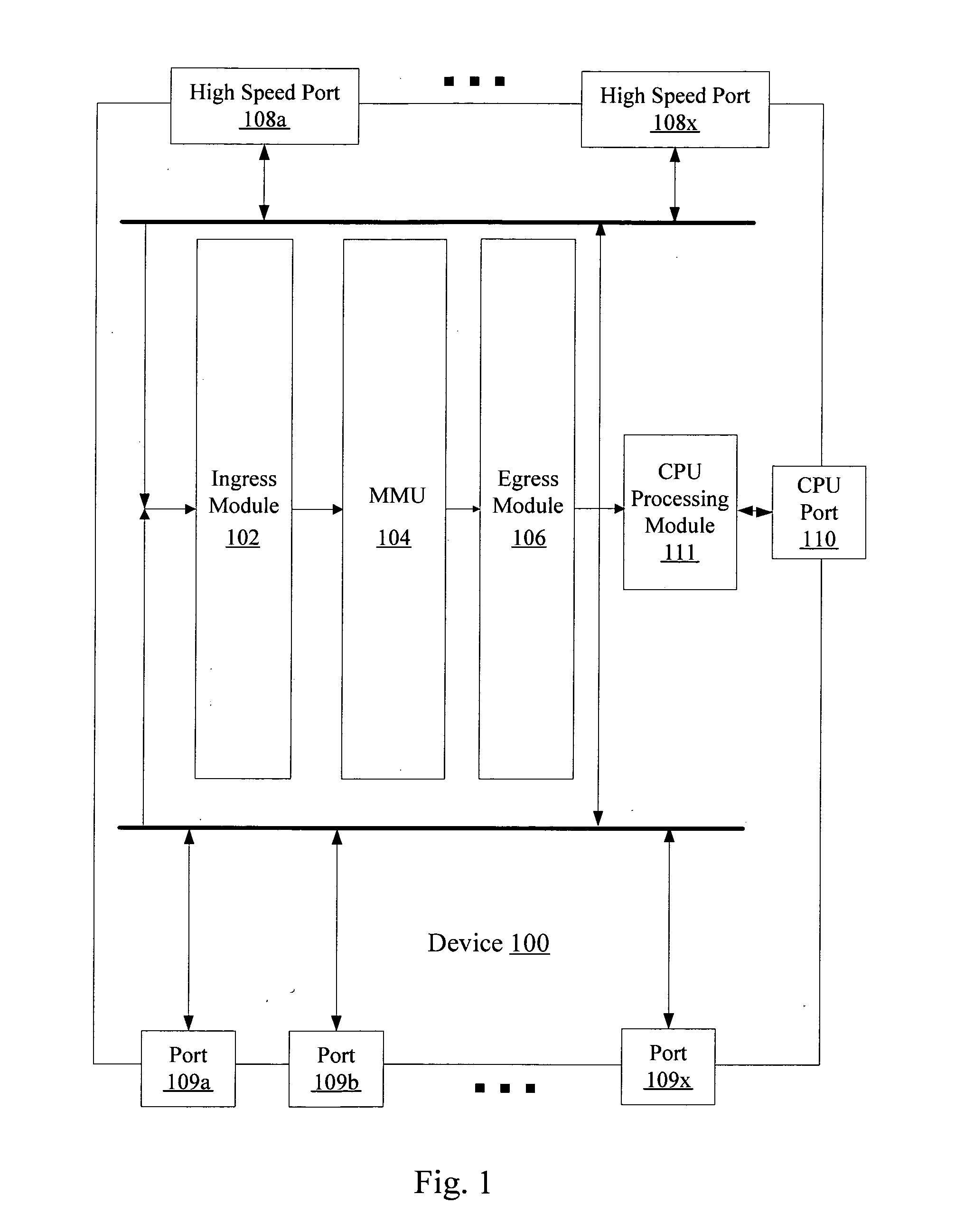
Rate limiting and minimum and maximum shaping in a network device
A network device for scheduling packets in a plurality of queues includes a plurality of leaky bucket modules, each of the plurality of leaky bucket mechanisms being associated with one of a plurality of queues and configured to process information based on a predefined bandwidth, a scheduler configured to schedule services of the plurality of queues and a metering module for tracking whether or not the plurality of queues has exceeded a predefined threshold through the leaky bucket modules. If the plurality of queues has exceeded the predefined threshold, the metering module is configured to compute a new bandwidth allocation for each of the plurality of queues, the new bandwidth allocation replacing the predefined bandwidth and being proportional to the predefined bandwidth for each of the plurality of queues.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
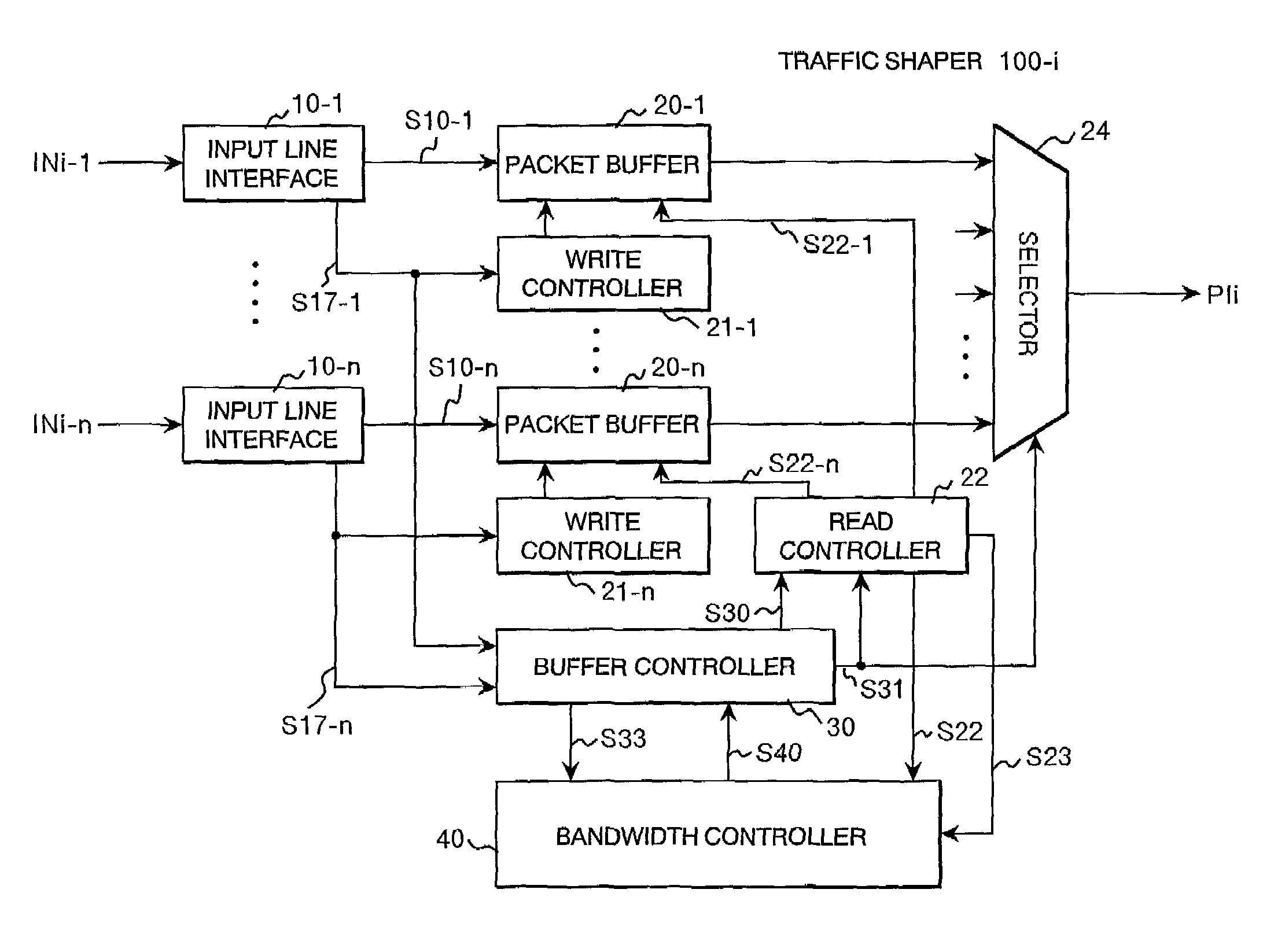
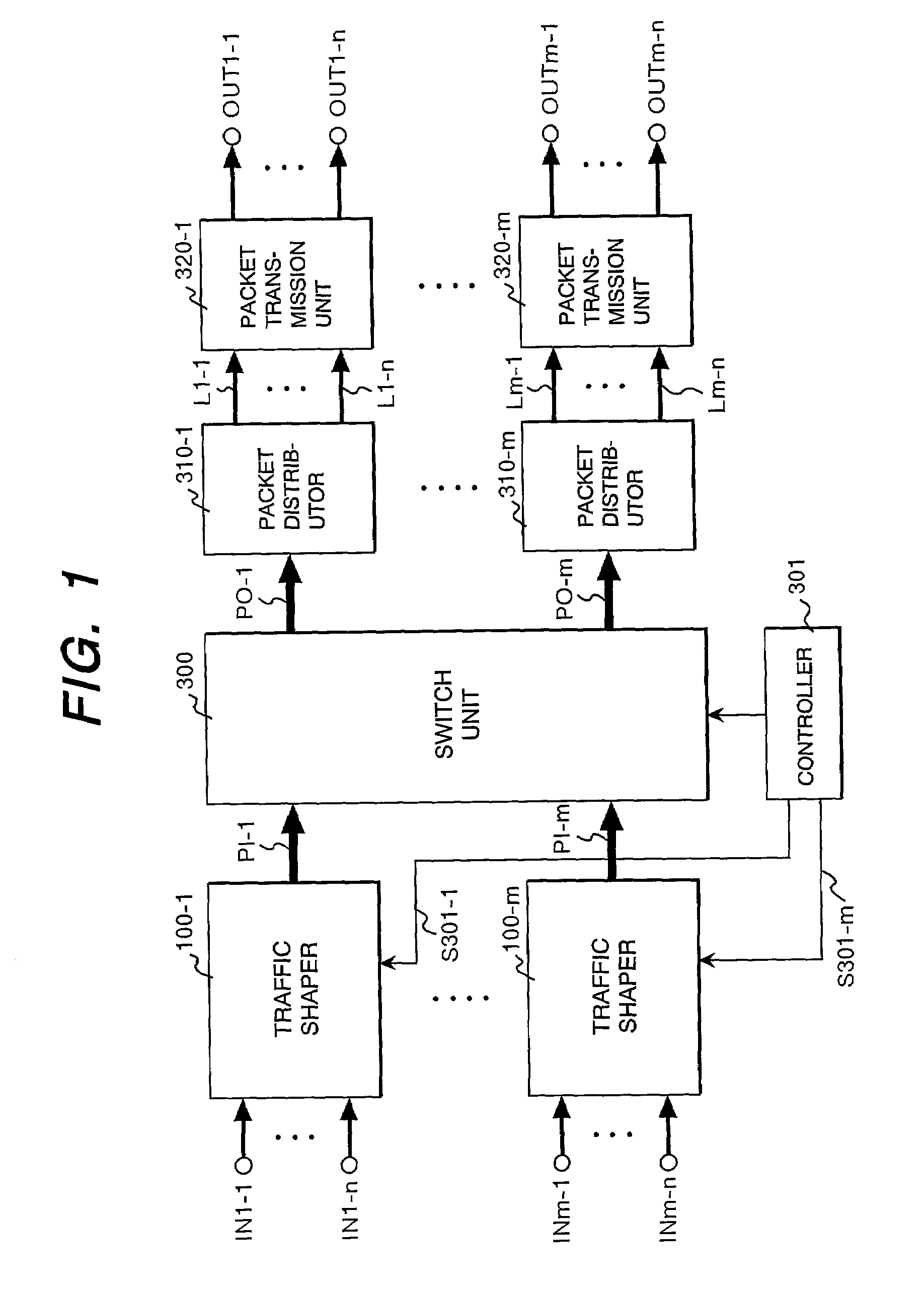
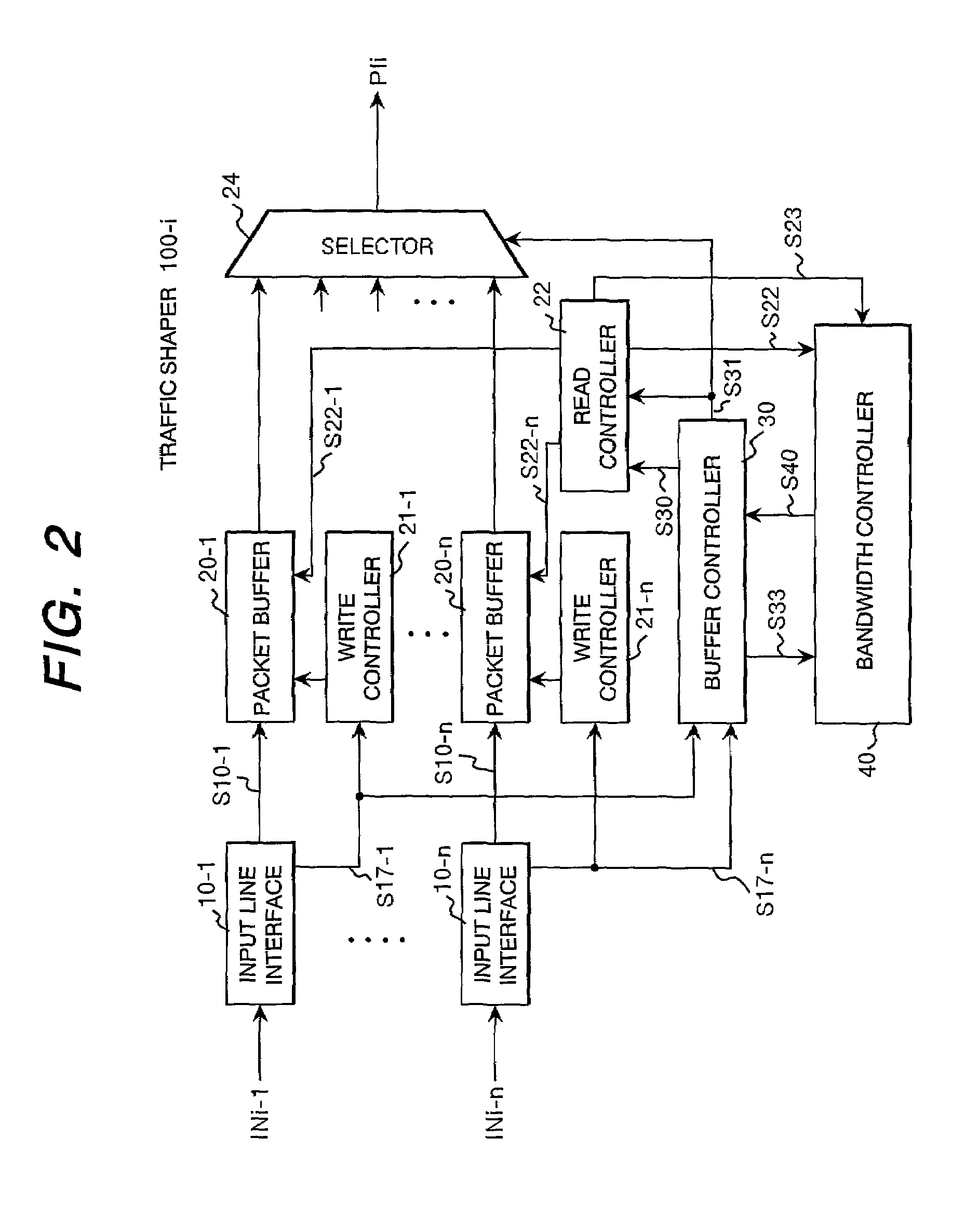
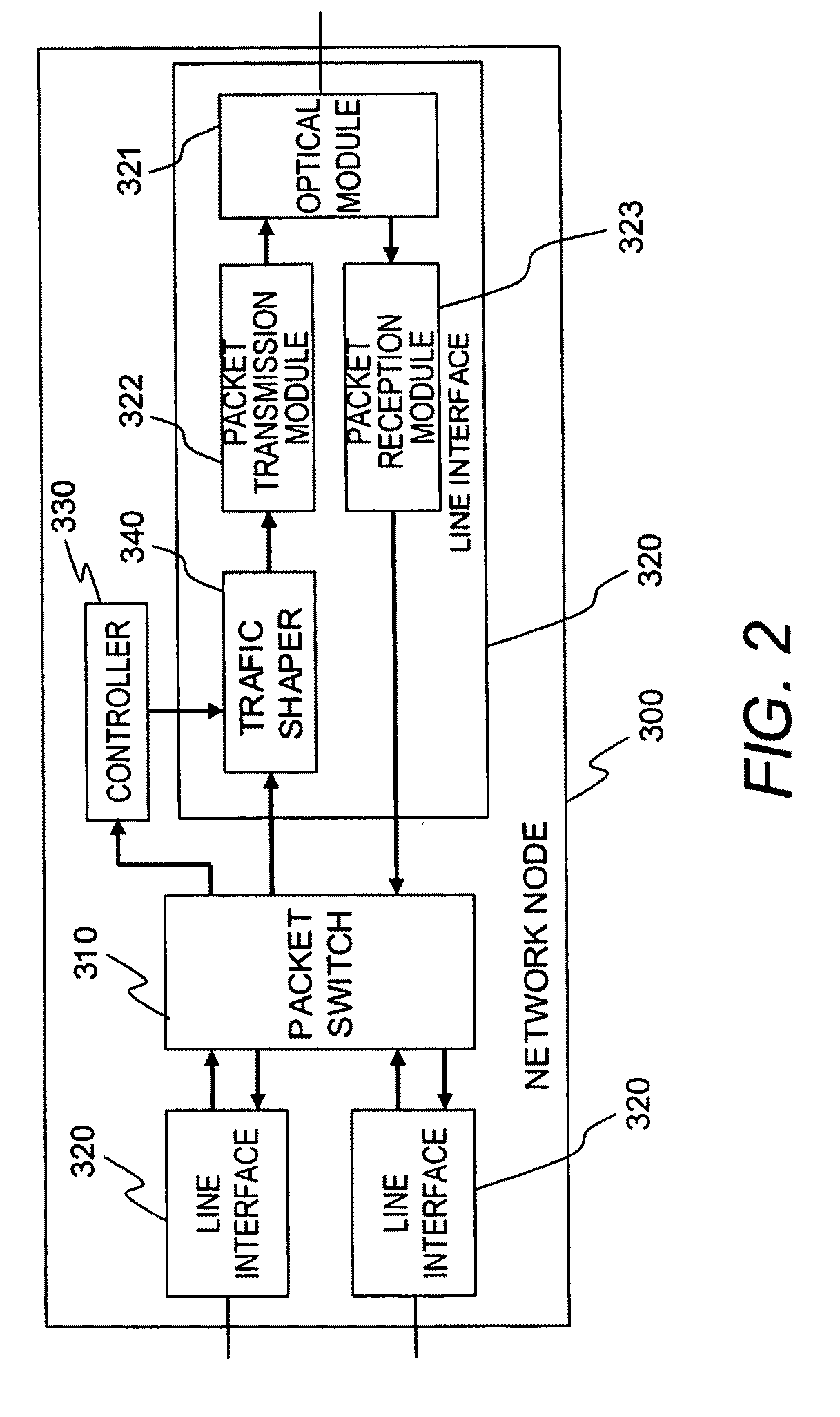
Leaky bucket type traffic shaper and bandwidth controller
InactiveUS7023799B2Easy to useGuaranteed bandwidthError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic shapingBand counts
A traffic shaper comprises a bandwidth controller 40 having a plurality of leaky bucket units 41-1 to 41-n prepared in correspondence with buffer memories 20-1 to 20-n, and an output queue designation unit 43 for specifying a buffer memory from which a packet is to be read out. Each of the leaky bucket units 41 has a level counter 416 for decrementing the count value at a predetermined rate, and a level increaser 411 to 417 for increasing the count value of the level counter by a value proportional to the product of the length of a transmitted packet and a unitary increment value which is variable depend on the current count value of the level counter.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Leaky-bucket thread scheduler in a multithreading microprocessor
ActiveUS7752627B2Digital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsThread schedulingParallel computing
A leaky-bucket style thread scheduler for scheduling concurrent execution of multiple threads in a microprocessor is provided. The execution pipeline notifies the scheduler when it has completed instructions. The scheduler maintains a virtual water level for each thread and decreases it each time the execution pipeline executes an instruction of the thread. The scheduler includes an instruction execution rate for each thread. The scheduler increases the virtual water level based on the requested rate per a predetermined number of clock cycles. The scheduler includes virtual water pressure parameters that define a set of virtual water pressure ranges over the height of the virtual water bucket. When a thread's virtual water level moves from one virtual water pressure range to the next higher range, the scheduler increases the instruction issue priority for the thread; conversely, when the level moves down, the scheduler decreases the instruction issue priority for the thread.
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
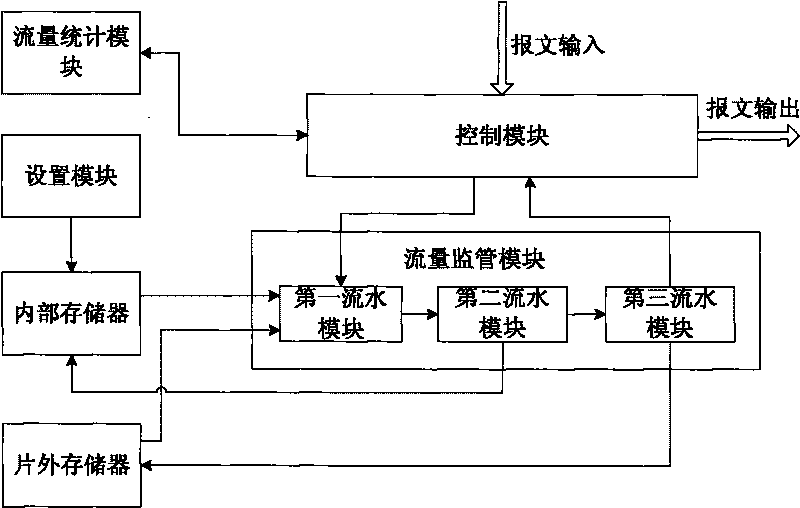
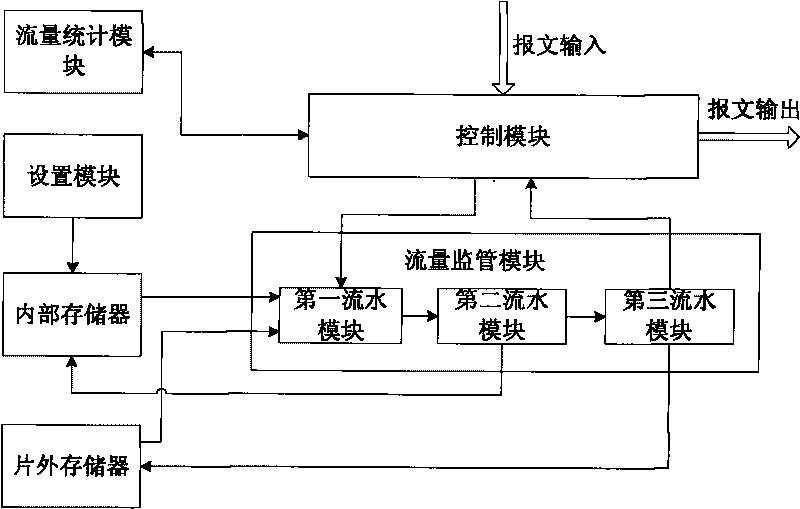
Method and device for supervising traffic based on token bucket
InactiveCN101741603AImprove compatibilityBreak through the bottleneck of processing powerData switching networksTraffic capacityLabelling algorithm
The invention discloses a method and a device for supervising traffic based on a token bucket. The device comprises a setting module, a memory, a control module and a traffic supervising module. The corresponding method comprises the following steps that: 1) setting different leaky bucket algorithm rules, and establishing a mapping relationship table between stream IDs and the leaky bucket algorithm rules; and 2) acquiring a message to be supervised; searching for the corresponding leaky bucket algorithm rule and a leaky bucket parameter by using a stream ID as an index; accordingly determining the number of available tokens in the current average leaky bucket and the peak leaky bucket; comparing the length of the message with the number of the available tokens in the current average leaky bucket and the peak leaky bucket respectively; coloring the message by adopting a corresponding leaky bucket algorithm rule and according to the comparison result; updating and storing the leaky bucket parameter serving as a standby parameter for processing the next stage of message with the same stream ID; and then discarding or forwarding the message according to the coloring result. The method and the device simultaneously support a single-rate marker algorithm and a double-rate marker algorithm, have excellent compatibility, break through the bottle neck of processing capacity and have high processing rate.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Timer adjustment for load control
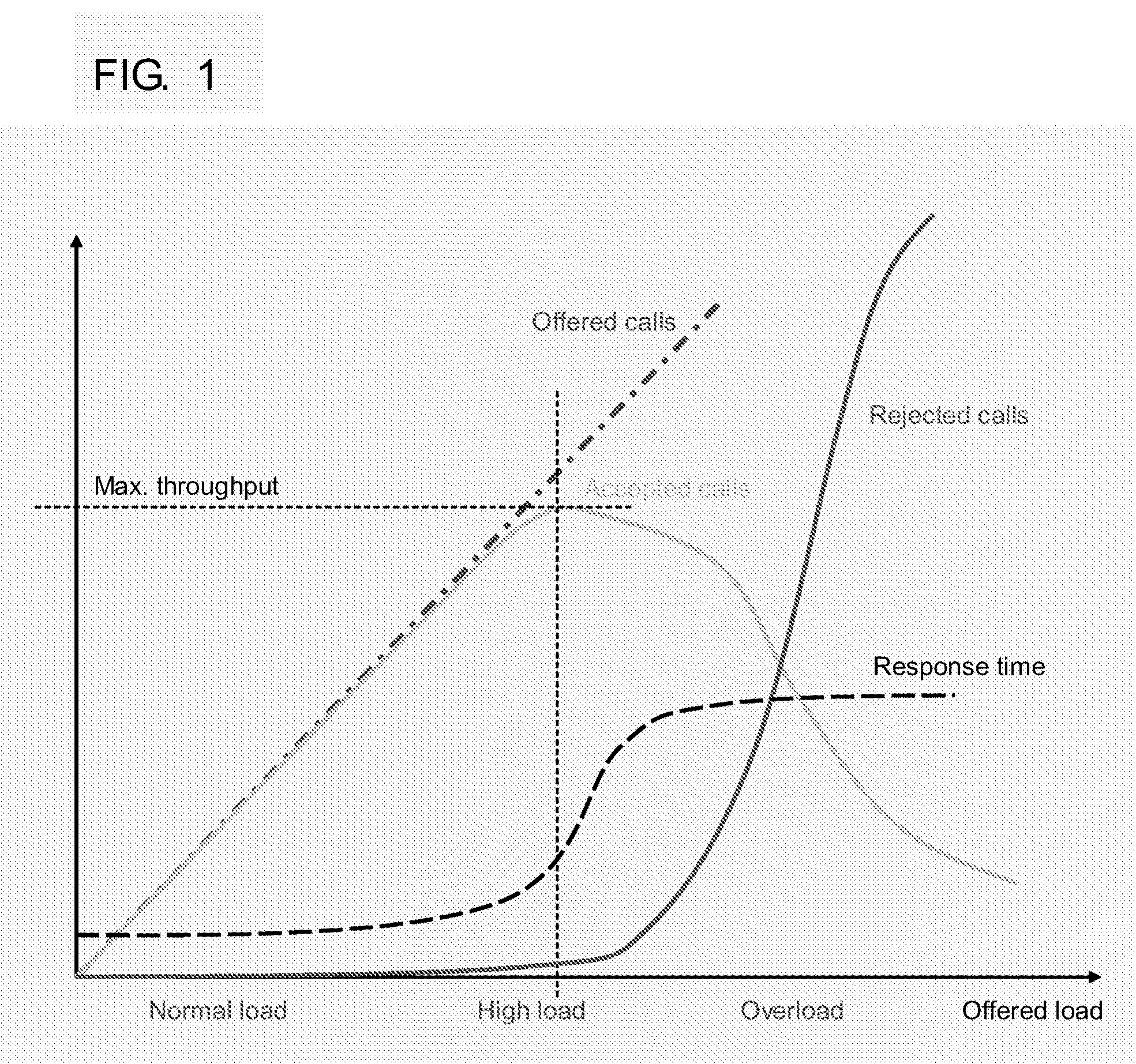
InactiveUS20100302950A1Prevention and reduction of service outageImprove usabilityError preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementCurrent loadWater level
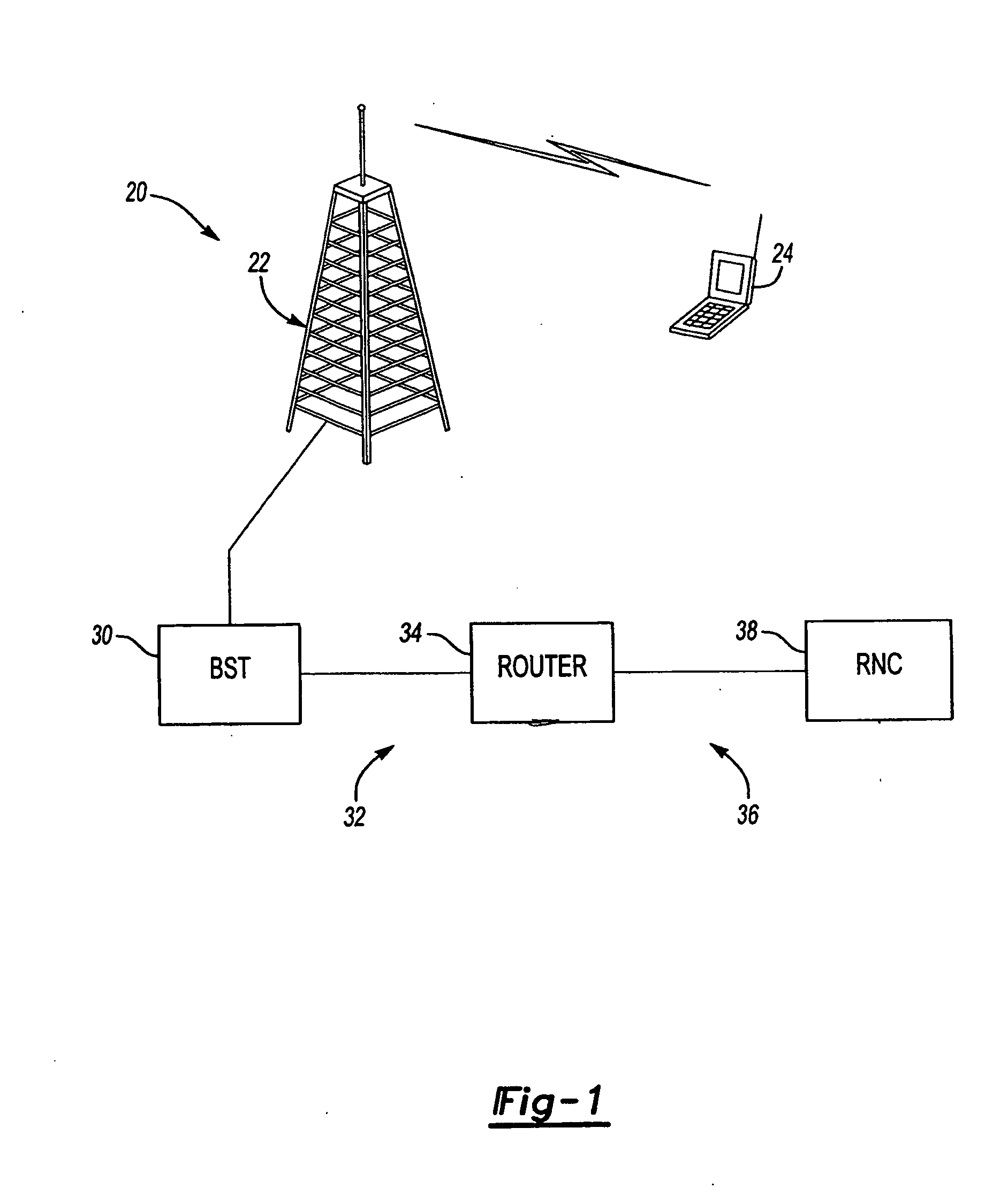
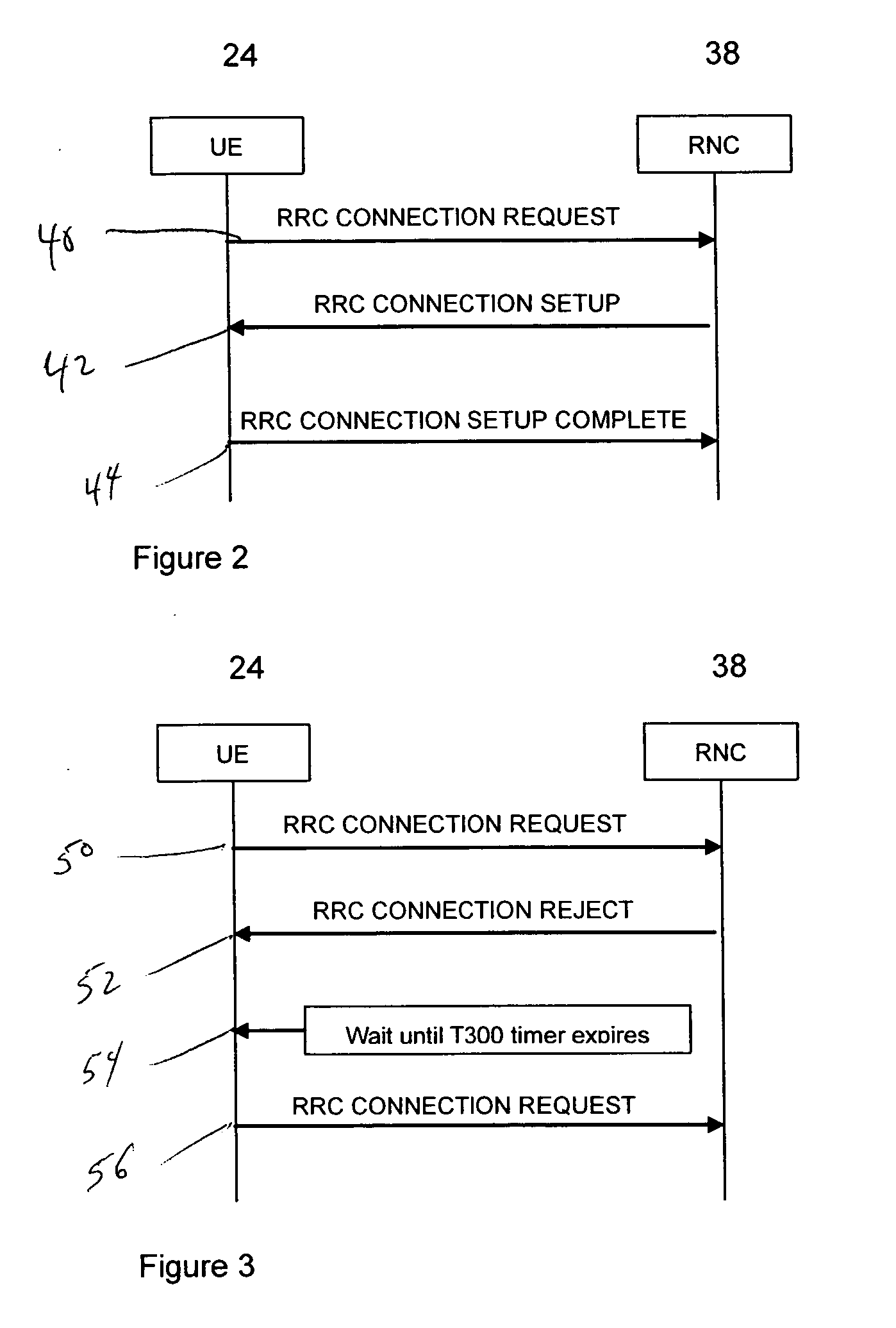
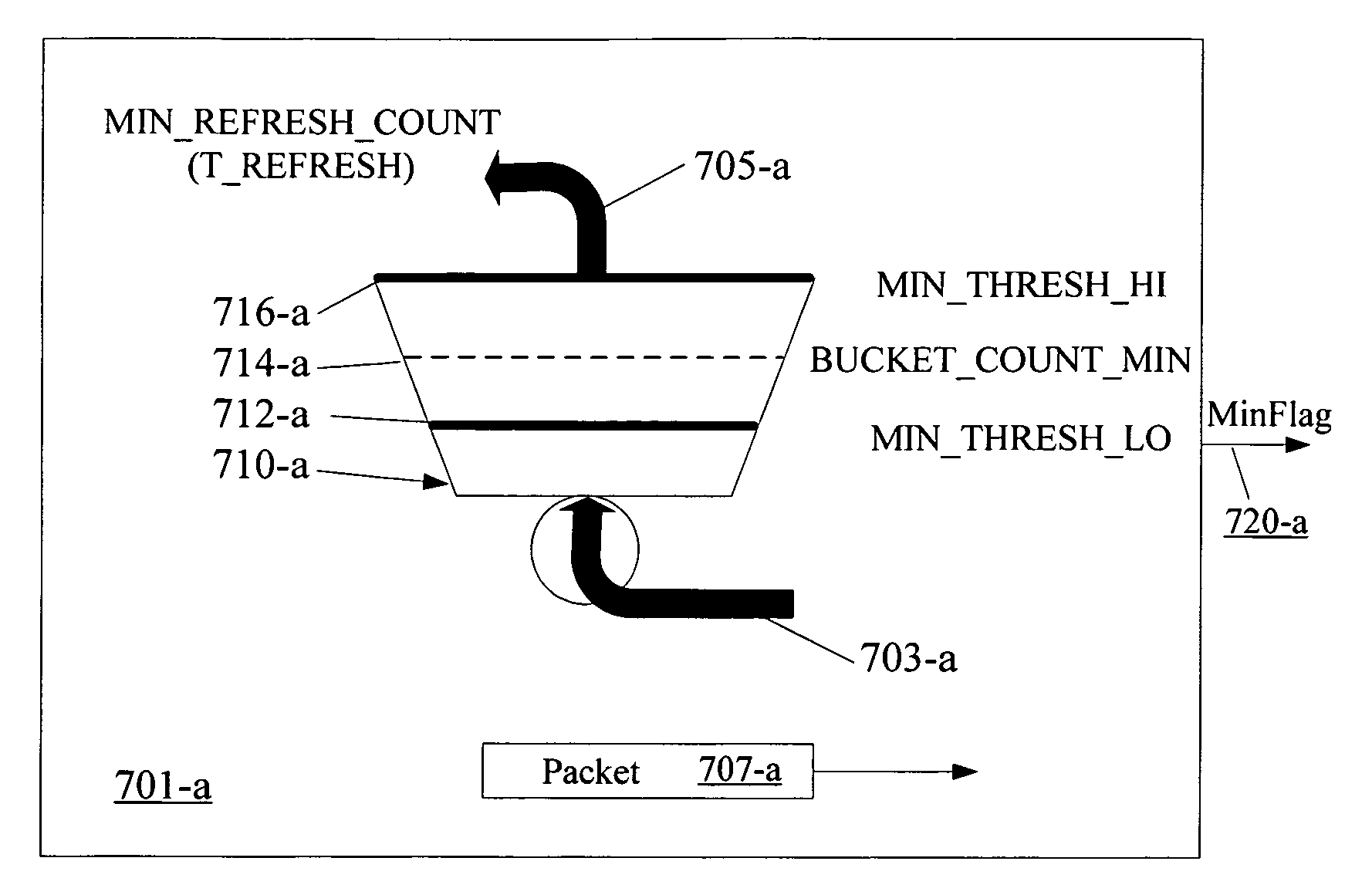
Method and apparatus embodiments are provided for dynamical adjusting a retry service request timer associated with User Equipment (UE) responsive to a service request based on a current load. In one embodiment, a method includes receiving a service request, and modifying a timer value associated with a User Equipment (UE) responsive to the service request based on a current load. The timer value is indicative of a period the UE is to wait before making a next service request. The timer value may be modified based on a leaky bucket algorithm. When the current load is indicative of an overload condition, the timer value is increased. For example, when the total number of service request establishment failures is above the high water mark, the timer value may be is increased. The timer value may be communicated to the UE.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
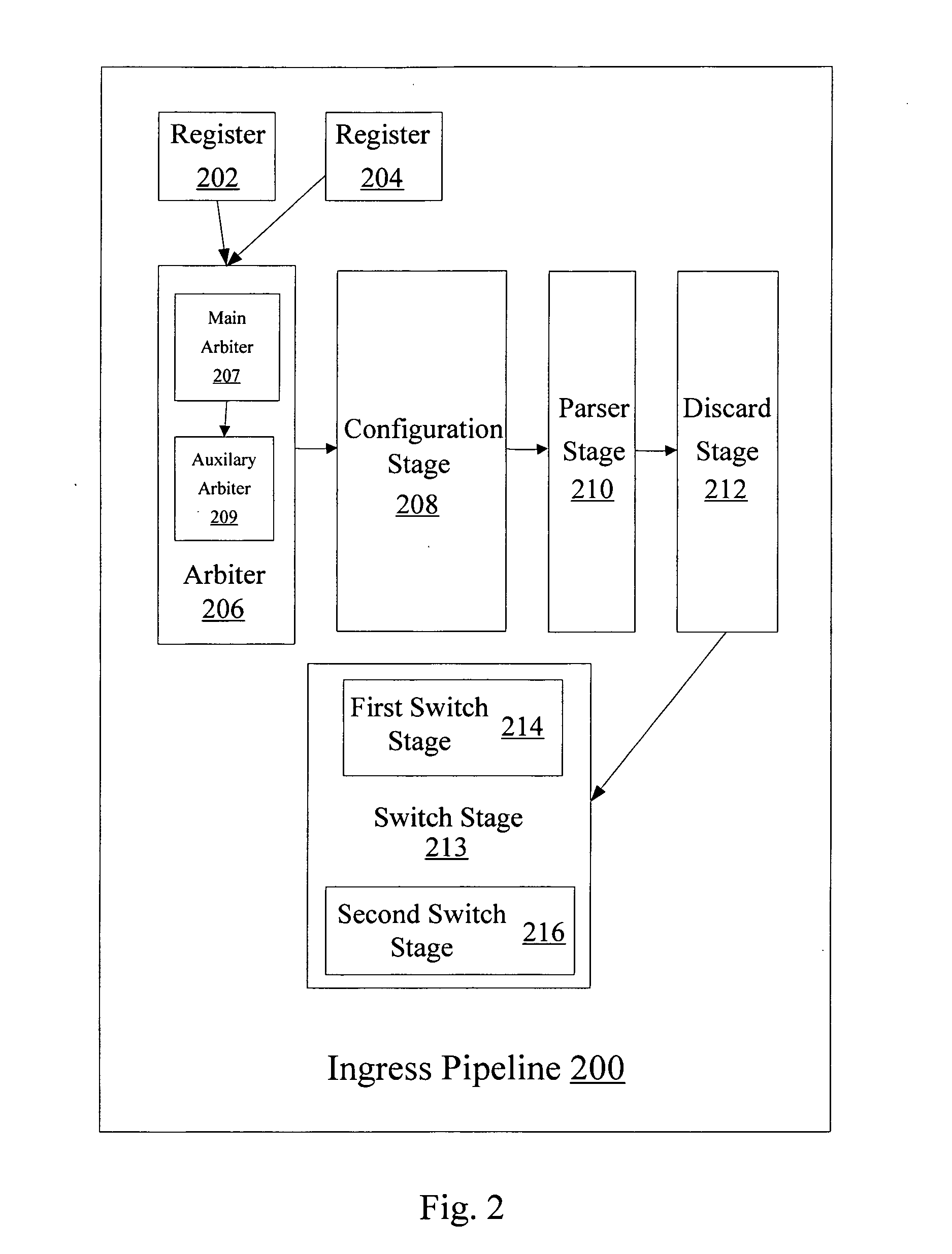
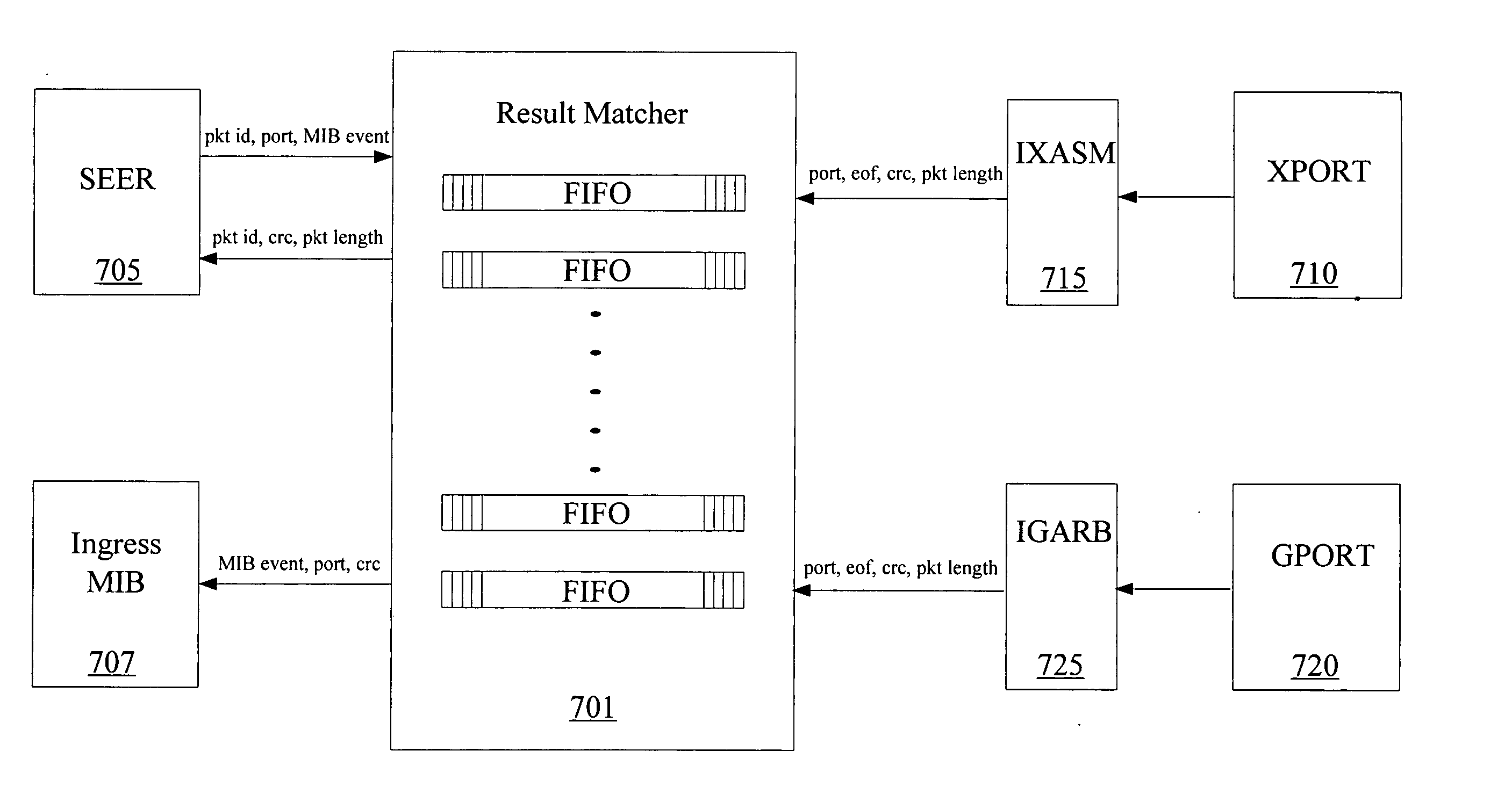
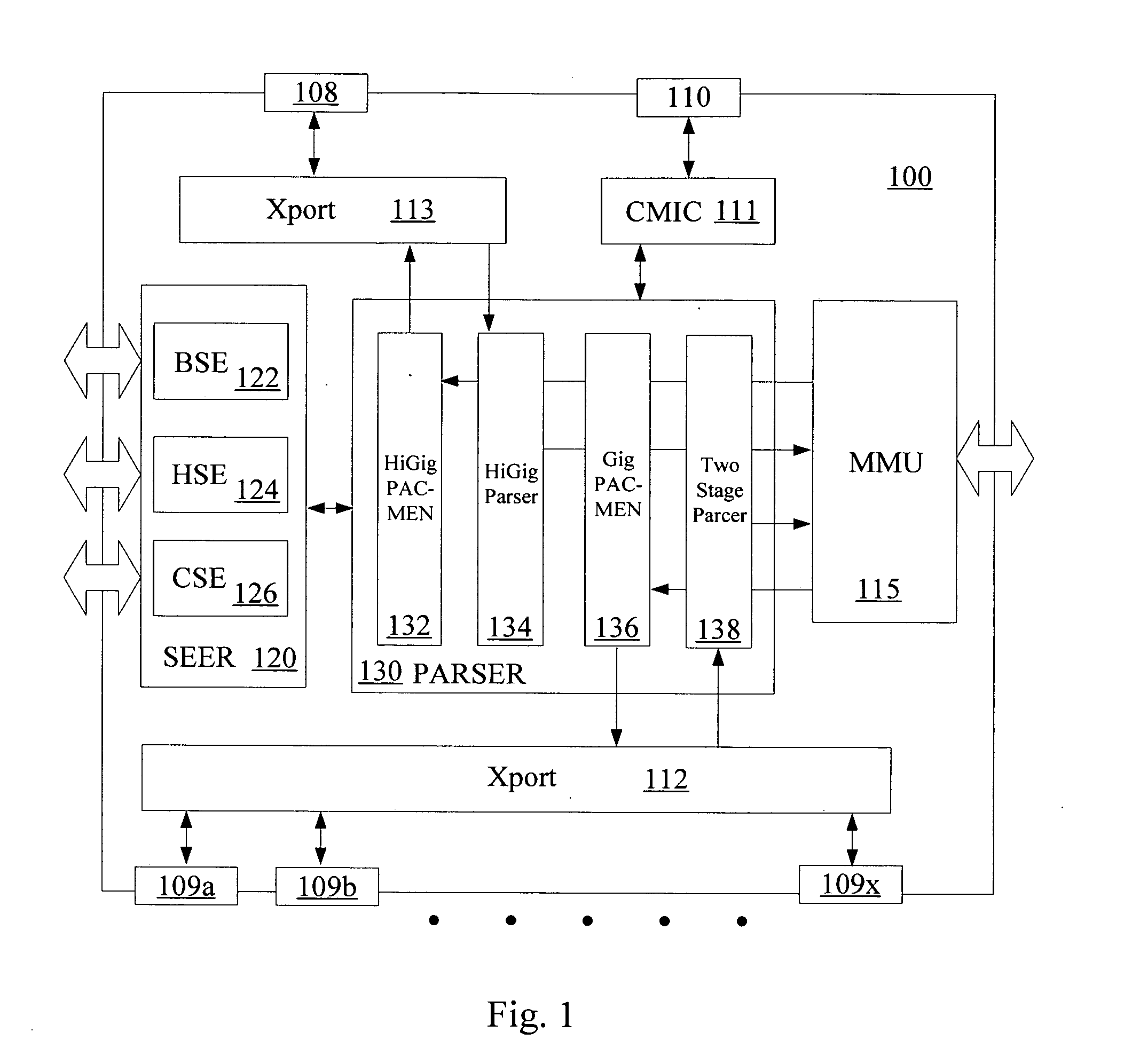
Timestamp metering and rollover protection in a network device
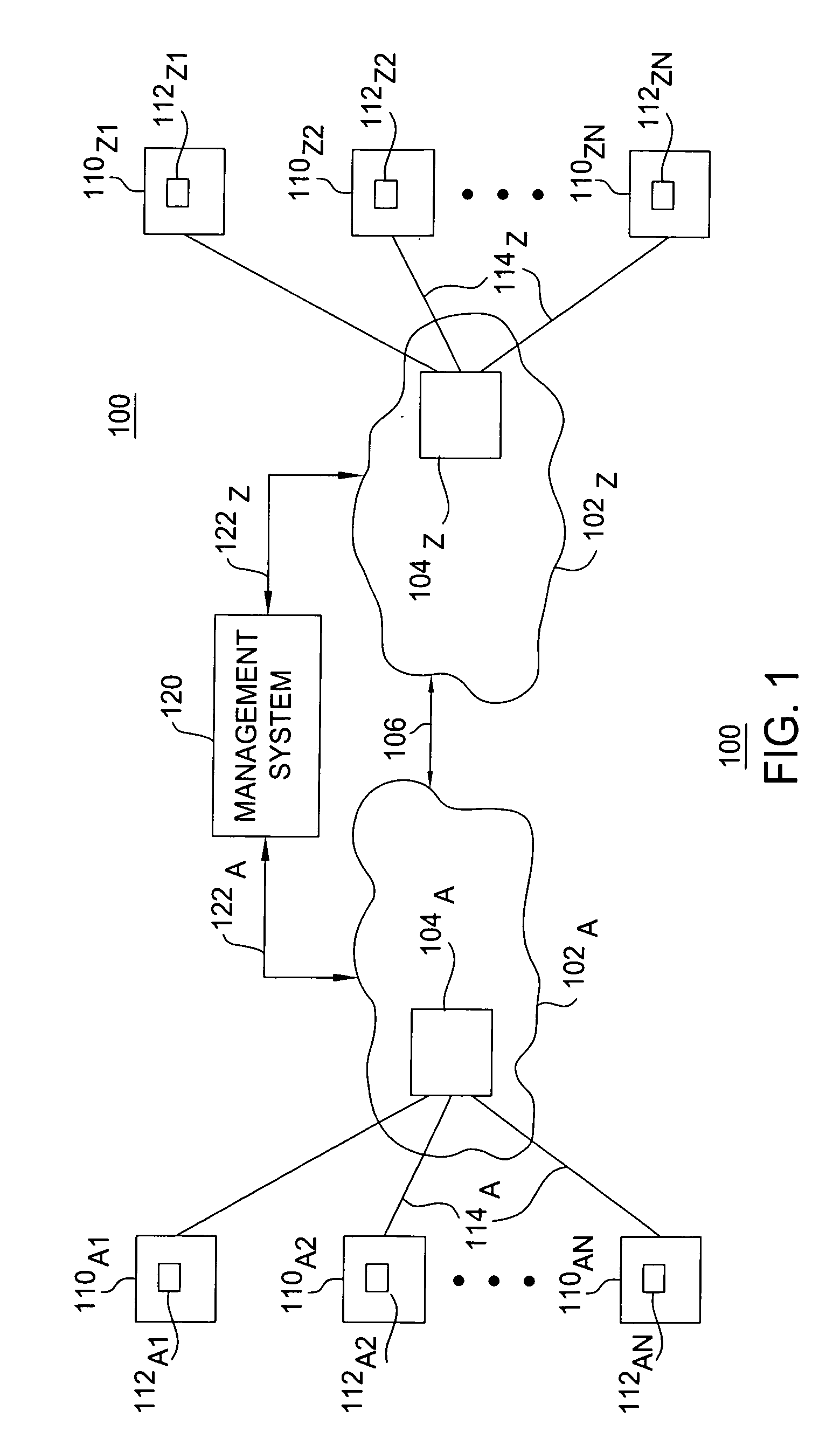
A network device for processing data on a data network includes a plurality of ports, configured to receive data from a data network and to send processed data to the data network, a memory management unit configured store data on and retrieve data from the memory and a metering unit configured to police a flow of the processed data to be sent to the network device. The metering unit is configured to utilize a series of leaky bucket units, where tokens are added to each leaky bucket unit only when that particular leaky bucket unit is accessed. The metering unit is also configured to add the tokens based on a prior timestamp value, a current timing value and an established rate and a multiplication to establish the tokens is accomplished by shifting a register of the established rate.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Aggregate rate transparent LAN service for closed user groups over optical rings
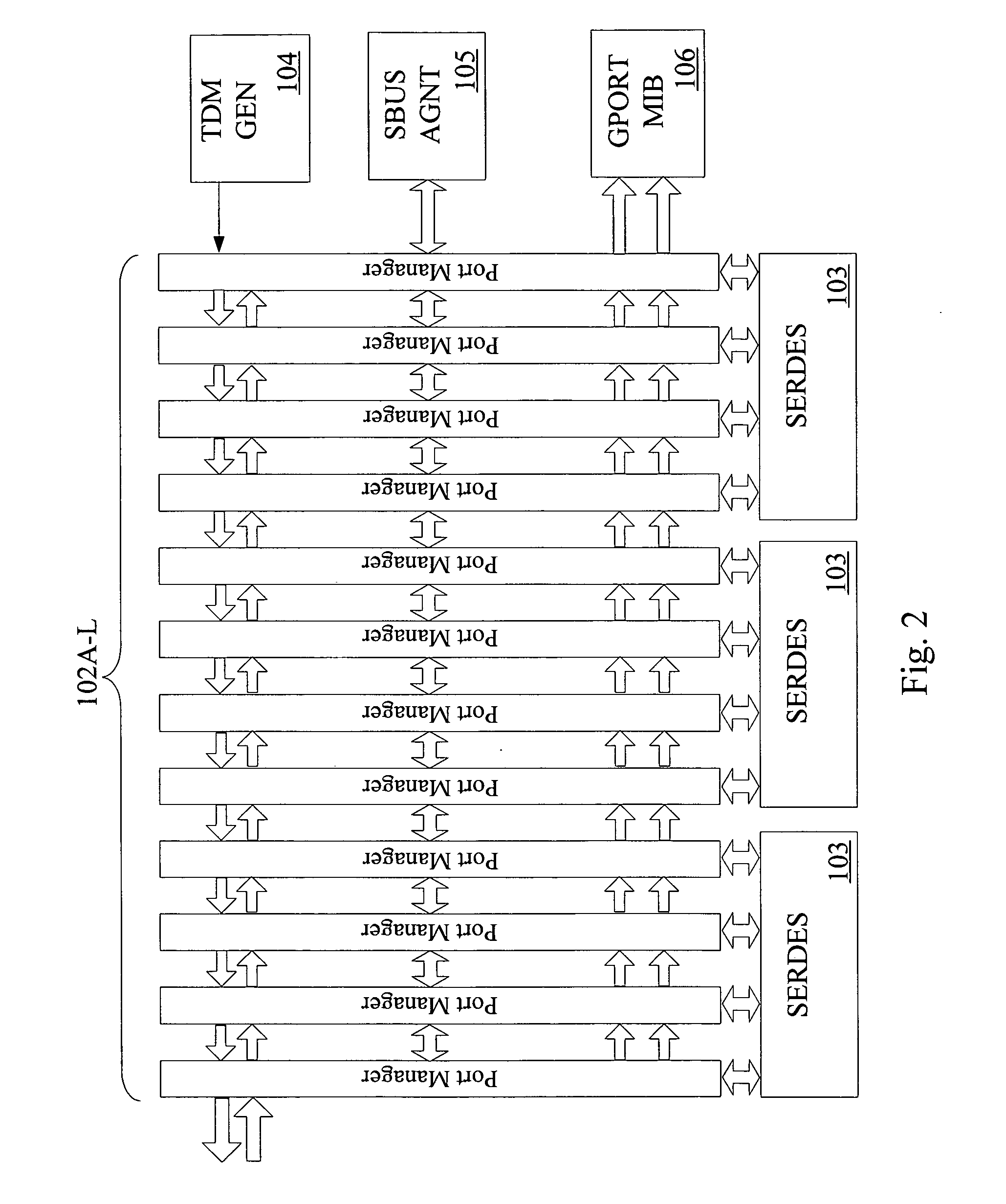
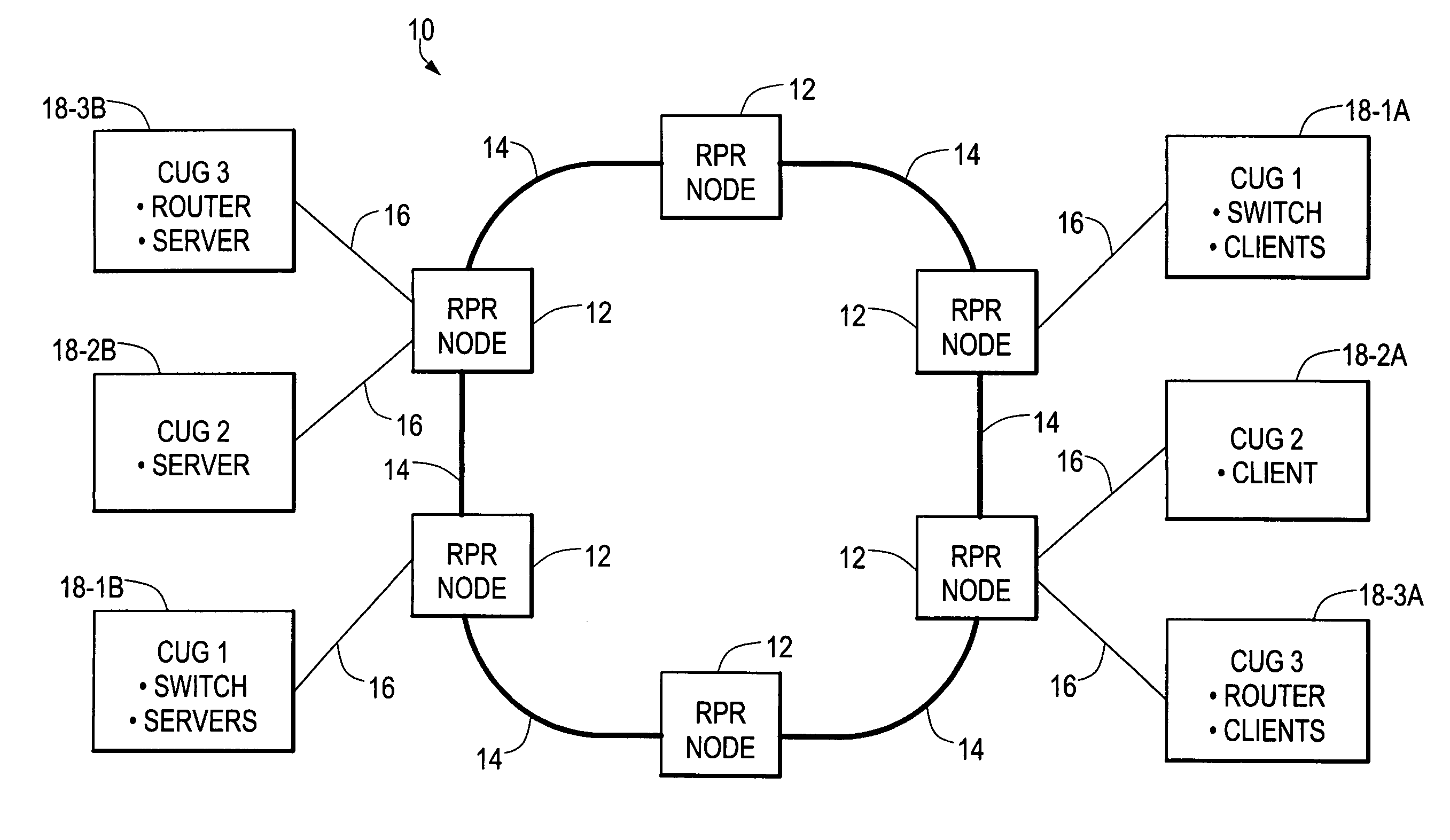
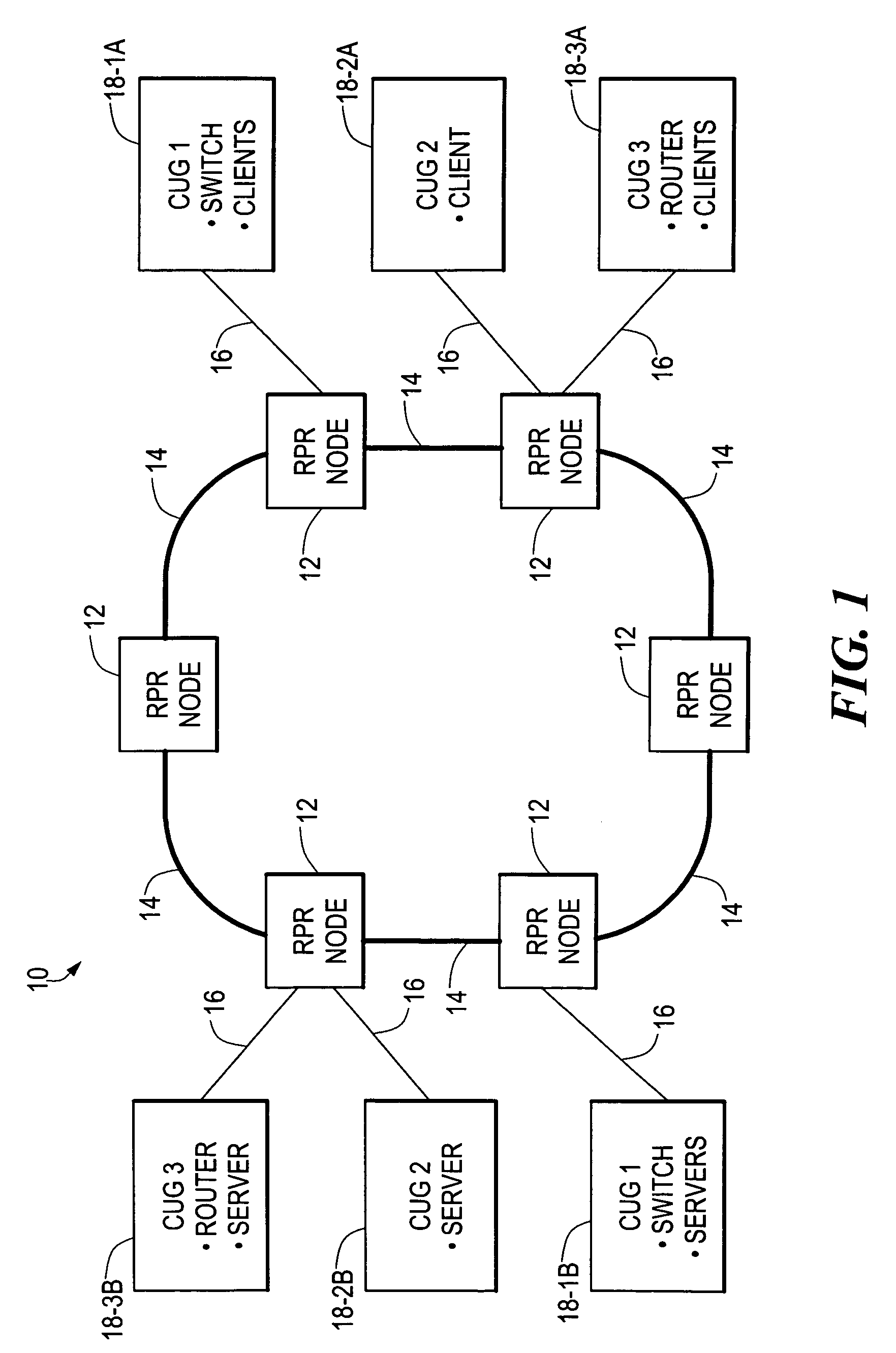
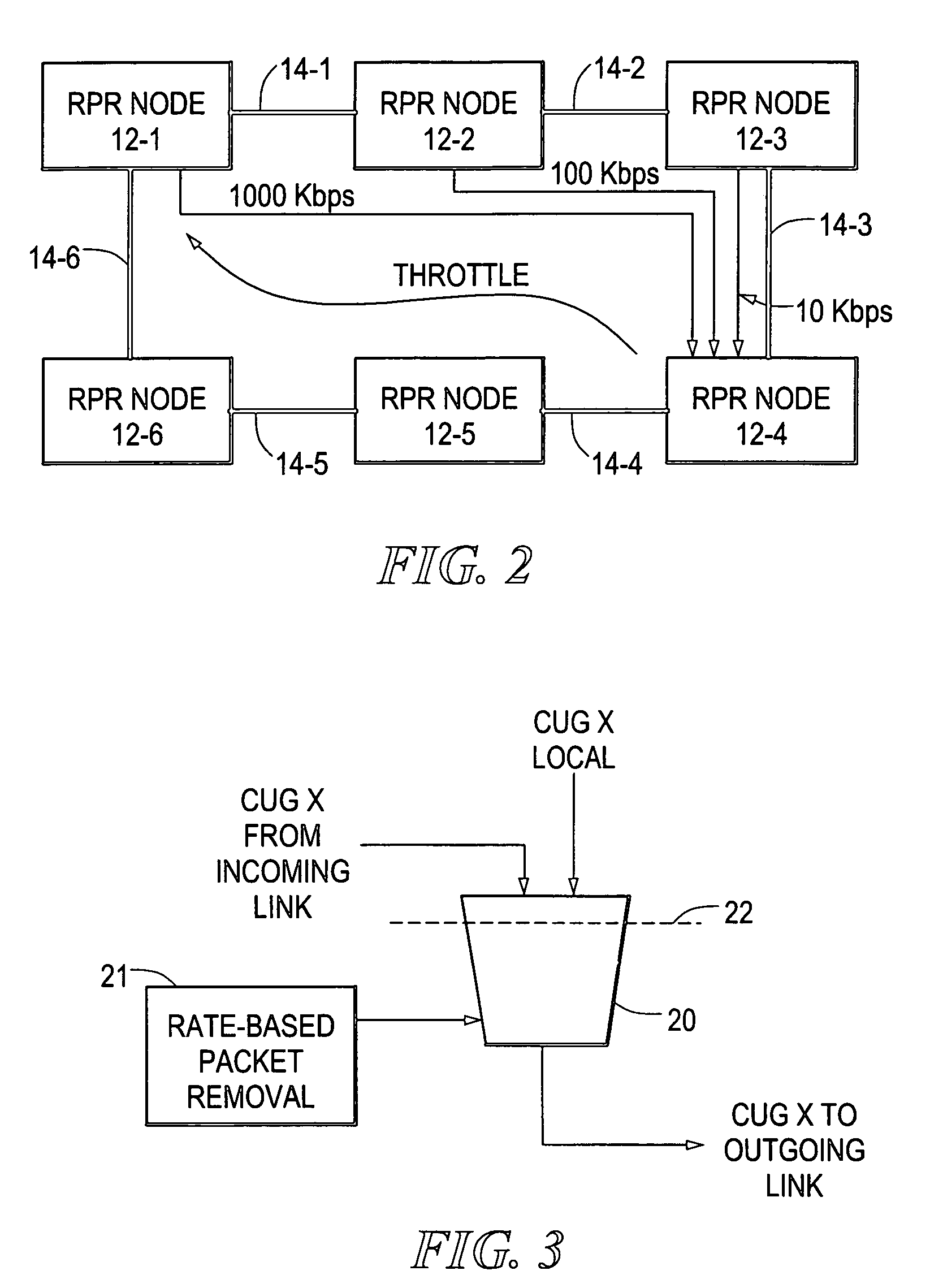
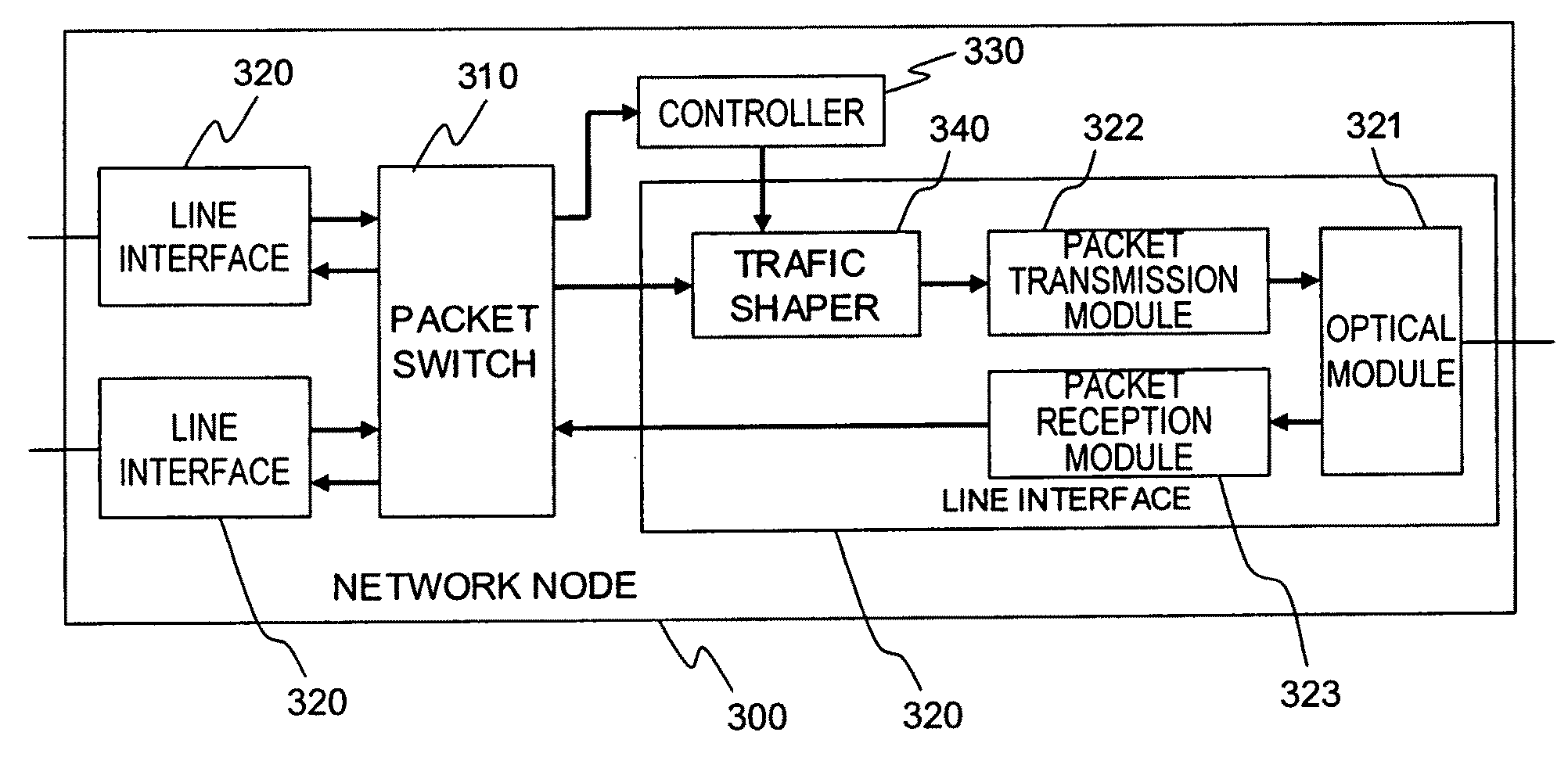
ActiveUS7102997B2Lighten the configuration burdenReduce data transfer rateEnergy efficient ICTTransmission systemsRing networkClient-side
A ring network provides transparent local area network (LAN) service by allocating respective proportions of data transmission capacity of the ring to different closed user groups (CUGs), each including a plurality of LAN clients. At each node of the ring, the use of a connected segment of the ring is monitored for both pass-through and locally-generated traffic by the LAN clients on a per-CUG basis. When it is detected that use of the connected segment for a CUG is approaching the allocated proportion, an active LAN client of the CUG is selected and sent a throttle message indicating that the LAN client is to reduce its data transmission rate. Rate monitoring for is accomplished using a “leaky bucket” mechanism. A “rate cache” identifying the active senders and their transmission rates can also be used in selecting a LAN client for receiving the throttle message.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Multi-flow multi-level leaky bucket policer
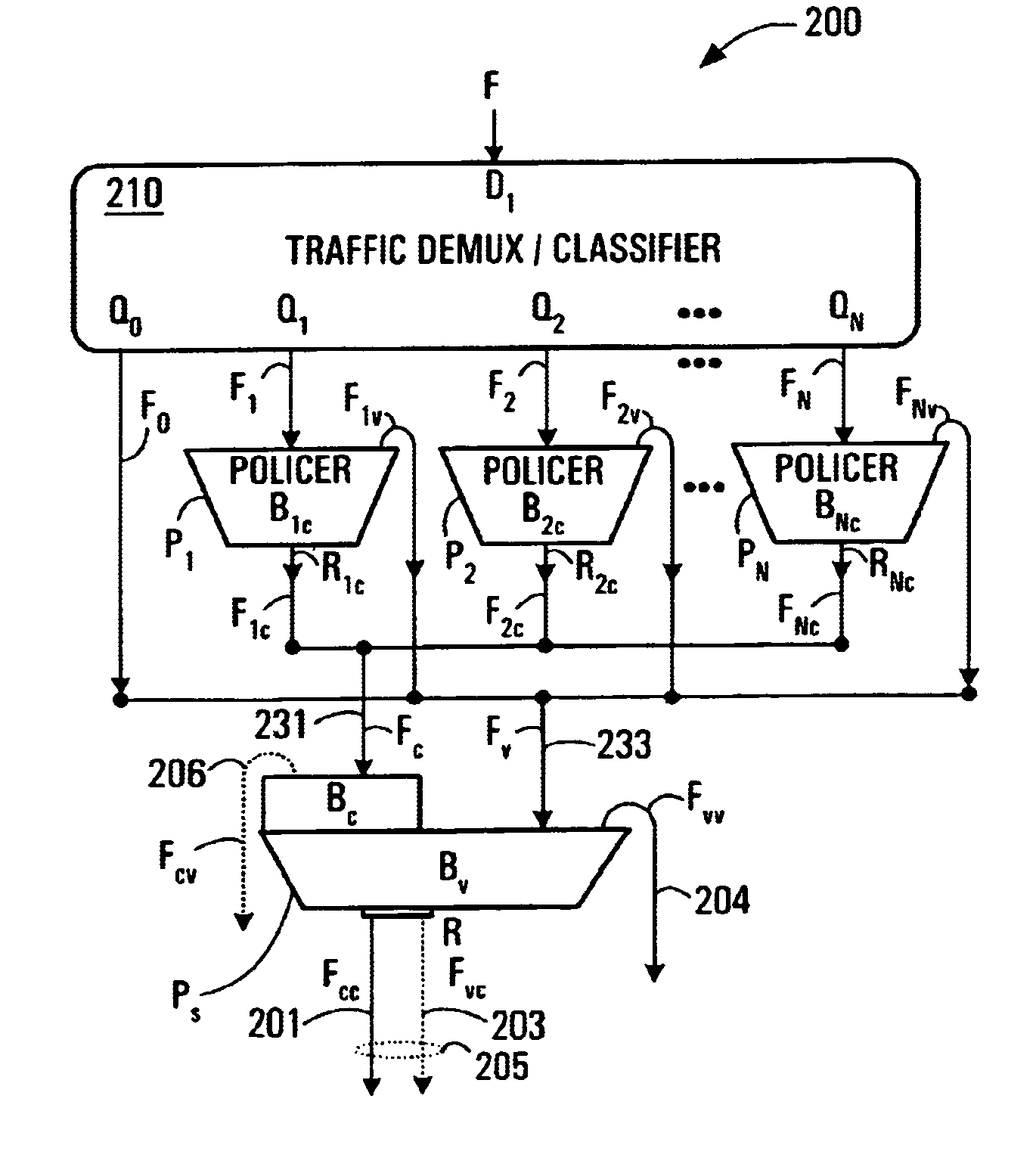
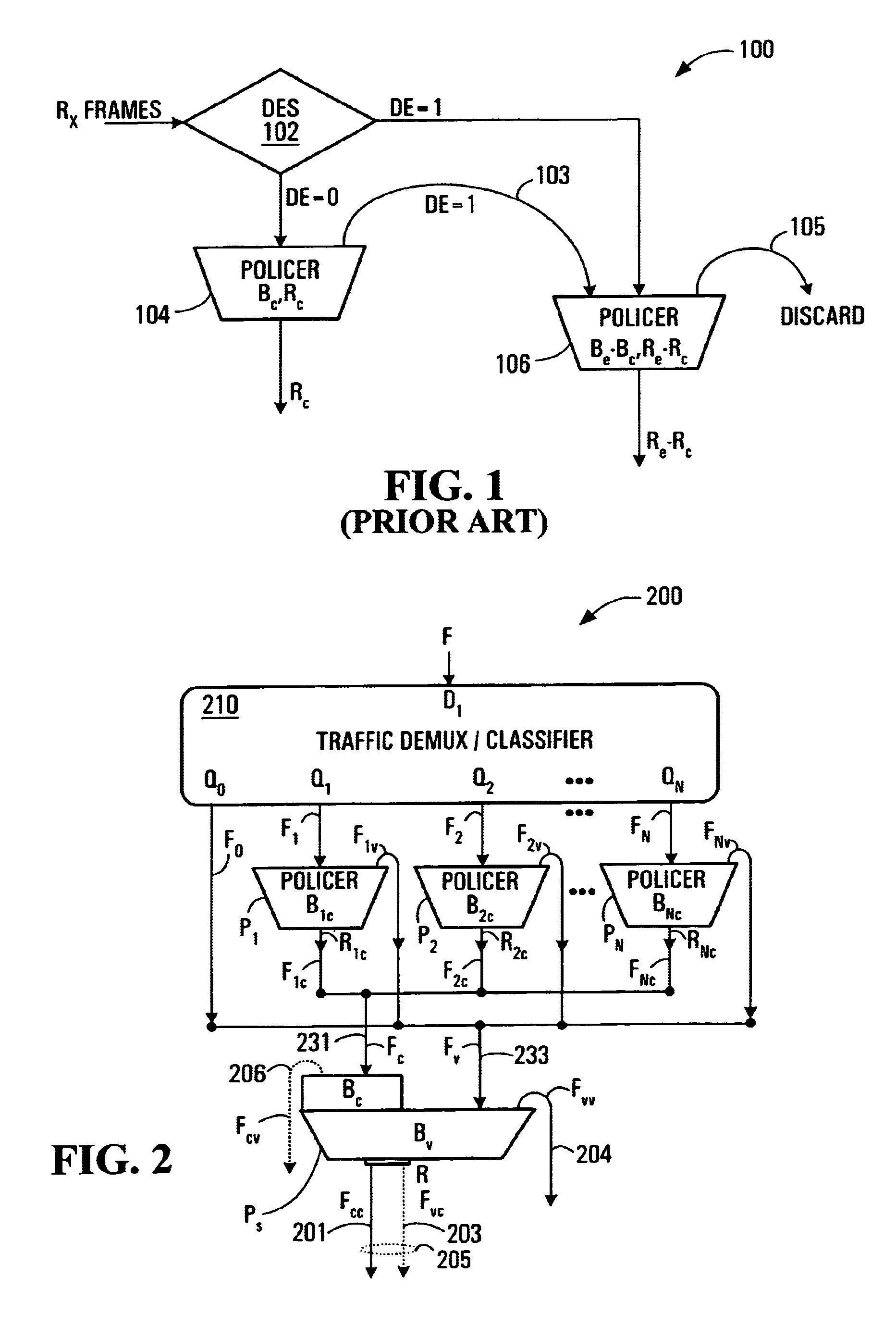
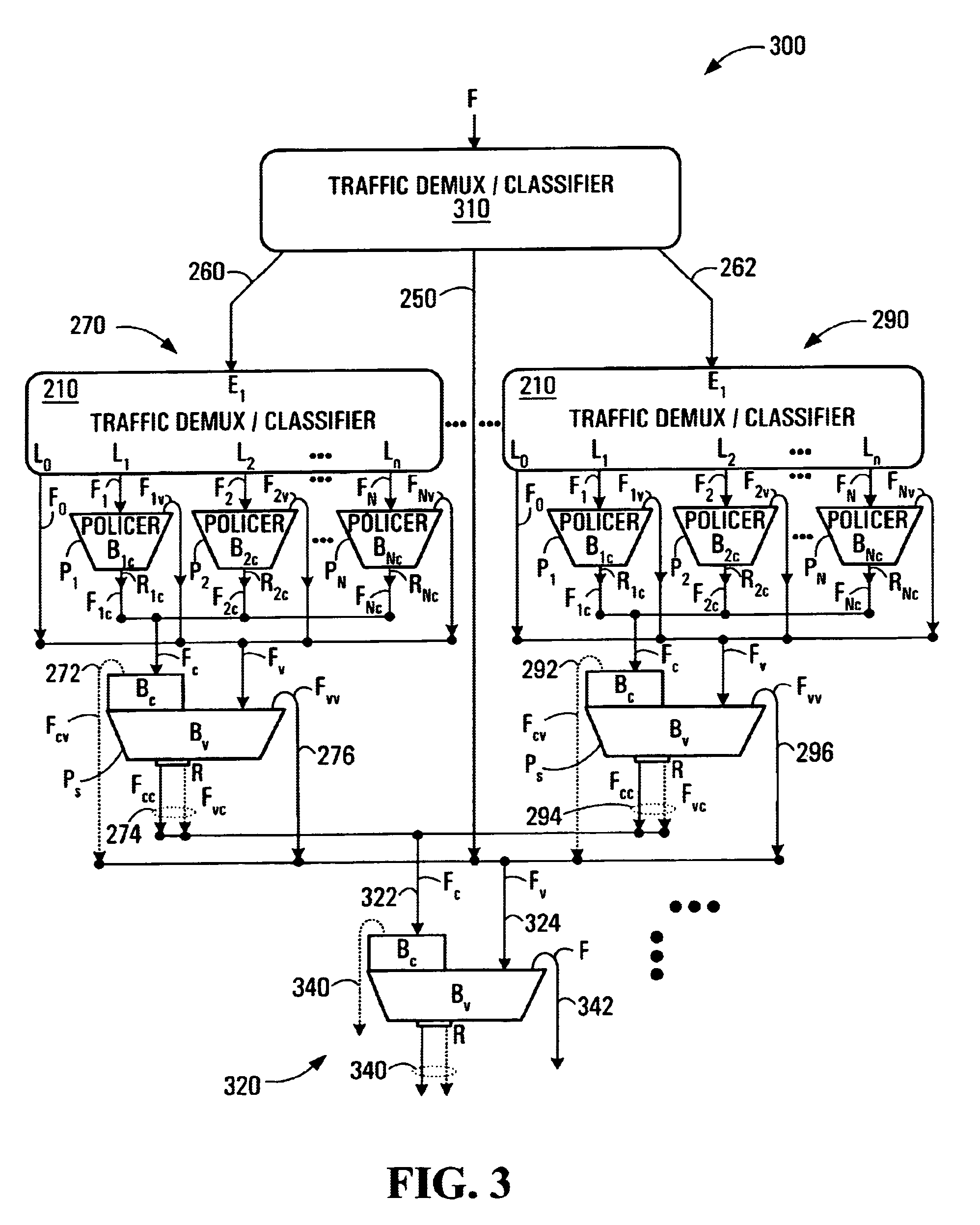
The invention provides a method and apparatus for policing a traffic flow in which a first stage of policing is performed on the traffic flow to produce a first stage conforming flow and a first stage violating flow. These two flows are then policed again in a second stage of policing, such that the first stage conforming flow can take advantage of a capacity allowed for the first stage violating flow which is unused by the first stage violating flow. In some embodiments, performing a first stage of policing involves associating each packet of the traffic flow with one of a plurality of sub-flows, policing at least one of the plurality of sub-flows individually to produce for each sub-flow a respective conforming sub-flow and a respective violating sub-flow. The conforming sub-flow(s) collectively are the first stage conforming flow. The violating sub-flows collectively are the first stage violating flow.
Owner:AVAYA MANAGEMENT LP
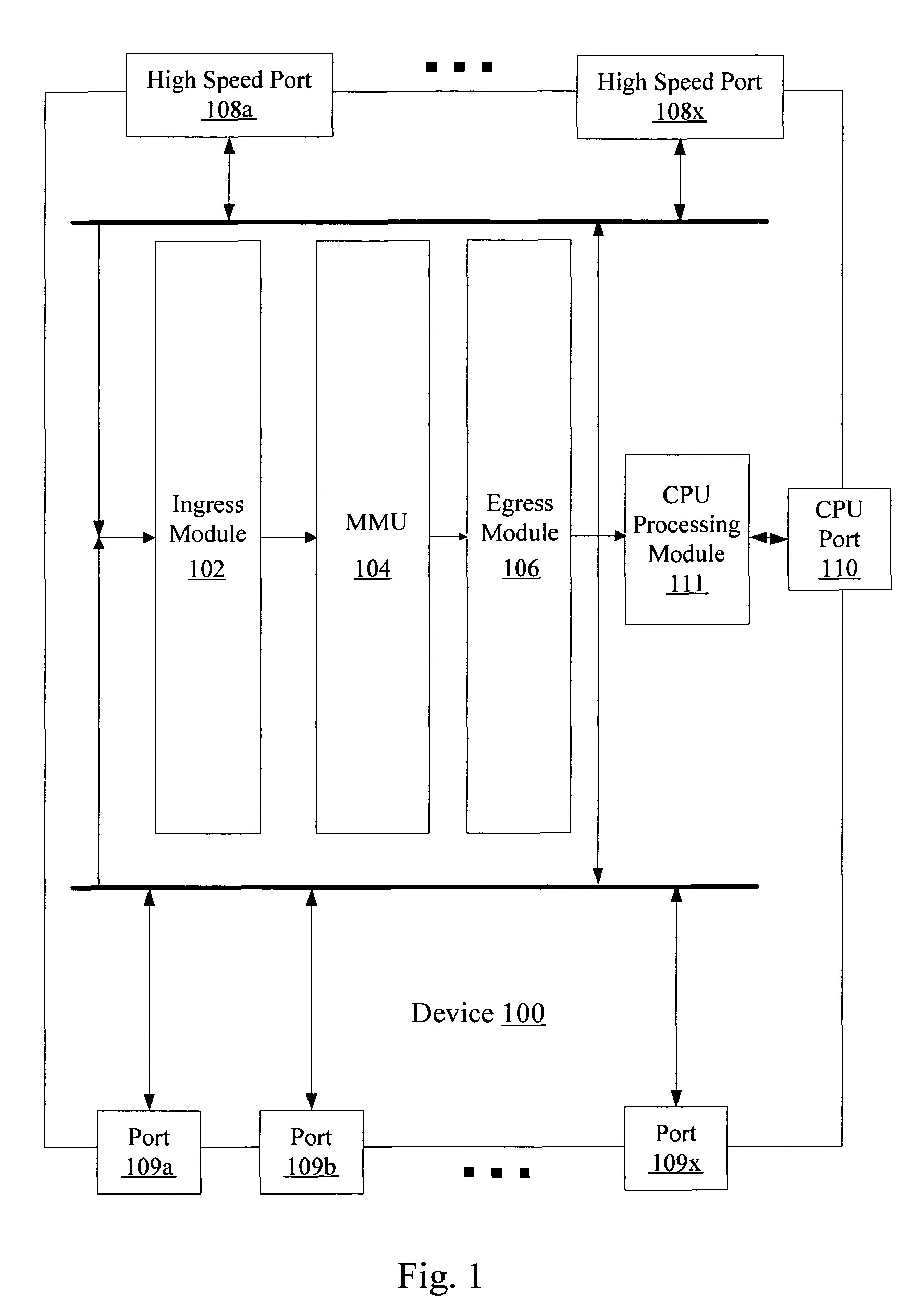
Packet forwarding apparatus using token bucket algorithm and leaky bucket algorithm
InactiveUS20090210553A1Strictly controlling bandwidthMultiplex system selection arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer networkAlgorithm
A packet forwarding apparatus and network system for providing different types of bandwidth control services to the user; in which a packet forwarding apparatus for transferring data comprises an interface unit for sending and receiving packets, and a traffic shaper for controlling the packet transmission timing and a packet switch for sending an output to the interface unit as the destination of the received packet; and the traffic shaper uses a token bucket algorithm when transmitting a packet to guarantee the minimum frame rate, and uses a leaky bucket algorithm when limiting the peak frame rate.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Flow control in packet-switched communication network using leaky bucket algorithm
InactiveCN1478345ANetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsData streamData traffic
A buffer in a packet control network unit may overflow or underflow during data transmission from an external network to a user terminal, thus causing many kinds of problems in data transmission. The problems can be prevented in a packet network providing a data flow control algorithm performed by the packet control unit. The packet control unit indicates to the network node, from which it receives data packets, the actual transmission rate of a specified data flow, as well as the buffering capacity for that flow. Then the said network node adjusts its transmission rate for the indicated flow.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
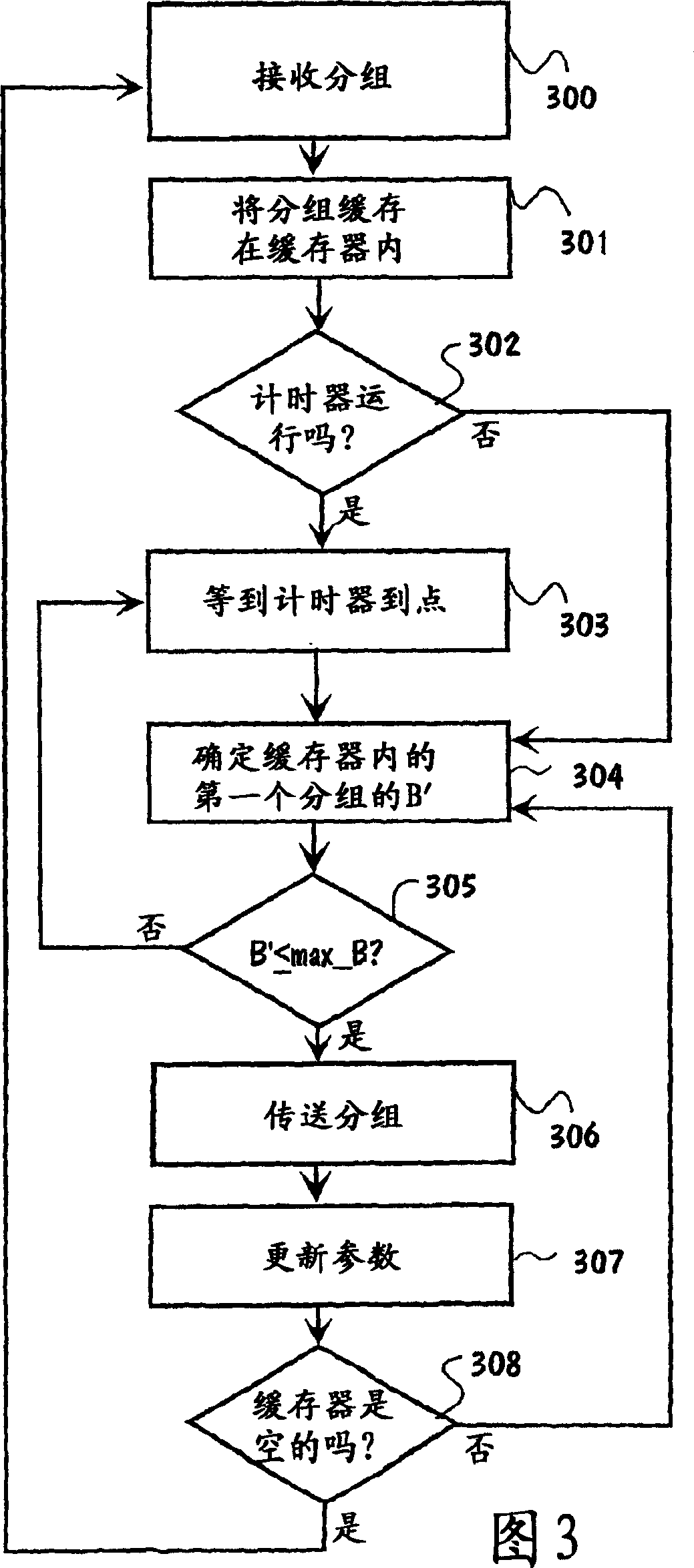
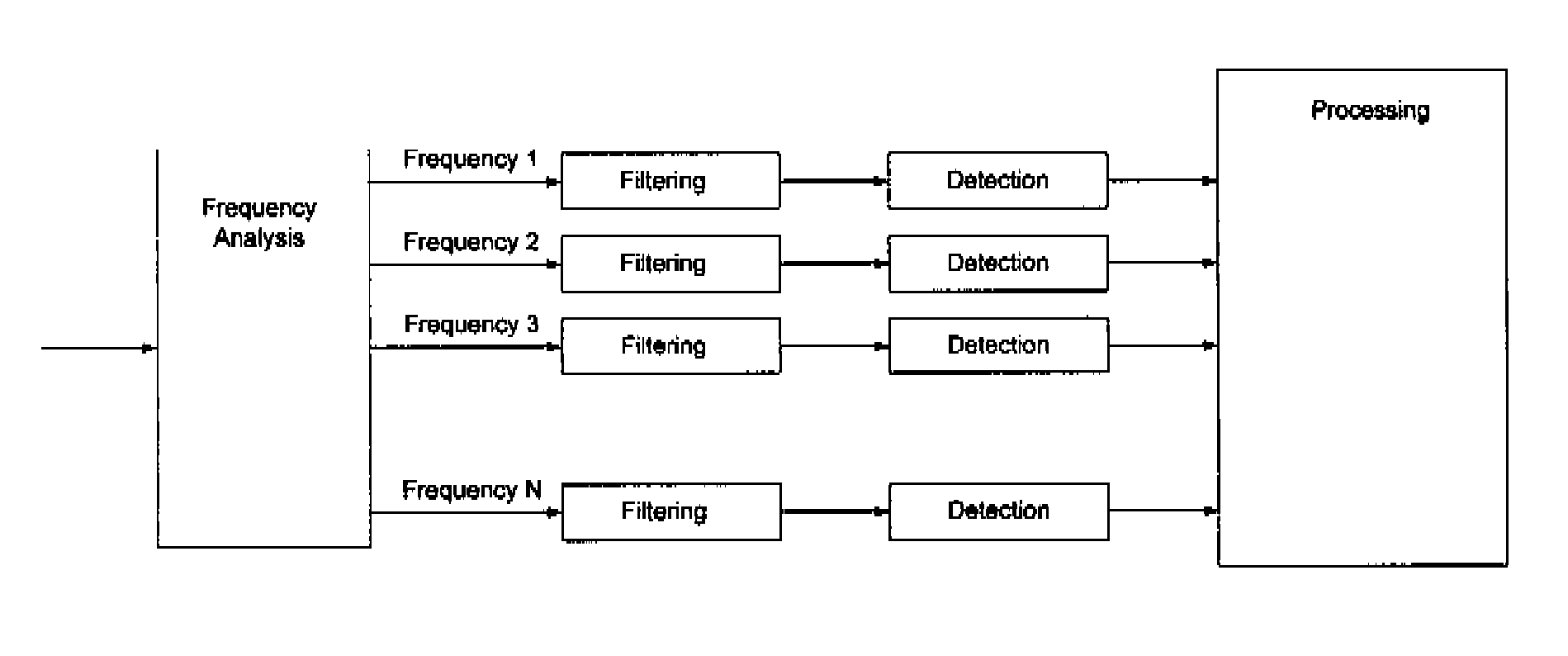
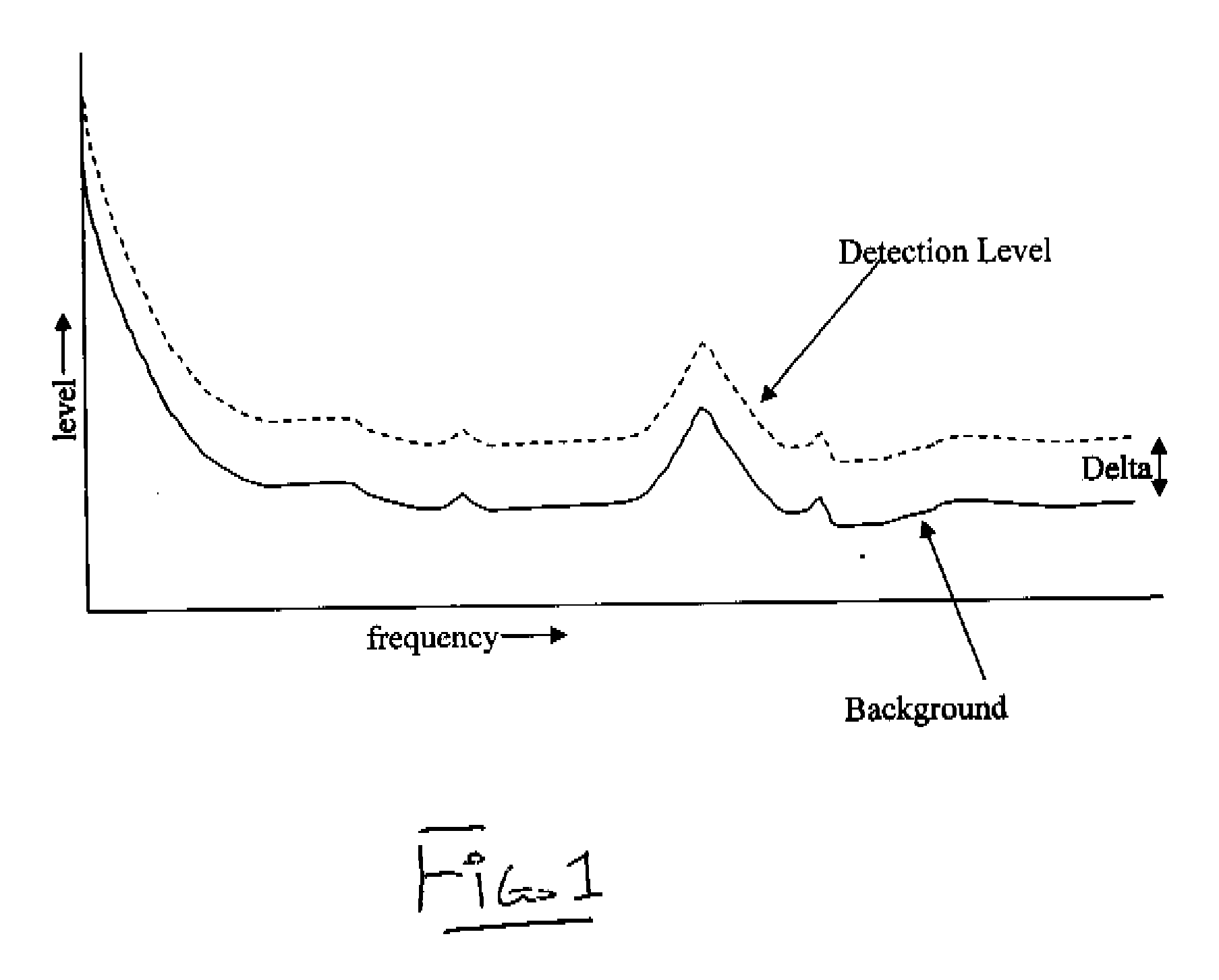
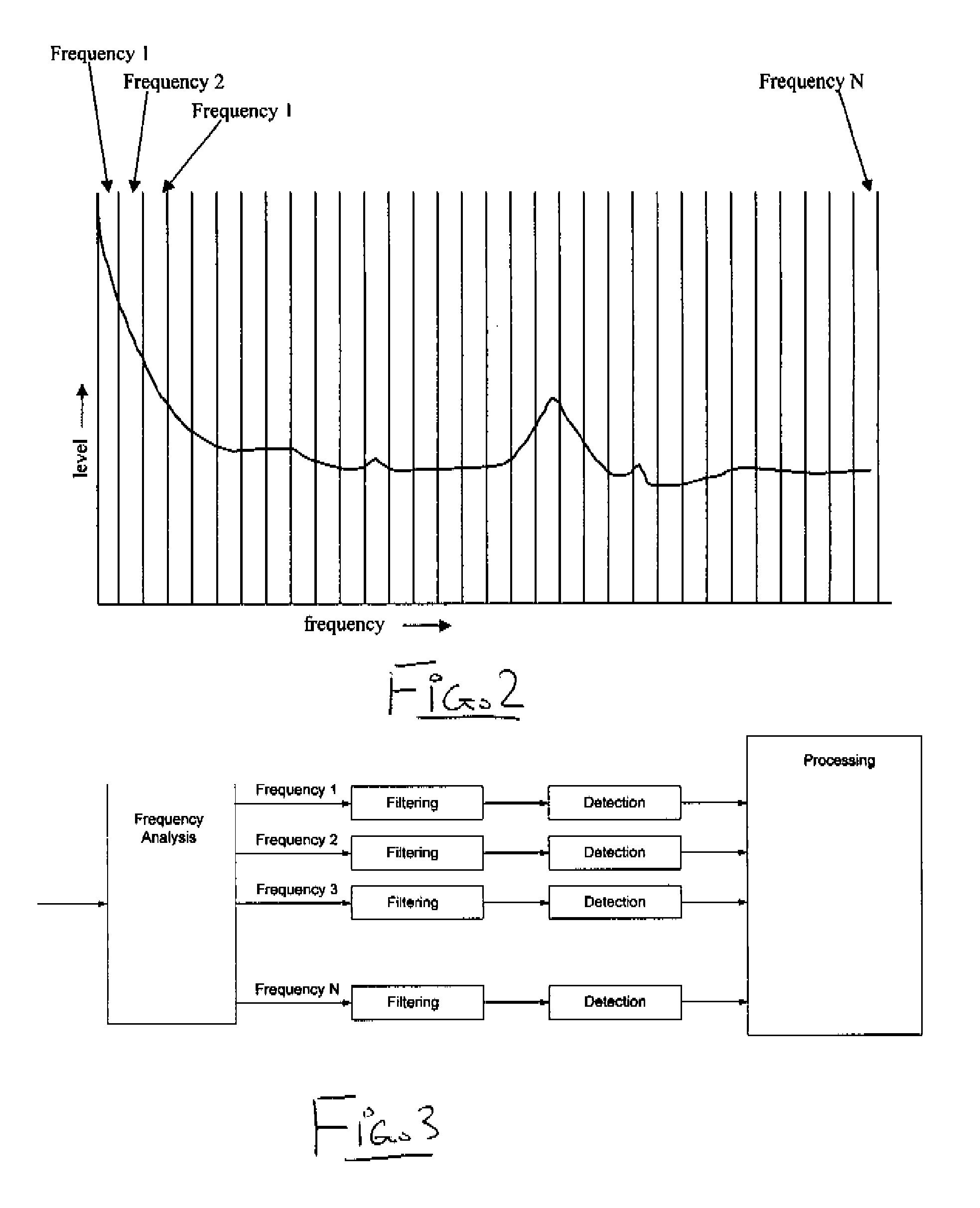
Frequency envelope detection method for signal analysis
A signal which varies over time is monitored to determine an alarm condition, where the sample stream of digital values from an A / D converter is divided in to equal length pieces and a Fourier Transform (FT) algorithm is used to transform each piece of the stream into a three dimensional dataset including frequency domain amplitude, frequency and time. A Frequency Envelope is calculated by taking the maxima over the time dimension for a period of time, leaving a two dimensional frequency domain amplitude vs frequency dataset which is compared with new data arriving to determine the alarm condition for each element of the Frequency Envelope either by applying a constant delta additively or multiplicatively or by using a “leaky bucket” algorithm.
Owner:NETWORK INTEGRITY SYST
Method and user device for triggering buffer area state report
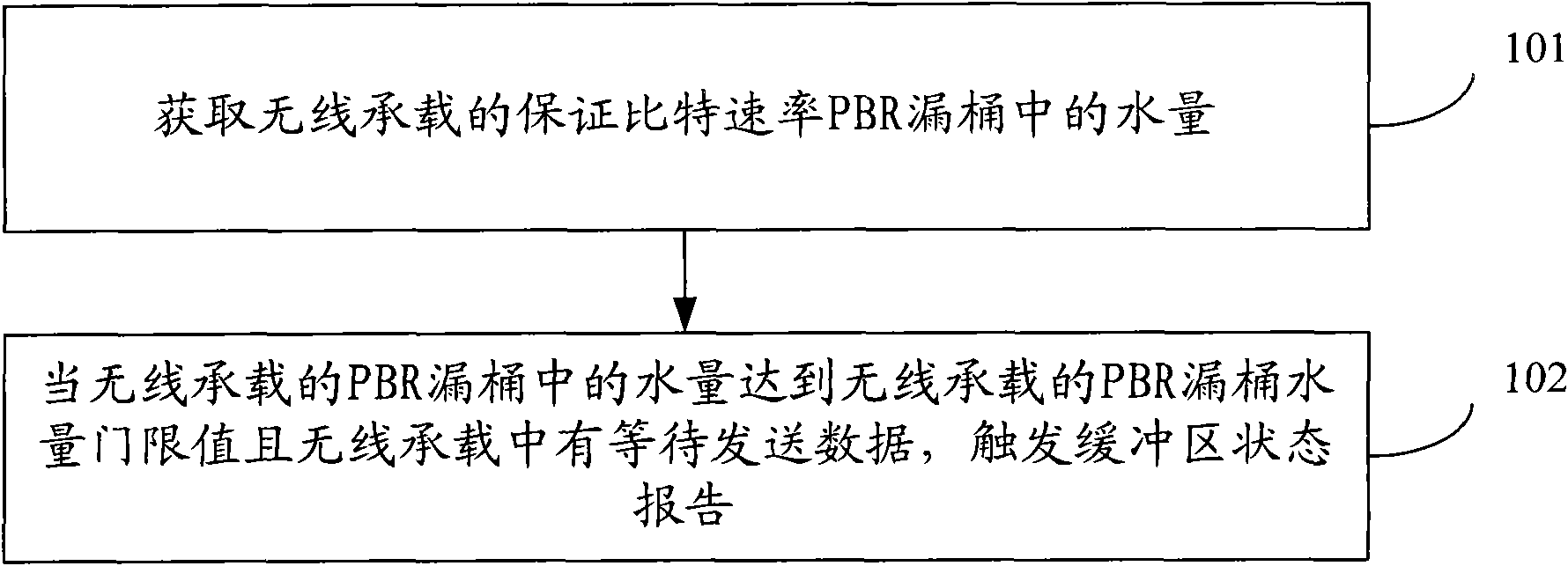
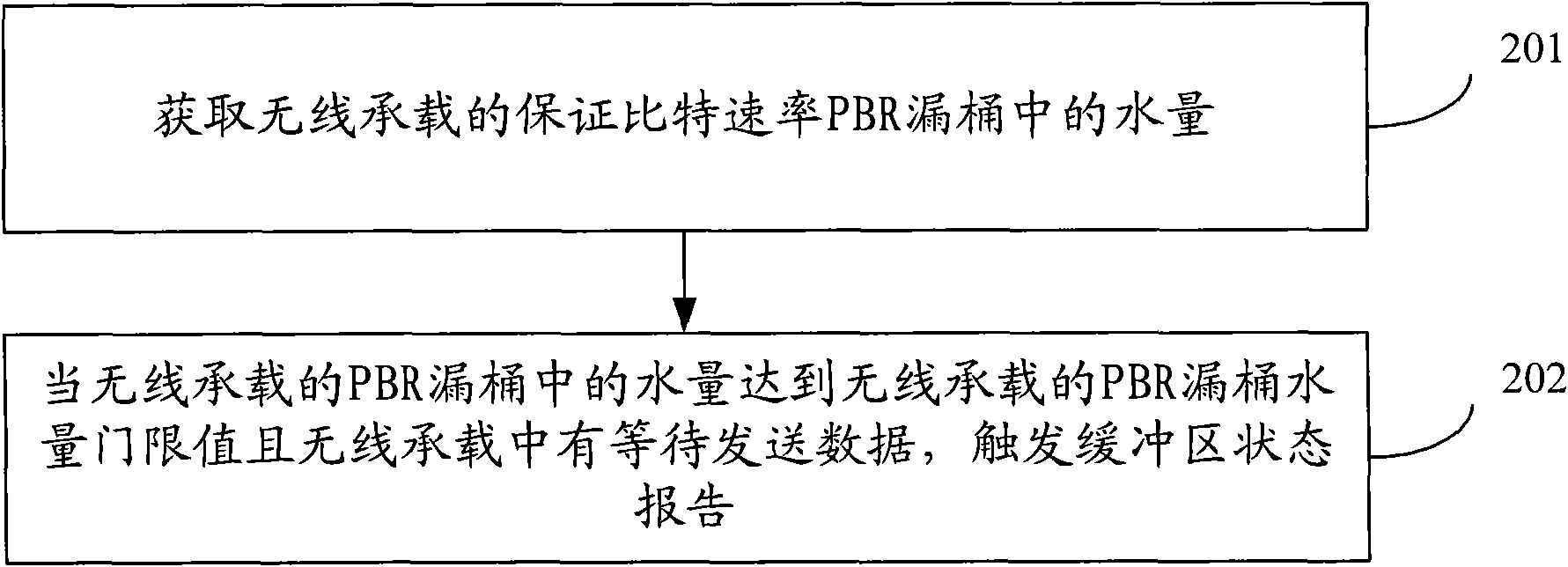
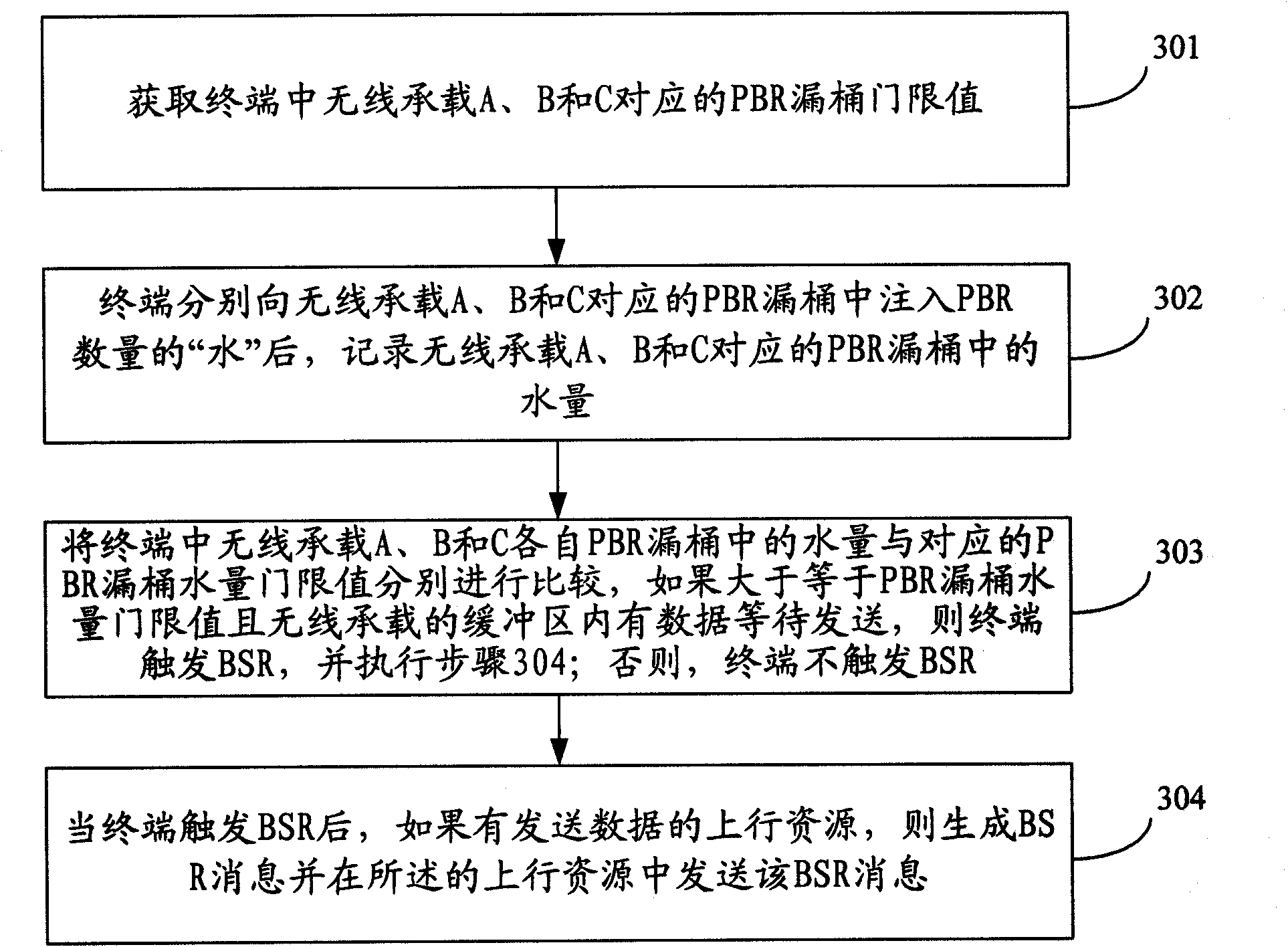
InactiveCN101772090AReduce overheadSolve the problem of hungerNetwork traffic/resource managementUplink schedulingUser equipment
The invention discloses a method and user device for triggering buffer area state report, belonging to the communication field. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining the water quantity for ensuring bit rate in PBR leaky bucket of radio bearer; and when the water quantity of PBR leaky bucket of radio bearer reaches the water quantity threshold of PBR leaky bucket of radio bearer and the radio bearer contains data to be sent, triggering the buffer area state report. The user device comprises an obtaining module and a triggering module. The method provided by the embodiment of the invention can timely trigger BSR, do not caused radio bearer resource starvation, reduce the cost used for sending BSR and provide efficient and fair buffer area state information needed by uplink scheduling so as to ensure the QoS requirements of various services.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Timestamp metering and rollover protection in a network device
A network device for processing data on a data network includes a plurality of ports, configured to receive data from a data network and to send processed data to the data network, a memory management unit configured store data on and retrieve data from the memory and a metering unit configured to police a flow of the processed data to be sent to the network device. The metering unit is configured to utilize a series of leaky bucket units, where tokens are added to each leaky bucket unit only when that particular leaky bucket unit is accessed. The metering unit is also configured to add the tokens based on a prior timestamp value, a current timing value and an established rate and a multiplication to establish the tokens is accomplished by shifting a register of the established rate.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and Apparatus for use in a communications network
InactiveUS20100118704A1Leakage rate therefore increaseReduce leak rateError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunications networkResponse delay
A method is provided of regulating a load placed on a first node of a telecommunications network caused by messages sent to the first node by a second node of the network according to a signalling protocol between the first node and the second node, comprising: using a leaky bucket restrictor associated with the second node to regulate the load, the leaky bucket having an adjustable leak rate; determining a roundtrip response delay relating to at least some of the messages during a measurement period; and adjusting the leak rate in dependence upon the determined response delay.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
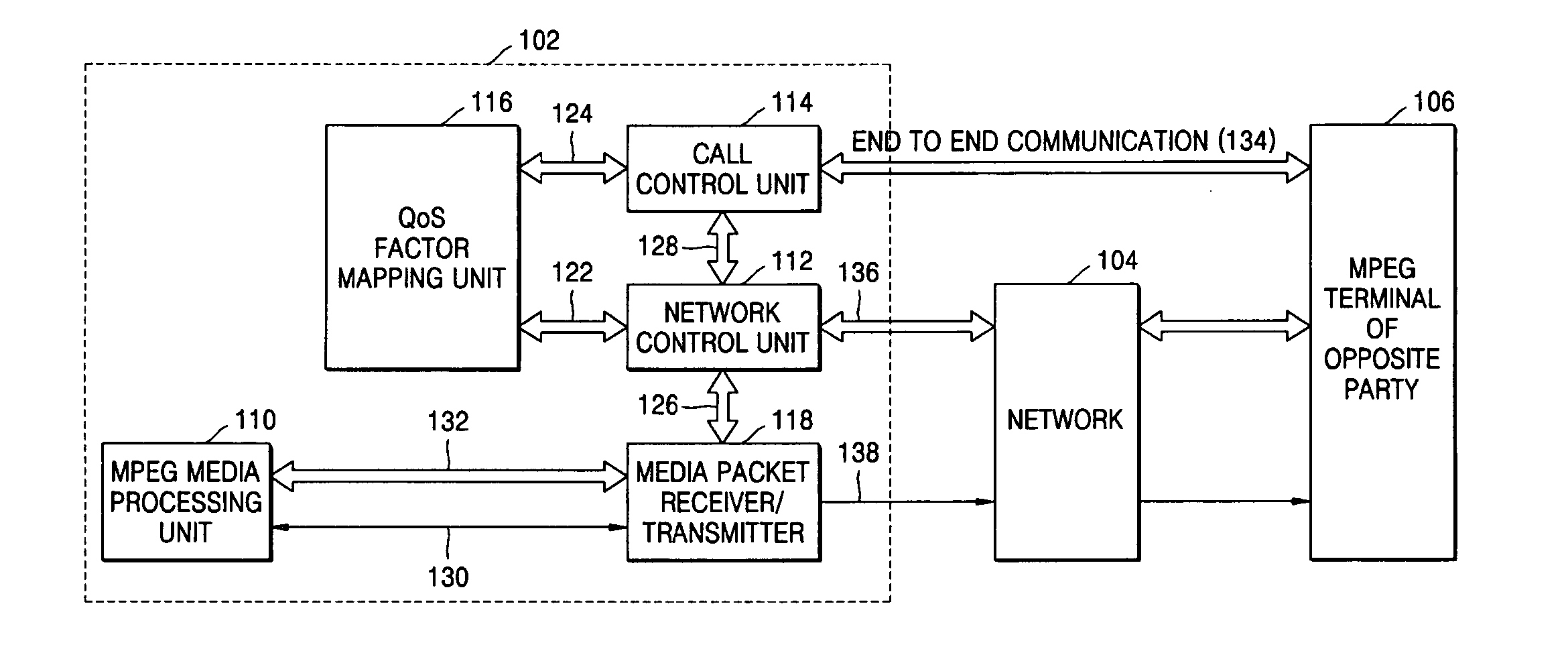
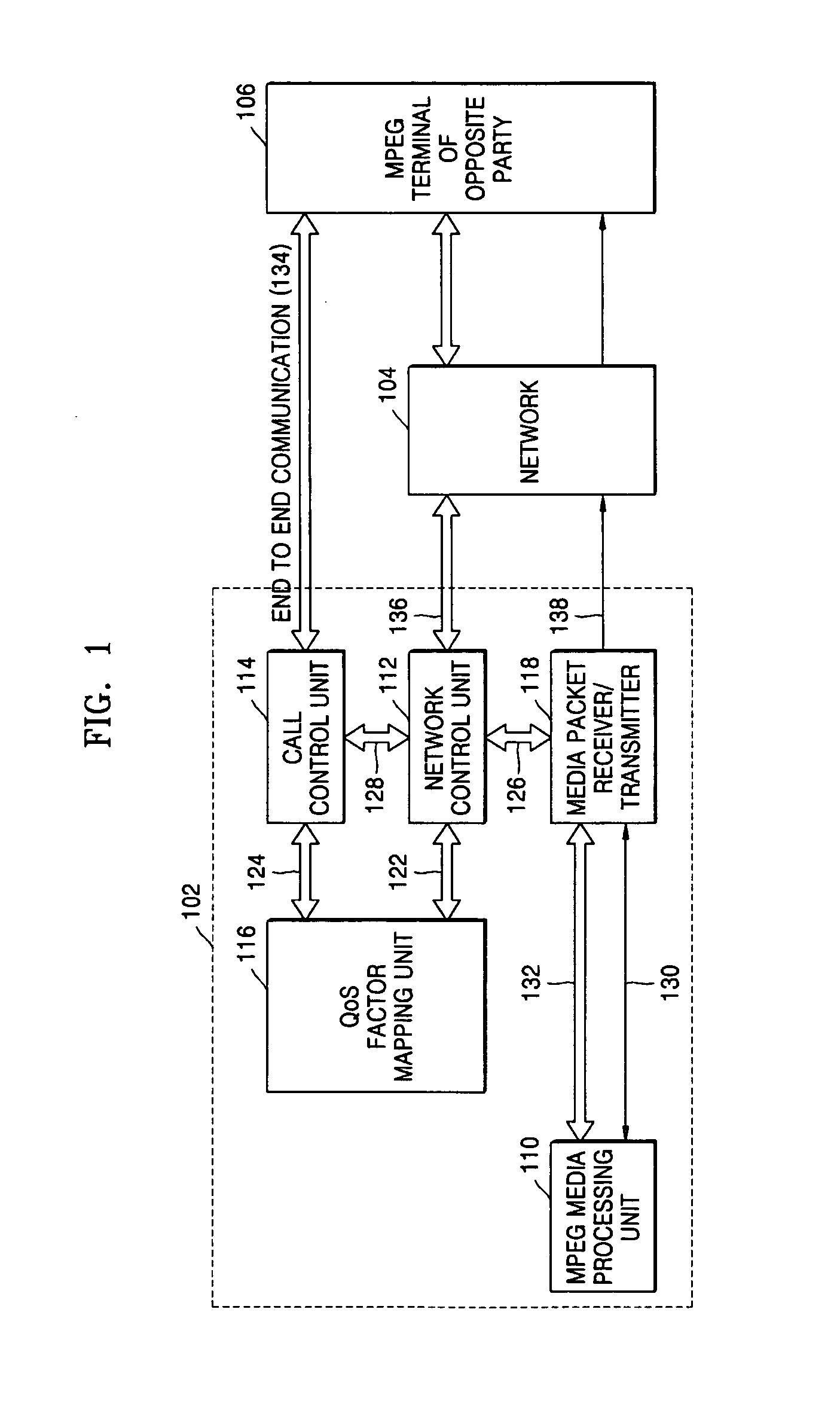
Method and device for delivering multimedia data using IETF QoS protocols
InactiveUS7450514B2Guaranteed normal transmissionData efficientPulse modulation television signal transmissionError preventionTransmission protocolReal-time computing
A method and device for delivering multimedia data using IETF QoS protocols. MPEG media data can be transmitted in packet units through a network using the IETF QoS protocol by mapping MPEG media traffic factors onto IETF QoS traffic factors. By encoding or transcoding MPEG media traffic according to a double leaky bucket model indicated by the four factors, a maximum bit rate, a first buffer size, a guaranteed bit rate, and a second buffer size, the MPEG media traffic factors may be transmitted using the IETF QoS protocol without having to go through the process of being mapped onto QoS traffic factors.
Owner:UNIV IND COOP GRP OF KYUNG HEE UNIV +1
Providing a high-speed defense against distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks
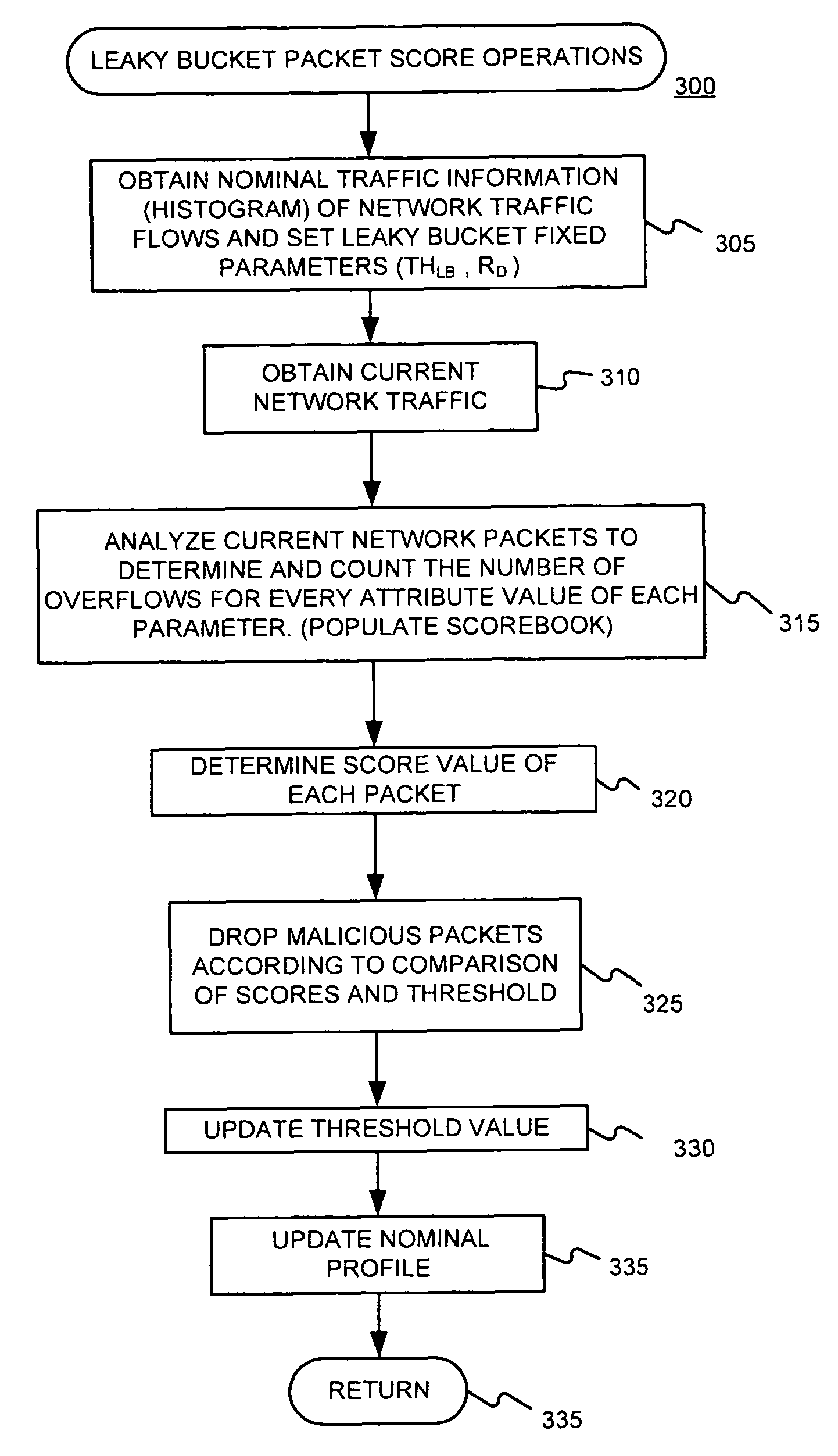
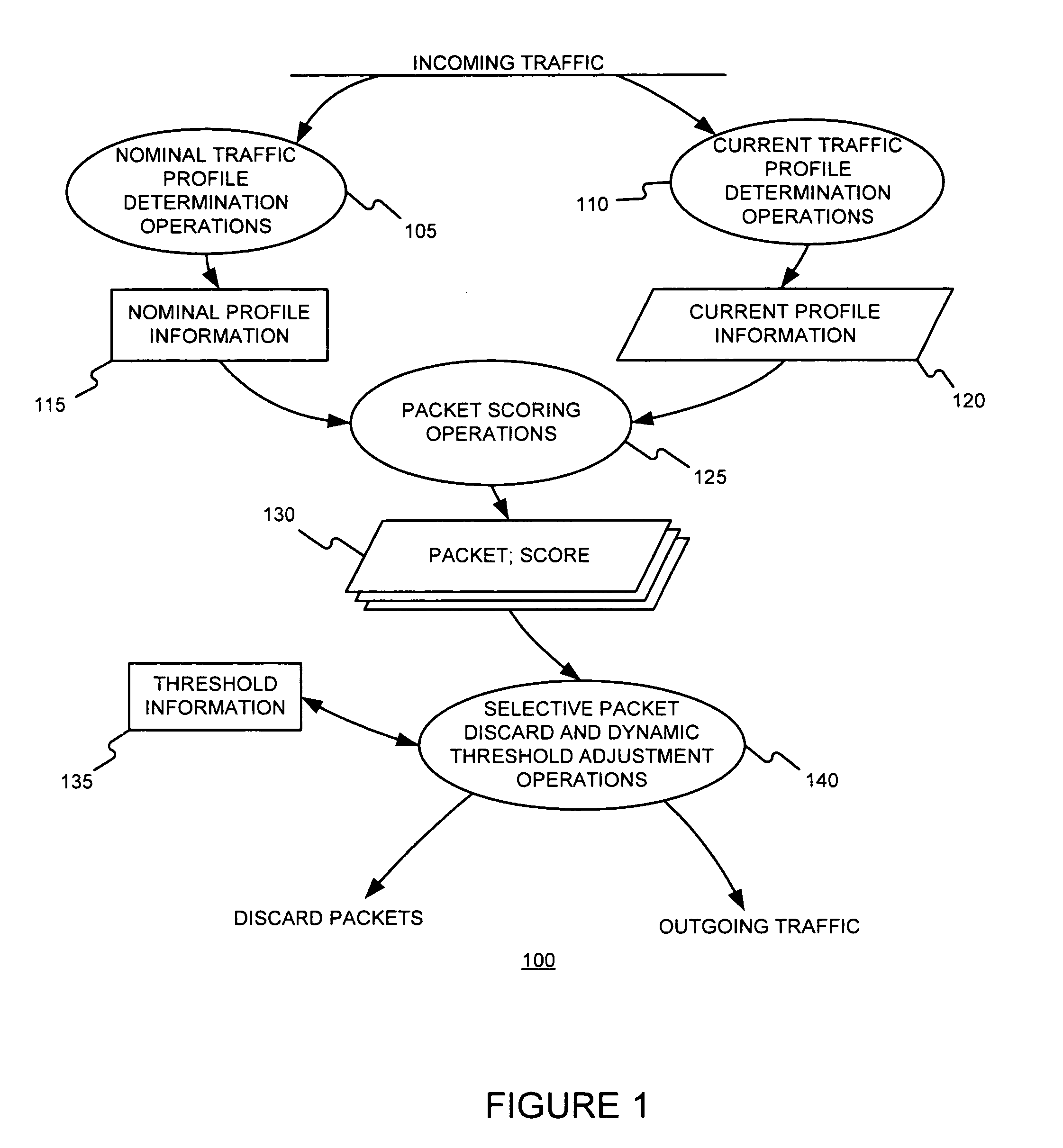
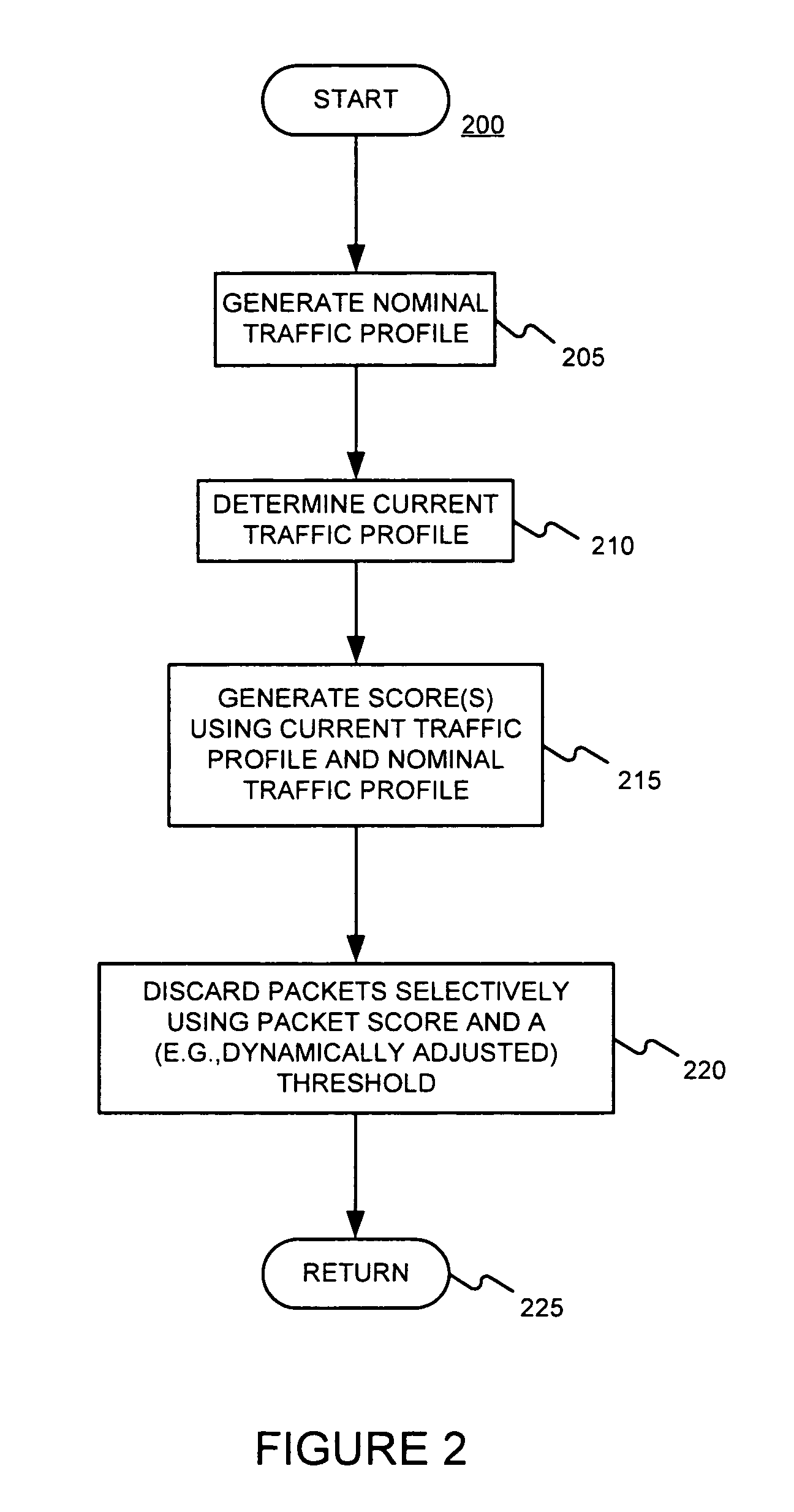
Effective control of communications traffic, even under fast-changing DDoS attacks, might be performed by (a) determining parameters of a leaky bucket using nominal communications traffic, (b) applying current communications traffic to the leaky bucket, (c) observing overflows, if any, of the leaky bucket, (d) scoring the current traffic based on the observed overflows, and (e) passing or dropping traffic based on the score. Alternatively, such control might be performed by (a) determining average mean and variance of each of one or more attribute values of nominal communications traffic, (b) determining a mean of each of the one or more attribute values of current communications traffic, (c) determining a probability that for each of the one or more attributes, its current mean value deviates more from its average mean that its current attribute value, (d) scoring the current traffic based on the determined probability or probabilities, and (e) passing or dropping traffic based on the score.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for policing connections using a leaky bucket algorithm with token bucket queuing
InactiveUS20070147404A1Data switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsDistributed computingShared memory
The invention includes a method and apparatus for performing packet policing by operating an input queue as a leaky bucket queue. The method includes storing a received packet in a shared memory shared by a plurality of input queues and a plurality of output queues, storing a corresponding packet pointer for the packet in one of the plurality of input queues, transferring the packet pointer from the one of the plurality of input queues to one of the plurality of output queues associated with an output port to which the packet is assigned, and transmitting the packet from the output port using the packet pointer. The packet pointer identifies a storage location in the shared memory. The packet pointer is removed from the one of the plurality of output queues and used for retrieving the packet from the shared memory.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Rate limiting and minimum and maximum shaping in a network device
ActiveUS8320240B2Special service provision for substationError preventionRate limitingProcess information
A network device for scheduling packets in a plurality of queues includes a plurality of leaky bucket modules, each of the plurality of leaky bucket mechanisms being associated with one of a plurality of queues and configured to process information based on a predefined bandwidth, a scheduler configured to schedule services of the plurality of queues and a metering module for tracking whether or not the plurality of queues has exceeded a predefined threshold through the leaky bucket modules. If the plurality of queues has exceeded the predefined threshold, the metering module is configured to compute a new bandwidth allocation for each of the plurality of queues, the new bandwidth allocation replacing the predefined bandwidth and being proportional to the predefined bandwidth for each of the plurality of queues.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com