Molecular marker for controlling corn plant height and applications thereof
A molecular marker and corn technology, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering, can solve problems such as plant dwarfing, discomfort, and the impact of yield and agronomic traits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1: Fine positioning of qPH3.1
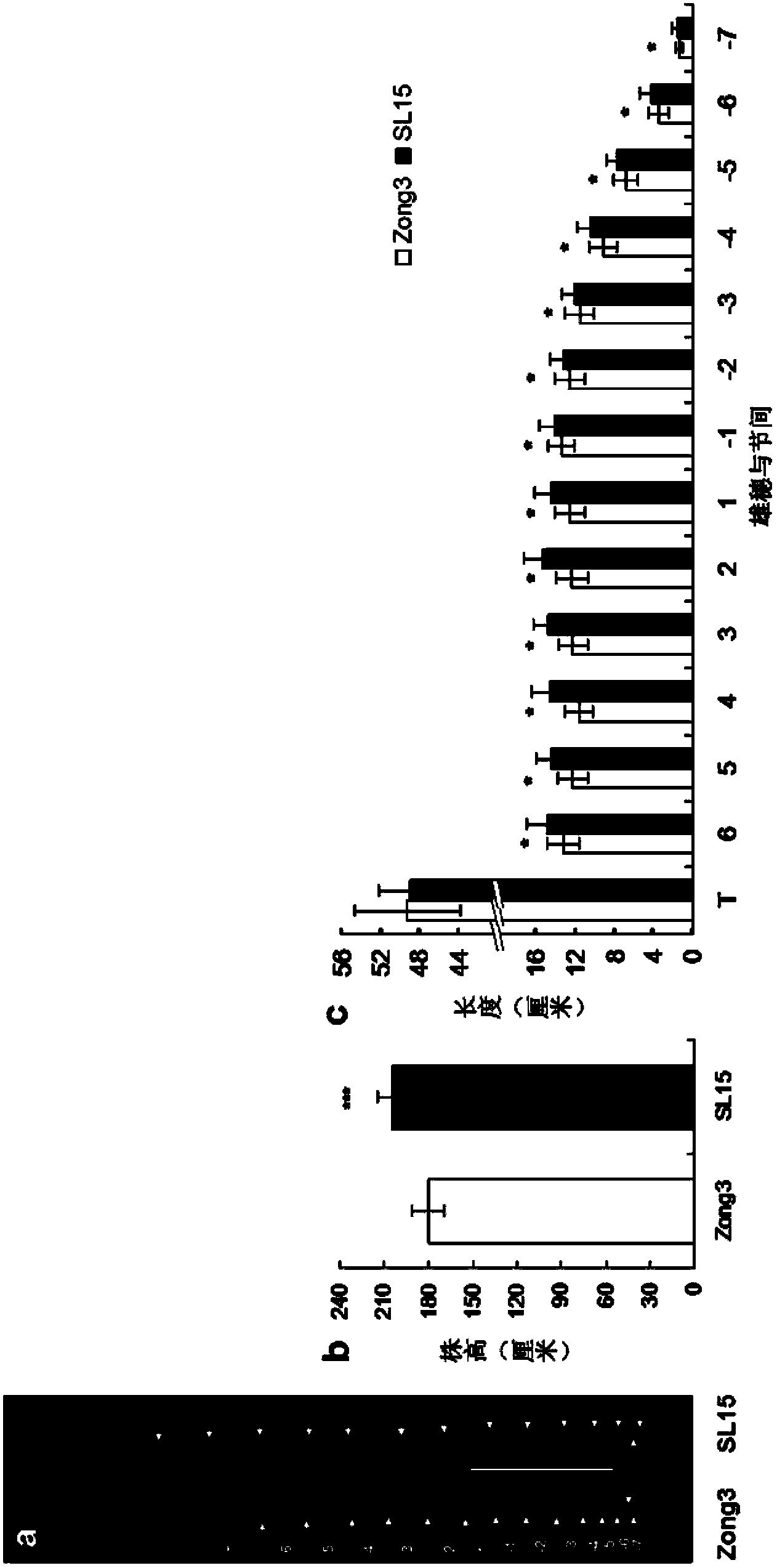
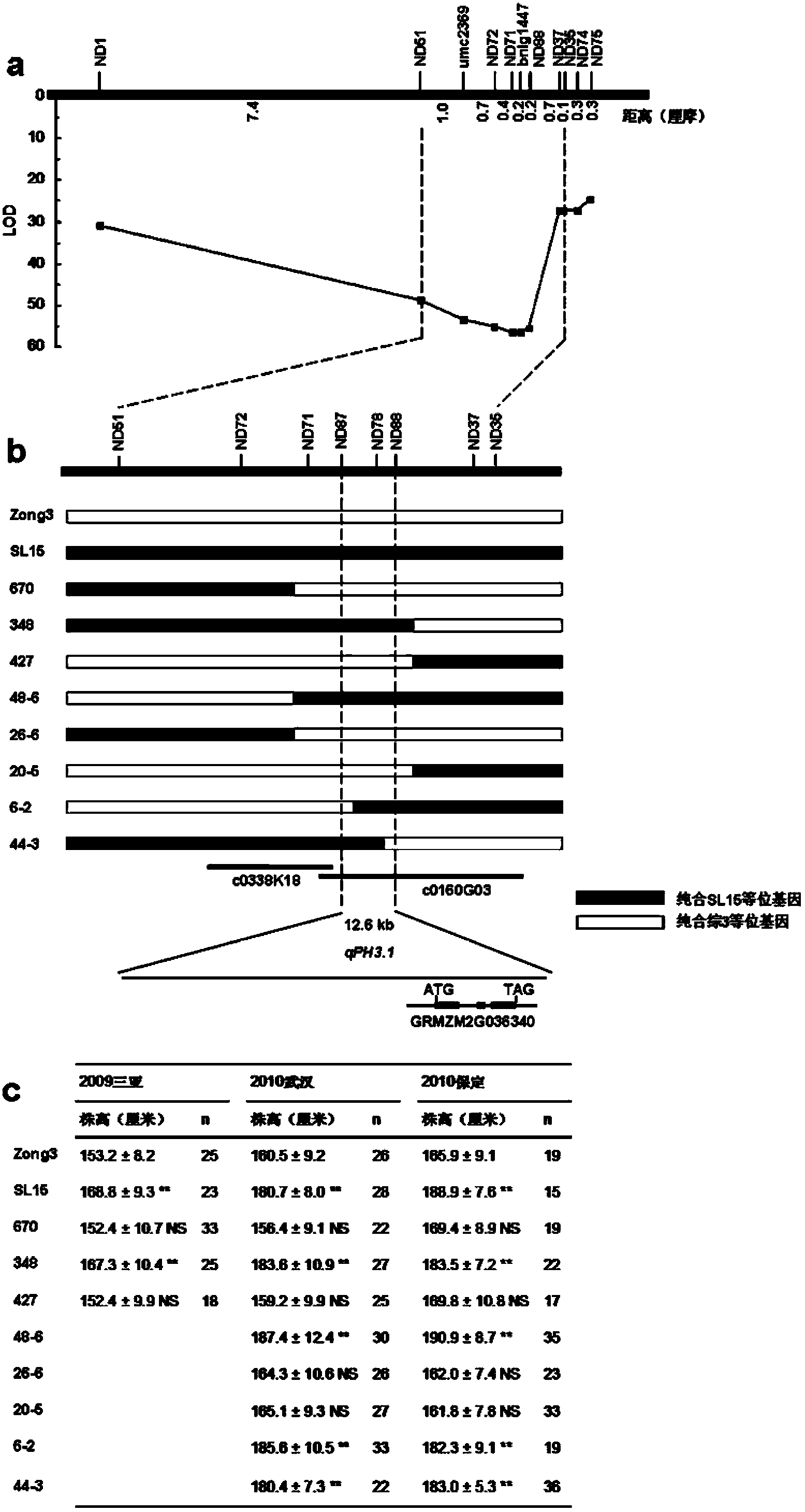
[0026] (1) Genetic composition of SL15 (HB522) and its phenotypic differences with Zong 3
[0027] SL15 (HB522, from the National Crop Germplasm Center) and Zong 3 (from the National Crop Germplasm Center) are the parental materials used in this experiment for the preparation of QTL mapping populations. SL15 is a chromosome segment substitution line, its main genetic background comes from Zong 3, and there is a difference between the chromosome segment near the umc2369 marker of chromosome 3 and Zong 3, and the imported fragment comes from HB522 (National Crop Germplasm Conservation Center germplasm bank). Applicants used 245 SSR markers evenly distributed across the genome to evaluate genetic differences between SL15 and Zong3. The results showed that the two sides of the imported fragment in SL15 could be preliminarily defined between bnlg1647~bnlg1447. In order to more accurately define the positions of both ends of the impo...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Example 2: Amplification and sequence analysis of candidate genes
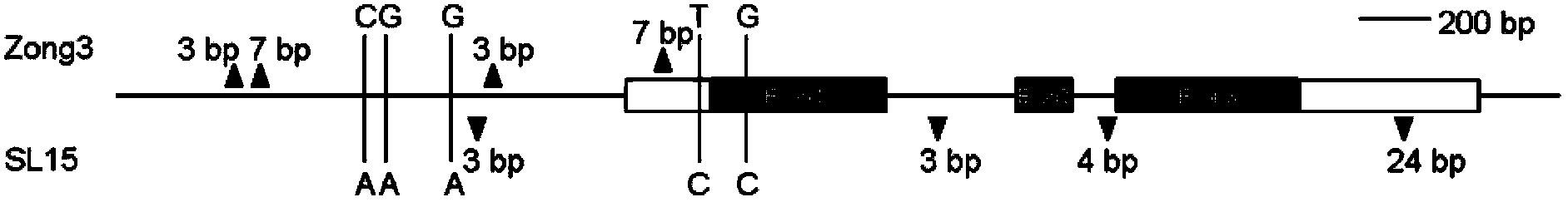
[0045] The complete coding sequence of the candidate gene (ZmGA3ox2), including genomic DNA and cDNA, was amplified from Zong3 and SL15 using primers 4046F and 6276R (see Table 4). The cDNA was amplified using the reverse transcription product of shoot apex RNA at the jointing stage as a template. PCR amplification uses high-fidelity LA Taq enzyme and GC Buffer II (purchased from Treasure Bioengineering Dalian Co., Ltd.). Primers 6107F and 7762R were used to amplify the sequence approximately 1.6 kb upstream of the ZmGA3ox2 start codon (ATG). Taq enzyme from Fermentas Company (product number: EP0621) was used for PCR amplification. Using the shoot tip RNA of the inbred line B73 ((Stock center USA), the RACE (Rapid-Amplification of cDNA Ends) technique was used to amplify the 5′ and 3′ ends of the candidate gene transcripts. RACE The kit used for amplification was the FirstChoice RLM-RACE kit (purchas...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Example 3: dwarf-1 gene encodes ZmGA3ox2
[0049] d1-6016 homozygous plants showed extreme dwarf phenotype at the seedling stage ( Figure 4 a). First, the applicant used primers 4046F and 7762R (see Table 4) to amplify the full-length ZmGA3ox2 gene of the d1-6016 homozygote. The expected size of the PCR product is approximately 3.7 kb in wild-type maize plants ( Figure 4 b), the positions of the primers on the ZmGA3ox2 gene are shown in Figure 4 c. PCR amplification found that only one band less than 2kb was obtained in the d1-6016 homozygote ( Figure 4 b), it is speculated that there may be a large fragment deletion in the gene. The amplified band was recovered and sequenced and analyzed. Compared with the B73 genome sequence, there was a 2304bp fragment deletion in the ZmGA3ox2 gene of d1-6016, including the 734bp upstream sequence of the start codon and the 1570bp coding region, and the loss of the core start subregion and almost the entire coding region, l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com