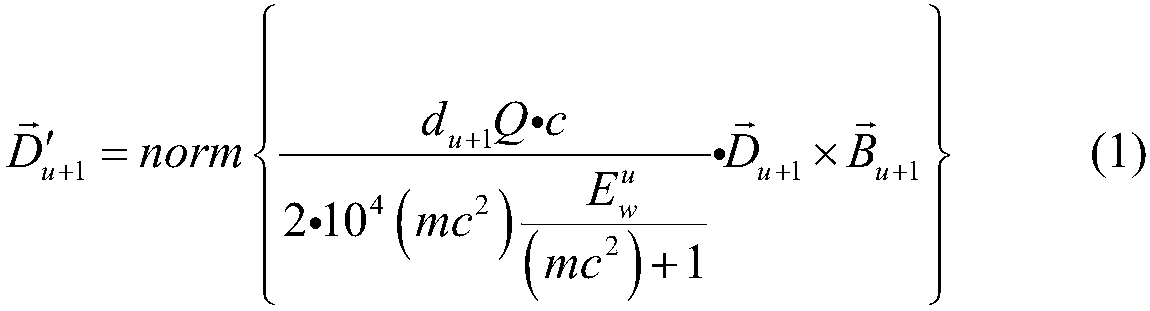Patents
Literature
37 results about "Heavy ion radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
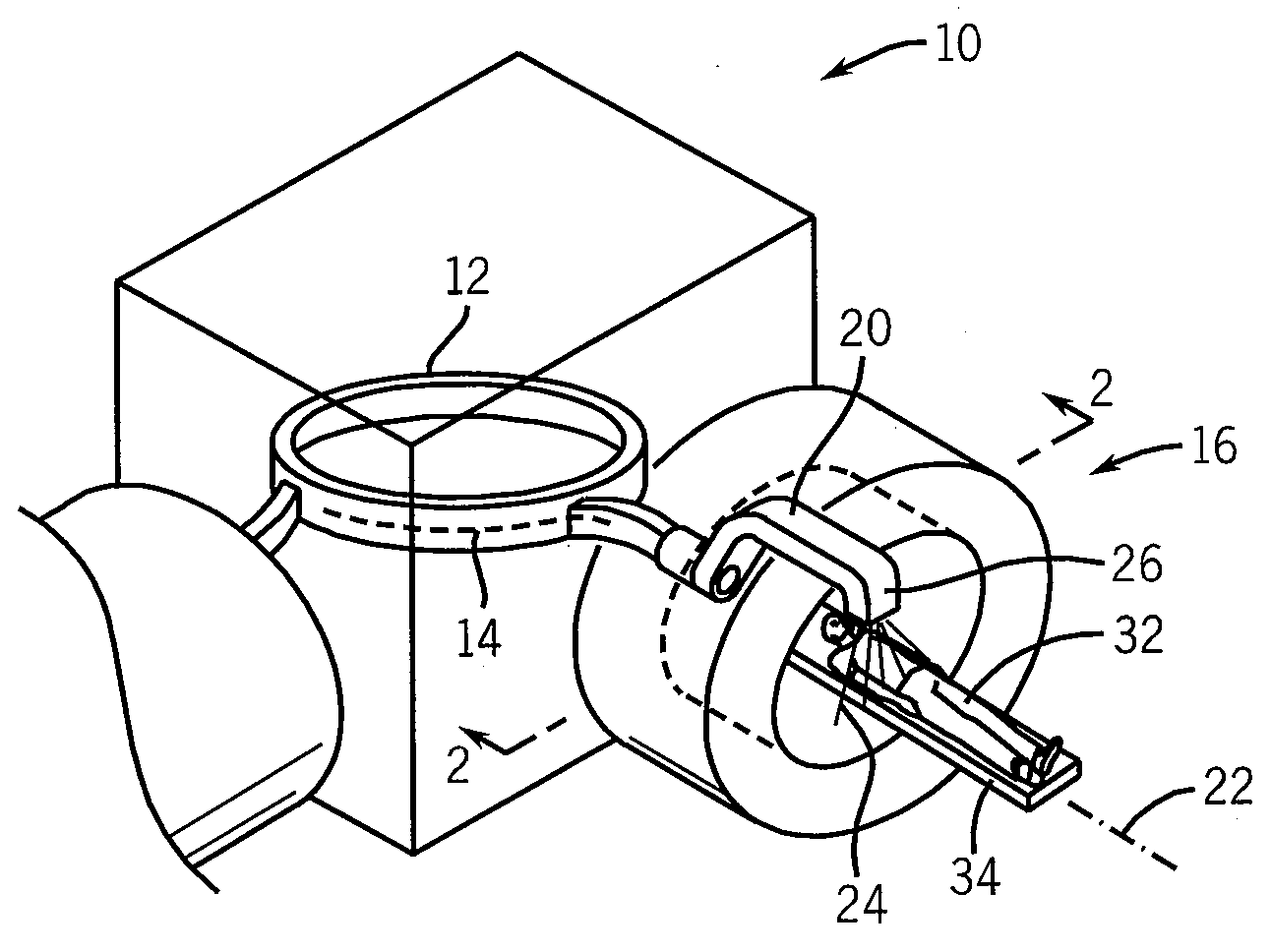
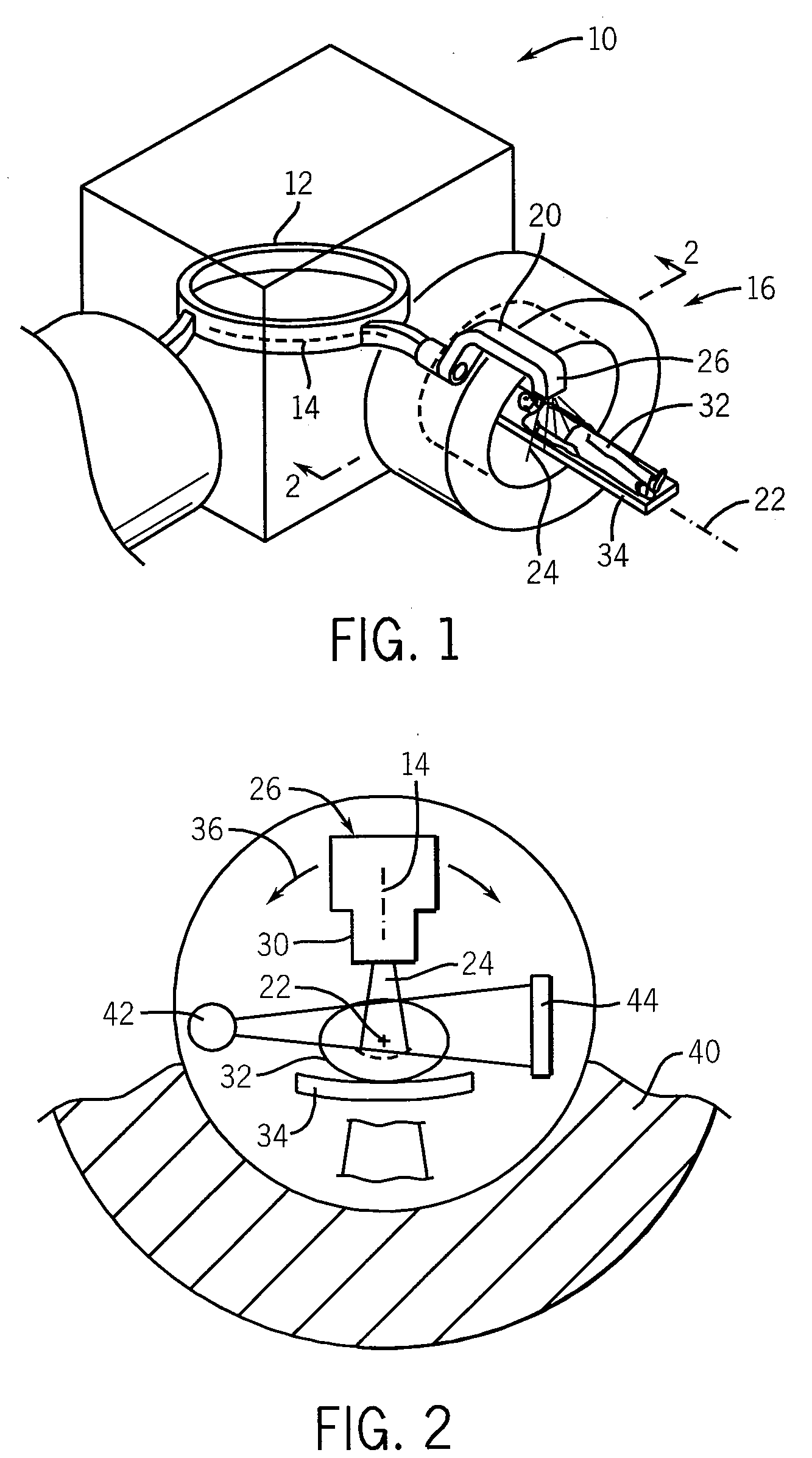
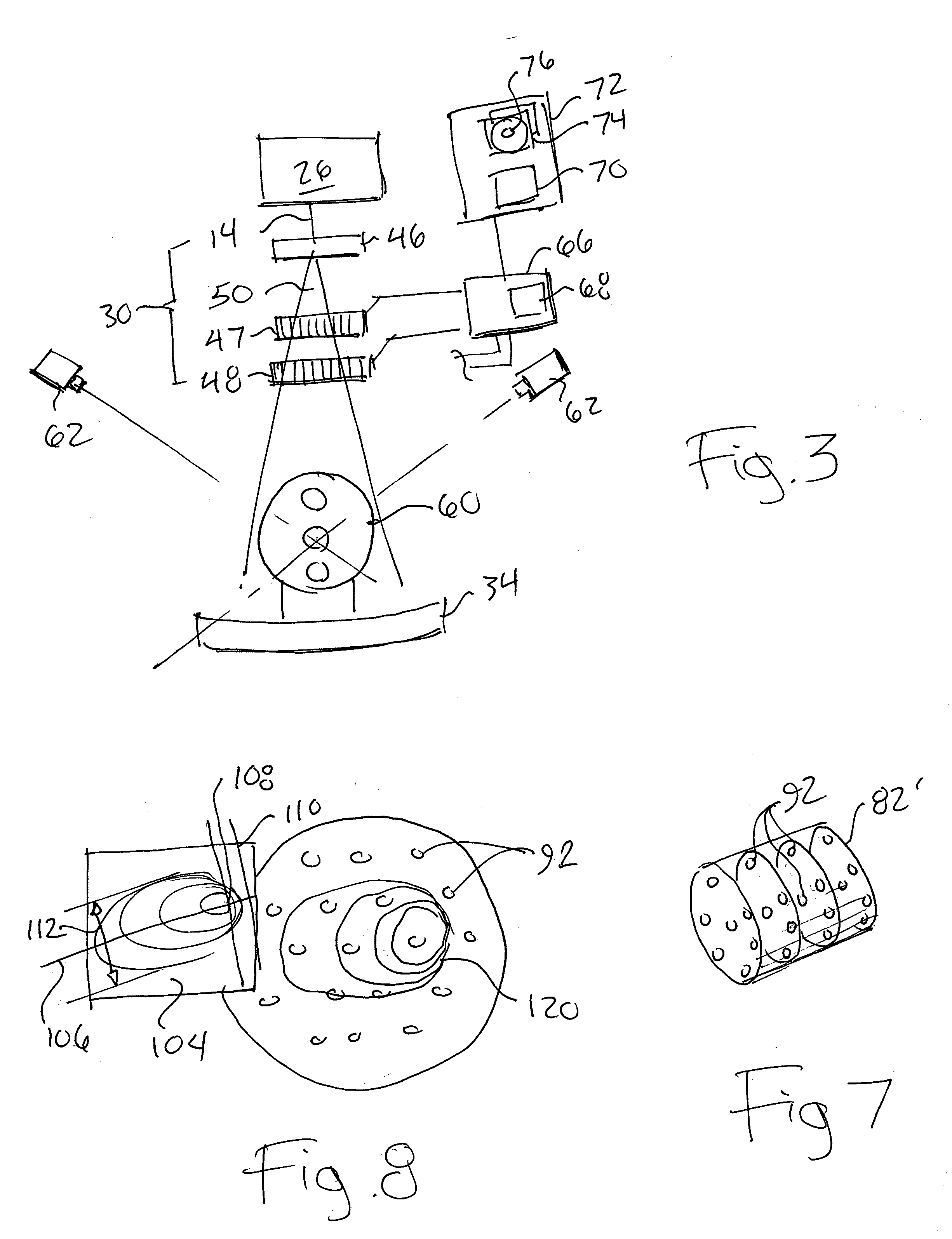
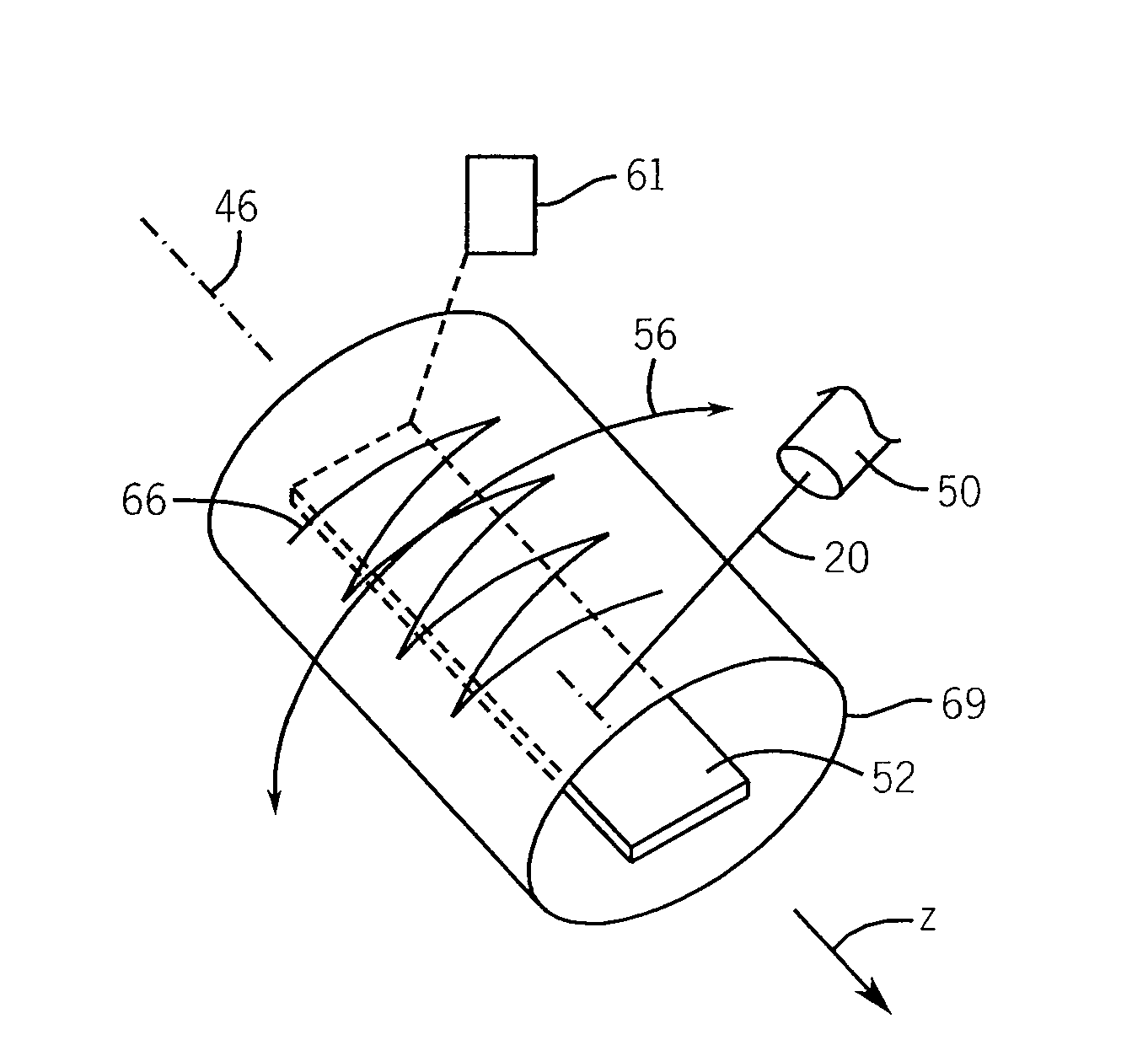
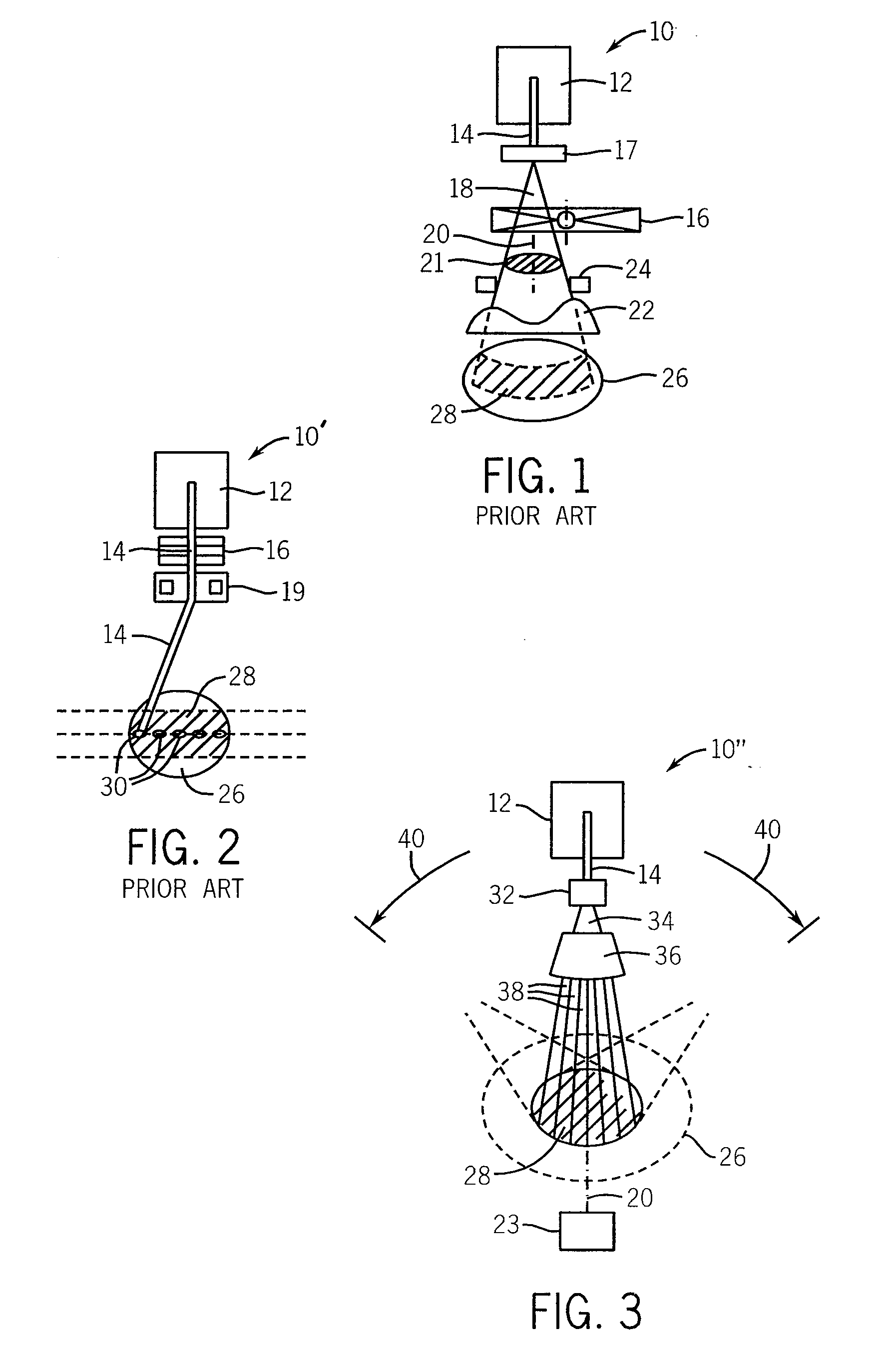
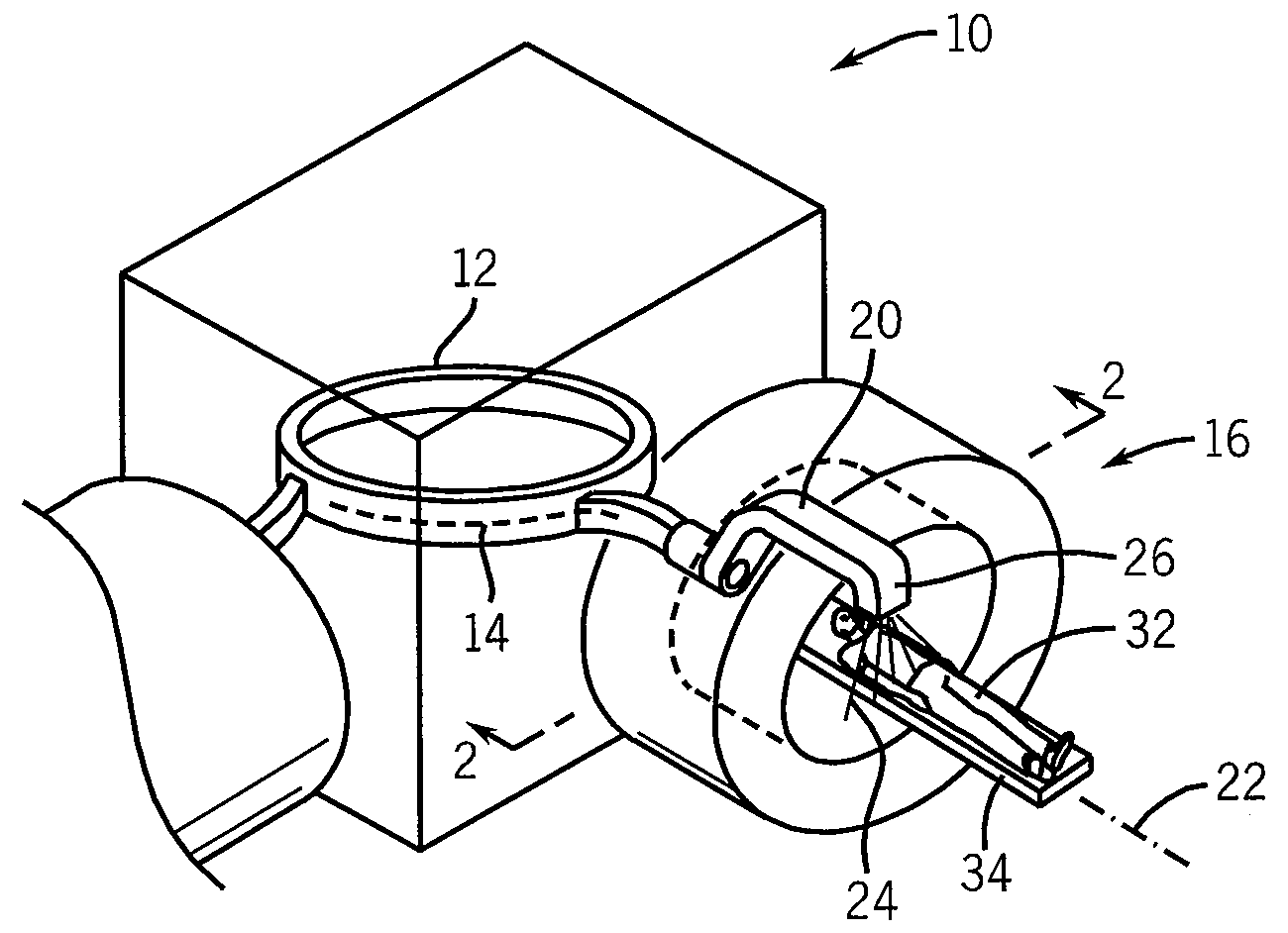
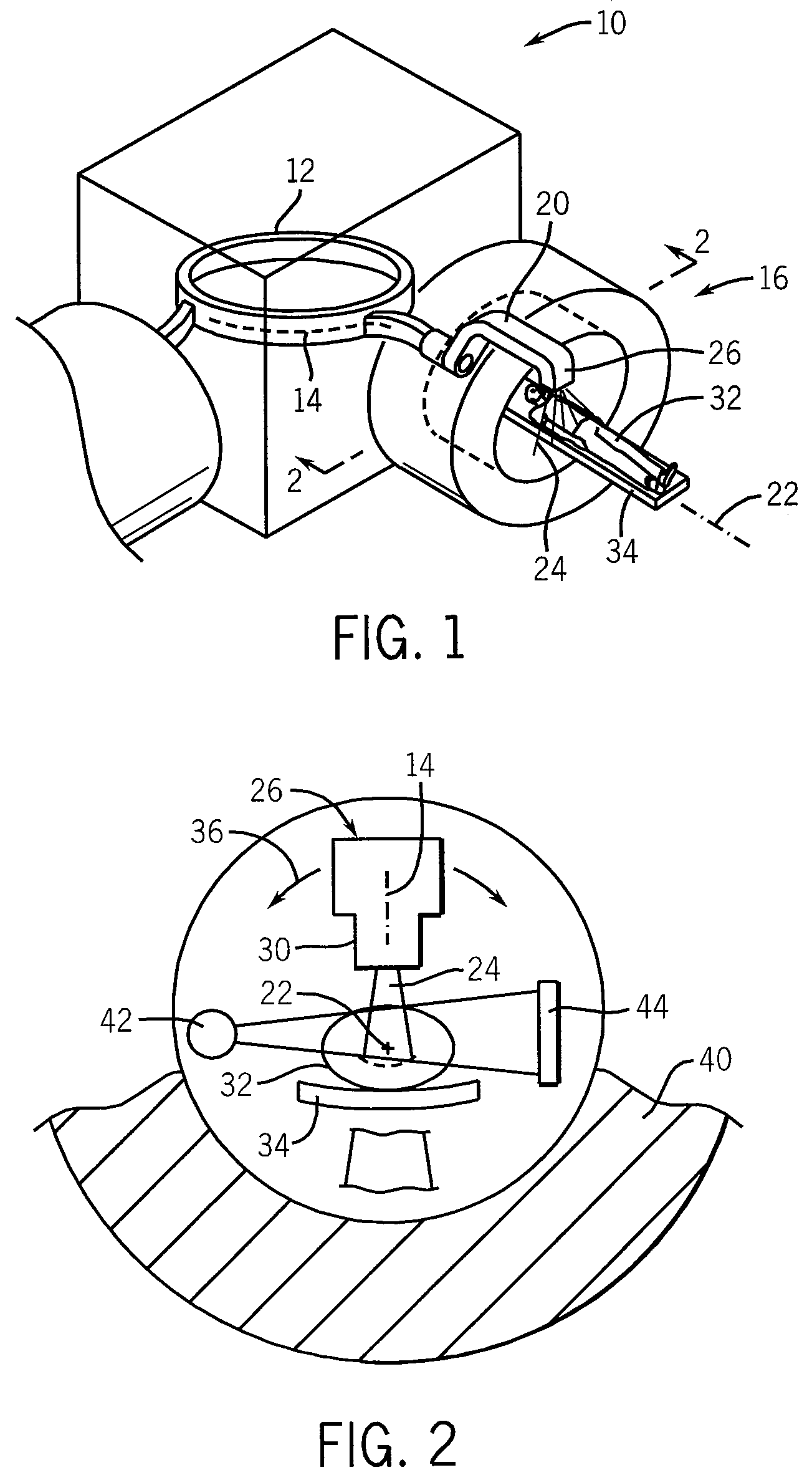
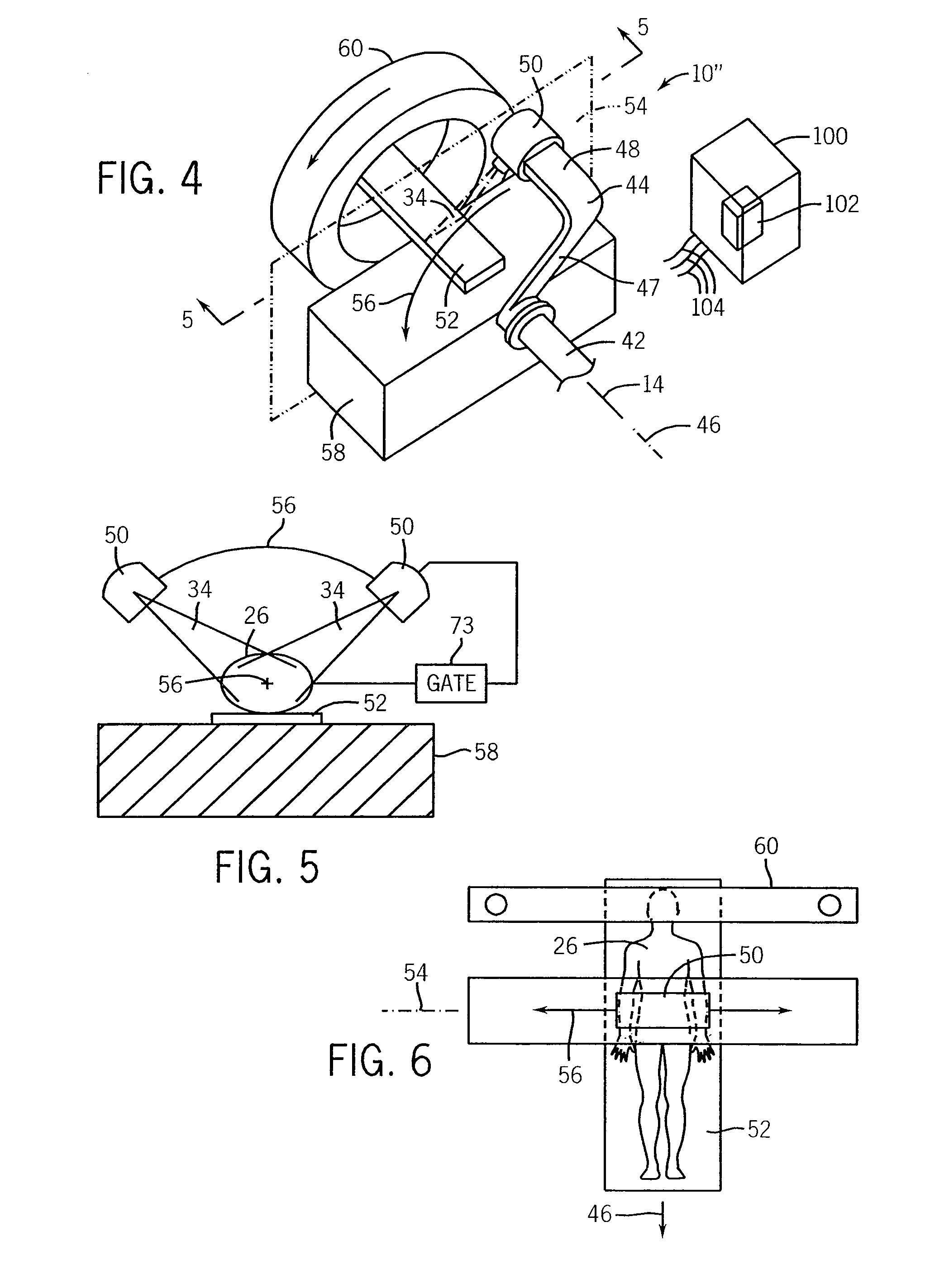
Phantom for ion range detection
ActiveUS20080217561A1Accurate representationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotometryBragg peakHeavy ion radiation
A phantom for heavy ion radiation therapy provides characterization of an ion beam that may enter but not exit from the phantom. The phantom may include multiple materials and multiple spatially dispersed ion detectors to obtain signals that may be fit to known beam curves to accurately characterize the location and other parameters of Bragg peak of a given ion beam within a patient.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
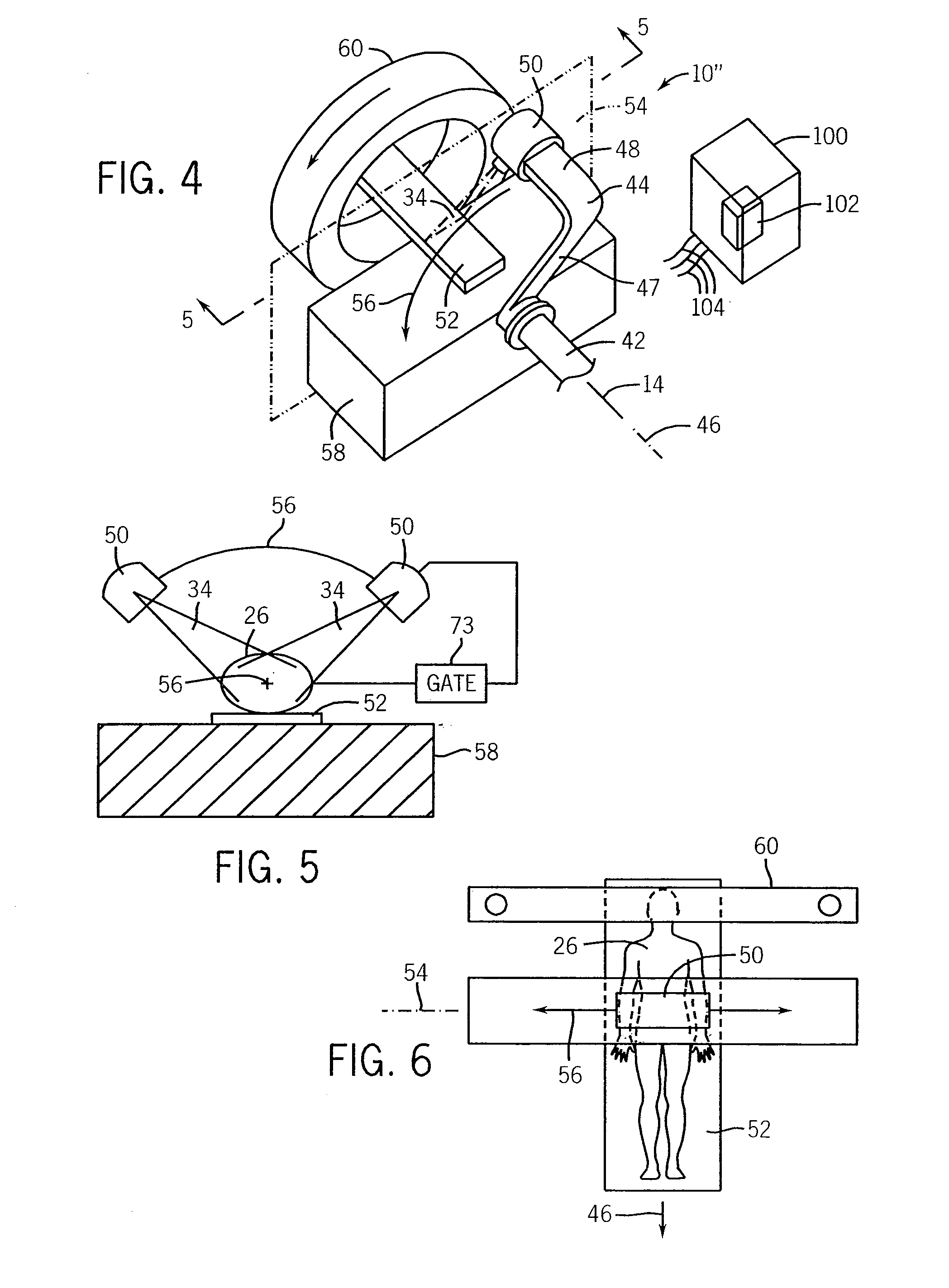
Heavy ion radiation therapy system with stair-step modulation
ActiveUS20090212231A1Reduce intensityHigh-speed and precise controlStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsHeavy ion radiationLight beam
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
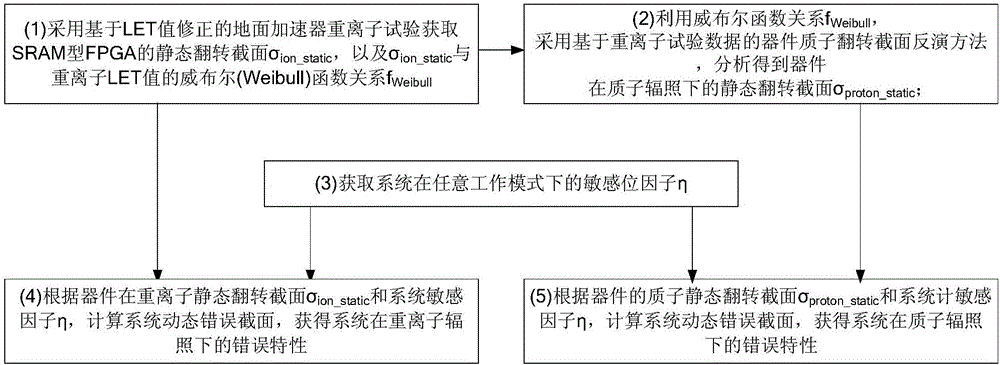
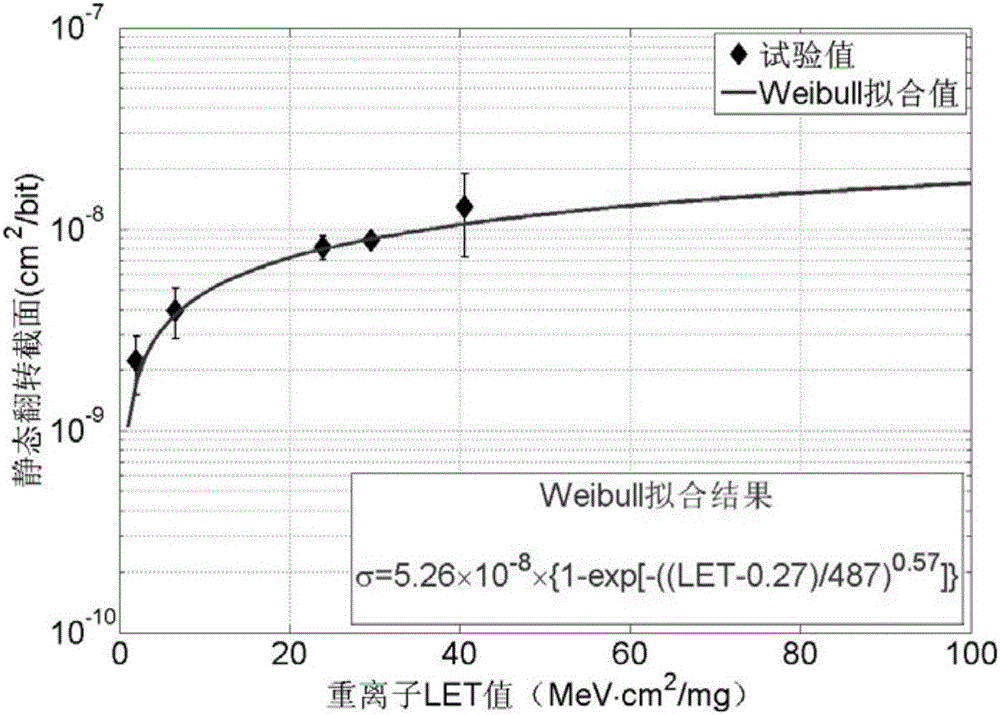
Method for verifying single particle soft error protection design based on heavy ion accelerator
ActiveCN105866573AReduced need for testingReduce design and development costsElectrical testingHeavy ion radiationHeavy ion irradiation
The invention discloses a method for verifying a single particle soft error protection design based on a heavy ion accelerator, and relates to the field of heavy ion and proton equivalent test verification of system single particle protection effect verification based on accelerator test data. The method includes the following steps: (1) adopting a ground accelerator heavy ion test which is determined on the basis of a LET value; (2) analyzing a proton static overturning cross section; (3) analyzing a sensitive bit factor of the system under any working mode; (4) analyzing a dynamic overturning cross section of the system under heavy ion radiation; (5) analyzing a dynamic overturning cross section of the system under proton radiation. The invention provides a method for verifying a single particle soft error protection design based on the heavy ion accelerator. The method can be intended for verifying single particle protection effects, and address the problems of tight time of domestic accelerators and difficulty in realizing high energy proton tests.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
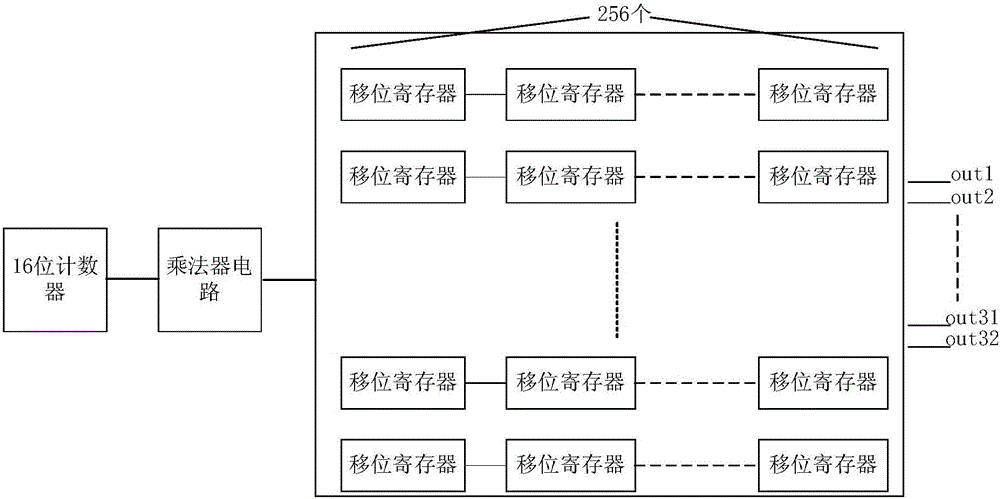
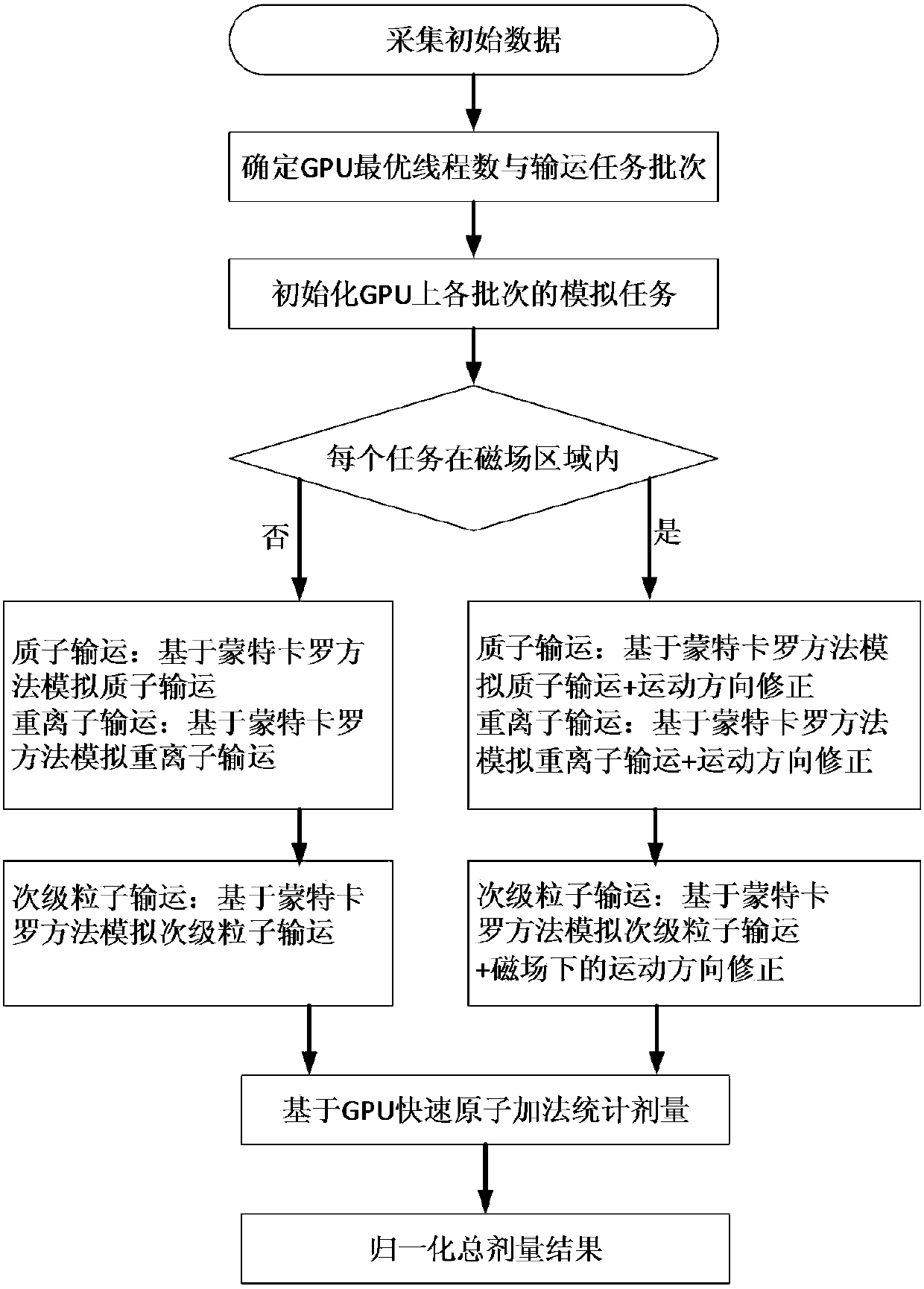
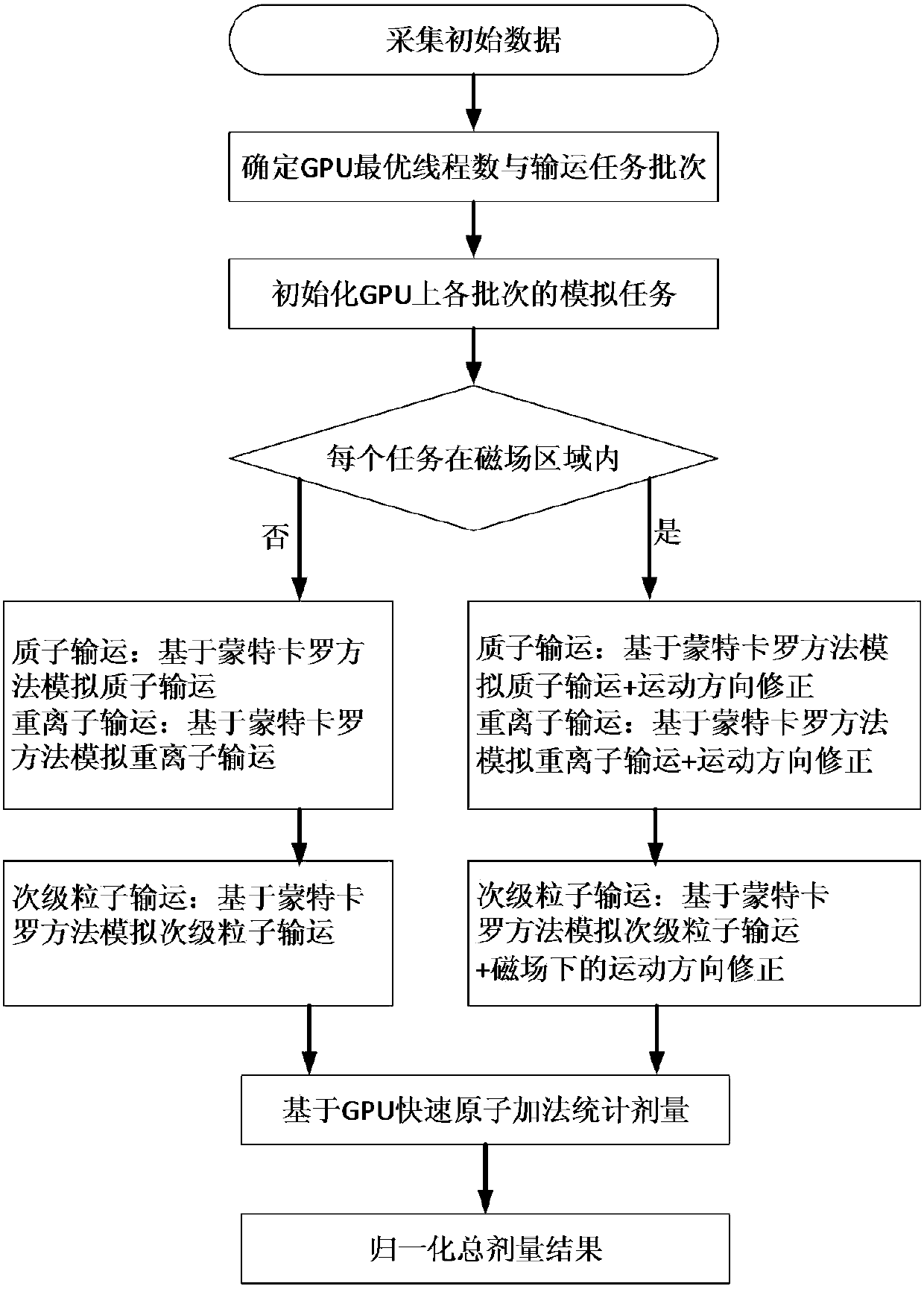
Proton and heavy ion dose calculation method under magnetic field based on GPU Monte-Carlo method
ActiveCN107050667AImprove the outcome of radiation therapyImprove inherent defectsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTreatment effectHeavy ion radiation
The invention discloses a proton and heavy ion dose calculation method under a magnetic field based on a GPU Monte-Carlo method. The method comprises the following steps: 1) collecting data; 2) determining an optimal thread count and transport task batches of a GPU; 3) calculating proton and heavy ion radiation dose of each batch under the magnetic field by utilizing the Monte-Carlo method; 4) calculating radiation dose of secondary particles of each batch under the magnetic field by utilizing the Monte-Carlo method; and 5) summarizing dose results based on a GPU fast atom addition method. The method can quickly and accurately calculate the proton and heavy ion radiation dose under the action of the magnetic field, and can be used for dose calculation of an MRI real-time guided proton and heavy ion treatment planning system, thereby improving accuracy and speed of dose calculation in the treatment planning system, and improving radiation treatment effect.
Owner:安徽慧软科技有限公司
Phantom for ion range detection
ActiveUS7714309B2Accurate representationElectrode and associated part arrangementsSolid-state devicesBragg peakHeavy ion radiation
A phantom for heavy ion radiation therapy provides characterization of an ion beam that may enter but not exit from the phantom. The phantom may include multiple materials and multiple spatially dispersed ion detectors to obtain signals that may be fit to known beam curves to accurately characterize the location and other parameters of Bragg peak of a given ion beam within a patient.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
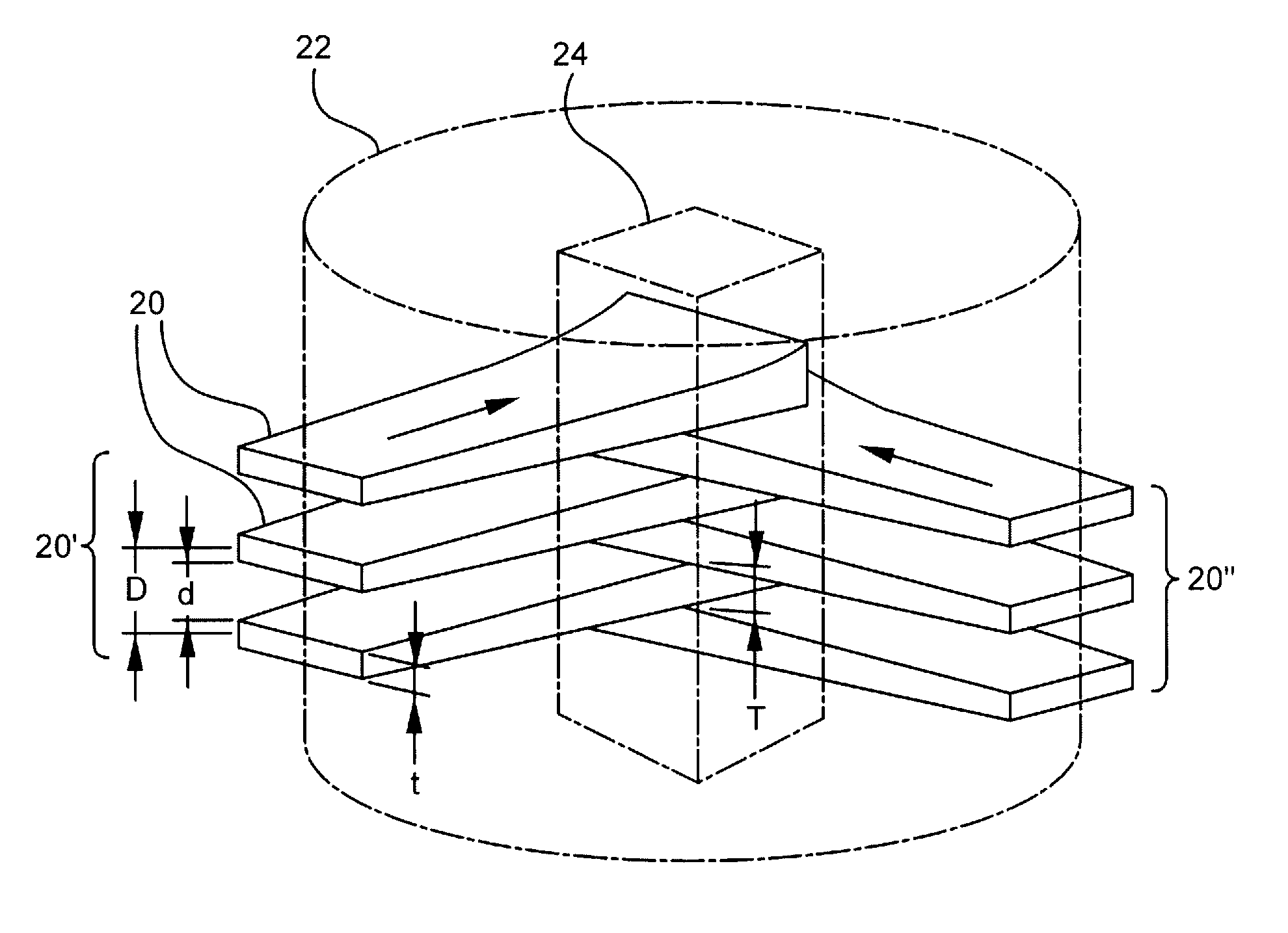
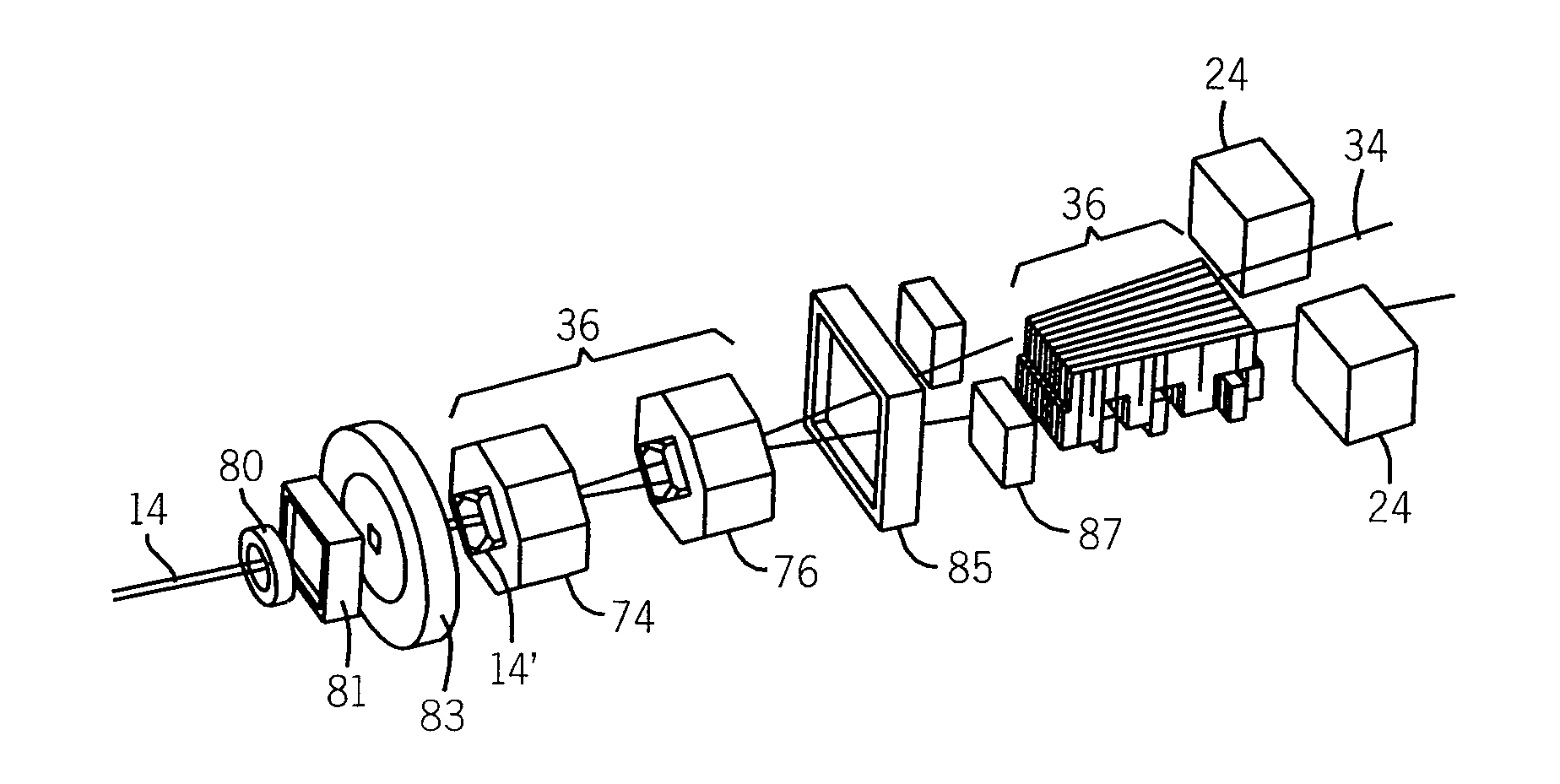
Heavy ion therapy with microbeams
ActiveUS8269198B2Reduce deliveryIncrease productionRadiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsHeavy ion radiationHeavy ion therapy
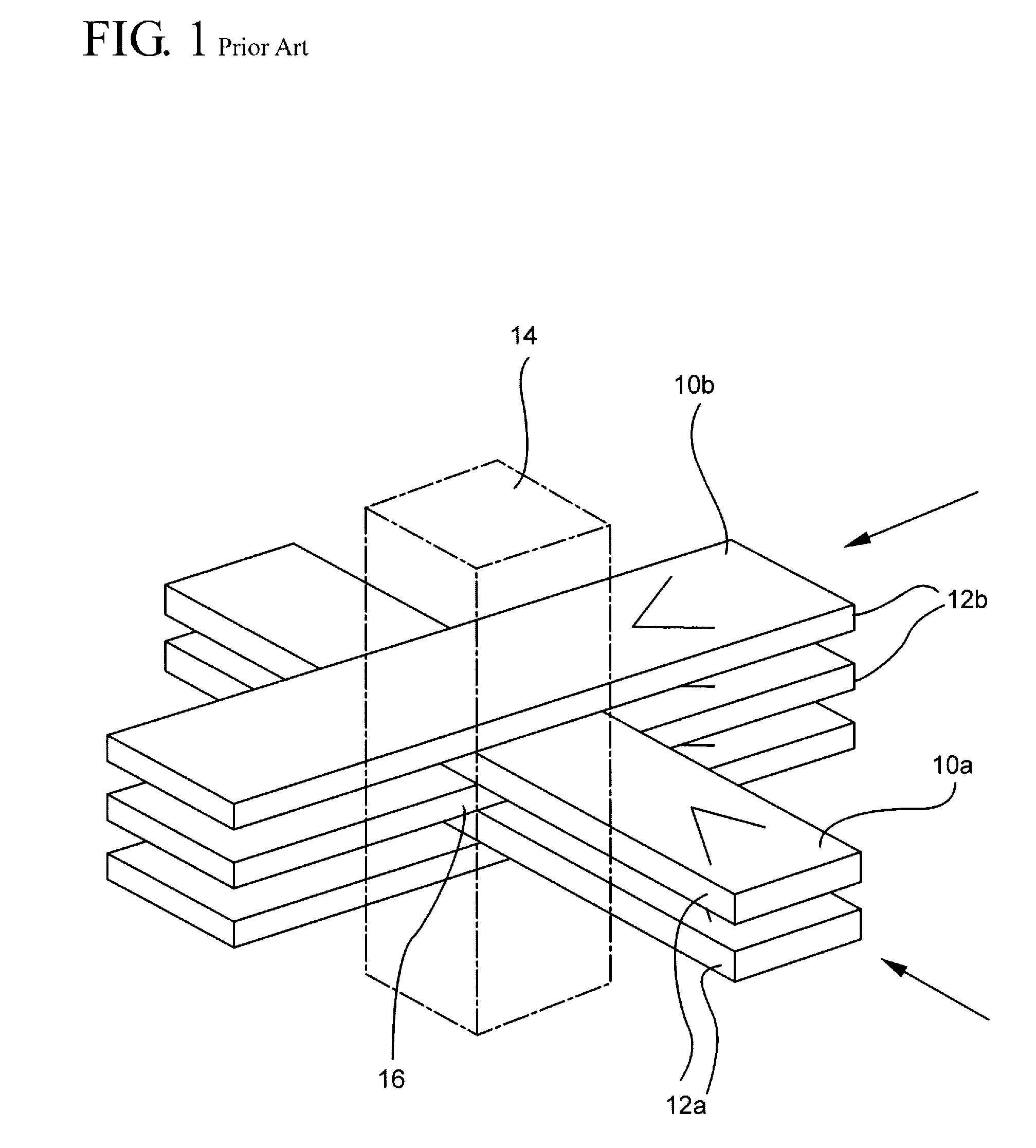
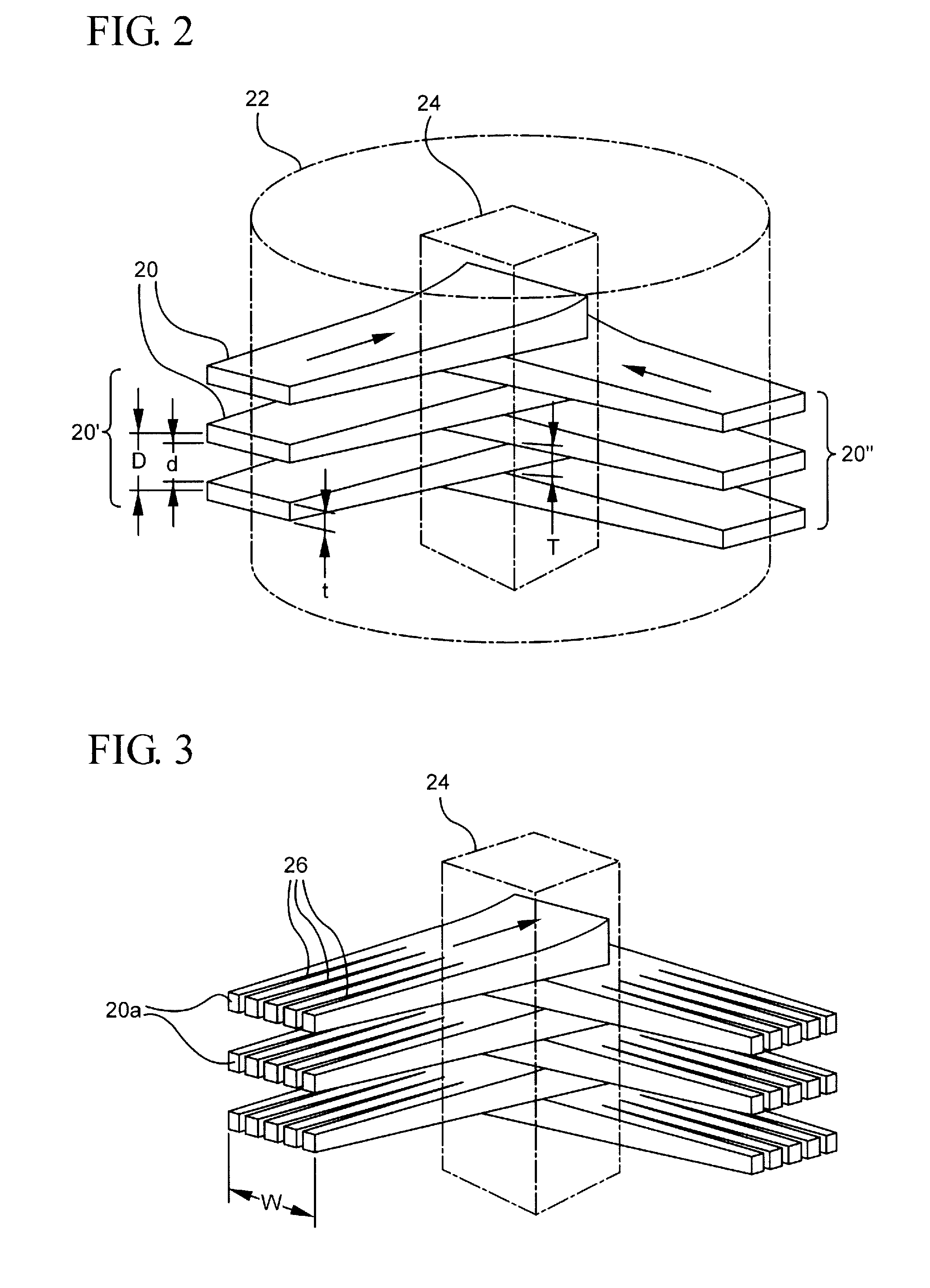
A method for delivering therapeutic heavy ion radiation to a subject, wherein a therapeutic dose of heavy ions is delivered substantially only to a target volume within the subject by generating a broad field of radiation effect substantially only within the target volume, and wherein the broad field of radiation effect is not generated in non-targeted tissue. The method includes the step of irradiating the target volume with at least two arrays of heavy ion microbeams, wherein the at least two arrays each have at least two parallel, spatially distinct heavy ion microbeams. The two arrays of microbeams are interleaved substantially only within the target volume to form a substantially continuous broad beam of radiation substantially only within the target volume.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
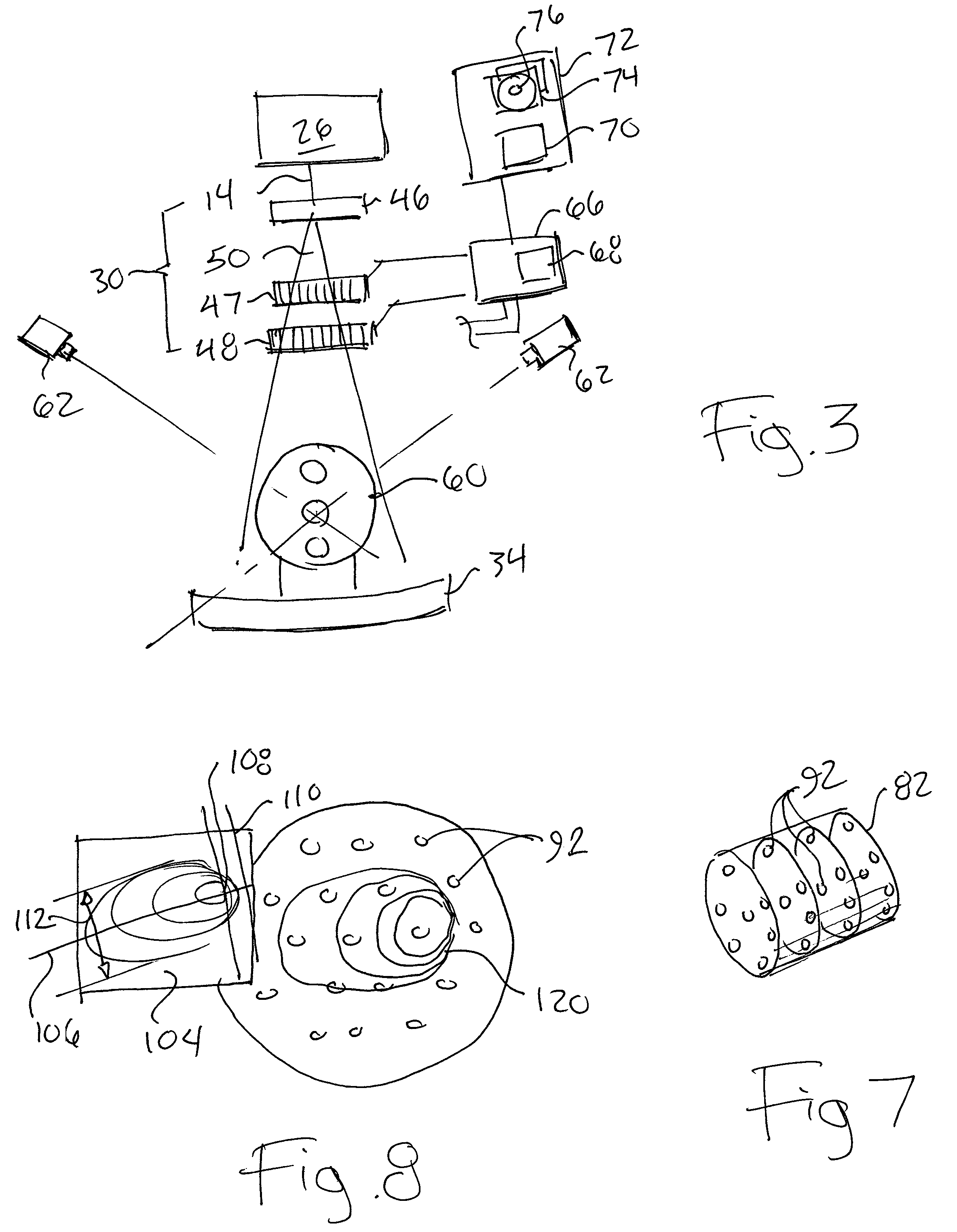
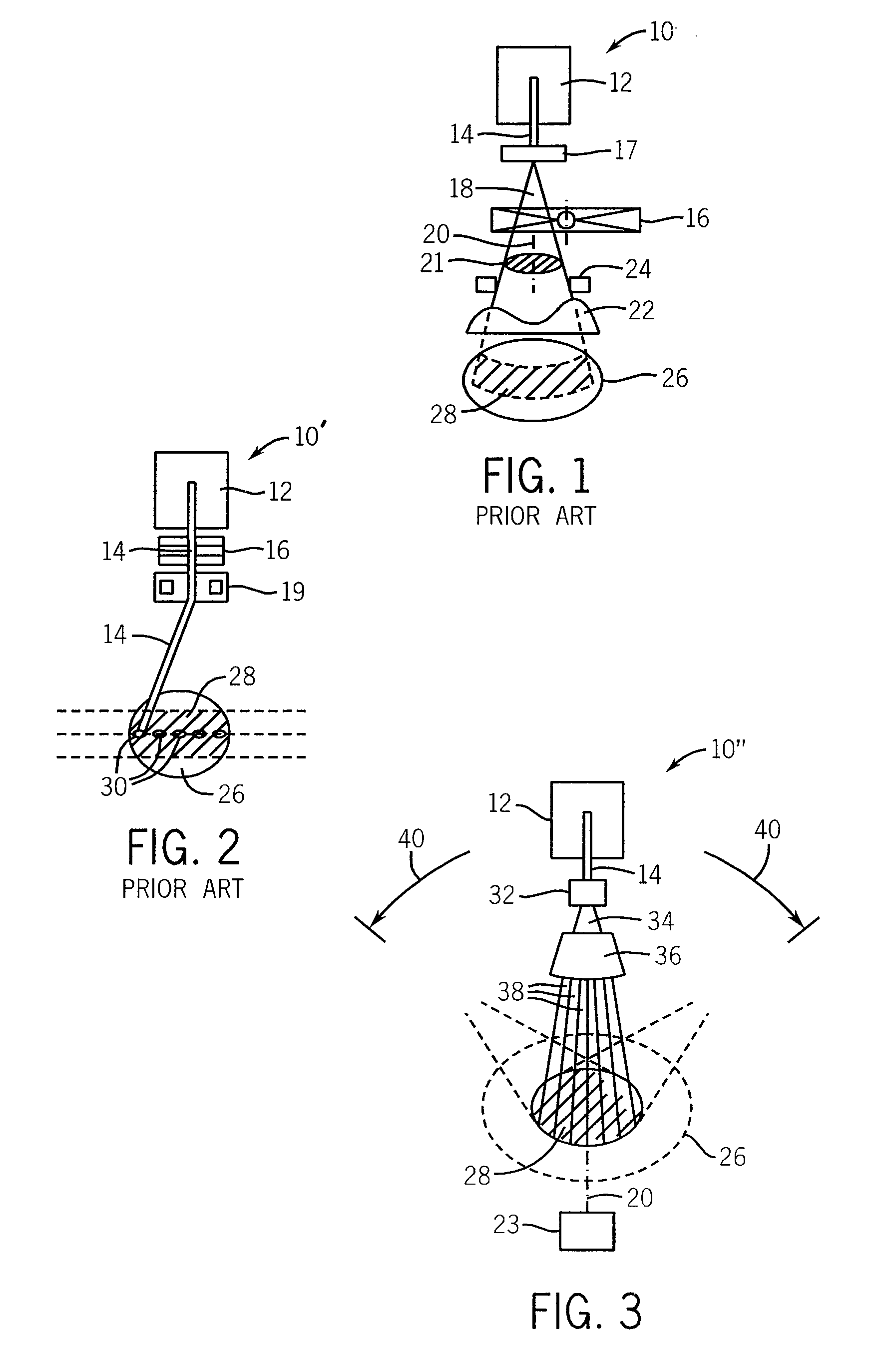
Positioning and verification method for radiation therapy of tumors
InactiveCN102671310AAccurate coincidenceReal-time display of shooting contentX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyVisual field lossGrating
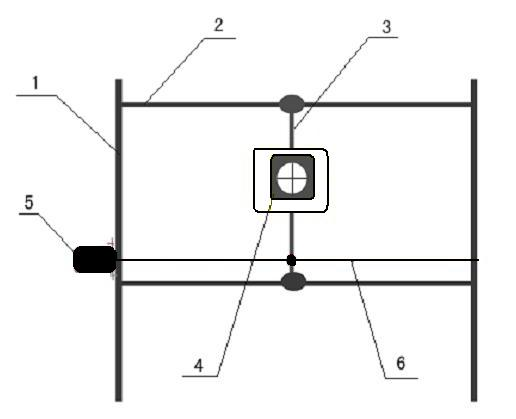
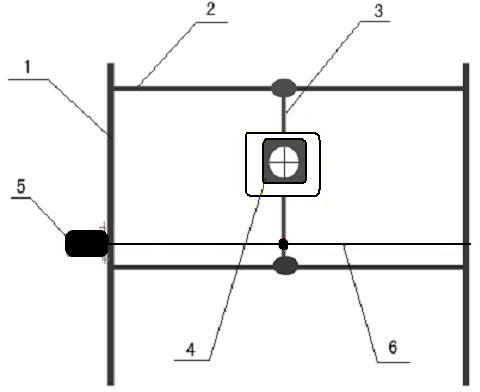
The invention relates to a positioning and verification method for radiation therapy of tumors. The method consists of a radiation therapy field positioning method and a multileaf collimator shape verification method. The radiation therapy field positioning method comprises the following steps of (1) marking the position of a field center cross on the body surface of a patient; (2) making the center cross of the visual field of a camera in a positioning and verification device for radiation therapy of tumors and the therapy field central axis coincide; (3) showing the shooting field of the camera on a displayer in real time; (4) making the center cross of the visual field and the field center cross on the body surface of the patient coincide; and (5) completing the positioning, and making the camera return to the initial position on a guide rail. The multileaf collimator shape verification method comprises the following steps of: performing the steps of (1) to (4) in the radiation therapy field positioning method; (5) obtaining a corresponding ratio on the optical grating distance of a multileaf collimator; (6) displaying a radiation field shape or virtual multileaf collimator shape of the patient in the visual field of the camera, and making the center of the radiation field shape or virtual multileaf collimator shape of the camera coincide with the center of the visual field of the camera; (7) forming a heavy ion radiation field shape; and (8) completing the multileaf collimator shape verification. The method is simple and convenient.
Owner:赵 瑞
Method for screening biomarkers of ionizing radiation as well as application of SZT2 protein determined by method
InactiveCN105803049AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingScreening methodMolecular biomarker
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
Novel kelp heavy ion radiation mutation breeding method
ActiveCN103766214AExcellent mutant plantsPreservation of new gene sourcesPlant genotype modificationHeavy ion radiationMutation breeding
The invention discloses a novel kelp heavy ion radiation mutation breeding method. The novel kelp heavy ion radiation mutation breeding method comprises the following steps: dispersing and filtering a kelp gametophyte cloning cell system to each gametophyte cell segment composed of 1-3 gametophyte cells; radiating by using 12C heavy ions; breeding a sporophore by using a kelp gametophyte cloning breeding technology; after the sporophore is ripen, carrying out phenotype and quality character determination; carrying out DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) variation detection on candidate plants with a large forward direction variation range; obviously improving phenotype and quality characters and taking the plants with obviously-varied DNA structures as breeding materials for breeding new varieties. The novel kelp heavy ion radiation mutation breeding method has the advantages that a lot of variation can be generated by radiating and inducing kelp gametophytes by the heavy ions; the variant plants can be obtained in shorter time and a new gene pool related with the good property is preserved.
Owner:SHANDONG ORIENTAL OCEAN SCI TECH
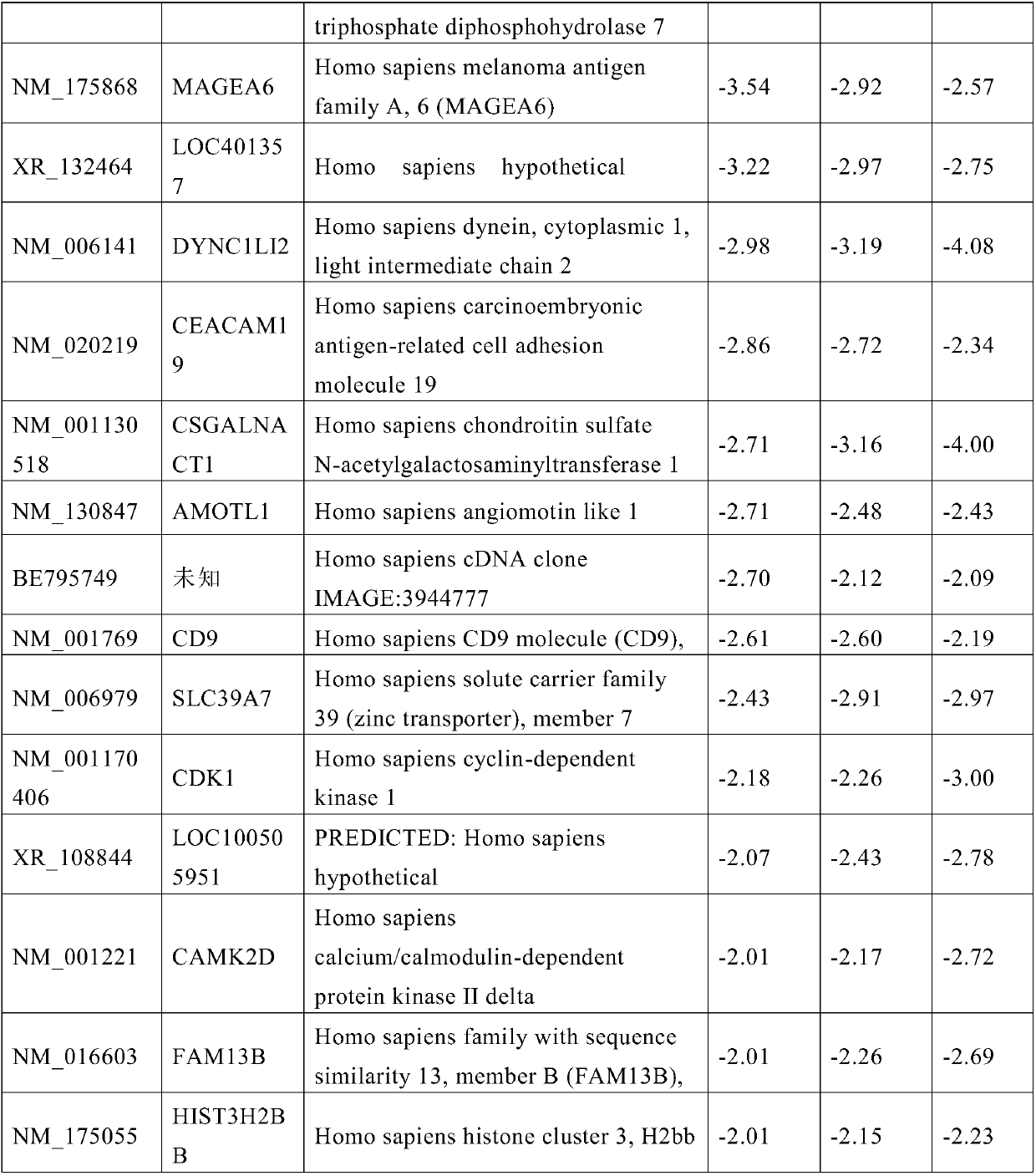
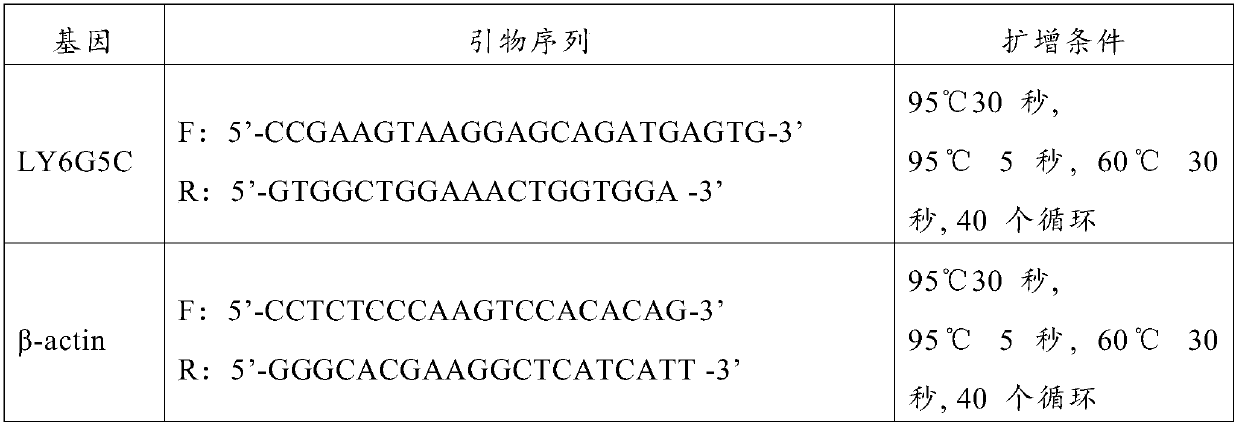
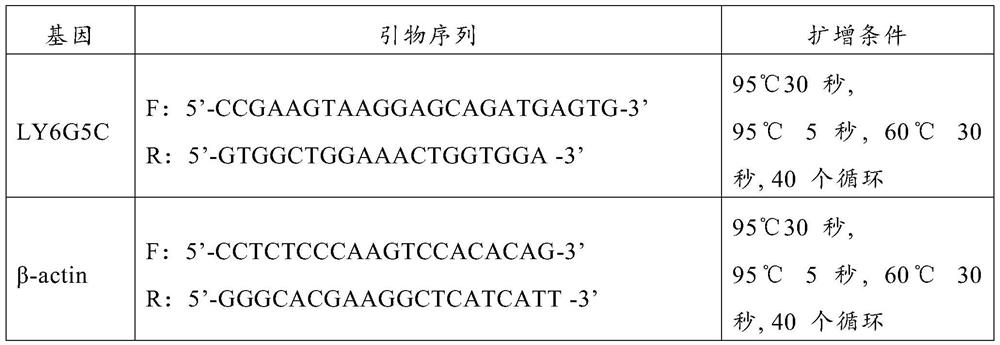
Application of LY6G5C gene as molecular marker for diagnosis of exposure to heavy ion radiation
The invention relates to application of an LY6G5C gene as a molecular marker to preparation of a reagent for diagnosis of exposure to heavy ion radiation, belonging to the field of application of genetic molecular markers. As the LY6G5C gene is used as the molecular marker for detection of exposure to heavy ion radiation, detection is more convenient and accurate and a radiation dose can be determined.
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
High-nitrogen yeast and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102337224AIrradiation mutagenesisEnriched mutagenesis methodFungiMutant preparationMicroorganismHeavy ion radiation
The invention relates to to a high-nitrogen yeast (particularly referring to Saccharomyces cerevisiae) and a preparation method thereof. Saccharomyces cerevisiae is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) with the preservation number of CGMCC No.5004; and Saccharomyces cerevisiae is obtained by heavy ion radiation mutation, the content of nitrogen in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is 40-60%. A heavy ion mutation technology has the following main advantages that (1) variation rate is high, generally 1000 times higher than natural variation rate; (2) variation spectrum is wide, namely type of variation is diverse, and a new type of microbe strain can be obtained; (3) variation stability is strong, relatively stable strains (coexistence of positive and negative mutations) can be obtained, and screening period can be shortened; and (4) mutation operability is strong, and the radiation mutation of the microbe can be easily completed.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Sweet sorghum breeding method
InactiveCN104782480AExcellent agronomic traitsImprove economyPlant genotype modificationRadiation DosagesDose rate
The invention belongs to the technical field of agriculture, relates to a sweet sorghum breeding method, in particular to a method for breeding sweet sorghum by using a heavy ionmutation breedingtechnique. The sweet sorghum breeding method is mainly characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) performing heavy ion beam radiation, namely, providing carbon, oxygen or argon heavy ion beams by using a heavy ion accelerator, and performing radiation treatment on sweet sorghum seeds at a vertical radiation terminal for 4-6 minutes under the conditions that the energy is 80-100MeV / mu, the radiation dosage is 80-120Gy and the dosage rate is 20-30Gy / minute; (2) performing mutant screening; (3) performing mutant detection; (4) performing hybridized combination optimization. Due to the adoption of the breeding method provided by the invention, after heavy ion radiation, mutant planting resources which are good in precocity property, high in sweet, high in yield and resistant to adversity can be obtained, after being planted for M3-M4 generations, the mutants can be stabilized, and the efficiency of mutant screening, mutant detection and hybridized combination blending is increased by more than 10% when being compared with that of a single crossbreeding method.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Heavy ion radiation therapy system with stair-step modulation
ActiveUS8269196B2Reduce intensityHigh-speed and precise controlRadiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsHeavy ion radiationLight beam
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
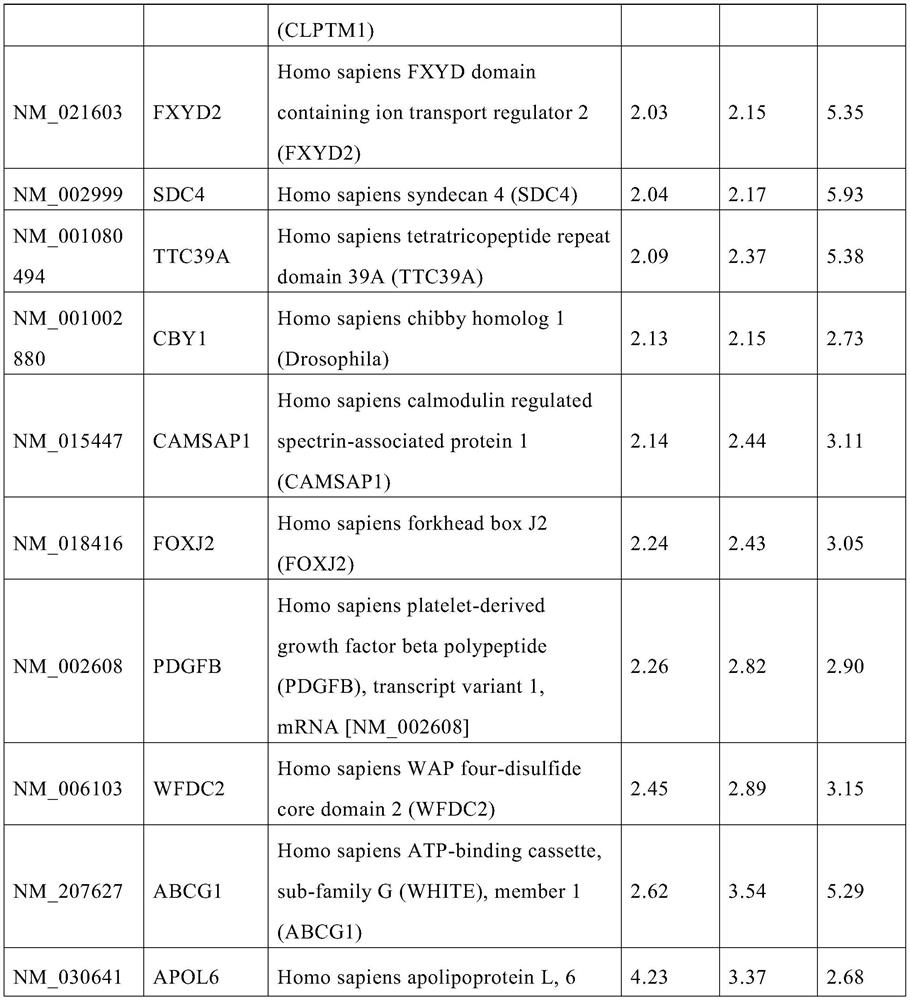
Application of ABCG1 gene as molecular marker for diagnosis of exposure to heavy ion radiation
The invention relates to application of an ABCG1 gene as a molecular marker to preparation of a reagent for diagnosis of exposure to heavy ion radiation, belonging to the field of application of genetic molecular markers. As the ABCG1 gene is used as the molecular marker for detection of exposure to heavy ion radiation, detection is more convenient and accurate and a radiation dose can be determined.
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
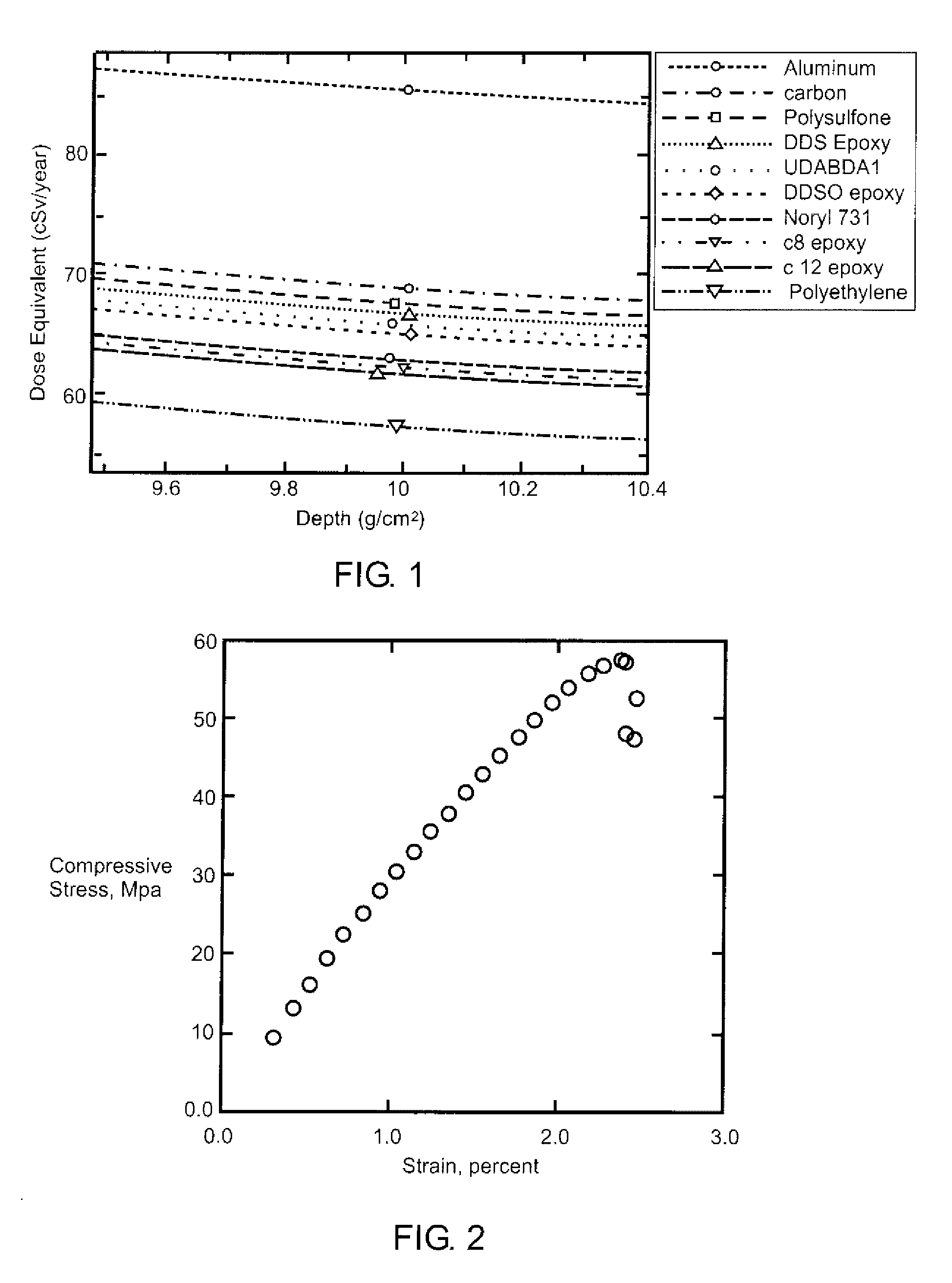
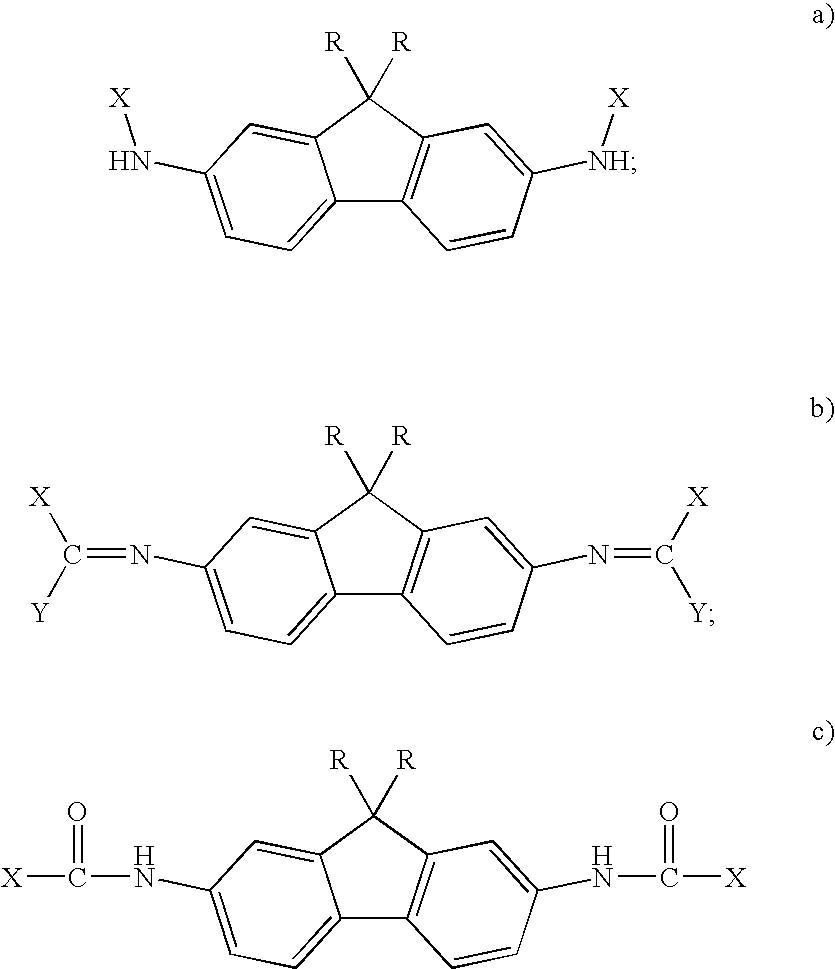
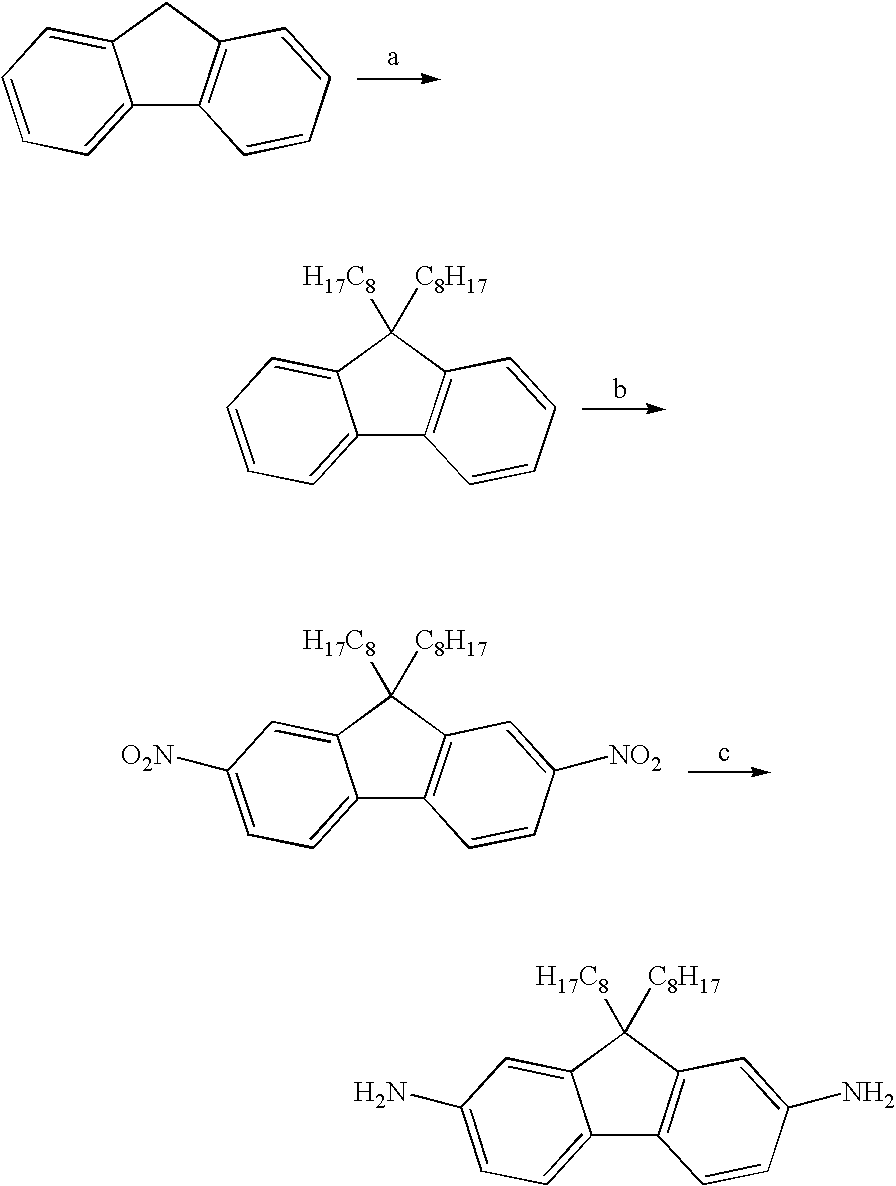
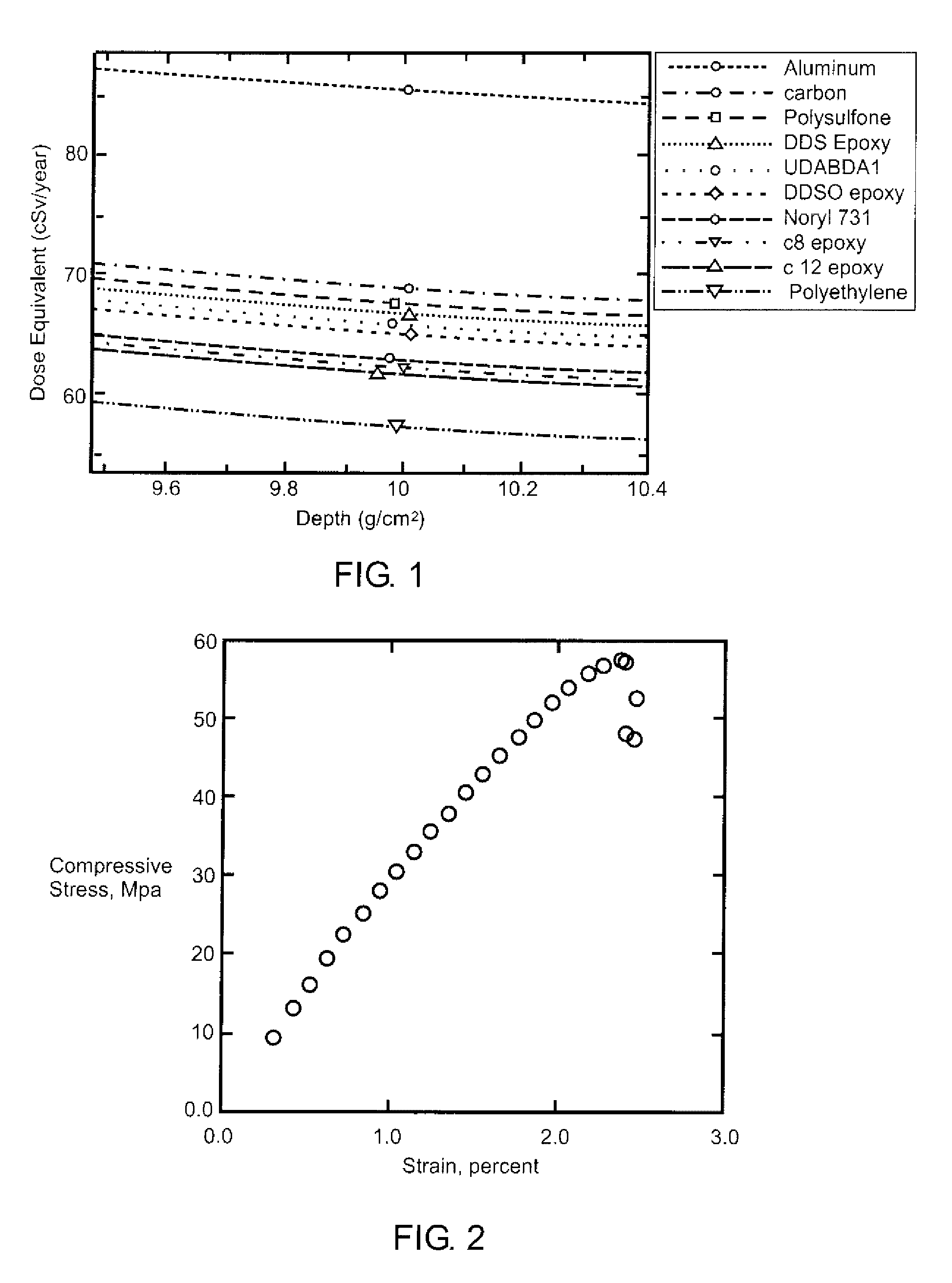
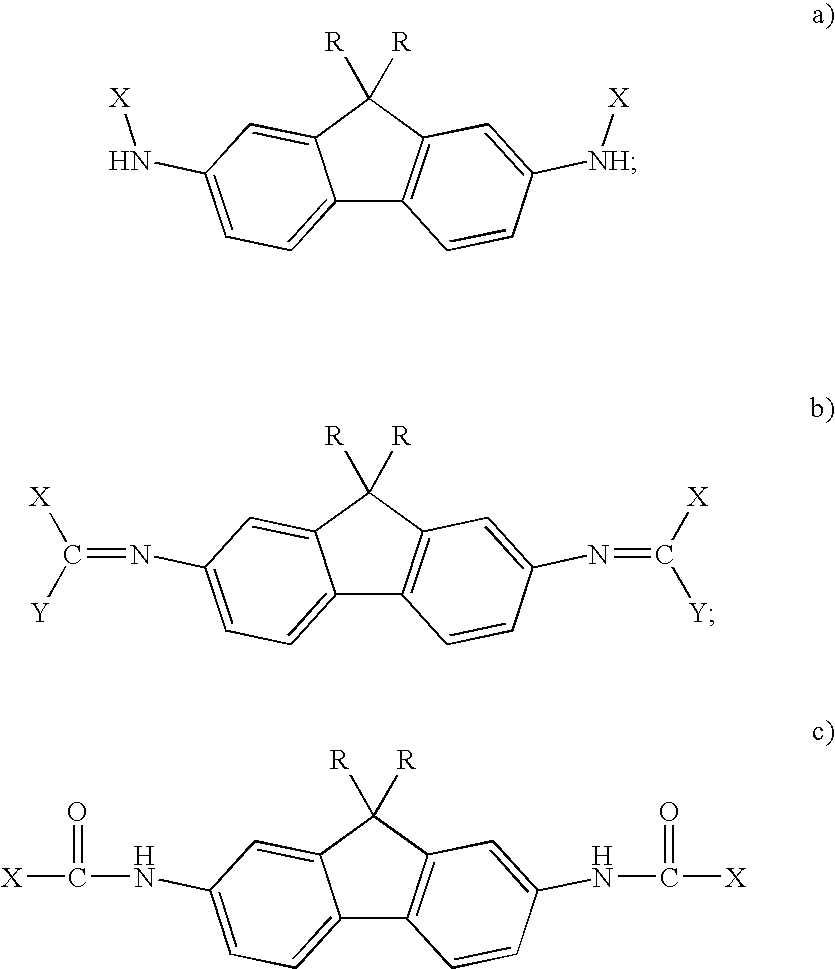
Novel Aromatic/Aliphatic Diamine Derivatives For Advanced Compositions And Polymers
InactiveUS20080004419A1Organic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensHeavy ion radiationDiamine
Novel compositions of matter comprise certain derivatives of 9,9-dialkyl fluorene diamine (AFDA). The resultant compositions, whether compositions of matter or monomers that are subsequently incorporated into a polymer, are unique and useful in a variety of applications. Useful applications of AFDA-based material include heavy ion radiation shielding components and components of optical and electronic devices.
Owner:NASA
Membrane separation method of sea cucumber polysaccharide fragments acting on simulation space heavy ion radiation oxidation stress
The invention relates to a preparation method of sea cucumber polysaccharides, particularly a membrane separation method of sea cucumber polysaccharide fragments acting on simulation space heavy ion radiation oxidation stress. The method solves the problems of low sea cucumber polysaccharide extraction rate, indefinite active sites and complex production technique in the existing traditional process. The method comprises the following steps: drying fresh sea cucumbers and taking dry sea cucumbers, pulverizing, extracting in a high-voltage pulse electric field, separating the extracting solution by an ultracentrifuge, carrying out membrane separation on the polysaccharide fragments through a plate-frame membrane component, screening the effective fragments through in-vivo and in-vitro experiments, carrying out vacuum scraper membrane concentration, and carrying out freeze-drying by using a vacuum freeze drier, thereby obtaining the sea cucumber polysaccharide fragment powder acting on simulation space heavy ion radiation oxidation stress. The sea cucumber polysaccharide fragments acting on simulation space heavy ion radiation oxidation stress are a natural extract with no side effects on the human body, have the effects of resisting oxidation, enhancing the immunity and the like, and are suitable for astronauts, air force soldiers, radar soldiers, chemoradiotherapeutic tumor patients and people with hypoimmunity. The sea cucumber polysaccharide fragments acting on simulation space heavy ion radiation oxidation stress are applicable to the fields of food, health products, cosmetics, medicine, biochemical engineering and the like.
Owner:卢卫红
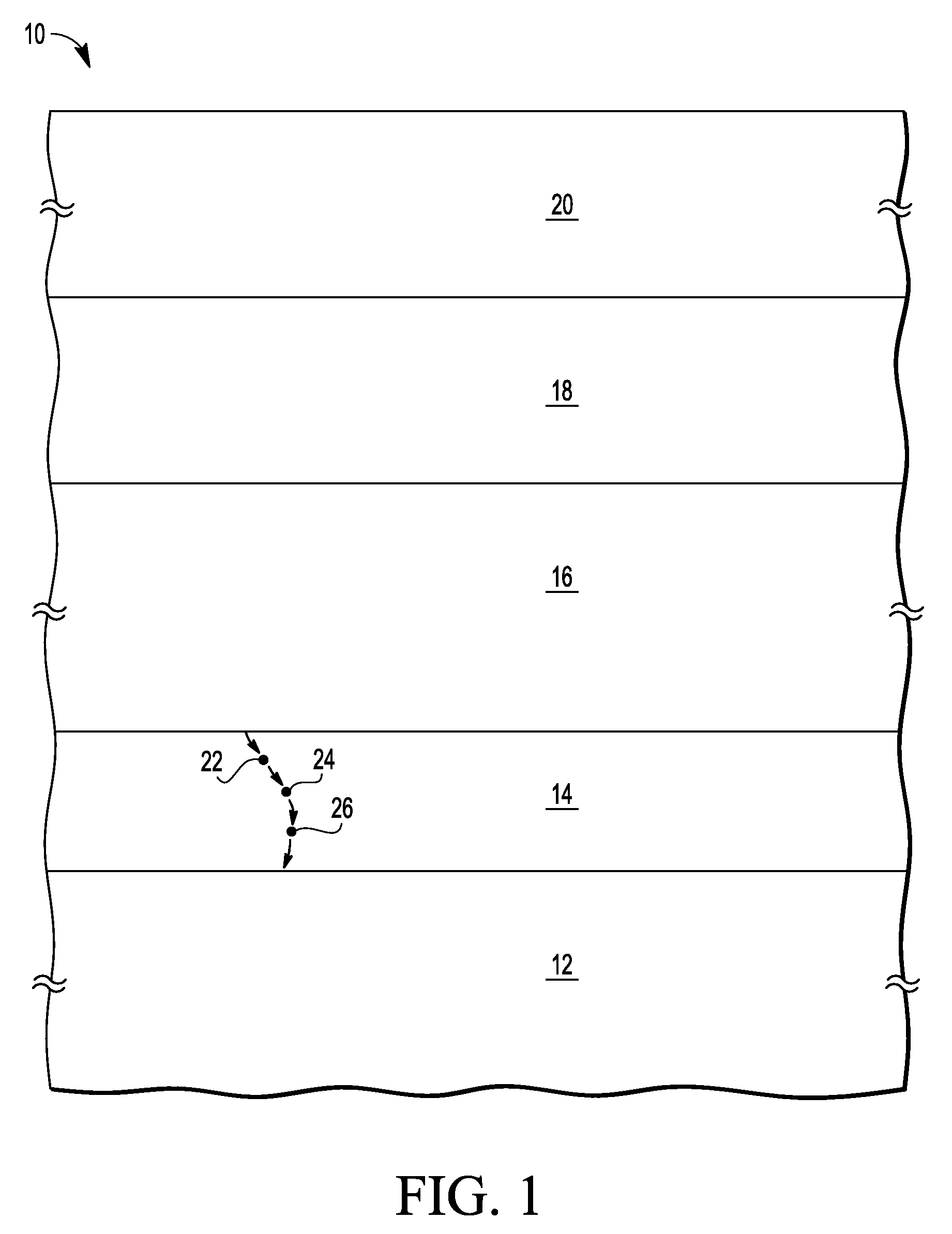
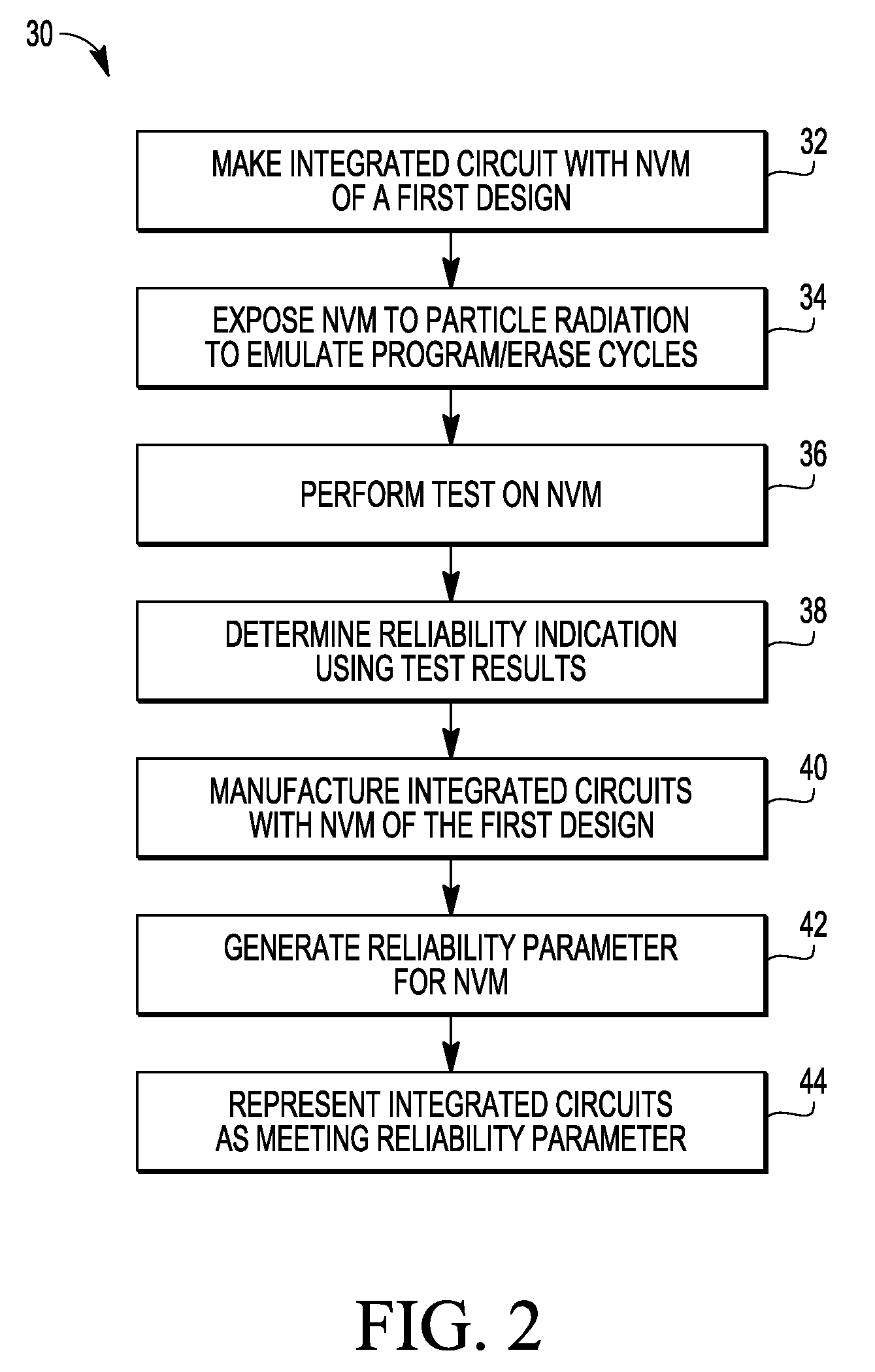
Method for simulating long-term performance of a non-volatile memory by exposing the non-volatile memory to heavy-ion radiation
InactiveUS7955877B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementRead-only memoriesHeavy ion radiationXenon
Testing a non volatile memory by exposing the non volatile memory to particle radiation (e.g. xenon ions) to emulate memory cell damage due to data state changing events of a non volatile memory cell. After the exposing, the memory cells are subjected to tests and the results of the tests are used to develop reliability indications of the non volatile memory. Integrated circuits with non volatile memories of the same design are provided. Reliability representations of the integrated circuits can be made with respect to a number of data state charging events based on the exposure and subsequent tests.
Owner:NXP USA INC
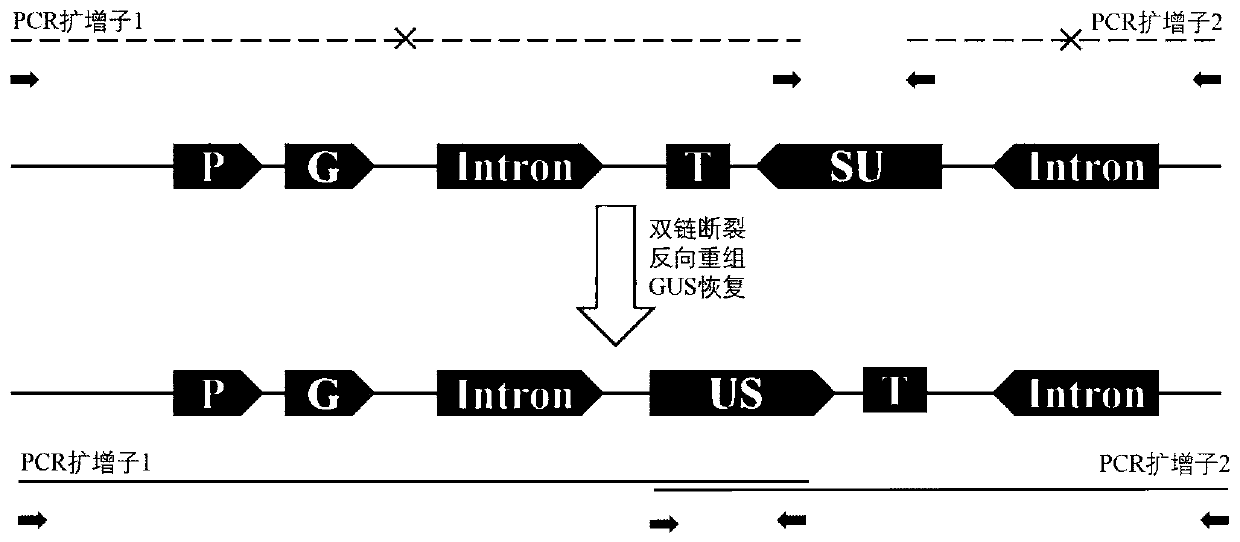
Efficient marking method for heavy ion radiation mouseearcress genome target spots
InactiveCN109777882AExperiment operation is simpleImprove labeling efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementHeavy ion radiationBioinformatics
The invention discloses an efficient marking method for heavy ion radiation mouseearcress genome target spots, and relates to the field of heavy ion plant radiation induction breeding mechanism research. In order to solve the problem that an existing reporter gene has defects for marking heavy ion radiation plant genome target spots, the method comprises the steps that a mouseearcress homologous recombination report system is adopted as an experimental material, the heavy ion radiation plant genome target spots are efficiently marked in the mode that the activity of the reporter gene is recovered after the reporter gene is damaged by DNA dual-chain breakage and subjected to homologous recombination repair, red recombination fragment and a flanking genome sequence thereof are amplified through PCR high fidelity, the sequencing detection amplification sequence basic group mutation condition is cloned, and therefore the heavy ion radiation plant genome target spots are marked. The methodhas the advantages that experiment operations are easy, the marking efficiency is high, and specific induction of DNA dual-chain breakage is achieved.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Heavy ion radiation induced chromosome fracture calculation method
InactiveCN101126697AAddressing bottlenecks in radiation susceptibility predictionRadiosensitivity DeterminationMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsRadiation sensitivityHeavy ion radiation
The utility model relates to a calculation method of chromosome breakage induced by heavy ion radiation, in particular to a number calculation method of broken cell of the chromosome after the cell accepts the irradiation of heavy ion. The calculation method of chromosome breakage induced by heavy ion radiation is characterized in that: A. The subject cell is cultured and the following operation is made when the subject cell is in exponential phase for a long term; B. Surface area of the cell is tested when the cell is at the spreading status inside the culture bottle; C. Cell content of G2 period is tested using a flow cytometer; D. Average LET of radiation ray is adopted when the cell is irradiated and tested. E. Number N of the irradiated cell is tested; F. Inner bottom area is tested for the cell culture bottle; G. The above testing value is brought into equation for solving. The utility model has the advantages that the establishment belonging to biological technology field of chromosome breakage theory calculation model occurring inside the cell after the tumor cells accepts the irradiation of the heavy ion can solve the predicted bottleneck for radiosensitivity of the tumor cells when heavy ion clinical radiotherapy plan is made and the application of the utility model also can quickly and accurately test radiation sensibility of tumor cells upon the heavy ion radiation for the tumor cells under the offline condition.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
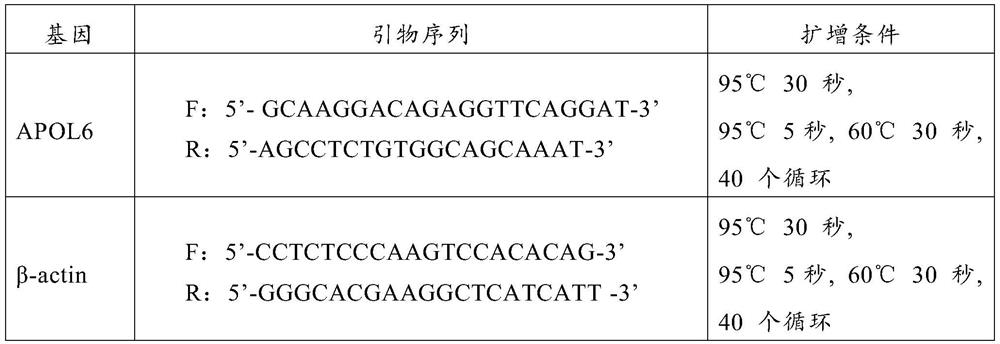
The use of apol6 gene as a molecular marker for the diagnosis of heavy ion radiation exposure
The invention belongs to the application field of gene molecular markers, and relates to the use of APOL6 gene as a molecular marker in preparing reagents for heavy ion radiation exposure diagnosis. Using the APOL6 gene as a molecular marker in the detection of heavy ion radiation exposure can be more convenient and accurate, and can determine the radiation dose.
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
Damage analysis method for heavy ion radiation silicon carbide diode under bias electric field
ActiveCN111554354AShorten the timeSave moneyChemical processes analysis/designComputational theoretical chemistryCarbide siliconHeavy ion radiation
A damage analysis method for a heavy ion radiation silicon carbide diode under a bias electric field comprises the steps of: constructing a simulation model of a silicon carbide diode through Geant4 based on the basic structure and material composition of the silicon carbide diode, and setting the size of the bias electric field and the type and energy of incident particles in the Geant4; performing analogue simulation in Geant4: injecting incident particles into the silicon carbide diode, and simulating the particle motion trails of the incident particles in the silicon carbide diode and theinitial defect damage distribution of the silicon carbide diode under different bias electric fields; and based on the simulation model and the initial defect damage distribution, simulating a defectdamage evolution process of the silicon carbide diode through TCAD software so as to analyze the influence of defect damage on the electrical property of the silicon carbide diode. The interaction relationship between the bias electric field and the radiation damage is disclosed, and a technical basis is provided for radiation effect mechanism analysis and reliability evaluation of silicon carbidedevices.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Preparation method of sub-nano porous PES film
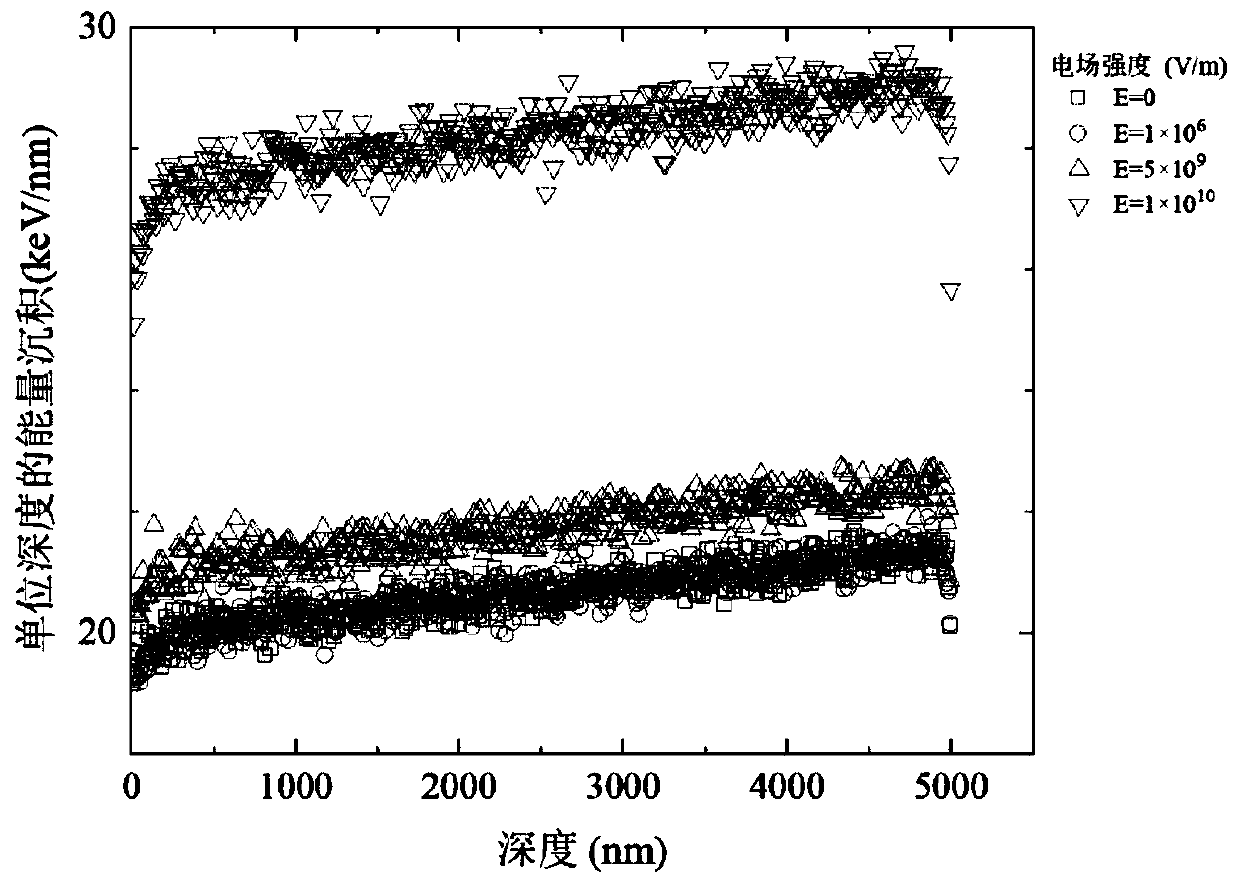
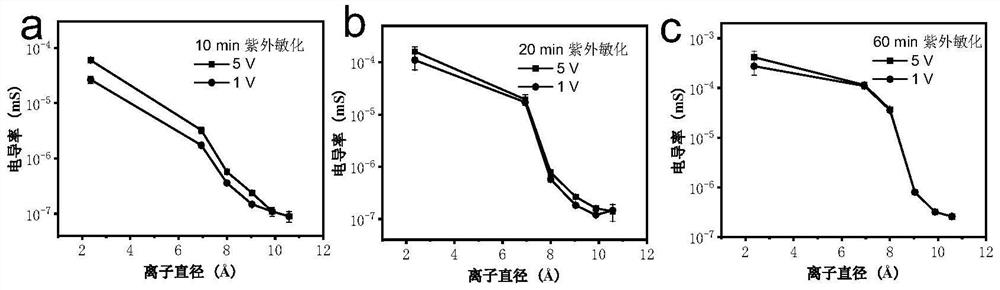
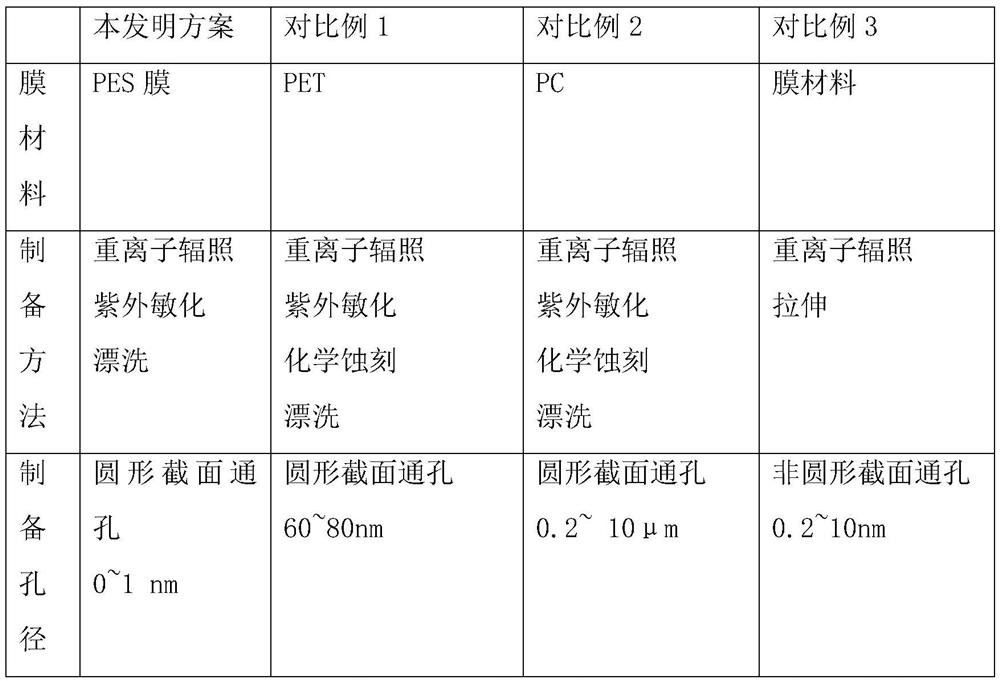
PendingCN114377567AGood chemical stabilityImprove physical stabilitySemi-permeable membranesUltraviolet lightsPolymer thin films
The invention discloses a preparation method of a sub-nano porous PES film, which sequentially comprises the following steps: heavy ion beam irradiation: uniformly irradiating the PES film with a heavy ion beam, the thickness of the PES film being 2-100 [mu] m; ultraviolet light sensitization: carrying out sensitization treatment on the double surfaces of the PES film by adopting ultraviolet light, and keeping the ultraviolet light intensity unchanged; and rinsing with water: immersing the sensitized PES membrane in water for rinsing at the water rinsing temperature of 70-90 DEG C for 4-7 minutes, taking out the membrane, and naturally airing to obtain the porous PES separation membrane with sub-nano pores. The PES film material is adopted, the porous polymer film with the pore diameter in the sub-nanometer size is prepared through heavy ion radiation, ultraviolet light sensitization and water rinsing, the preparation process is simple, efficient and low in cost, large-scale preparation can be achieved, compared with an existing conventional preparation method, the pore diameter of pores prepared through the method is smaller, and the pore diameter is smaller. And the prepared porous PES film has good chemical and physical stability.
Owner:先进能源科学与技术广东省实验室
Use of ly6g5c gene as molecular marker for diagnosis of heavy ion radiation exposure
The invention belongs to the application field of gene molecular markers, and relates to the use of LY6G5C gene as a molecular marker in the preparation of reagents for the diagnosis of heavy ion radiation exposure. Using the LY6G5C gene as a molecular marker for the detection of heavy ion radiation exposure can be more convenient and accurate, and the radiation dose can be determined.
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
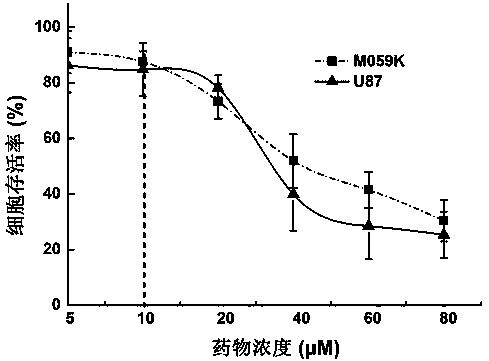
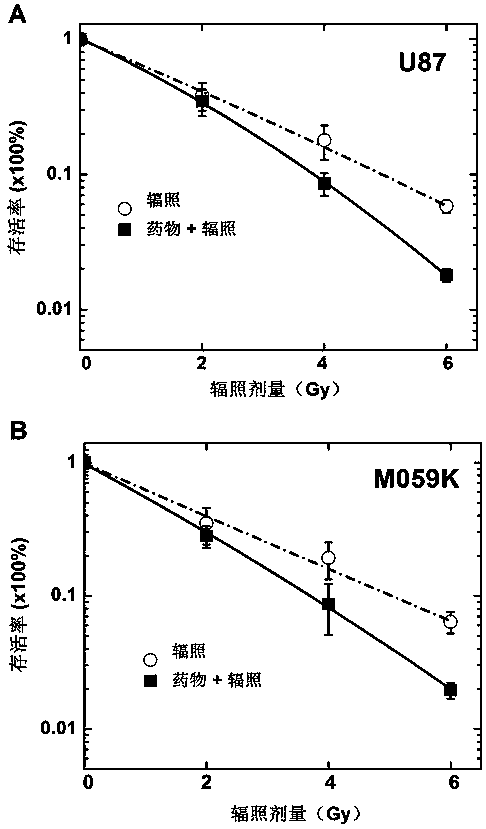
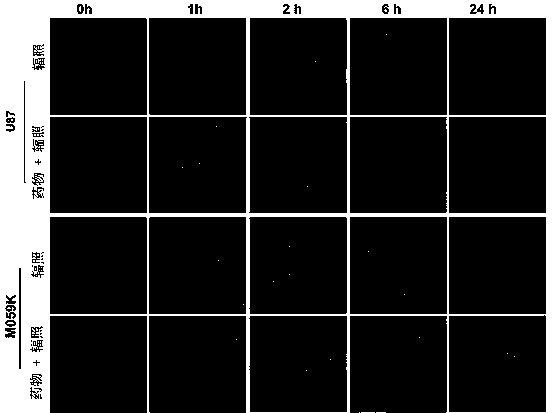
Application of genistein in preparation of heavy ion radiation-sensitizing drug
InactiveCN107693512ASmall side effectsPromote apoptosisOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsTreatment effectHeavy ion radiation
The invention relates to application of genistein in the preparation of a heavy ion radiation-sensitizing drug. Effective concentration of the genistein as a radiation-sensitizing drug in the preparation of a heavy ion radiation-sensitizing drug for inhibiting tumor proliferation of patients is 5-20 microns. The drug can remarkably inhibit heavy ion radiation induced DNA double-strand break repairand promote tumor cell apoptosis so as to further raise tumor cell killing efficiency of heavy ions, has potential application value in the preparation of a radiosensitivity drug, and is helpful forenhancing the effect of single irradiation in heavy ion treatment, reducing the number of treatment, shortening treatment course and lowering treatment cost.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
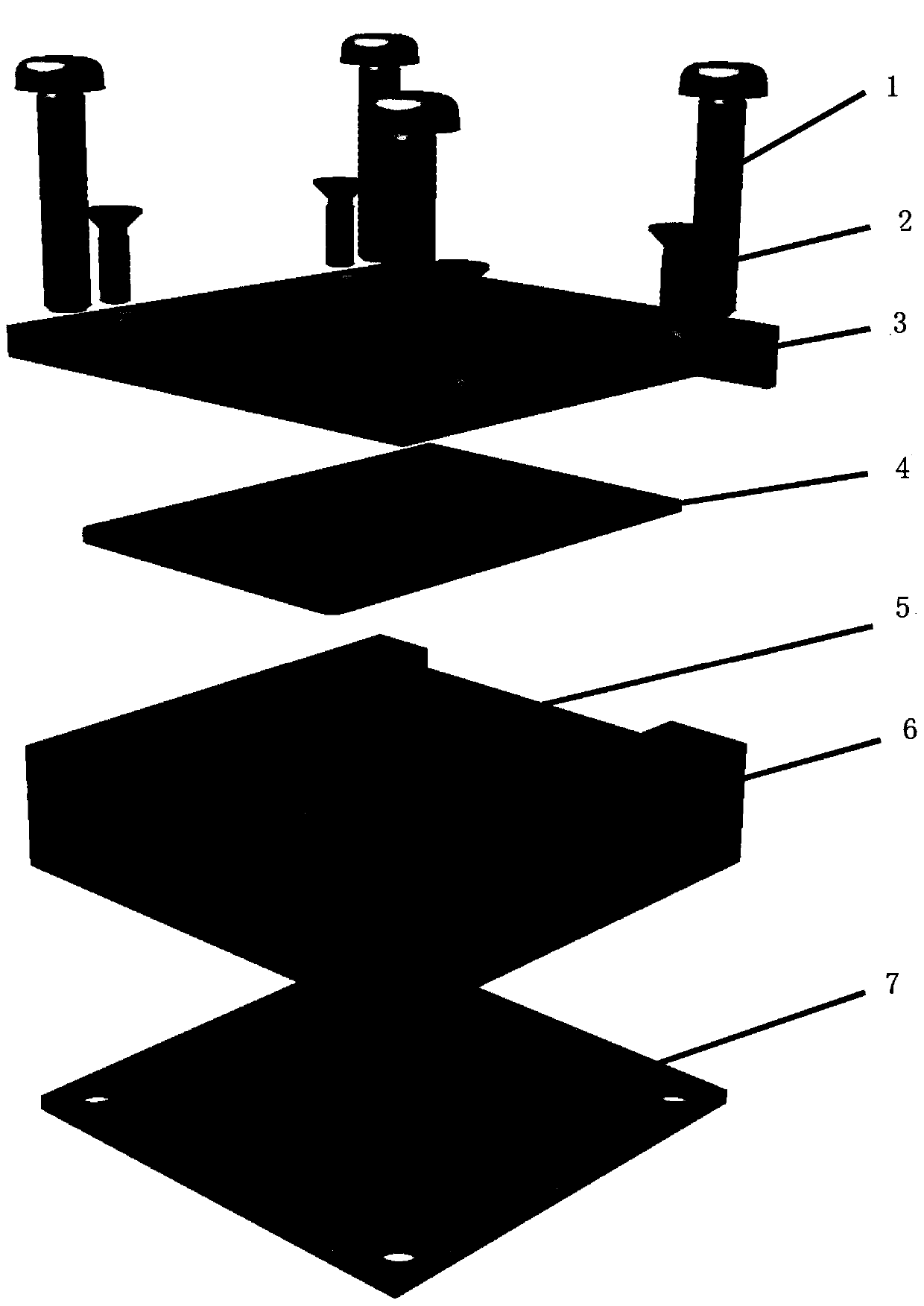
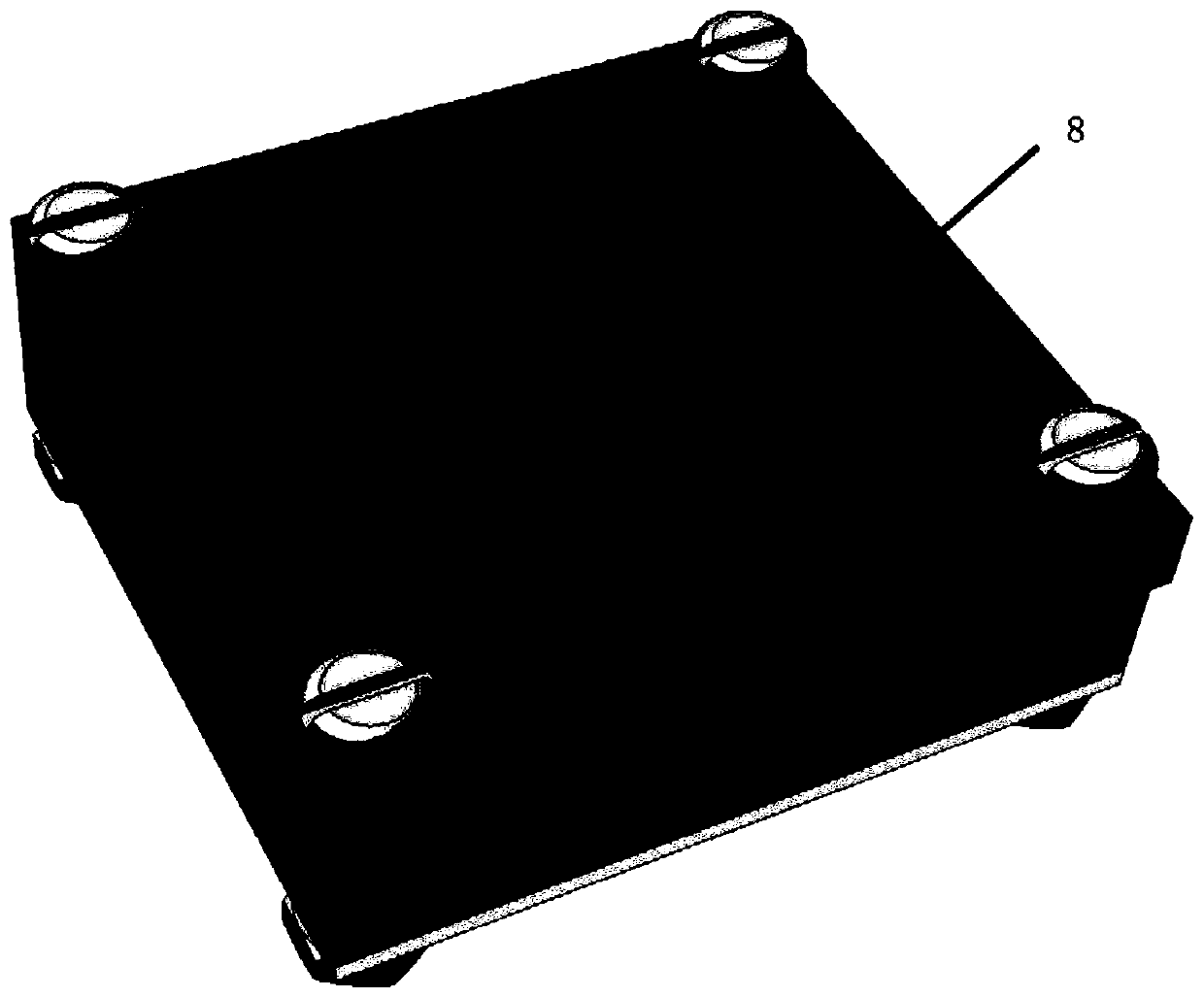
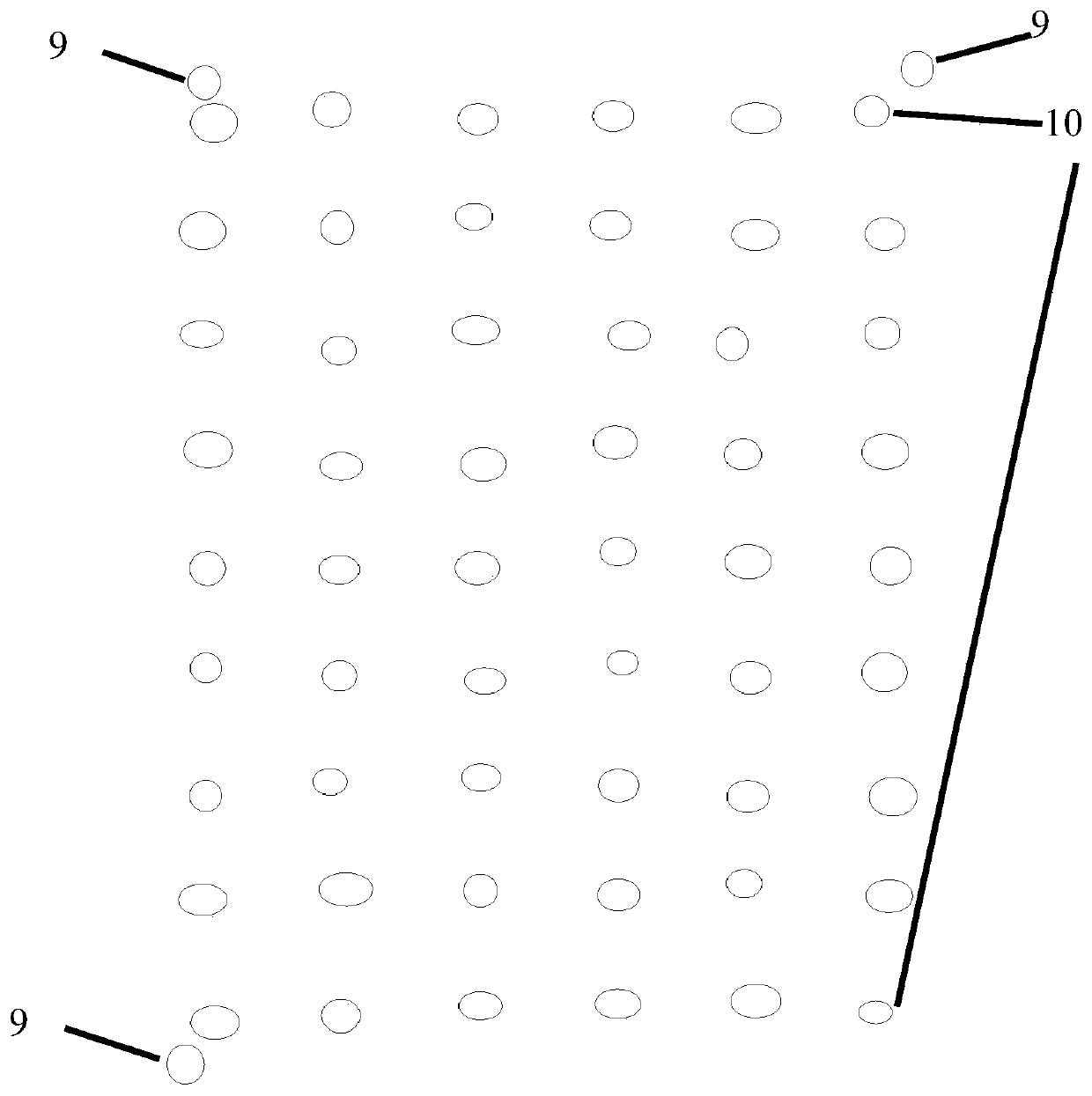
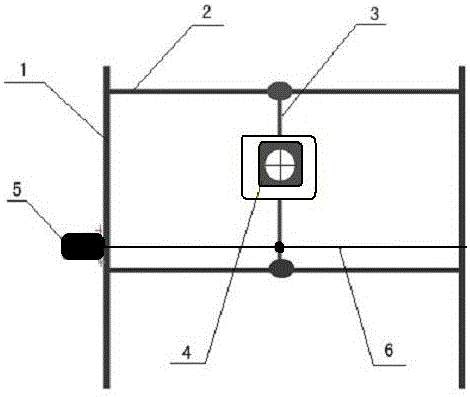
A device and method for measuring rice seed embryos exposed to heavy ion radiation
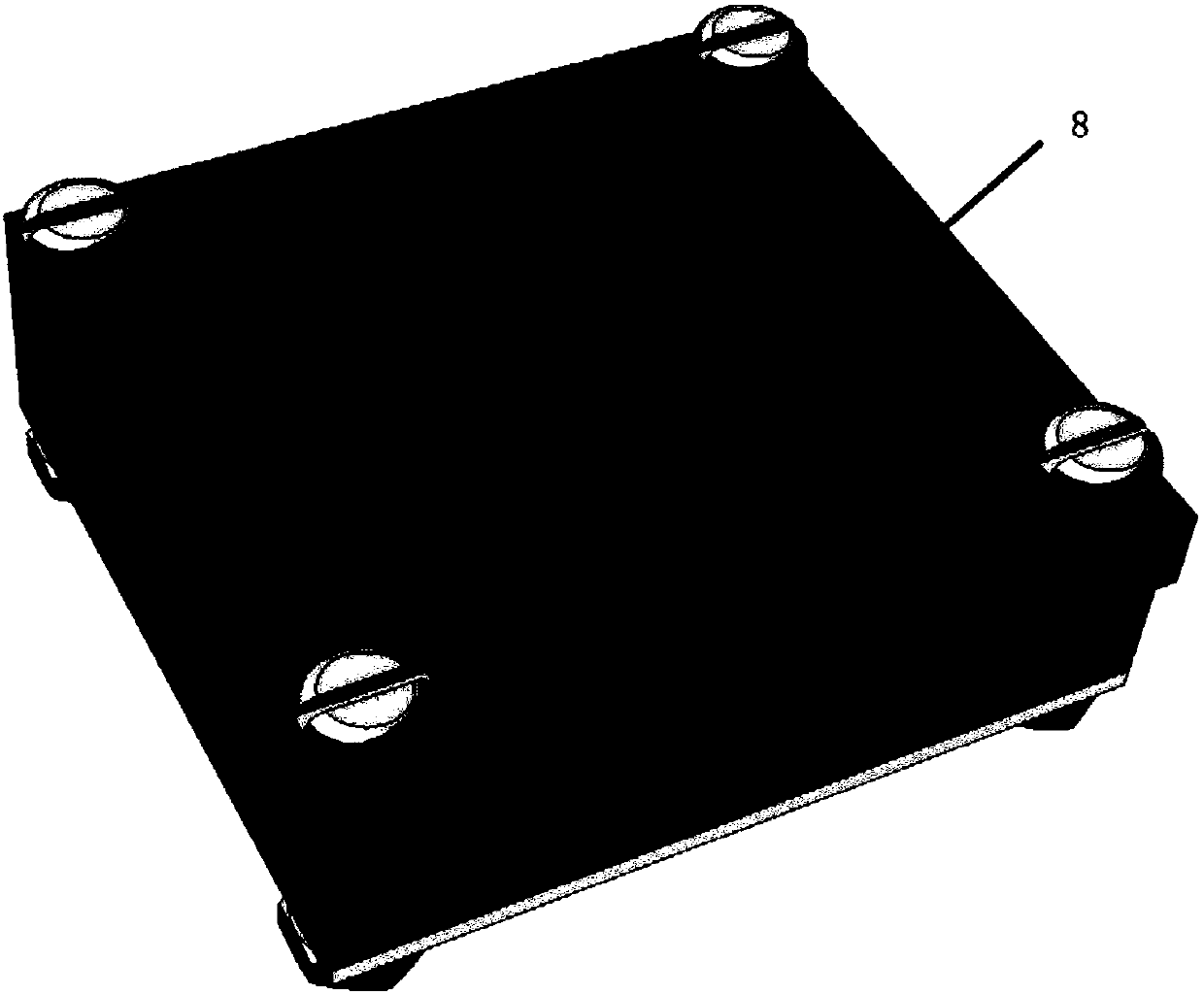
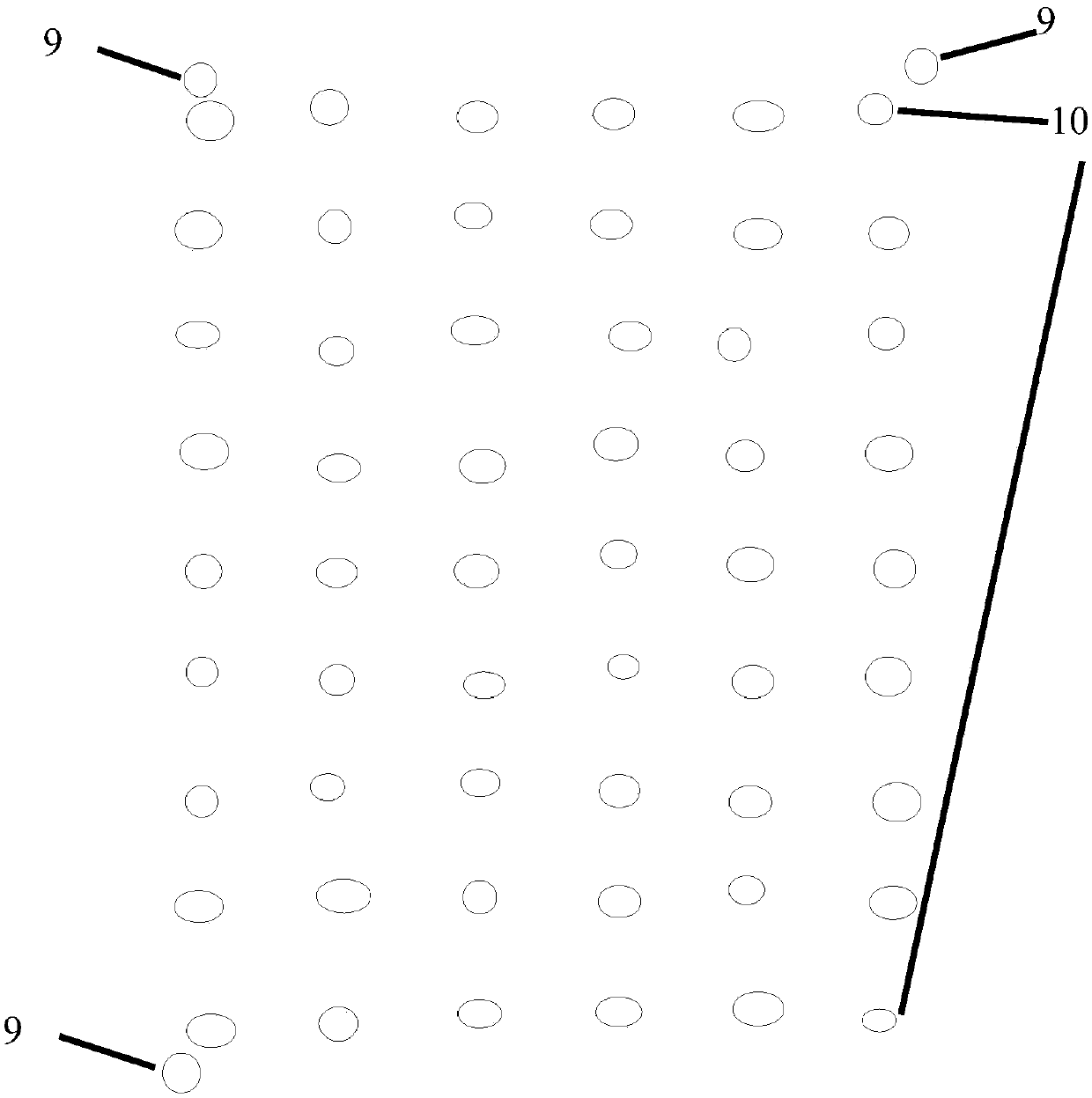
The invention discloses a device for measuring the exposure of rice seed embryos to heavy ion radiation. The device is a seed box for study of rice seed space radiation effect. The device consists ofan upper cover plate (3), a nuclear track detector (4), a matrix (6) and a lower cover plate (7) from top to bottom in order, the matrix (6) is a square groove equipped with a plurality of ellipticalholes (5), the elliptical holes (5) are through-holes and are used for installing and fixing rice seeds (8), the nuclear track detector (4) is installed in the square groove, and is fixed through theupper cover plate (3) and the lower cover plate (7). Based on the device, the invention also discloses a method for measuring the exposure of rice seed embryos to heavy ion radiation, and the method can acquire the linear energy transfer information of heavy ion radiation to the seed embryos. The method provided by the invention can accurately acquire the heavy ion radiation to the seed embryos, in addition to high energy and long-range heavy ions, the heavy ions also include low energy and short-range heavy ions.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Aromatic/aliphatic diamine derivatives for advanced compositions and polymers
Novel compositions of matter comprise certain derivatives of 9,9-dialkyl fluorene diamine (AFDA). The resultant compositions, whether compositions of matter or monomers that are subsequently incorporated into a polymer, are unique and useful in a variety of applications. Useful applications of AFDA-based material include heavy ion radiation shielding components and components of optical and electronic devices.
Owner:NASA
A tumor radiotherapy positioning and verification method
InactiveCN102671310BAccurate coincidenceReal-time display of shooting contentX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyVisual field lossGrating
The invention relates to a positioning and verification method for radiation therapy of tumors. The method consists of a radiation therapy field positioning method and a multileaf collimator shape verification method. The radiation therapy field positioning method comprises the following steps of (1) marking the position of a field center cross on the body surface of a patient; (2) making the center cross of the visual field of a camera in a positioning and verification device for radiation therapy of tumors and the therapy field central axis coincide; (3) showing the shooting field of the camera on a displayer in real time; (4) making the center cross of the visual field and the field center cross on the body surface of the patient coincide; and (5) completing the positioning, and making the camera return to the initial position on a guide rail. The multileaf collimator shape verification method comprises the following steps of: performing the steps of (1) to (4) in the radiation therapy field positioning method; (5) obtaining a corresponding ratio on the optical grating distance of a multileaf collimator; (6) displaying a radiation field shape or virtual multileaf collimator shape of the patient in the visual field of the camera, and making the center of the radiation field shape or virtual multileaf collimator shape of the camera coincide with the center of the visual field of the camera; (7) forming a heavy ion radiation field shape; and (8) completing the multileaf collimator shape verification. The method is simple and convenient.
Owner:赵 瑞
A kind of kelp heavy ion radiation mutation breeding method
ActiveCN103766214BExcellent mutant plantsPreservation of new gene sourcesPlant genotype modificationHeavy ion radiationMutation breeding
Owner:SHANDONG ORIENTAL OCEAN SCI TECH
Device and method for measuring exposure of rice seed embryos to heavy ion radiation
The invention discloses a device for measuring the exposure of rice seed embryos to heavy ion radiation. The device is a seed box for study of rice seed space radiation effect. The device consists ofan upper cover plate (3), a nuclear track detector (4), a matrix (6) and a lower cover plate (7) from top to bottom in order, the matrix (6) is a square groove equipped with a plurality of ellipticalholes (5), the elliptical holes (5) are through-holes and are used for installing and fixing rice seeds (8), the nuclear track detector (4) is installed in the square groove, and is fixed through theupper cover plate (3) and the lower cover plate (7). Based on the device, the invention also discloses a method for measuring the exposure of rice seed embryos to heavy ion radiation, and the method can acquire the linear energy transfer information of heavy ion radiation to the seed embryos. The method provided by the invention can accurately acquire the heavy ion radiation to the seed embryos, in addition to high energy and long-range heavy ions, the heavy ions also include low energy and short-range heavy ions.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Method for increasing starch yield of duckweed mutants through induced mutation by heavy ion radiation
InactiveCN111657142AHigh genetic stabilityPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsInduced mutationHeavy ion radiation
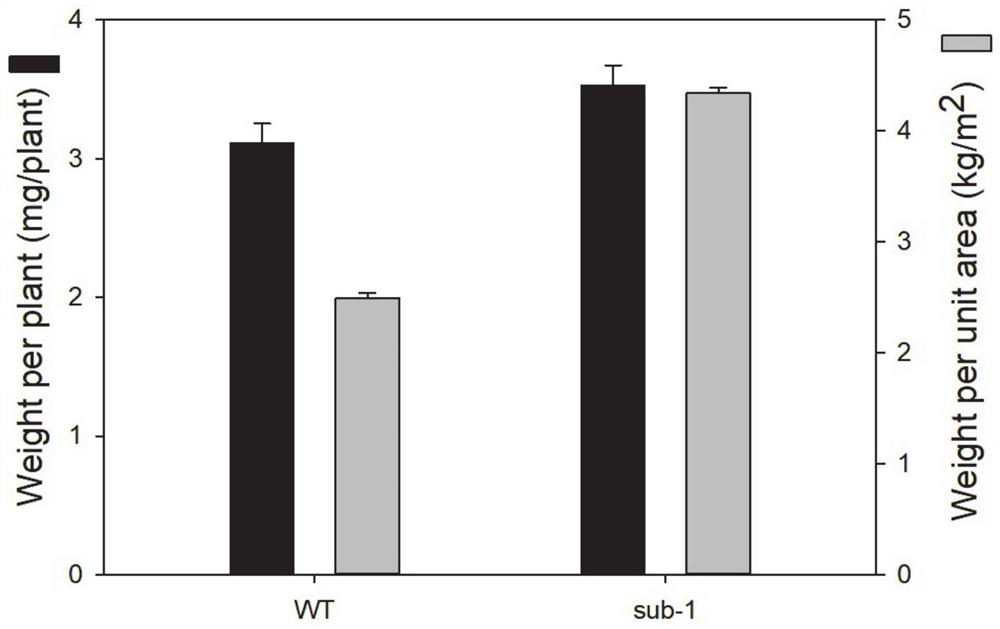
The invention specifically relates to a method for increasing the starch yield of duckweed mutants through induced mutation by heavy ion radiation. Duckweed is an ideal plant material for starch production. In order to further improve the starch production efficiency of duckweed, the invention provides a method for increasing the starch yield of duckweed mutants through induced mutation by heavy ion radiation. The method comprises the specific steps: performing induced mutation on duckweed callus through heavy ion radiation, performing differentiation culture so as to obtain regenerated plants, screening plants with high-yield starch, and performing combination with certain culture conditions so as to achieve further increase of the starch yield. The starch yield of one mutant with a goodeffect is significantly increased compared to the starch yield of a control group. As an energy plant, the accumulation amount of biomass is crucial for production of bioethanol, the mass per mutant is increased by 13.5% compared with the mass of a wild type, and the biomass per unit area is increased by 74.0% compared with that of the wild type; and the mutants which are obtained by using the method have good genetic stability of traits, and are ideal engineering strains for production of bio-energy.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com