Patents
Literature
56 results about "Multileaf collimator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
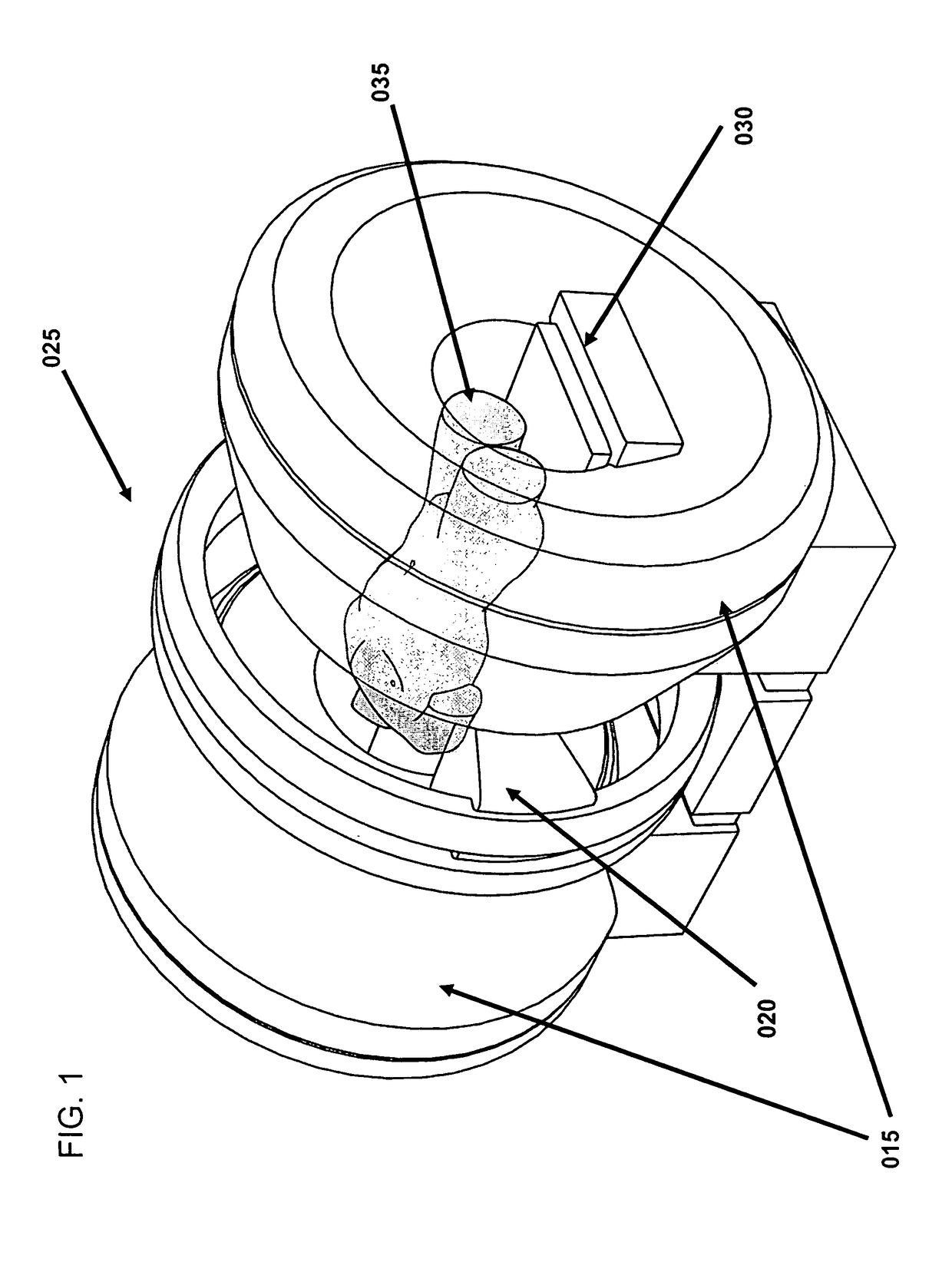
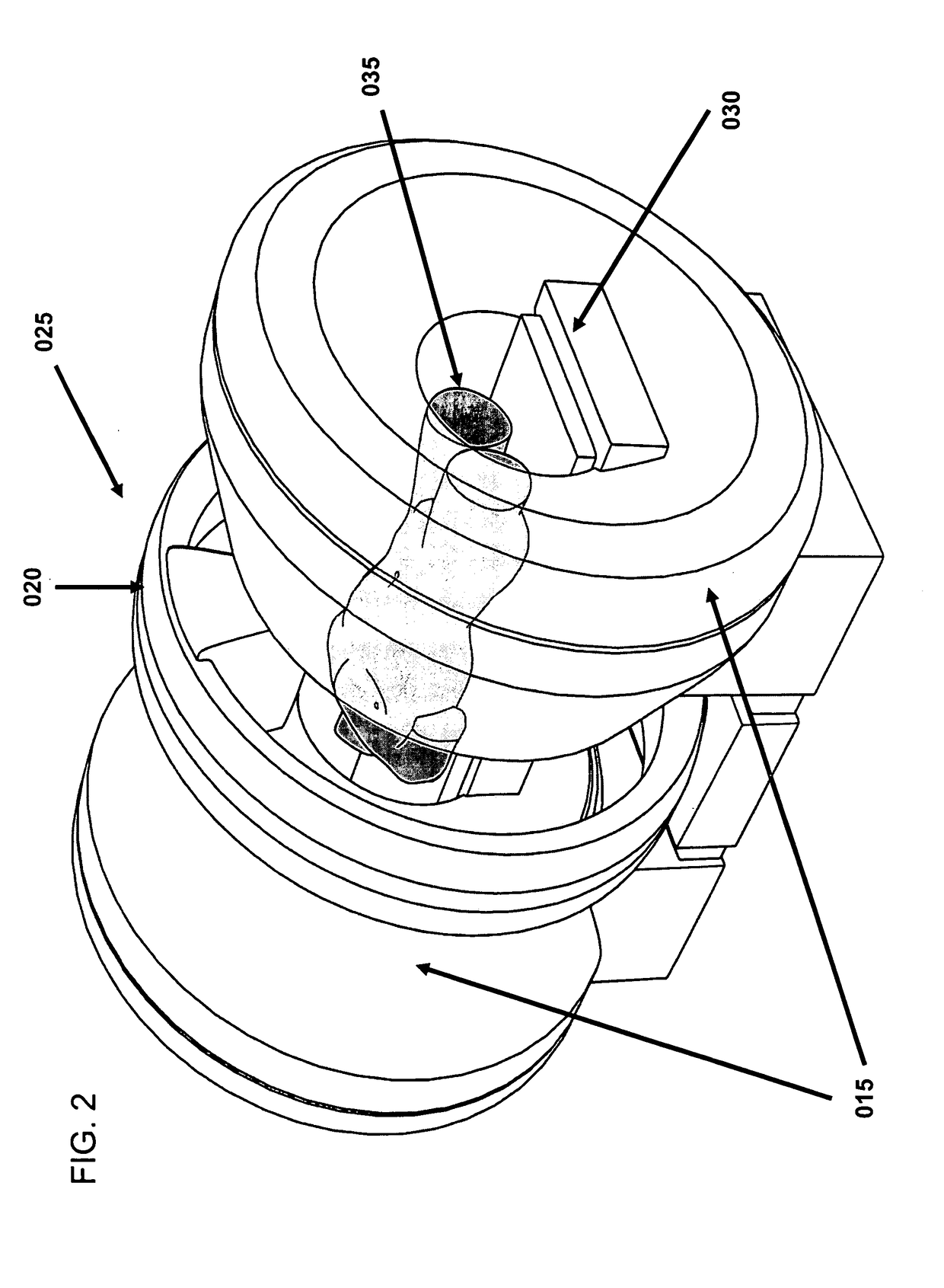
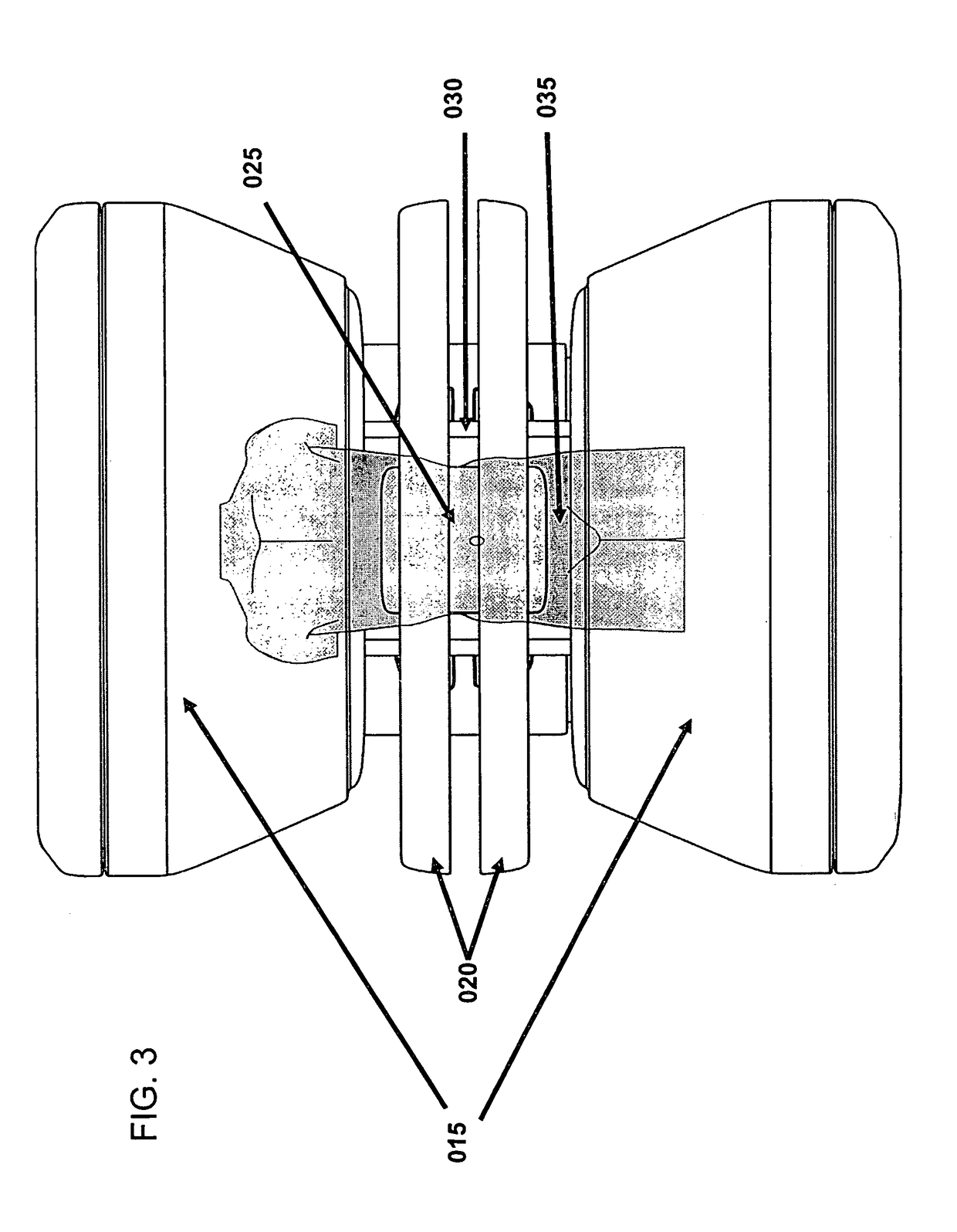
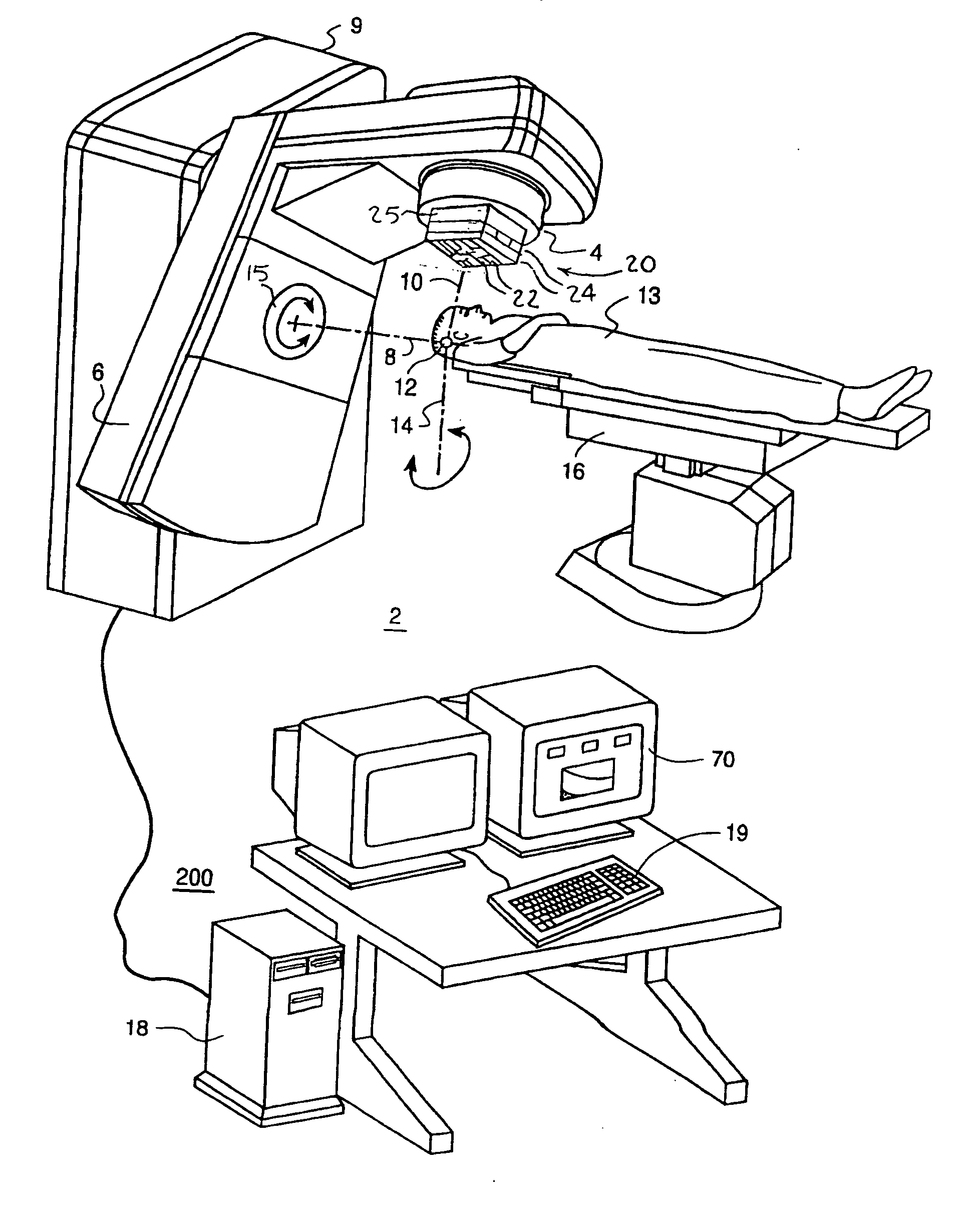
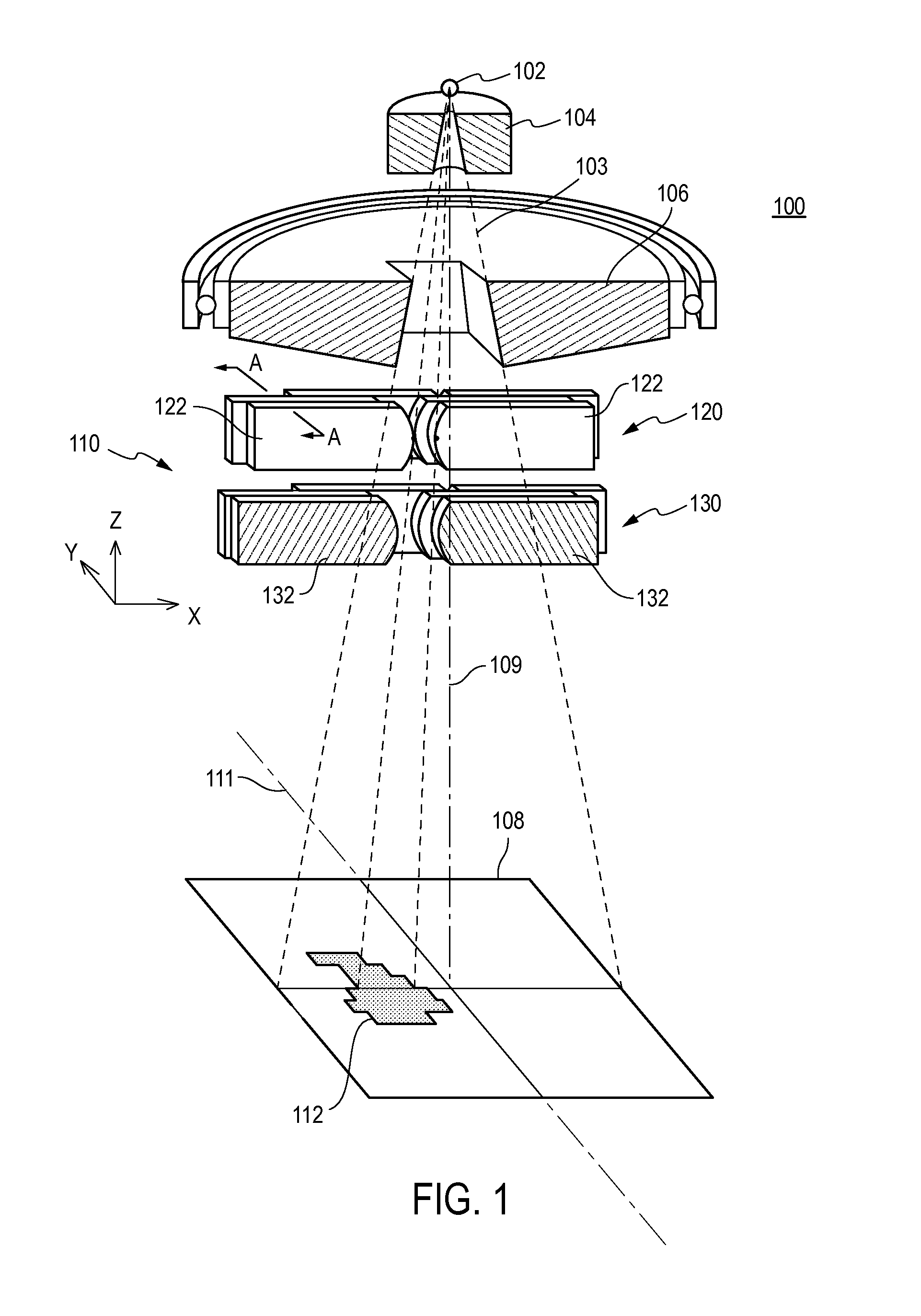
A multileaf collimator (MLC) is a device made up of individual "leaves" of a high atomic numbered material, usually tungsten, that can move independently in and out of the path of a radiotherapy beam in order to shape it and vary its intensity.
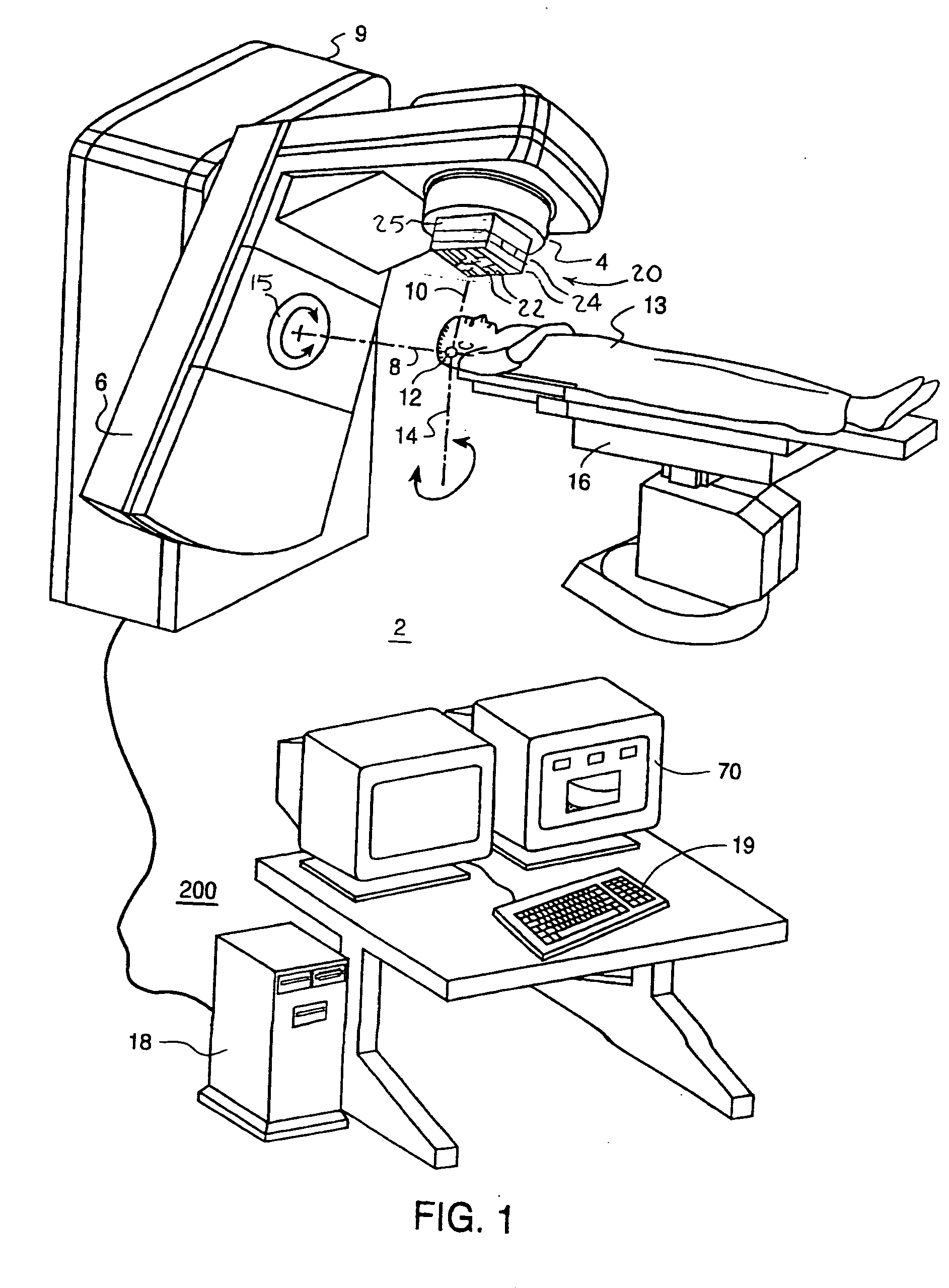
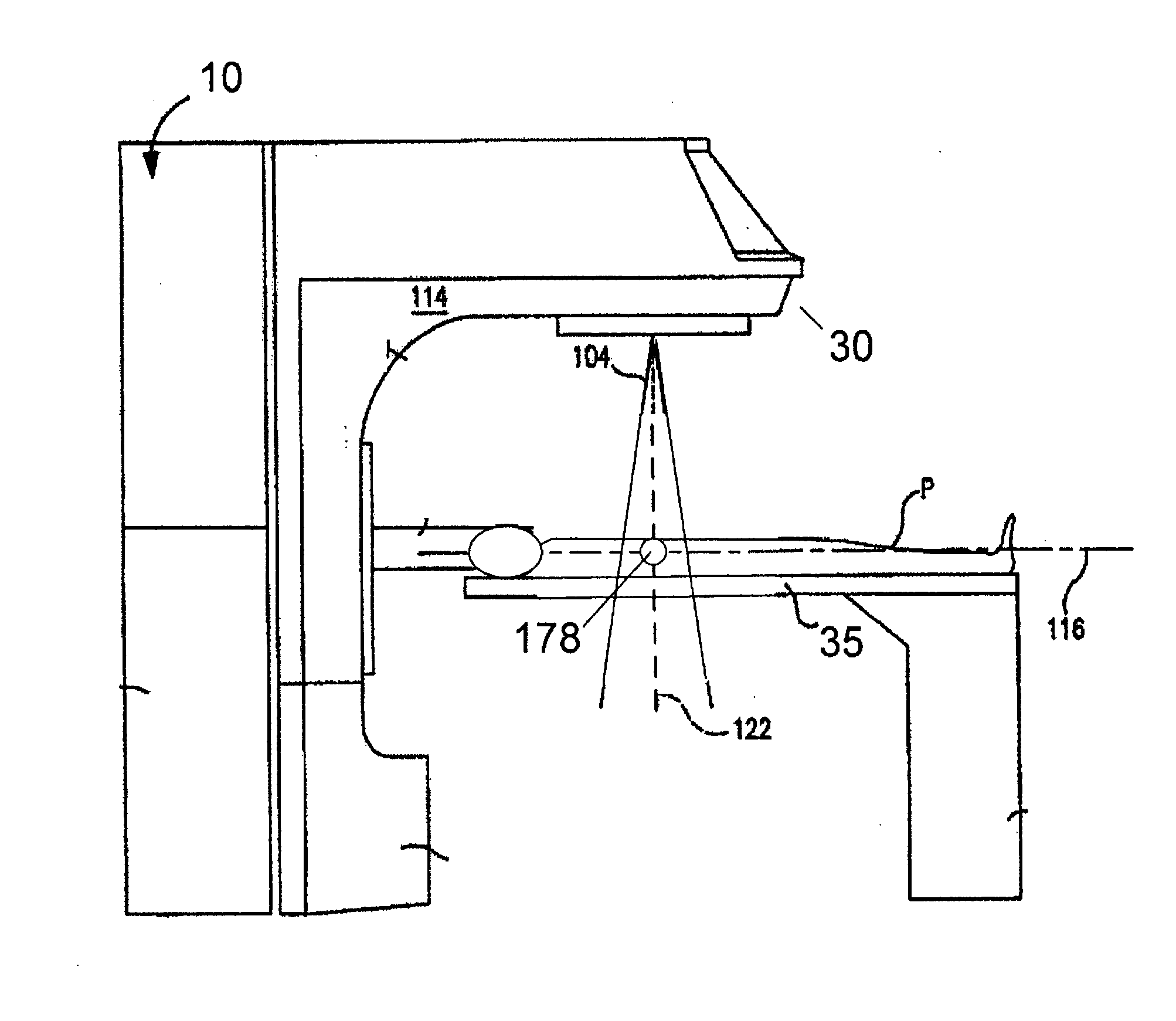
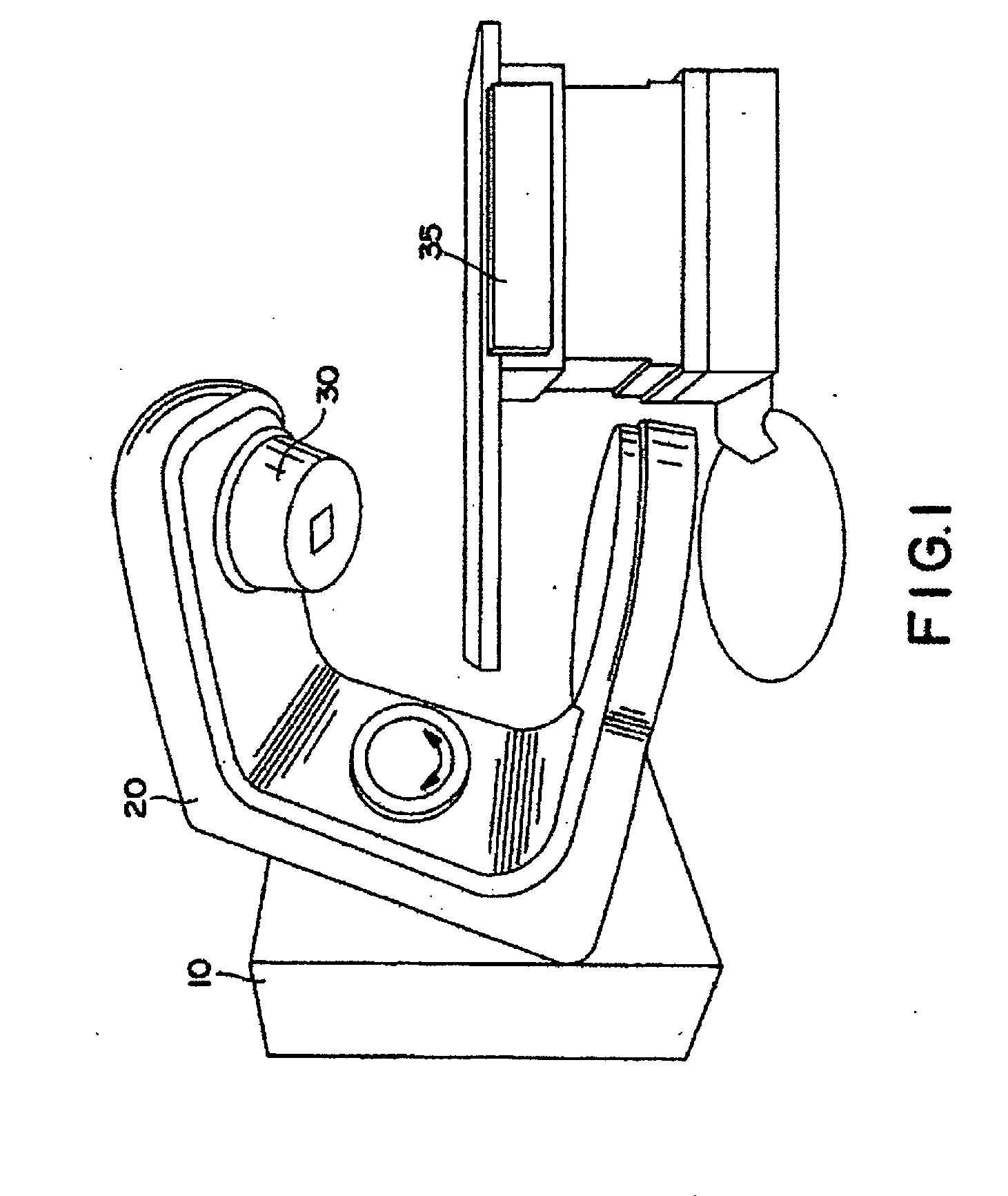
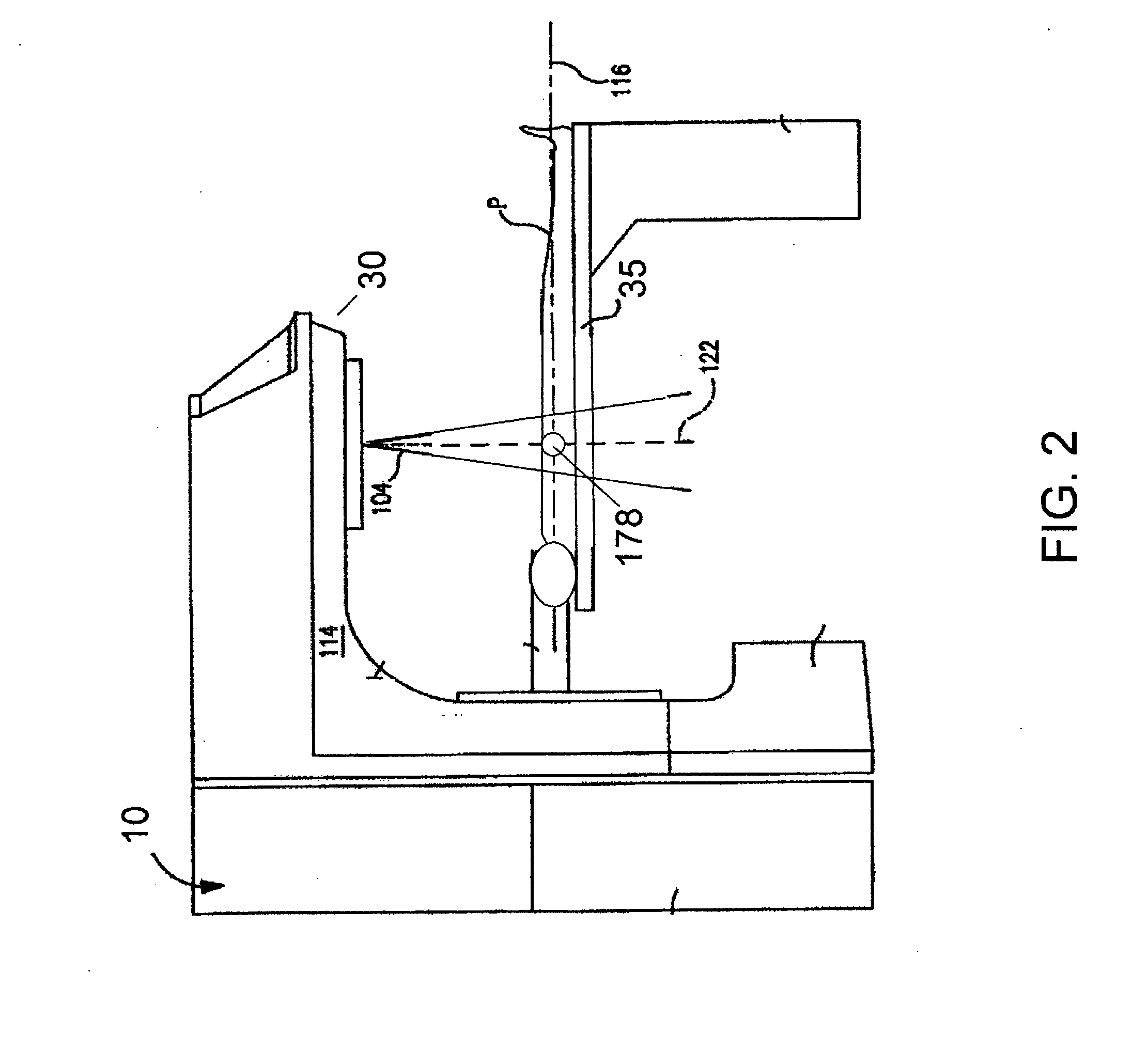
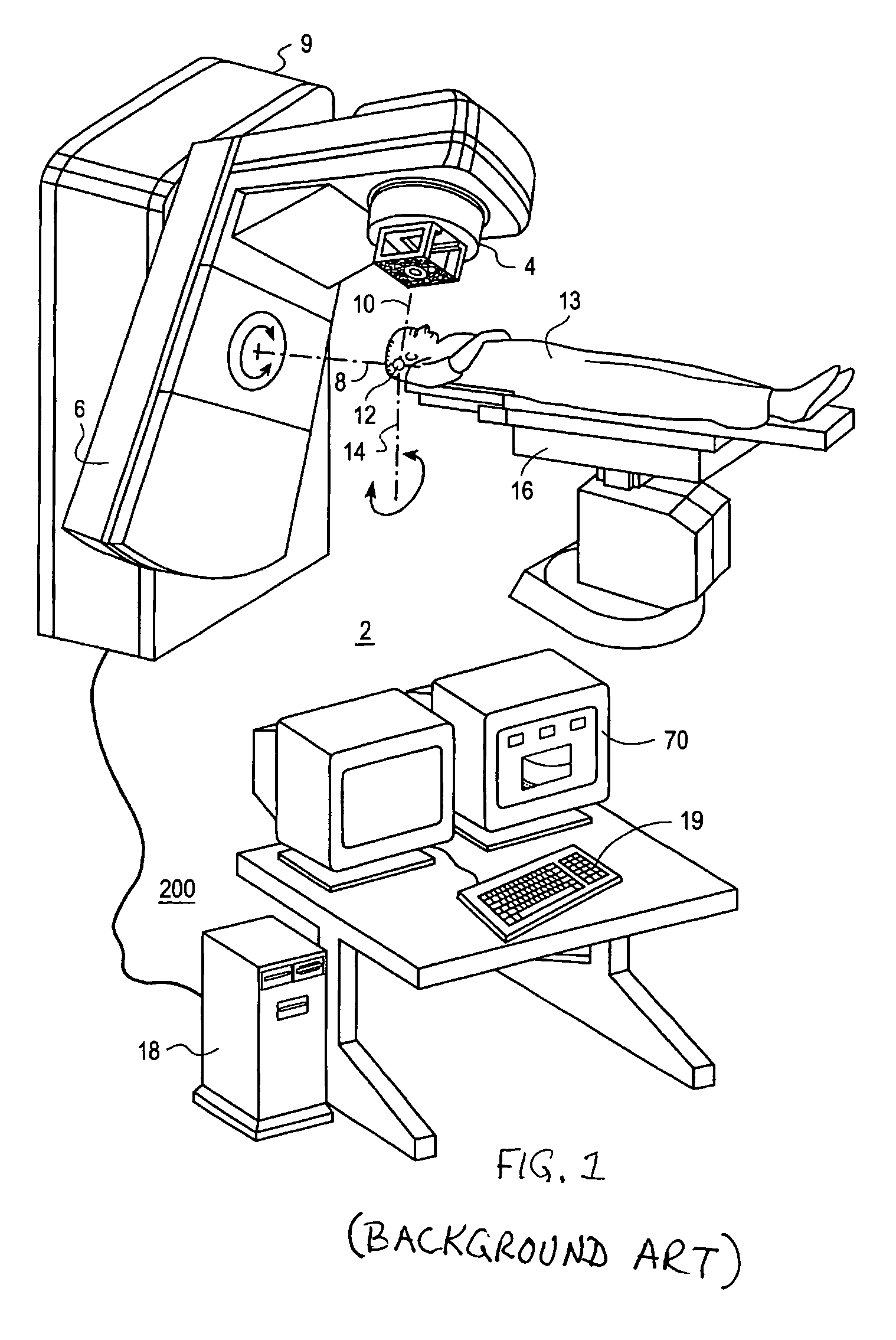
System for delivering conformal radiation therapy while simultaneously imaging soft tissue
InactiveUS7907987B2Accurate guideIncrease speedMagnetic measurementsMicrowave therapyImage resolutionConformal radiation therapy
A device and a process for performing high temporal- and spatial-resolution MR imaging of the anatomy of a patient during intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) to directly measure and control the highly conformal ionizing radiation dose delivered to the patient for the treatment of diseases caused by proliferative tissue disorders. This invention combines the technologies of open MRI, multileaf-collimator or compensating filter-based IMRT delivery, and cobalt teletherapy into a single co-registered and gantry mounted system.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
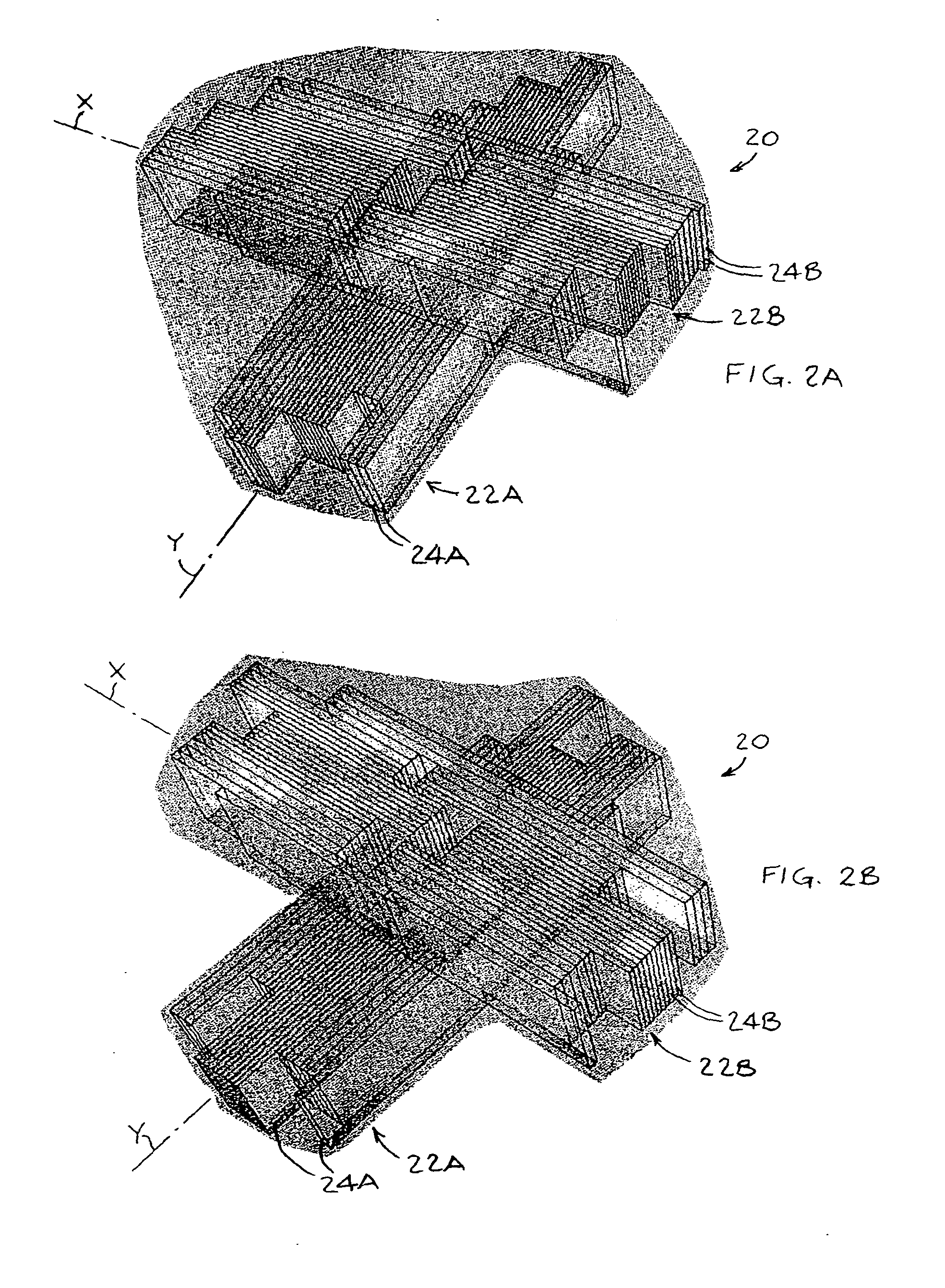
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy with a multilayer multileaf collimator
InactiveUS20050058245A1Handling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapySpatial OrientationsControl system
An intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) system including a radiation beam delivery device positionable in a plurality of spatial orientations, an IMRT control system adapted to modulate at least an intensity of a radiation beam emanating from the radiation beam delivery device depending on at least one of the spatial orientations of the radiation beam delivery device and in accordance with an IMRT intensity map, and a multilayer multileaf collimator placed in a path of the radiation beam emanating from the radiation beam delivery device, the multilayer multileaf collimator including a plurality of layers of radiation blocking leaves, the layers being at different positions along the path of the radiation beam generally traverse to the radiation beam.
Owner:EIN GAL MOSHE
Radiation therapy system and method of using the same
A method of using a radiation system having a multileaf collimator (“MLC”) to adjust for unevenness in the radiation emitted by the system is disclosed. By appropriately controlling the MLC in accordance with the invention the system can be operated without a flattening filter. In addition, the invention allows the system user to vary the radiation beam energy in the course of a single treatment, without the need to use or change flattening filters. A map of the uneven radiation beam intensity in the treatment area is obtained, and the map information is combined with a treatment plan to control movement of the leaves of the MLC such that each area receives the correct radiation dose.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
System for Delivering Conformal Radiation Therapy While Simultaneously Imaging Soft Tissue
ActiveUS20100113911A1Accurate guideIncrease speedMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringDiseaseTherapeutic Technique
A device and a process for performing high temporal- and spatial-resolution MR imaging of the anatomy of a patient during intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) to directly measure and control the highly conformal ionizing radiation dose delivered to the patient for the treatment of diseases caused by proliferative tissue disorders. This invention combines the technologies of open MRI, multileaf-collimator or compensating filter-based IMRT delivery, and cobalt teletherapy into a single co-registered and gantry mounted system.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
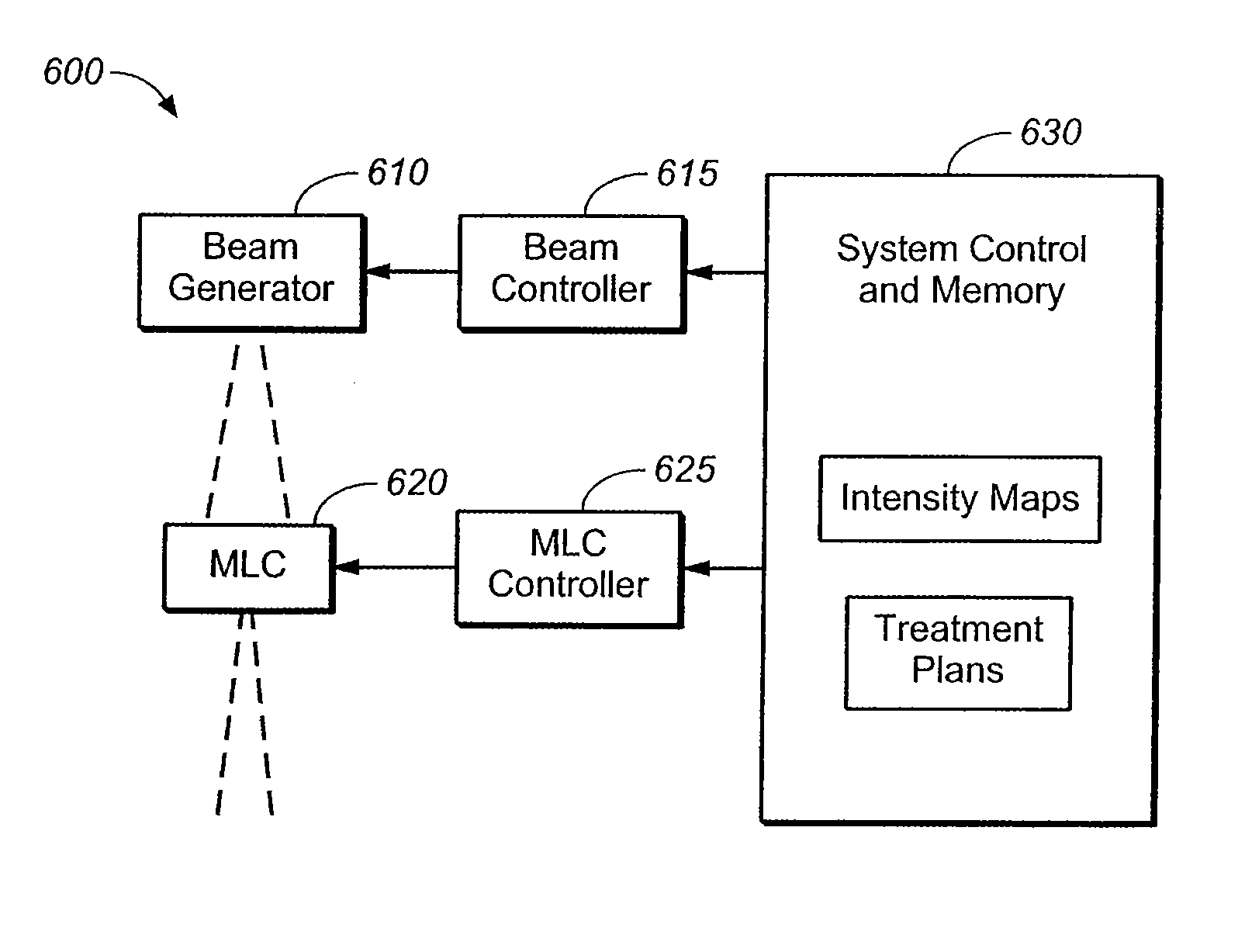
Method for controlling modulation strength in radiation therapy
ActiveUS7809107B2Increase the number ofSmall sizeLight therapyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyMultiple formsLight beam
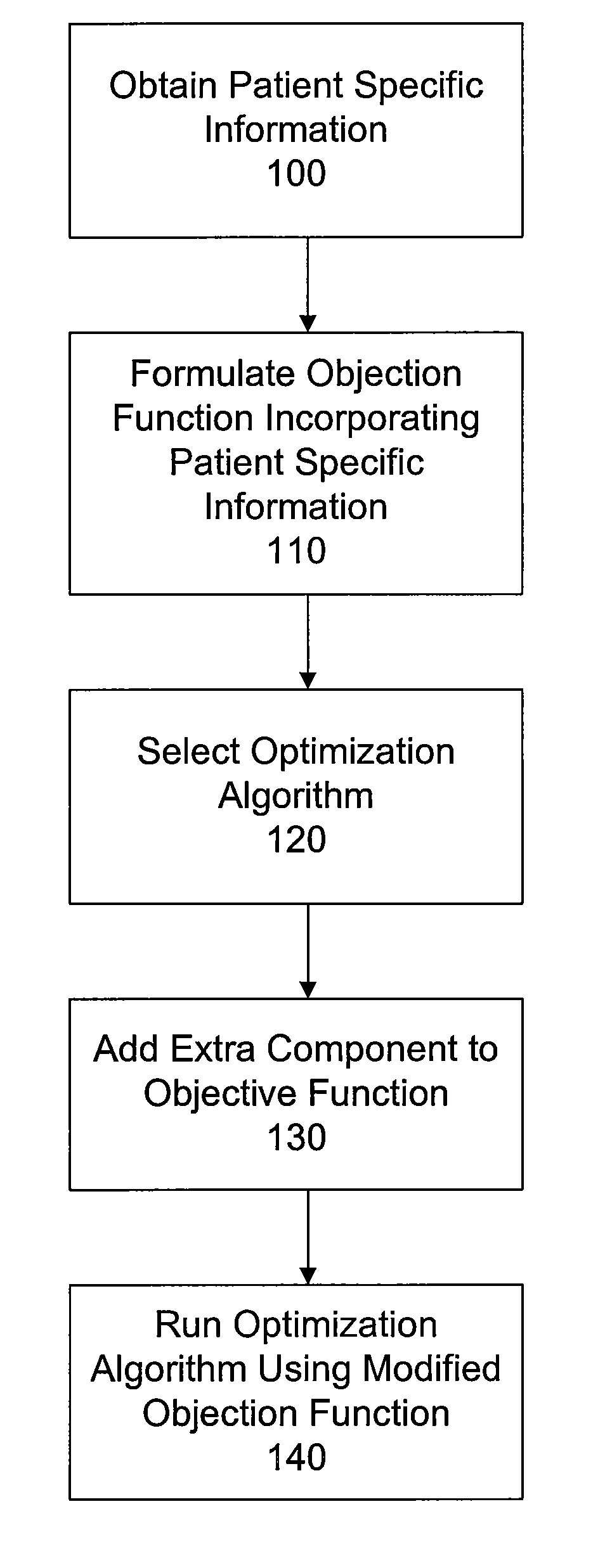
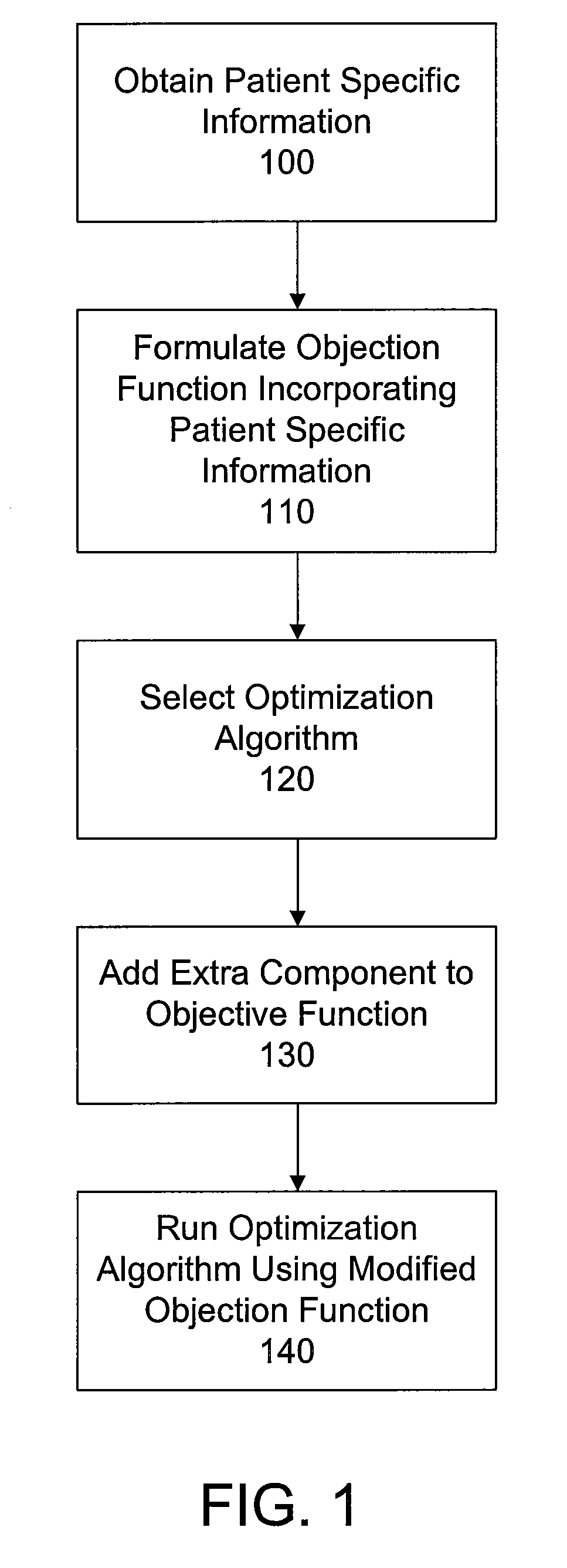
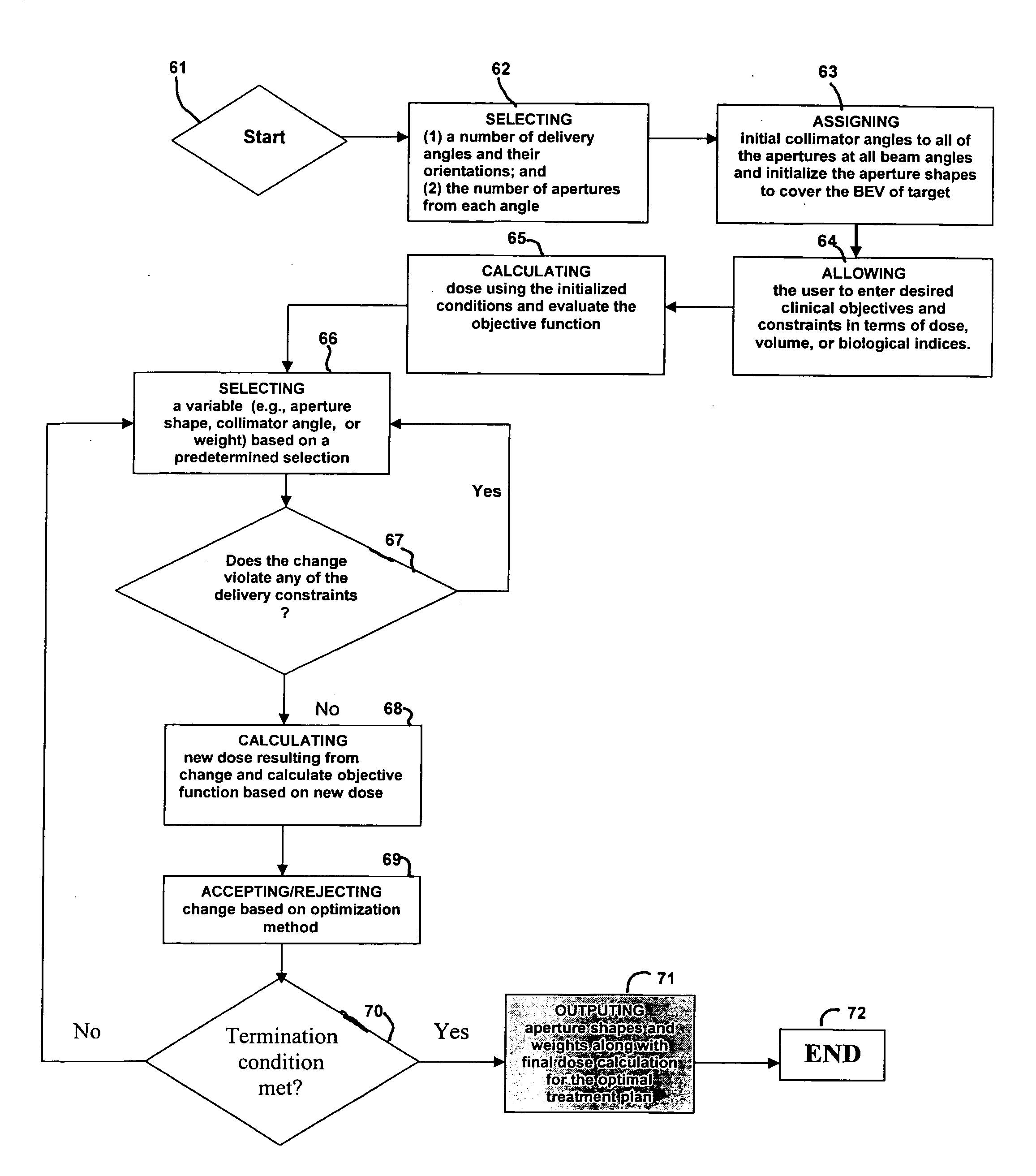
Methods for developing and using treatment plans with improved modulation for radiation therapy are disclosed. The methods involve adding an extra component to the patient-related objective function in order to make the optimization algorithm used to develop the treatment plan arrive at a solution with increased modulation. The extra component may take many forms. For example, the user may specify that the treatment plan favor solutions using a range of monitor units. The present invention is particularly useful in conjunction with radiotherapy systems having multileaf collimators for beam shaping, and in connection with advanced radiotherapy techniques, such as IMRT and arc therapy.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
Method for intensity modulated radiation treatment using independent collimator jaws
InactiveUS20060045238A1Increase freedomHighly conformalHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyIntensity-modulated radiation therapyTreatment use
The present invention is a method for treatment planning and delivery of the radiation treatment plan for the intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) treatment using linear accelerators (LINACs) not equipped with a multileaf collimator (MLC). The present invention makes the use of a simpler collimator consisting of only 4 collimator jaws. In addition, the method for treatment planning of the present invention may be performed on a computer separate from the LINAC control computer, so that the treatment planning system can generate IMRT treatment plans for LINACs and collimator jaws from different vendors.
Owner:PROWESS
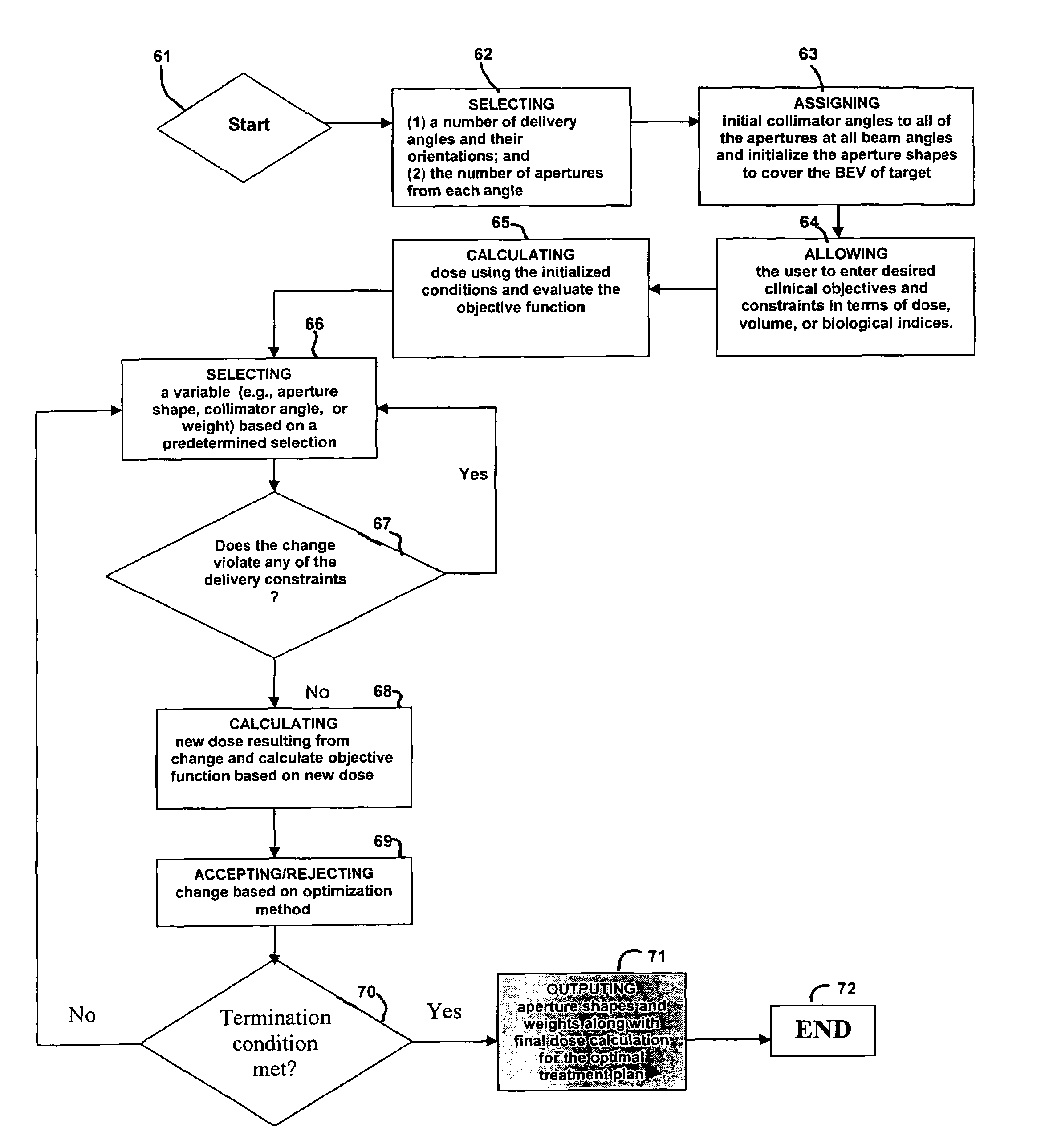
Radiation therapy inverse treatment planning using a regularization of sparse segments
InactiveUS20110085643A1Reduce in quantityReduce the numberX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyInverse treatment planningTherapy planning
A method of reducing a total number of beam segments in a dose distribution for a radiation therapy field is provided. The method includes providing a multiobjective radiation therapy treatment plan using a suitably programmed computer, where the multiobjective radiation therapy treatment plan includes a radiation beam dose performance objective and a fluence map sparsity objective in a given fluence function domain, and providing a Pareto frontier of tradeoff criteria between the beam dose performance and a total number of radiation segments (or sub-fields) of the multiobjective radiation therapy treatment plan using the suitably programmed computer, where an achieved set of radiation beam dose distributions associated with efficiency points of the Pareto frontier are evaluated using a clinical acceptance criteria, where a clinically acceptable radiation beam dose distribution having a smallest number of the multileaf collimator segments is a final solution for the multiobjective radiation therapy treatment plan.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Radiation therapy system and method of using the same
A method of using a radiation system having a multileaf collimator (“MLC”) to adjust for unevenness in the radiation emitted by the system is disclosed. By appropriately controlling the MLC in accordance with the invention the system can be operated without a flattening filter. In addition, the invention allows the system user to vary the radiation beam energy in the course of a single treatment, without the need to use or change flattening filters. A map of the uneven radiation beam intensity in the treatment area is obtained, and the map information is combined with a treatment plan to control movement of the leaves of the MLC such that each area receives the correct radiation dose.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
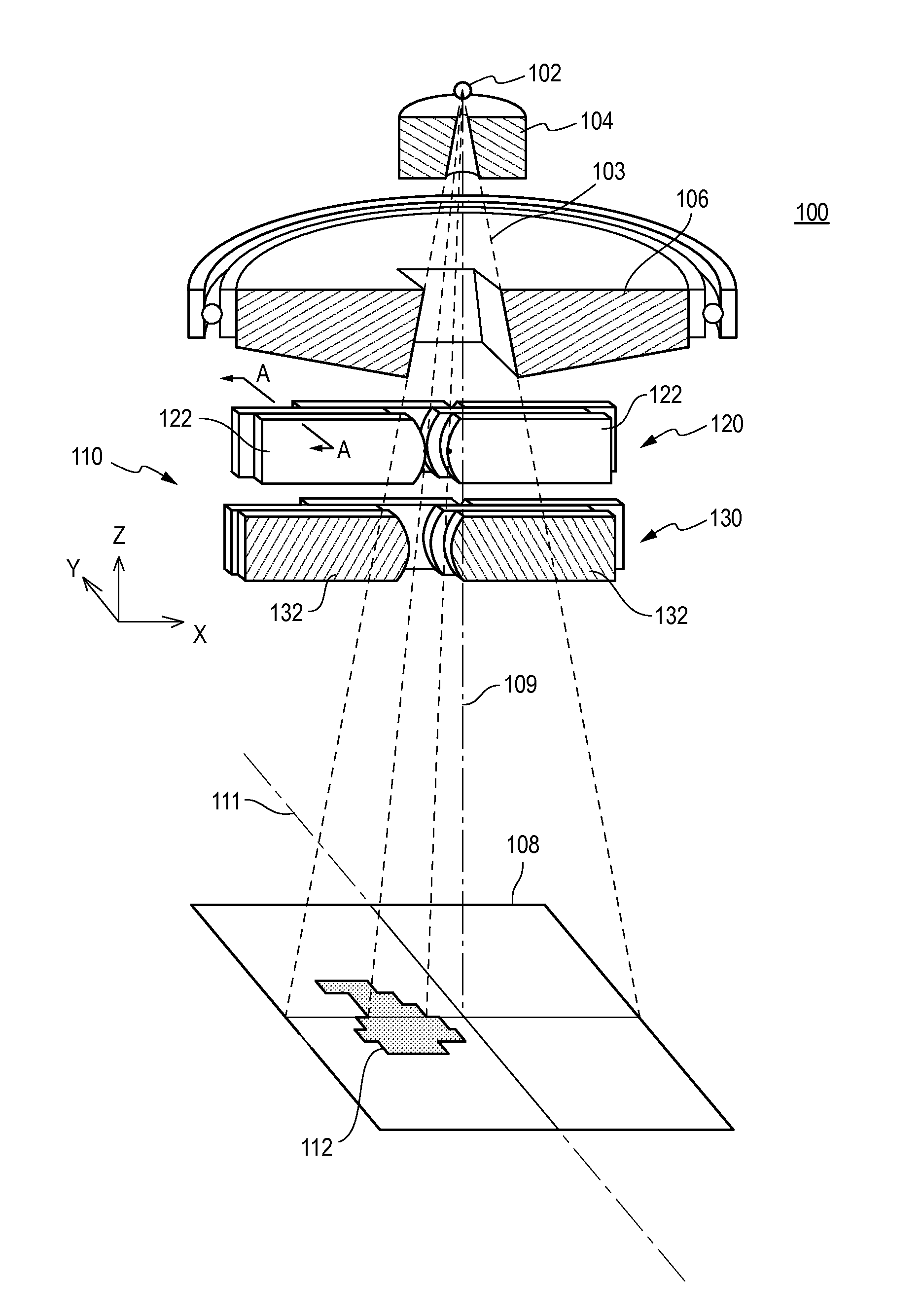
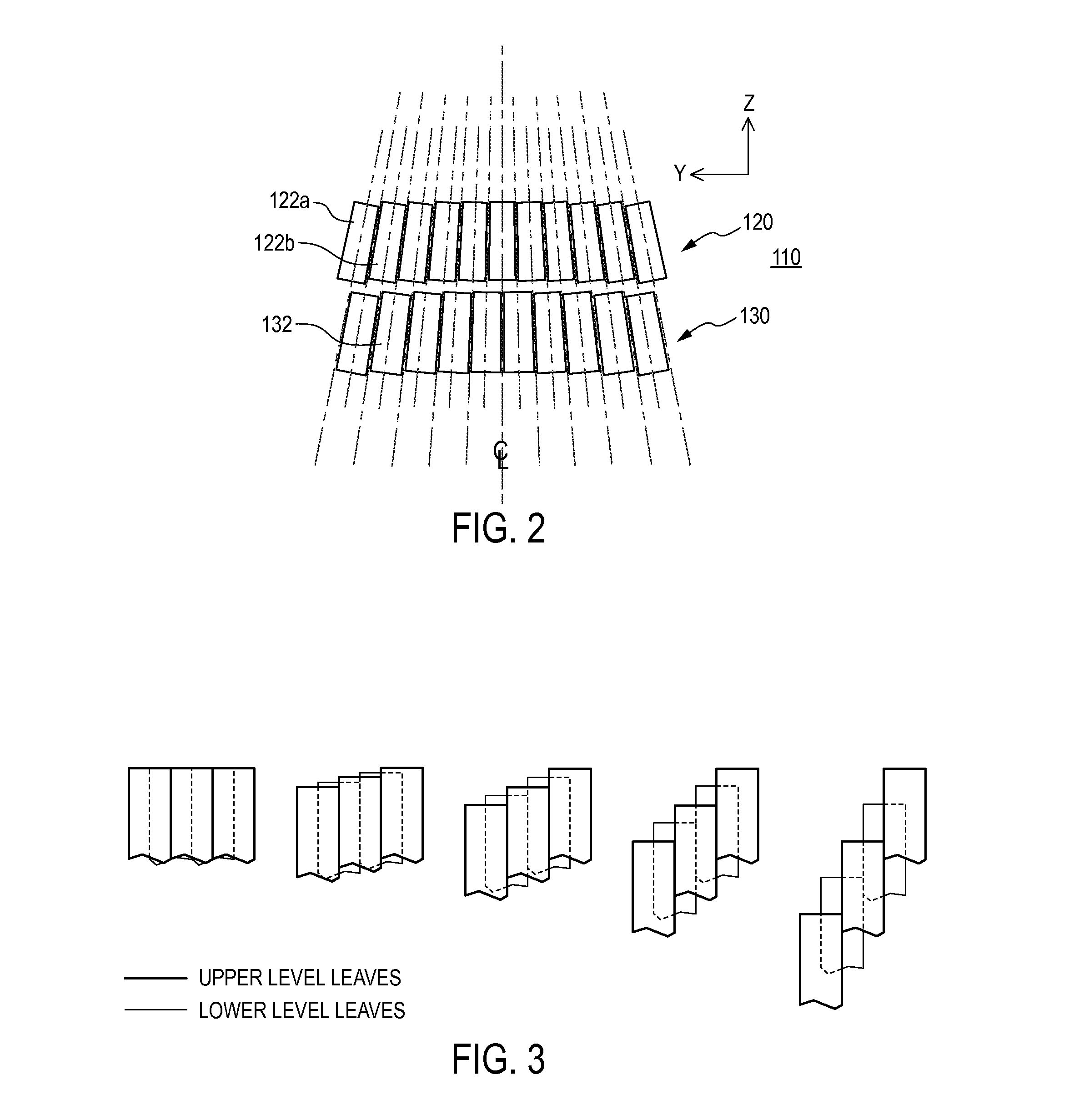
Multi level multileaf collimator leaf tip shape effects and penumbra optimization
ActiveUS20150273239A1Easy to shapeHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyLight beamField of view
A multi level multileaf collimator employs leaves with leaf tips having a non-square shape in a beam's eye view to improve beam shaping effect and penumbra performance. The multi level multileaf collimator includes a first multileaf collimator in a first level comprising beam blocking leaves longitudinally movable in a first direction, and a second multileaf collimator in a second level comprising beam blocking leaves longitudinally movable in a second direction. The first direction may be generally parallel with the second direction and the leaves of the first multileaf collimator may laterally offset the leaves of the second multileaf collimator. The beam blocking leaves of the first multileaf collimator may comprise an end portion having a non-square shape in a beam's eye view.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG +1
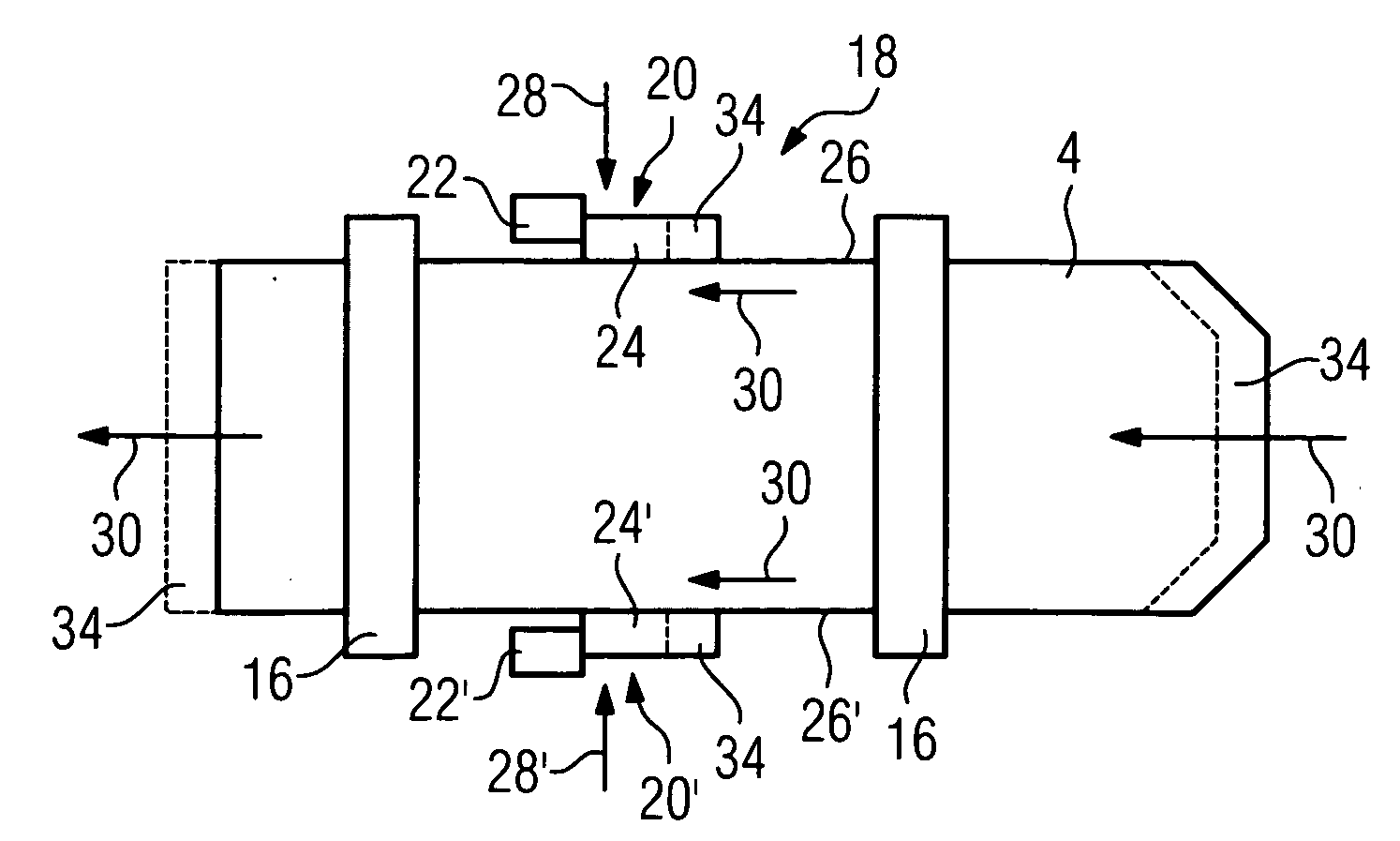
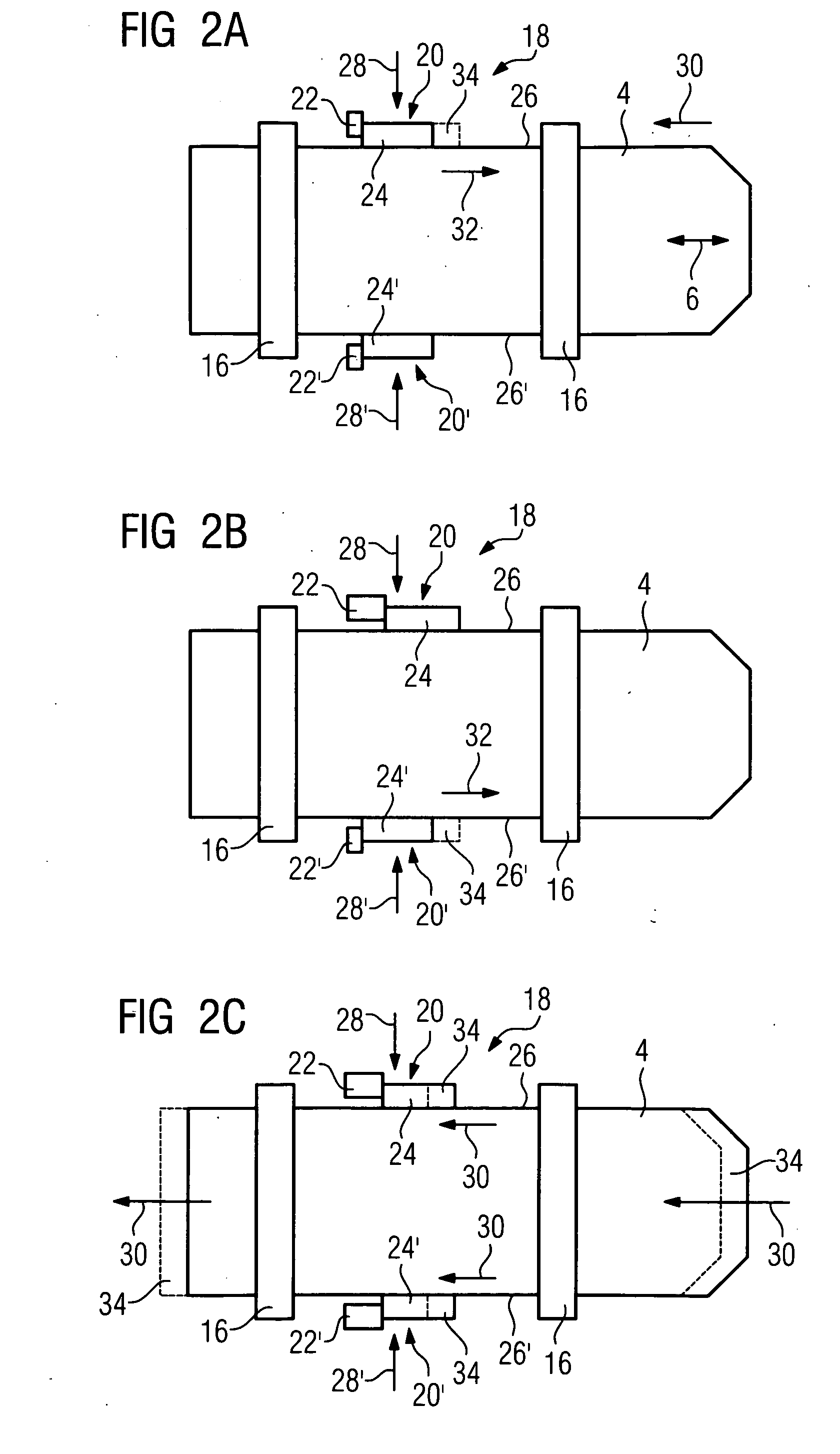
Multileaf collimator and radiation therapy device
InactiveUS7792252B2Improve accuracyHigh degreeHandling using diaphragms/collimetersRadiation therapyPiezoelectric actuatorsRadiation therapy
The invention relates to a multileaf collimator having a plurality of leaves mounted displaceably in an adjusting direction for establishing a contour of a beam path. Each displaceably mounted leaf is assigned at least one linear drive having at least one piezoelectric actuator for displacing the leaf in the adjusting direction. Because the piezoelectric actuator can be driven precisely, an improved radiation therapy can be achieved, particularly in the case of a radiation therapy device having a multileaf collimator of said kind, owing to precise establishing of the contour.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
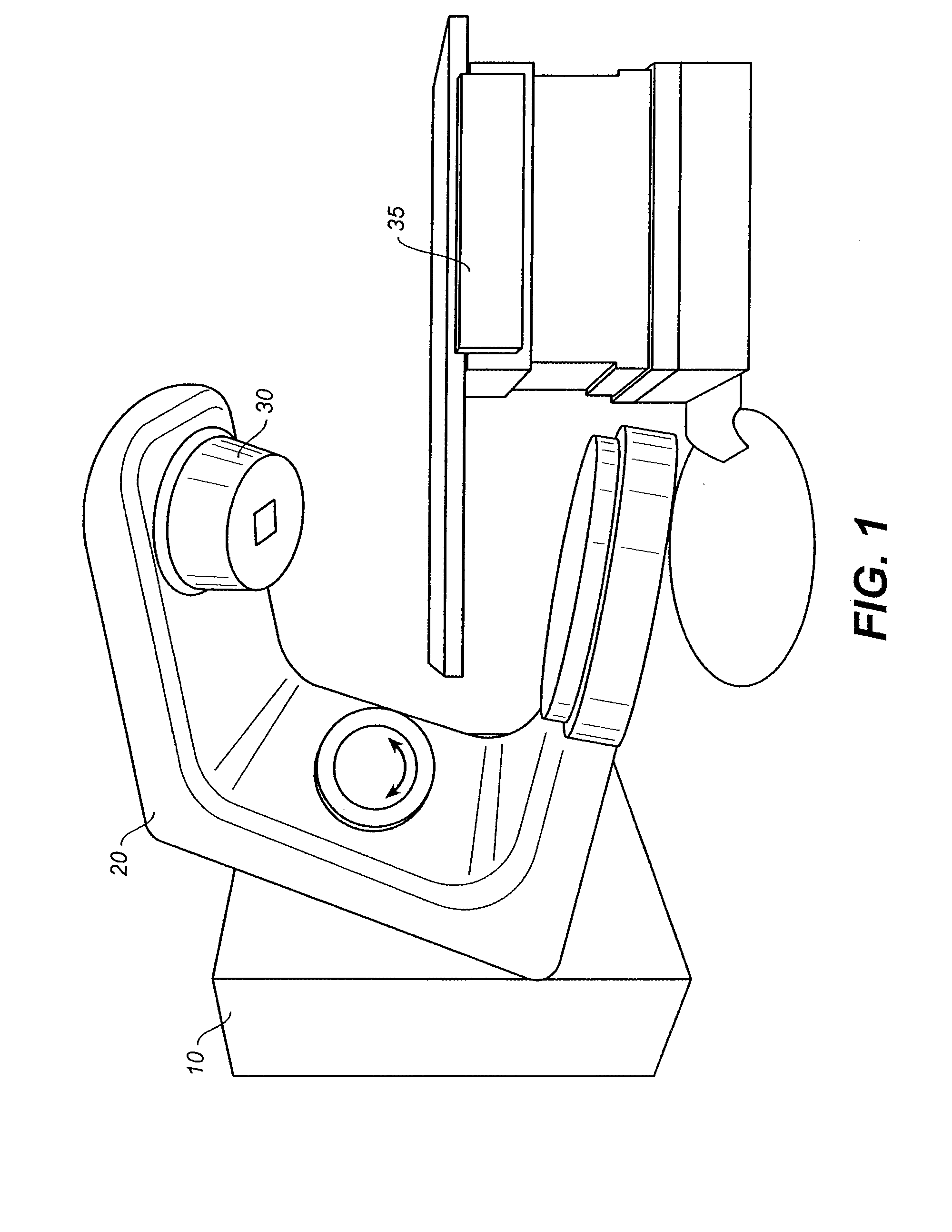
Multileaf collimator
InactiveUS7564951B2Accurate settingHandling using diaphragms/collimetersRadiation therapyComputer scienceMultileaf collimator
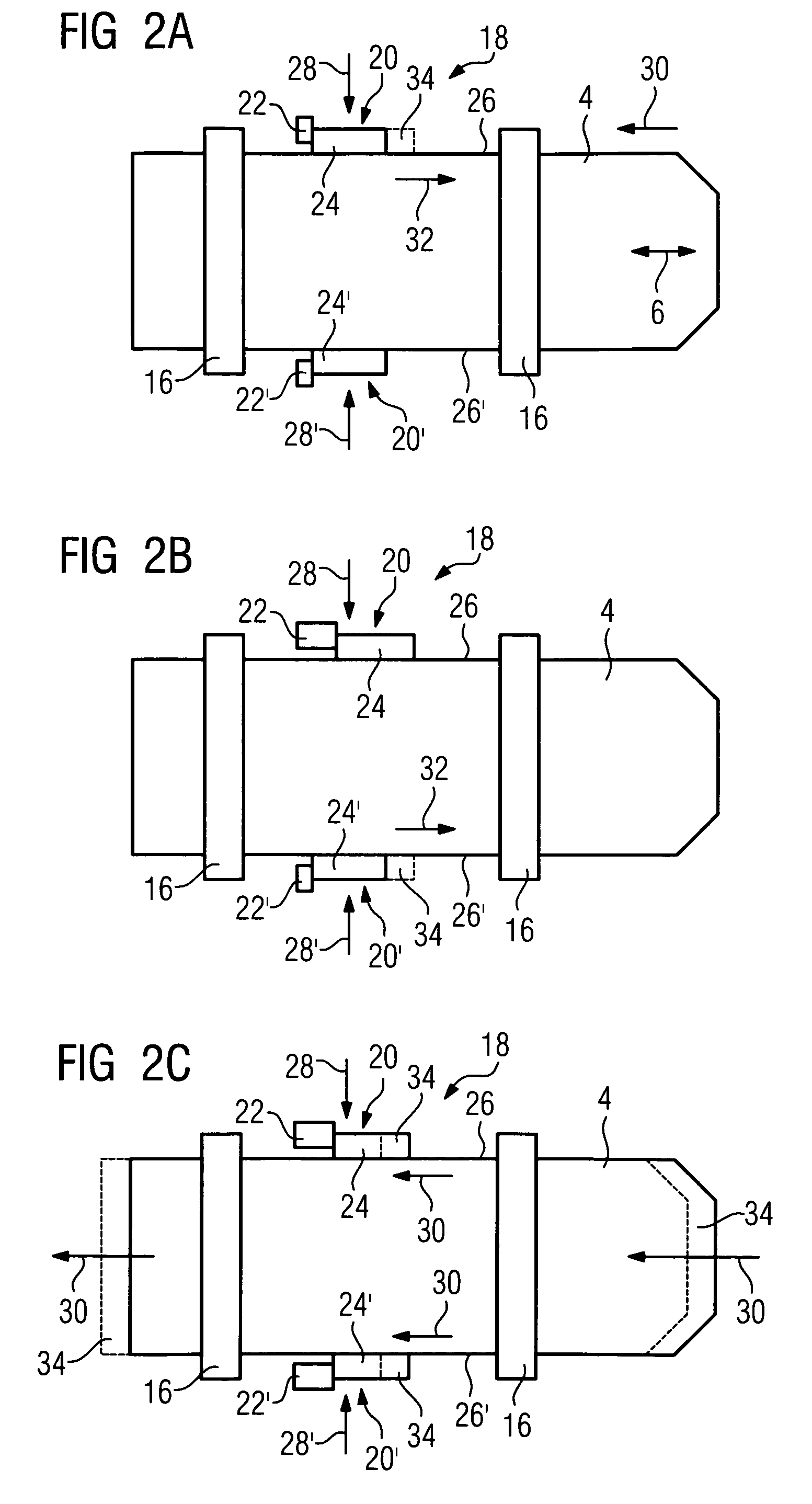
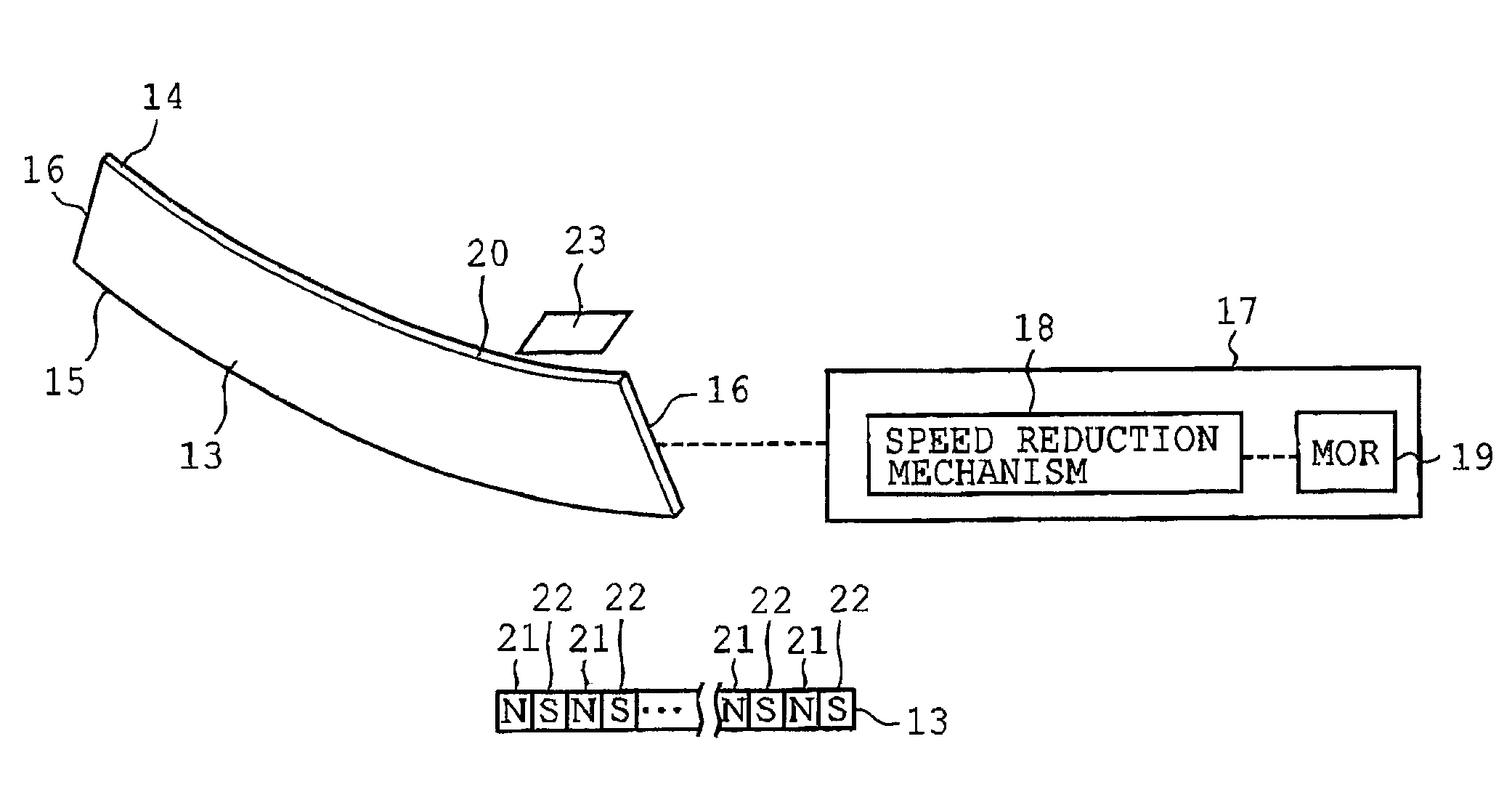
A multileaf collimator includes a first leaf block group including plural leaf blocks, a second leaf block group including plural leaf blocks arranged in the same direction as the first leaf block group and disposed opposite the leaf blocks of the first leaf block group, plural magnetic layers located on the respective leaf blocks of the first and second leaf block groups so as to be positioned on faces of the leaf blocks along a moving direction of the leaf blocks, plural magnetic sensors mounted on the respective leaf blocks and varying output signals when the respective leaf blocks are moved in an oncoming direction or a departing direction, and a control device controlling drive mechanisms according to the output signals delivered by the respective magnetic sensors so that spacing between the leaf blocks of the first and second leaf blocks is adjusted into a target configuration.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
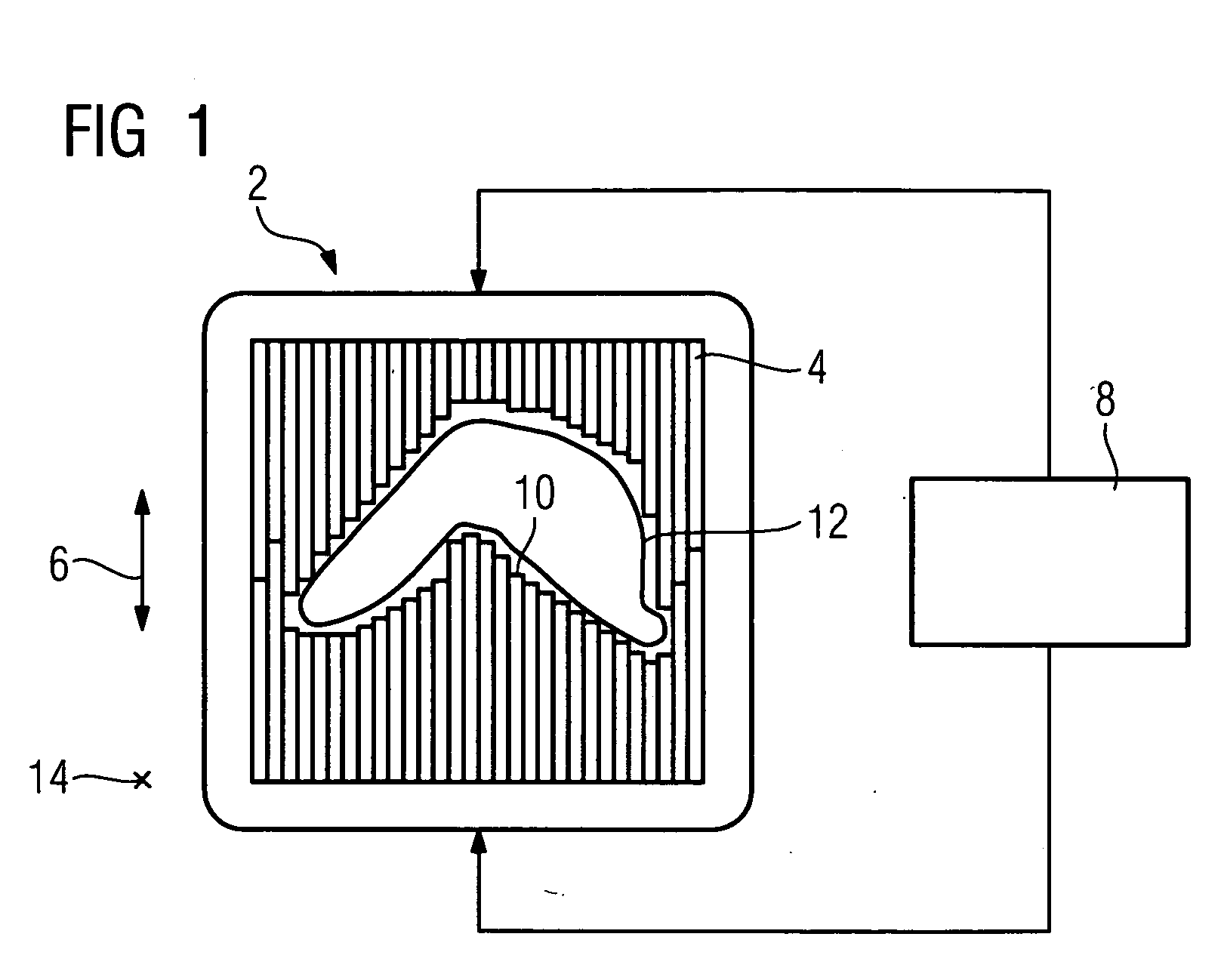
Particle-Beam Treatment System
ActiveUS20080298553A1Avoid radiationPrevent inappropriateHandling using diaphragms/collimetersDiagnostic recording/measuringParticle beamEngineering
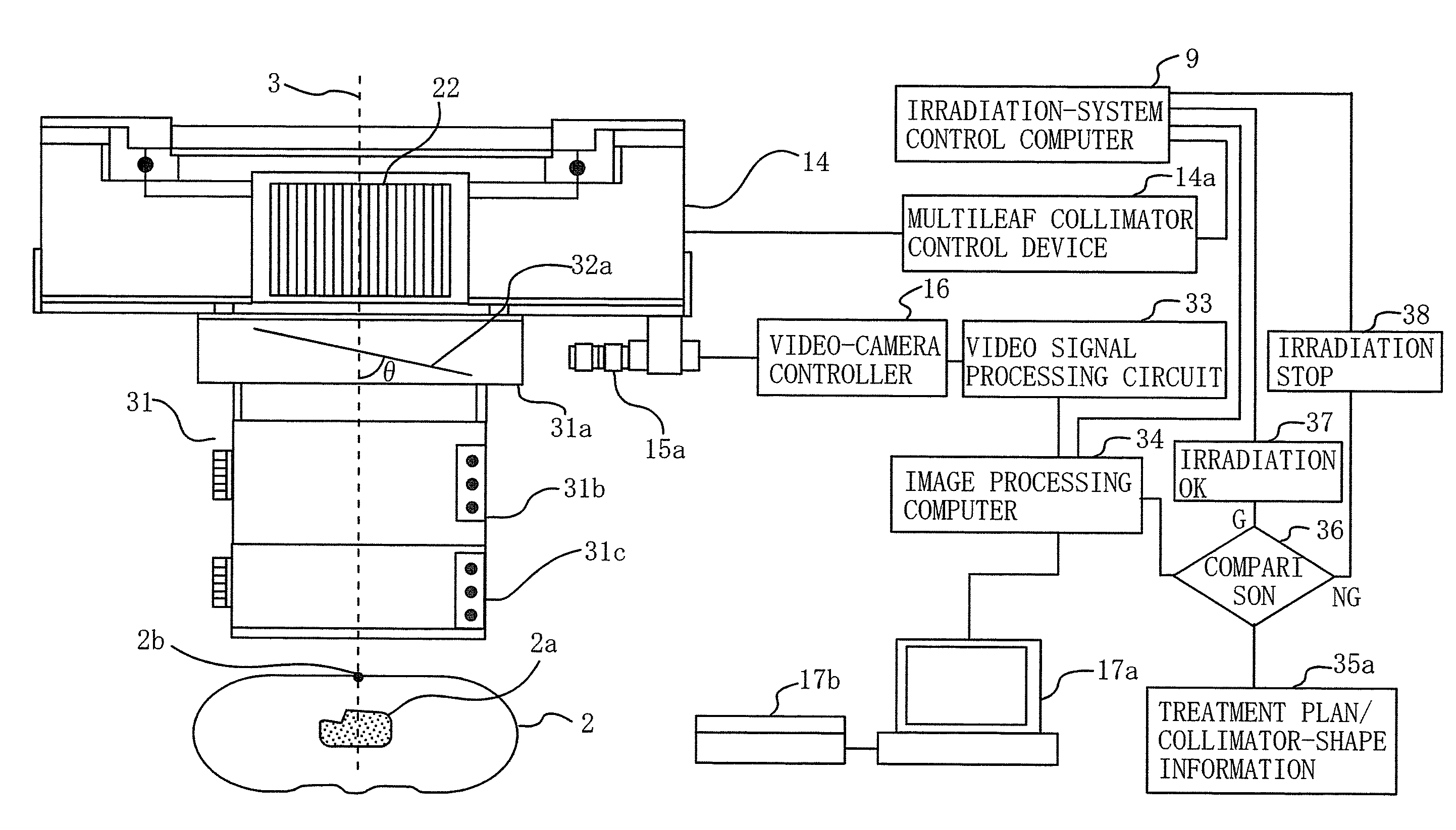
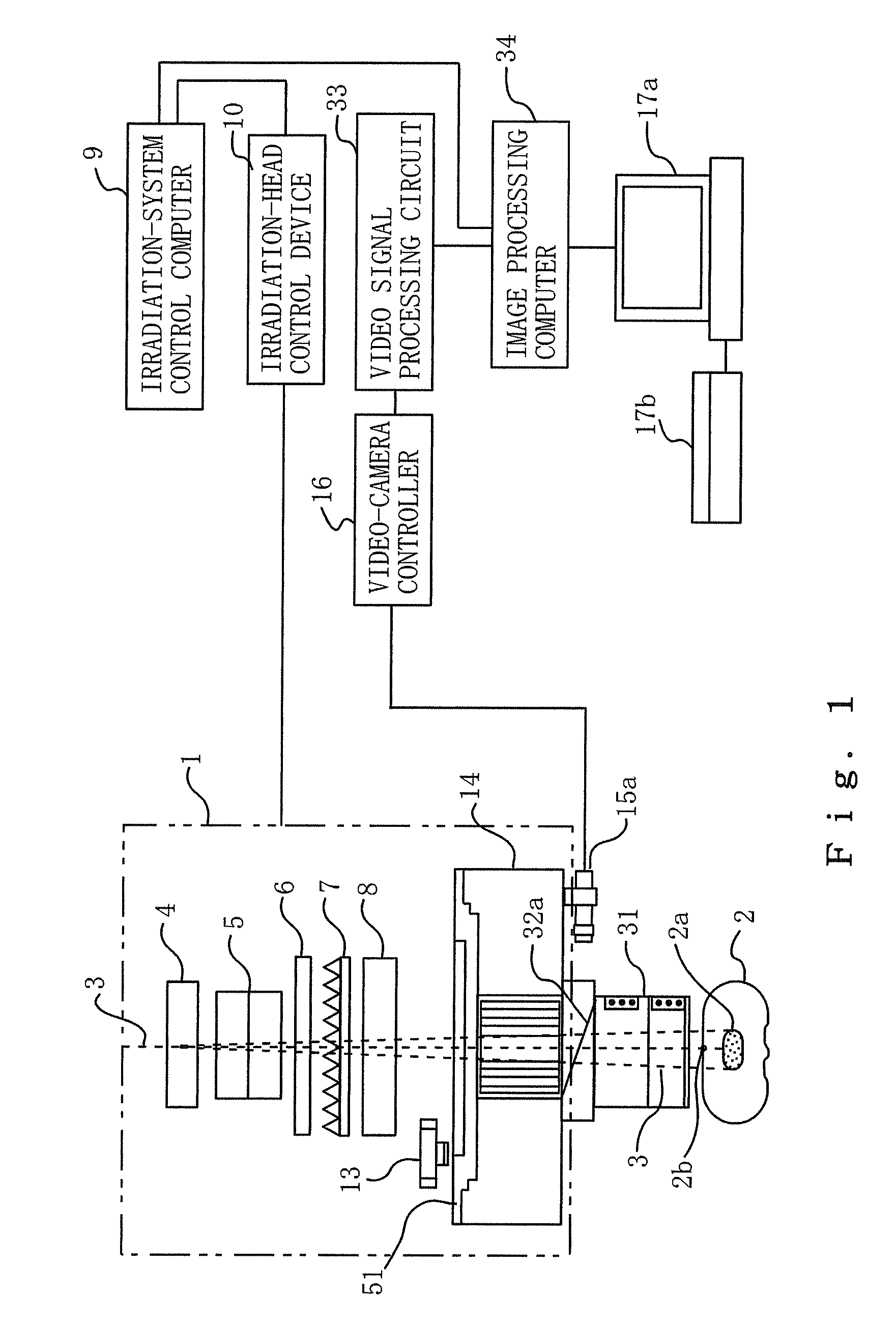
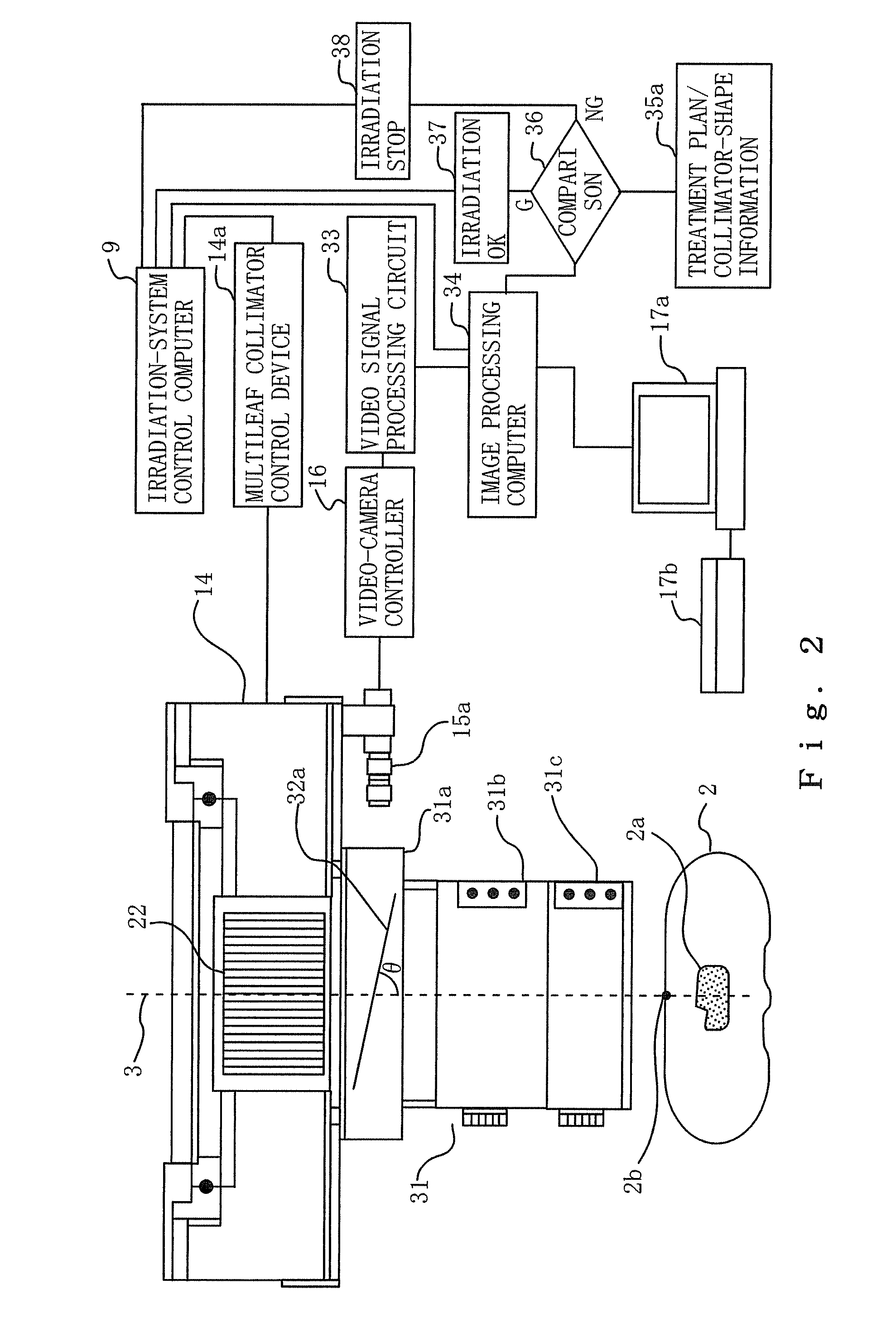
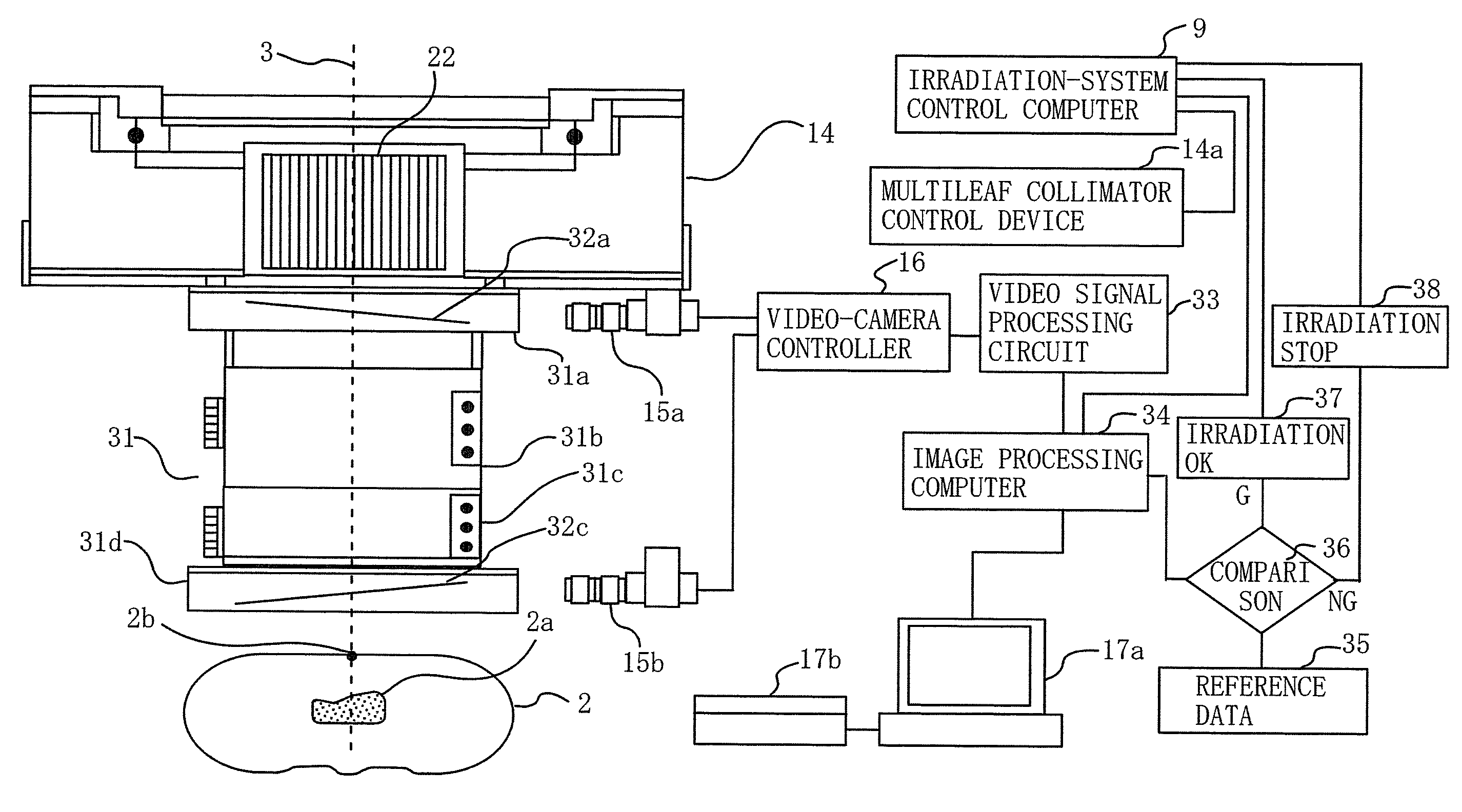
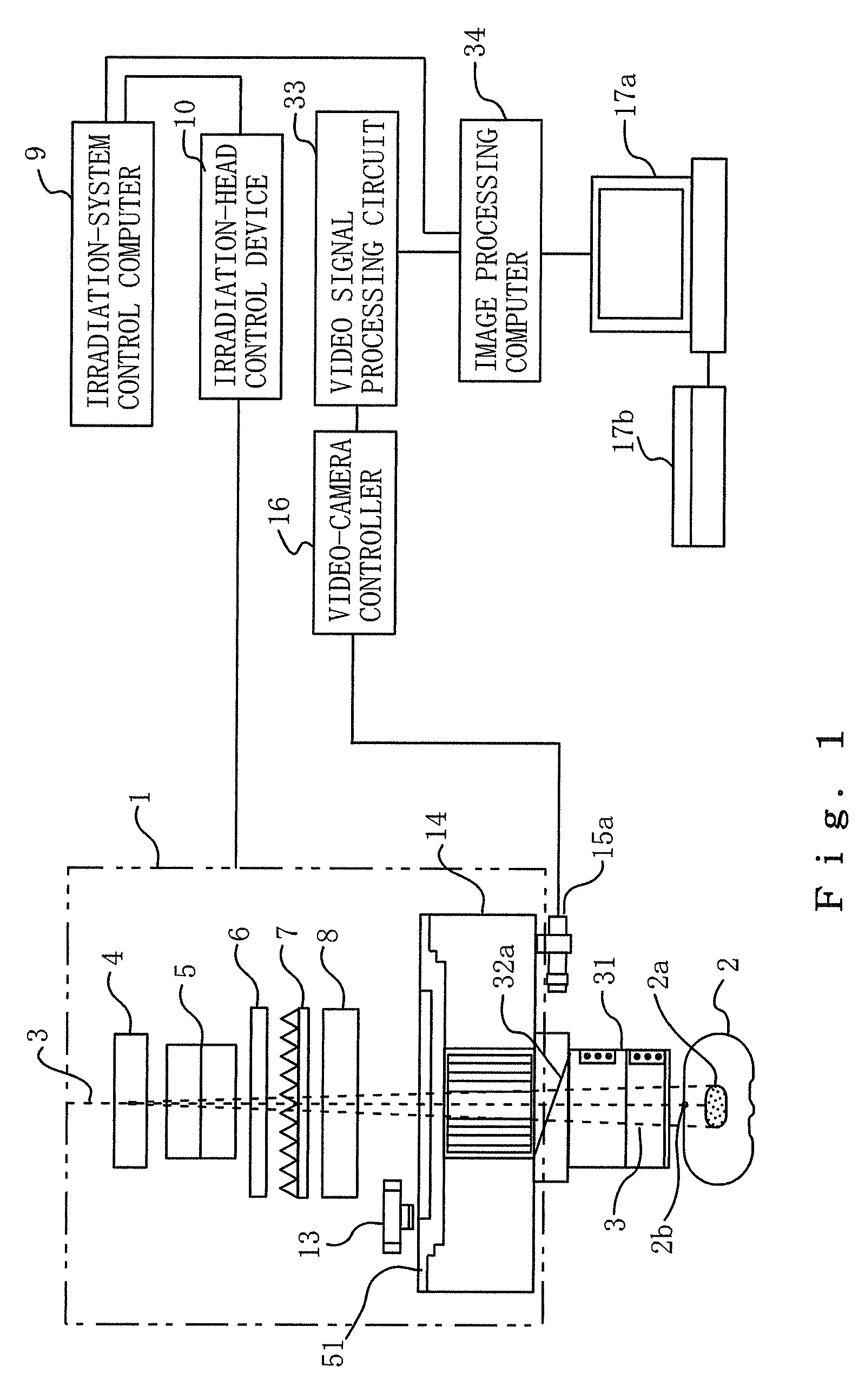
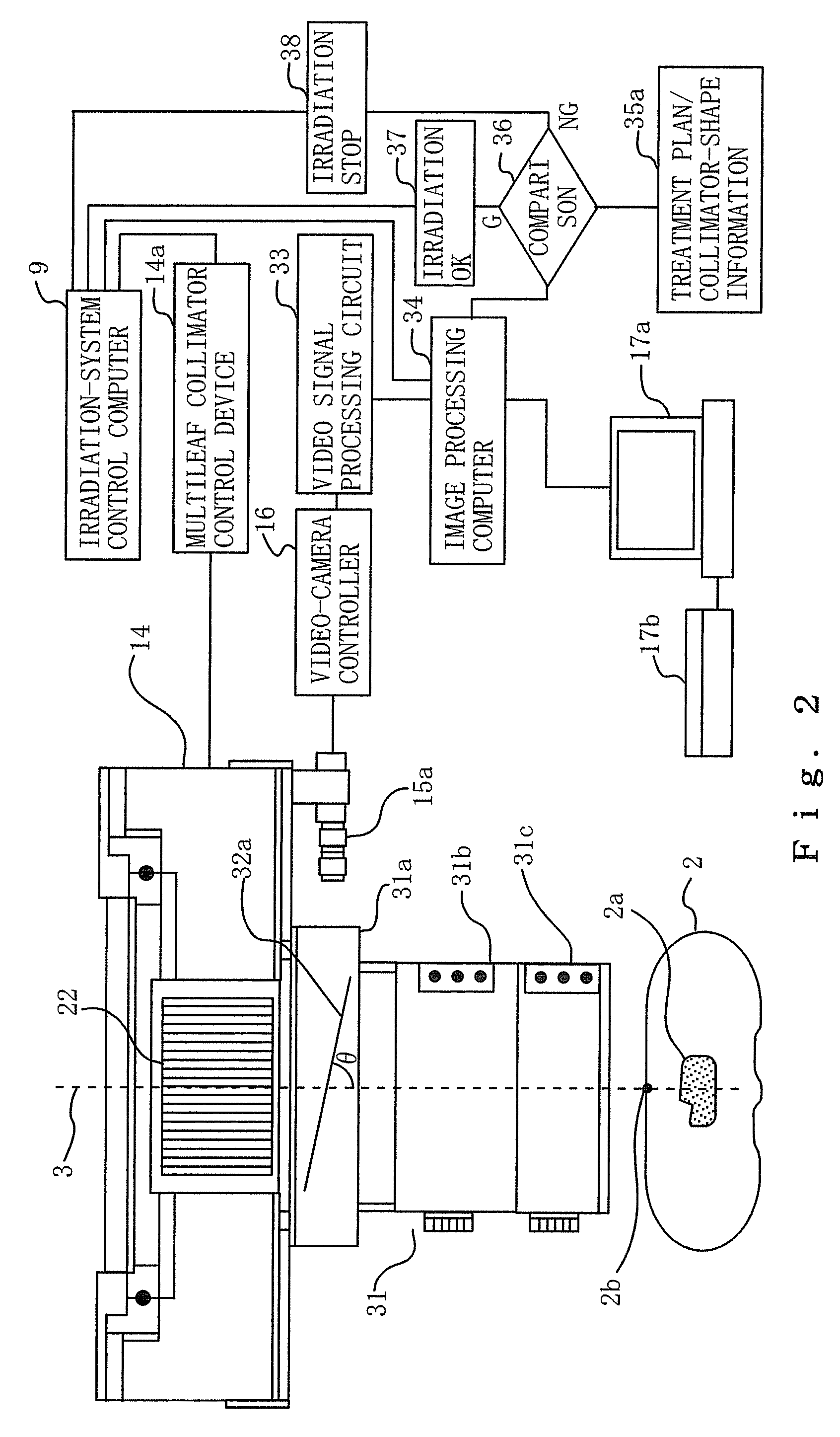
Provision is made for a particle-beam treatment system in which, even during particle-beam irradiation, the shape of a multileaf collimator is monitored. The particle-beam treatment system, in which multi-layer conformal irradiation is performed while the setting of the shape of the multileaf collimator in an irradiation head is changed during particle-beam irradiation, is provided with an optical shape-monitoring unit mounted attachably and detachably in the snout portion at the downstream side of the multileaf collimator, the optical shape-monitoring unit having a shape-monitoring mirror, opposing the multileaf collimator, for monitoring the shape of the multileaf collimator; a video camera for shooting the multileaf-collimator shape reflected by the shape-monitoring mirror; and an image monitor for displaying an image of the video camera that shoots the shape of the multileaf collimator.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Helical electron beam generating device and method of use
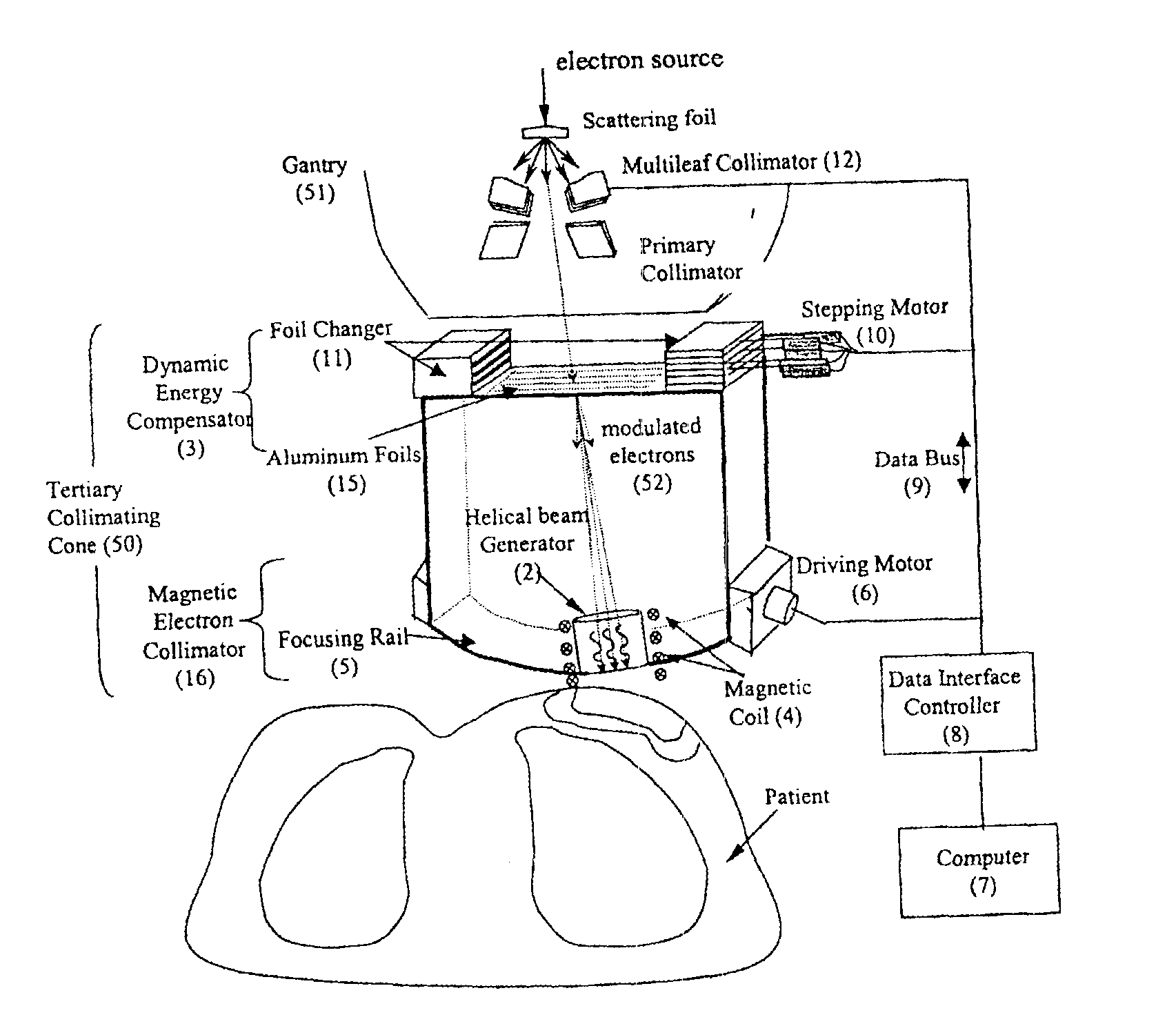
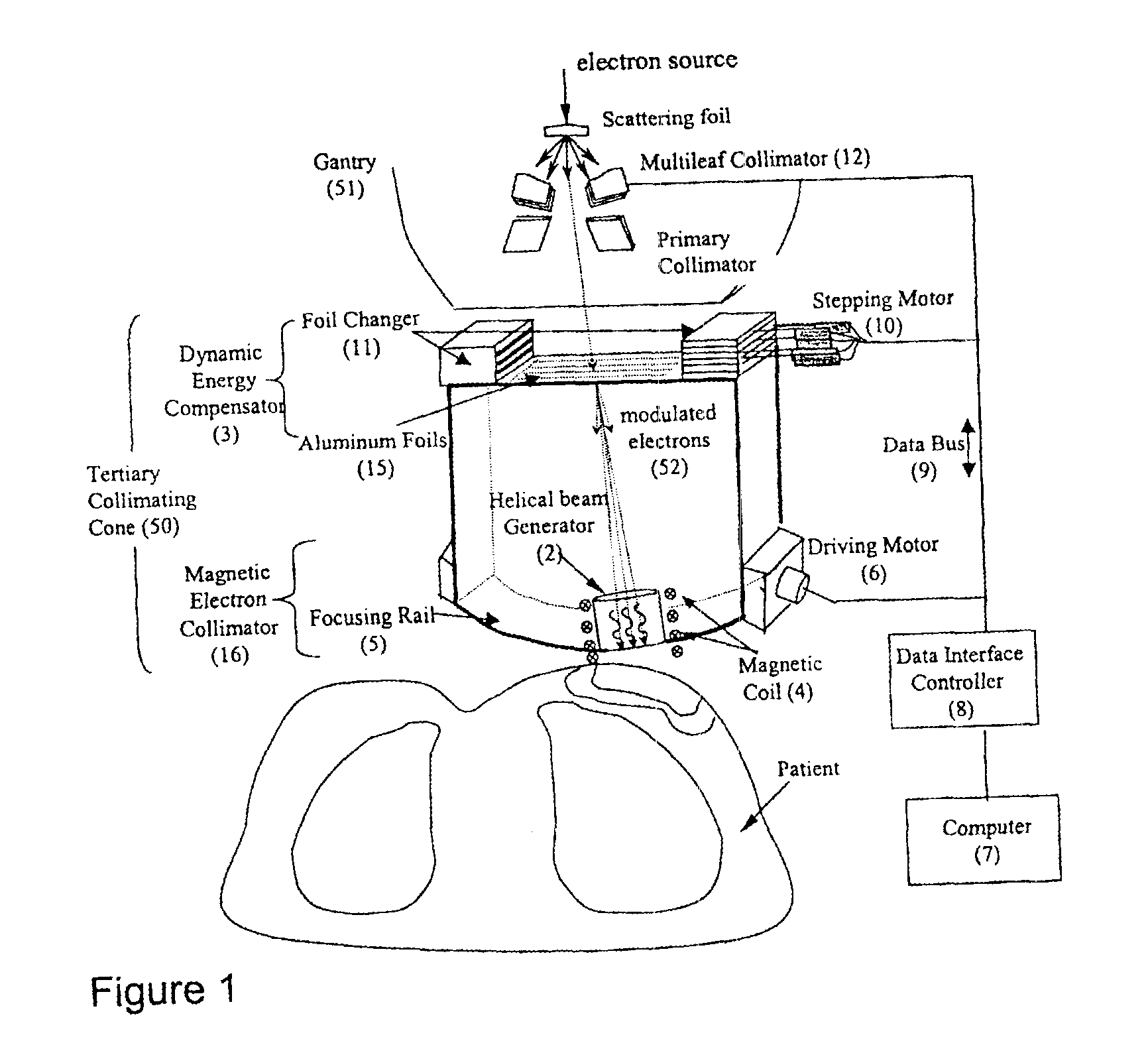
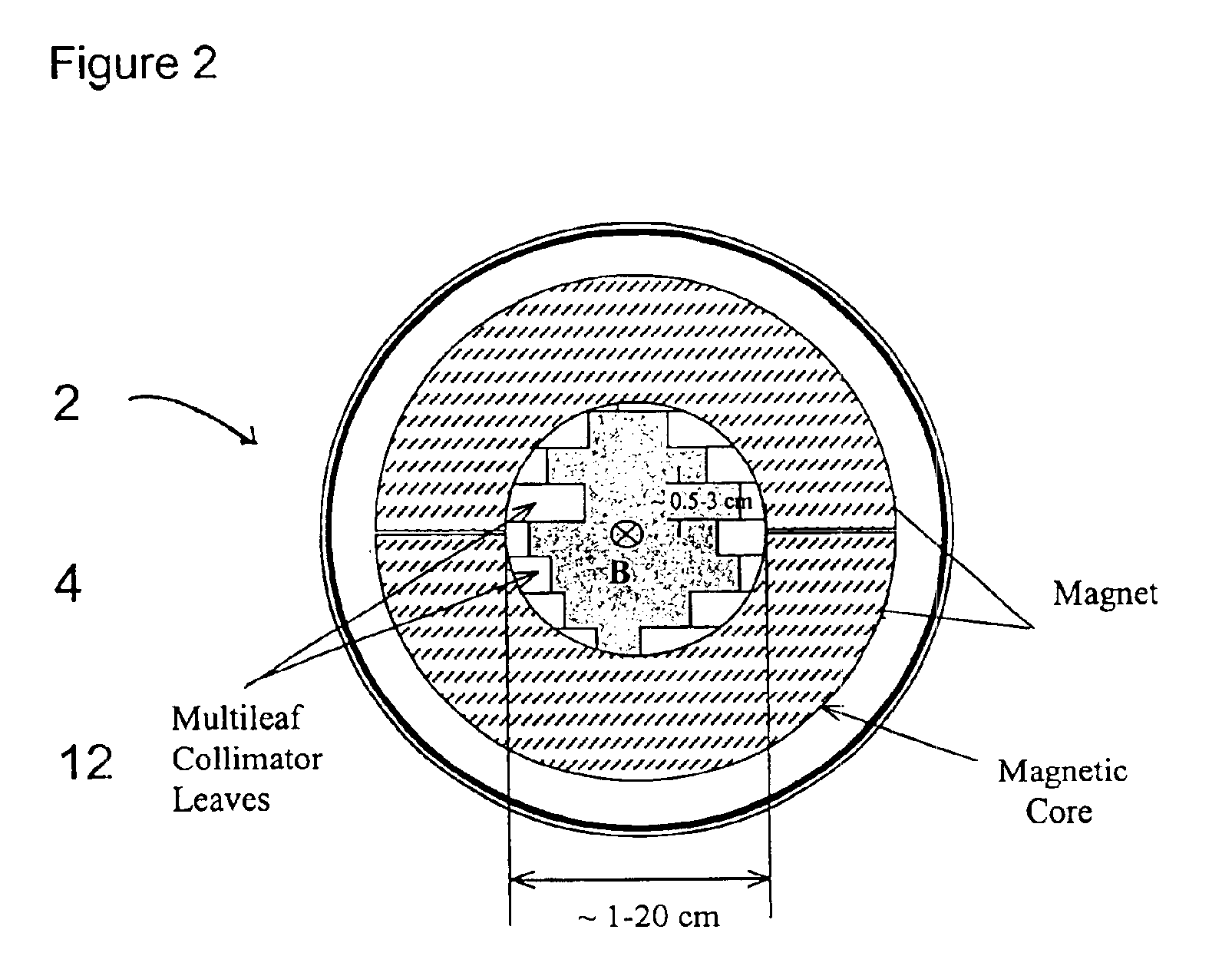
InactiveUS6878951B2Reduce amountQuickly and easily into proper position for treatmentLaser detailsElectrode and associated part arrangementsElectronMultileaf collimator
A device for generating helical electron beams that can be used for radiation therapy is disclosed. The device contains a tertiary collimating cone that can be attached to a gantry of a linear accelerator or placed directly below the gantry. The tertiary collimating cone has a dynamic energy compensator and a magnetic electron collimator to modify the energy of electrons and to generate a helical trajectory. A multileaf collimator may be present within the tertiary collimating cone. A computer coordinates the movements of various components. The helical electron beam produced by this device can be targeted to tumors better and safer and reduce the amount of radiation hitting normal tissue than current devices.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
Method for intensity modulated radiation treatment using independent collimator jaws
InactiveUS7180980B2Increase freedomHighly conformalHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyIntensity-modulated radiation therapyTreatment use
The present invention is a method for treatment planning and delivery of the radiation treatment plan for the intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) treatment using linear accelerators (LINACs) not equipped with a multileaf collimator (MLC). The present invention makes the use of a simpler collimator consisting of only 4 collimator jaws. In addition, the method for treatment planning of the present invention may be performed on a computer separate from the LINAC control computer, so that the treatment planning system can generate IMRT treatment plans for LINACs and collimator jaws from different vendors.
Owner:PROWESS
Multi level multileaf collimators
ActiveCN103079643AHandling using diaphragms/collimetersRadiation safety meansEngineeringMultileaf collimator
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Optimal configuration of photon and electron multileaf collimators in mixed beam radiotherapy
ActiveUS6937693B2Reduce dosageSmall penumbraX-ray apparatusX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyMixed beamLight beam
A radiation therapy method that includes directing a beam along a beam path toward a treatment area. Performing a correction process on the beam, the process includes selectively collimating the beam based on a dose that takes into account bremsstrahlung interactions caused by the beam.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Multileaf collimator
InactiveUS20090080619A1Accurate settingHandling using diaphragms/collimetersRadiation therapyComputer scienceMagnetic layer
A multileaf collimator includes a first leaf block group including plural leaf blocks, a second leaf block group including plural leaf blocks arranged in the same direction as the first leaf block group and disposed opposite the leaf blocks of the first leaf block group, plural magnetic layers located on the respective leaf blocks of the first and second leaf block groups so as to be positioned on faces of the leaf blocks along a moving direction of the leaf blocks, plural magnetic sensors mounted on the respective leaf blocks and varying output signals when the respective leaf blocks are moved in an oncoming direction or a departing direction, and a control device controlling drive mechanisms according to the output signals delivered by the respective magnetic sensors so that spacing between the leaf blocks of the first and second leaf blocks is adjusted into a target configuration.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
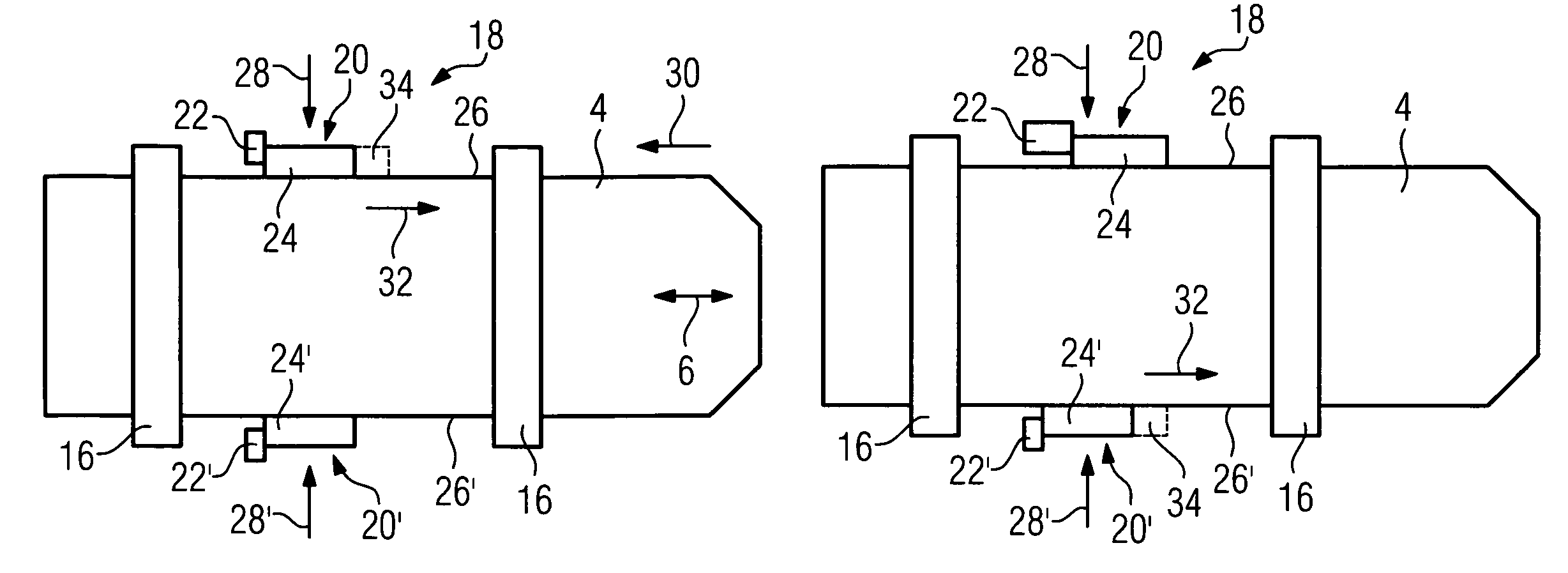
Method for checking positional accuracy of the leaves of a multileaf collimator
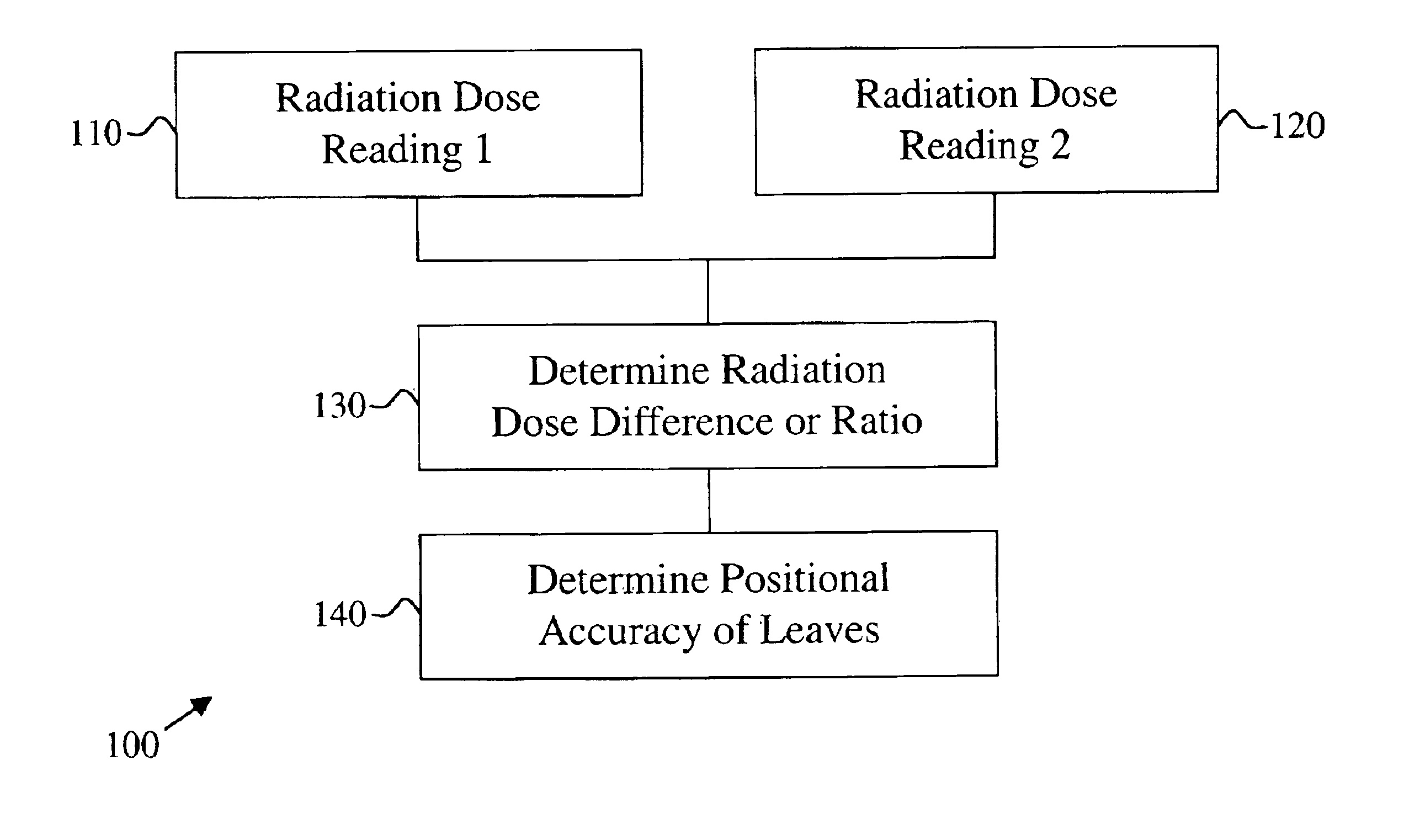
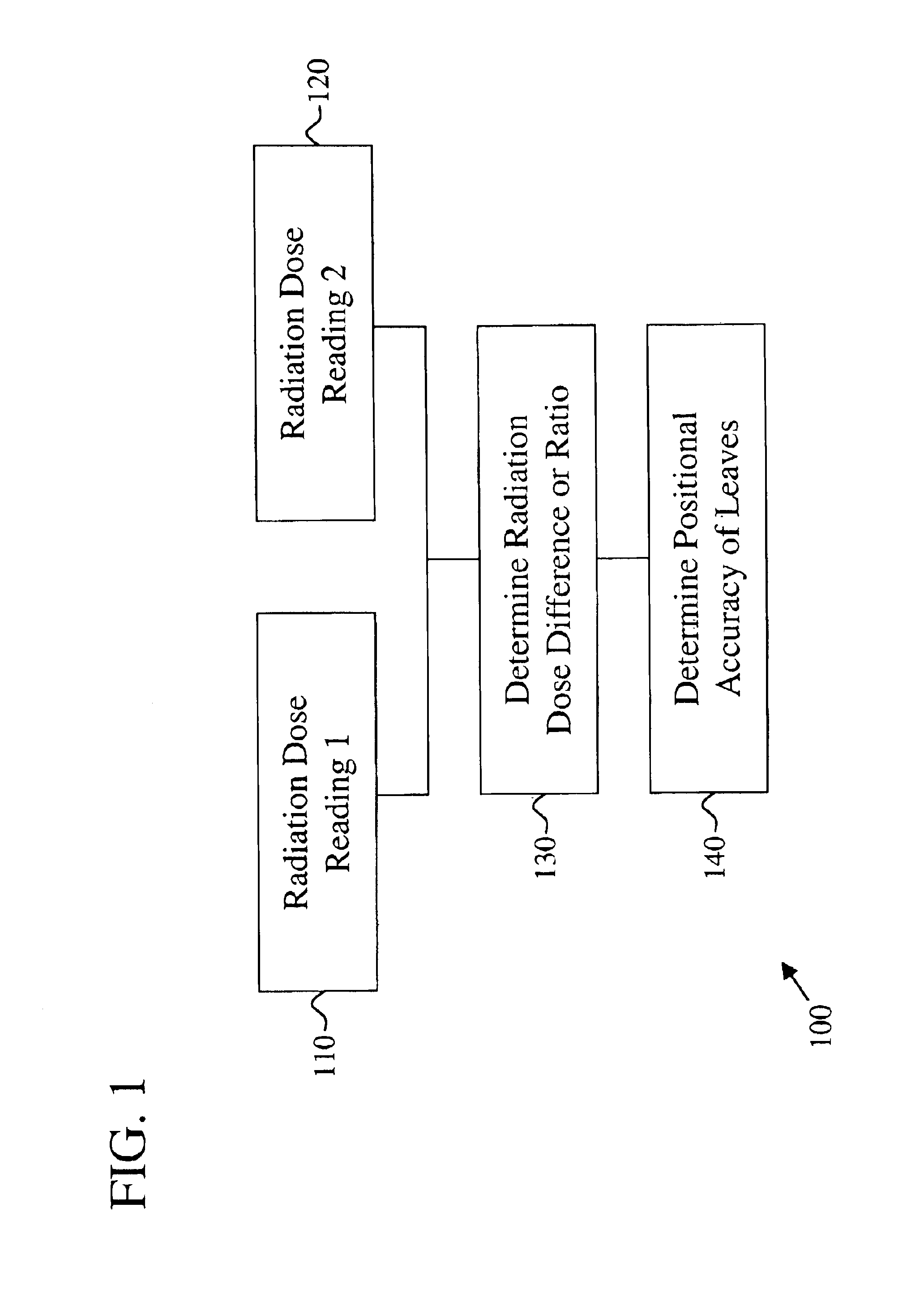
InactiveUS6891178B2Simplified and accurate methodEfficient and reliable in determiningThermometer detailsElectrode and associated part arrangementsDosimeterQuality assurance
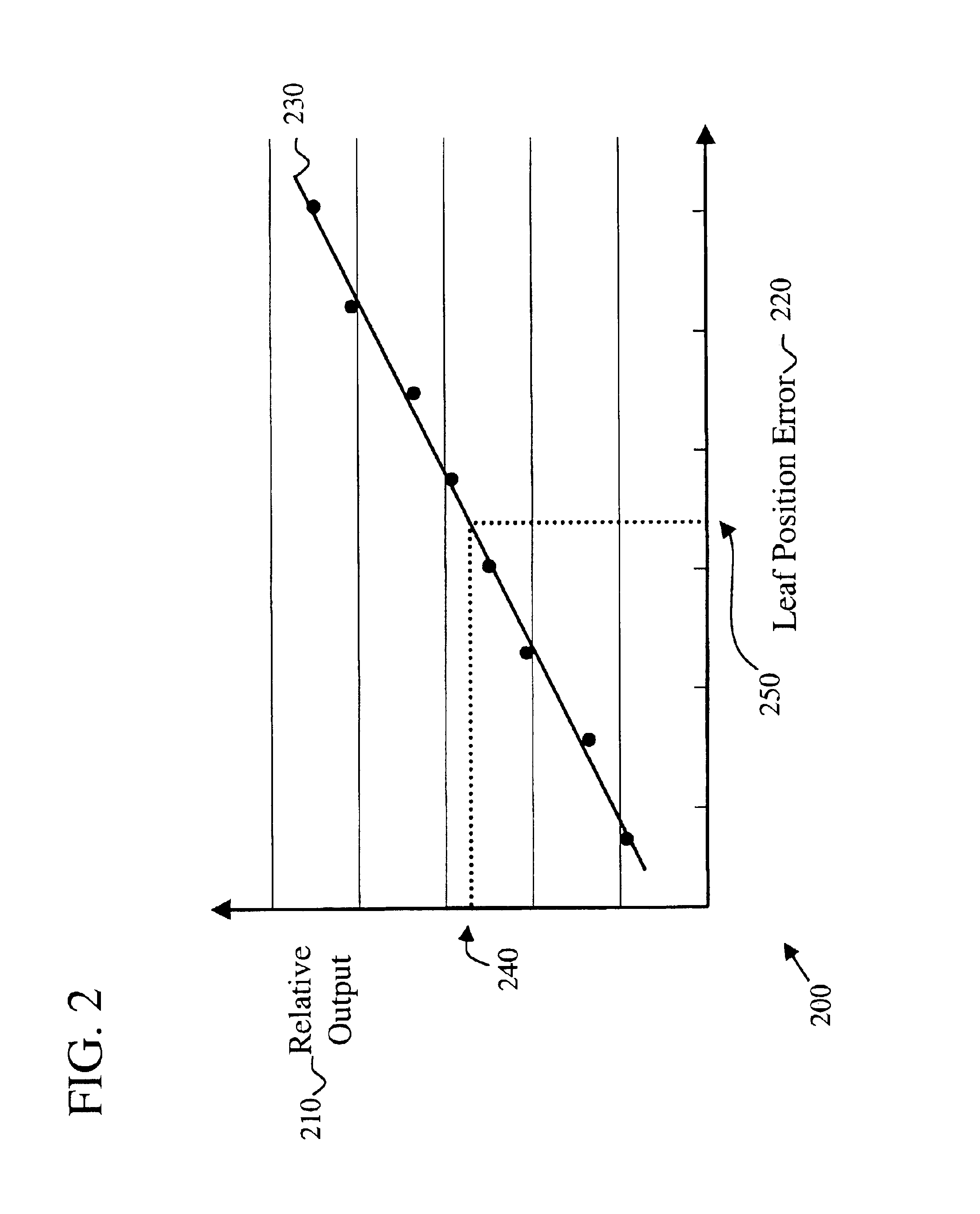
A method is provided for determining the positional accuracy of leaves of a multileaf collimator for delivering doses of radiation to a particular spatial location for treatment purpose. The method could be implemented as routine quality assurance check of the multileaf collimator leaf positioning errors. The method includes producing a first field and producing a second field, which is different from the first field. A dosimeter means is included for measuring a radiation dose difference or ratio between the first field and the second field at at least one spatial location. The dose difference or ratio is then used to determine the positional accuracy of the leaves by comparing with a known relationship between leaf positional errors and relative dosimeter outputs. The method provides a more simplified, accurate, efficient and reliable method over currently used methods.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Radiation therapy treatment planning machine
InactiveUS6999556B2Avoid stopHandling using diaphragms/collimetersComputerised tomographsEngineeringConformal Therapy
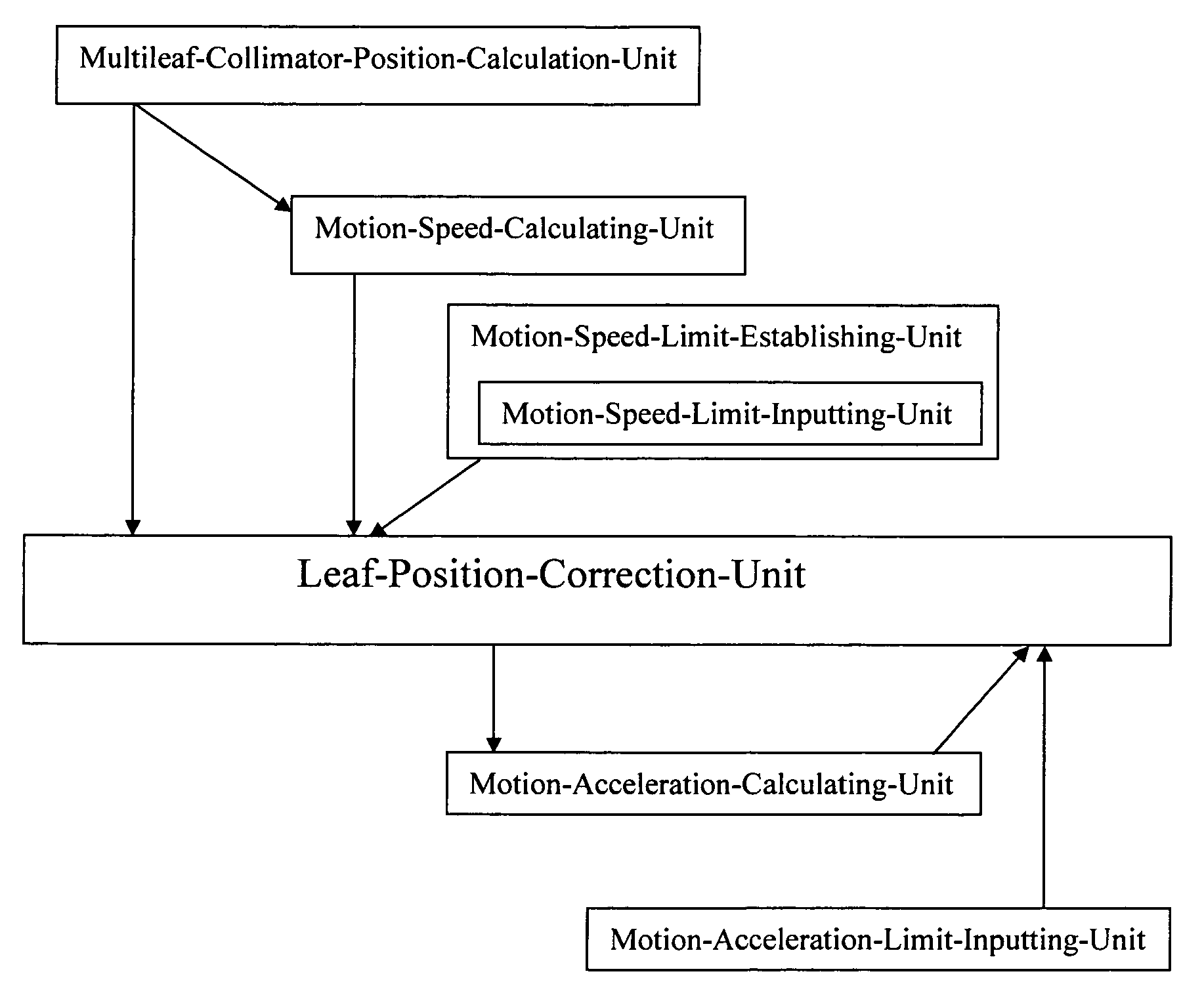
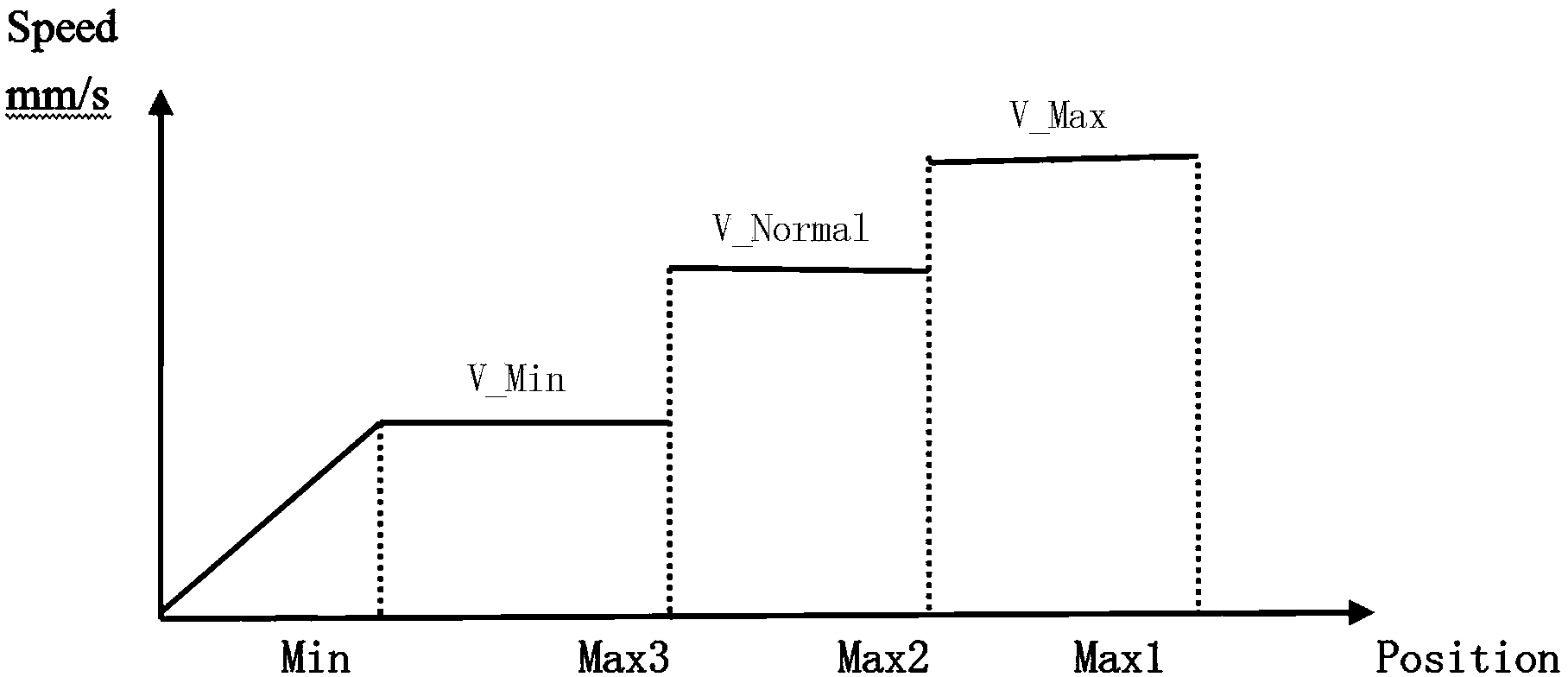
In an RTP machine, for a series of leaf positions which are generated by a Multileaf-Collimator-Position-Calculation-Unit, a speed limit is established by a Motion-Speed-Limit-Establishing-Unit. Further, a Motion-Display-Unit indicates the area where motion speed exceeds the established speed and / or a Leaf-Position-Correction-Unit controls the area in order to be equal to or less than the established speed limit. Furthermore, a Motion-Acceleration-Calculating-Unit calculates motion acceleration of the multileaf collimator, and the Motion-Display-Unit indicates the area where the calculated motion acceleration exceeds the established limit and / or the Leaf-Position-Correction-Unit controls the area in order to be equal to or less than the established acceleration limit. An interruption of irradiation due to a multileaf collimator positioning error is prevented while the treatment is being conducted by the multileaf collimator motion limit control in radiation therapy such as conformal therapy or others which the multileaf collimator moves in during irradiation.
Owner:NAKANO SYST
Multileaf collimator and radiation therapy device
InactiveUS20090041199A1Improve accuracyHigh degreeHandling using diaphragms/collimetersRadiation therapyPiezoelectric actuatorsRadiation therapy
The invention relates to a multileaf collimator having a plurality of leaves mounted displaceably in an adjusting direction for establishing a contour of a beam path. Each displaceably mounted leaf is assigned at least one linear drive having at least one piezoelectric actuator for displacing the leaf in the adjusting direction. Because the piezoelectric actuator can be driven precisely, an improved radiation therapy can be achieved, particularly in the case of a radiation therapy device having a multileaf collimator of said kind, owing to precise establishing of the contour.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
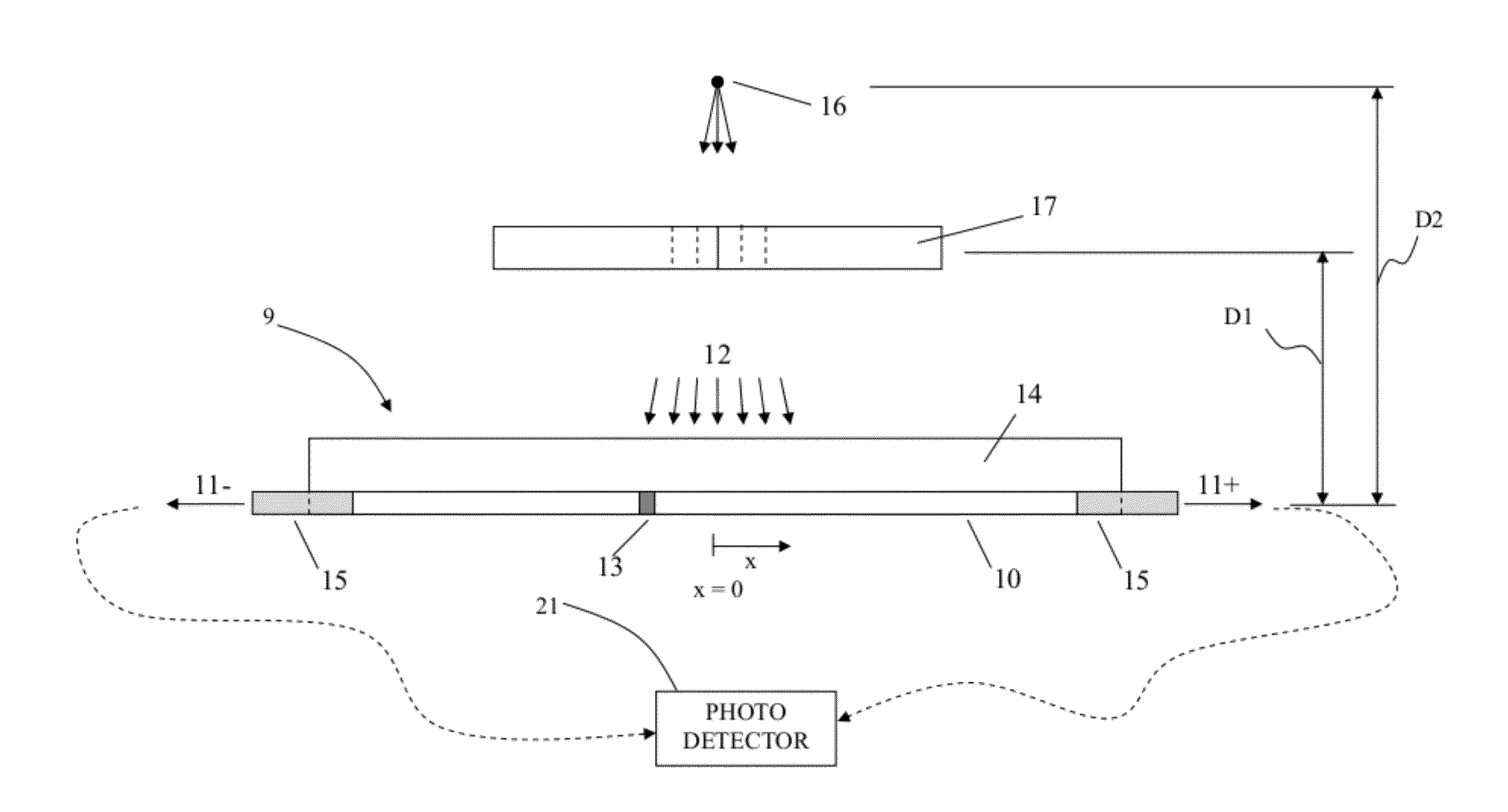
Fluence monitoring devices with scintillating fibers for x-ray radiotherapy treatment and methods for calibration and validation of same
ActiveUS20120205530A1Minimize attenuationMaterial analysis by optical meansCalibration apparatusFiberCalibration and validation
According to one aspect, a fluence monitoring detector for use with a multileaf collimator on a radiotherapy machine having an x-ray radiation source. The fluence monitoring detector includes a plurality of scintillating optical fibers, each scintillating optical fiber configured to generate a light output at each end thereof in response to incident radiation pattern thereon from the radiation source and multileaf collimator, a plurality of collection optical fibers coupled to the opposing ends of the scintillating optical fibers and operable to collect the light output coming from both ends of each scintillating optical fiber, and a photo-detector coupled to the collection optical fibers and operable to converts optical energy transmitted by the collection optical fibers to electric signals for determining actual radiation pattern information.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Radiation therapy inverse treatment planning using a regularization of sparse segments
InactiveUS8315357B2Reduce in quantityReduce the numberX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyInverse treatment planningTherapy planning
A method of reducing a total number of beam segments in a dose distribution for a radiation therapy field is provided. The method includes providing a multiobjective radiation therapy treatment plan using a suitably programmed computer, where the multiobjective radiation therapy treatment plan includes a radiation beam dose performance objective and a fluence map sparsity objective in a given fluence function domain, and providing a Pareto frontier of tradeoff criteria between the beam dose performance and a total number of radiation segments (or sub-fields) of the multiobjective radiation therapy treatment plan using the suitably programmed computer, where an achieved set of radiation beam dose distributions associated with efficiency points of the Pareto frontier are evaluated using a clinical acceptance criteria, where a clinically acceptable radiation beam dose distribution having a smallest number of the multileaf collimator segments is a final solution for the multiobjective radiation therapy treatment plan.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
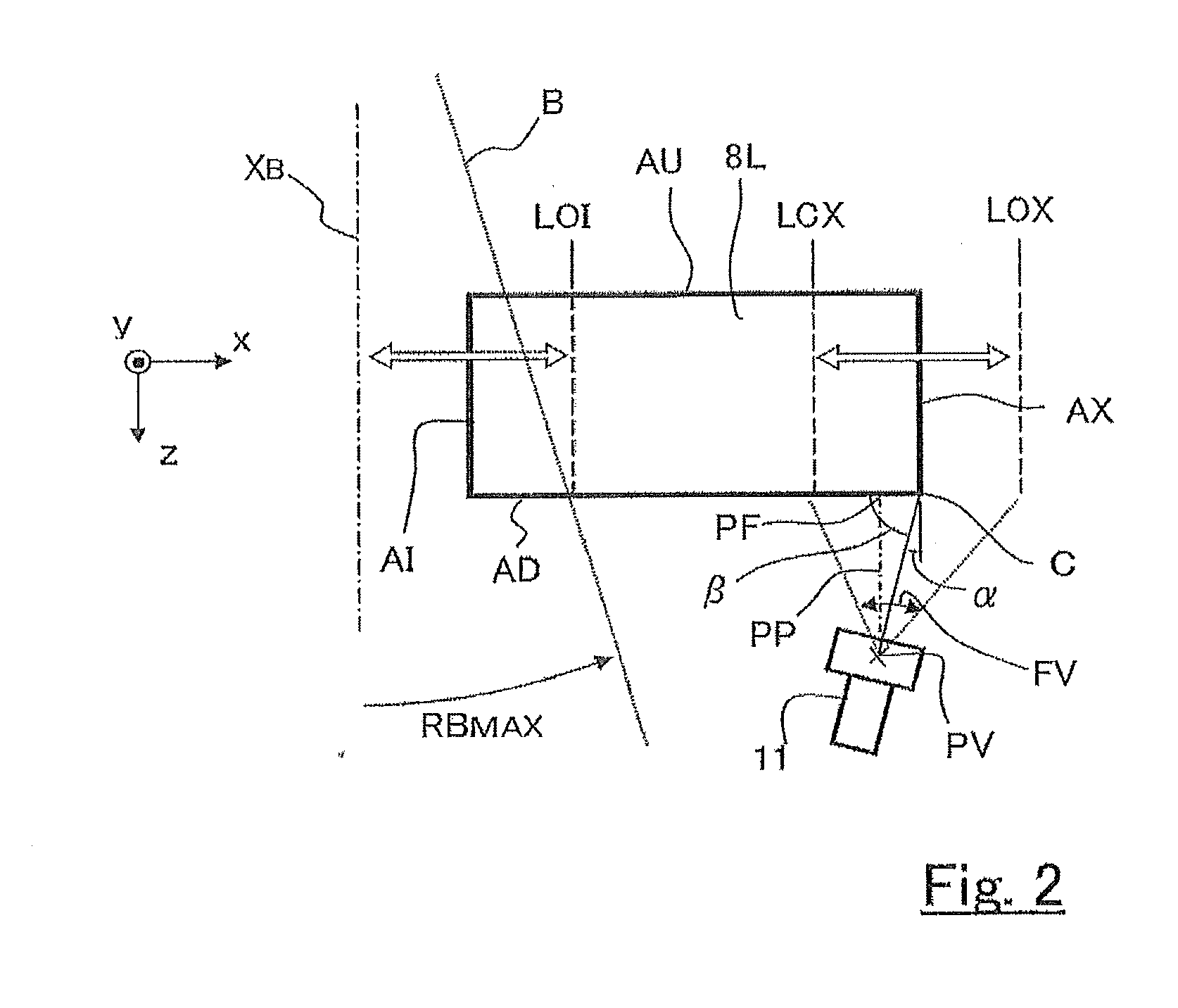
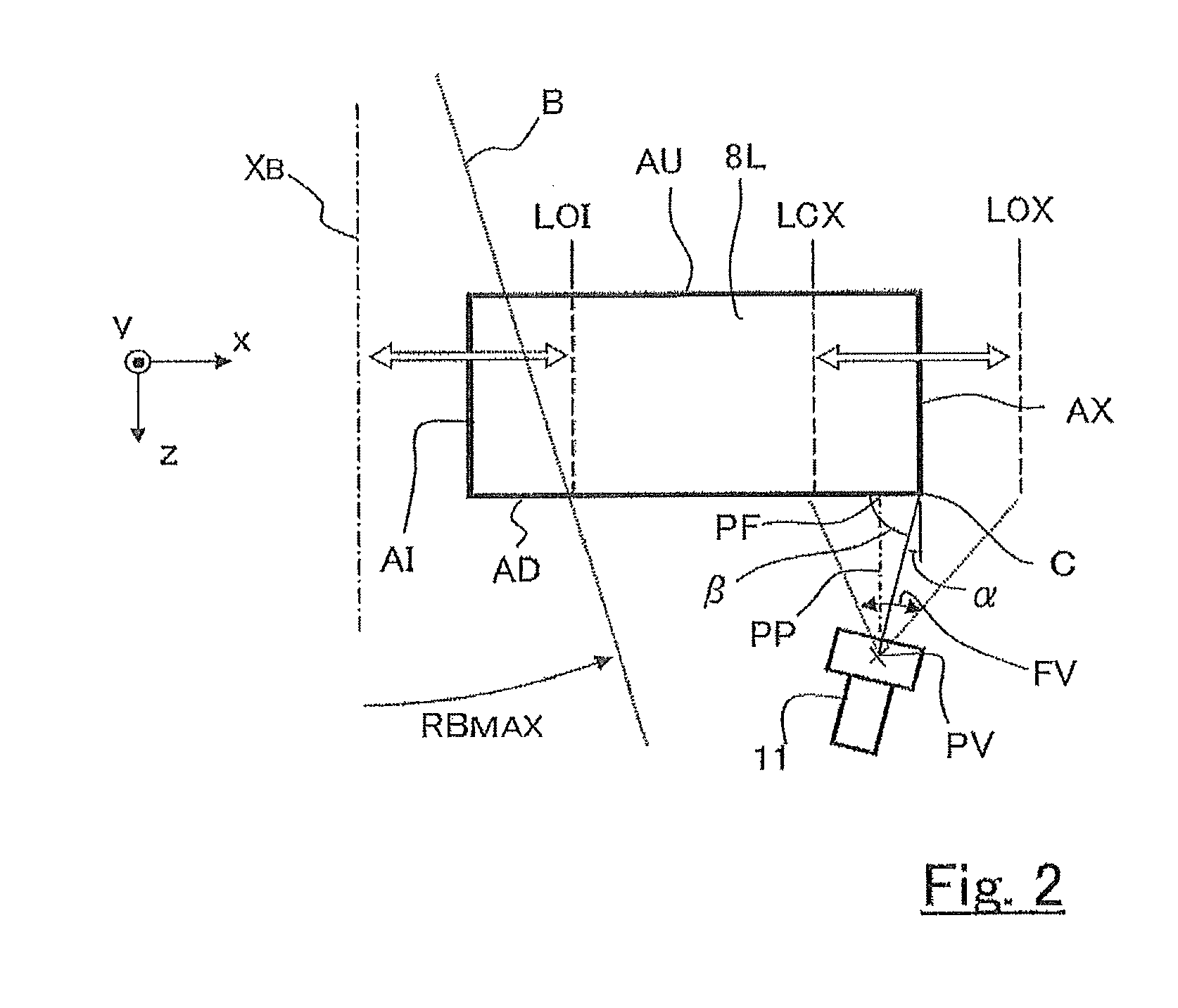
Multilear collimator, particle beam therapy device and therapy planning device
InactiveCN103068441AIncrease contrastUnaffected by penumbraRadiation/particle handlingX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyParticle beamEngineering
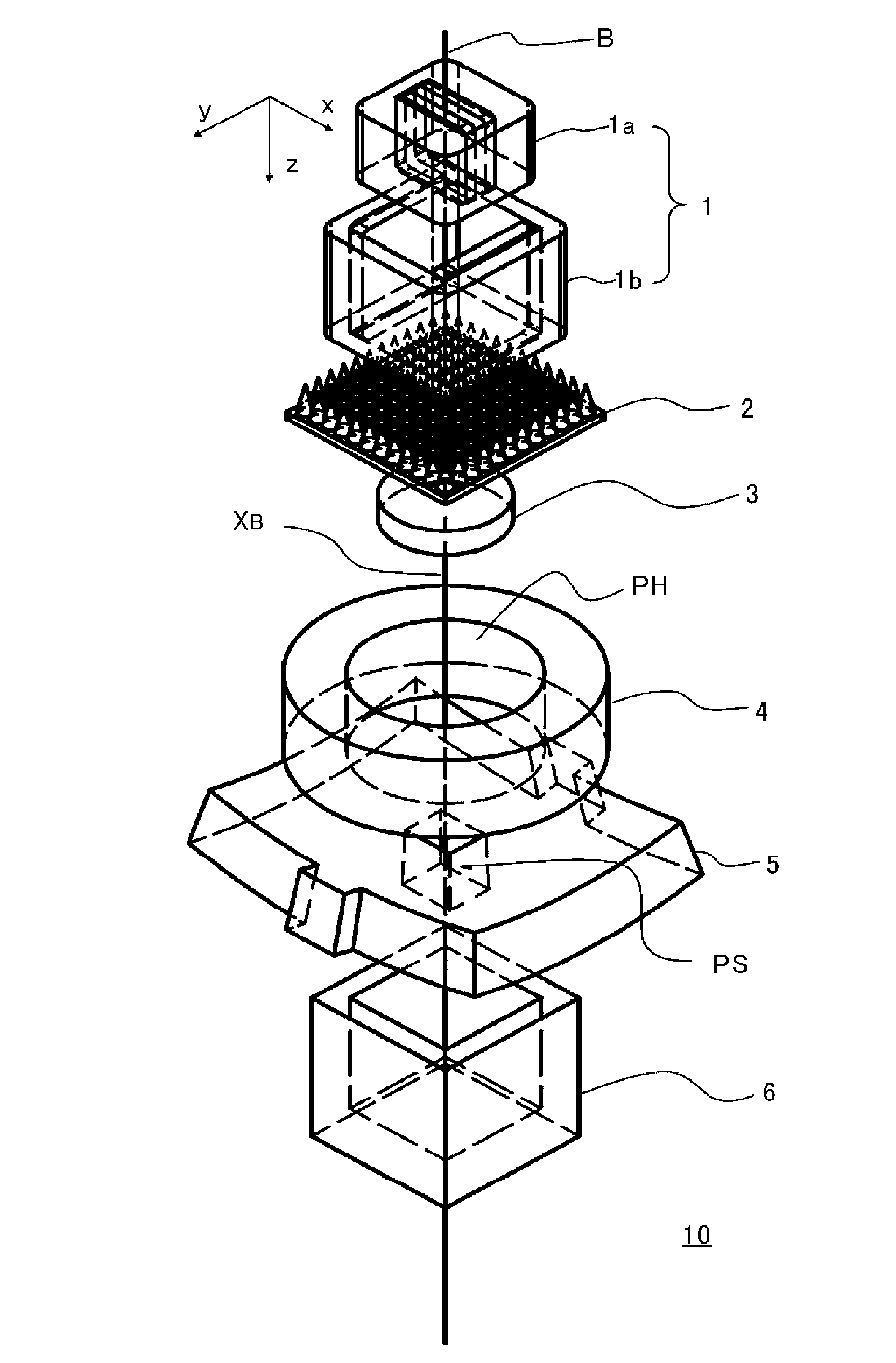
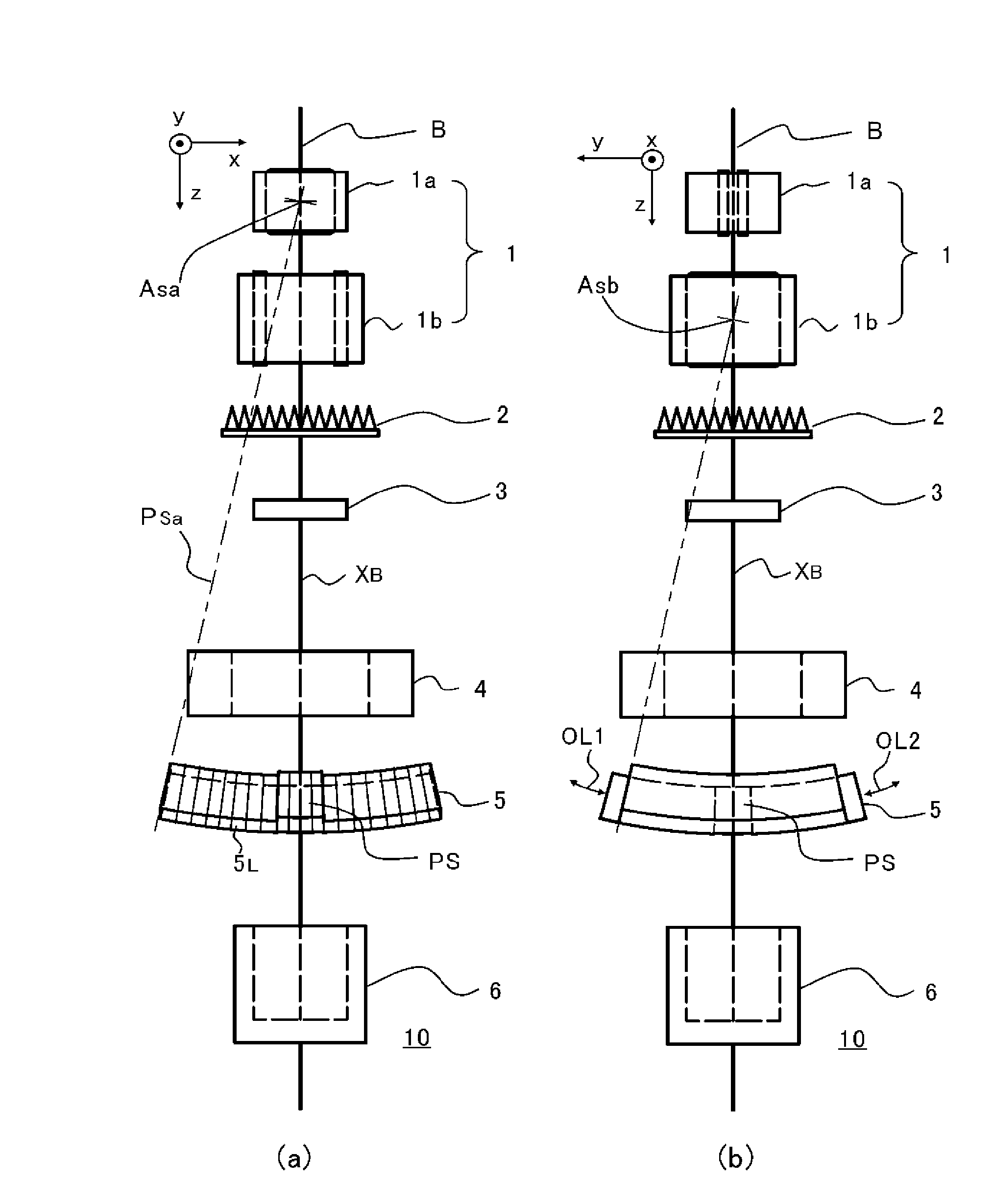
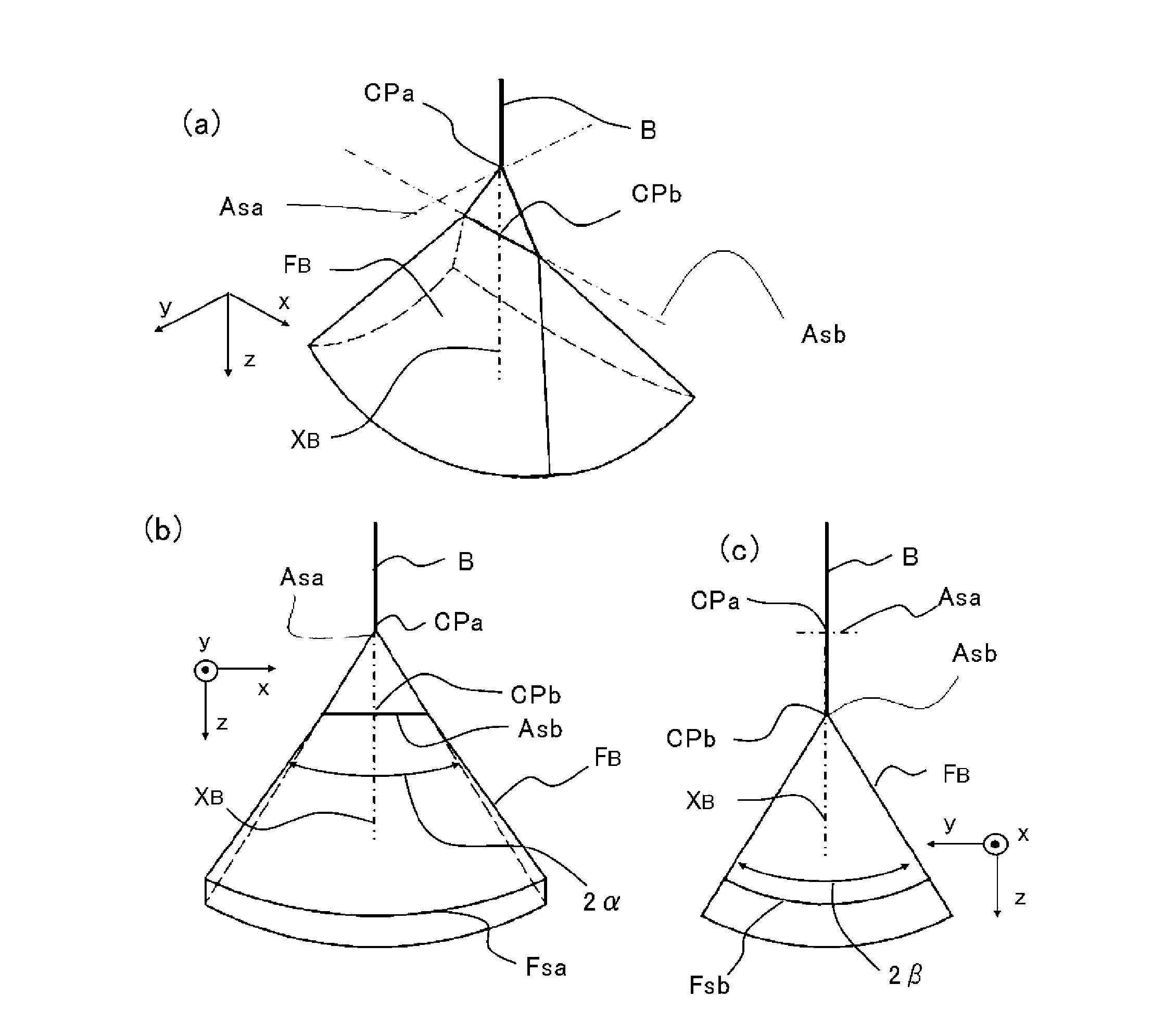
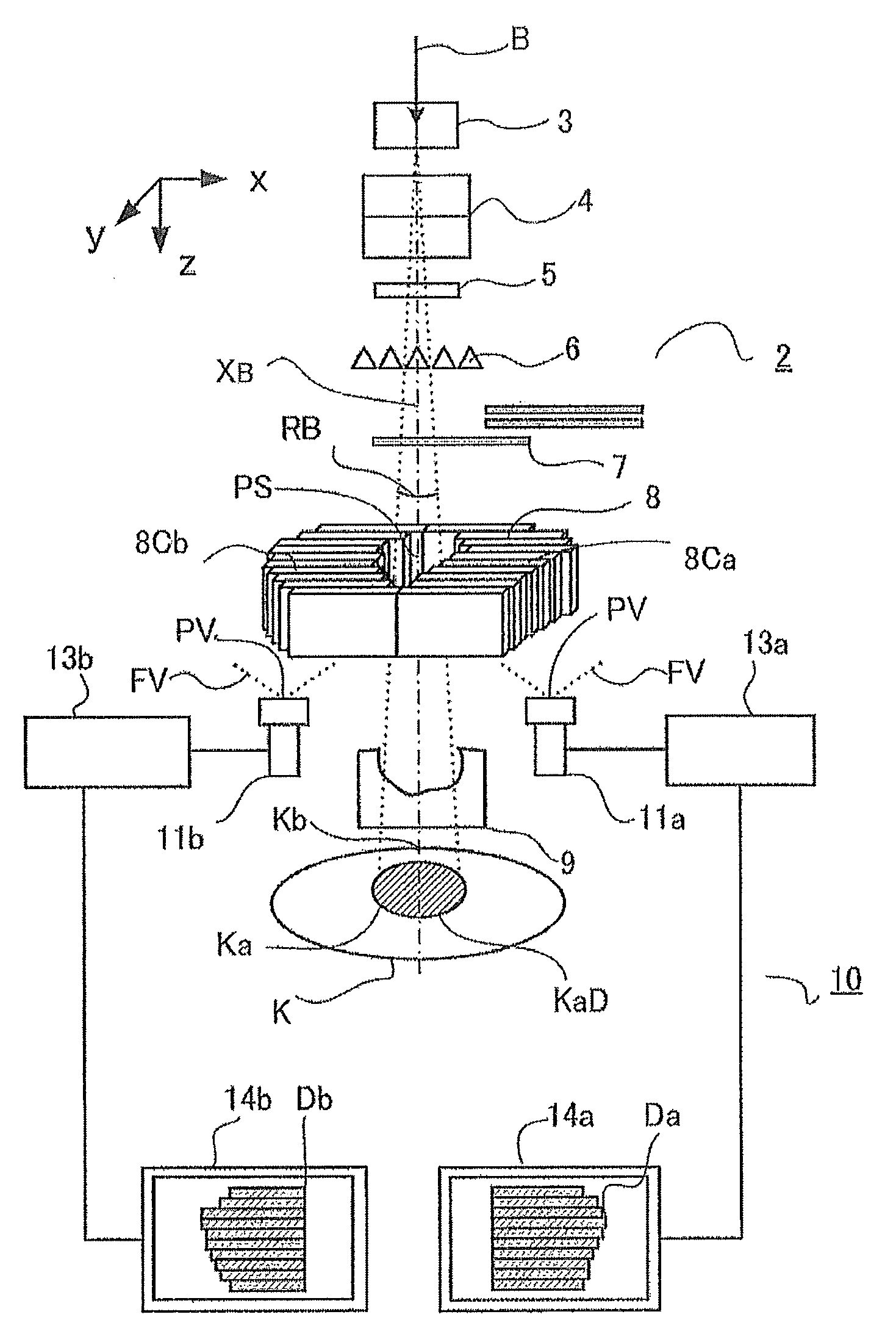
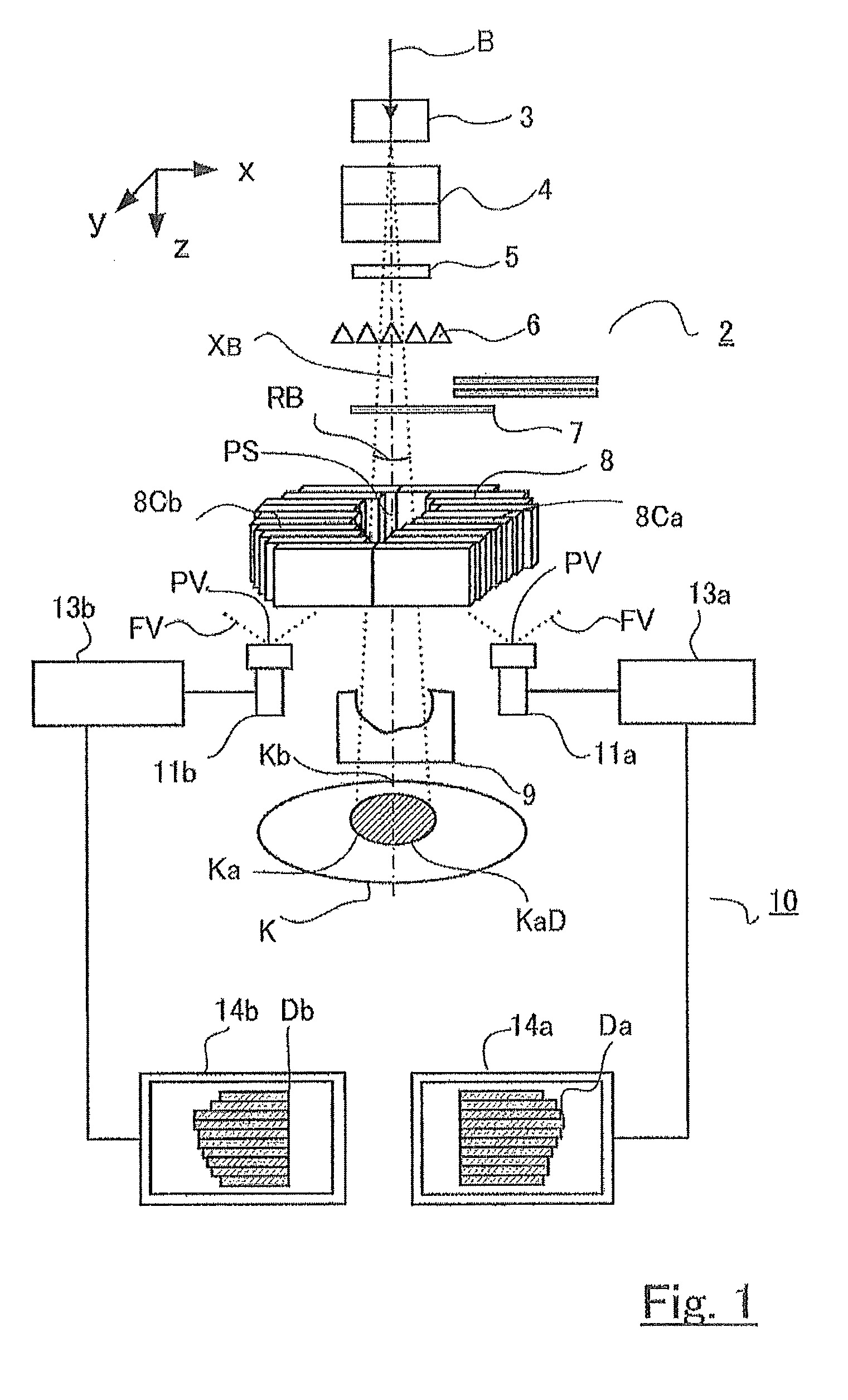
The purpose of the invention is to obtain a multileaf collimator and a particle beam therapy device that can form high contrast irradiation fields without being affected by the penumbra. The multileaf collimator is provided with an array of leaves (5C) wherein a plurality of leaf plates (5L) are stacked in the thickness direction with one of the end faces (EL) aligned, and with a leaf plate driving mechanism (5D) that drives the one end face (EL) of each leaf plate (5L) towards or away from the beam axis (XB). For each of the leaf plates (5L), the surface (PL) of said leaf plate that faces the adjacent leaf plate in the thickness direction is formed by a plane (PSa) containing a first axis (ASa) that is on the beam axis (XB). The leaf plate driving mechanism (5D) drives the leaf plates (5L) along a circular orbit (OL) having, as the center, a second axis (Asb) that is on the beam axis (XB) and is perpendicular to the beam axis (XB) and to the first axis (Asa).
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Particle-beam treatment system
ActiveUS7579608B2Avoid radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersDiagnostic recording/measuringParticle beamEngineering
Provision is made for a particle-beam treatment system in which, even during particle-beam irradiation, the shape of a multileaf collimator is monitored. The particle-beam treatment system, in which multi-layer conformal irradiation is performed while the setting of the shape of the multileaf collimator in an irradiation head is changed during particle-beam irradiation, is provided with an optical shape-monitoring unit mounted attachably and detachably in the snout portion at the downstream side of the multileaf collimator, the optical shape-monitoring unit having a shape-monitoring mirror, opposing the multileaf collimator, for monitoring the shape of the multileaf collimator; a video camera for shooting the multileaf-collimator shape reflected by the shape-monitoring mirror; and an image monitor for displaying an image of the video camera that shoots the shape of the multileaf collimator.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Anti-collision control method for leaves of multileaf collimator
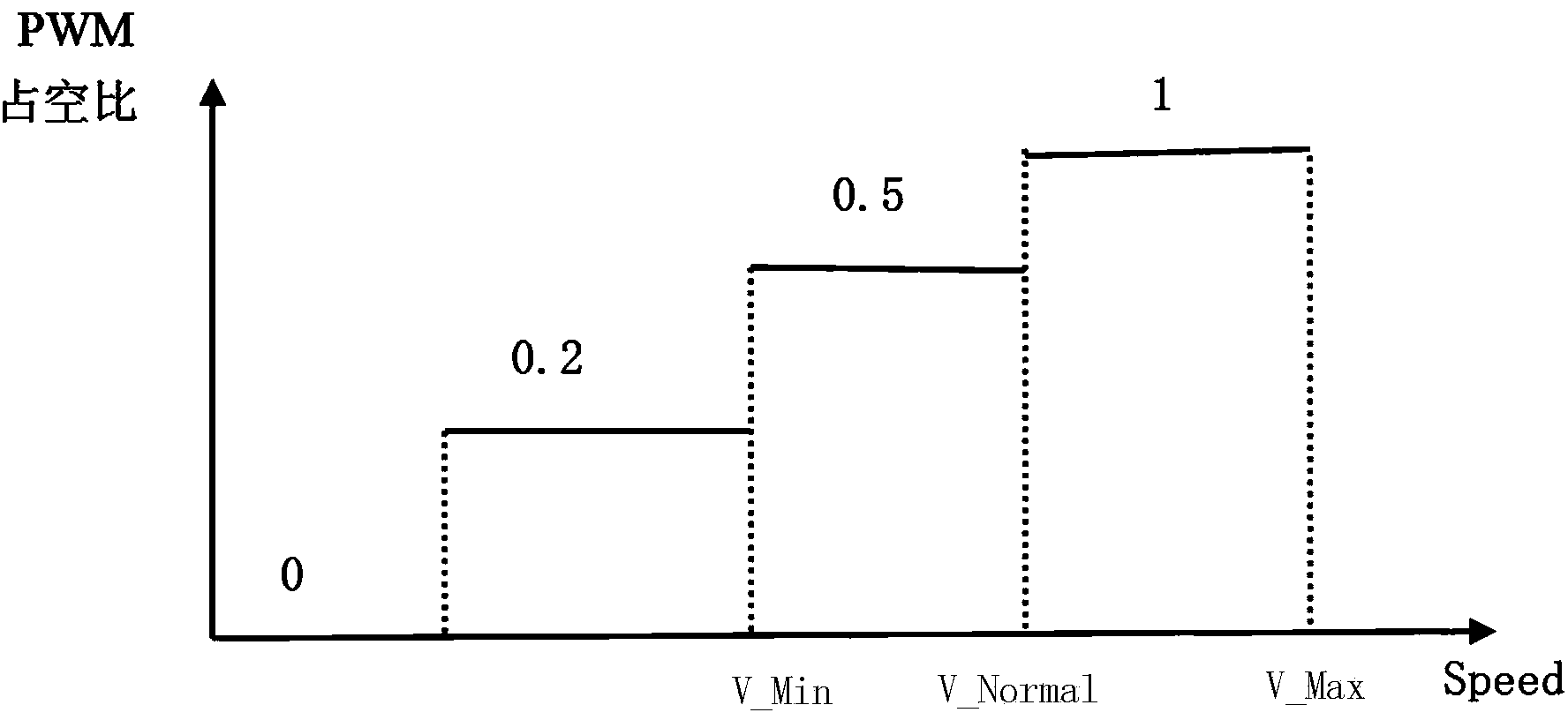
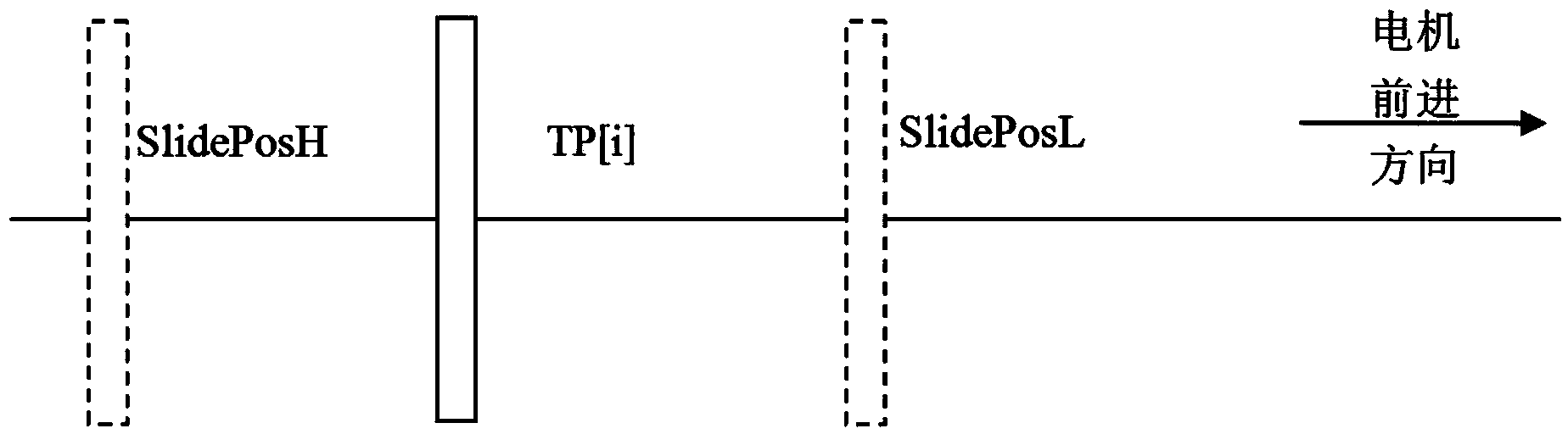
InactiveCN104240785AAvoid collisionPrevent failures such as mechanical damageHandling using diaphragms/collimetersRadiation therapyLower limitIntensity modulate radiotherapy
The invention relates to an anti-collision control method for leaves of a multileaf collimator. The anti-collision control method for the leaves of the multileaf collimator includes the following steps that in static intensity modulated radiotherapy, the difference between the real-time positions and the target positions to which the leaves move is compared with the difference between the initial positions of the leaves and the target positions to which the leaves move to keep adjusting the operating speed of a motor for driving the leaves to move; the closer the real-time positions of the leaves are to the target positions, the lower the operating speed of the motor is, and then collision between the leaves caused when the two sets of leaves are closed can be effectively prevented; in dynamic intensity modulated radiotherapy, when whether the motor moves forward or backward is judged, the number of pulses emitted by an actual motor position coder and measured by the i sub-field in real time is compared with the upper limit value SlidePosH and the lower limit value SlidePosL to judge whether the motor brakes or keeps sliding forward due to inertia or keeps running at a certain speed of Vo[i]. Thus, the position actually reached by the motor in the operating process is basically identical to the target position, it is guaranteed that the error of the position is within + / -e, faults such as mechanical damage caused by leaf collision are prevented, and the end faces of the leaves are prevented from leaking rays.
Owner:SHANDONG JIAOTONG UNIV
Particle beam therapy system
ActiveUS20120215049A1Easy to adjustAccurate monitoringElectrode and associated part arrangementsHandling using diaphragms/collimetersParticle beamParticle physics
The objective is to obtain a particle beam therapy system that prevents dispersion of a charged particle beam, reduction of the energy thereof, and upsizing of the system and that can accurately monitor the opening shape of a multileaf collimator so as to perform high-accuracy particle beam therapy. An image-capturing unit that takes an image of an outer end of a respective downstream side face of a leaf plate is provided for each row of leaves in such a way as to be situated at a position that is at an outer side of an irradiation field; and adjusted in such a way that the base of a perpendicular from a viewpoint to the downstream side face, is situated at a position that is at an inner side of the position of the outer end when the leaf plate is maximally driven in the departing direction.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
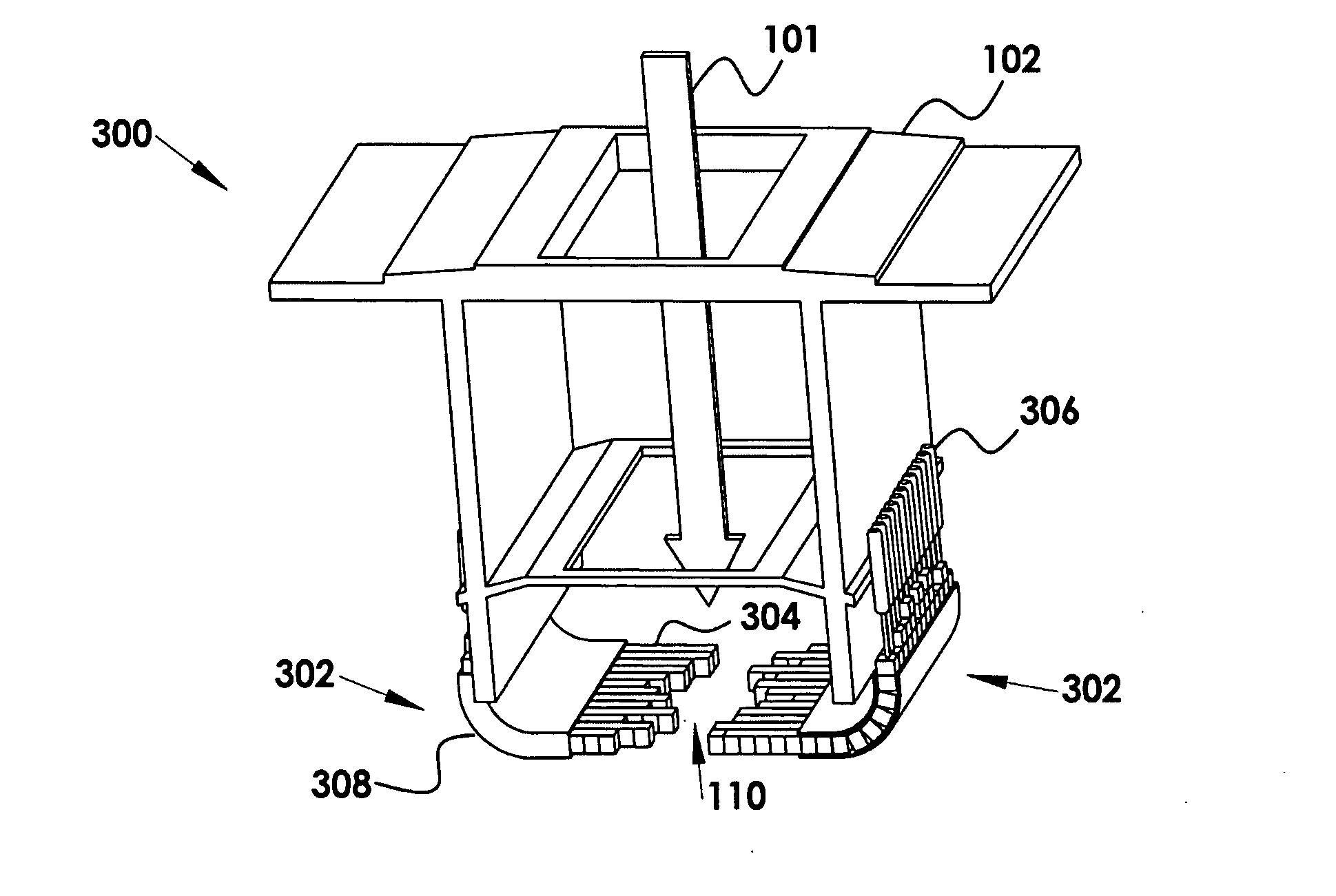
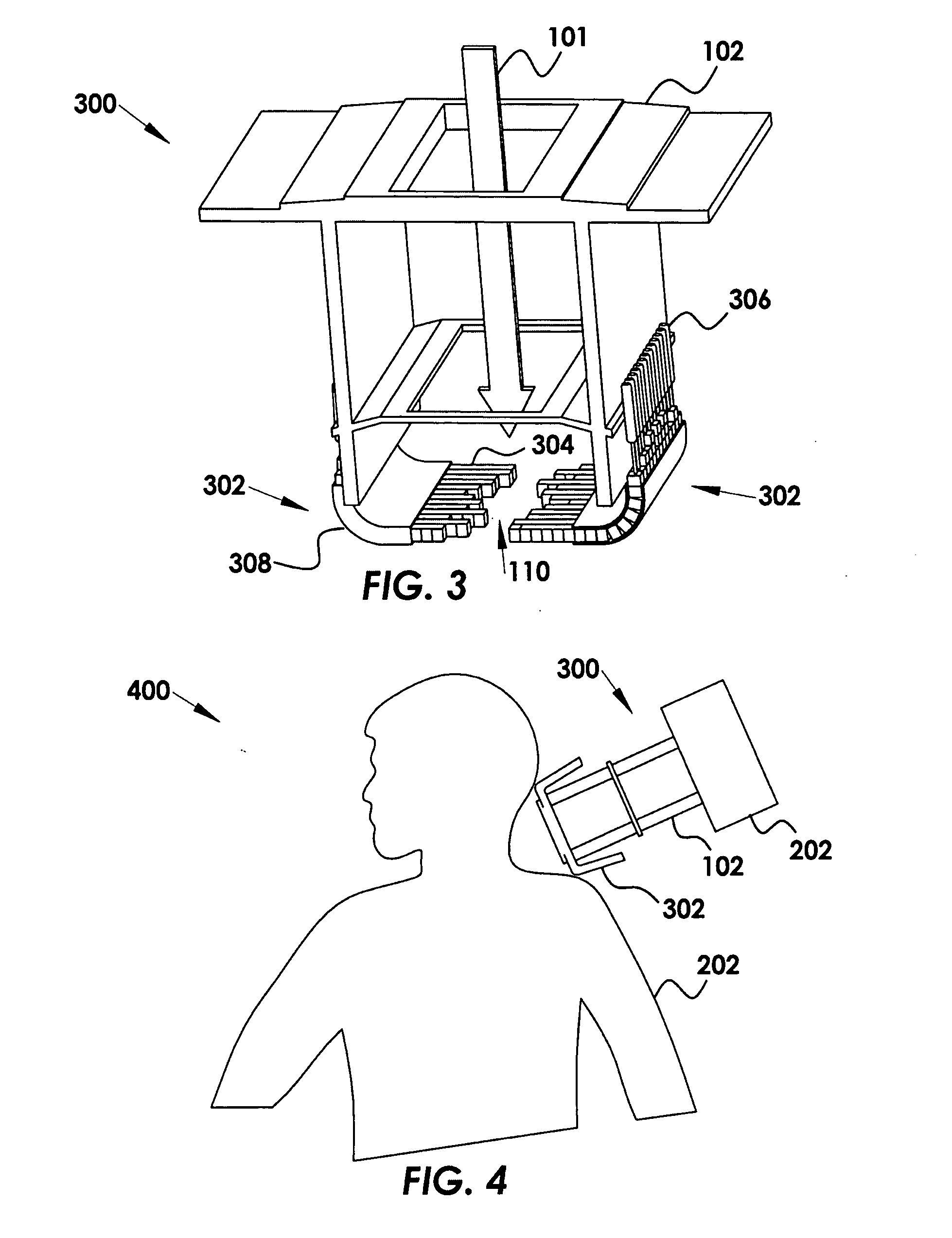
Multileaf collimator for electron radiotherapy
InactiveUS20090001295A1Easy accessFaster patient treatmentElectrode and associated part arrangementsHandling using diaphragms/collimetersEngineeringMechanical engineering
A flexible multi-leaf collimator for electron radiotherapy is provided, where the leaves are not a single rigid component, but are configured in a manner that curves away from the patient to provide greater clearance. The invention includes a plurality of flexible assemblies, at least one guide supporting the assemblies, and a plurality of assembly drivers. The driver engages the assembly and moves the assembly along the guide. The assembly has an extended state and a retracted state relative to the guide, such that when in the extended state the assembly is held in the aperture plane and when in the retracted state the assembly conforms along the guide. When in the extended state the assemblies are disposed as a treatment aperture.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Method for calibrating a multileaf collimator
InactiveCN102526885AReduce complexityHandling using diaphragms/collimetersRadiation therapyPosition biasMultileaf collimator
The invention relates to a method for calibrating a multileaf collimator by determining a value for a drift of a position of a collimator leaf carriage. The method comprises the steps of: a) defining a reference position of the collimator leaf carriage; b) determining a first value for a drift of a first position of a leaf from a first defined absolute position, the leaf being arranged on the collimator leaf carriage and the collimator leaf carriage being located at the reference position; c) moving the collimator leaf carriage to a position to be checked; d) determining a second value, the second value being for a drift of a second position of the leaf from a second defined absolute position, the collimator leaf carriage being located at the position to be checked; e) determining a difference value by forming the difference between the first value and the second value for the drift of the position of the leaf; and f) using the difference value as a value for the drift of the position of the collimator leaf carriage for the position to be checked.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Multileaf collimator
A collimating device for controlling a radiation field of an X-ray radiated from an X-ray radiator. The device includes a plurality of first collimating leaves, a plurality of second collimating leaves, a beam generator, a detector, a memory, and a controller. The plurality of second collimating leaves oppose the first collimating leaves. The beam generator is configured to generate a beam. The beam emanates between the first collimating leaves and the second collimating leaves. The detector is configured to detect the beam. The memory is configured to store position information of each leaf of the first and second collimating leaves when the each leaf is determined to intersect the beam based on the detection. The controller is configured to position the each leaf based on the position information so as to control the radiation field.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Particle beam therapy system
ActiveUS8536548B2Easy to adjustAccurate monitoringElectrode and associated part arrangementsHandling using diaphragms/collimetersViewpointsParticle beam
A particle beam therapy system that prevents dispersion of a charged particle beam, reduction of the energy thereof, and upsizing of the system and can accurately monitor the opening shape of a multileaf collimator so as to perform high-accuracy particle beam therapy. An image-capturing unit that takes an image of an outer end of a respective downstream side face of a leaf plate is provided for each row of leaves in such a way as to be situated at a position that is at an outer side of an irradiation field; and adjusted in such a way that a foot of a perpendicular line from a viewpoint, of the image capturing unit, to the downstream side face of a leaf plate, is situated at a position that is at an inner side of the position of the outer end when the leaf plate is maximally driven in the departing direction.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com