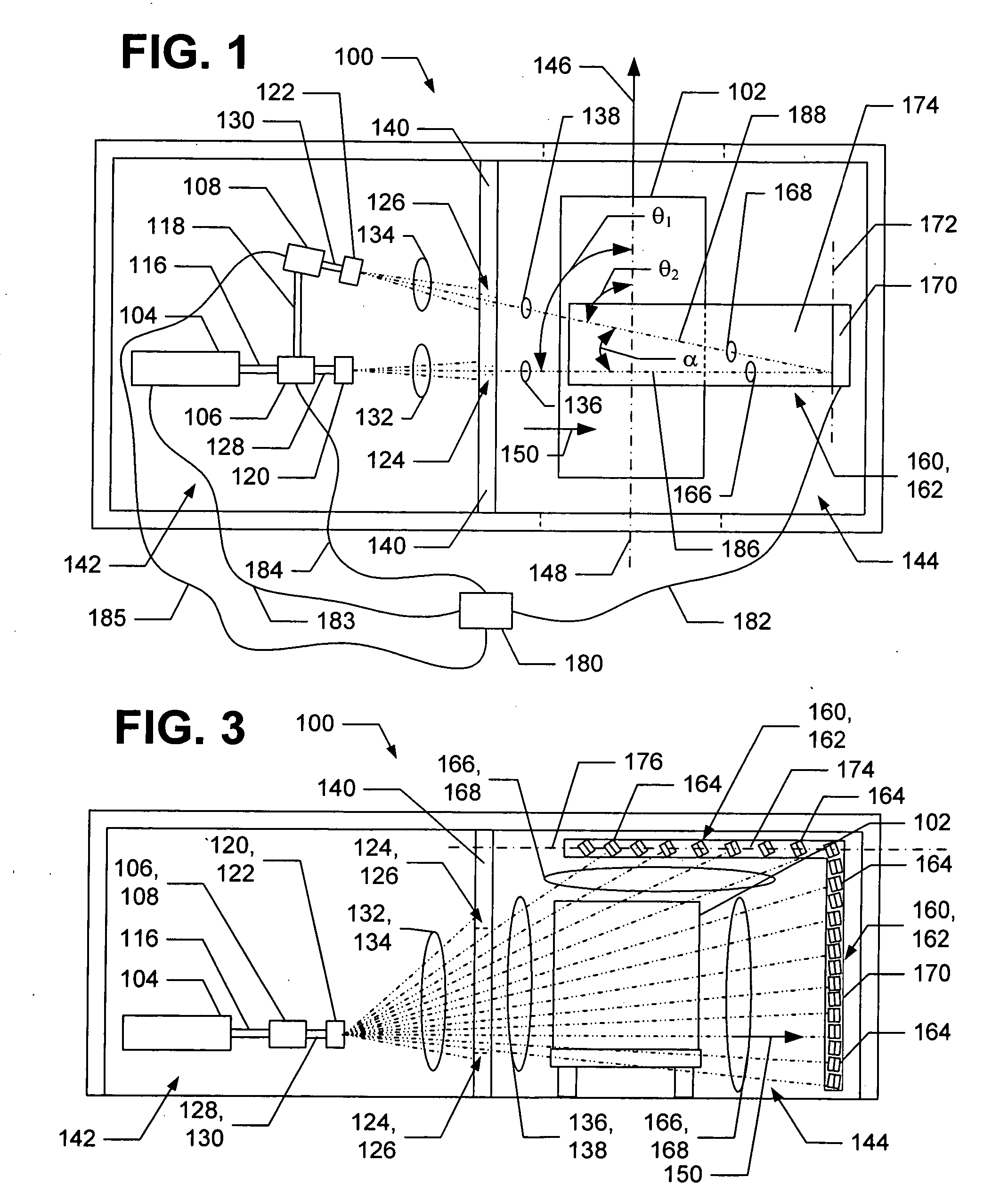
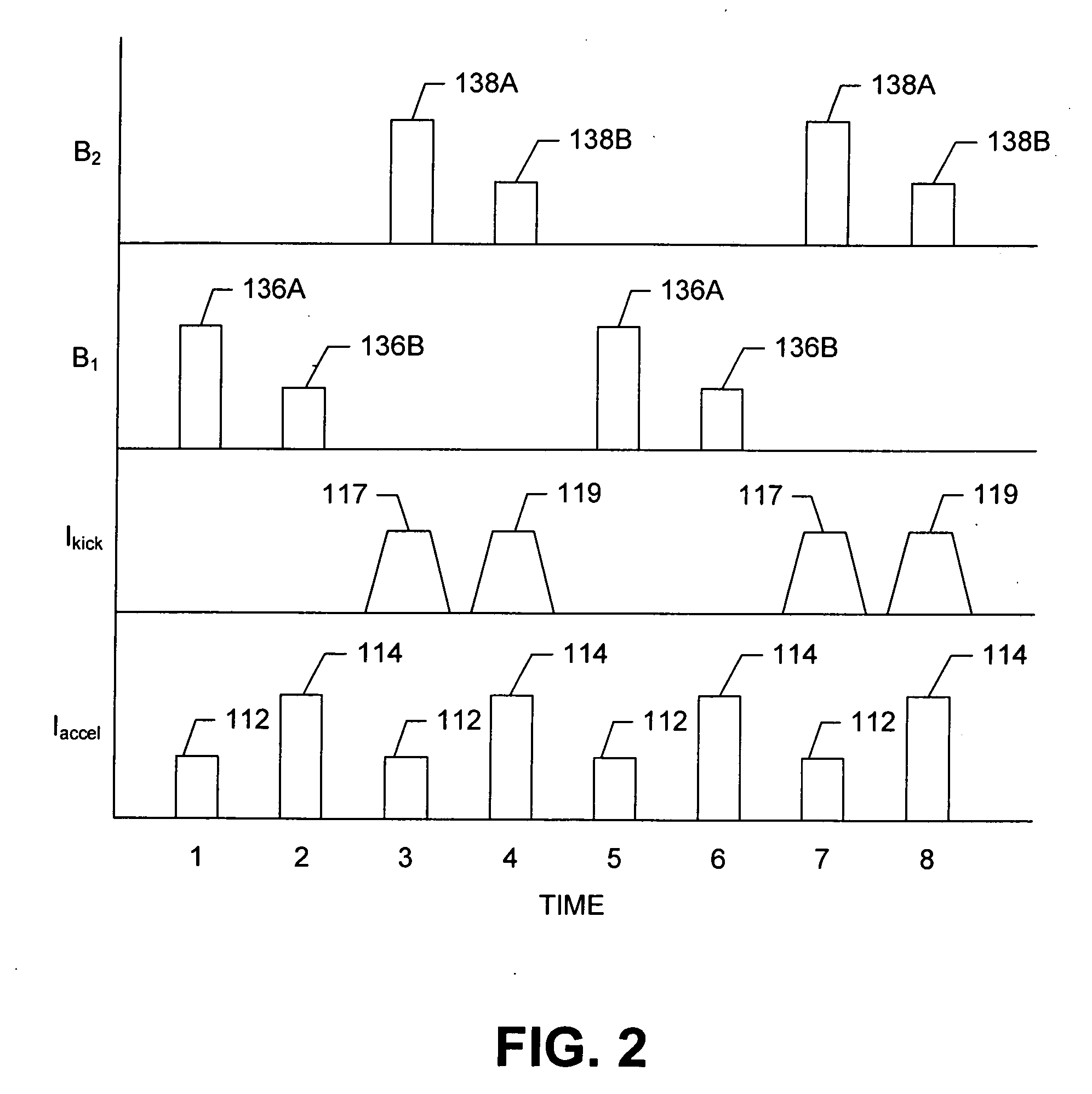
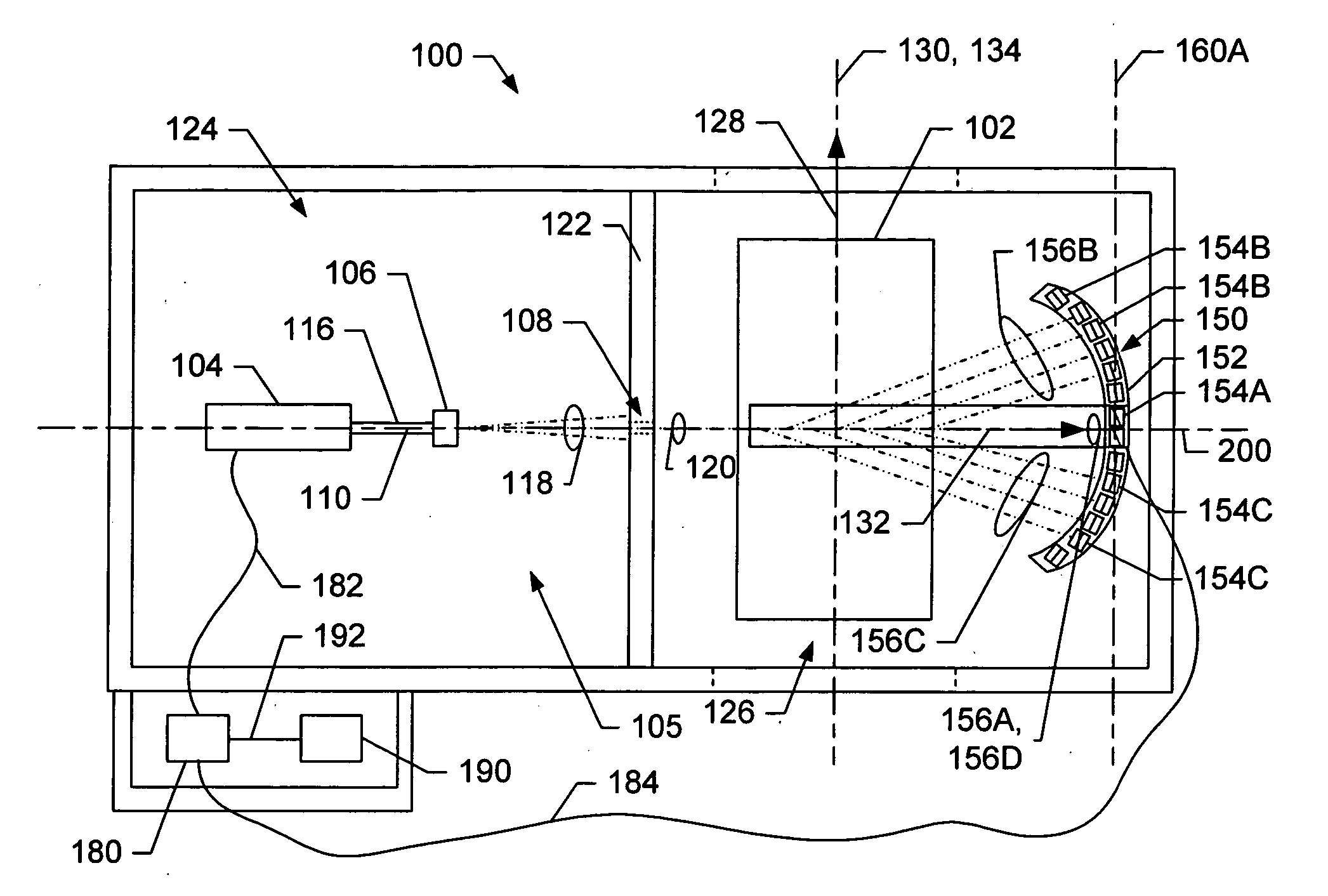
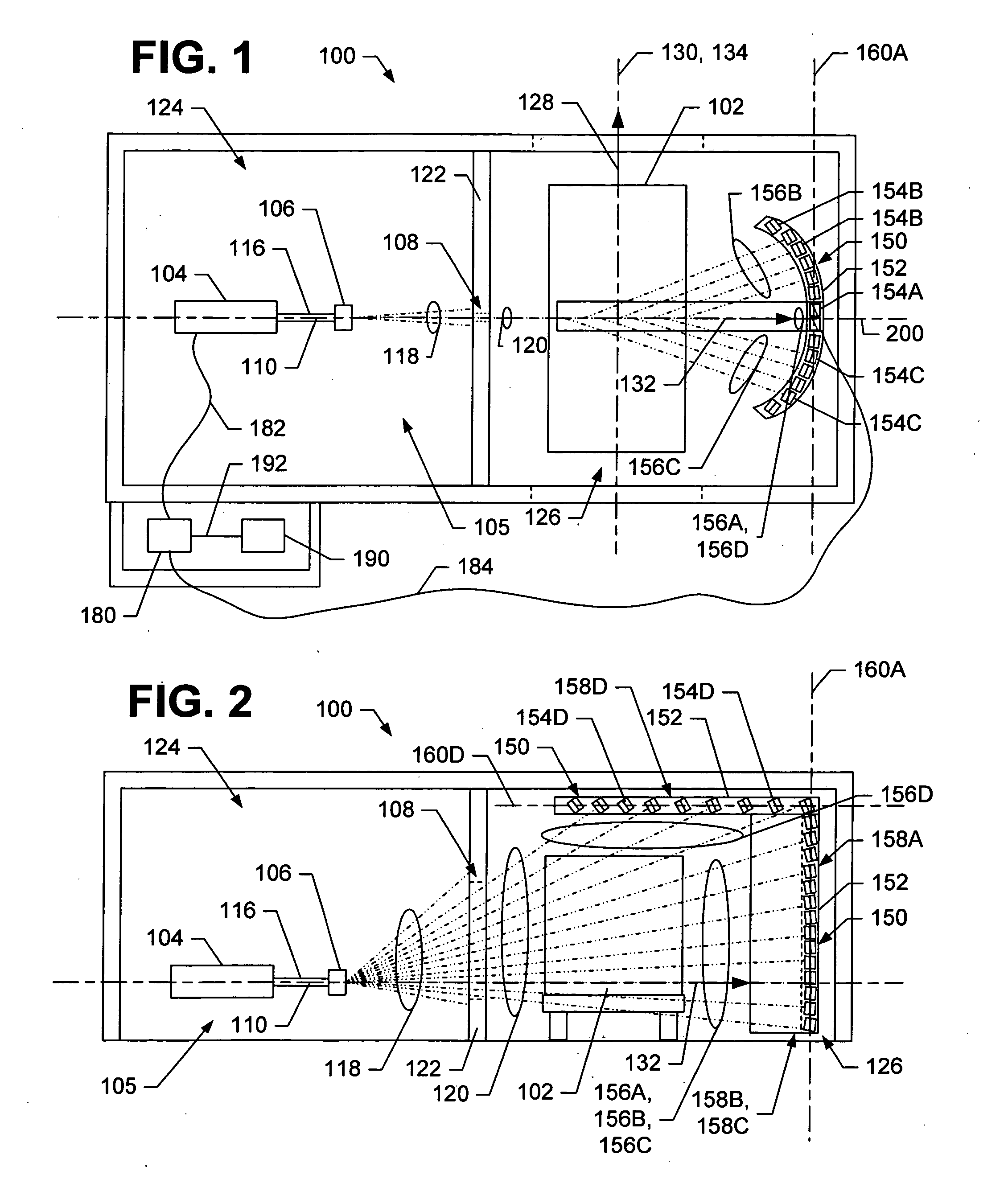
Patents
Literature
90 results about "Bremsstrahlung" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bremsstrahlung ([ˈbʁɛmsˌʃtʁaːlʊŋ] ), from bremsen "to brake" and Strahlung "radiation"; i.e., "braking radiation" or "deceleration radiation", is electromagnetic radiation produced by the deceleration of a charged particle when deflected by another charged particle, typically an electron by an atomic nucleus. The moving particle loses kinetic energy, which is converted into radiation (i.e., a photon), thus satisfying the law of conservation of energy. The term is also used to refer to the process of producing the radiation. Bremsstrahlung has a continuous spectrum, which becomes more intense and whose peak intensity shifts toward higher frequencies as the change of the energy of the decelerated particles increases.
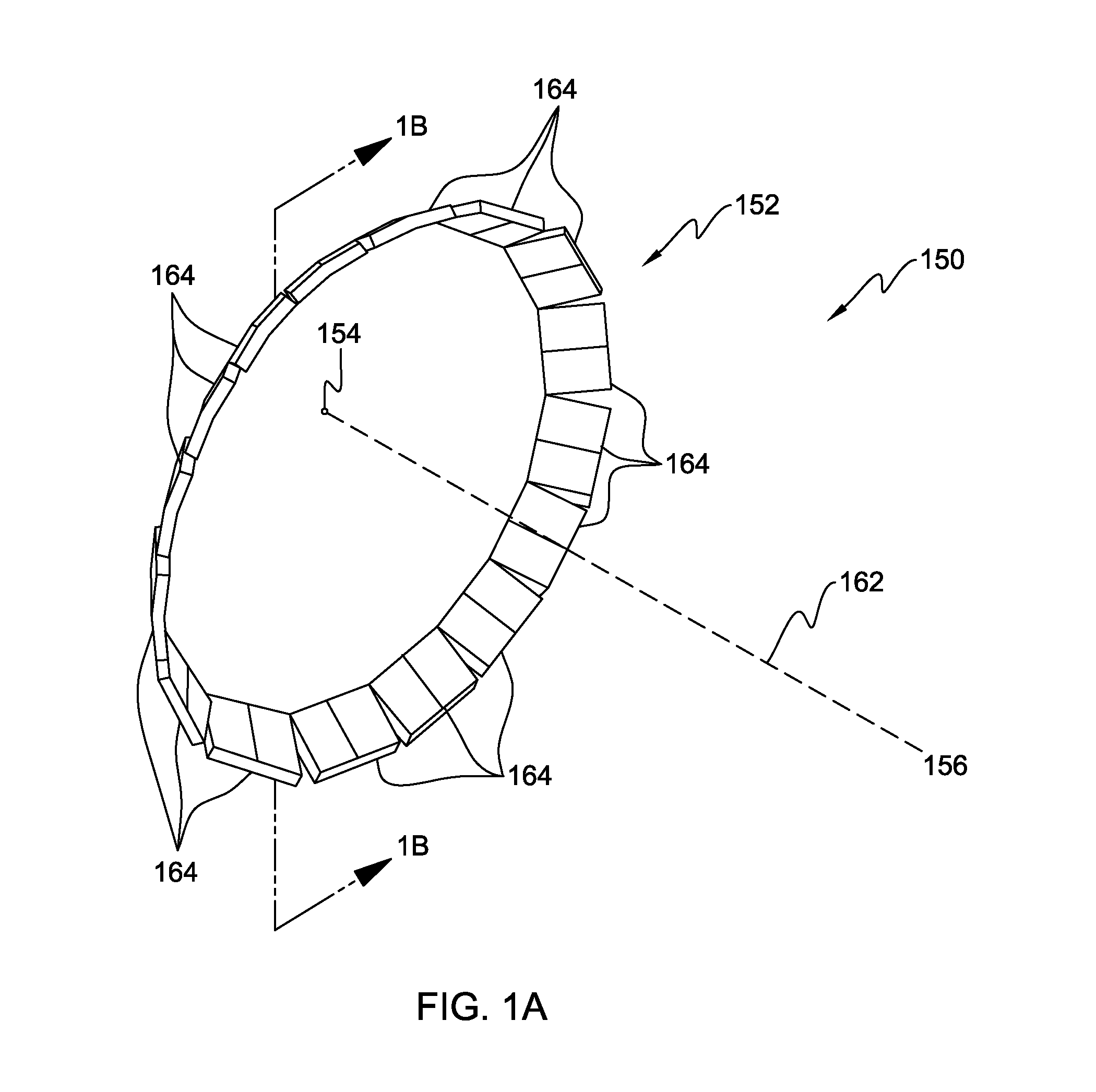
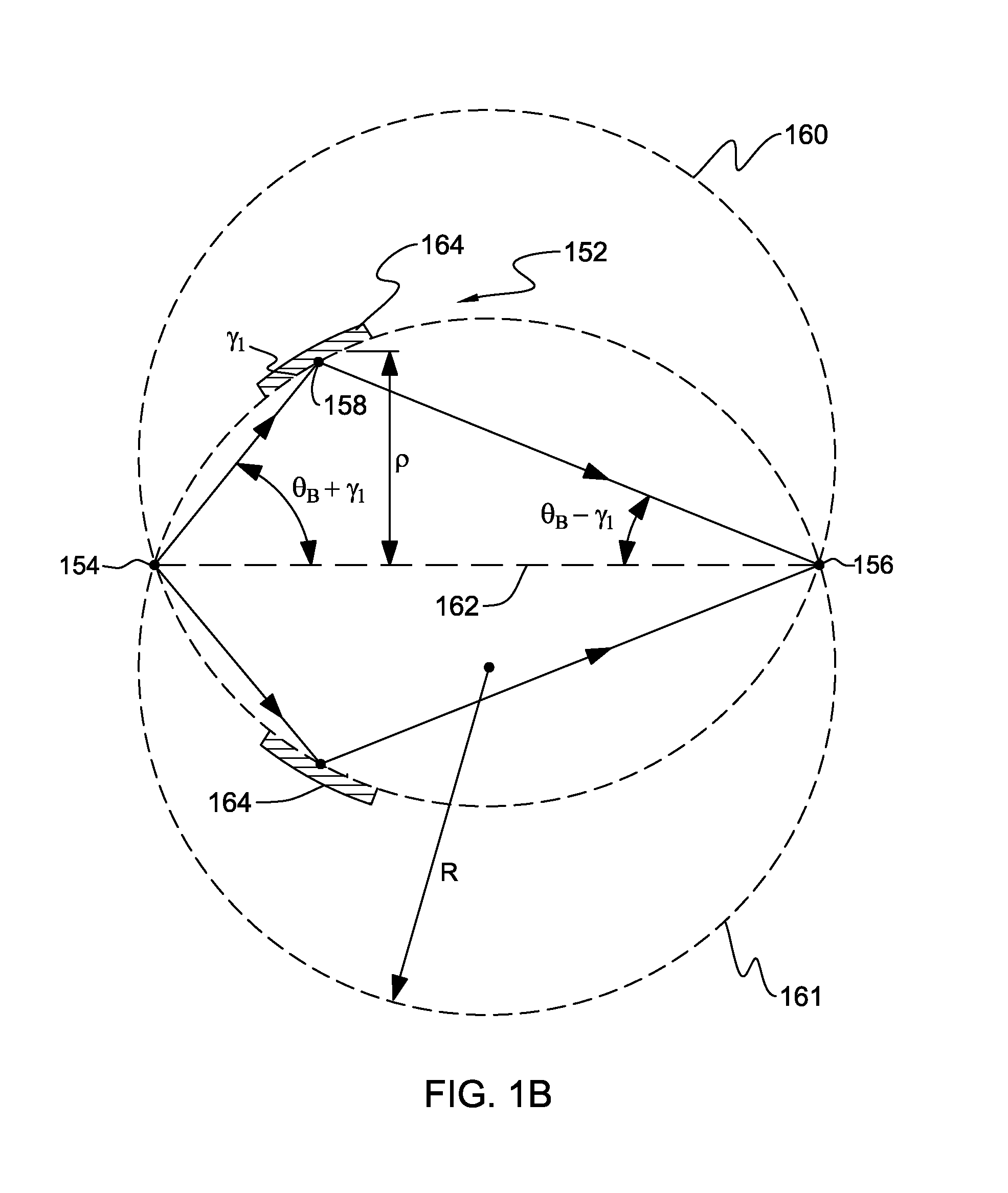
Bremsstrahlung laser (“blaser”)
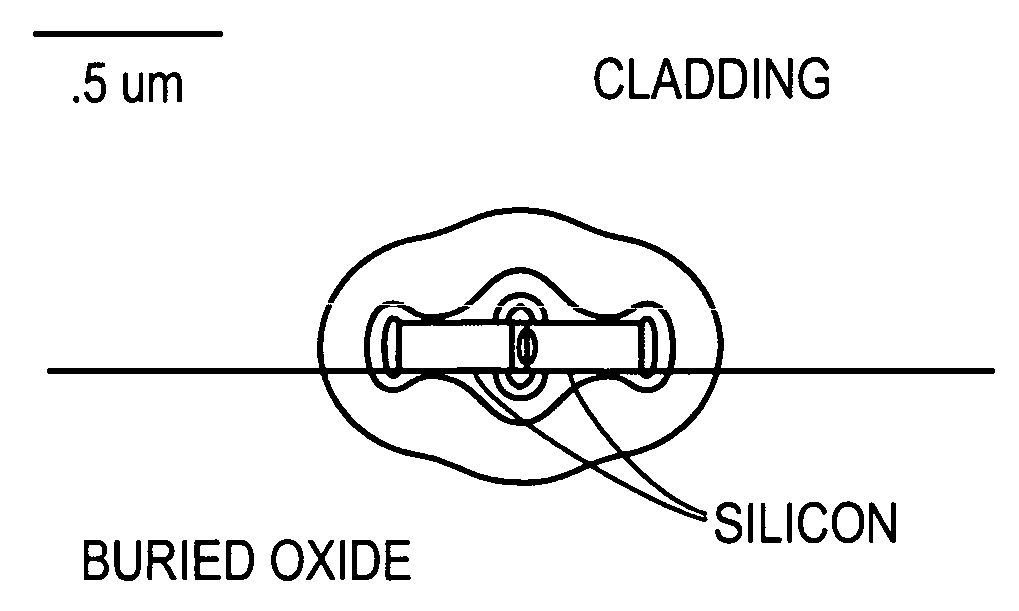
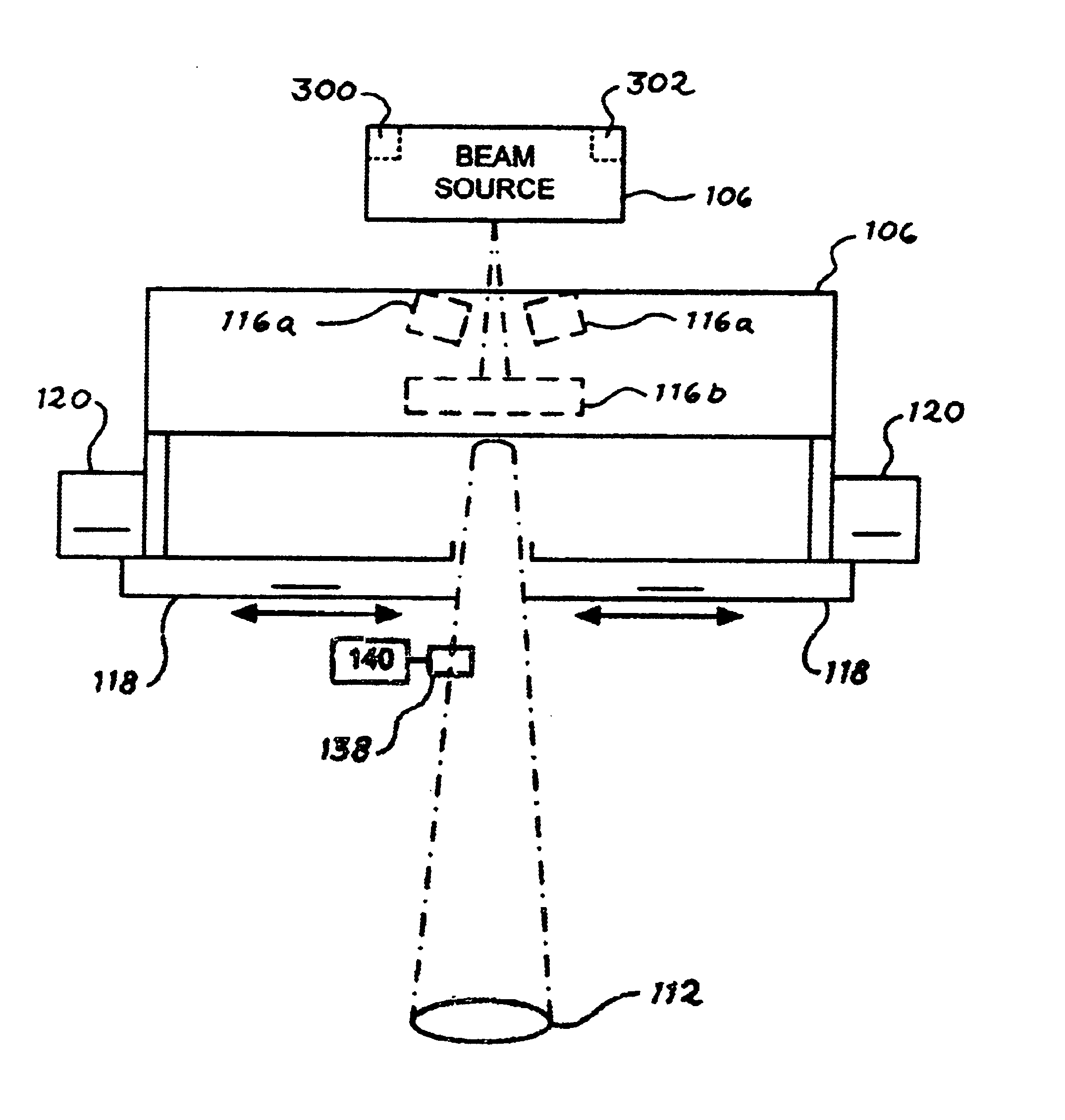
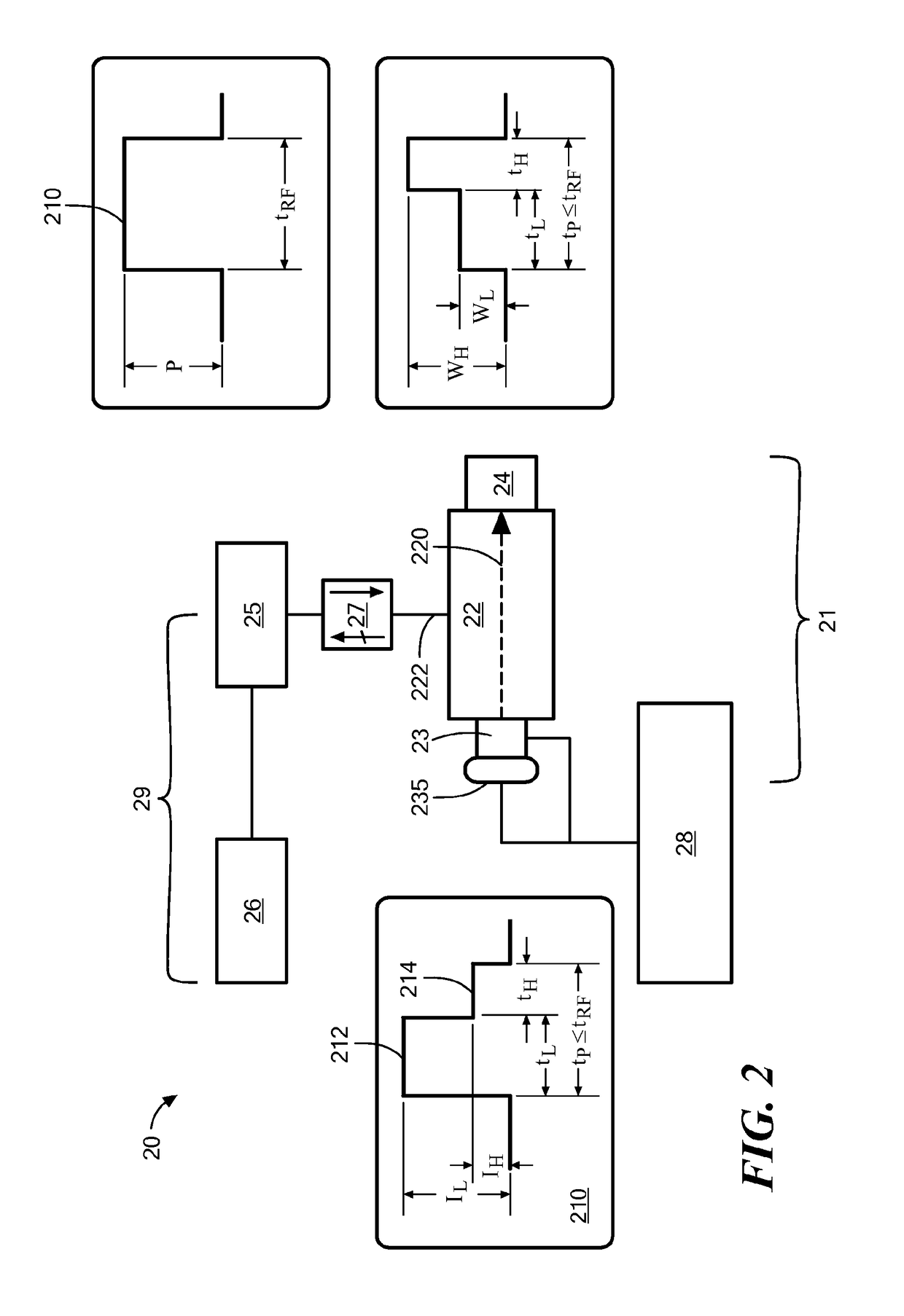
A light generating system that comprises a narrow evacuated slot defined between at least two high index contrast waveguide elements. The apparatus can be fabricated using a material such as a SOI wafer having an oxide layer thickness of the order of 1 micron and a top silicon layer thickness of the order of 100-150 nm. Electrode contacts are provided to at least two waveguide elements fabricated in the top silicon layer, each waveguide element having a thickness comparable to the top silicon layer thickness, a width of some hundreds of nm, and having a slot having dimensions in the range of 50-200 nm defined therebetween. The length of the slot is at least as long as the slot width. Charged particles, such as electrons, that are emitted and accelerated across the slot by an applied electrical signal provide a source of photons as a consequence of being accelerated and / or decelerated.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
XRF system having multiple excitation energy bands in highly aligned package
ActiveUS8559597B2Increased signal noiseSmall intensityX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX ray analysisX-ray optics
An x-ray analysis apparatus for illuminating a sample spot with an x-ray beam. An x-ray tube is provided having a source spot from which a diverging x-ray beam is produced having a characteristic first energy, and bremsstrahlung energy; a first x-ray optic receives the diverging x-ray beam and directs the beam toward the sample spot, while monochromating the beam; and a second x-ray optic receives the diverging x-ray beam and directs the beam toward the sample spot, while monochromating the beam to a second energy. The first x-ray optic may monochromate characteristic energy from the source spot, and the second x-ray optic may monochromate bremsstrahlung energy from the source spot. The x-ray optics may be curved diffracting optics, for receiving the diverging x-ray beam from the x-ray tube and focusing the beam at the sample spot. Detection is also provided to detect and measure various toxins in, e.g., manufactured products including toys and electronics.
Owner:X-RAY OPTICAL SYSTEM INC
Bremsstrahlung laser ("blaser")
InactiveUS20080007817A1Increases tunneling probabilityIncrease probabilityLaser detailsRefractive indexElectrode Contact
A light generating system that comprises a narrow evacuated slot defined between at least two high index contrast waveguide elements. The apparatus can be fabricated using a material such as a SOI wafer having an oxide layer thickness of the order of 1 micron and a top silicon layer thickness of the order of 100-150 nm. Electrode contacts are provided to at least two waveguide elements fabricated in the top silicon layer, each waveguide element having a thickness comparable to the top silicon layer thickness, a width of some hundreds of nm, and having a slot having dimensions in the range of 50-200 nm defined therebetween. The length of the slot is at least as long as the slot width. Charged particles, such as electrons, that are emitted and accelerated across the slot by an applied electrical signal provide a source of photons as a consequence of being accelerated and / or decelerated.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Use of nearly monochromatic and tunable photon sources with nuclear resonance fluorescence in non-intrusive inspection of containers for material detection and imaging
Methods and systems for detecting potential items of interest in target samples, using nuclear resonance fluorescence, utilize incident photon spectra that are narrower than traditional bremsstrahlung spectra but overlap nuclear resonances in elements of interest for purposes of detection, such as but not limited to the detection of threats in luggage or containers being scanned.
Owner:PASSPORT SYSTEMS INC
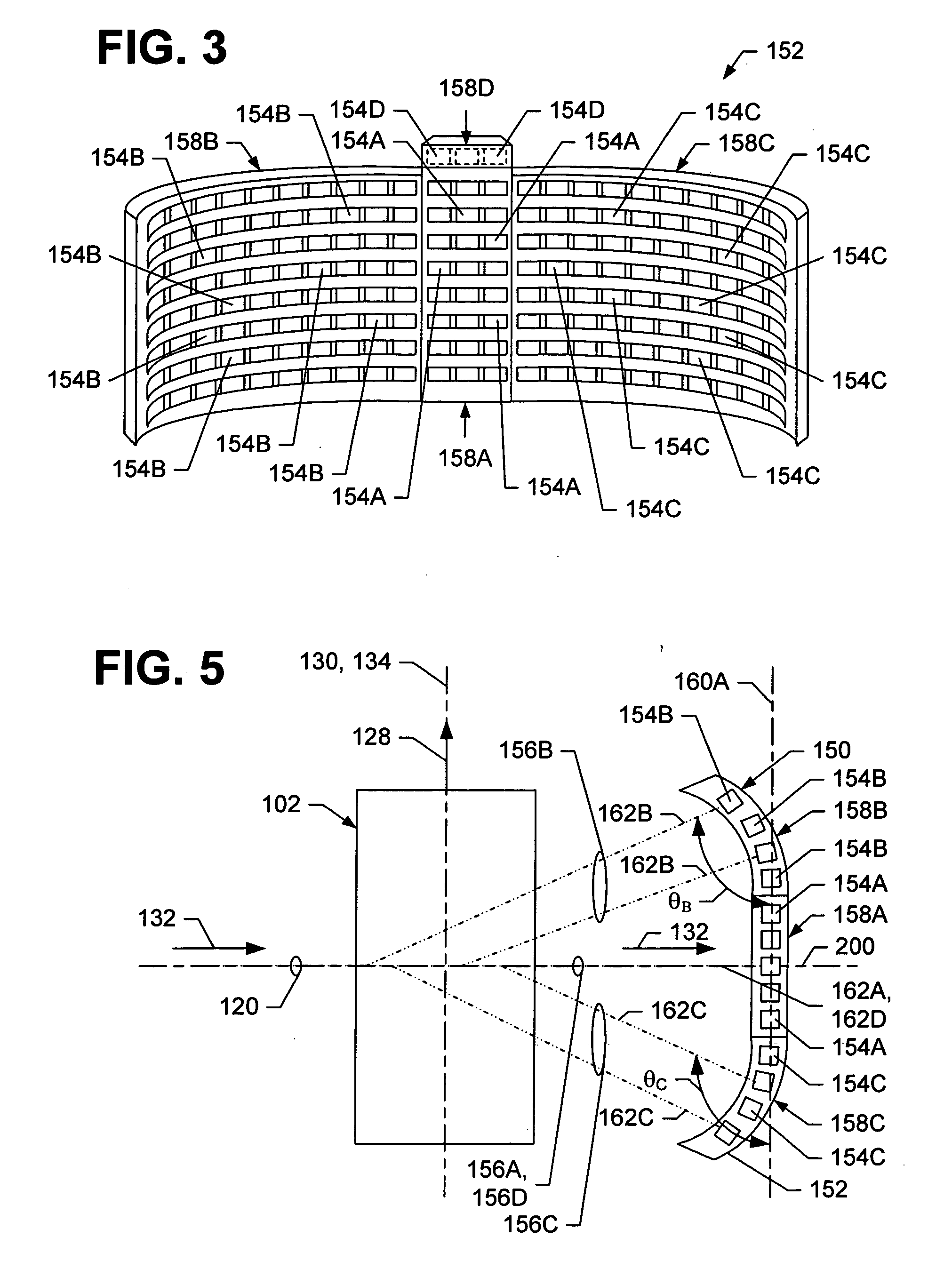
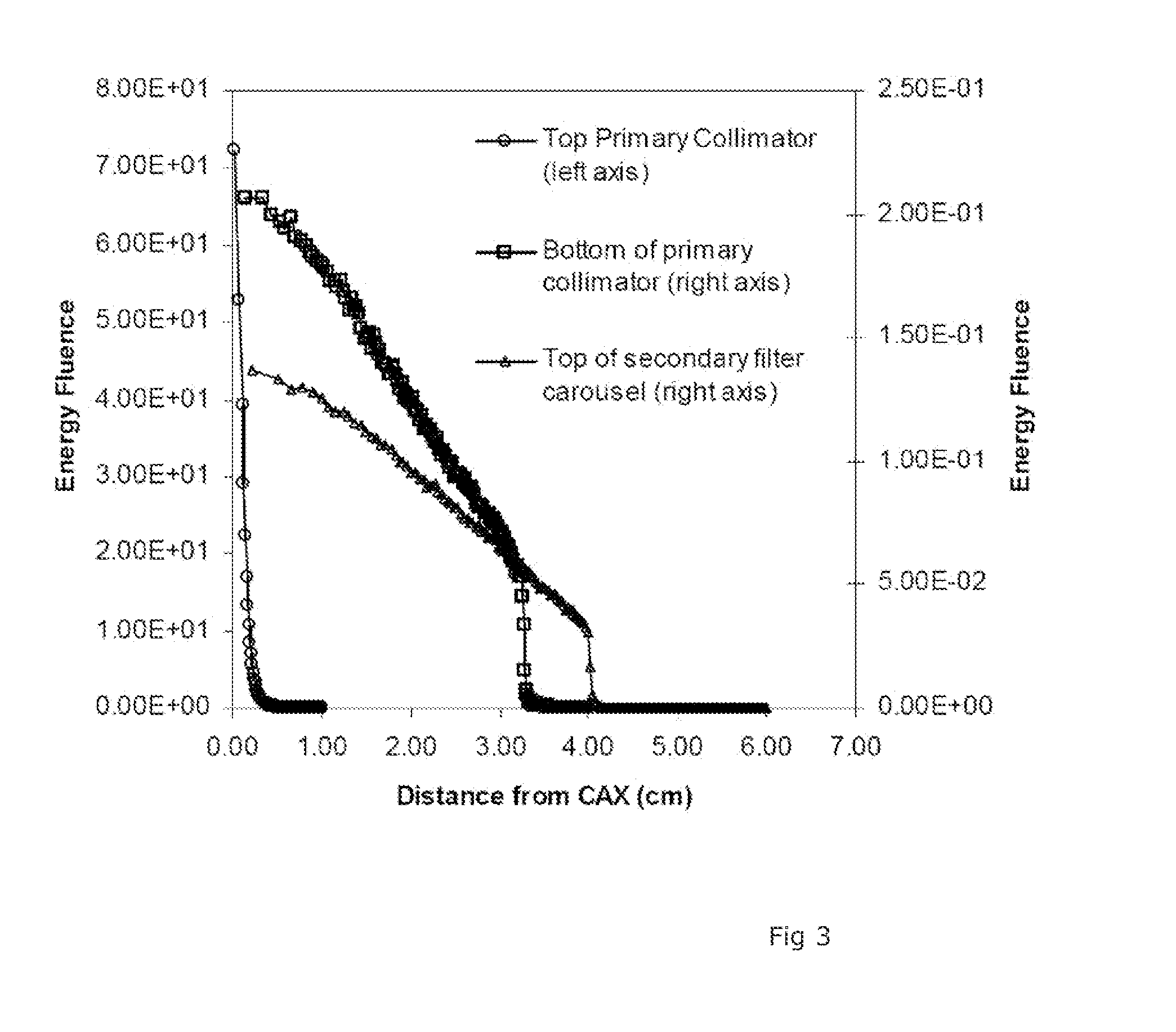
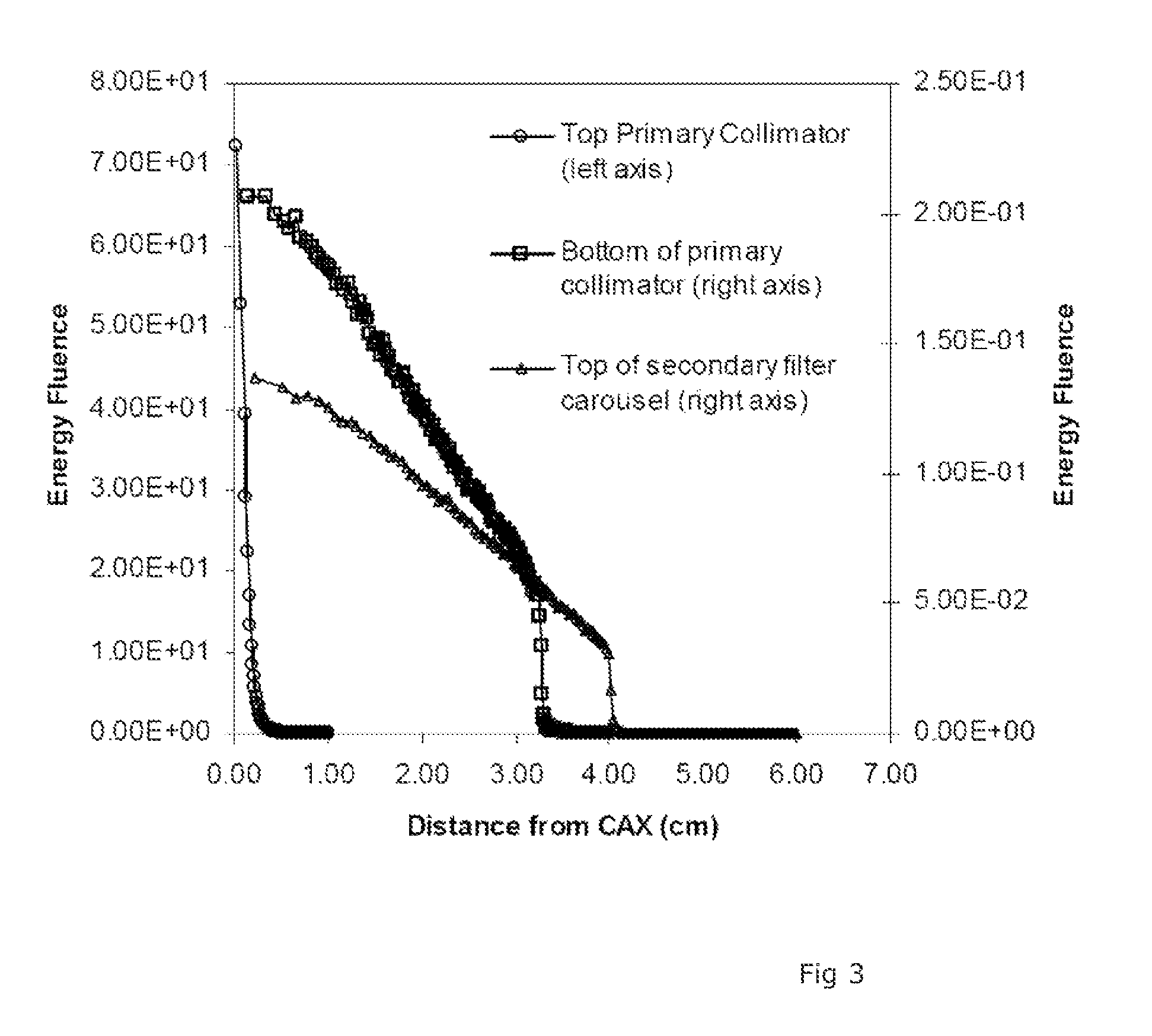
Optimal configuration of photon and electron multileaf collimators in mixed beam radiotherapy
ActiveUS6937693B2Reduce dosageSmall penumbraX-ray apparatusX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyMixed beamLight beam
A radiation therapy method that includes directing a beam along a beam path toward a treatment area. Performing a correction process on the beam, the process includes selectively collimating the beam based on a dose that takes into account bremsstrahlung interactions caused by the beam.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Angled-beam detection system for container inspection
InactiveUS20060233302A1Reduces number of orientation and geometryCostly and time-consumeRadiation/particle handlingStructural/machines measurementMulti materialHazardous substance
A non-intrusive inspection system, including apparatuses and methods, for non-intrusively inspecting containers such as, without limitation, those employed to transport items in international commerce. The non-intrusive inspection system is configured to generate and scan a container with multiple bremsstrahlung, or x-ray, beams having multiple spectra and directed at the container in multiple directions and planes separated by one or more angle(s). Using data collected from such scanning, software of the non-intrusive inspection system generates three-dimensional images of the items present in a container, calculates the volumes and densities of such items, computes effective “Z” numbers, and distinguishes between multiple materials, or elements, of such items. By employing multiple bremsstrahlung beams directed upon a container in multiple planes, the non-intrusive inspection system reduces the number of orientations and geometries of items within a container that might otherwise be employed to avoid the detection of harmful materials being transported within a container.
Owner:SCANTECH IDENTIFICATION BEAM SYST
Non-intrusive container inspection system using forward-scattered radiation
InactiveUS20060256914A1Low costEnhance the imageMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionForward scatterMulti material
A non-intrusive container inspection system, including apparatuses and methods, for non-intrusively scanning and inspecting containers employed to transport items therewithin that utilizes forward-scattered bremsstrahlung, or x-rays, for generating multi-plane images of items present within the containers and for distinguishing between multiple materials present in such items. The system is adapted to direct a pulsed bremsstrahlung, or x-ray, beam having multiple spectra in a substantially single direction at a container being scanned and to produce data that corresponds to portions of the beam that either pass through items within the container without being scattered or that are forward-scattered by items within the container. The system employs a detector array having sections specially configured and oriented to receive and produce data corresponding to the non-scattered and forward-scattered portions of the beam.
Owner:SCANTECH HLDG
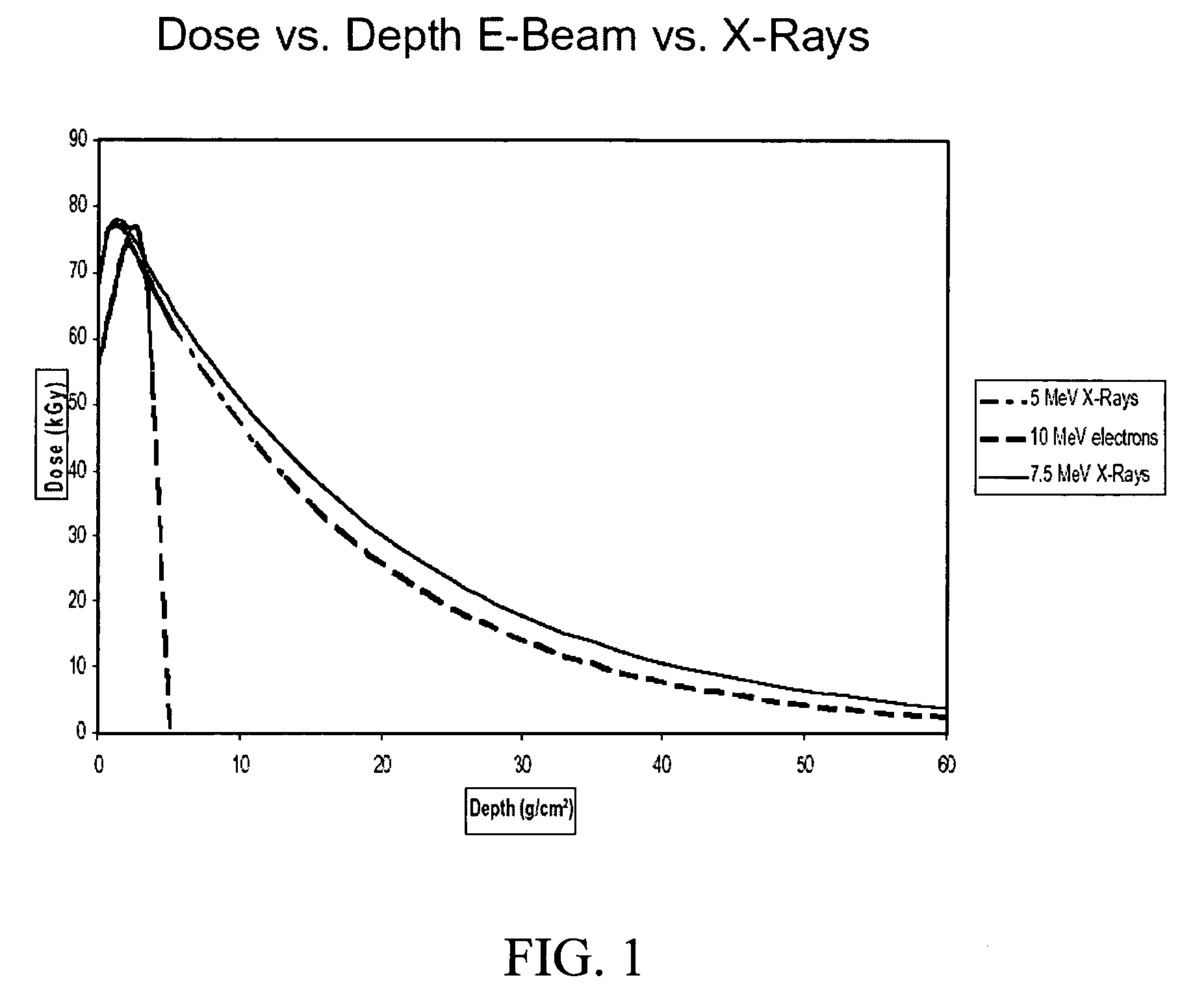
Processes for chemically affecting reactive materials with X-rays
InactiveUS20080196829A1Fast and energy efficientLess complicatedLamination ancillary operationsElectric discharge tubesPolymer scienceHigh energy
The present invention describes a method for curing polymers and polymer composites with X-rays generated by the bremsstrahlung effect, using a high power, high energy electron beam. The process generates X-rays with sufficient throughput and penetration for commercial use. The present invention employs high power, high energy electron beams to create the X-rays. The beams are typically run at energies ranging from 1 MeV to 10 MeV, preferably from 3 MeV to 10 MeV, and more preferably from 5 MeV to 7 MeV. The beams typically have powers ranging from 30 kW or higher, preferably 80 kW or higher, more preferably 100 kW of higher, and ideally at least 200 kW. Suitable polymers and polymer composites include, but are not limited to, polymeric molding materials, fiber reinforced molding materials, reactive monomer impregnated wood, similar and dissimilar materials bonded through adhesives.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Apparatus and Method for Fluid Phase Fraction Determination Using X-Rays
ActiveUS20140355737A1Reduce complexityLow costMaterial testing goodsVolume/mass flow by differential pressureElectricityFluid phase
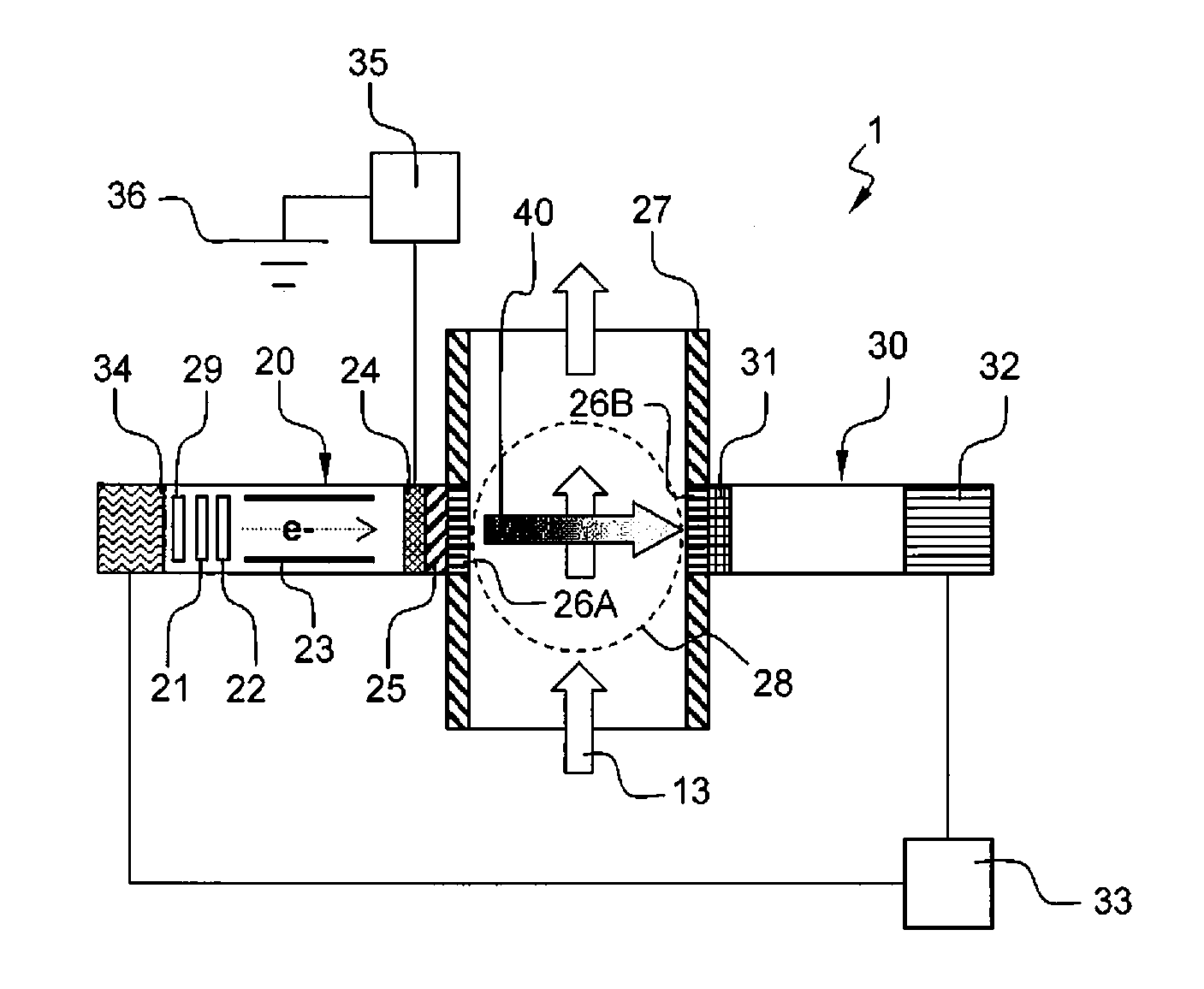
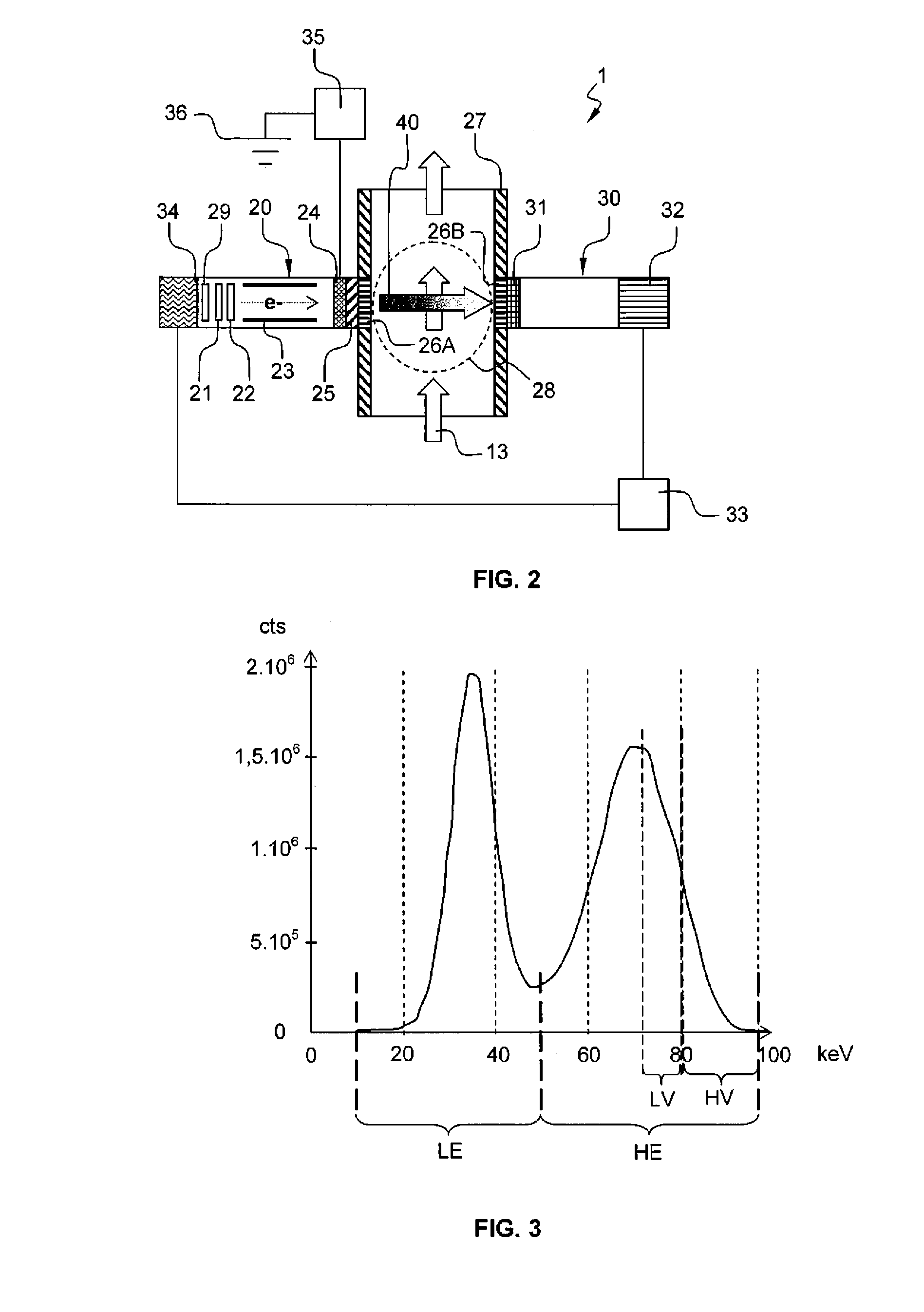
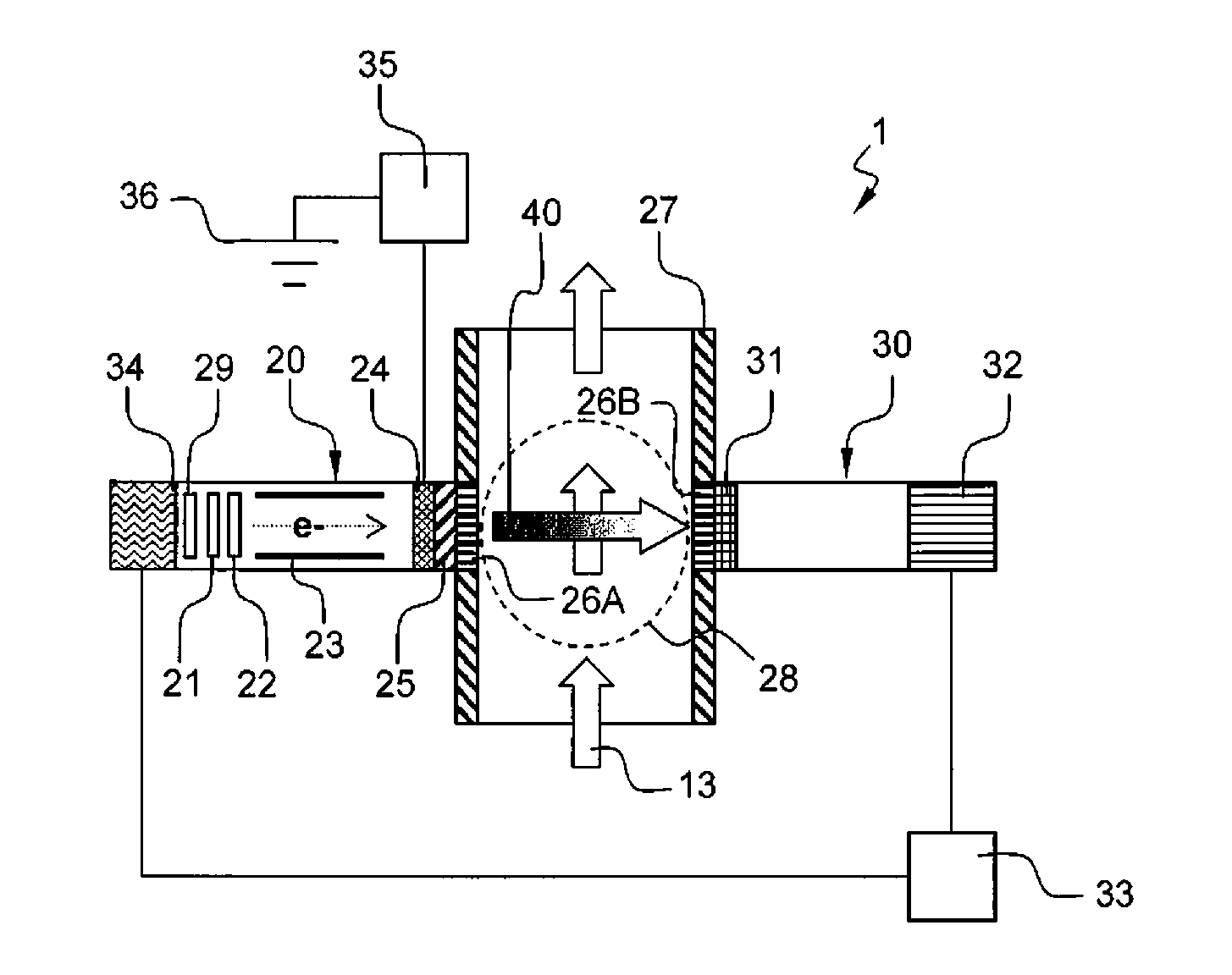
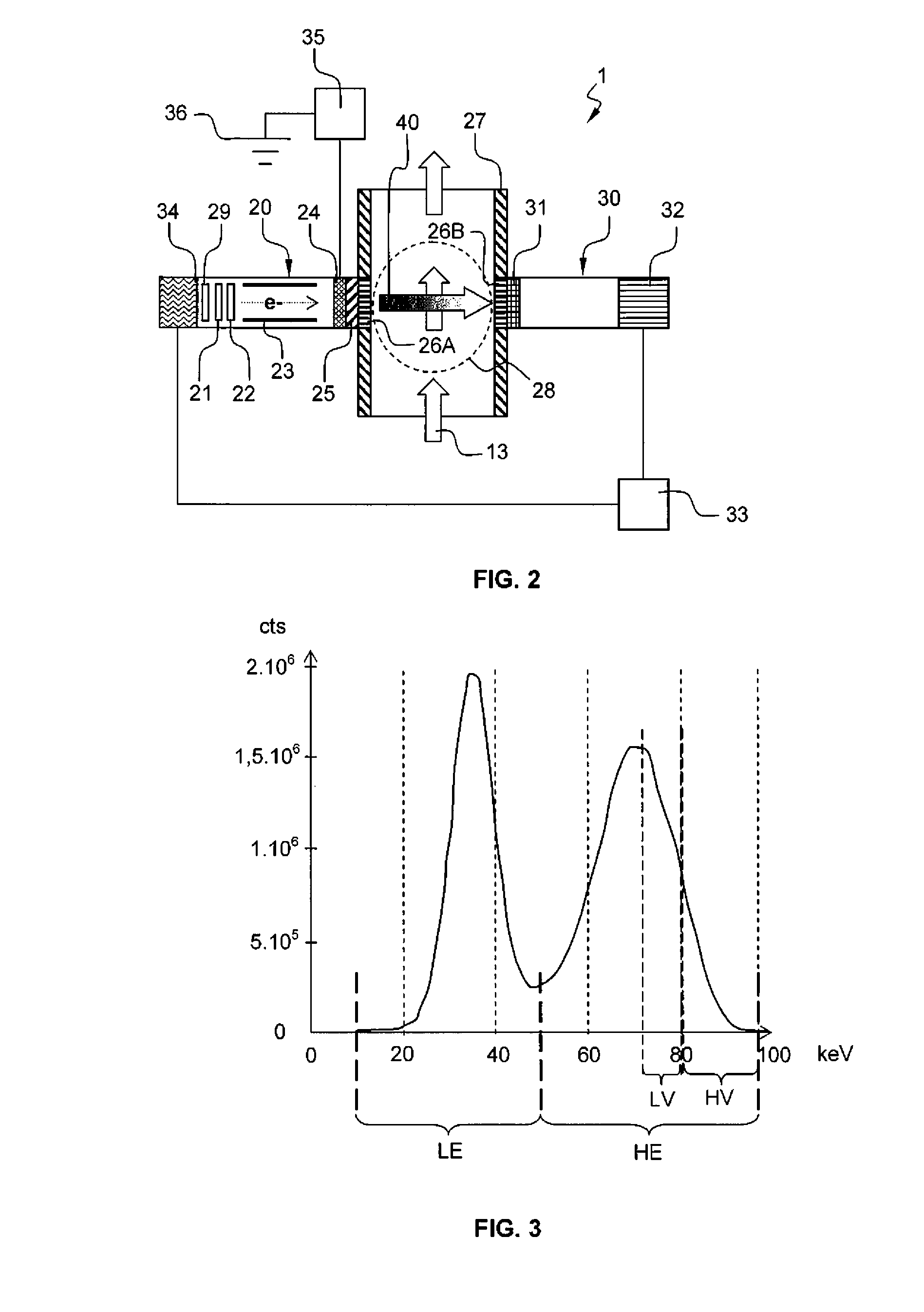
An apparatus for determining fluid phase fraction of a multiphase fluid mixture (13) comprises:—a x-ray generator (20) arranged to emit a x-ray radiation spectrum comprising a low energy region and a high energy region, the high energy region including a Bremsstrahlung spectrum;—a pipe section (27) through which the multiphase fluid mixture (13) flows comprising a measurement section (28), said measurement section (28) being coupled to said x-ray generator (20);—a detector (30) coupled to said measurement section (28) and arranged to detect x-ray radiation that has passed through said multiphase fluid mixture (13), the detector (30) being coupled to a multichannel analyzer (32) producing a measurement output comprising a low energy (LE) and high energy (HE) measurement counts; wherein the measurement output further comprises a low energy (LV) and high energy (HV) control counts, in a low energy and high energy control windows located on an edge of the Bremsstrahlung spectrum, respectively; and wherein the apparatus further comprises an electrical parameter control arrangement (33) coupled to the x-ray generator (20) and the detector (30), the electrical parameter control arrangement (33) being arranged to calculate a first ratio of the high energy control count relative to the low energy control count (RV=HV / LV) and a second ratio of the high energy measurement count relative to the low energy measurement count (RE=HE / LE), and to adjust the electrical operation of the x-ray generator (20) based on an electrical parameter control function (FC(V)) of said ratios that minimize a dependence of the electrical operation of the x-ray generator on the fluid phase fraction of the multiphase fluid mixture (13) flowing in the measurement section (28).
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
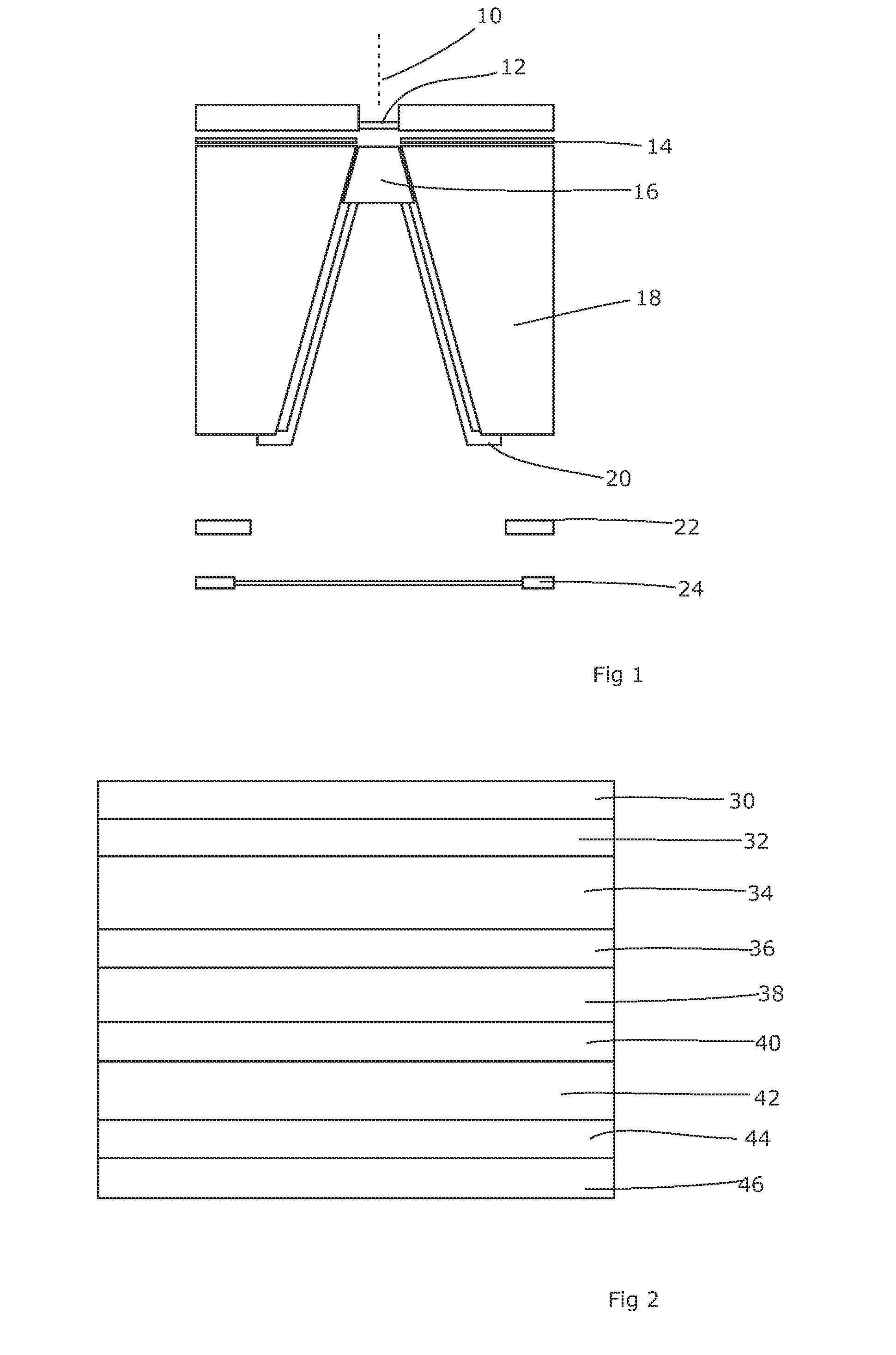
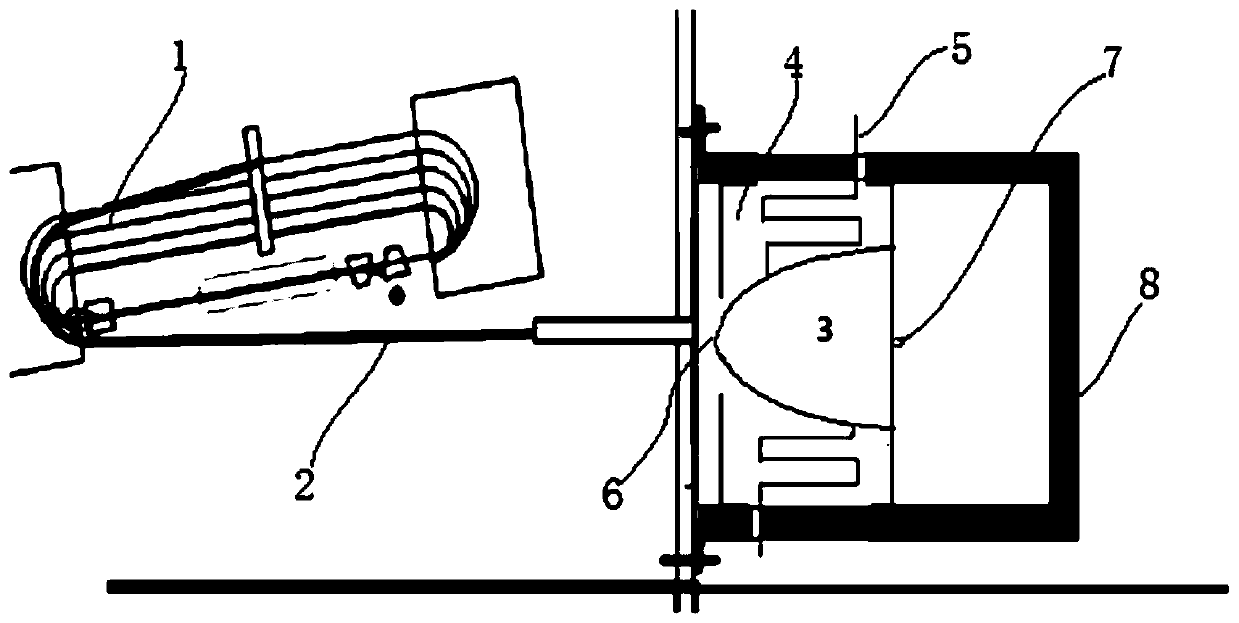
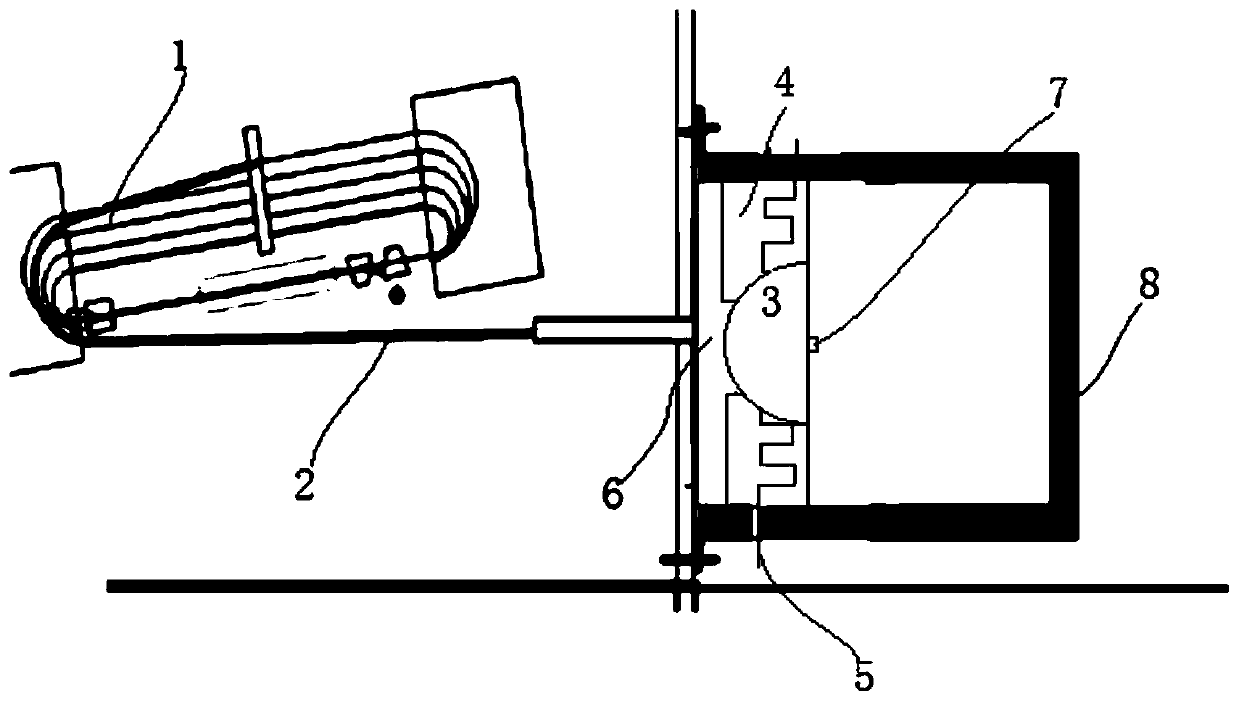
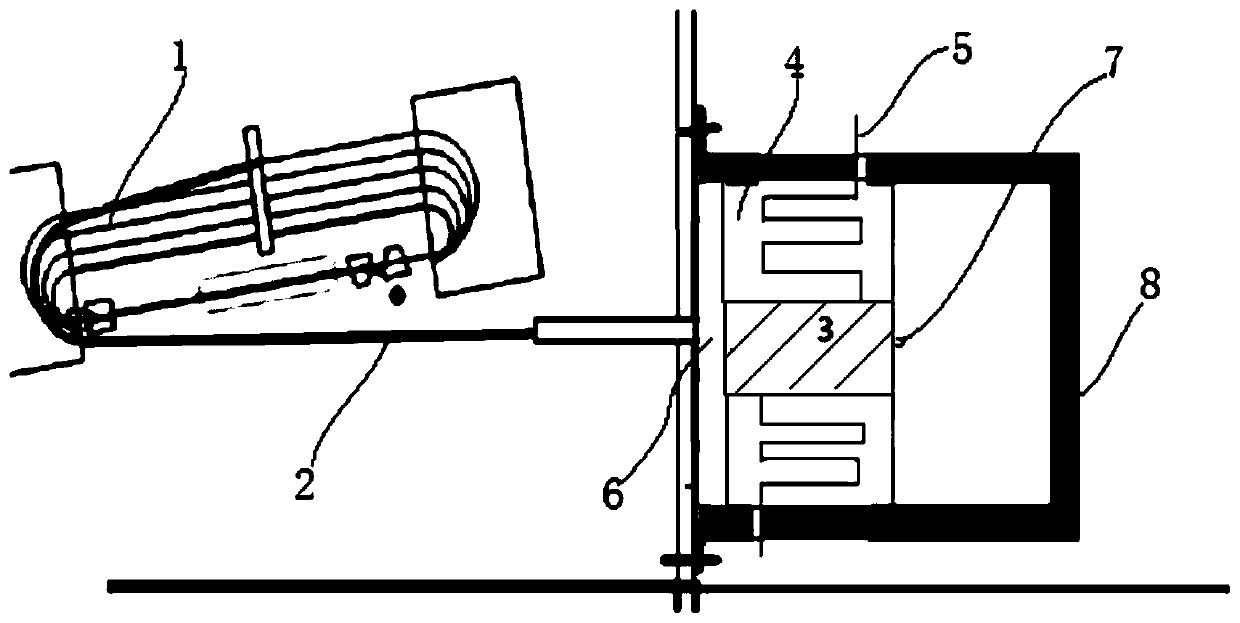
Radiotherapy Apparatus
ActiveUS20110142202A1Reduce skin doseAvoid insufficient thicknessX-ray tube electrodesHandling using diaphragms/collimetersHigh energyX-ray
It is desirable to achieve a co-incident investigative kV source for a therapeutic MV source—a so-called “beams-eye-view” source. It has been suggested that bremsstrahlung radiation from an electron window be employed; we propose a practical structure for achieving this which can switch easily between a therapeutic beam and a beam-eye-view diagnostic beam capable of offering good image resolution. Such a radiation source comprises an electron gun, a pair of targets locatable in the path of a beam produced by the electron gun, one target of the pair being of a material with a lower atomic number than the other, and an electron absorber insertable into and withdrawable from the path of the beam. In a preferred form, the electron gun is within a vacuum chamber, and the pair of targets are located at a boundary of the vacuum chamber. The lower atomic number target can be Nickel and the higher atomic number target Copper and / or Tungsten. The electron absorber can be Carbon, and can be located within the primary collimator, or within one of a plurality of primary collimators interchangeably locatable in the path of the beam. Such a radiation source can be included within a radiotherapy apparatus, to which the present invention further relates. A flat panel imaging device for this source can be optimised for low energy x-rays rather than high energy; Caesium Iodide-based panels are therefore suitable.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Radiation irradiation device, radiation irradiation method and program storage medium
InactiveUS9079027B2High therapeutic effectReduce harmX-ray tube electrodesHandling using diaphragms/collimetersSoft x rayFluence
A radiation irradiation device is provided that includes: a metal target that emits bremsstrahlung X-rays as a radiation beam due to irradiation with an electron beam; a radiation shielding member that includes a slit-shaped radiation passage portion and that is disposed downstream of the metal target in the radiation beam emission direction and is disposed such that a portion of the radiation beam passes through the radiation passage portion and the radiation beam incident to regions other than the radiation passage portion is blocked; and an electron beam generating device that irradiates, onto the metal target, an electron beam such that a diameter at a generation point of the emitted radiation beam is smaller than a length of an entry portion of the radiation passage portion along a length direction of the entry portion.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Angled-beam detection system for container inspection
InactiveUS7356118B2Reduces number of orientation and geometryCostly and time-consumeRadiation/particle handlingStructural/machines measurementMulti materialHazardous substance
A non-intrusive inspection system, including apparatuses and methods, for non-intrusively inspecting containers such as, without limitation, those employed to transport items in international commerce. The non-intrusive inspection system is configured to generate and scan a container with multiple bremsstrahlung, or x-ray, beams having multiple spectra and directed at the container in multiple directions and planes separated by one or more angle(s). Using data collected from such scanning, software of the non-intrusive inspection system generates three-dimensional images of the items present in a container, calculates the volumes and densities of such items, computes effective “Z” numbers, and distinguishes between multiple materials, or elements, of such items. By employing multiple bremsstrahlung beams directed upon a container in multiple planes, the non-intrusive inspection system reduces the number of orientations and geometries of items within a container that might otherwise be employed to avoid the detection of harmful materials being transported within a container.
Owner:SCANTECH IDENTIFICATION BEAM SYST
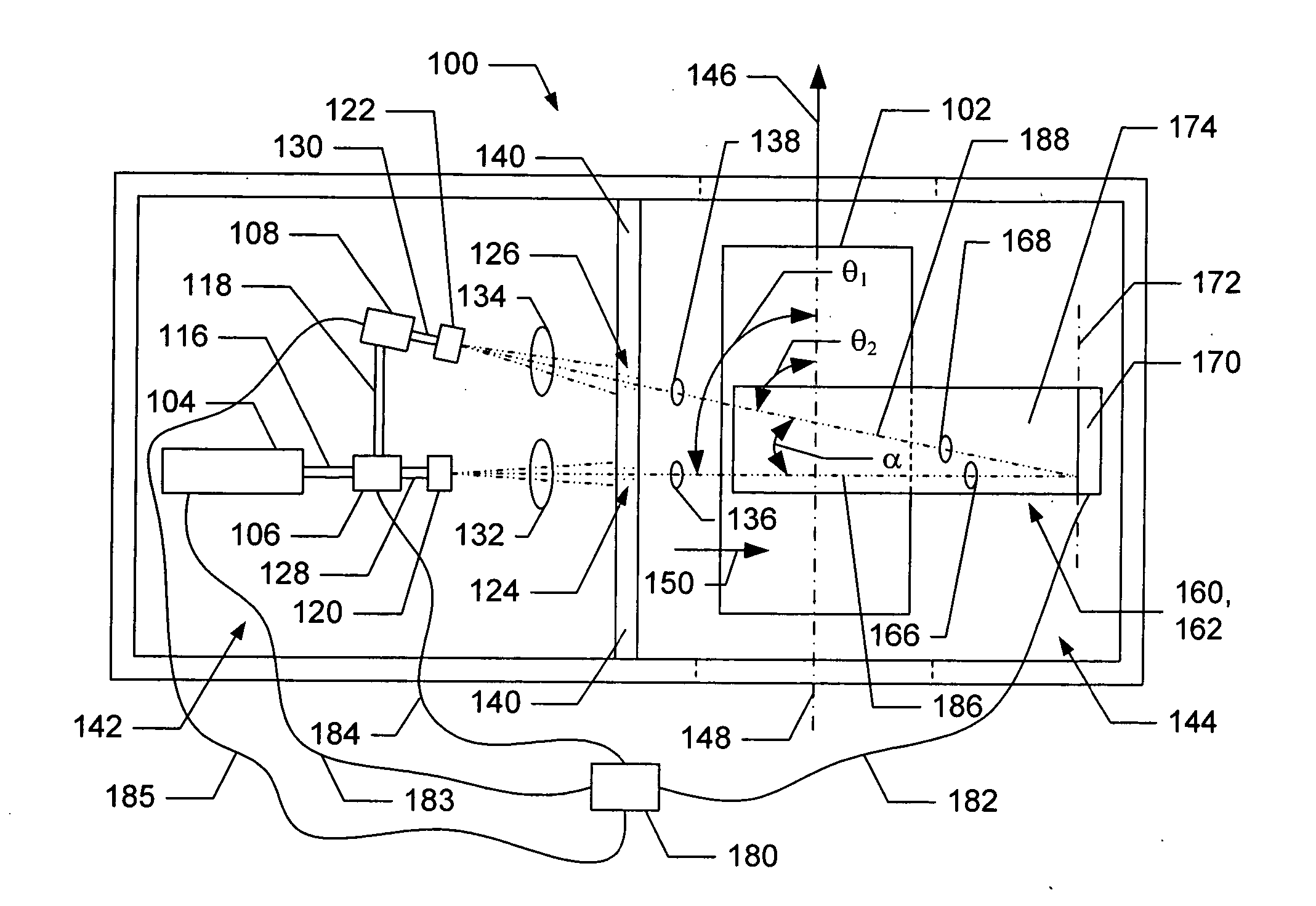
X-ray source and X-ray generating method
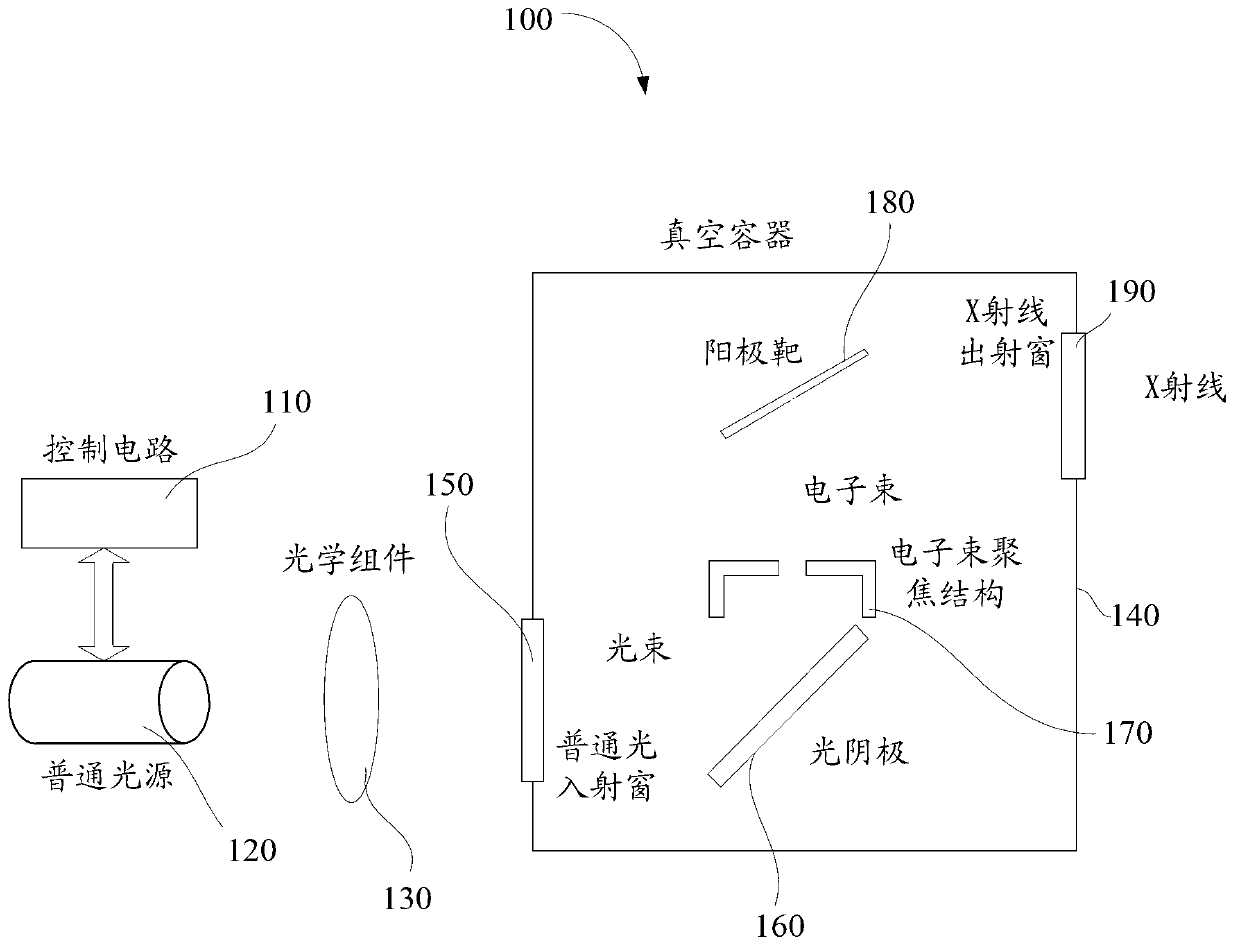
ActiveCN103219211AImprove time resolutionExposure Precise ControlX-ray tube electrodesOptical ModulePhotocathode
Provided is an X-ray source. The X-ray source comprises a control circuit, an ordinary light source, an optical module, a photocathode, an electron beam focusing structure, an anode target, an X-ray exit window, an ordinary light incidence window and a vacuum container, wherein the control circuit is used for controlling a working state of the ordinary light source, the ordinary light source is used for emitting light rays with a specific wave length range, the optical module is used for focusing the light rays emitted by the ordinary light source, the photocathode is used for generating electrons through optical excitation, the electron beam focusing structure is used for focusing electro beams generated by the photocathode, the anode target receives bombardment of accelerated electrons, and generates X-rays through bremsstrahlung, the X-ray exit window and the ordinary light incidence window are arranged on the vacuum container, and the vacuum container is used for packaging the photocathode, the electron beam focusing structure and the anode target. The X-ray source has the advantages of being high in time resolution, programmable, capable of achieving impulse type emission, changeable in size and shape of an emission area, capable of enabling a high voltage to be easily connected, low in difficulty of connection, capable of enabling heat dissipation of the anode target to be easy, and relatively simple in structure. The invention further provides an X-ray generating method.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED MEDICAL DEVICES SHENZHEN
Double-spectrum imaging device driven by laser to generate X-ray source
InactiveCN102778294AImprove conversion efficiencyIncrease total brightnessRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSoft x rayX-ray
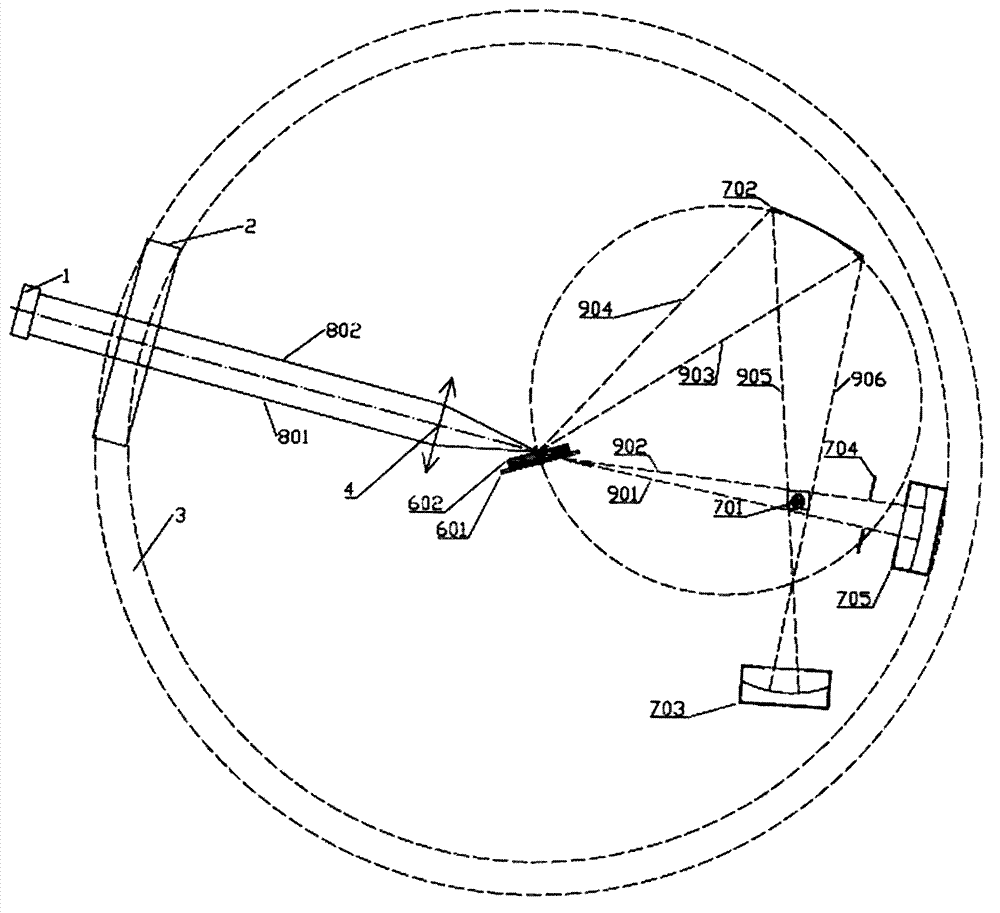
A double-spectrum imaging device driven by laser to generate an X-ray source comprises a laser device (1), a vacuum chamber (3),a driving laser inlet (2) and a target assembly. The driving laser inlet (2) is arranged on the vacuum chamber (3) and is matched with the laser device (1), the target assembly is arranged in the vacuum chamber (3) and consists of a plane foil target (601) and a support (602), the plane foil target (601) is positioned in the middle of the vacuum chamber (3), andthe plane with the plane foil target (601) divides the vacuum chamber (3) into target-front space and target-rear space. The double-spectrum imaging device is characterized in that spherical bent crystals capable of being gathered are distributed at the front or the rear of the target to diffract X-rays, to-be-measured samples are distributed on a sample support (701) at the downstream of the spherical bent crystals, and backlight imaging information is received by an imager; and bremsstrahlung spectral lines are led to the front or the rear of the target to directly transmit through the to-be-measured samples on the sample support, and backlight imaging information is received by an imager at a signal receiving end.
Owner:INST OF FLUID PHYSICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Bremsstrahlung reflection triode
ActiveCN110047721ATake advantage ofLower average energyX-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingHard X-raysStrong pulse
The invention relates to a bremsstrahlung reflection triode for generating strong pulse hard X rays. The problems that the gap potentials of two cathodes and anodes of an existing bremsstrahlung reflection triode are inconsistent, and a radiation field cannot be fully utilized are solved. The triode comprises a reflection triode cavity, an anode base, an anode, cathodes, transverse cover plates, aforward cover plate, an insulation plate fixing nut, an insulation plate transition piece and an insulation plate. The part, connected with the insulation plate, of the reflection triode cavity is acylinder, the part, away from the insulation plate, of the reflection triode cavity is transited into a closed cavity, and two parallel flat plates are arranged on the opposite surfaces of the closedcavity; the two cathodes are respectively arranged on the two flat plates of the closed cavity; the anode is positioned between the two cathodes; the anode is arranged on the anode base, the anode base is installed on a water line inner cylinder through the insulation plate transition piece, and the insulation plate transition piece is fixed through the insulation plate fixing nut. The transversecover plates are arranged on the two flat plates of the closed cavity respectively, and the forward cover plate is arranged at the axial tail end of the closed cavity.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
Blades of multi-blade collimator for electronic wire conformation and intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT)
The invention discloses blades of a multi-blade collimator for electronic wire conformation and intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), which are mainly characterized in that: the blade of the electronic multi-blade collimator is made of tungsten with thickness of 1.50 to 2cm so as to block most of electrons and generate relatively less bremsstrahlung; the end face of the blade is an upright end face, an inclined end face of which the inclined plane forms an angle of 3.75 to 60 degrees with a ray center shaft, and an arc-shaped end face with curvature radius of 0.75 to 0.85cm, and dosage penumbrae generated by the three end faces are basically the same; and the width of the blade is 0.8 to 1.2cm, so that radiated field edge dosage is relatively accurate and the accurate input of the subfield dosage is facilitated. Compared with the photon multi-blade collimator which is commonly used at present, the electronic multi-blade collimator has the advantages of simple structure, small occupied space, low cost, and more suitability for the electronic wire conformation and intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) to better treat superficial tumors.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Source for intra-pulse multi-energy X-ray cargo inspection
ActiveUS9867271B2Cathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingLinear acceleratorsX-rayRadio frequency
Methods for generating a multiple-energy X-ray pulse. A beam of electrons is generated with an electron gun and modulated prior to injection into an accelerating structure to achieve at least a first and specified beam current amplitude over the course of respective beam current temporal profiles. A radio frequency field is applied to the accelerating structure with a specified RF field amplitude and a specified RF temporal profile. The first and second specified beam current amplitudes are injected serially, each after a specified delay, in such a manner as to achieve at least two distinct endpoint energies of electrons accelerated within the accelerating structure during a course of a single RF-pulse. The beam of electrons is accelerated by the radio frequency field within the accelerating structure to produce accelerated electrons which impinge upon a target for generating Bremsstrahlung X-rays.
Owner:AMERICAN SCI & ENG INC
Medical isotope generation method and device based on laser wake-field accelerator
The invention provides a medical isotope generation method and device based on a laser wake-field accelerator. Interaction between super-strong and super-short lasers and plasma is utilized to generate a strong flow relativity electron beam. The electron beam is utilized to irradiate a high atomic number target to generate high-flow-strength bremsstrahlung gamma light. The bremsstrahlung gamma light bombards an interested object target to induce a ([gamma], xn+yp) photonuclear reaction or a ([gamma], [gamma]') optical excitation reaction, and object isotopes including gamma rays, electrons, positive electrons and [alpha] particle emitters are generated. By adopting the method provided by the invention, radio isotopes higher in activity are generated, and the cost is relatively low; in addition, the device provided by the invention is compact and convenient to carry, and the device is capable of being placed near a large-sized medical mechanism to be better applied to and serve radiation diagnosis, targeting treatment and other medical applications.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV +1
Radiotherapy apparatus
ActiveUS8355482B2High contrast imageEasy to switchX-ray tube electrodesHandling using diaphragms/collimetersHigh energyX-ray
Owner:ELEKTA AB
<99>Mo production method and <99>Mo production equipment based on bremsstrahlung and photonuclear reaction bifunctional target
PendingCN110473645AOvercoming strong self-attenuationIncrease productivitySpecific isotope recoveryIrradiation devicesSelf attenuationRadioactive decay
The invention belongs to the field of medical radioactive diagnosis nuclides, and relates to a <99>Mo production method and <99>Mo production equipment based on a bremsstrahlung and photonuclear reaction bifunctional target. In the prior art, the introduction of a conversion target can cause the low bremsstrahlung efficiency of a method for producing <99>Mo by using electron beams. A purpose of the present invention is to solve the problem in the prior art. According to the present invention, a high-energy electron beam emitted from an electron accelerator directly bombards an integrated bremsstrahlung and photonuclear reaction <100>Mo target; the production equipment comprises an electron accelerator, a target box, a target plate arranged in the target box, and a cooling system, wherein the target plate is a bremsstrahlung and photonuclear reaction bifunctional target plate, the bremsstrahlung and photonuclear reaction bifunctional target plate is a <100>Mo target, the target box hasan opening for the entering of an electron beam, and the electron beam enters the target box and directly bombards the bremsstrahlung and photonuclear reaction bifunctional target to produce <99>Mo. According to the present invention, by using the <100>Mo integrated bremsstrahlung and photonuclear reaction target, the strong self-attenuation on the bremsstrahlung twice in the traditional conversion target methods of high atomic number tungsten (W) and the like can be well overcome so as to greatly improve the production efficiency of <99>mo.
Owner:西安迈斯拓扑科技有限公司
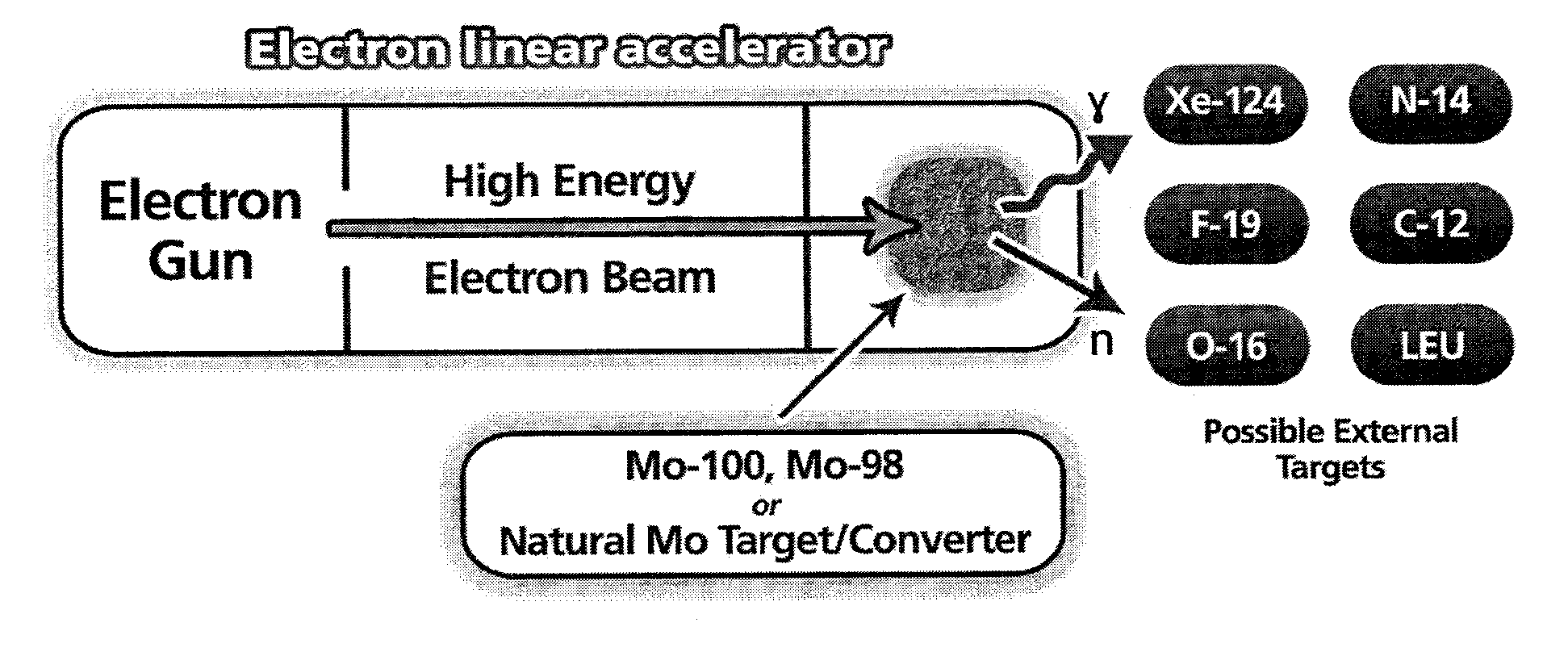
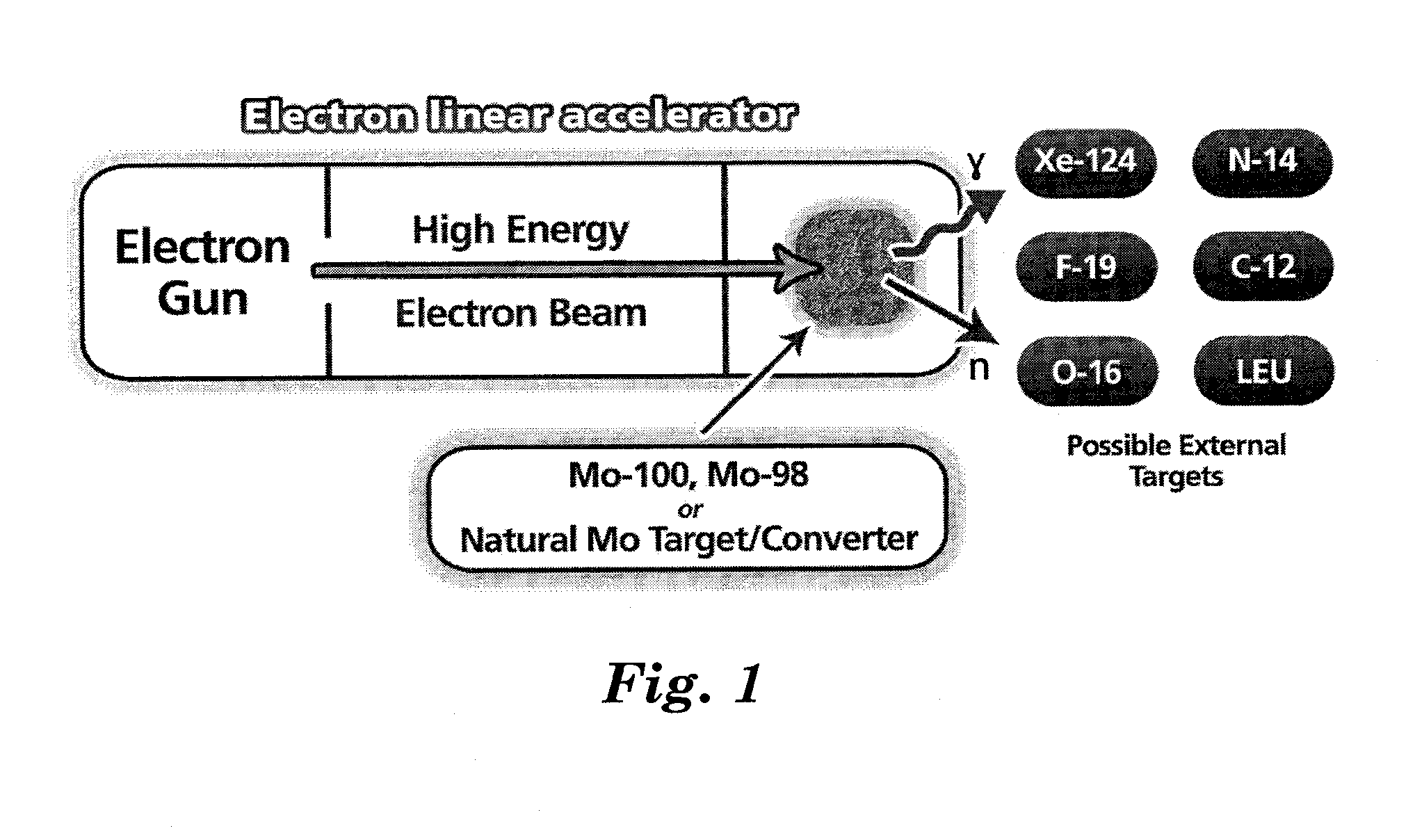
Molybdenum-converter based electron linear accelerator and method for producing radioisotopes
ActiveUS20140192942A1Specific isotope recoveryConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNeutron captureDistilled water
The present invention provides a method for producing molybdenum-99 comprising: i) providing an electron accelerator; ii) providing a molybdenum converter / target unit (Mo-CTU) comprising one or more metallic components, wherein each one of said metallic components is made of a material selected from the group consisting of natural molybdenum, molybdenum-100, molybdenum-98, and mixtures thereof; iii) directing an electron beam generated via said electron accelerator onto said Mo-CTU to produce a braking radiation (bremsstrahlung); iv) employing said bremsstrahlung onto said Mo-CTU to produce molybdenum-99 and neutrons via a photo-neutron reaction; v) slowing down the neutrons produced in step iv) with a low atomic liquid, e.g. distilled water; and optionally vi) employing the neutrons produced in step iv) to produce a complementary amount of molybdenum-99 via a neutron capture reaction on said Mo-CTU. The invention further provides an apparatus for producing molybdenum-99.
Owner:B G NEGEV TECH & APPL LTD
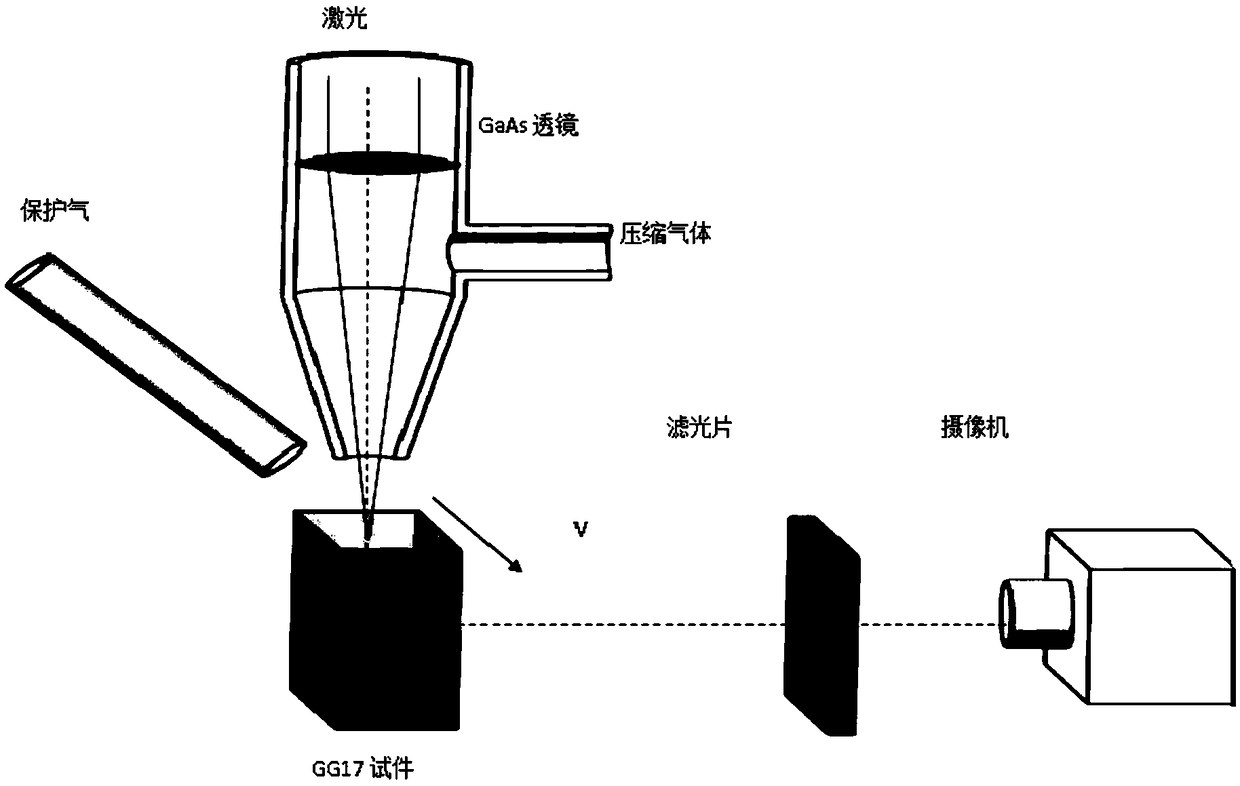
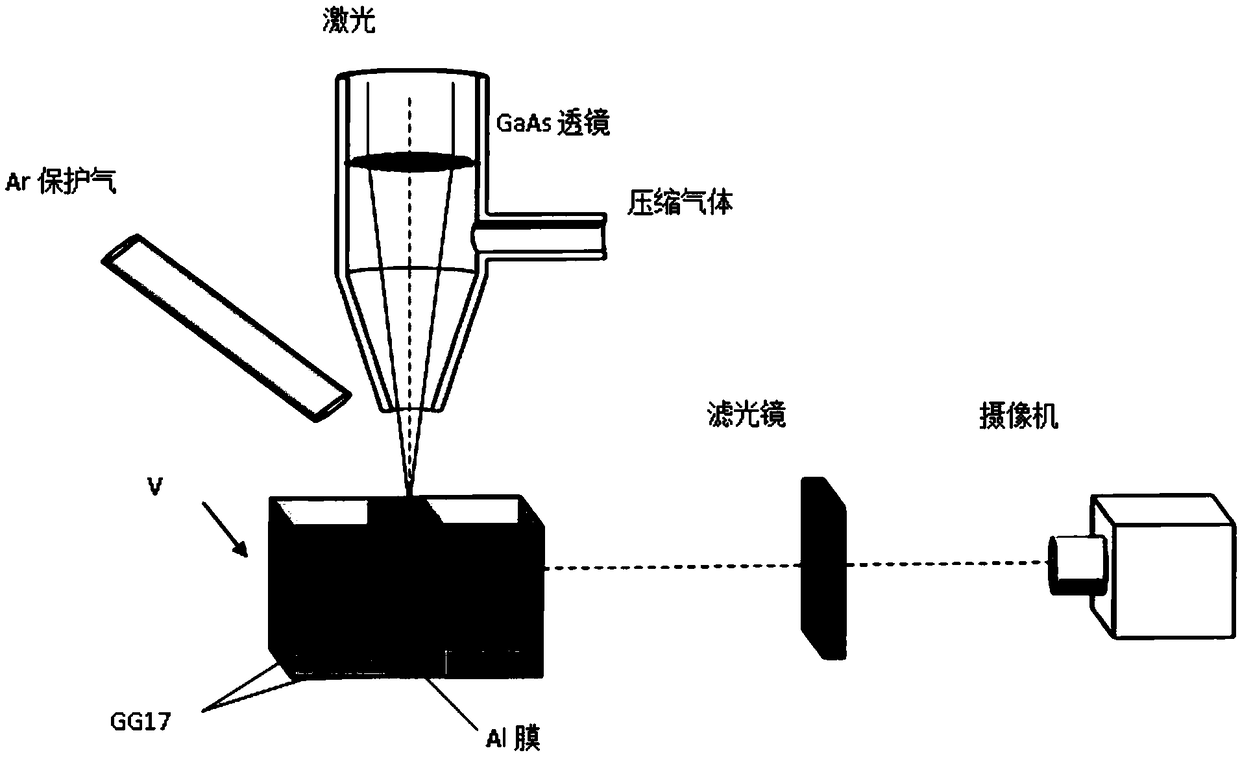
Composite test specimen for all-dimensional direct observation of metal material penetration fusion welding micropores
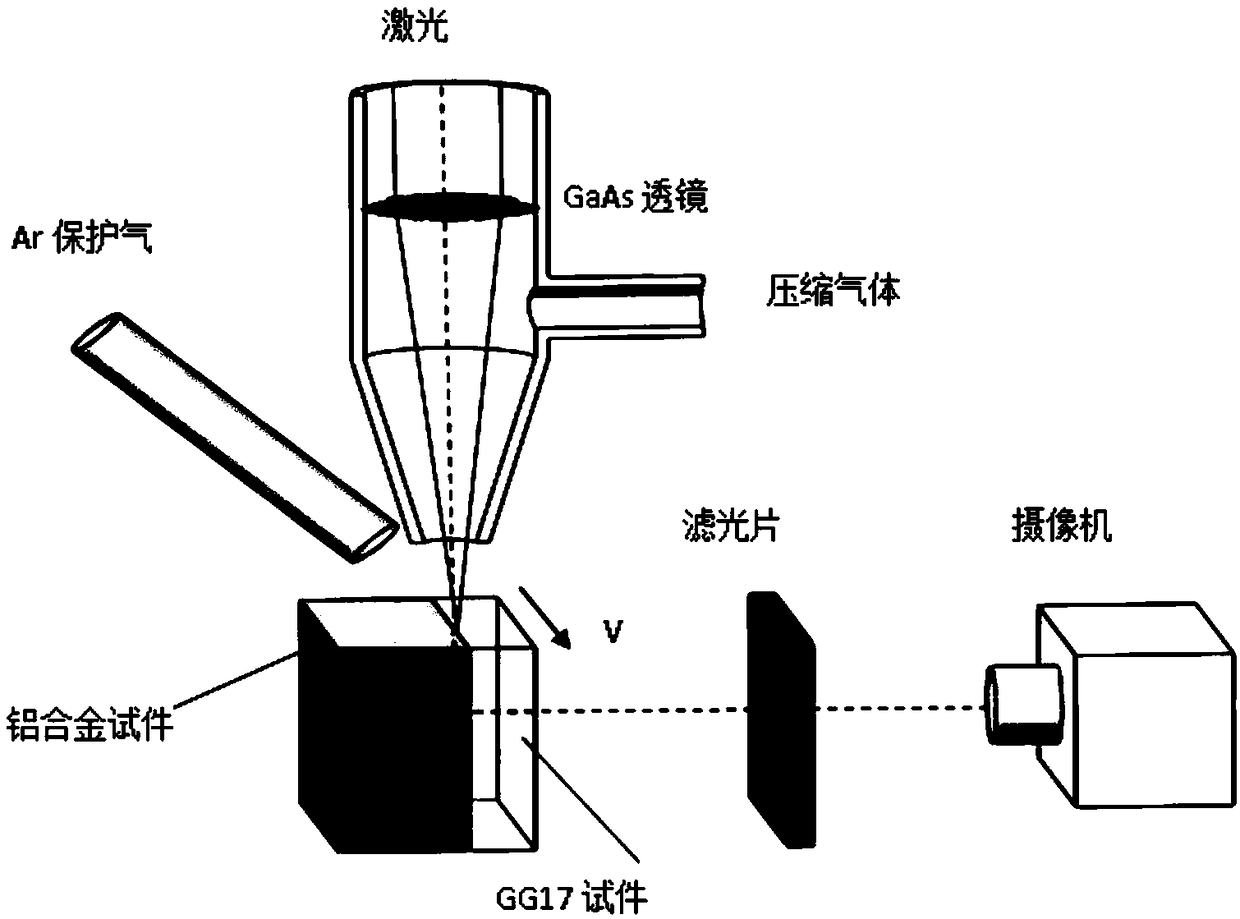
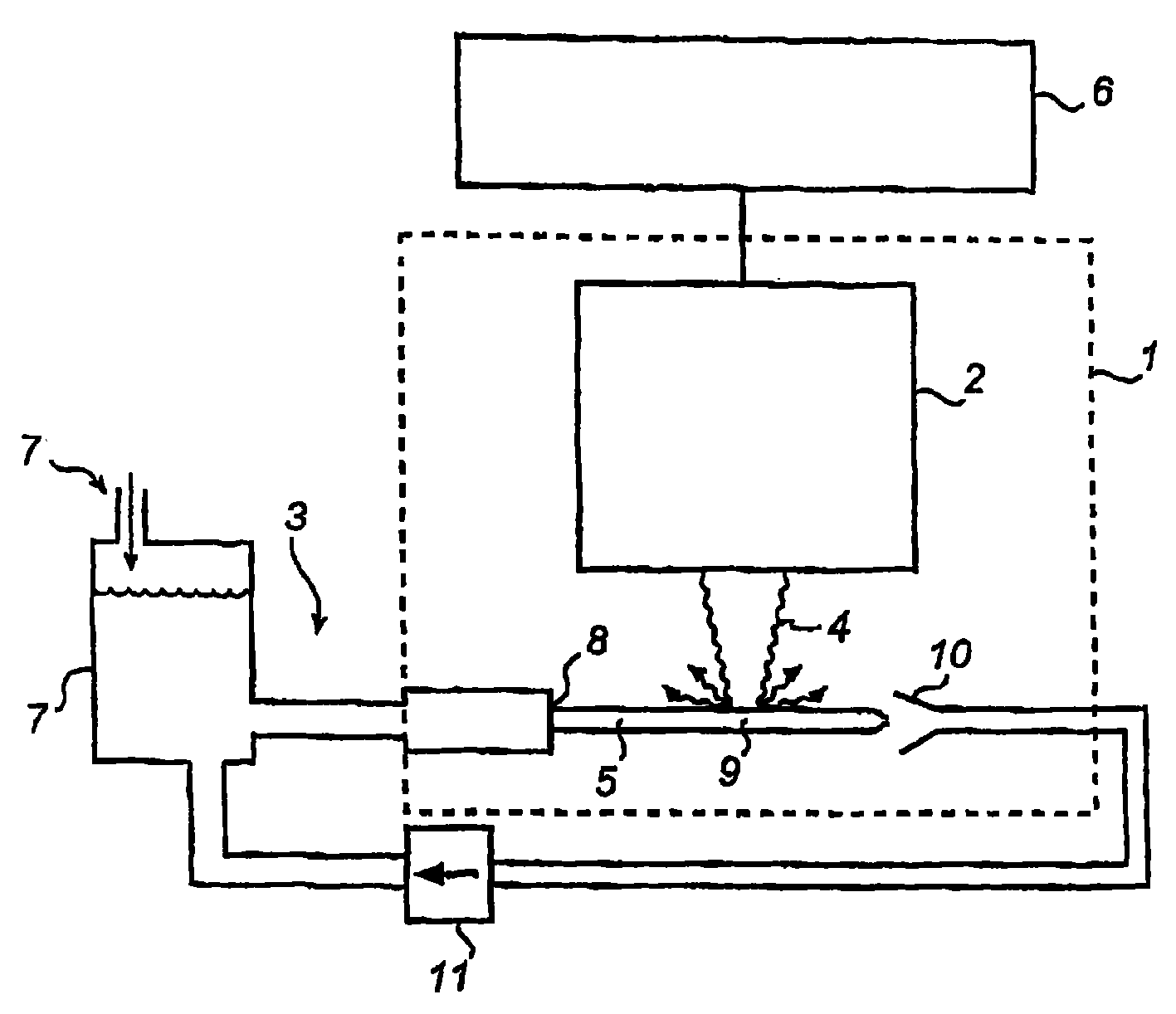
ActiveCN109470169AObservation is clear and accurateImprove accuracyUsing optical meansEnergy absorptionDirect observation
The invention provides a composite test specimen for all-dimensional direct observation of metal material penetration fusion welding micropores. The composite test specimen comprises an upper metal test specimen body and a lower GG17 test specimen body, the top face of the whole composite test piece, namely the top face of the metal test specimen body is a plane, the bottom face of the metal testspecimen body and the top face of the GG17 test specimen body are smooth binding faces, and an included angle of n degrees is formed between the binding face of the metal test specimen body and the GG17 test specimen body and top face of the composite test specimen, wherein n is larger than 0 degree and smaller than 90 degrees. The composite test specimen can be used for all-dimensional direct observation of shapes of the metal material penetration fusion welding micropores and all-dimensional direct observation of plasma in the micropores, observation dead corners do not exist, more precise micropore shapes are provided for study of micropore behaviors and energy absorption mechanisms in the micropores, and accurate in-pore plasma parameters are also provided for study of inverse bremsstrahlung absorption of the plasma.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
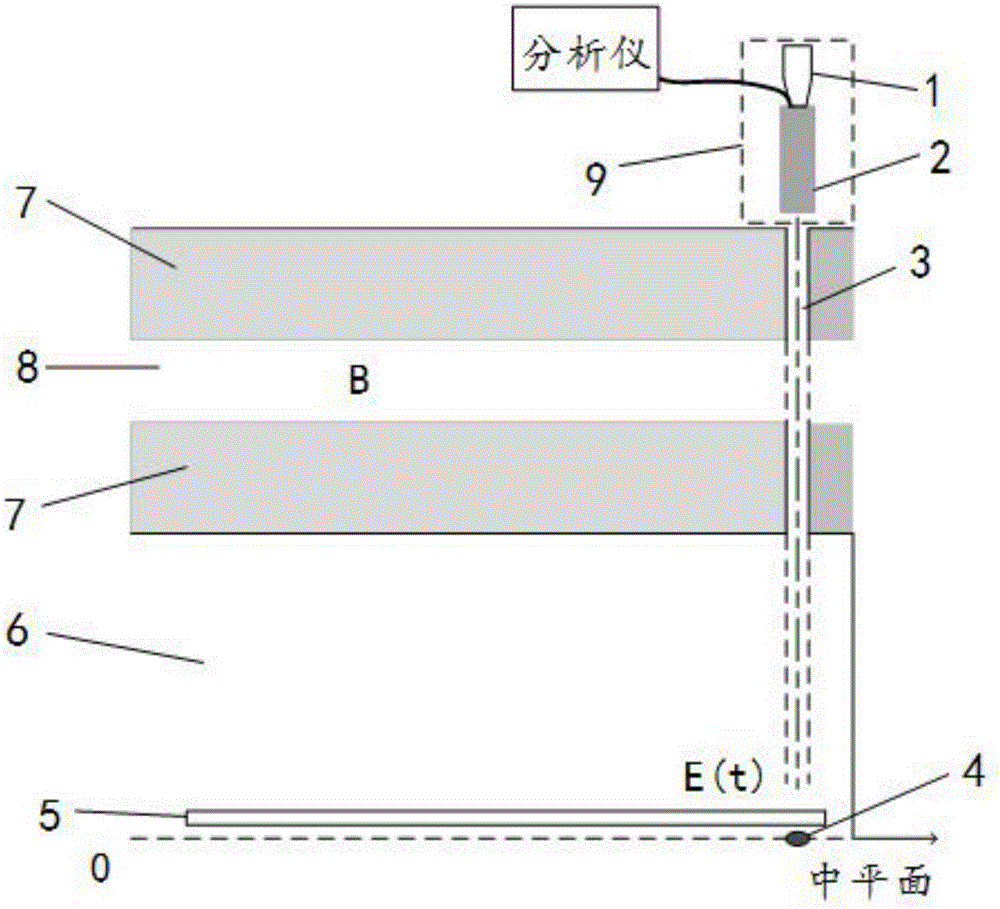
Hard X-ray flux detection system of J-TEXT Tokamak device
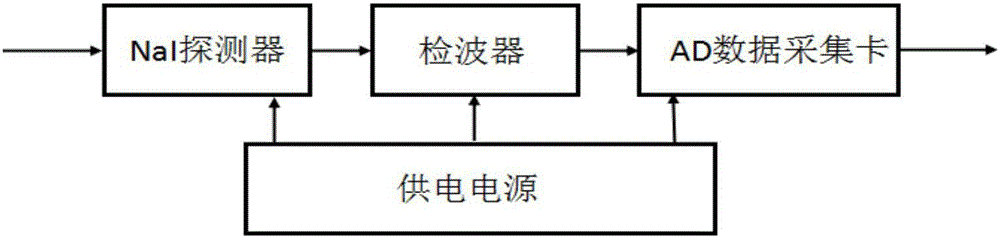
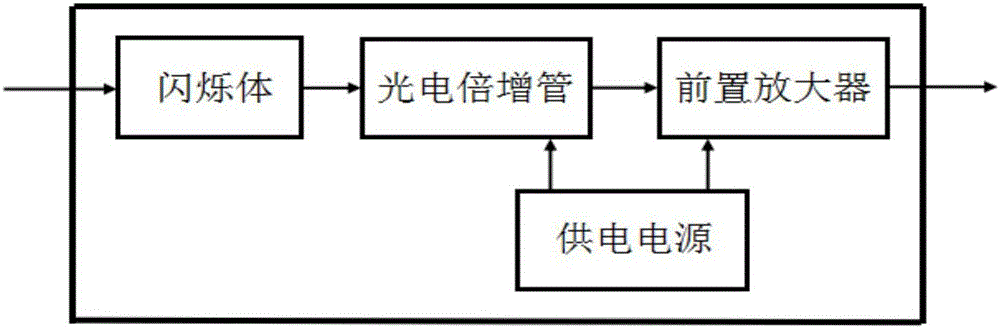
InactiveCN106772540ASimple structureAccurately Measure RadiationX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentHard X-raysData acquisition
The invention discloses a hard X-ray flux detection system of a J-TEXT Tokamak device. The hard X-ray flux detection system comprises a hard X-ray detection module, a detection circuit and an AD data acquisition module; the J-TEXT Tokamak device generates a large number of high-speed escape electrons when disruption is operated; the high-speed escape electrons bombard the material of the first wall of the device so as to directly damage the material; great importance should be attached to the density monitoring of the escape electrons; when the escape electrons damage the first wall, thick target bremsstrahlung occurs between the escape electrons and the material, and hard X-rays are generated, and the energy of the hard X-rays can be up to 0.5 to 10MeV; the more escape electrons strike the wall of the device, the higher the energy of the generated hard X-rays is, and the higher pulse voltage outputted by the detector is; hard X-ray optical signals are converted to pulse voltage signals through the hard X-ray detection module; the peak signals of the pulse signals are detected by the detection circuit; the peak signals are transmitted to a computer terminal through the data acquisition card; the computer terminal stores the peak signals; radiation intensity can be determined; and since the radiation intensity is proportional to the amplitude of the pulse signals, the distribution condition of the escape electrons can be obtained.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Apparatus and method for fluid phase fraction determination using X-rays
ActiveUS9448189B2Reduce complexityLow costMaterial testing goodsVolume/mass flow by differential pressureFrequency spectrumFluid phase
An apparatus for determining fluid phase fraction of a multiphase fluid mixture (13) comprises: —a x-ray generator (20) arranged to emit a x-ray radiation spectrum comprising a low energy region and a high energy region, the high energy region including a Bremsstrahlung spectrum; —a pipe section (27) through which the multiphase fluid mixture (13) flows comprising a measurement section (28), said measurement section (28) being coupled to said x-ray generator (20); —a detector (30) coupled to said measurement section (28) and arranged to detect x-ray radiation that has passed through said multiphase fluid mixture (13), the detector (30) being coupled to a multichannel analyzer (32) producing a measurement output comprising a low energy (LE) and high energy (HE) measurement counts; wherein the measurement output further comprises a low energy (LV) and high energy (HV) control counts, in a low energy and high energy control windows located on an edge of the Bremsstrahlung spectrum, respectively; and wherein the apparatus further comprises an electrical parameter control arrangement (33) coupled to the x-ray generator (20) and the detector (30), the electrical parameter control arrangement (33) being arranged to calculate a first ratio of the high energy control count relative to the low energy control count (RV=HV / LV) and a second ratio of the high energy measurement count relative to the low energy measurement count (RE=HE / LE), and to adjust the electrical operation of the x-ray generator (20) based on an electrical parameter control function (FC(V)) of said ratios that minimize a dependence of the electrical operation of the x-ray generator on the fluid phase fraction of the multiphase fluid mixture (13) flowing in the measurement section (28).
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Partial vacuum laser welding and two-sided annealing device for aluminum alloys
ActiveCN109079352AHigh yield strengthHigh tensile strengthFurnace typesLaser beam welding apparatusVacuum chamberLaser beams
The invention discloses a partial vacuum laser welding and two-sided annealing device for aluminum alloys. The exhaust flow of an air outlet pipe of a partial vacuum chamber is larger than the intakeflow of an air inlet pipe, and a negative pressure environment is provided during welding; a resistance heating plate is arranged to preheat a welded plate, and a laser annealing module is arranged; after an aluminum alloy plate is welded with laser and is slightly cooled, laser annealing is carried out with the residual heat of preheating; and grain refinement and residual pressure layers are formed on the upper surface and the lower surface of a welded joint, and therefore the yield strength and tensile strength of the welded joint are improved. The ambient air pressure is reduced by the laser welding under partial vacuum, the discharging of bubbles in a molten pool is facilitated, pore defects are reduced, meanwhile the generation of a laser induced plasma and metal vapor is inhibited,and the inverse bremsstrahlung absorption for laser beam energy is reduced. In addition, the preheating treatment of the welded plate improves the stability of the welding process, and splashing is greatly reduced. The fish-scale patterns on the weld surface tend to be fine, and therefore the defect of pits in the weld surface is reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Self-shielded sterilization apparatus using electron beam irradiation
InactiveUS20070176116A1Facilitates and miniaturizesSimple structureMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiationMiniaturizationAtomic physics
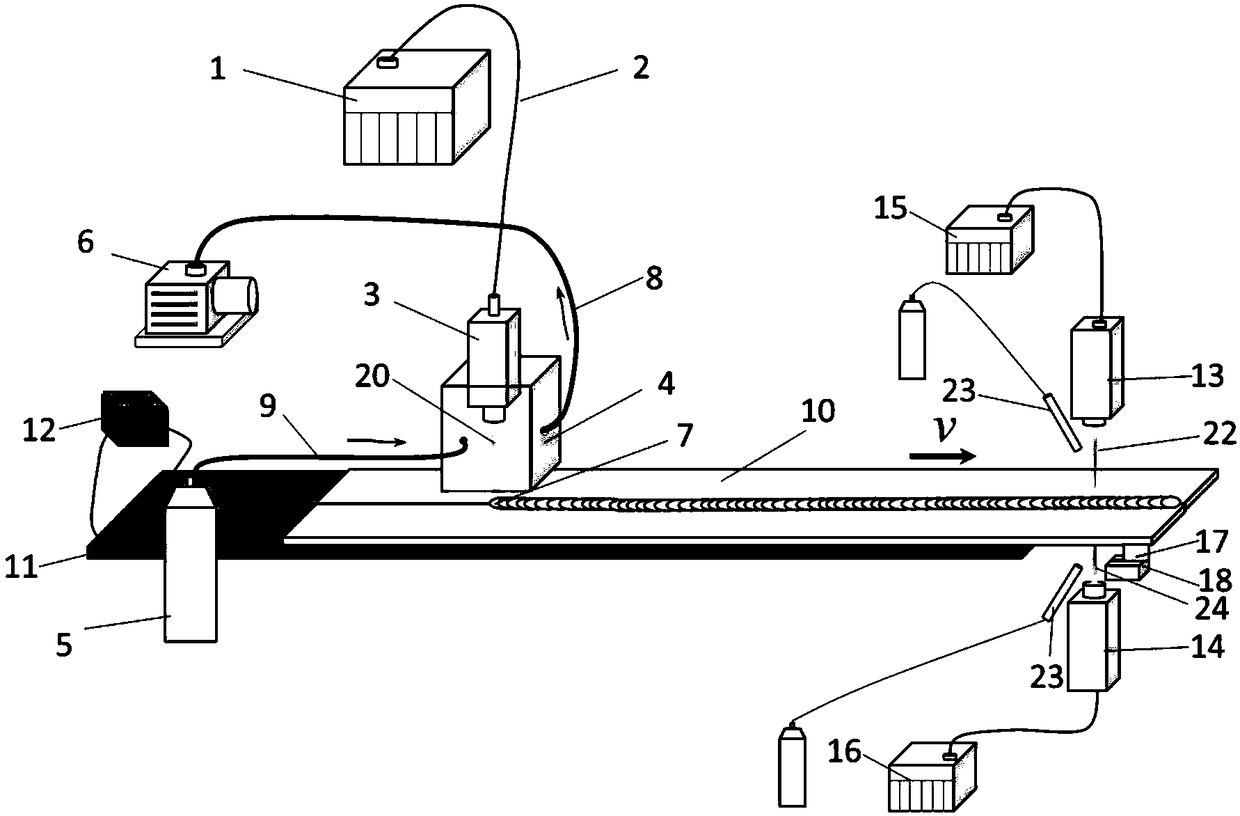
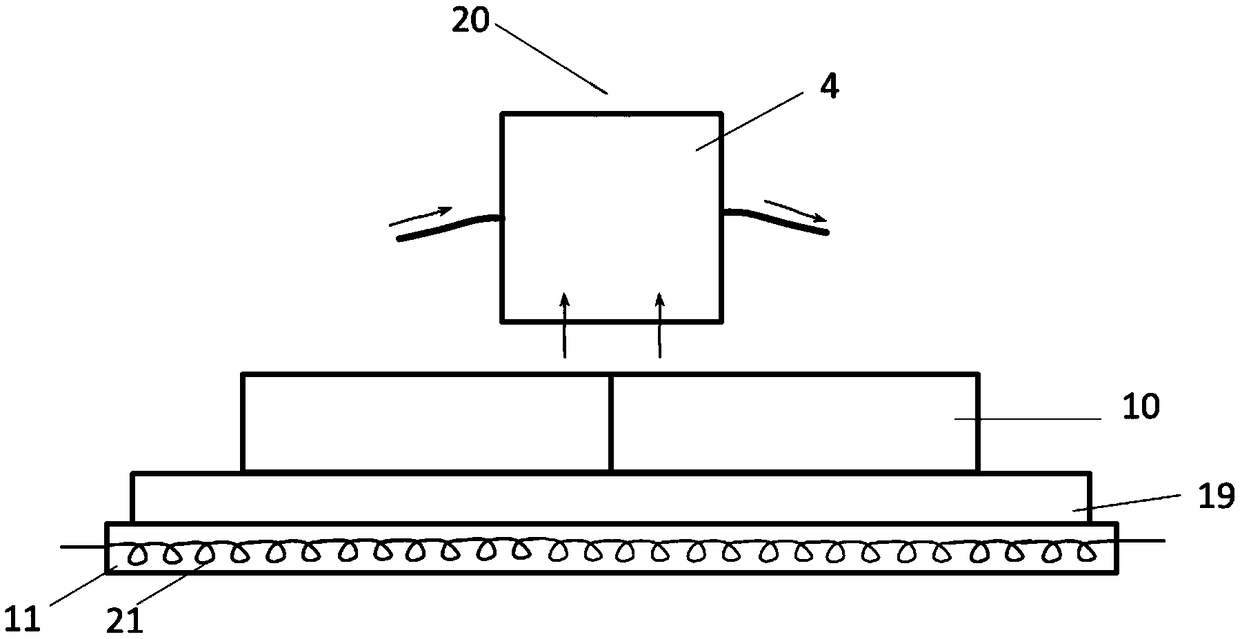
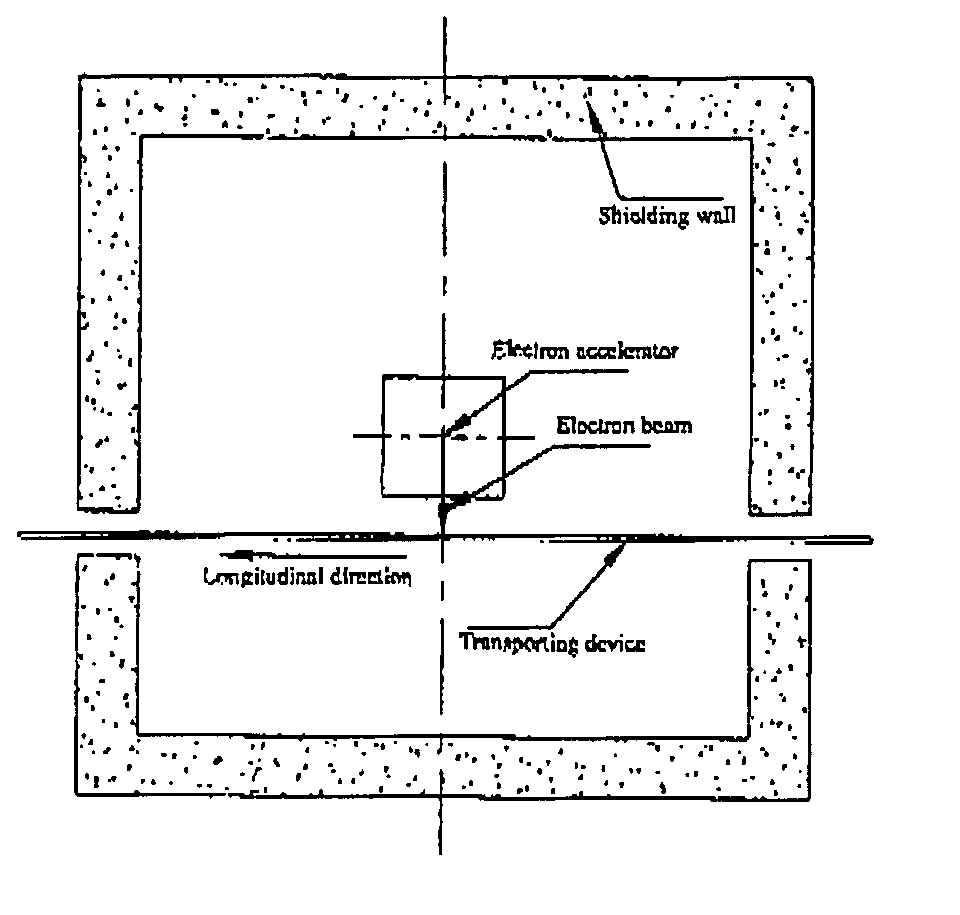
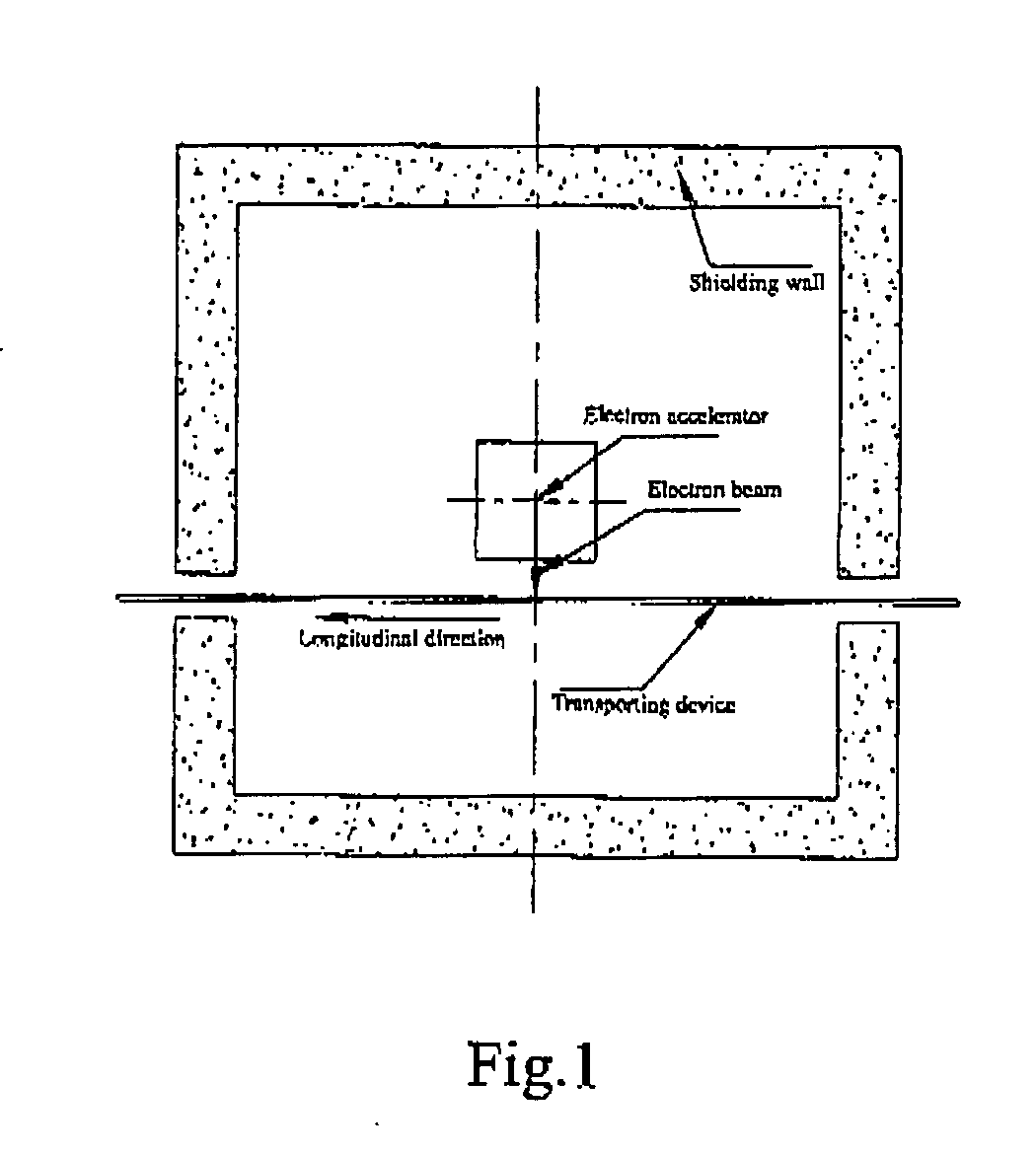
A self-shielded sterilization apparatus using an electron beam, comprising: an electron beam irradiator for irradiating an electron beam; a shielding for shielding the electron beam irradiated from the electron beam irradiator and a bremsstrahlung of the electron beam; a tray disposed within the shielding for placing thereon an object to be irradiated; an opening for placing an object into and taking the object out of the shielding; and a shielding door for closing the opening. With the above configurations, the apparatus avoids the shield construction taking a large area and the complicated transporting device, which facilitates a miniaturization of the apparatus.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Method for identifying substance by simulating dual energy X-ray imaging by utilizing Monte Carlo method
InactiveCN102662196AEfficient identificationExtract comprehensiveNuclear radiation detectionX-rayDual energy
The invention discloses a method for identifying substance by simulating dual energy X-ray imaging by utilizing a Monte Carlo method, which relates to the method for identifying the substance by utilizing the dual energy X-ray imaging and aims at solving the problem of a low substance identification rate in the current security check process. The method comprises the following steps of: step 1, simulating processes of bombarding a tungsten target by electron beams with energies being 9 MeV and 6 MeV by utilizing the Monte Carlo method, generating bremsstrahlung radiation, and obtaining an X-ray spectrum; step 2, carrying out alignment for the X-ray spectrum obtained in the step 1, scanning a sample to be detected after the alignment, and obtaining a scanning image; and step 3, analyzing the scanning image obtained in the step 2, obtaining an identification curve of the sample to be detected, and realizing the substance identification according to the relationship between the identification curve and substance atoms. The method disclosed by the invention is suitable for the security check.
Owner:TECHN PHYSICS INST HEILONGJIANG ACADOF SCI
Laser shock peening method for improving intensity of laser induced shock wave by adopting time sequence double laser pulse
The invention discloses a laser shock peening method for improving the intensity of a laser induced shock wave by adopting a time sequence double laser pulse, and belongs to the field of laser processing. The laser shock peening method aims at solving the problem that existing laser shock peening systems are generally insufficient in laser energy utilization so as to affect the intensity of shockwaves. The method comprises the step that a laser pulse A and a laser pulse B sequentially irradiate and shock the same position of a workpiece surface in a relative delay mode. The specific process comprises the following steps that firstly, the pulse A irradiates and shocks the surface of the workpiece to form an initial plasma, when the electron density of the initial plasma is reduced to be below the critical density of forming the plasma shielding effect, the pulse B which reaches in delay irradiates and shocks a target area, and a part of the laser energy of the pulse B reaches the surface of an absorption layer so as to continue to gasify and ionize the material of the workpiece; and the other part of the laser energy of the pulse B is subjected to inverse bremsstrahlung absorptionby the initial plasma formed through the pulse A. Under the conditions that the output capability of a laser device is not increased and the irradiation area of a light spot is not changed, the purpose of improving the intensity of the shock wave is achieved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for generating X-ray
InactiveCN1272989CIncrease brightnessX-ray tube electrodesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSoft x rayHard X-rays
In a method and an apparatus for generating X-ray or EUV radiation, an electron beam is brought to interact with a propagating target jet, typically in a vacuum chamber. The target jet is formed by urging a liquid substance under pressure through an outlet opening. Hard X-ray radiation may be generated by converting the electron-beam energy to Bremsstrahlung and characteristic line emission, essentially without heating the jet to a plasma-forming temperature. Soft X-ray or EUV radiation may be generated by the electron beam heating the jet to a plasma-forming temperature.
Owner:伊克斯勒姆股份公司
Method for measuring voltage of compact superconductive circular accelerator high frequency resonant cavity
The invention discloses a method for measuring voltage of a compact superconductive circular accelerator high frequency resonant cavity. Based on Bremsstrahlung principles, the method specifically comprises the following steps: Bremsstrahlung X rays sent out from detecting points in the accelerator high frequency cavity are propagated to an outer part of an accelerator via a collimating aperture, full energy peak energy spectra of the above rays can be detected via a detector, cavity peak value voltage in the accelerator high frequency cavity is in a certain corresponding relation with maximum energy of the rays, and peak value voltage of the high frequency cavity can be measured based on maximum value of the detected energy spectra of the rays. The method disclosed in the invention is simple and reliable in principles, high in feasibility and strong in operability; the peak value voltage of the high frequency cavity can be accurately obtained; compared with a conventional electronics measurement method, cavity distribution parameters can be prevented from being affected by a plurality of factors, the peak value voltage of the high frequency cavity can be accurately reflected, and physical beam tuning requirements for the accelerator can be satisfied.
Owner:HEFEI CAS ION MEDICAL & TECHNICAL DEVICES CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com