Patents
Literature
30results about How to "Small intensity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
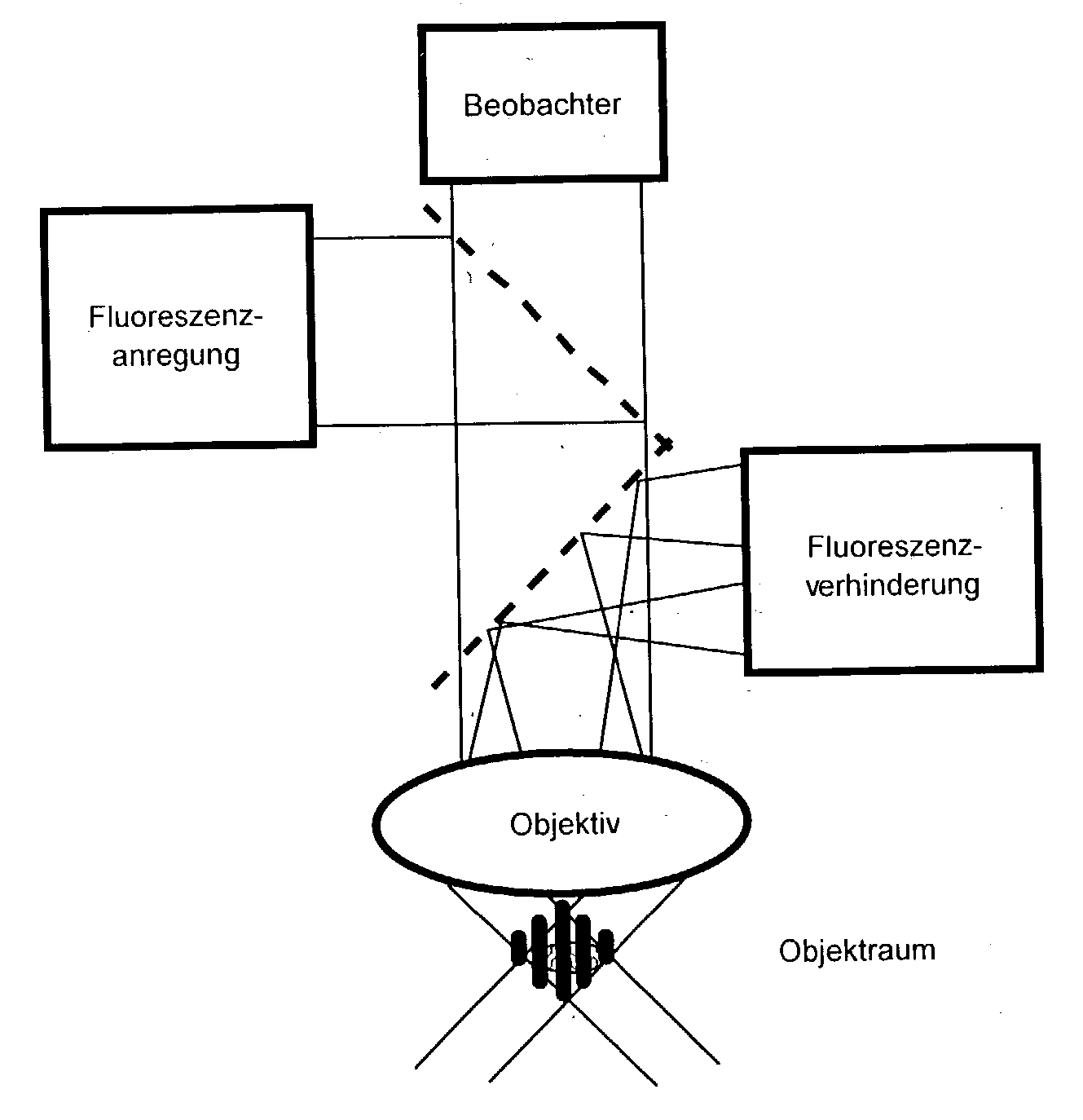
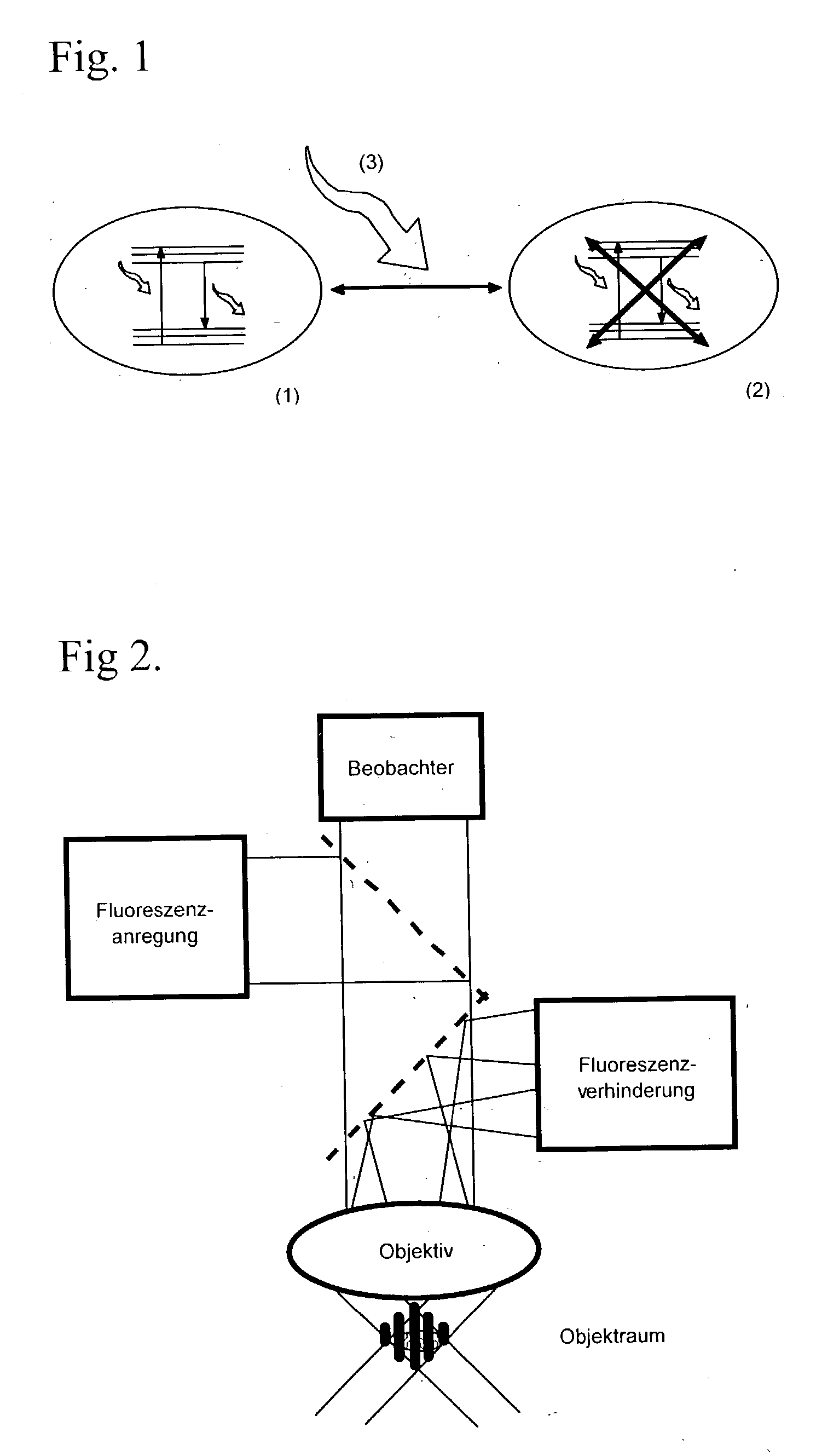
High spatial resoulution imaging and modification of structures
ActiveUS20040212799A1Small intensityLong lastingSpectrum investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical propertyImage resolution
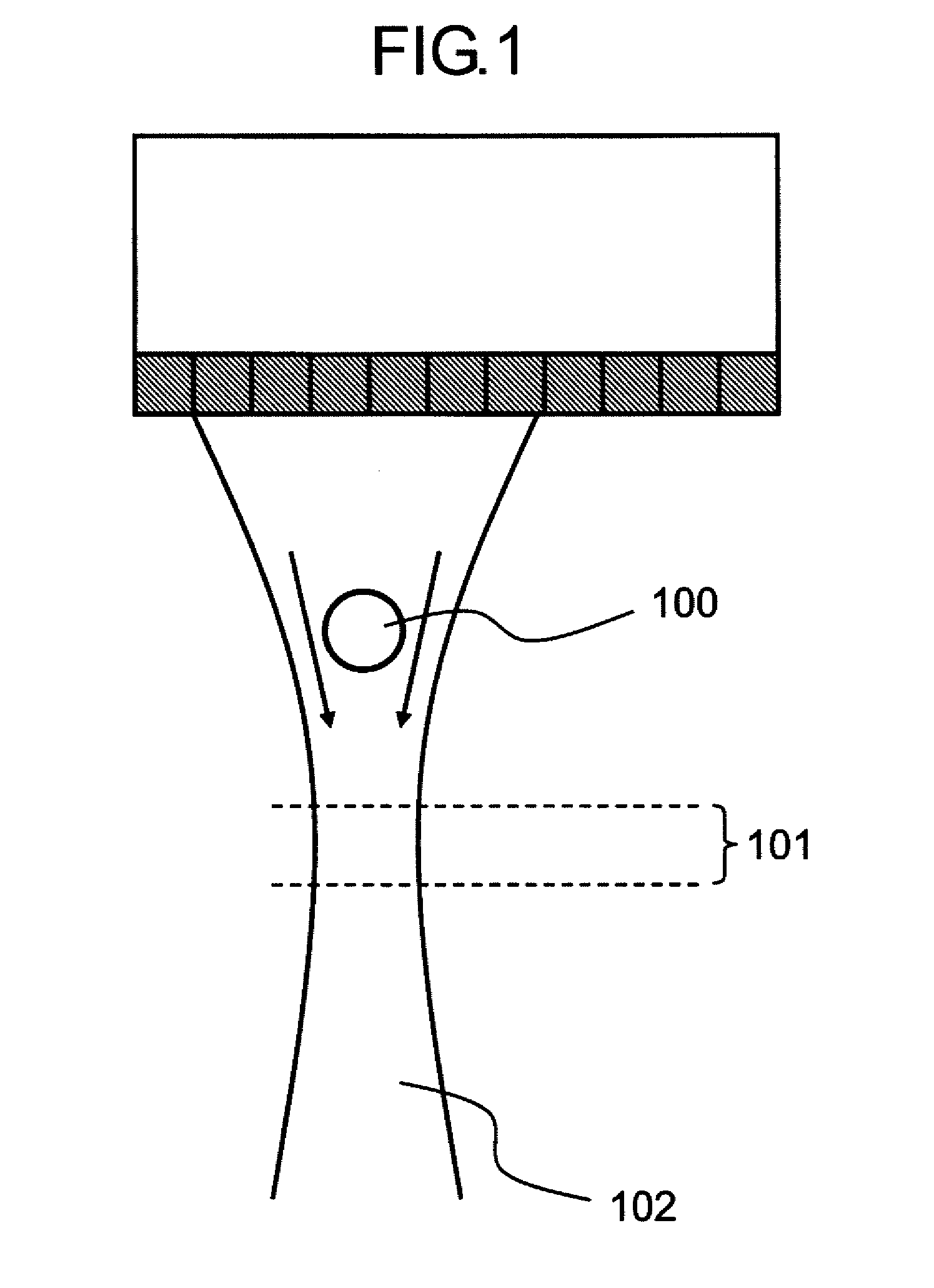
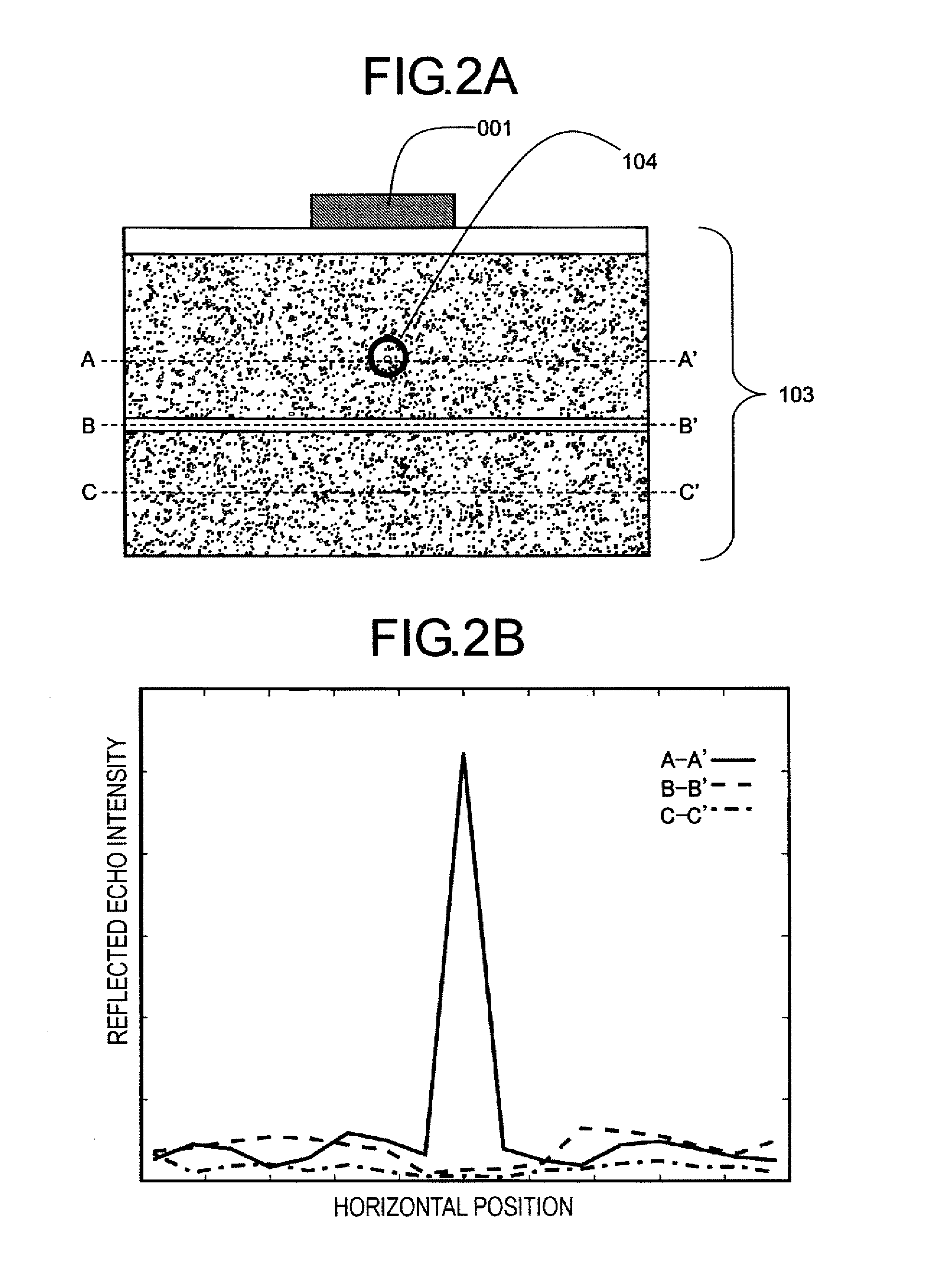
In a method of high spatial resolution imaging or modifying a structure, the structure is marked with a substance which is selected from the group of substances which can be transferred from a first state having first optical properties to a second state having second optical properties by means of an optical switch over signal. Then, the second state of the substance is adjusted with the switch over signal except for a spatially limited area. If the substance and the switch over signal are adapted to each other in such a way, that everywhere where the switch over signal exceeds a threshold value essentially the second state of the substance is adjusted, and if the spatial area purposefully omitted by the switch over signal is an intensity minimum of an interference pattern, the spatial area of the structure in which the substance is within the first state becomes smaller than the diffraction limit for the switch over signal.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
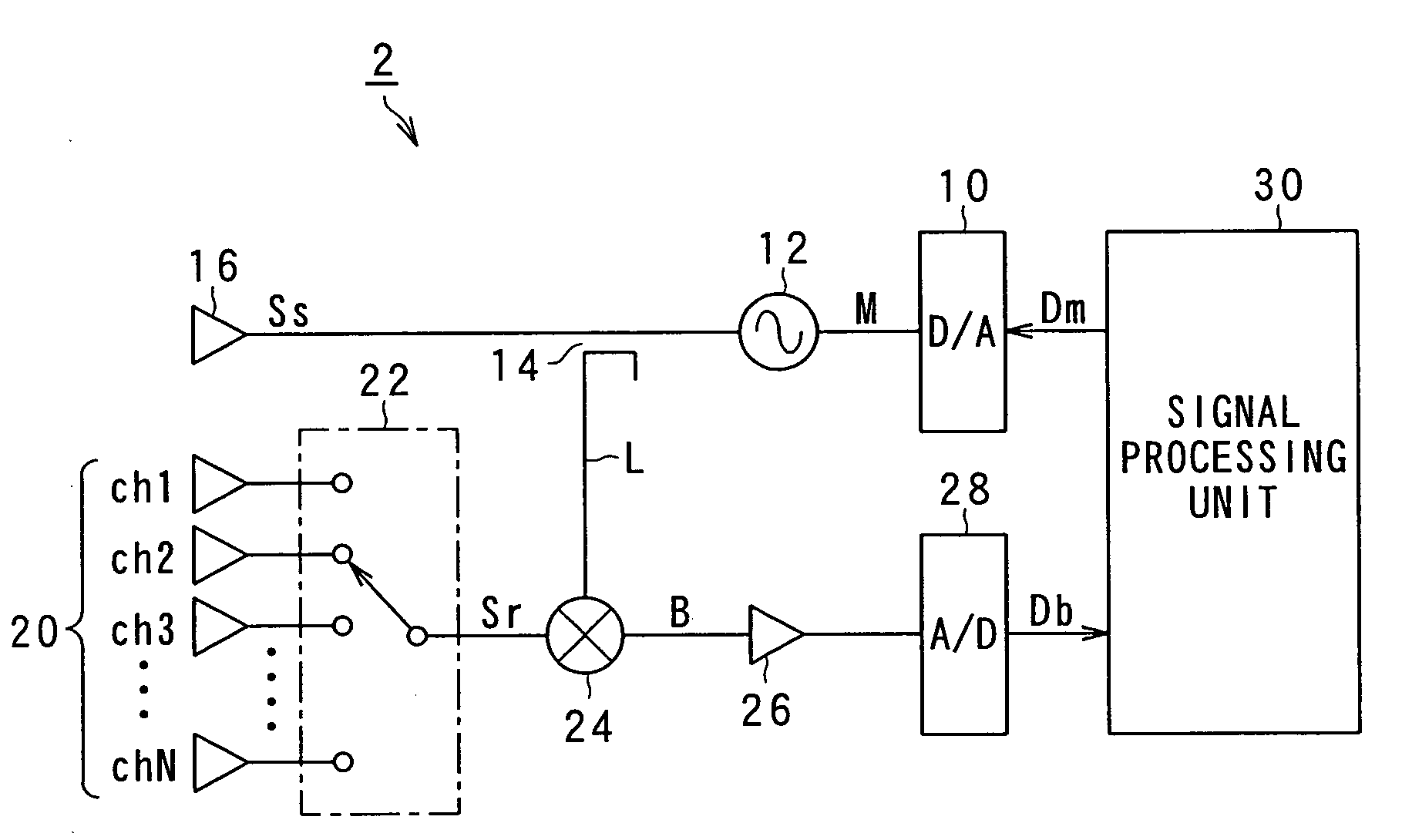
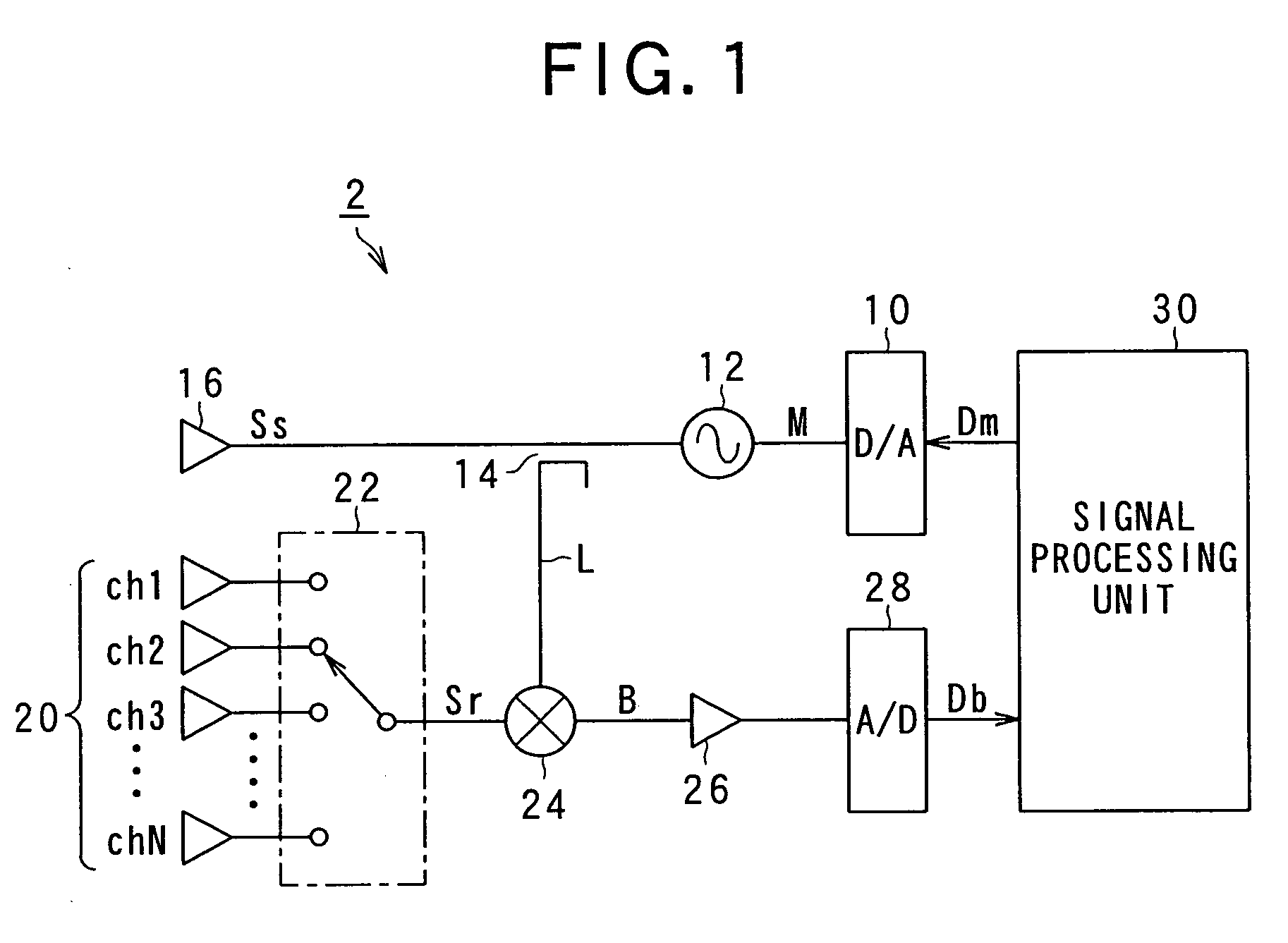
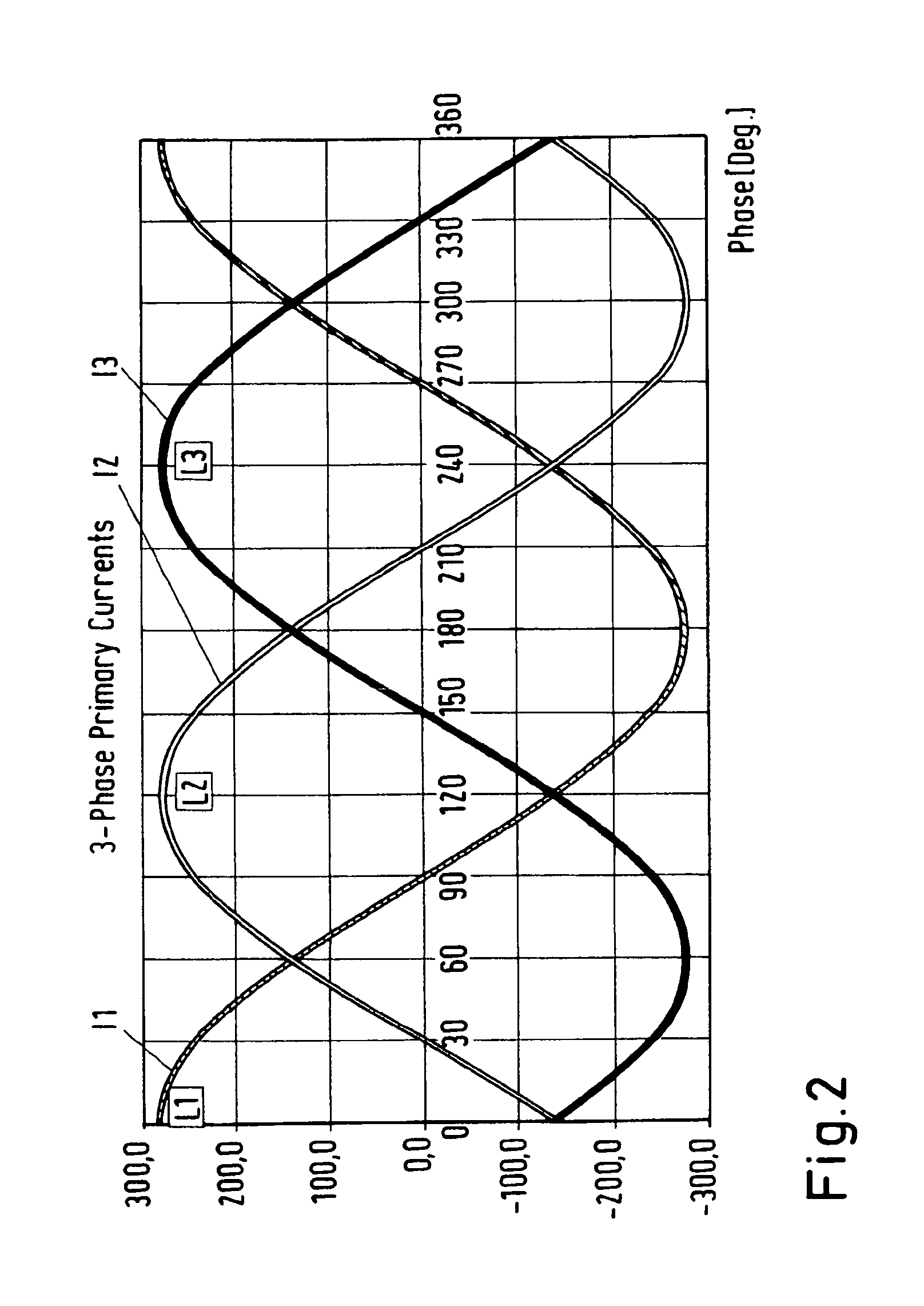
Method for detecting interference in radar system and radar using the same
InactiveUS20090096661A1Small intensityExclude influenceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumRadar systems
A method for a radar for determining a level of interference of return of a radar wave transmitted by the radar from a target object and radio wave transmitted by some other radar, and a radar, in particular a frequency modulated continuous wave (FMCW) radar, that performs the method for determining the level of interference between the radar and some other radar is provided. In the method according to the present invention, after incident radio wave received by the radar is subjected by a frequency analysis to obtain frequency spectrum characteristic of the incident radio wave, one of frequency components of incident radio wave, the one of the frequency components having larger intensity than a predetermined intensity threshold value is not used to calculate a reference value that indicates the level of interference.
Owner:DENSO CORP
XRF system having multiple excitation energy bands in highly aligned package
ActiveUS8559597B2Increased signal noiseSmall intensityX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX ray analysisX-ray optics
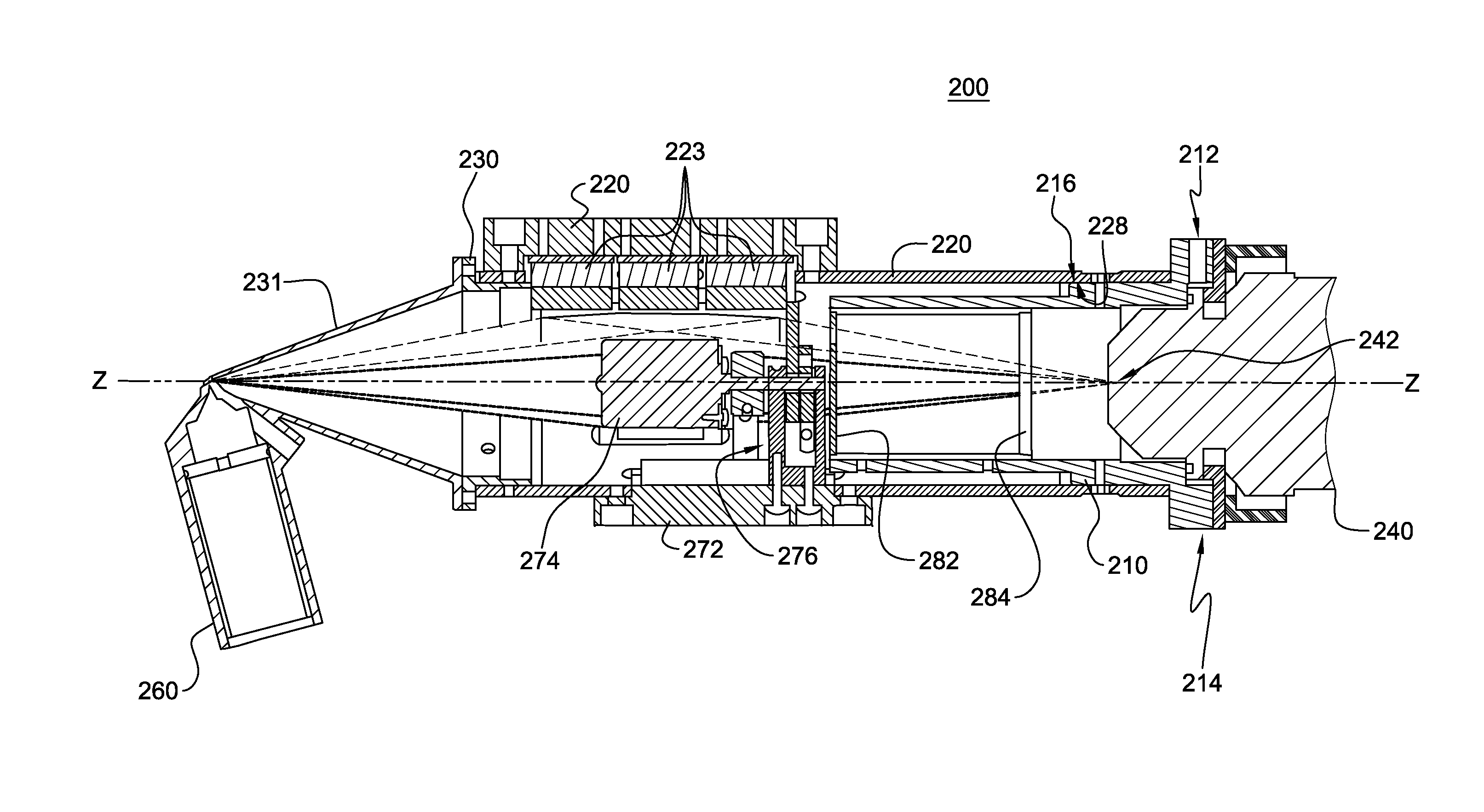
An x-ray analysis apparatus for illuminating a sample spot with an x-ray beam. An x-ray tube is provided having a source spot from which a diverging x-ray beam is produced having a characteristic first energy, and bremsstrahlung energy; a first x-ray optic receives the diverging x-ray beam and directs the beam toward the sample spot, while monochromating the beam; and a second x-ray optic receives the diverging x-ray beam and directs the beam toward the sample spot, while monochromating the beam to a second energy. The first x-ray optic may monochromate characteristic energy from the source spot, and the second x-ray optic may monochromate bremsstrahlung energy from the source spot. The x-ray optics may be curved diffracting optics, for receiving the diverging x-ray beam from the x-ray tube and focusing the beam at the sample spot. Detection is also provided to detect and measure various toxins in, e.g., manufactured products including toys and electronics.
Owner:X-RAY OPTICAL SYSTEM INC
LED lamp for homogeneously illuminating hollow bodies
ActiveUS20130010460A1Small intensityReduce overlapNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceEngineeringOn board
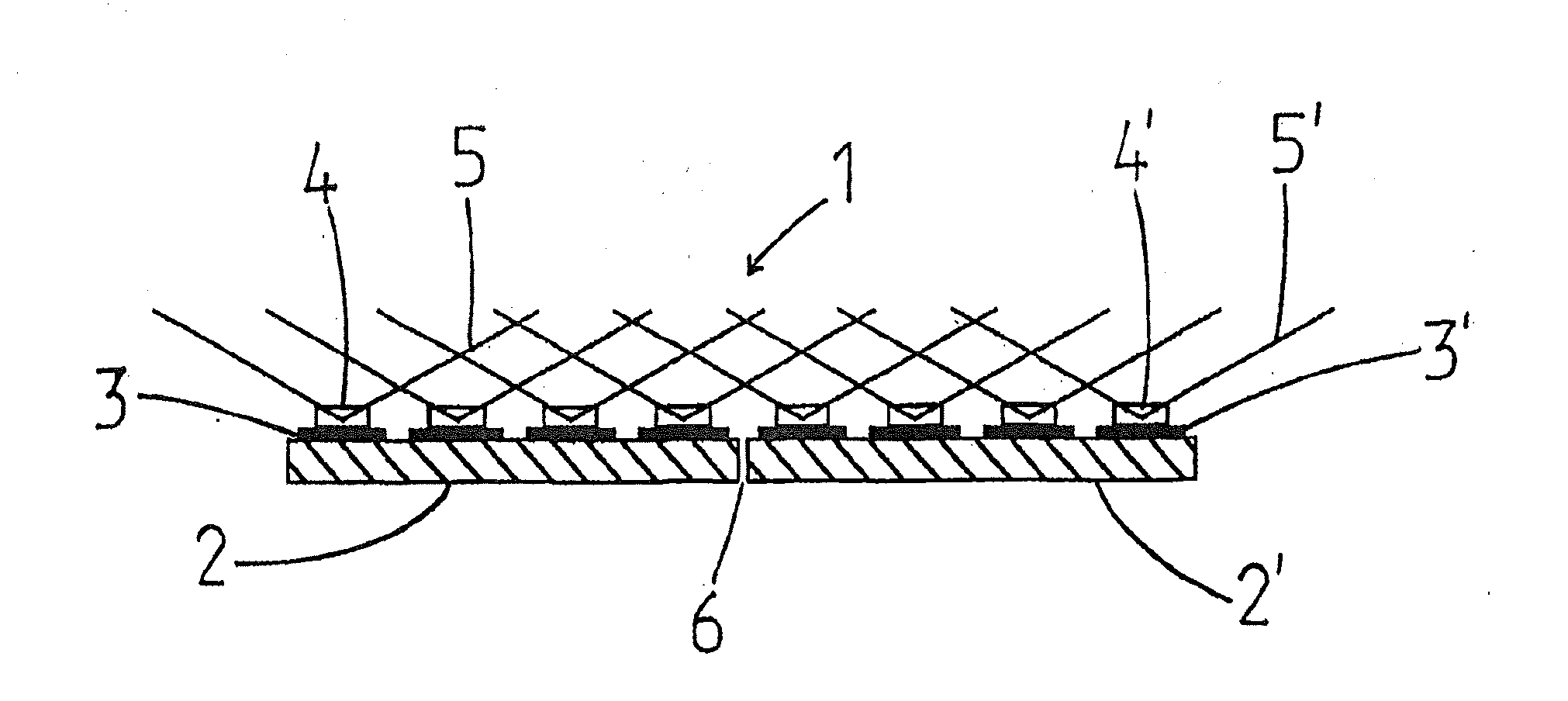
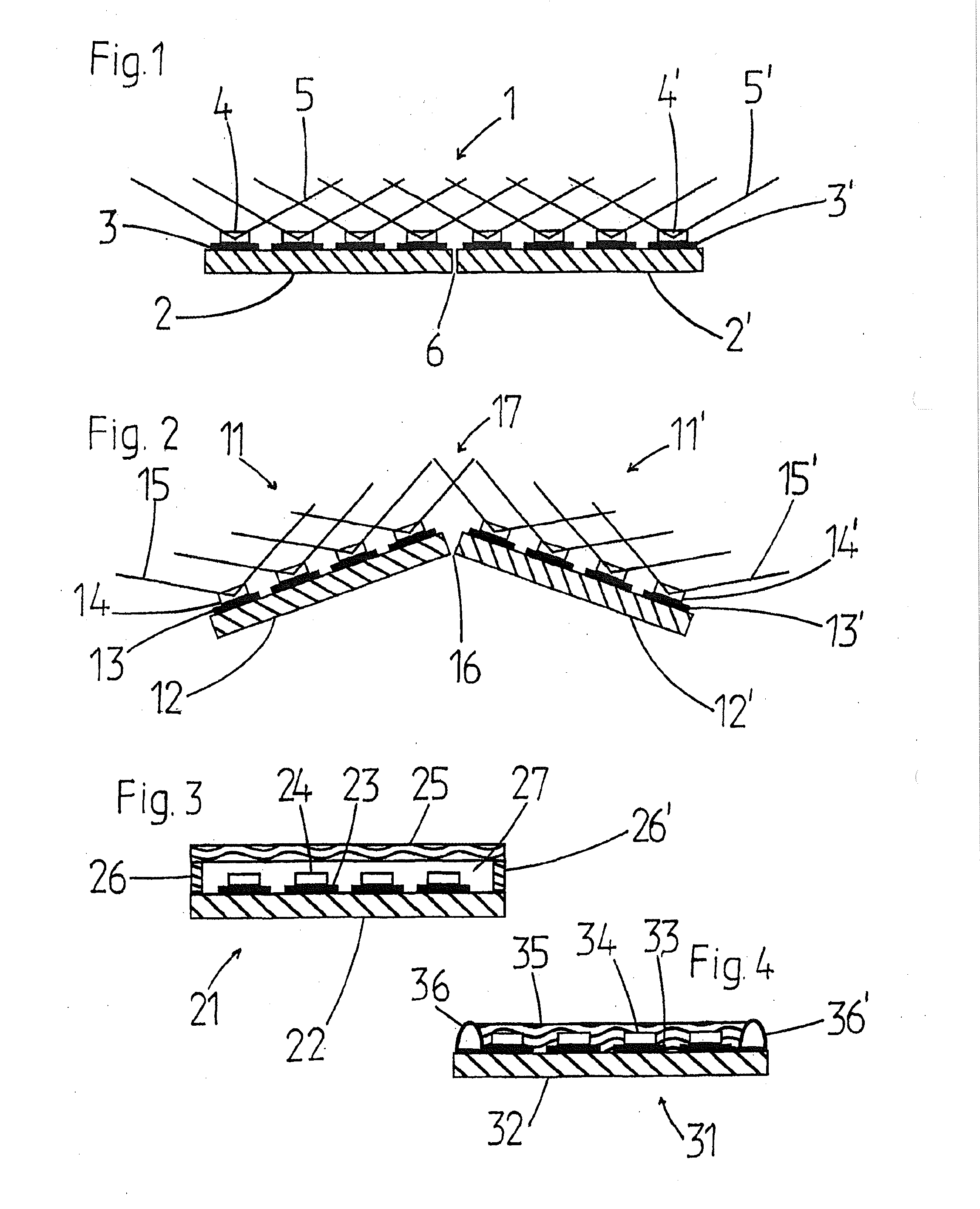
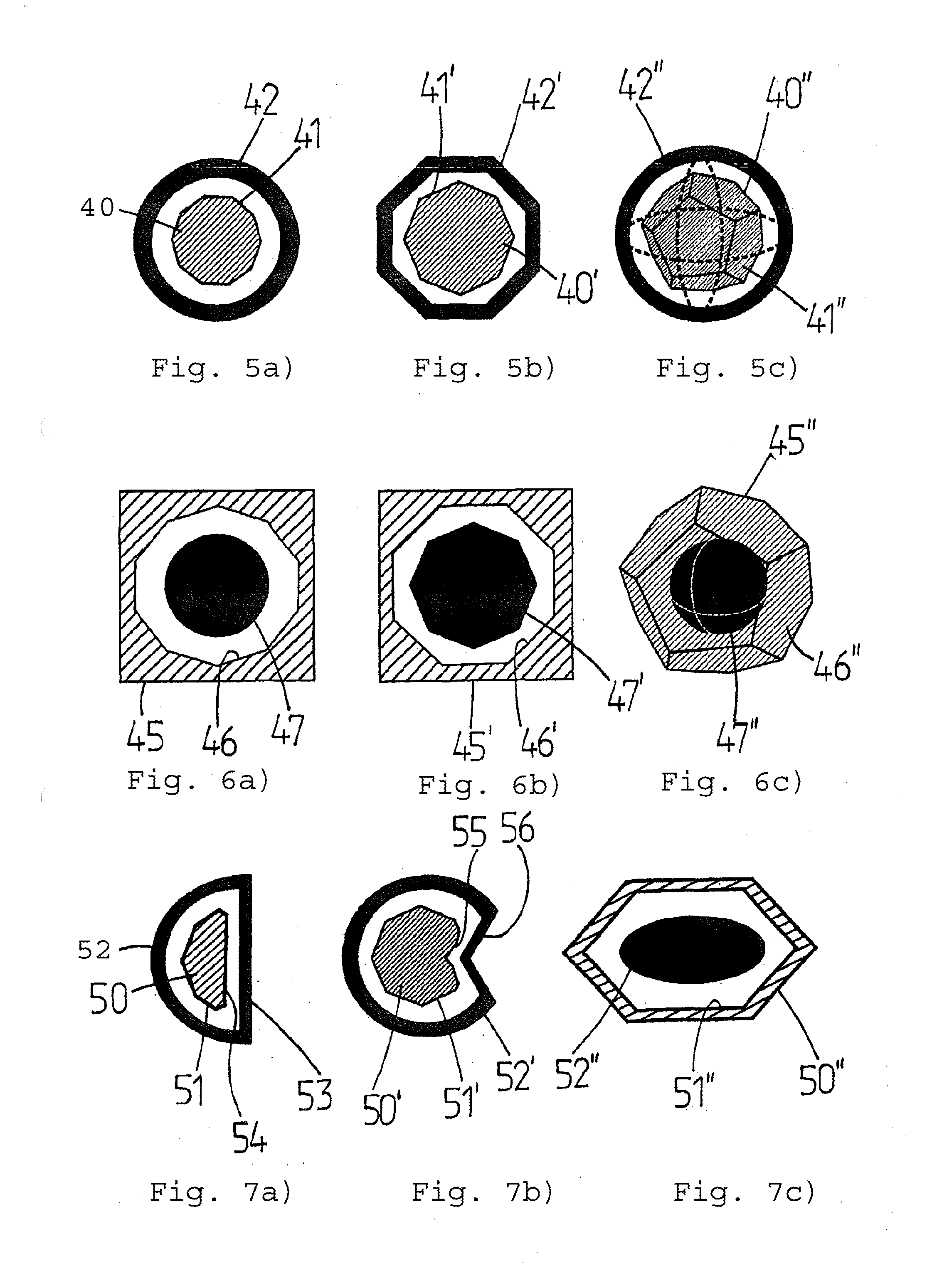
A lighting device (40-40″, 45-45″, 50-50″, 60, 80, 93-93″) is provided for the uniform illumination of curved, uneven, or polyhedral surfaces. The lighting device has a plurality of flat chip-on-board LED modules (1, 11, 11′, 21, 31, 41-41″, 46-46″, 51-51″, 61-61″, 71-71′″, 811-818), which are arranged adjacent to each other at least in pairs. Each chip-on-board LED module (1, 11, 11′, 21, 31, 41-41″, 46-46″, 51-51″, 61-61″, 71-811-818) has a plurality of light-emitting LEDs (4, 4′, 14, 14′, 24, 34, 64, 72). The lighting device (40-40″, 45-45″, 50-50″, 60, 80, 93-93″) is characterized by at least one pair of the adjacent chip-on-board LED modules (1, 11, 11′, 21, 31, 41-41″, 46-46″, 51-51″, 61-61″, 71-71′″, 811-818) being arranged at an angle greater than 0° with respect to the surface normals of the modules.
Owner:HERAEUS NOBLELIGHT GMBH
Xrf system having multiple excitation energy bands in highly aligned package
ActiveUS20110170666A1Great interestIncreased signal noiseMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray spectral distribution measurementPhysicsSoft x ray
An x-ray analysis apparatus for illuminating a sample spot with an x-ray beam. An x-ray tube is provided having a source spot from which a diverging x-ray beam is produced having a characteristic first energy, and bremsstrahlung energy; a first x-ray optic receives the diverging x-ray beam and directs the beam toward the sample spot, while monochromating the beam; and a second x-ray optic receives the diverging x-ray beam and directs the beam toward the sample spot, while monochromating the beam to a second energy. The first x-ray optic may monochromate characteristic energy from the source spot, and the second x-ray optic may monochromate bremsstrahlung energy from the source spot. The x-ray optics may be curved diffracting optics, for receiving the diverging x-ray beam from the x-ray tube and focusing the beam at the sample spot. Detection is also provided to detect and measure various toxins in, e.g., manufactured products including toys and electronics.
Owner:X-RAY OPTICAL SYSTEM INC
Electrical Conductor for Transporting Electrical Energy and Corresponding Production Method
InactiveUS20130264093A1Small catenary sagImprove electrical performanceNon-insulated conductorsConductive materialElectrical conductorSkin effect
An electrical conductor for transmission of electrical power, having a total cross-section equal to or above 10 mm2 and comprising a plurality of stranded filamentary members, where at least one of the filamentary members is made from microalloyed copper or microalloyed aluminium having annealing temperatures higher than 250° C., and has the side surface thereof totally coated with a fluorinated polymer. The conductor has a better behavior relative to the skin effect and allows operation at high temperatures. Furthermore, if the electrical conductor is suspended, it has a smaller sag and prevents or reduces the accumulation of ice and / or snow.
Owner:LA FARGA LACAMBRA
Method and Its Apparatus for Inspecting Defects
InactiveUS20090257058A1High sensitivityIncrease speedOptically investigating flaws/contaminationLight polarisation measurementEdge surfaceUltimate tensile strength
A defect inspection apparatus is capable of inspecting an extremely small defect present on the top and edge surfaces of a sample such as a semiconductor substrate or a thin film substrate with high sensitivity and at high speed. The defect inspection apparatus has an illumination optical system, a plurality of detection optical units and a signal processor. One or more of the detection optical units receives either light diffracted from an edge portion of the sample or light diffracted from an edge grip holding the sample. The one or more of the detection optical units shields the diffracted light received by the detection optical unit based on a signal obtained by monitoring an intensity of the diffracted light received by the detection optical unit in order to inspect a sample portion located near the edge portion and a sample portion located near the edge grip.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Signal processing apparatus, ultrasonic apparatus, control method for signal processing apparatus, and control method for ultrasonic apparatus
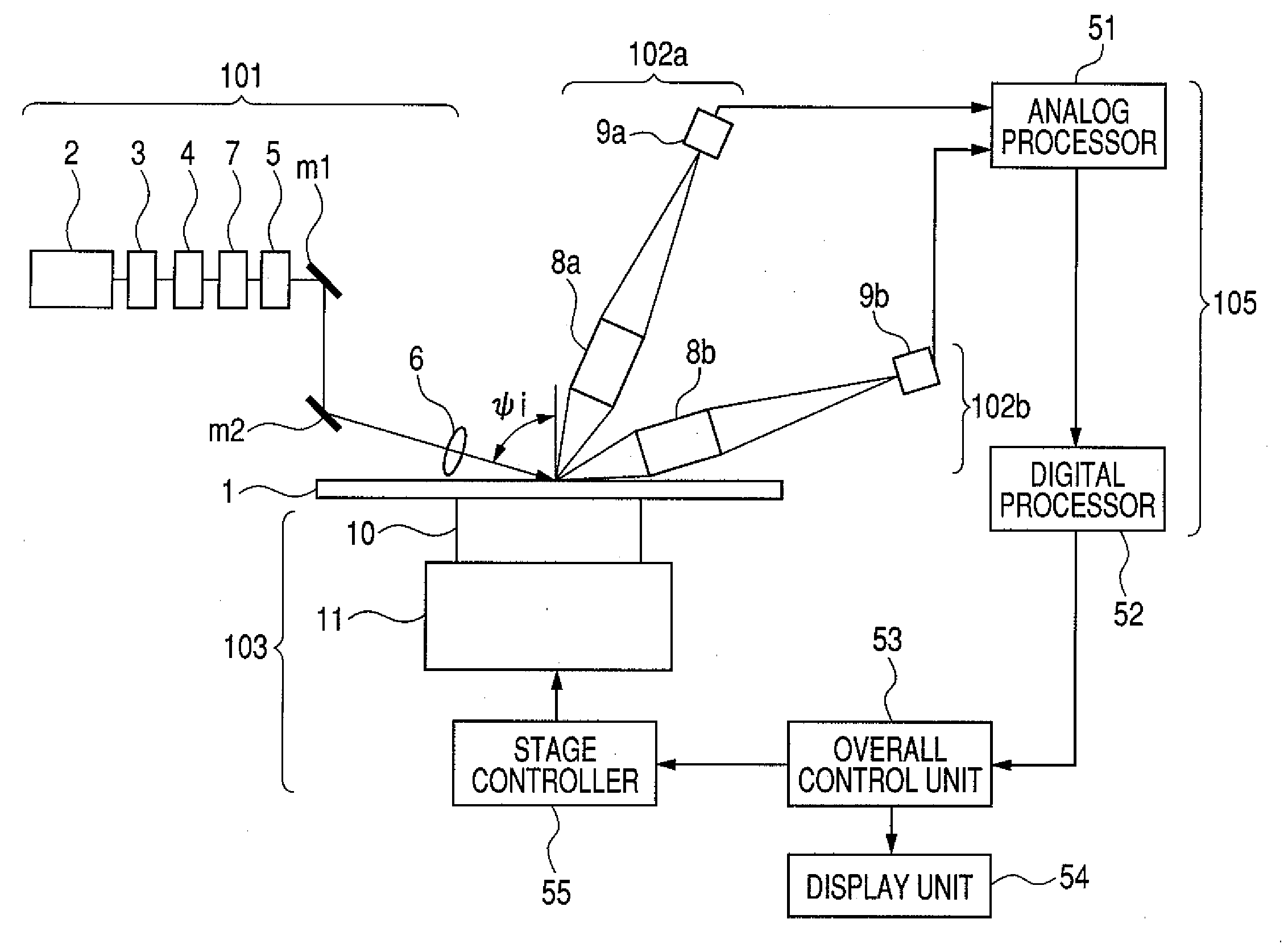
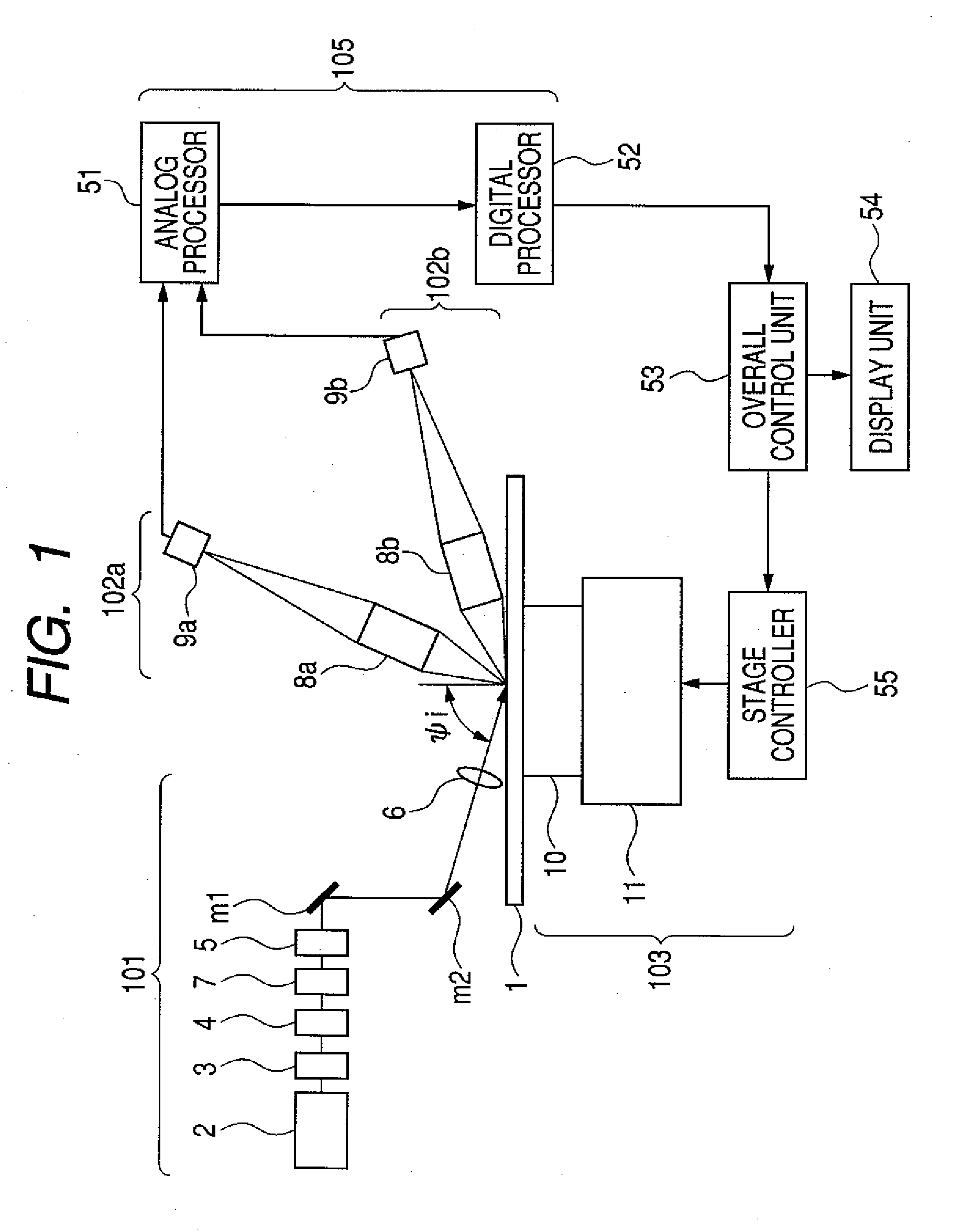
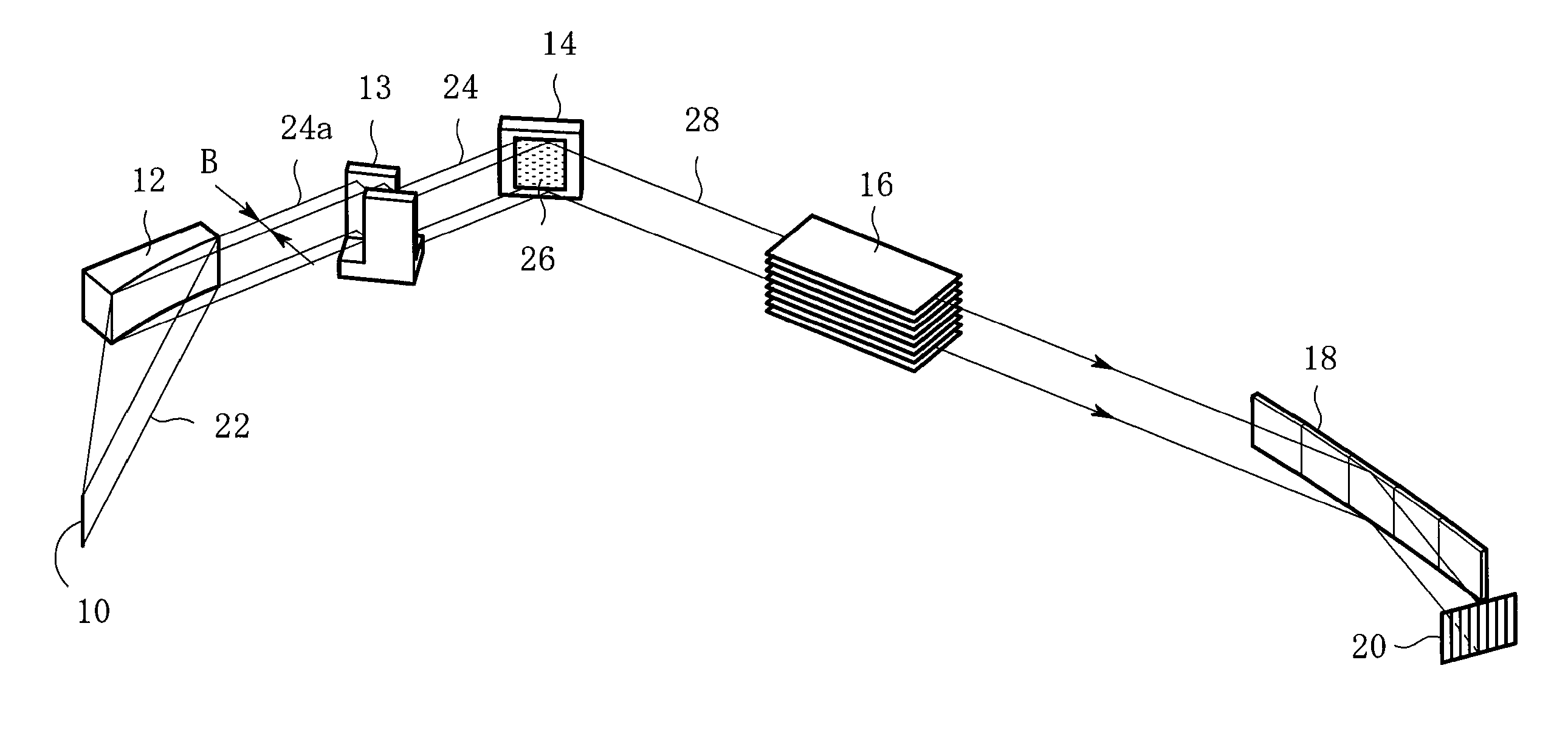
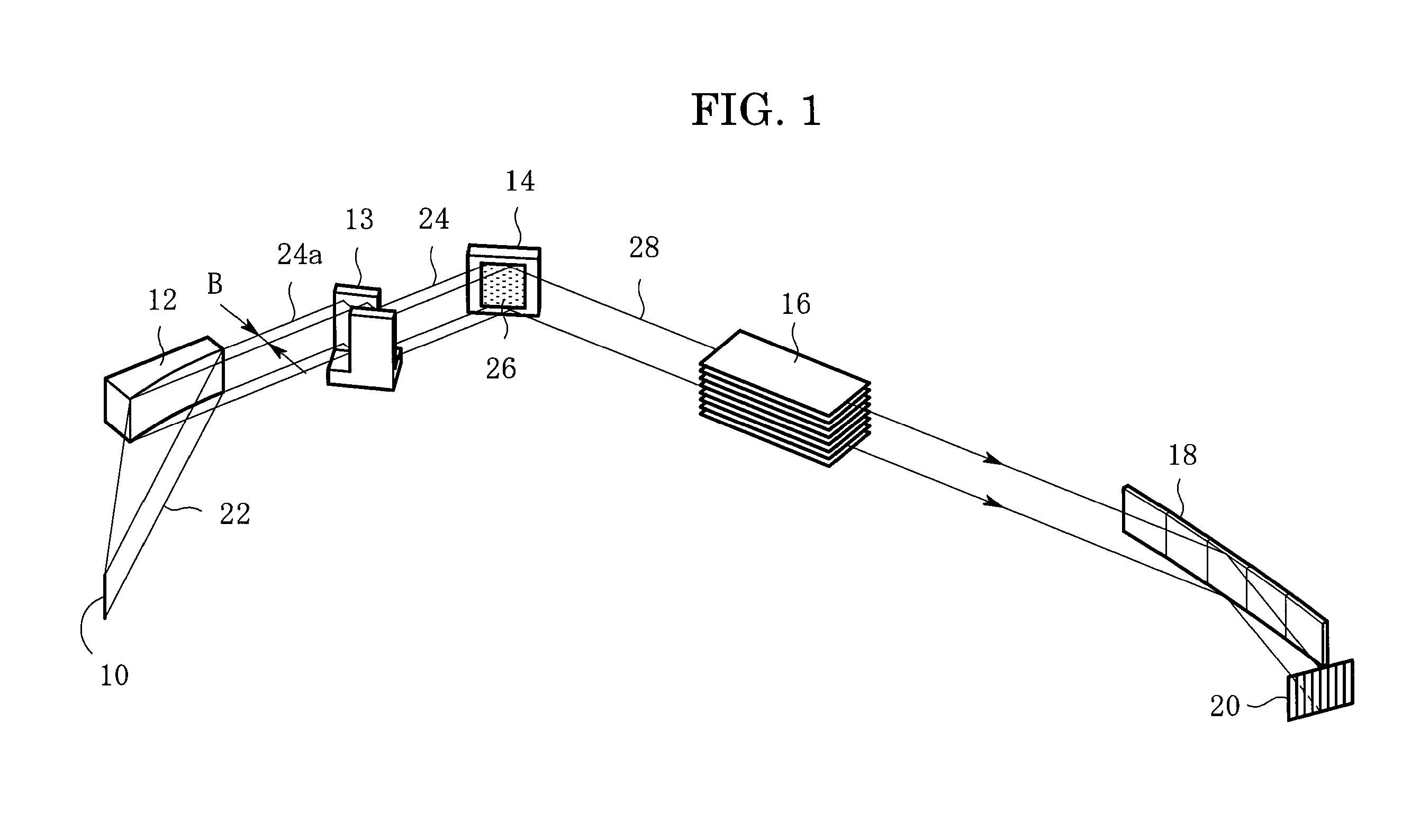
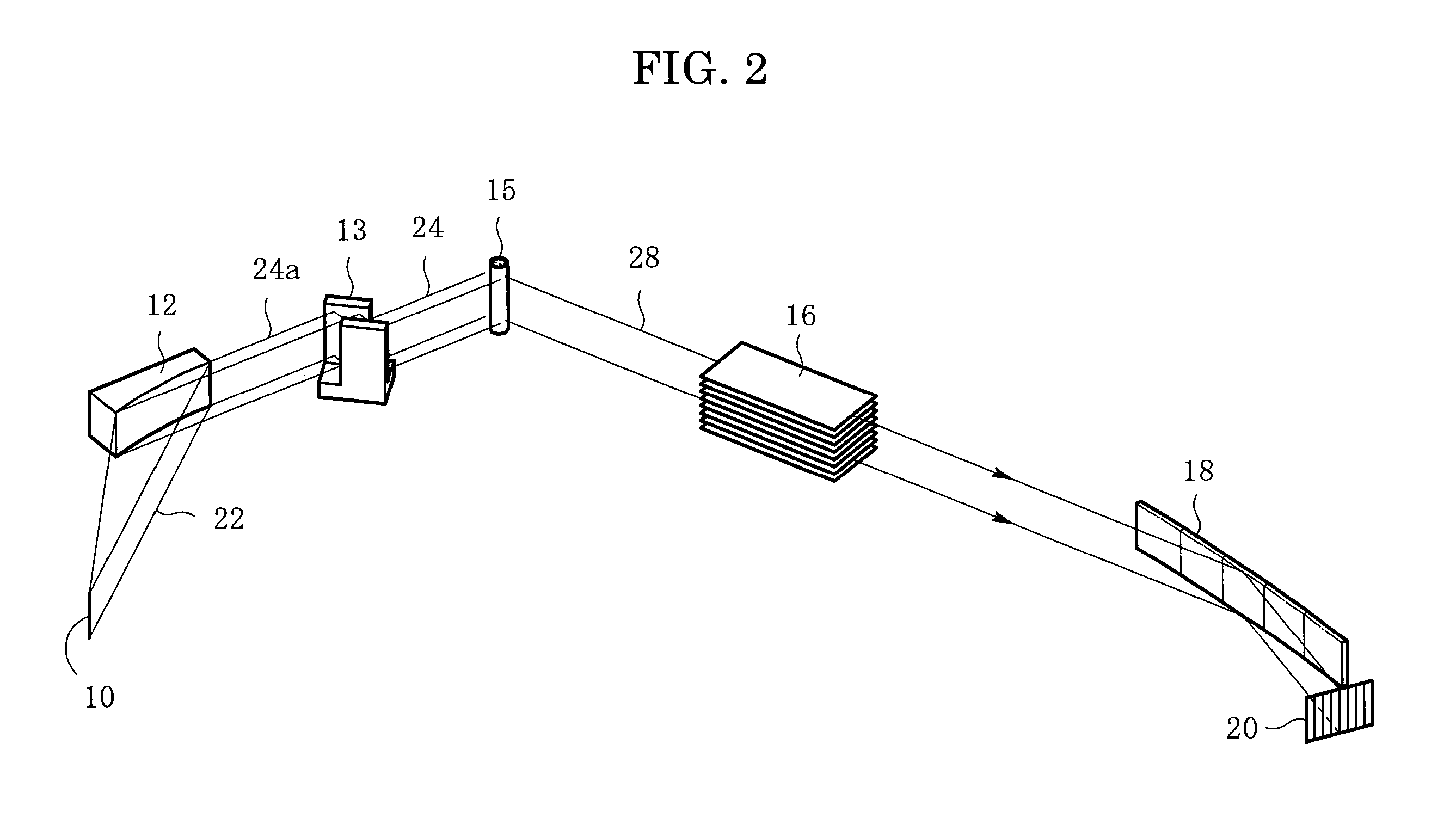
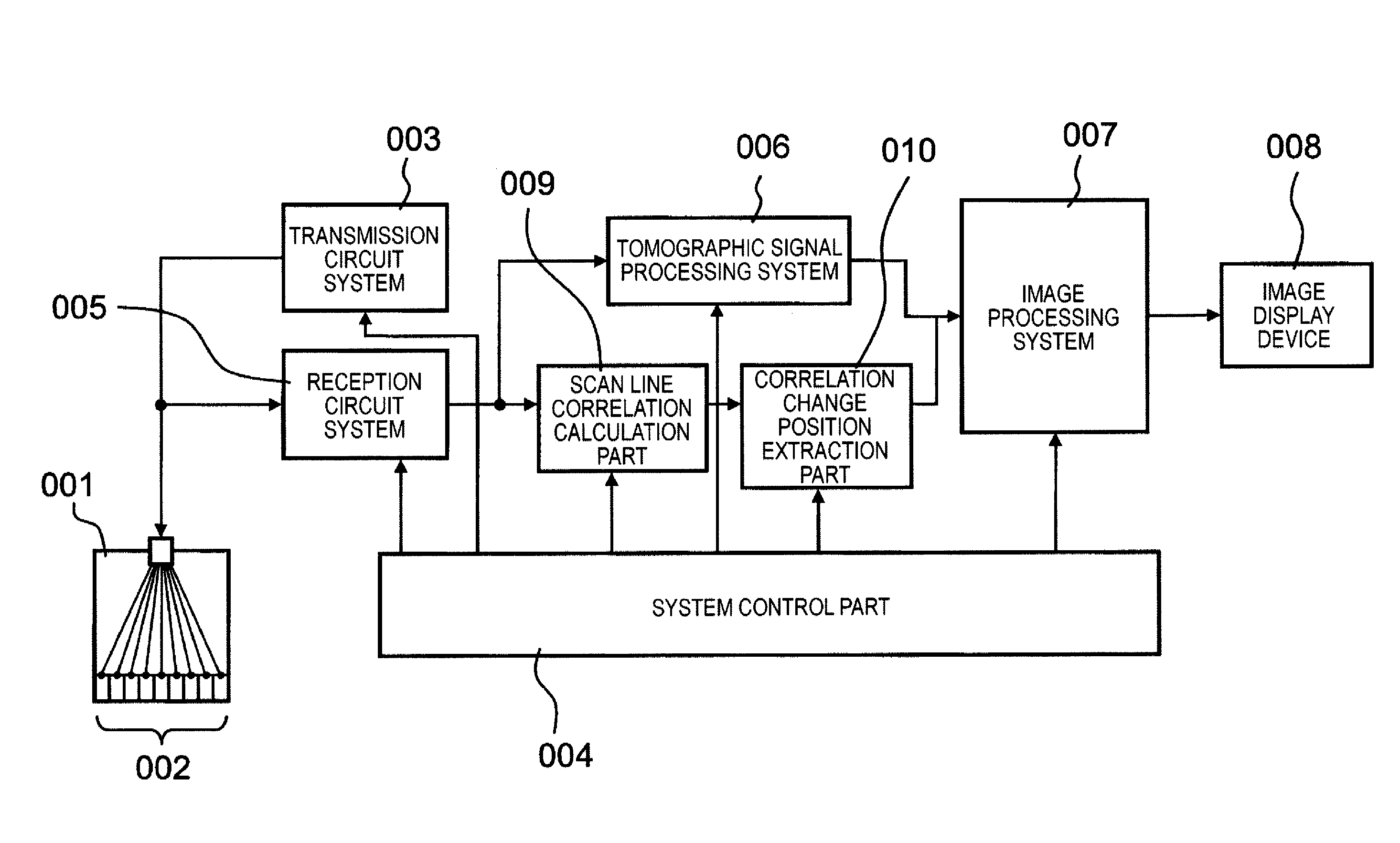
ActiveUS20110083511A1Improve resolutionDetection signal be so smallUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTomographic imageUltrasound
A signal processing apparatus scans a beam of elastic waves into an object to be examined, acquires received waveform data of a plurality of scan lines, and performs signal processing to form a tomographic image of said object to be examined from the received waveform data of the plurality of scan lines. The signal processing apparatus includes a scan line correlation calculation part (009) that calculates a correlation value of received waveform data between a first scan line and a second scan line that has a prescribed correlation with the first scan line, for a plurality of positions on the scan lines, and a correlation change position extraction part (010) that extracts, from among the plurality of positions on said scan lines, a position at which the correlation value becomes a value different from a prescribed value as a position at which a unique region can exist.
Owner:CANON KK
Gaming System
InactiveUS20070246883A1Facilitate automatic electronic paymentSmall intensityLottery apparatusBoard gamesComputer hardware
Owner:CUDLIPP WILLIAM OWEN
Method and apparatus for performing a magnetic pulse welding operation
InactiveUS6921013B1Small intensityFacilitate subsequent performanceMetal working apparatusTubular articlesInductorEngineering
A pair of metallic components are co-axially aligned prior to full energization of the magnetic pulse welding inductor to provide for improved control of the magnetic pulse welding process. To accomplish this, either or both of the components are supported in a floating manner. An electromagnetic coil is then energized so as to generate a magnetic field of relatively small intensity within or about one of the components. This relatively small intensity magnetic field exerts a relatively small force on the two components, causing them to move to a co-axially aligned position relative to one another and to the coil. Then, while the components are co-axially aligned, they are subjected to a magnetic field of relatively large intensity for the purpose of permanently joining such components together. This relatively large intensity magnetic field exerts a large pressure on one of the two components, causing it to deform toward the other of the two components at a high velocity. The high velocity impact of these two components, as well as the large pressures exerted thereon, caused the two components to become permanently joined together.
Owner:METALSA SA DE CV
X-ray diffraction apparatus and X-ray diffraction method
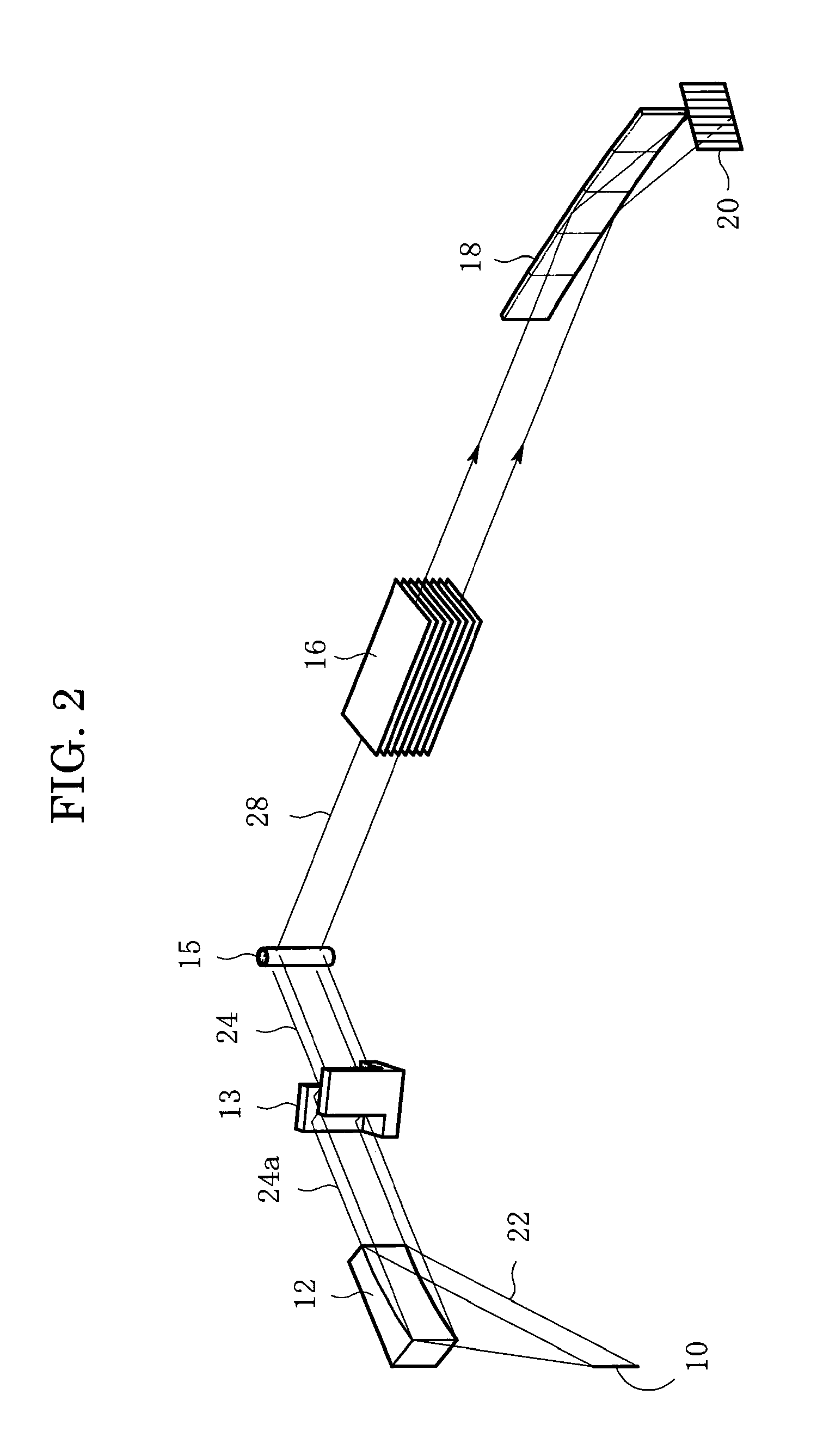
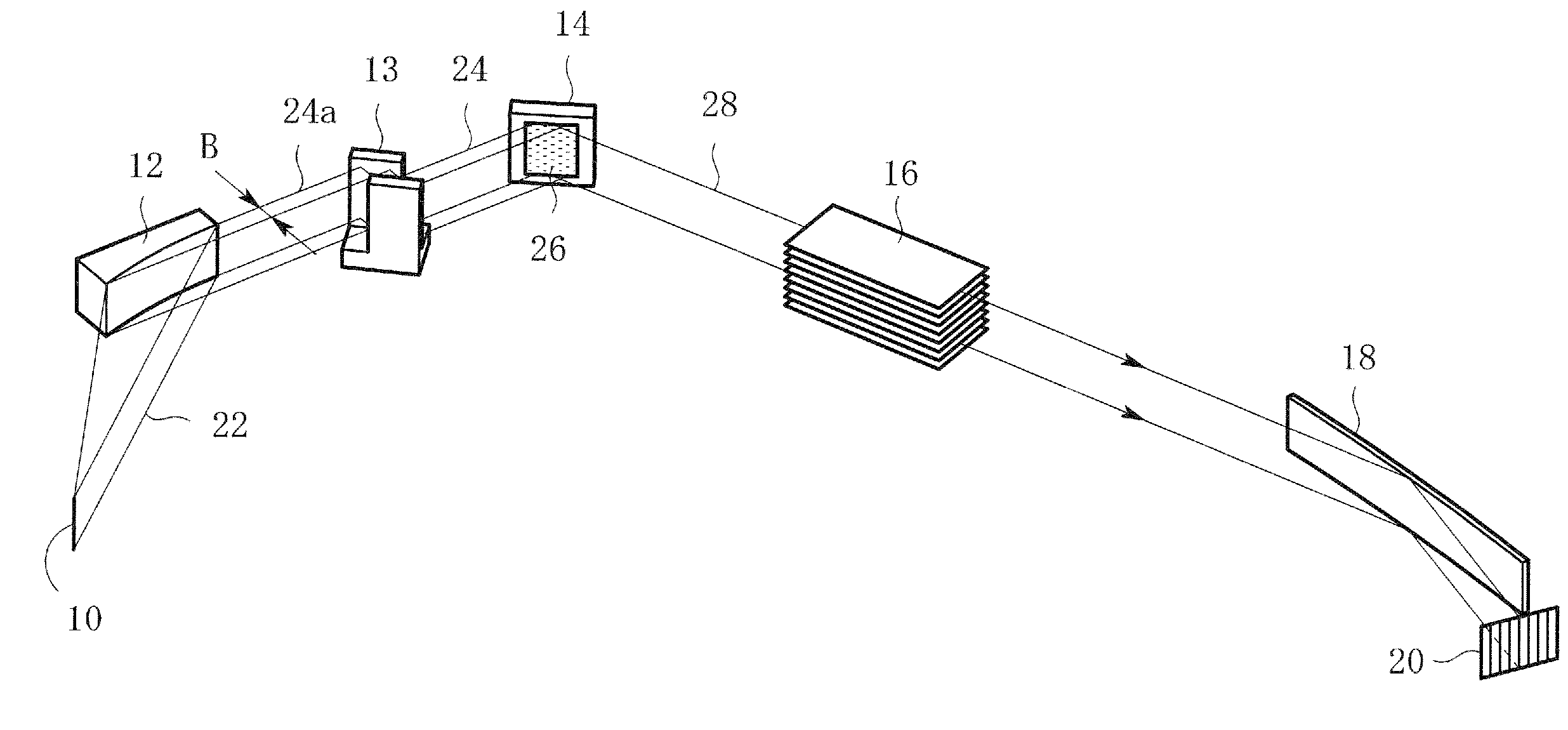
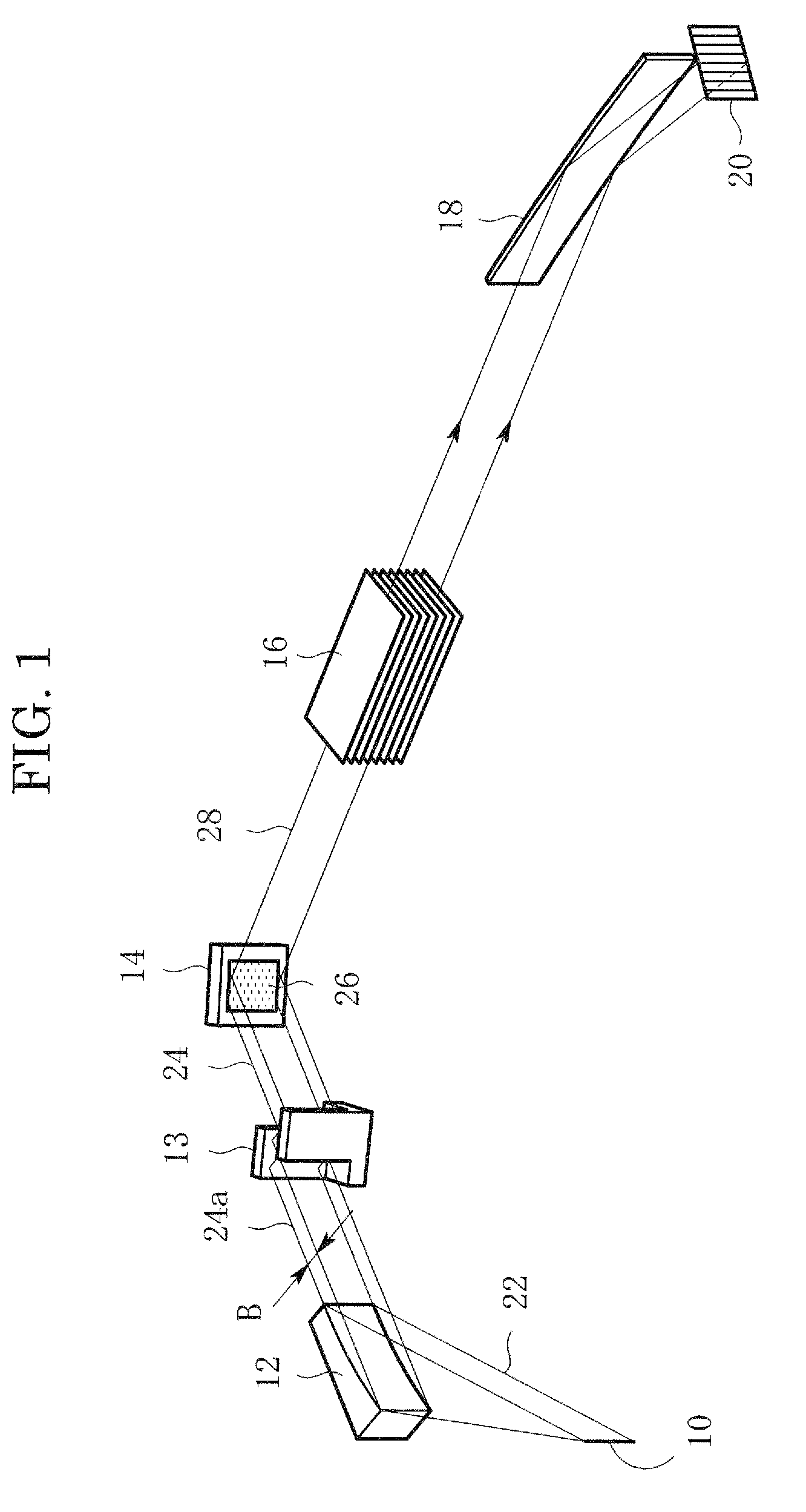
InactiveUS7801272B2Convenient angleSmall intensityHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionLattice planeX-ray
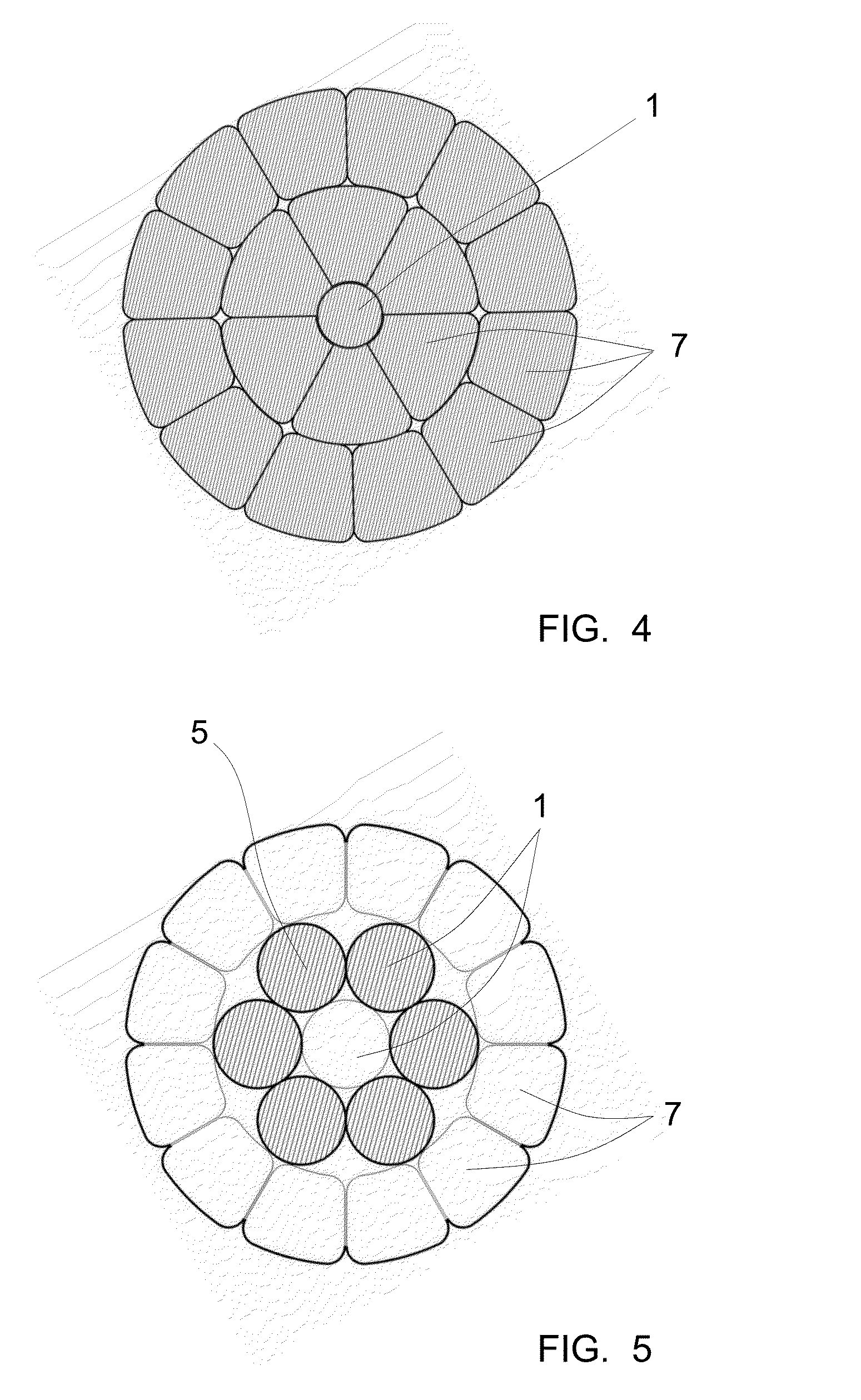
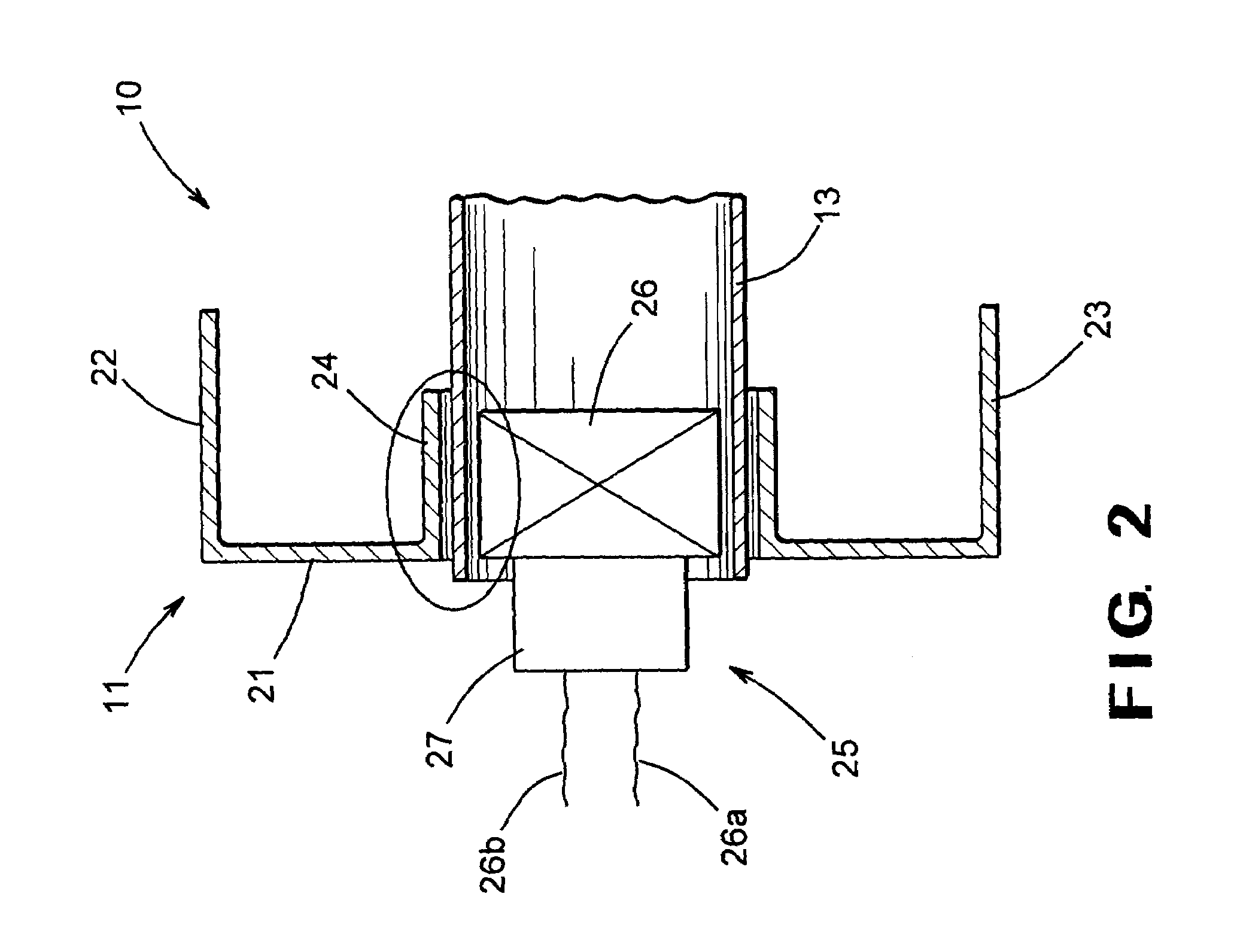
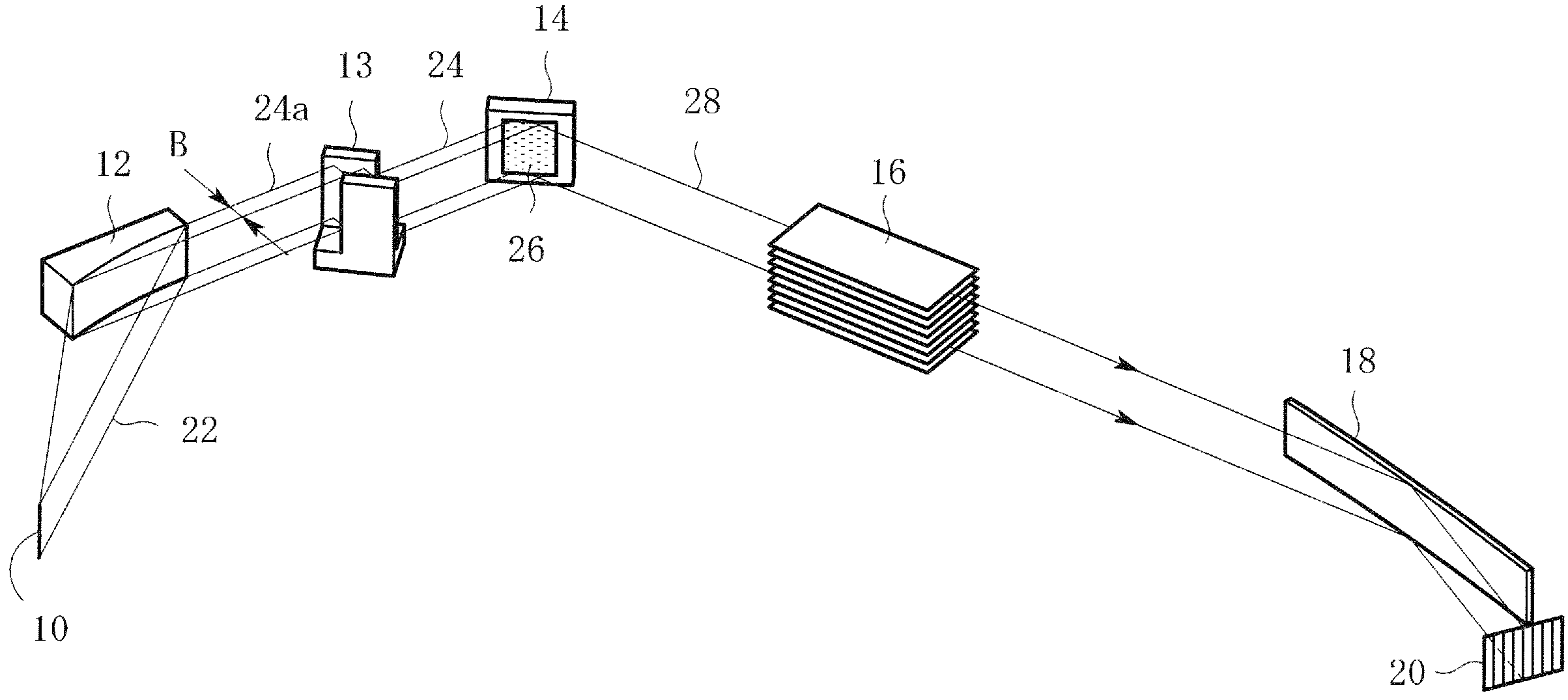
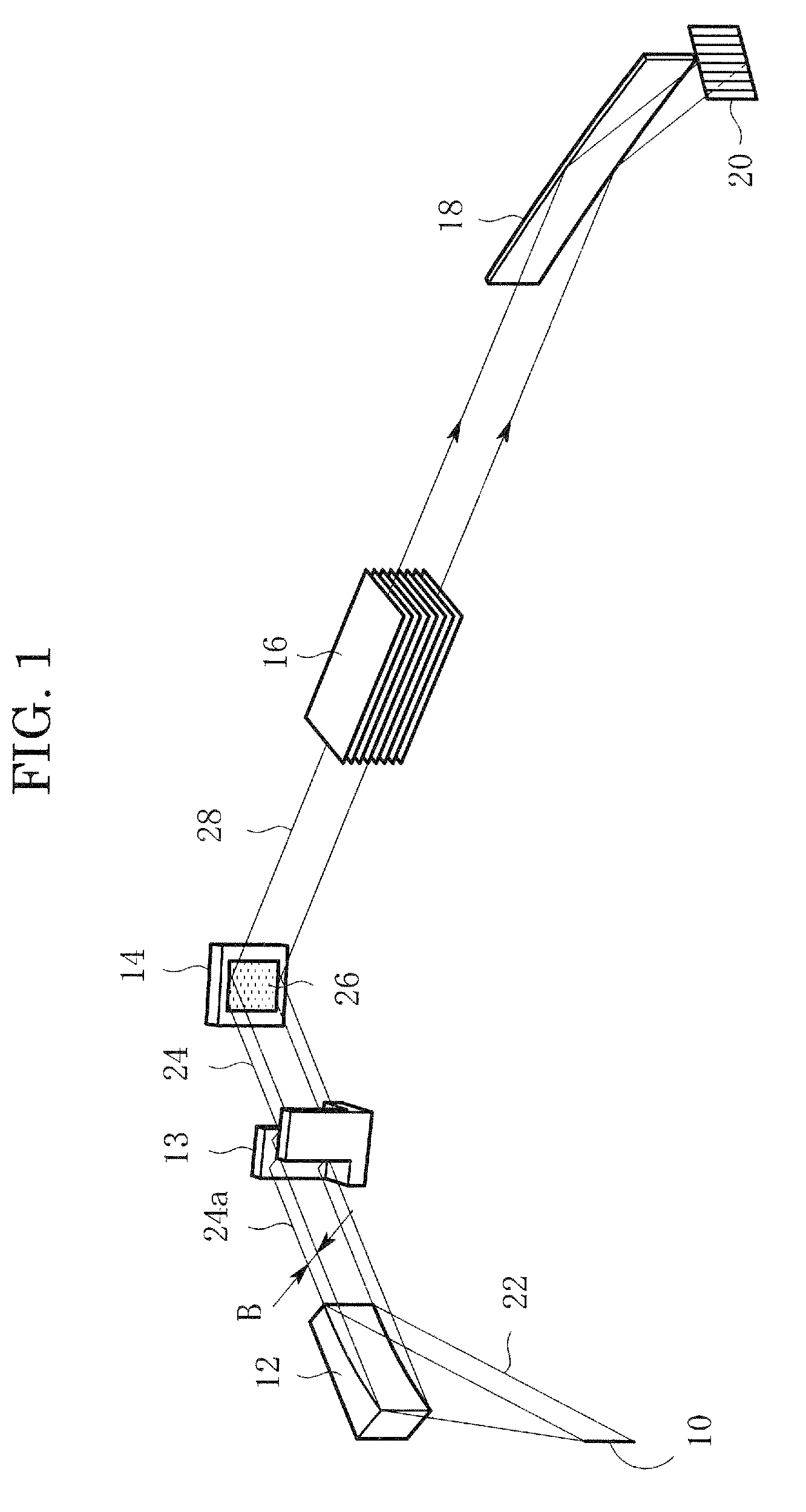
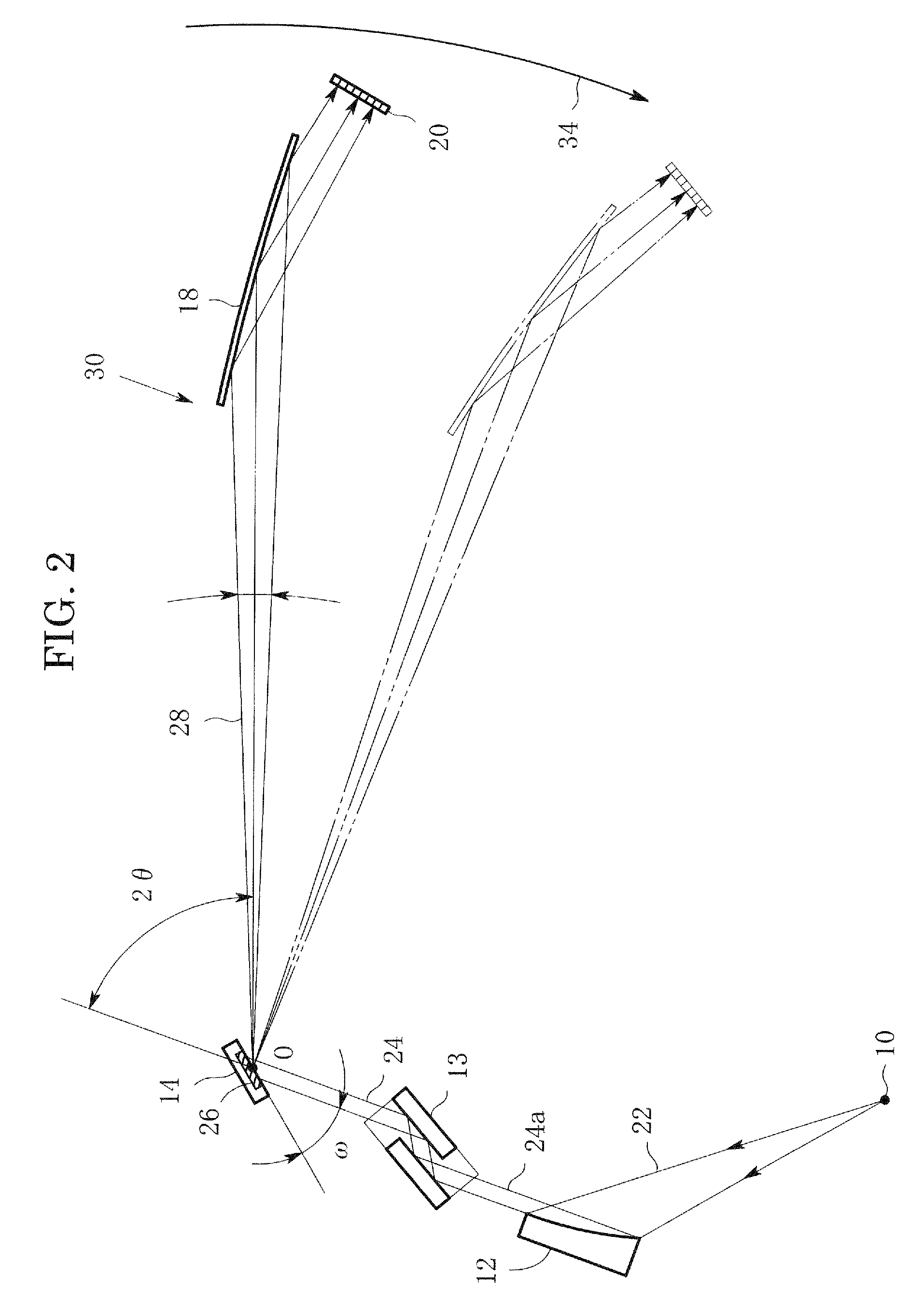
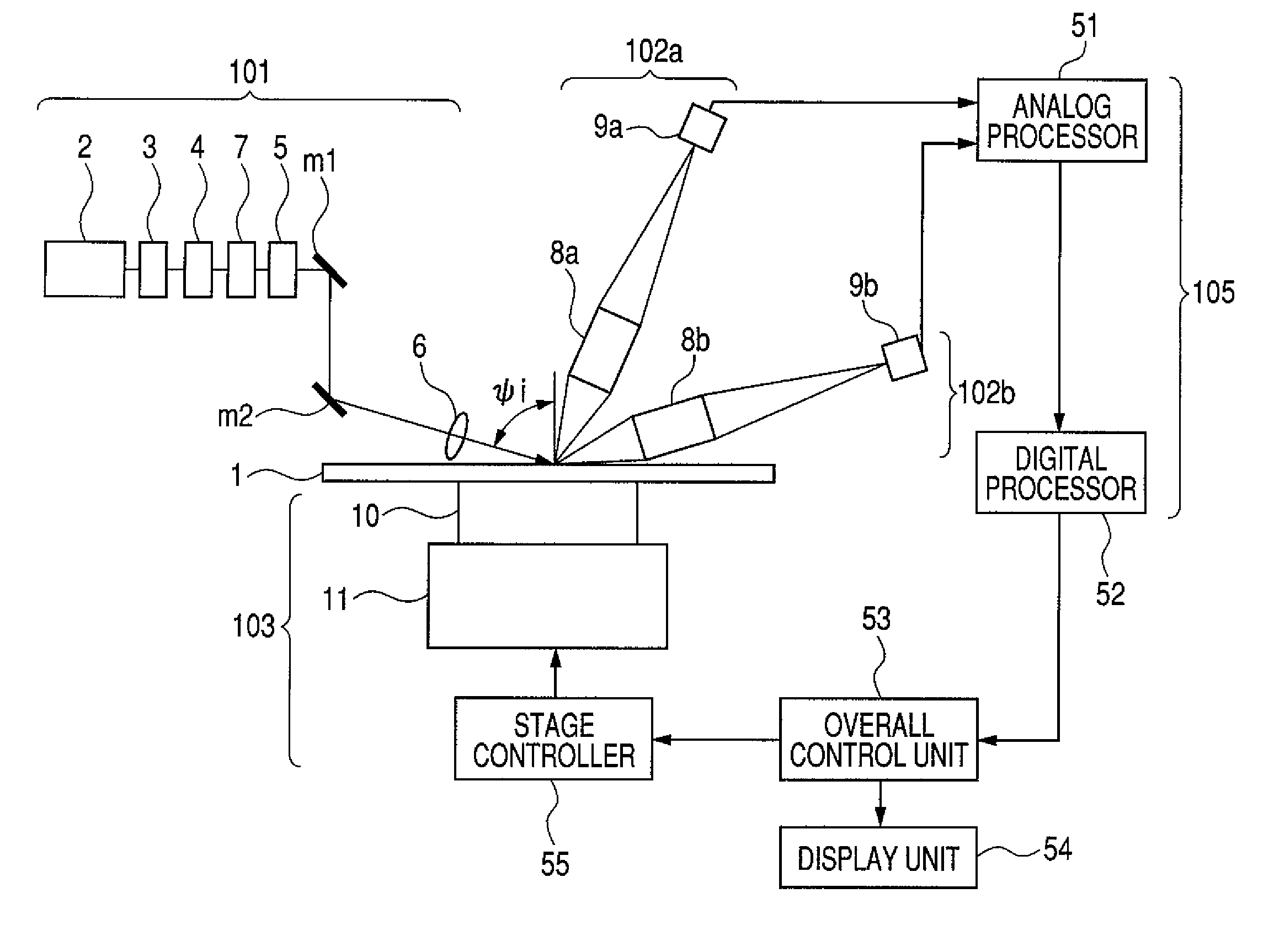
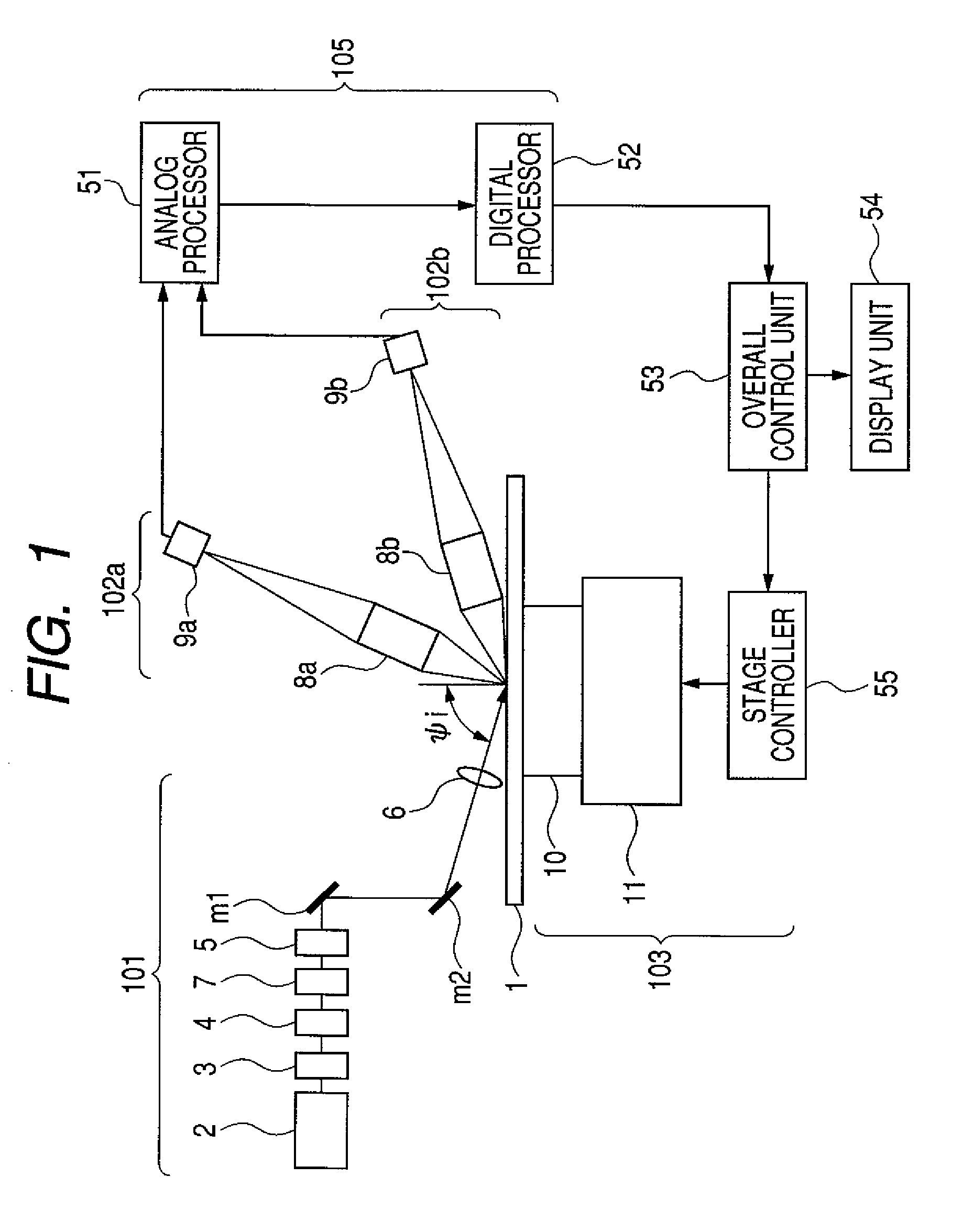
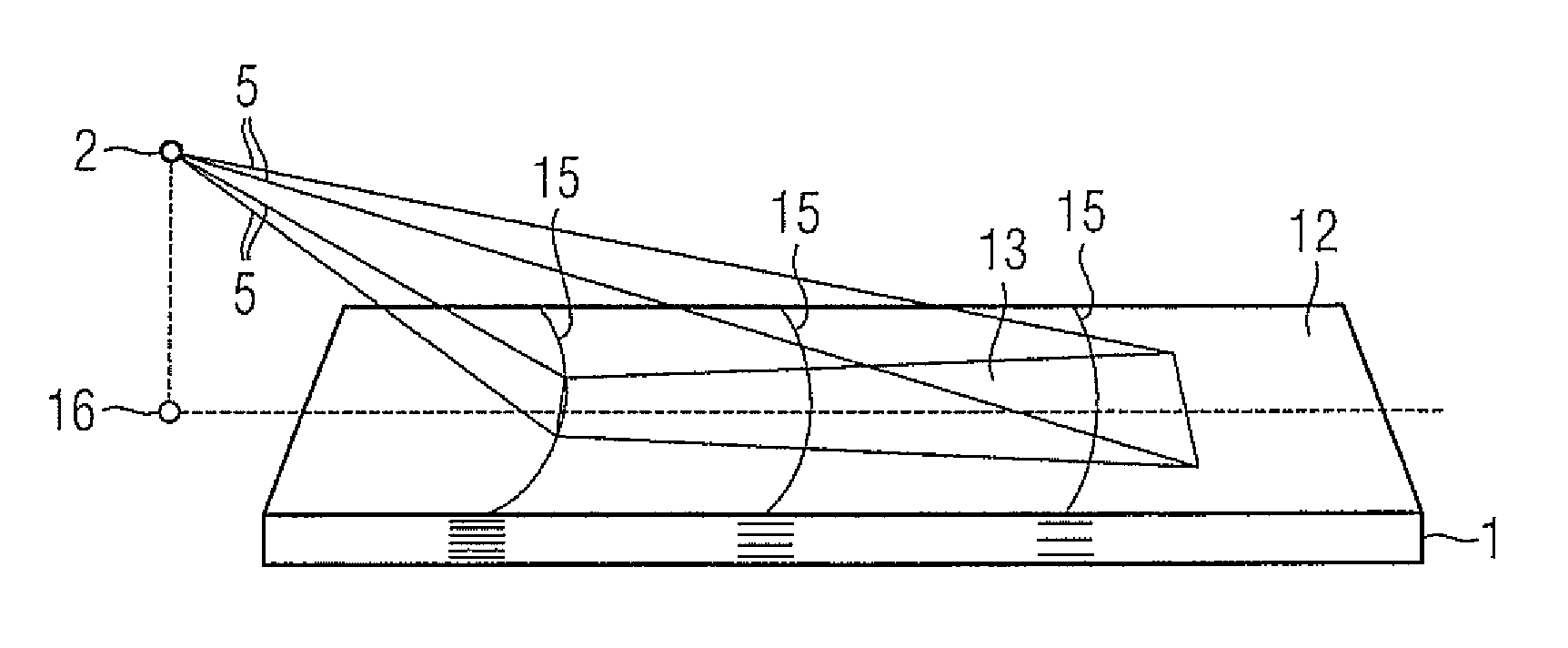
In an X-ray diffraction method using the parallel beam method, an X-ray parallel beam is incident on a sample, and diffracted X-rays from the sample are reflected at a mirror and thereafter detected by an X-ray detector. The reflective surface of the mirror has a shape of an equiangular spiral that has a center located on the surface of the sample. A crystal lattice plane that causes reflection is parallel to the reflective surface at any point on the reflective surface. The X-ray detector is one-dimensional position sensitive in a plane parallel to the diffraction plane. A relative positional relationship between the mirror and the X-ray detector is determined so that reflected X-rays from different points on the reflective surface of the mirror reach different points on the X-ray detector respectively. This X-ray diffraction method is superior in angular resolution, and is small in X-ray intensity reduction, and is simple in structure.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
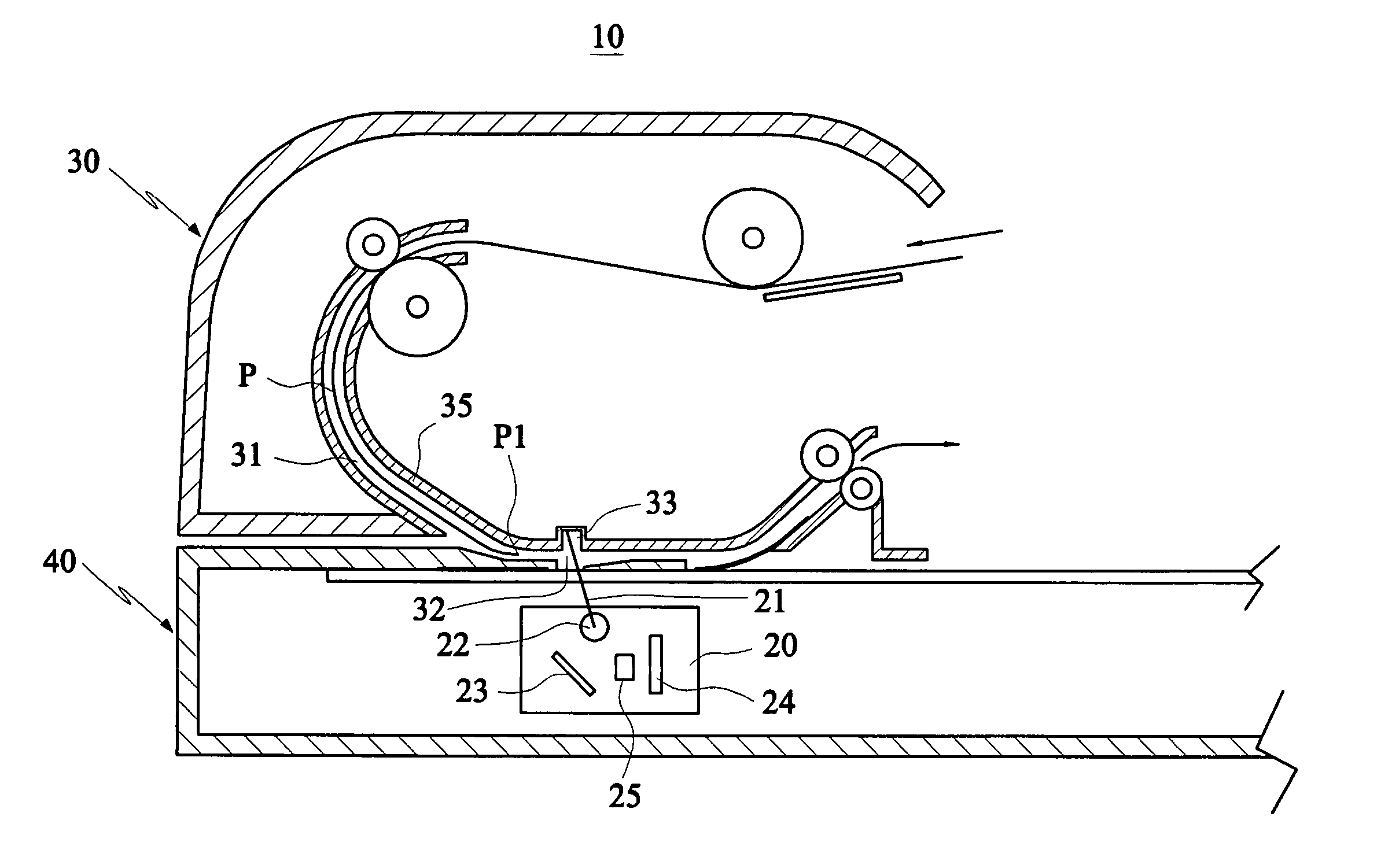
Sheet-fed scanning device capable of detecting a document edge
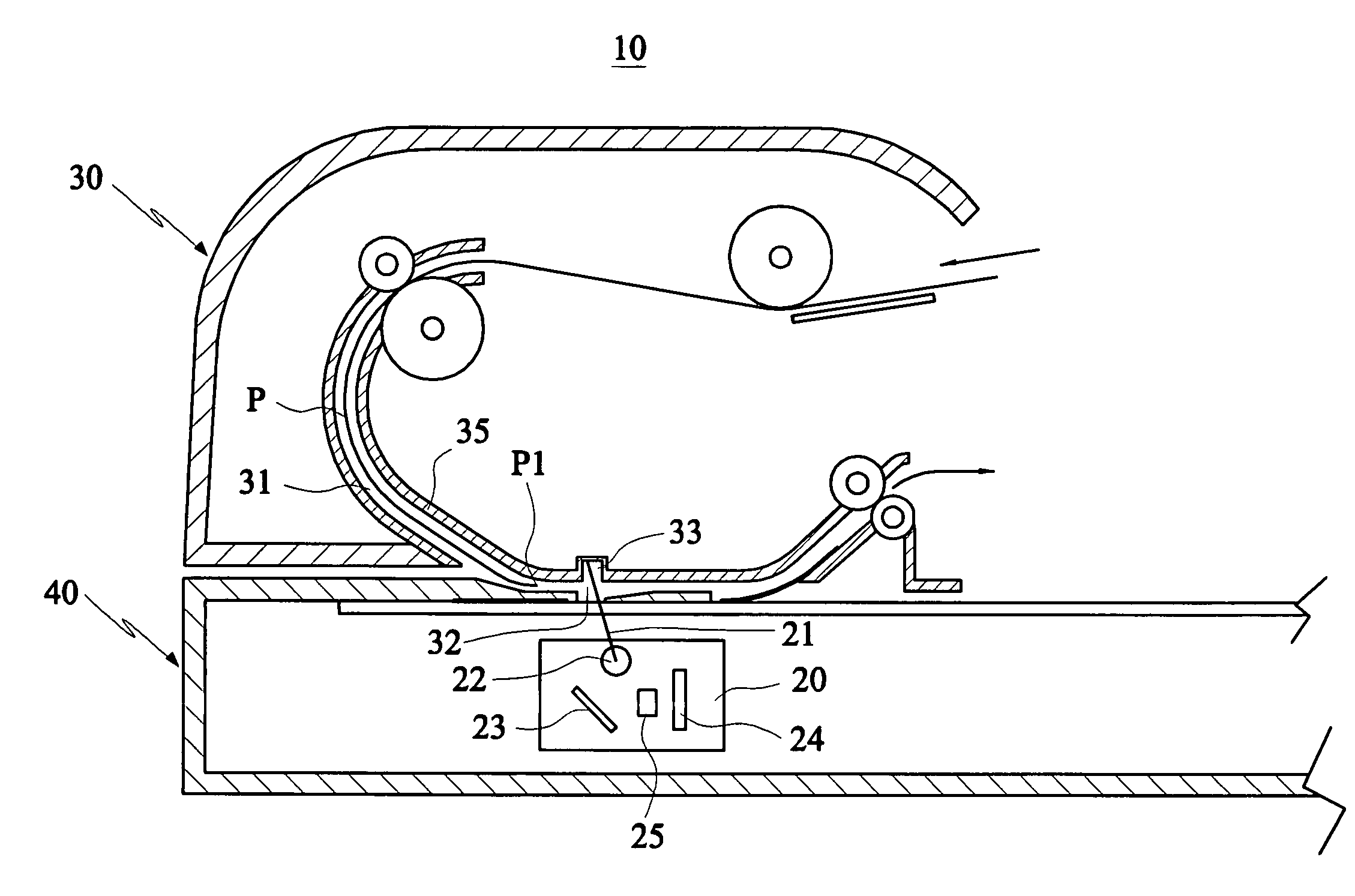
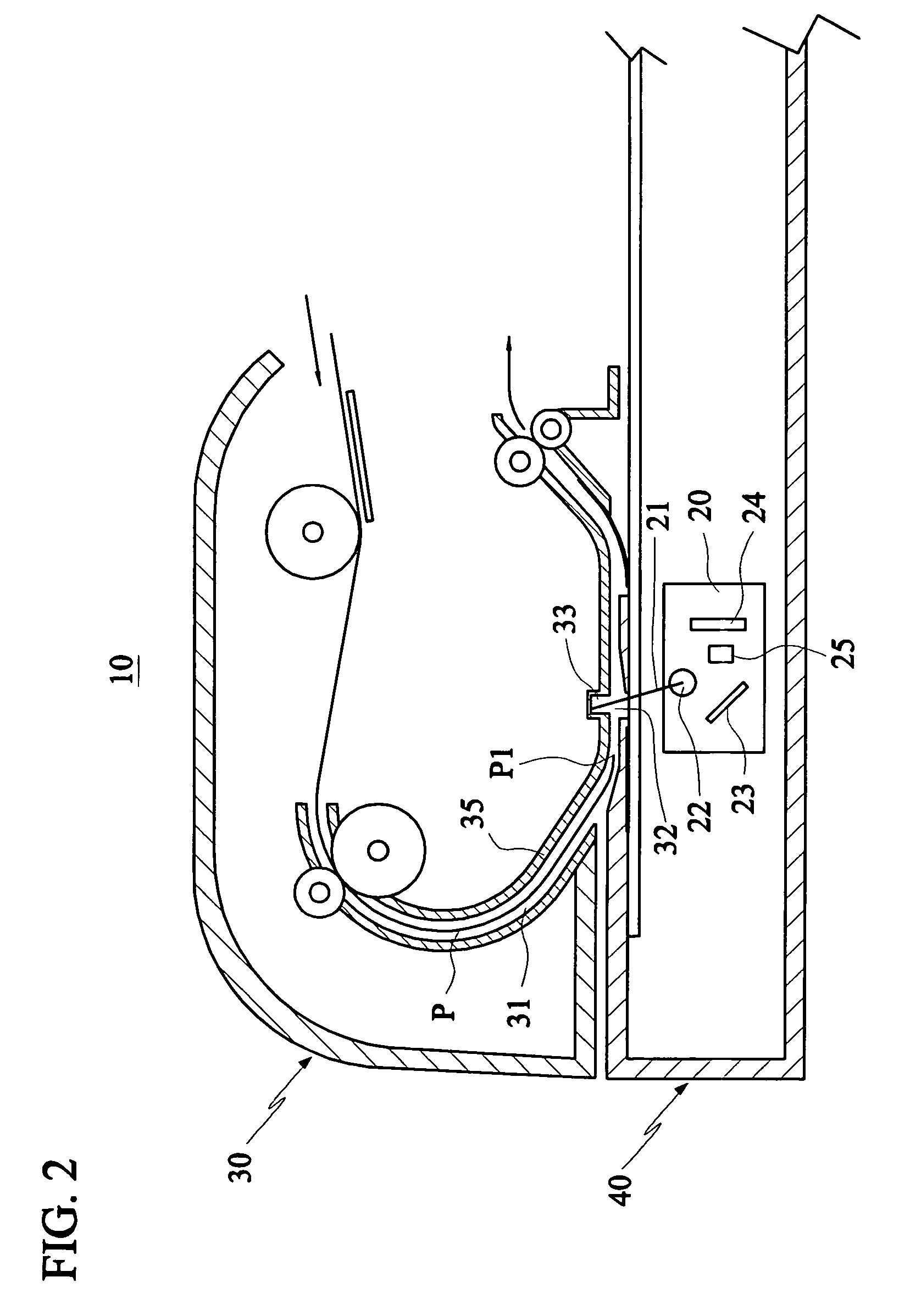
ActiveUS7327502B2Easy to detectAvoid the errors caused by the wear of the backgroundPictoral communicationComputer scienceBrightness perception
A sheet-fed scanning device capable of detecting a document edge includes a scanning module and an automatic document feeder. The scanning module scans a document with a light ray. The automatic document feeder feeds the document across a scanning region on a sheet passageway for the scanning module to scan. In this invention, a section of a guide plate of the sheet passageway located within the scanning region is formed with a concave portion, wherein the document moving across the scanning region is located between the concave portion and the scanning module, such that the intensity of a first brightness of the concave portion sensed by the scanning module is far smaller than the intensity of a second brightness of the document sensed by the scanning module. Thus, it is possible to facilitate the document edge detection and the document skew correction.
Owner:AVISION
Group iii nitride semiconductor light-emitting device and method for producing the same
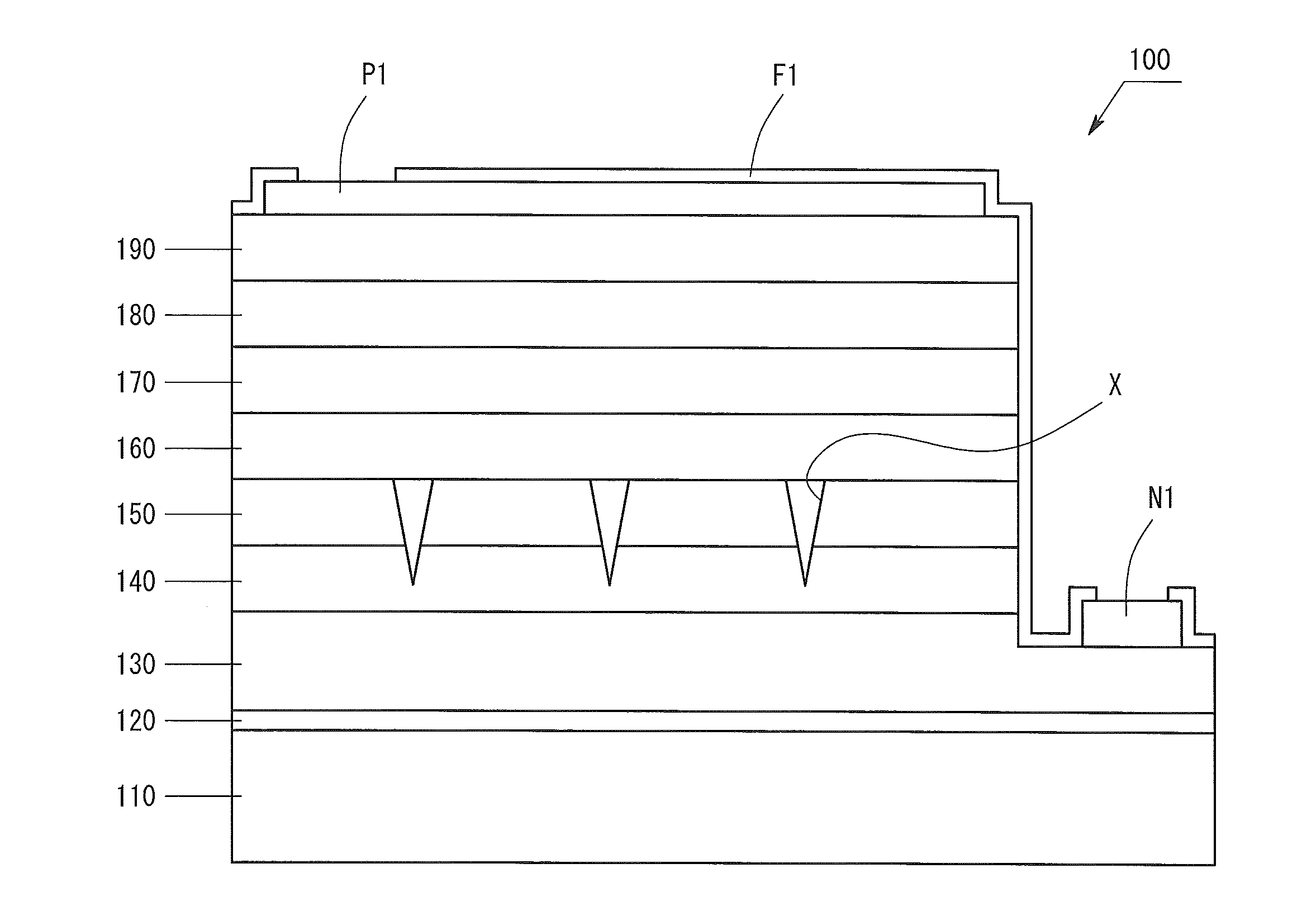
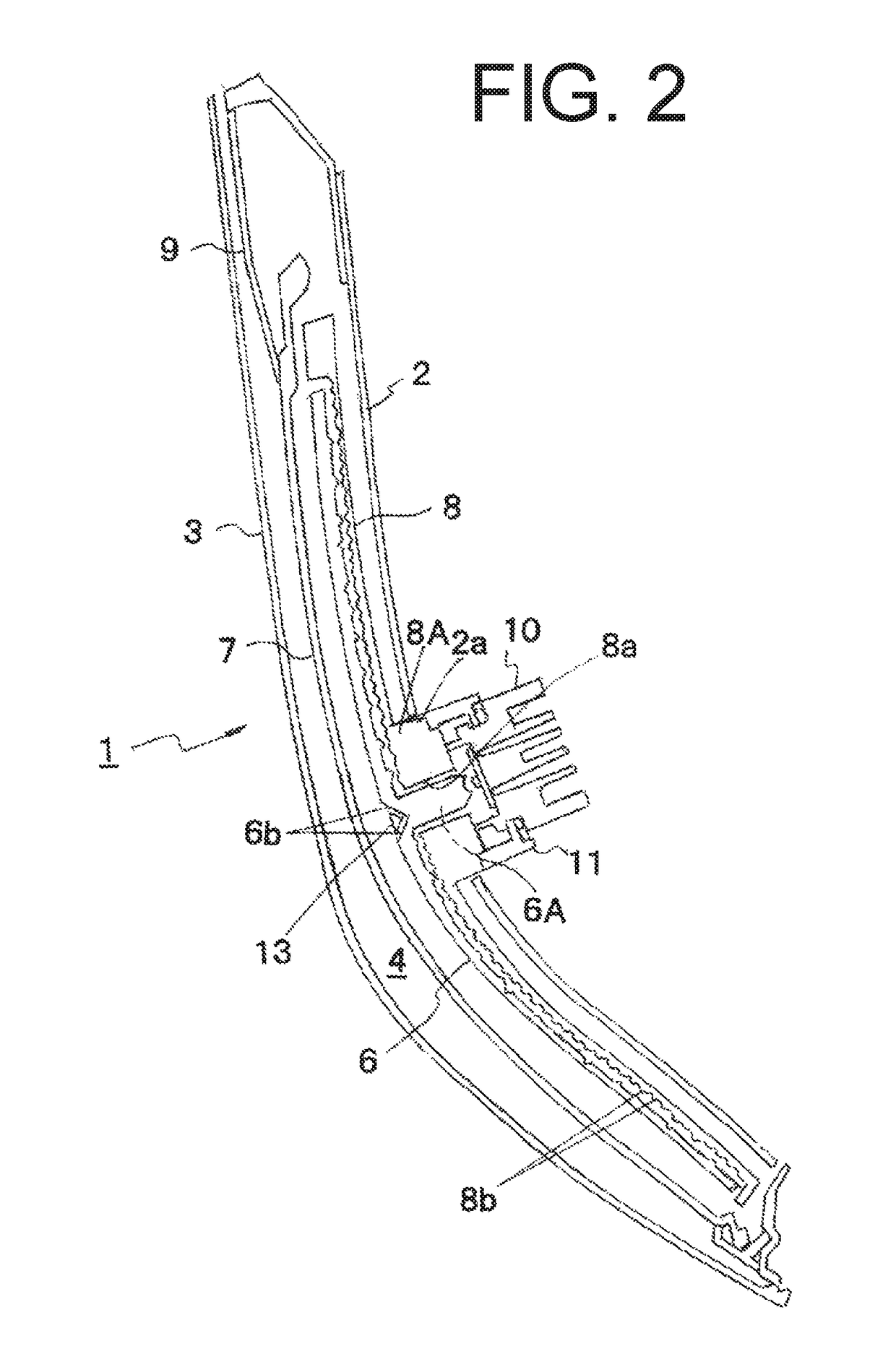
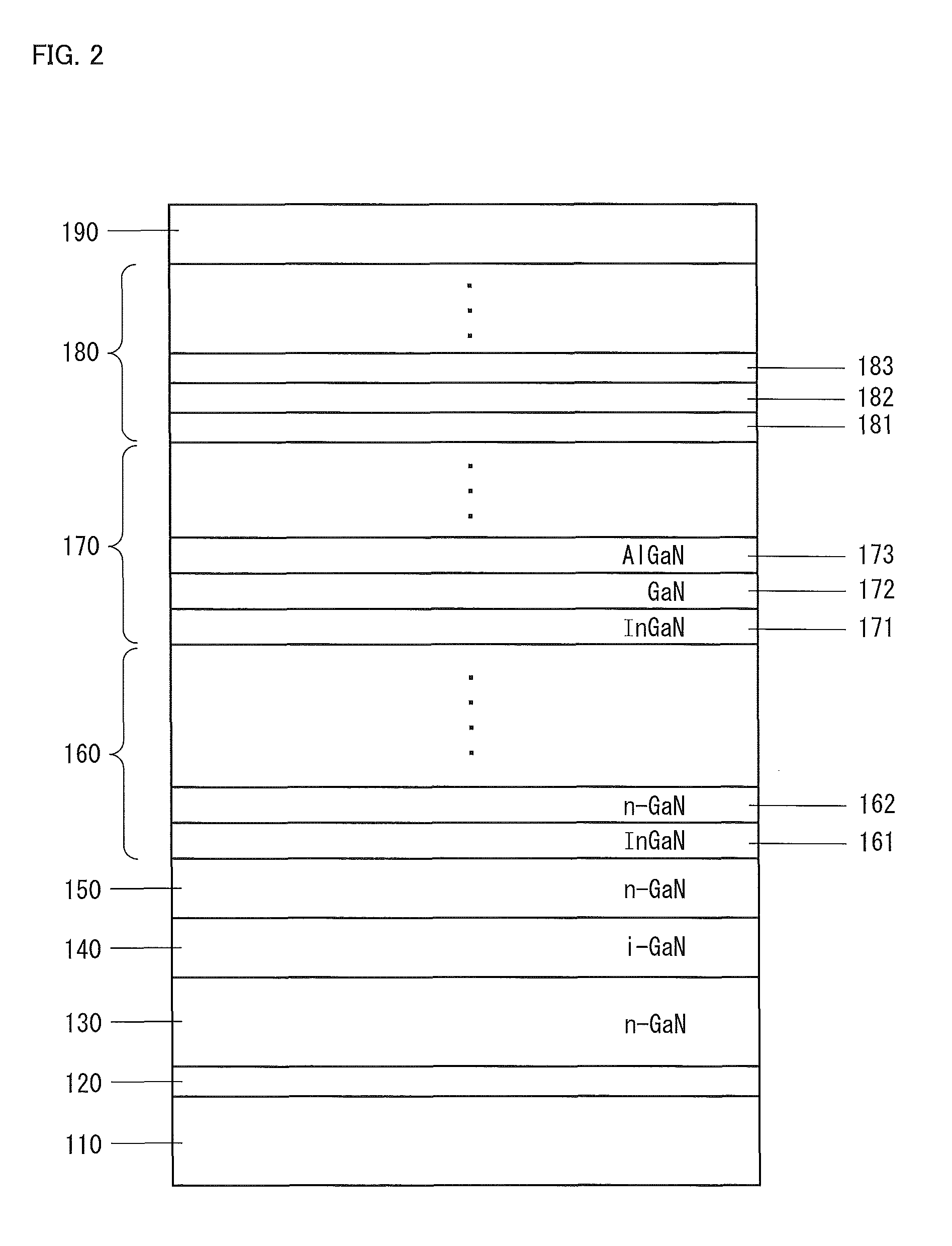
ActiveUS20140084241A1Strain applied to the light-emitting layer is relaxedEnhanced glowSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesContact layerLight emission
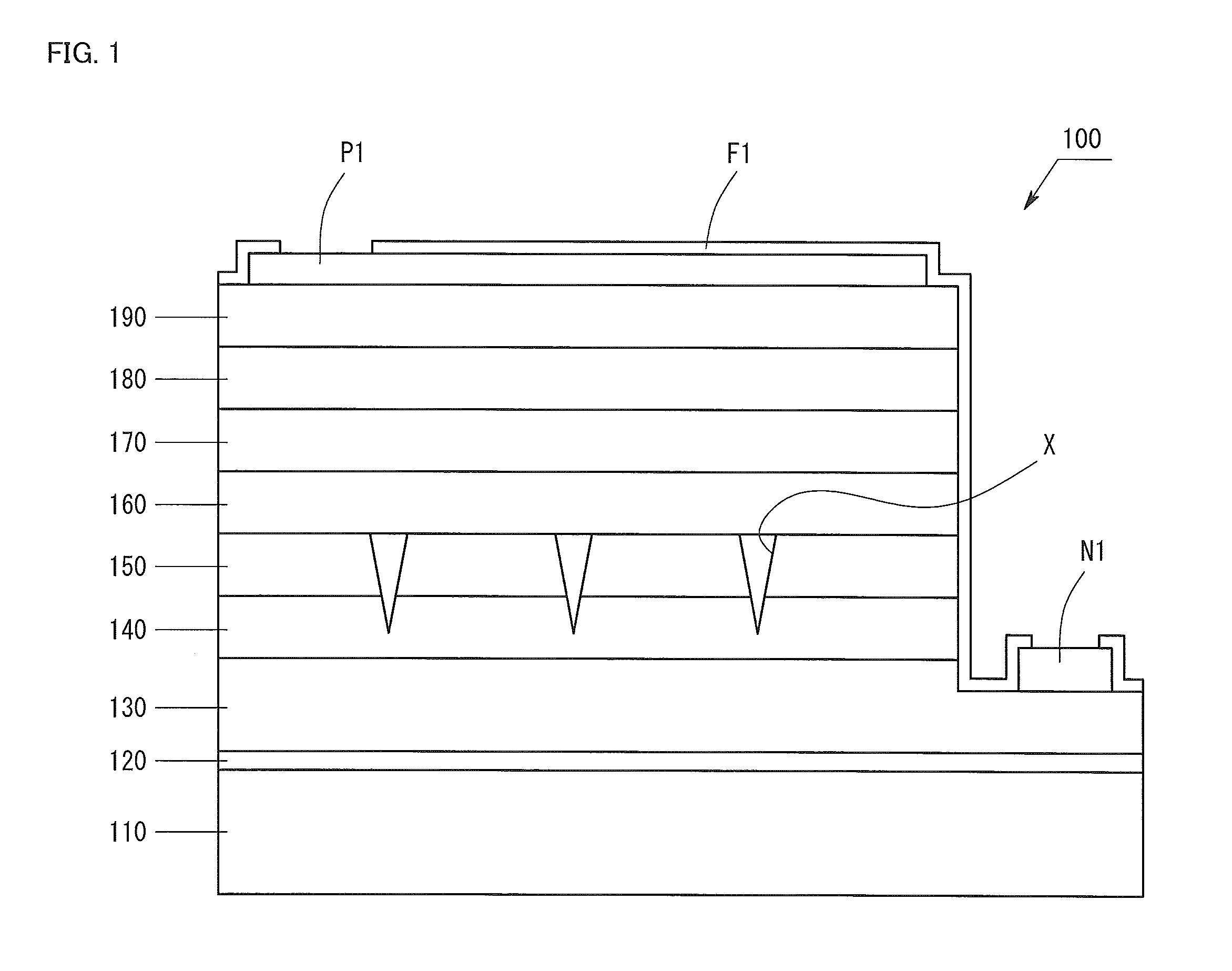
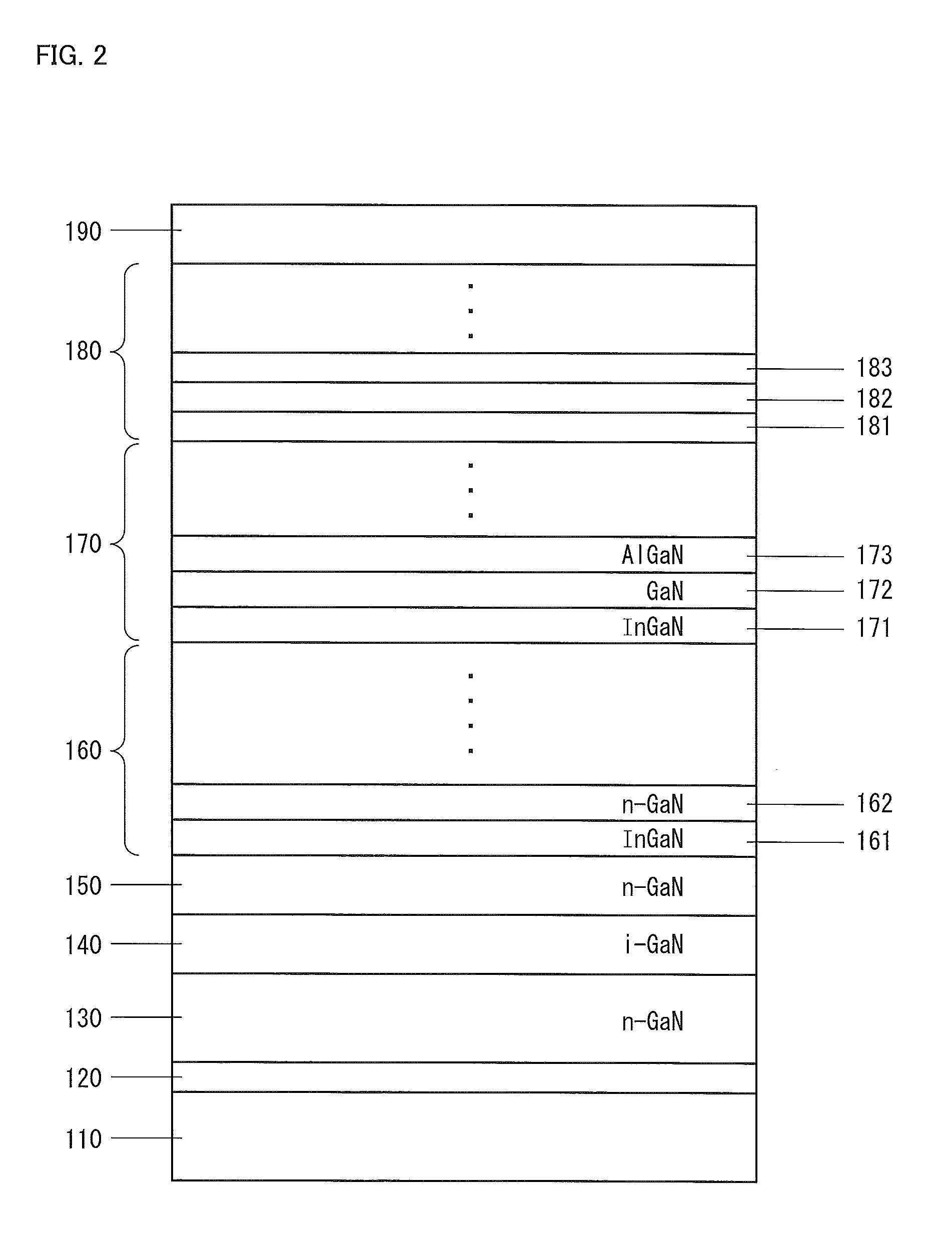
The invention provides a Group III nitride semiconductor light-emitting device in which the strain in the light-emitting layer is relaxed, thereby attaining high light emission efficiency, and a method for producing the device. The light-emitting device of the present invention has a substrate, a low-temperature buffer layer, an n-type contact layer, a first ESD layer, a second ESD layer, an n-side superlattice layer, a light-emitting layer, a p-side superlattice layer, a p-type contact layer, an n-type electrode N1, a p-type electrode P1, and a passivation film F1. The second ESD layer has pits X having a mean pit diameter D. The mean pit diameter D is 500 Å to 3,000 Å. An InGaN layer included in the n-side superlattice layer has a thickness Y satisfying the following condition: −0.029×D+82.8≦Y≦−0.029×D+102.8.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
X-ray diffraction method and X-ray diffraction apparatus
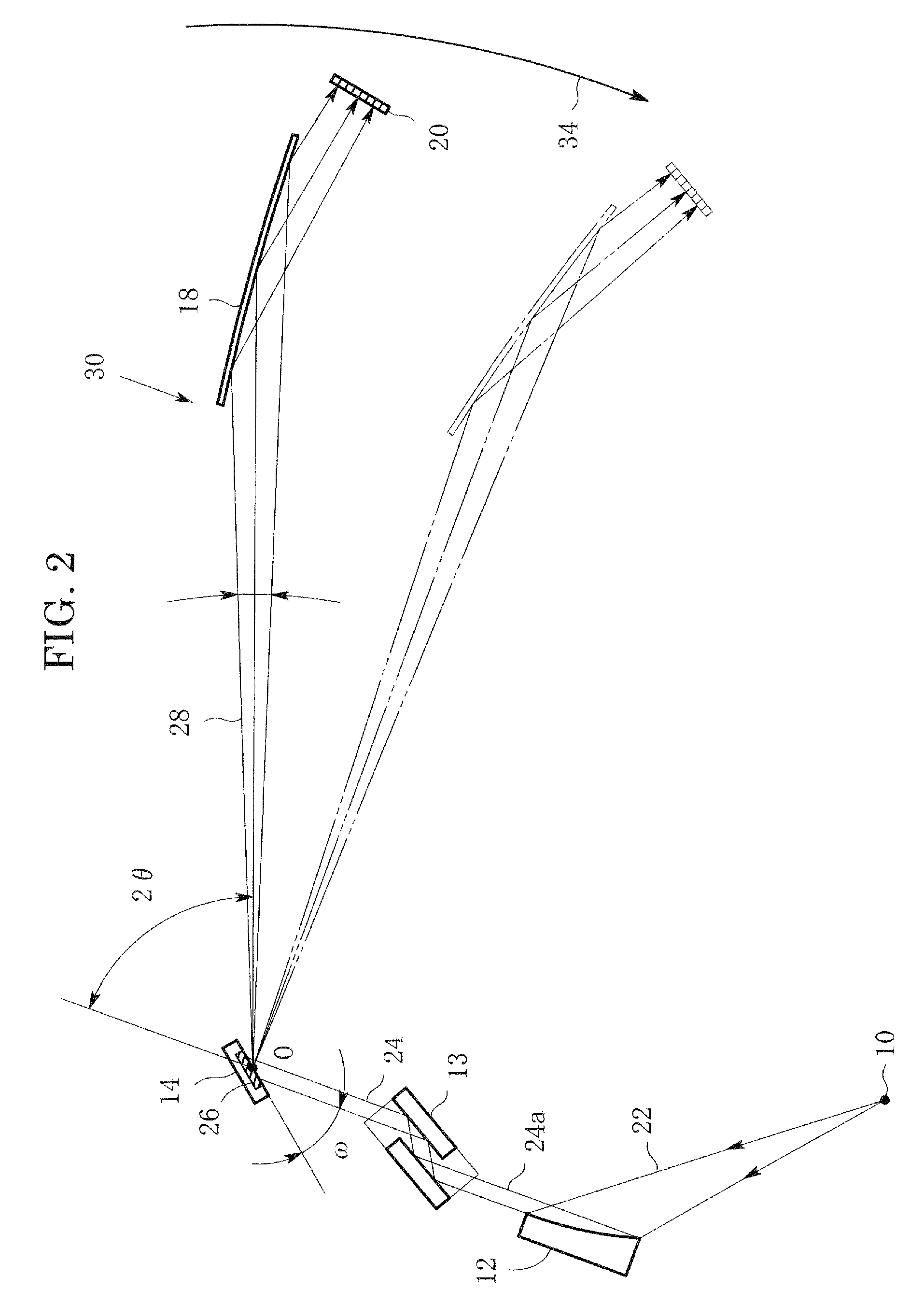
InactiveUS8340248B2Convenient angleSmall intensityX-ray spectral distribution measurementNanoinformaticsSoft x rayLight beam
In an X-ray diffraction method, an X-ray parallel beam is incident on a sample, and diffracted X-rays from the sample are reflected at a mirror and thereafter detected by an X-ray detector. The reflective surface of the mirror is a combination of plural flat reflective surfaces, the respective centers of which are located on an equiangular spiral having a center that is located on a surface of the sample. The X-ray detector is one-dimensional position-sensitive in a plane parallel to the diffraction plane. X-rays that have been reflected at different flat reflective surfaces reach different points on the X-ray detector respectively. A correction is performed for separately recognizing different reflected X-rays that may have been reflected at the different flat reflective surfaces, and might be mixed with each other on the same detecting region of the X-ray detector.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
X-ray diffraction apparatus and x-ray diffraction method
InactiveUS20090086921A1Superior angular resolutionLess reductionHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionLattice planeX-ray
In an X-ray diffraction method using the parallel beam method, an X-ray parallel beam is incident on a sample, and diffracted X-rays from the sample are reflected at a mirror and thereafter detected by an X-ray detector. The reflective surface of the mirror has a shape of an equiangular spiral that has a center located on the surface of the sample. A crystal lattice plane that causes reflection is parallel to the reflective surface at any point on the reflective surface. The X-ray detector is one-dimensional position sensitive in a plane parallel to the diffraction plane. A relative positional relationship between the mirror and the X-ray detector is determined so that reflected X-rays from different points on the reflective surface of the mirror reach different points on the X-ray detector respectively. This X-ray diffraction method is superior in angular resolution, and is small in X-ray intensity reduction, and is simple in structure.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
Method and its apparatus for inspecting defects
InactiveUS7869024B2High sensitivityIncrease speedMaterial analysis by optical meansLight polarisation measurementEdge surfaceUltimate tensile strength
A defect inspection apparatus is capable of inspecting an extremely small defect present on the top and edge surfaces of a sample such as a semiconductor substrate or a thin film substrate with high sensitivity and at high speed. The defect inspection apparatus has an illumination optical system, a plurality of detection optical units and a signal processor. One or more of the detection optical units receives either light diffracted from an edge portion of the sample or light diffracted from an edge grip holding the sample. The one or more of the detection optical units shields the diffracted light received by the detection optical unit based on a signal obtained by monitoring an intensity of the diffracted light received by the detection optical unit in order to inspect a sample portion located near the edge portion and a sample portion located near the edge grip.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
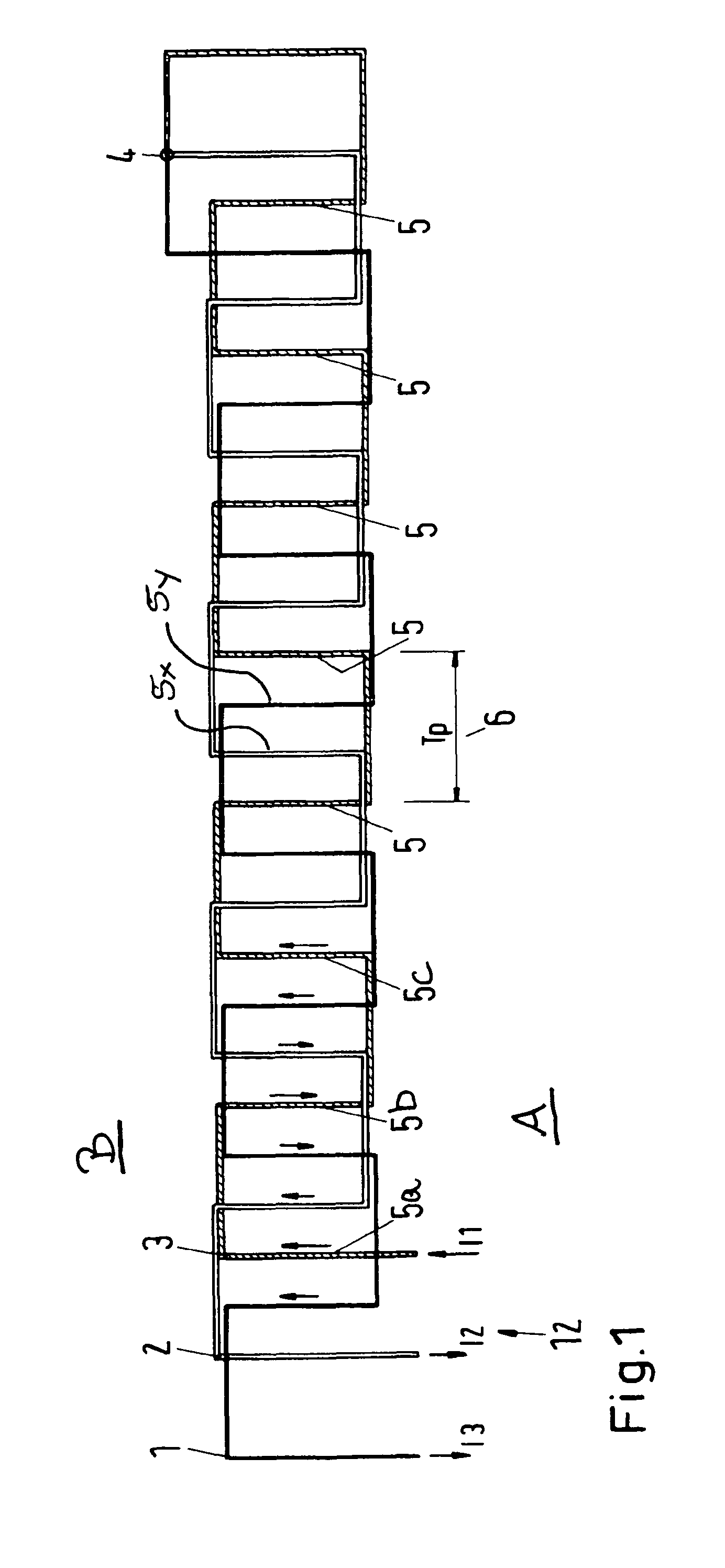
Transferring electric energy to a vehicle
ActiveUS8590682B2Easily realizedLeakage inductivityRail devicesCircuit arrangementsElectricityElectrical conductor
The invention relates to a system for transferring electric energy to a track bound vehicle, in particular to a light rail vehicle, such as a tram, wherein the system comprises an electric conductor arrangement (12) for producing an electromagnetic field and for thereby transferring the energy to the vehicle, the electric conductor arrangement (12) comprises at least one line (1, 2, 3) for carrying one phase of an alternating voltage or current, the line (1, 2, 3) extends along the track, the line (1, 2, 3) is arranged in such a manner that it produces—at each point in time while the alternating electric current is flowing through the line (1, 2, 3)—a row of successive magnetic poles (at sections 5) of an electromagnetic field, wherein the successive magnetic poles have alternating magnetic polarities, the row of successive magnetic poles extends in the travel direction of the vehicle which is defined by the track.
Owner:BOMBARDIER TRANSPORTATION GMBH
Sheet-fed scanning device capable of detecting a document edge
ActiveUS20050141055A1Facilitate document edge detectionFacilitate document edge detection documentPictoral communicationPaper documentDocument preparation
A sheet-fed scanning device capable of detecting a document edge includes a scanning module and an automatic document feeder. The scanning module scans a document with a light ray. The automatic document feeder feeds the document across a scanning region on a sheet passageway for the scanning module to scan. In this invention, a section of a guide plate of the sheet passageway located within the scanning region is formed with a concave portion, wherein the document moving across the scanning region is located between the concave portion and the scanning module, such that the intensity of a first brightness of the concave portion sensed by the scanning module is far smaller than the intensity of a second brightness of the document sensed by the scanning module. Thus, it is possible to facilitate the document edge detection and the document skew correction.
Owner:AVISION
Crash box arrangement and method of detecting the intensity of an impact
InactiveUS20120319413A1Risk minimizationInhibition effectPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementBumpersEngineeringHardness
A crash box arrangement includes a hollow member having a first hardness and defining a hollow space in communication with at least one ventilation opening; and a damper having a second hardness which is smaller than the first hardness. The damper has an impulse cavity in communication with the hollow space of the hollow member.
Owner:BENTELER AUTOMOBILTECHNIK GMBH
X-ray diffraction method and x-ray diffraction apparatus
InactiveUS20100246768A1Convenient angleSmall intensityX-ray spectral distribution measurementNanoinformaticsSoft x rayImage resolution
In an X-ray diffraction method using the parallel beam method, an X-ray parallel beam is incident on a sample, and diffracted X-rays from the sample are reflected at a mirror and thereafter detected by an X-ray detector. The reflective surface of the mirror consists of a combination of plural flat reflective surfaces. The respective centers of the flat reflective surfaces are located on an equiangular spiral having a center that is located on a surface of the sample. The X-ray detector is one-dimensional position-sensitive in a plane parallel to the diffraction plane. X-rays that have been reflected at different flat reflective surfaces reach different points on the X-ray detector respectively. A corrective operation is performed for separately recognizing the different reflected X-rays on the assumption that the different reflected X-rays that have been reflected at the different flat reflective surfaces might be unfortunately mixed each other on the same detecting region of the X-ray detector. This X-ray diffraction method is superior in angular resolution, and is small in X-ray intensity reduction, and is simple in structure.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
Signal processing apparatus, ultrasonic apparatus, control method for signal processing apparatus, and control method for ultrasonic apparatus
ActiveUS8784317B2Promote generationSpeed up extractionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesScan lineChange positions
A signal processing apparatus scans a beam of elastic waves into an object to be examined, acquires received waveform data of a plurality of scan lines, and performs signal processing to form a tomographic image of said object to be examined from the received waveform data of the plurality of scan lines. The signal processing apparatus includes a scan line correlation calculation part (009) that calculates a correlation value of received waveform data between a first scan line and a second scan line that has a prescribed correlation with the first scan line, for a plurality of positions on the scan lines, and a correlation change position extraction part (010) that extracts, from among the plurality of positions on said scan lines, a position at which the correlation value becomes a value different from a prescribed value as a position at which a unique region can exist.
Owner:CANON KK
X-ray radiator to generate quasi-monochromatic x-ray radiation, and radiography x-ray acquisition system employing same
ActiveUS8537970B2Increase radiation intensityIncrease the areaNanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionLattice planeCrystalline materials
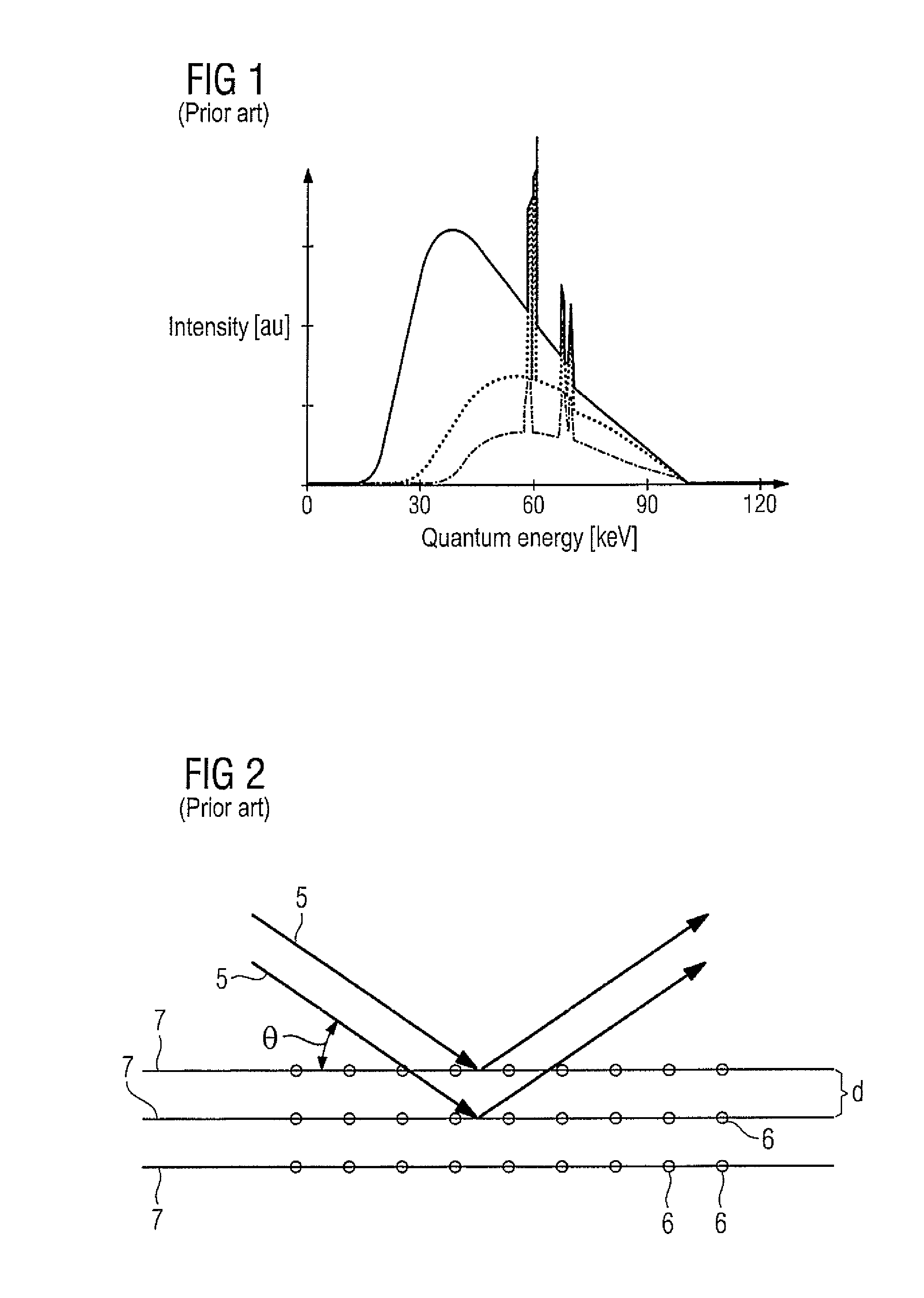
For a quasi-monochromatic x-ray radiation with high radiation intensity, an x-ray radiator generates quasi-monochromatic x-ray radiation to expose a subject from a point-shaped radiation source that emits a polychromatic x-ray radiation, and having a diffraction device to diffract the polychromatic x-ray radiation. The diffraction device has a super-mirror made of crystalline material with a flat surface. In the super-mirror, the crystalline material has at least one (in particular continuous) variation of the lattice plane spacing of the crystal lattice. The radiation source and the diffraction device are arranged such that quasi-monochromatic x-ray radiation is generated from the polychromatic x-ray radiation by partial reflection at the super-mirror.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
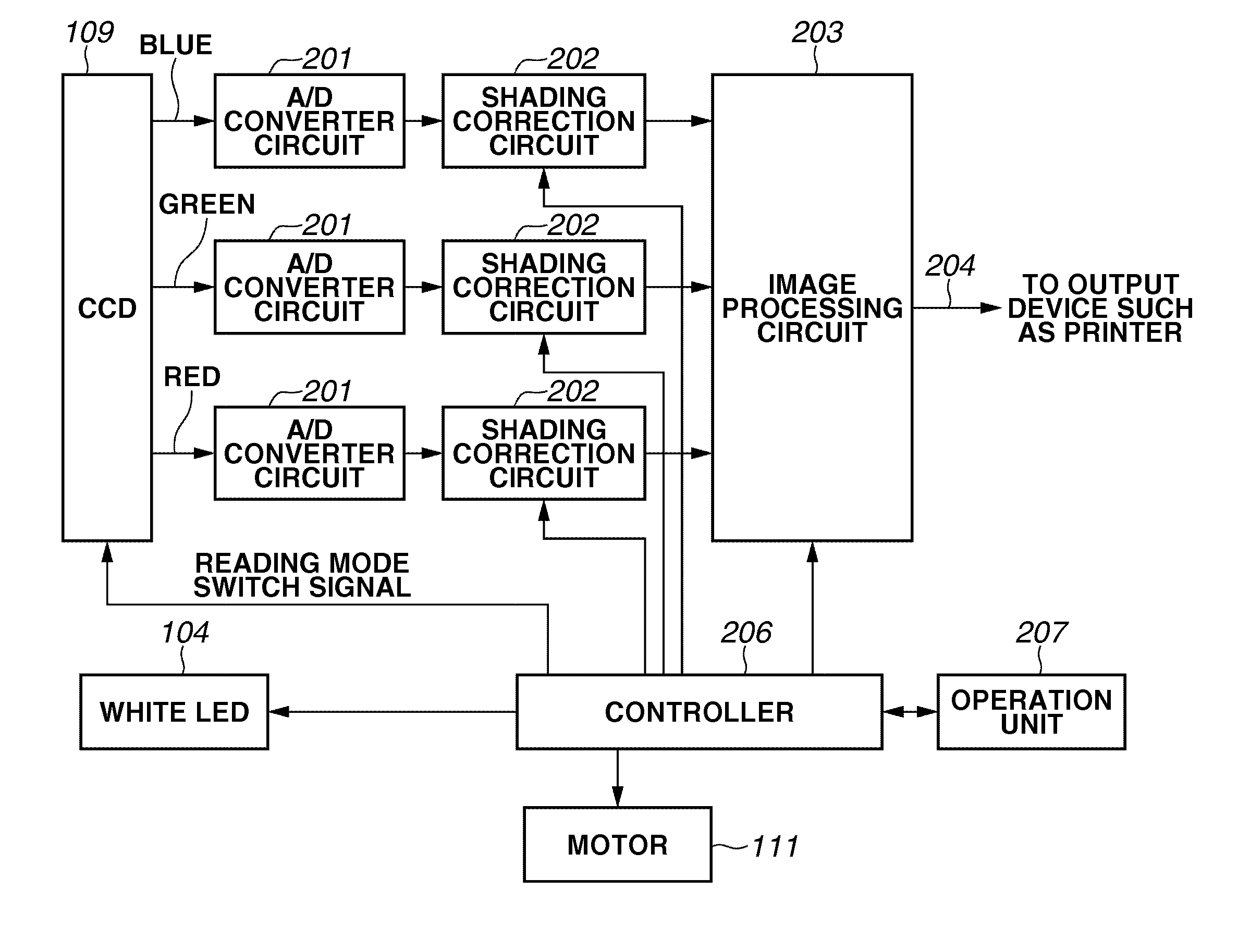
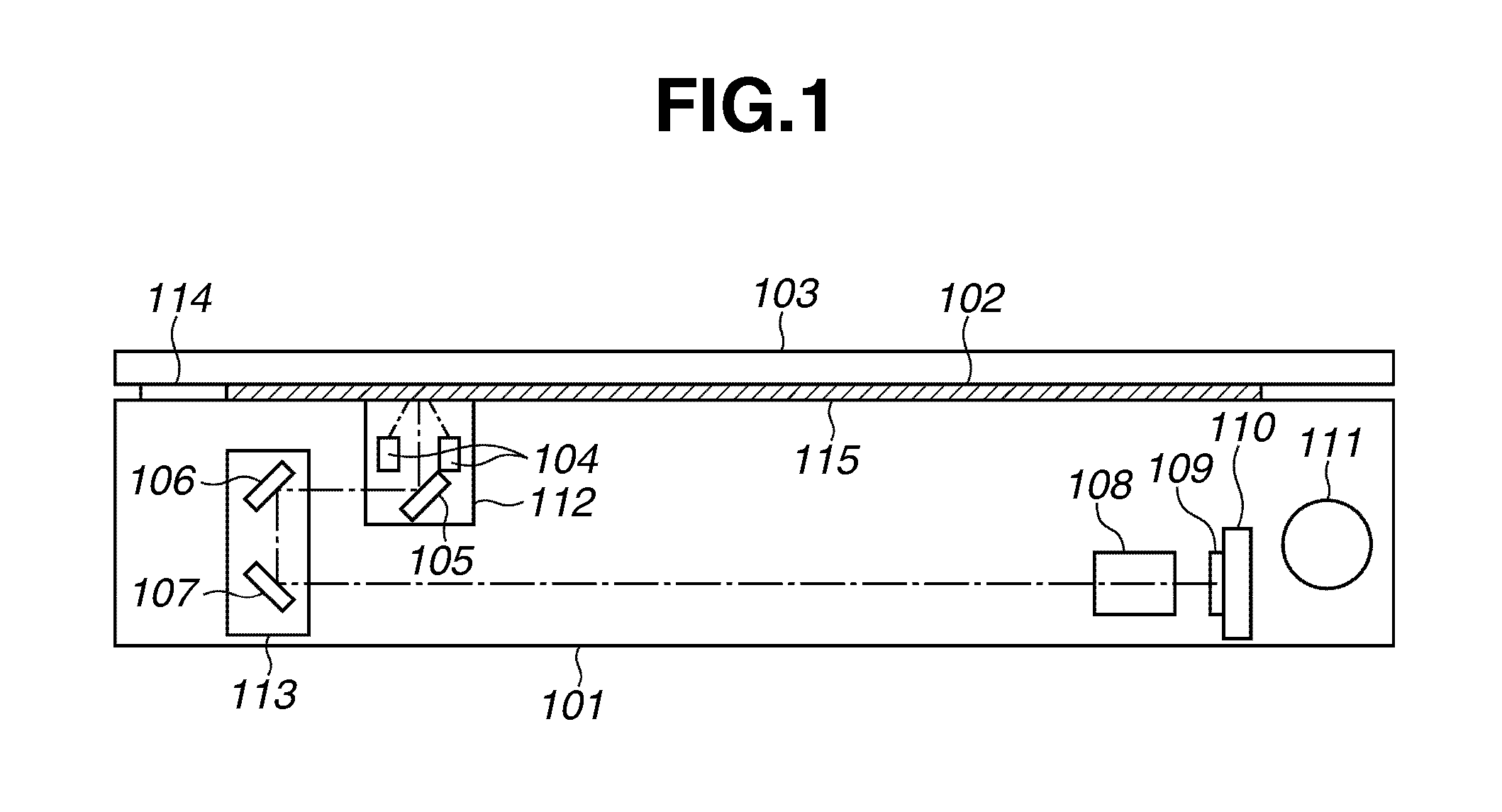
Document reading apparatus
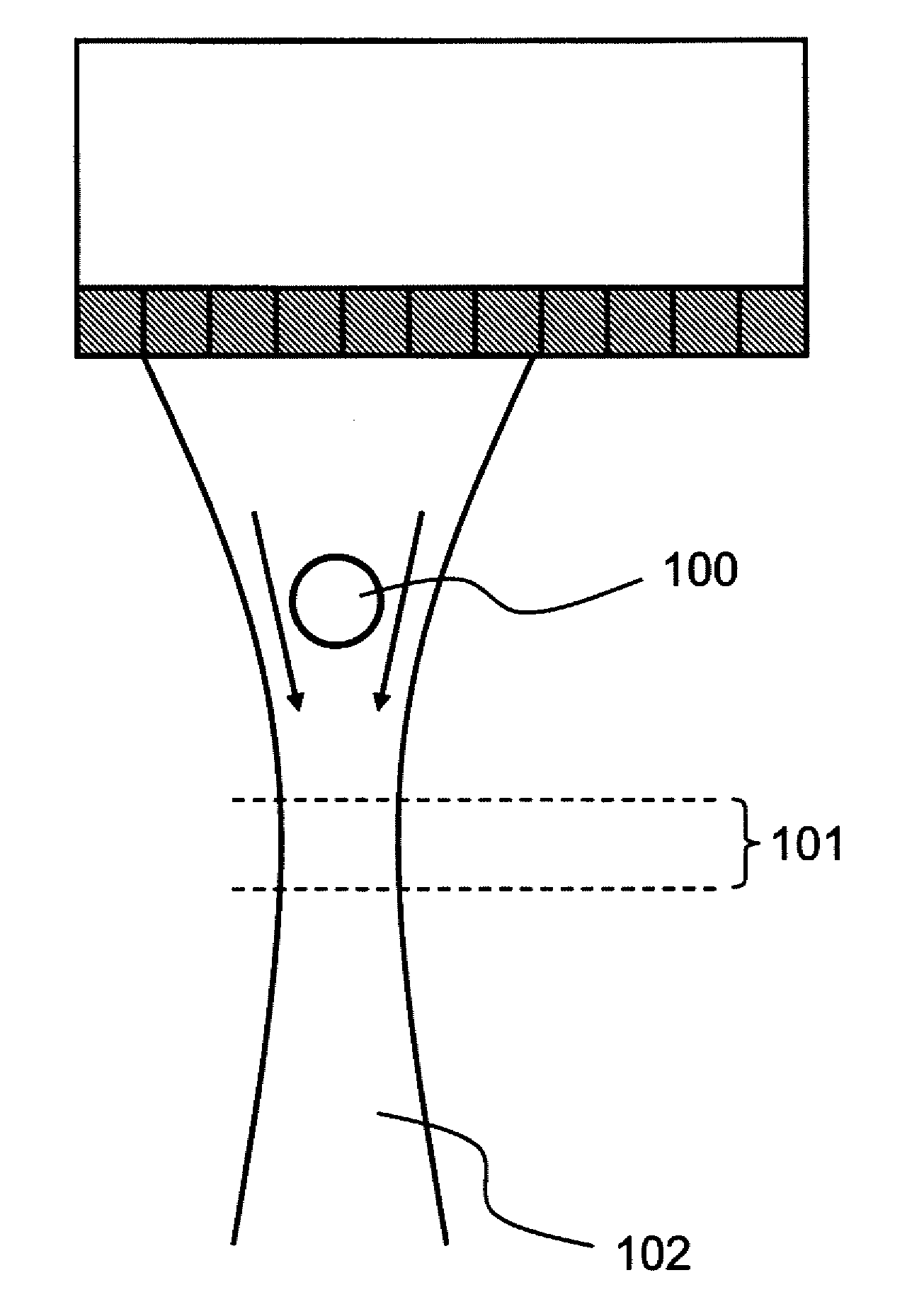
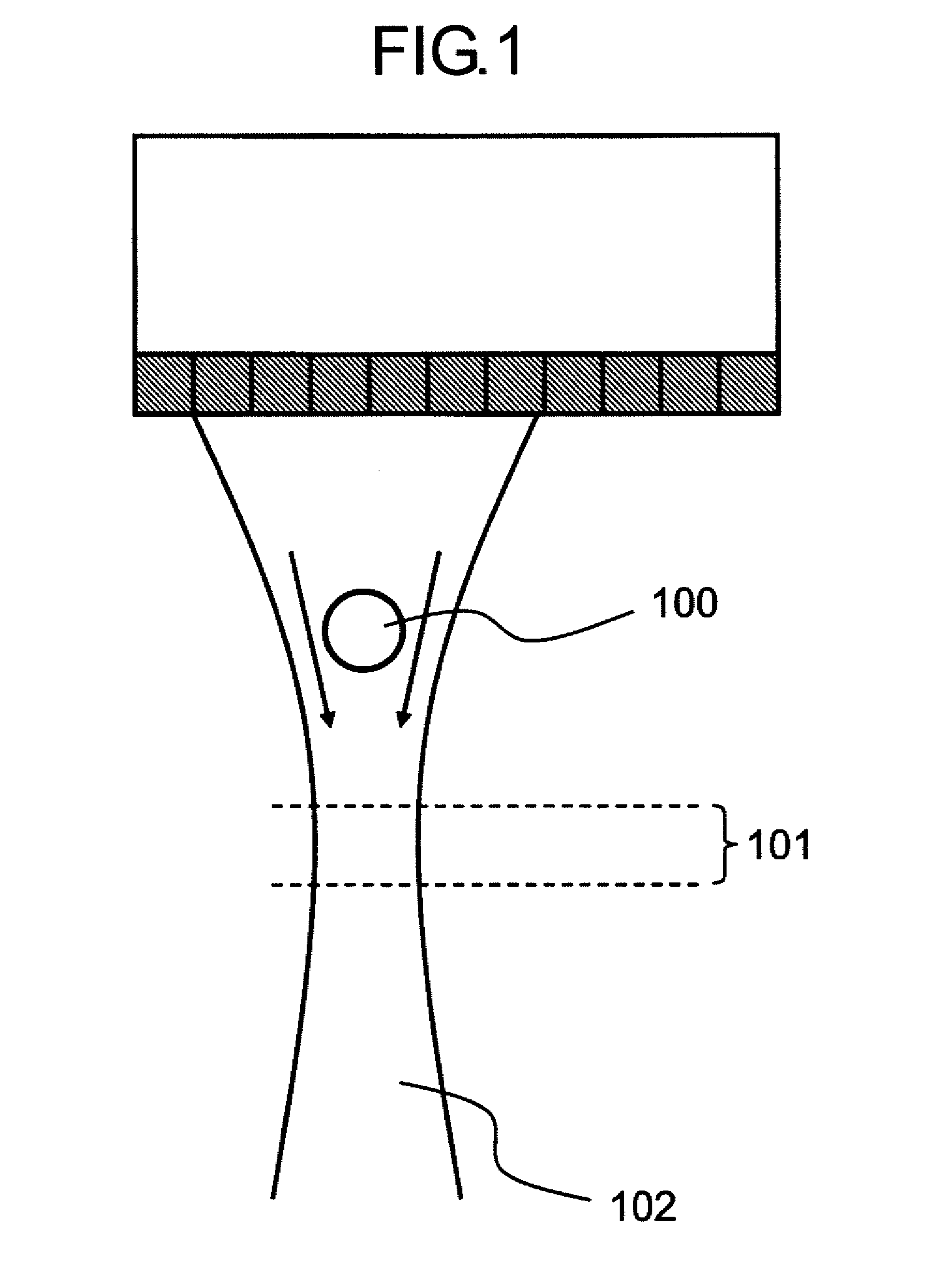
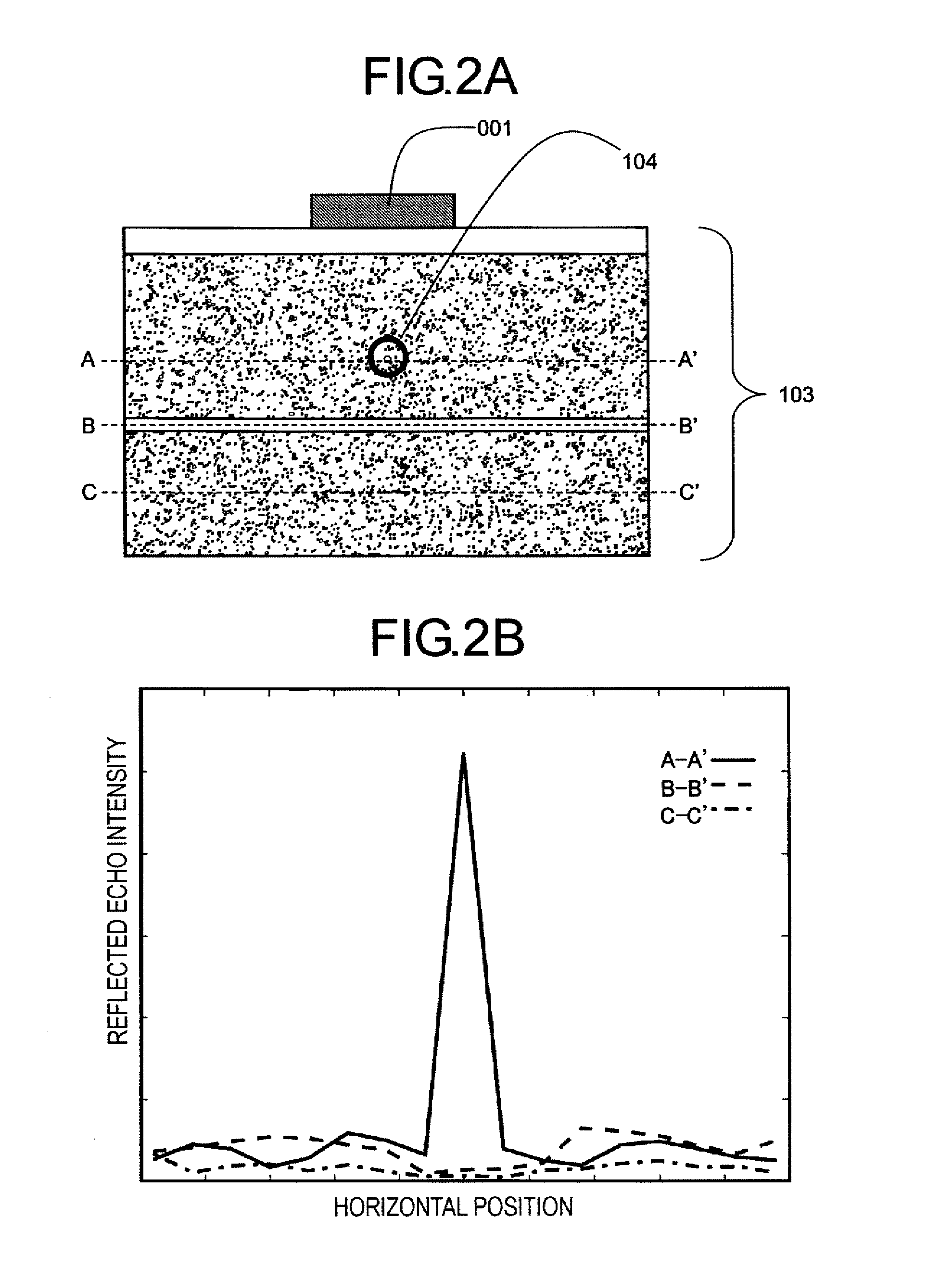
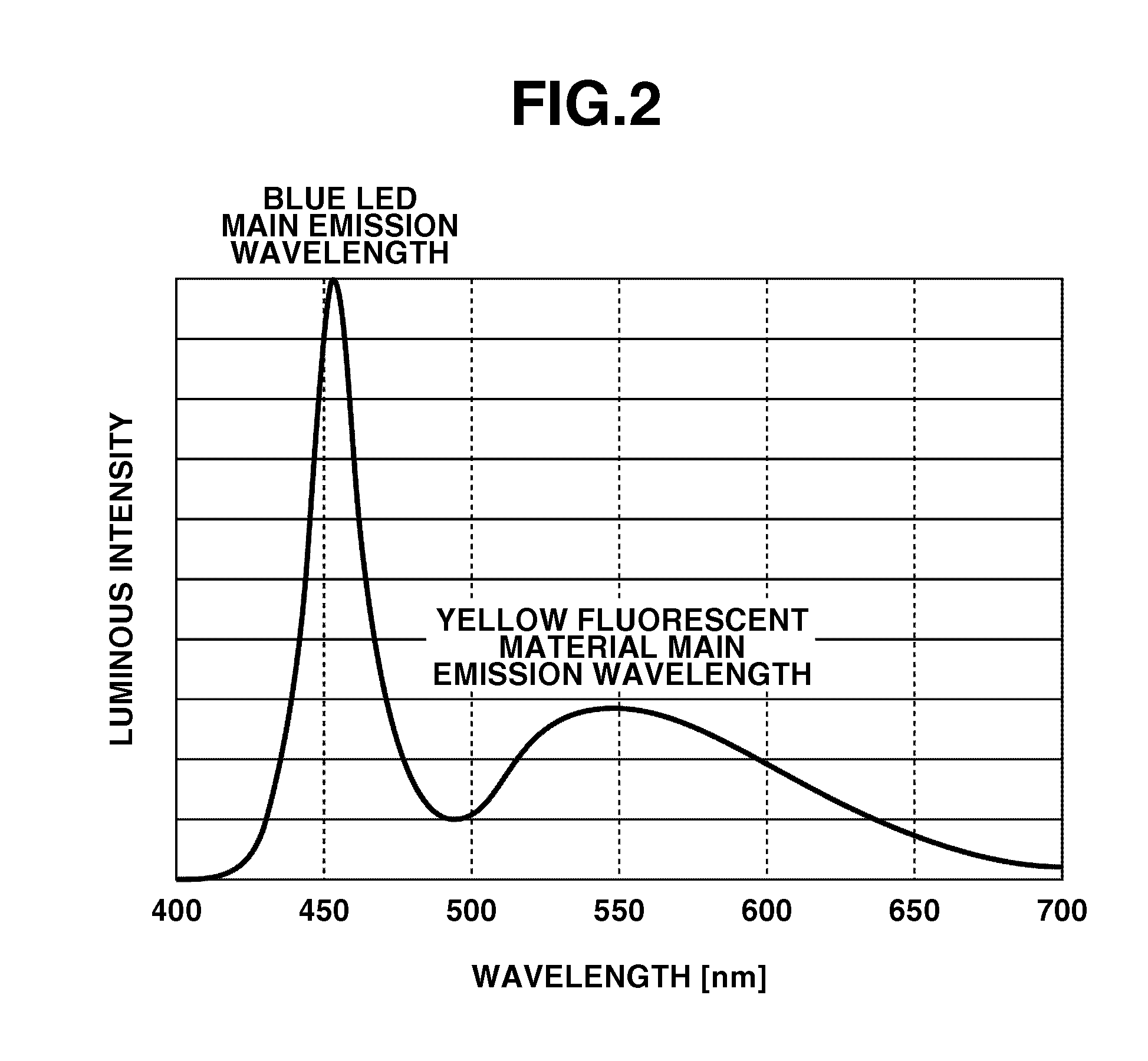
ActiveUS20100195171A1Small intensityDigitally marking record carriersDischarge tube luminescnet screensLine sensorPeak value
A document reading apparatus includes a white LED including an LED and a fluorescent material and configured to illuminate a document reading position with light, a reading unit having a color line sensor and a monochrome line sensor and configured to read an image of a document illuminated with the light emitted from the white LED, and a filter arranged on an optical path between the monochrome line sensor and the document, and wherein the filter is configured to suppress transmission of light at a peak wavelength of the LED so that, regarding an intensity of light to be received on the monochrome line sensor, the intensity of the light at the peak wavelength of the LED is smaller than the intensity of the light at the peak wavelength of the fluorescent material when the light emitted from the LED is received.
Owner:CANON KK
Gaming system
InactiveUS7780165B2Small intensityHandling be eliminatedLottery apparatusBoard gamesComputer hardwareHome position
Owner:CUDLIPP WILLIAM OWEN
Vehicle lighting fixture
ActiveUS10174902B2Even projectionImproved luxurious senseMechanical apparatusOptical signallingLight guidePrism
A vehicle lighting fixture can achieve uniform projection of light while being capable of providing improved luxurious sense of projected light. The vehicle lighting fixture can include a housing, an outer lens configured to cover an opening of the housing to define a lighting chamber; and a light source and a light guiding lens located in the lighting chamber. The light guiding lens is configured so as to receive light from the light source and guide the light to a light exiting surface thereof for light projection. The light guiding lens has a functional surface which is opposite to the light exiting surface and can include a plurality of flute cuts configured to diffuse light and a plurality of prism cuts configured to reflect light. The plurality of prism cuts are arranged at random on the functional surface.
Owner:STANLEY ELECTRIC CO LTD
Group III nitride semiconductor light-emitting device and method for producing the same
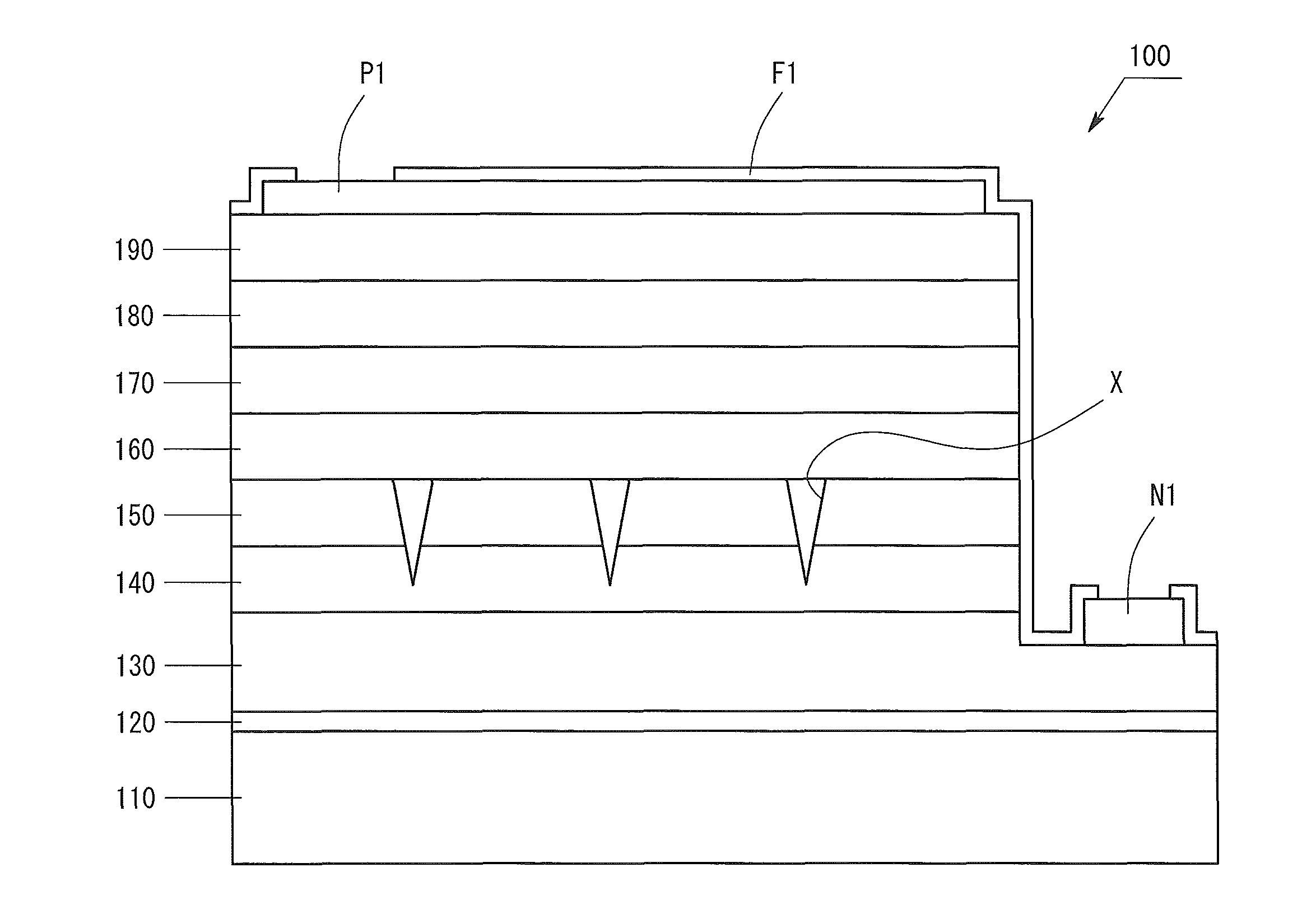
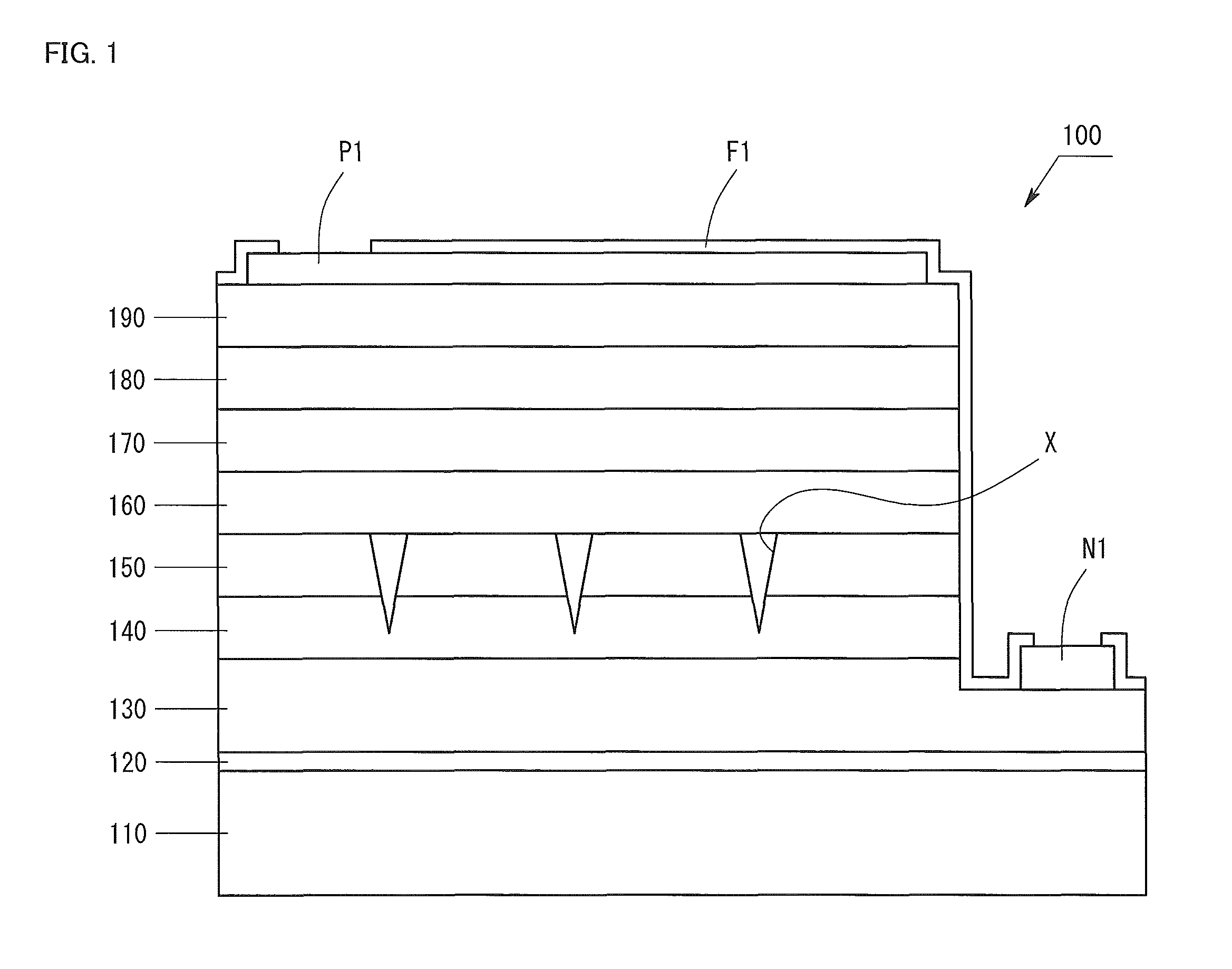
ActiveUS9029832B2Strain applied to the light-emitting layer is relaxedEnhanced glowSemiconductor devicesContact layerLight emission
The invention provides a Group III nitride semiconductor light-emitting device in which the strain in the light-emitting layer is relaxed, thereby attaining high light emission efficiency, and a method for producing the device. The light-emitting device of the present invention has a substrate, a low-temperature buffer layer, an n-type contact layer, a first ESD layer, a second ESD layer, an n-side superlattice layer, a light-emitting layer, a p-side superlattice layer, a p-type contact layer, an n-type electrode N1, a p-type electrode P1, and a passivation film F1. The second ESD layer has pits X having a mean pit diameter D. The mean pit diameter D is 500 Å to 3,000 Å. An InGaN layer included in the n-side superlattice layer has a thickness Y satisfying the following condition: −0.029×D+82.8≦Y≦−0.029×D+102.8.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
X-ray radiator to generate quasi-monochromatic x-ray radiation, and radiography x-ray acquisition system employing same
ActiveUS20110299658A1Increase radiation intensityIncrease exposure areaNanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionLattice planeCrystalline materials
For a quasi-monochromatic x-ray radiation with high radiation intensity, an x-ray radiator generates quasi-monochromatic x-ray radiation to expose a subject from a point-shaped radiation source that emits a polychromatic x-ray radiation, and having a diffraction device to diffract the polychromatic x-ray radiation. The diffraction device has a super-mirror made of crystalline material with a flat surface. In the super-mirror, the crystalline material has at least one (in particular continuous) variation of the lattice plane spacing of the crystal lattice. The radiation source and the diffraction device are arranged such that quasi-monochromatic x-ray radiation is generated from the polychromatic x-ray radiation by partial reflection at the super-mirror.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
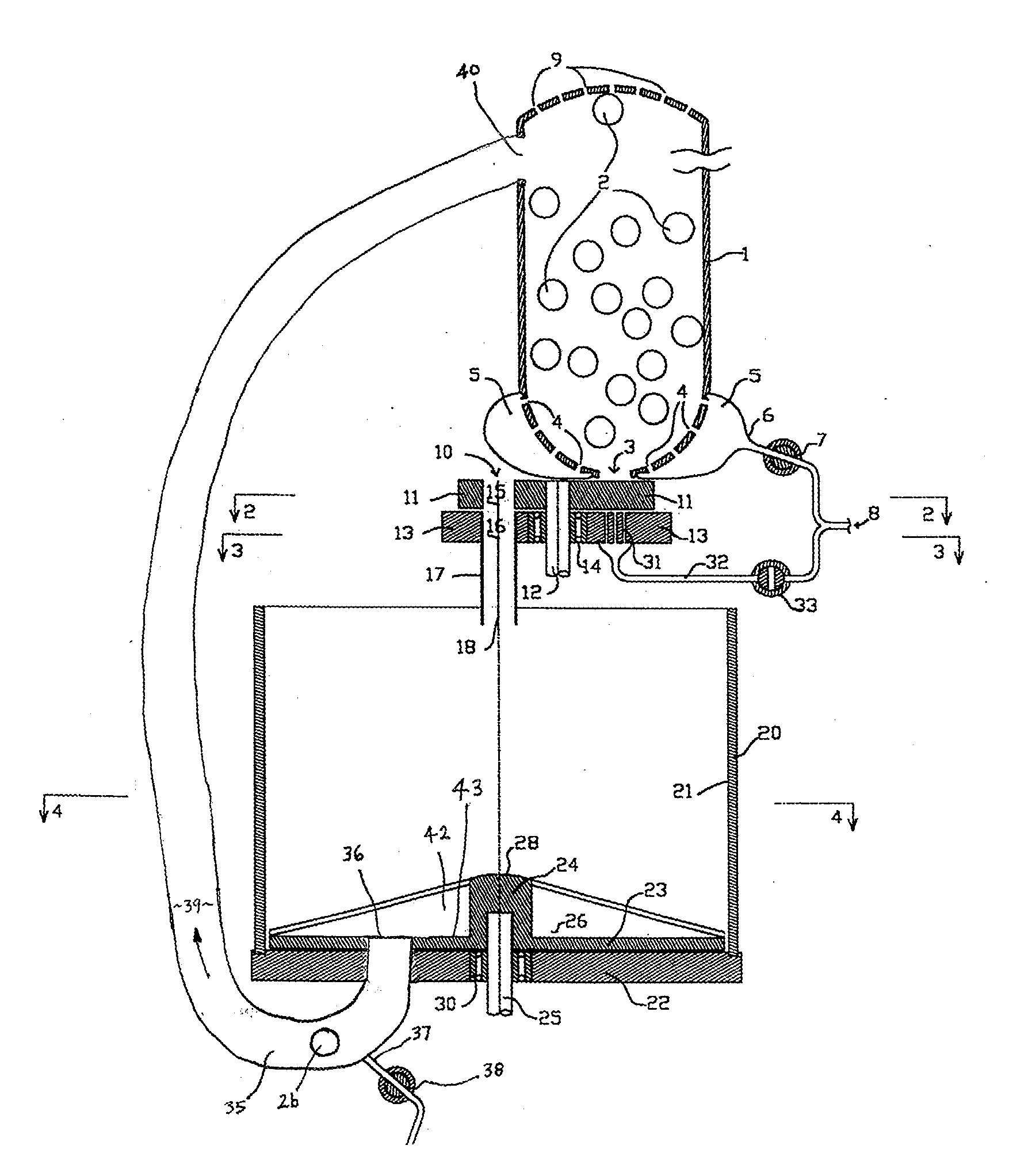
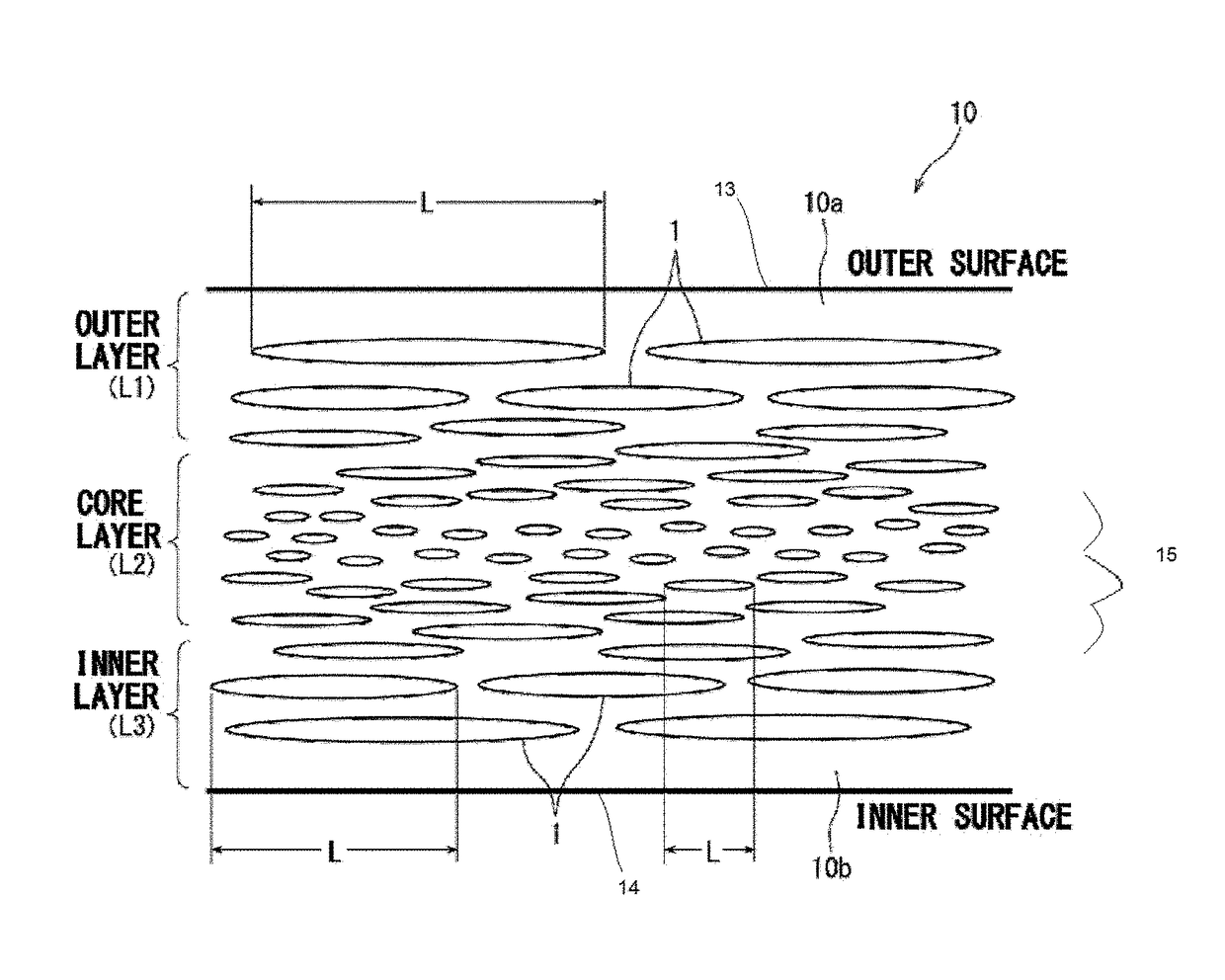
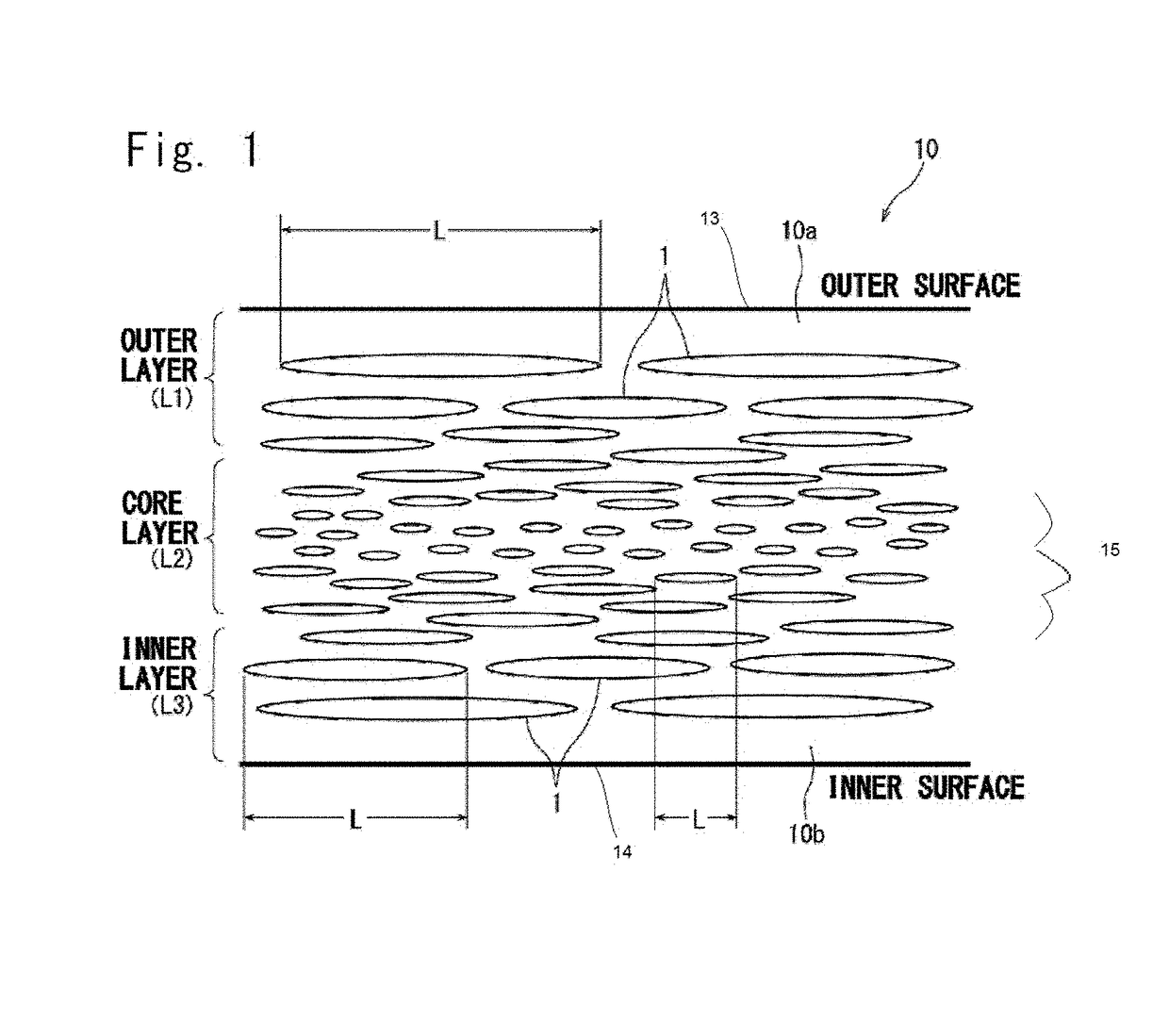
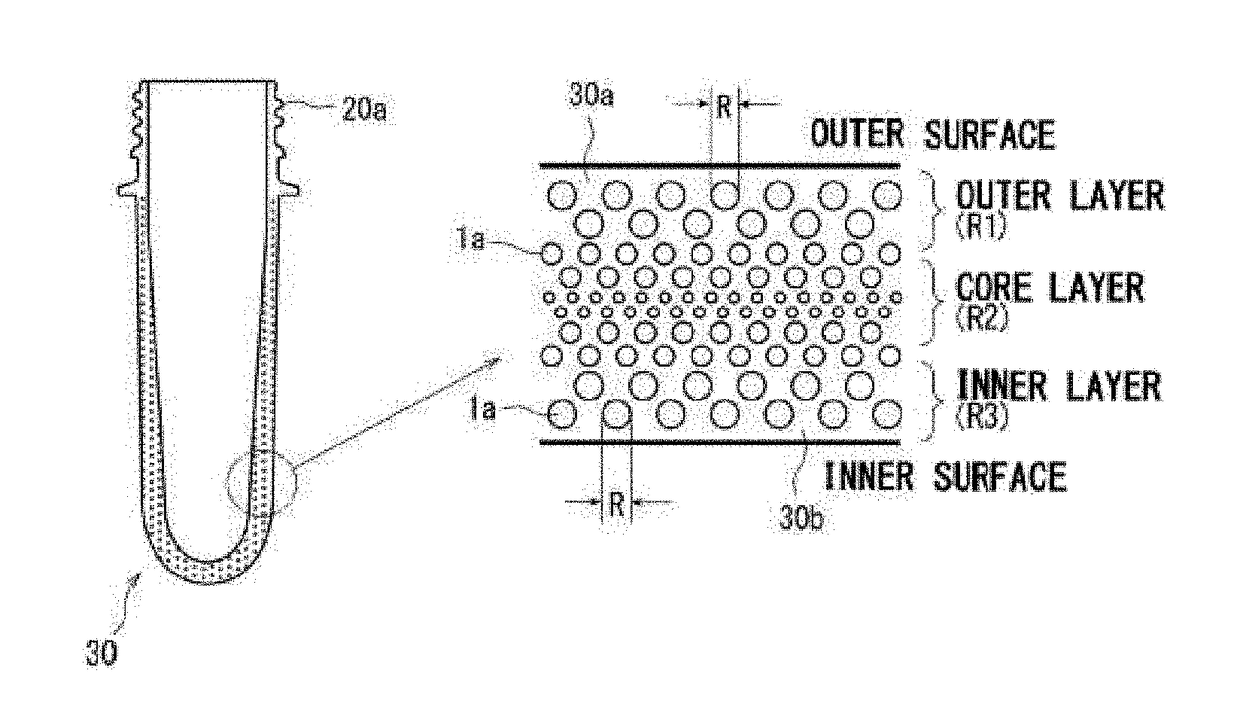
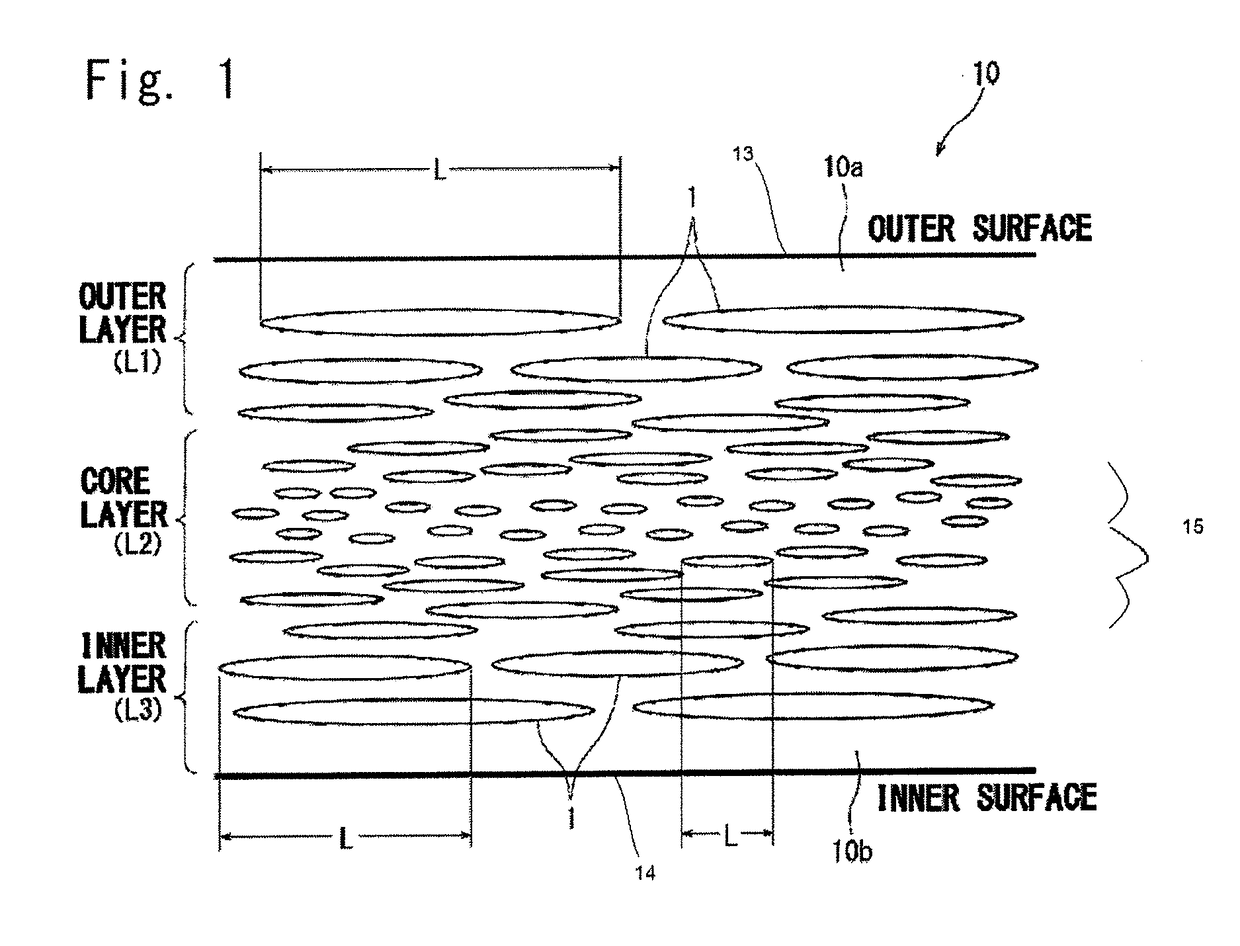
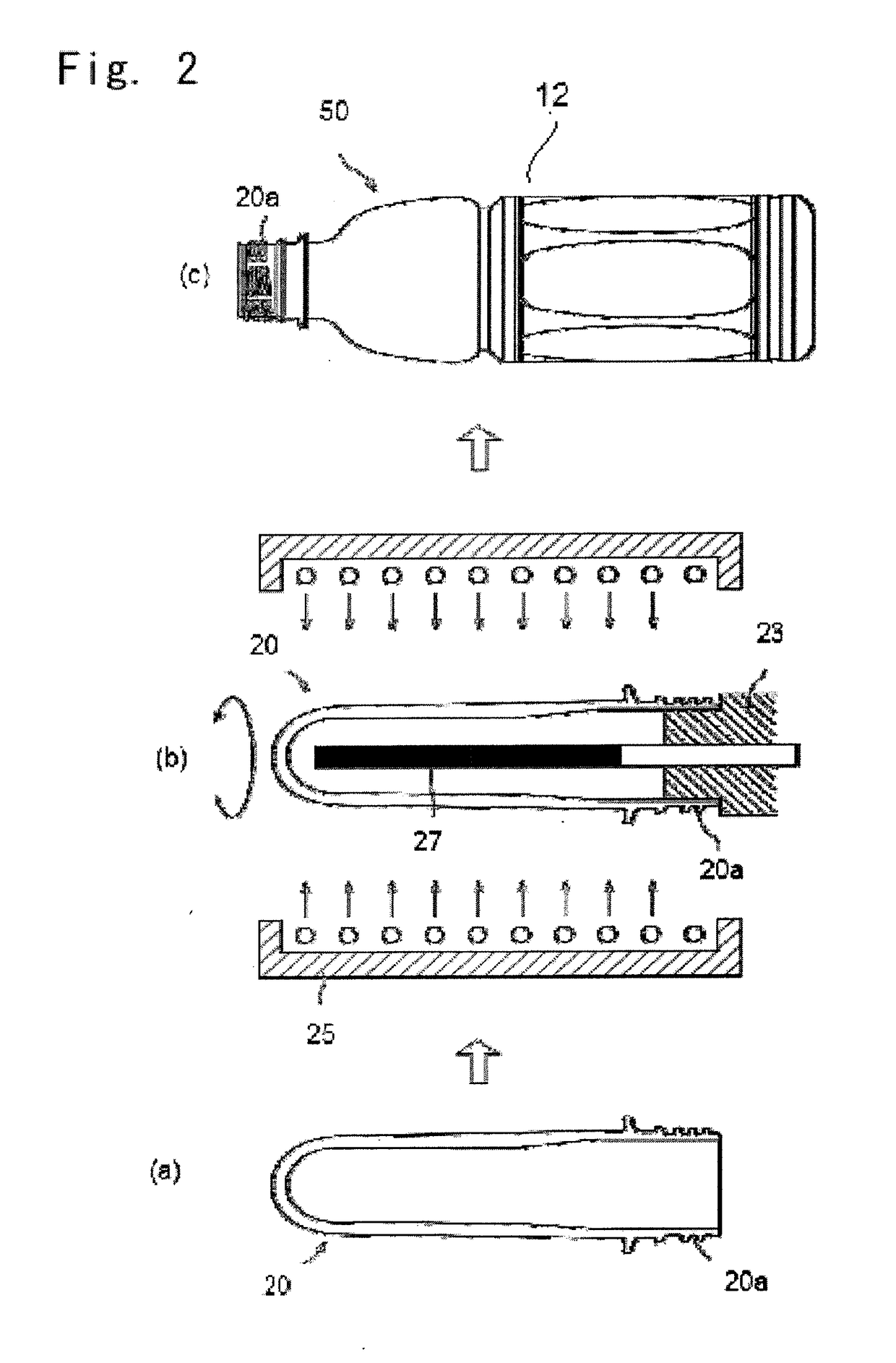
Foamed and stretched plastic bottle
A foamed and stretched plastic bottle having, in the body portion thereof, a foamed region in which foamed cells are distributed, wherein, in at least a portion of the foamed region, the lengths of the foamed cells in the axial direction of the bottle are so distributed as to gradually decrease as the positions of the foamed cells shift from the outer surface side of the body portion toward the central portion thereof and then gradually increase as their positions shift from the central portion thereof toward the inner surface side thereof. The foamed and stretched plastic bottle of the invention exhibits excellent light-shielding property.
Owner:TOYO SEIKAN GRP HLDG LTD
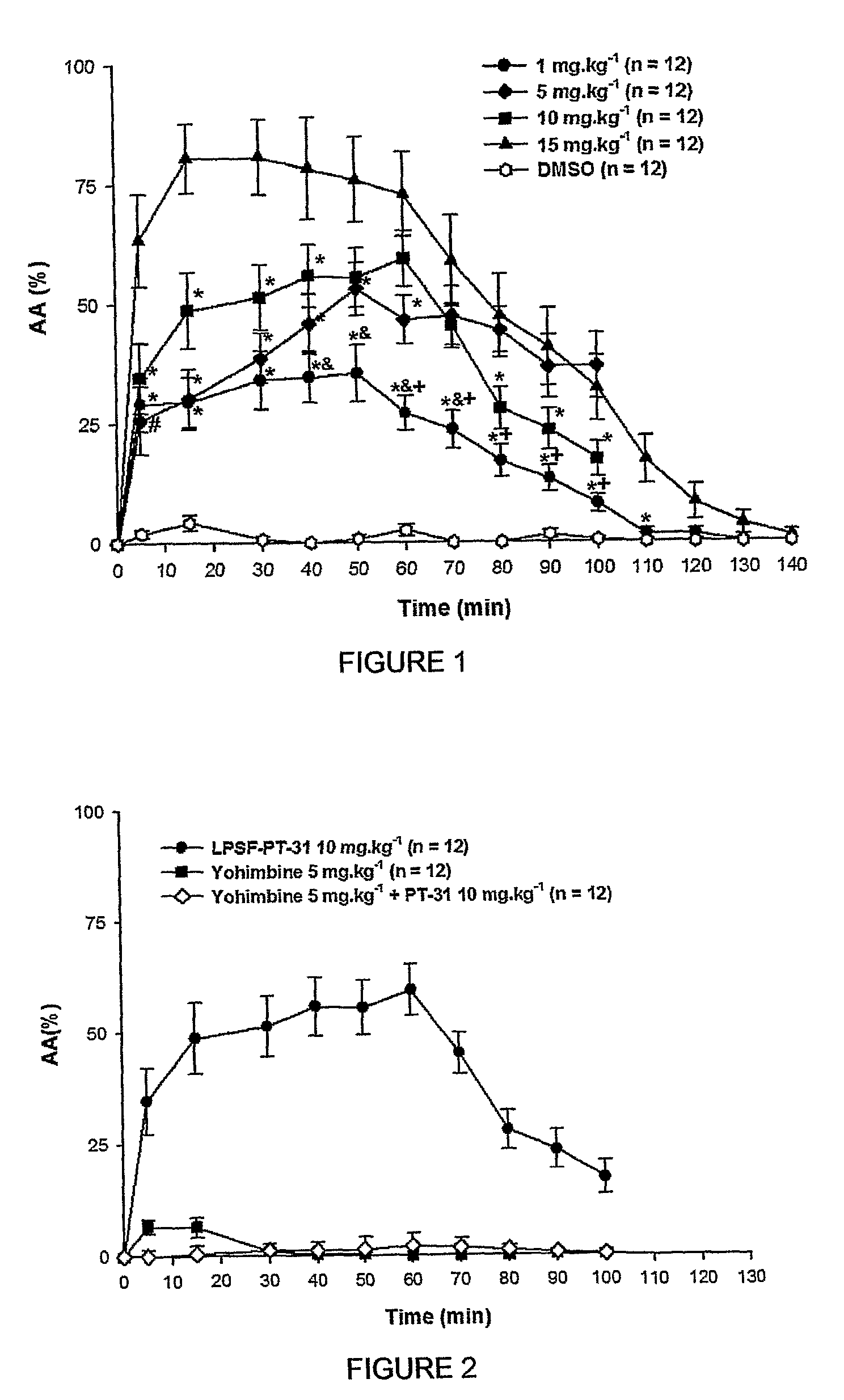
Compound with anesthetics activity, methods for its production and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same
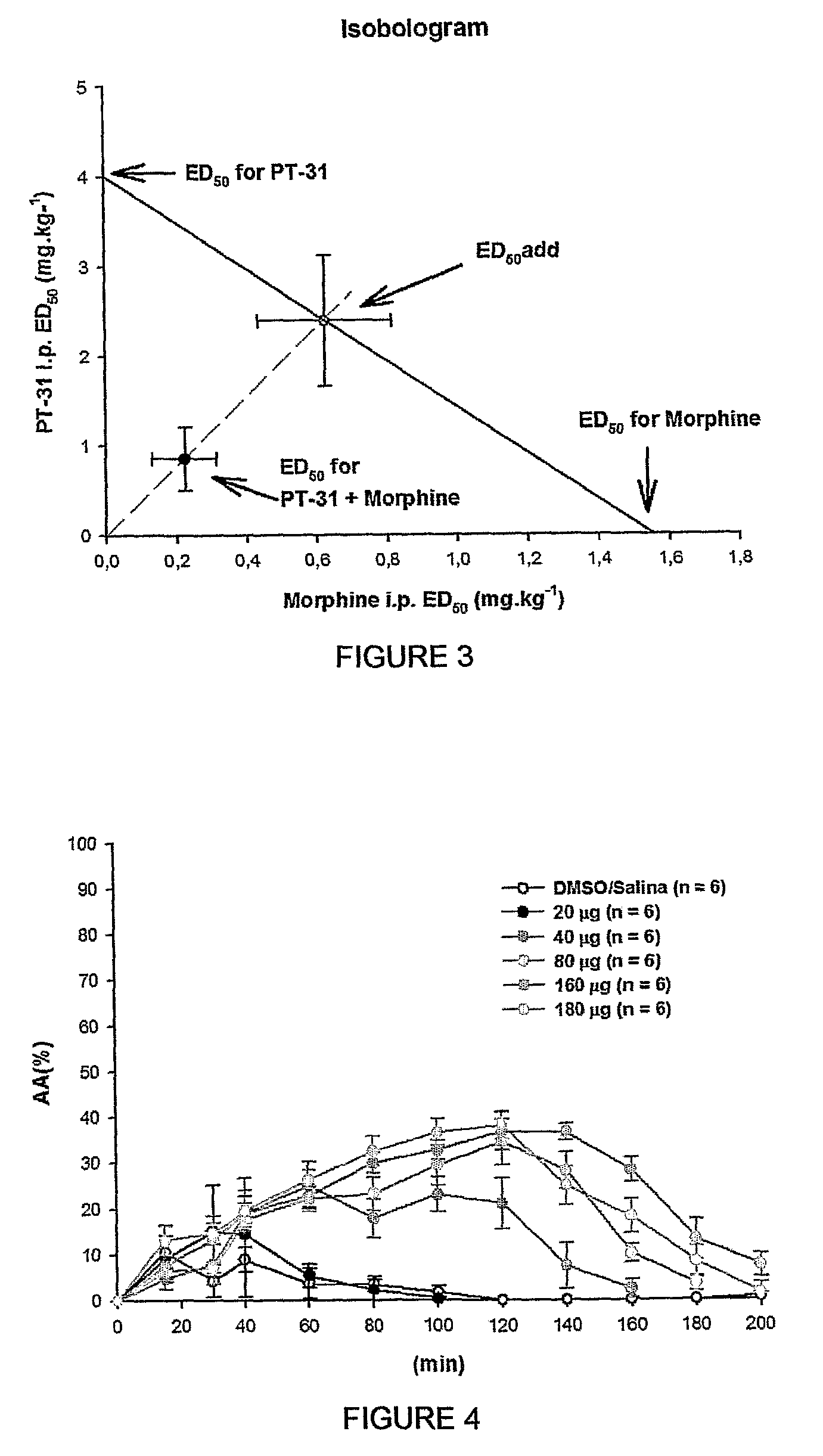
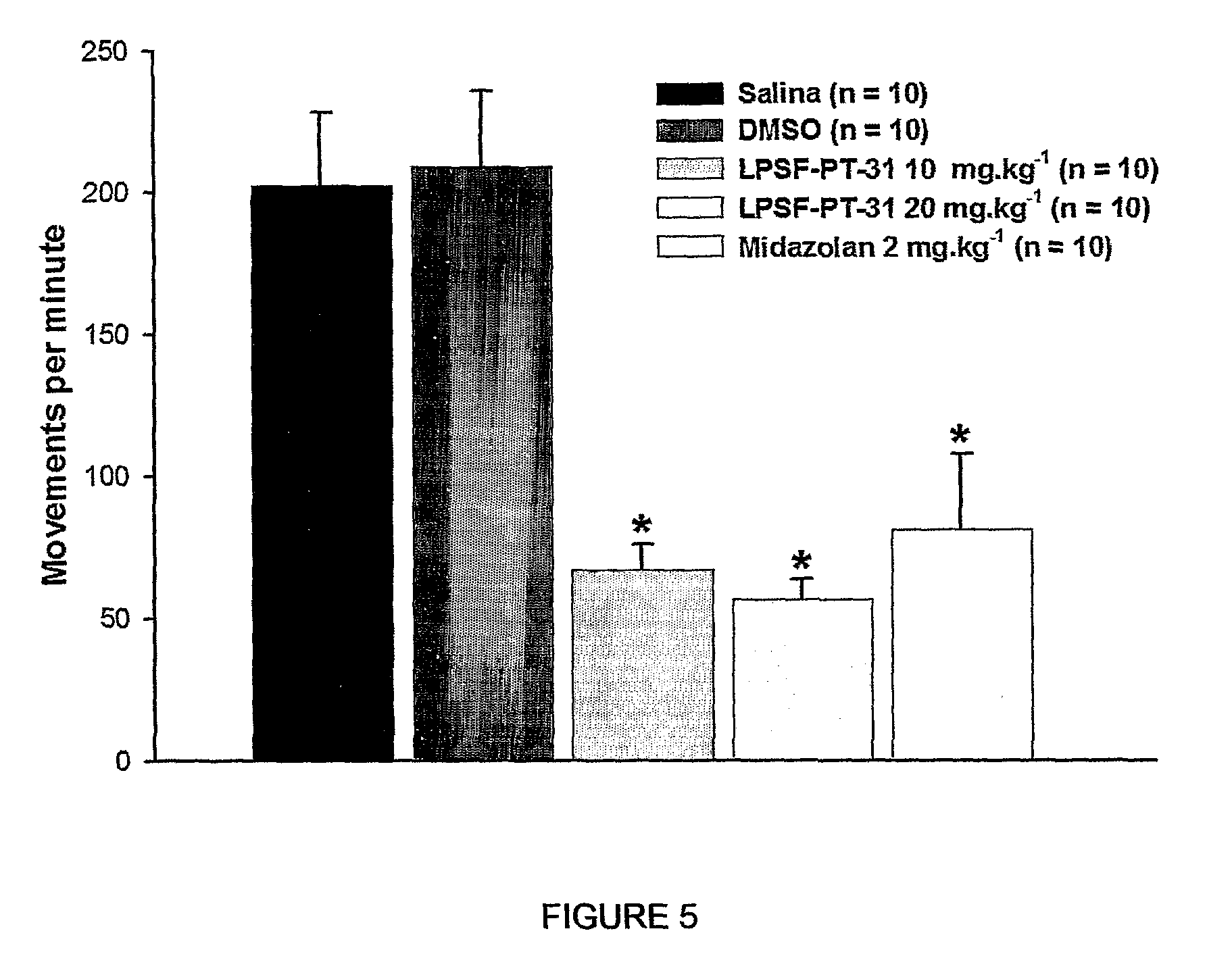
The present invention is related to a new series of chemical compounds, namely 3-benzyl-imidazolidine-2,4-dione substituted in the position 2 and / or 6 of benzyl ring by halogens as presented to the molecule named LPSF-PT-31, GIRSUPAN and its therapeutic use as drug with analgesic, sedative and adjuvant of anesthetics activities. The invention is also related to a process for production of said compounds as well as pharmaceutical compositions comprising them.
Owner:UFPE +1
Foamed and stretched plastic bottle
ActiveUS20170174383A1Novel distributionHigh strengthBottlesMachines/enginesPosition shiftPlastic bottle
Owner:TOYO SEIKAN GRP HLDG LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com