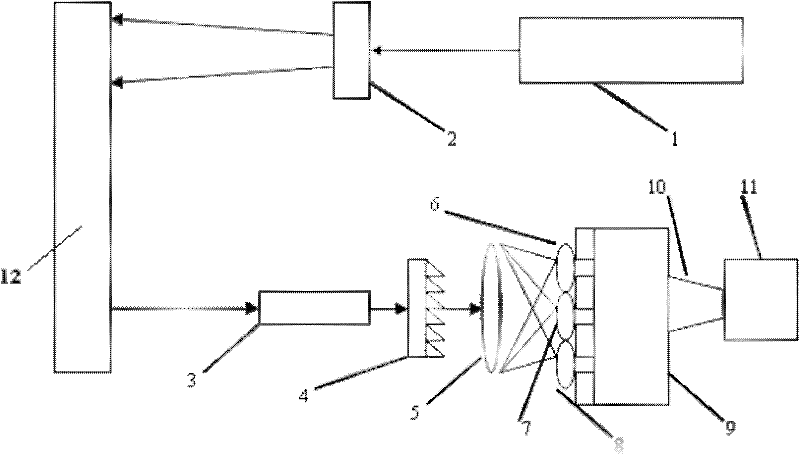
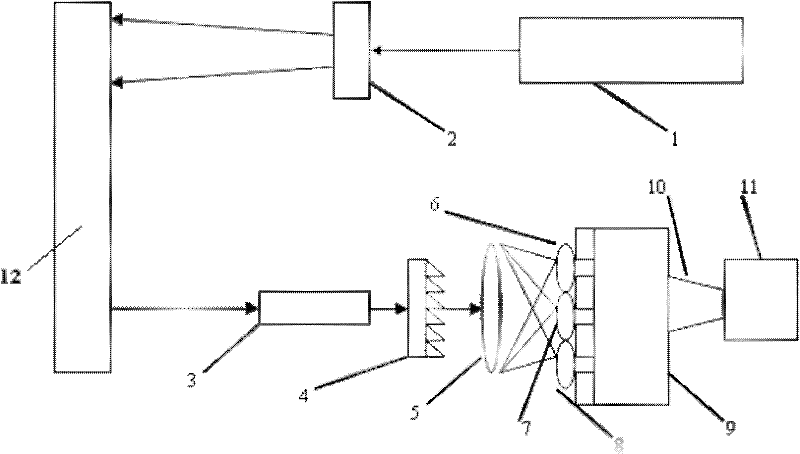
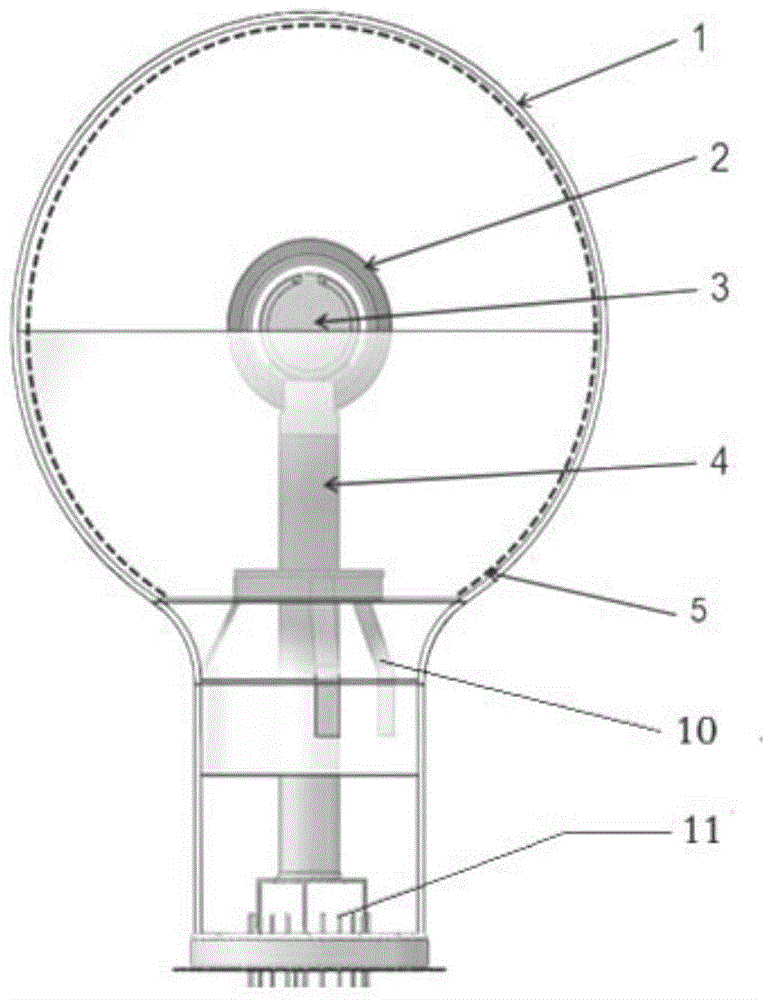
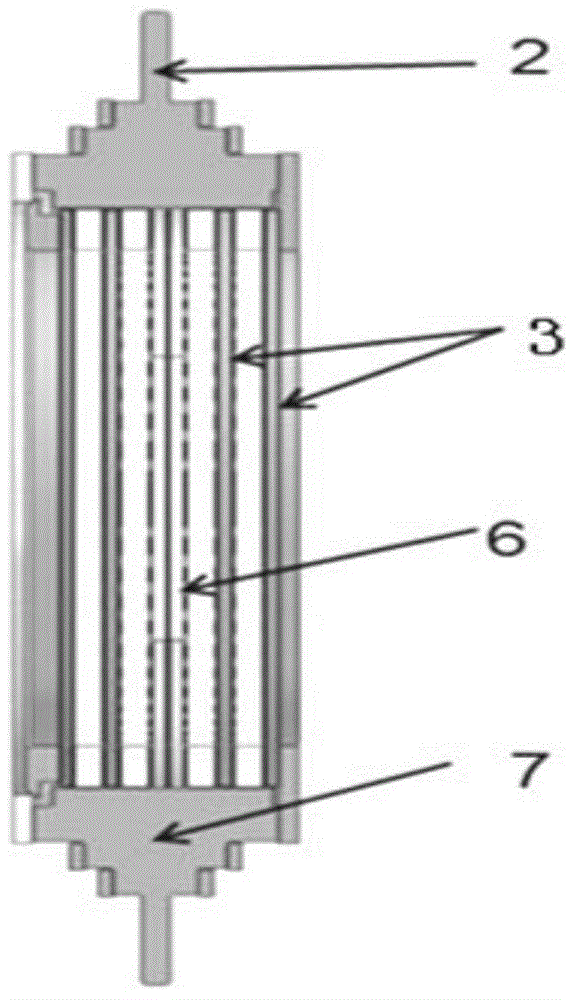
Patents
Literature
1058 results about "Photocathode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A photocathode is a negatively charged electrode in a light detection device such as a photomultiplier or phototube that is coated with a photosensitive compound. When this is struck by a quantum of light (photon), the absorbed energy causes electron emission due to the photoelectric effect.
Semiconductor X-ray photocathodes devices
InactiveUS6201257B1Reduce noiseHigh x-ray energy discriminationDischarge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesPhotocathodePhotonic sensor
An energy dispersive x-ray and gamma-ray photon counter is described. The counter uses a photon sensor which incorporates a unique photocathode called Advanced Semiconductor Emitter Technology for X-rays (ASET-X) as its critical element for converting the detected photons to electrons which are emitted into a vacuum. The electrons are multiplied by accelerations and collisions creating a signal larger than the sensor noise and thus allowing the photon to be energy resolved very accurately, to within ionization statistics. Because the signal is already above the sensor noise it does not have to be noise filtered therefore allowing high-speed counting. The photon sensor can also be used as a device to visualize and image gamma-ray and x-ray sources.
Owner:ADVANCED SCI CONCEPTS
Time resolution fluorescence spectral measuring and image forming method and its device
InactiveCN1912587ADifferent temporal resolutionsAchieving high-sensitivity detectionFluorescence/phosphorescencePhotocathodePicosecond
A method of using picosecond scan camera to simultaneously obtain fluorescent light spectrum and fluorescent lifetime of sample includes focusing blue violet light emitted by laser on sample by objective to excite sample single photon, collecting fluorescent from sample then splitting it and focusing it to be image on photoelectric cathode of picosecond scan camera, setting dispersion direction of fluorescent to be the same as slit direction of said camera but to be vertical to scan direction in order to measure out fluorescent lifetime of different light spectrum simultaneously under coaction of scan circuit and image intensifier deflection system.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
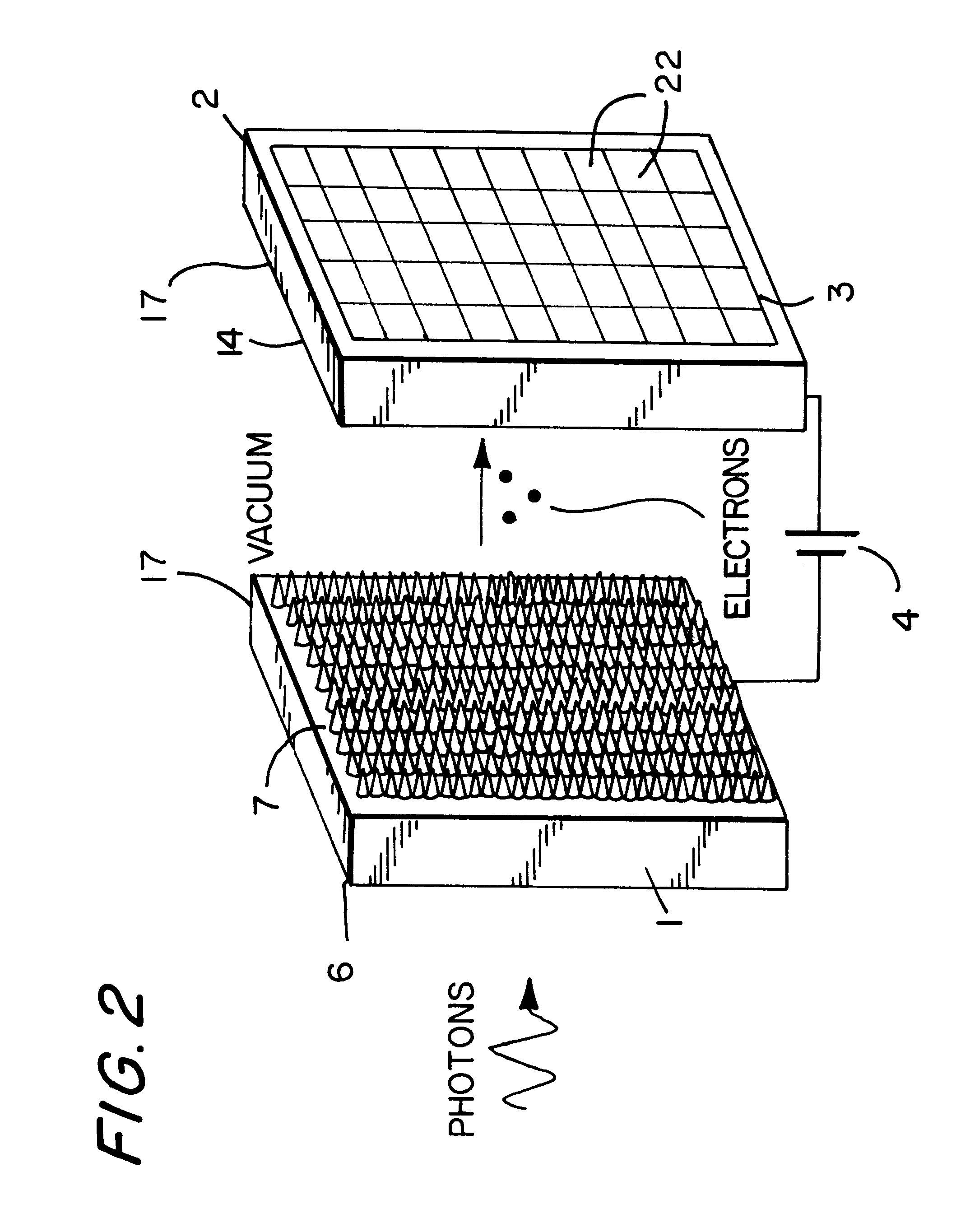
Low-photon flux image-intensified electronic camera
ActiveUS20060081770A1Low backgroundZero effective read noiseSolid-state devicesMultiplier circuit arrangementsGallium arsenide phosphidePhotocathode
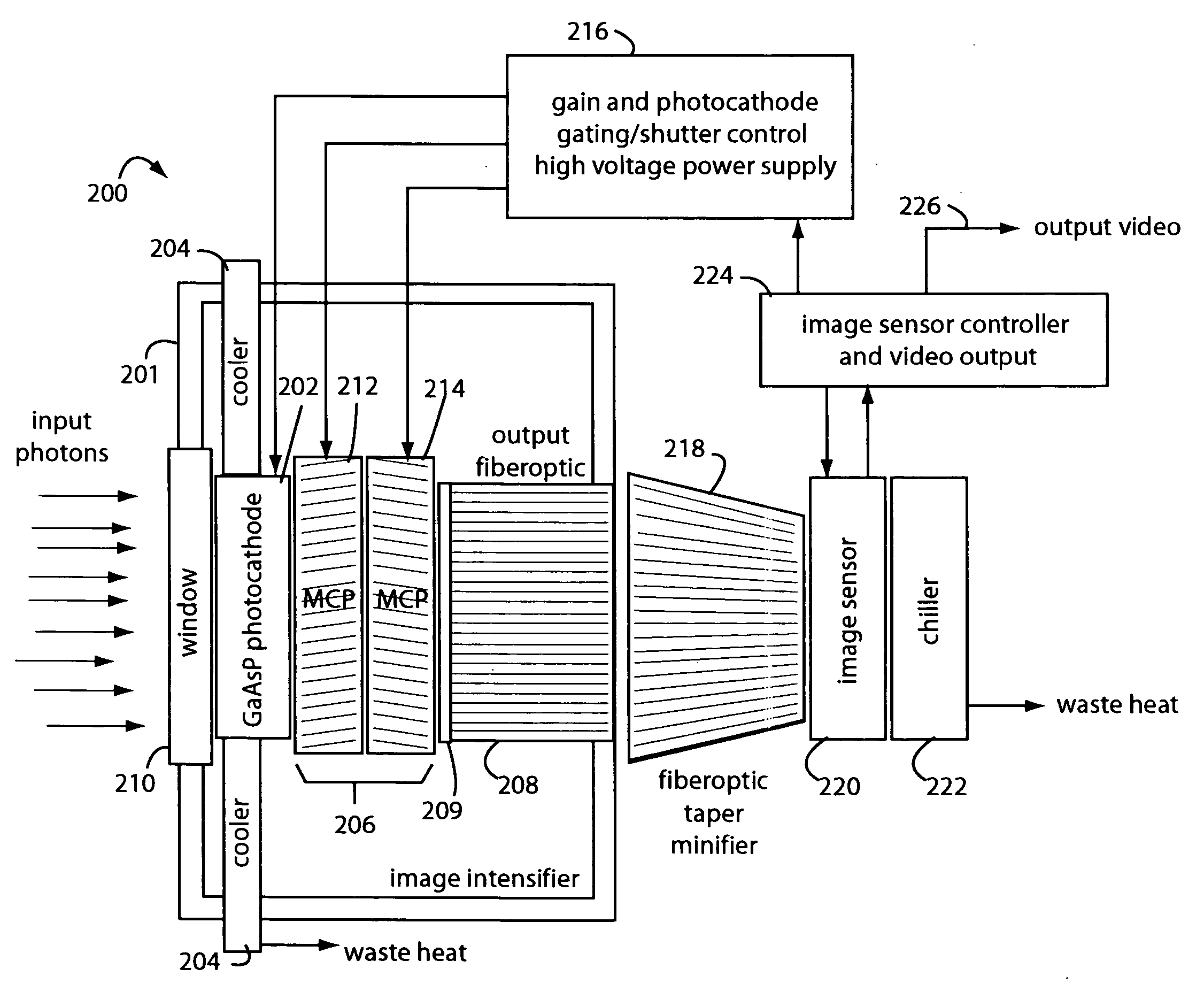
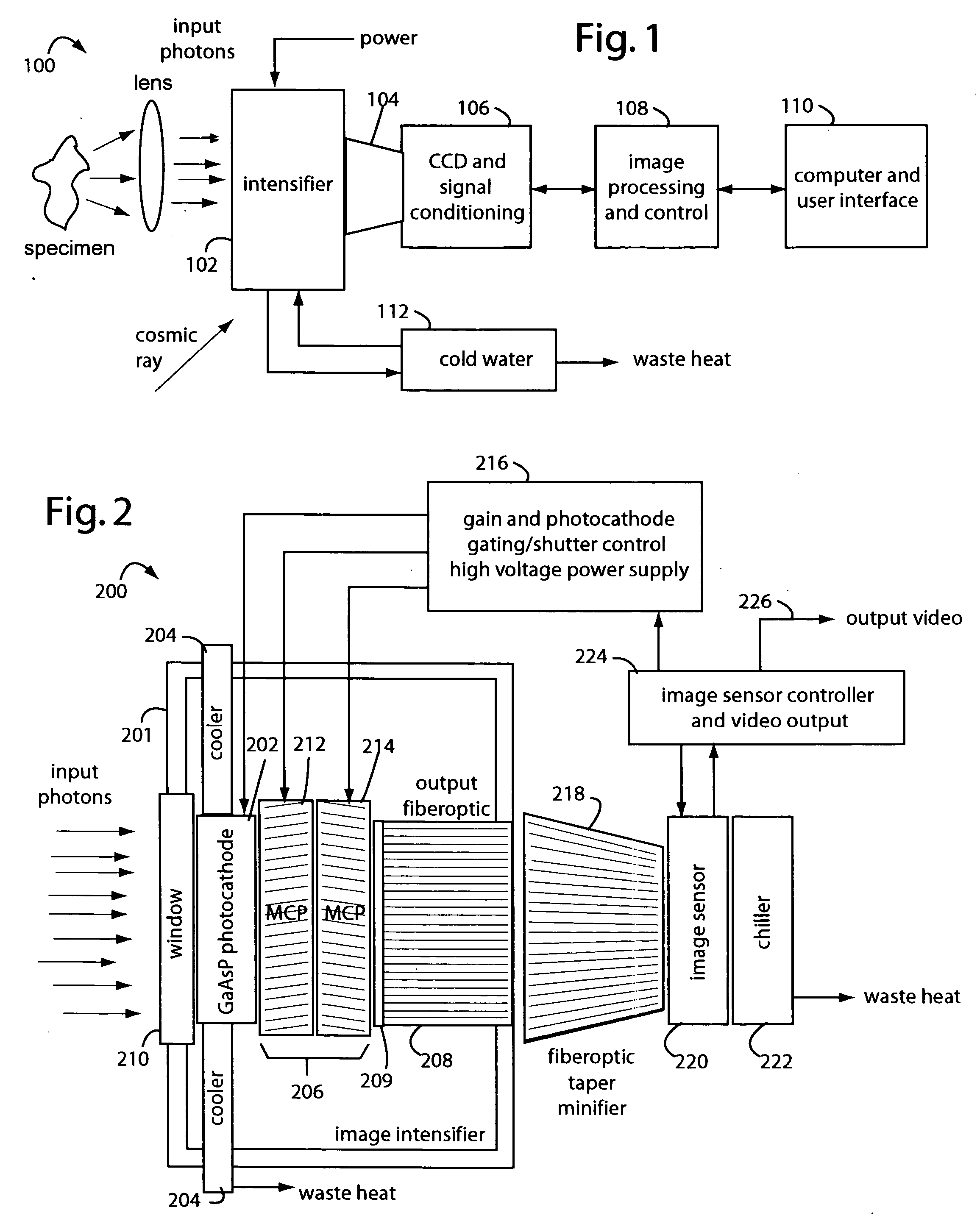
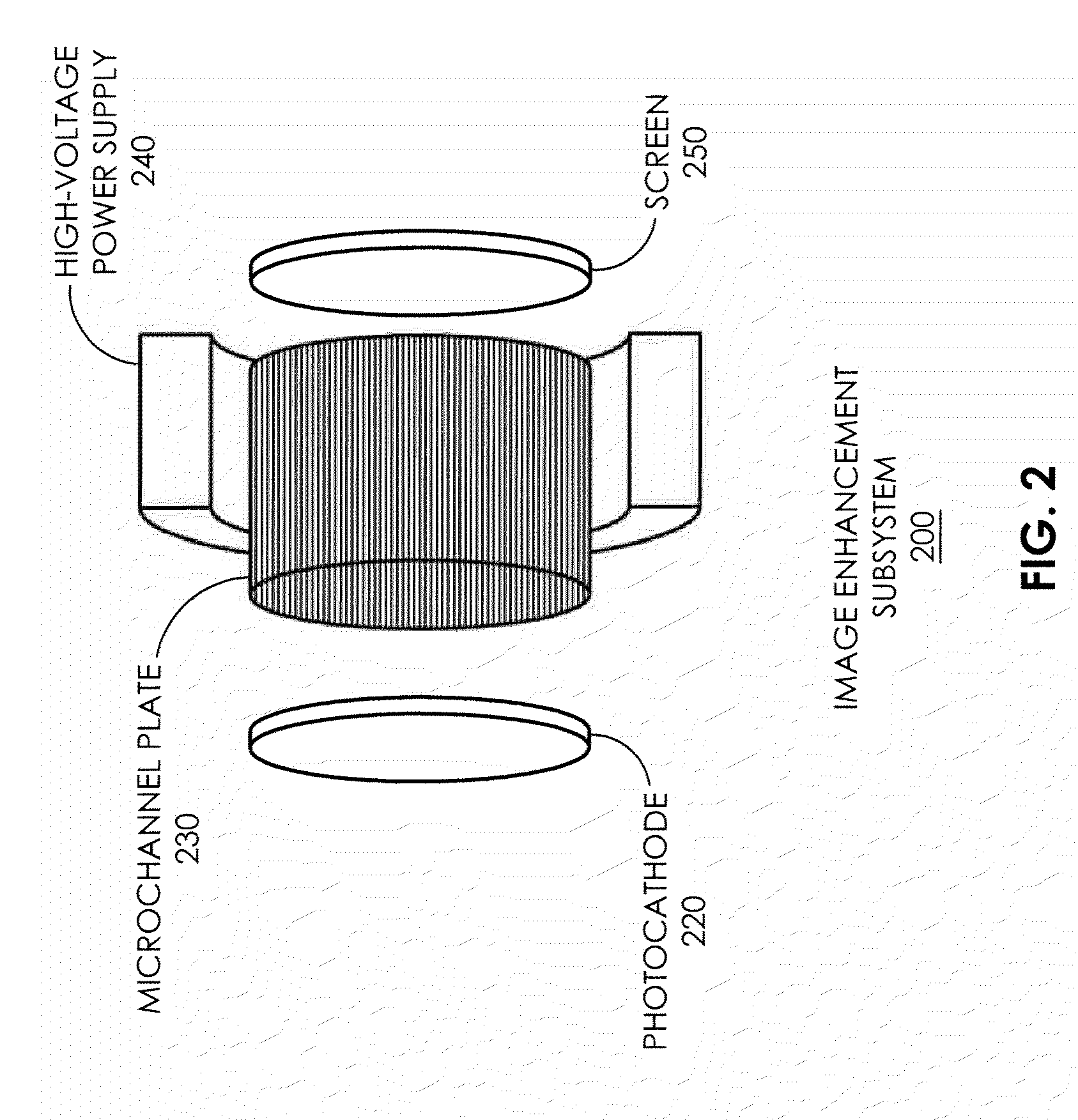
A low-photon flux image-intensified electronic camera comprises a gallium arsenide phosphide (GaAsP) photocathode in a high vacuum tube assembly behind a hermetic front seal to receive image photons. Such is cooled by a Peltier device to −20° C. to 0° C., and followed by a dual microchannel plate. The microchannels in each plate are oppositely longitudinally tilted away from the concentric to restrict positive ions that would otherwise contribute to the generation high brightness “scintillation” noise events at the output of the image. A phosphor-coated output fiberoptic conducts intensified light to an image sensor device. This too is chilled and produces a camera signal output. A high voltage power supply connected to the dual microchannel plate provides for gain control and photocathode gating and shuttering. A fiberoptic taper is used at the output of the image intensifier vacuum tube as a minifier between the internal output fiberoptic and the image sensor.
Owner:STANFORD PHOTONICS
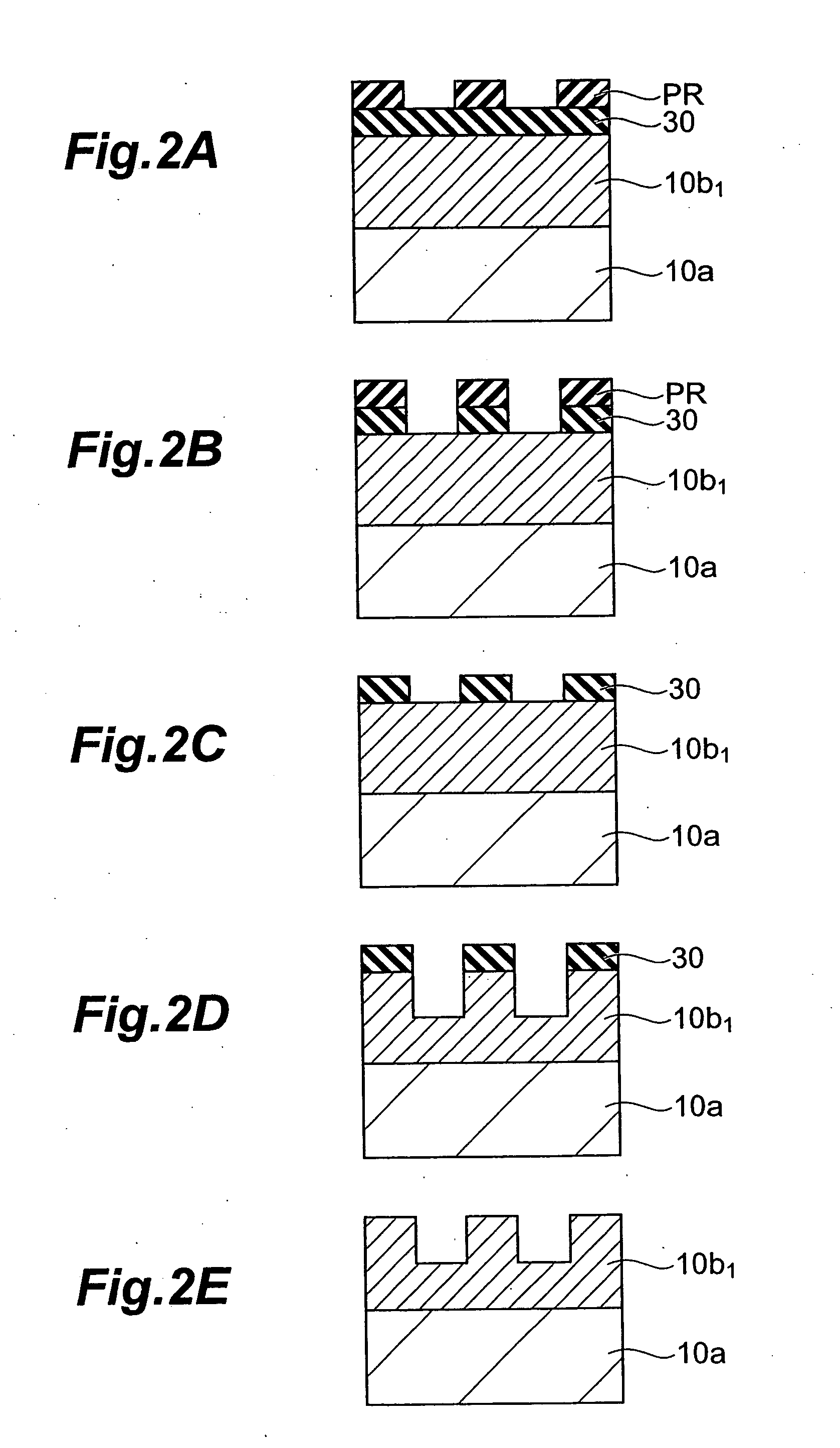
Photocathode
InactiveUS20070096648A1Bias voltage can be appliedReduce contact resistancePhoto-emissive cathodesPhotoelectric discharge tubesSemiconductor materialsPhotocathode
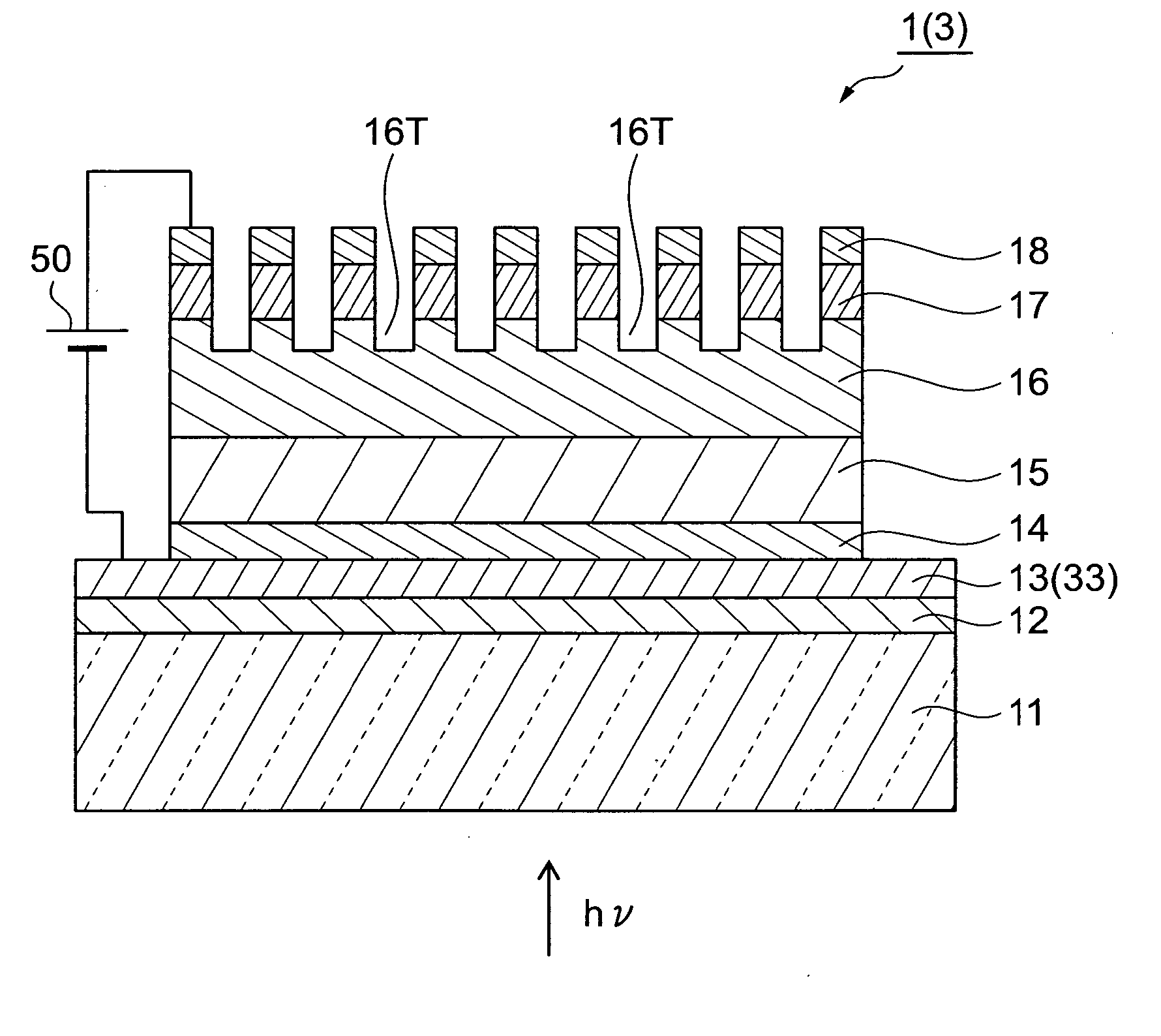
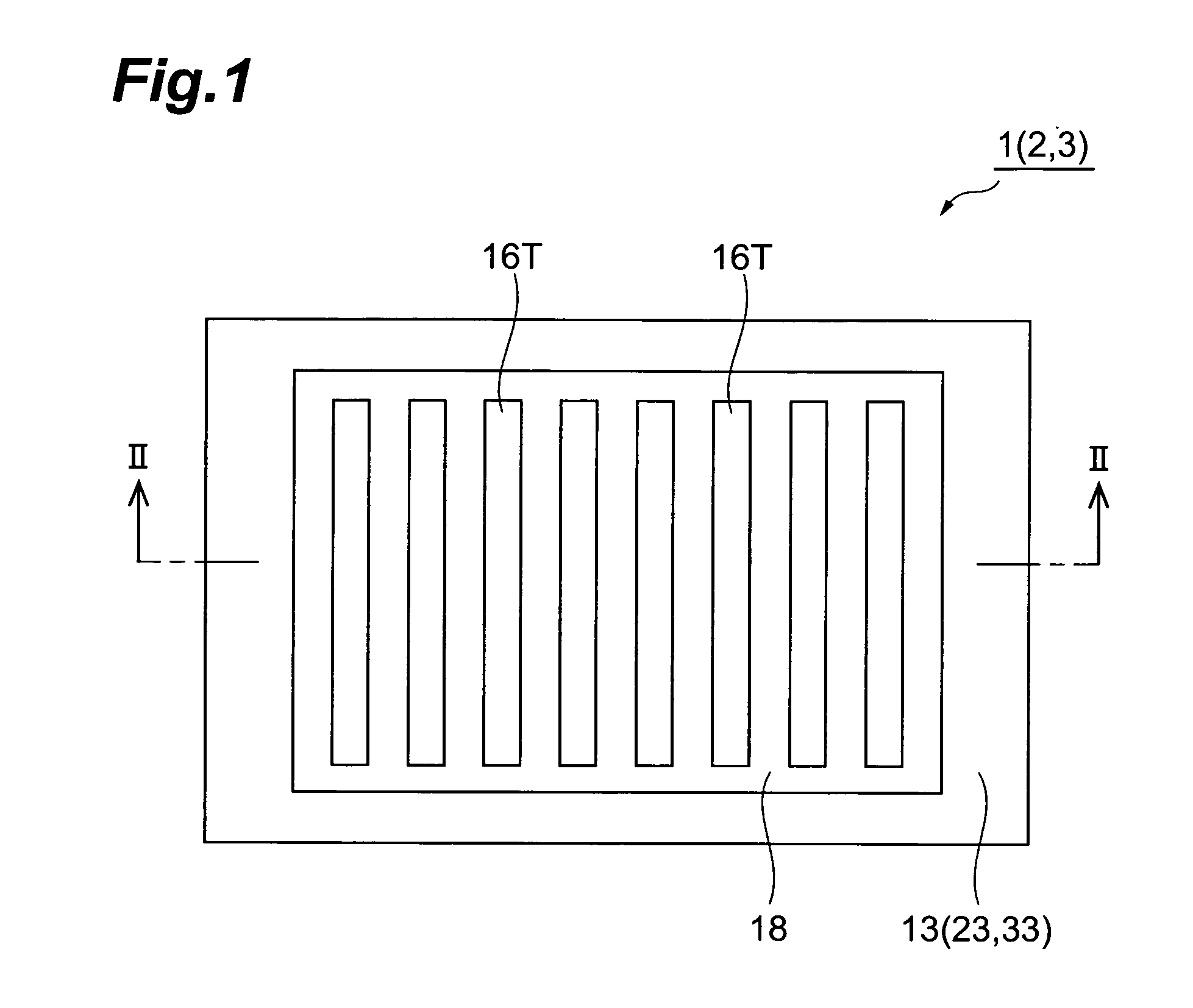
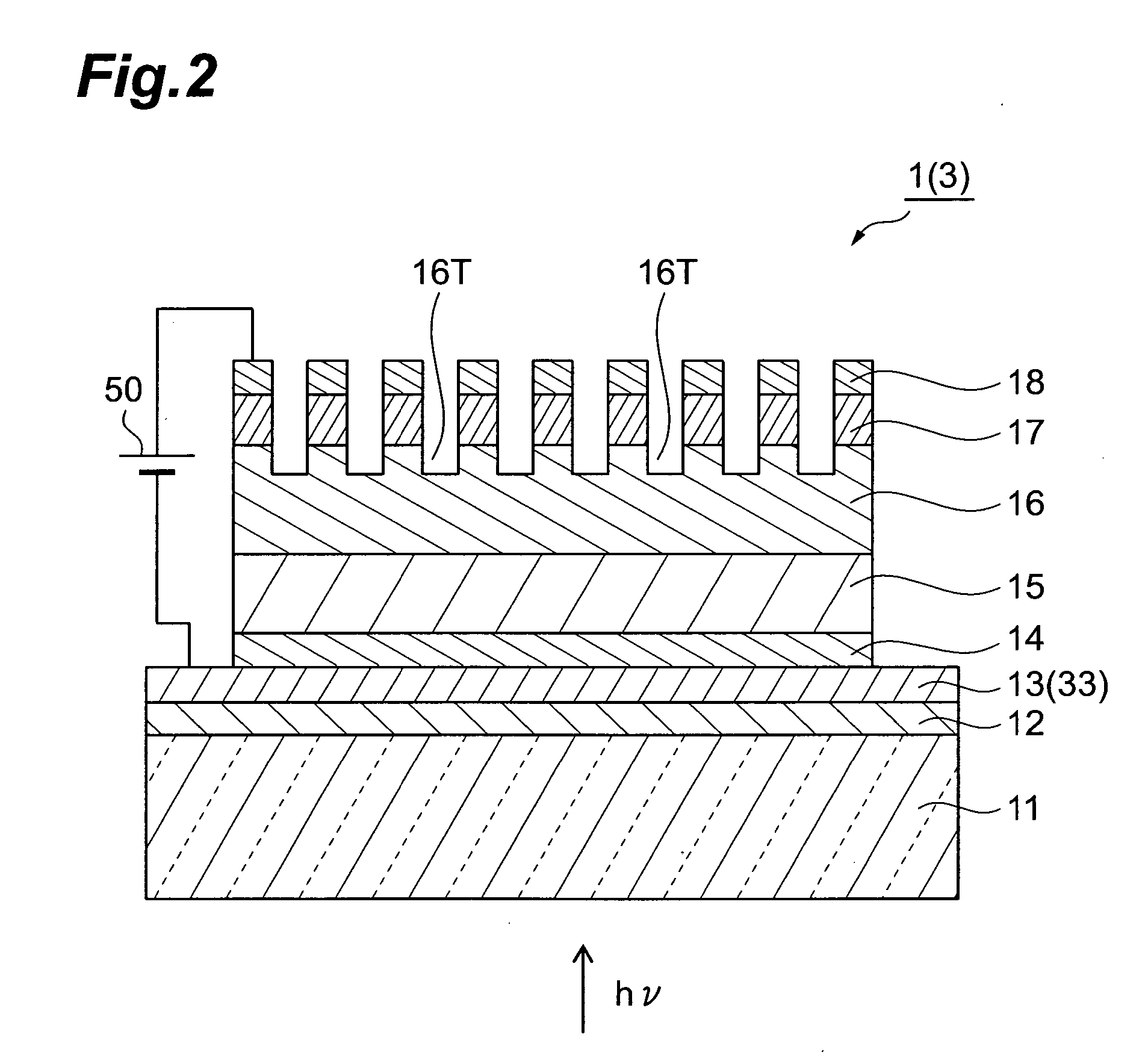
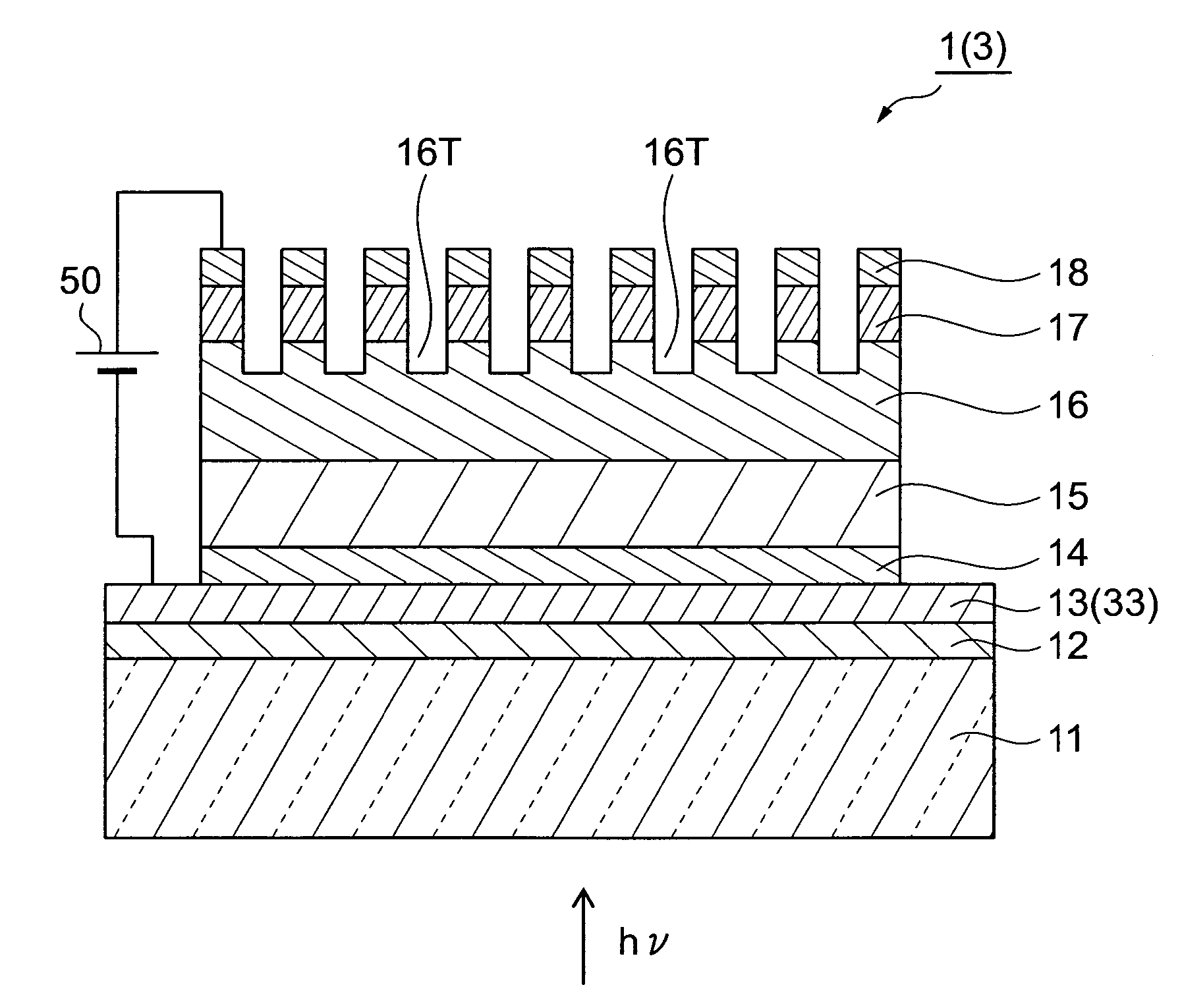
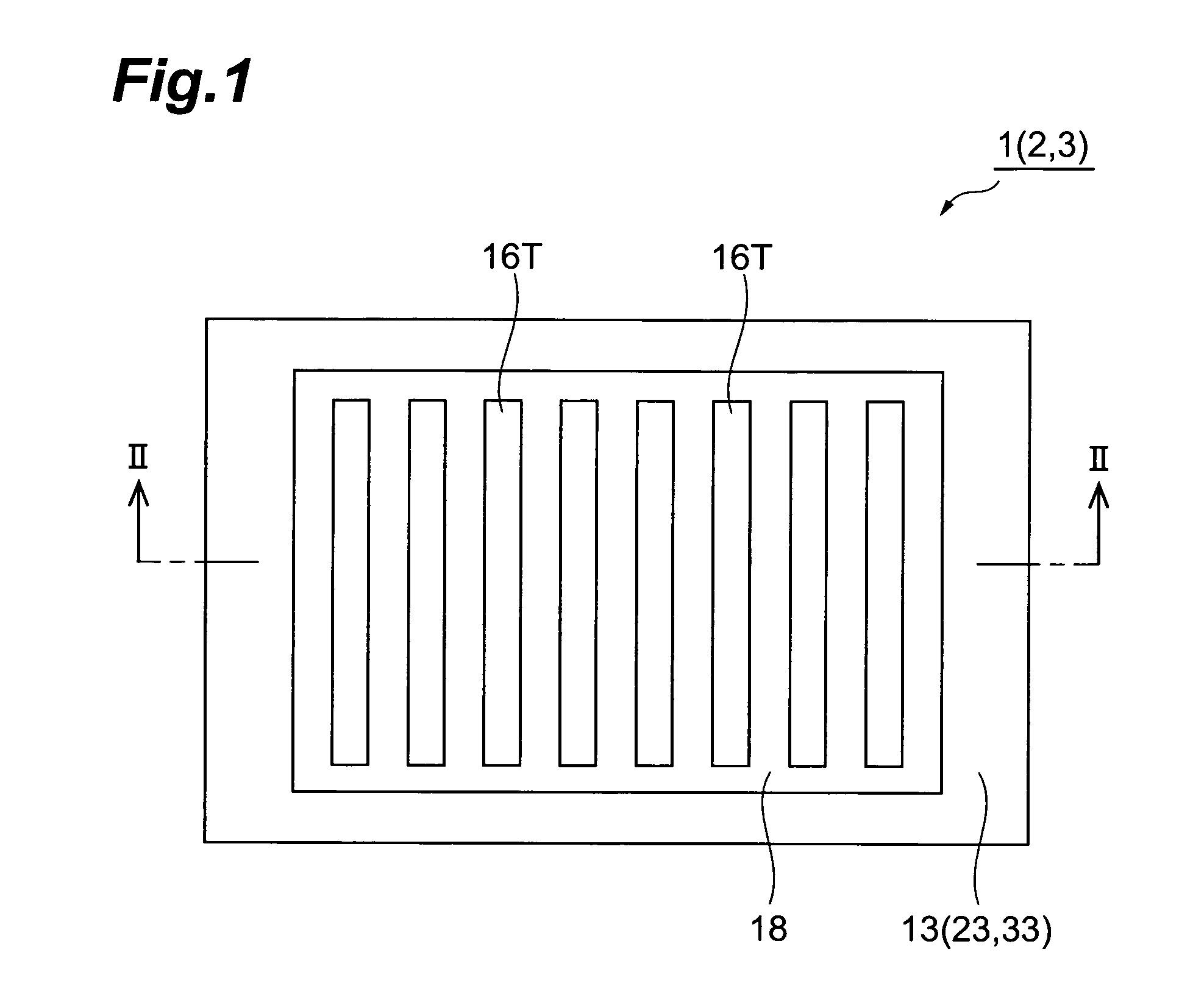
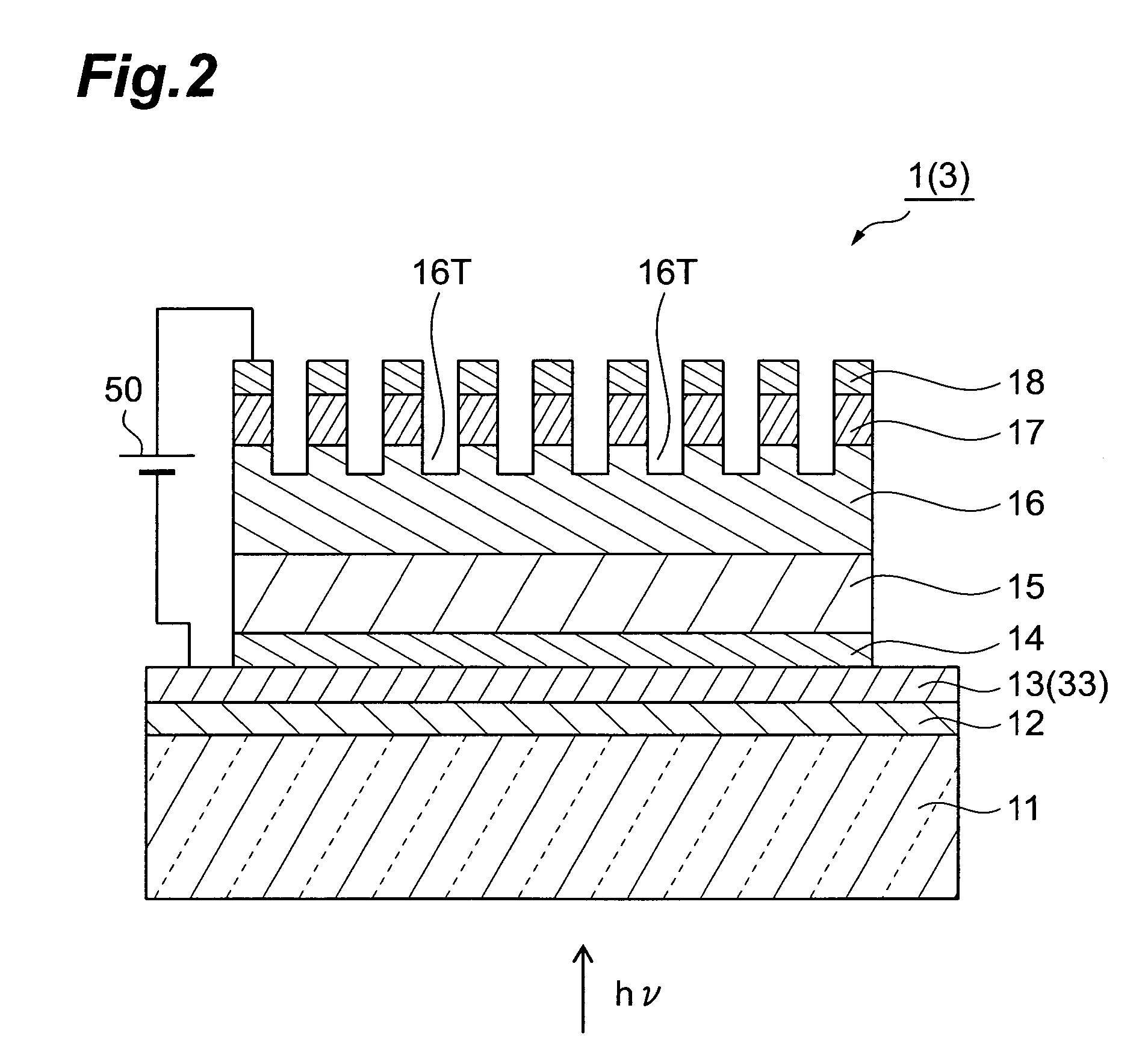
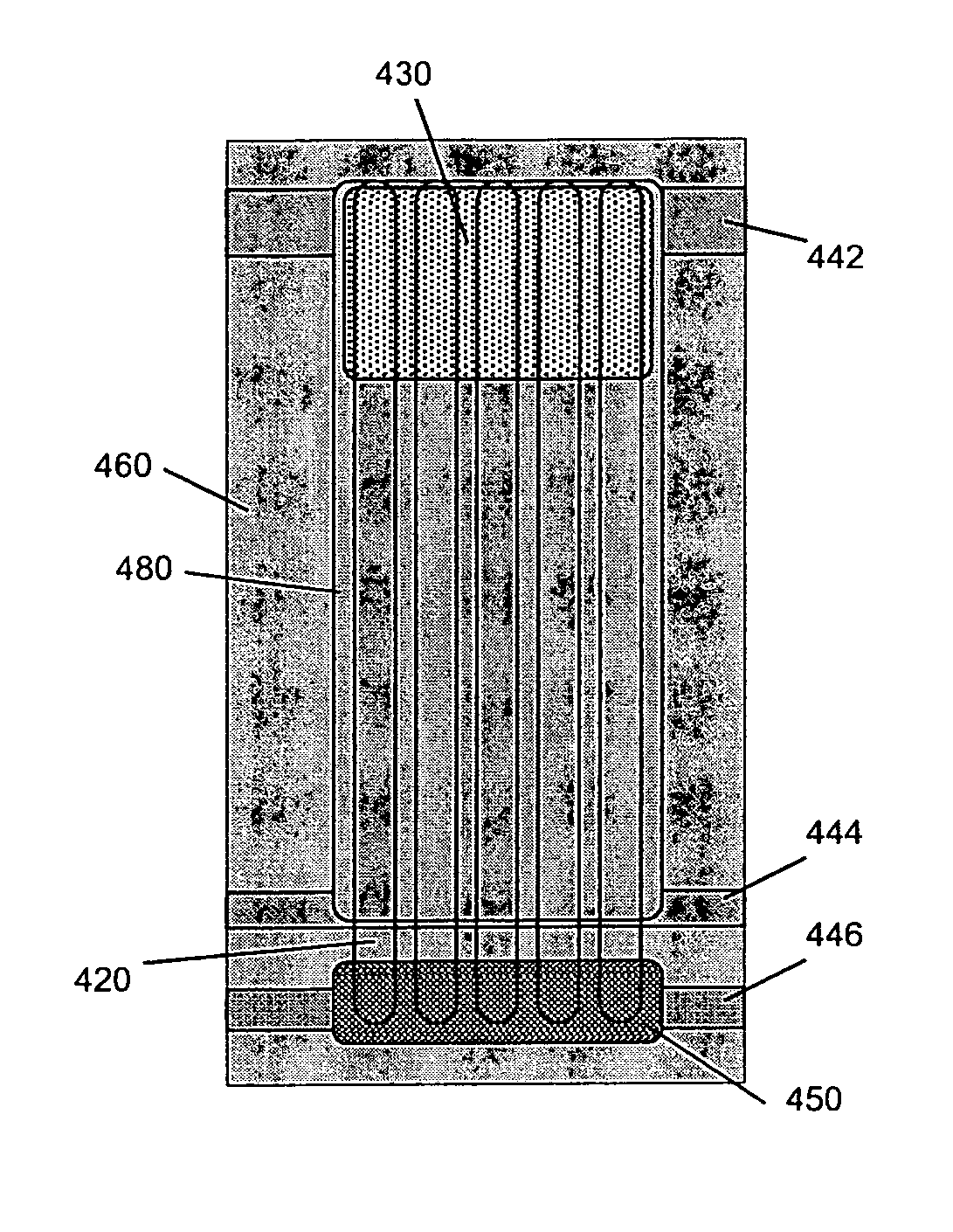
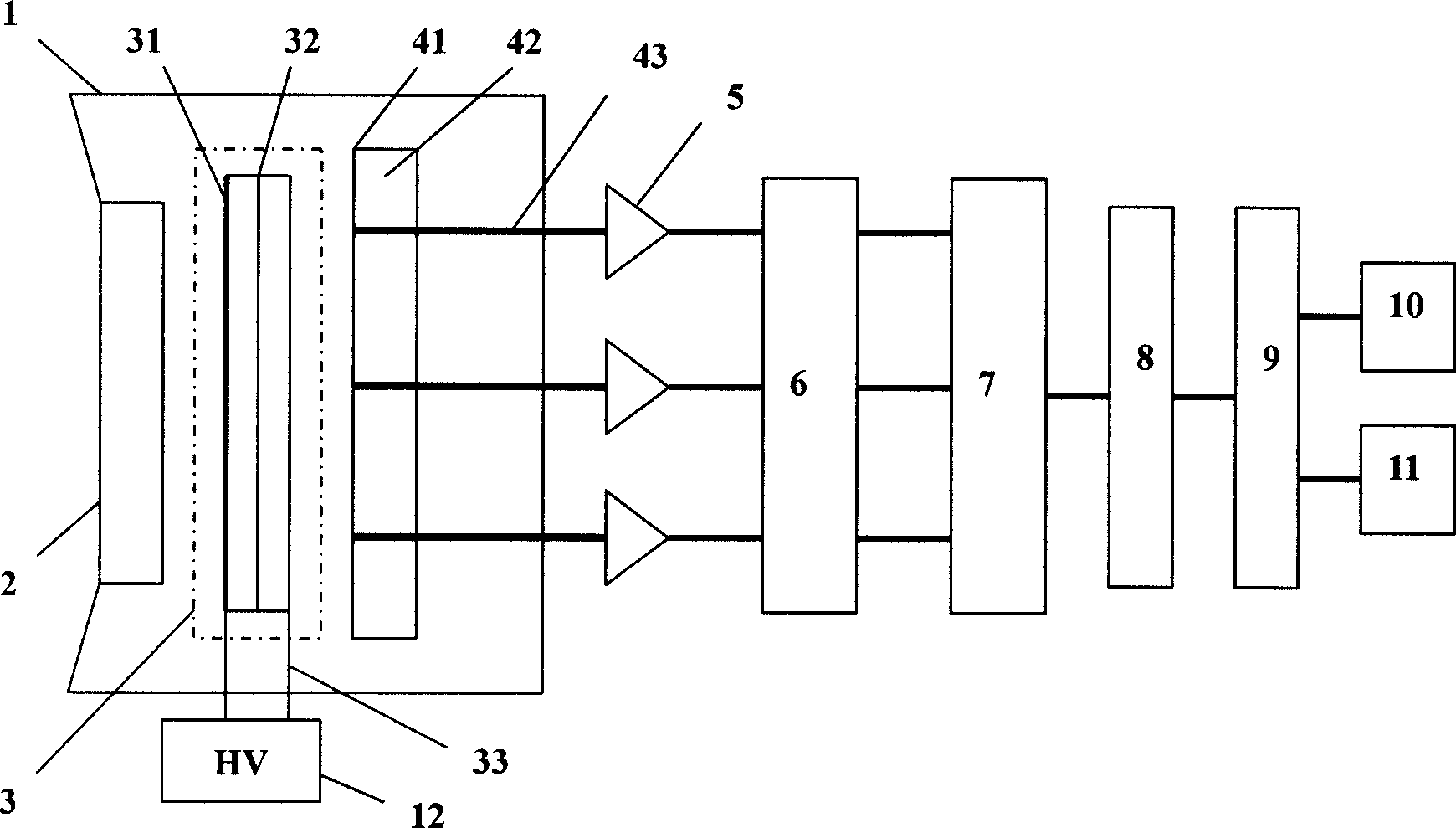
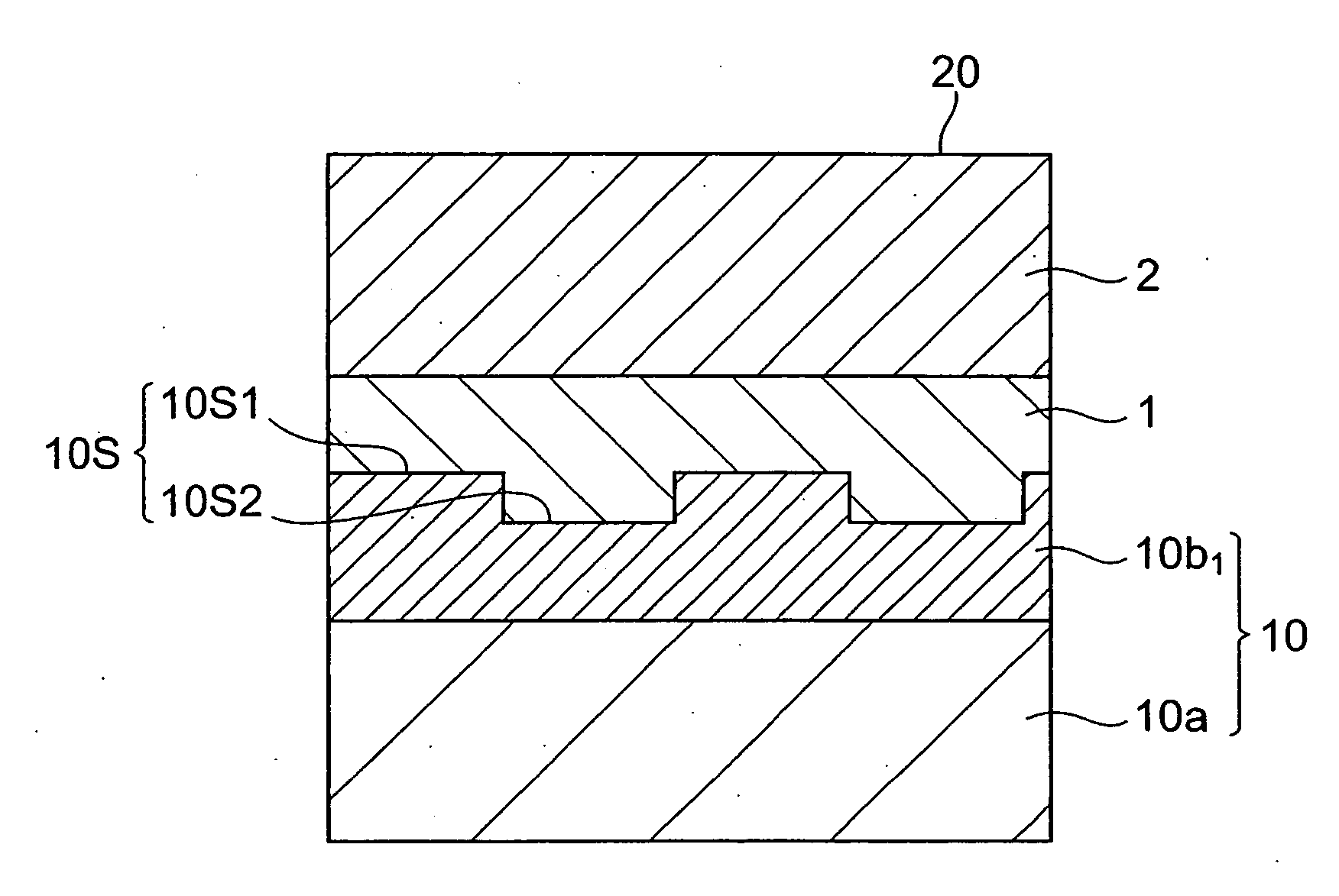
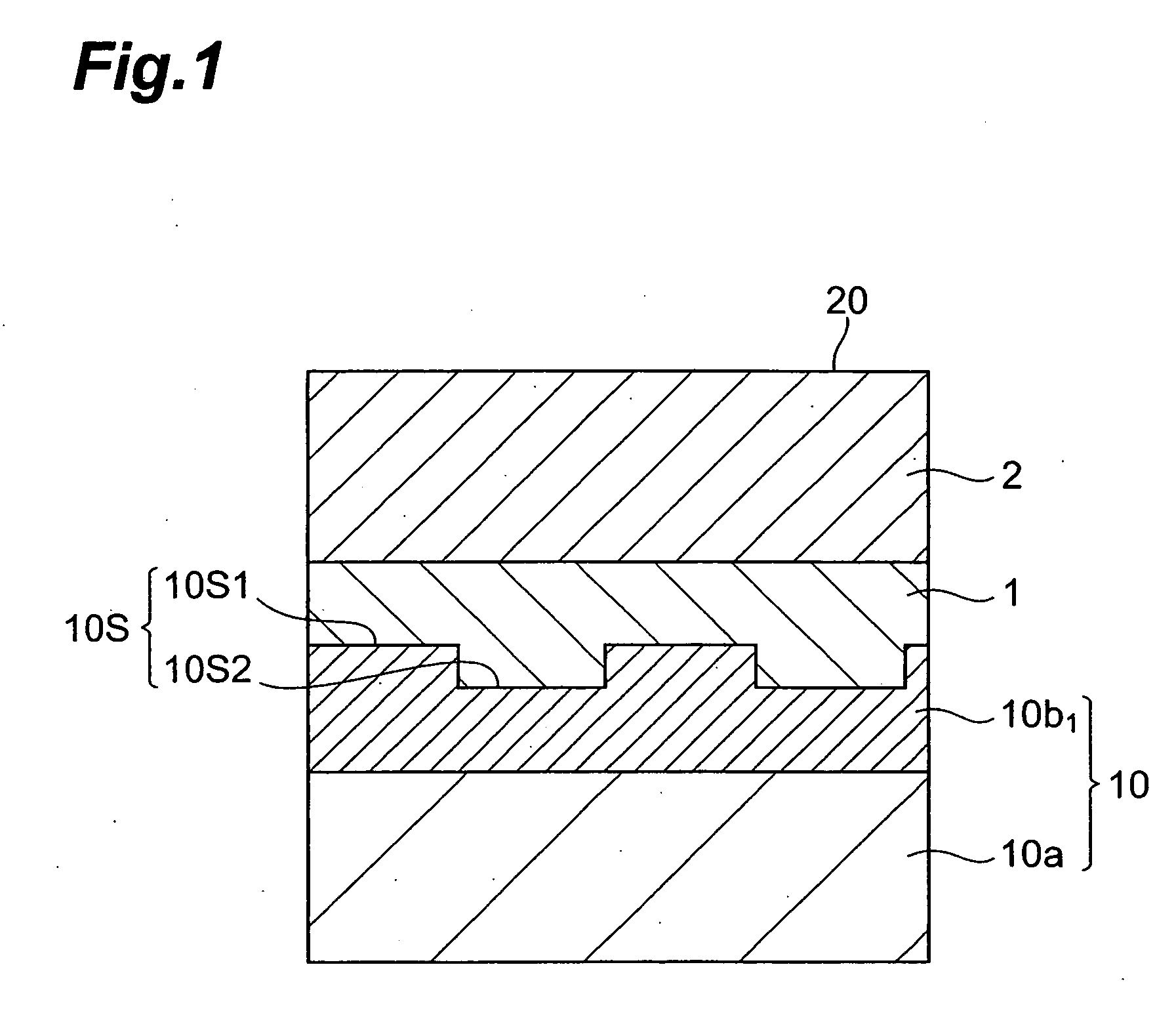
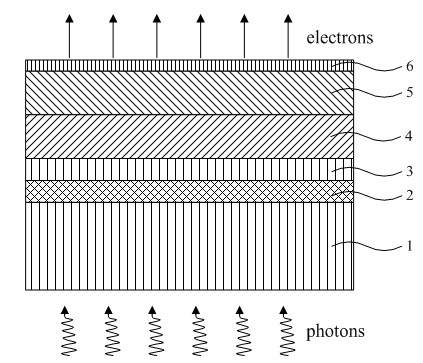
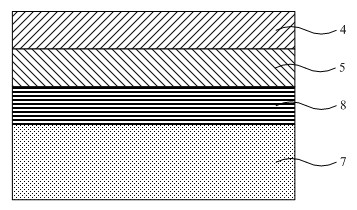
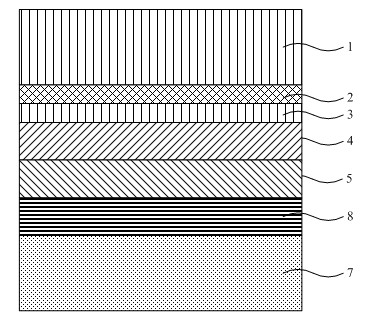
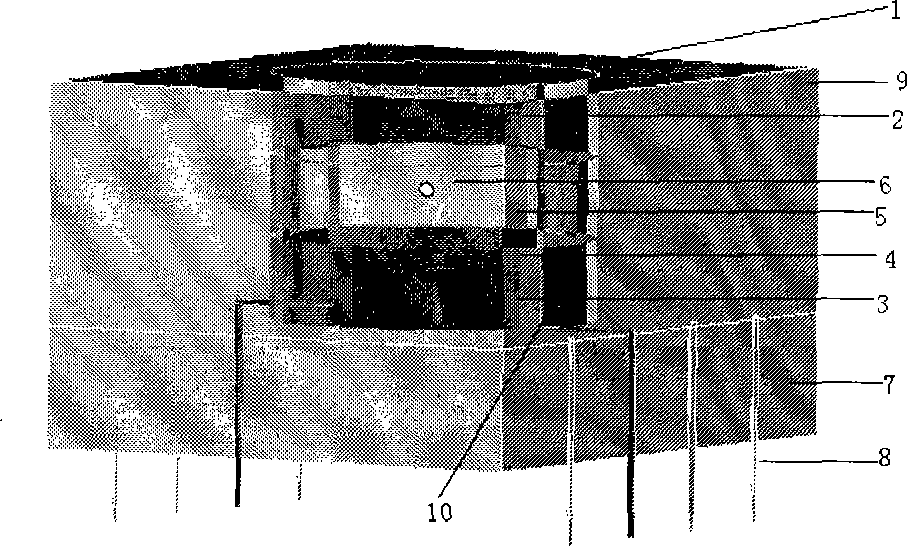
A semiconductor photocathode 1 includes: a transparent substrate 11; a first electrode 13, formed on the transparent substrate 11 and enabling passage of light that has been transmitted through the transparent substrate 11; a window layer 14, formed on the first electrode 13 and formed of a semiconductor material with a thickness of no less than 10 nm and no more than 200 nm; a light absorbing layer 15, formed on the window layer 14, formed of a semiconductor material that is lattice matched to the window layer 14, is narrower in energy band gap than the window layer 14, and in which photoelectrons are excited in response to the incidence of light; an electron emission layer 16, formed on the light absorbing layer 15, formed of a semiconductor material that is lattice matched to the light absorbing layer 15, and emitting the photoelectrons excited in the light absorbing layer 15 to the exterior from a surface; and a second electrode 18, formed on the electron emission layer.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Photocathode comprising a plurality of openings on an electron emission layer
InactiveUS7816866B2Bias voltage can be appliedReduce contact resistancePhoto-emissive cathodesPhotoelectric discharge tubesSemiconductor materialsPhotocathode
A semiconductor photocathode 1 includes: a transparent substrate 11; a first electrode 13, formed on the transparent substrate 11 and enabling passage of light that has been transmitted through the transparent substrate 11; a window layer 14, formed on the first electrode 13 and formed of a semiconductor material with a thickness of no less than 10 nm and no more than 200 nm; a light absorbing layer 15, formed on the window layer 14, formed of a semiconductor material that is lattice matched to the window layer 14, is narrower in energy band gap than the window layer 14, and in which photoelectrons are excited in response to the incidence of light; an electron emission layer 16, formed on the light absorbing layer 15, formed of a semiconductor material that is lattice matched to the light absorbing layer 15, and emitting the photoelectrons excited in the light absorbing layer 15 to the exterior from a surface; and a second electrode 18, formed on the electron emission layer.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
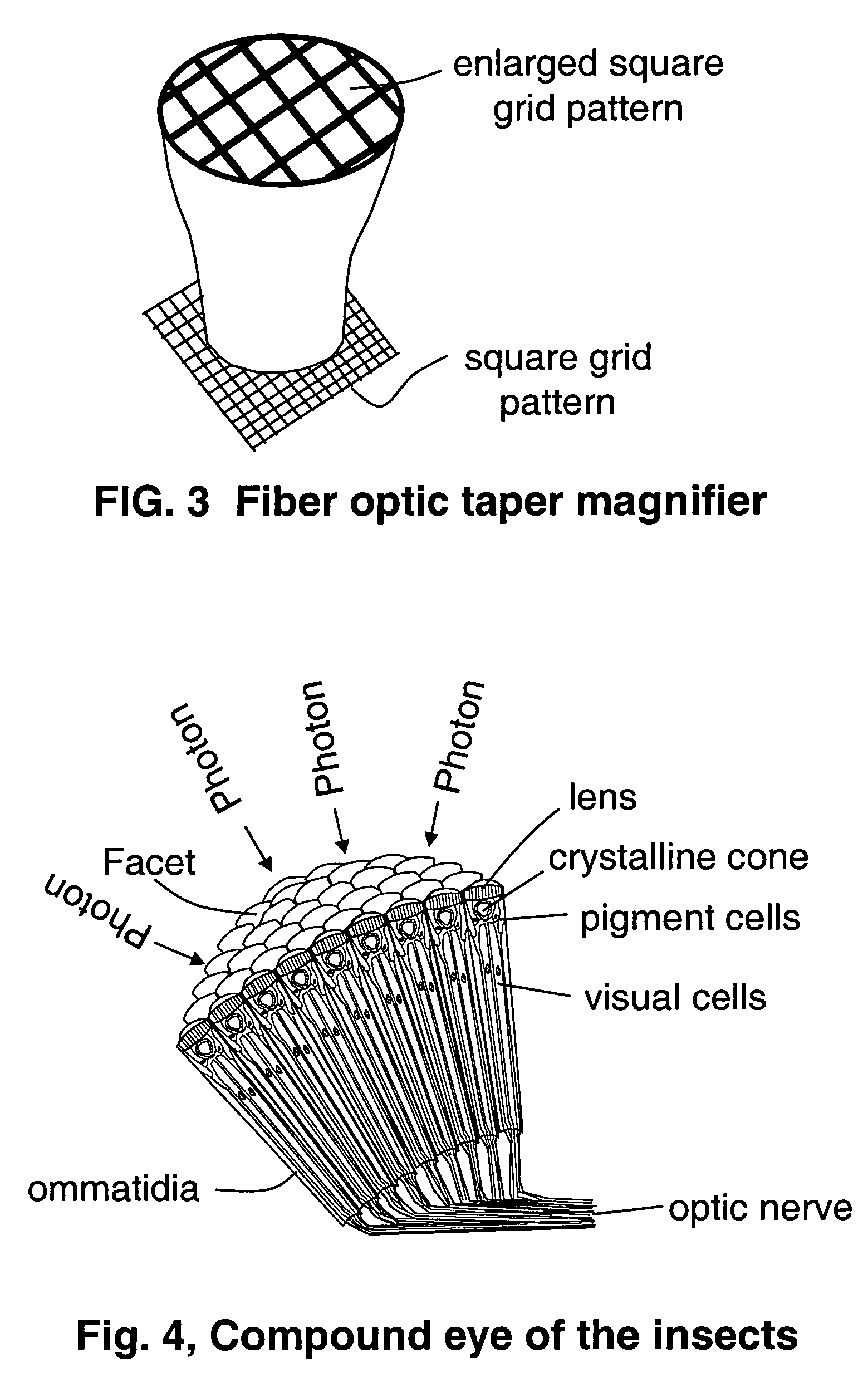
Contact-field optical microscope
InactiveUS7006741B1Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingBundled fibre light guidePhotocathodeOpto electronic
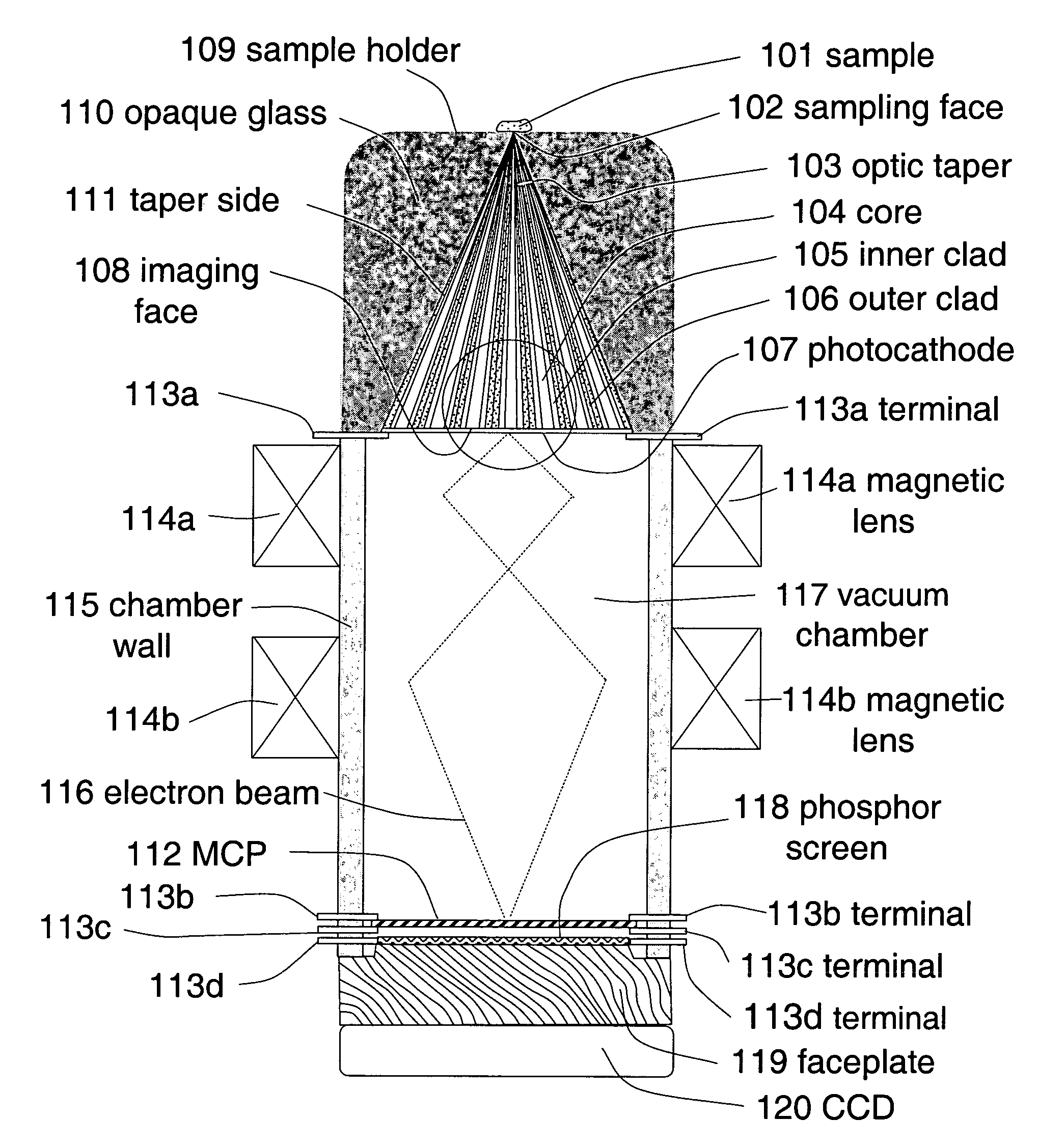
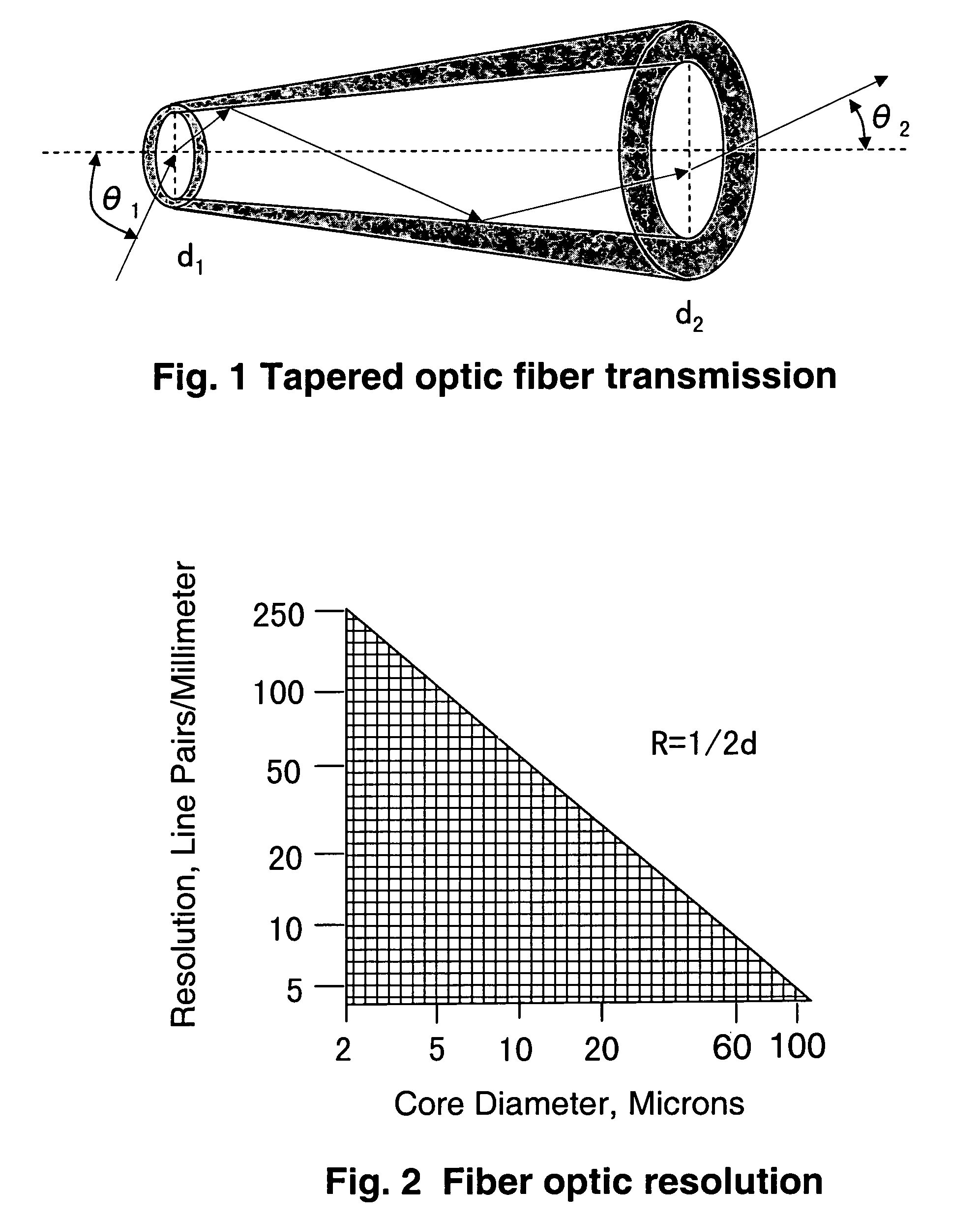
A broad-spectrum, high spatial and time resolution contact-field optical microscope comprises a fiber optical taper, a vacuum chamber, a photocathode, a magnetic lens photoelectron image enlarger, a micro-channel plate image intensifier, a phosphor screen and a CCD. Sample is placed directly in contact with a smaller sampling face of the optical taper. Light which is emitted, reflected or transmitted by the sample is launched into each of the fiber core ends on the sampling face and conveyed by the optical fibers to a larger imaging face of the optical taper, thereby presenting an enlarged image at the imaging face. The image is converted into a photoelectron image by photocathode which is deposited on the surface of the imaging face. The photoelectron image is further enlarged by magnetic lenses and intensified by micro-channel plate. The enlarged and enhanced electron image is displayed on phosphor screen and coupled through faceplate to CCD.
Owner:YU BI
Field emission display device in separated structure
InactiveCN1805105AImprove display qualityReduce difficultyImage/pattern display tubesNon-linear opticsLiquid crystal light valvePhotocathode
The invention relates to a separated field emission display device, which comprises a glass basic plate and the three primary colors fluorescent powder and aluminum film mounted on the glass basic plate. Wherein, there is a sealed vacuum chamber between the glass basic plate and the ITO glass basic plate; the aluminum film and the ITO glass basic plate are individually connected to the anode and cathode of direct current and high voltage; the ITO glass basic plate is plated with a photo-electric cathode array; the liquid crystal light valve is mainly formed by a upper ITO glass basic plate with directional layer, a liquid crystal layer and a lower ITO glass basic plate with directional layer, while the lower end of said liquid crystal light valve has a negative light source of light-emitting diode. The invention uses the electric beam to impact the fluorescent powder, the liquid crystal light valve and the negative light source, therefore, it has the energy saving, portable and better display properties of CRT and plane display, and compared to the surface conductive electric emitting display, it can avoid the preparation of nanometer slit to reduce the difficulty of technique and process.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
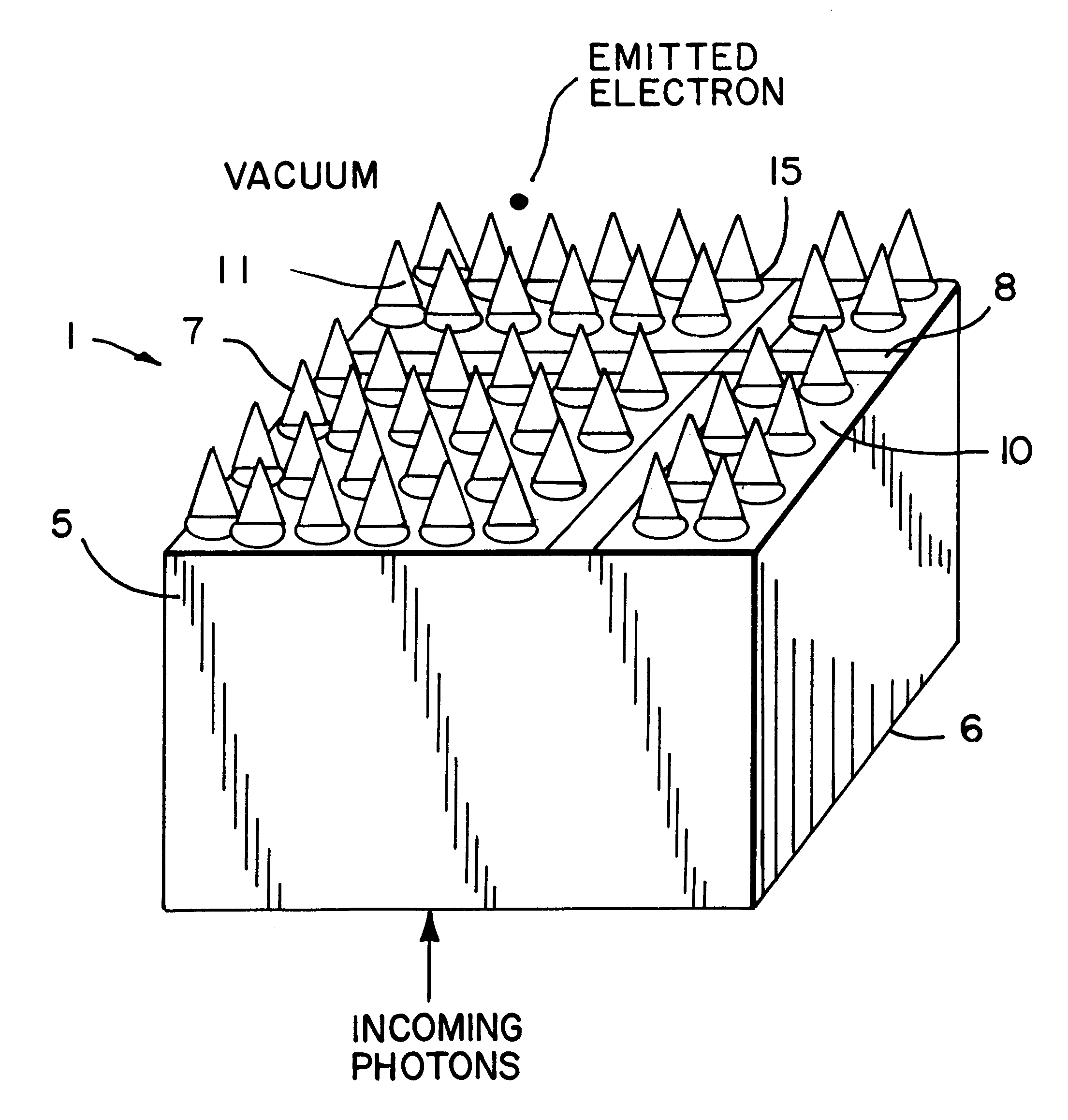
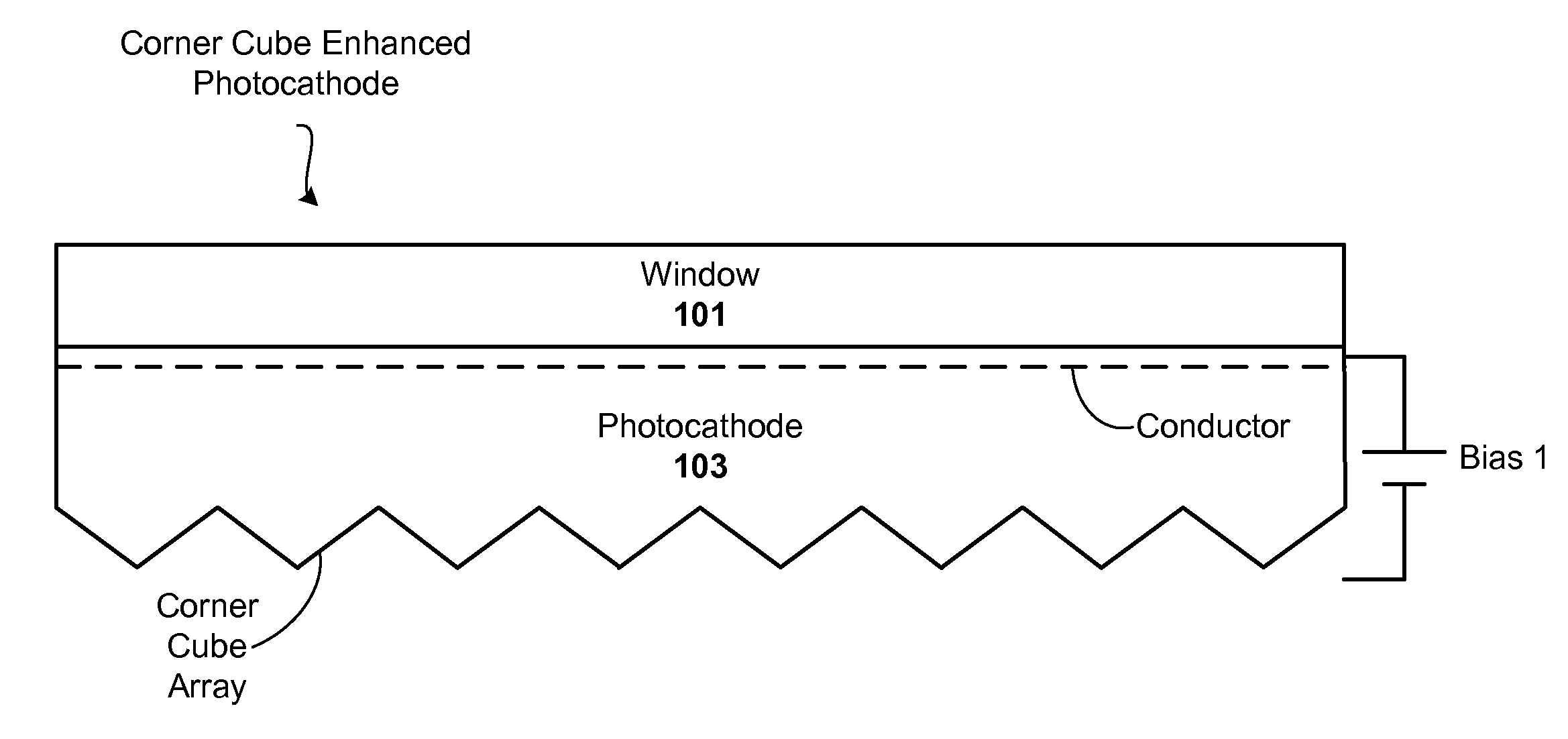
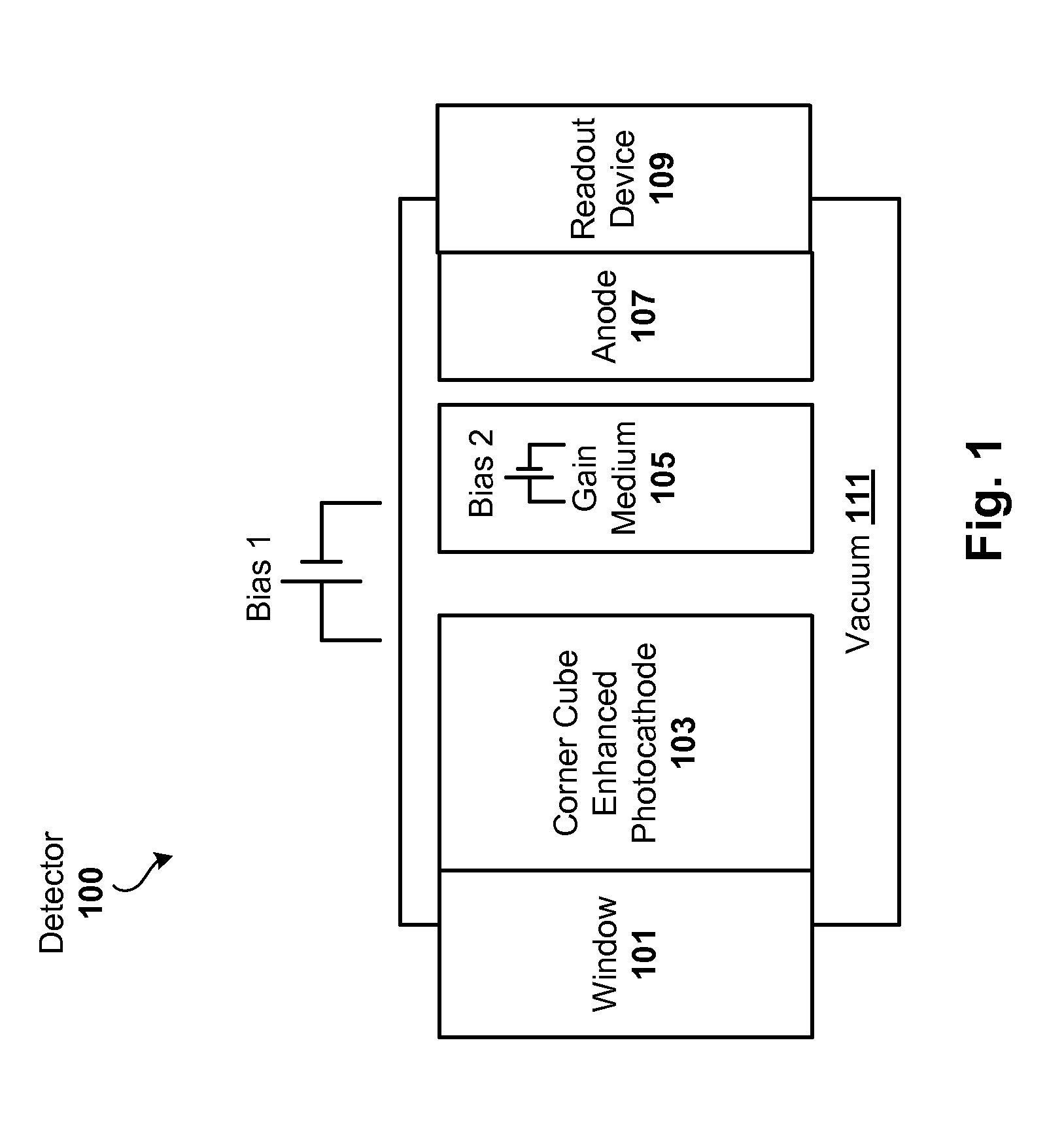
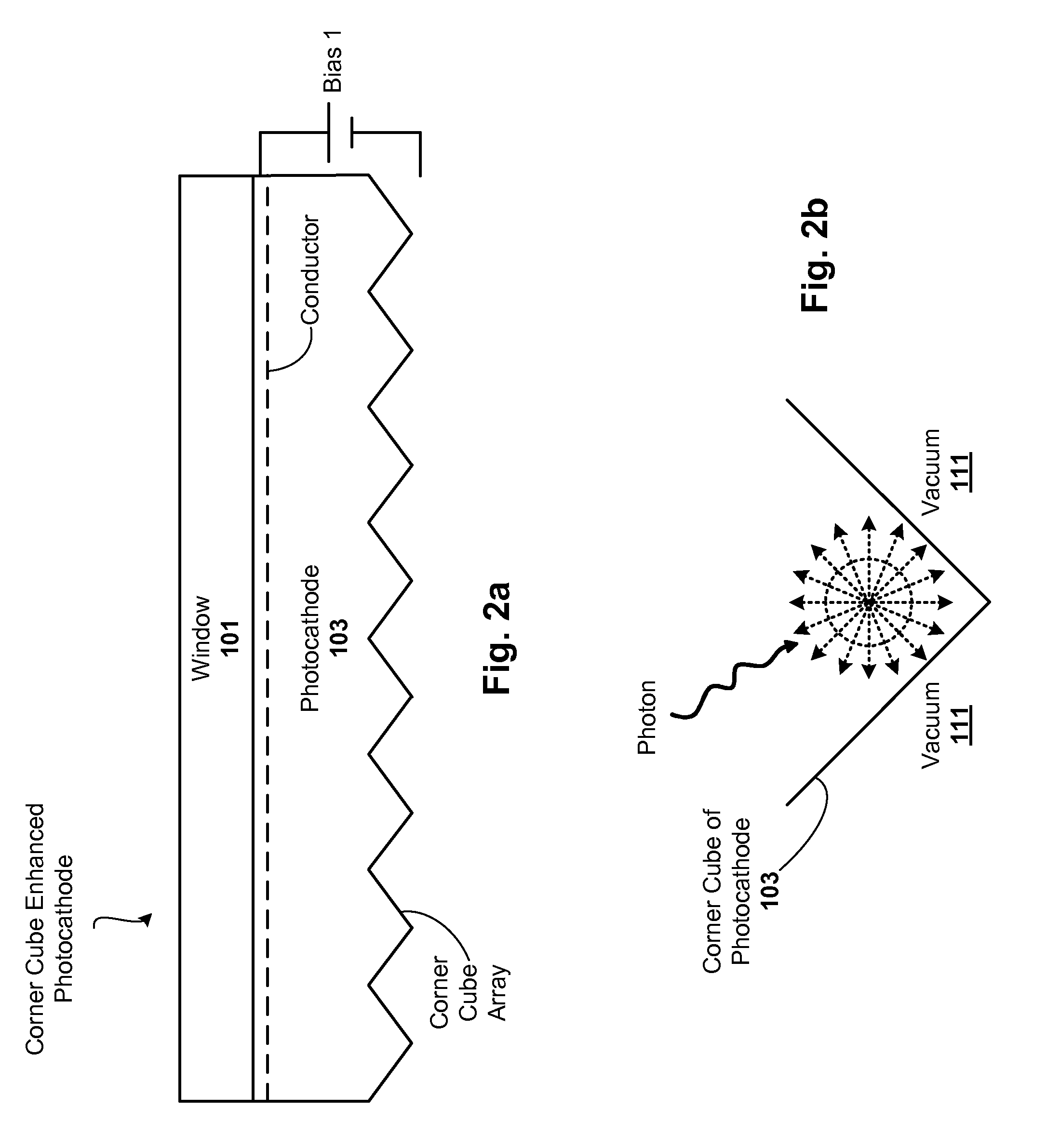
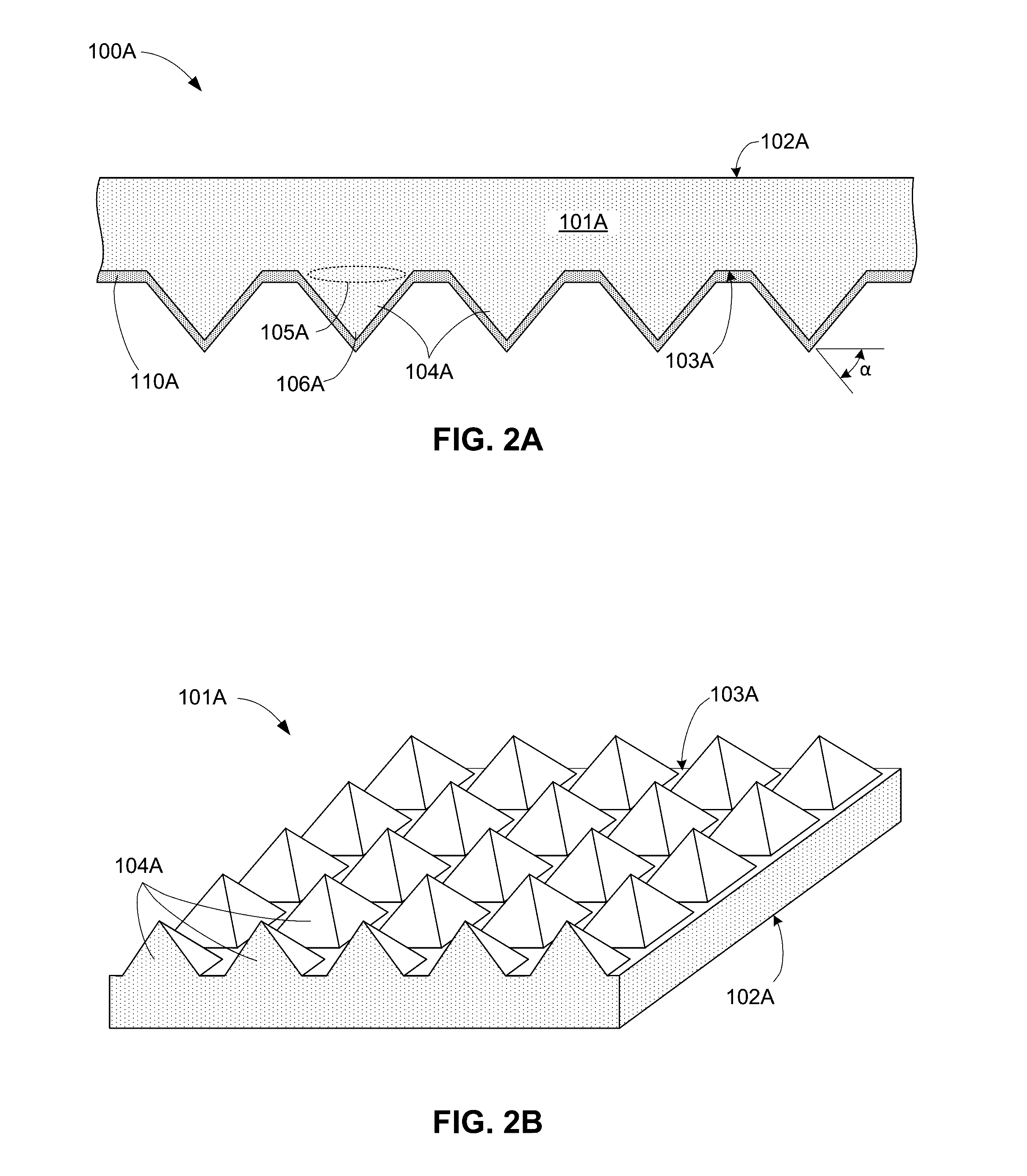
Corner cube enhanced photocathode
ActiveUS20120012811A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhoto-emissive cathodes manufactureQuantum efficiencyPhotocathode
Techniques are disclosed for improving the quantum efficiency of photocathode devices. The techniques allow for an increase in the optical thickness of the photocathode device, while simultaneously allowing for an increase in the probability of electron escape into the vacuum of the device. The techniques are particularly useful in detector and imaging. In one embodiment, a photocathode device is provided that has an array of corner cubes fabricated in a surface of the photocathode. The corner cube array is made of the same material as the photocathode layer. The device may be, for example, a detector or image intensifier that operates in the UV, visible, and IR light spectrums, and may further include a gain medium, anode, and readout device. Techniques for forming the device are also provided.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Photoelectrode for producing hydrogen and oxygen by photoelectro-chemically decomposing water, preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN104762634AEasy to separateImprove transmission performanceEnergy inputElectrode shape/formsHydrogenPhotocathode
A photoelectrode for producing hydrogen and oxygen by photoelectro-chemically decomposing water is characterized in that the photoelectrode is composed of a photocathode and a photoanode, wherein the photocathode and a photoanode are provide with quantum dots being assembled with assistance of a double-functional molecule. The invention achieves the establishment and the application of the photoelectrode for producing hydrogen and oxygen on the basis of semiconductors, quantum dots and catalysts. The photoelectrode is high in stability, is free of a sacrificial agent, is simple in operation, is good in repeatability, is strong in universality and is high in utilization rate on visible light. In addition, the catalyst is free of requirement of noble metals, is low in cost and is easy to obtain.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Confocal-reflection streak lidar apparatus with strip-shaped photocathode, for applications at a wide range of scales
InactiveUS6873716B1Eliminate needEnhances target signatureUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryPulse beamPhotocathode
The system images the volume of a turbid medium and detects the contents. The medium can be water or air, or living tissue, or almost any other material which is at least partially light-transmissive. The system includes a light source for producing a series of discrete fan-shaped pulse beams that are substantially uniform in intensity or have been peaked at the edges of the fan to illuminate sections of the medium, a streak tube with a large, thin-slit-shaped photocathode for collecting the maximum amount of light from weak returns, a field-limiting slit disposed in front of the cathode for removing multiply scattered light, a large-aperture optical element for collecting and focusing the reflected portions of the pulse beam on the field-limiting slit and the cathode, and an array of detectors. A volume display of the medium is generated by translating the transmitter and receiver normal to the longitudinal axis of the pulse beam, to illuminate adjacent sections of the medium, and combining the sections to provide a volume display. All, or substantially all, of the light returned from each pulse beam is used. Vehicle motion can be used to provide the scan of the beam. Applications range from foggy sky surveillance at multiple-kilometer scale to location of fractional-millimeter tumors in a human breast.
Owner:ARETA ASSOC
Method for preparing hydrogen through photoanode-photovoltaic battery coupled dual-illumination fully-photic-driven decomposition of water
InactiveCN104711627AImprove visible light absorptionHigh catalytic activityElectrolysis componentsLight-sensitive devicesSemiconductor materialsHydrogen
The invention relates to a method for preparing hydrogen through photoanode-photovoltaic battery coupled dual-illumination fully-photic-driven decomposition of water. Efficient decomposition of water is realized under sunlight illumination conditions by using coupling of a photoelectrocatalysis technology with a photovoltaic battery technology, adopting a water oxidation cocatalsyt modified semiconductor material as a photoanode, placing a proton reduction cocatalyst modified Si battery in an electrolyte as a photocathode, directly connecting the positive electrode of the Si battery with the anode through a lead and allowing the surface of the cathode to contact with the electrolyte. The method realizes fully photic driven decomposition of water without applied bias conditions, and the solar energy utilization efficiency STH of the method reaches 2.2% or above.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
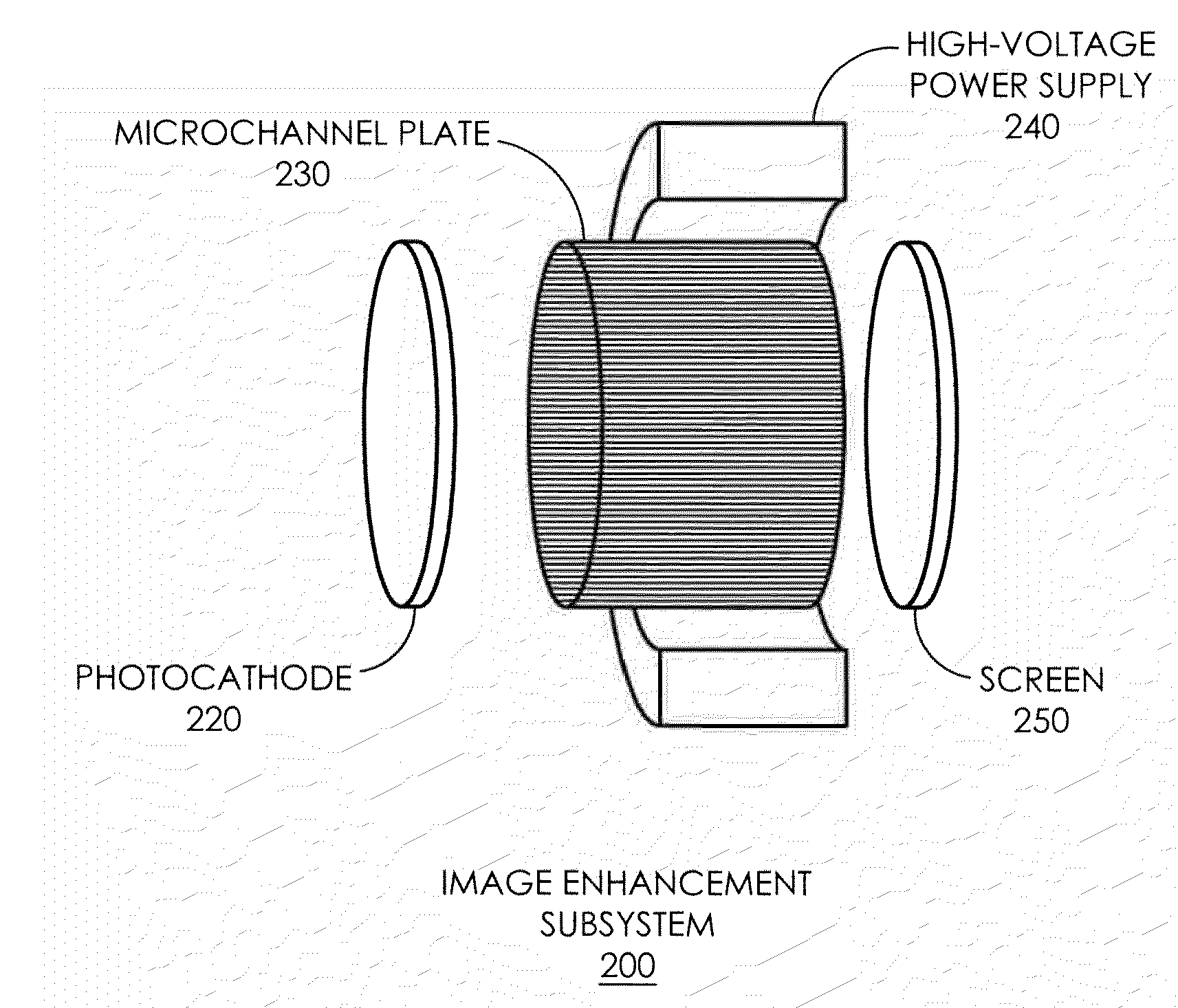
Advanced Image Intensifier Assembly
InactiveUS20090108180A1Function increaseImprove abilitiesMultiplier cathode arrangementsMultiplier circuit arrangementsPhotocathodeElectromagnetic interference
An advanced image intensifier assembly provides enhanced functionality. A grounded photocathode provides shielding from electromagnetic interference, improving the ability to work in multiple light conditions. Bi-directional wireless communication and non-volatile storage allow critical information to be permanently stored and read wirelessly at a scanning station, easing in identification of units. Because bi-directional communication components can be embedded within an image intensifier assembly, existing end-user night vision devices can be upgraded by simply replacing the image intensifier assembly. For enhanced safety, a programmable shutdown capability is provided. This renders the device inoperative in the absence of continuous input, either wireless or manual, from an authorized operator, thus rendering the device useless if captured by enemy combatants. Finally, direct 1-volt operation enables the device to be powered by, for example, a single AA battery.
Owner:SALDANA MICHAEL R
Microbial photoelectrochemical system for simultaneously generating electricity and hydrogen and treating sewage
ActiveCN102329006AElectrolysis componentsFinal product manufactureSemiconductor materialsPhotocathode
The invention relates to a microbial photoelectrochemical system for simultaneously generating electricity and hydrogen and treating sewage, which comprises an electrolytic bath and an ion exchange membrane, wherein the ion exchange membrane is arranged in the electrolytic bath and divides the electrolytic bath into an anode chamber and a cathode chamber; an anode and a photocathode are respectively arranged in the anode chamber and the cathode chamber; the anode and the photocathode are connected with a resistor through wires; one side of the photocathode is provided with a completely transparent quartz glass window; the anode is composed of electrogenesis microbes and an anode substrate; the photocathode is made of a sunlight-responsive semiconductor material; sewage containing organic pollutants is contained in the anode chamber; and an electrolyte solution is contained in the cathode chamber. In one microbial photoelectrochemical pool, the organic pollutants in the sewage are oxidized into carbon dioxide by electrogenesis microbes attached to the anode, and release electrons and protons, the protons are transferred to the cathode through the electrolyte so as to be reduced into hydrogen by the photocathode, and the electrons are transferred to the cathode through an external circuit so as to generate electric energy.
Owner:DONGGUAN WOJIESEN WATER TREATMENT
Fully-integrated in-plane micro-photomultiplier
An integrated micro-photomultiplier is disclosed which employs sub-micron-wide channels for electron amplification. These channels are created with standard lithographic and planar-fabrication techniques, and sealed with a vacuum-deposition process. A photocathode, continuous dynode, anode and signal-collector are fabricated along the channels. This photomultiplier design obviates the needs for through-substrate etching, and mechanical assembly of separate layers. Because large-scale-integration techniques can be used to fabricate multiple micro-photomultipliers, significant reductions in device cost and size are expected. The integrated micro-photomultiplier is useful for high-speed, low-light-level optical detection, and may find applications in optical communications, visible or infrared imaging, and chemical or biological sensing.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
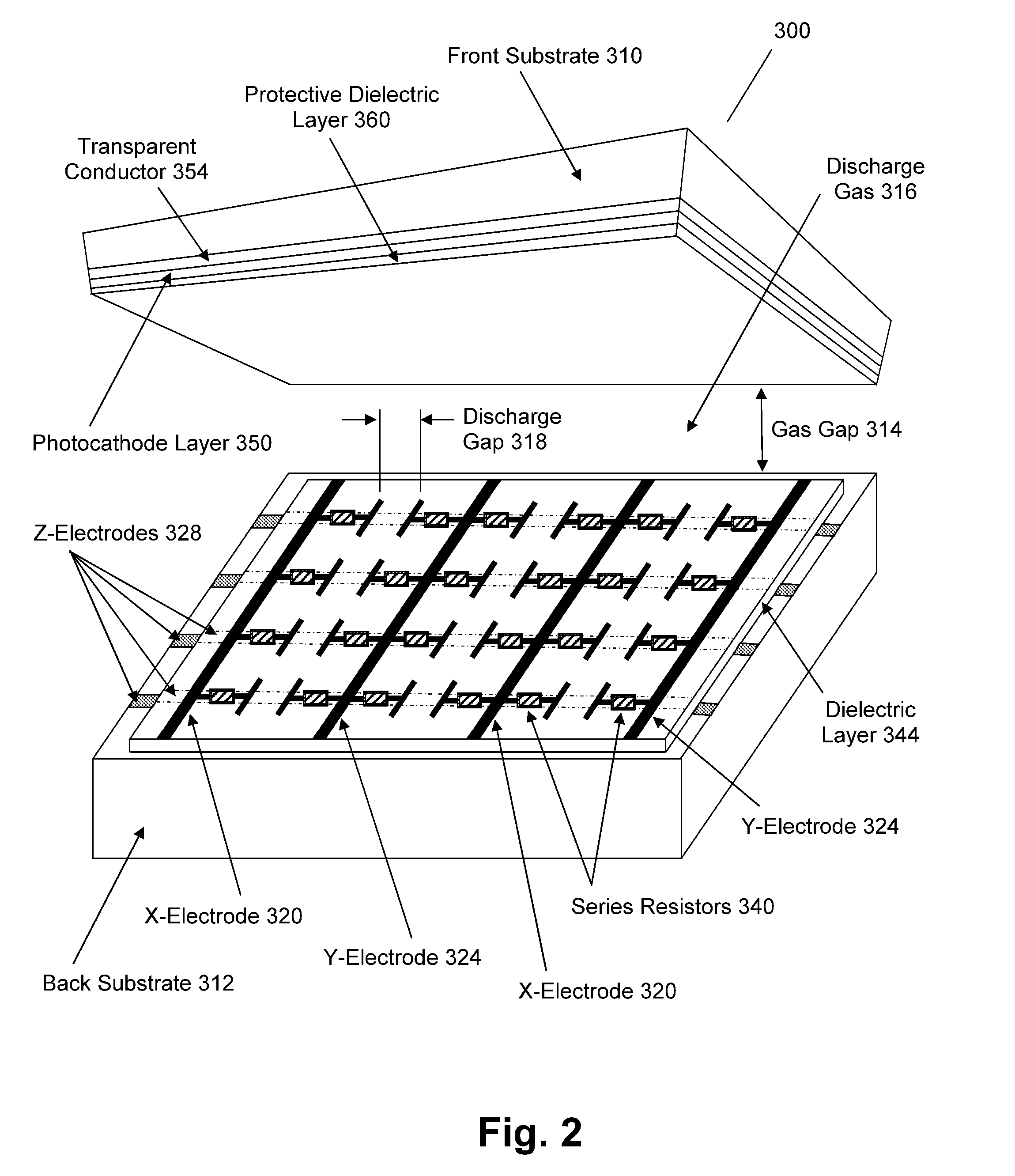
Plasma Panel Based Radiation Detector
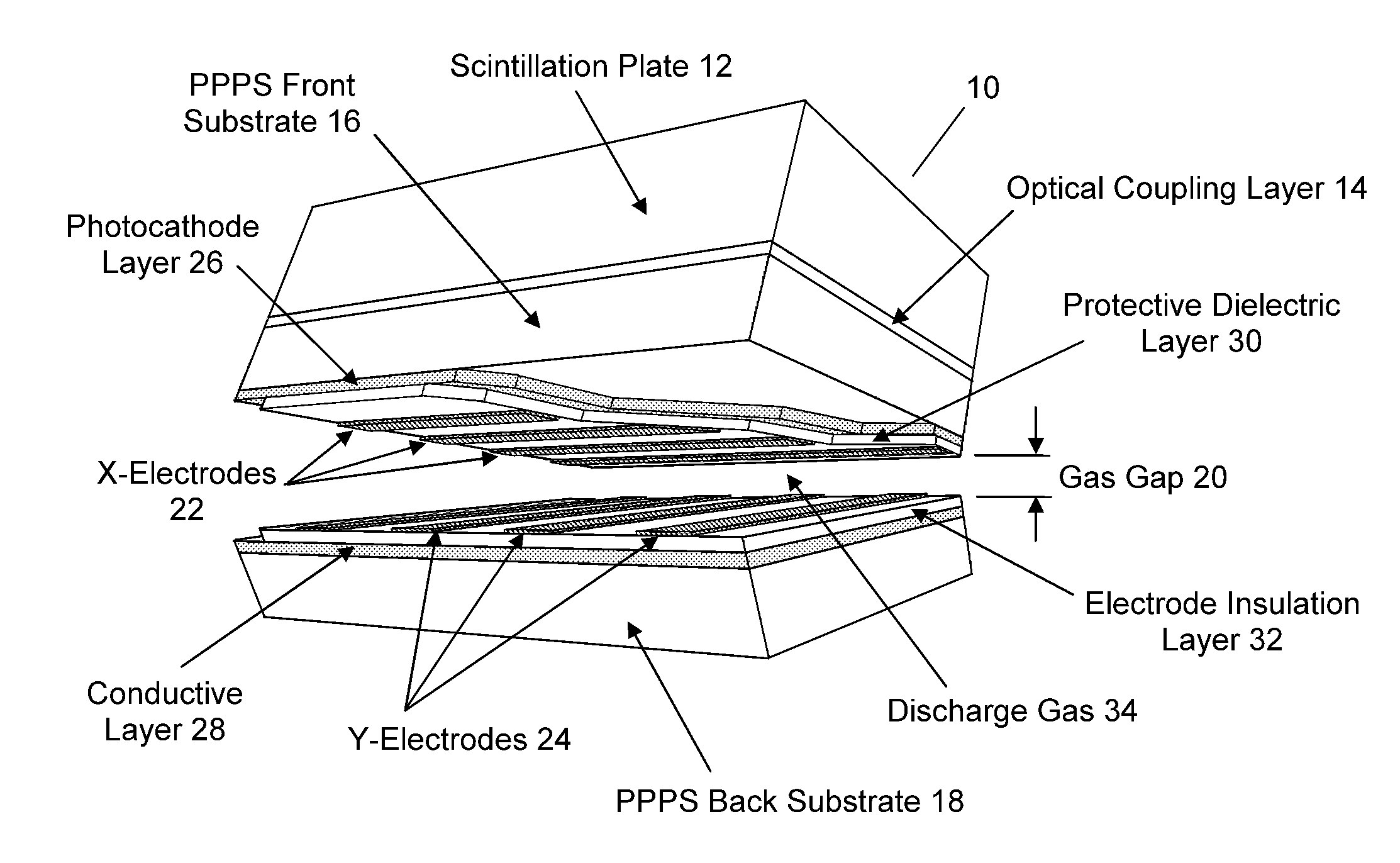
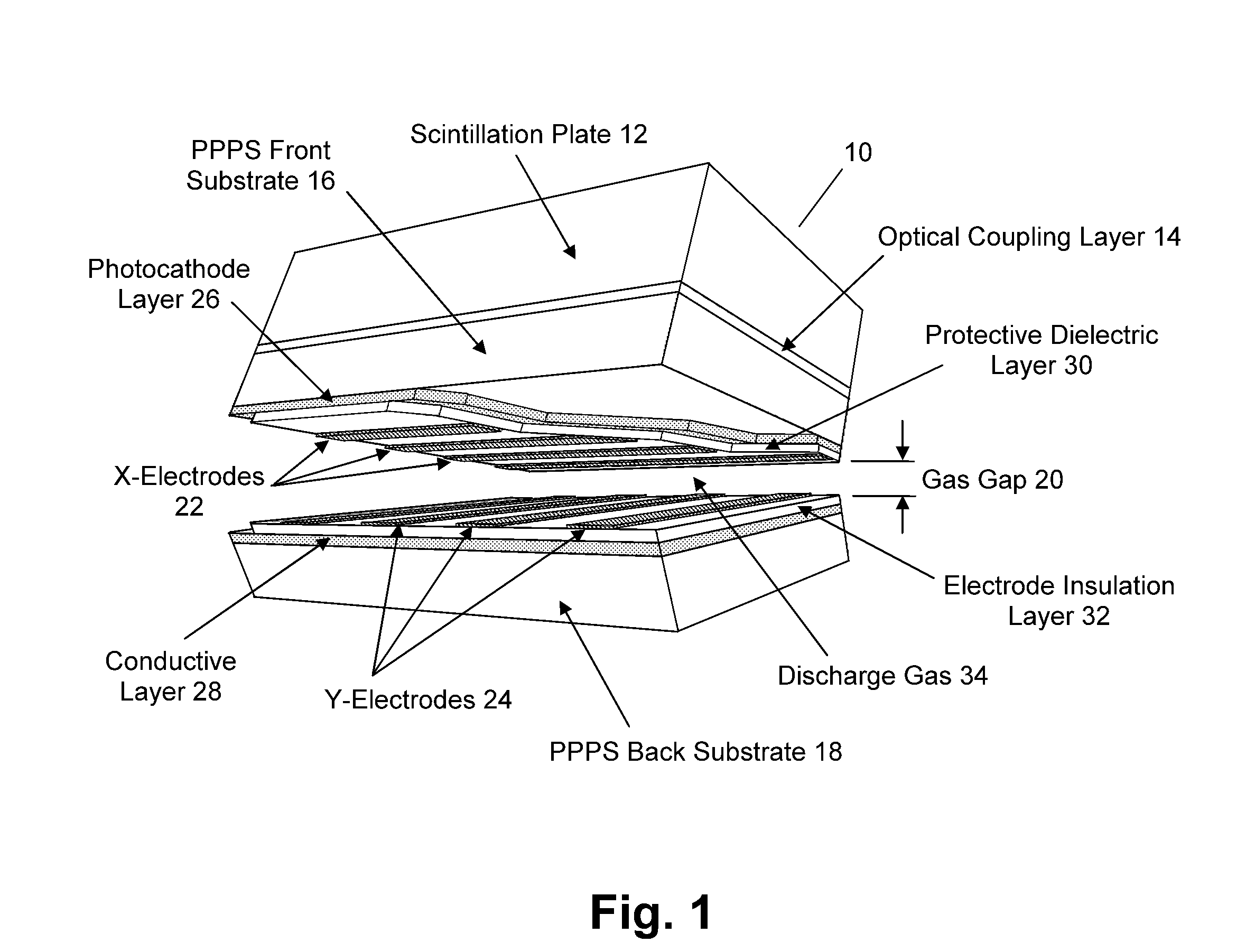
InactiveUS20080210878A1Electric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansElectricityPhotocathode
A radiation counting detector includes a first substrate and a second substrate that is generally parallel to first substrate and forms a gap with the first substrate. A gas is contained within the gap. A photocathode layer is coupled to one side of the first substrate and faces the second substrate. A first electrode is coupled to the second substrate and a second electrode is electrically coupled to the first electrode. A first impedance is coupled to the first electrode and a second impedance is coupled to the second electrode. A power supply is coupled to at least one of the electrodes. A first discharge event detector is coupled to the first impedance and a second discharge event detector is coupled to the second impedance. The radiation counting detector further includes a plurality of pixels, each capable of outputting a gas discharge pulse upon interaction with radiation received from the photocathode. Each gas discharge pulse is counted as having an approximately equal value. The radiation counting detector further includes circuitry for detecting if a gas discharge pulse is output from the pixels, and for counting each gas discharge pulse as an individual event.
Owner:INTEGRATED SENSORS
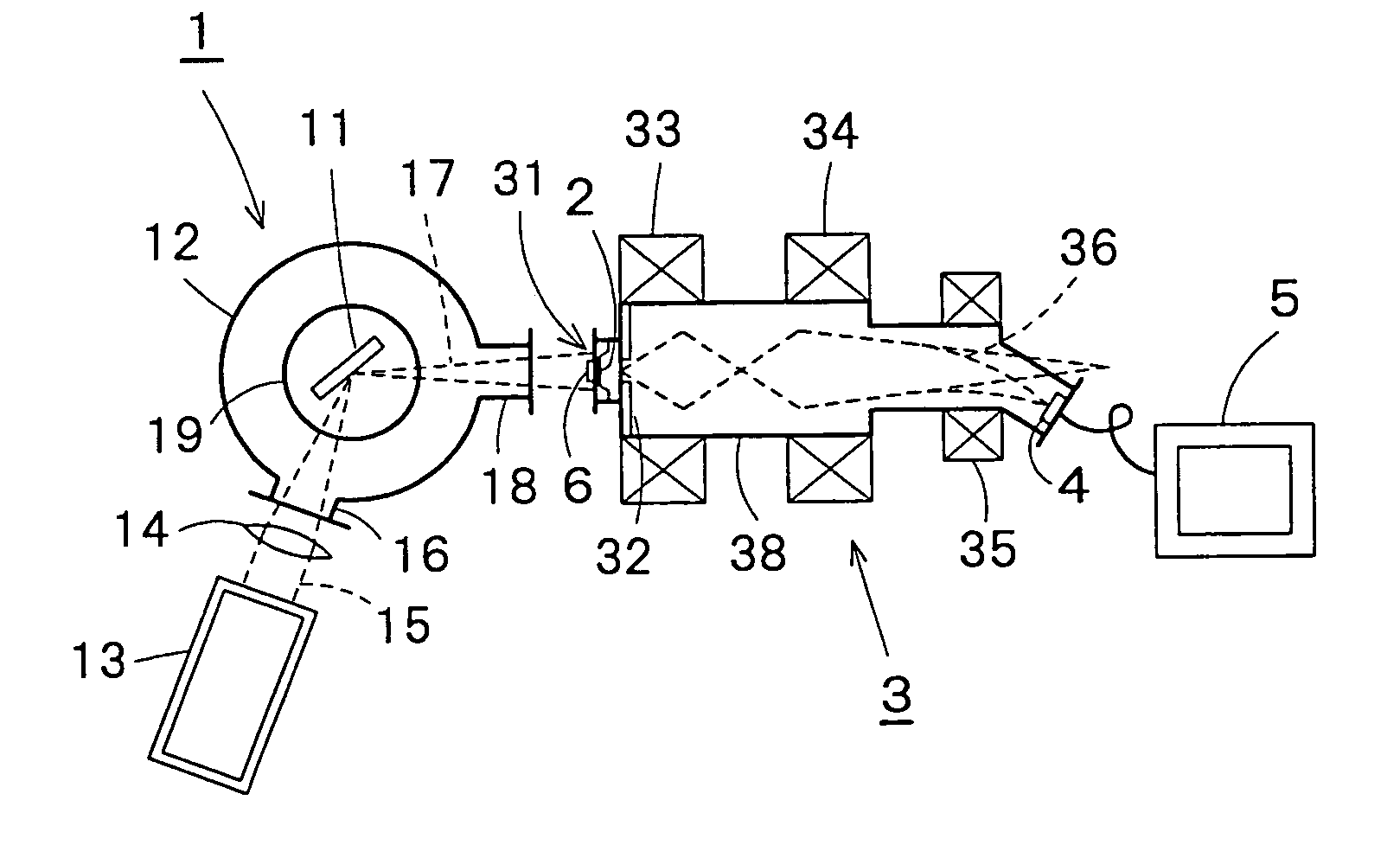
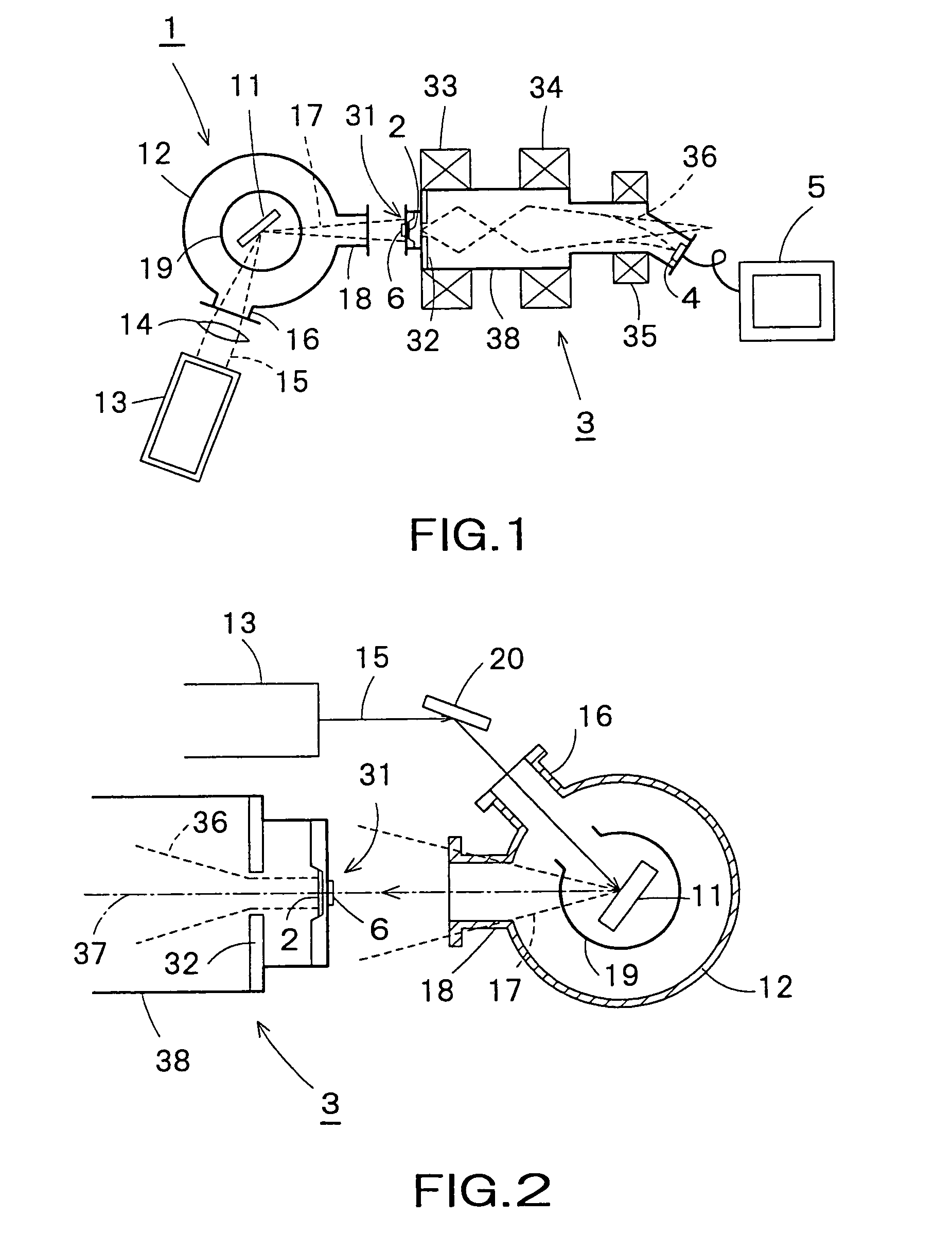
X-ray microscope apparatus
InactiveUS7039157B2Small sizeEasy to useImage-conversion/image-amplification tubesMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationImaging processingPhotocathode
An X-ray microscope apparatus includes an X-ray generator, a photocathode disposed on a path of X-rays for producing electrons when irradiated with X-rays generated by the X-ray generator, an electron image enlarging device having an acceleration anode for accelerating electrons produced by the photocathode and a magnetic lens for enlarging and focusing an electron beam of electrons emitted by the photocathode, an electron beam detecting device for detecting the electron beam focused thereon by the electron image enlarging device; and an image processing device for processing an electron image formed by the electron beam detecting device. The X-ray microscope apparatus can be formed in compact construction.
Owner:KAWASAKI HEAVY IND LTD
Single photon counting formatter
InactiveCN101387548AStitching is not requiredHigh sensitivityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMicro imagingPhotocathode
The invention relates to a single photon counting and imaging detection device. A high-voltage power supply of the device is connected with a micro-imaging reinforced tube through a high tension lead; a display, an image processing device and a printer are connected with a computer respectively; an anode collector is arranged between the micro-imaging reinforced tube and a preamplifier; the anode collector comprises a substrate, an electrode plated on the substrate and a signal lead; an anode is connected with the preamplifier through the signal lead; and the micro-imaging reinforced tube comprises a photocathode and a microchannel plate connected with the photocathode which are arranged sequentially along a light path. The device has the characteristics that the device can read out a time mark for arriving time and a general image of integral in a period, realize the single photon counting and two-dimensional imaging detection of an extremely-weak object, has the function of single photon counting, and can perform two-dimensional imaging on the extremely-weak luminous object. The device has the advantages of large area array, high sensitivity, low dark count, high resolution factor, good imaging linearity and the real-time measurement and processing.
Owner:陕西光电子先导院科技有限公司
Multi-layer photon counting electronic module
InactiveUS20110084212A1Reduce noiseWide dynamic rangeSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotocathodeComputer module
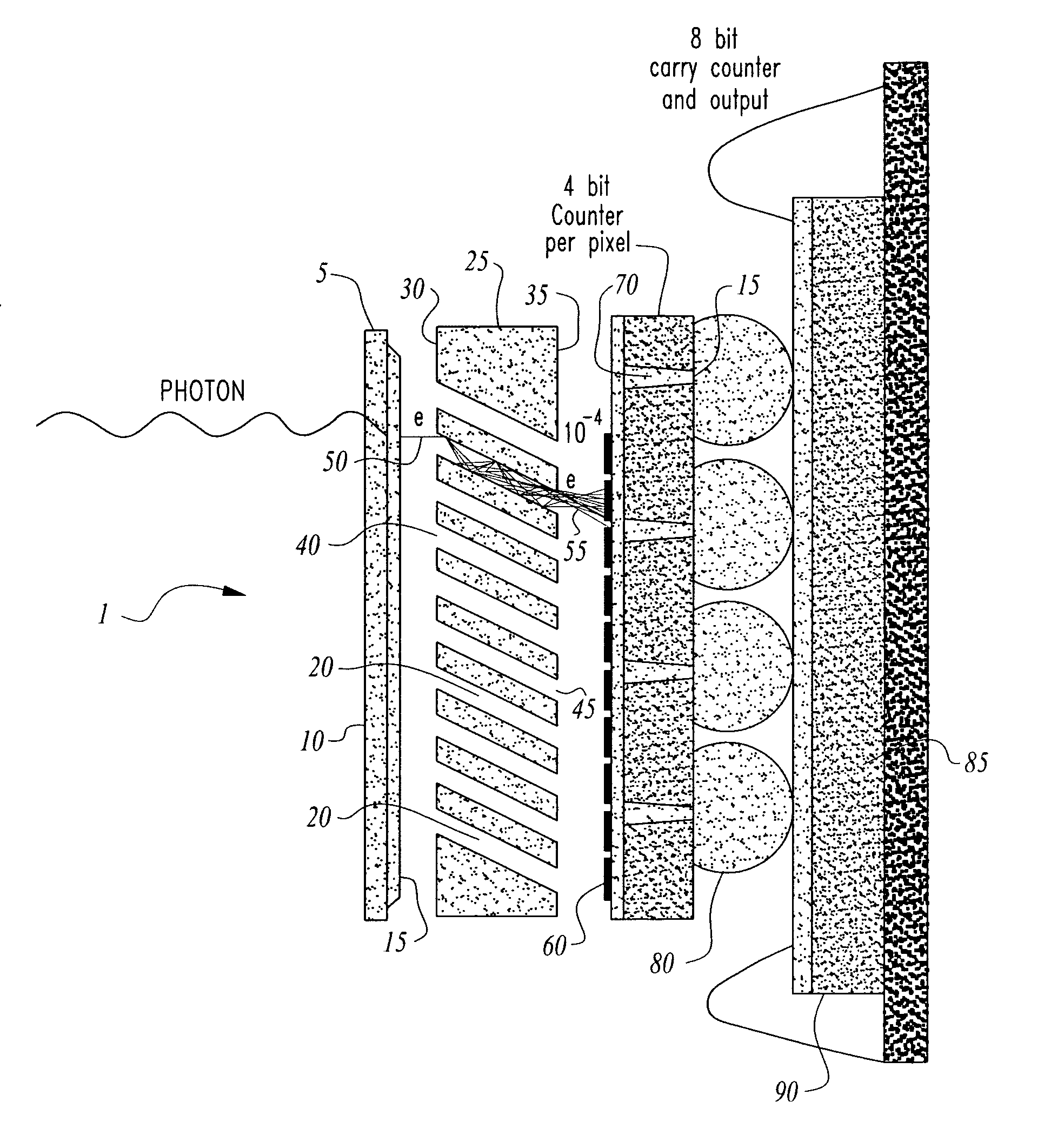
A multilayer electronic module for photon counting such as in the solar blind region of the ultraviolet electromagnetic spectrum is provided.The device comprises a photocathode for detecting photons and generating an electron output, a micro-channel plate for receiving the output electrons emitted from the photocathode in response to the photon input and amplifying same, readout circuitry and one or more bit-counting circuit layers used to count the electron output of the micro-channel plate.
Owner:PFG IP +1
Photoelectrolysis of water using proton exchange membranes
ActiveUS7037414B2Improve efficiencyImprove stabilityMachining electrodesCellsElectro catalystWater use
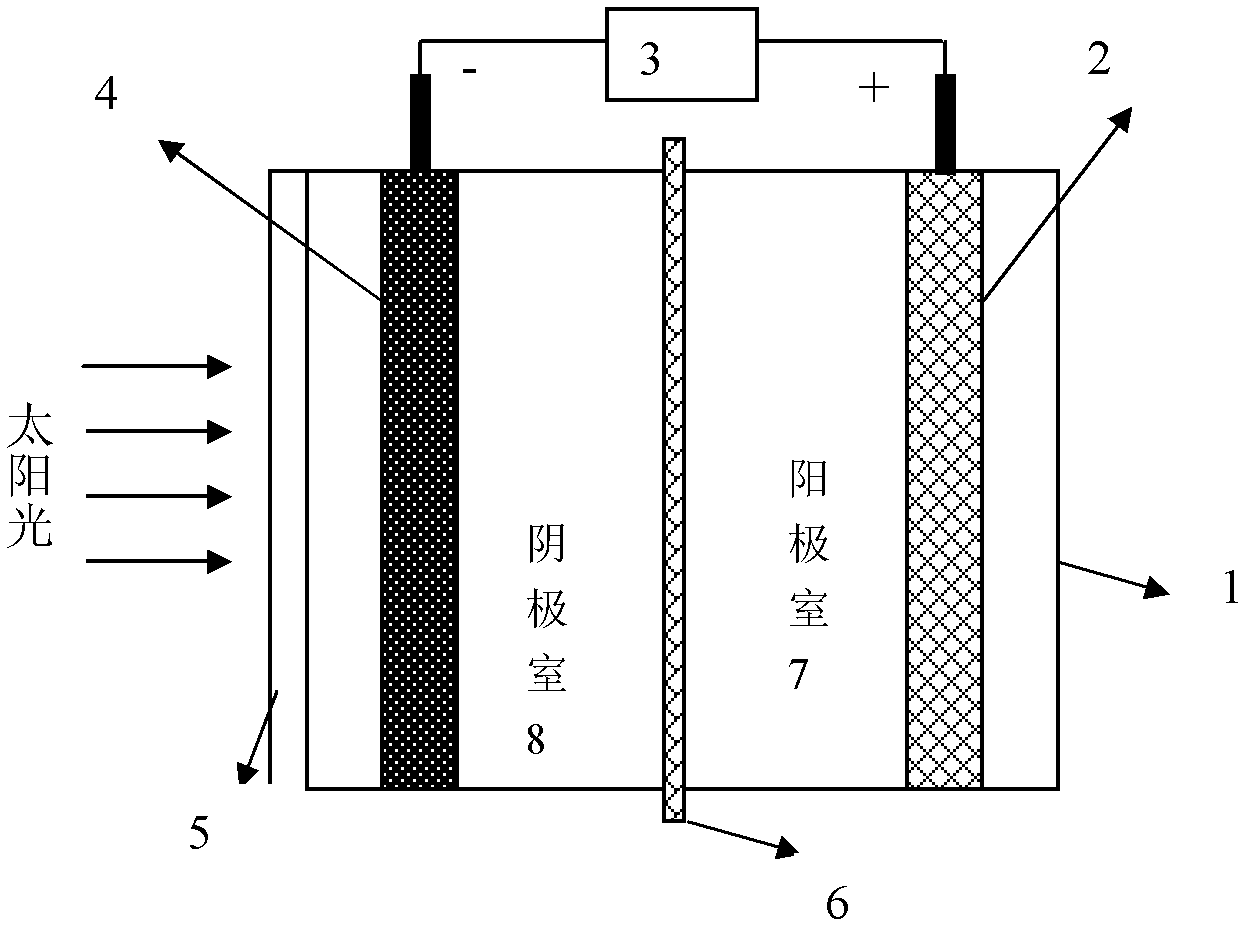
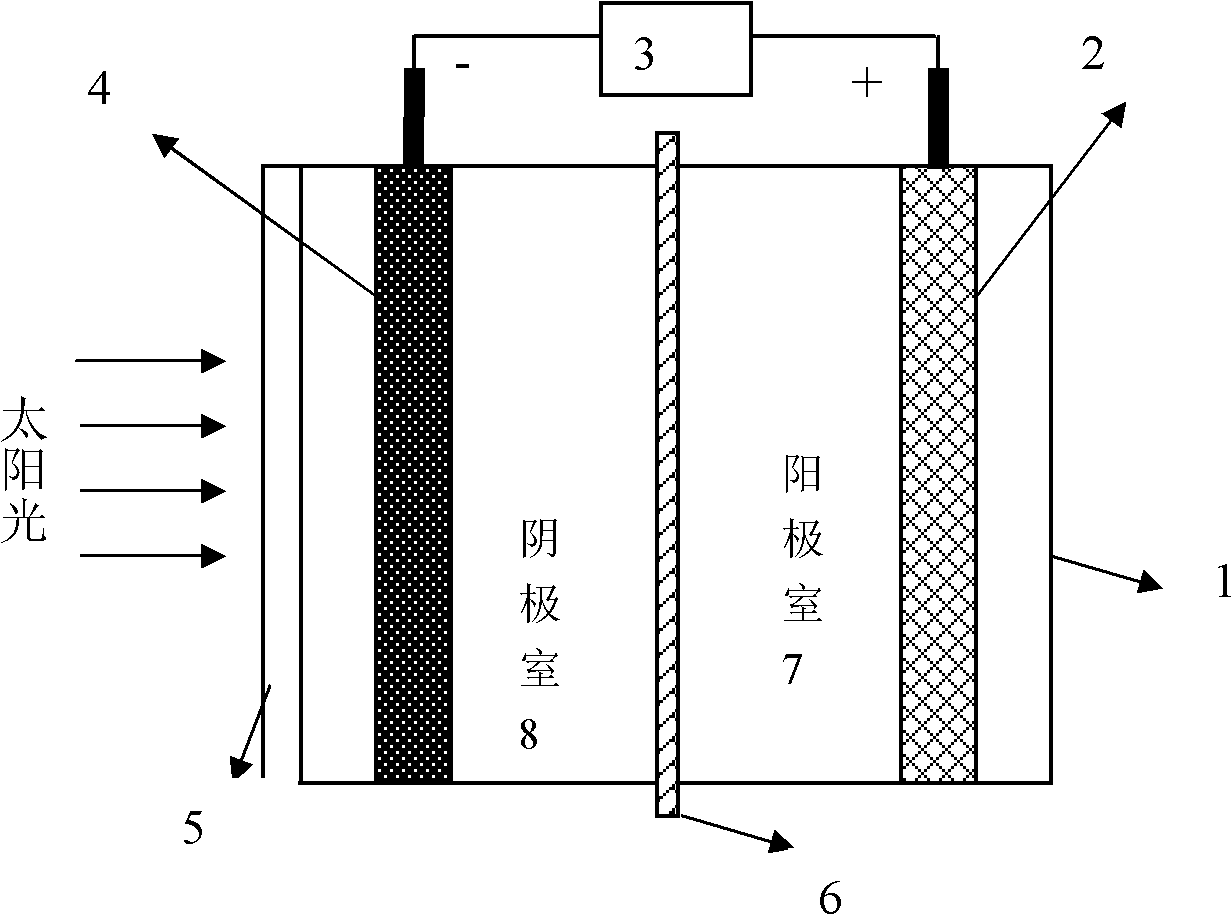
A photoelectrochemical cell which includes a light transmissive enclosure, a semiconductor photoanode disposed within the light transmissive enclosure, a semiconductor photocathode disposed within the light transmissive enclosure, and an electrolytic solution disposed entirely between the semiconductor photoanode and the semiconductor photocathode. This is achieved by the use of semiconductor photoelectrodes (photoanodes and photocathodes) which include a proton exchange membrane having an electrolyte facing surface in contact with the electrolytic solution and a light transmissive wall facing surface, and having a photo electro-catalyst disposed on the light transmissive wall facing surface.
Owner:GAS TECH INST
Field emission photo-cathode array for lithography system and lithography system provided with such an array
InactiveUS20030178583A1Increase productionEfficiency of electron generation in the converter layer will be increasedElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsElectron sourceLithographic artist
The present invention relates to the use of an electron source in a lithography system for producing a plurality of electron beams directed towards an object to be processed, said electron source comprising a plurality of field emitters, characterized in that said electron source comprises a semiconductor layer with a plurality of tips, said use including the steps of: producing a plurality of light spots on said electron source, producing one light spot on one field emitter; exciting electrons to a conduction band (Ec) by light from a light spot within said field emitter by a photo-electric effect; accelerating said electrons in said conduction band (Ec) towards said tips and tunnelling them outside tips in order to generate electrons for said plurality of electron beams, causing tips to generate electrons for said electron beam having a spot smaller than 100 nm on an object to be processed, each spot of light triggering an electron beam from one tip.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Imaging system
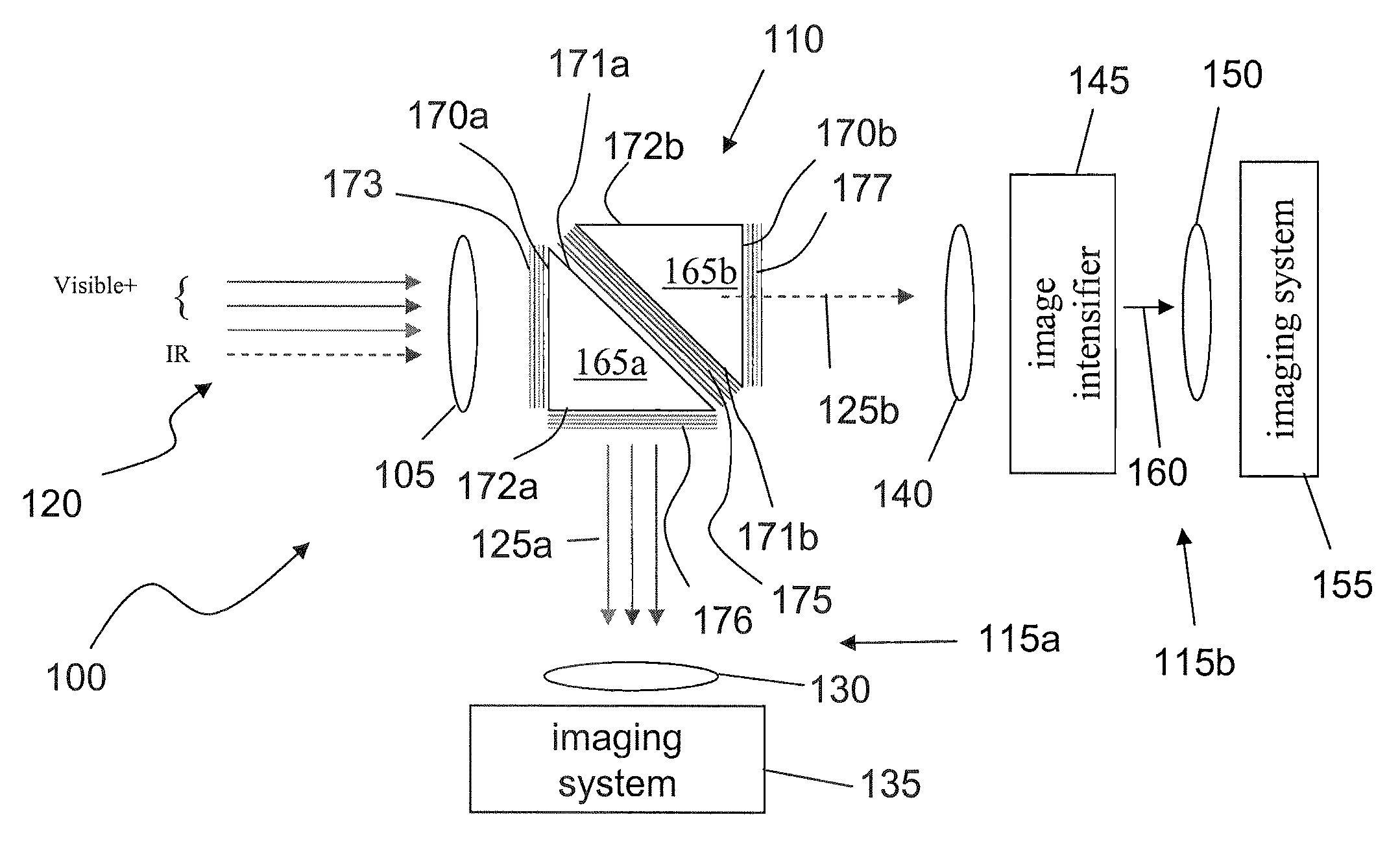
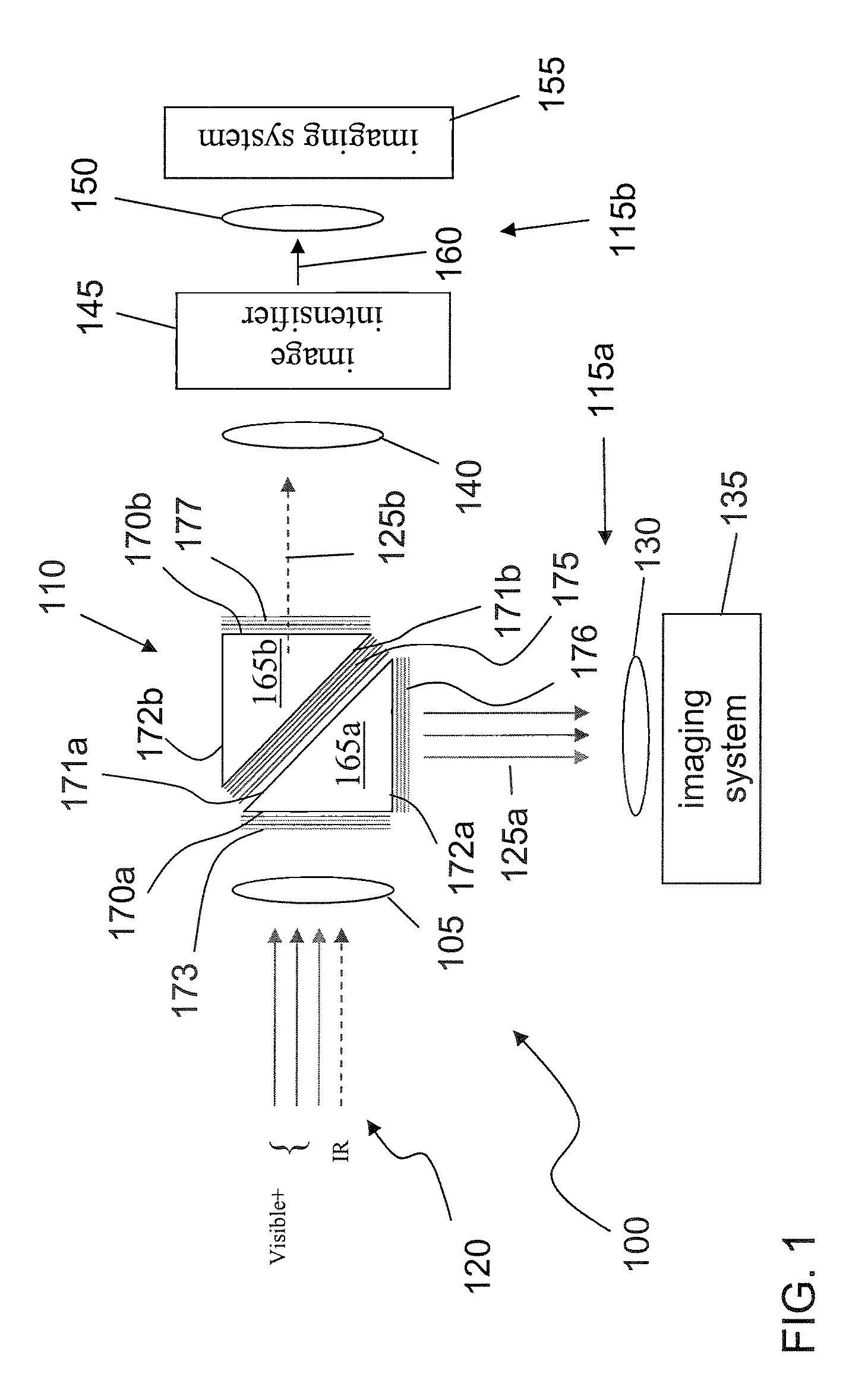
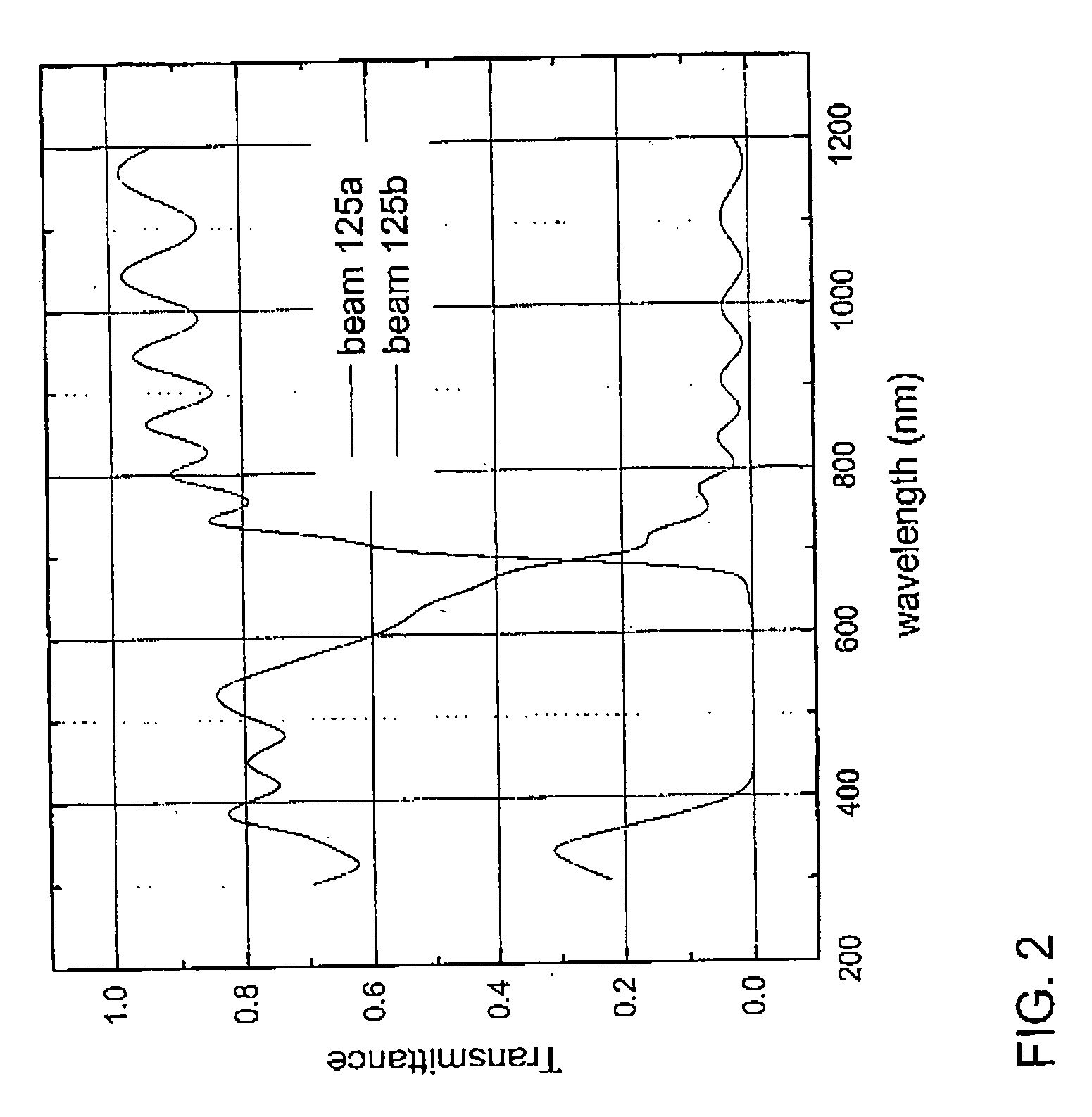
InactiveUS20080237771A1Extended service lifeAvoid lostTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesSpectral bandsPhotocathode
A viewing system configured to combine multiple spectral images of a scene, the system includes a spectral beam separator configured to split an incoming beam of radiation into a first and a second beam of radiation, the first beam of radiation including radiations substantially in a first spectral band and the second beam of radiation including radiations substantially in a second spectral band; an image intensifier configured to intensify the second beam of radiation, the image intensifier including a photocathode configured to produce a flux of photoelectrons with substantially increased efficiency when exposed to the second beam of radiation, the photocathode constructed and arranged to substantially absorb all the radiations in the second beam of radiation; a current amplifier configured to amplify the flux of photoelectrons; and a display system configured to display an image of the scene in the second spectral band based on the amplified flux of electrons simultaneously with an image of the scene in the first spectral band.
Owner:SUBRAHMANYAM PILLA
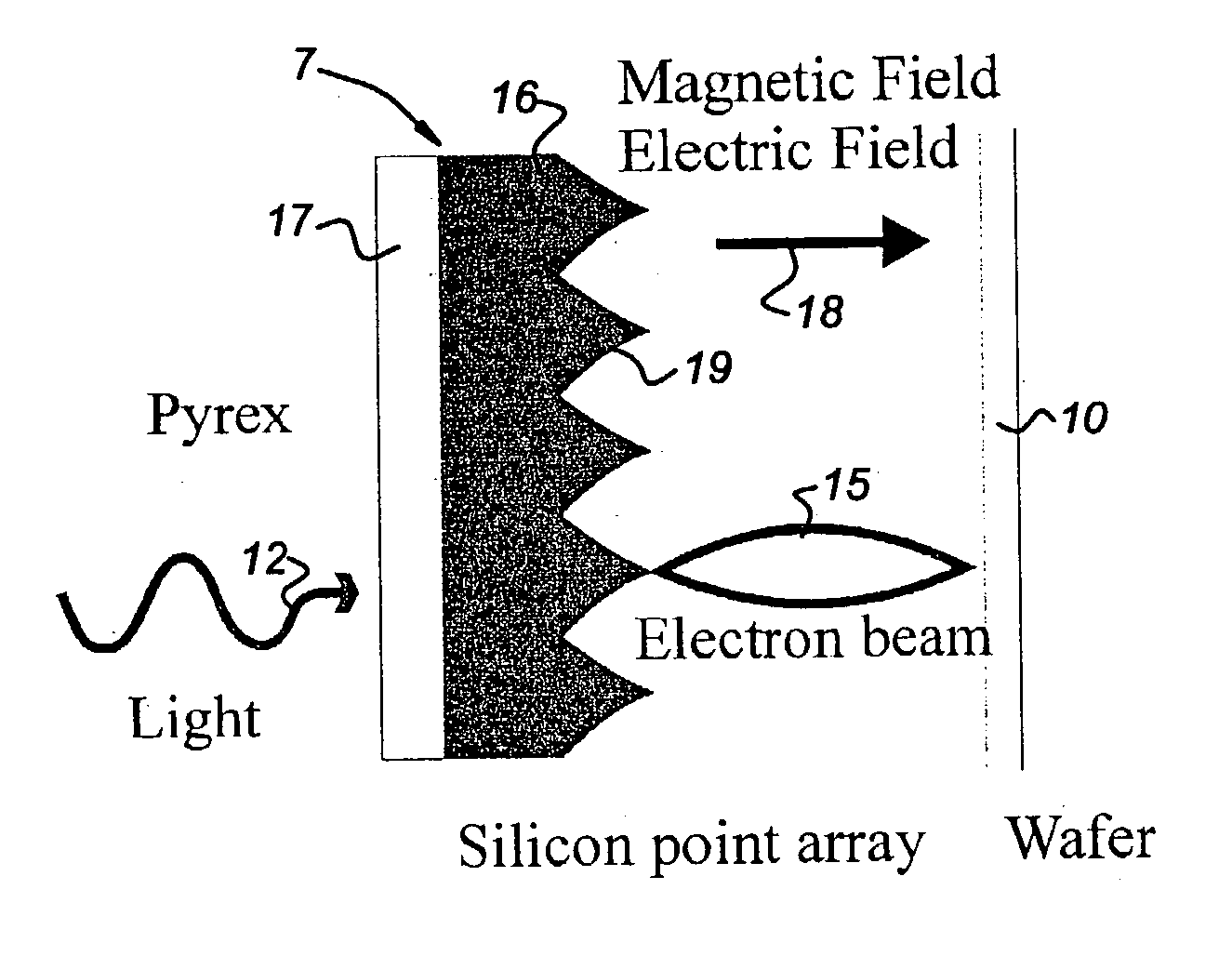
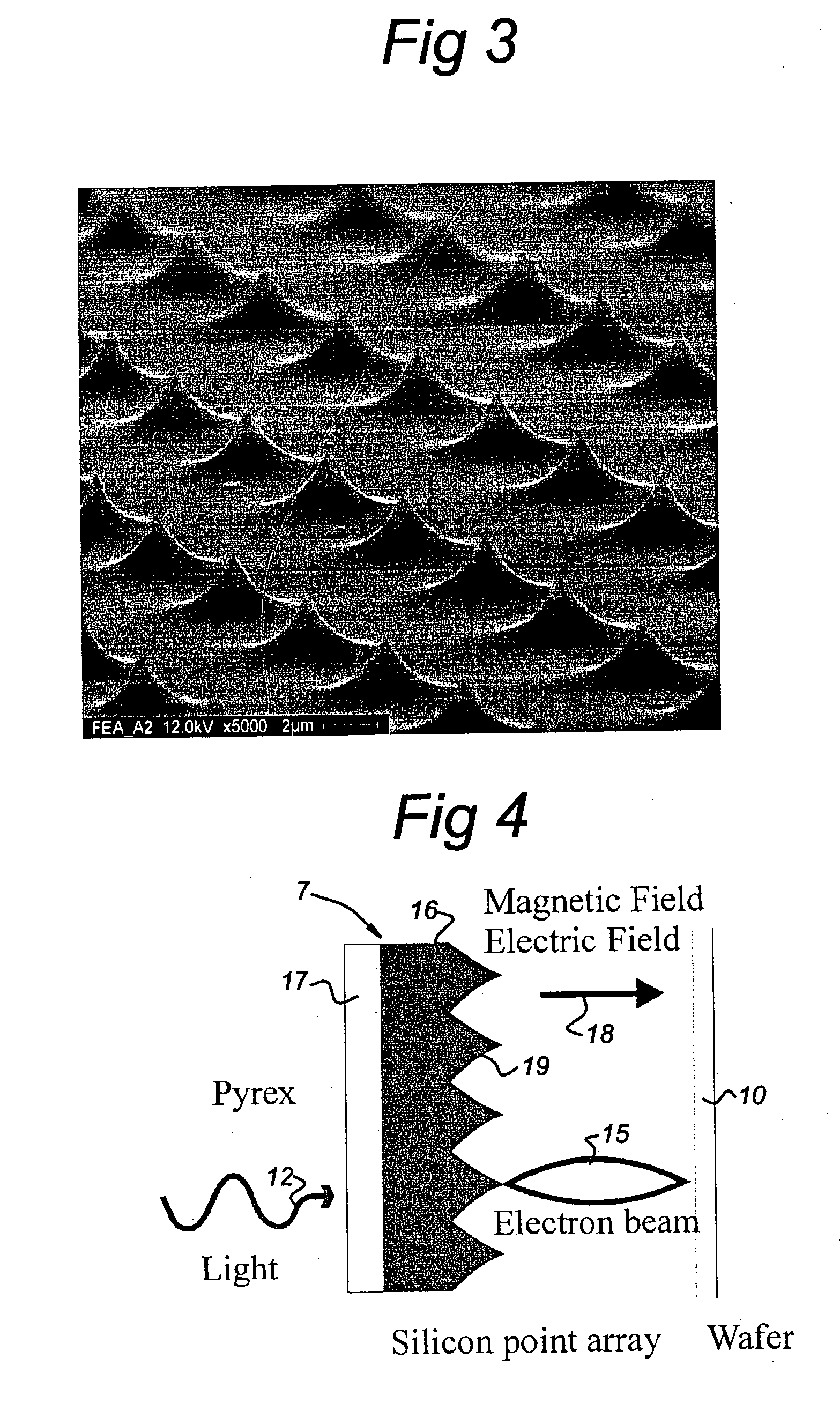
Photocathode including field emitter array on a silicon substrate with boron layer
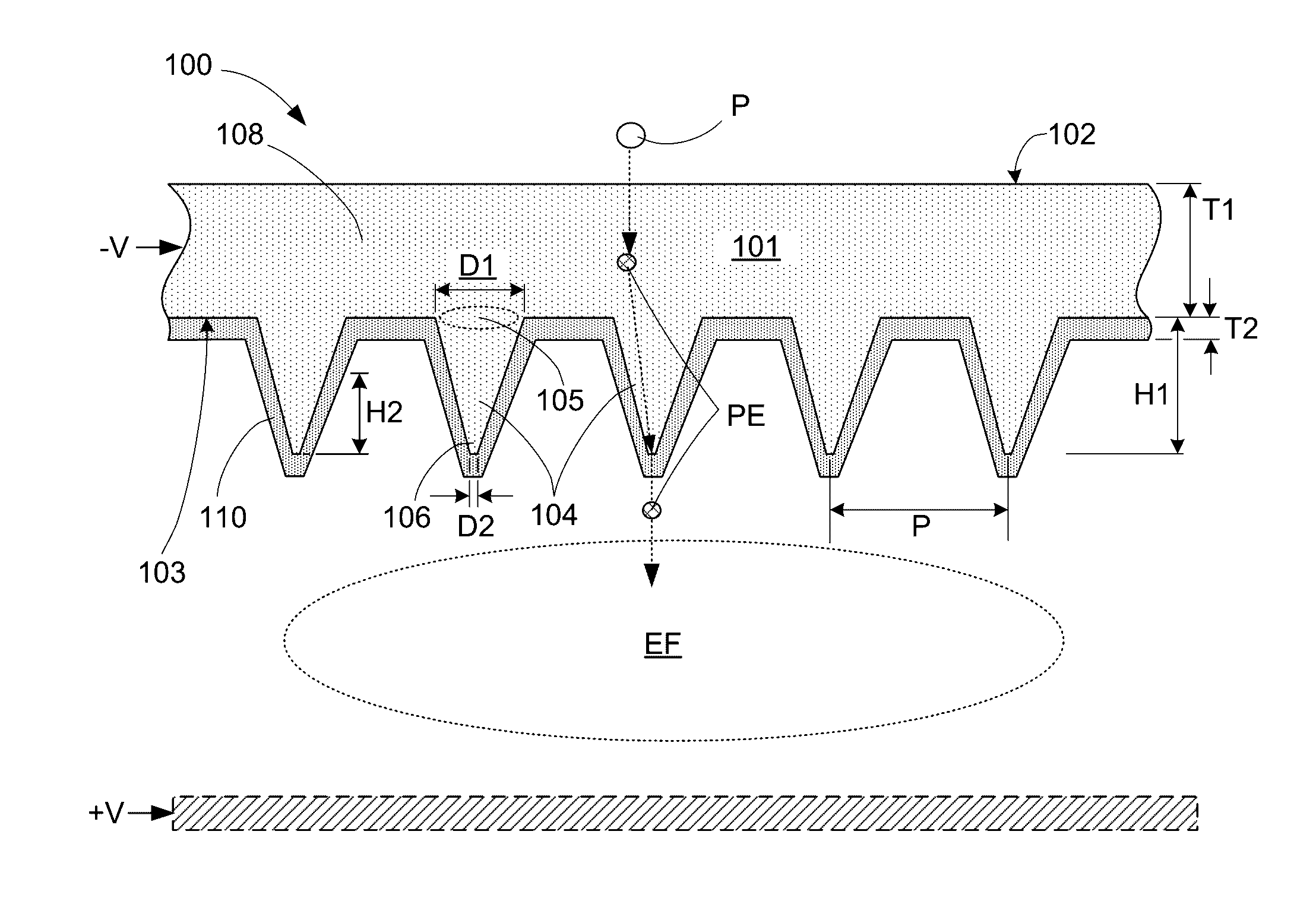
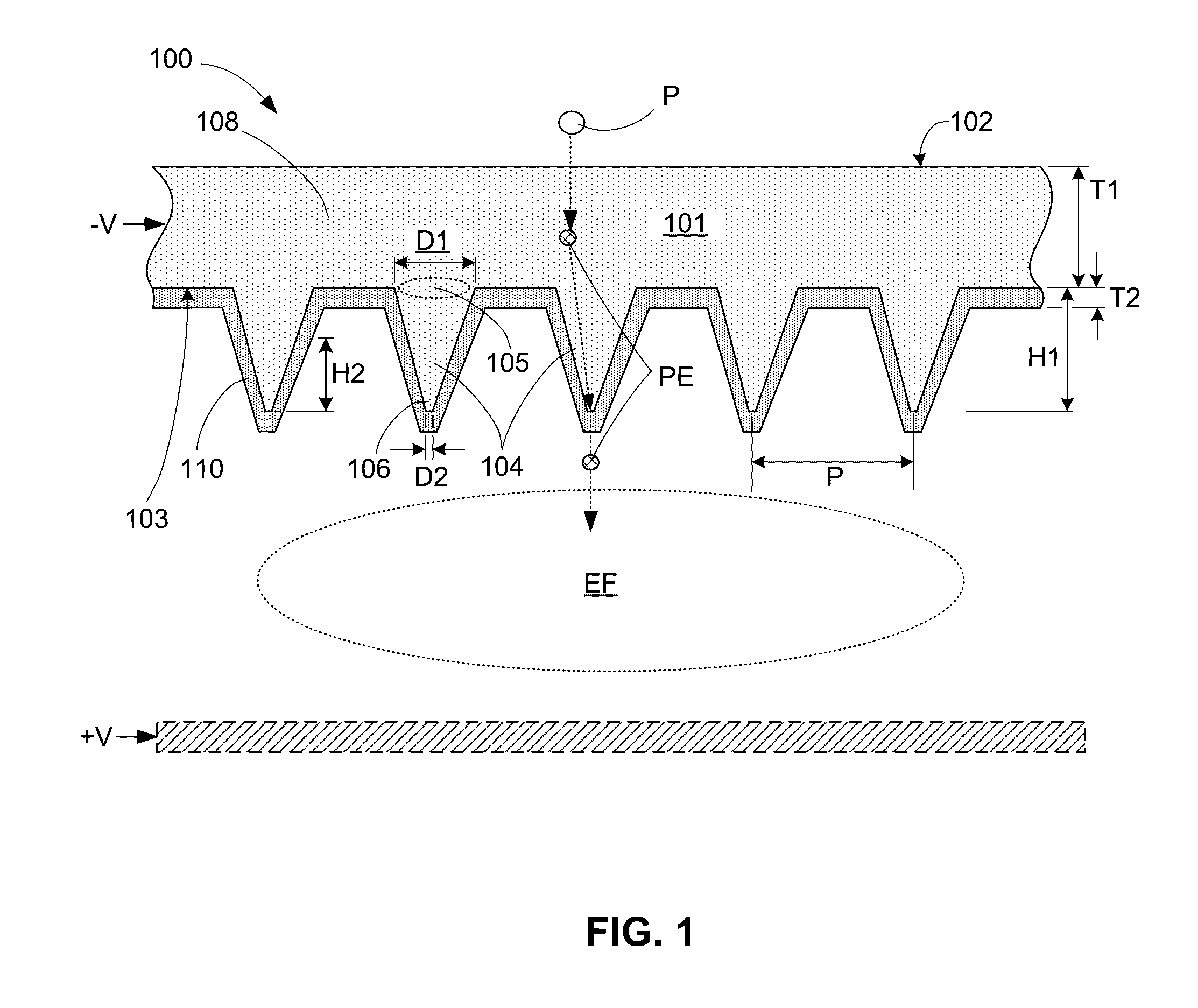
ActiveUS20160343532A1Improve work functionReduce potential barrierSolid-state devicesImage pickup tubesPhotocathodeWhiskers
A photocathode utilizes an field emitter array (FEA) integrally formed on a silicon substrate to enhance photoelectron emissions, and a thin boron layer disposed directly on the output surface of the FEA to prevent oxidation. The field emitters are formed by protrusions having various shapes (e.g., pyramids or rounded whiskers) disposed in a two-dimensional periodic pattern, and may be configured to operate in a reverse bias mode. An optional gate layer is provided to control emission currents. An optional second boron layer is formed on the illuminated (top) surface, and an optional anti-reflective material layer is formed on the second boron layer. An optional external potential is generated between the opposing illuminated and output surfaces. An optional combination of n-type silicon field emitter and p-i-n photodiode film is formed by a special doping scheme and by applying an external potential. The photocathode forms part of sensor and inspection systems.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
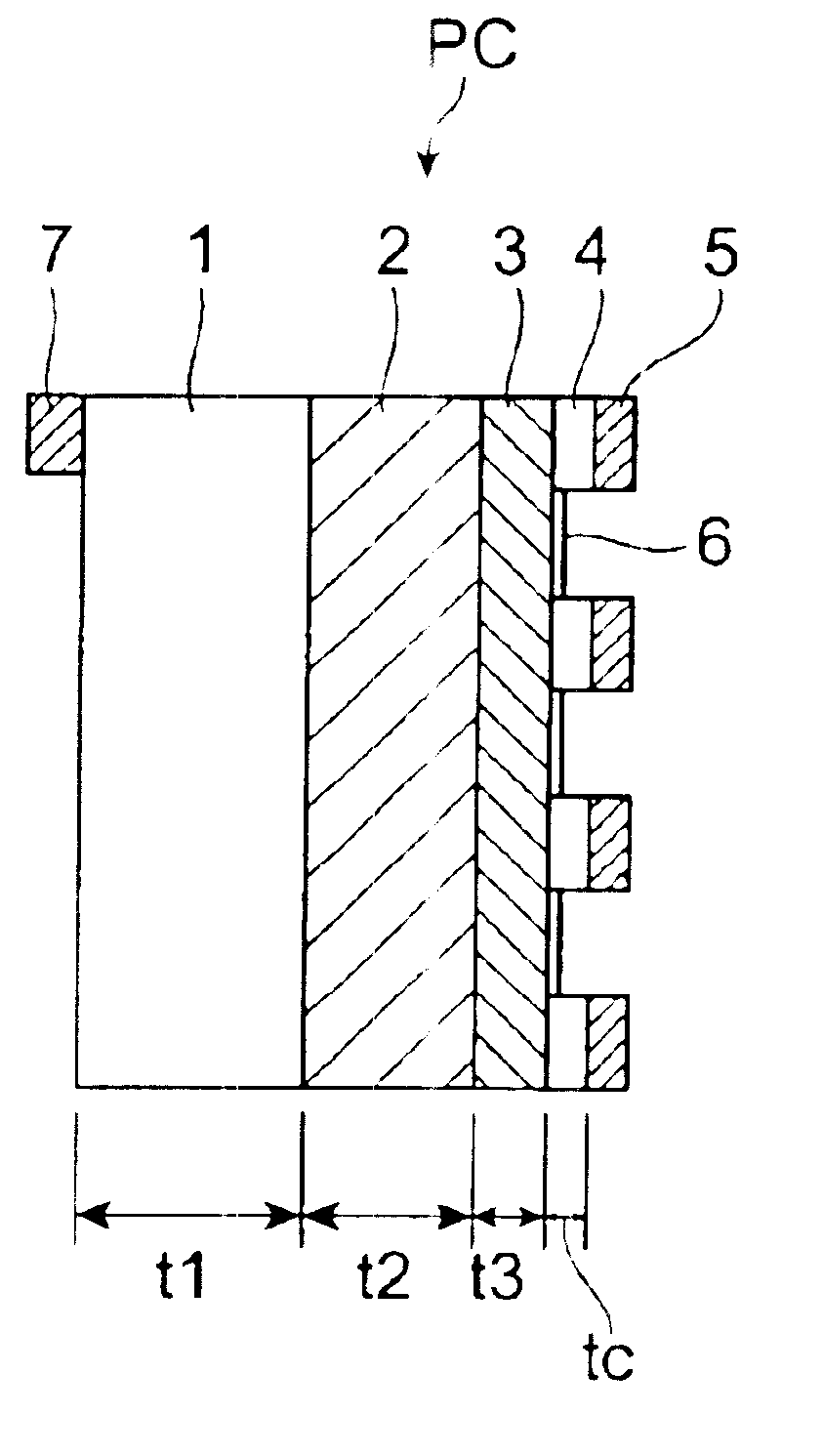
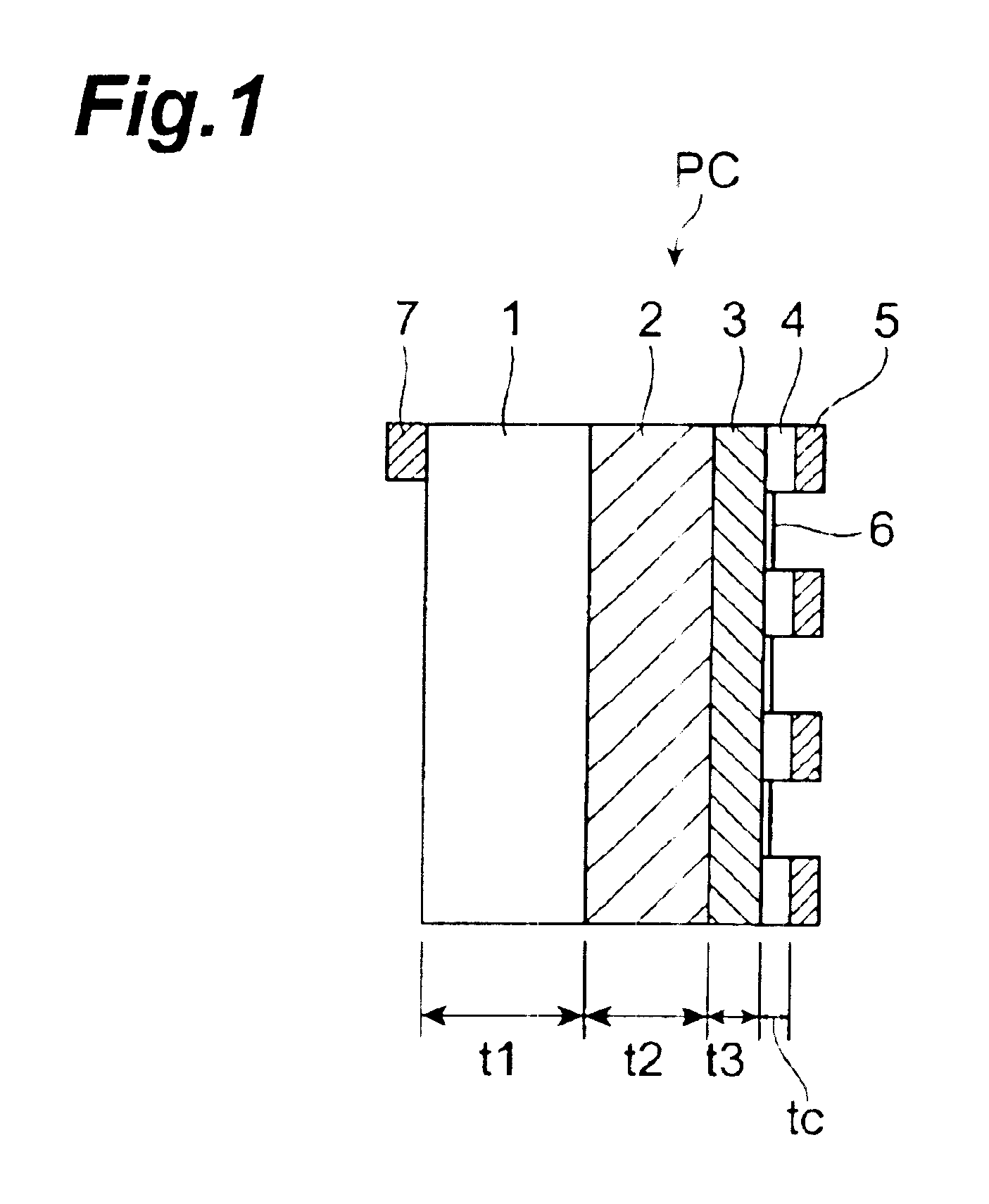
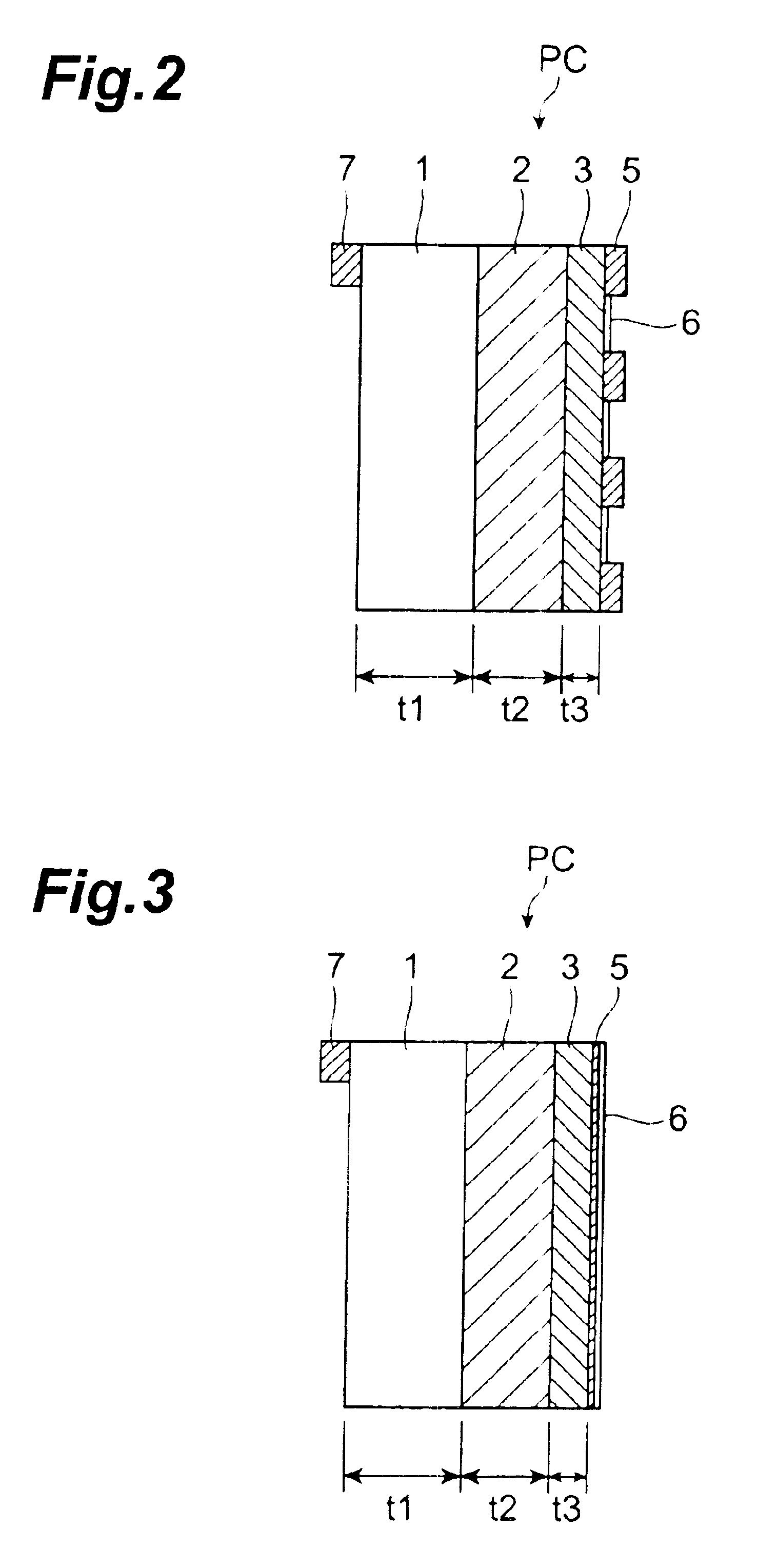
Semiconductor photocathode
InactiveUS6917058B2Decrease in time resolutionIncrease the electric field strengthSolid-state devicesPhoto-emissive cathodesInfraredPhotocathode
In the case of a thick light-absorbing layer 2, a phenomenon of a decrease in the time resolution occurs. However, when the thickness of the light-absorbing layer 2 is limited, a portion of low electron concentration in one electron group is cut out, and hence overlap regions of adjacent electron concentration distributions decrease. Therefore, by shortening the transit time necessary for the passage of electrons, regions of overlapping electron distributions due to diffusion can also be suppressed. Furthermore, the strength of an electric field within a light-absorbing layer can be increased by thinning the light-absorbing layer. Therefore, the time resolution of infrared rays can be remarkably improved by a synergistic action of these effects. If it is assumed that the time resolution is 40 ps (picoseconds), for example, when the thickness of a light-absorbing layer is 1.3 μm which is nearly equal to the wavelength of infrared, then a possible time resolution is 7.5 ps when this thickness is 0.19 μm.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
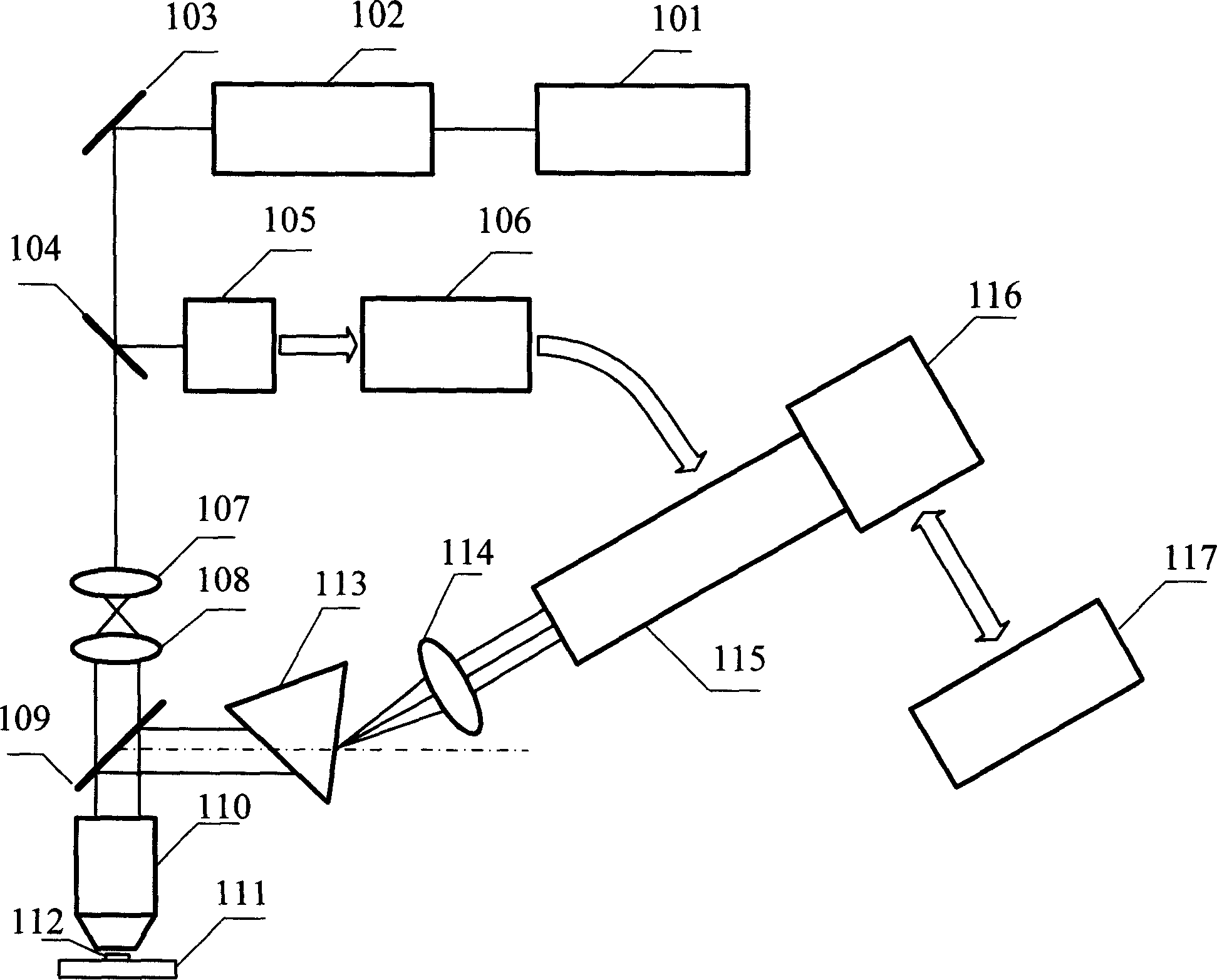
Multispectral stripe tube three-dimensional lidar imaging apparatus
InactiveCN102253394AImprove accuracyIncrease richnessElectromagnetic wave reradiationPhotocathodeImage detection
The invention, which belongs to the photoelectric imaging technology field, relates to a multispectral stripe tube three-dimensional lidar imaging apparatus. The apparatus comprises: a multi-wavelength laser, a beam expanding prism, a reception telescope, a diffraction grating spectroscope, a convex lens, optical filters, a stripe tube, a coupling light cone, and a CCD camera. A mixing multi-wavelength laser beam that is emitted by the multi-wavelength laser passes through the beam expanding prism and then is shot at an object and is reflected; the reflected laser beam is received by the reception telescope and is gathered to the diffraction grating spectroscope; and then the gathered laser beam passes through the convex lens and is focused on the optical filters; the focused laser beam bombards a photoelectric cathode of the stripe tube to generate a plurality of electron beams though a slit and the plurality of electron beams bombard a fluorescent screen in the stripe tube; and then a multispectral strip image is coupled through the coupling light cone and is imaged on the CCD camera. According to the invention, a multi-spectral detection technology is integrated into a stripe tube lidar imaging apparatus, so that accuracy of object imaging and richness of information are improved; and a specific wavelength can detect a weak signal; therefore, an application arrange of the stripe tube lidar imaging detection apparatus is expanded.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Photomultiplier of electrostatic focusing micro-channel plates
ActiveCN103915311AAchieve electrical connectionReduce transit time differenceMultiplier anode arrangementsPhotocathodePhotomultiplier
The invention discloses a photomultiplier of electrostatic focusing micro-channel plates. The photomultiplier comprises a photocathode, an electron multiplier, an anode, a focusing electrode, a power supply electrode and a supporting post for supporting the focusing electrode, the electron multiplier and the anode, the focusing electrode, the electron multiplier and the anode are arranged in a glass vacuum container, and a signal lead of the anode and the power supply electrode penetrate through the glass vacuum container to be connected with an external circuit. The photomultiplier is characterized in that the centers of the focusing electrode, the electron multiplier and the anode are coaxial, the electron multiplier comprises the two pairs of micro-channel plates arranged in parallel, and certain gaps are reserved between the micro-channel plates. Compared with the prior art, all stages of voltages of the micro-channel plates are independently adjusted, and high gains and good photoelectron spectra are achieved.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
Temporal-spatial resolution radiant flux diagnosis system
ActiveCN106526654AImprove time resolutionHigh spatial resolution measurementX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentTemporal resolutionMicrometer
The invention provides a temporal-spatial resolution radiant flux diagnosis system, which is used for conducting precise diagnosis on the temporal and spatial evolution process of an X-ray radiant flux in a hohlraum. The hohlraum emits X-rays which undergo imaging by means of a pinhole in a pinhole plate, a portion of the X-rays is imaged onto an imaging plate; the other portion of the X-ray passes through a slit I in the imaging plate and then passes through a slit II in a time resolution plate to irradiate on an X-ray photocathode, further passes through a streak camera focusing deflection system and is recorded in a streak camera. According to the recorded signal, the temporal and spatial evolution process of the X-ray radiant flux emitted at a specified position of the hohlraum can be obtained. The temporal-spatial resolution radiant flux diagnosis system has time resolution with picosecond magnitude and temporal resolution with dozens of micrometer magnitude, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Electron tube
InactiveUS20070176160A1Reduced crystal defectHigh sensitivityPhoto-emissive cathodesPhotoelectric discharge tubesPhotocathodeCrystallographic defect
A GaN-based semiconductor photocathode is applied to an electron tube. A GaN-based compound semiconductor layer is laterally grown on a substrate, and incorporated in the electron tube. The crystal defects of the compound semiconductor layer are reduced, whereby an electron tube which has inconceivably high sensitivity is realized.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
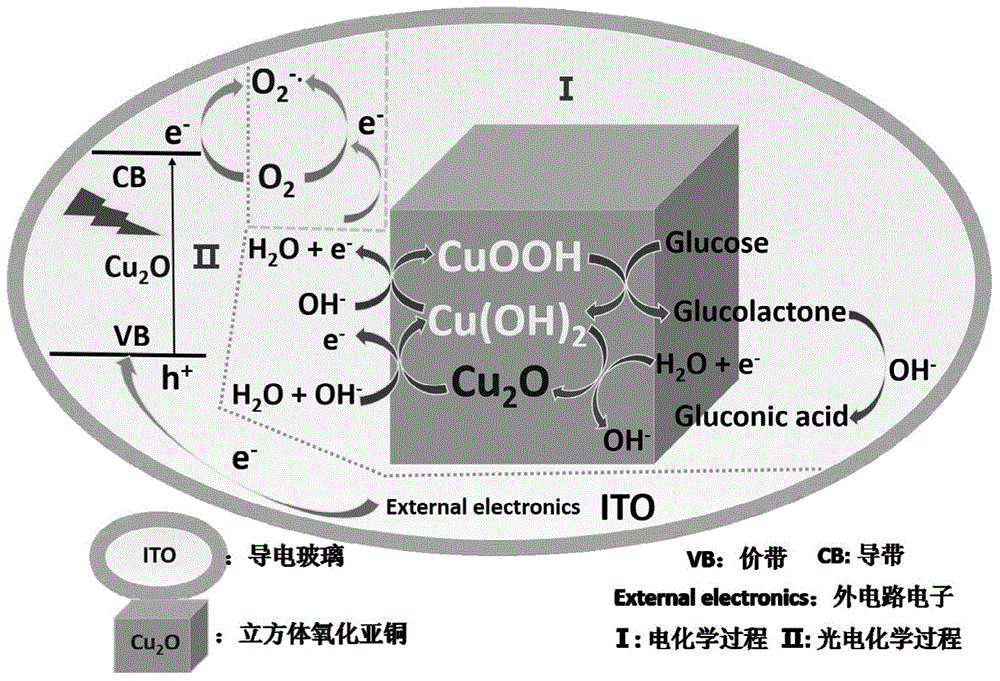
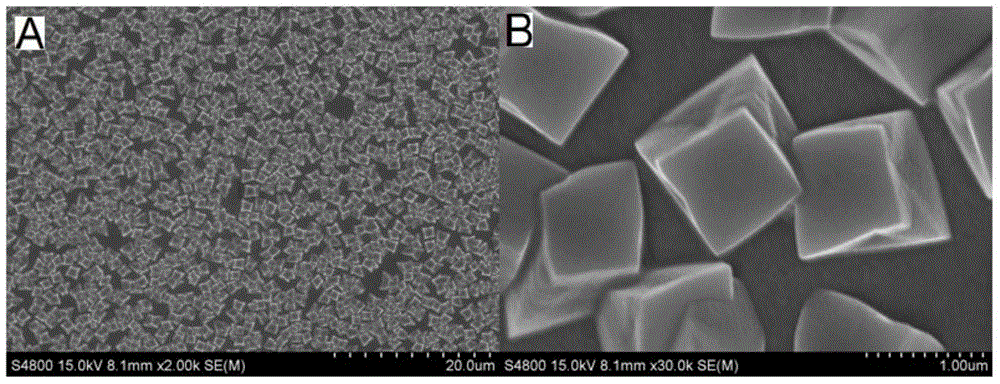
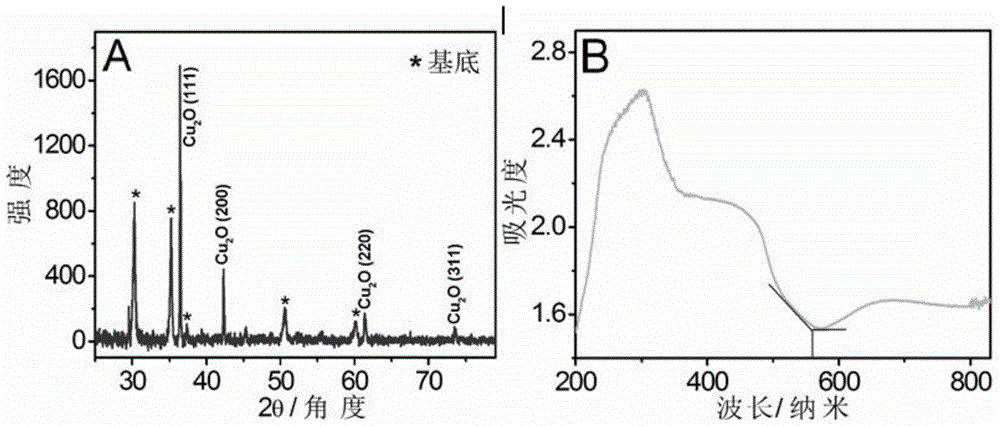
Construction method and detection method of cuprous oxide membrane-based enzyme free-oxygen sensitive glucose photo electrochemical sensor
InactiveCN104569096ALow detection signal backgroundLow costMaterial electrochemical variablesPhotocathodeOxygen
The invention discloses a construction method of a cuprous oxide membrane-based enzyme free-oxygen sensitive glucose photo electrochemical sensor. The construction method comprises the following steps: with an ITO conductive glass as a working electrode, a platinum wire as a counter electrode and a silver / silver chloride electrode as a reference electrode, inserting the three electrodes into a sodium hydroxide solution containing 0.05mol / L copper sulfate and 0.1mol / L sodium citrate, and regulating a pH value to be 11; under the conditions that the deposition temperature is 60 DEG C, the deposition potential is -0.4V and the deposition time is 20 minutes, forming a cuprous oxide membrane on the surface of the ITO conductive electrode; and rinsing residual solution on the surface with pure water, drying for 1h at the temperature of 100 DEG C, and forming a stable cuprous oxide membrane-based photocathode. According to the construction method disclosed by the invention, photocurrent detection based on light excitation is low in detection signal background and can have high detection sensitivity and stability without needing expensive instrument and equipment and complex sample treatment.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
Blue-stretch variable-bandgap AlGaAs/GaAs photocathode and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102306600AChange bandgapImprove quantum efficiencyCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesCold cathode manufactureQuantum efficiencyPhotocathode
The invention discloses a blue-stretch variable-bandgap AlGaAs / GaAs photocathode and a manufacturing method thereof. The cathode consists of a 9741 glass, an SiO2 passivation layer, an Si3N4 anti-reflection film, a variable-bandgap AlxGa1-xAs buffer layer, a GaAs emission layer and a Cs / O activation layer. In the AlxGa1-xAs buffer layer with a certain thickness, a variable-bandgap buffer layer with gradually-reduced Al component from the AlxGa1-xAs buffer layer to the GaAs emission layer can be generated, and a built-in electric field from the AlxGa1-xAs buffer layer to the GaAs emission layer is constructed; under the action of the built-in electric field, photoelectrons generated in the AlxGa1-xAs layer are transported to the emission layer in a diffusion and drifting mode, thus the photoelectric emission quantum efficiency of short wave photons can be improved and the purpose of blue stretch can be reached.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Ultraviolet flame sensor and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101251416AThe overall structure is small and beautifulGuaranteed spacingSpectrum investigationPhotometryGlass chipPhotocathode
An ultraviolet flame sensor and a manufacturing method thereof relate to a solar blind type ultraviolet flame sensor. The invention provides the ultraviolet flame sensor with simple structure, small size, high stability, high strength and high linearity and sensitivity, and the sensor manufacturing method with good versatility, simple technique and low cost. The invention is characterized in that: the ultraviolet flame sensor comprises a uviol piece, a meshed anode which is arranged on the uviol piece, a cathode substrate glass piece, a photocathode which is arranged on the cathode substrate glass piece, a glass ring which is arranged between the cathode and the anode, a vacuum orifice which is arranged on the glass ring, a plastic packaged base which is arranged under the cathode substrate glass piece, a cathode and an anode lead which are adhered to the plastic packaged base and are respectively connected with the cathode and the anode, and a plastic casing which is arranged around the plastic packaged base, the glass ring and the glass piece.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com