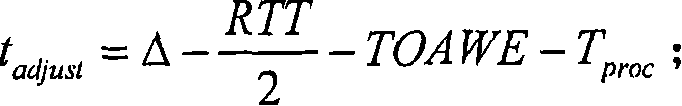Patents
Literature
800 results about "Time mark" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
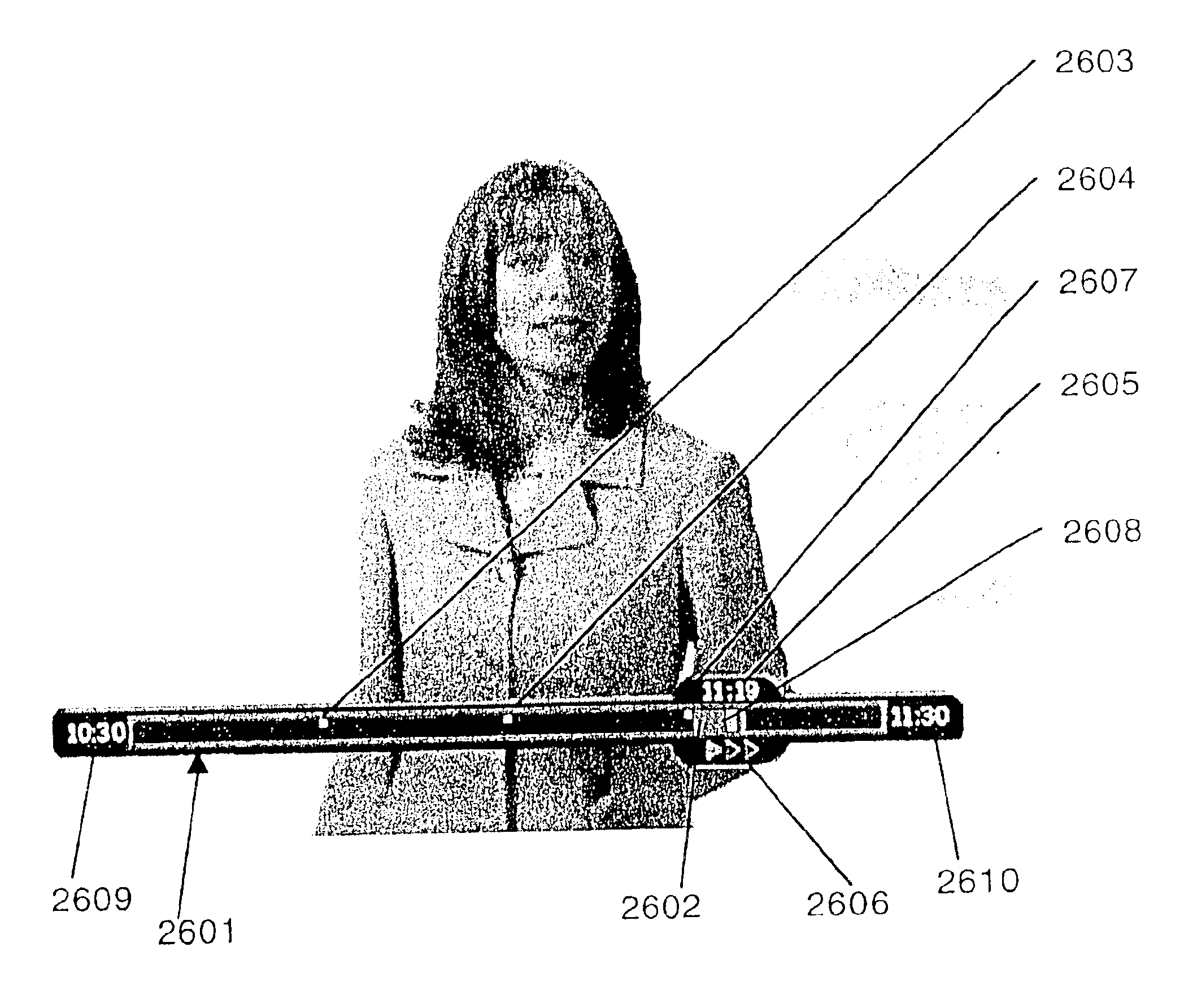
Multimedia visual progress indication system
InactiveUS6847778B1Enhanced interactionTelevision system detailsDisc-shaped record carriersTime markComputer graphics (images)
A multimedia visual progress indication system that provides a trick play bar that is overlaid onto the program material or displayed on a dedicated display. A cache bar inside of the trick play bar indicates the length of a recording session or the length of stored program material and expands to the right when material is being recorded. Every half hour (or selected increment), the cache bar slides to the left. Time marks are displayed inside the trick play bar giving the user a visual reference point from which to judge the current time and visual time reference points. The time marks are in any increment of time needed. The total length of the stored program material or next time or counter increment in the recording cycle is displayed on the right hand end of the trick play bar. A position indicator moves within the trick play bar and tells the user visually where his current position is within the program material. A slider moves along the trick play bar and on top of the cache bar and is linked to the position indicator and can be moved anywhere within the cache bar by the user. The slider displays the numeric time or counter mark of the current position. A mode indicator is positioned below the slider and follows the slider's movement and displays whether the user is in play, record, pause, slow play, fast play, fast forward (1×, 2×, and 3×), slow reverse play, slow reverse, and fast reverse (1×, 2×, and 3×) modes. The 1×, 2×, and 3× speeds are adjustable by the system to be any variable desired (e.g., 2×, 16×, and 32×). The trick play bar and its associated components are displayed for a predetermined time period when overlaid onto the program material.
Owner:TIVO SOLUTIONS INC
System for Monitoring Vehicle Use
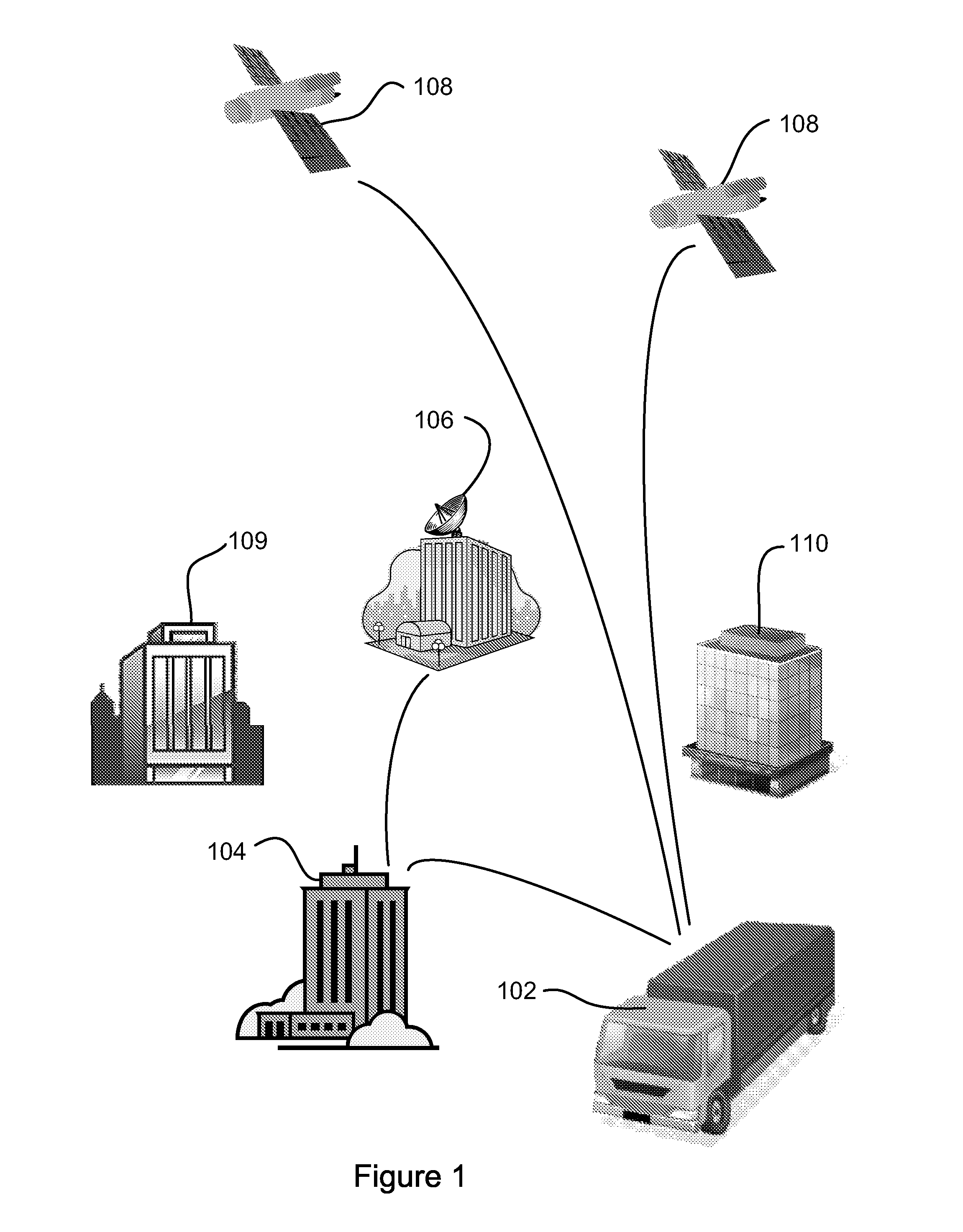
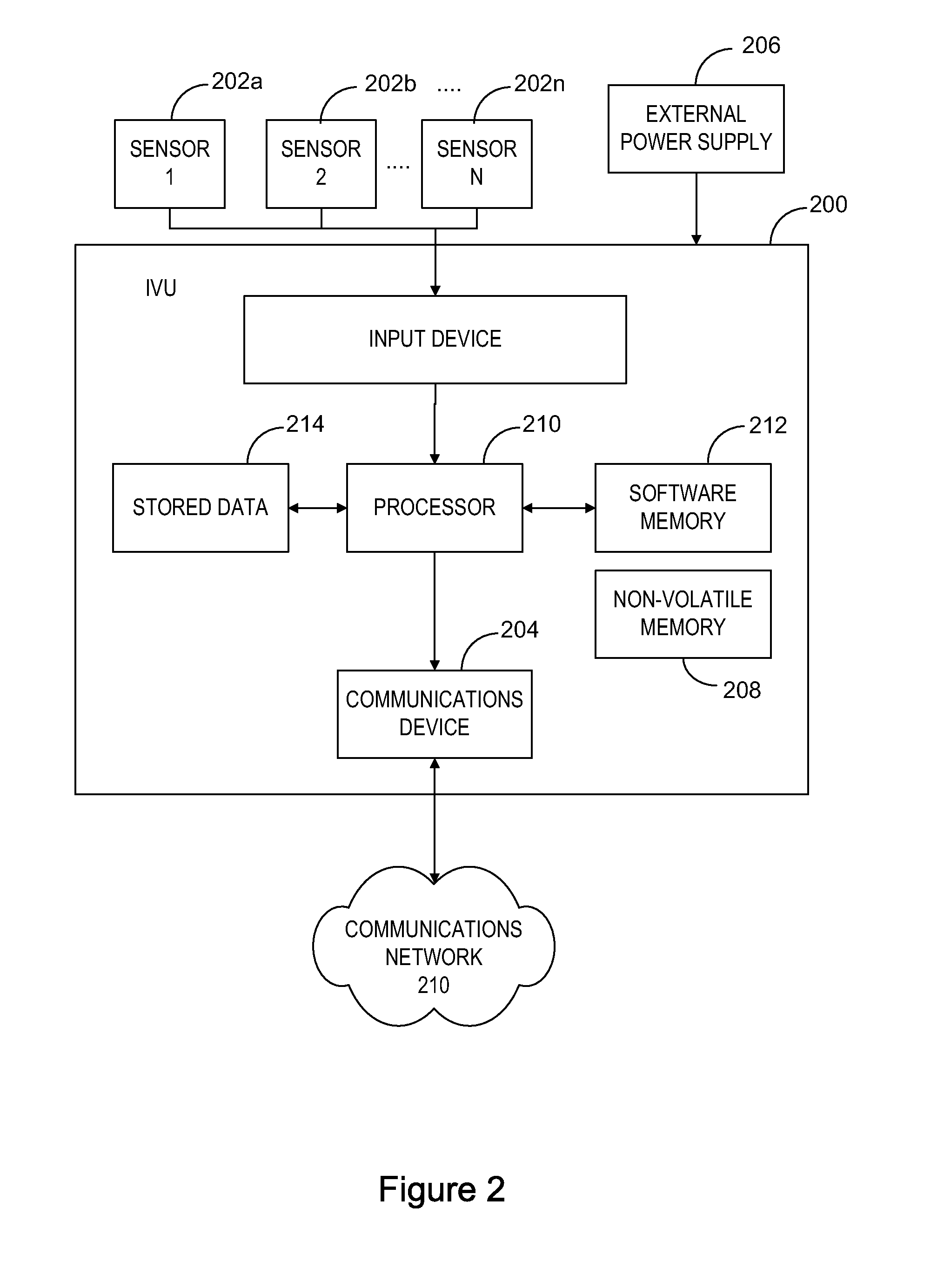
ActiveUS20110035139A1Analogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficTime markNon compliance
A system for monitoring of vehicles and particularly heavy vehicles and their compliance with specific network (e.g. road) access conditions uses vehicle telematics solutions. The system includes an in-vehicle unit (IVU) associated with a vehicle being monitored. The IVU includes a receiver for receiving positioning signals, a processor for processing a time-marked log of vehicle data, a storage element for storing the time-marked log and a first wireless communication element for communicating time marked data to a Service Provider (SP) processing apparatus. One or more Service Providers operate Service Provider (SP) processing apparatus. The SP processing apparatus include a SP wireless communication element for receiving time-marked data from one or more IVUs and a SP processor for processing received data. The SP processor is adapted to compare received data from the time-marked log of a vehicle with one or more vehicle-use conditions applicable to that vehicle, and to generate a non-compliance report where the comparison indicates that non-compliant activity has occurred. A SP storage element stores non-compliance reports and relevant time-marked data.
Owner:TRANSPORT CERTIFICATION AUSTRALIA
Propagating web transaction context into common object model (COM) business logic components
ActiveUS20050039190A1Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsStart timeTime mark
Owner:MICRO FOCUS LLC
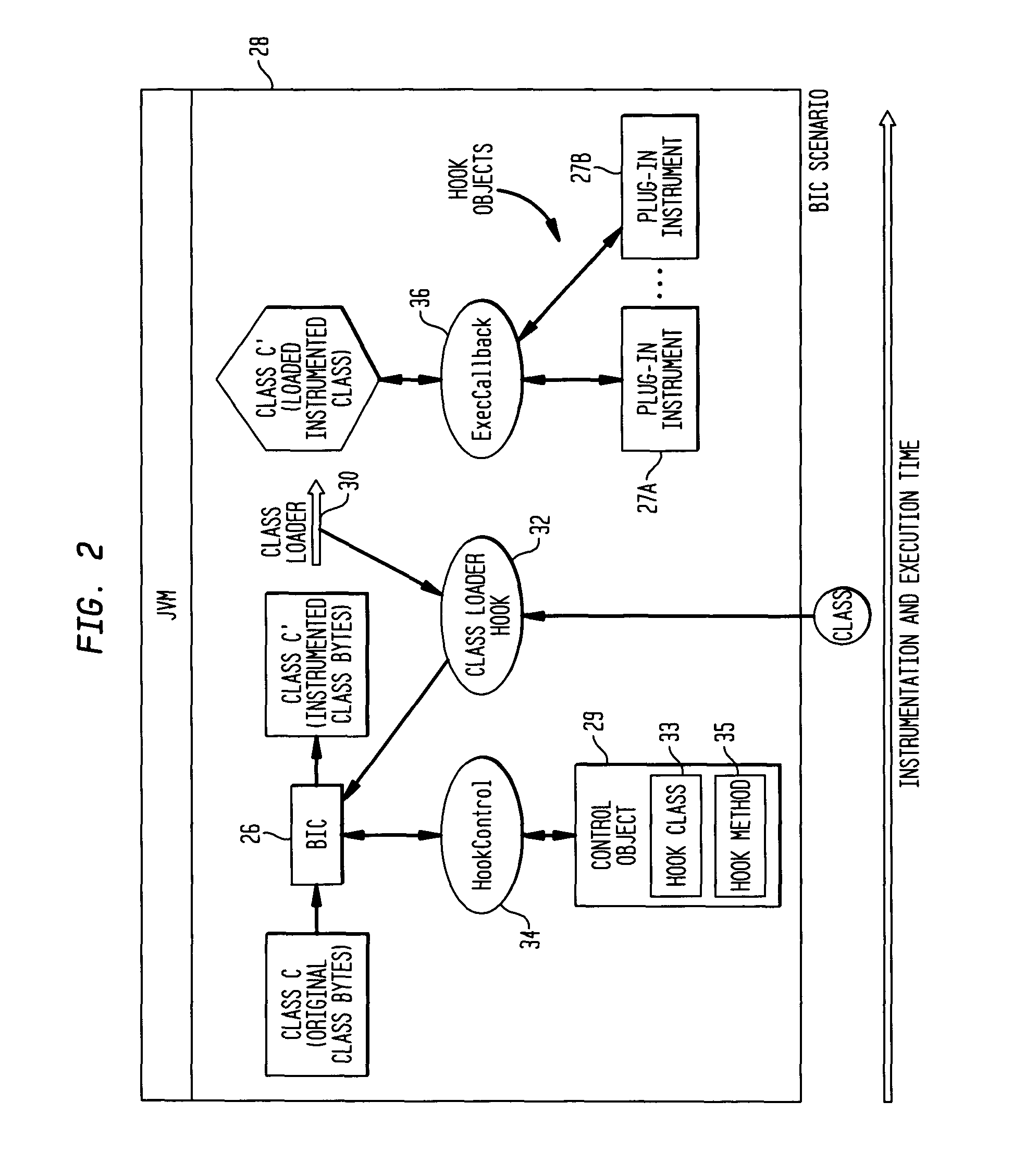
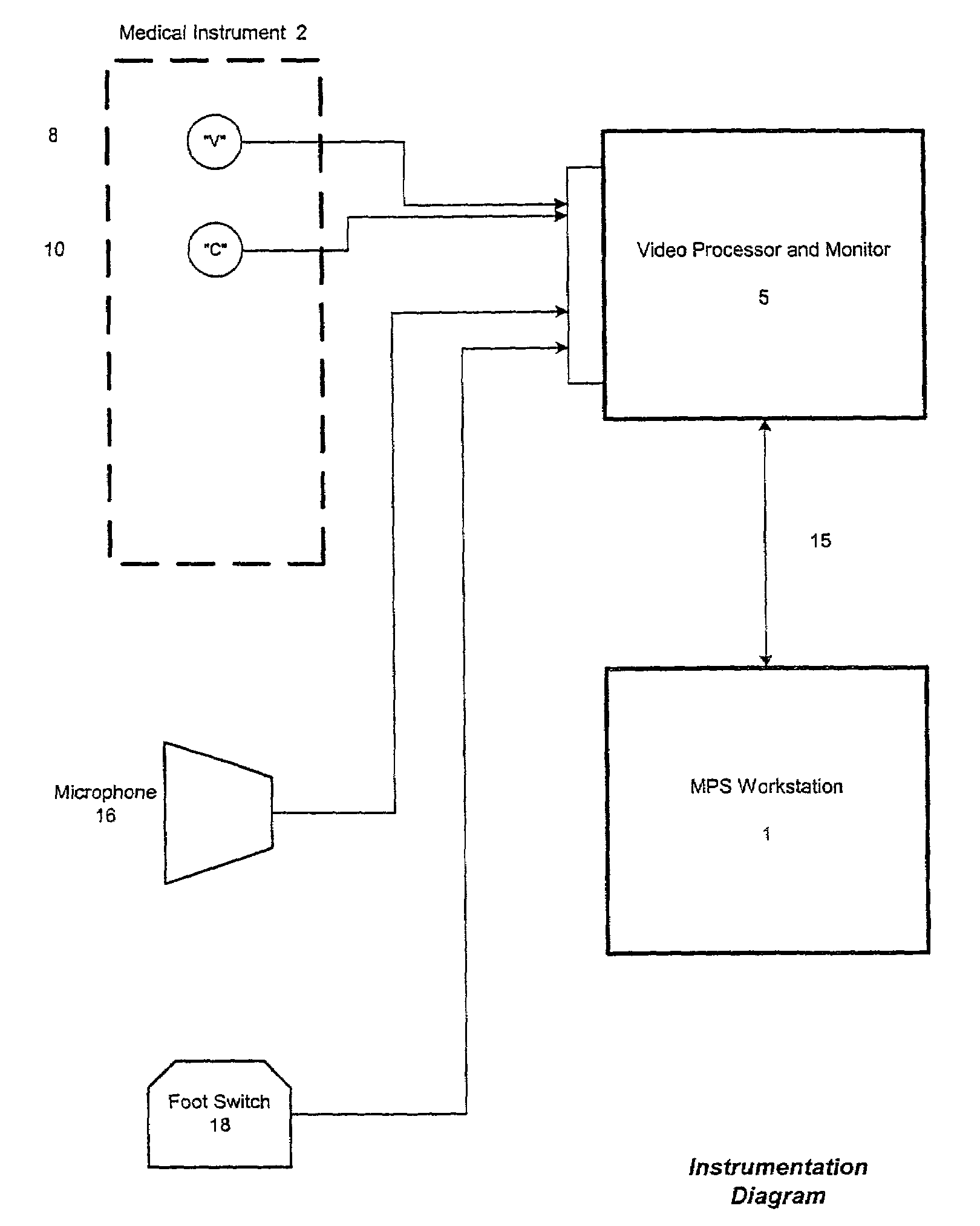
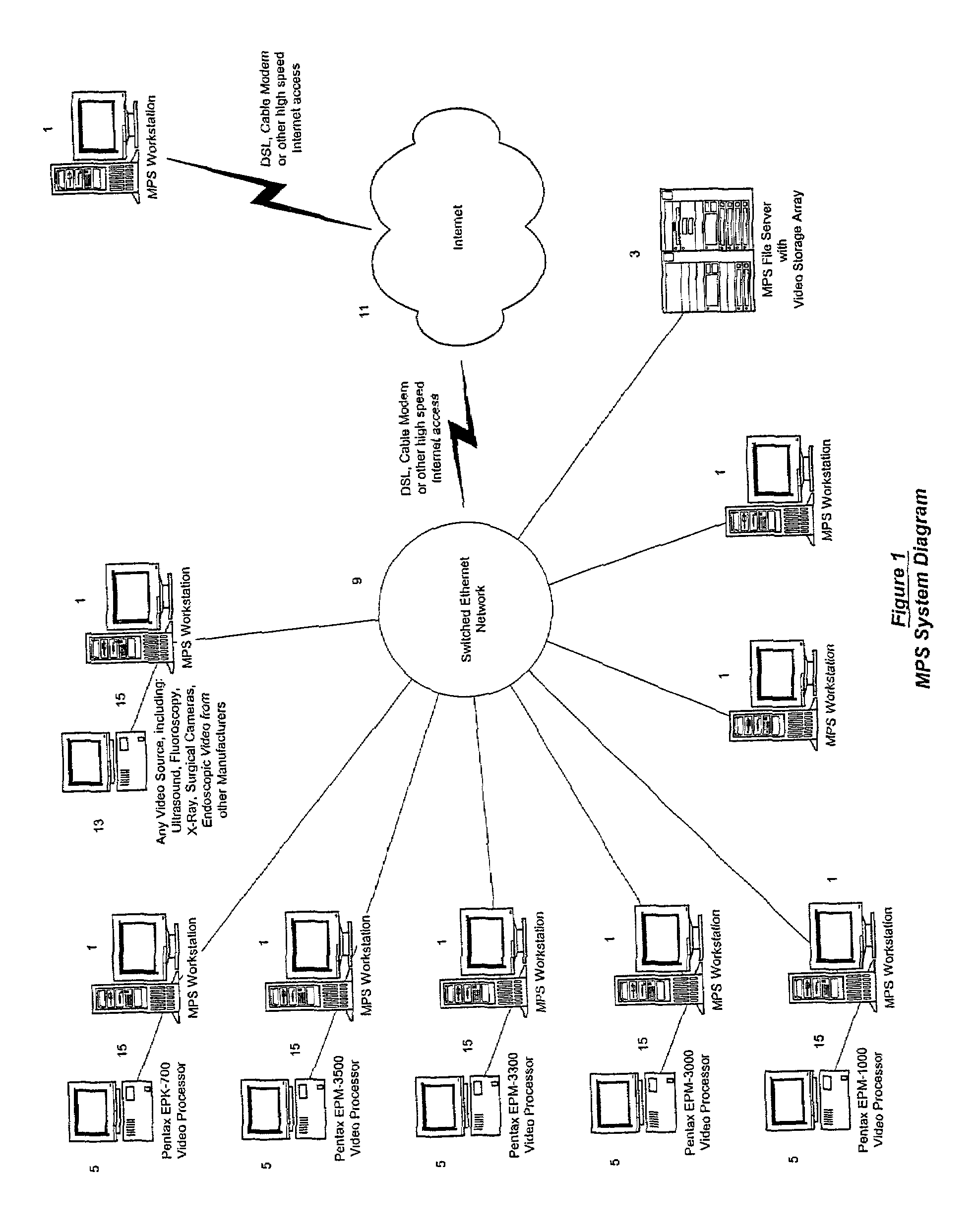
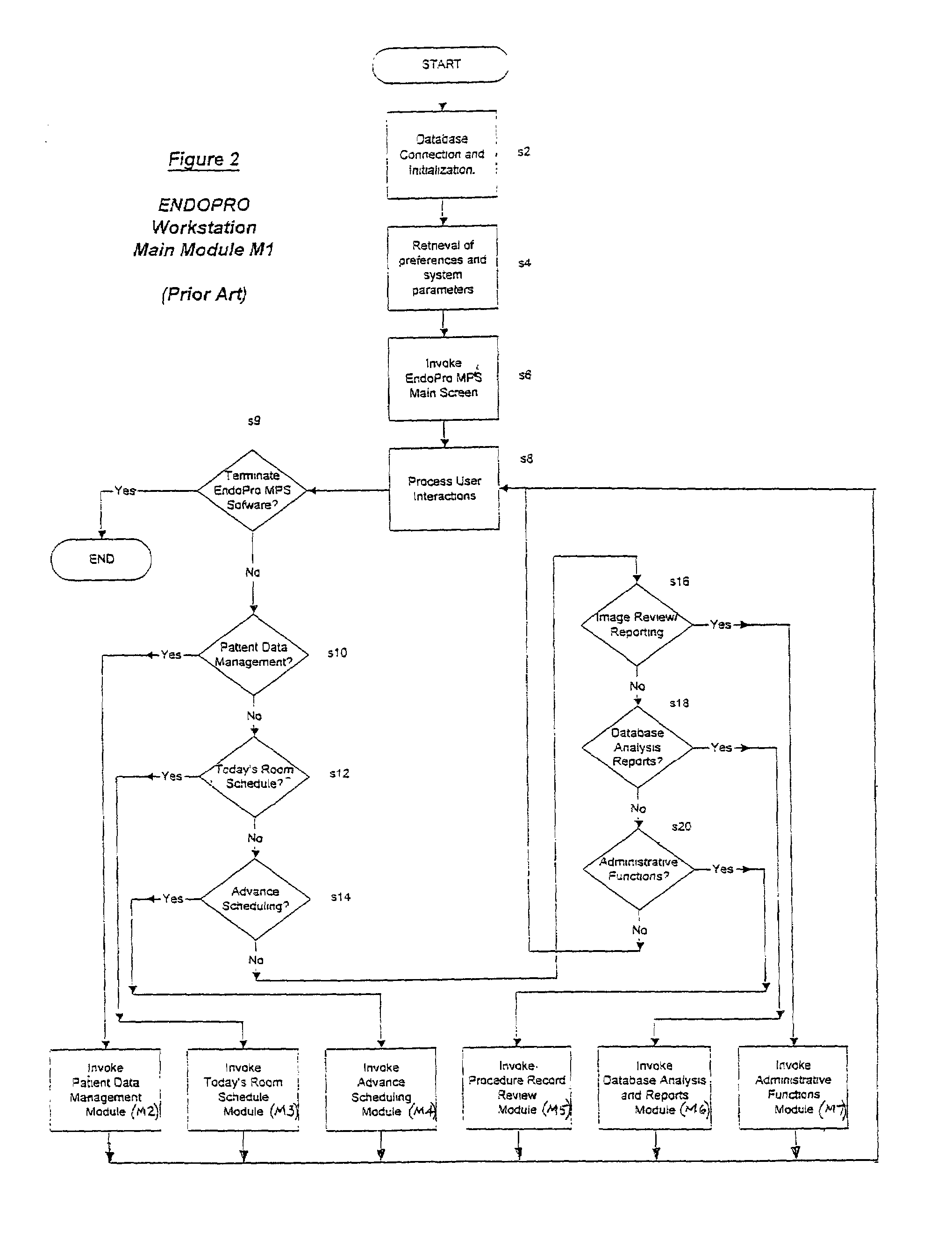
Computer-based video recording and management system for medical diagnostic equipment
ActiveUS7231135B2Storage problemQuality improvementTelevision system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsPatient dataVideo recording
Owner:INTEL CORP +1
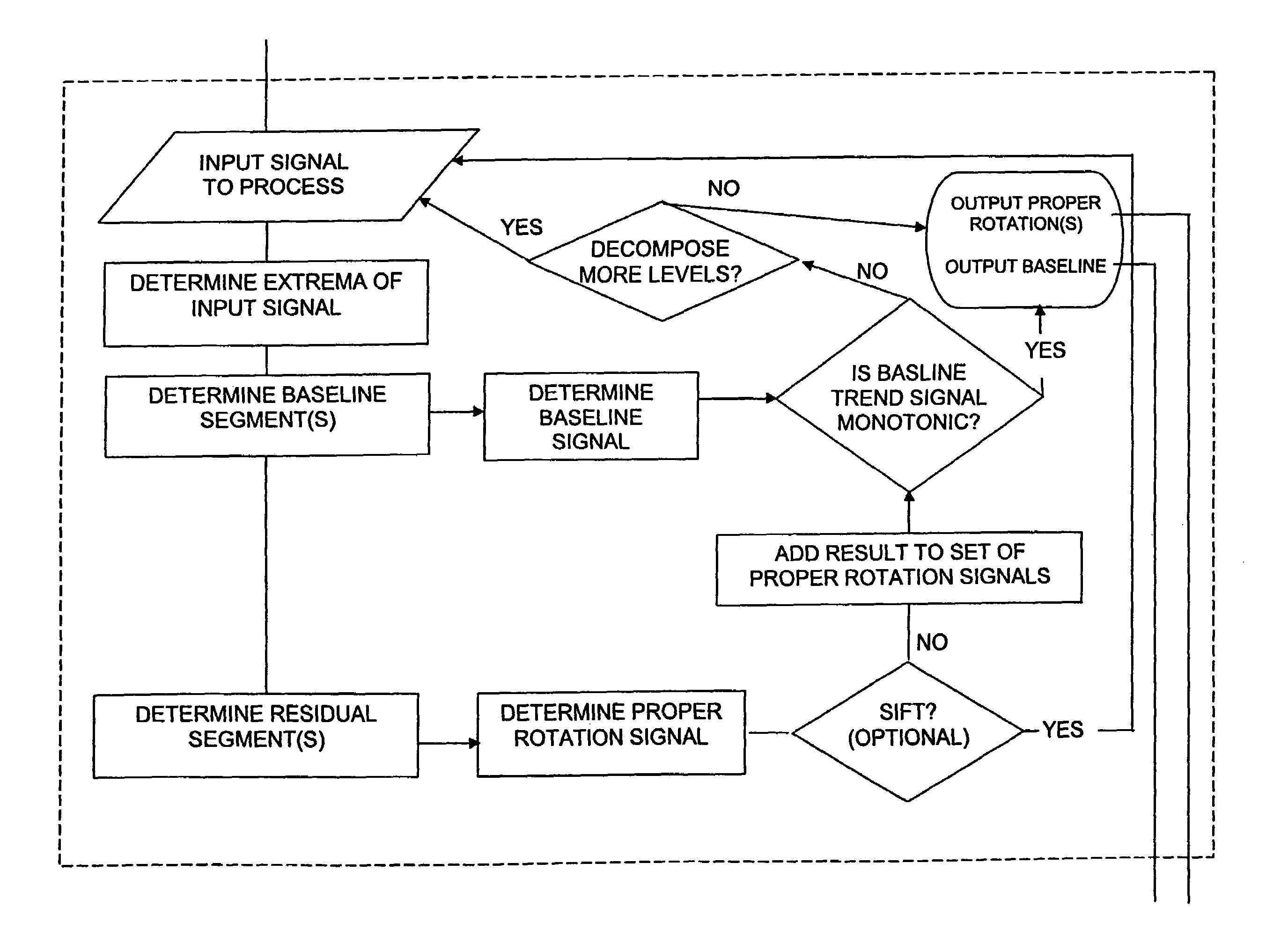
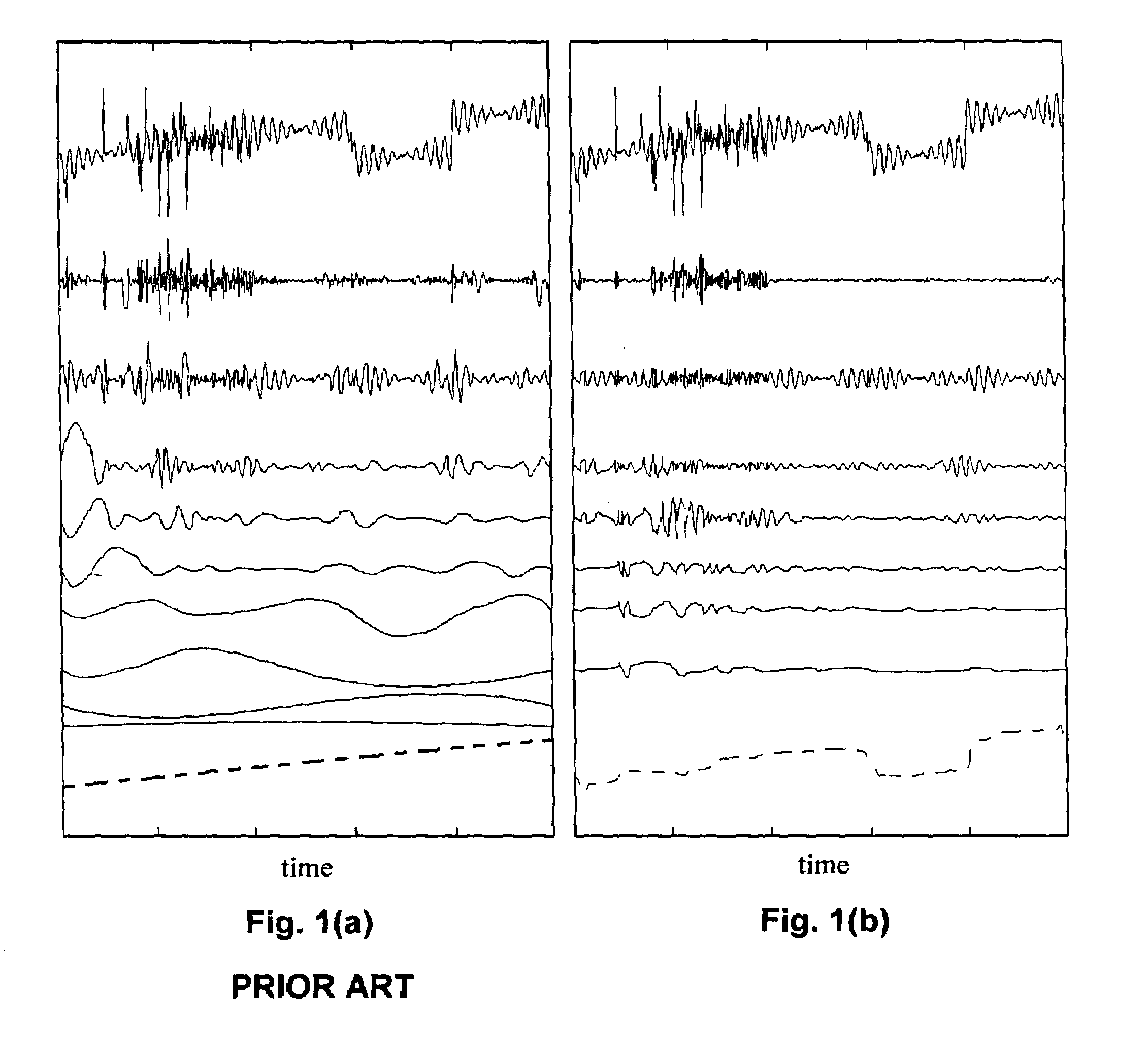
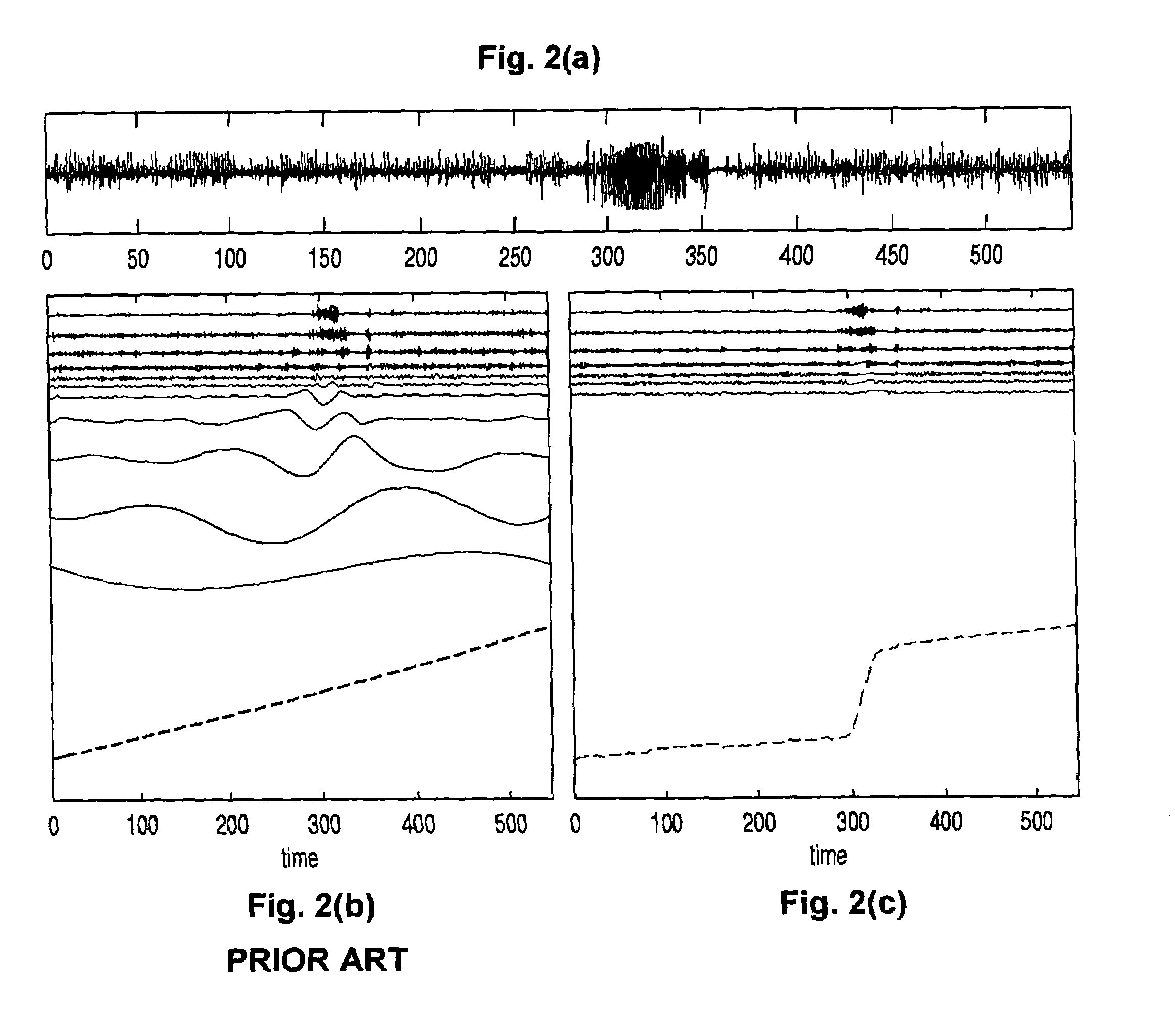
Method, computer program, and system for intrinsic timescale decomposition, filtering, and automated analysis of signals of arbitrary origin or timescale
ActiveUS7054792B2Easy to operateImprove performanceAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceTesting/monitoring control systemsTime markDecomposition
A method and system for intrinsic timescale decomposition, filtering, and automated analysis of signals of arbitrary origin or timescale including receiving an input signal, determining a baseline segment and a monotonic residual segment with strictly negative minimum and strictly positive maximum between two successive extrema of the input signal, and producing a baseline output signal and a residual output signal. The method and system also includes determining at least one instantaneous frequency estimate from a proper rotation signal, determining a zero-crossing and a local extremum of the proper rotation signal, and applying interpolation thereto to determine an instantaneous frequency estimate thereof. The method and system further includes determining at least one instantaneous frequency estimate from a proper rotation signal, extracting an amplitude-normalized half wave therefrom and applying an arc sine function to the amplitude-normalized half wave to determine an instantaneous frequency estimate of the proper rotation signal.
Owner:FLINT HILLS SCI L L C
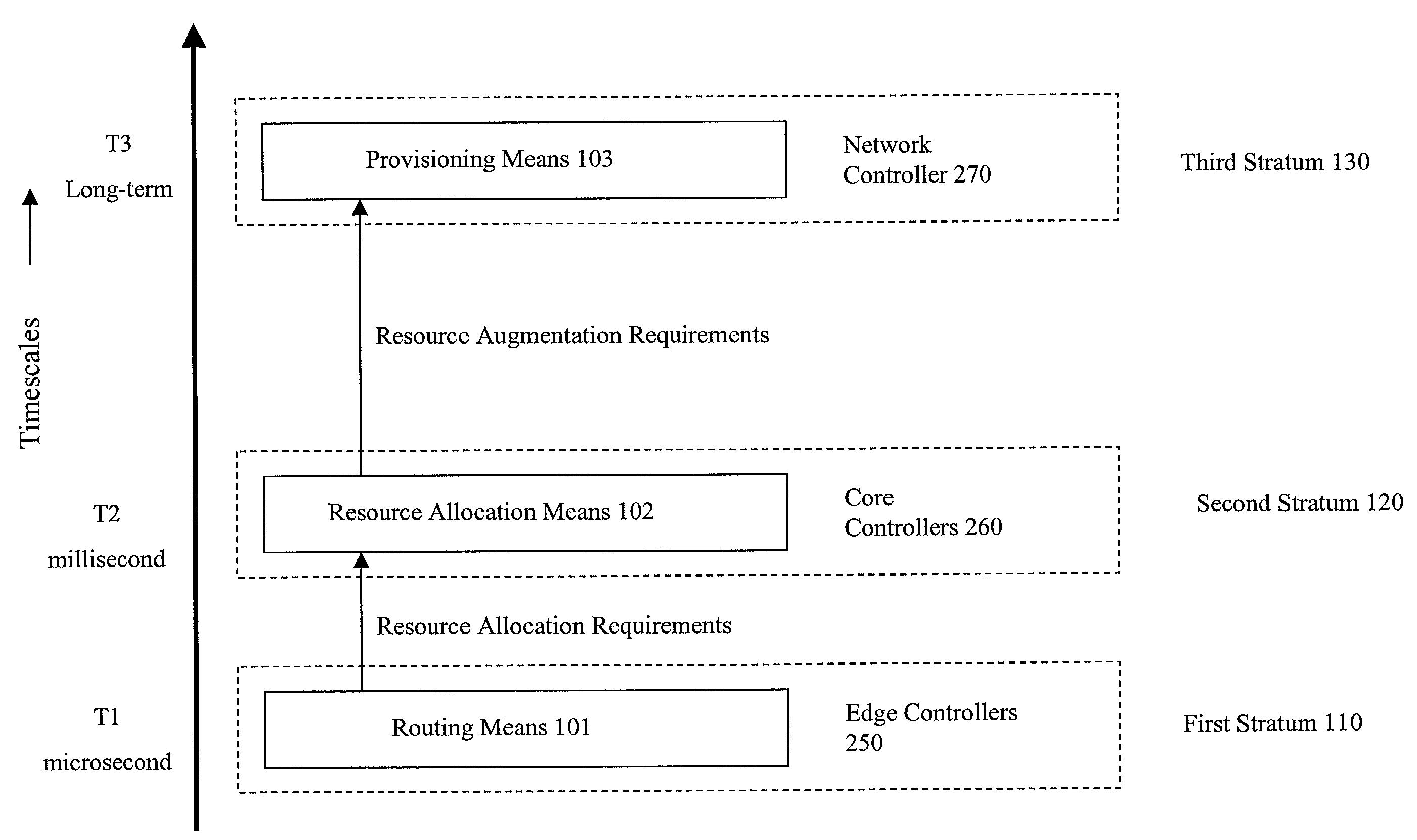
System and method for network control and provisioning
ActiveUS7249169B2High degree of automationHigh degreeMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksTraffic capacityState variation
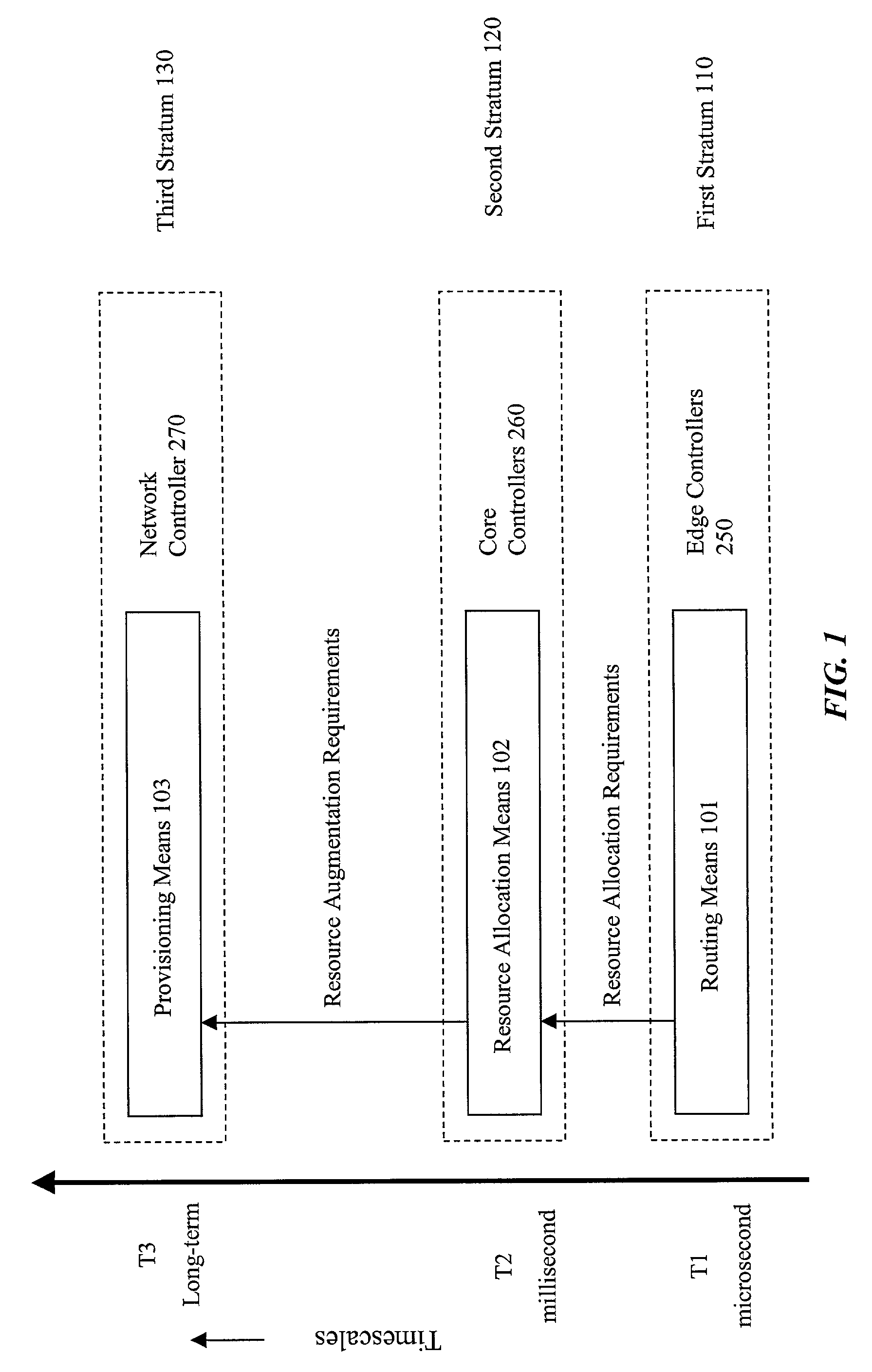
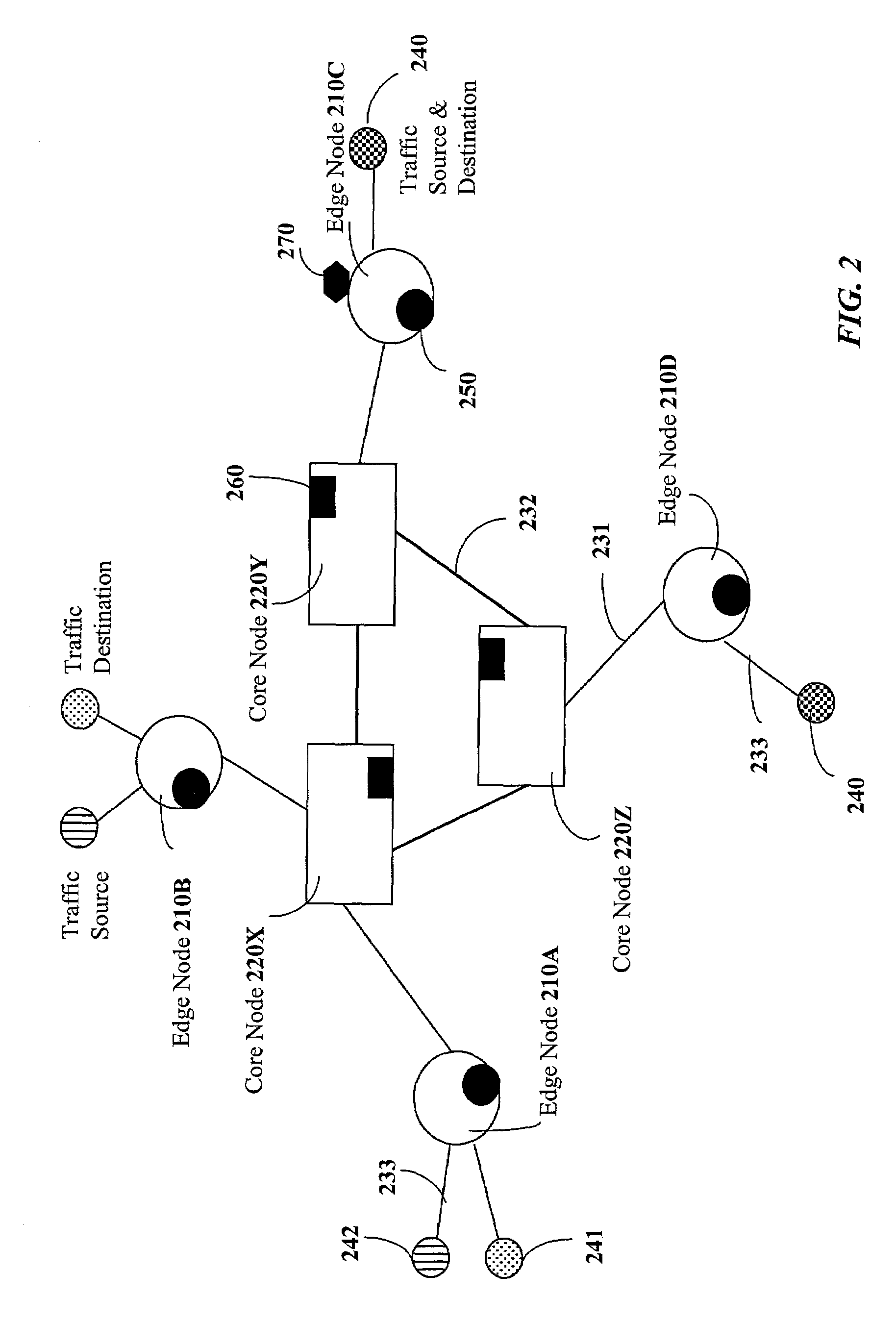
A multi-stratum multi-timescale control for self-governing networks provides automatic adaptation to temporal and spatial traffic changes and to network state changes. Microsecond timescale reacting through the routing function, a facet of the lowest stratum, allows a source node to choose the best available route from a sorted list of routes, and to collect information on the state of these routes. Millisecond timescale correcting through the resource allocation function, a facet of the intermediate stratum, allows the network to correct resource allocations based on requirements calculated by the routing function. Long-term provisioning through the provisioning function at the higher stratum allows the network to recommend resource augmentations, based on requirements reported by the resource allocation function. The control is implemented in the network through coordination across edge node controllers, core node controllers, and network controllers. Metrics based on automated measurements of network performance are used by the control to adjust network resources. The Routing index is collected by the routing function and is the average rank of the selected route within a route-set. The routing function also collects measurements on route Constituent Traffic, which quantifies traffic in each of three categories: (carried) first-class, (carried) secondary, and rejected. The Resource Allocation Index is a metric collected by the resource allocation function. It quantifies the number of failures in re-allocating resources. In another aspect of this invention, a provisioning method is provided, which recommends appropriate link capacity increments based on the afore-mentioned Constituent Traffic measurements, and based on rules provided by the network operator.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Method and apparatus for implementing persistent and reliable message delivery
ActiveUS7376092B2Special service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime markMessage routing
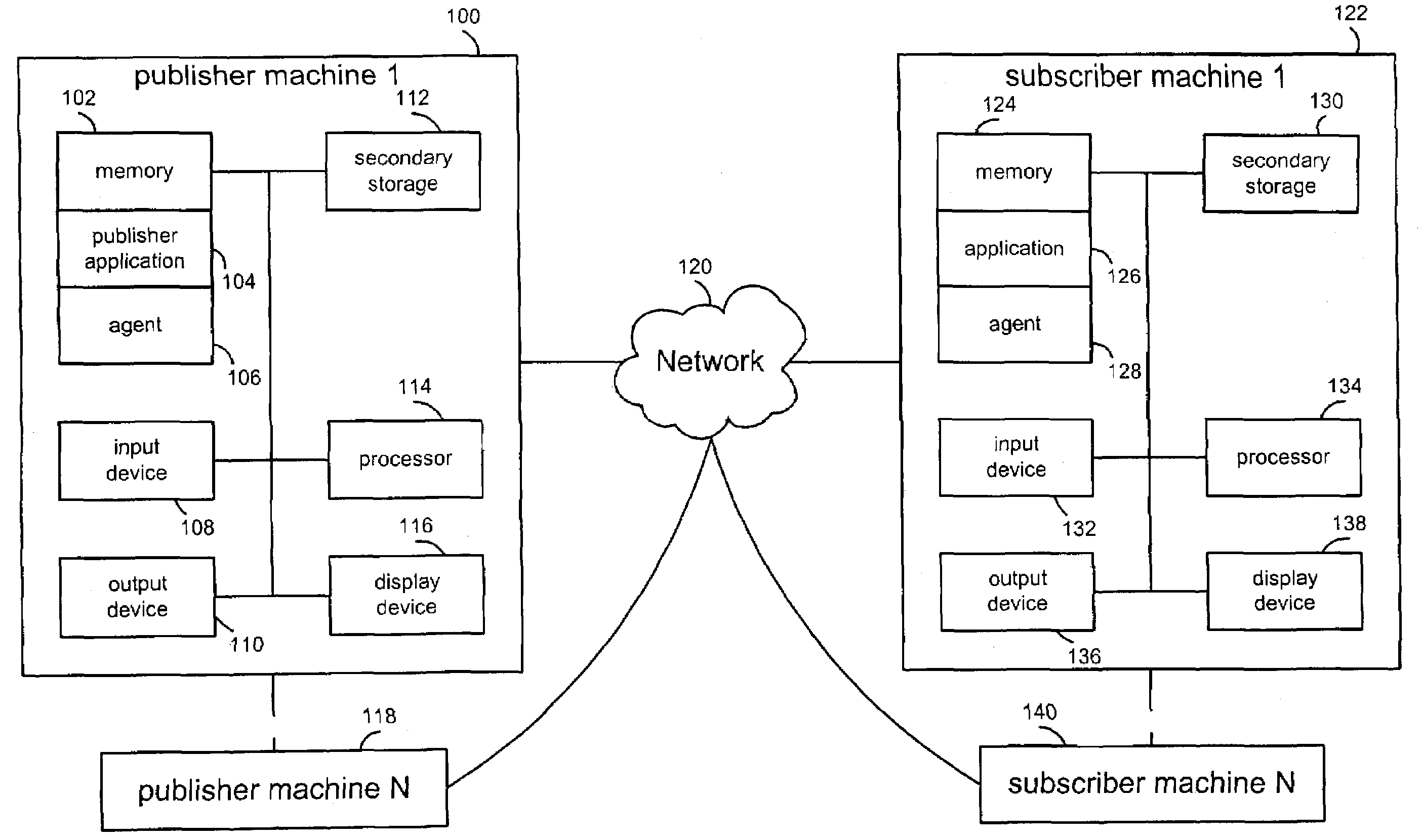
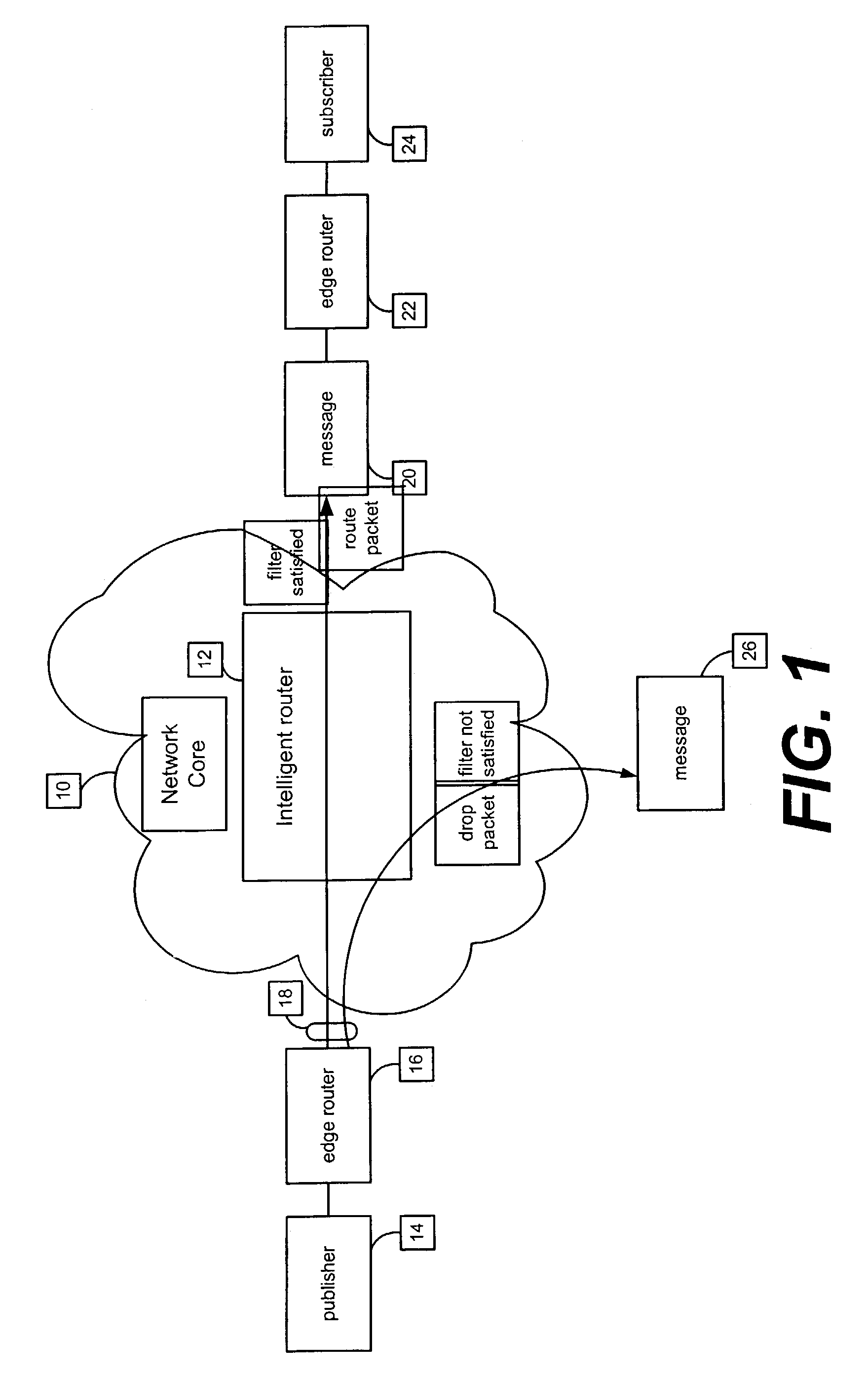
A method and apparatus provide for persistent caching of methods delivered via a publish-subscribe network. At a first node, a message having data via the network is received. The data is time-marked. The data is cached in a cache memory at the first node. The message is routed to a second node using content-based routing. These steps are repeated at a second node. A router that includes modules for executing this method is provided. A publish-subscribe network that includes nodes that include modules for executing this method is provided. A computer-readable medium that includes instructions for executing this method is provided.
Owner:PRECACHE
Safety data transmission method and paying method, paying terminal and paying server
ActiveCN101098225AProtection securityEnsure safetyUser identity/authority verificationPayment architectureTime markPassword
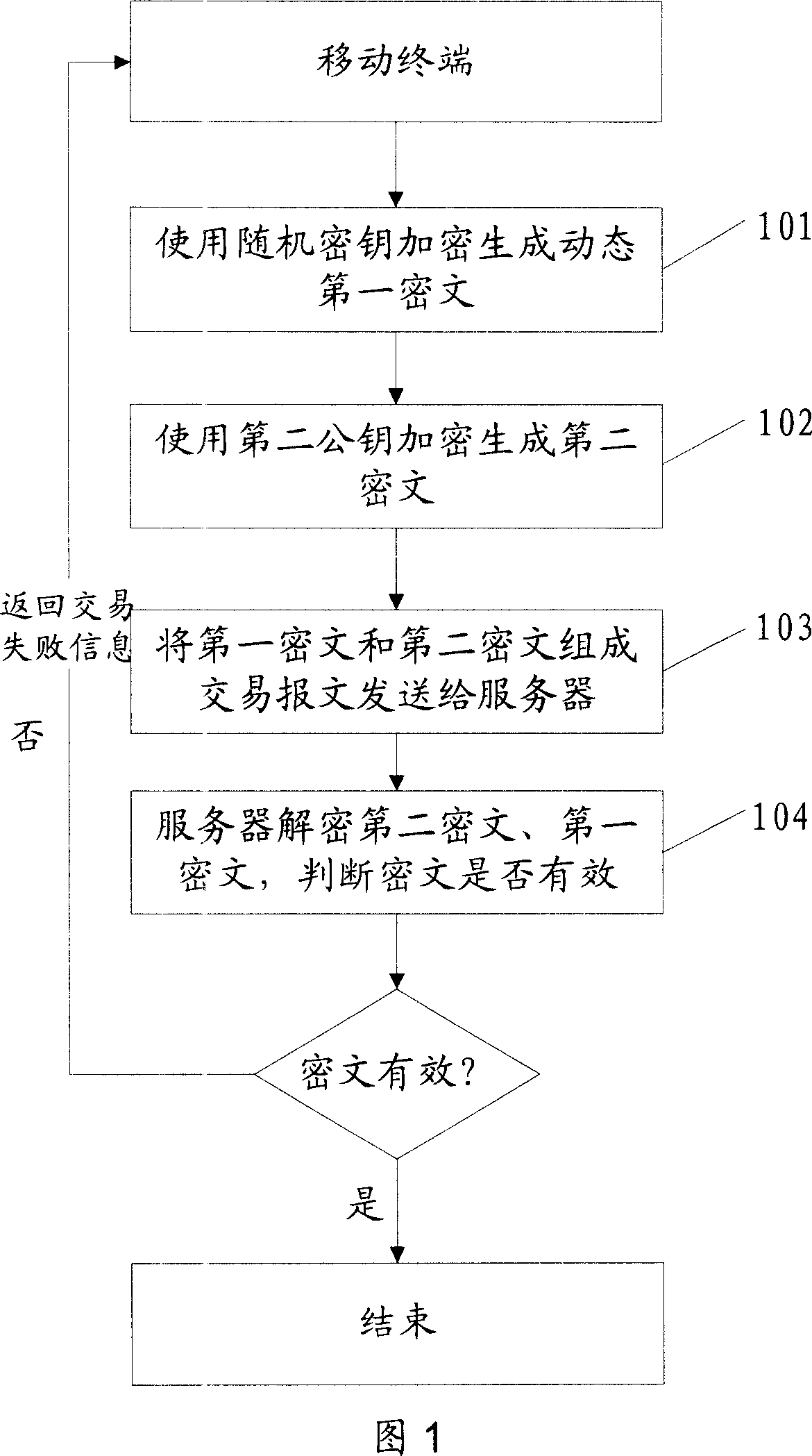
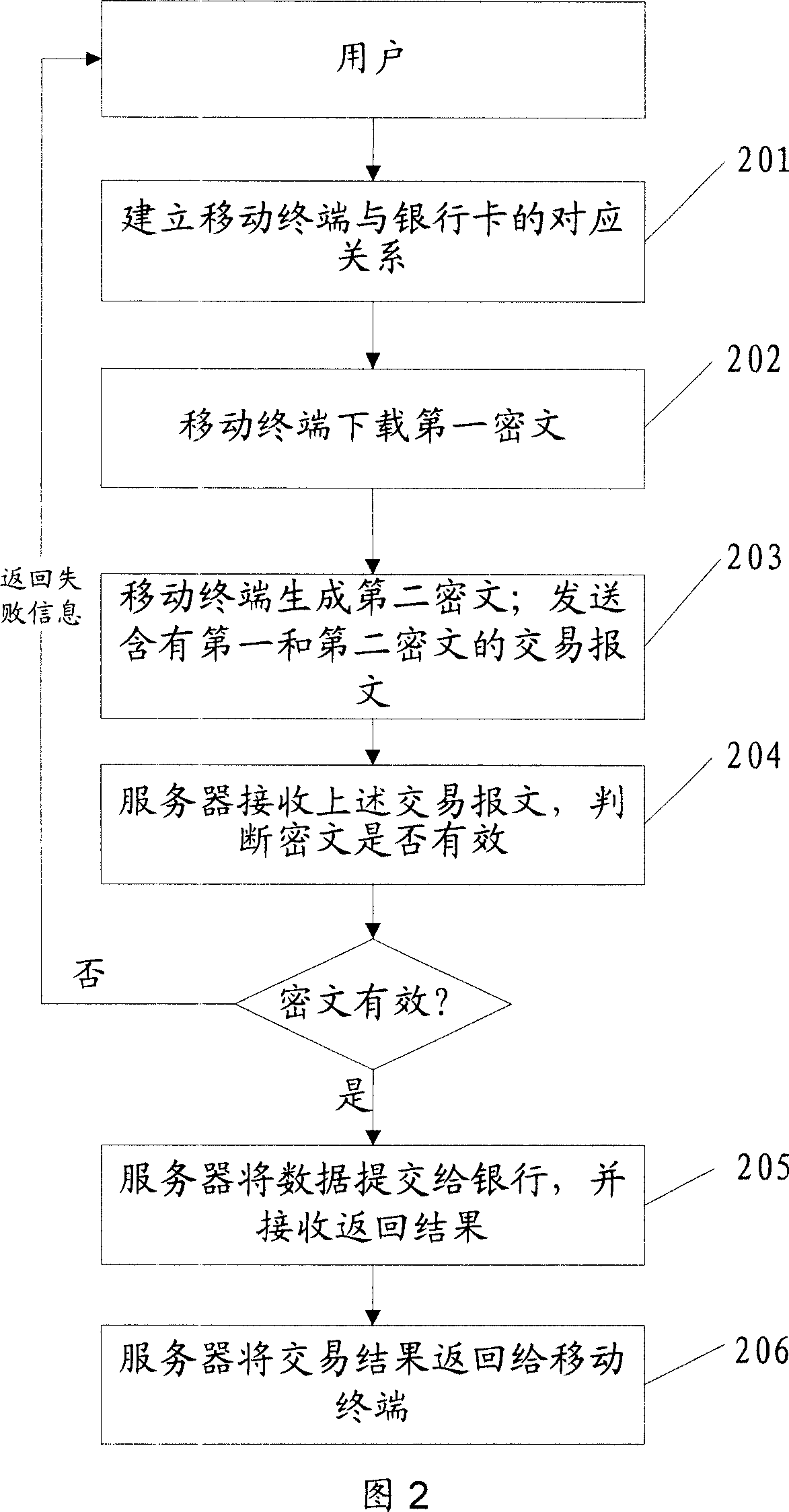
The invention discloses a safe data transmission method, comprising that a mobile terminal uses a second public key to encrypt the personal password of bank card to generate a second cryptogram, the mobile terminal combines the first and second cryptograms into a trade report to be sent to a server, while the first cryptogram contains card track information stored in the mobile terminal, the server decrypts the first and second cryptograms, for best, the mobile terminal can use random password to encrypt the first cryptogram to generate a dynamic first cryptogram, while the random password is generated by relative algorism according to dynamic factor. The invention uses asymmetry encrypt technique to encrypt the data sent by mobile terminal, and uses random password to generate dynamic cryptogram, and generates the cryptogram with living period according to time mark, therefore, the transmission safety of finance data as cark track information or the like is effectively protected via the combined encrypt methods, to realize mobile payment.
Owner:CHINA UNIONPAY
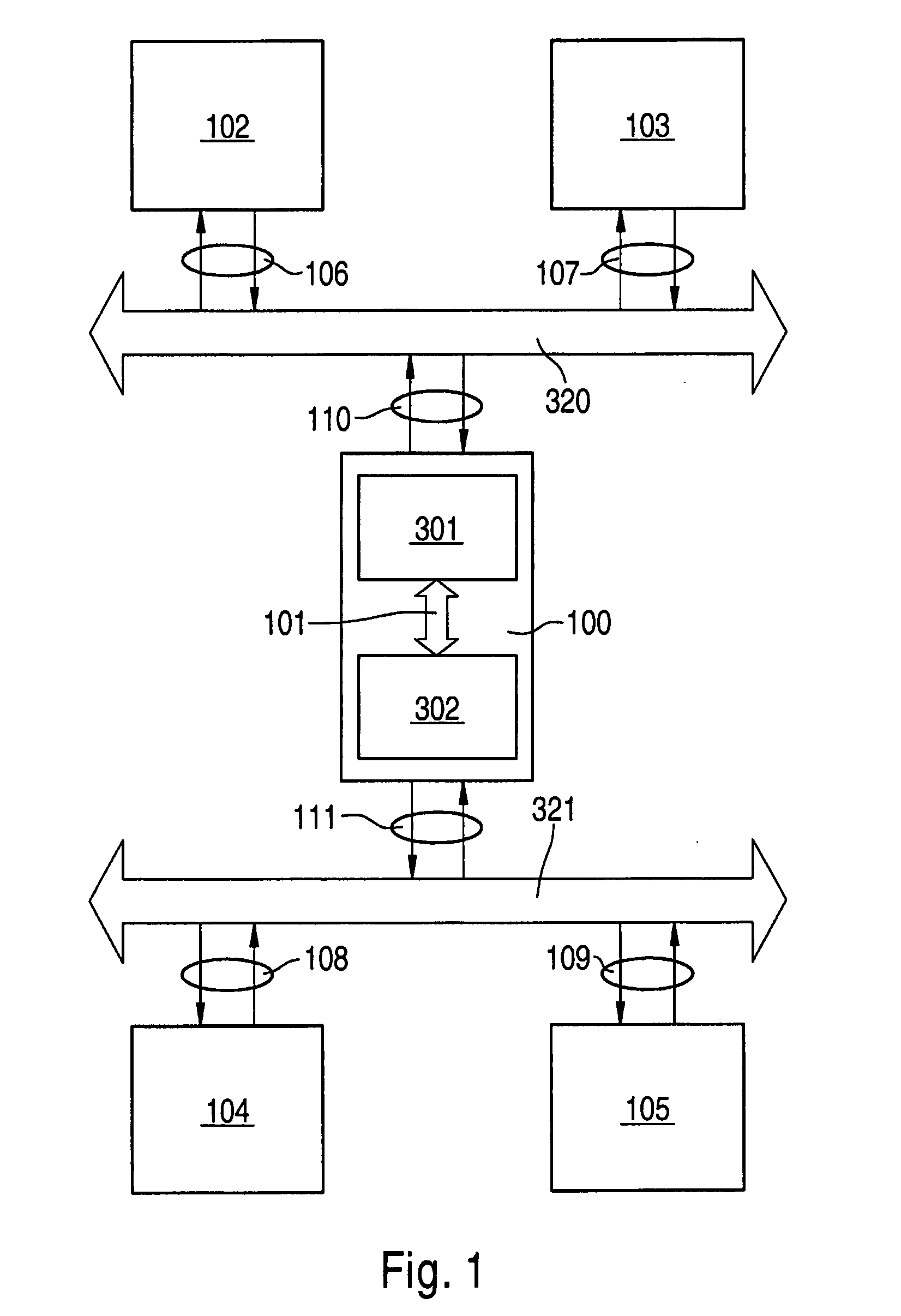
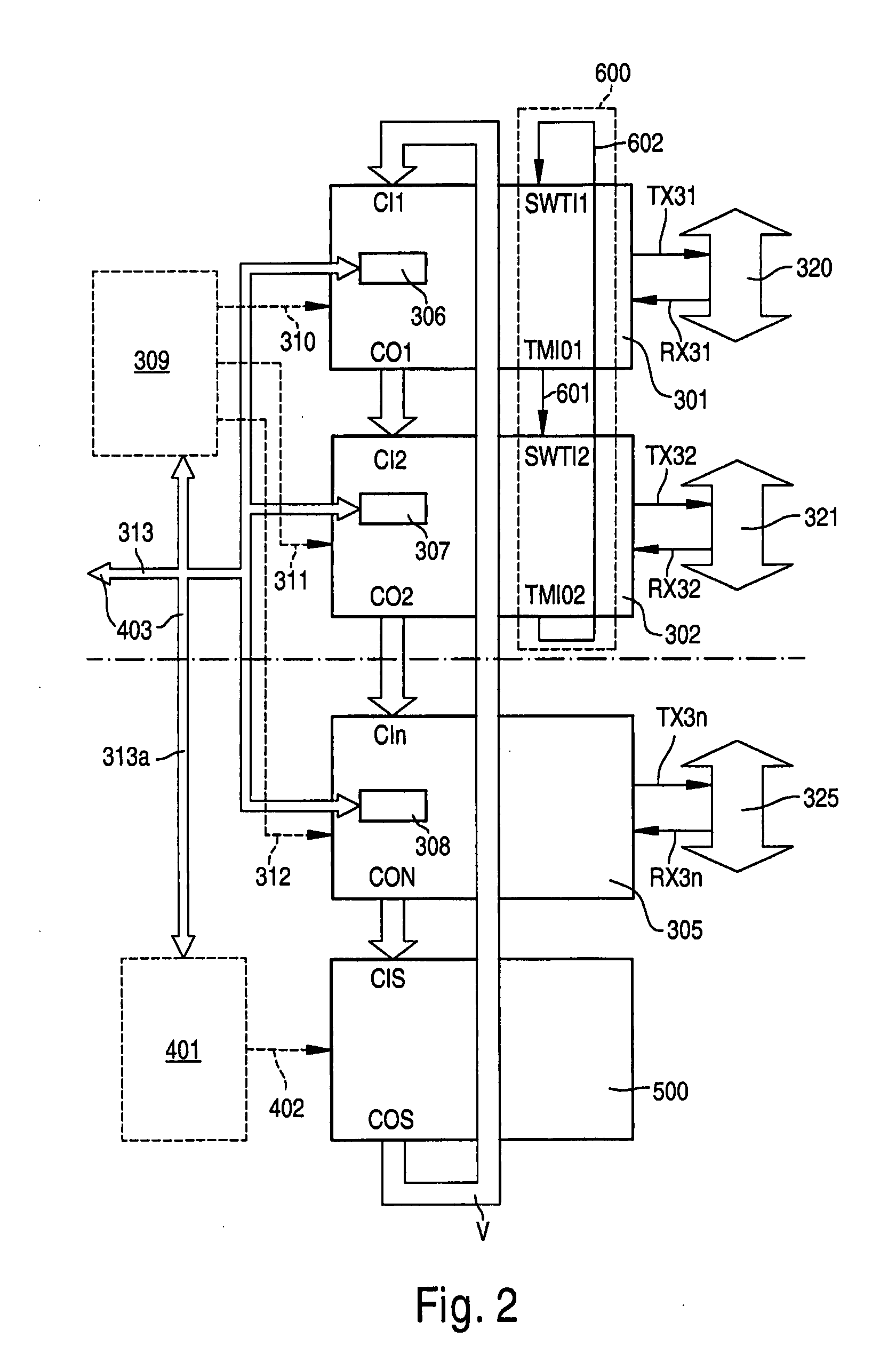
Base band and RF system synchronization and time delay compensation process
ActiveCN101098328AAchieve precise compensationTime-division multiplexMultiple carrier systemsTransmission protocolTime delays
Owner:ZTE CORP
Apparatus and method for identifying cable phase in a three-phase power distribution network
InactiveUS7031859B2Noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementCurrent/voltage measurementDifferential phaseTime mark
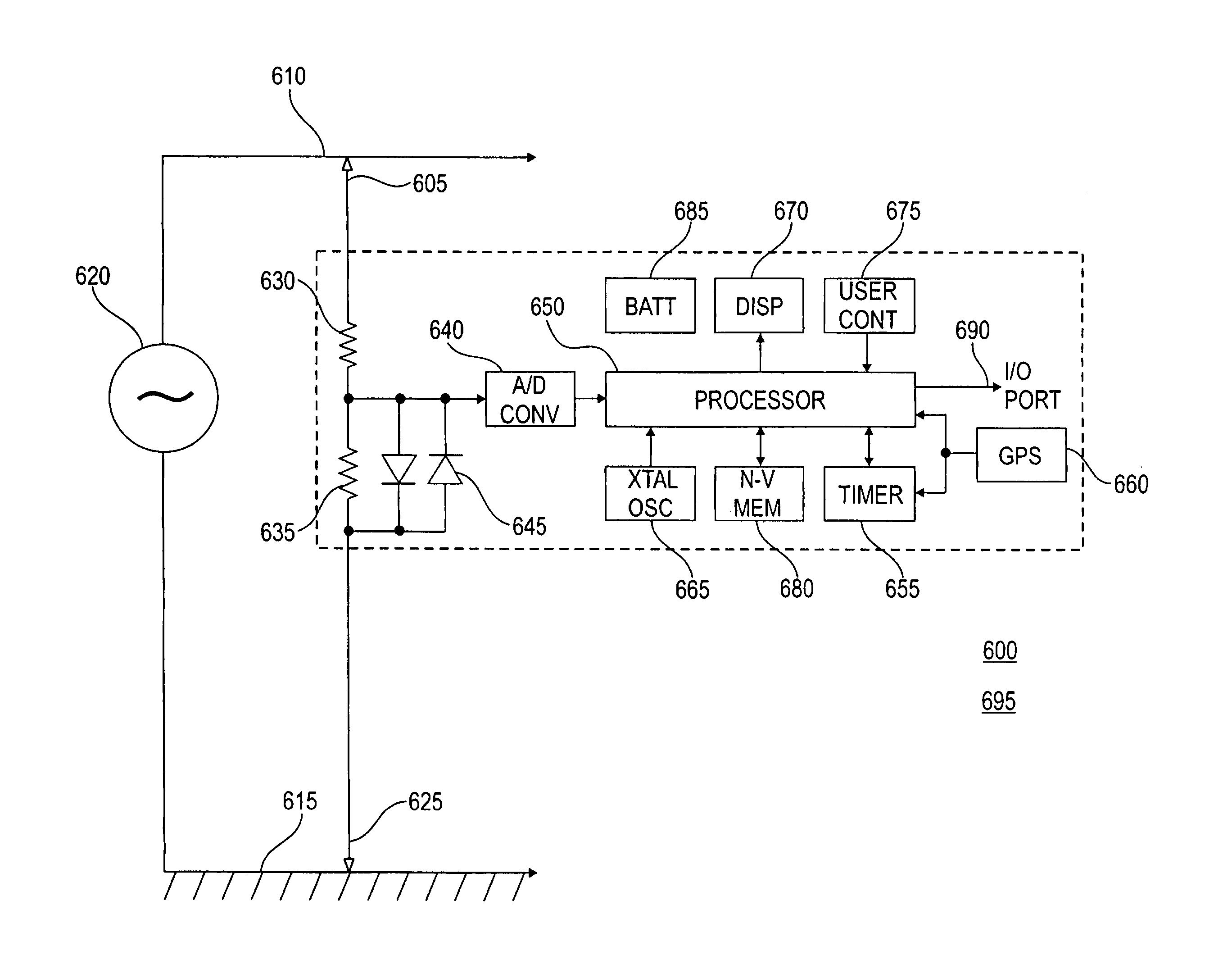
A line phase identification system and method identifies the phase of a power line at a remote unknown-phase line (160) in a three-phase power distribution network (100). The instantaneous phase of a known-phase line (150) is measured and saved each GPS second using a 1-pps time mark of a GPS receiver (660). The instantaneous phase at the unknown-phase line (160) is measured at a single GPS second using the 1-pps time mark of a GPS receiver (660) and compared to the phase measurement taken from the known-phase line (150) at the same GPS second. The differential phase between these simultaneously taken known and unknown instantaneous phases will be close to either 0, +120, or −120 degrees, thus identifying the line phase at the line under test (160).
Owner:PIESINGER GREGORY H
Multi-event sequential recording and testing system
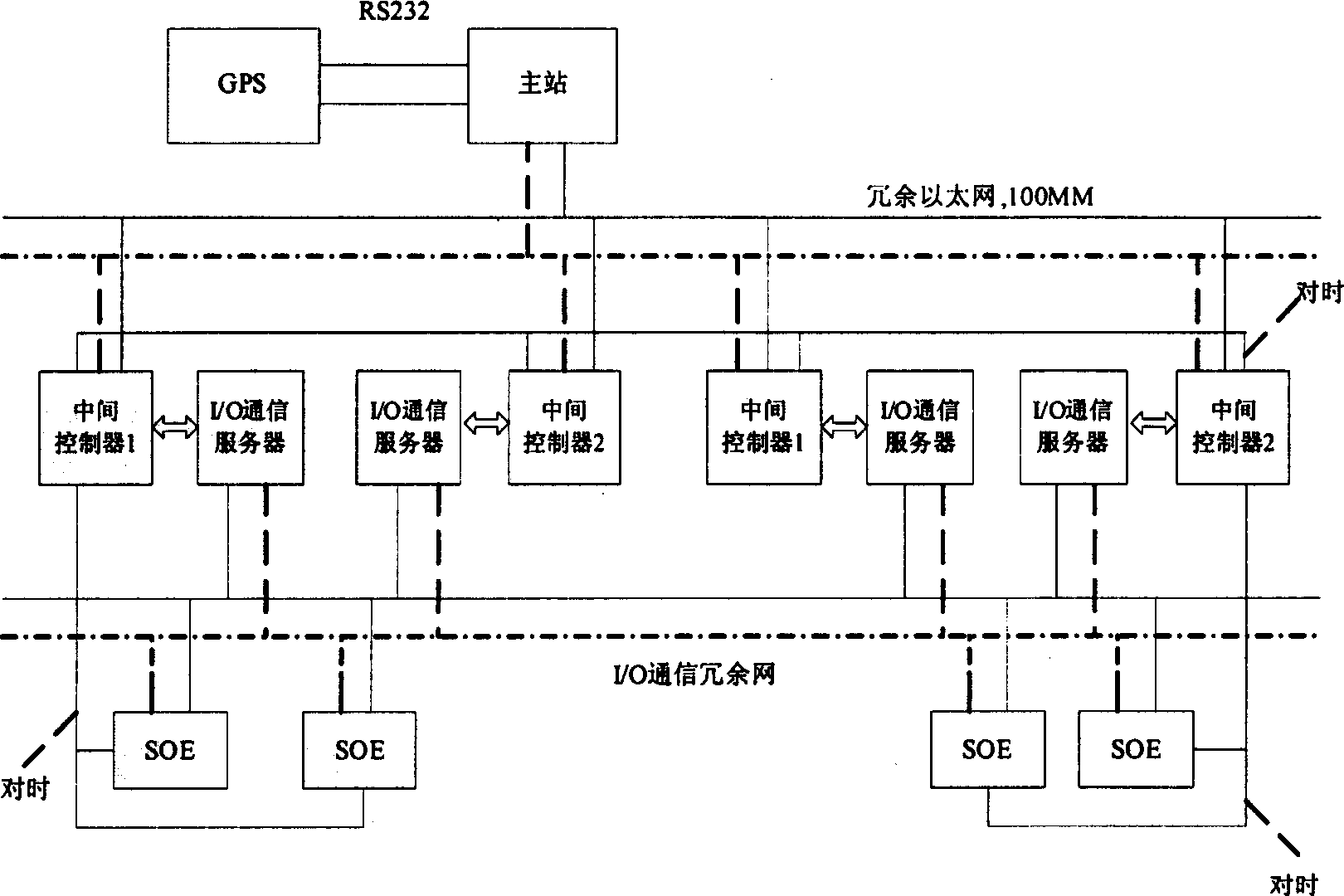
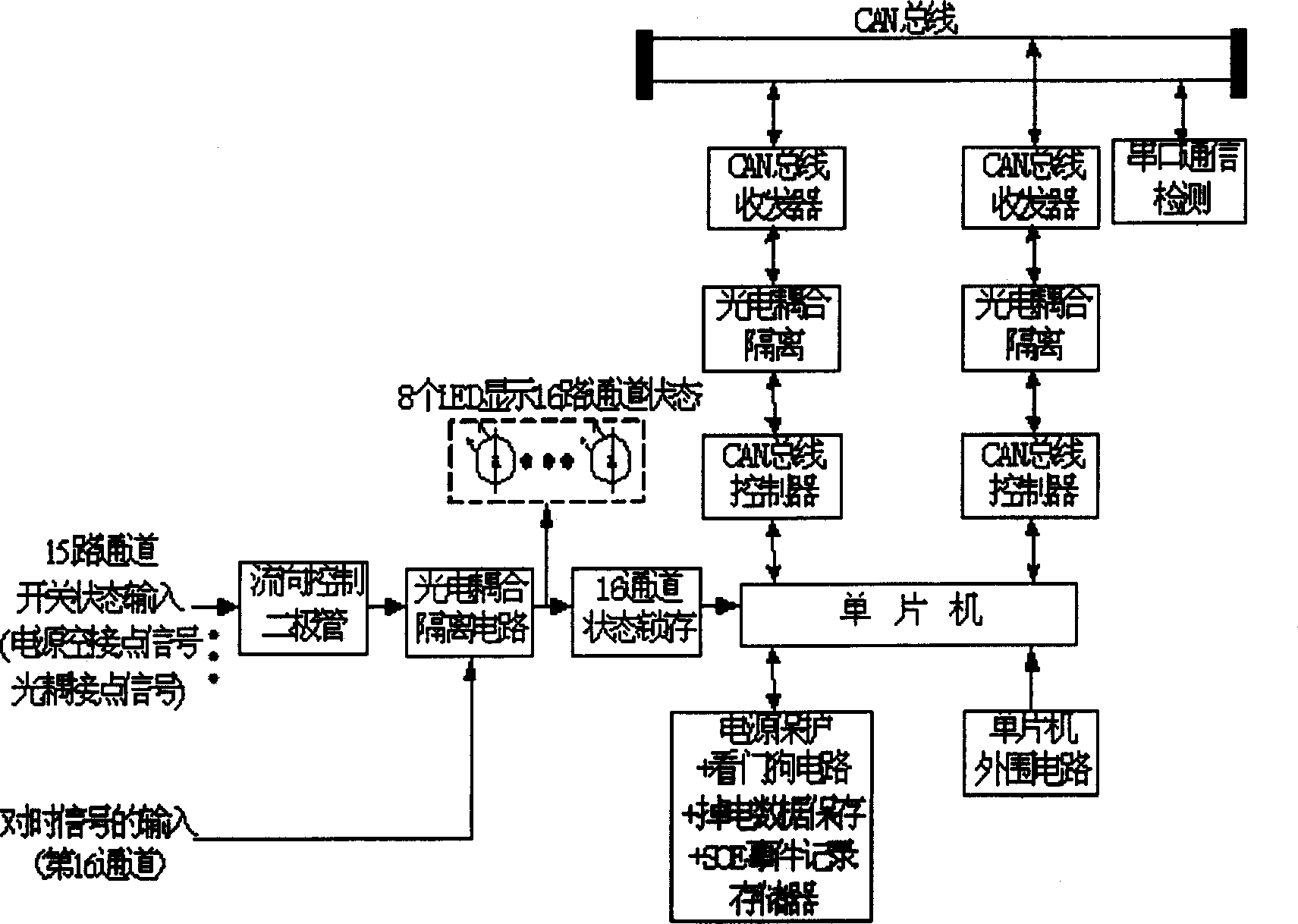
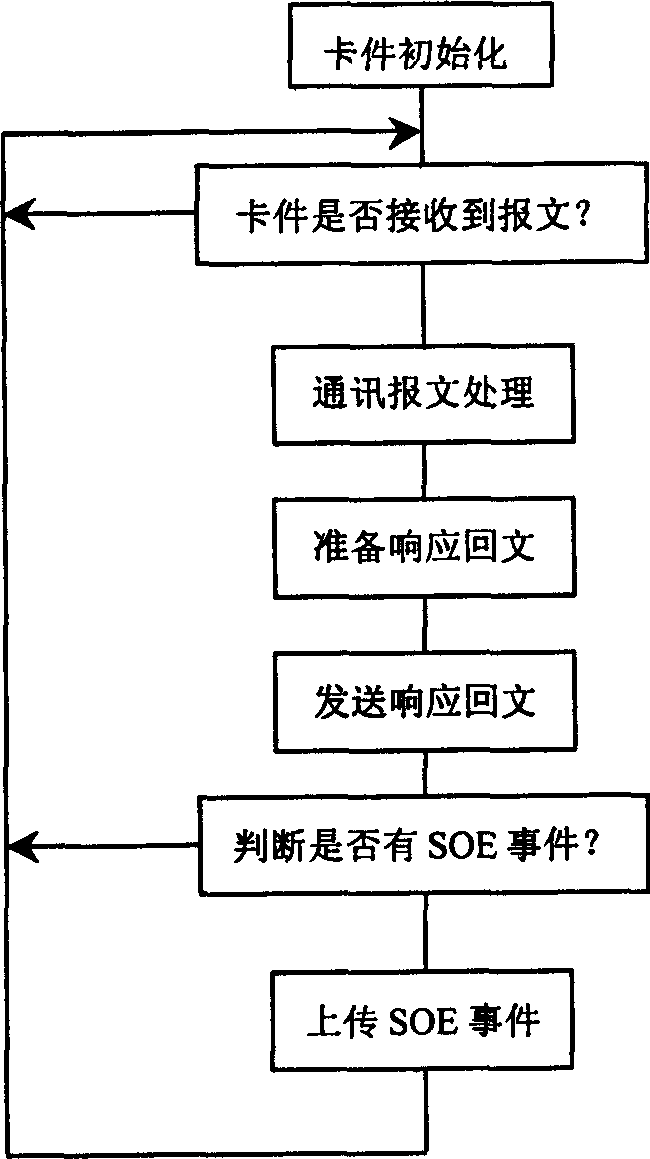
InactiveCN1801023AReduce expression bytesSolve paralysisElectric testing/monitoringPrimary stationTime mark
The invention discloses a record and test system of multiple-event sequence, which is characterized by the following: adapting on-site CAN bus to do communication connection; recording the sequence of happening time corresponding to the condition deflection when the monitored object occurs SOE case. The system contains a case of GPS, main station computer, at lest two middle controllers, at least two communication servers and at least four SOE substations, wherein the GPS provides time mark; the computer sends clock signal A to all middle controllers, which select one controller as datum clock station to send time setting signal B,C to other middle controllers and all substations; the communication server transmits clock signal A to all SOE substations to affirm and record SOE event; the millisecond clock in the SOE substation is started by signal C to generate millisecond clock signal D and integrate with A to form clock signal E of SOE substation, which judges and uploads SOE event. The invention confines the synchronous and monitoring resolution error not more than 1 millisecond.
Owner:杨卫民 +2
Method and device for synchronizing two bus systems and arrangement composed to two bus systems
ActiveUS20100049891A1Easy to adjustTime-division multiplexSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlTemporal informationTime mark
A device for synchronizing at least two bus systems, having a first communications module for a first bus system and a second communications module for a second bus system, wherein in the first communications module first trigger information is present by which a trigger signal is triggered in the first bus system, characterized in that the device is configured in such a manner that the first and second communications modules are connected to each other and the first trigger information is transmitted to the second communications module, and the second communications module is configured in such a manner that a time information value is determined from the first trigger information and that time information value is compared with a second time mark of the second bus system, a time difference being determined and the next reference message being triggered in the second bus system in dependence upon the second time mark and the time difference.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
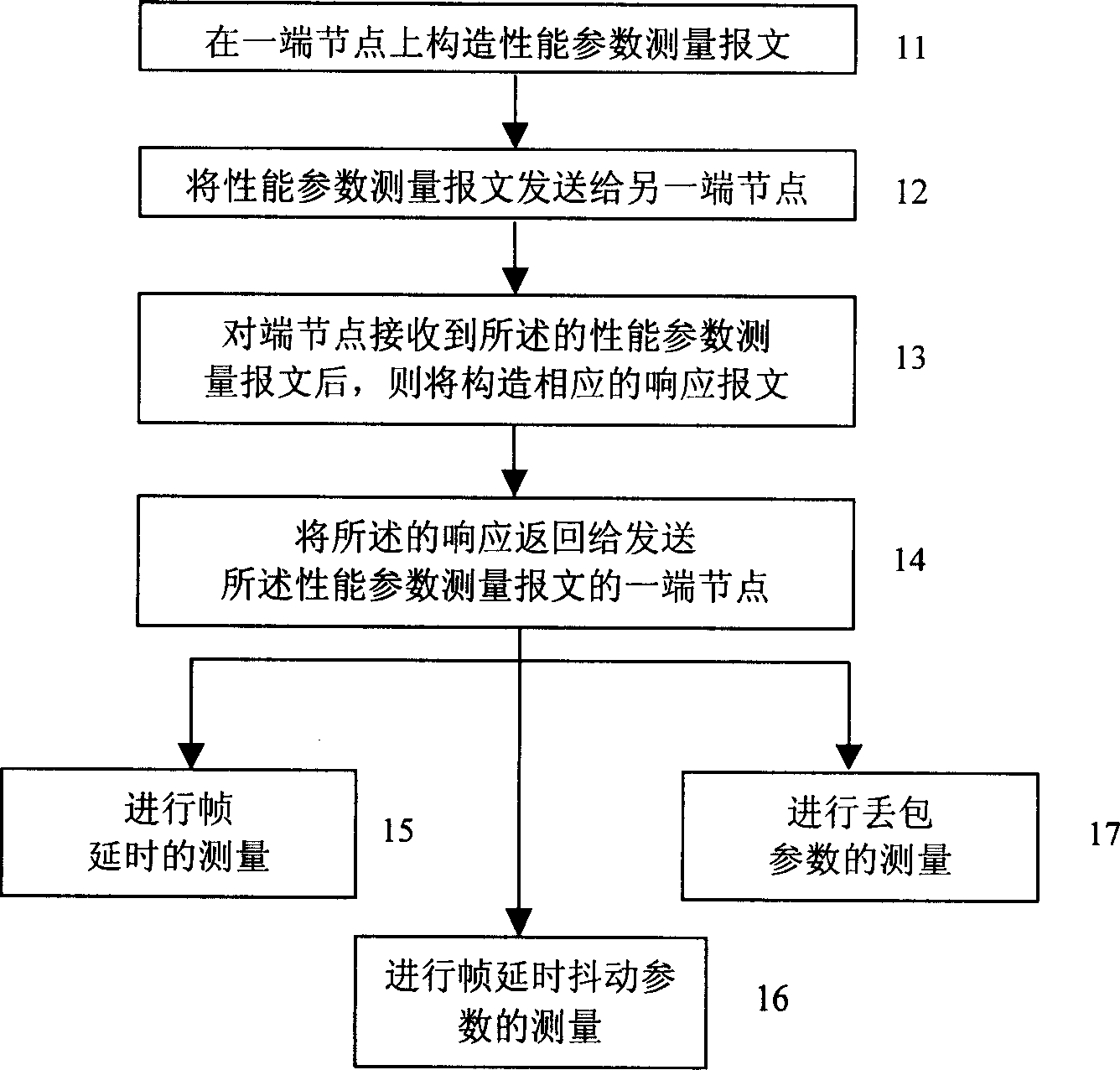
Method for measuring MPLS network performance parameter
InactiveCN1881908AGive full play to superior performanceData switching networksTime markMulti protocol
The invention relates to a method for measuring the property parameter of MPLS network, which comprises: first, setting serial number and receiving / sending mark information at the report of multi-protocol mark exchange MPLS network; then, based on said serial number and receiving / sending time mark information, measuring the property parameters. The invention supports the check of SLA consistence of present MPLS network, and supports the optimized MPLS distribution, to fully utilize the property of MPLS network.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
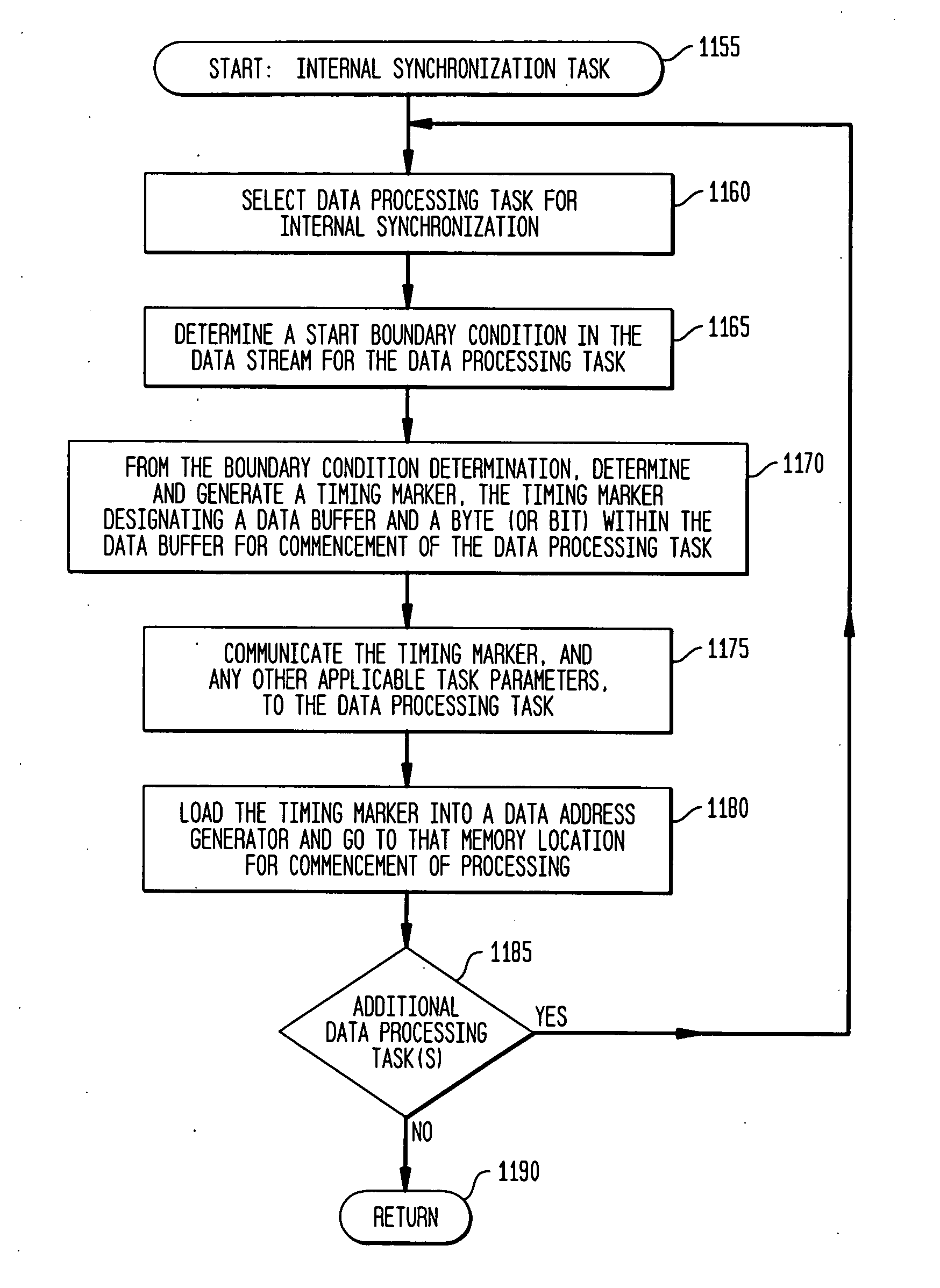
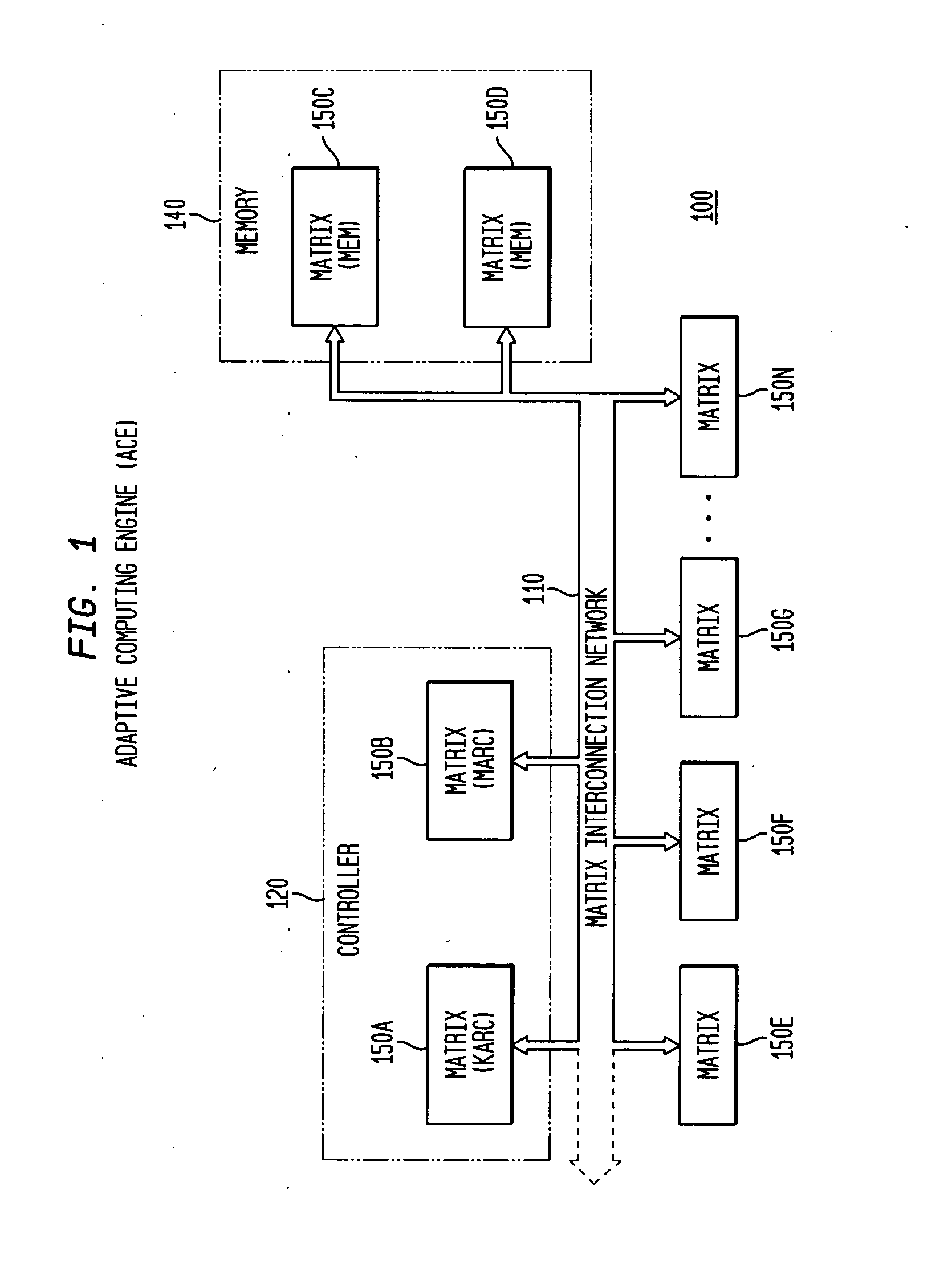
Internal synchronization control for adaptive integrated circuitry
ActiveUS20050038984A1Program synchronisationMultiple digital computer combinationsData streamTime mark
The present invention concerns internal synchronization in adaptive integrated circuitry which utilizes a data flow model for data processing. The present invention controls task initiation and execution based upon data consumption measured in data buffer units, with initiation of and transitions between tasks based on determined boundary condition within the data stream. In the various embodiments, when a data processing task is selected for synchronization, a boundary condition in a data stream is determined for commencement of the selected data processing task. From the boundary condition determination, a timing marker for the commencement of the selected data processing task is determined, relative to the data stream. The timing marker is dual-valued, providing a designated buffer unit and a designated byte or bit location within the designated buffer. The timing marker is communicated to the selected data processing task, which then commences data processing at a location in the data stream designated by the timing marker. The various apparatus embodiments include a hardware task manager, a node sequencer, a programmable node, and use of a synchronization task within an adaptive execution unit.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
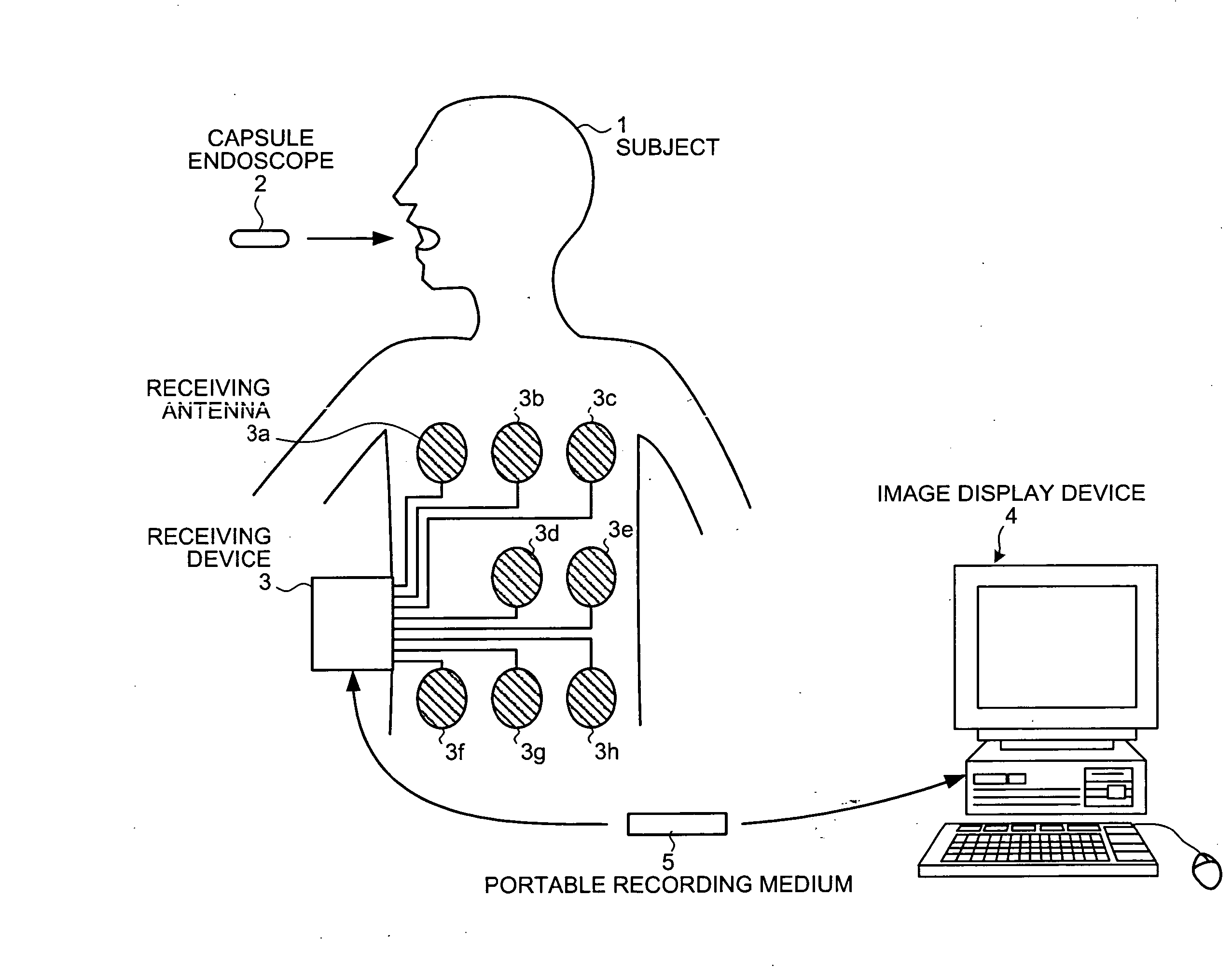
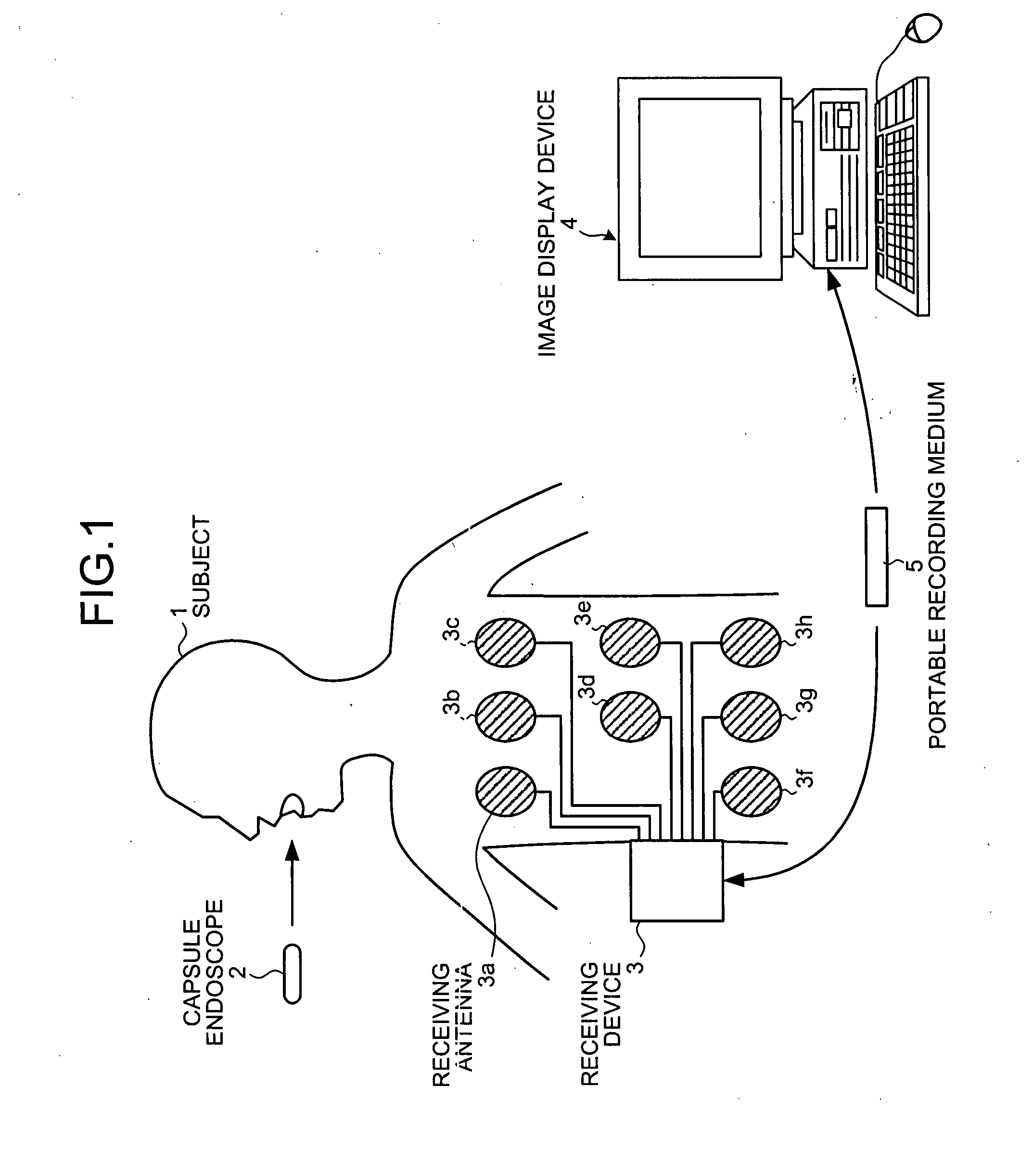
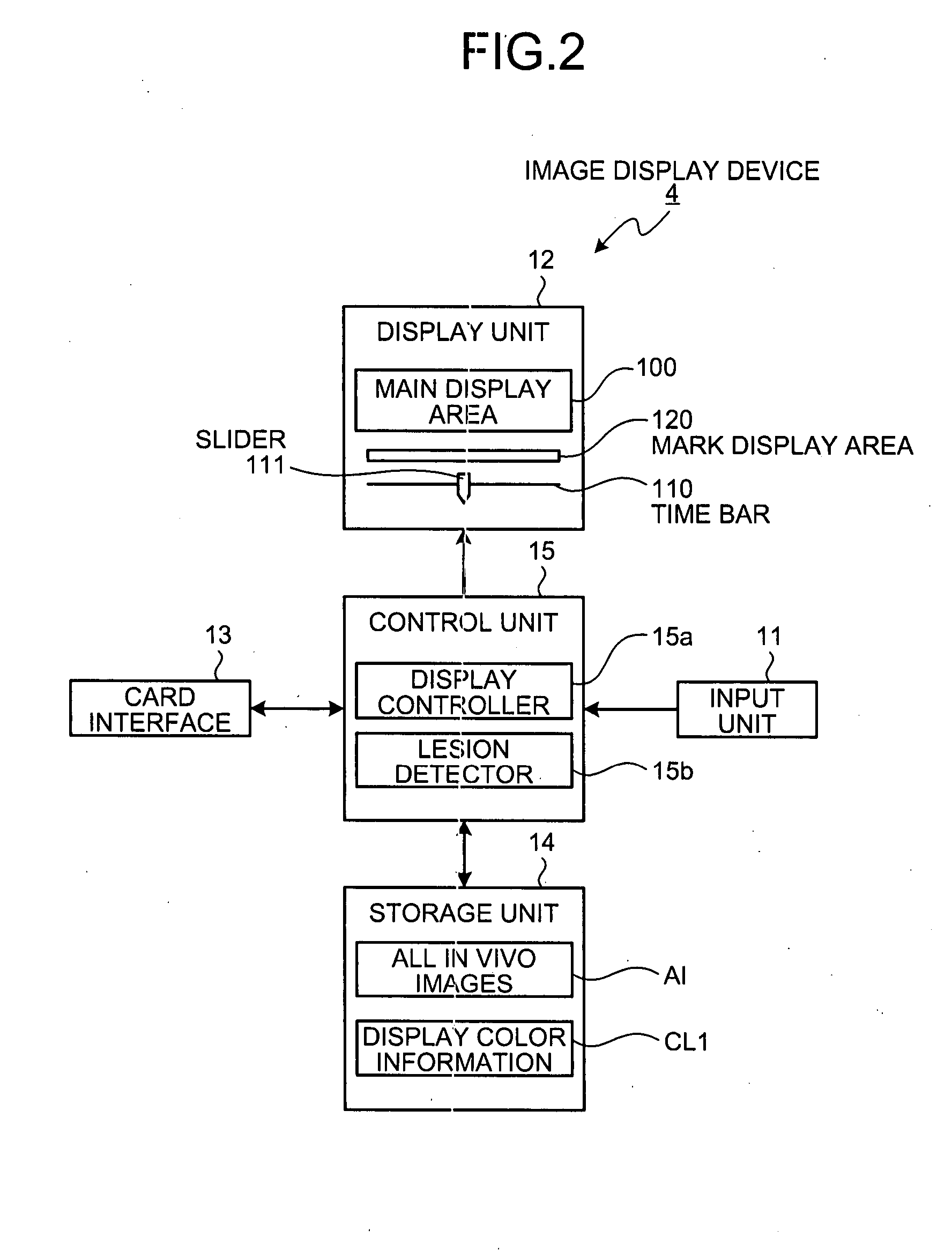
Image display device
A device for displaying in vivo images picked up inside a subject in a time series. The device automatically detects lesion images contained in all in vivo images picked up over the time series. The device displays an elongated display area having a time scale assigned along a longitudinal direction thereof and an indicator which moves along the time scale to indicate a time position in the time scale which corresponds to a current in vivo image currently displayed in a main display area. In response to a detection of the lesion image, the device makes pixels located at a time position in the elongated display area which position corresponds to the lesion image to emit light in a predetermined pixel-display mode. The display mode of the indicator is controlled in response to information on a lesion that is possible to be contained in the current in vivo image.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Daylight saving time support for mobile devices
InactiveUS20060002236A1Accurate displayAccurate operationVisual indicationElectric indicationTime markDaylight saving time
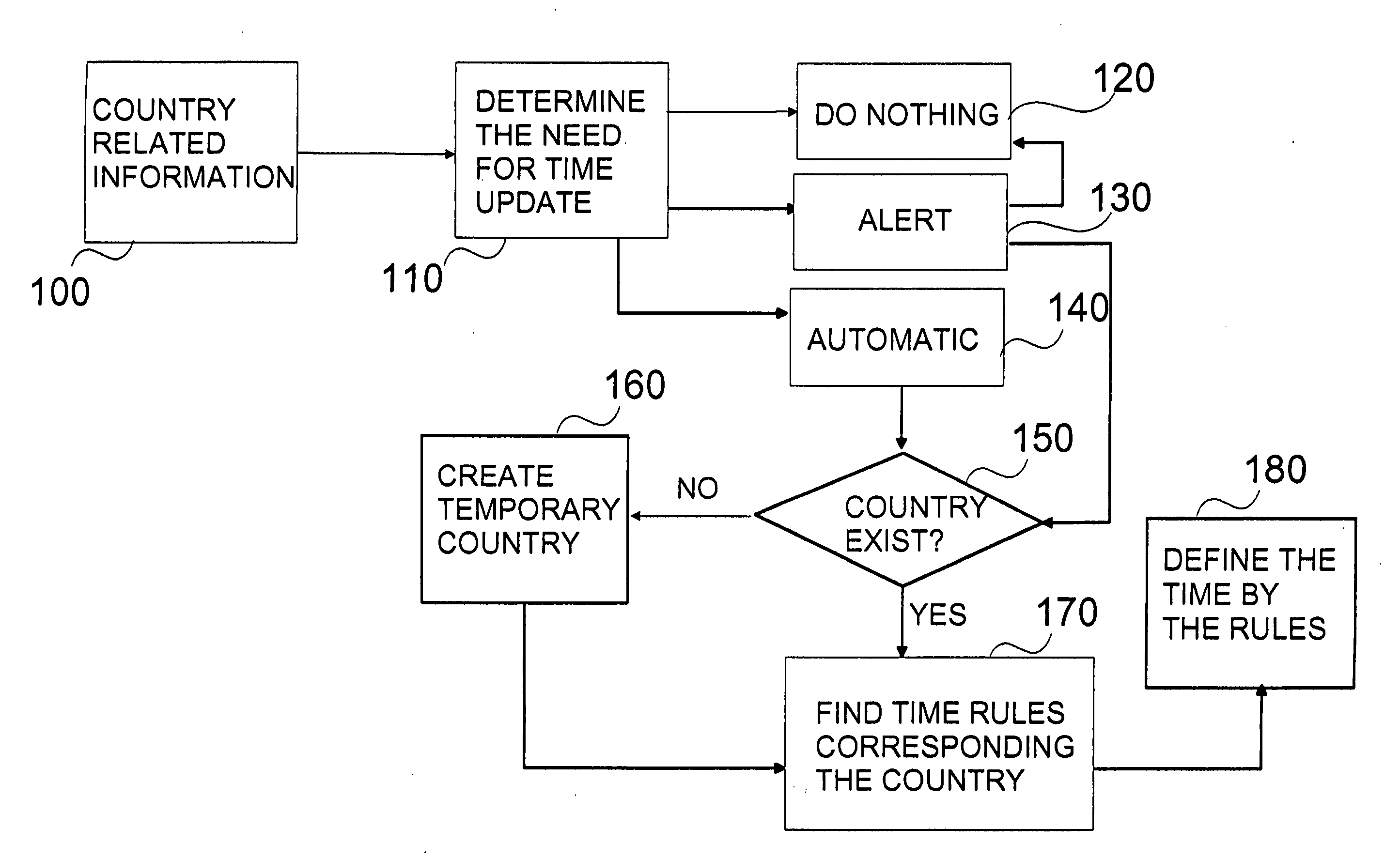
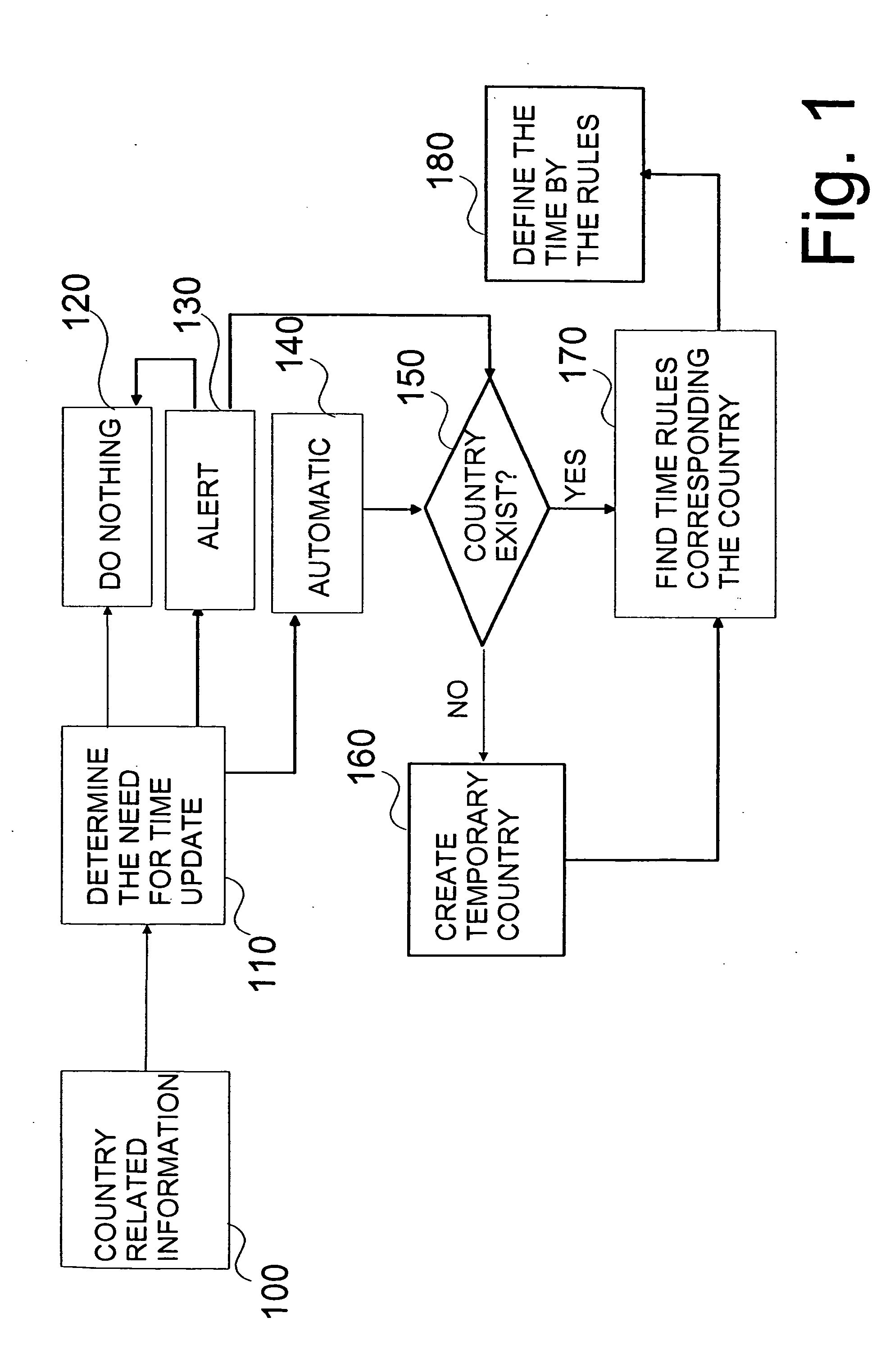
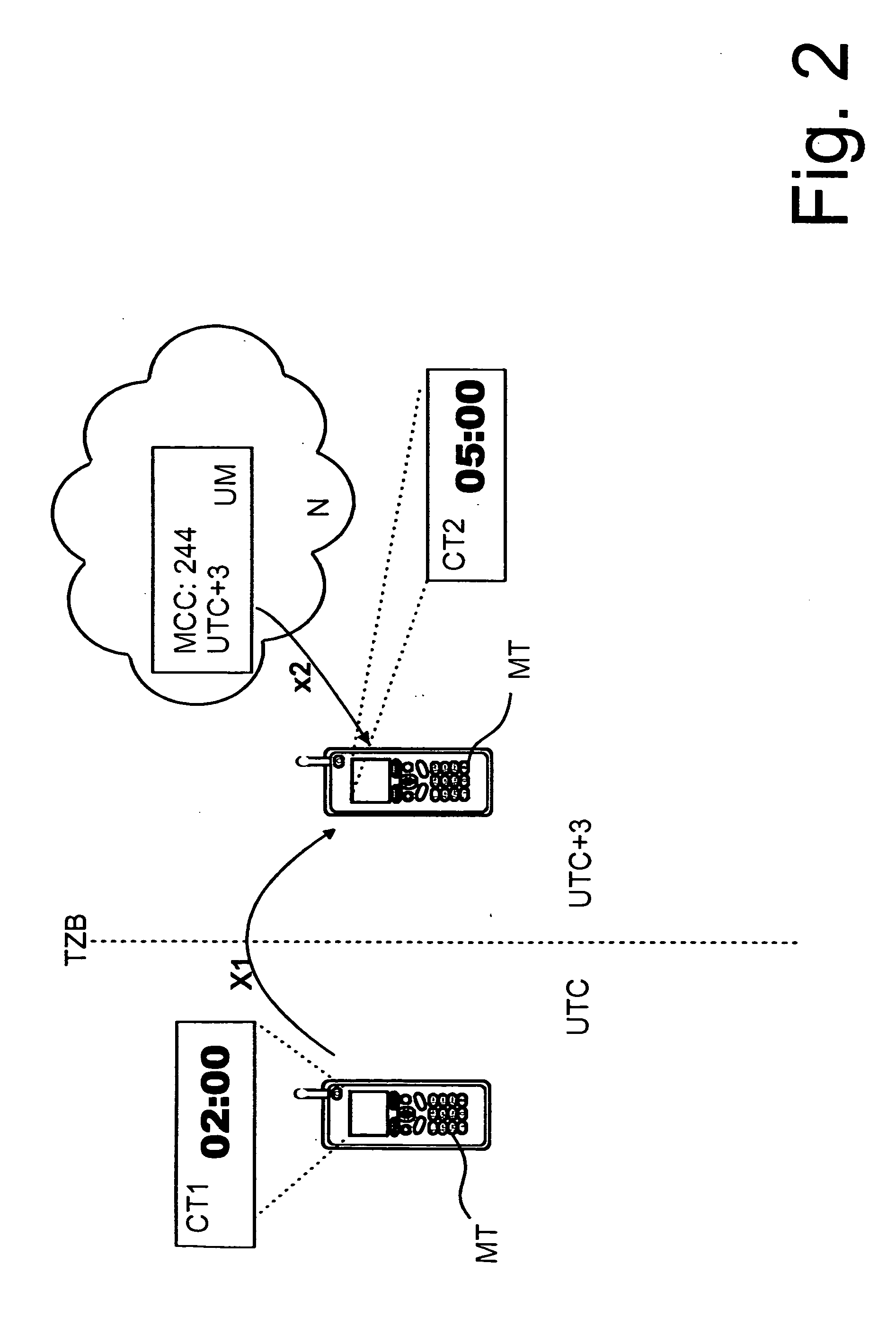
The invention relates to a method for updating a time marking according to new location, wherein a country related information is detected, a need for time update is determined, and if needed, time rules corresponding to said country related information is retrieved and the time is updated according to said rules. The invention relates also to a system, to a device, to a update converter and to computer program product.
Owner:RPX CORP
System and method for distributing time and frequency over a network
ActiveUS20090117928A1Timing tightElectric power transfer ac networkRadio-controlled time-piecesTime markClock rate
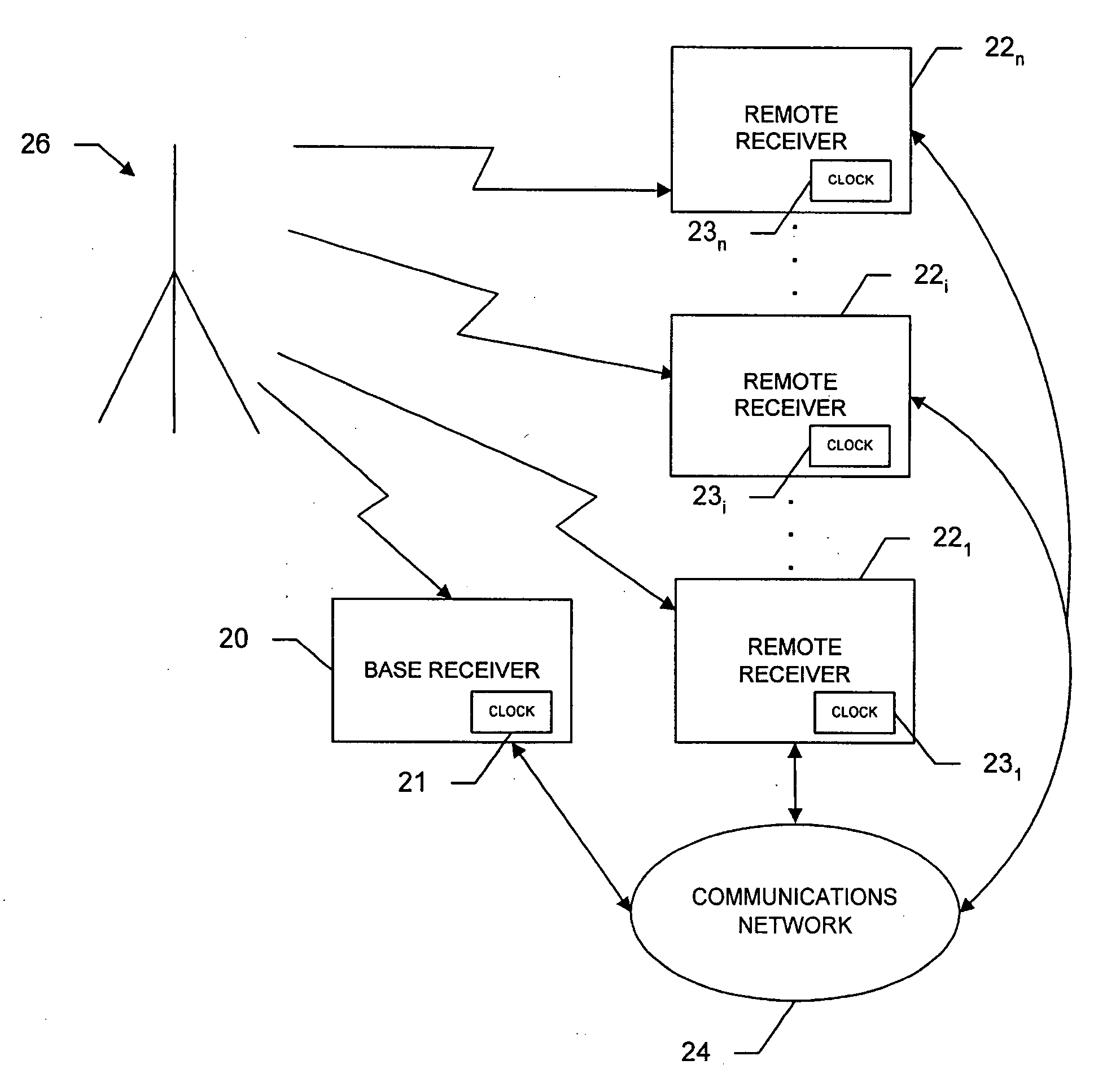
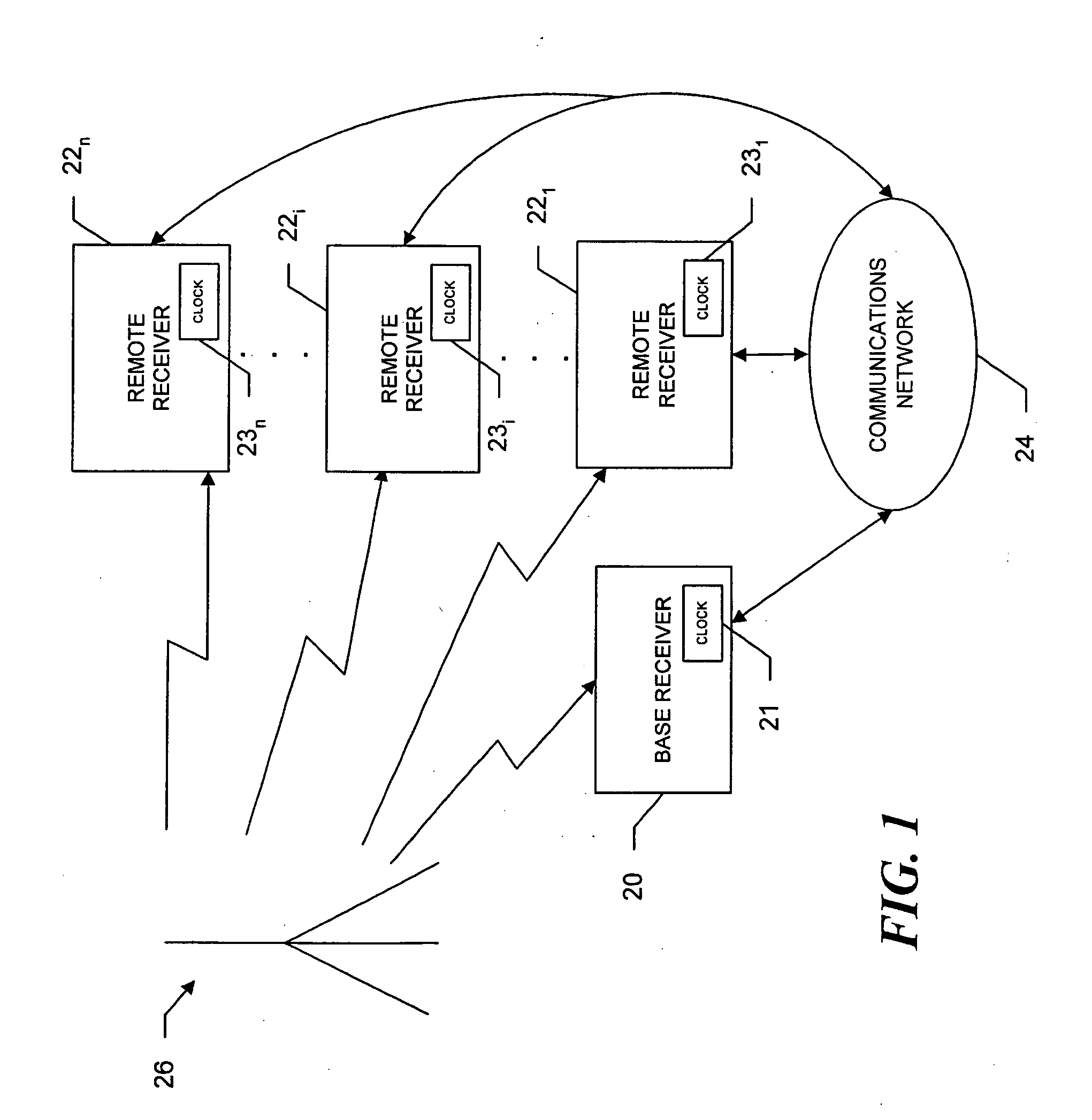
A system to distribute accurate time and / or frequency over a network utilizing signals of opportunity transmitted by one or more local transmitters with known locations, the system includes a base receiver with a clock synchronized to a reference time scale such as GNSS or UTC time that saves a series of samples of the signals of opportunity and time tags the series with a calculated time of broadcast. A remote receiver saves samples of the signals of opportunity and correlates the series with the saved samples. The remote receiver calculates a time of transmission of saved samples that correspond to the series, determines a time offset as a difference in the time of broadcast calculated at the remote receiver and the time of broadcast calculated at the base receiver, and determines the time offset with respect to the base receiver. The base receiver further or instead phase locks to the signal opportunity and at predetermined intervals determines phase measurements of the integrated carrier frequency of the signal of opportunity and provides the phase information to the remote receiver. The remote receiver, which is also phase locked to the same signal of opportunity, uses the phase measurement information to frequency lock its clock to the base receiver clock by determining a frequency error based on the rate of change of phase measurements made at the base receiver and the remote receiver.
Owner:NOVATEL INC
Multi-node synchronization sampling and data transmission method
ActiveCN101316160AStable delayStable transmission bandwidthElectric signal transmission systemsSynchronising arrangementStart timeTime mark
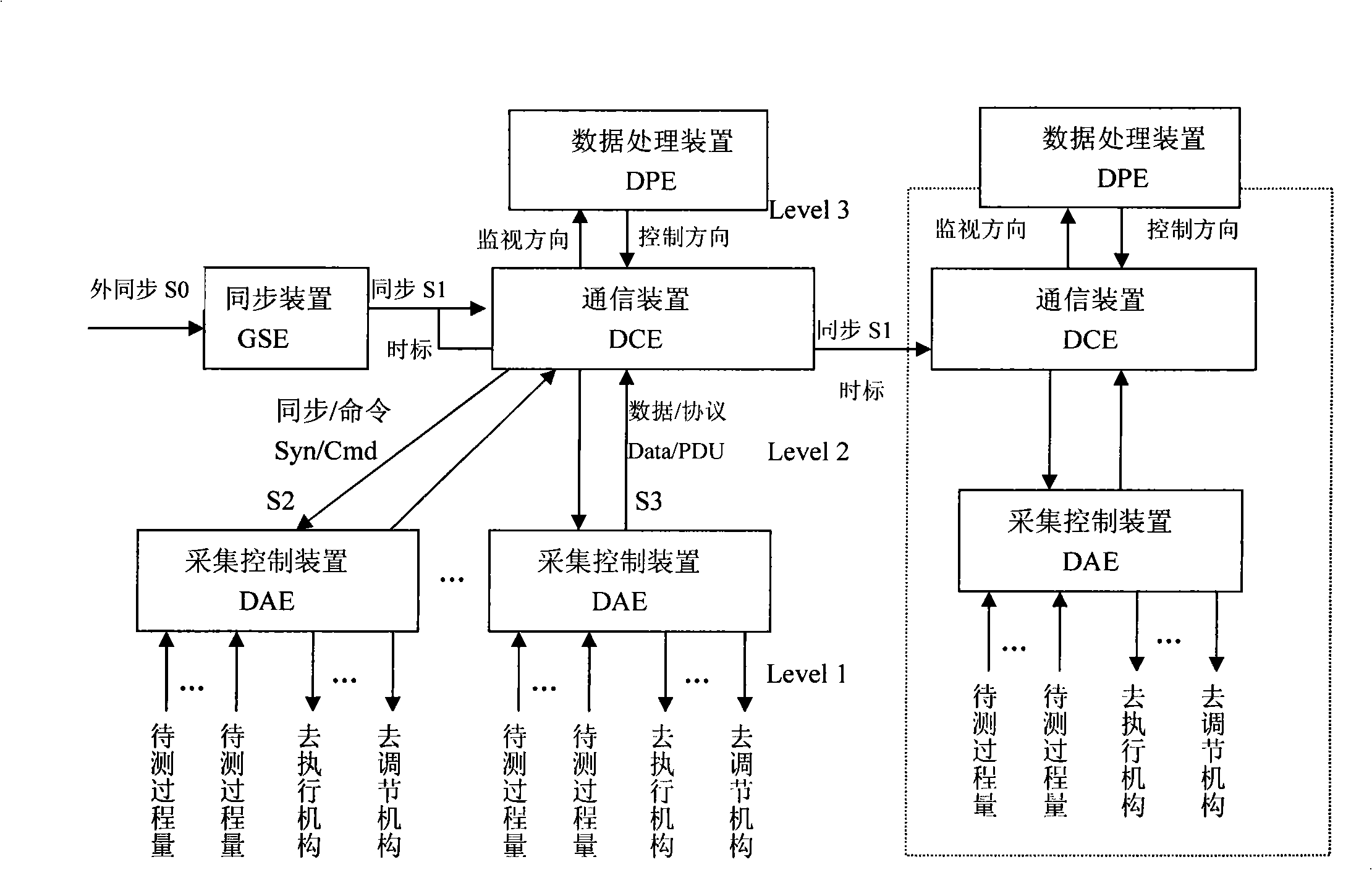
The invention provides a multi-node synchronous sampling control and data transmission method, the steps are as follows:(1) an overall synchronizer that matches with the upper layer data processing equipment and the process variable acquisition control equipment (DAE) is constructed, the equipment produces an overall synchronous signal S1 by utilizing an outer sync source or a local timer; (2) the overall synchronous signal is accessed to one or more data communication equipment (DCE), which produce a synchronous signal S2 for each accessed process variable acquisition control equipment; (3) the absolute time scale in the signal S1 and the overall sampling counter are utilized to realize the secondary synchronous sampling on the process variable among the data communication equipment; (4) the acquisition control equipment (DAE) for acquiring and outputting the process variable detects the synchronous signal and order data after receiving the signal S2; (5) the acquisition control equipment dynamically adjusts the start time of the S2 signal according to Delta ti and realizes the long-distance multinode synchronous sampling.
Owner:NANJING PANENG TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT CO LTD
Method and device for synchronizing two bus systems by transmission of a time associated trigger signal from one system to another
ActiveUS8321612B2Easy to adjustTime-division multiplexSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlTemporal informationTime mark
A device for synchronizing at least two bus systems, having a first communications module for a first bus system and a second communications module for a second bus system, wherein in the first communications module first trigger information is present by which a trigger signal is triggered in the first bus system, characterized in that the device is configured in such a manner that the first and second communications modules are connected to each other and the first trigger information is transmitted to the second communications module, and the second communications module is configured in such a manner that a time information value is determined from the first trigger information and that time information value is compared with a second time mark of the second bus system, a time difference being determined and the next reference message being triggered in the second bus system in dependence upon the second time mark and the time difference.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
High-accuracy failure wave-recording device and its transmission line combined failure distance-measuring method
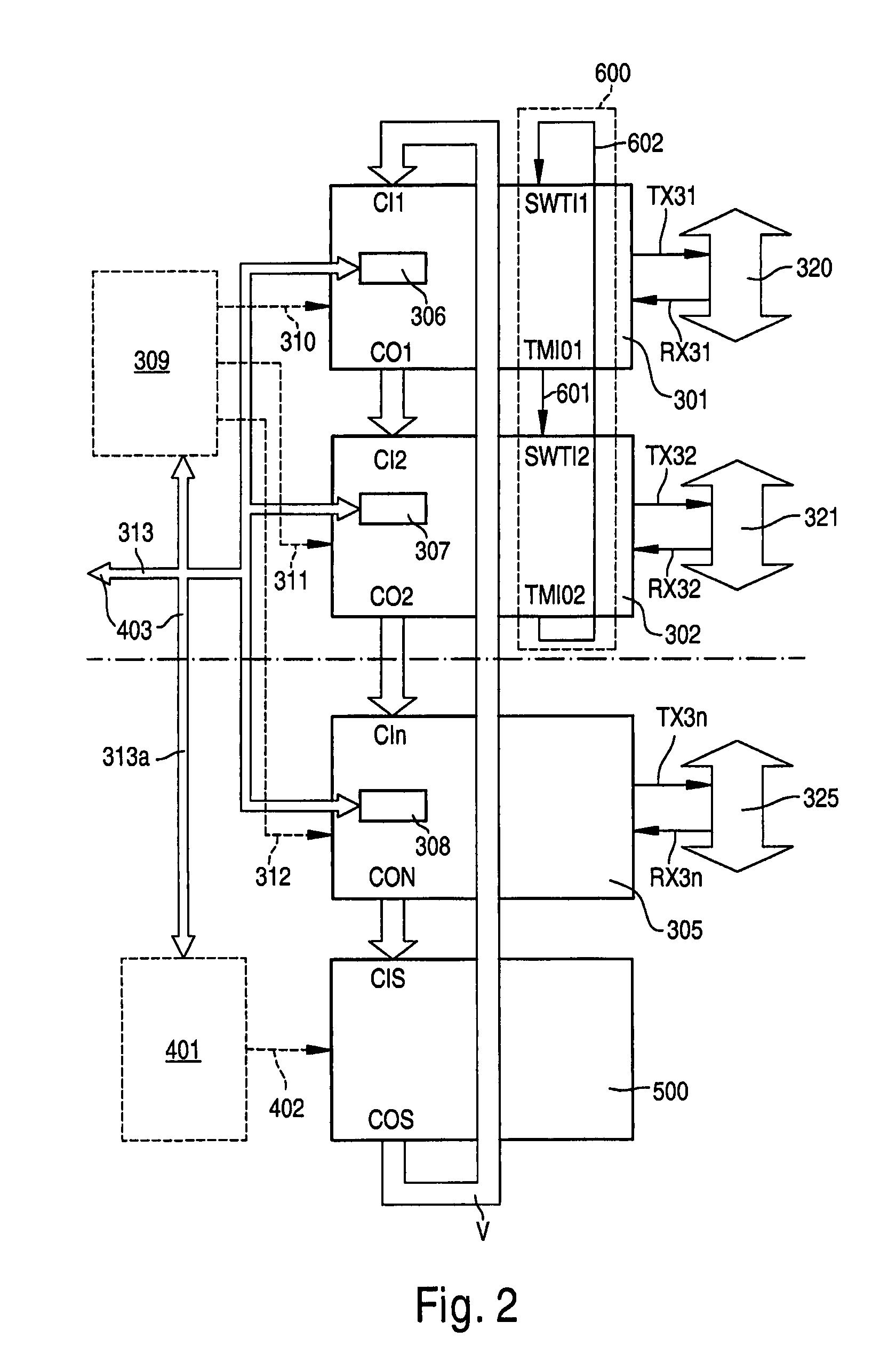
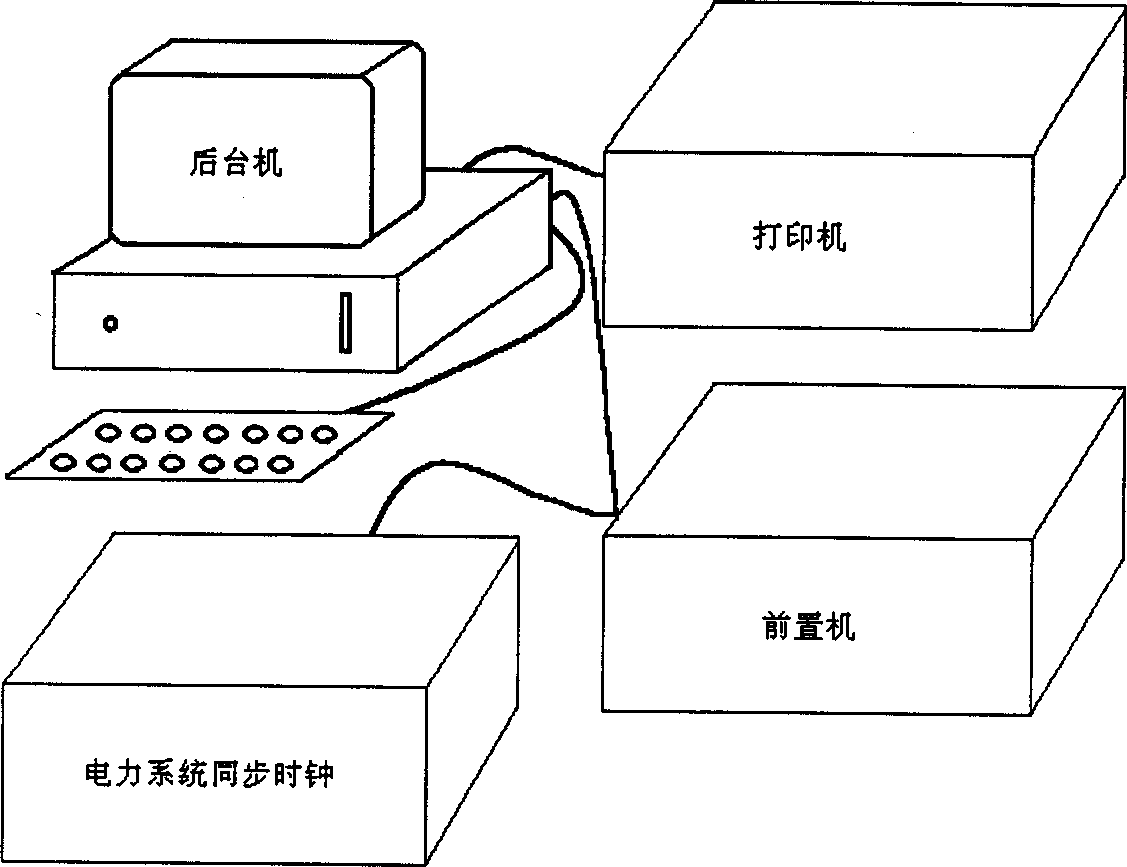
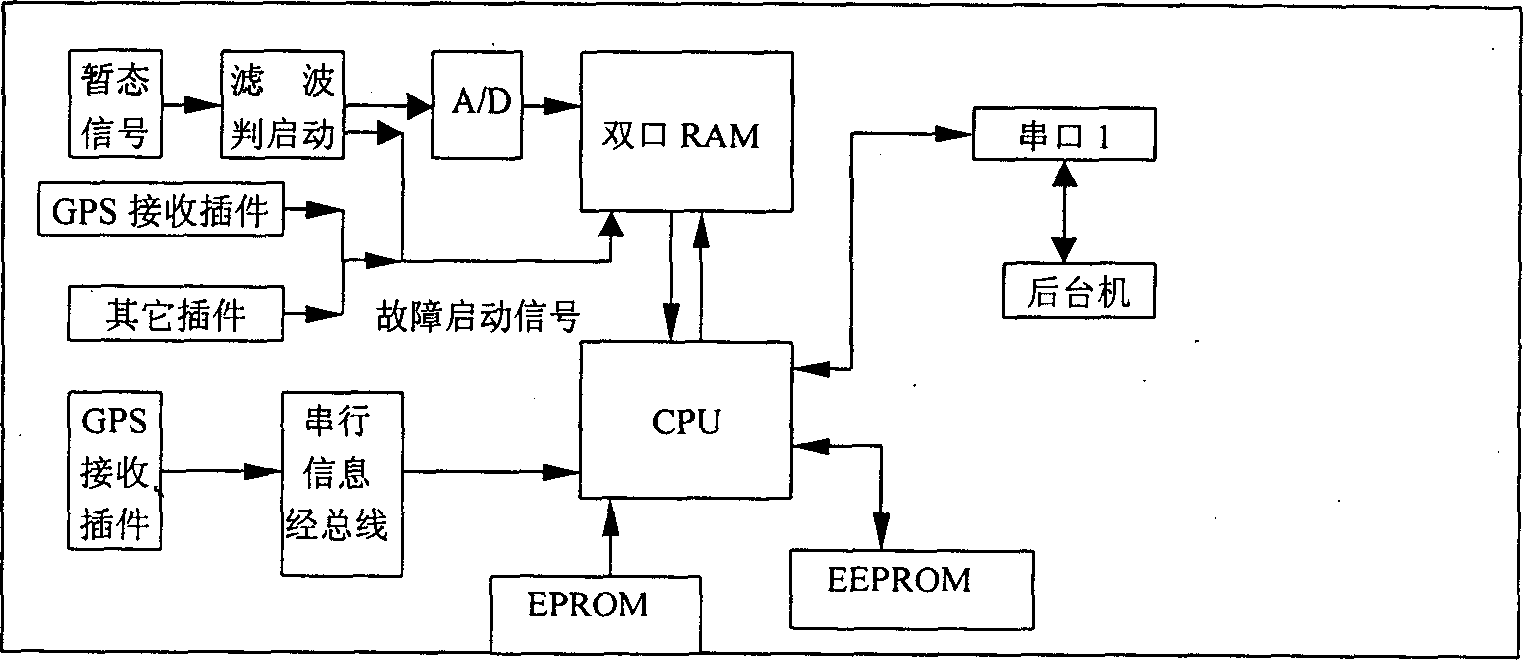
The present invention belongs to the field of power system, including four portions of topping machine, background machine, power system synchroclock and printer, in which the topping machine includes steady-state voltage and current collecting unit, transient voltage and current collecting unit, high-frequency collecting unit and GPS (global navigational satellite timing and distance-measuring system) time synchronization unit which can be used for providing accurate time mark and interfaced with power system synchroclock. The background machine adopts industrial control computer for fault data analysis and processing, the power system synchroclock is used for providing accurate time information and the printer can be used for printing fault record and fault distance-reasuring result.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method And System For Time Synchronization Of Phase Of Signals From Respective Measurement Devices
ActiveUS20130018620A1Improve accuracyFast response timeElectrical measurementsTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesMeasurement deviceTime mark
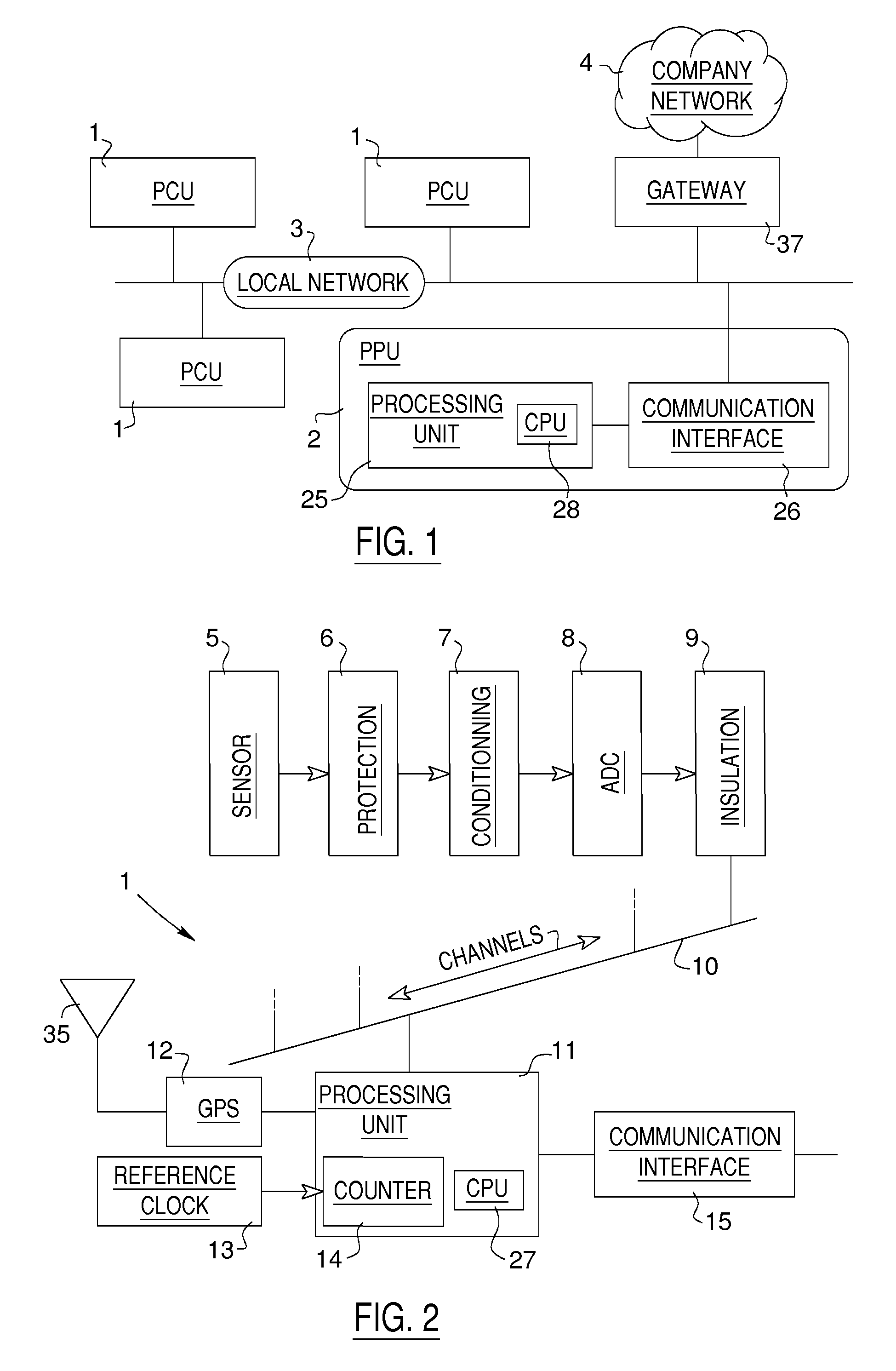
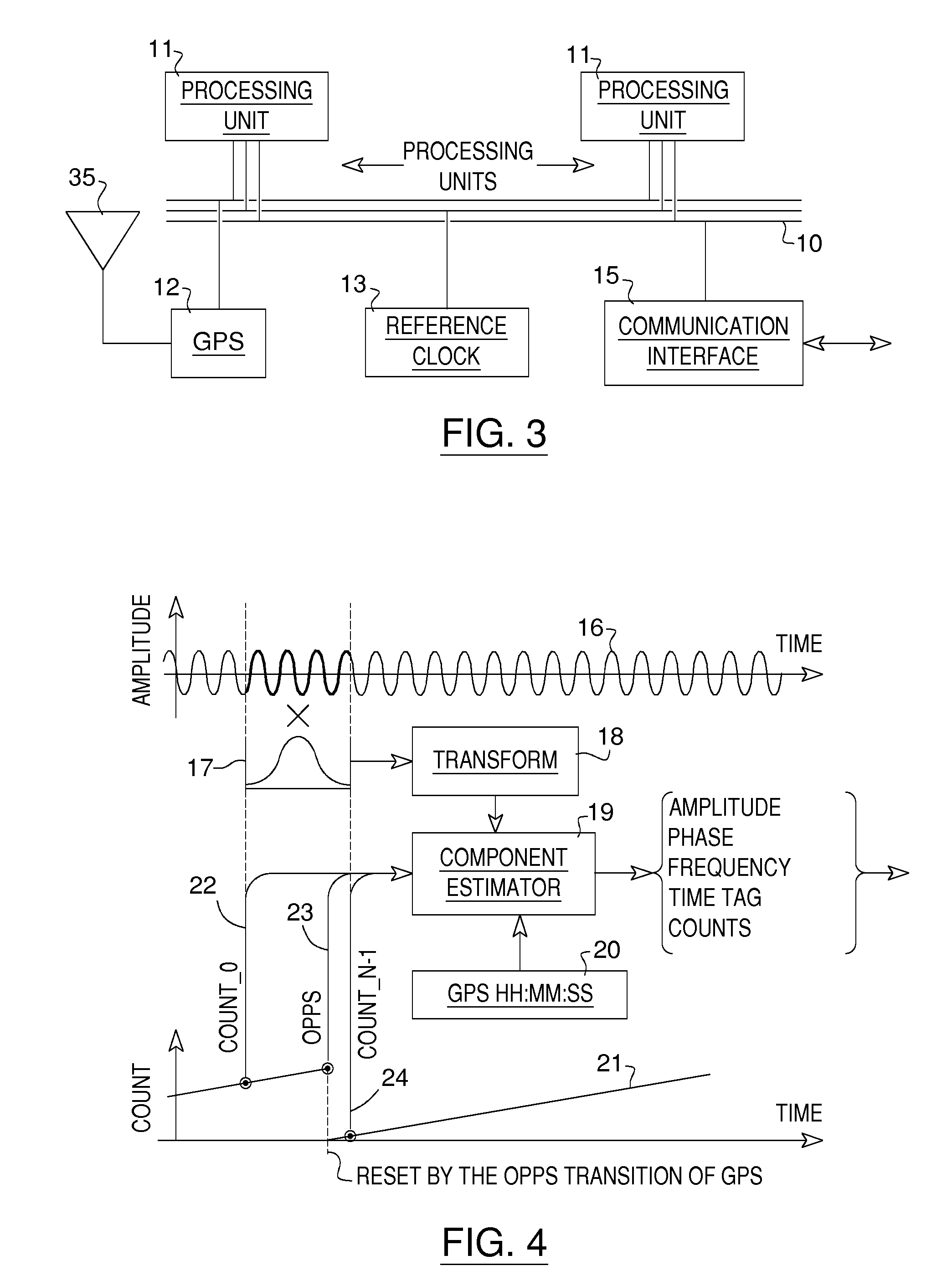
According to the invention, a time synchronization of phase between measurement devices that do not share a same clock for their respective sampling of the signals is carried out by a time tagging of samples of the signals in time blocks followed by an adjustment of the phase values of components of interest of the signals in the regrouped time blocks so that the values refer to common time references between the measurement devices. The tagging is carried out with a synchronization signal available to the measurement devices, completed with count values provided by a counter operated by a reference clock for each measurement device.
Owner:HYDRO QUEBEC CORP
Measuring device and measuring method for continuous physical quantity
InactiveCN101614554AAvoid aliasingImprove accuracyMeasurement arrangements for variableRecording measured valuesStart timeTime mark
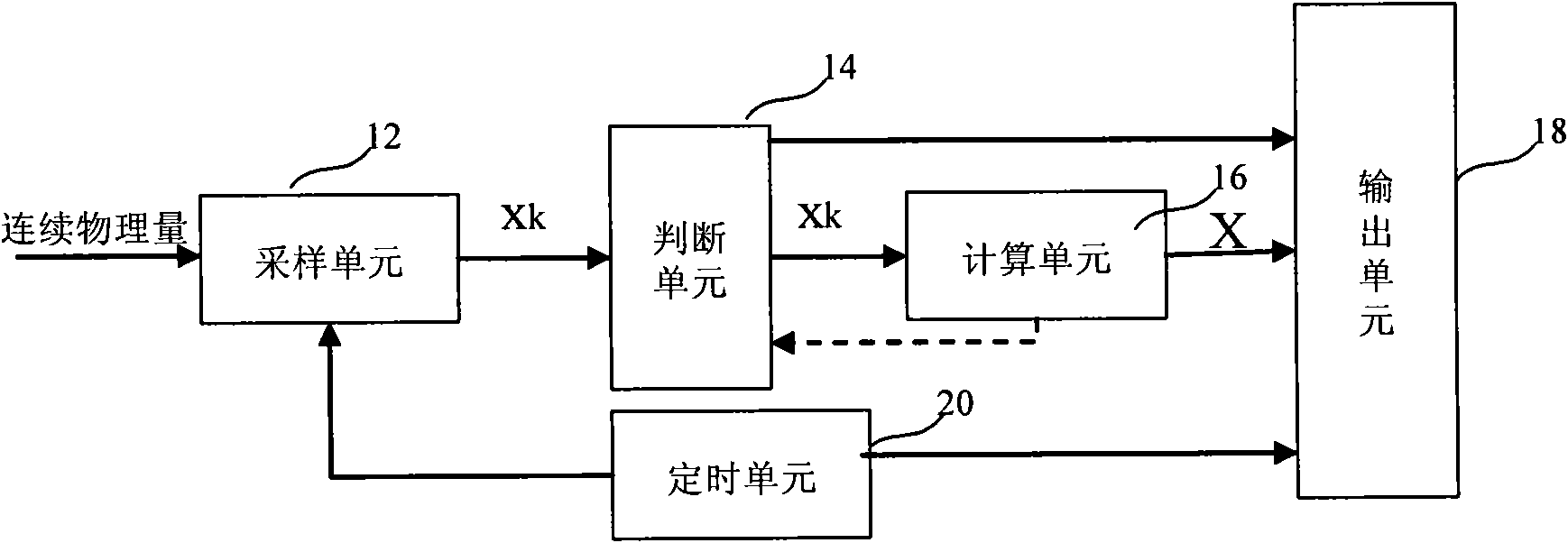
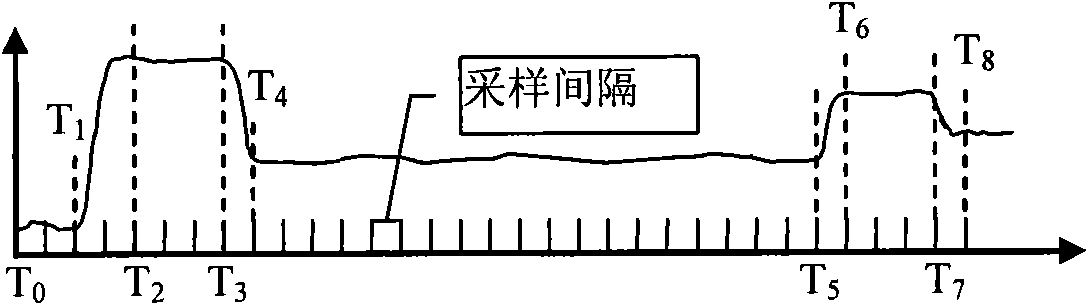
The invention discloses a measuring device and a measuring method for continuous physical quantity. The measuring device comprises a timing unit, a sampling unit, a judgment unit, a calculating unit and an output unit, wherein the timing unit is used for outputting a time base and a time scale; the sampling unit samples the continuous physical quantity at time intervals of satisfying the Nyquist sampling theorem under the control of the time base and outputs a sampling value; the judgment unit judges whether the sampling value turns or gets off a steady state process; the calculating unit calculates a steady state value for the sampling value of the sampling unit in the steady state process; and the output unit outputs the start time and the end time of the steady state process and the steady state value according to the judgment result and the time scale. The device and the method can reduce the output data quantity and do not produce aliasing simultaneously.
Owner:SANCHUAN ELECTRIC POWER EQUIP
Metadata time marking information for indicating a section of an audio object
InactiveUS9105300B2Small sizeLow costElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsSpeech analysisTime markComputer science
The application relates to a method for encoding time marking information within audio data. According to the method, time marking information is encoded as audio metadata within the audio data. The time marking information indicates at least one section of an audio object encoded in the audio data. E.g. the time marking information may specify a start position and an end position of the section or only a start position. The at least one section may be a characteristic part of the audio object, which allows instant recognition by listening. The time marking information encoded in the audio data enables instantaneous browsing to a certain section of the audio object. The application further relates to a method for decoding the time marking information encoded in the audio data.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
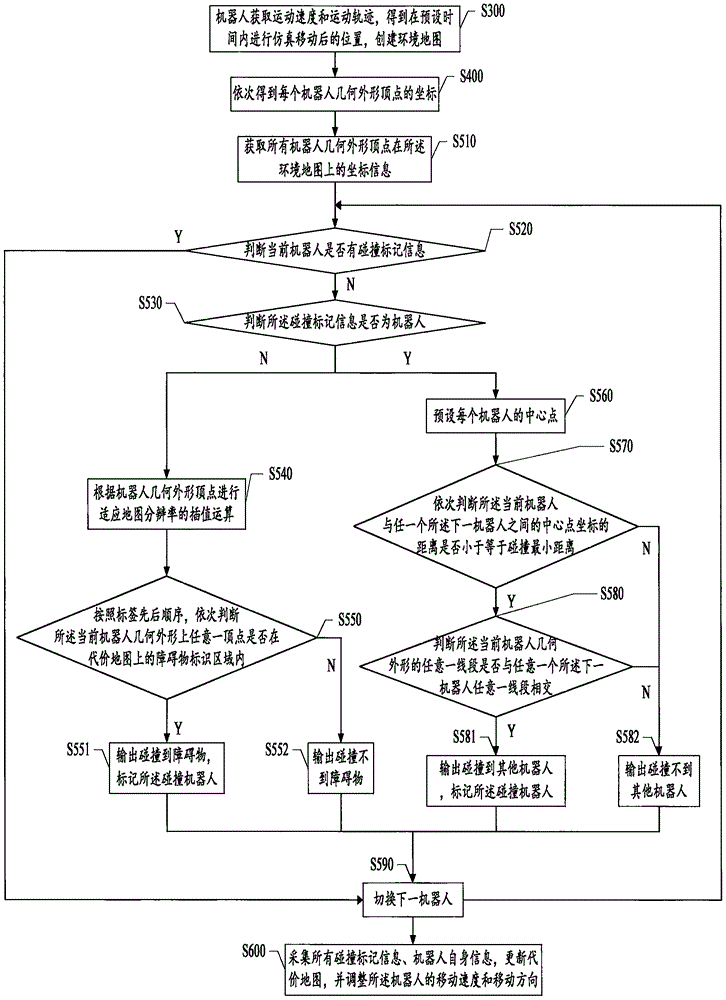
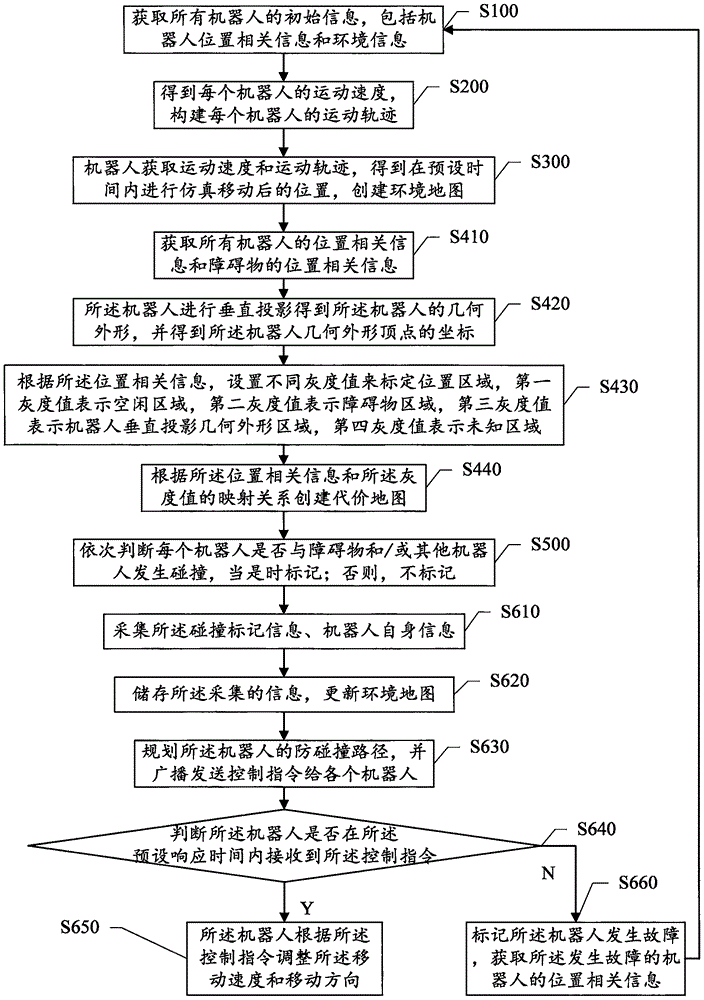
Multirobot collision preventing method and system
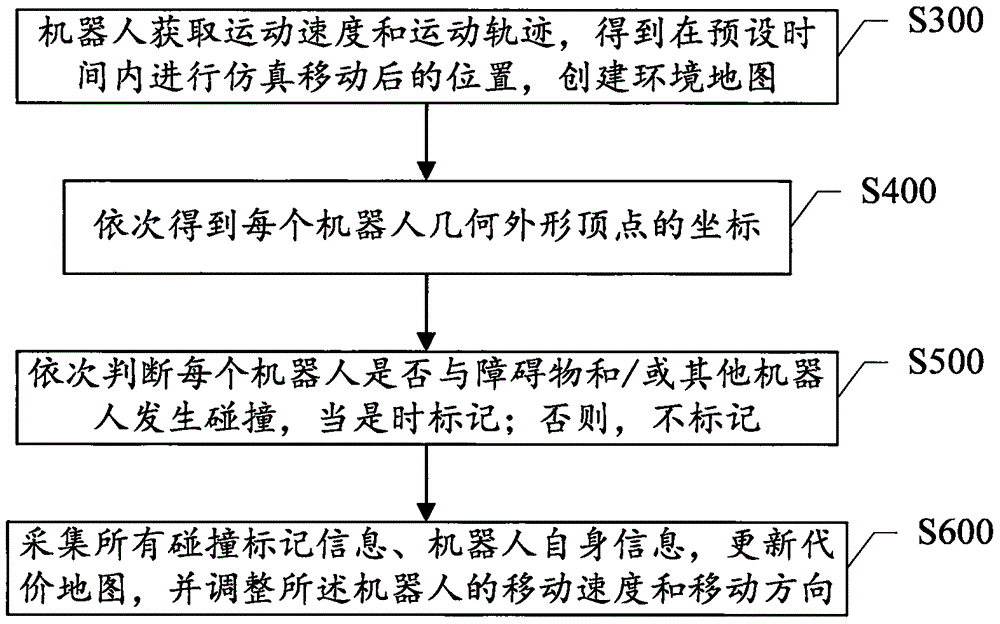
ActiveCN106325280AAvoid stickingPrevent the situationPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesTime markRobot position
The invention discloses multirobot collision preventing method and system. Robots obtains motion speeds and motion tracks to obtain positions of simulated movements within a preset time and create an environmental map; coordinates of the geometric profile peaks of the robots are sequentially obtained; whether the robots collide with obstacles or other robots or not according to different judgment methods, and time marks are made; all collision marking information and robot position related information are acquired, the environmental map is updated, and the moving speeds and the moving tracks of the robots are adjusted. The collision between the robots and the obstacles or other robots can be greatly avoided, normal operation of most of robots can be effectively ensured, different judgment times can be adopted for predicted collision between the robots and the obstacles and predicted collision between the robots, and the calculation time can be greatly shortened.
Owner:SHANDONG ZHONGHAO PLASTIC IND CO LTD
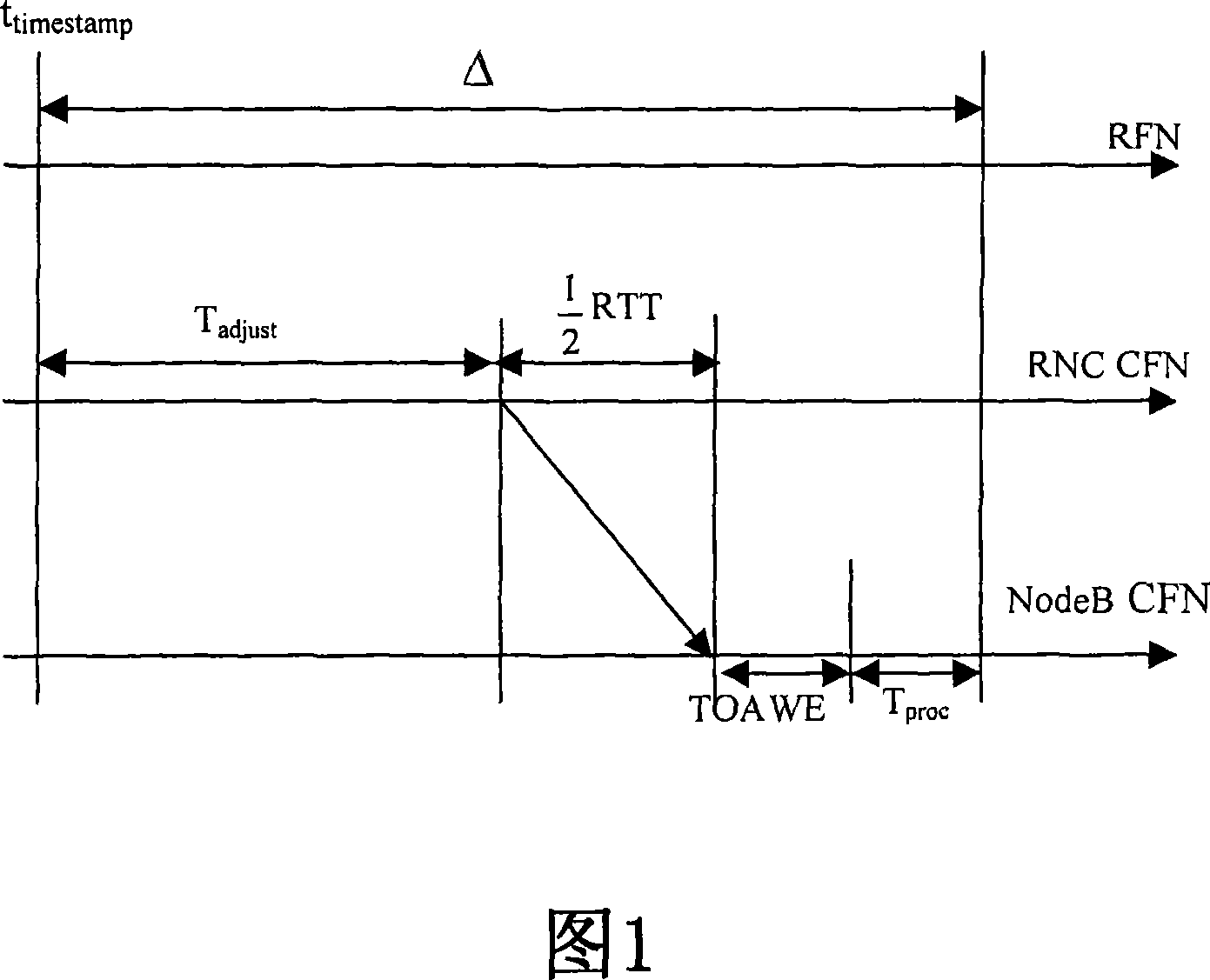
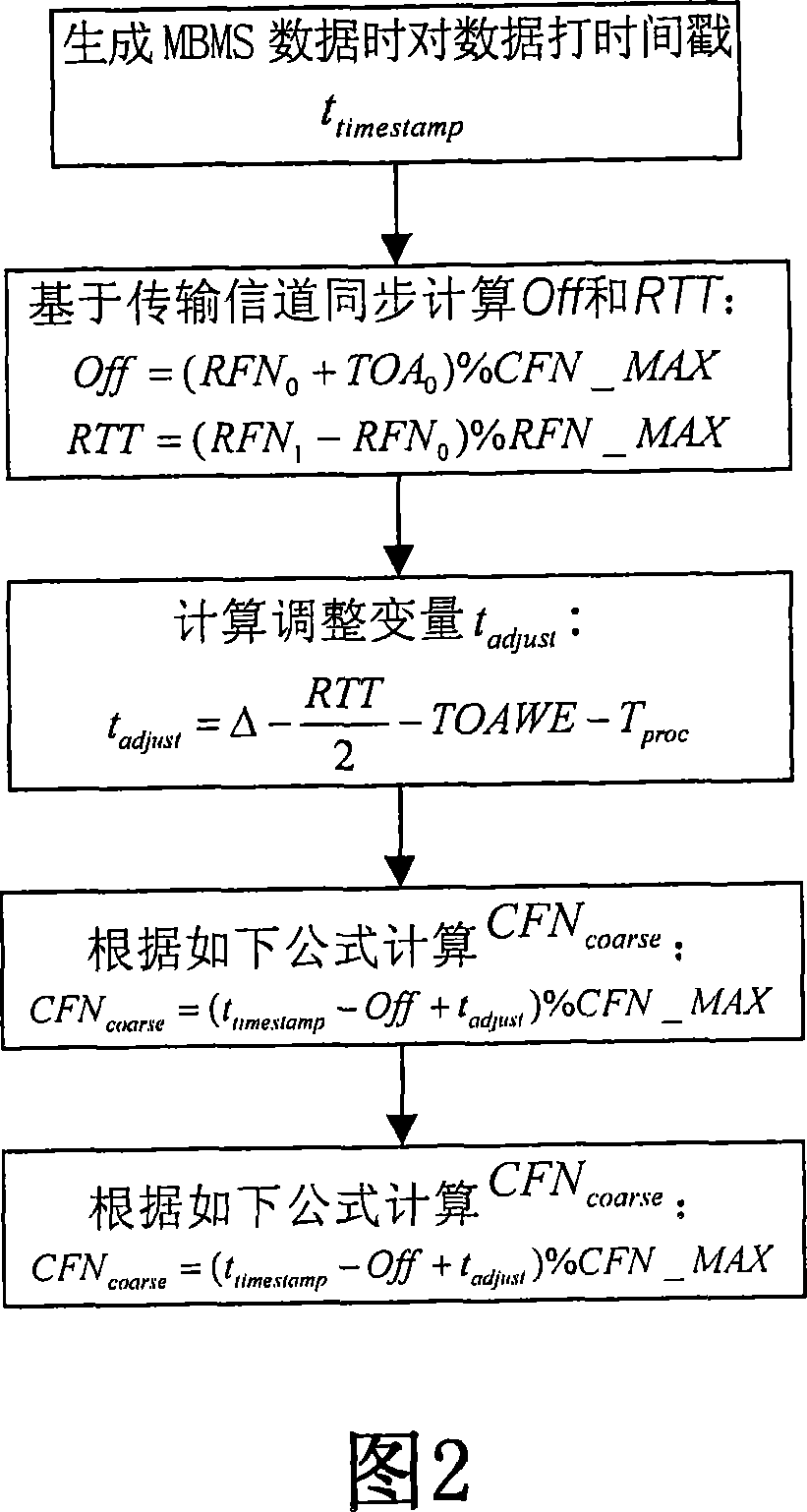
Method for realizing multimedia broadcasting and multicasting service data synchronized transmission
ActiveCN101043265ARealize synchronous sendingSpecial service provision for substationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsData synchronizationTime mark
The invention provides a method of realizing multimedia broadcasting and group broadcasting operation transmission in-phase, the method includes: data is marked with time when generating multimedia broadcasting and group broadcasting operation data, and deciding the transmission time of empty port according to the time mark; calculating the data transmission frame number of areola based on the transmission time of empty port. The implement of the invention can realize the synchronization transmission of MBMS operation in an areola on condition that base station does not support node synchronization.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
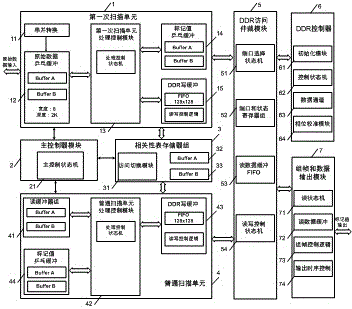
Real-time binary image connected domain mark realizing method based on FPGA
ActiveCN104881666AProcessing speedReal-time processingCharacter and pattern recognitionProcessor architectures/configurationTime markImage resolution
The invention discloses a real-time binary image connected domain mark realizing method based on FPGA, which belongs to the large scale integrated circuit design, object identification and visual measurement technical field. The invention aims to achieve real-time connected domain marking of large scale moving objects on the basis of field programmable gate array devices in a hardware way. Four symmetrical processing nodes are used. A newest serial exchange architecture (VPX architecture) is adopted. Each processing node comprises XC5VX95TI-2FPGA of the XILINX corporation and a DDR memory cell of a 16G-bit storage capacity. The nodes are interconnected through 16 pairs of 2.5GHz RocketIO. Each processing node is composed of a first-time scanning unit, a main controller module, a correlation memory group, a common scanning unit, a DDR access arbitration module, a DDR controller, and a framing and data output module. Real-time marking of large scale moving objects is achieved through superscalar streamline and dynamic delay streamline technologies. Adaption to various resolutions is further realized. The performance is not affected when the moving object shape and number are changed. Strong robustness is achieved. The calculation result is completely consistent with the MATLAB bwlabel function.
Owner:成都靖尧通信技术有限公司
Photon counting multi-channel time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay system and counting method
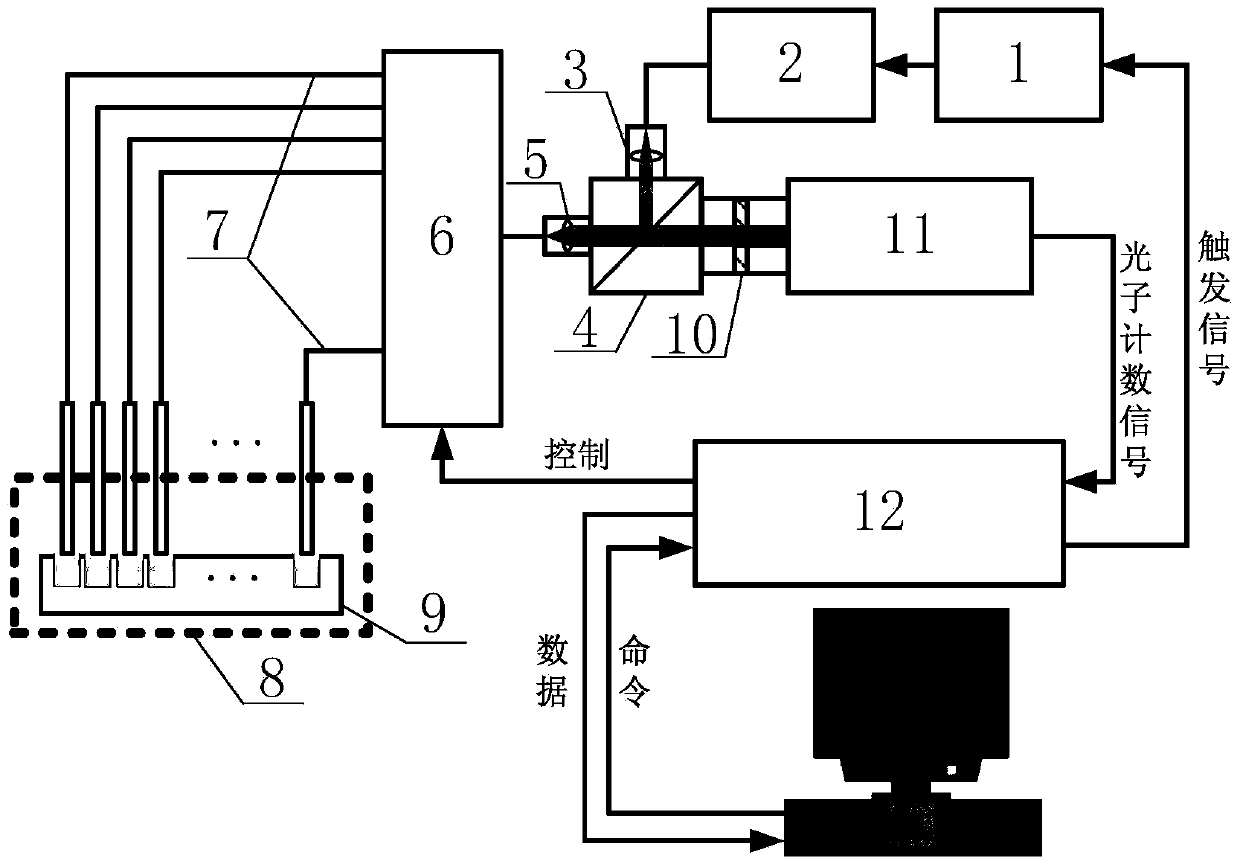
InactiveCN103728446AAvoid interferenceEasy to assembleBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceTime resolved fluorescence immunoassayTime mark
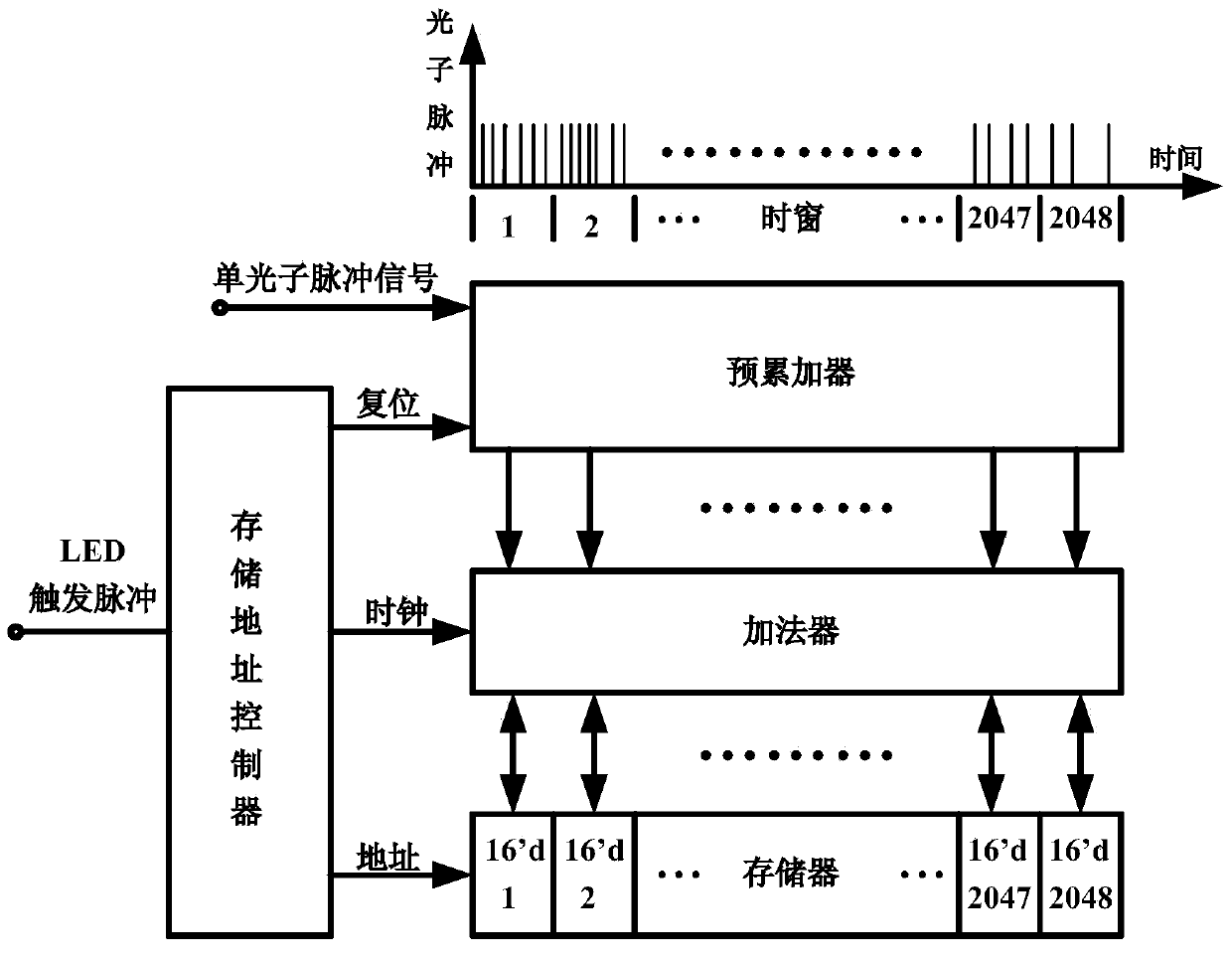
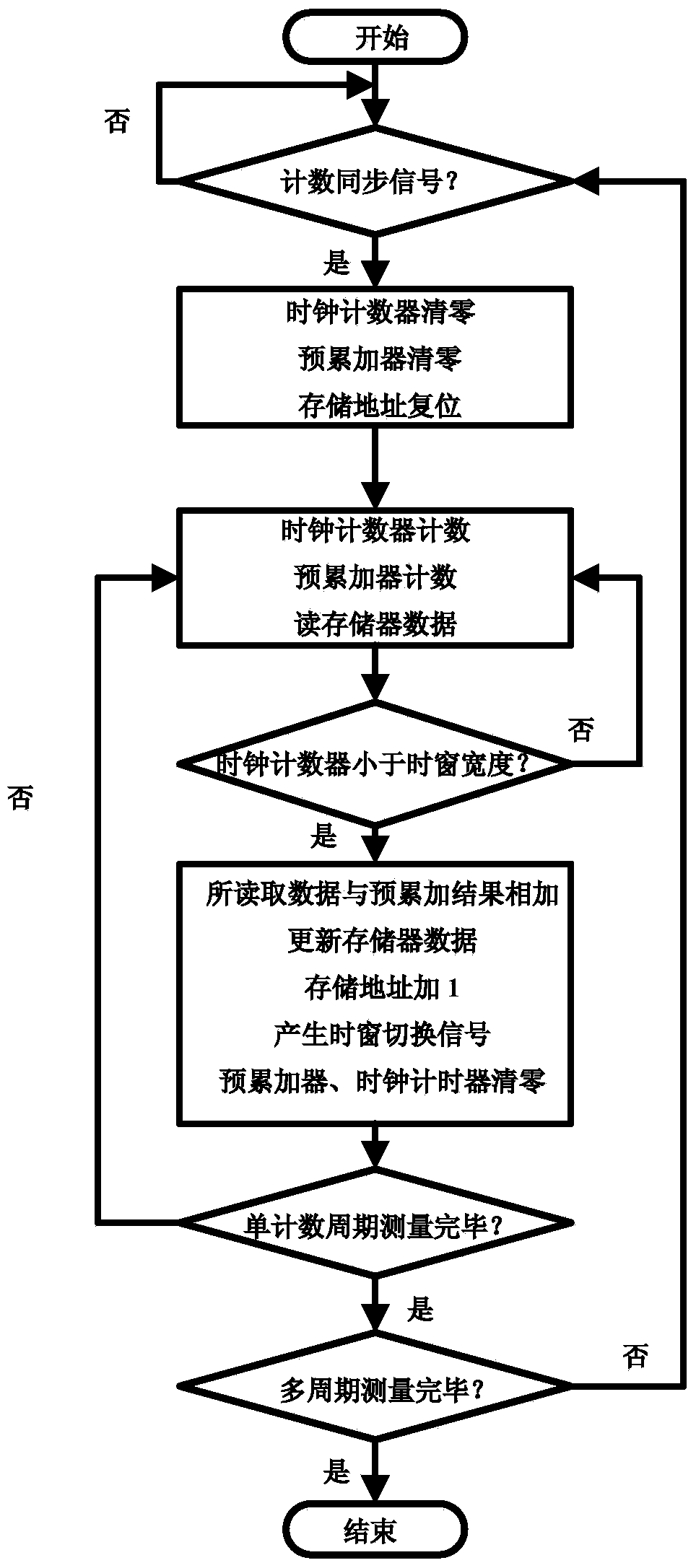
The invention belongs to the technical field of fluorescence immunoassay and relates to a photon counting multi-channel time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay system which comprises a light source module, a detection module and a time marked photon counting analysis / control module. At the same time, the invention relates to a counting method adopted by the system. The counting method of exciting a sample to be detected with pulse light, sending a fluorescence signal generated by the sample after excitation into a PMT (Photo Multiplier Tube) photon counting head and outputting a pulse signal comprises the following steps of taking cycles of the excitation pulse light as counting cycles, dividing each counting cycle into a plurality of time intervals with the same width, accumulating photons detected after sending excitation light pulses of each counting cycle into a memory corresponding to a corresponding time window, that is marking the positions of the photons in the pulse cycles with the intervals where the time windows are located, and uploading data in the memory into an upper computer after counting for the cycles. The multi-channel time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay system is low in cost and has very high sensitivity.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Single photon counting formatter
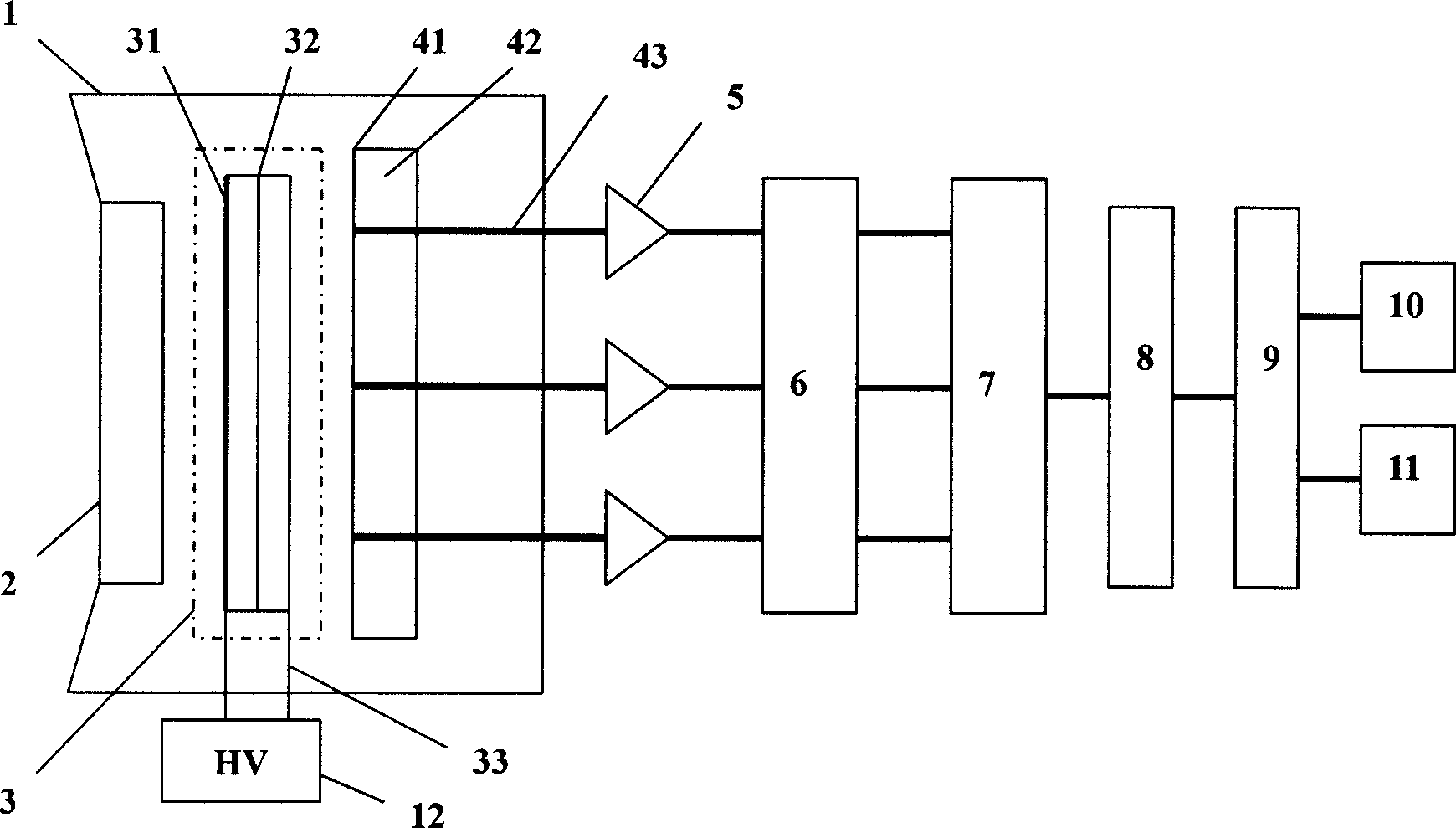
InactiveCN101387548AStitching is not requiredHigh sensitivityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMicro imagingPhotocathode
The invention relates to a single photon counting and imaging detection device. A high-voltage power supply of the device is connected with a micro-imaging reinforced tube through a high tension lead; a display, an image processing device and a printer are connected with a computer respectively; an anode collector is arranged between the micro-imaging reinforced tube and a preamplifier; the anode collector comprises a substrate, an electrode plated on the substrate and a signal lead; an anode is connected with the preamplifier through the signal lead; and the micro-imaging reinforced tube comprises a photocathode and a microchannel plate connected with the photocathode which are arranged sequentially along a light path. The device has the characteristics that the device can read out a time mark for arriving time and a general image of integral in a period, realize the single photon counting and two-dimensional imaging detection of an extremely-weak object, has the function of single photon counting, and can perform two-dimensional imaging on the extremely-weak luminous object. The device has the advantages of large area array, high sensitivity, low dark count, high resolution factor, good imaging linearity and the real-time measurement and processing.
Owner:陕西光电子先导院科技有限公司
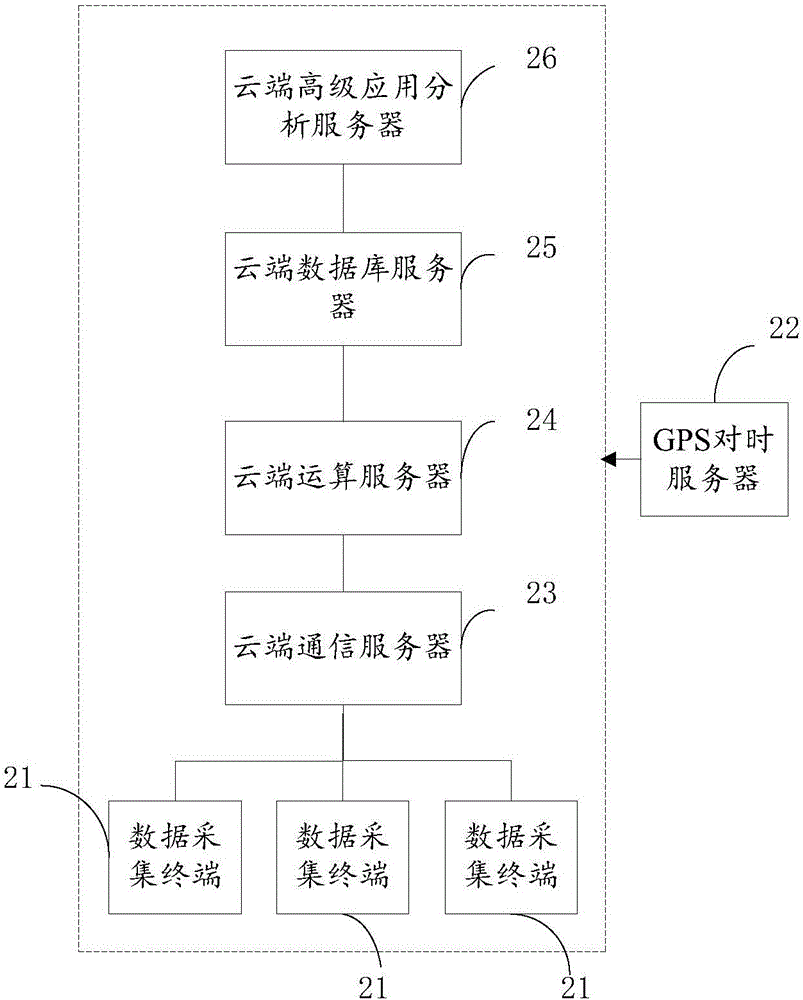
Power quality monitoring method and system
The invention discloses a power quality monitoring method. Through a data acquisition terminal which is arranged in a substation, a GPS timing server carries out unified timing. The electrical amount real-time data of a monitor point are synchronously acquired. The data acquisition terminal sends the acquired electrical amount real-time data with a time mark to a cloud operation server through a cloud communication server via a high-speed wireless communication network. The cloud operation server carries out operation on the electrical amount real-time data to acquire power quality data and non power quality data. The acquired data are saved in a cloud database server. A cloud advanced application analysis server extracts the power quality data and the non power quality data, and carries out real-time display, historical trend statistics, report generation and output, waveform playback display and harmonic source retrospective analysis on monitor data to complete power quality analyzing and managing. According to the invention, operation and maintenance costs of a system are greatly reduced, so that the scalability of a monitoring system is fundamentally improved.
Owner:南京国臣直流配电科技有限公司 +1
Synchronous compression transformation order analysis method for rolling bearing fault diagnosis
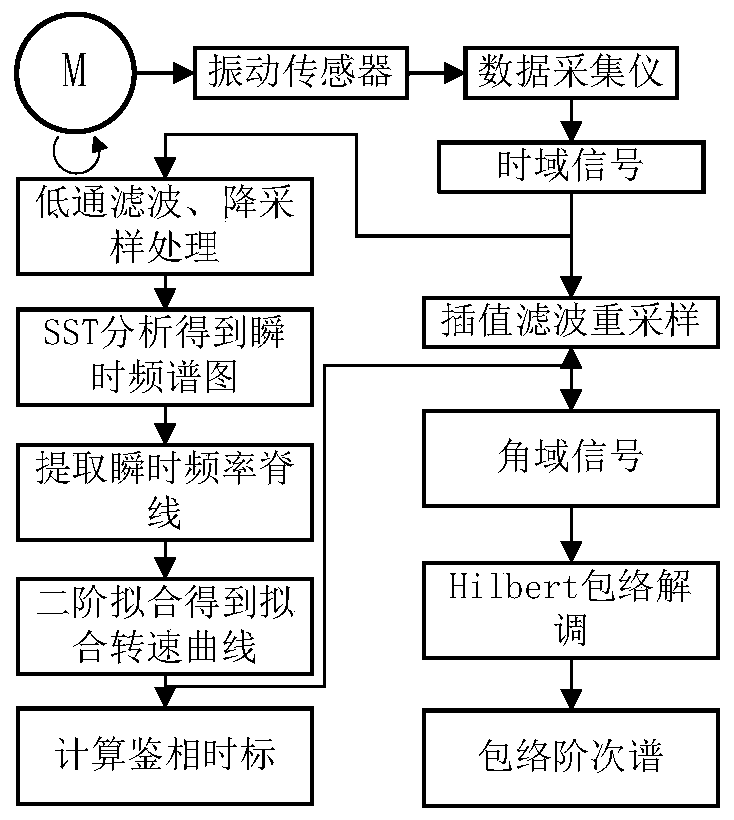
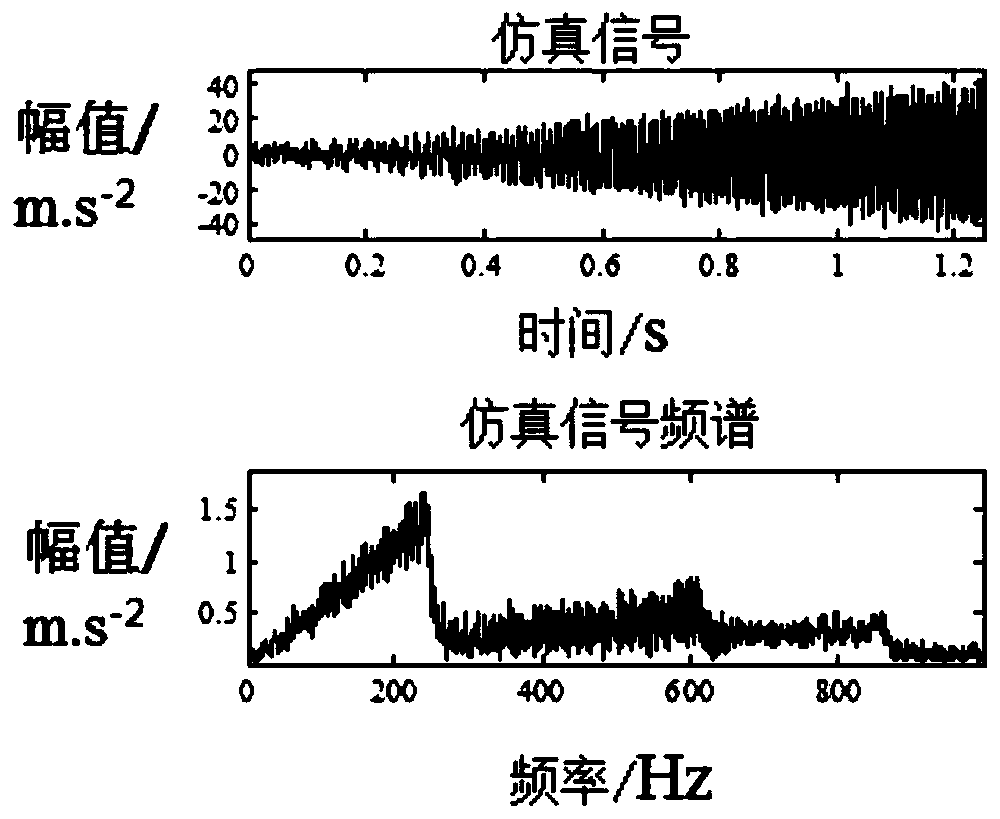
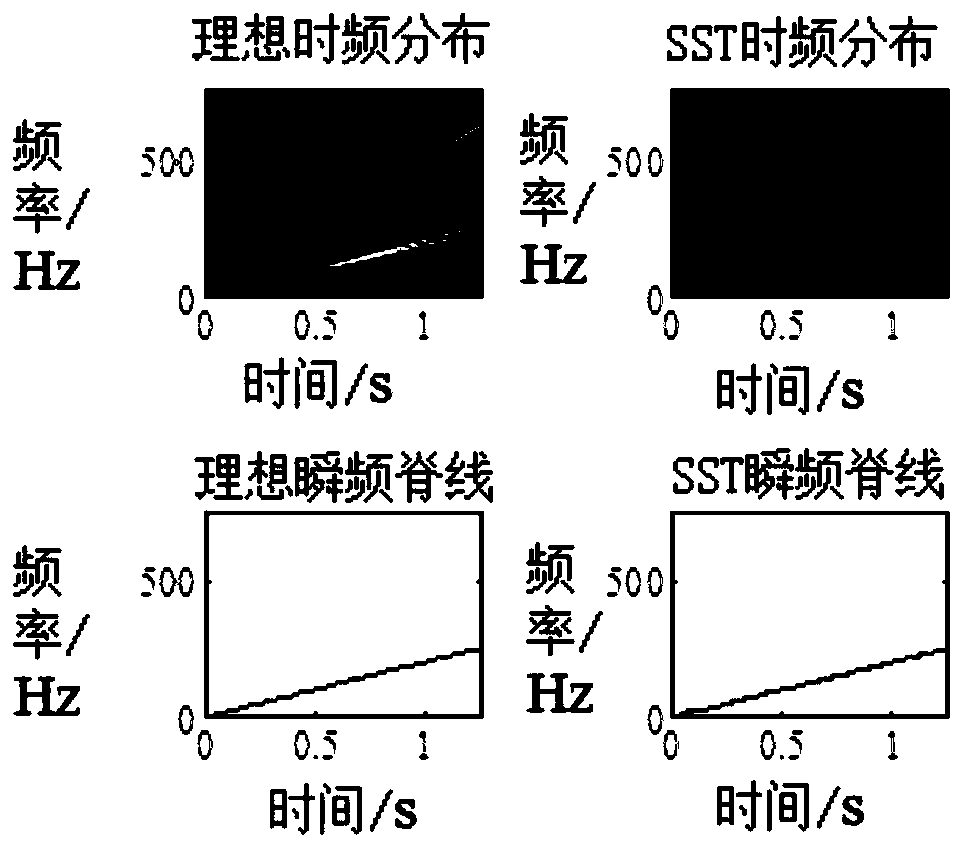
InactiveCN110617964AGood ability concentrationAccurate extractionMachine part testingTime markFrequency conversion
The invention discloses a synchronous compression transformation order analysis method for rolling bearing fault diagnosis. According to the method, firstly, SST is utilized to analyze a variable-speed vibration signal of a bearing to obtain time-frequency distribution of the vibration signal; secondly, an instantaneous frequency ridge of frequency conversion is extracted and subjected to high-order polynomial fitting, a fitted instantaneous frequency curve is obtained, and phase discrimination time marks are solved according to the fitted instantaneous frequency curve; thirdly, equal-angle resampling is performed on the original vibration signal to obtain an angular domain signal; and fourthly, Hilbert envelope demodulation is performed on the angular domain signal, an envelope order spectrum of the angular domain signal is solved, whether the rolling bearing has a fault or not and the fault type are judged by analyzing the envelope order spectrum, a diagnosis result is given, maintenance suggestions are proposed, and therefore normal running of a metro vehicle is guaranteed. Through the synchronous compression transformation order analysis method, instantaneous frequency conversion information contained in the vibration signal can be precisely extracted, order tracking is realized, a specific hardware device is not needed, the installing process is greatly simplified, and thefault monitoring cost is lowered.
Owner:中国铁道科学研究院集团有限公司城市轨道交通中心
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com