Patents
Literature
461 results about "Instantaneous phase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
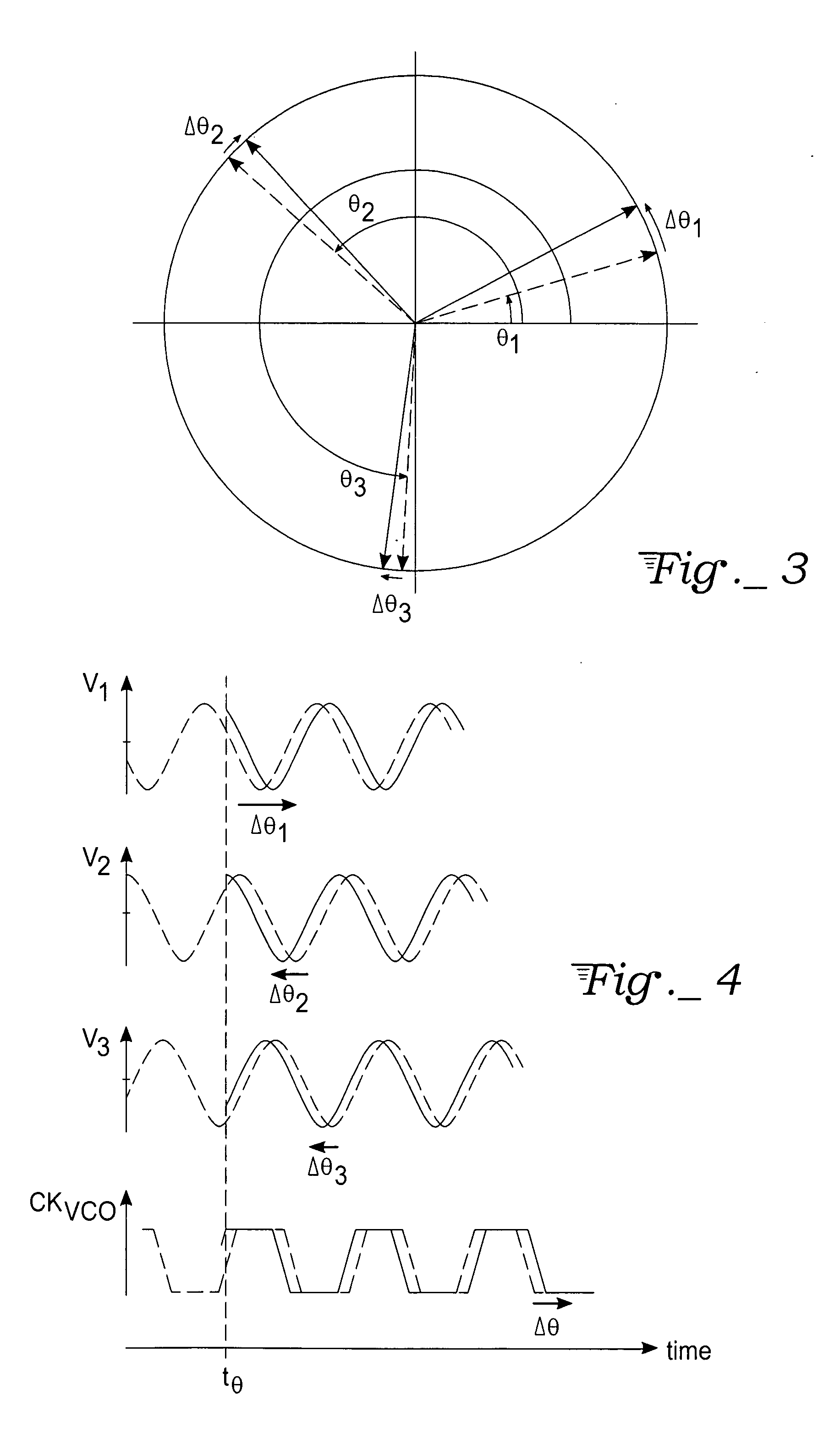
Instantaneous phase and frequency are important concepts in signal processing that occur in the context of the representation and analysis of time-varying functions. where arg is the complex argument function. The instantaneous frequency is the temporal rate of the instantaneous phase.
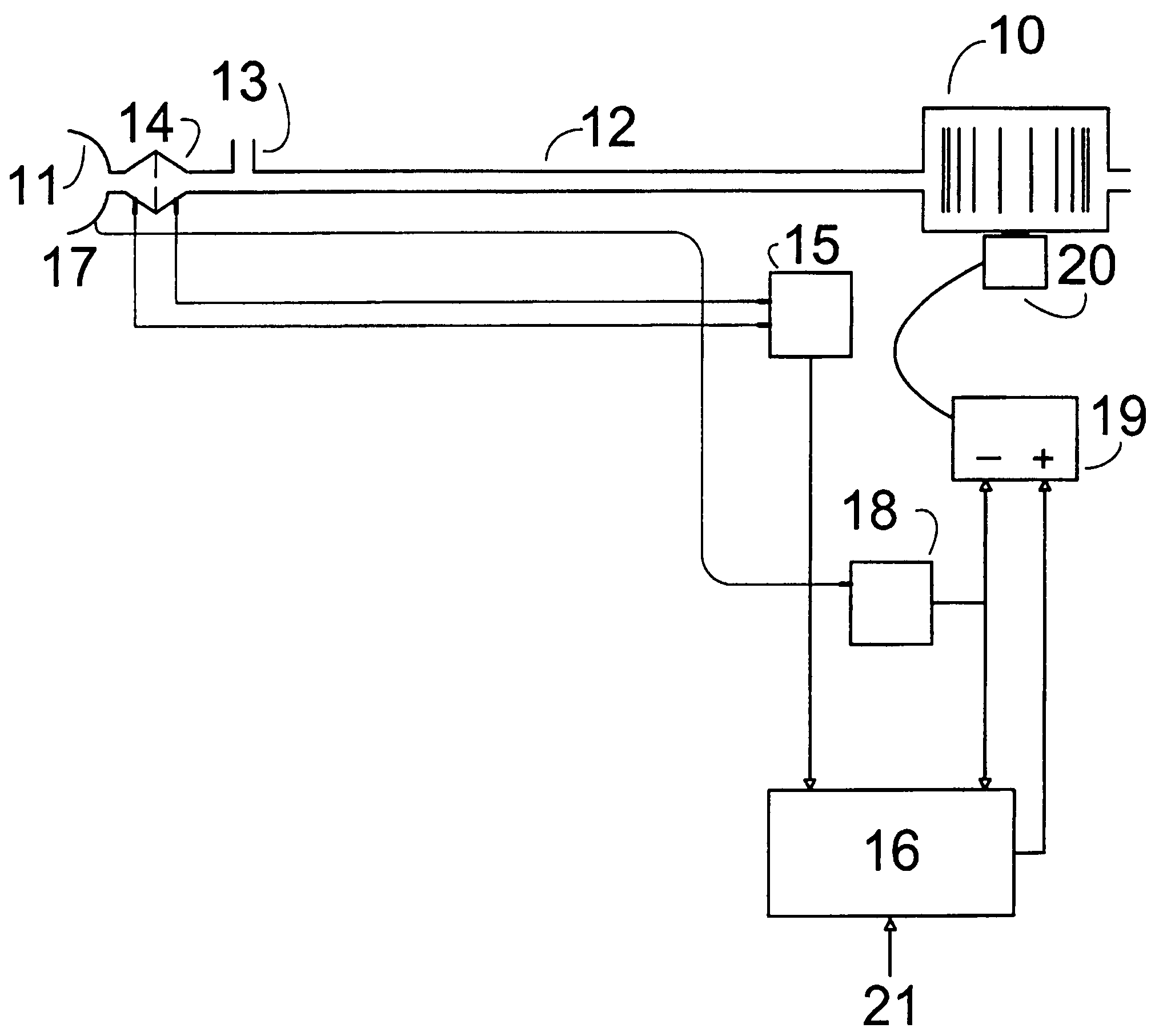
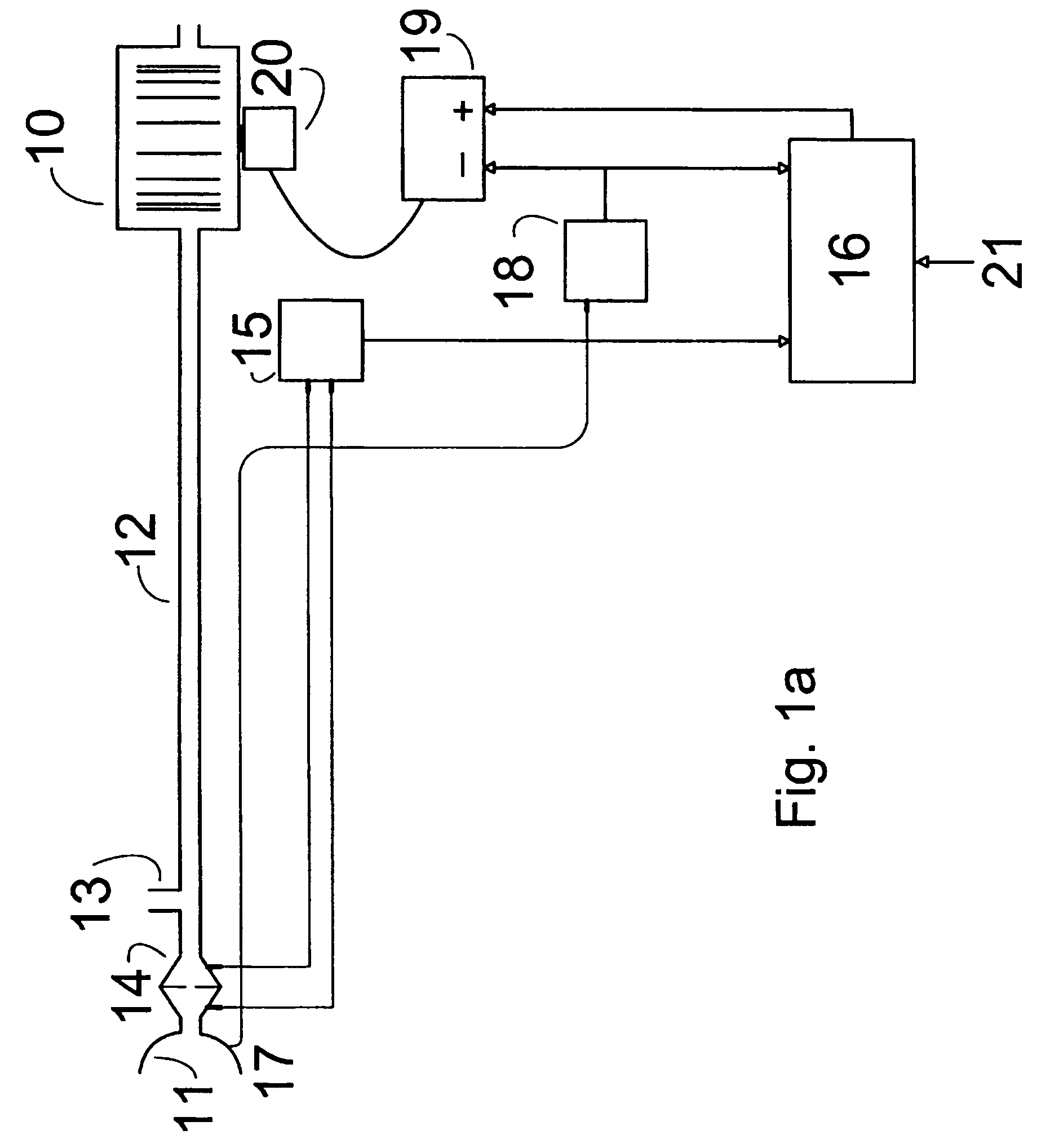
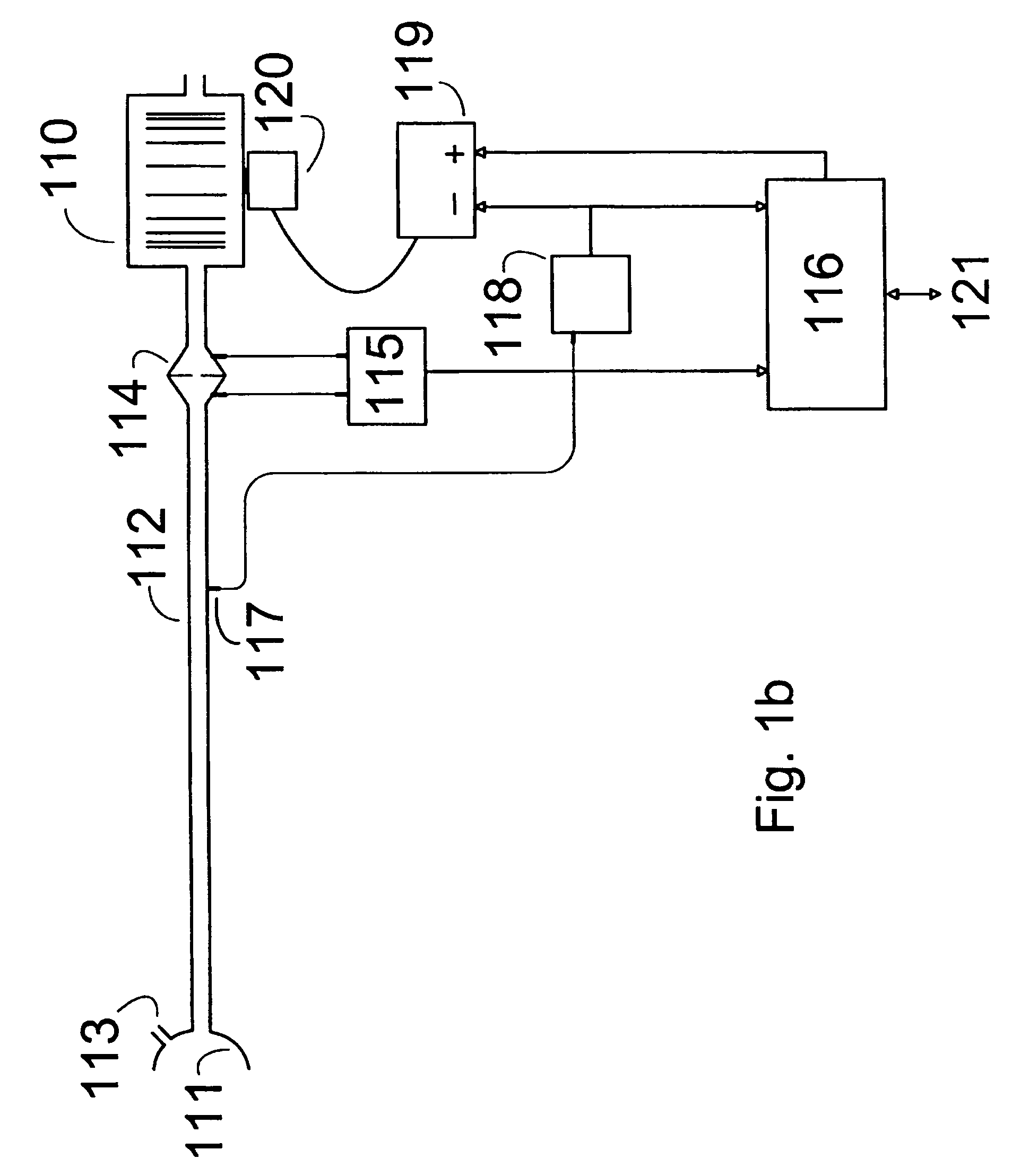
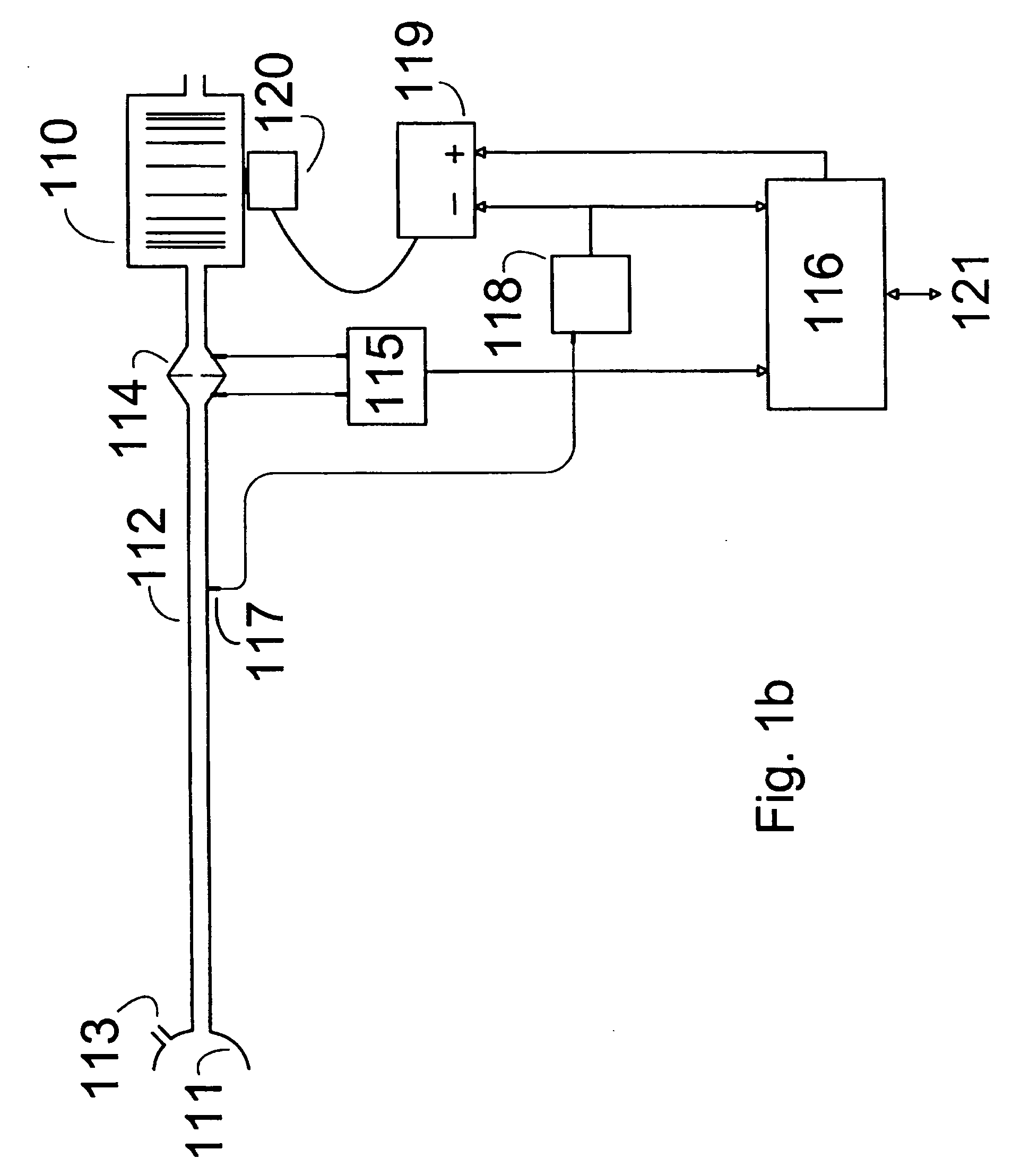
Method and apparatus for determining instantaneous inspired volume of a subject during ventilatory assistance
InactiveUS7137389B2Reduce noiseOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksEngineeringRespiration rate
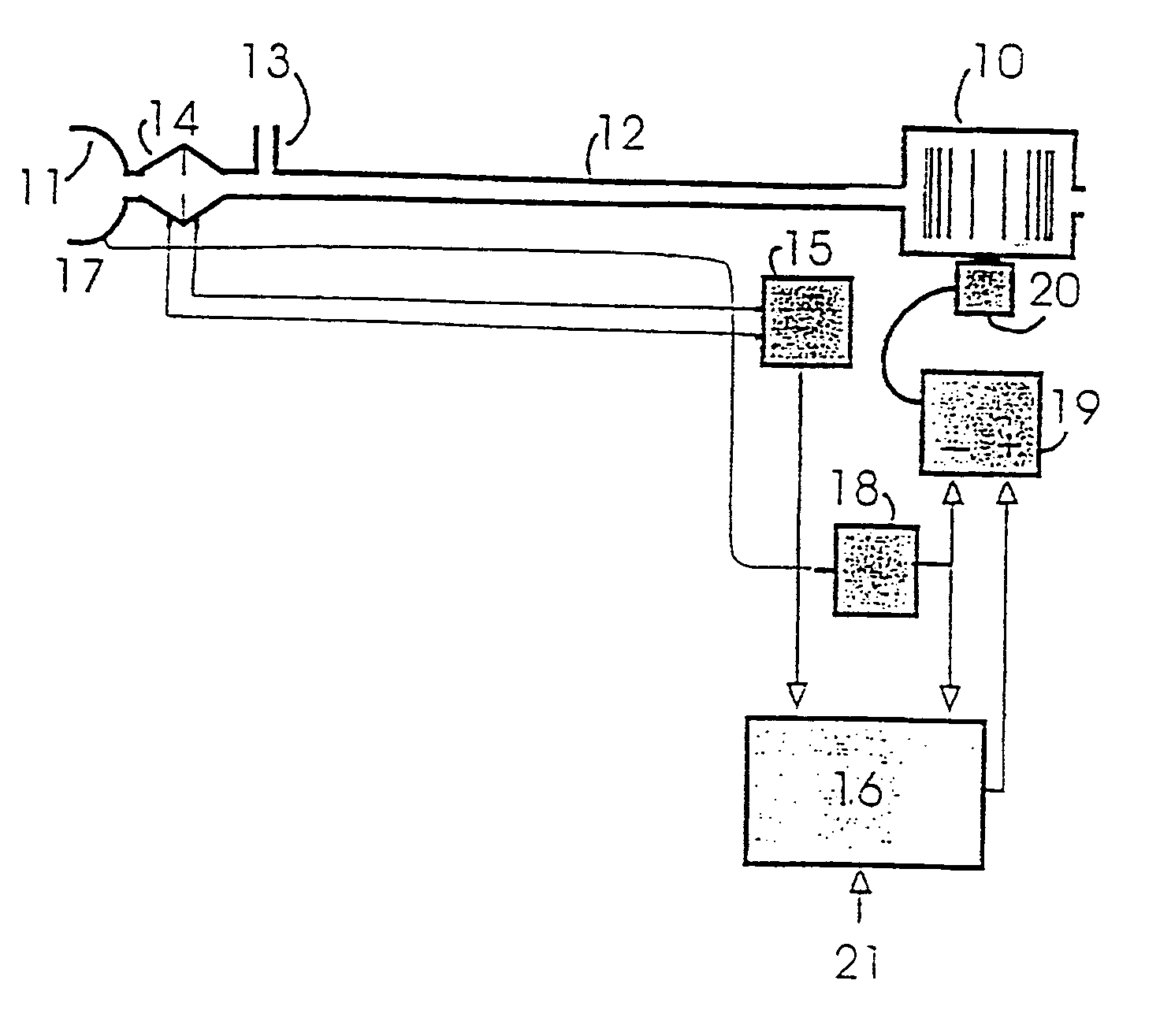
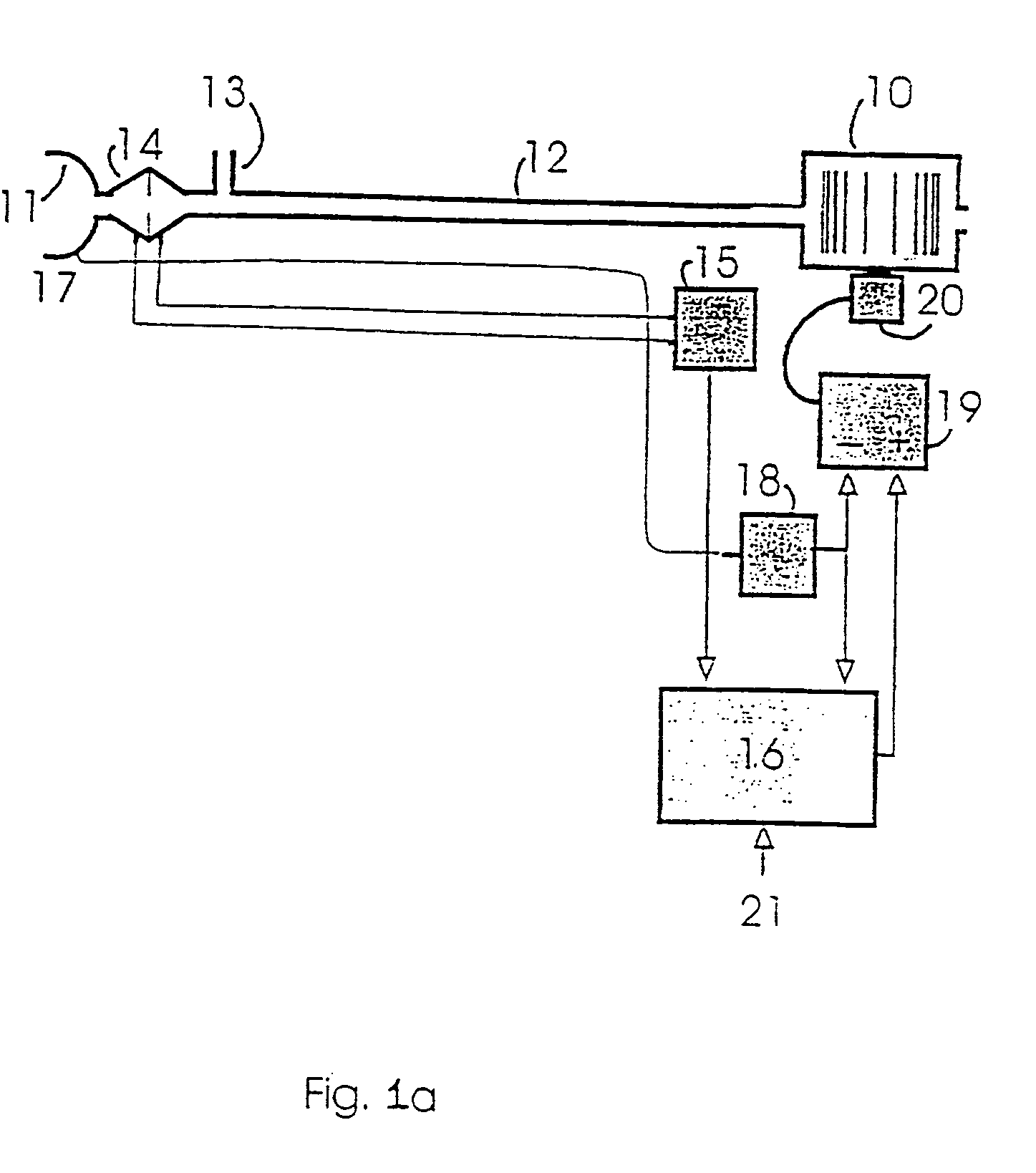
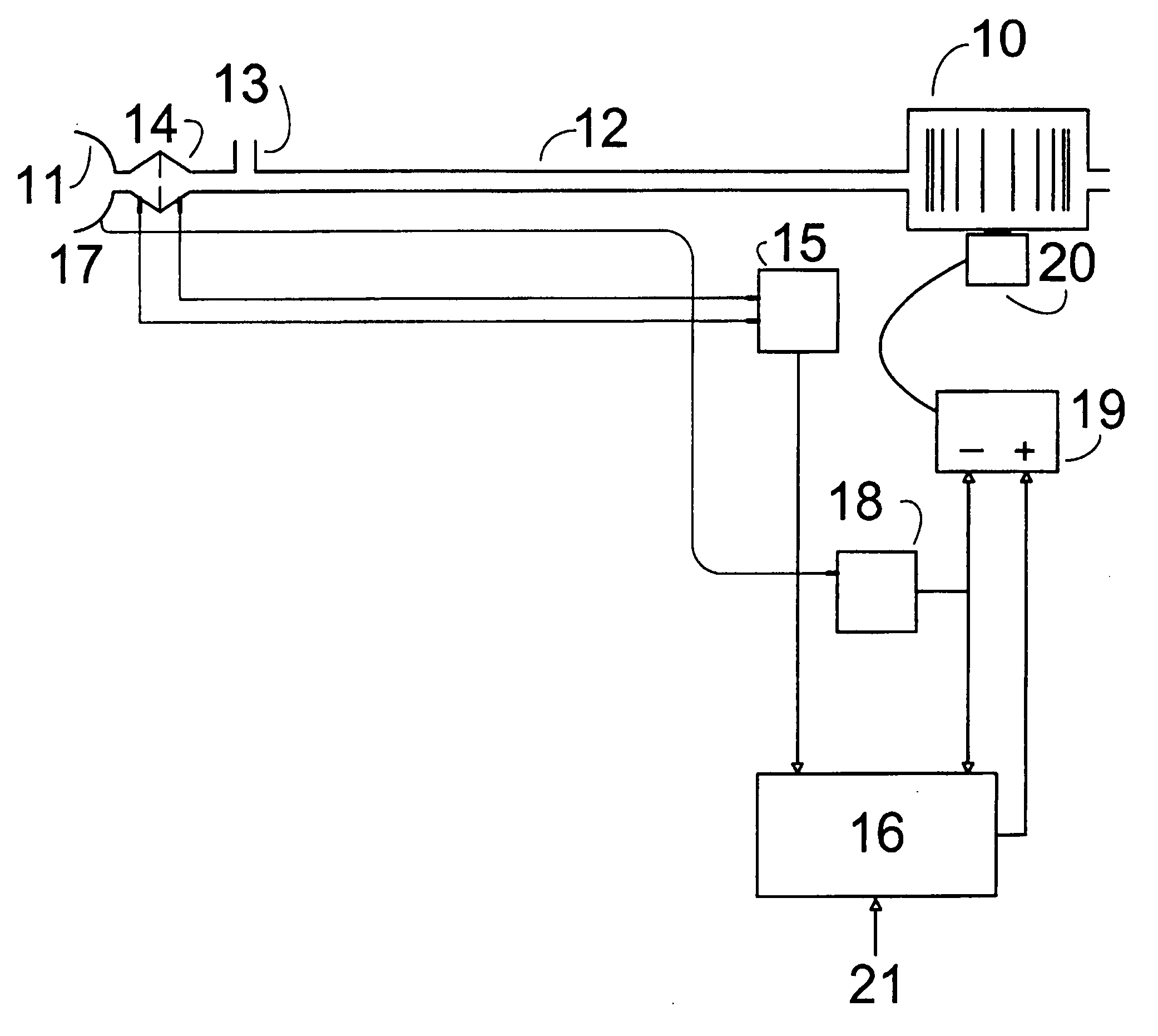
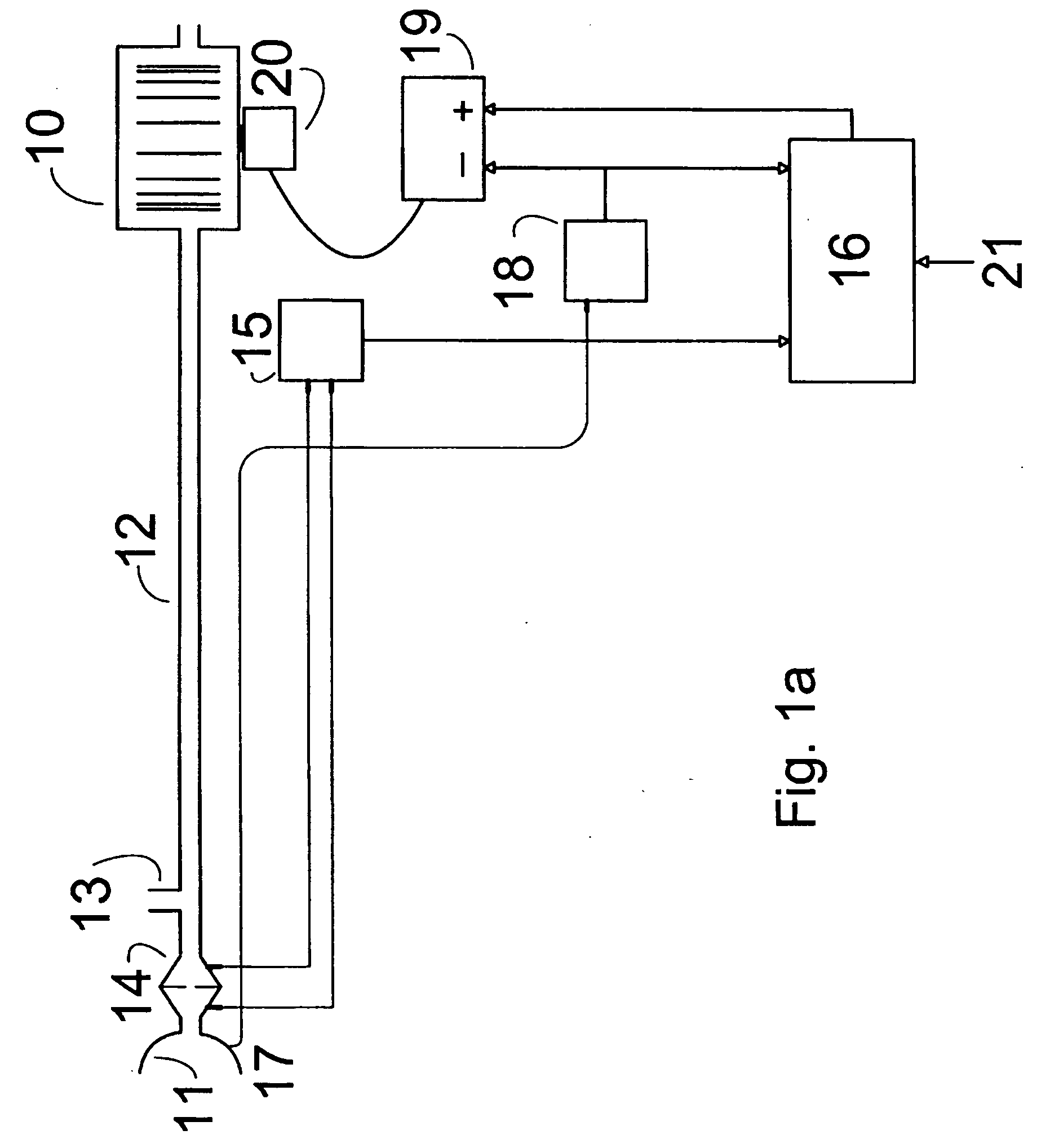
The apparatus provides for the determination of the instantaneous phase in the respiratory cycle, subject's average respiration rate and the provision of ventilatory assistance. A microprocessor (16) receives an airflow signal from a pressure transducer (18) coupled to a port (17) at a mask (11). The microprocessor (16) controls a servo (19), that in turn controls the fan motor (20) and thus the pressure of air delivered by the blower (10). The blower (10) is coupled to a subject's mask (ii) by a conduit (12). The invention seeks to address the following goals: while the subject is awake and making substantial efforts the delivered assistance should be closely matched in phase with the subject's efforts; the machine should automatically adjust the degree of assistance to maintain at least a specified minimum ventilation without relying on the integrity of the subject's chemoreflexes; and it should continue to work correctly in the presence of large leaks.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Method and apparatus for transmitting a digital information signal and vending system incorporating same
A cashless business transaction system (e.g., a vending system, a material tracking system, or a highway toll system) incorporates a method and apparatus for transmitting a digital information signal. A signal generator (311) generates a constant frequency signal. A phase modulator (305) varies the instantaneous phase of the constant frequency signal to represent digital information, thereby producing a phase modulated signal (325). A tuned resonant circuit (307) filters and averages the phase modulated signal to produce a simulated FM signal, and transmits the simulated FM signal via its antenna (309). One such business transaction system (e.g., a vending system) incorporates such a transmitter to facilitate transmission of billing information from a device located within a substantially electrically shielded environment. Another such business transaction system preferably incorporates such a transmitter to facilitate half-duplex transmission of digital information regardless of whether or not the digital information is transmitted from a device located within a substantially electrically shielded environment.
Owner:POLE ZERO ACQUISITION
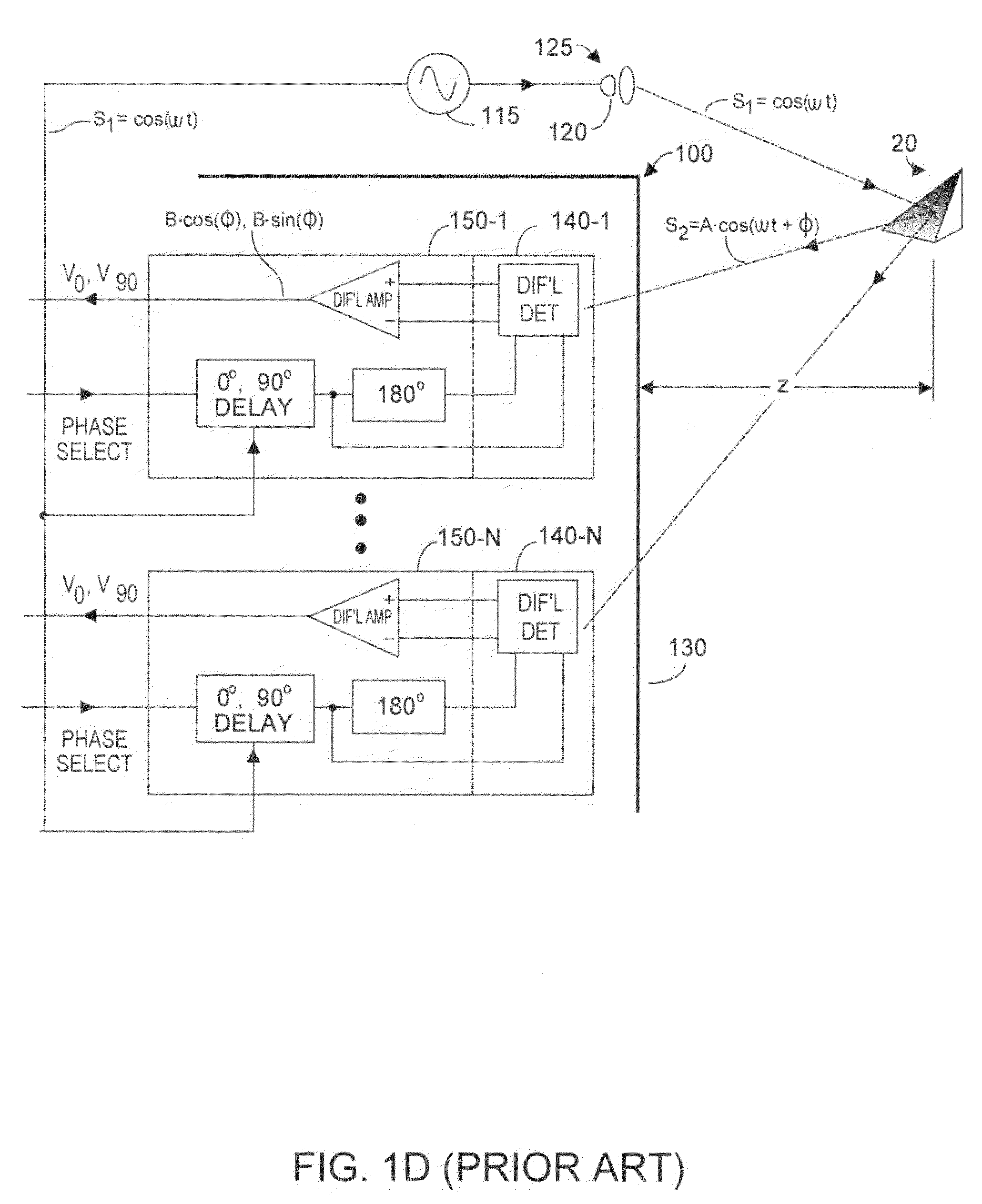
Method and system to avoid inter-system interference for phase-based time-of-flight systems
ActiveUS7405812B1Likelihood of interferenceReduce distractionsOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationClock rateOptical energy
Inter-system interference cross-produce P12 is reduced in a phase-based TOF system by randomizing instantaneous phase and / or frequency within a capture interval (or detection integration period). In one aspect, the TOF clock system frequency preserves long-term clock frequency stability but intentionally includes random or pseudo-random clock noise. The noise ensures the generated clock signals are temporally imperfect and lack substantial perfect periodicity. A second aspect causes the TOF clock system to hop frequency, preferably pseudo-randomly. TOF system homodyning favors detection of optical energy whose frequency correlates to the time-varying frequency of the emitted optical energy. Thus, the varying spectral spacing of the emitted optical energy reduces likelihood that an adjacent TOF system at any given time will emit optical energy of an interfering frequency. At least one aspect is employed, both aspects being mutually complementary to reduce the cross-correlation product P12 without substantially affecting TOF system performance.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for determining instantaneous leak during ventilatory assistance
InactiveUS7644713B2Reduce noiseOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksTransducerEngineering
The apparatus provides for the determination of the instantaneous phase in the respiratory cycle, subject's average respiration rate and the provision of ventilatory assistance. A microprocessor (16) receives an airflow signal from a pressure transducer (18) coupled to a port (17) at a mask (11). The microprocessor (16) controls a servo (19), that in turn controls the fan motor (20) and thus the pressure of air delivered by the blower (10). The blower (10) is coupled to a subject's mask (ii) by a conduit (12). The invention seeks to address the following goals: while the subject is awake and making substantial efforts the delivered assistance should be closely matched in phase with the subject's efforts; the machine should automatically adjust the degree of assistance to maintain at least a specified minimum ventilation without relying on the integrity of the subject's chemoreflexes; and it should continue to work correctly in the presence of large leaks.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Linear phase robust carrier recovery for QAM modems
InactiveUS6904098B1Large loop bandwidthLower latencyDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionAutomatic frequency control detailsQam modulationBlind equalization
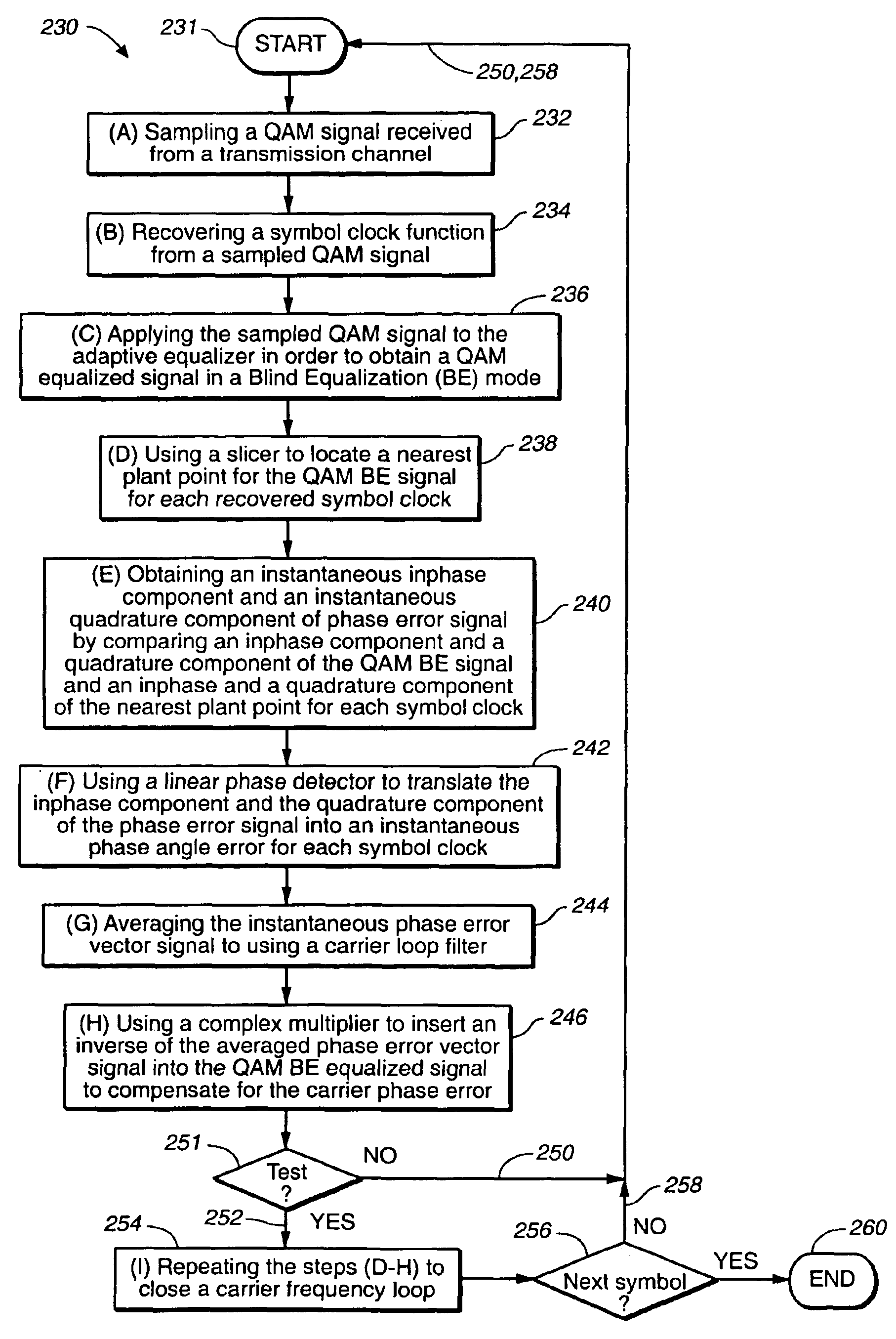
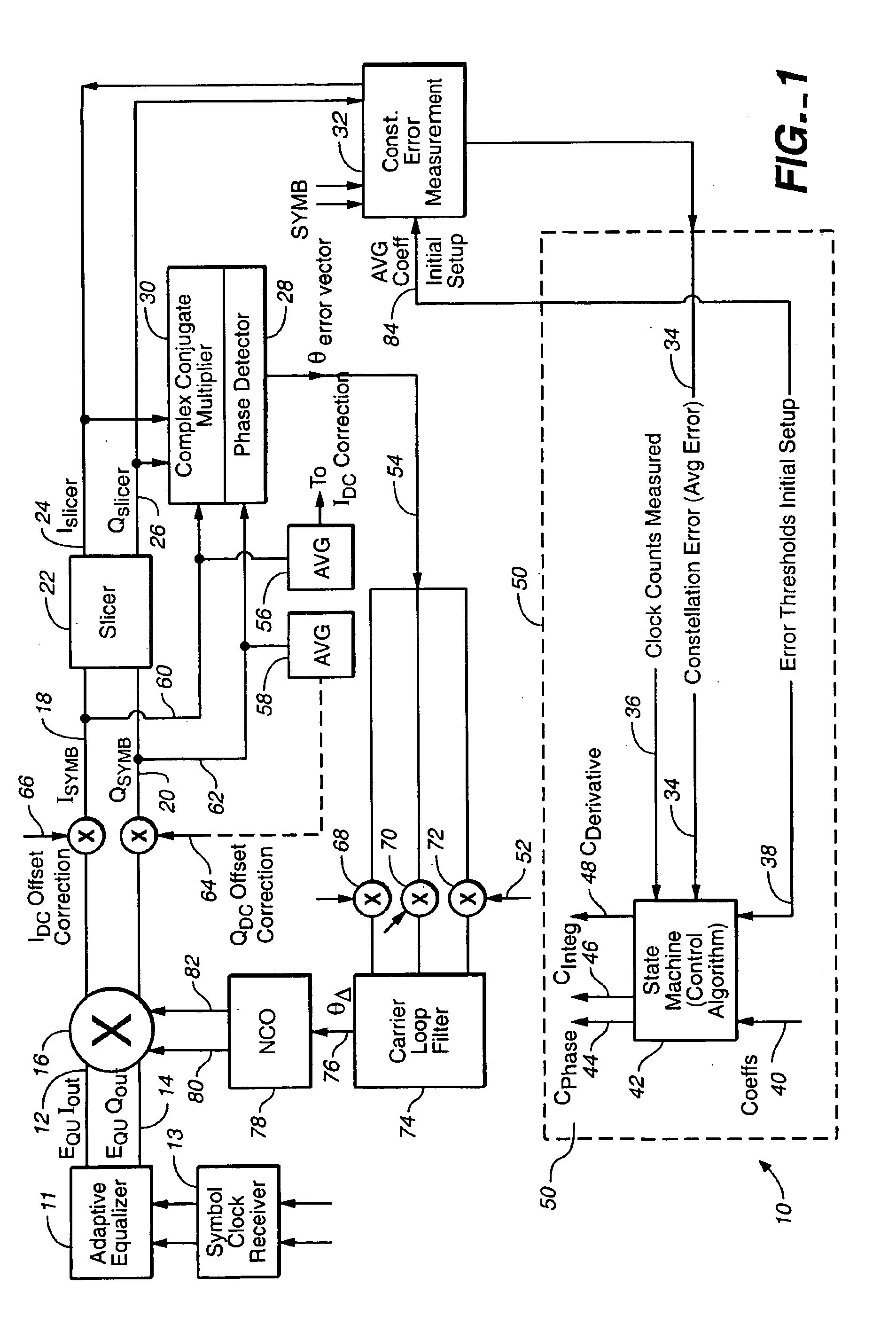
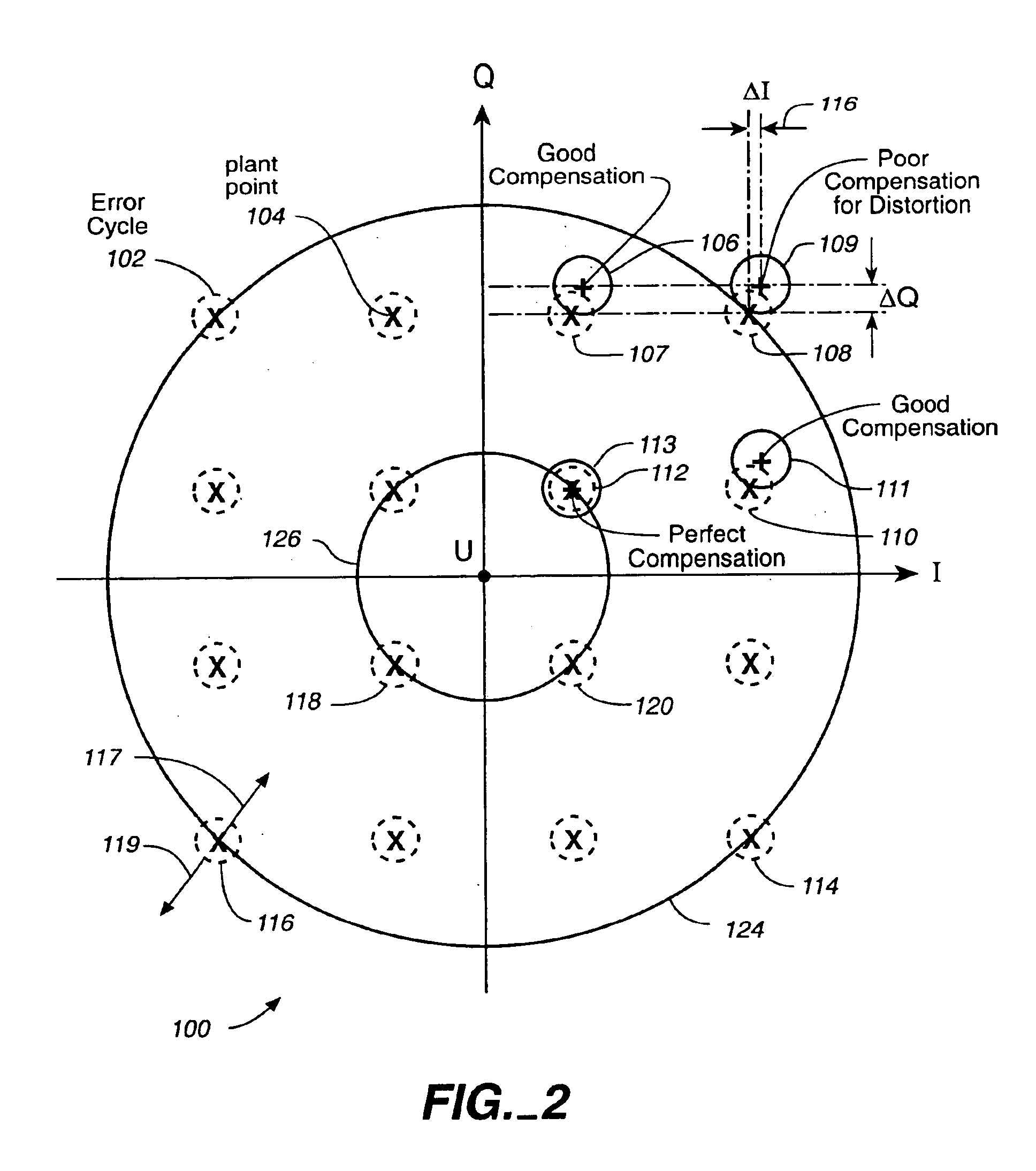
In a QAM demodulator including an adaptive equalizer, a method of carrier tracking comprising the following steps is disclosed: (A) sampling a QAM signal received from a transmission channel; (B) recovering a symbol clock function from the sampled QAM signal; (C) applying the sampled QAM signal to the adaptive equalizer in order to obtain a QAM equalized signal in a Blind Equalization (BE) mode; (D) using a slicer to locate a nearest plant point for the QAM Blind equalized signal for each recovered symbol clock; (E) using a complex conjugate multiplier to obtain an instantaneous inphase component and an instantaneous quadrature component of a phase angle error signal; (F) using a linear phase detector to obtain an instantaneous phase angle error for each symbol clock; (G) averaging the instantaneous phase angle error signal by using a carrier loop filter; (H) using a complex multiplier to insert an inverse of the averaged phase angle error signal into the QAM Blind equalized signal to compensate for the carrier phase angle error; and (I) repeating the steps (D-H) to close a carrier frequency loop.
Owner:REMEC BROADBAND WIRELESS NETWORKS LLC
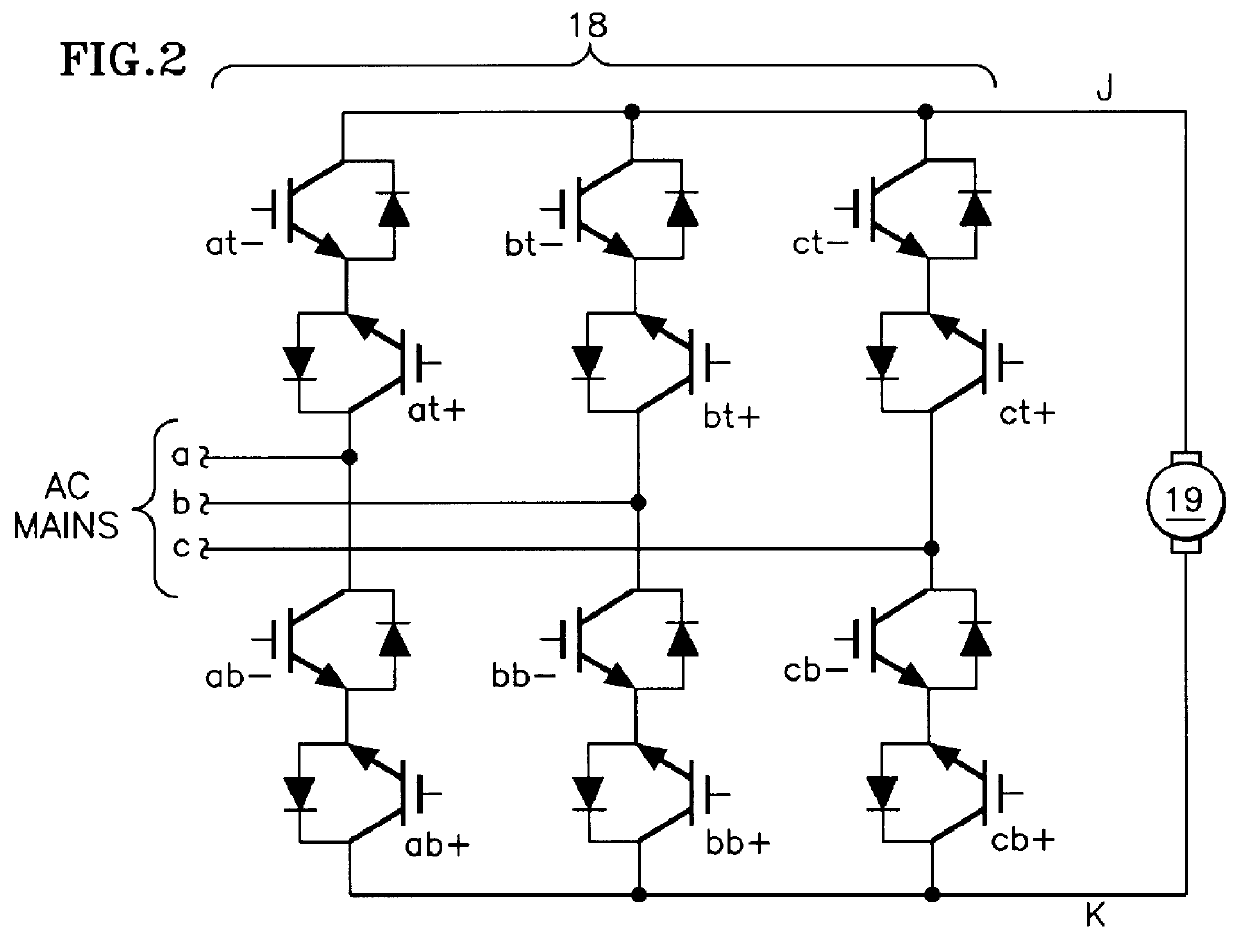
Reduced common voltage in a DC matrix converter
InactiveUS6166930AReducing common mode output voltageReduce size of magneticAC motor controlElectric motor controlMatrix convertersReverse current
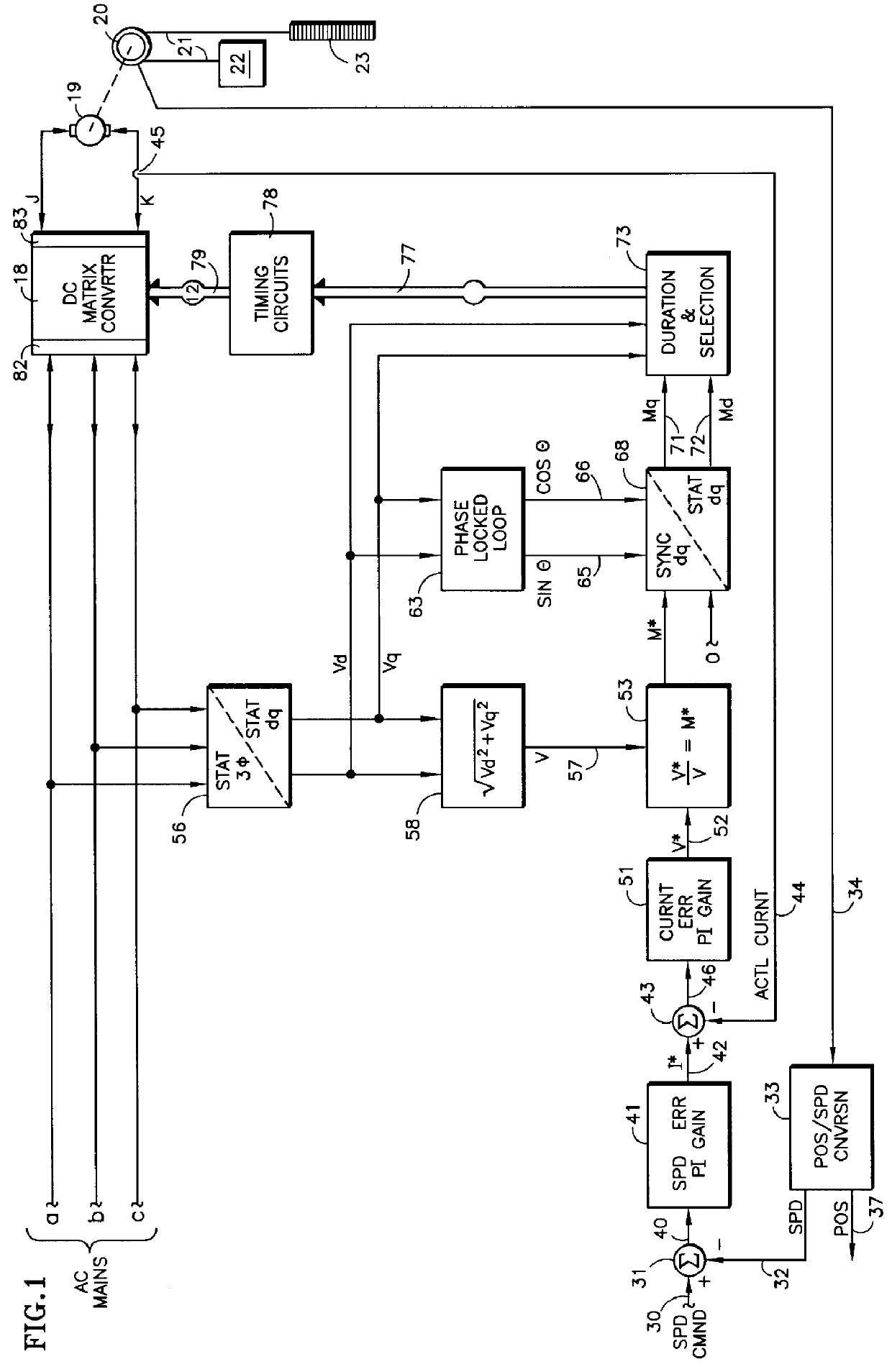
A DC matrix converter having six forward current conducting power switches and six reverse current conducting power switches has the on time duration of each power switch within each pulse width modulation period controlled by relationships between d, q components of a modulation index determined by the ratio of a voltage command to the instantaneous voltage of the AC mains expressed in stationary d, q coordinates, the selection of which is made based on inequalities between the AC mains voltage components expressed in dq coordinates, and relationships of the AC main voltage components expressed in d, q coordinates. Zero vectors are related to the one AC main having lower line-to-neutral voltage than the other AC mains, using relationships between the instantaneous AC mains voltage in d, q coordinates.
Owner:SUBAIR +1
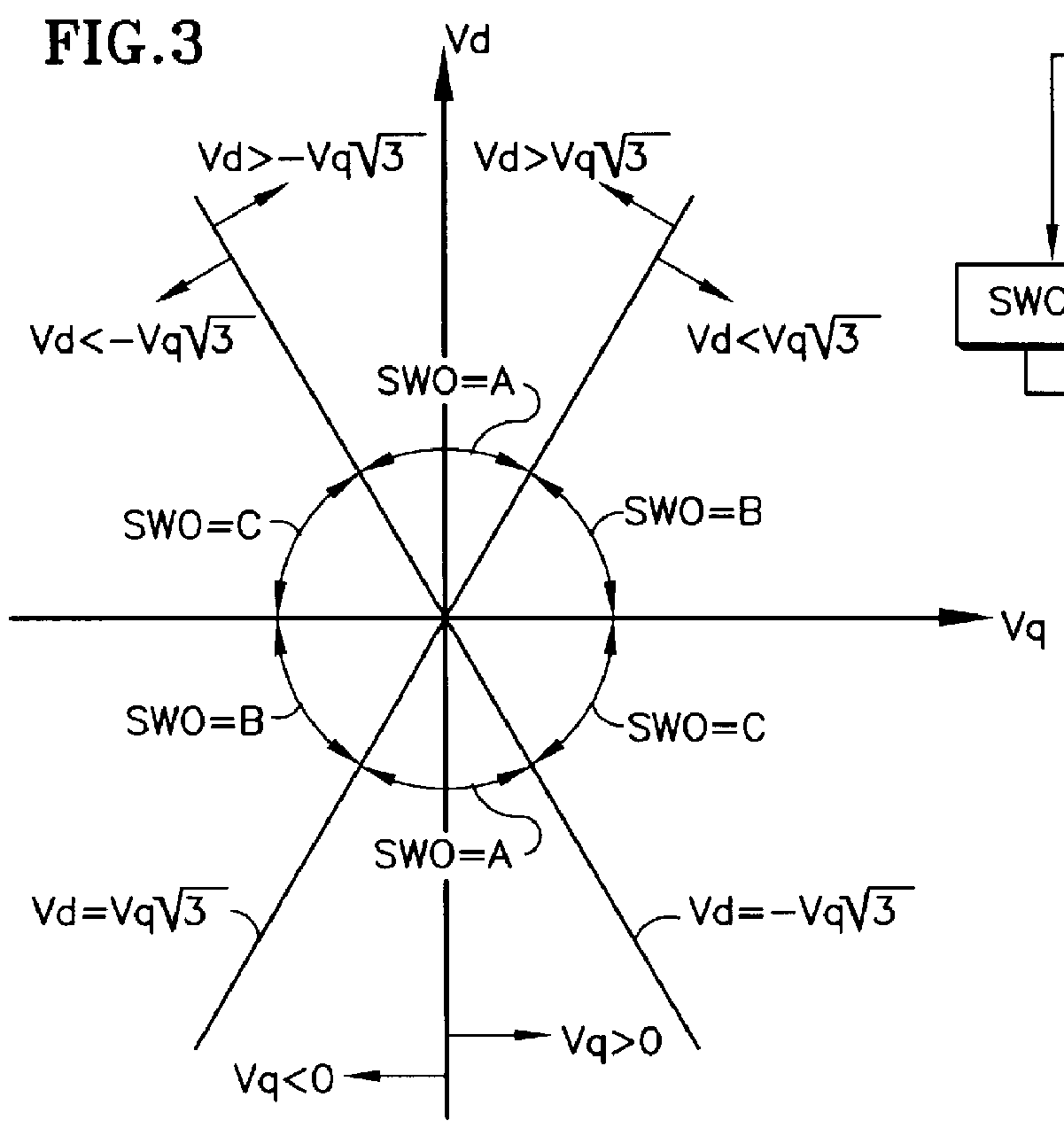
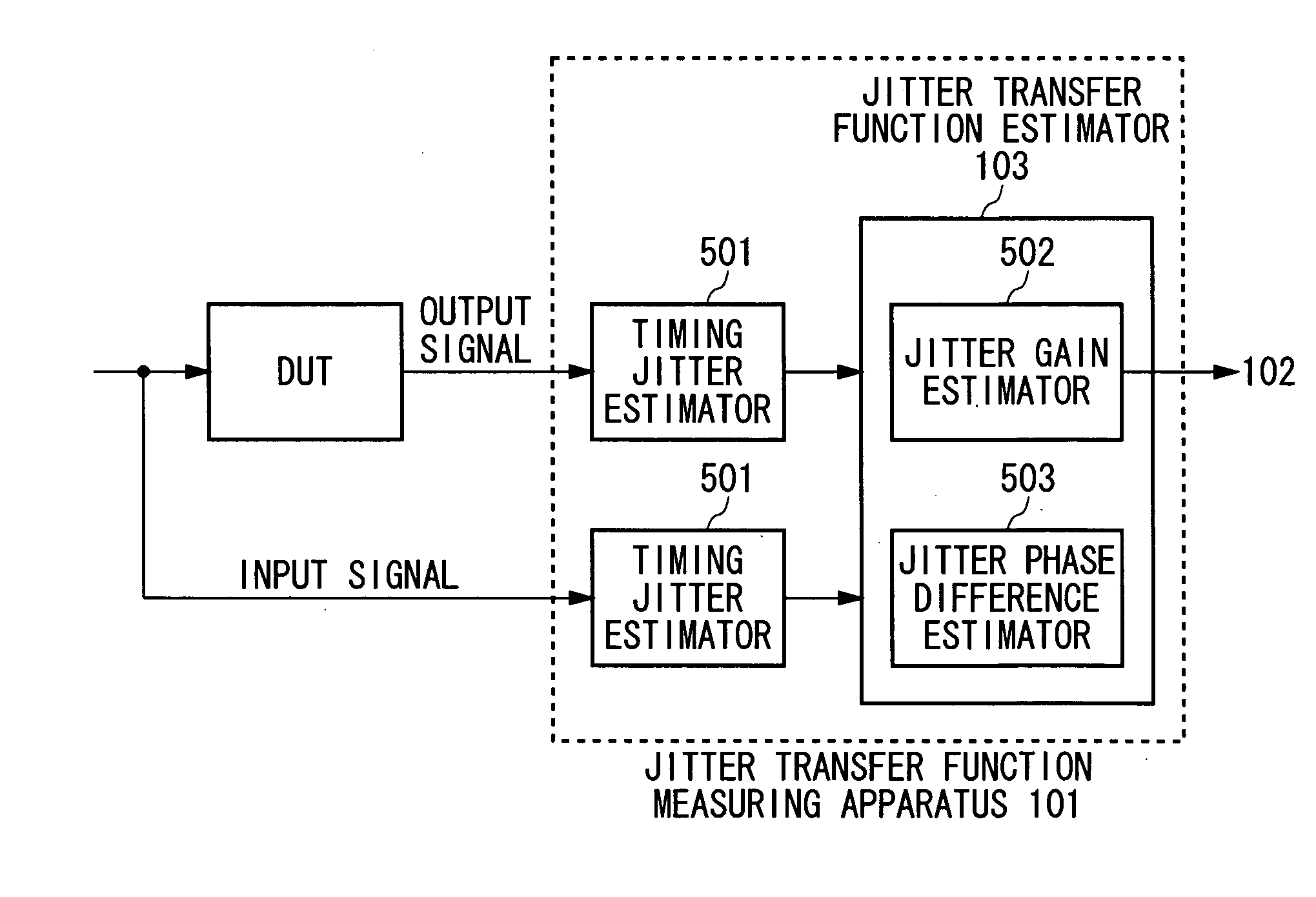
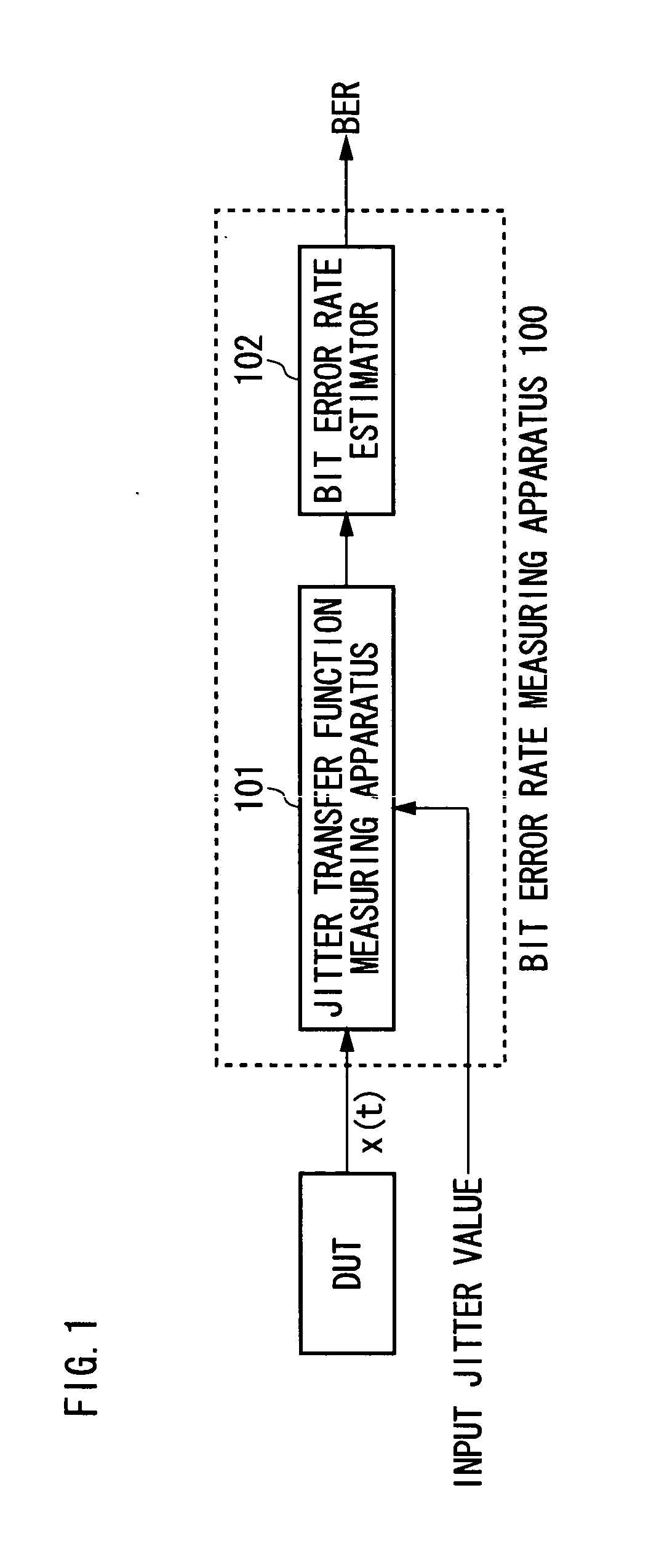
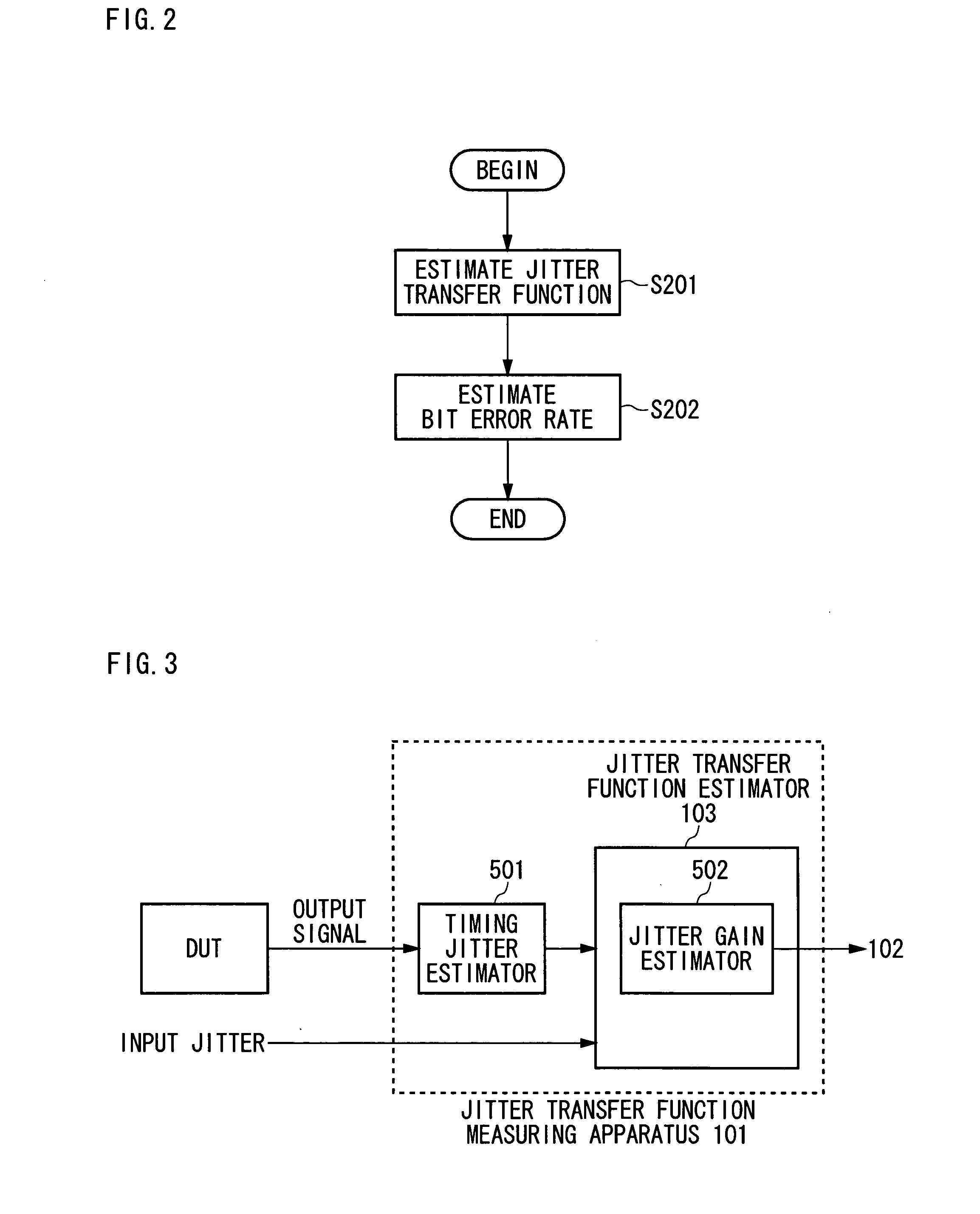
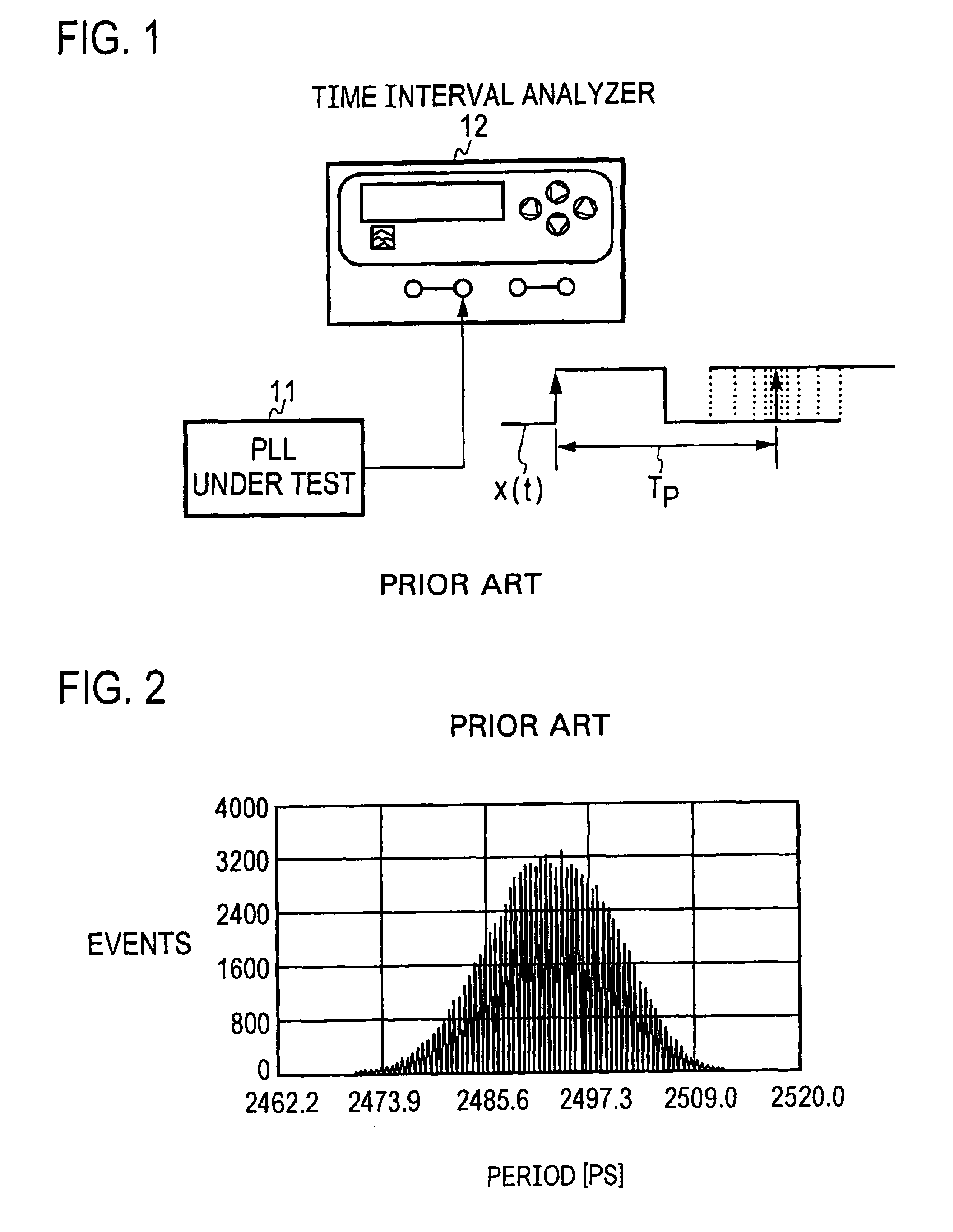
Measuring apparatus and measuring method
ActiveUS20050031029A1Digital circuit testingError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorPhase noiseMeasurement device
A measuring apparatus including a timing jitter estimator which estimates an output timing jitter sequence which indicates the output timing jitter of an output signal based on an output signal output from a DUT in response to an input signal input to the DUT, and a jitter transfer function estimator which estimates a jitter transfer function in the DUT based on the output timing jitter sequence. The jitter transfer function estimator includes an instantaneous phase noise estimator which estimates an instant phase noise of the output signal based on an output signal, and a resampler which generates the output timing jitter sequence by resampling the instantaneous phase noise at predetermined timing.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
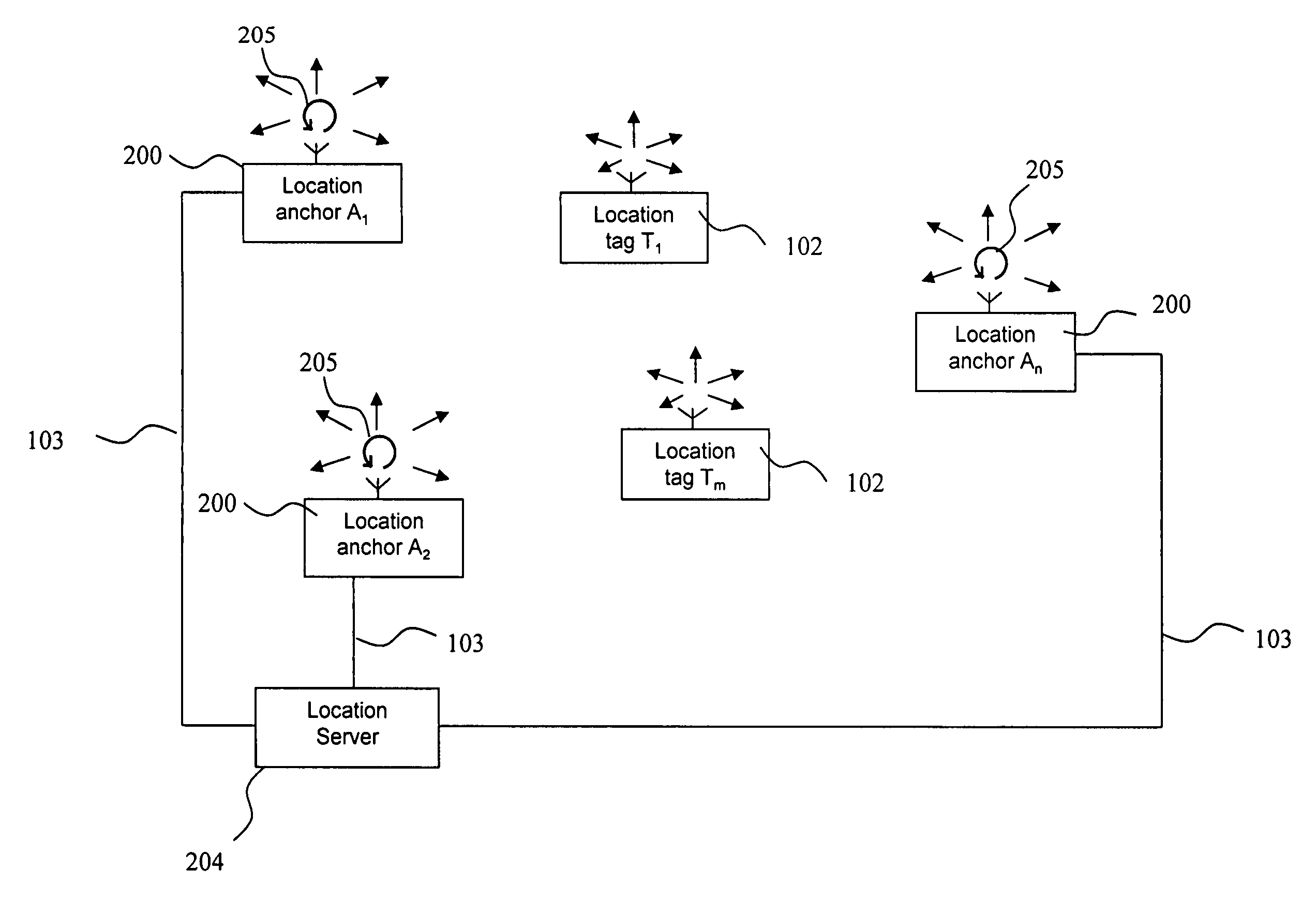
Method and System for Multipath Reduction for Wireless Synchronizing and/or Locating
ActiveUS20130021206A1Minimize air timeMaximize capacityDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationBroadcast transmissionSynchronizing
A method for determining an instantaneous phase difference between time bases of at least two location anchors for a desired point in time (t), each of the location anchors having transmitting and receiving access to a joint broadcast transmission medium and a respective time base for measuring time, wherein a first of the location anchors broadcasts a first broadcast message at least twice; the first location anchor and at least a second of the location anchors receive the first broadcast messages; the second location anchor broadcasting a second broadcast message at least twice; and the second location anchor and at least the first location anchor receive the second broadcast messages. The location server calculates the instantaneous phase difference from a determined first and second clock model functions and from a time elapsed between a reference point in time and the desired point in time t.
Owner:NANOTRON GES FUR MIKROTECHN
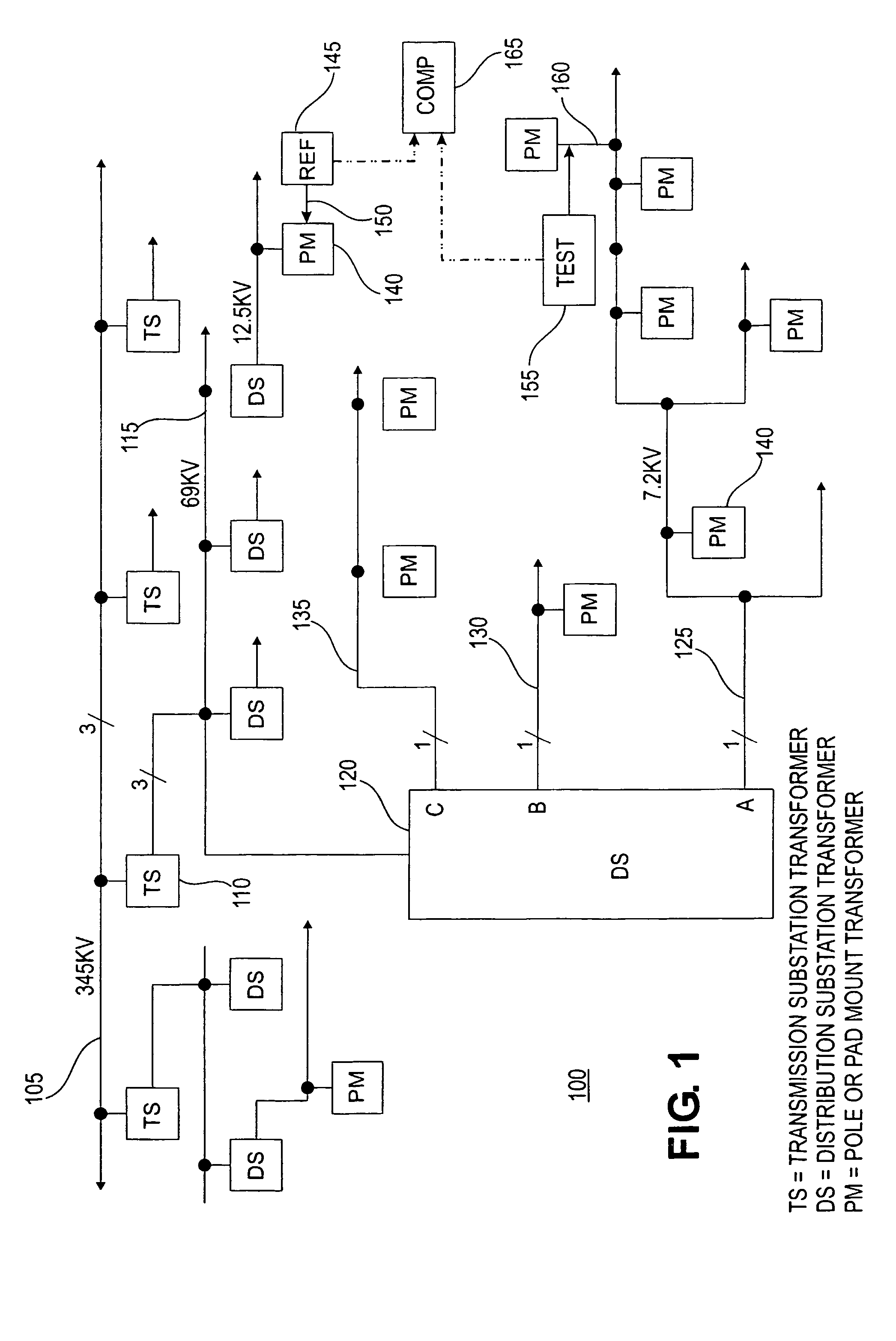
Apparatus and method for identifying cable phase in a three-phase power distribution network
InactiveUS7031859B2Noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementCurrent/voltage measurementDifferential phaseTime mark
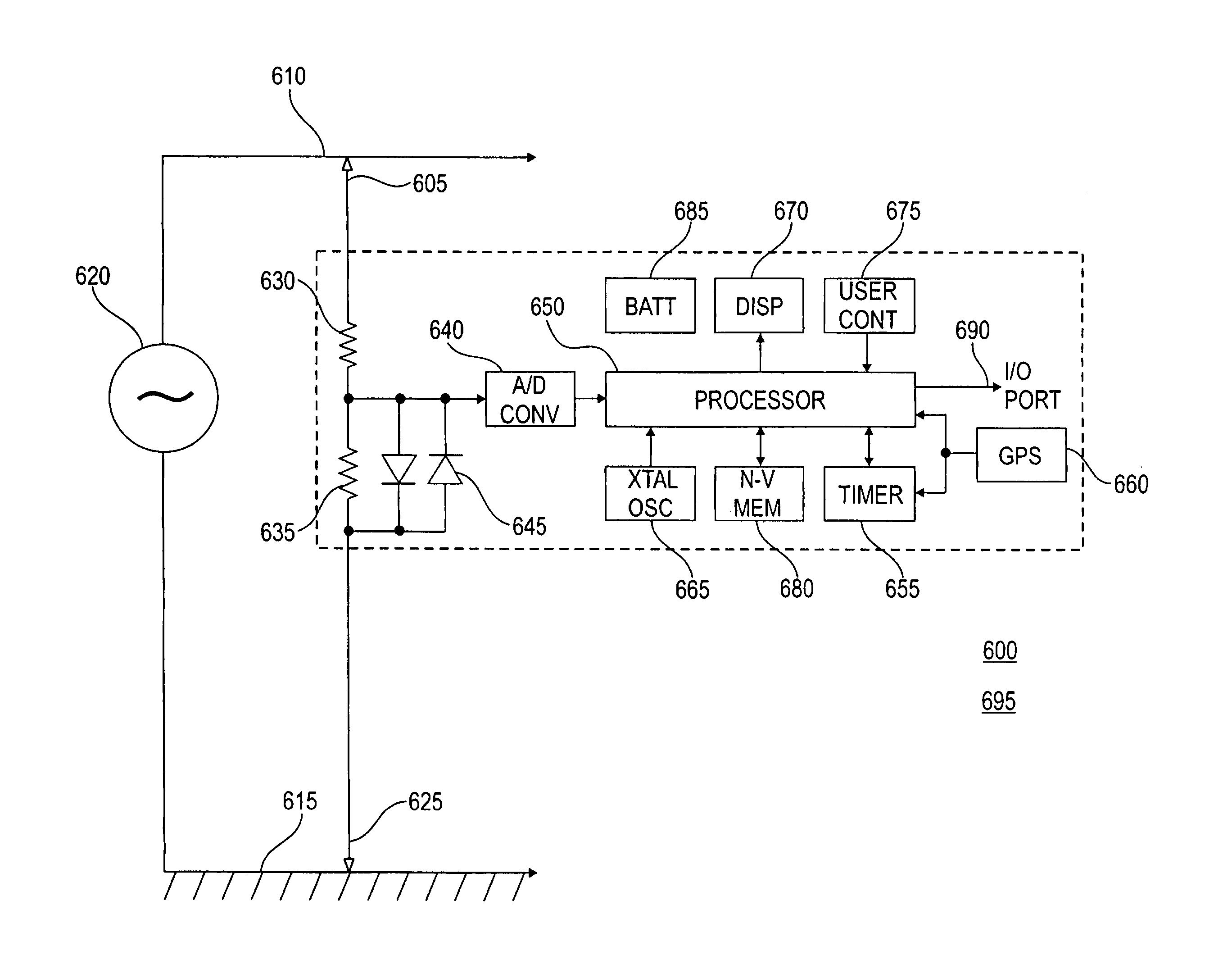
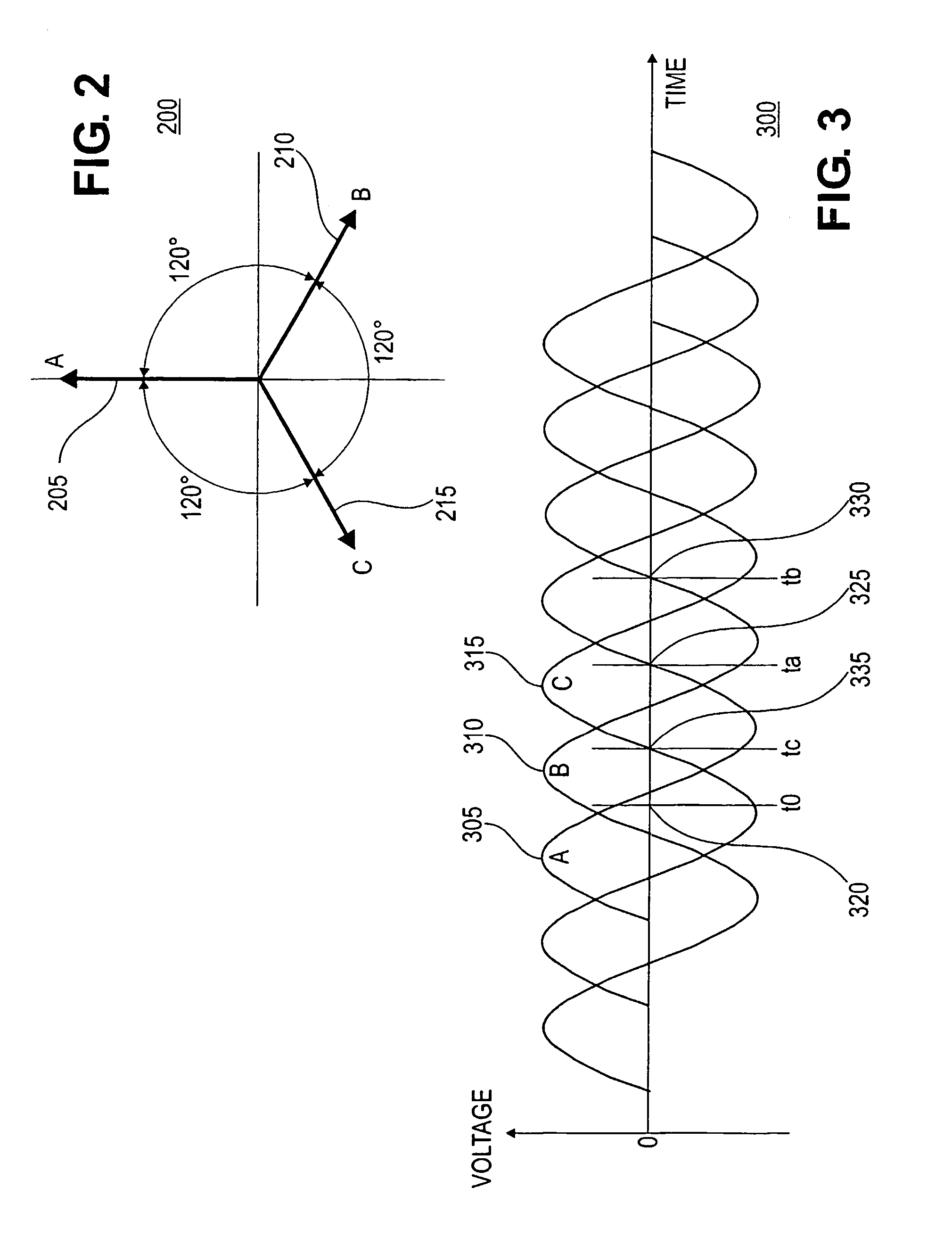
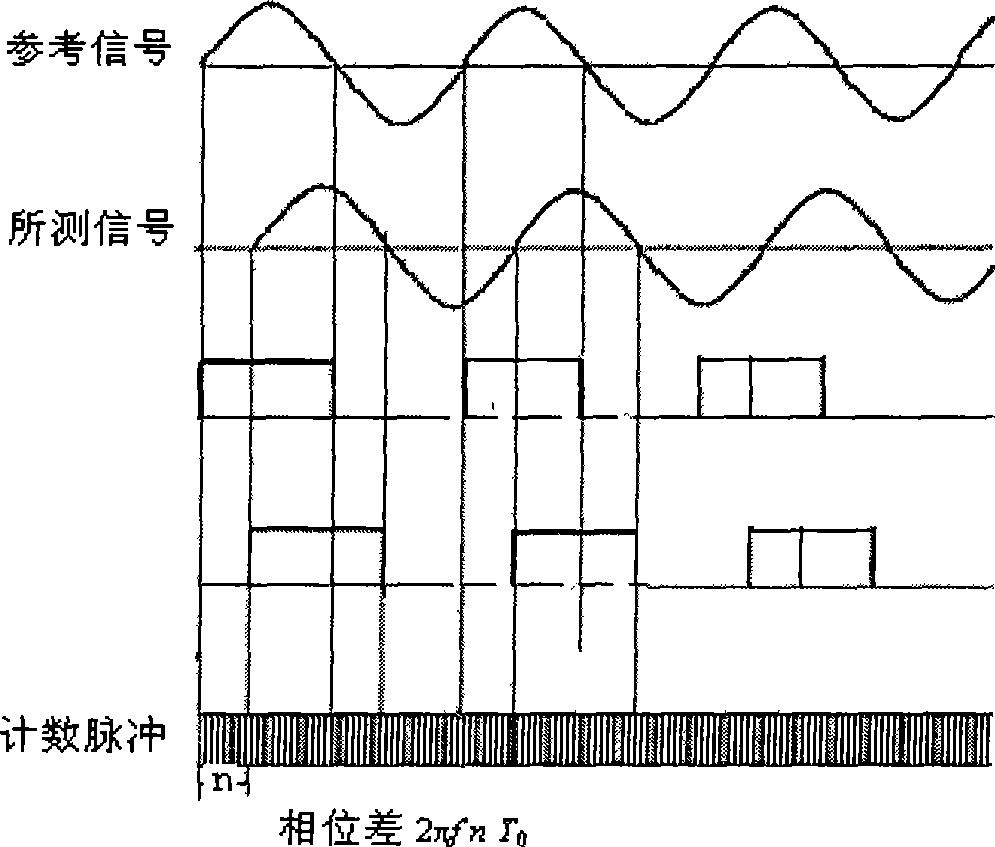
A line phase identification system and method identifies the phase of a power line at a remote unknown-phase line (160) in a three-phase power distribution network (100). The instantaneous phase of a known-phase line (150) is measured and saved each GPS second using a 1-pps time mark of a GPS receiver (660). The instantaneous phase at the unknown-phase line (160) is measured at a single GPS second using the 1-pps time mark of a GPS receiver (660) and compared to the phase measurement taken from the known-phase line (150) at the same GPS second. The differential phase between these simultaneously taken known and unknown instantaneous phases will be close to either 0, +120, or −120 degrees, thus identifying the line phase at the line under test (160).
Owner:PIESINGER GREGORY H
High precision instant phase estimation method based on full-phase FFT
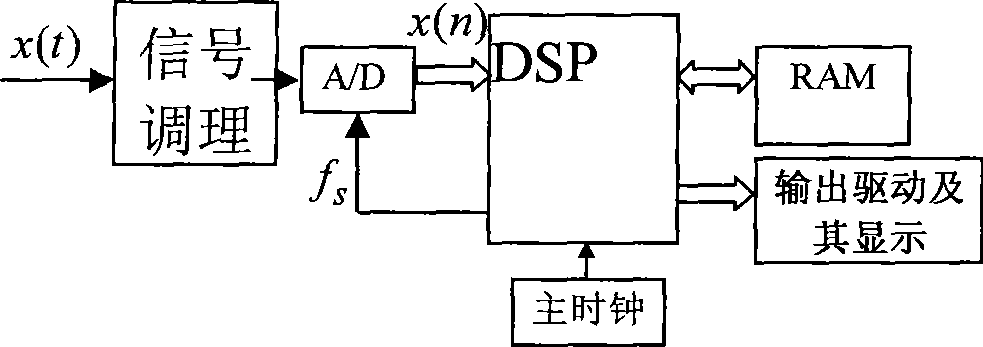
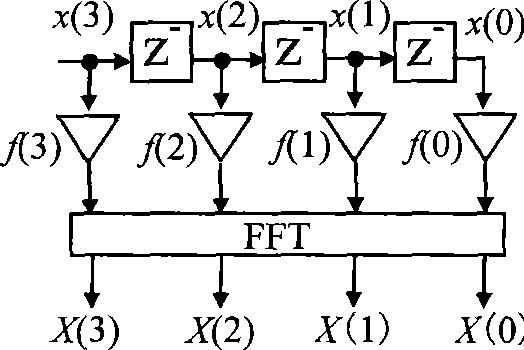
InactiveCN101388001ALow costComplex mathematical operationsDigital signal processingEstimation methods
The invention belongs to the technical field of digital signal processing, and relates to a high-accuracy instantaneous phase estimation method based on the full-phase FFT. The steps of the estimation method comprise directly sampling an input signal x(t) to obtain a discrete data sequence (x(n-N+1)..., x(n), ..., x(n+N-1)), storing 2N-1 data obtained by sampling in the RAM of a DSP, utilizing a convolution window of which the length is 2N-1 in number to perform windowing for the sequence, superimposing the data of which the distance is N sampling intervals, fast performing Fourier transformation to the N data, outputting N plurals which namely correspond as N spectral values Y(k), performing spectral peak searching, finding a spectral Y(k*) with the highest amplitude in the N spectral values Y(k), and performing rating to the imaginary part and the real part of the spectral Y(k*), thereby an instantaneous phase estimation result of a time n can be obtained by performing arctangent calculation to the ratio.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Assisted ventilation to match patient respiratory need
InactiveUS20060150974A1Reduce noiseOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksAssisted ventilationTransducer
The apparatus provides for the determination of the instantaneous phase in the respiratory cycle, subject's average respiration rate and the provision of ventilatory assistance. A microprocessor (16) receives an airflow signal from a pressure transducer (18) coupled to a port (17) at a mask (11). The microprocessor (16) controls a servo (19), that in turn controls the fan motor (20) and thus the pressure of air delivered by the blower (10). The blower (10) is coupled to a subject's mask (ii) by a conduit (12). The invention seeks to address the following goals: while the subject is awake and making substantial efforts the delivered assistance should be closely matched in phase with the subject's efforts; the machine should automatically adjust the degree of assistance to maintain at least a specified minimum ventilation without relying on the integrity of the subject's chemoreflexes; and it should continue to work correctly in the pesence of large leaks.
Owner:RESMED LTD
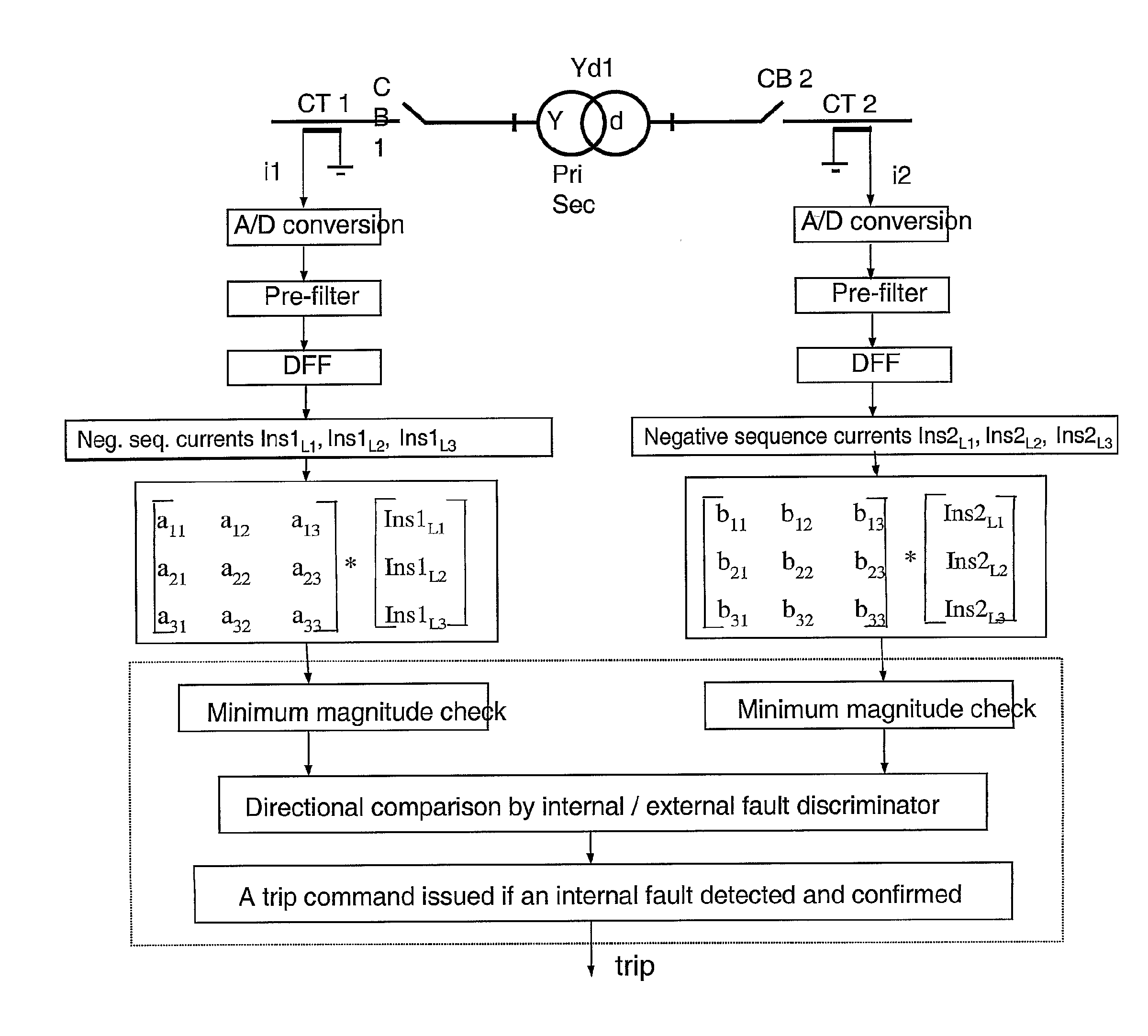
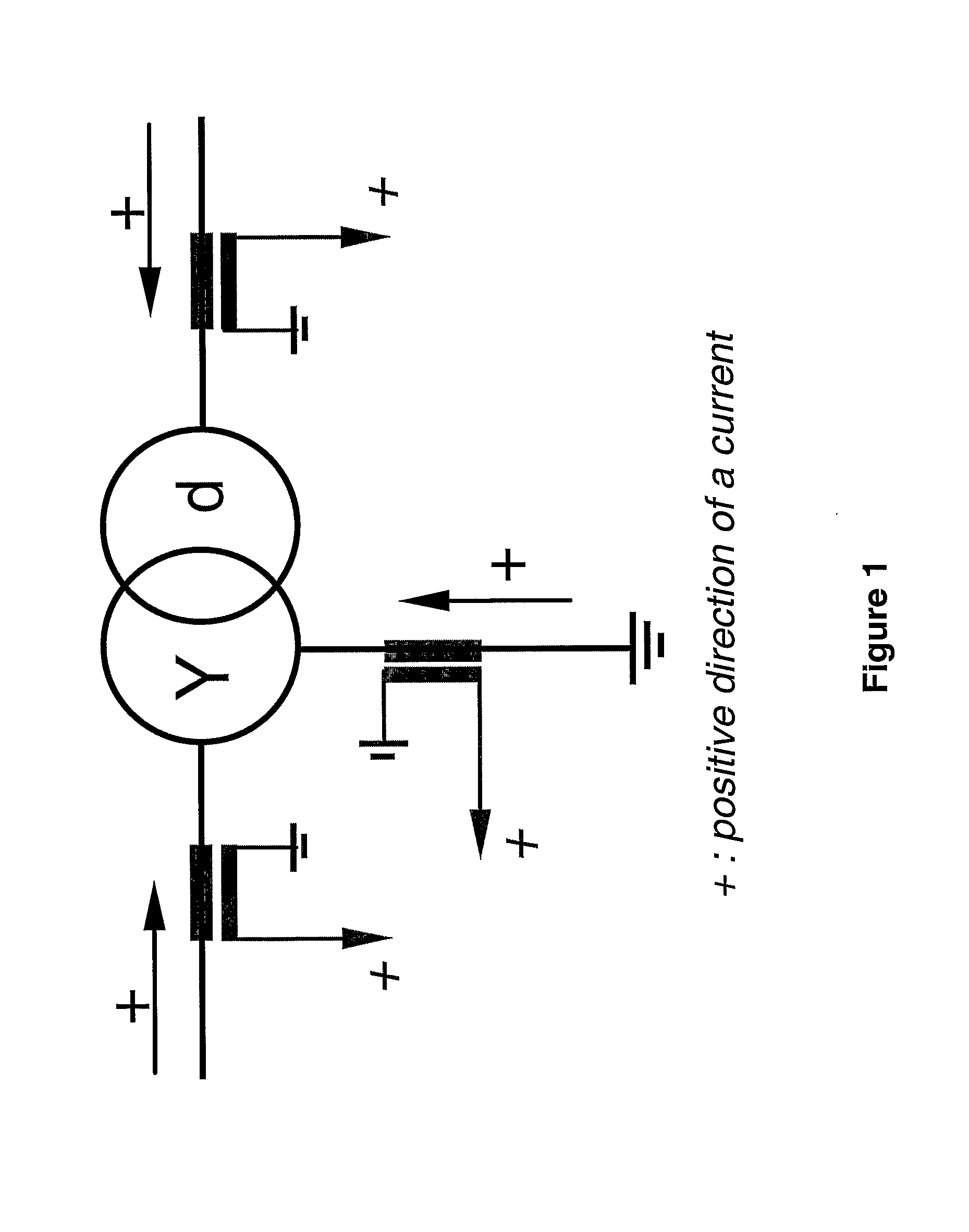
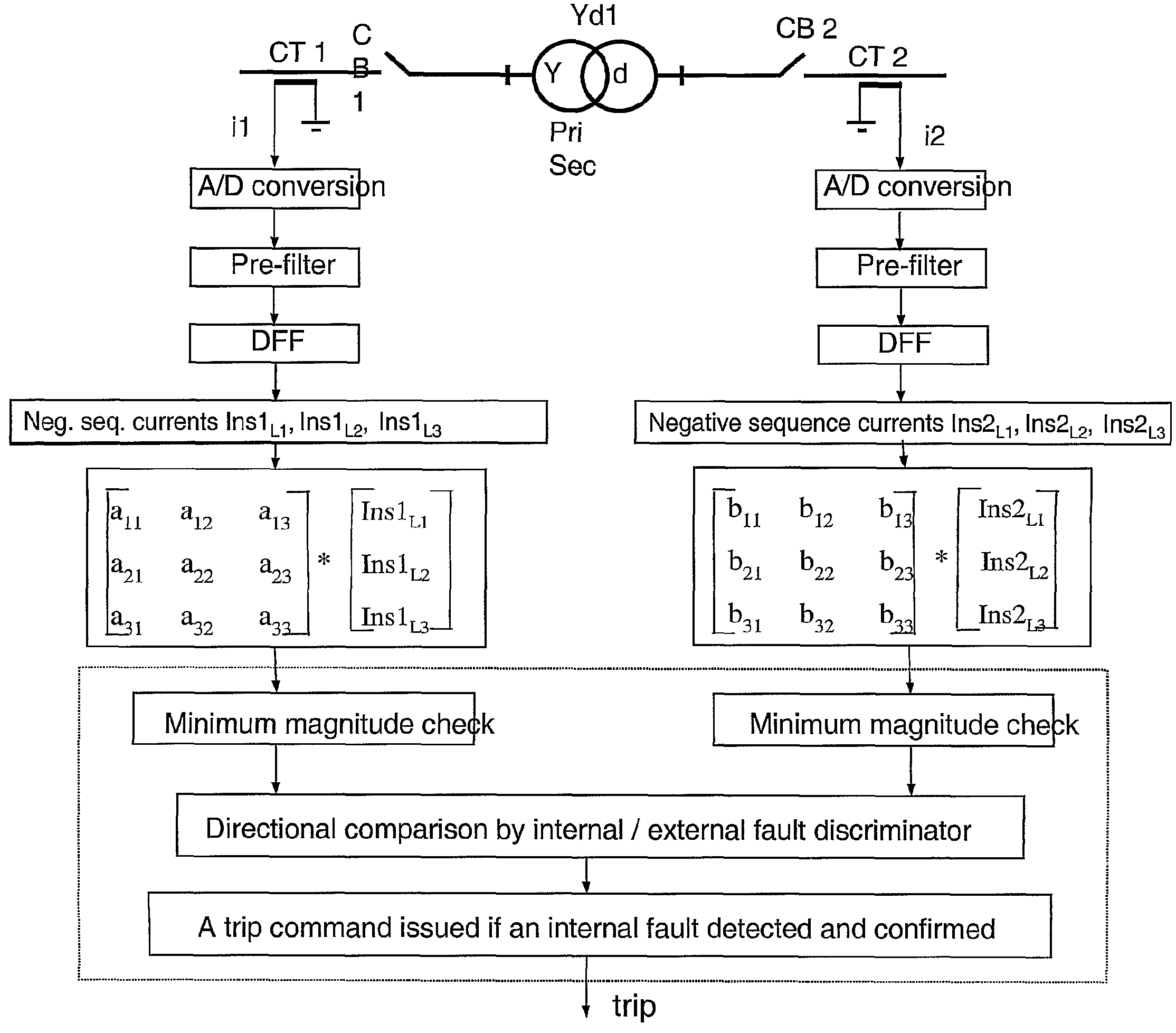
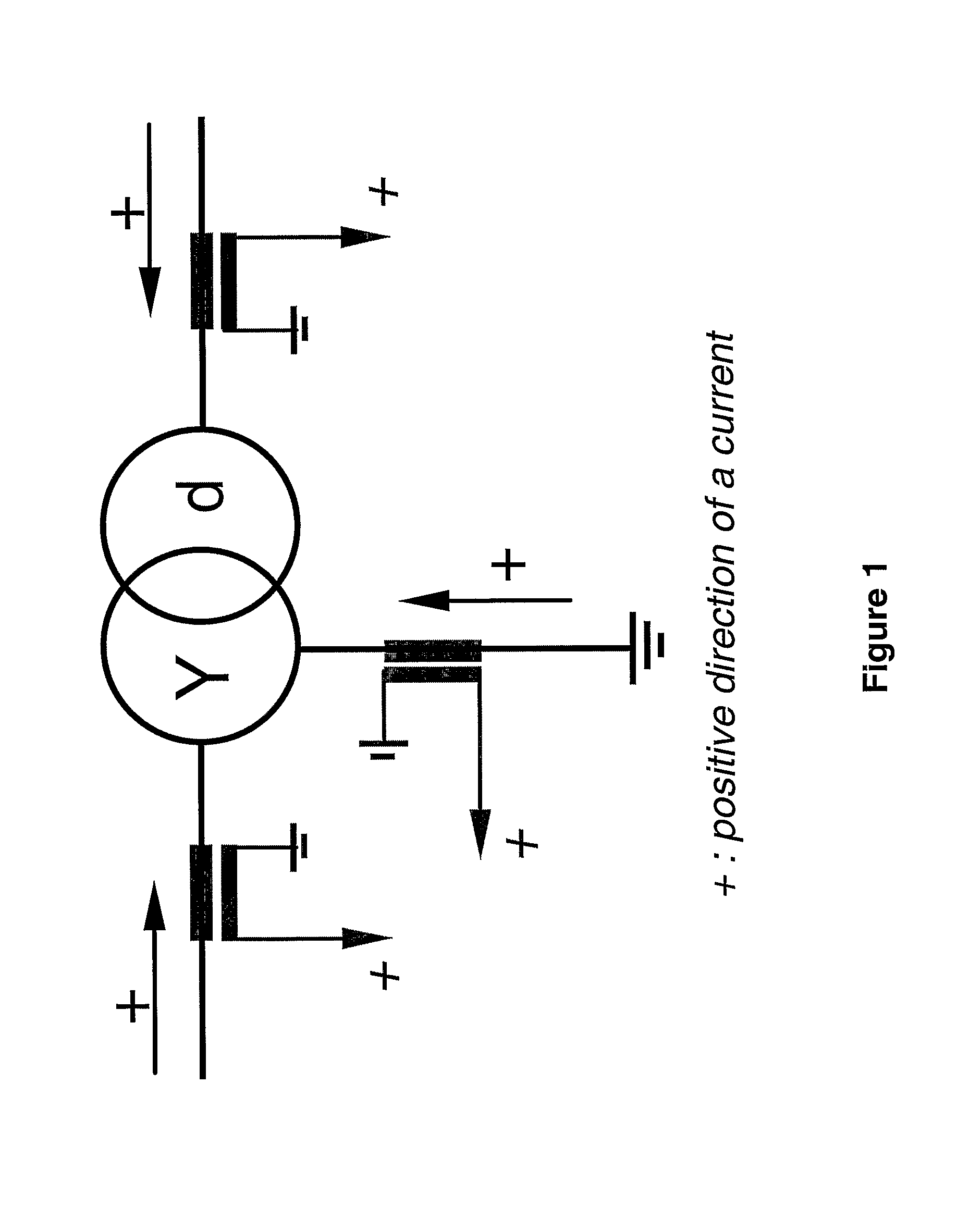
Method And Device For Fault Detection In Transformers Or Power Lines
ActiveUS20080130179A1Reduce usageRapid responseTransformers testingEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionPhase currentsAutotransformer
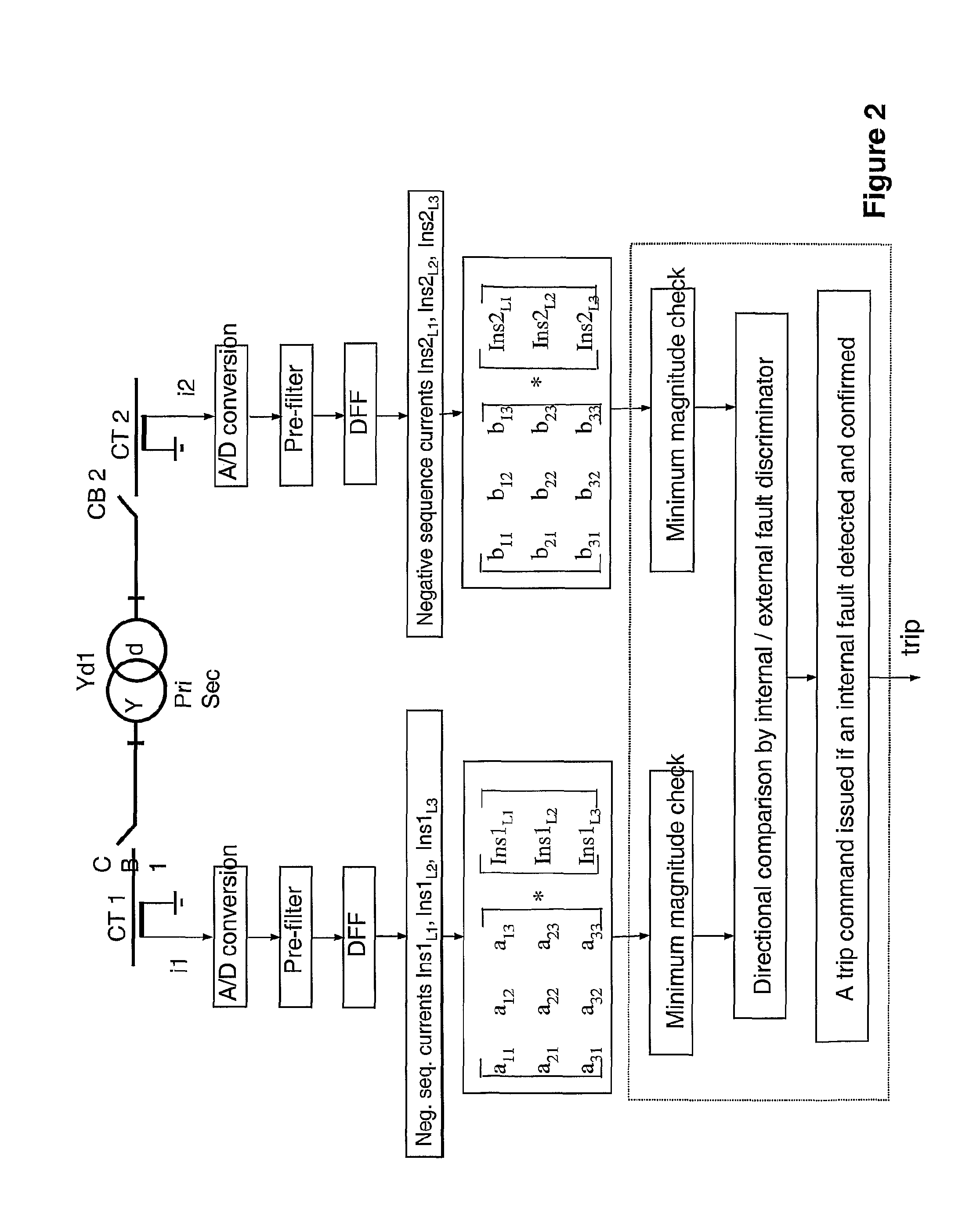
A method for fault detection in a power transformer / autotransformer and / or interconnected power lines, which are within the zone protected by the differential protection, and particularly suitable for detecting turn-to-turn faults in power transformer / autotransformer windings. All individual instantaneous phase currents of the protected object are measured, individual phase currents as fundamental frequency phasors are calculated, the contributions of the individual protected object sides negative sequence currents to the total negative sequence differential current are calculated by compensating for the phase shift of an eventual power transformer within the protected zone, the relative positions of the compensated individual sides negative sequence currents in the complex plane are compared, in order to determine whether the source of the negative sequence currents, i.e. the fault position, is within the protected zone or outside of the protected zone, delimited with current transformer locations, the protected object is disconnected if determined that the source of the negative sequence currents is within the protected zone.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
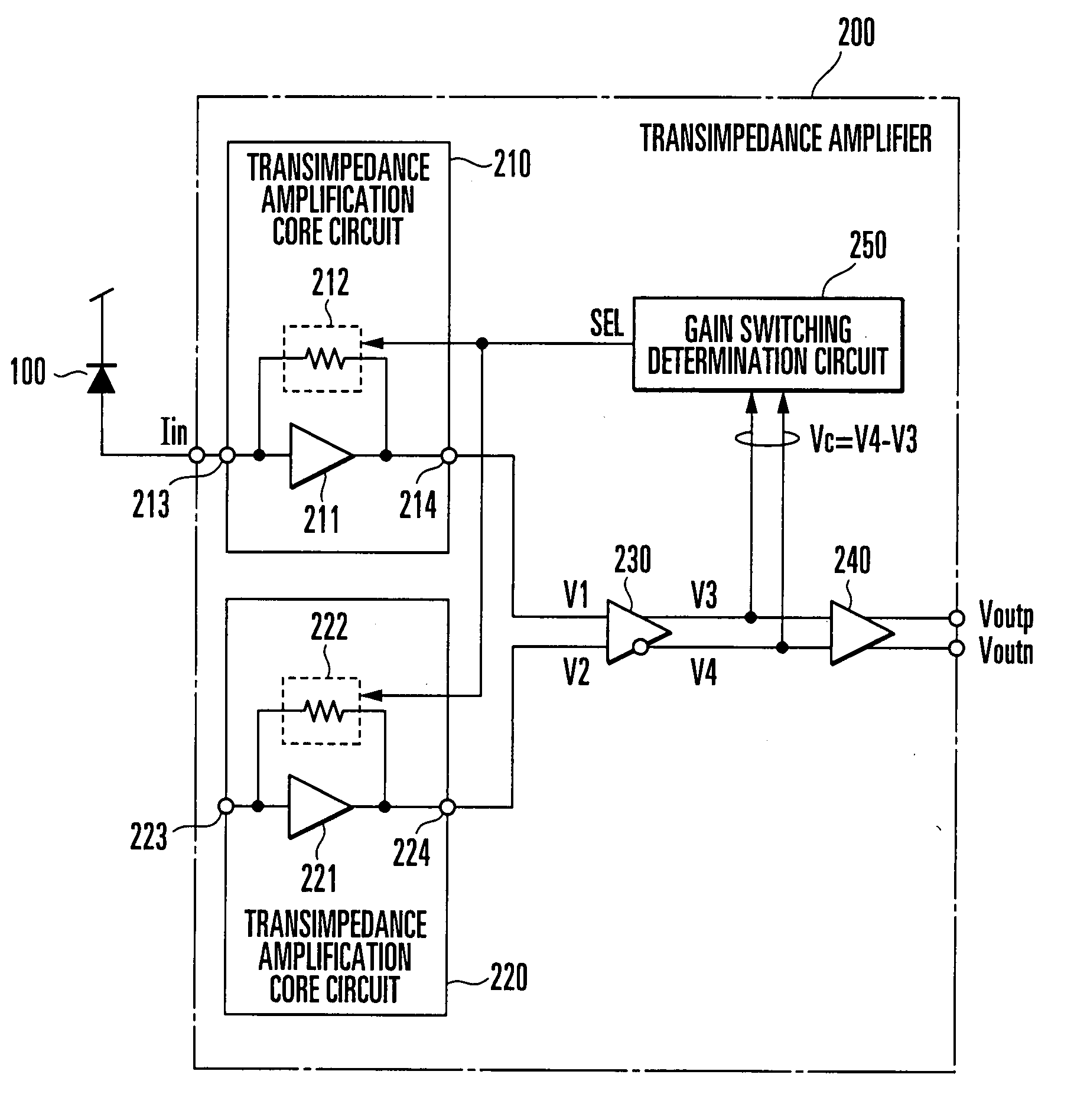
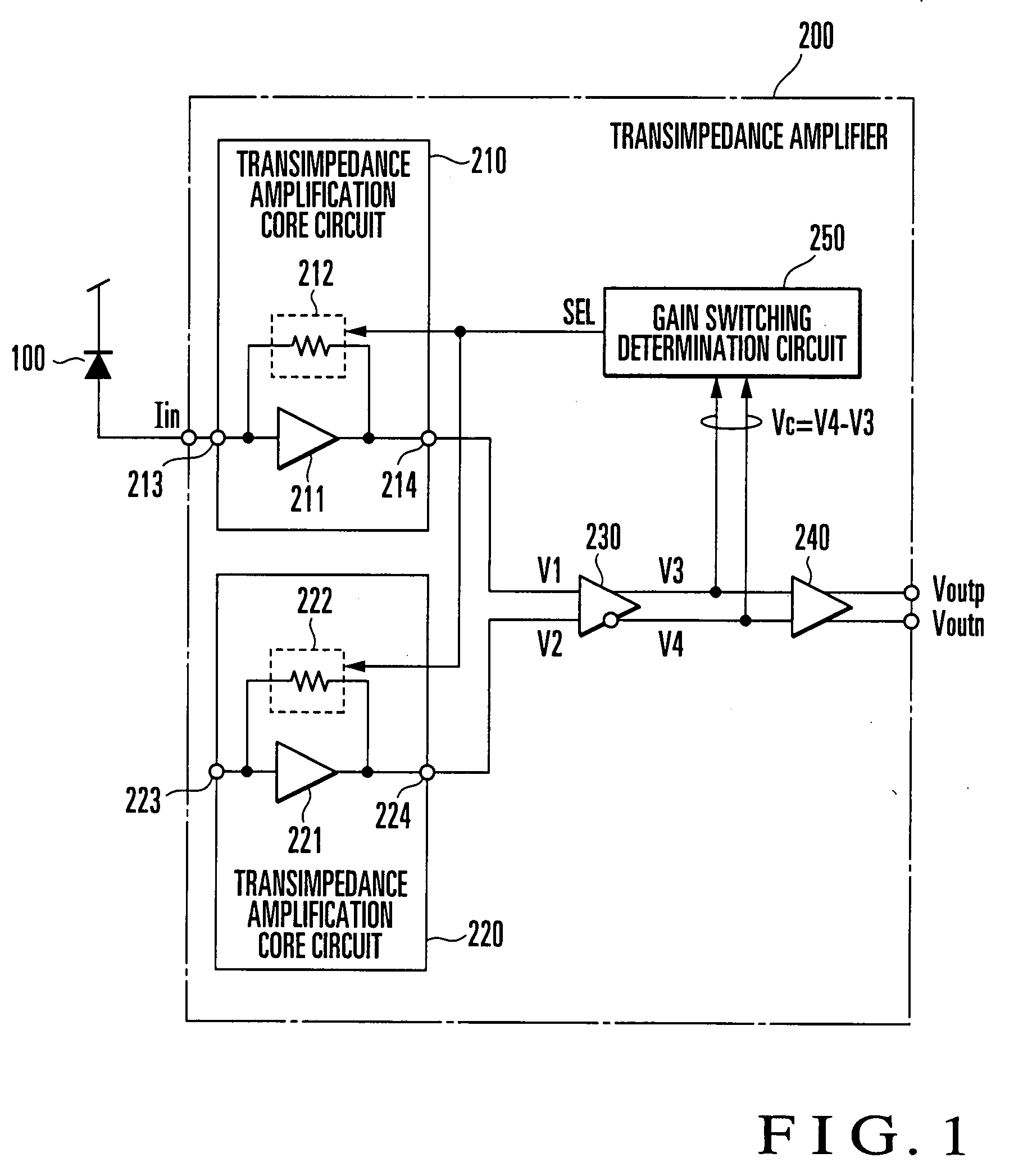
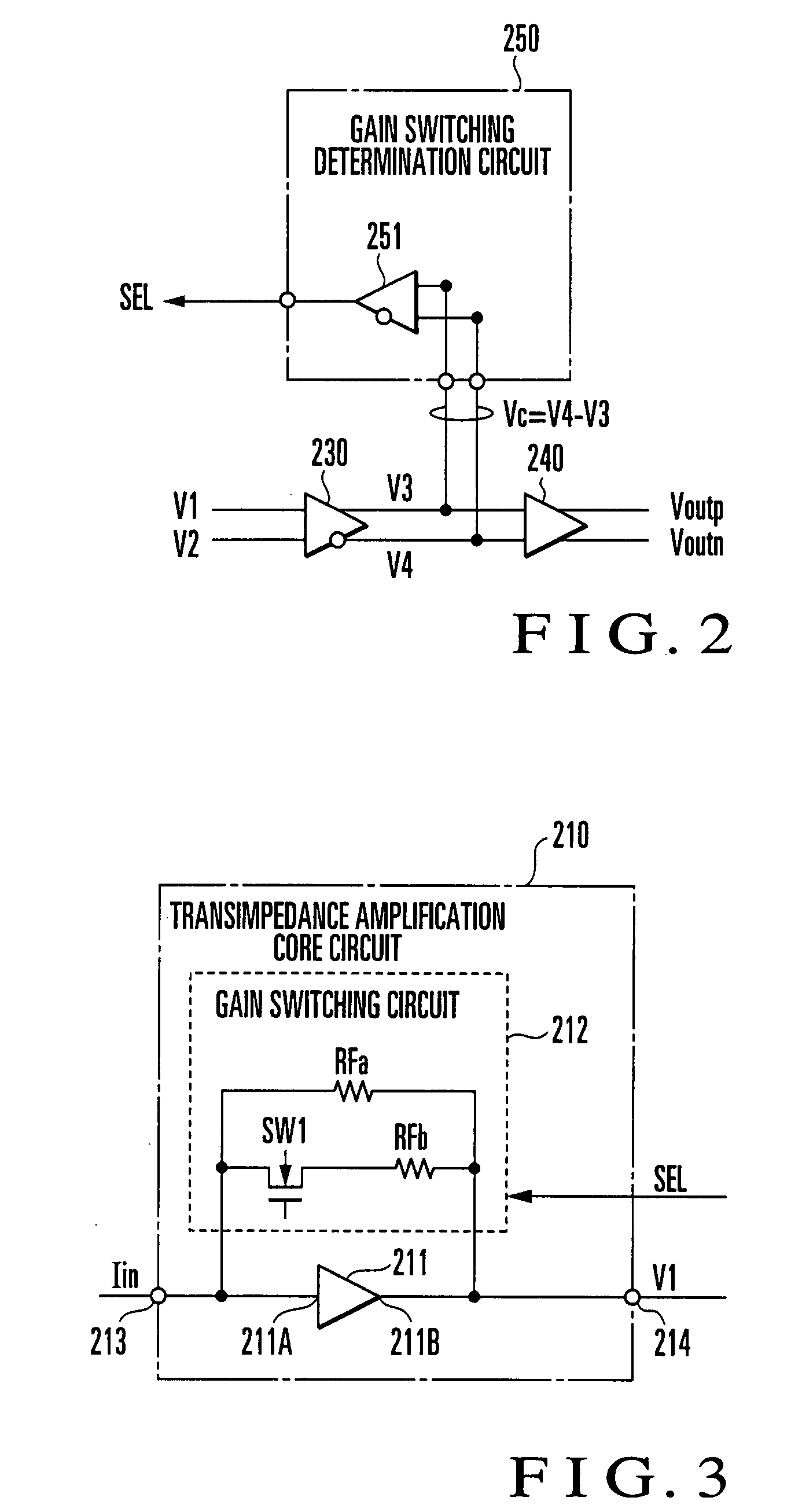
Transimpedance Amplifier
ActiveUS20080309407A1Gain controlAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceHysteresisAudio power amplifier
A gain switching determination circuit (250) compares / determines a comparative input voltage (Vc) from an inter-stage buffer (230) with a first hysteresis characteristic, and outputs a gain switching signal (SEL) based on the comparison / determination result to first and second transimpedance amplifier core circuits (210, 220), thereby switching the gains of the core circuits. This obviates holding a comparison input voltage with long response time in a level holding circuit for gain switching determination, which allows instantaneous gain switching determination and instantaneous response corresponding to burst data.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP +1
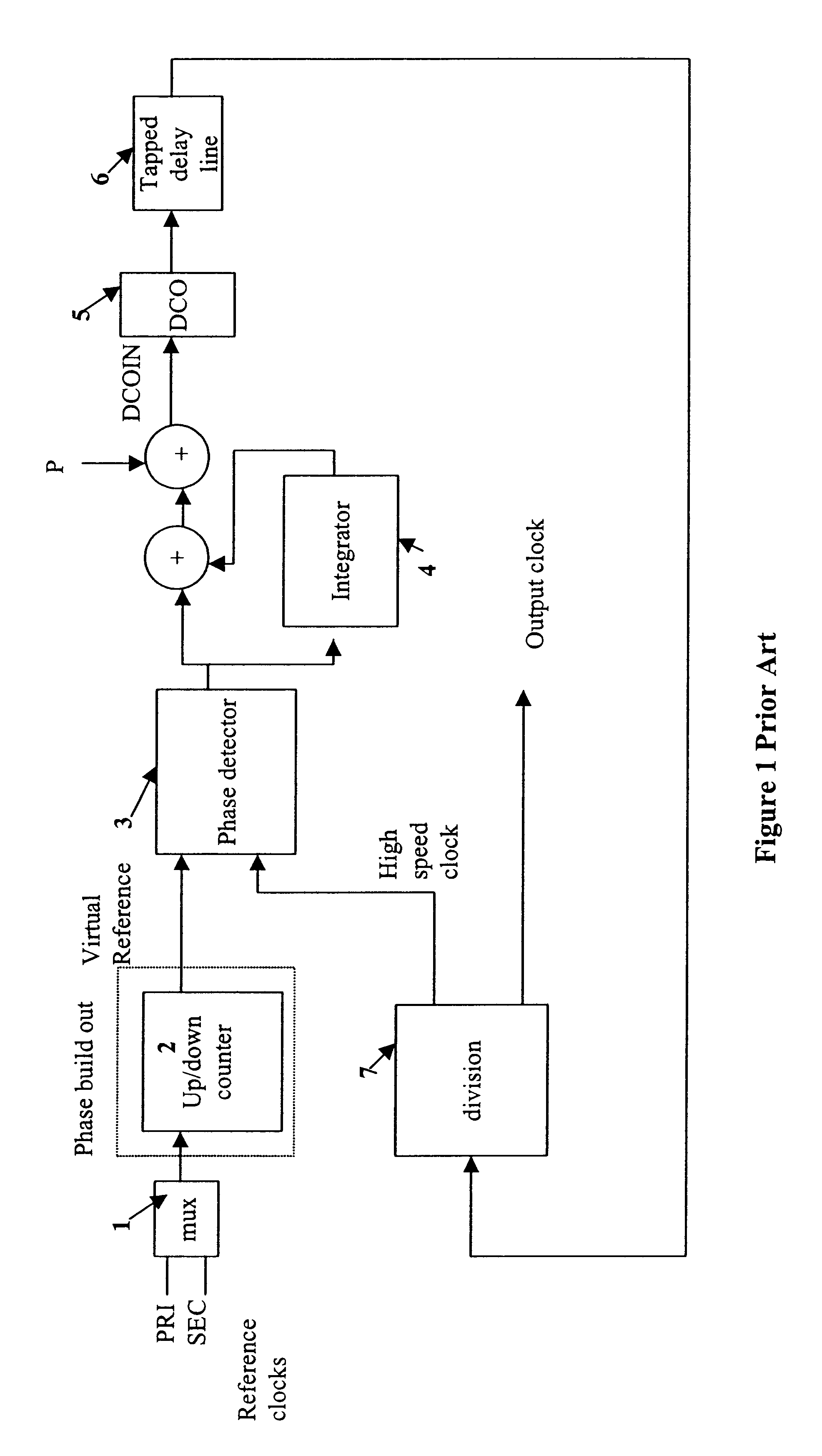
Multiple input phase lock loop with hitless reference switching
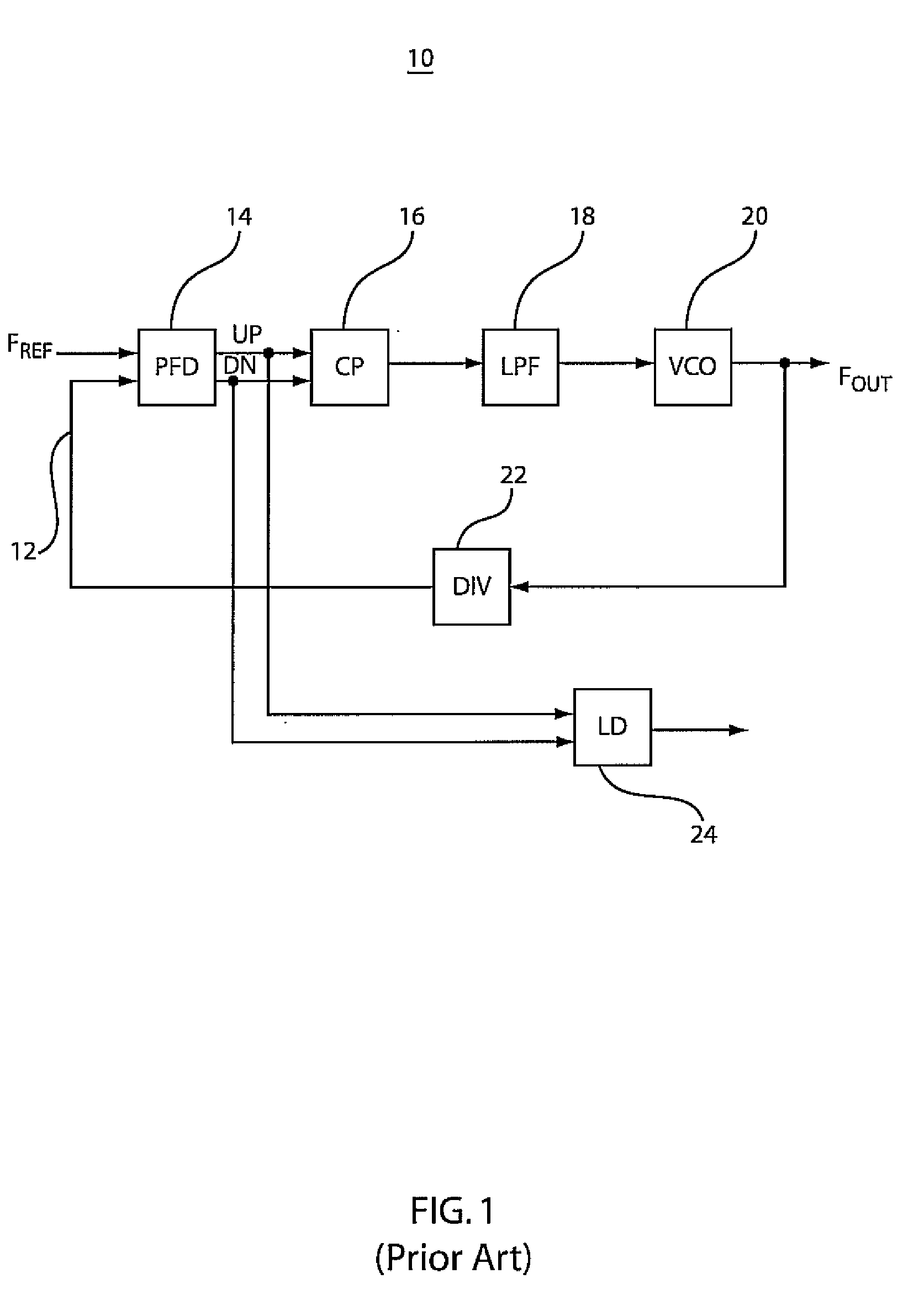
InactiveUS6570454B2Reduce jitterPulse automatic controlTime-division multiplexClock recoveryDigital controlled oscillator
Owner:ZARLINK SEMICON LTD
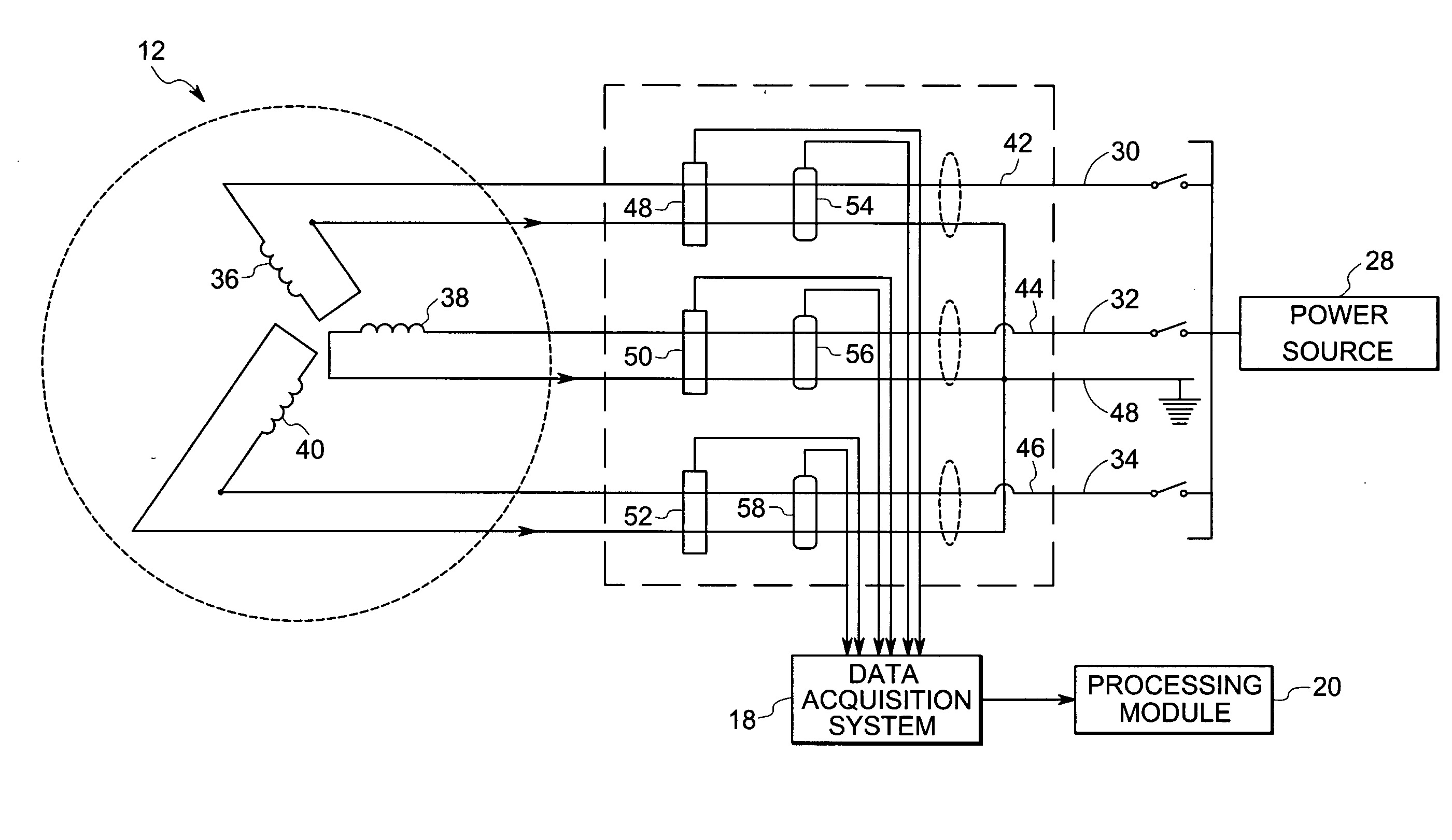
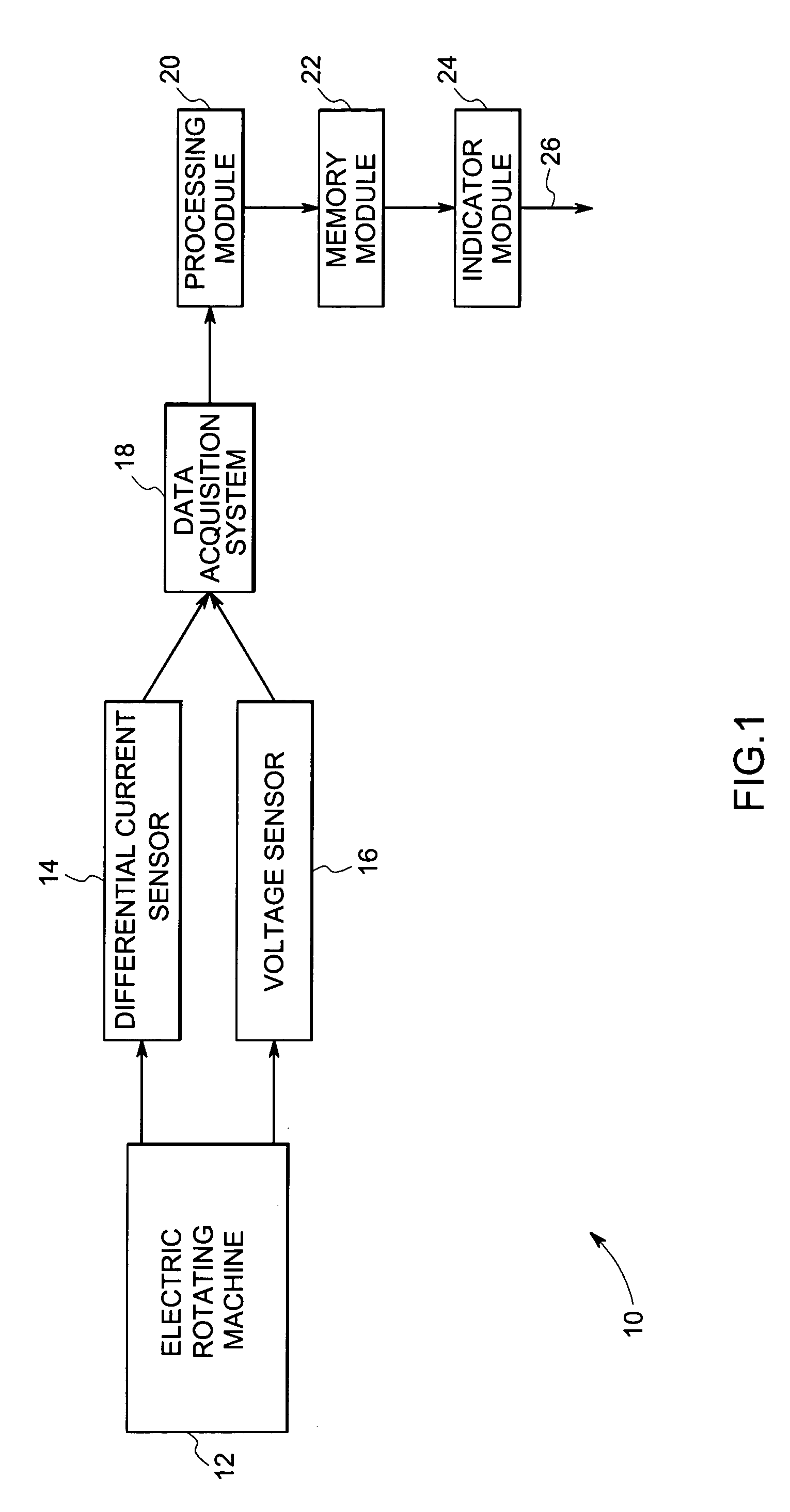
System and method for monitoring of insulation condition
InactiveUS20050218906A1Emergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionAir-break switch detailsElectric machineEngineering
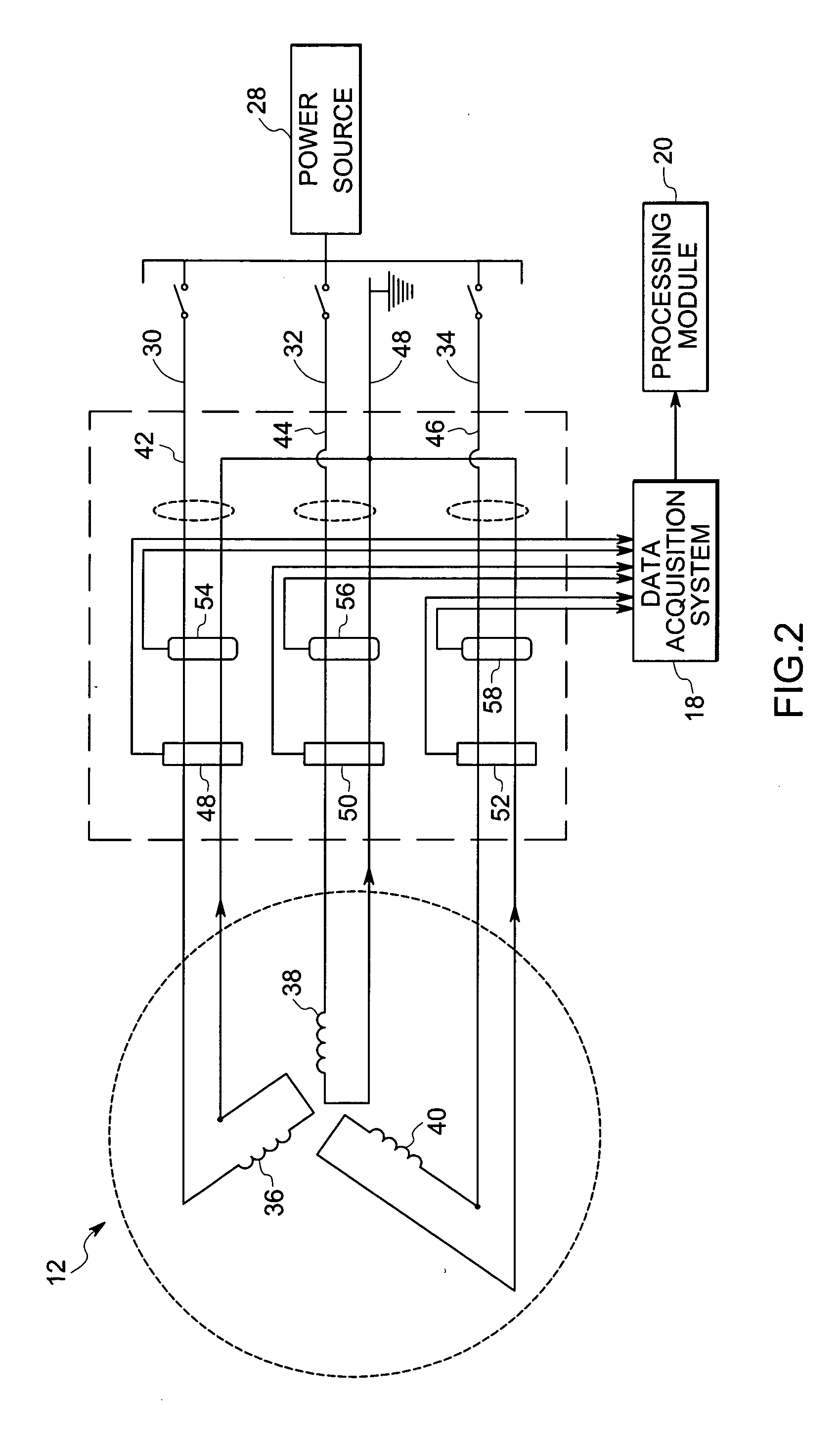
An online insulation condition monitoring system for a rotating electric machine, includes a differential current sensor and a voltage sensor coupled to the machine, for measuring values for the instantaneous differential current and the instantaneous phase voltage respectively. A processing module is configured for converting the values for the instantaneous differential current and the instantaneous phase voltage to respective values for phasor current and phasor voltage. The processing module further calculates an angular relationship between phasor current and phasor voltage and generates an output based on the calculated angular relationship, as an indication of insulation condition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for on-chip phase error measurement to determine jitter in phase-locked loops
ActiveUS20080172193A1Noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementElectrical testingPhase locked loop circuitPhase frequency detector
An apparatus includes a phase-locked loop (PLL) circuit including a phase-frequency detector configured to output phase error signals. A phase error monitor circuit is configured to determine instantaneous peak phase error by logically combining the phase error signals and comparing pulse widths of the logically combined phase error signals to a programmable delay time at each reference clock cycle to determine instantaneous phase error change. A storage element is configured to store the instantaneous phase error change.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Hybrid polar/cartesian digital modulator
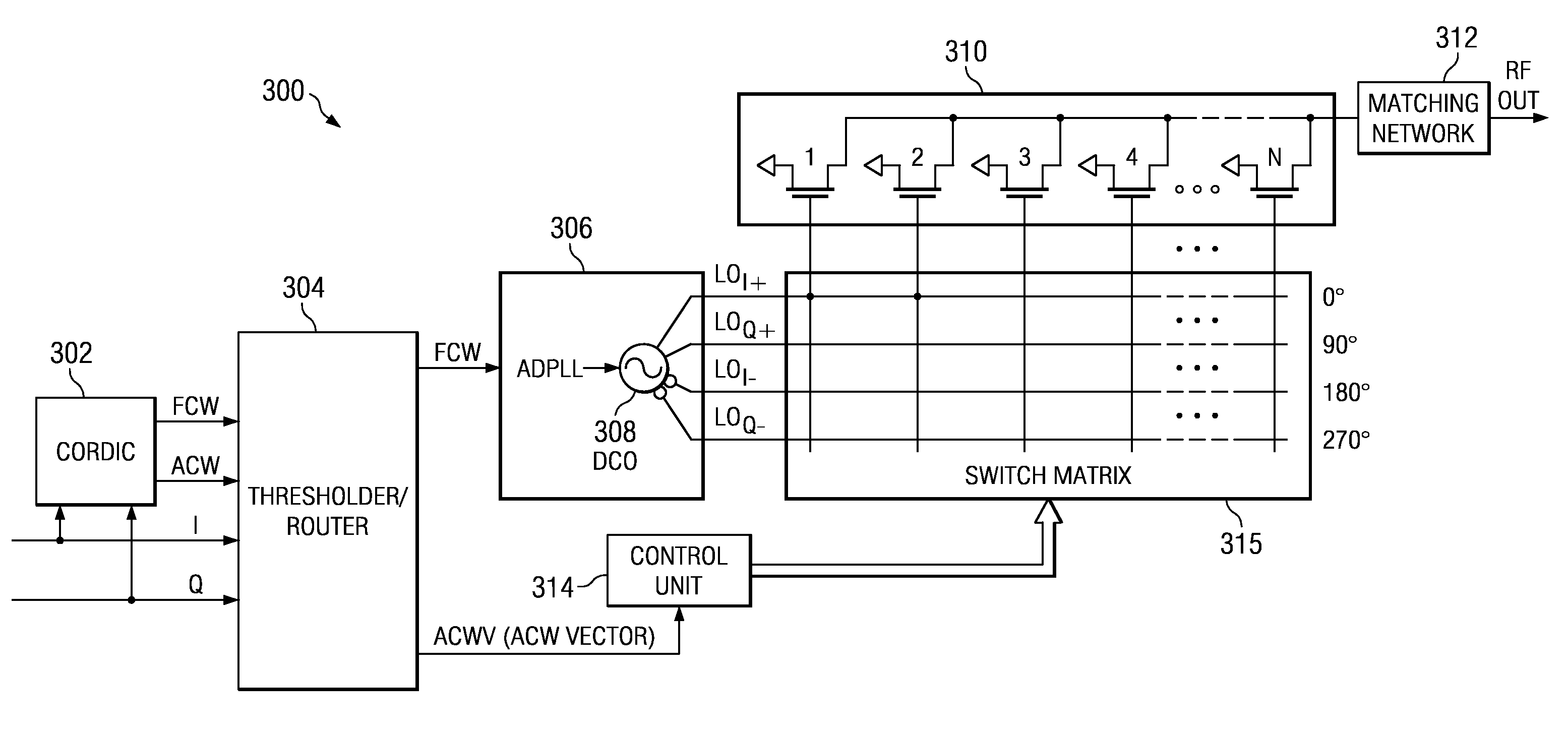
ActiveUS7532679B2Reconfigurable analogue/digital convertersAnalogue conversionControl powerQam modulation
A novel apparatus and method for a hybrid Cartesian / polar digital QAM modulator. The hybrid technique of the present invention utilizes a combination of an all digital phase locked loop (ADPLL) that features a wideband frequency modulation capability and a digitally controlled power amplifier (DPA) that features interpolation between 90 degree spaced quadrature phases. This structure is capable of performing either a polar operation or a Cartesian operation and can dynamically switch between them depending on the instantaneous value of a metric measured by a thresholder / router. In this manner, the disadvantages of each modulation technique are avoided while the benefits of each are exploited.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Apparatus for and method of measuring jitter
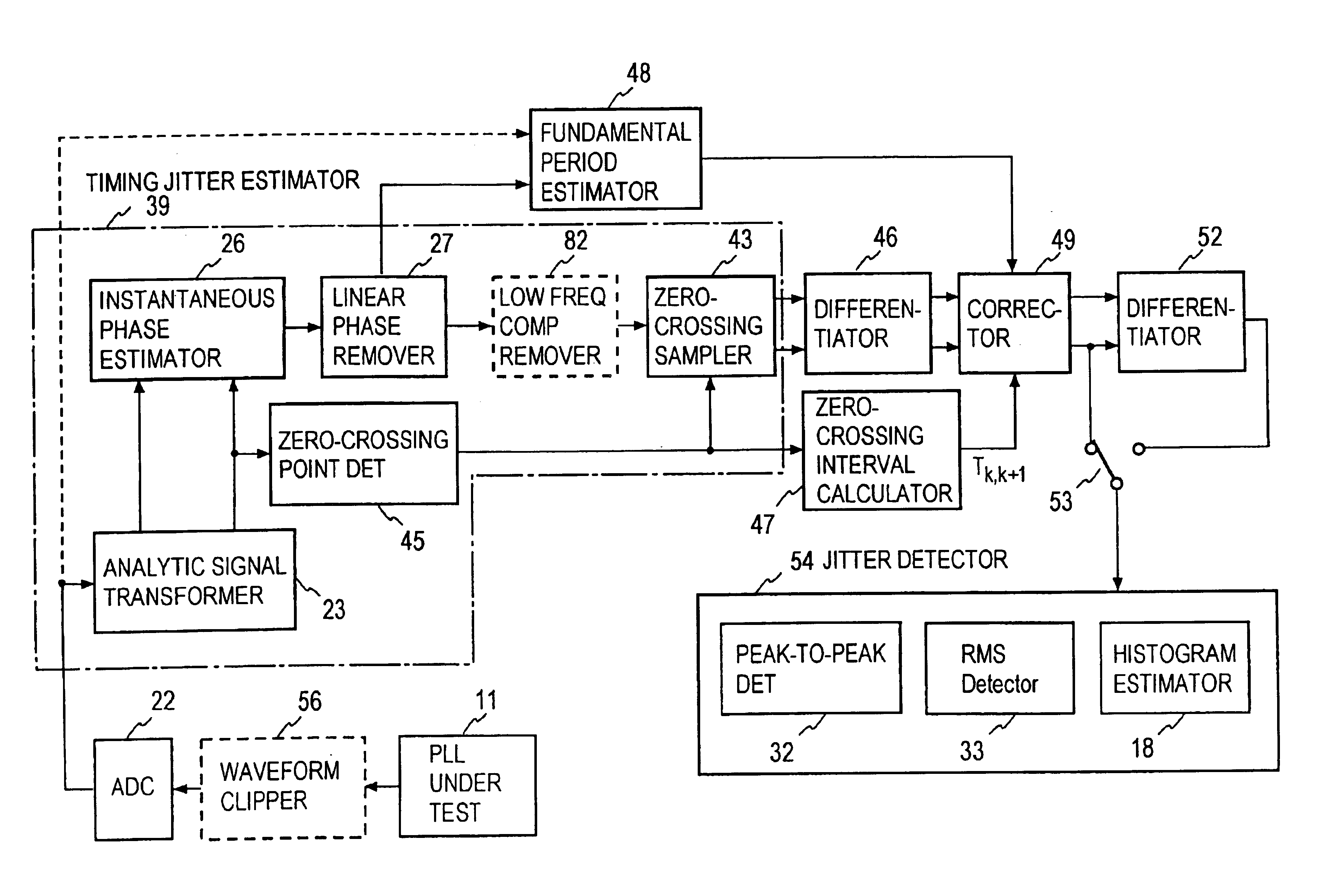
InactiveUS6922439B2Period jitter can beOver-sampling ratioMultiple input and output pulse circuitsError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorPhase noiseAnalytic signal
A signal under measurement x(t) is transformed into a complex analytic signal zc(t), and an instantaneous phase of the xc(t) is estimated using the zc(t). A linear phase is removed from the instantaneous phase to obtain a phase noise waveform Δφ(t) of the x(t), and the Δφ(t) is sampled at a timing close to a zero-crossing timing of the x(t) to obtain a timing jitter sequence. Then a difference sequence of the timing jitter sequence is calculated to obtain a period jitter sequence. The period jitter sequence is multiplied by a ratio T0 / Tk,k+1 of the fundamental period T0 of the x(t) and the sampling time interval Tk,k+1 to make a correction of the period jitter sequence. A period jitter value of the x(t) is obtained from the corrected period jitter sequence.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
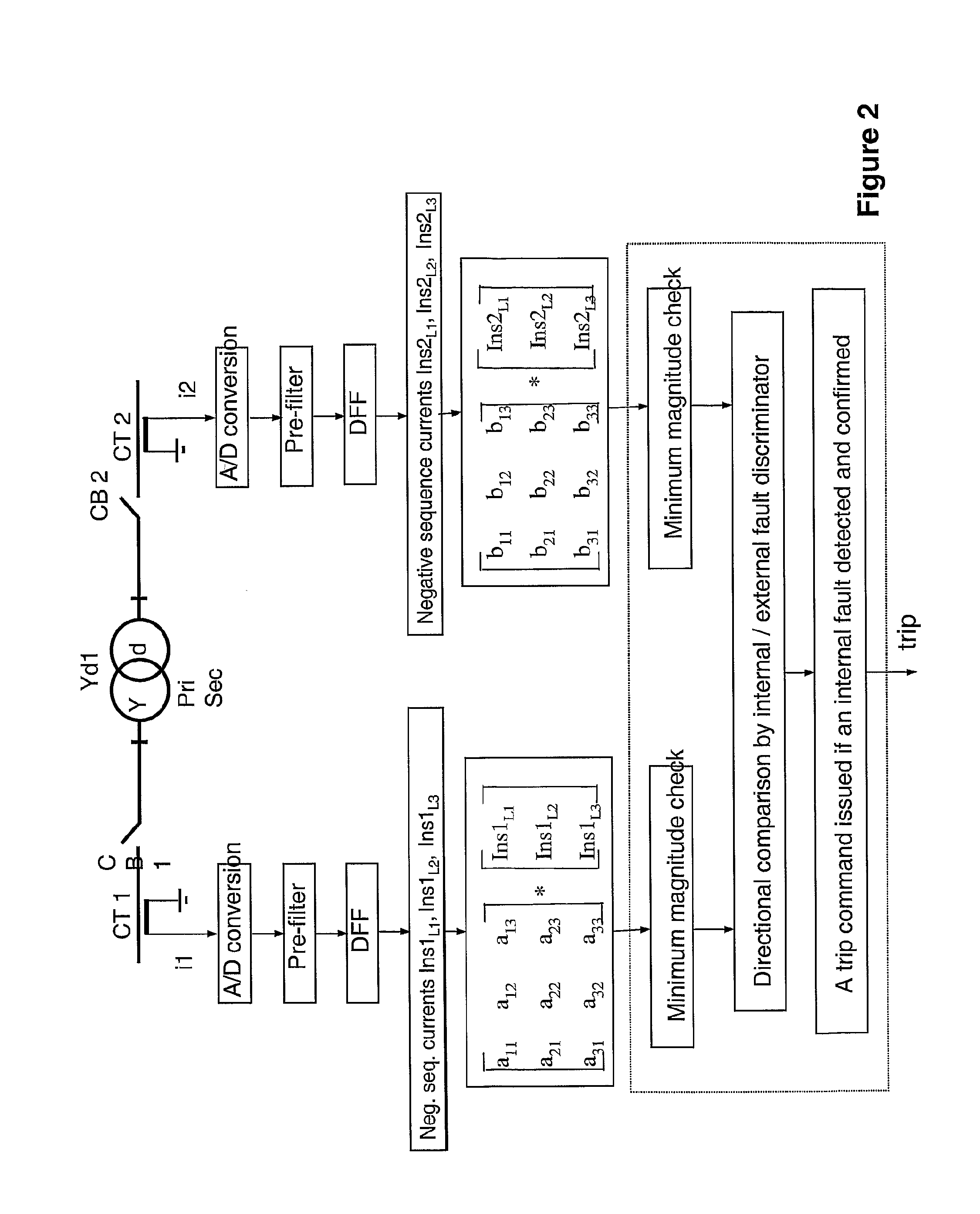
Method and device for fault detection in transformers or power lines
ActiveUS7812615B2Rapid responseEfficient detectionTransformers testingEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionPhase currentsAutotransformer
A method for fault detection in a power transformer / autotransformer and / or interconnected power lines, which are within the zone protected by the differential protection, and particularly suitable for detecting turn-to-turn faults in power transformer / autotransformer windings. All individual instantaneous phase currents of the protected object are measured, individual phase currents as fundamental frequency phasors are calculated, the contributions of the individual protected object sides negative sequence currents to the total negative sequence differential current are calculated by compensating for the phase shift of an eventual power transformer within the protected zone, the relative positions of the compensated individual sides negative sequence currents in the complex plane are compared, in order to determine whether the source of the negative sequence currents, i.e. the fault position, is within the protected zone or outside of the protected zone, delimited with current transformer locations, the protected object is disconnected if determined that the source of the negative sequence currents is within the protected zone.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY LTD
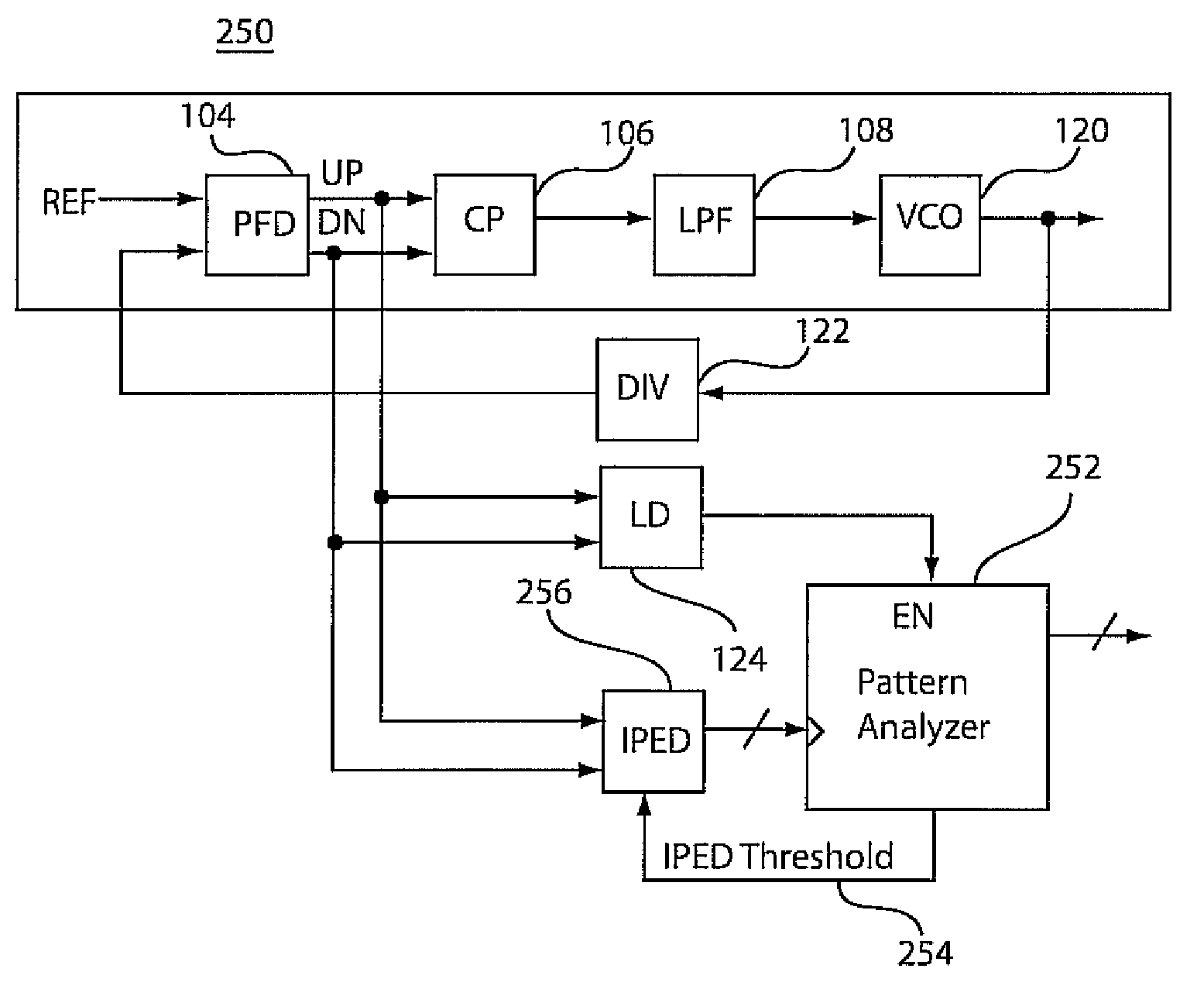
Automatic static phase error and jitter compensation in PLL circuits
InactiveUS7511543B2Enhance the shake effectEffective wayPulse automatic controlVoltage-current phase angleEngineeringLag
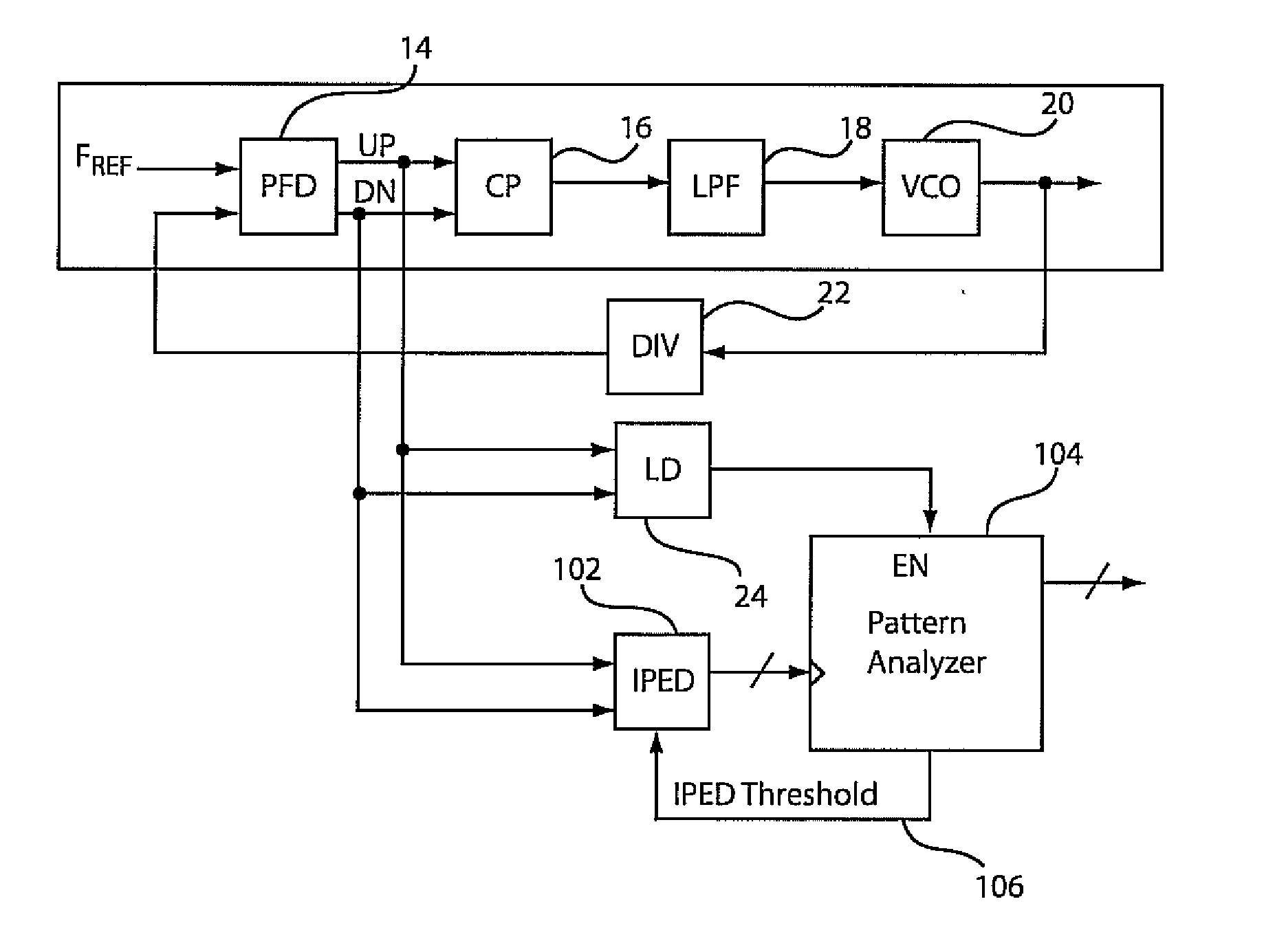
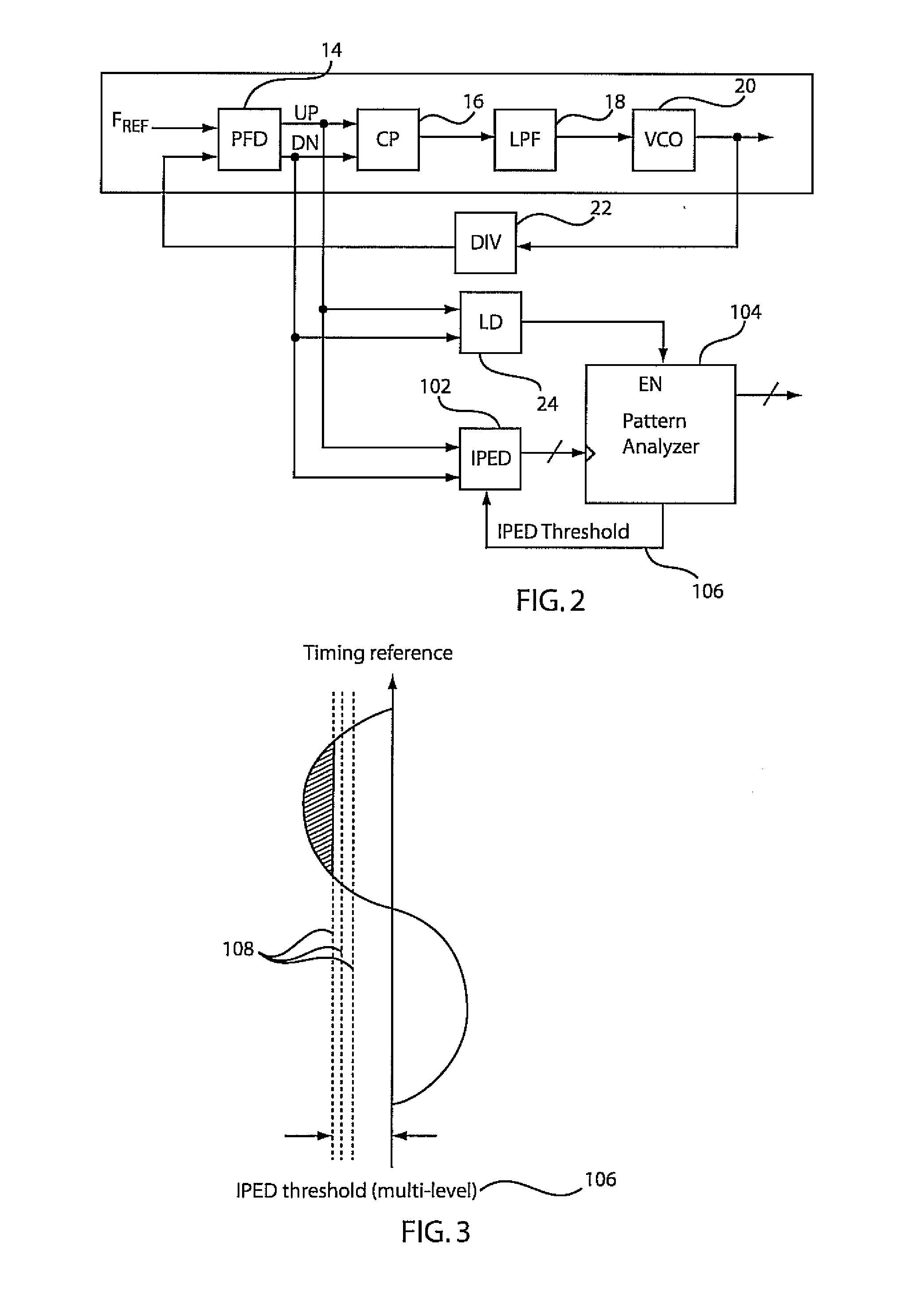
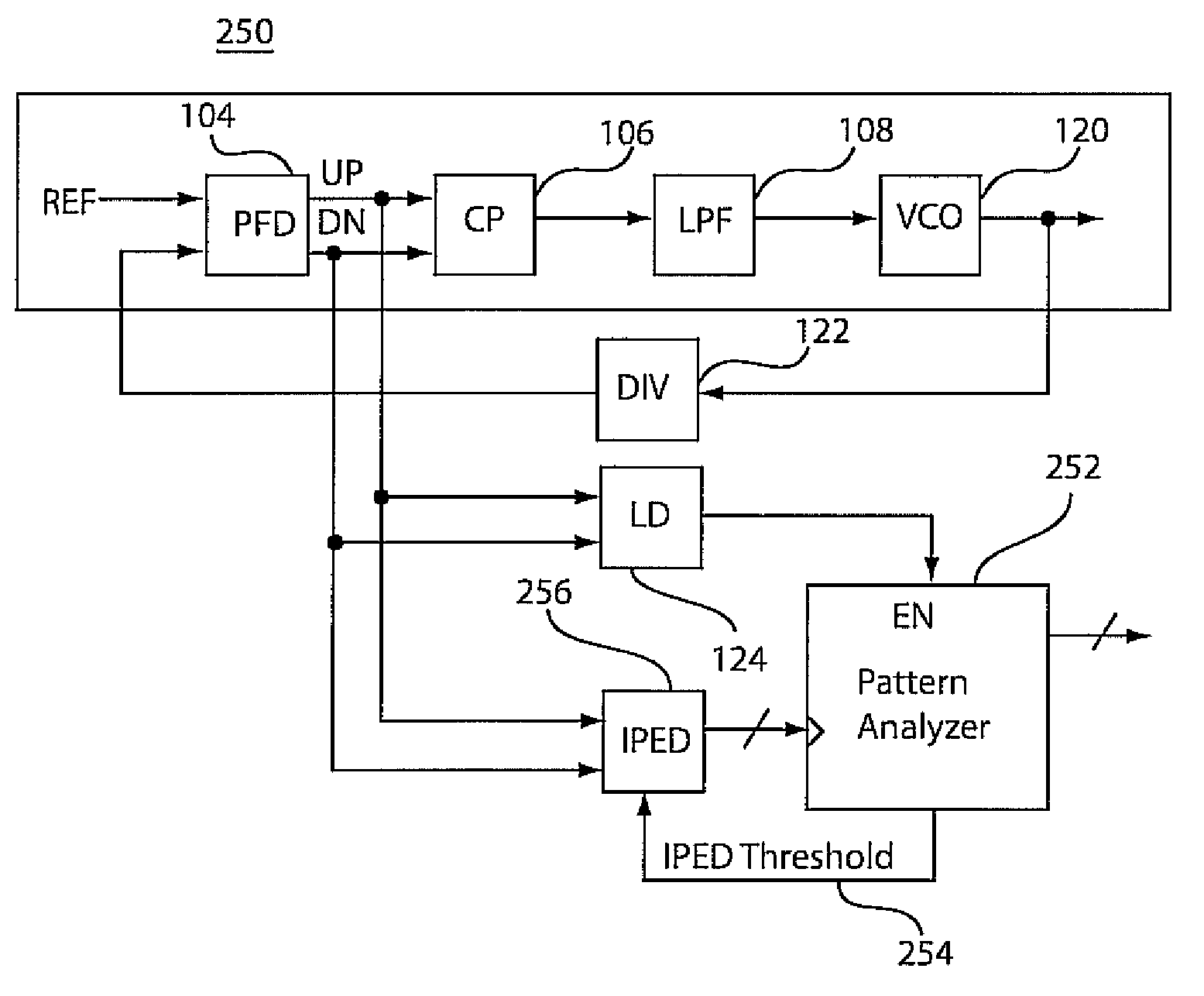
An instantaneous phase error detector (IPED) and method includes a first gate configured to logically OR output phase error signals as data to a first latch, and a second gate configured to logically combine the output phase error signals to clock the first latch. A delay element delays to the data to the first latch where the output of the first latch provides instantaneous phase error change information. A second latch is coupled to the output phase error signals to output a lead / lag signal to indicate which of the output phase error signals is leading. A phase-locked loop employing the output of the IPED is also disclosed along with static phase measurement and jitter optimization features.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Fusion-based spatio-temporal feature detection for robust classification of instantaneous changes in pupil response as a correlate of cognitive response
InactiveUS20090171240A1Computationally efficientComputationally robustMedical data miningPerson identificationPupil diameterFeature extraction
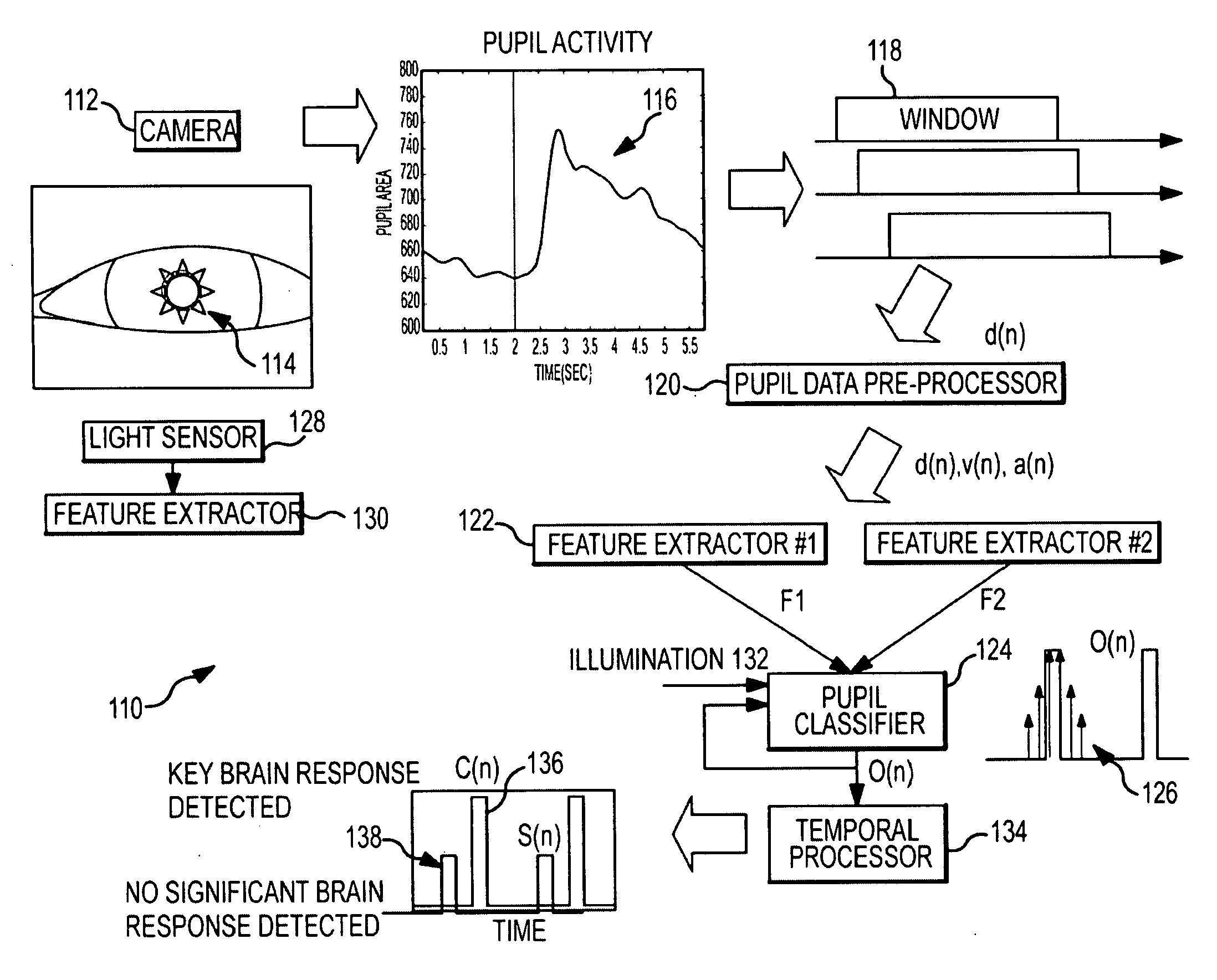
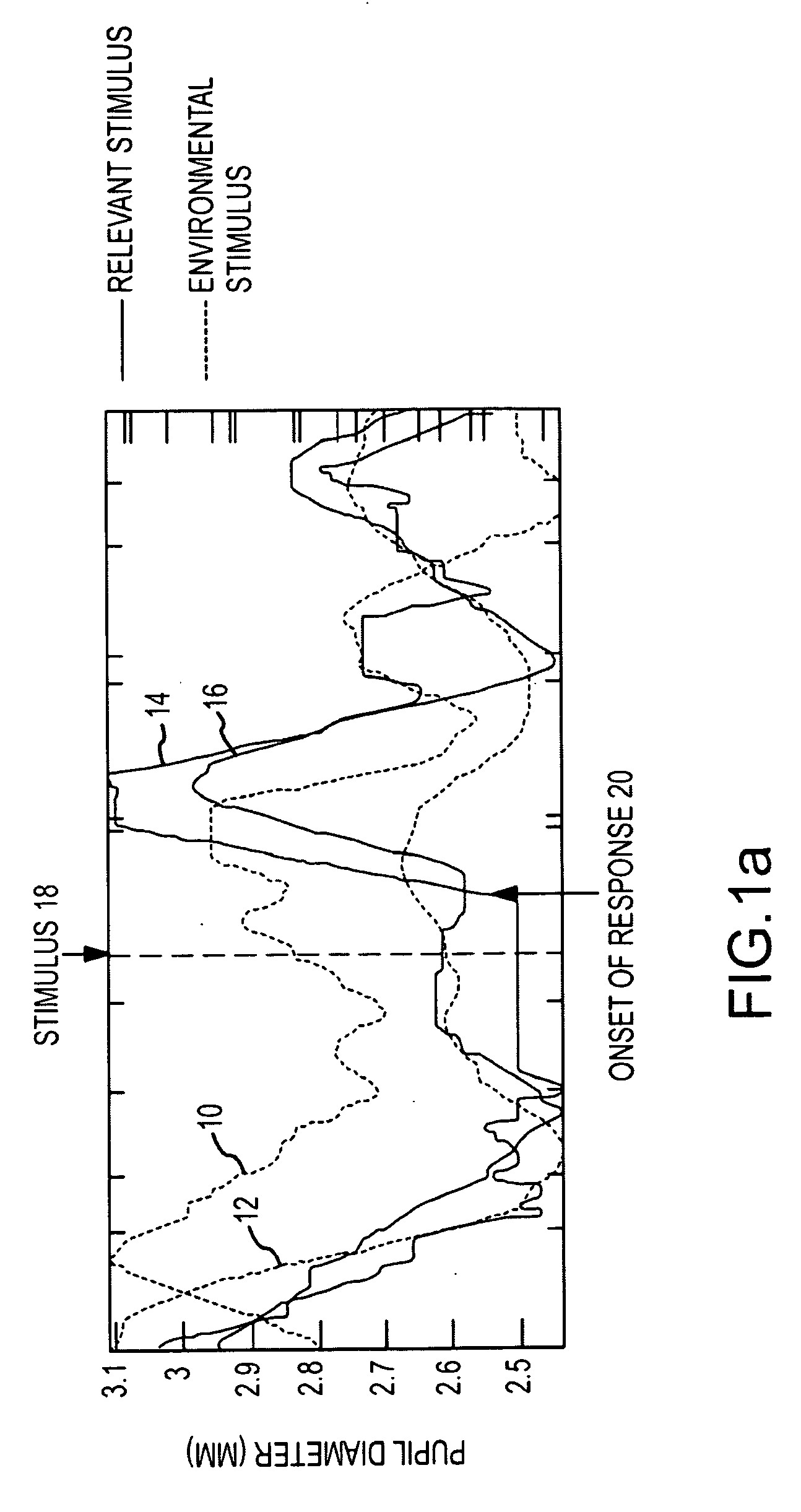
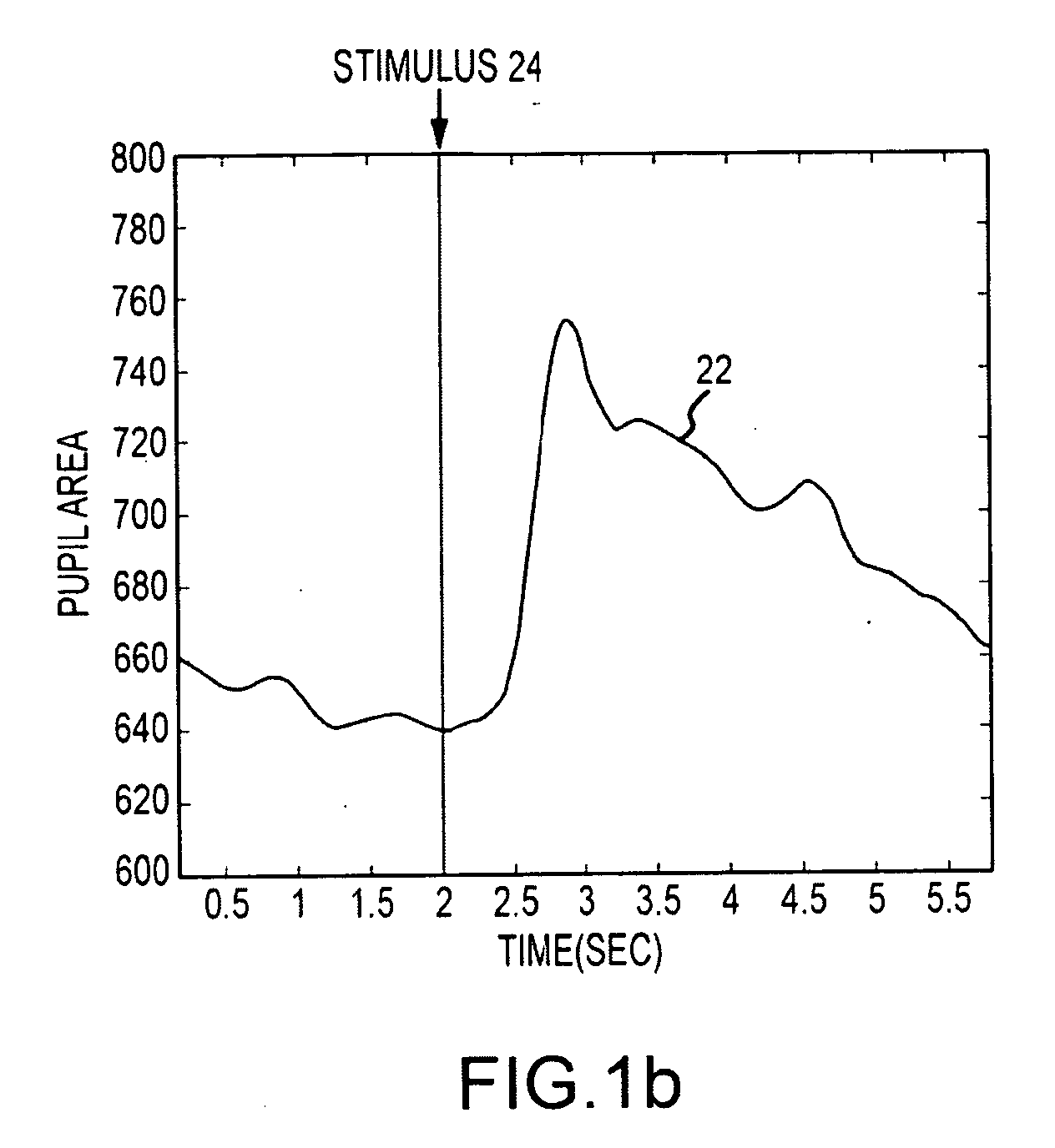
A computationally efficient and robust approach for monitoring the instantaneous pupil response as a correlate to significant cognitive response to relevant stimuli derives data samples d(n) of the pupil diameter (area), v(n) of pupil velocity and a(n) of pupil acceleration from the pupillary response and segments the data samples into a sequence of time-shifted windows. A feature extractor extracts a plurality of spatio-temporal pupil features from the data samples from the response and baseline periods in each window. A classifier trained to detect patterns of the extracted spatio-temporal pupil features for relevant stimuli generates an output indicative of the occurrence of absence of a significant cognitive response in the subject to a relevant stimulus.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
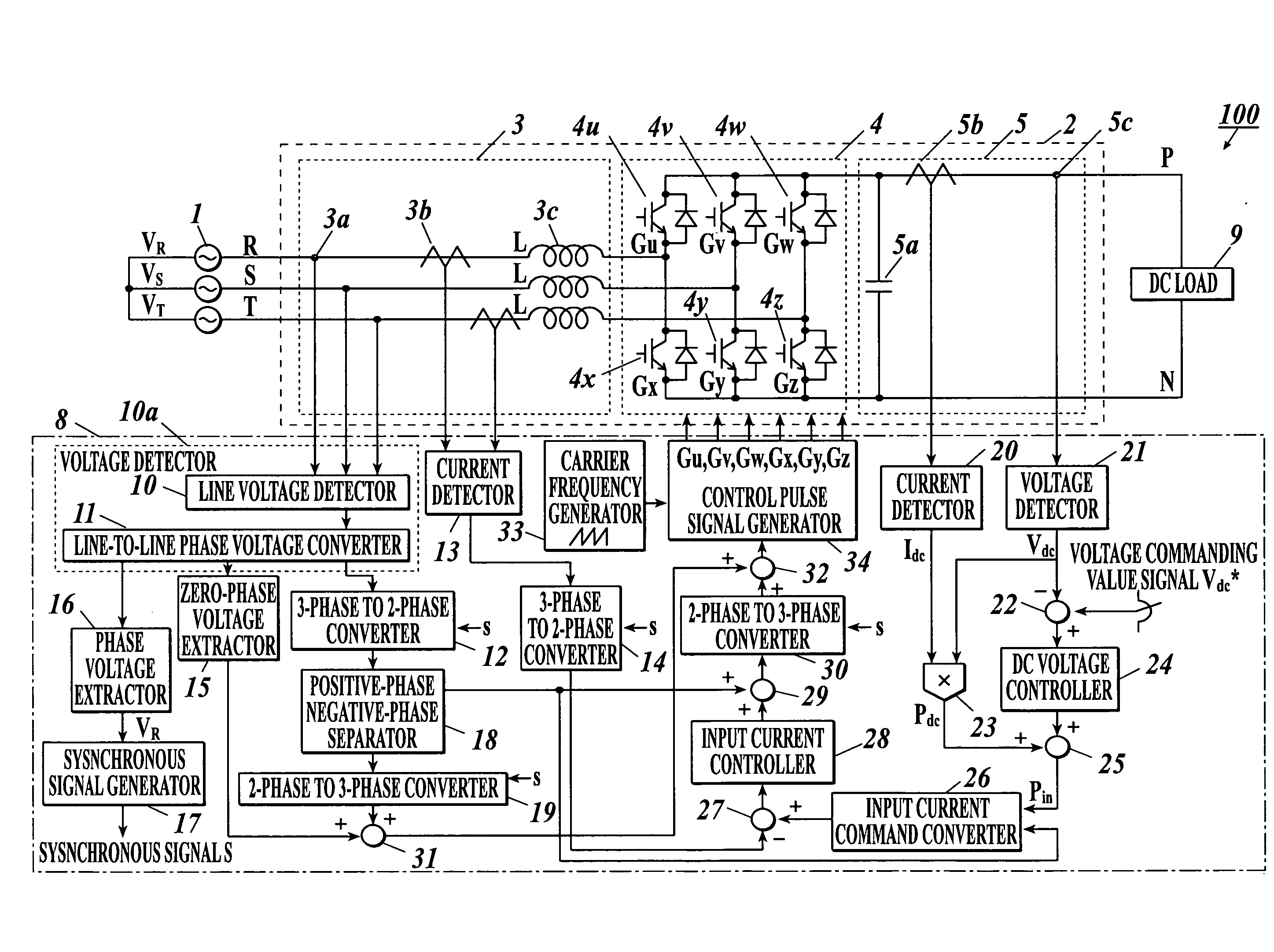
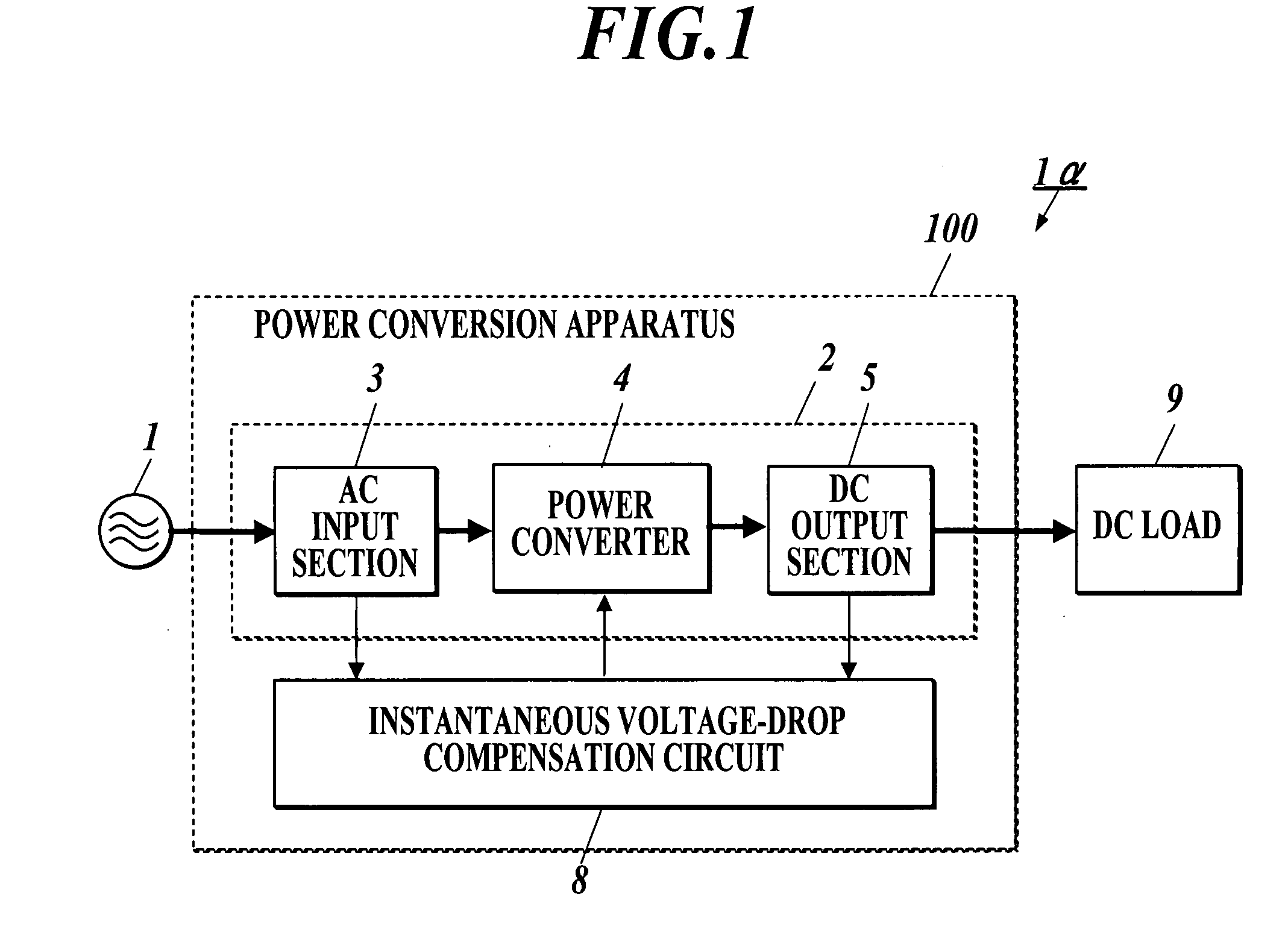
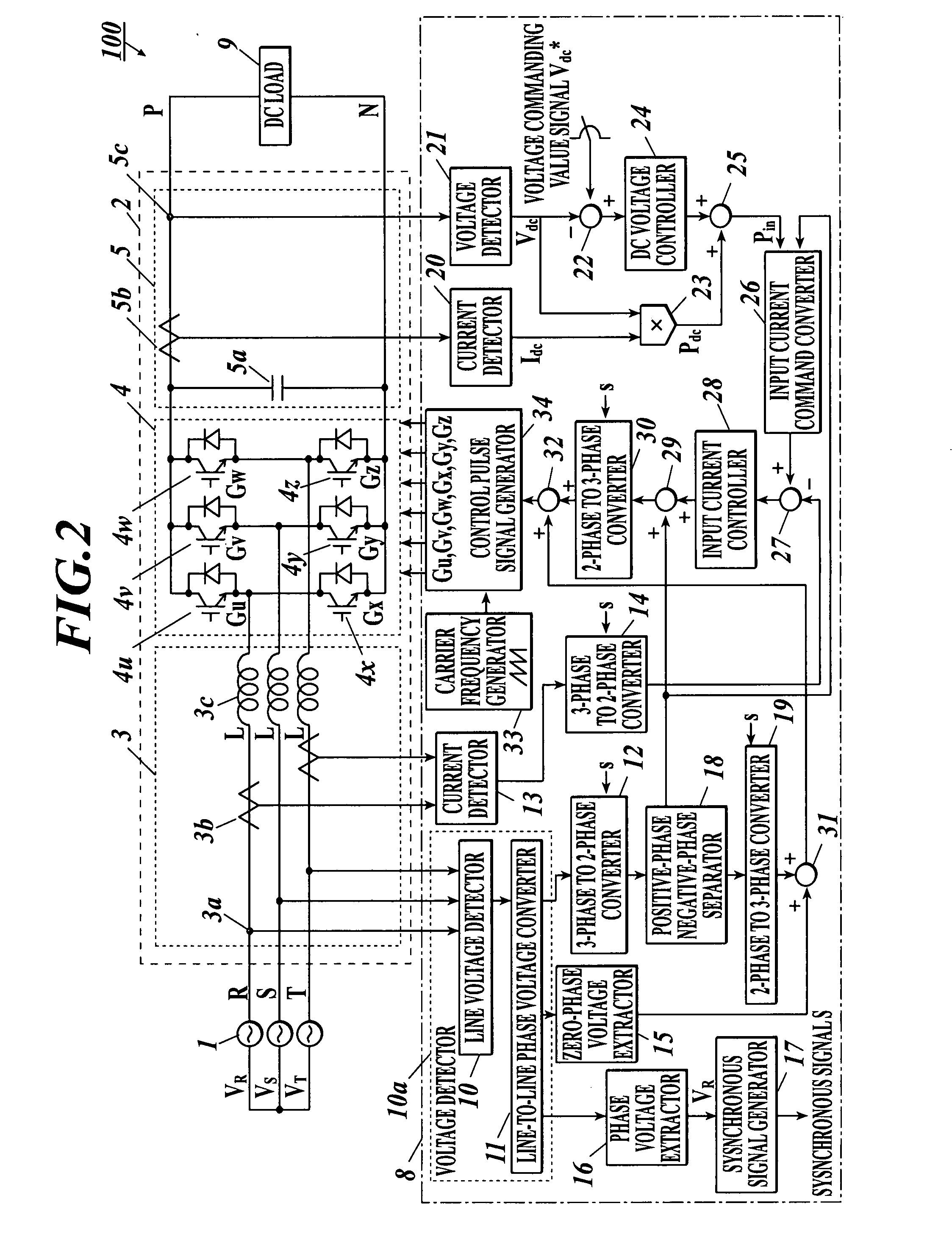
Instantaneous voltage-drop compensation circuit, power conversion apparatus, instantaneous voltage-drop compensation method and computer readable medium storing instantaneous voltage-drop compensation program
ActiveUS20080130335A1Easy maintenanceSolution to short lifeAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcPhase currentsControl signal
An instantaneous voltage-drop compensation circuit including: a first voltage detector detecting three-phase voltages to be input to a power converter converting three-phase AC to DC based on control pulse signals, and outputting three-phase voltage signals; a first three-phase to two-phase converter converting the detected signals to two-phase voltage signals; a first current detector detecting three-phase currents to be input to the power converter and outputting three-phase current signals; a second three-phase to two-phase converter converting the detected current signals to two-phase current signals; a first subtracter generating a first deviation signal from input current command signals and the two-phase current signals; an input current controller generating input current control signals based on the first deviation signal; and a first adder adding the two-phase voltage signals to the input current control signals, to generate control pulse signals for the power converter.
Owner:KYOSAN ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD
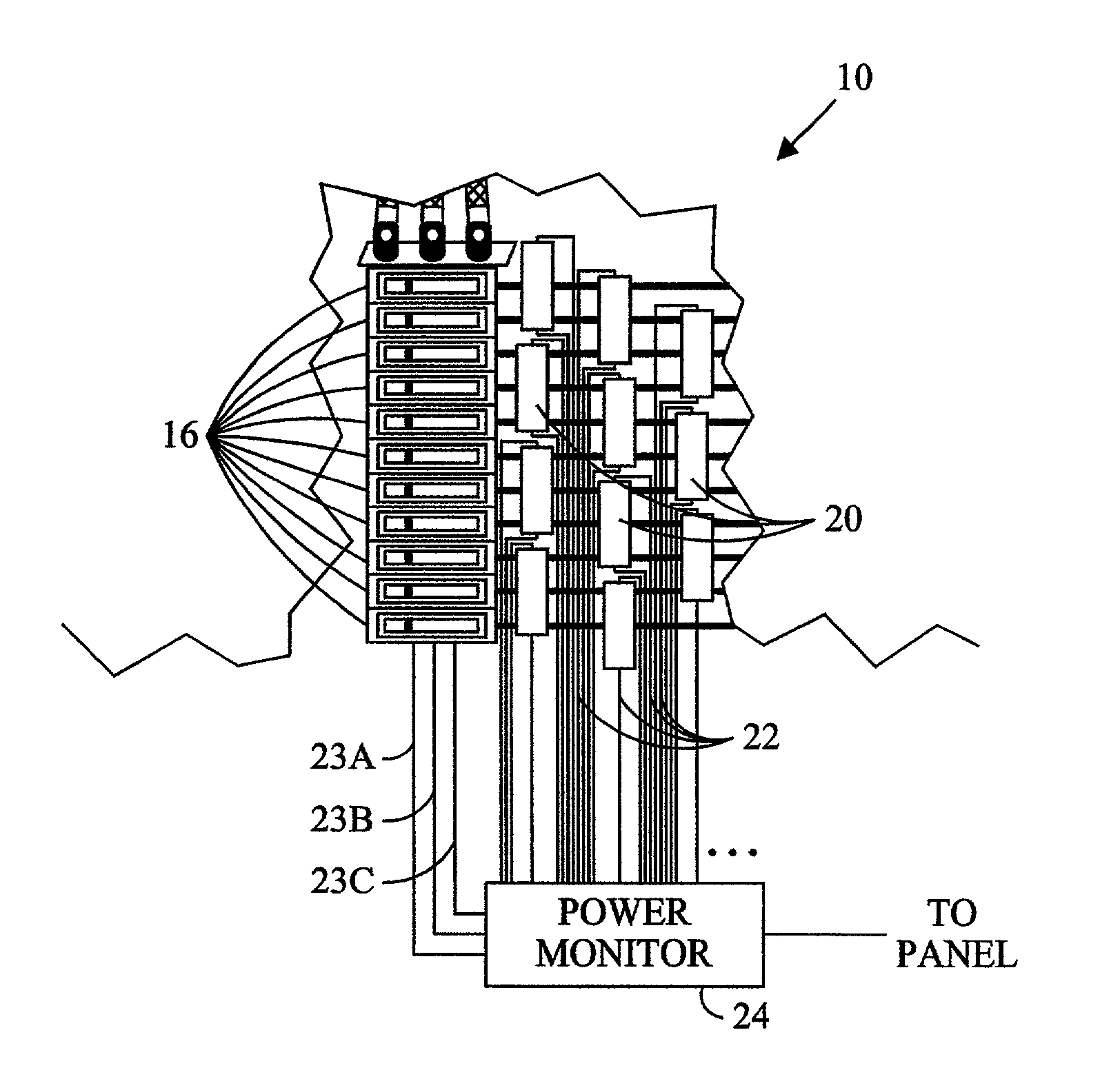
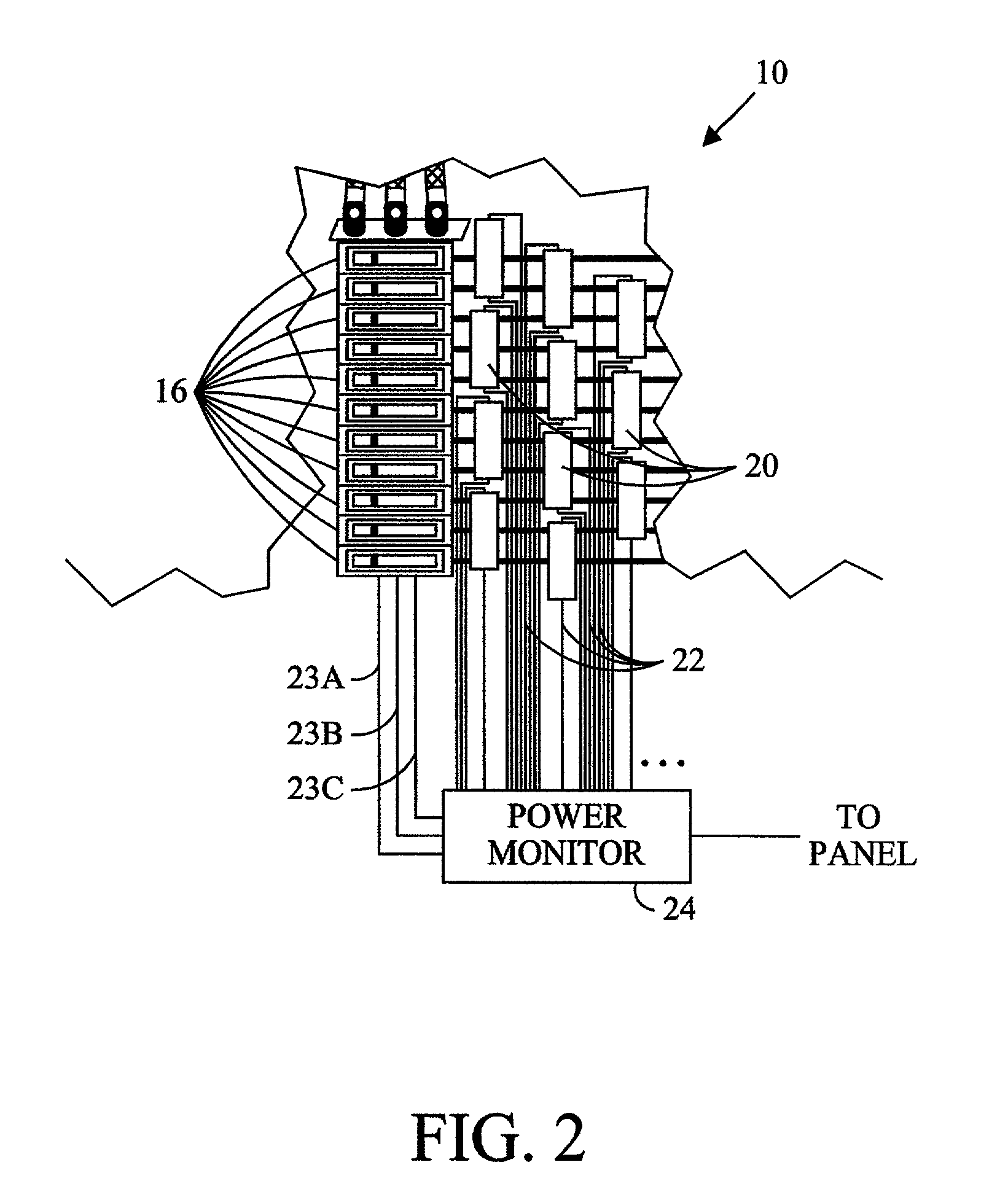
Simplified power monitoring system for electrical panels
InactiveUS7221145B2Electric devicesElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical conductorMonitoring system
A power monitoring system for electrical panels providing multi-phase power, with multiple current sensors. The disclosed power monitoring system preferably determines the instantaneous power provided to each of multiple loads by sensing the potential and phase of each conductor that supplies power to one or more of the respective loads.
Owner:VERIS INDS
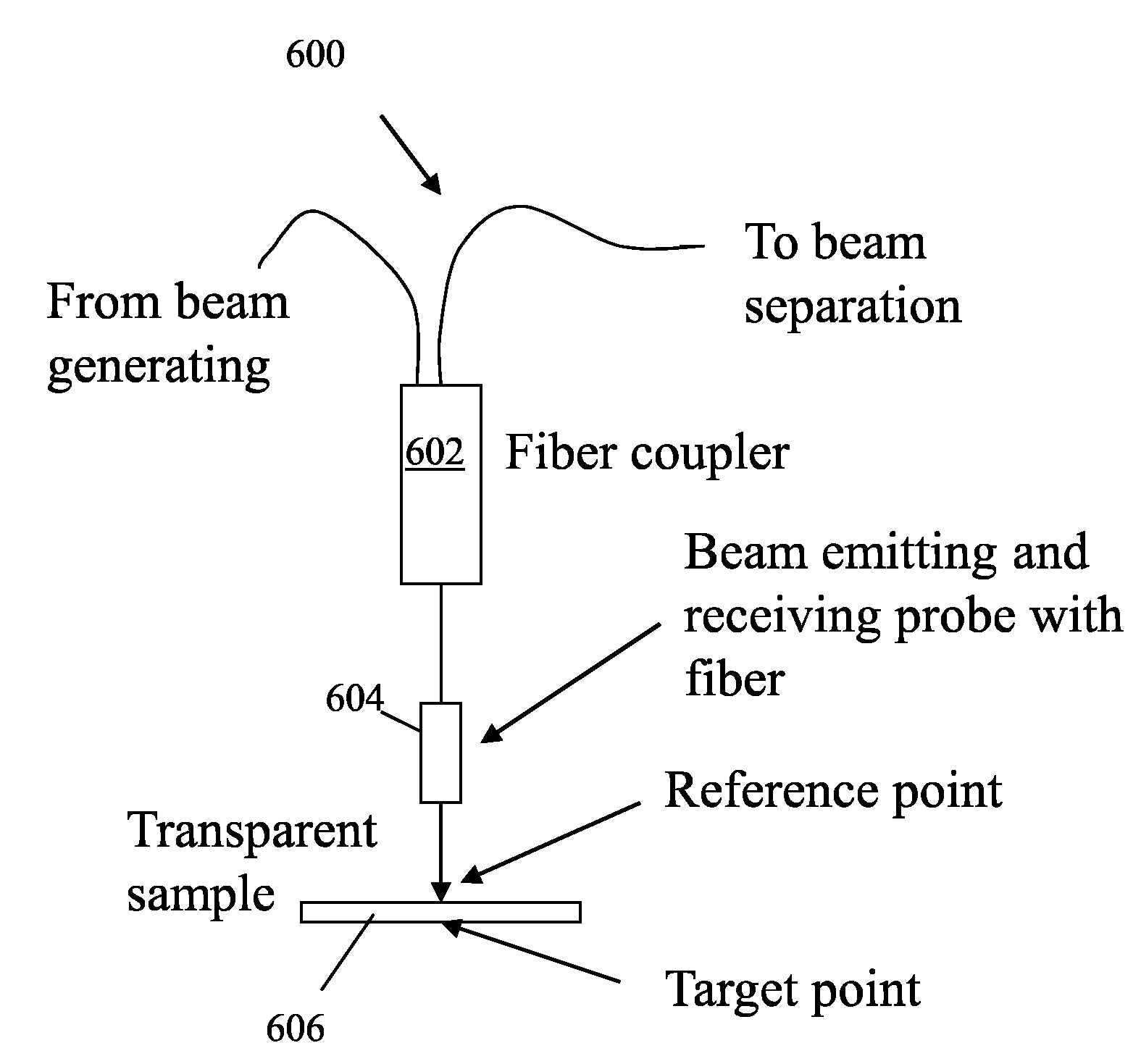
Instantaneous, phase measuring interferometer apparatus and method
The present invention generally relates to measuring and testing in the area of optics, and more specifically to a plurality of interacting coherent light beams to produce a cancellation or reinforcement of wave energy for measuring or testing. The present invention is directed to an improved interferometer system wherein a measurement is derived from phase measurements, wherein measurements include: distance, angular speed, as well as other physical or metrological properties. The present invention includes an interferometer that uses an illumination source comprised a plurality of simultaneously activated laser beams, each possessing a different wavelength contained in a coherent composite laser beam.
Owner:LISI
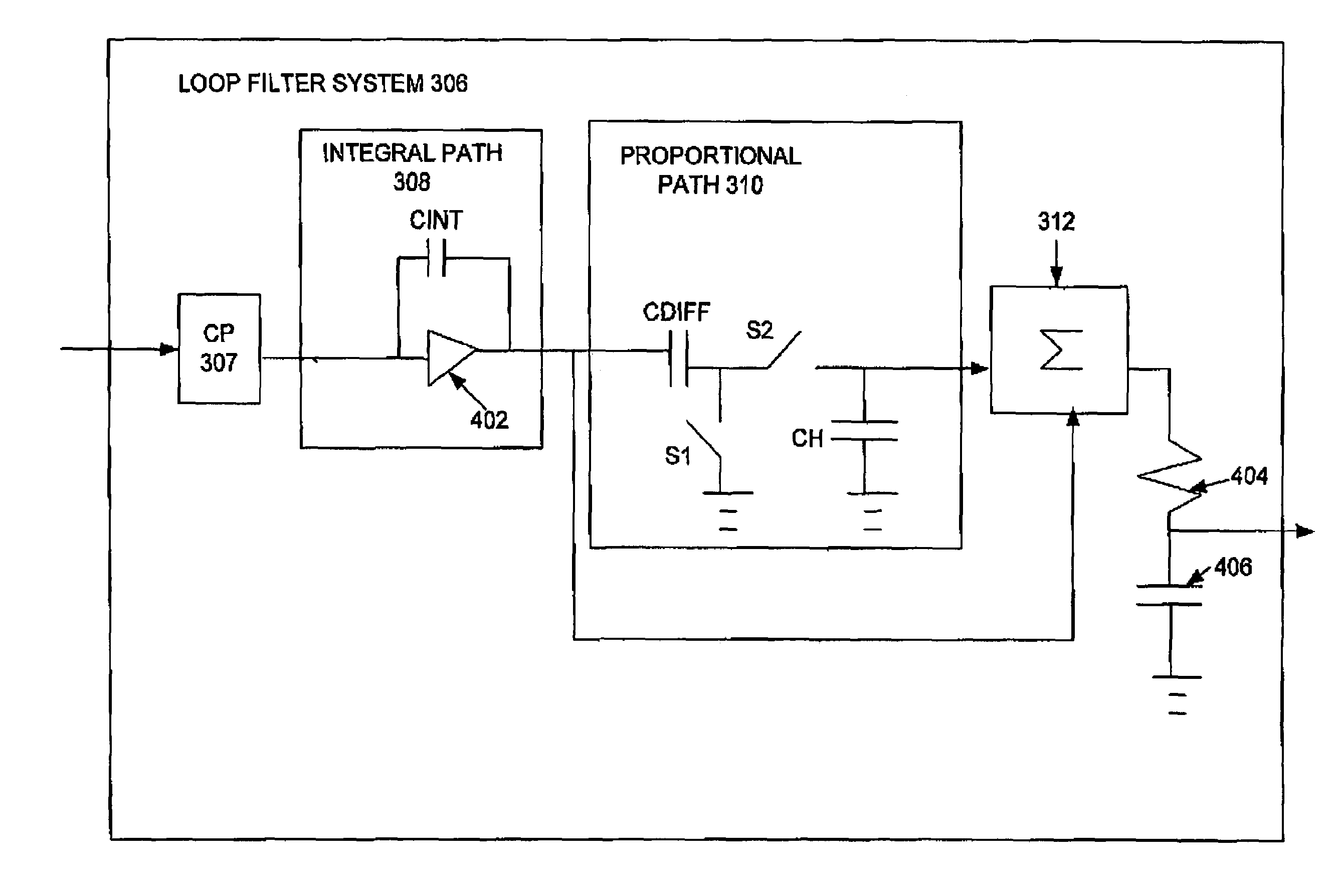
Low-noise loop filter for a phase-locked loop system
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Automatic static phase error and jitter compensation in pll circuits
InactiveUS20080191746A1Enhance the shake effectEffective wayPulse automatic controlVoltage-current phase angleLagData delay
An instantaneous phase error detector (IPED) and method includes a first gate configured to logically OR output phase error signals as data to a first latch, and a second gate configured to logically combine the output phase error signals to clock the first latch. A delay element delays to the data to the first latch where the output of the first latch provides instantaneous phase error change information. A second latch is coupled to the output phase error signals to output a lead / lag signal to indicate which of the output phase error signals is leading. A phase-locked loop employing the output of the IPED is also disclosed along with static phase measurement and jitter optimization features.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Multi-phase realigned voltage-controlled oscillator and phase-locked loop incorporating the same
InactiveUS20060197614A1Pulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsPhase detectorCharge injection
A multi-phase realigned voltage-controlled oscillator (MRVCO) achieves phase realignment based on charge injection in the VCO stages with the injection amount proportional to the instantaneous phase error between the VCO output clock and a reference clock. The MRVCO may be incorporated as part of an implementation of a multi-phase realigned phase-locked loop (MRPLL). A separate phase detector, as well as a specific realignment charge pump, may be provided in the PLL for controlling the VCO. The VCO has lower phase modulation noise, so that the PLL has very large equivalent bandwidth.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Damage detection method based on instantaneous phase changing degree
InactiveCN101995435AAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalSonificationRandom noise
The invention discloses a damage detection method based on instantaneous phase changing degree in the technical field of mechanical structural detection, comprising the following steps: fixing an energy converter on the surface of an object to be detected or inlaying the energy converter in the structure of the object to be detected and constructing a detection area; detecting and calculating the objected to be detected in a non-damage state by utilizing ultrasonic guided wave to obtain the flight time of the wave signal scattered by the damage; calculating to obtain the damaged coordinate position by adopting a triangle positioning method according to the flight time, and drawing multiple coordinate tracks by combining ToF assessed by each sensing path in a sensing network, wherein the converging area of the coordinate tracks is the area in which the damage can appear. The method of the invention has preferable ability of resisting the random noise interference; even though signal noise ratio (SNR) of the collected wave signal is lower, the method still can be used for accurately assessing the ToF scattered by the damage in a basic order symmetrical (S0) mode, and further successfully identifies and positions the damage by combining a triangle positioning method.
Owner:GARBSEN ELECTRIC SHANGHAI CO LTD
Passive distance measurement using spectral phase gradients
ActiveUS20060007423A1Avoid dependenceLong distanceOptical rangefindersSatellite radio beaconingTelevision receiversPassive radar
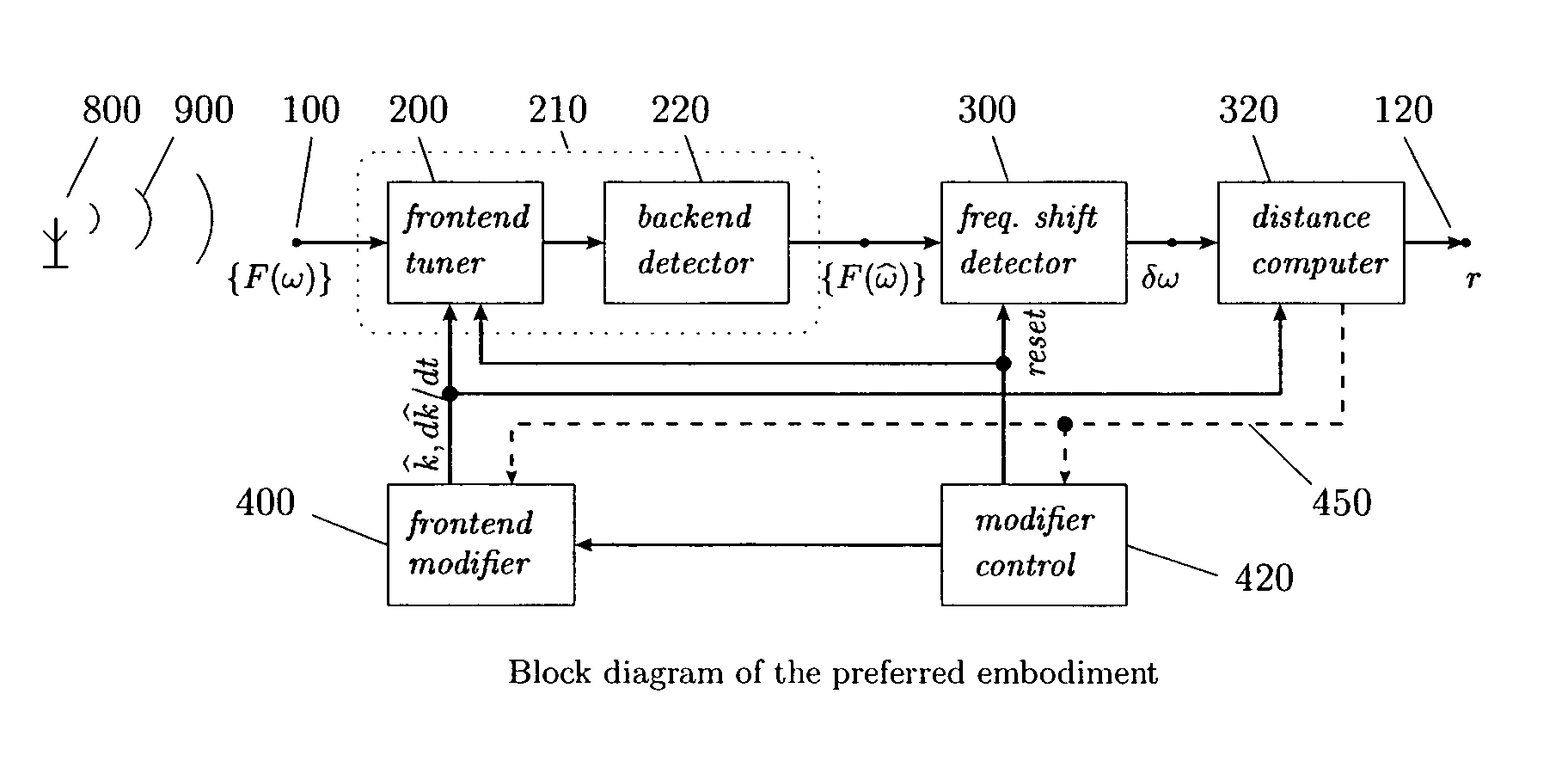
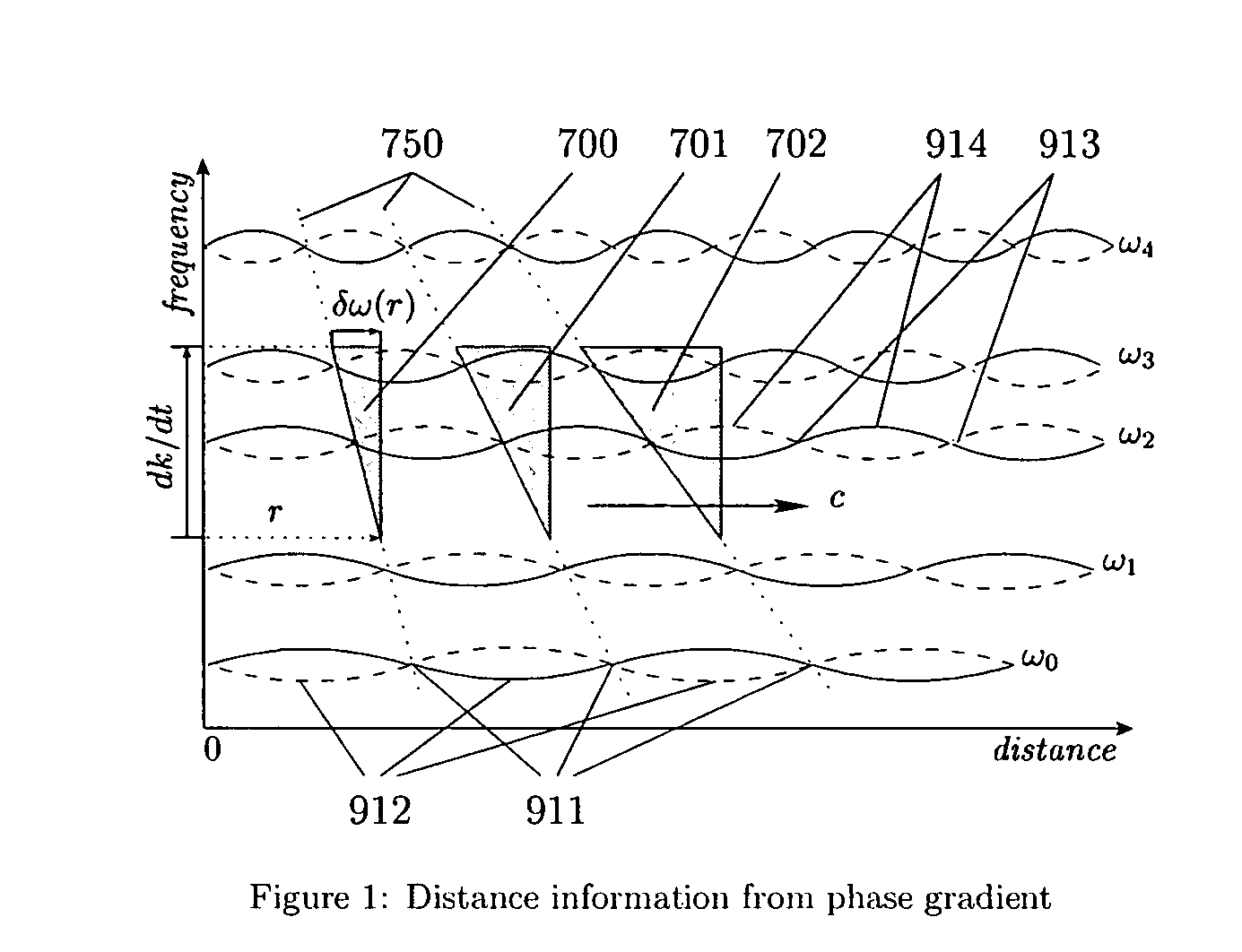
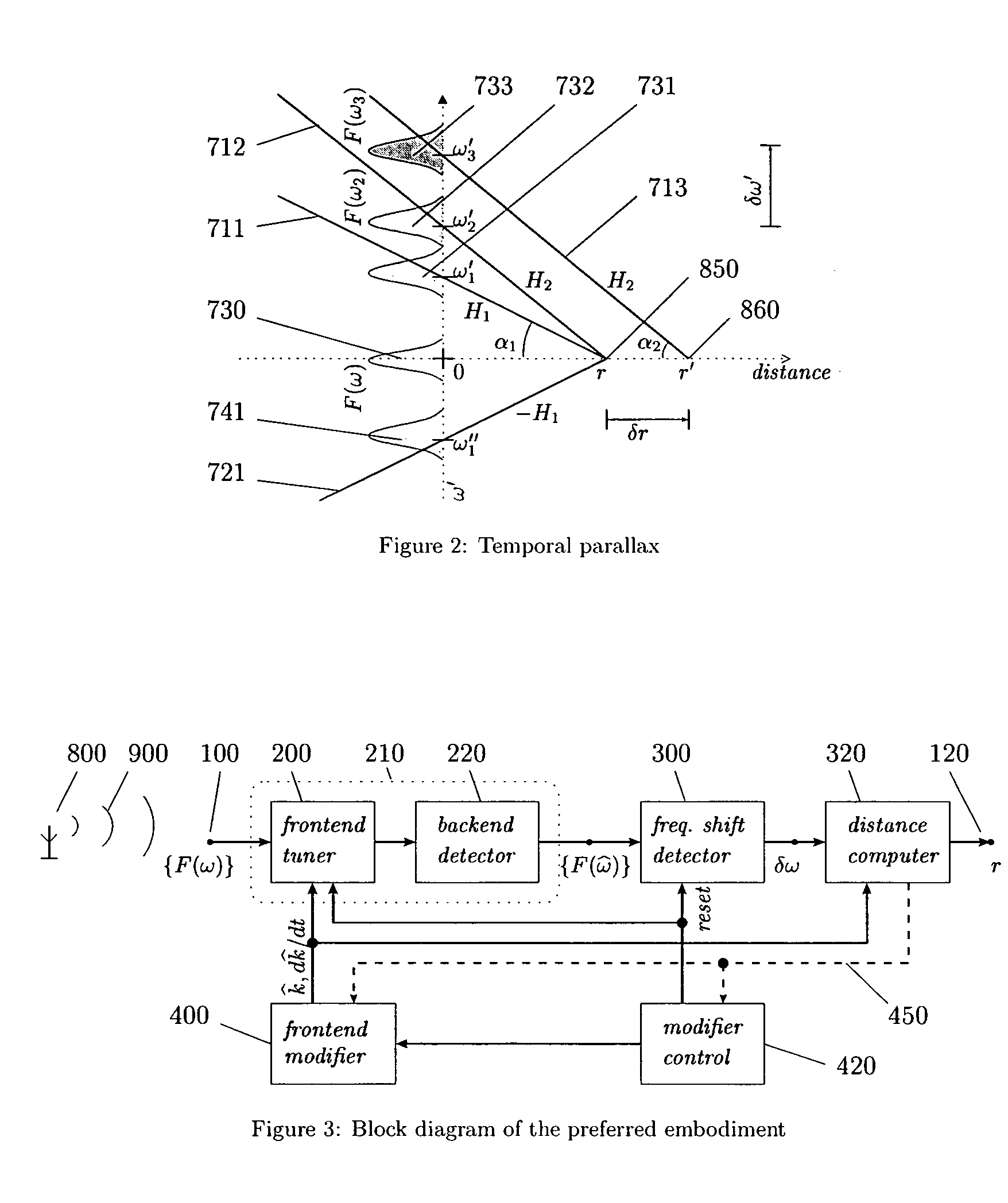
General method for extracting source distance information from any kind of received radiation, including electromagnetic and acoustic, without involving round-trip time or phase in any form, and thus more truly passive than existing passive radars. The method exploits the facts that radiation from a real source must comprise wavepackets of nonzero bandwidth, that the individual frequency components of a wavepacket must have consistent phase at the source, and that their instantaneous phases must increase linearly along the path in proportion to the respective frequencies, so that the phase gradient across the components must be proportional to the distance travelled. The invention simplifies over naïve phase gradient measurement by scanning the phase gradient at a controlled rate, thereby converting the gradient into normalized frequency shifts proportional to the scanning rate and the source distance. It mimics the cosmological redshift and acceleration, but at measurable levels over any desired range and even with sound. Potential applications include stealth and “unjammable” radars for the military, ranging capability for emergency services, commodity low-power vehicular and personal radars, simplification and improvements in radar and diagnostic imaging, improved ranging in general all the way from ground to inter-galactic space, “interference-free” communication systems including radio and television receivers, source-distance (or range-division) multiplexing improved cellphone power control and battery life, and continuous, transparent diagnostics for optical fibres, integrated circuits and transmission lines.
Owner:GURUPRASAD VENKATA
Adaptive GDFE
ActiveUS20060276918A1Minimize error propagation effectImprove performanceMultiple-port networksModulated-carrier systemsSpatial correlationCommunications system
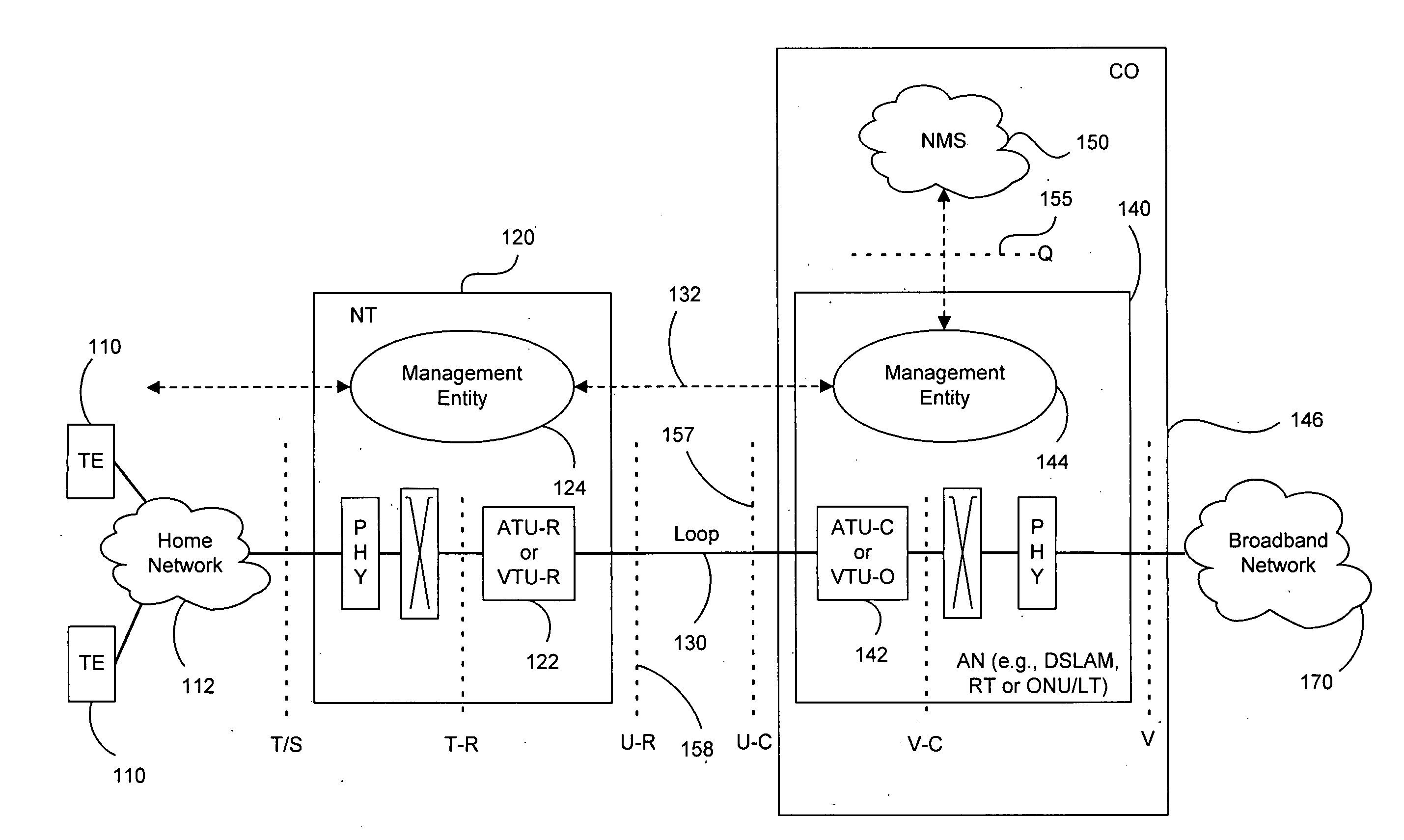
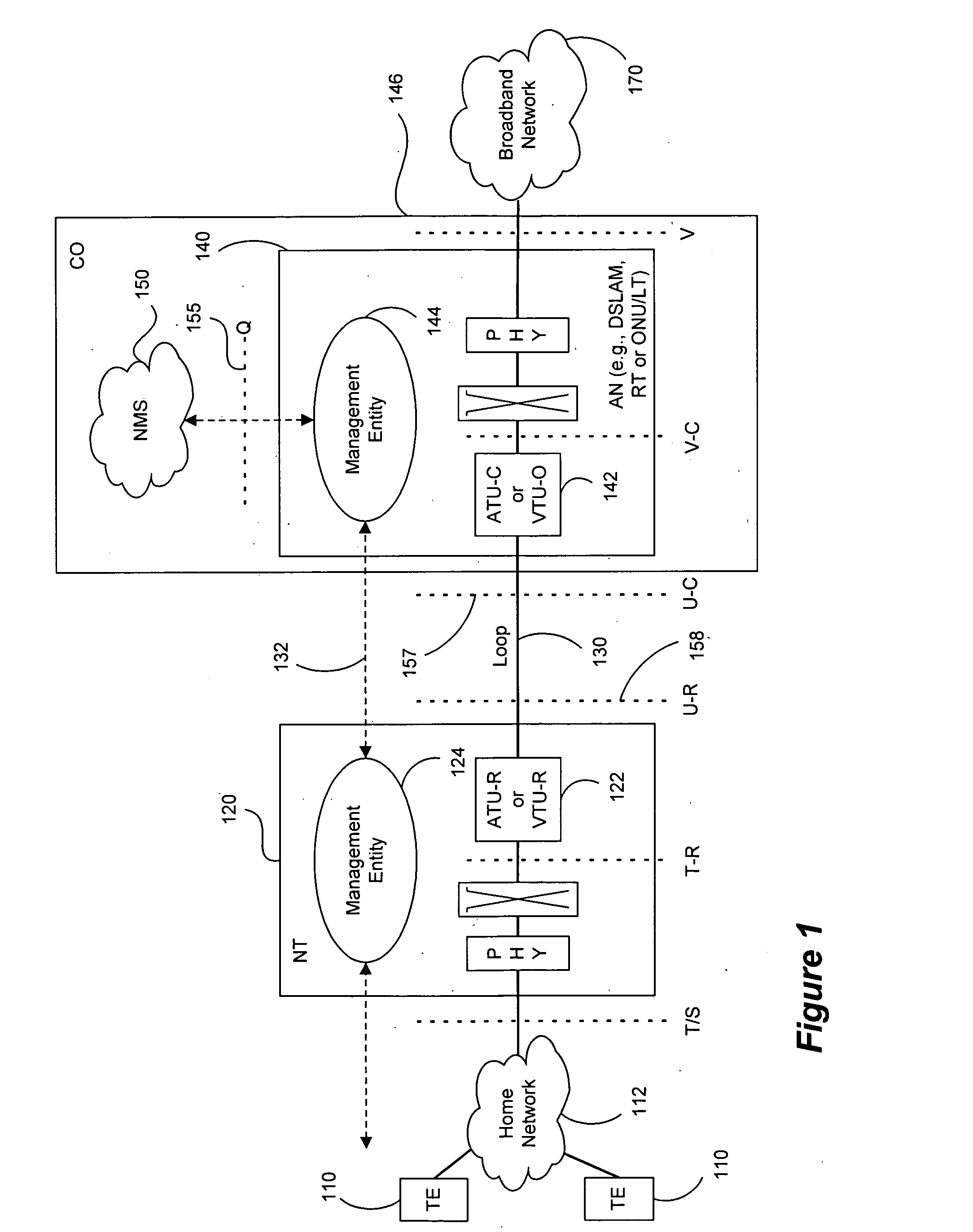
Adaptive generalized decision feedback equalization (GDFE) allows variations in one or more channels and noise of a multi-line / multi-channel communication system to be tracked. Such tracking can be used in vector upstream (one-sided) situations in communication systems such as ADSL and VDSL, among others. The GDFE may be separated into adaptive and static portions and / or components. Either a feedforward section or a feedback section (or both) can be separated to create a static component and an adaptive component. The adaptive components adjust to the instantaneous channel and noise changes (for example, using the instantaneous errors and simple LMS algorithms). When the channel and noise do not exhibit any time-variation, the adaptive filters can zero themselves. Local updating of adaptive feedforward and / or feedback filters addresses rapid changes to the spatial correlation of noise and / or changes to the multi-line channel (for example, time-variation due to temperature changes, component variations, mechanical stress, and other reasons), without disruption to separate static feedforward and / or feedback filters supplied by a controller, such as a DSL optimizer or the like that can assist by doing the heavier calculations and providing vectoring information and data to the DSL line components. An efficient implementation is provided of any triangularization of the binder channel that characterizes multi-user vectored-DMT DSL. Adaptation also allows correction of any inaccuracy in initially or previously reported crosstalk transfer functions and noise spatial correlation.
Owner:ASSIA SPE LLC CO THE CORP TRUST CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com